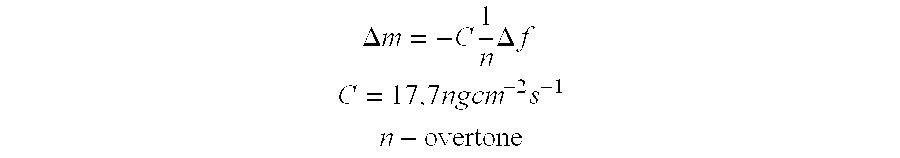Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
125 results about "Heparan sulfate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Heparan sulfate (HS) is a linear polysaccharide found in all animal tissues. It occurs as a proteoglycan (HSPG) in which two or three HS chains are attached in close proximity to cell surface or extracellular matrix proteins. It is in this form that HS binds to a variety of protein ligands, including Wnt, and regulates a wide range of biological activities, including developmental processes, angiogenesis, blood coagulation, abolishing detachment activity by GrB (Granzyme B), and tumour metastasis. HS has also been shown to serve as cellular receptor for a number of viruses including the respiratory syncytial virus.
Methods and compositions related to modulating the extracellular stem cell environment
This invention relates, in part, to methods and compositions that modulate the stem cell environment. More specifically, the invention relates, in part, to methods and compositions for modulating stem cell differentiation. Such modulation, in some aspects of the invention, is accomplished by agents that modulate glycosaminoglycans in the stem cell microenvironment (i.e., at or on the cell surface and / or in the extracellular matrix). Therefore, methods and compositions are provide for modulating glycosaminoglycan moieties, e.g., heparan sulfate glycosaminoglycan (HSGAG) moieties, in the microenvironment of stem cells. Methods and compositions for promoting or inhibiting embryonic stem cell differentiation (e.g., differentiation into endothelial cells) are also provided. This invention also relates, therefore, in part, to cell populations (e.g., endothelial cell populations or impoverished endothelial cell populations) that can be produced with the methods and compositions provided. Furthermore, the invention relates, in part, to tissues, and uses thereof, formed by the methods and compositions provided. Moreover, the invention also relates, in part, to methods of treatment using the methods and compositions provided.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
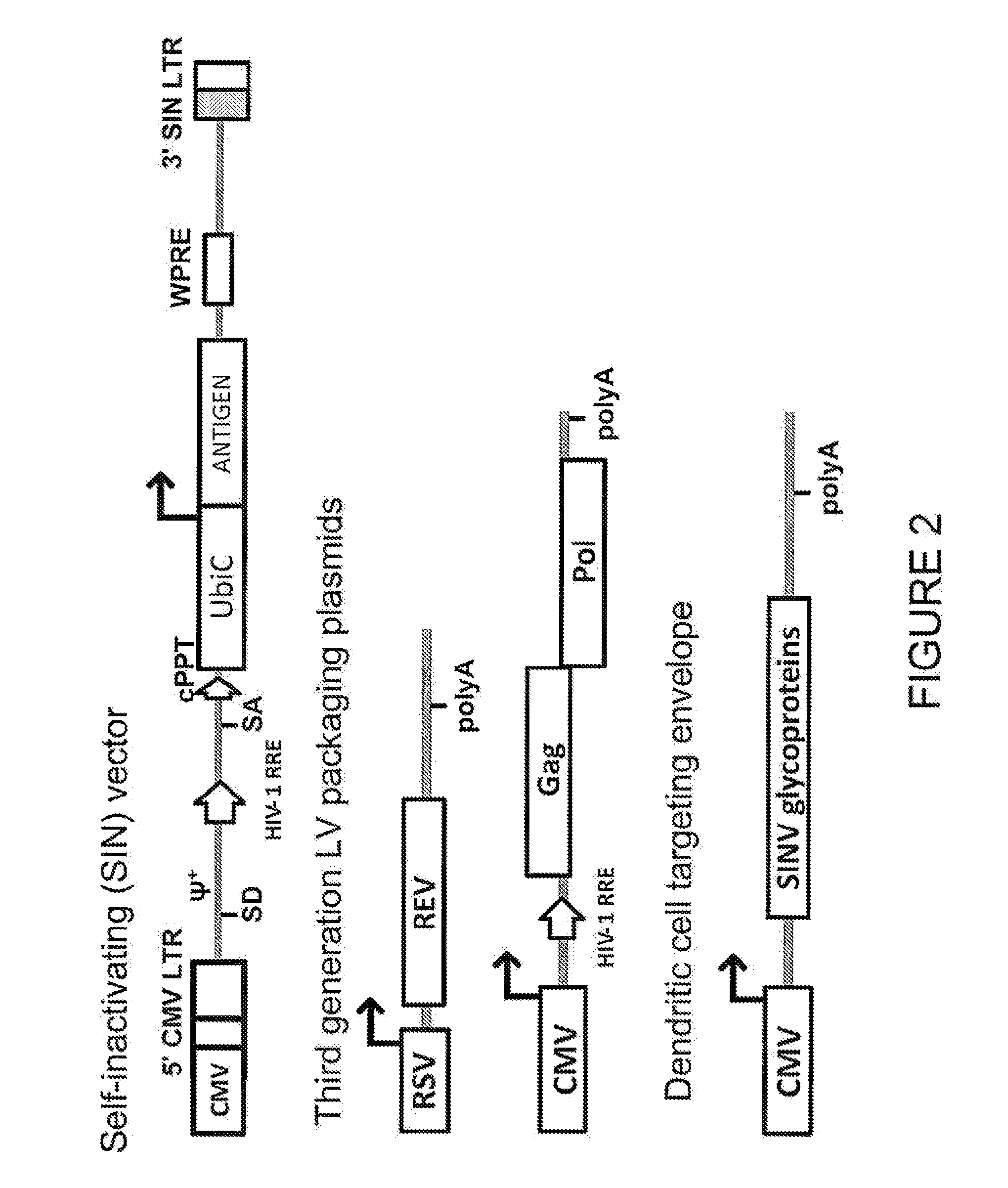
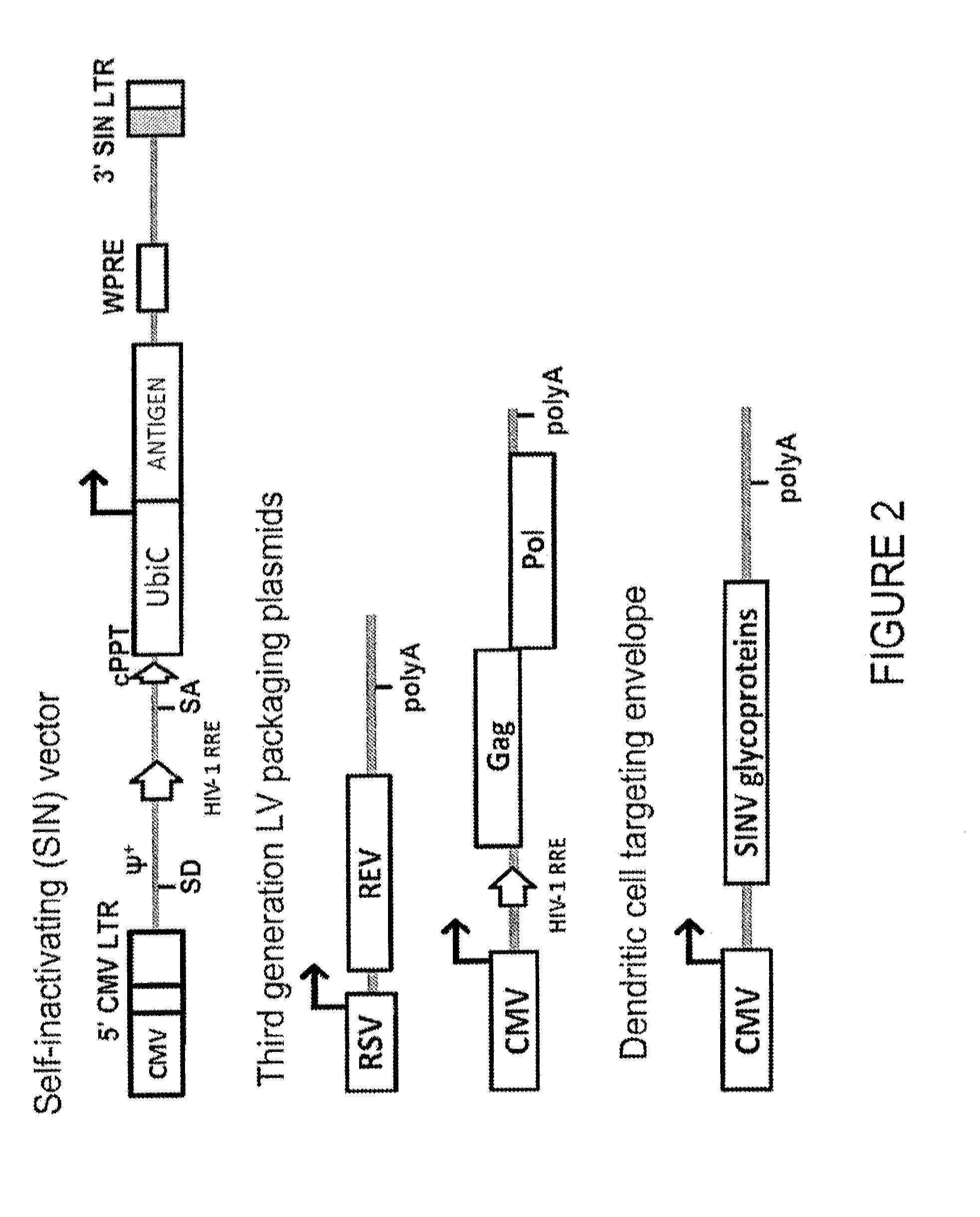
Lentiviral vectors pseudotyped with a sindbis virus envelope glycoprotein
InactiveUS20110064763A1Promote infectionSsRNA viruses positive-senseAntiviralsDendritic cellSindbis virus
Lentiviral vector particles comprising a Sindbis virus E2 glycoprotein variant and a lentiviral vector genome comprising a sequence of interest are provided. A lentiviral vector particle comprising: (a) an envelope comprising a Sindbis virus E2 glycoprotein variant; and (b) a lentiviral vector genome comprising a sequence of interest; wherein the E2 glycoprotein variant facilitates infection of dendritic cells by the lentiviral vector particle, and wherein the E2 glycoprotein variant has reduced binding to heparan sulfate compared to a reference sequence (HR strain).
Owner:IMMUNE DESIGN CORP
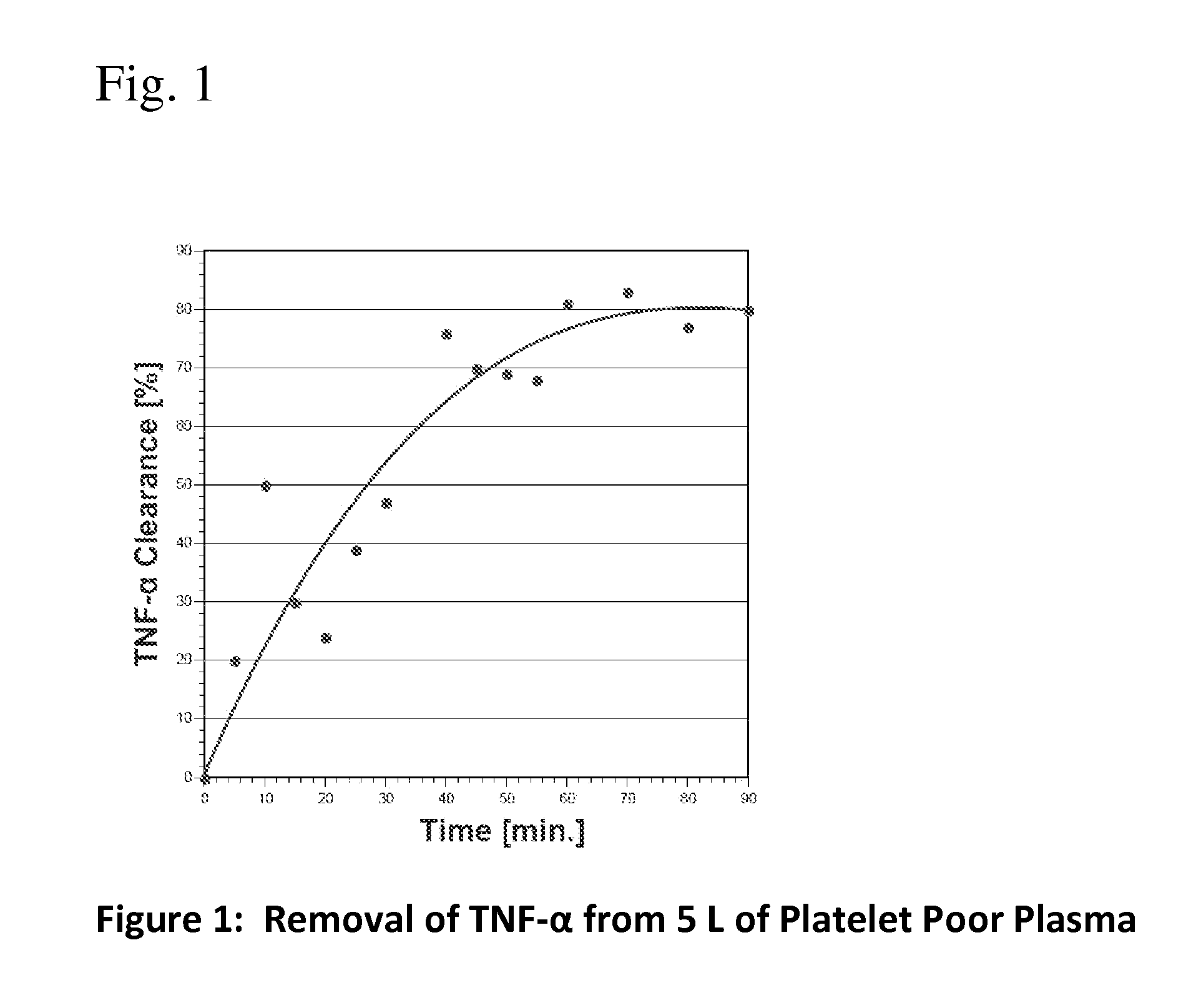
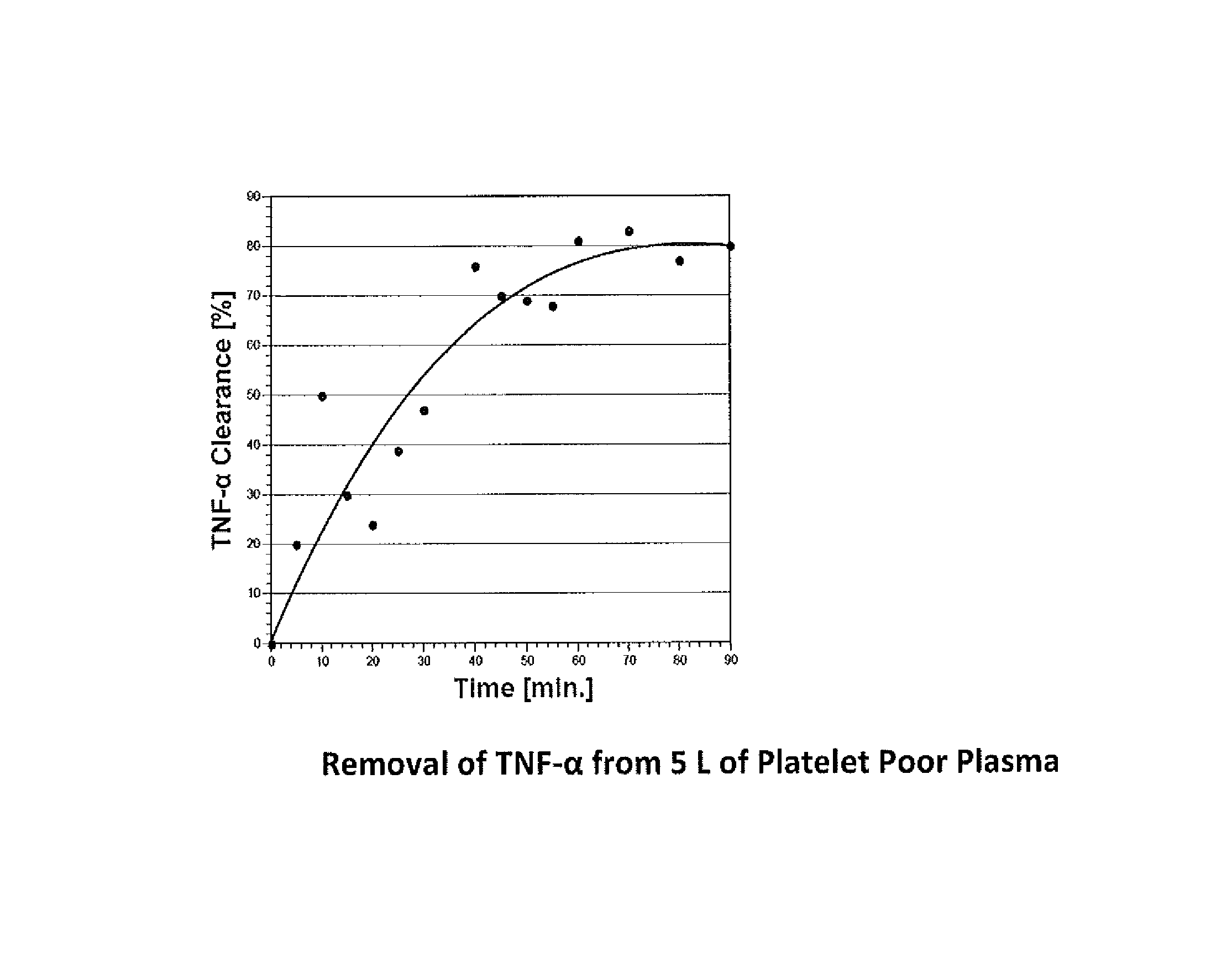
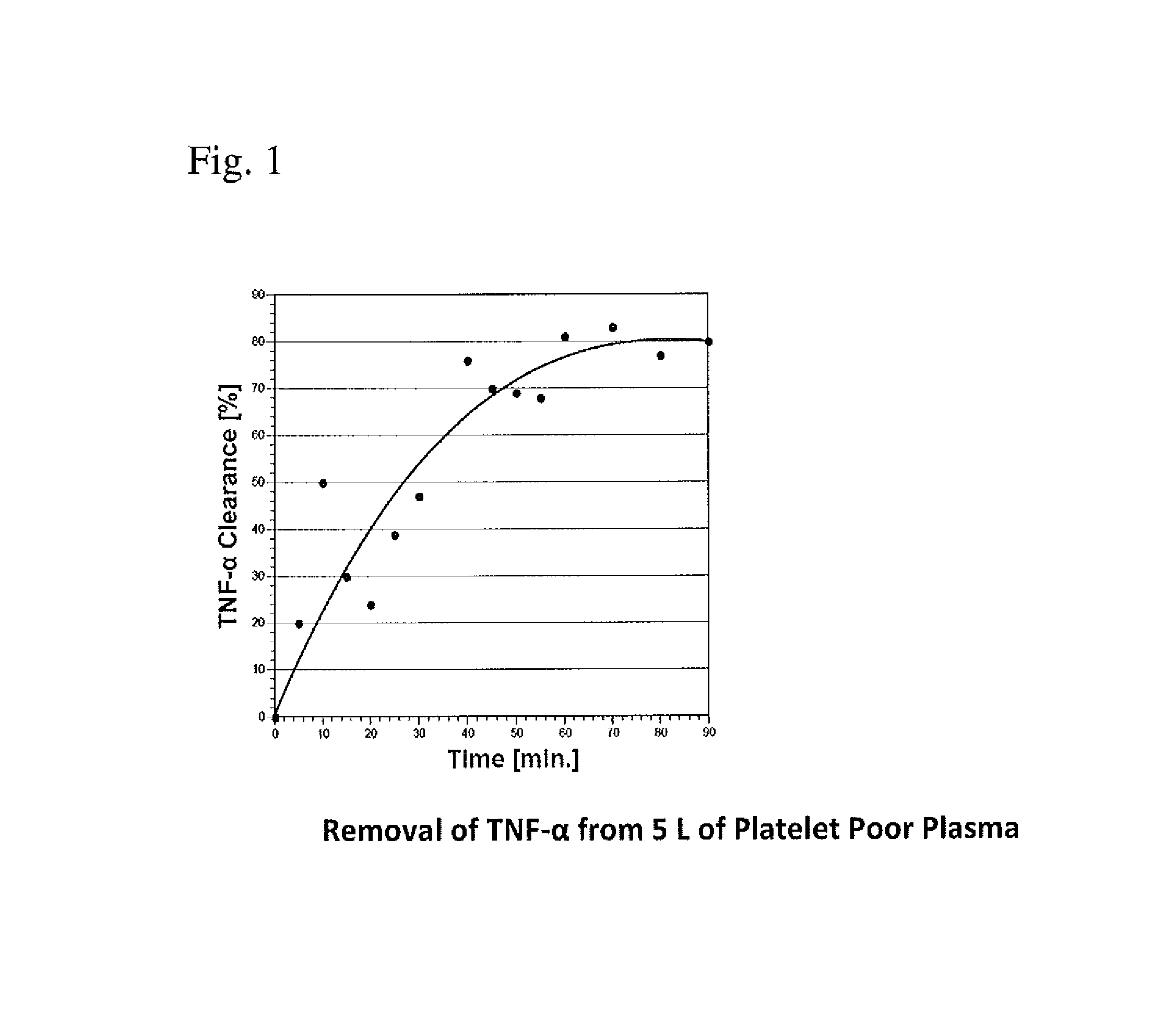
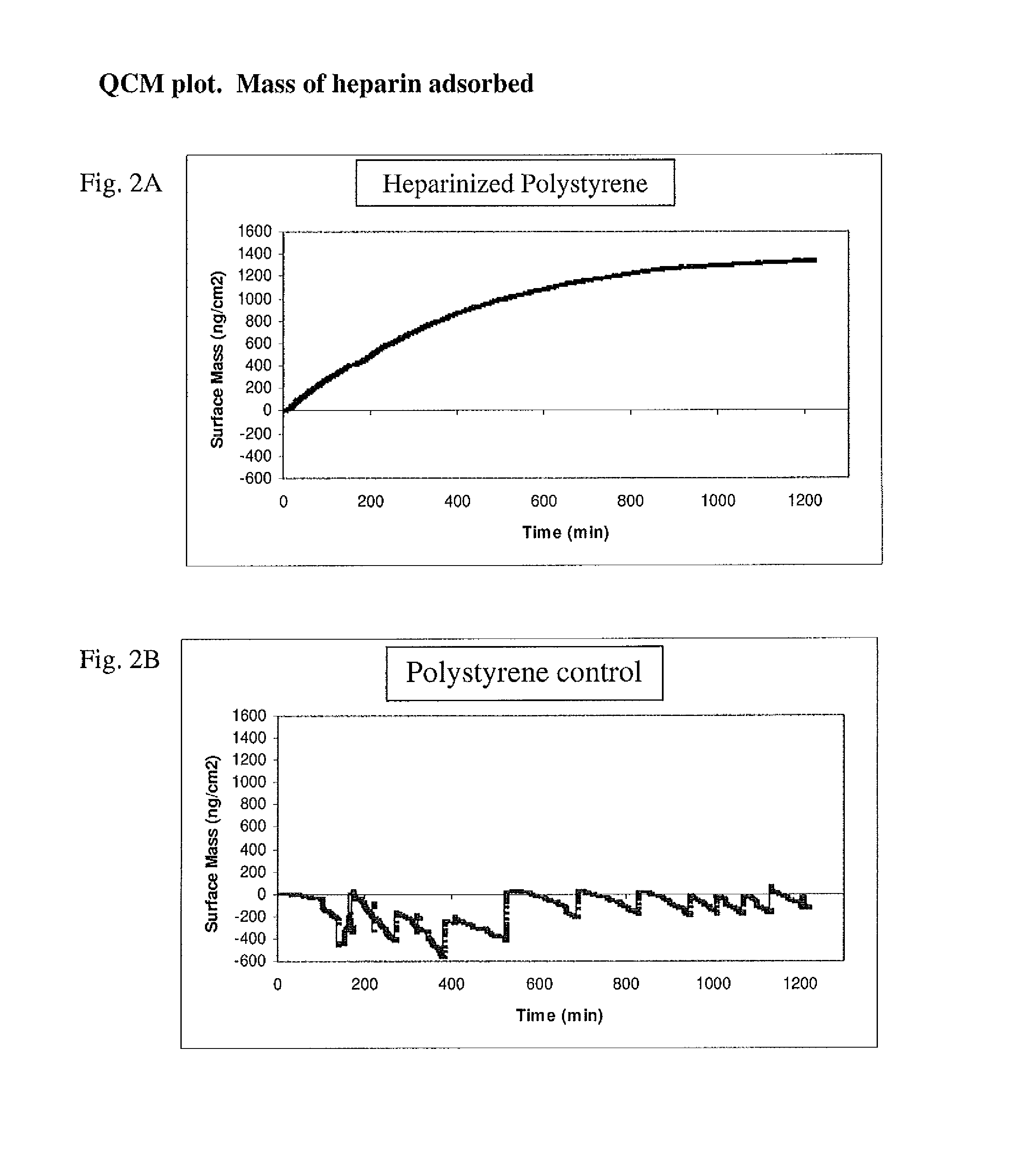
Method for removing cytokines from blood with surface immobilized polysaccharides
ActiveUS20110184377A1Lessen and eliminate spreadPrevent diseaseAntibacterial agentsSalicyclic acid active ingredientsPorous substrateSurface concentration
The present invention is directed to a method for removing cytokines and / or pathogens from blood or blood serum (blood) by contacting the blood with a solid, essentially non micro-porous substrate which has been surface treated with heparin, heparan sulfate and / or other molecules or chemical groups (the adsorbent media or media) having a binding affinity for the cytokine or pathogen(s) to be removed (the adsorbates), and wherein the size of the interstitial channels within said media is balanced with the amount of media surface area and the surface concentration of binding sites on the media in order to provide adequate adsorptive capacity while also allowing relatively high flow rates of blood through the adsorbent media.
Owner:EXTHERA MEDICAL
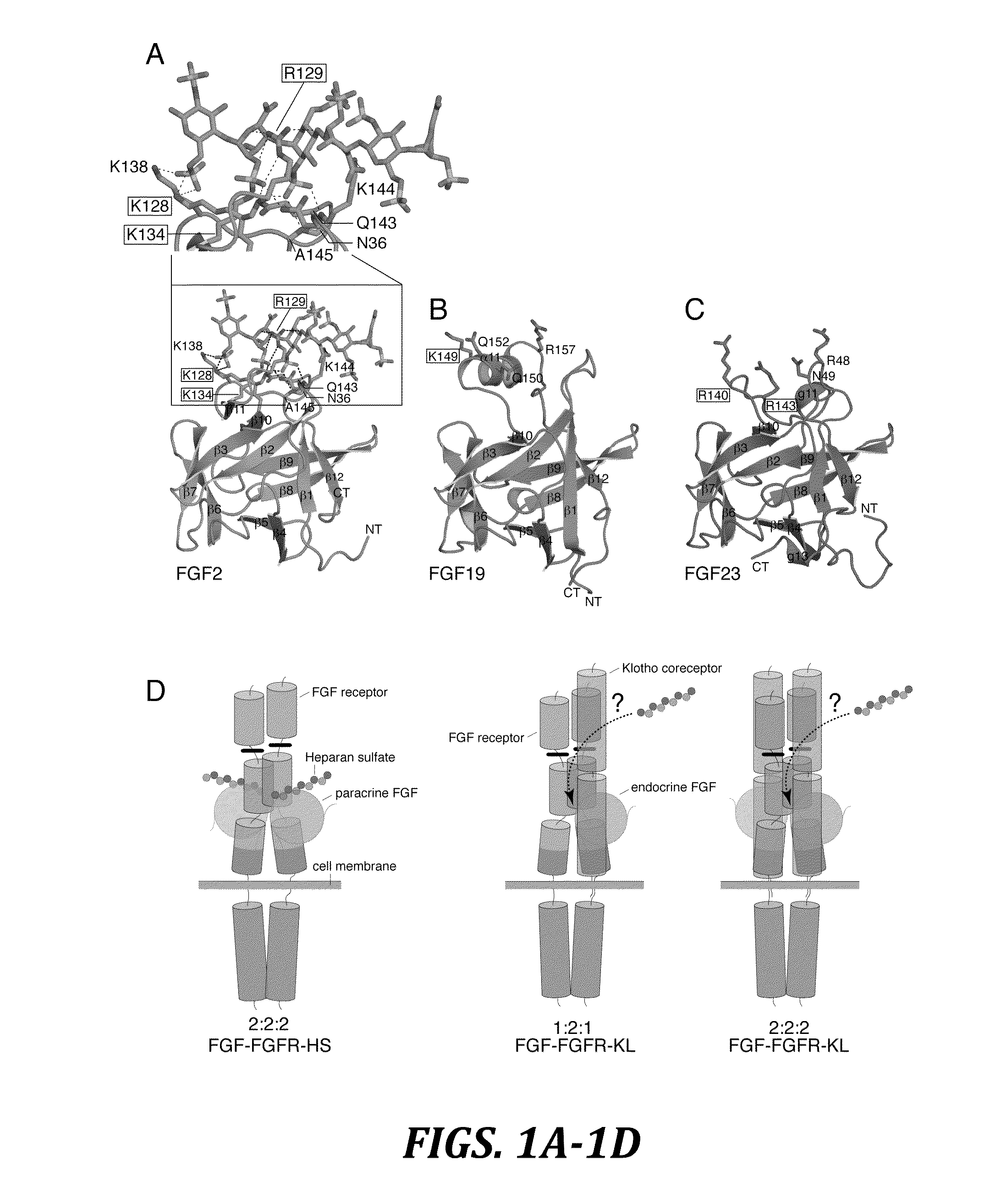
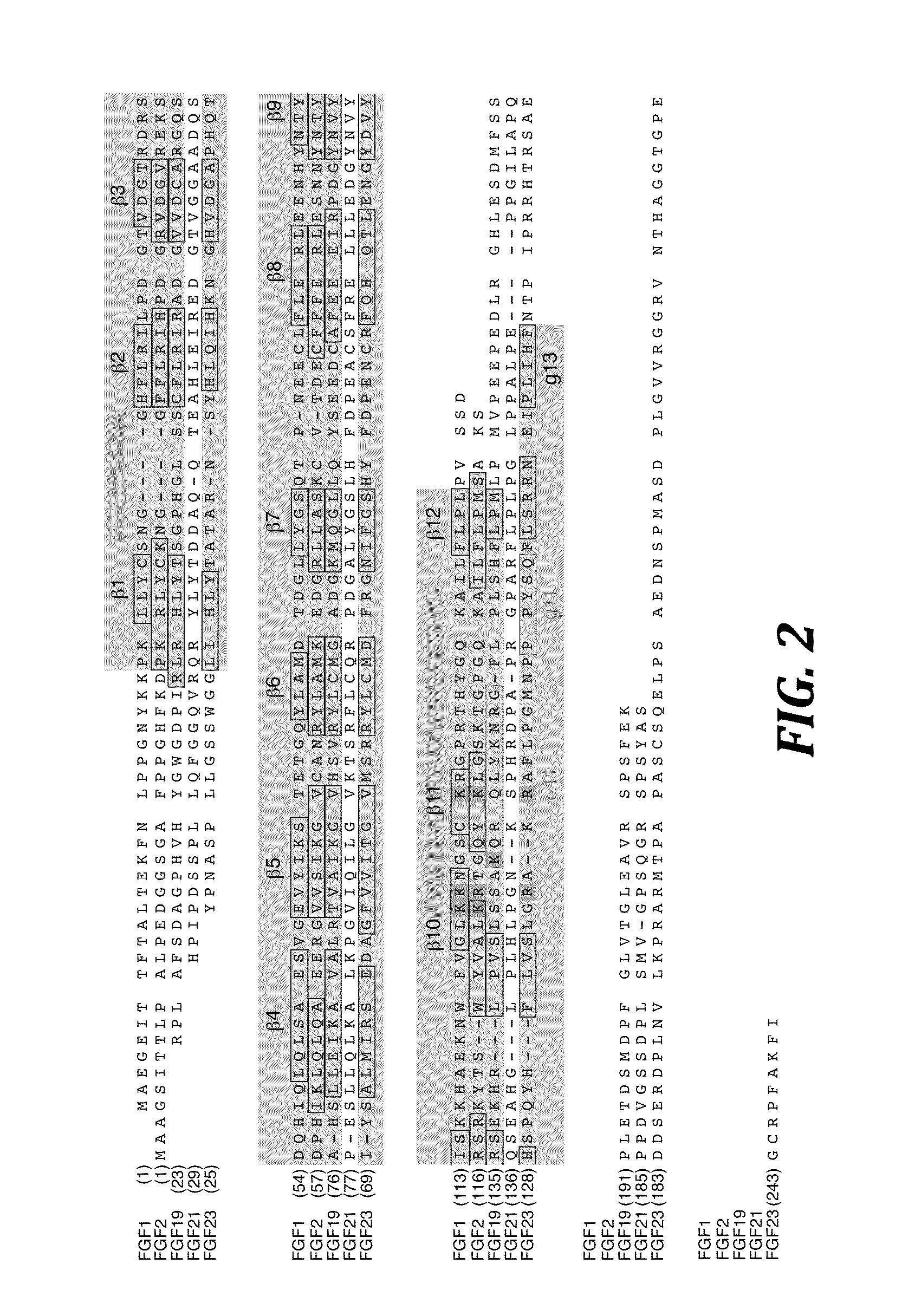
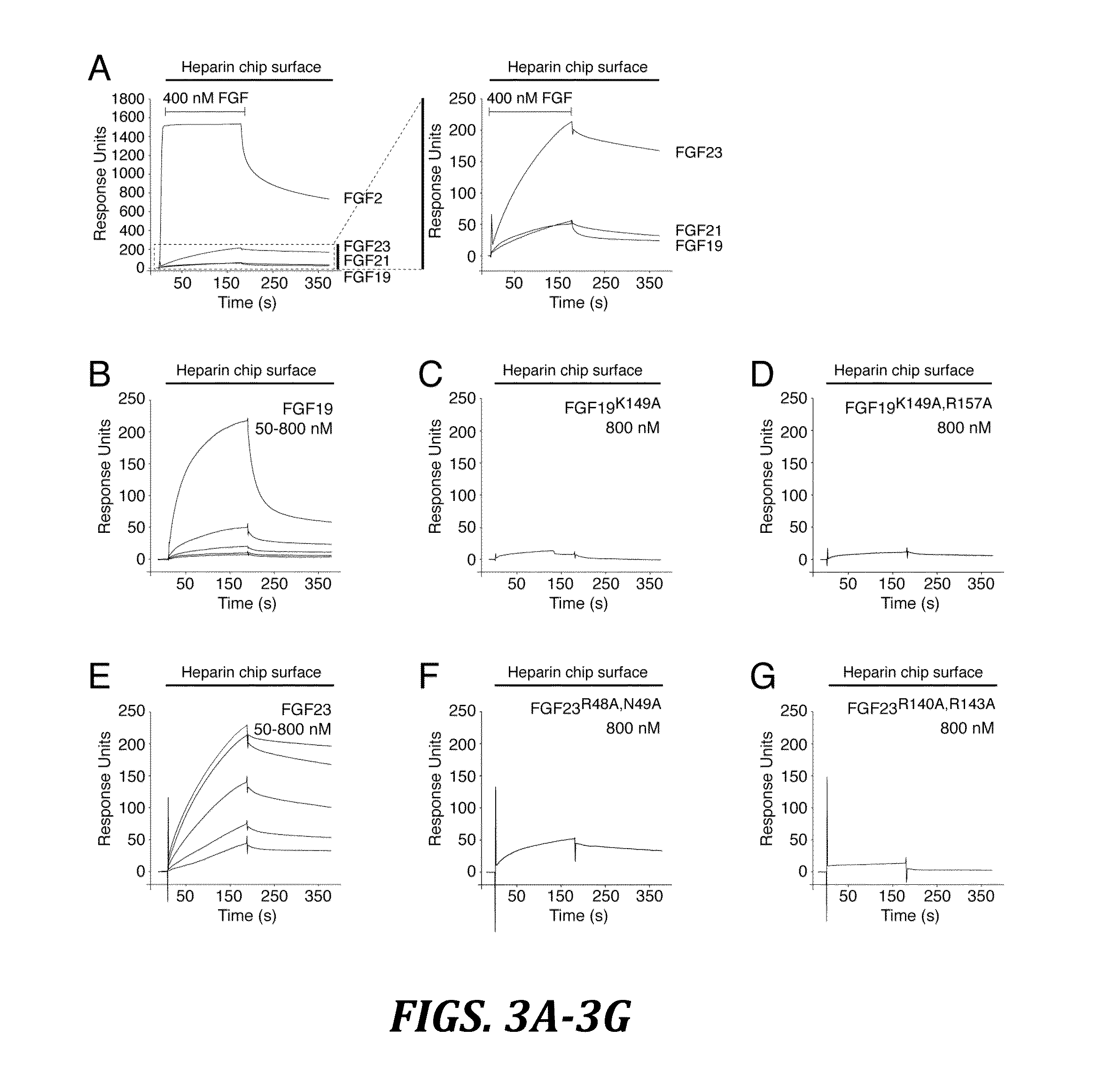
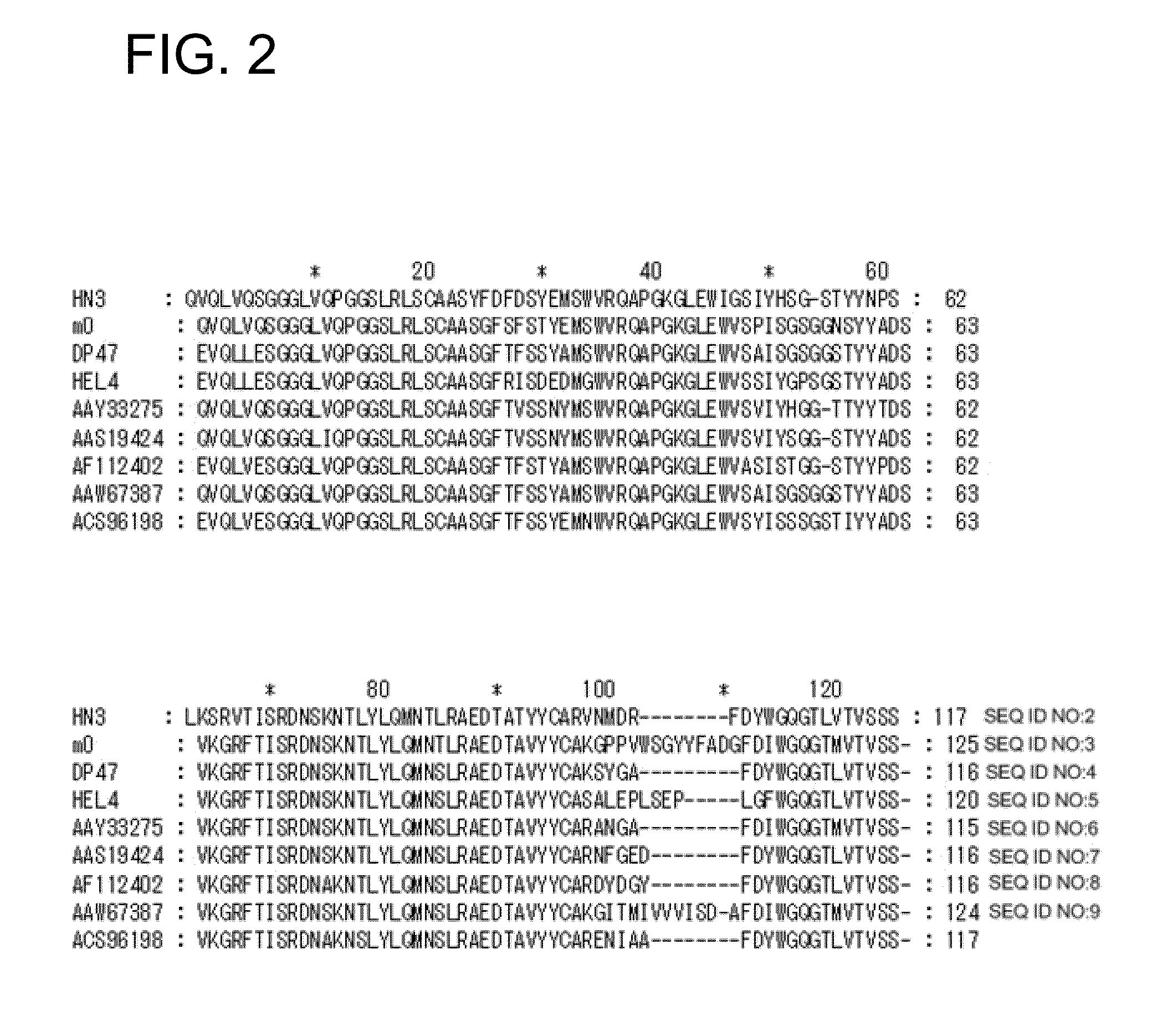
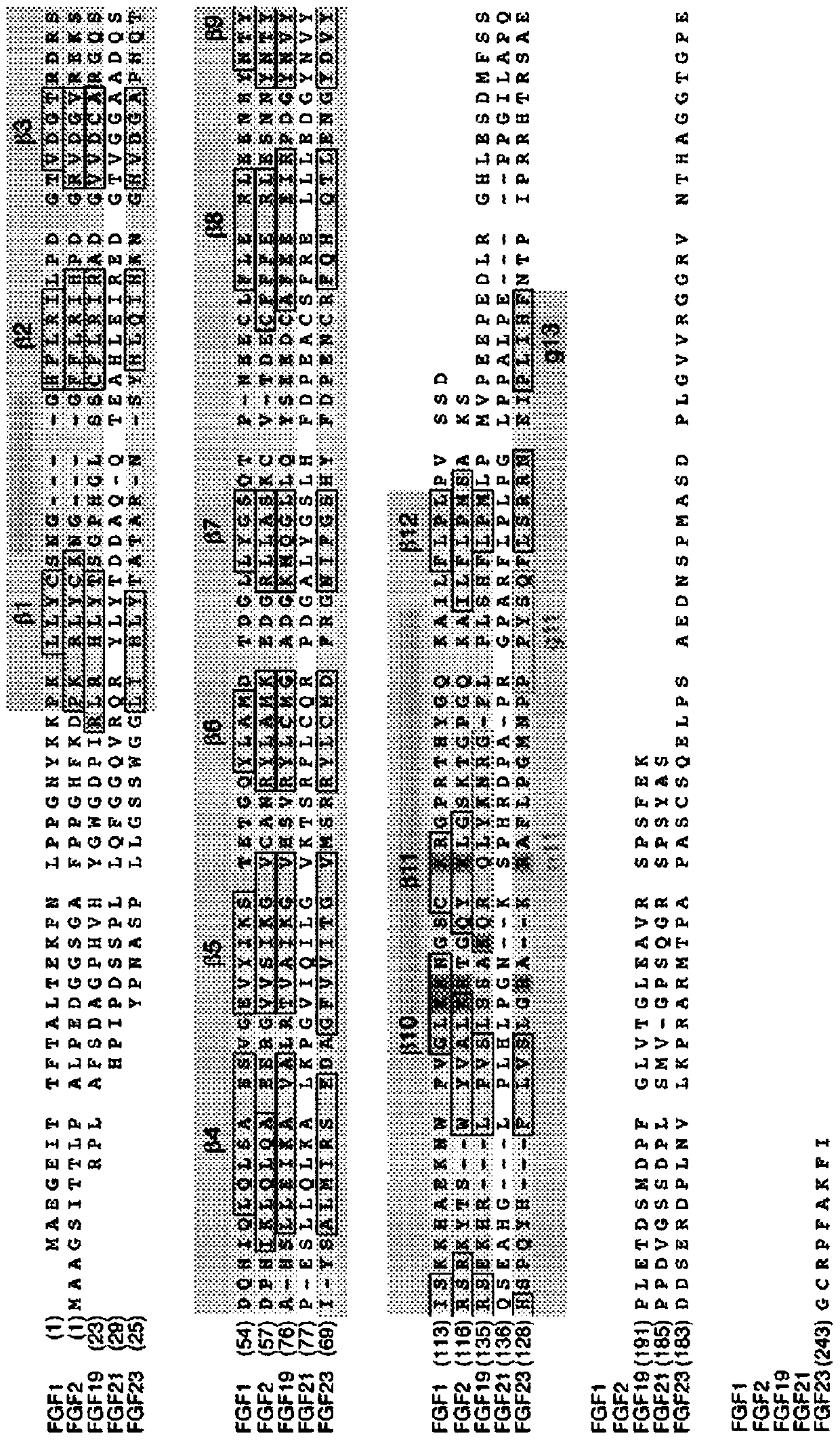
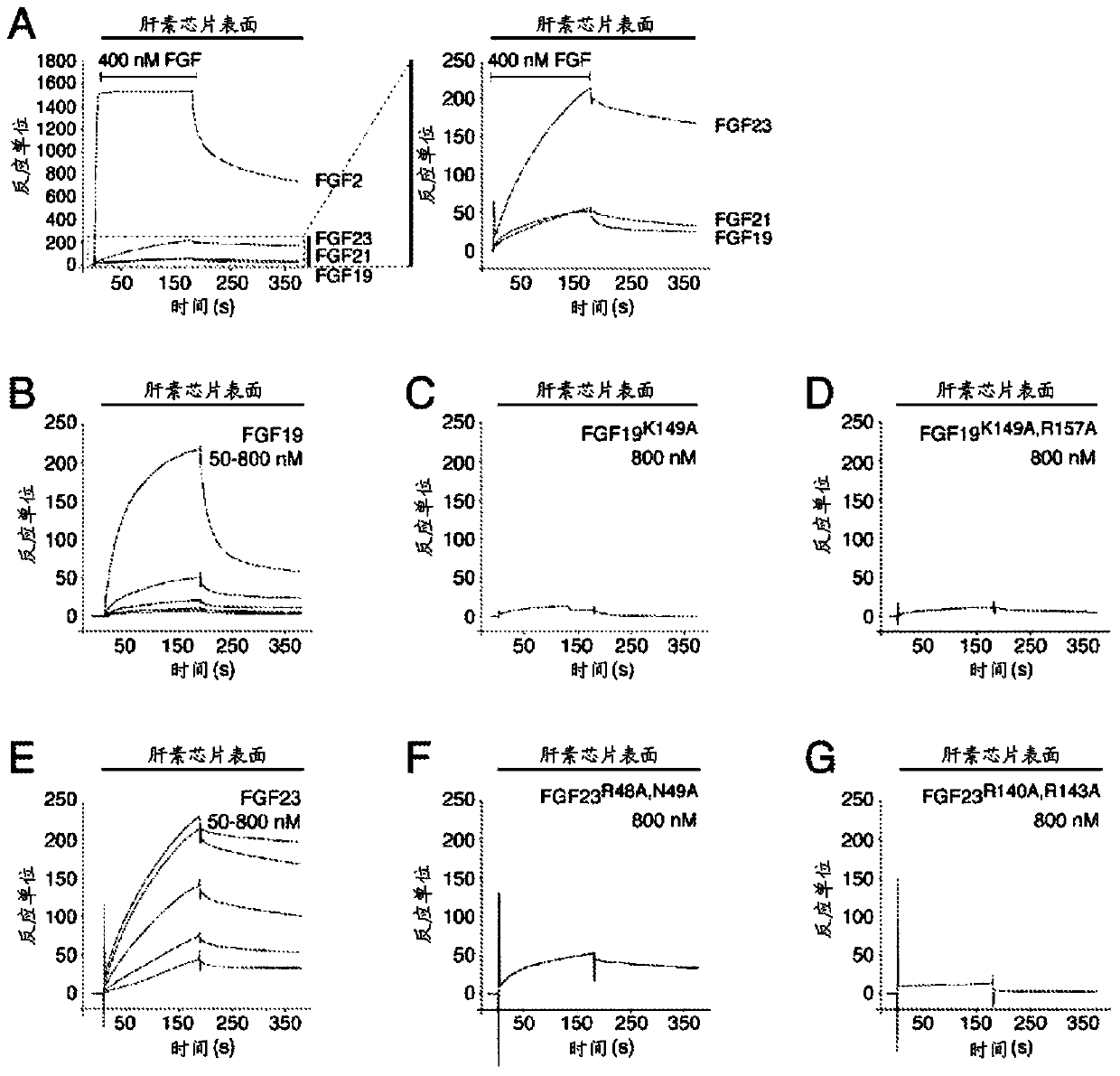
Chimeric fibroblast growth factor 19 proteins and methods of use
ActiveUS20130331317A1Enhanced endocrine activityLow affinityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsKlothoHeparin-DHE
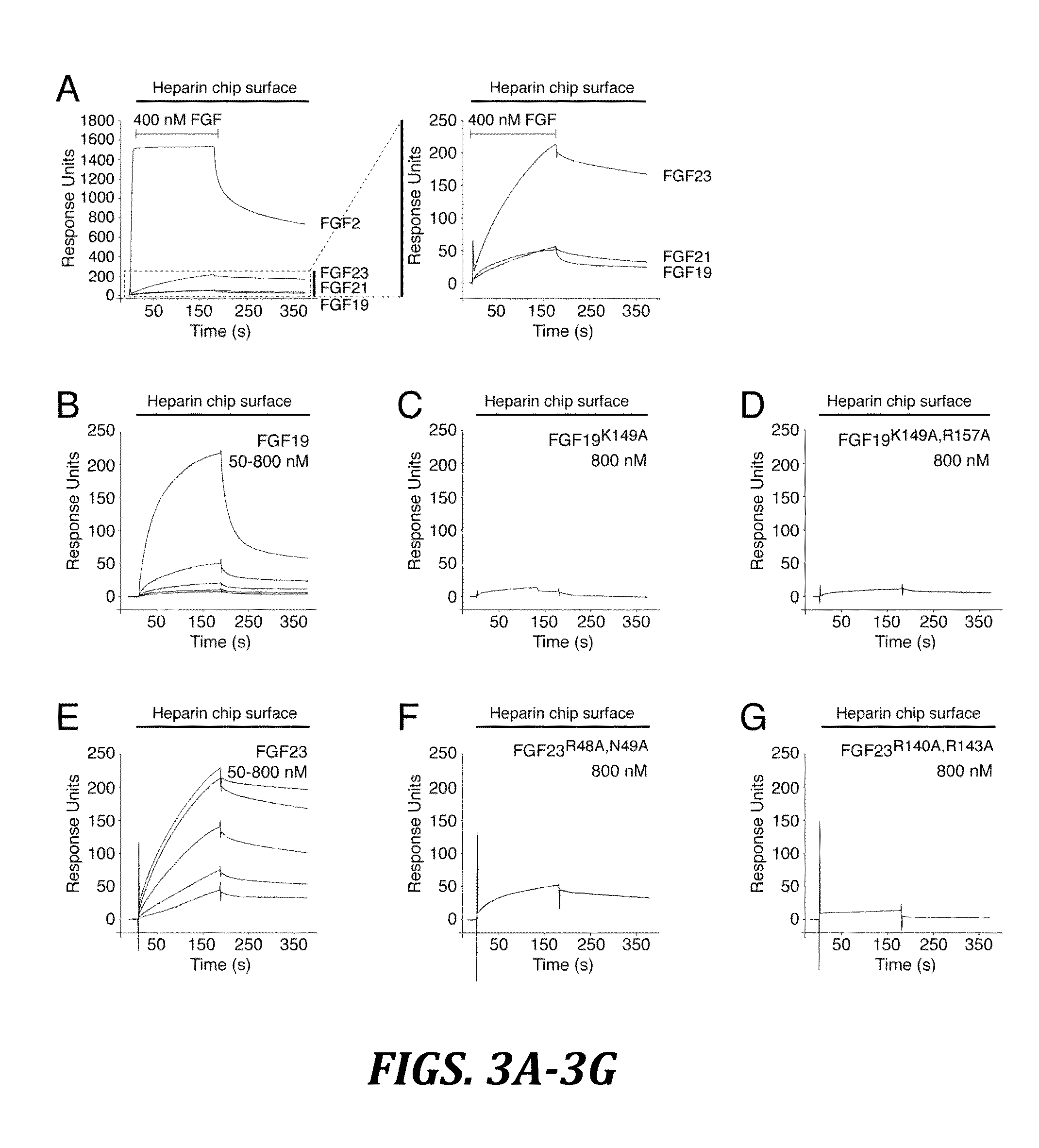
The present invention relates to a chimeric protein that includes an N-terminus coupled to a C-terminus, where the N-terminus includes a portion of a paracrine fibroblast growth factor (“FGF”) and the C-terminus includes a C-terminal portion of an FGF19 molecule. The portion of the paracrine FGF is modified to decrease binding affinity for heparin and / or heparan sulfate compared to the portion without the modification. The present invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions including chimeric proteins according to the present invention, methods for treating a subject suffering from diabetes, obesity, or metabolic syndrome, and methods of screening for compounds with enhanced binding affinity for the βKlotho-FGF receptor complex involving the use of chimeric proteins of the present invention.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES +2
Method for stimulating angiogenesis and wound healing
InactiveUS20070141101A1Effective combinationPromote angiogenesisPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsWound healingCell-Extracellular Matrix
A device comprising an extracellular matrix having an internal pH between 4.0 and 6.0 is discussed. This matrix contains heparin or a heparin-related compound such as heparan sulfate. Preferably the matrix also contains fibronectin or a fragment thereof. The matrix will bind to a protein having a pH dependent binding to heparin such as VEGF, preferably VEGF 121 or VEGF 165. The device will release the protein as the pH increases to physiological pH, such as 7.0 to 7.5. The device can be used to deliver a drug to a specific site. For example, with VEGF to a site in need of angiogenesis.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Method for removing cytokines from blood with surface immobilized polysaccharides
ActiveUS8758286B2Lessen and eliminate spreadAntibacterial agentsSalicyclic acid active ingredientsPorous substratePolysaccharide
The present invention is directed to a method for removing cytokines and / or pathogens from blood or blood serum (blood) by contacting the blood with a solid, essentially non micro-porous substrate which has been surface treated with heparin, heparan sulfate and / or other molecules or chemical groups (the adsorbent media or media) having a binding affinity for the cytokine or pathogen(s) to be removed (the adsorbates), and wherein the size of the interstitial channels within said media is balanced with the amount of media surface area and the surface concentration of binding sites on the media in order to provide adequate adsorptive capacity while also allowing relatively high flow rates of blood through the adsorbent media.
Owner:EXTHERA MEDICAL
Stem cells
InactiveUS20090148420A1Culture is increasedHigh cell proliferation rateBiocideOrganic active ingredientsHeparan sulfateMolecular biology
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
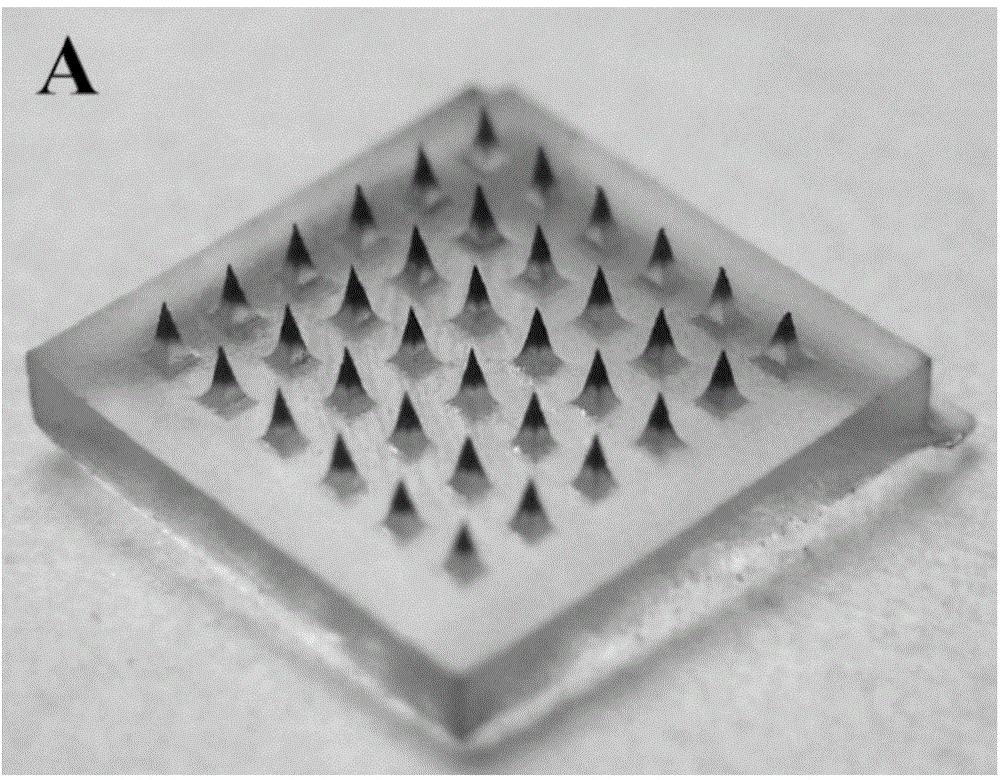
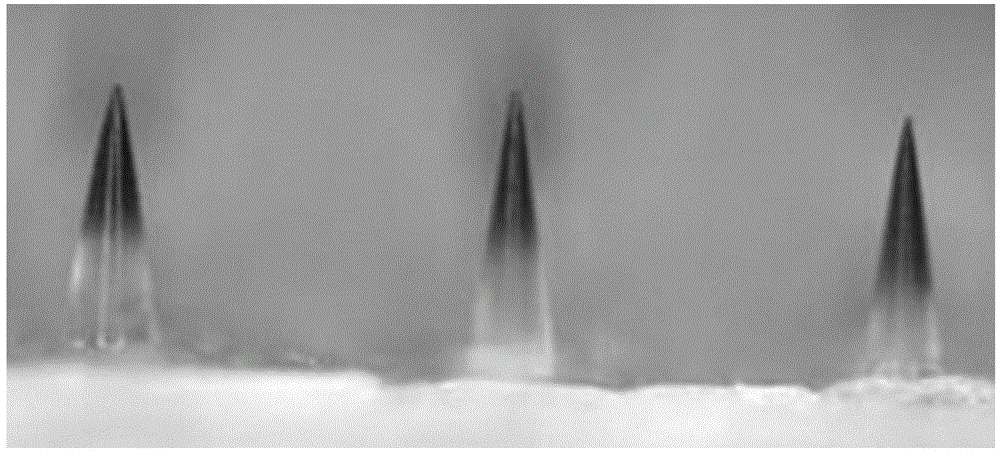
Autolytic microneedle transdermal patch and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105311000AImproving immunogenicitySolve the problem that it is difficult to induce Th1 type cellular immunityPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsImmunological disordersTransdermal patchIntramuscular injection
The invention belongs to an autolytic microneedle in the technical field of transdermal drug delivery and especially relates to an autolytic microneedle transdermal patch and a preparation method thereof. In the invention, endogenic oligomerized hyaluronic acid and / or low-molecular-weight heparan sulfate are employed as a microneedle substrate material and a vaccine adjuvant at the same time to prepare the autolytic microneedle in which a vaccine is loaded, thereby preparing the autolytic microneedle transdermal patch in the invention. The autolytic microneedle transdermal patch can achieve effective transcutaneous immune of the vaccine and enhance humoral immune response of the vaccine. Compared with intramuscular injection immune and other autolytic microneedle transcutaneous immune in the prior art, the autolytic microneedle transdermal patch can significantly enhance cellullar immunologic response of the vaccine.
Owner:BEIJING CAS MICRONEEDLE TECH LTD
Human monoclonal antibodies specific for glypican-3 and use thereof
ActiveCN103596985AAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBiological material analysisLymphatic SpreadImmunglobulin e
Described herein is the identification of human monoclonal antibodies that bind GPC3 or heparan sulfate (HS) chains on GPC3 with high affinity. The antibodies described herein are capable of inhibiting HCC cell growth and migration. Provided are human monoclonal antibodies specific for GPC3 or HS chains on GPC3, including immunoglobulin molecules, such as IgG antibodies, as well as antibody fragments, such as single-domain VH antibodies or single chain variable fragments (scFv). Further provided are compositions including the antibodies that bind GPC3 or HS chains on GPC3, nucleic acid molecules encoding these antibodies, expression vectors comprising the nucleic acids, and isolated host cells that express the nucleic acids. Methods of treating cancer and / or inhibiting tumor growth or metastasis are also provided. Further provided are methods of detecting cancer in a subject and confirming a diagnosis of cancer in a subject.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
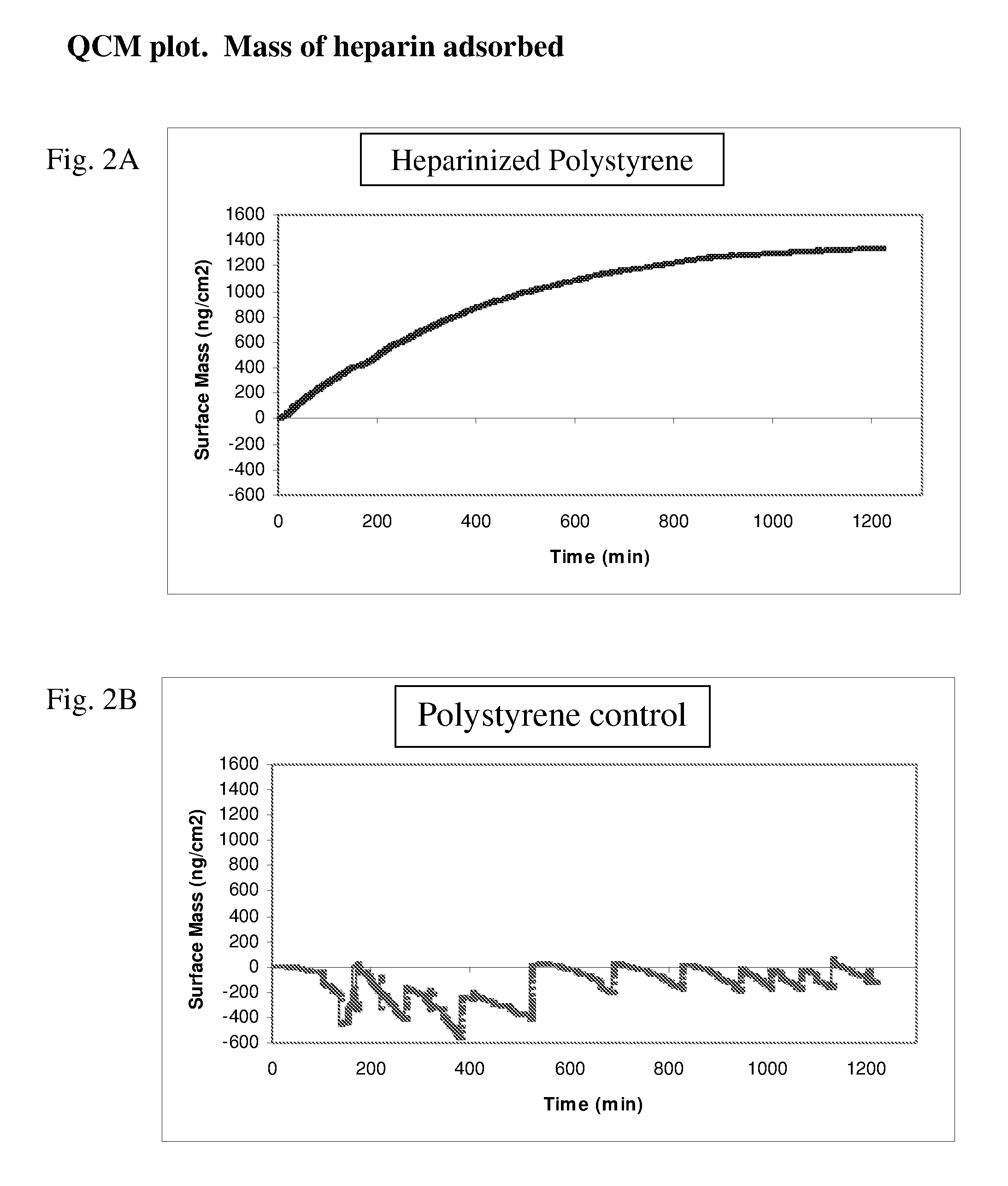
Heparin-binding protein modified with heparan sulfate sugar chains, process for producing the same and pharmaceutical compositions containing the same
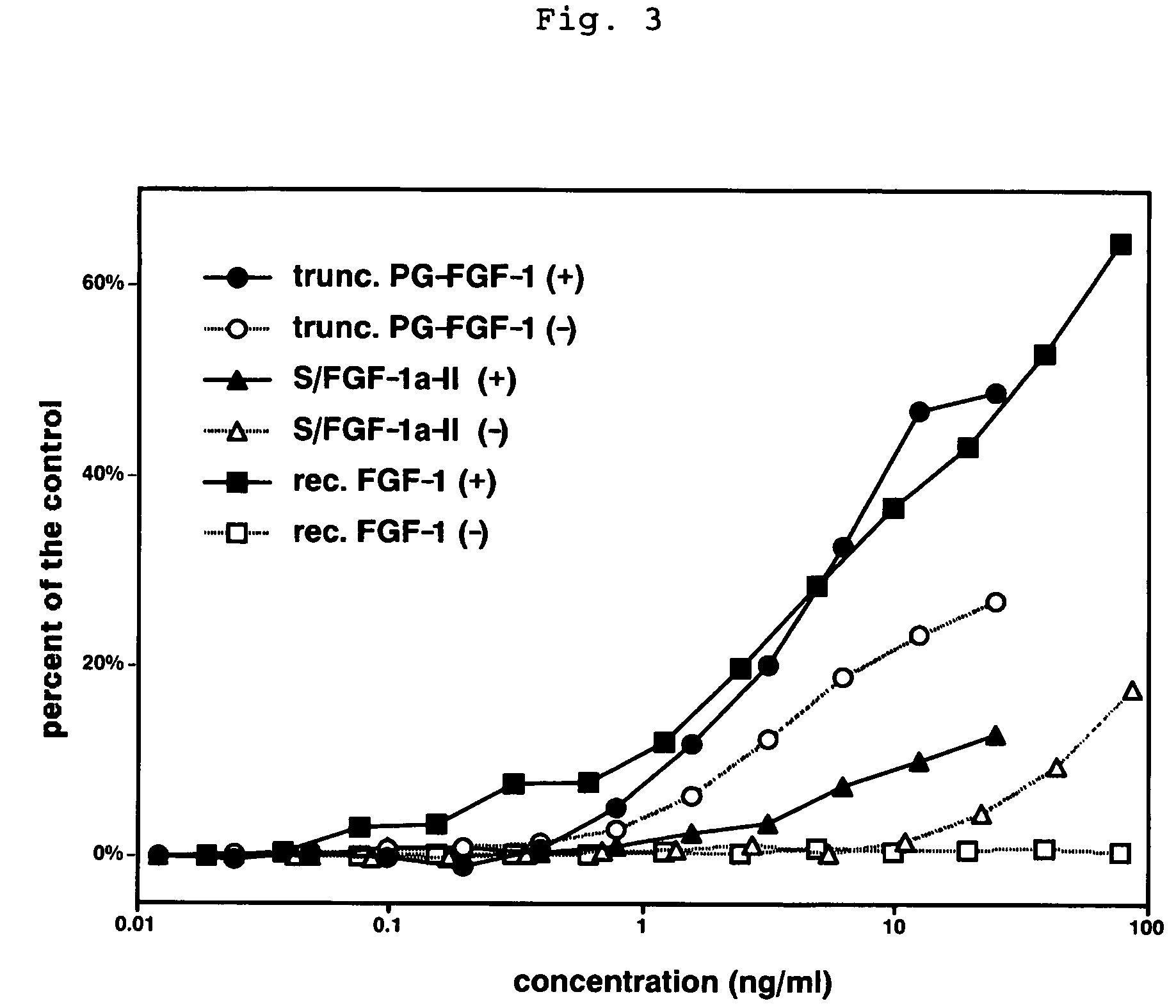
A heparin-binding protein having covalently bonded heparan sulfate sugar chains within its molecule is produced by ligating a cDNA encoding a peptide which can be modified with heparan sulfate sugar chains selectively to a cDNA encoding a heparin-binding protein and producing in an animal cell the gene product of the resultant ligated cDNA. This heparan sulfate sugar chain-modified heparin-binding protein is functionalized by covalently bonding thereto glycosaminoglycan sugar chains containing little chondroitin sulfate. For example, this heparin-binding protein is excellent in stabilities, such as thermostability, acid resistance, alkali resistance and in vivo stability. Further, the heparan sulfate sugar chain-modified heparin-binding protein is effective in cell proliferation and tissue regeneration, and has effect of regulating the physiological functions of FGFs. Thus, this heparin-binding protein is extremely useful as a medicine for preventing or treating various FGF-related diseases.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Chimeric fibroblast growth factor 19 proteins and methods of use
The present invention relates to a chimeric protein that includes an N-terminus coupled to a C-terminus, where the N-terminus includes a portion of a paracrine fibroblast growth factor (“FGF”) and the C-terminus includes a C-terminal portion of an FGF19 molecule. The portion of the paracrine FGF is modified to decrease binding affinity for heparin and / or heparan sulfate compared to the portion without the modification. The present invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions including chimeric proteins according to the present invention, methods for treating a subject suffering from diabetes, obesity, or metabolic syndrome, and methods of screening for compounds with enhanced binding affinity for the βKlotho-FGF receptor complex involving the use of chimeric proteins of the present invention.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Use of heparin and carbohydrates to treat cancer
ActiveUS20150111849A1Reduce flow rateEffective combinationOrganic active ingredientsHaemofiltrationPorous substrateDiffusion transport
The method is described as the removal of mediators that contribute to the pathogenesis of cancer from blood by contacting the blood with a solid, essentially non-micro-porous substrate which has been surface treated with heparin, heparan sulfate and, optionally, other molecules or chemical groups (the adsorbent media or media) having a binding affinity to the mediator, and wherein the size of the interstitial channels within said substrate are balanced with the amount of interstitial substrate surface area such that high flow rates of blood past said substrate creates a flow transport that is characterized by convection transport more than Brownian diffusion transport.
Owner:EXTHERA MEDICAL
Method for removing bacteria from blood using high flow rate
InactiveUS20170035956A1Reduce bacterial loadShorten the construction periodOther blood circulation devicesOther chemical processesHeparan sulfateGram-positive bacterium
The present invention provides methods for removing a significant amount of bacteria (e.g., gram-negative bacteria and gram-positive bacteria, including bacteria with no or low affinity for heparan sulfate) from whole blood, serum or plasma using an adsorption media. The method can be used in extracorporeal treatments involving high volumetric flow rates and high linear flow rates.
Owner:EXTHERA MEDICAL
Lentiviral Vectors Pseudotyped with a Sindbis Virus Envelope Glycoprotein
ActiveUS20120039932A1Promote infectionSsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsDendritic cellSindbis virus
Lentiviral vector particles comprising a Sindbis virus E2 glycoprotein variant and a lentiviral vector genome comprising a sequence of interest are provided. A lentiviral vector particle comprising: (a) an envelope comprising a Sindbis virus E2 glycoprotein variant; and (b) a lentiviral vector genome comprising a sequence of interest; wherein the E2 glycoprotein variant facilitates infection of dendritic cells by the lentiviral vector particle, and wherein the E2 glycoprotein variant has reduced binding to heparan sulfate compared to a reference sequence (HR strain).
Owner:IMMUNE DESIGN CORP
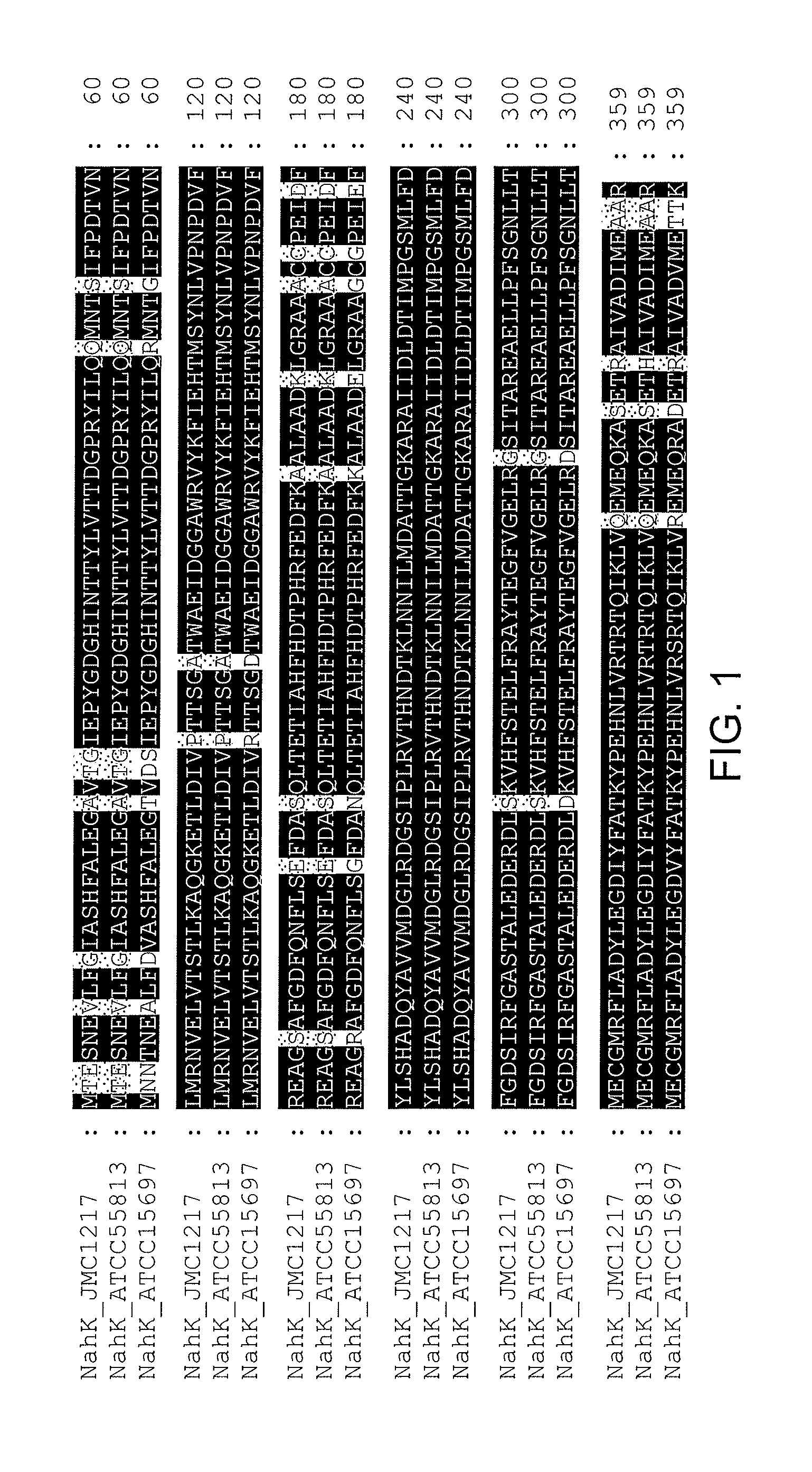
Method for separating and purifying heparin sodium and heparan sulfate from heparin byproducts
ActiveCN102911290AHigh purityEfficient removalOrganic active ingredientsBlood disorderMaterial resourcesIon-exchange resin
The invention discloses a method for separating and purifying heparin sodium and heparan sulfate from heparin byproducts. The method comprises the steps of dissolving raw heparin byproducts, adding potassium acetate to precipitate and separate heparin sodium, adding potassium acetate to precipitate heparin sodium after precipitating and dissolving heparin sodium, collecting a precipitate, dissolving and then conducting fractional precipitation repeatedly with anhydrous alcohol to prepare the heparin sodium with a higher purity, adding a benedict reagent and a saturated sodium hydroxide solution to supernate, centrifuging to obtain a solution containing the heparan sulfate, removing copper ions with a decoppering agent, adding active carbon to absorb the precipitate, decolorizing and filtering, and then absorbing and eluting with anion exchange resin to obtain the high-purity heparan sulfate by separation. According to the method, the high-purity heparin sodium and heparan sulfate can be separated again from the byproducts used for producing the heparin sodium, so that financial resources and material resources required for storing or discarding a large number of heparin byproducts can be saved, wastes can be changed into valuables, the byproducts are recycled, the cost is saved greatly, and a value is created.
Owner:NANJING KING FRIEND BIOCHEM PHARMA CO LTD +1
Gelatin-chitosan-hyaluronic acid-heparan sulfate composite three-dimensional stent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101920045AEvenly distributedProliferation and growth are in good conditionProsthesisFreeze-dryingIn vivo
The invention relates to a gelatin-chitosan-hyaluronic acid-heparan sulfate composite three-dimensional stent and a preparation method thereof. The gelatin-chitosan-hyaluronic acid-heparan sulfate porous three-dimensional composite stent is prepared by mixing gelatin, chitosan, hyaluronic acid and heparan sulfate in different ratios to obtain mixtures at different concentrations and freeze-dryingthe mixtures. The pore diameter, porosity, degradation, water absorption and the like of the stent can be regulated and controlled through each component content and freeze drying condition and can meet the basic requirement of a stent material. The stent can be used for the study of the growth, propagation and differentiation of NS / PCs. Through the hyaluronic acid, cells are distributed in the stent uniformly, and the heparan sulfate can bond growth factors, so that the growth propagation condition of the cells is similar to in-vivo condition; and the composite stent contains more functionalgroups such as amino groups, carboxyl groups, hydroxyl groups, sulfo groups, amide groups and the like, and is suitable for the conglutination, growth, propagation and the like of the cells.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Heparan sulfate proteoglycan composition and use thereof
The present invention relates to method for the preparation of glycosaminoglycan compositions, isolated glycosaminoglycan compositions obtainable therefrom, glycosaminoglycan compositions, kits and use thereof. More specifically, the present invention provides a method for isolating glycosaminoglycan compositions of the invention from human follicular fluid. The compositions, related methods and uses according to the present invention are useful in the treatment and / or prevention of thrombotic diseases, cell proliferation disorders, proteolysis and inflammation mediated cell invasion and infertility.
Owner:HOPITAUX UNIVS DE GENEVE +1
Carbohydrate composition with wound healing promoting effect and application of carbohydrate composition
ActiveCN108553481ARaw materials are easy to getEasy to manufactureOrganic active ingredientsDermatological disorderCarbohydrate compositionOligosaccharide
The invention provides a carbohydrate composition with a wound healing promoting effect and application of the carbohydrate composition. The carbohydrate composition contains at least five types of carbohydrate including carboxymethyl chitosan, rhizoma bletillae polysaccharides, fucoidan from fucus vesiculosus, heparan sulfate, chondroitin sulfate, oligosaccharides of hyaluronan and gulose aldehyde acid oligosaccharides. The carbohydrate composition and the application have the advantages that VEGFA (vascular endothelial growth factor A), FGF2 (fibroblast growth factor 2) and VE-cadherin protein mRNA (messenger ribonucleic acid) expression can be obviously improved by the carbohydrate composition, VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) secretion and skin fibroblast (HSF) and human immortalized keratinocyte (HaCaT) proliferation can be obviously promoted by the carbohydrate composition, and the obvious wound healing promoting effect can be realized by the carbohydrate composition; raw materials required by the carbohydrate composition are easily available, composition methods for the carbohydrate composition are simple, the carbohydrate composition is low in cost, easy to industrialize and wide in application range, and the like.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Pharmaceutical compositions comprising anti-inflammatory quinazolinecarboxamide derivatives
InactiveUS20070191400A1Avoid interactionOrganic active ingredientsBiocideAutoimmune conditionAutoimmune disease
The present invention provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising quinazolinecarboxamide derivative, and certain novel quinazolinecarboxamide derivatives capable of inhibiting heparan sulfate-glycosaminoglycan (HS-GAGs) interactions with L-selectin, and useful in the prevention or treatment of various diseases, disorders and conditions mediated by HS-GAGs, particularly inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, viral diseases, cancer, and amyloid disorders.
Owner:RIMONYX PHARMA
Sulphated heparan sulfated for inhibiting cell proliferation
InactiveCN103288981AAvoid diversionPrevent relapseOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsEthanol precipitationTrimethyloxamine
A heparan sulfated derivative is prepared from heparan sulfated by sulphating. A preparation method comprises: swelling heparan sulfated by anhydrous dimethyl formamide, adding a sulfur trioxide-trimethylamine complex, heating for esterification, dissolving, dialyzing, freeze-drying precipitation components of the reactant by distilled water, then dissolving by sodium chloride solution, precipitating by ethanol, centrifuging, removing a supernatant, drying, and then obtaining sulphated heparan sulfated. The heparan sulfated derivative can inhibit activities of tumor cells and umbilical vein endothelial cell proliferation.
Owner:SHENZHEN HEPALINK PHARMA GRP CO LTD
Haparin-Binding Protein Modified with Heparan Sulfate Sugar Chains, Process for Producing the Same and Pharmaceutical Compositions Containing the Same
A heparin-binding protein having covalently bonded heparan sulfate sugar chains within its molecule is produced by ligating a cDNA encoding a peptide which can be modified with heparan sulfate sugar chains selectively to a cDNA encoding a heparin-binding protein and producing in an animal cell the gene product of the resultant ligated cDNA. This heparan sulfate sugar chain-modified heparin-binding protein is functionalized by covalently bonding thereto glycosaminoglycan sugar chains containing little chondroitin sulfate. For example, this heparin-binding protein is excellent in stabilities, such as thermostability, acid resistance, alkali resistance and in vivo stability. Further, the heparan sulfate sugar chain-modified heparin-binding protein is effective in cell proliferation and tissue regeneration, and has effect of regulating the physiological functions of FGFs. Thus, this heparin-binding protein is extremely useful as a medicine for preventing or treating various FGF-related diseases.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Method for removing bacteria from blood using high flow rate
The present invention provides methods for removing a significant amount of bacteria (e.g., gram-negative bacteria and gram-positive bacteria, including bacteria with no or low affinity for heparan sulfate) from whole blood, serum or plasma using an adsorption media. The method can be used in extracorporeal treatments involving high volumetric flow rates and high linear flow rates.
Owner:EXTHERA MEDICAL
Human monoclonal antibodies specific for glypican-3 and use thereof
ActiveUS20150368340A1Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsLymphatic SpreadAntibody fragments
Described herein is the identification of human monoclonal antibodies that bind GPC3 or heparan sulfate (HS) chains on GPC3 with high affinity. The antibodies described herein are capable of inhibiting HCC cell growth and migration. Provided are human monoclonal antibodies specific for GPC3 or HS chains on GPC3, including immunoglobulin molecules, such as IgG antibodies, as well as antibody fragments, such as single-domain VH antibodies or single chain variable fragments (scFv). Further provided are compositions including the antibodies that bind GPC3 or HS chains on GPC3, nucleic acid molecules encoding these antibodies, expression vectors comprising the nucleic acids, and isolated host cells that express the nucleic acids. Methods of treating cancer and / or inhibiting tumor growth or metastasis are also provided. Further provided are methods of detecting cancer in a subject and confirming a diagnosis of cancer in a subject.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Chemoenzymatic synthesis of heparin and heparan sulfate analogs
The present invention provides a one-pot multi-enzyme method for preparing UDP-sugars from simple sugar starting materials. The invention also provides a one-pot multi-enzyme method for preparing oligosaccharides from simple sugar starting materials.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Chimeric fibroblast growth factor 21 proteins and methods of use
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV +1
Neural Progenitor Cell Differentiation
ActiveUS20140271905A1Restore motor functionEffective amountNervous system cellsMammal material medical ingredientsDiseaseProgenitor
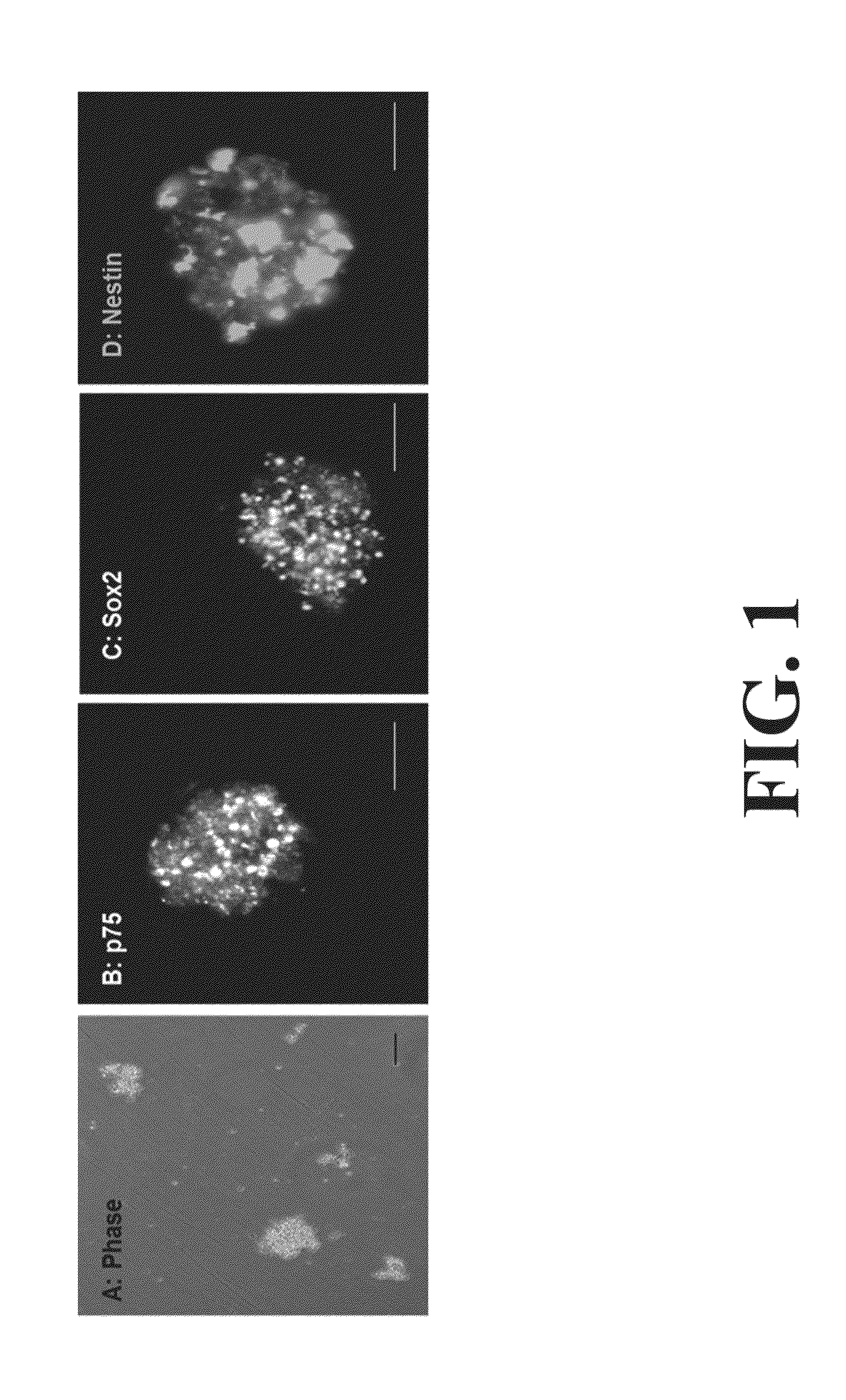
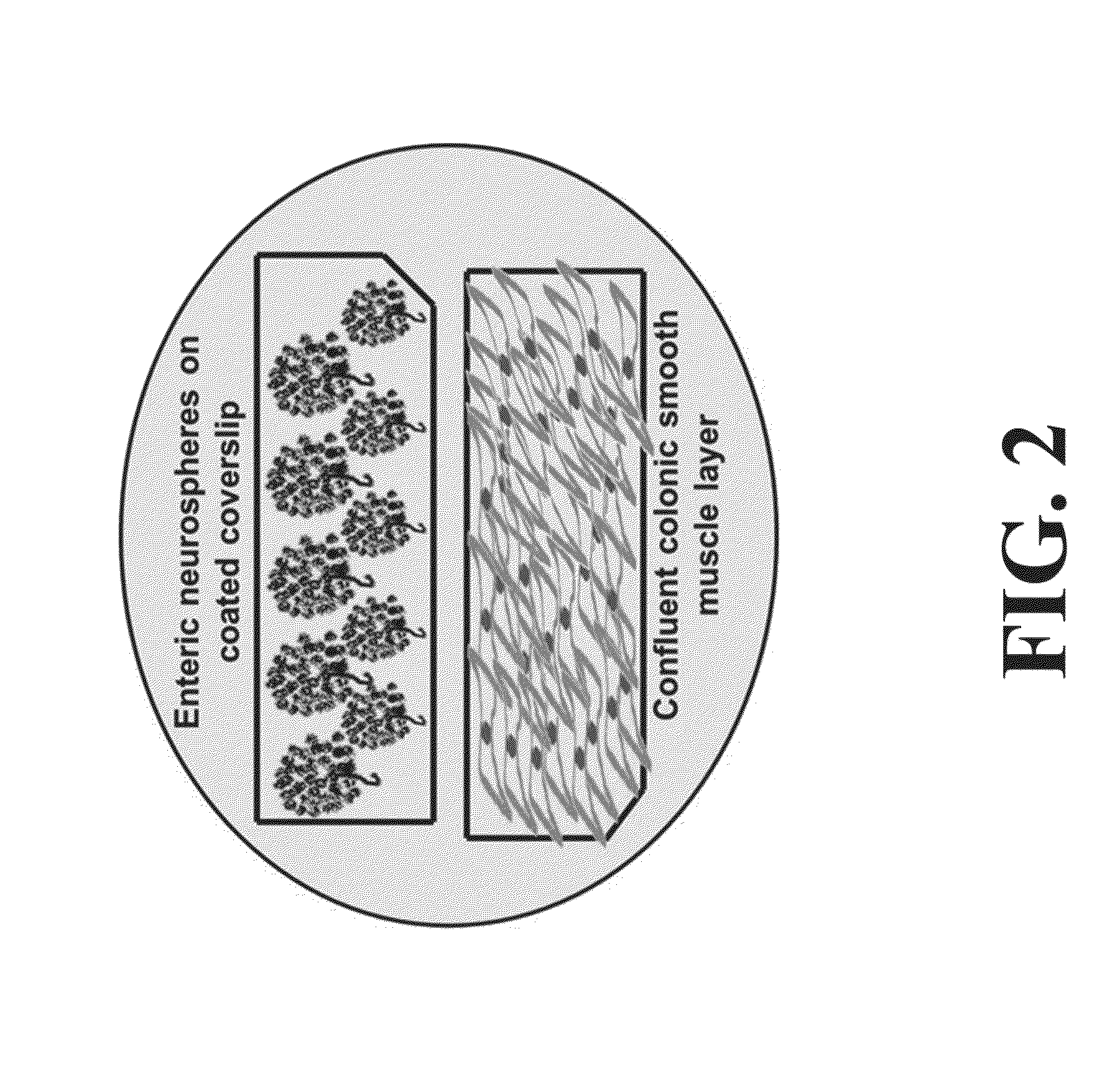
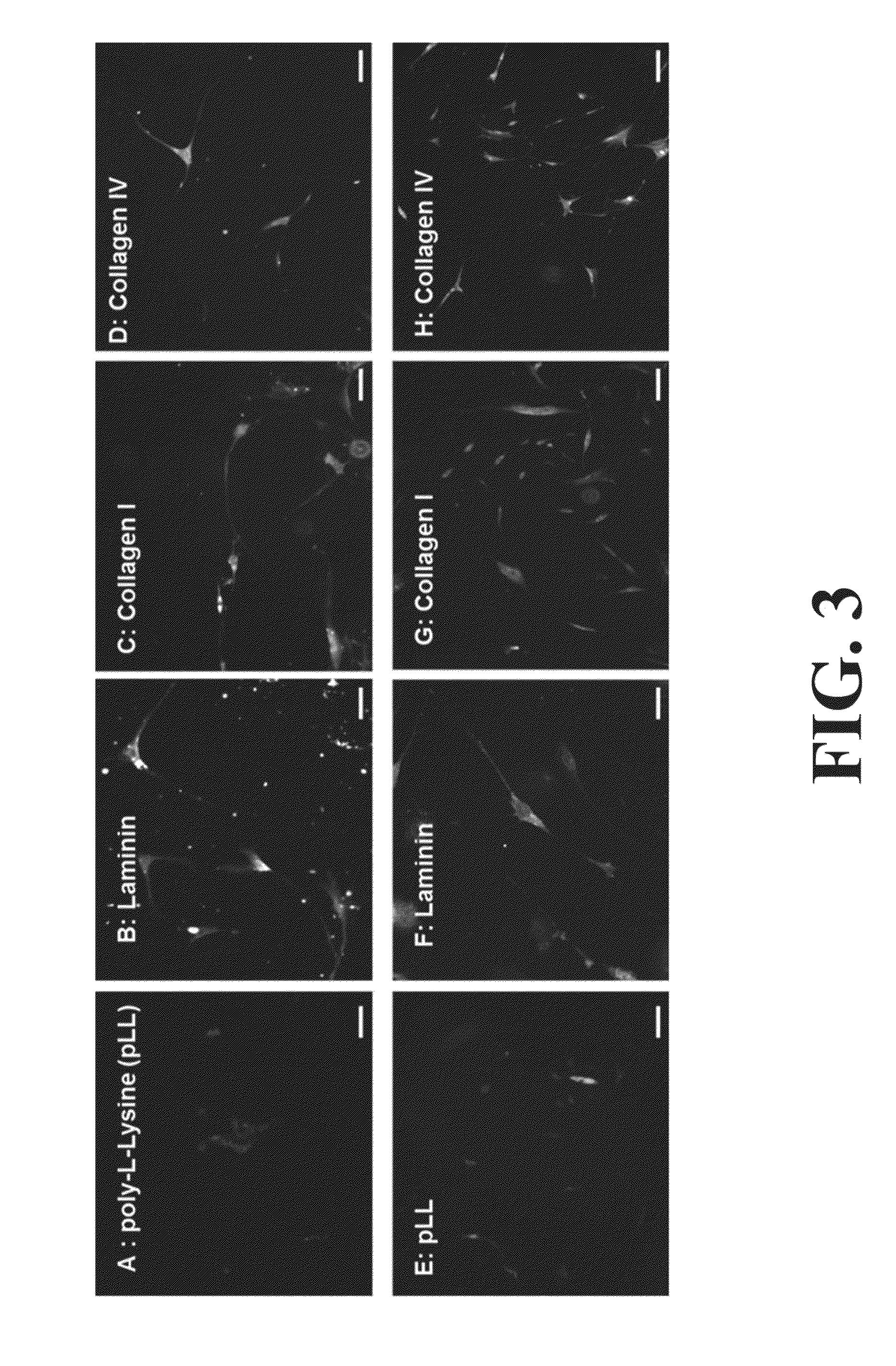
Differentiation and stability of neural stem cells can be enhanced by in vitro or in vivo culturing with one or more extracellular matrix (ECM) compositions, such as collagen I, IV, laminin and / or a heparan sulfate proteoglycan. In one aspect of the invention, adult mammalian enteric neuronal progenitor cells can be induced to differentiate on various substrates derived from components or combinations of neural ECM compositions. Collagen I and IV supported neuronal differentiation and extensive glial differentiation individually and in combination. Addition of laminin or heparan sulfate to collagen substrates unexpectedly improved neuronal differentiation, increasing neuron number, branching of neuronal processes, and initiation of neuronal network formation. In another aspect, neuronal subtype differentiation was affected by varying ECM compositions in hydrogels overlaid on intestinal smooth muscle sheets. The matrix compositions of the present invention can be used to tissue engineer transplantable innervated GI smooth muscle constructs to remedy aganglionic disorders.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
Multifunctional composite hydrogel for injection and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108295029AImprove stabilityImprove water retentionOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsCell-Extracellular MatrixBone tissue
The invention relates to multifunctional composite hydrogel for an injection and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of biological medicines. Such multifunctional composite hydrogelfor the injection, which is provided by the invention, is Col-HA-PVP (Collagen-Hyaluronic Acid-Polyvinyl Pyrrolidone)-Nanoparticles quaternary composite hydrogel which is formed by compositing collagen (Col), hyaluronic acid (HA), polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP) and poly(lactic-co-glycotic acid) (PLGA) clad heparan sulfate (HS) and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta), and the multifunctional composite hydrogel is used for highly simulating the composition and structure of an extracellular matrix (ECM), has better stability, water retention rate and mechanical performance, and meanwhile, can be used for promoting the regeneration and restoration of bone tissue.
Owner:无锡凯尔富医药科技有限公司
Methods of culturing mesenchymal stem cells
InactiveUS8287853B2Culture is increasedHigh rateOrganic active ingredientsBiocideMesenchymal stem cellHeparan sulfate
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Method for extracting high-purity heparan sulfate from heparan production wastes
The method discloses a method for extracting high-purity heparan sulfate from heparan production wastes, and aims at providing a method used for extracting purified heparan sulfate taking the heparanproduction wastes as raw material. The method has the advantages of low cost, convenient operation and easy industrial scaling. The method is characterized by comprising the steps that 1), the heparanproduction wastes are prepared into a solution; 2), acid is added to adjust the pH to 1.9-2.3, ethanol is added, and stirring, centrifugation and standing are conducted; 3), supernatant liquid is collected, aqueous alkali is added to adjust pH to 6-8, and water is added; 4), absorbent is added to the solution is step 3), and stirring is conducted until all mucopolysaccharide in the solution is absorbed by the absorbent; 5), the absorbent is collected and washed with clean water, a sodium chloride solution is added to conduct elution, elution liquid is collected after the elution is completed,and precipitant is added for precipitation; 6), precipitations are collected and dried; the method belongs to the field of mucopolysaccharide pharmaceuticals.
Owner:深圳市格利科生物科技有限公司
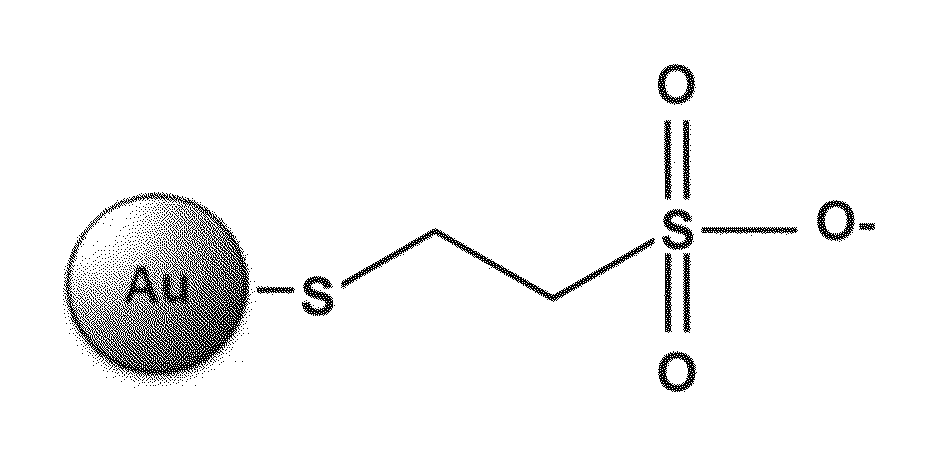
Pharmaceutical compositions comprising water-soluble sulfonate-protected nanoparticles and uses thereof
InactiveUS20120027809A1Inhibition is effectiveEffective preventionAntibacterial agentsPowder deliverySulfonateMicroorganism
The present invention provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising water-soluble sulfonate-protected nanoparticles, more particularly, pharmaceutical compositions comprising water-soluble sulfonate-protected silver or gold nanoparticles. The pharmaceutical compositions of the invention are useful in prevention or treatment of infections or conditions or disorders caused by microorganisms capable of binding to heparan sulfate, e.g., herpes simplex viruses.
Owner:BAR ILAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com