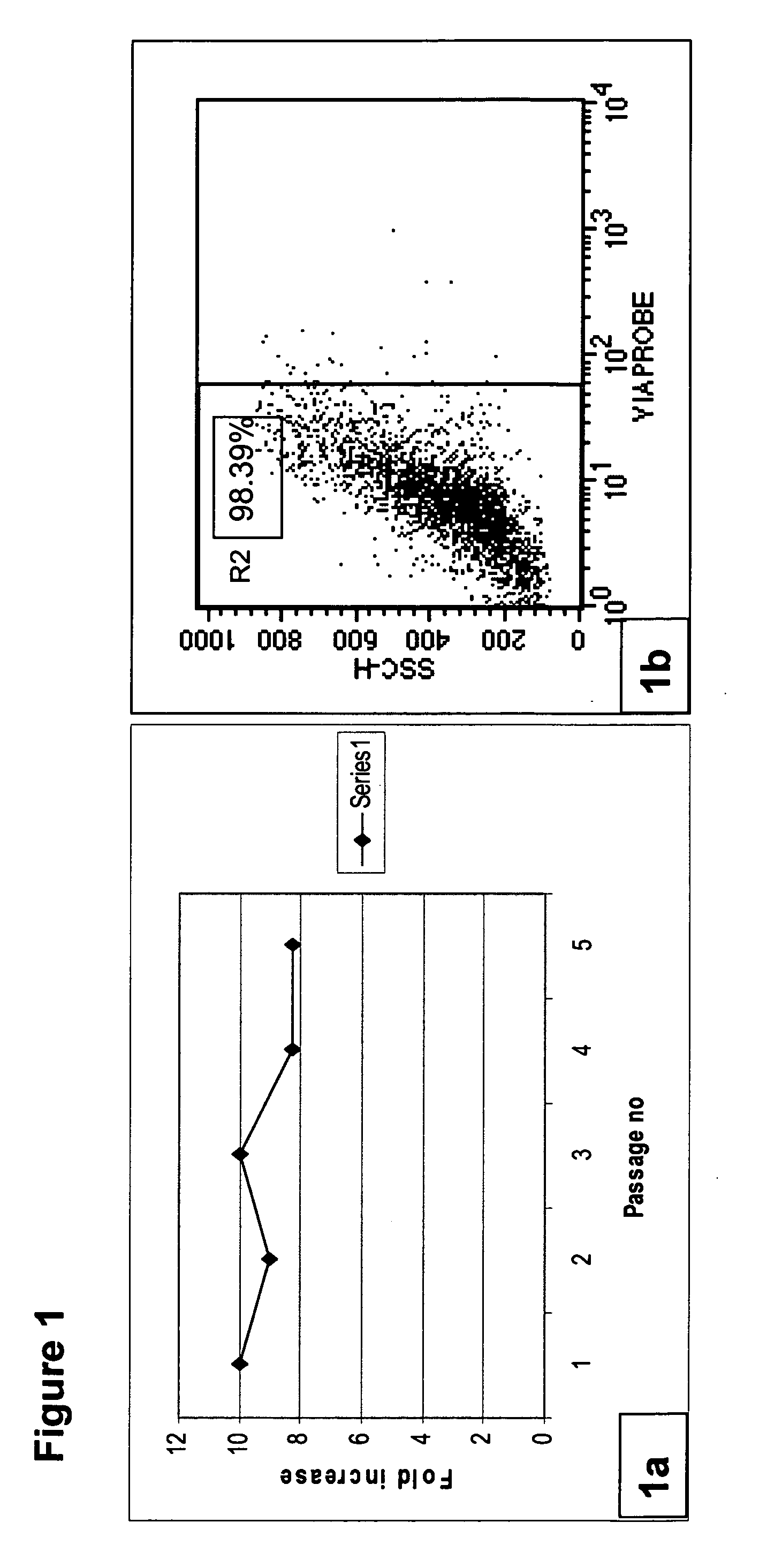
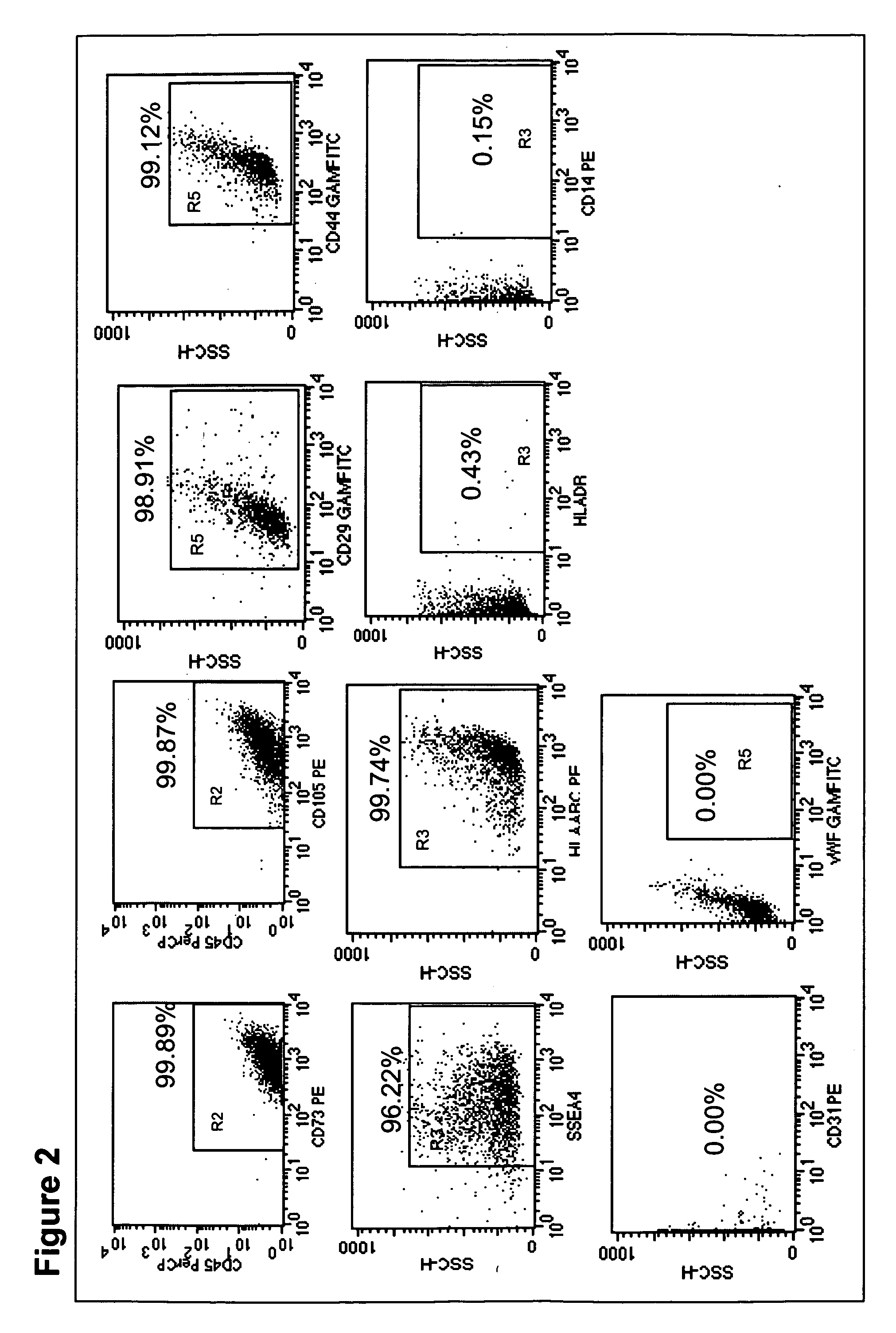
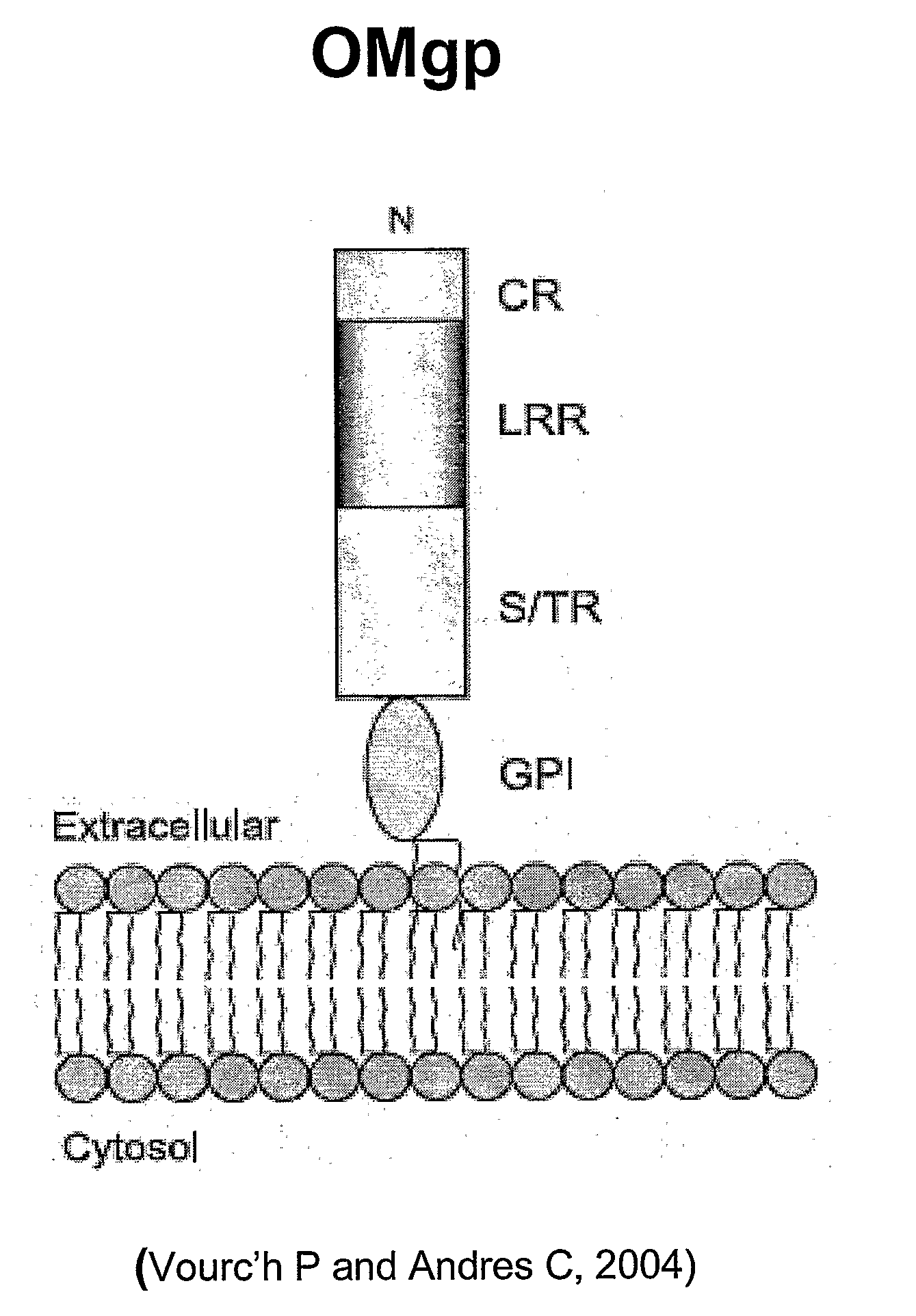
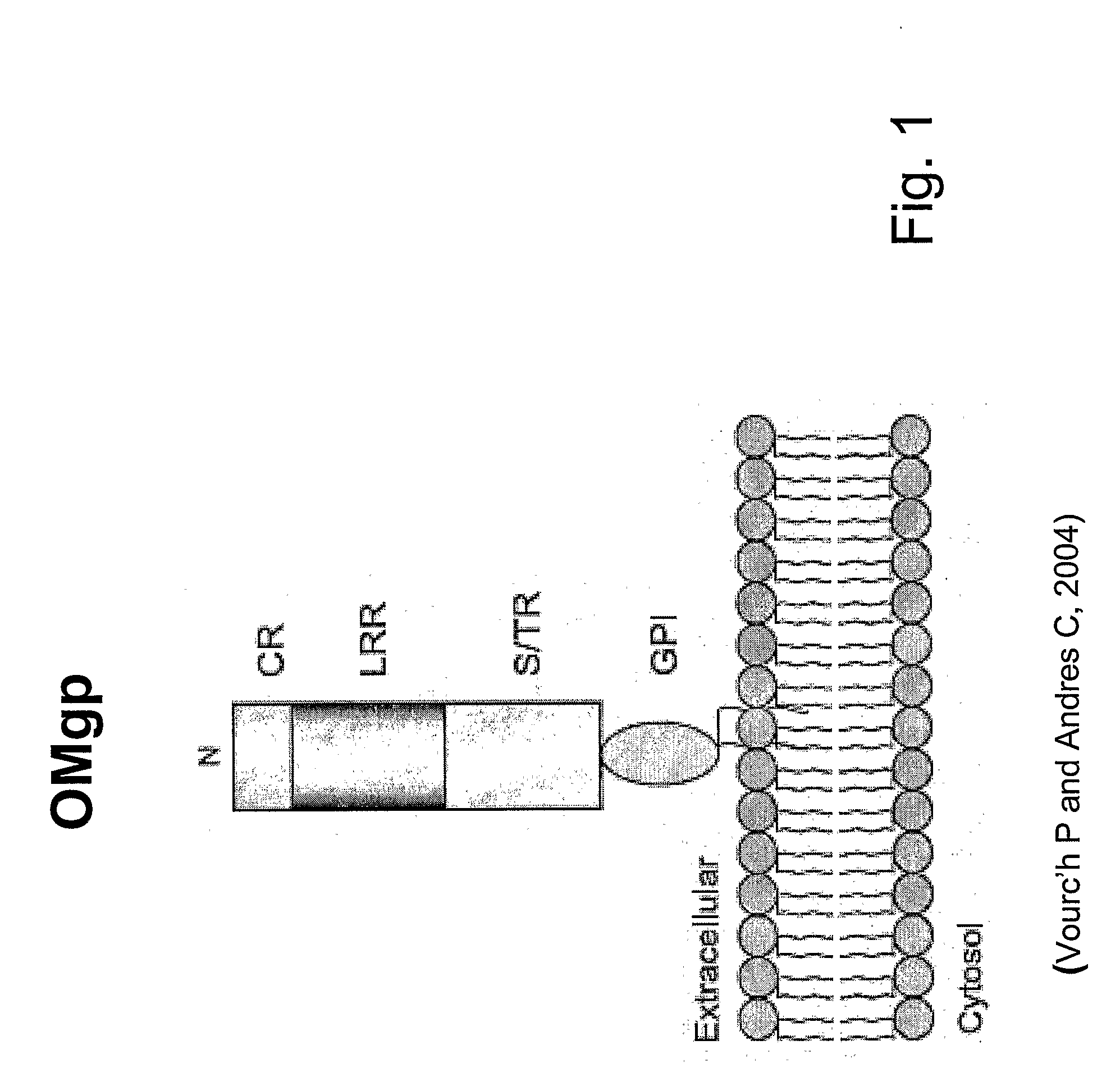
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
70 results about "Neuronal differentiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Neuronal Differentiation. Definition. The process whereby uncommitted neuronal precursor cells gradually accumulate gene products specific to, and required for, the eventual form and function of a specialized neuronal cell type.
Nerve Regeneration Promoting Agent
InactiveUS20100254951A1Promote differentiationIncrease the number ofBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
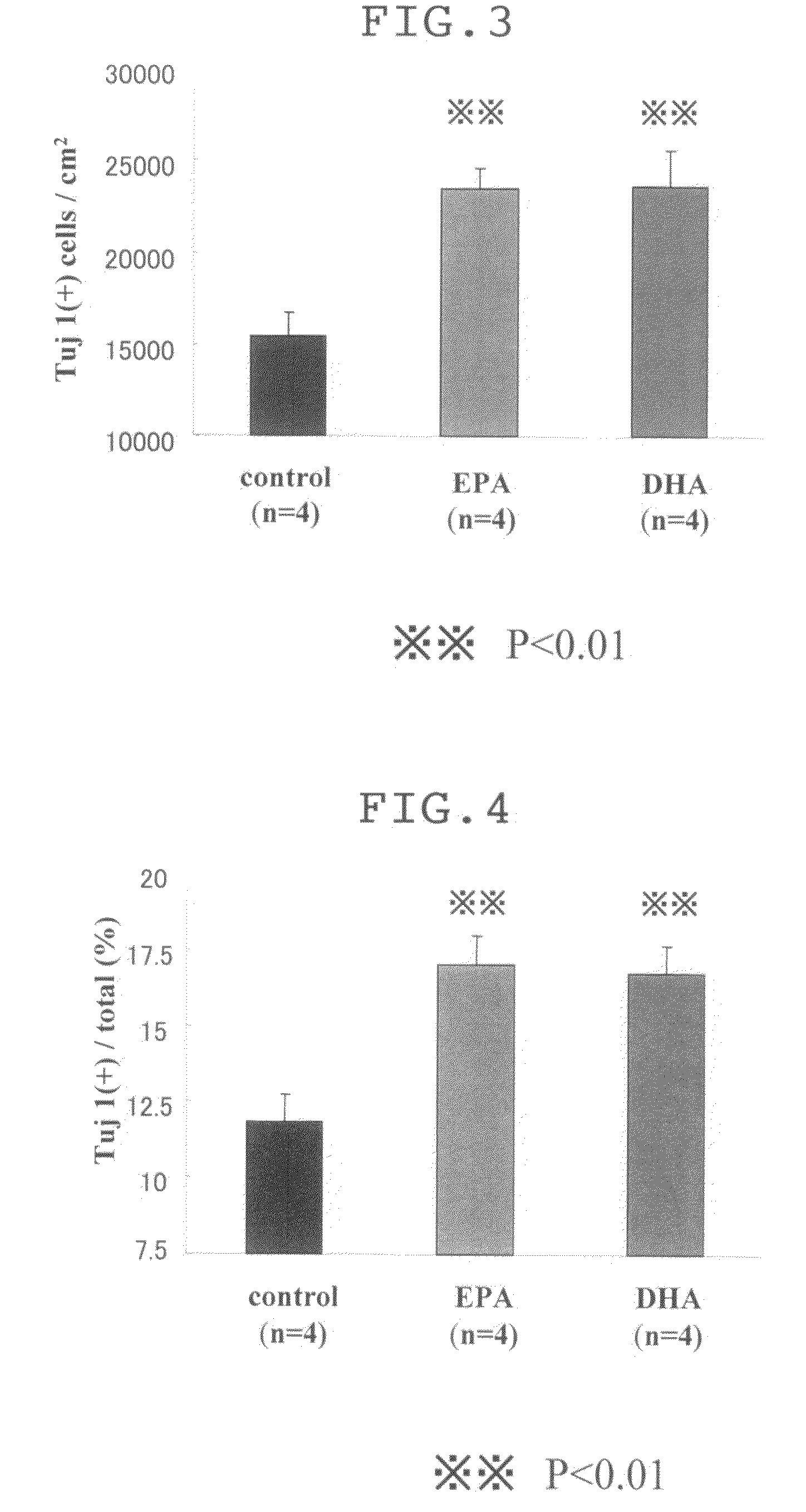
A neuronal differentiation promoting agent for neural stem cells comprising, as an active ingredient, at least one member selected from the group consisting of ω-3 unsaturated fatty acids and ω-6 unsaturated fatty acids having 18 to 22 carbon atoms, and derivatives thereof. The agent can be used for induction of differentiation of neural stem cells and is useful for treating and / or preventing a variety of neurological diseases, and in the fields of nerve transplantation and / or regenerative medicine for nerves.
Owner:MOCHIDA PHARM CO LTD +1
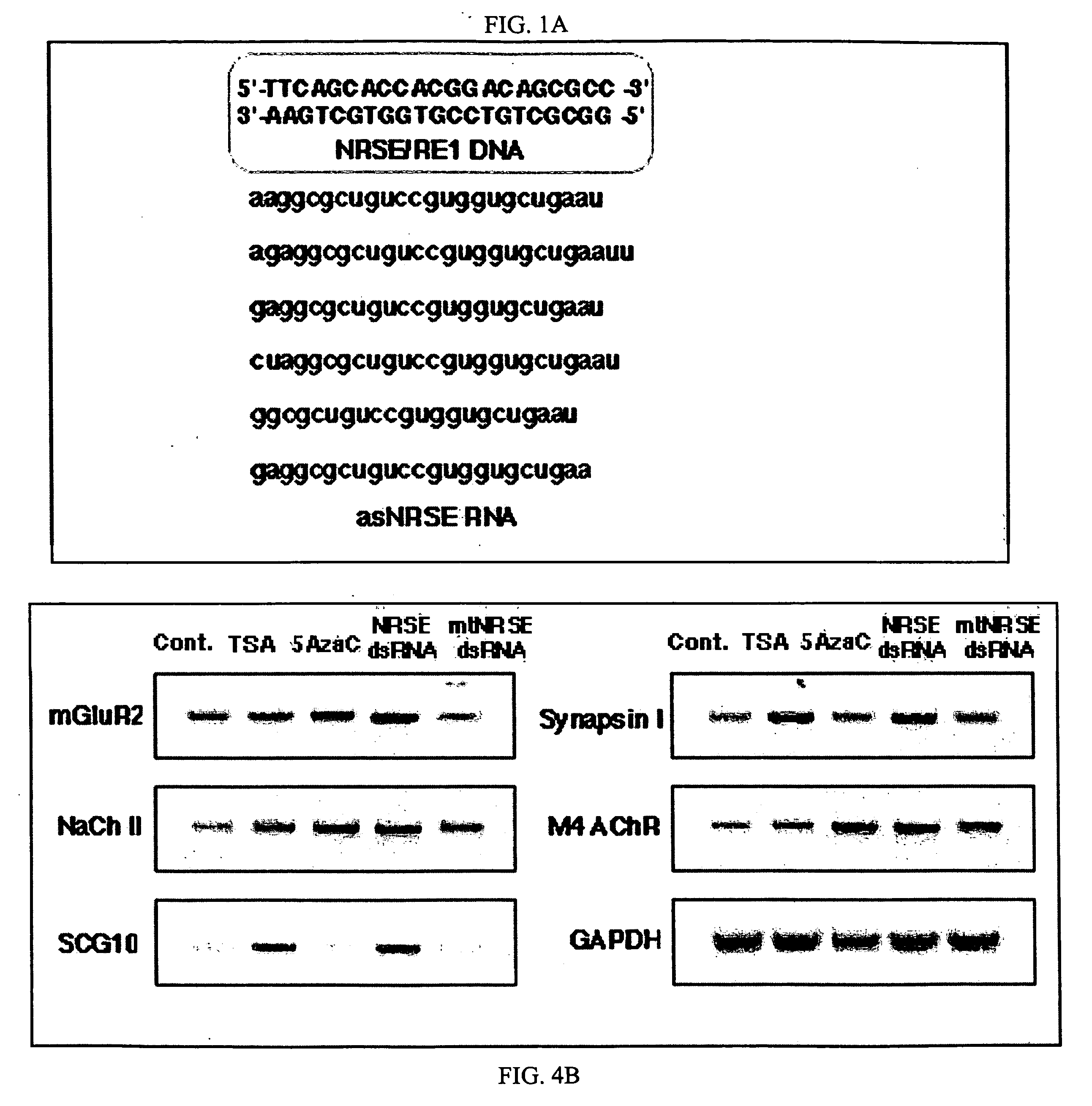
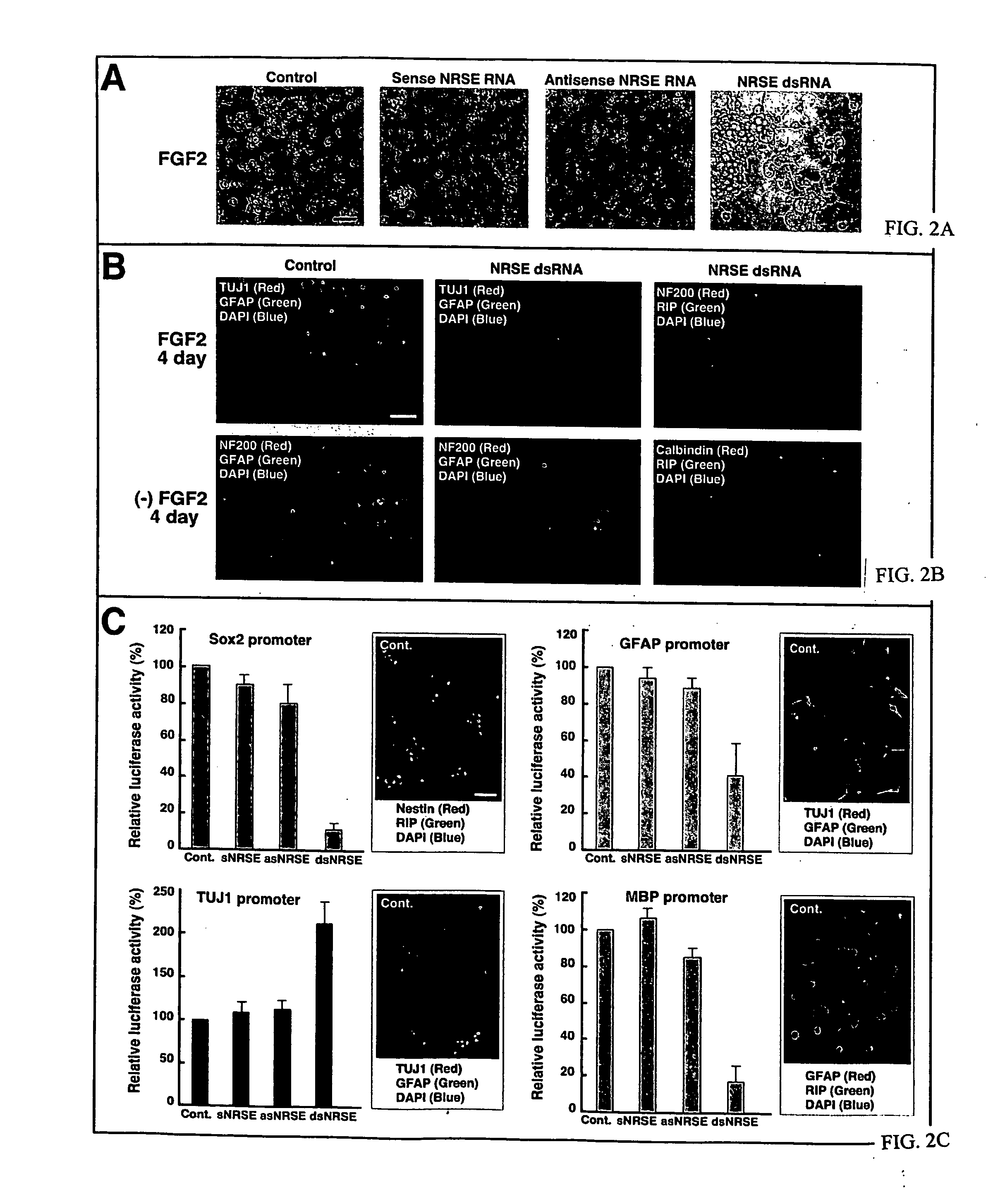
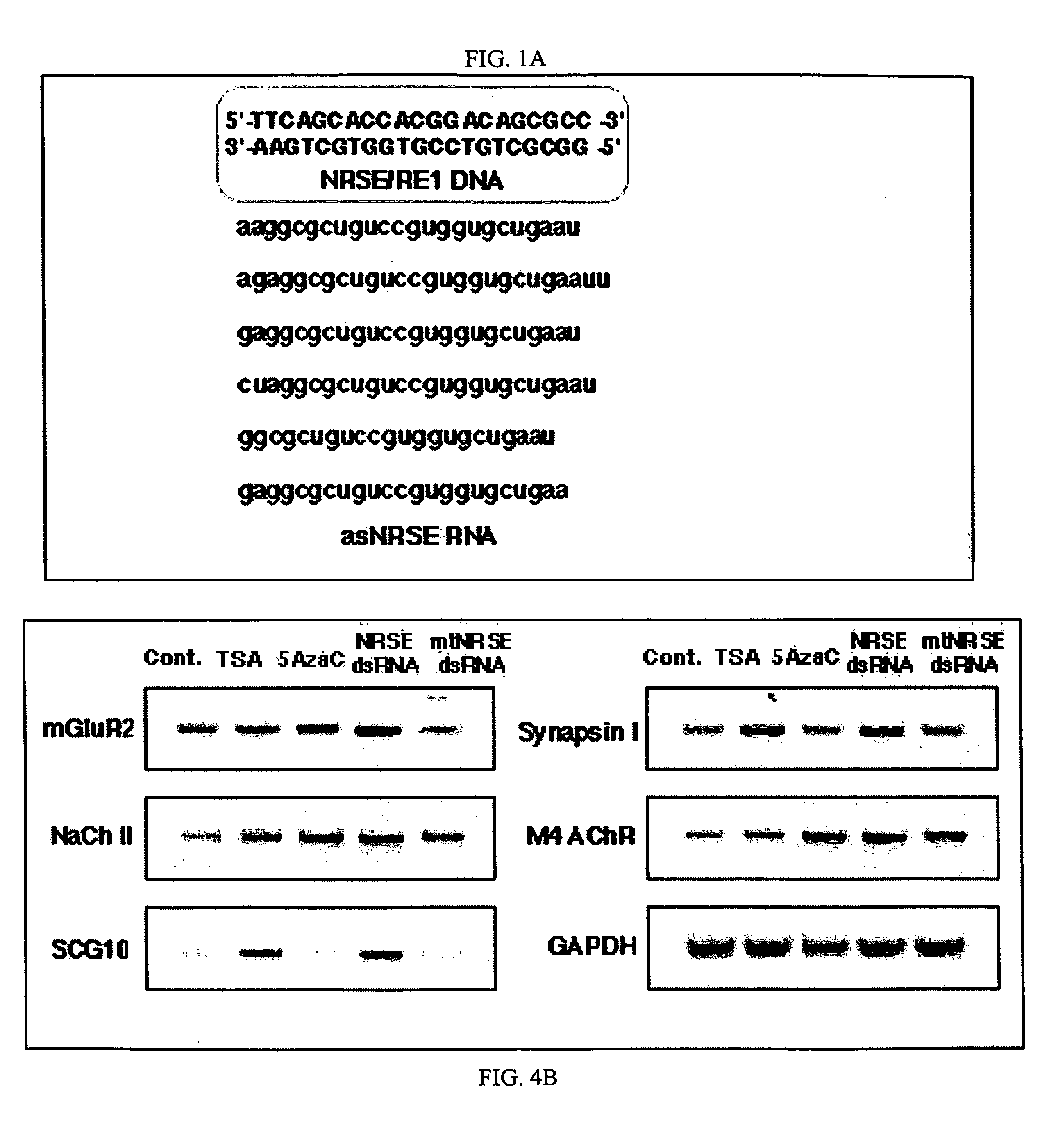
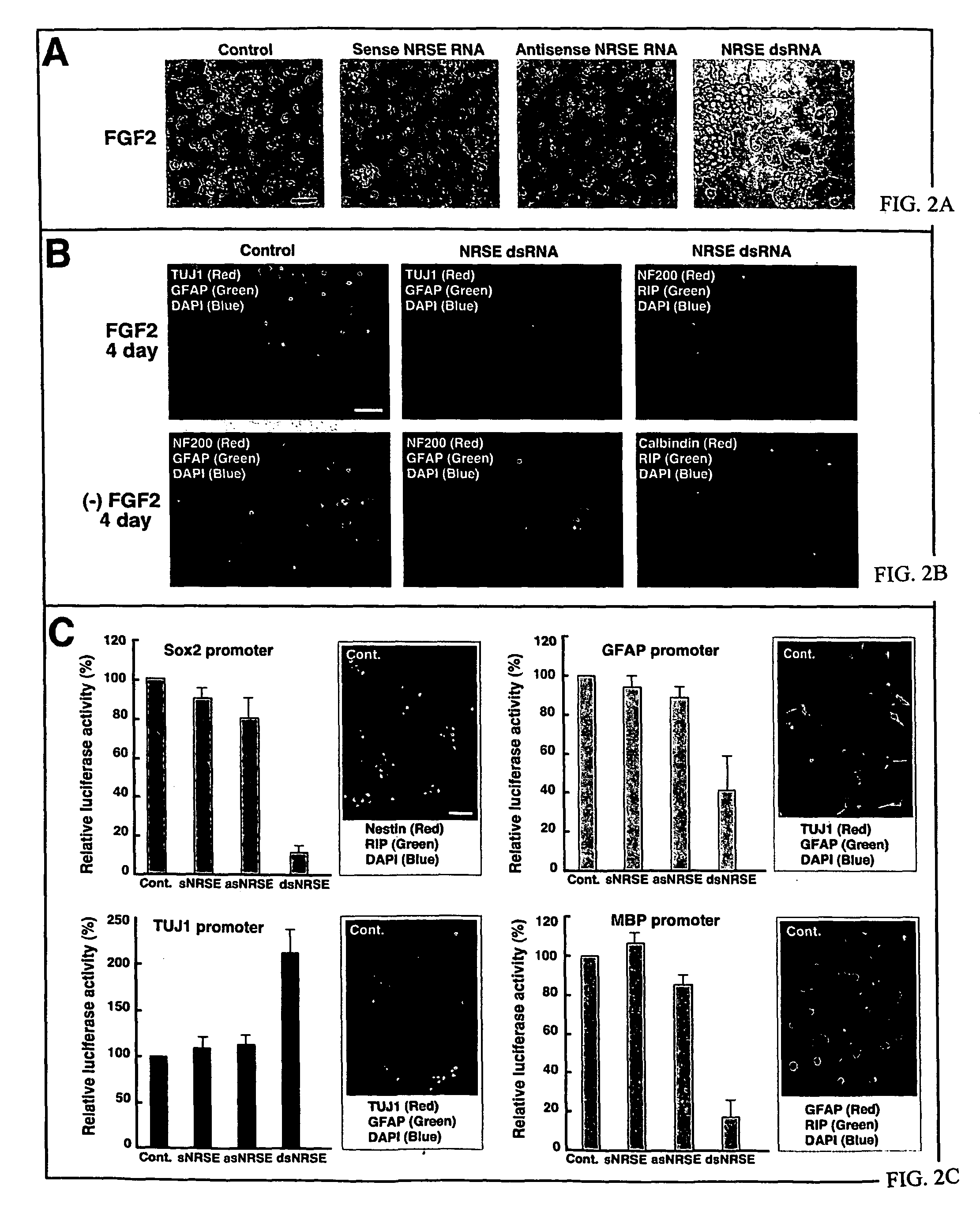
Transcriptional regulation of gene expression by small double-stranded modulatory RNA
The invention provides a method for modulating gene expression by contacting a cellular system with a double-stranded ribonucleic acid molecule capable of associating with a regulatory machinery that controls transcription of one or more genes, wherein the association results in altered expression of the one or more genes. The invention is further directed to method for directing the differentiation of neuronal stem cells into neurons by contacting a cellular system with a double-stranded ribonucleic acid molecule capable of associating with a regulatory machinery that controls transcription of one or more genes involved in neuronal differentiation and directing the transcription of the one or more genes. In related embodiments, the invention provides particular compositions of double-stranded ribonucleic acid molecules as well as therapeutic and screening applications of the invention.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
Method of inducing and maintaining neuronal cells
InactiveUS20080261879A1Avoid deathPrevent degenerationNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsGerm layerNeurulation
The present invention makes available a method for inducing neuronal differentiation and preventing the death or degeneration of neuronal cells both in vitro and in vivo. The subject method stems from the unexpected finding that, contrary to traditional understanding of neural induction, the default fate of ectodermal tissue is neuronal rather than mesodermal and / or epidermal. In particular, it has been discovered that preventing or antagonizing a signaling pathway in a cell for a growth factor of the TGF-β family can result in neuronal differentiation of that cell.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Chemical inducers of neurogenesis
InactiveUS20090036451A1Promotes and enhances well-beingReduce frequencyBiocideNervous disorderNervous systemNeurogenesis
The present invention relates to compounds and methods for inducing neuronal differentiation in normal neural stem cells and brain cancer stem cells. The methods may take place in vitro, such as in isolates from the adult mammalian brain, or in vivo. Compounds and methods described herein may find use in the treatment of neurodegenerative and psychiatric diseases, the repair and regeneration of the nervous system, and in treatment of neurologic malignancy.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Method of growing mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow
InactiveUS20090004661A1Function increaseGood potential sourceMicrobiological testing/measurementCulture processCord blood stem cellMesenchymal stem cell
The present invention provides a method for culturing mesenchymal stem cells using cord blood serum, for therapeutic purposes in regenerative medicine; and in particular the present invention provides for the use of these cells in the treatment of PD, and the present invention has provided proliferation and neuronal differentiation of the MSCs in a xenofree culture system for clinical applications in a simple two step protocol, and the in vivo functional efficacy was tested in Parkinson's animal model.
Owner:RELIANCE LIFE SCI PVT
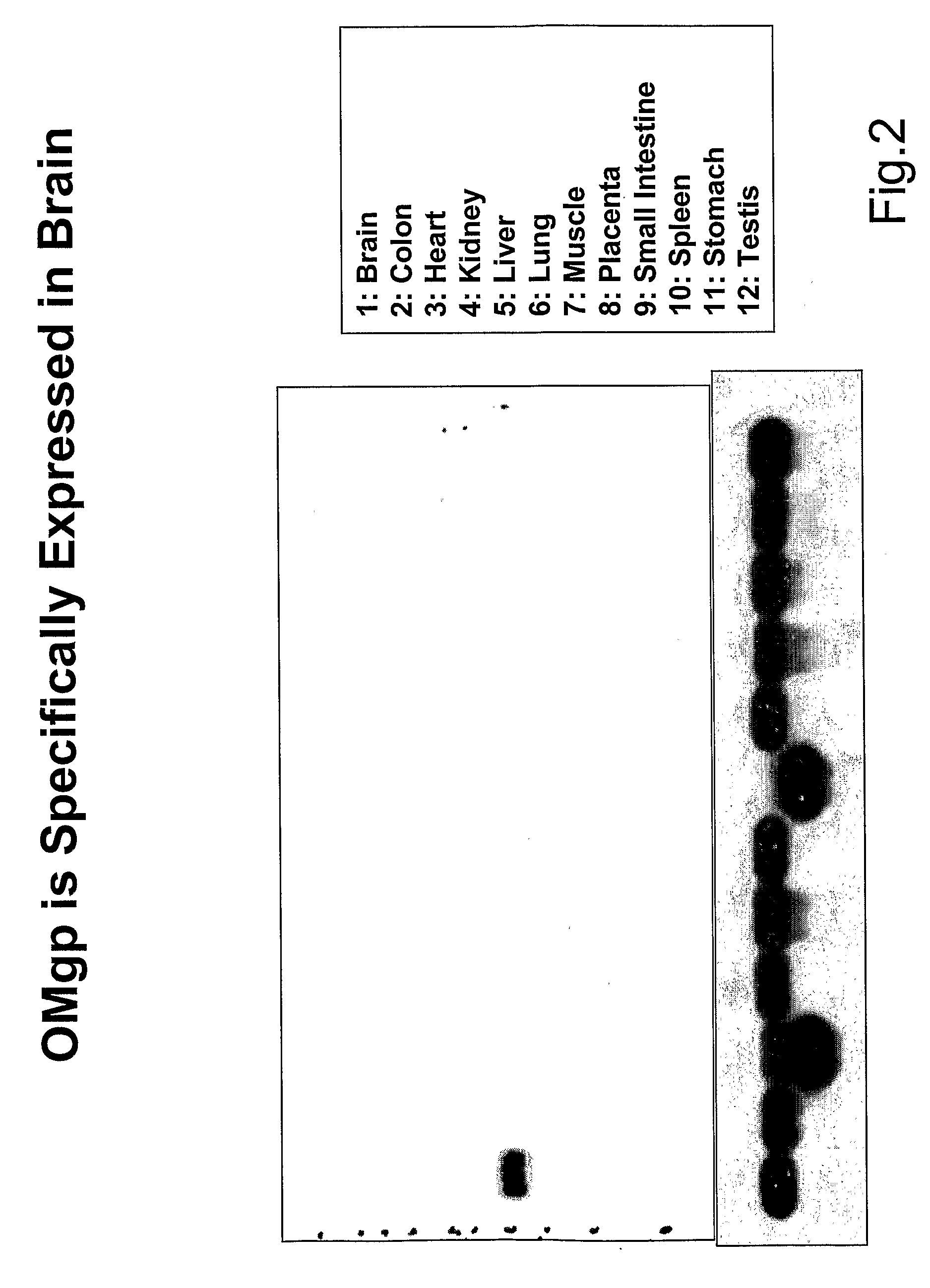
Oligodendrocyte-Myelin Glycoprotein Compositions and Methods of Use Thereof
InactiveUS20090175846A1Promoting neuronalPromoting oligodendrocyte survivalOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseMyelin glycoprotein
The present invention is based on the discovery that oligodendrocyte-myelin glycoprotein (OMgp), which is ex-pressed by oligodendrocytes and CNS myelin, negatively regulates oligodendrocyte and neuronal differentiation and survival. Based on these discoveries, the invention relates generally to methods of promoting neuronal and oligodendrocyte survival and differentiation by administration of an OMgp anatagonist. Additionally, the invention generally relates to methods of treating various diseases, disorders or injuries associated with demyelination, dysmyelination, oligodendrocyte / neuronal cell death, axonal injury and / or differentiation by the administration of an OMgp antagonist.
Owner:BIOGEN IDEC MA INC
Neuronal differentiation-inducing peptide and use thereof
InactiveUS20090253618A1Easy to produceEasy to distinguishNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsSOCS ProteinsInducer
A neuronal differentiation inducer comprising at least one peptide which can induce the differentiation of at least one cell into a neurocyte. The peptide is an artificially synthesized peptide comprising an amino acid sequence derived from a BC-box of at least one protein belonging to the SOCS protein family or an amino acid sequence having a partial modification in the BC-box-derived amino acid sequence, wherein the BC-box-derived amino acid sequence is composed of at least 10 contiguous amino acid residues selected in the amino acid sequence constituting the BC-box.
Owner:TOAGOSEI CO LTD
Transcriptional regulation of gene expression by small double-stranded modulatory RNA
The invention provides a method for modulating gene expression by contacting a cellular system with a double-stranded ribonucleic acid molecule capable of associating with a regulatory machinery that controls transcription of one or more genes, wherein the association results in altered expression of the one or more genes. The invention is further directed to method for directing the differentiation of neuronal stem cells into neurons by contacting a cellular system with a double-stranded ribonucleic acid molecule capable of associating with a regulatory machinery that controls transcription of one or more genes involved in neuronal differentiation and directing the transcription of the one or more genes. In related embodiments, the invention provides particular compositions of double-stranded ribonucleic acid molecules as well as therapeutic and screening applications of the invention.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
Neuronal differentiation-inducing peptide and use thereof
A neuronal differentiation inducer provided by the present invention contains an artificially synthesized peptide which includes an amino acid sequence constituting a signal peptide in amyloid precursor protein (APP), or a partial sequence of the amino acid sequence constituting this signal peptide.
Owner:TOAGOSEI CO LTD
Neuronal differentiation method of adult stem cells using small molecules
The present invention relates to a neuronal differentiation method of adult stem cells using small molecules, more particularly to a method for inducing differentiation of adult stem cells into nerve cells using small molecules, which enables effective differentiation into nerve cells and, thus, is useful in treating intractable CNS disorders such as Parkinson's disease, dementia, Alzheimer's disease and spinal cord injury.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF CHEM TECH
Differentiation of bone marrow cells into neuronal cells and uses therefor
The present invention relates to methods of inducing differentiation of mammalian bone marrow stromal cells into neuronal cells by contacting marrow stromal cells with a neuronal differentiation-inducing compounds. Neuronal differentiation-inducing compounds of the invention include anti-oxidants such as, but not limited to, beta-mercaptoethanol, dimethylsulfoxide, butylated hydroxyanisole, butylated hydroxytoluene, ascorbic acid, dimethylfumarate, and n-acetylcysteine. Once induced to differentiate into neuronal cells, the cells can be used for cell therapy, gene therapy, or both, for treatment of diseases, disorders, or conditions of the central nervous system.
Owner:PHILADELPHIA HEALTH & EDUCATION CORP +1
Neural cell system obtained by enabling human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSC) to differentiate by means of directional induction, and induction method and application of neural cell system
ActiveCN107326013ASuppress generationEffective treatmentGenetically modified cellsMutant preparationBone Marrow Stromal CellInjury brain
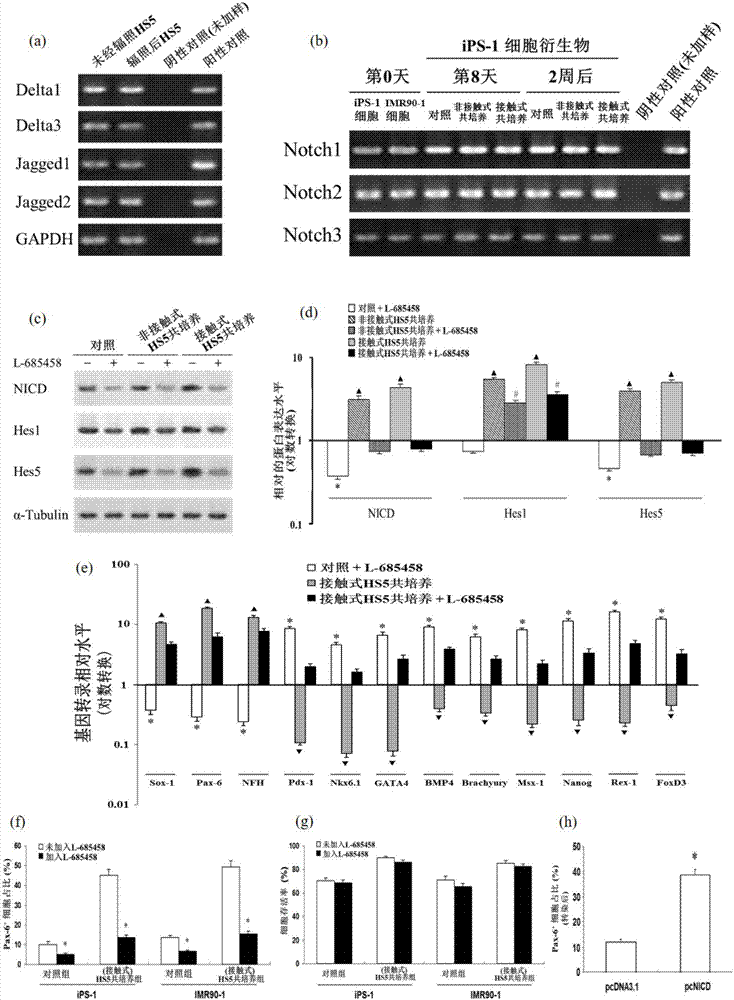
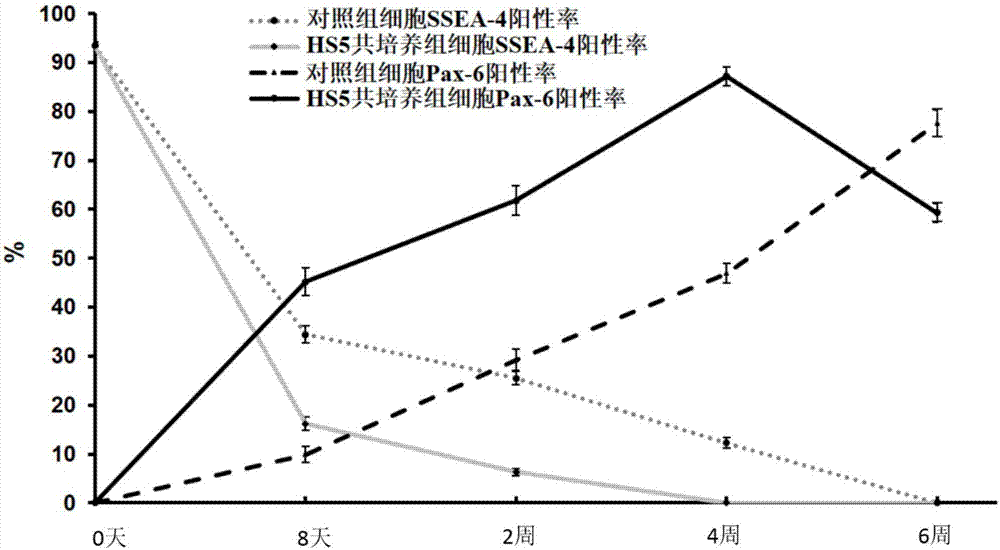
The invention discloses a neural cell system obtained by enabling human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSC) to differentiate by means of directional induction, and an induction method and application of the neural cell system. The method comprises the step of culturing the hiPSC by stages so as to induce the neuronal differentiation of the hiPSC, wherein the stages comprises a. carrying out co-culture on the hiPSC and bone marrow stromal cells (HS5) in an induced medium; b. continuously culturing the hiPSC by using an HS5 conditioned medium; c. using a basic medium for culturing neuronal cells to continuously culture the hiPSC. The method provided by the invention can induce the hiPSC to directionally differentiate into nervous system cells and inhibit the generation of non-nervous system cells at the same time, thus obtaining a mature and broad-spectrum neural cell group. The neural cell group is not only proved to be mature neurons having electrical impulse discharge by means of in vitro validation, but is also confirmed to have a function of effectively treating nervous system diseases (such as brain stroke and brain injury) in experiments of mice in vivo.
Owner:杨涛
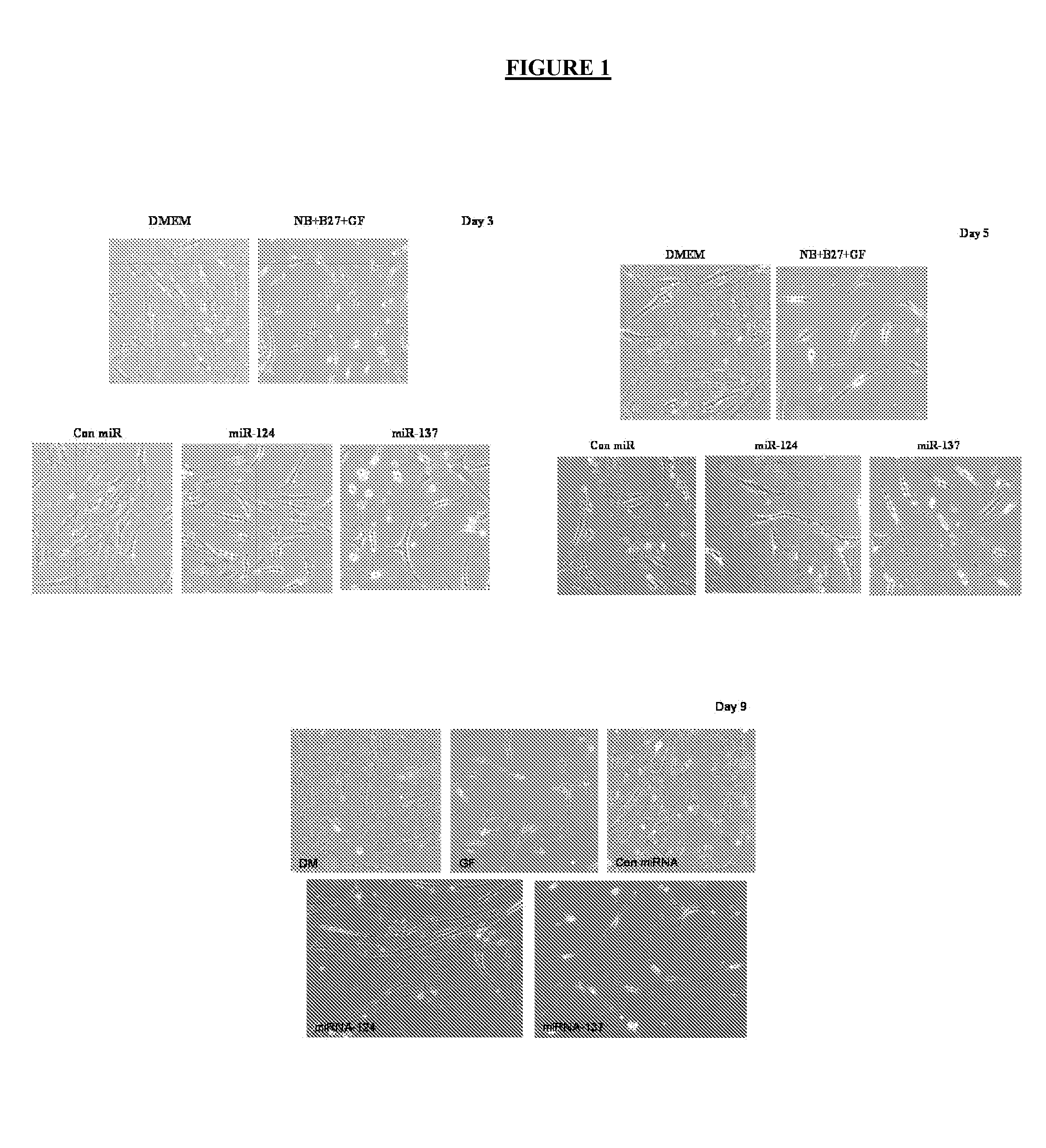
Methods, systems, and compositions for neuronal differentiation of multipotent stromal cells
ActiveUS20120148550A1Decreased cellDecreased system functionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseNervous system
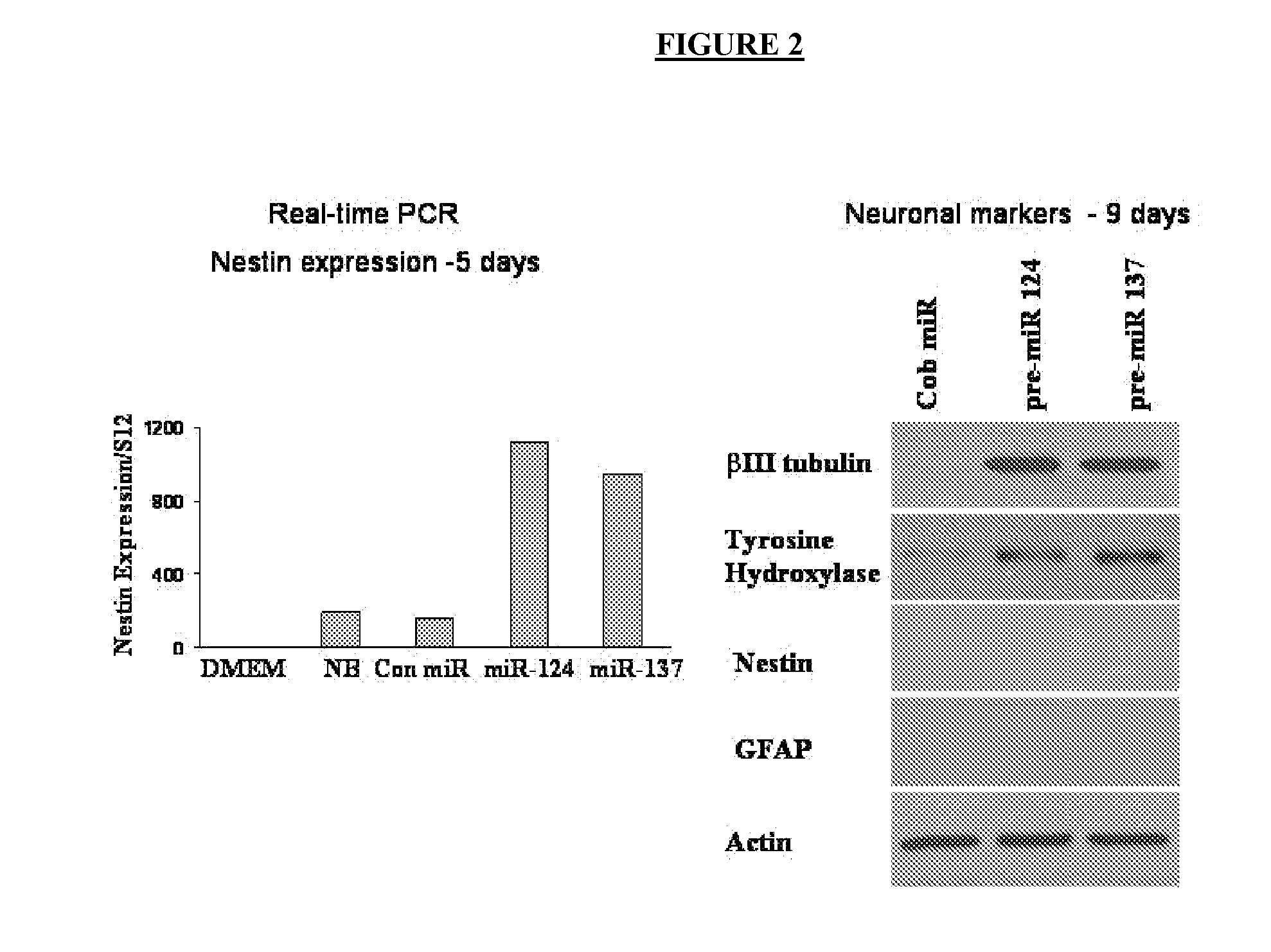
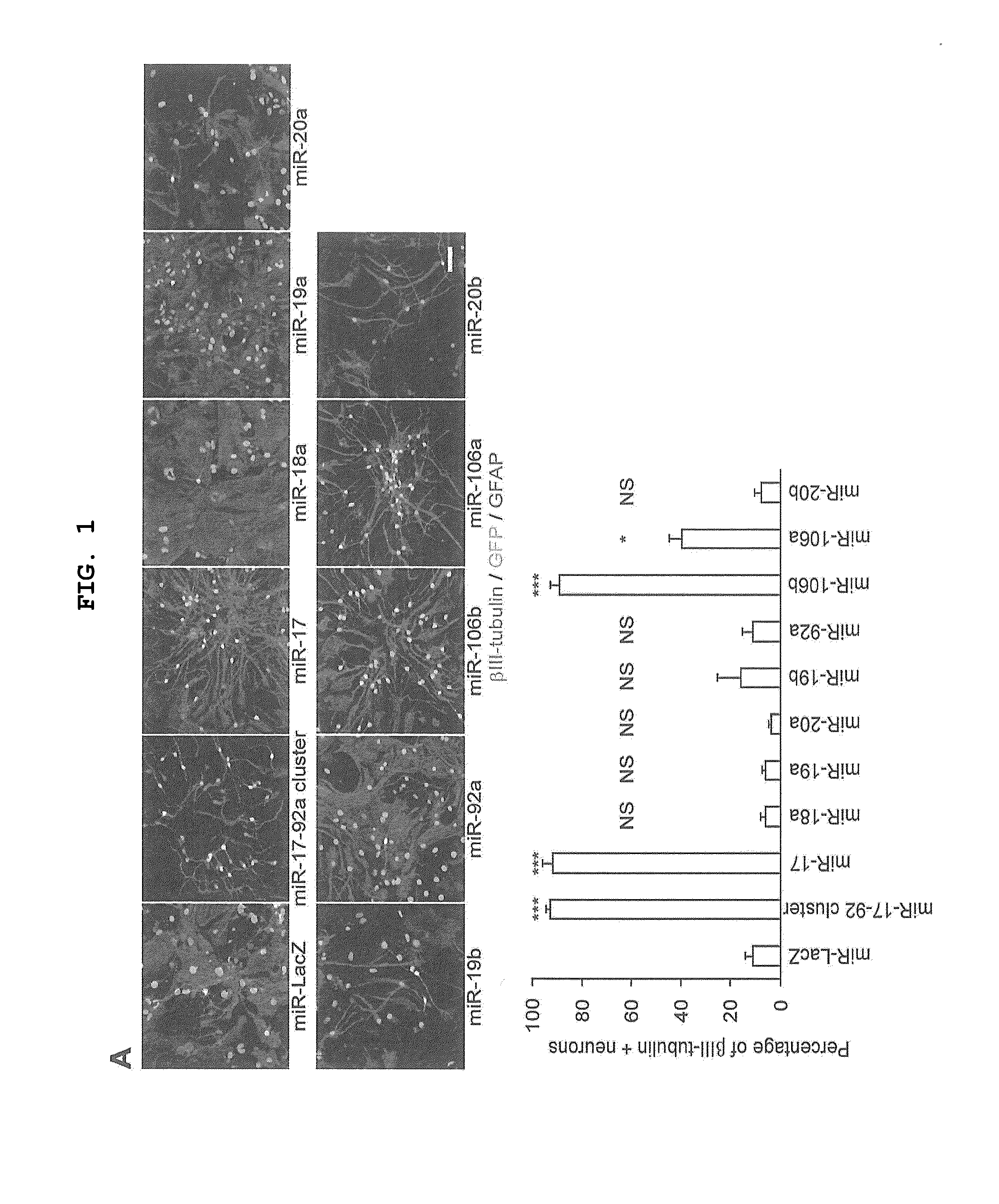
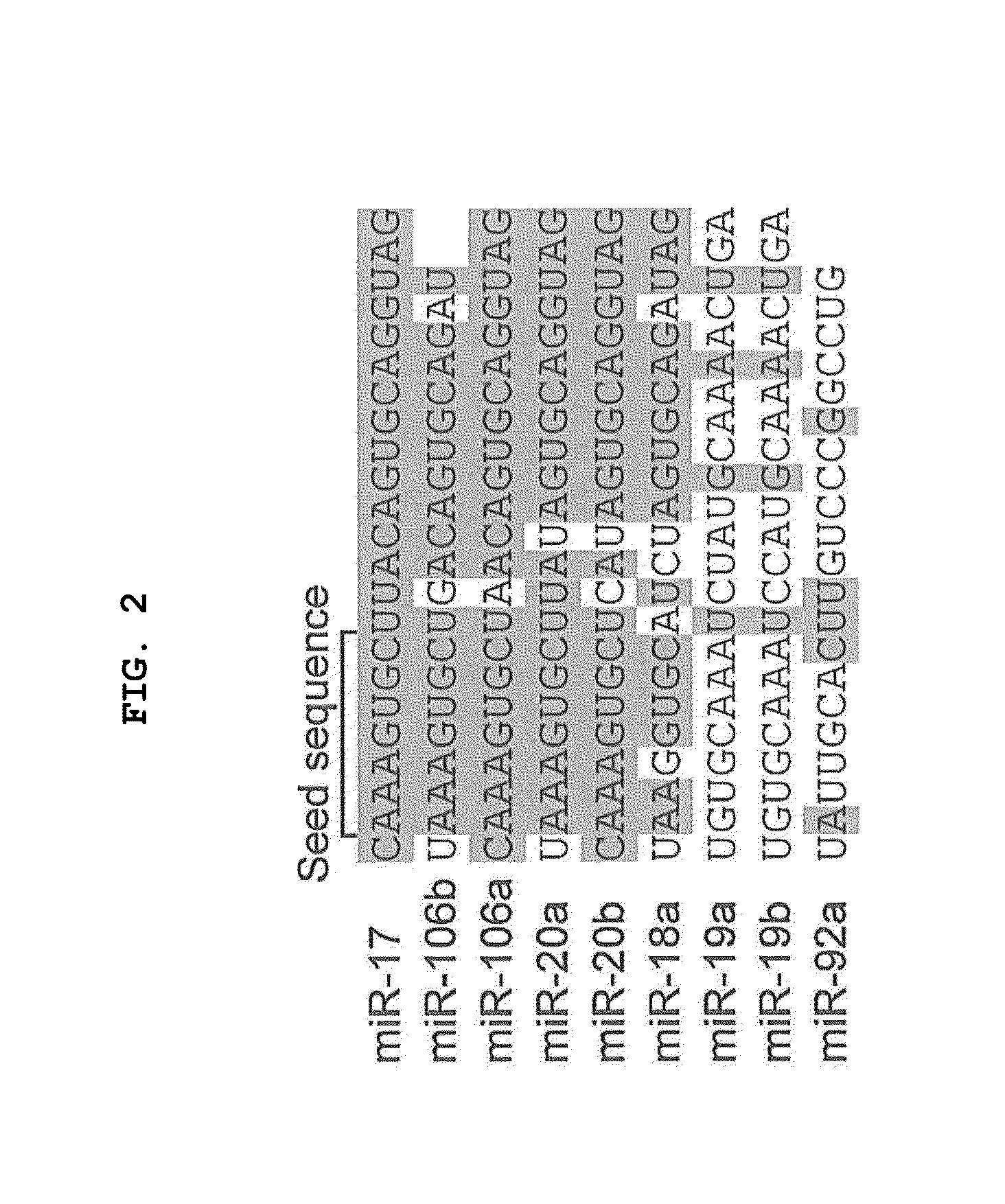
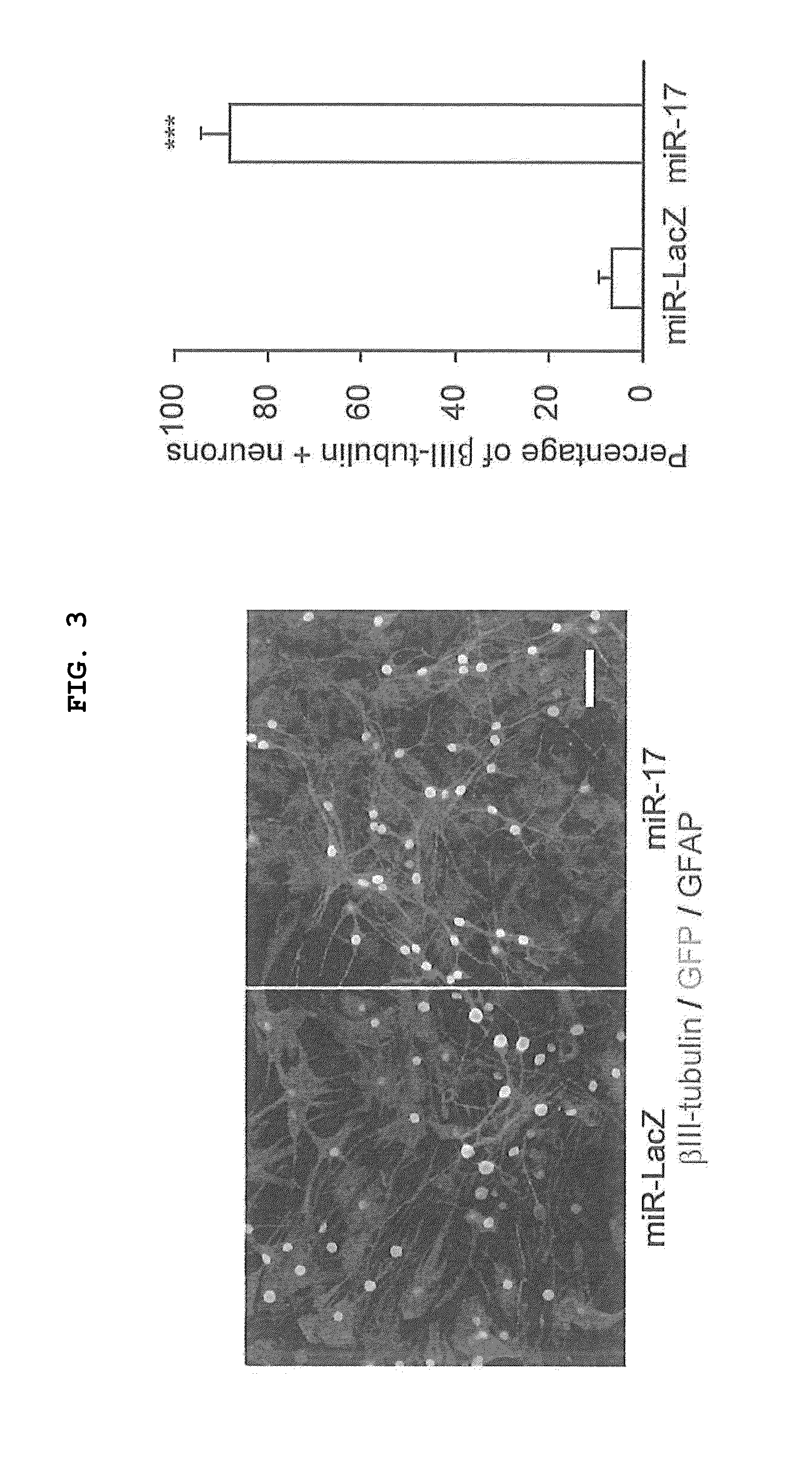
Some embodiments of the invention comprise methods, systems, and compositions to selectively induce, whether in vitro or in vivo, the neuronal differentiation of multipotent stromal cells through the application of microRNAs, including but not limited to miRNA-124, miRNA-137 and / or miRNA-9* expression products of those miRNAs, and molecules and compositions containing functional elements of those miRNAs. Some embodiments of the invention also comprise the therapeutic administration and use of such induced cells to treat mammalian injuries and diseases, including but not limited to, nervous system injuries or diseases that may otherwise result in decreased cell or system function.
Owner:EXOSTEM BIOTEC LTD
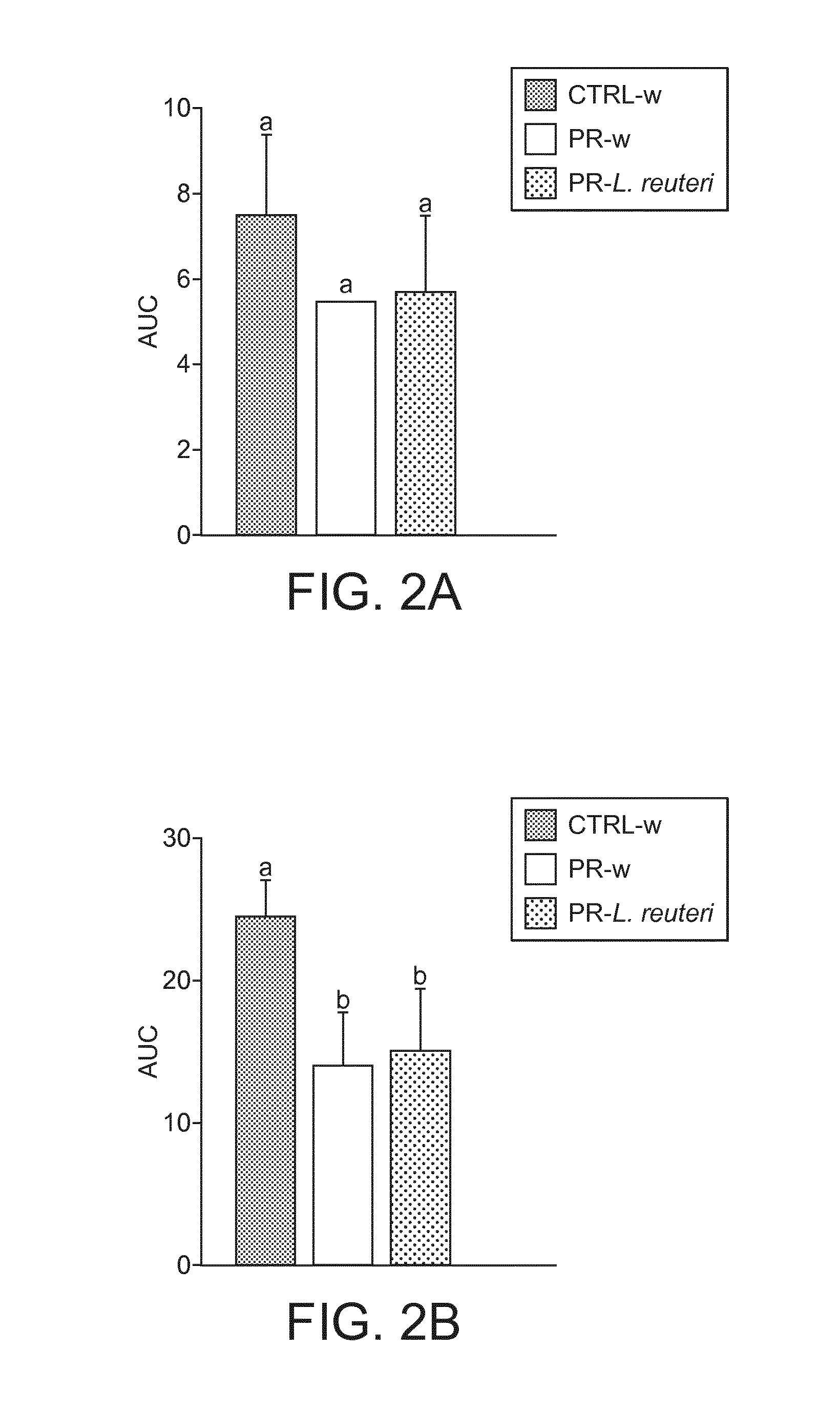
Lactobacillus reuteri dsm 17938 for the development of the enteric nervous system
InactiveCN104244736ABacteria material medical ingredientsDigestive systemNervous systemEnteric nervous system
Owner:BIOGAIA AB
Neural Progenitor Cell Differentiation
ActiveUS20140271905A1Restore motor functionEffective amountNervous system cellsMammal material medical ingredientsDiseaseProgenitor
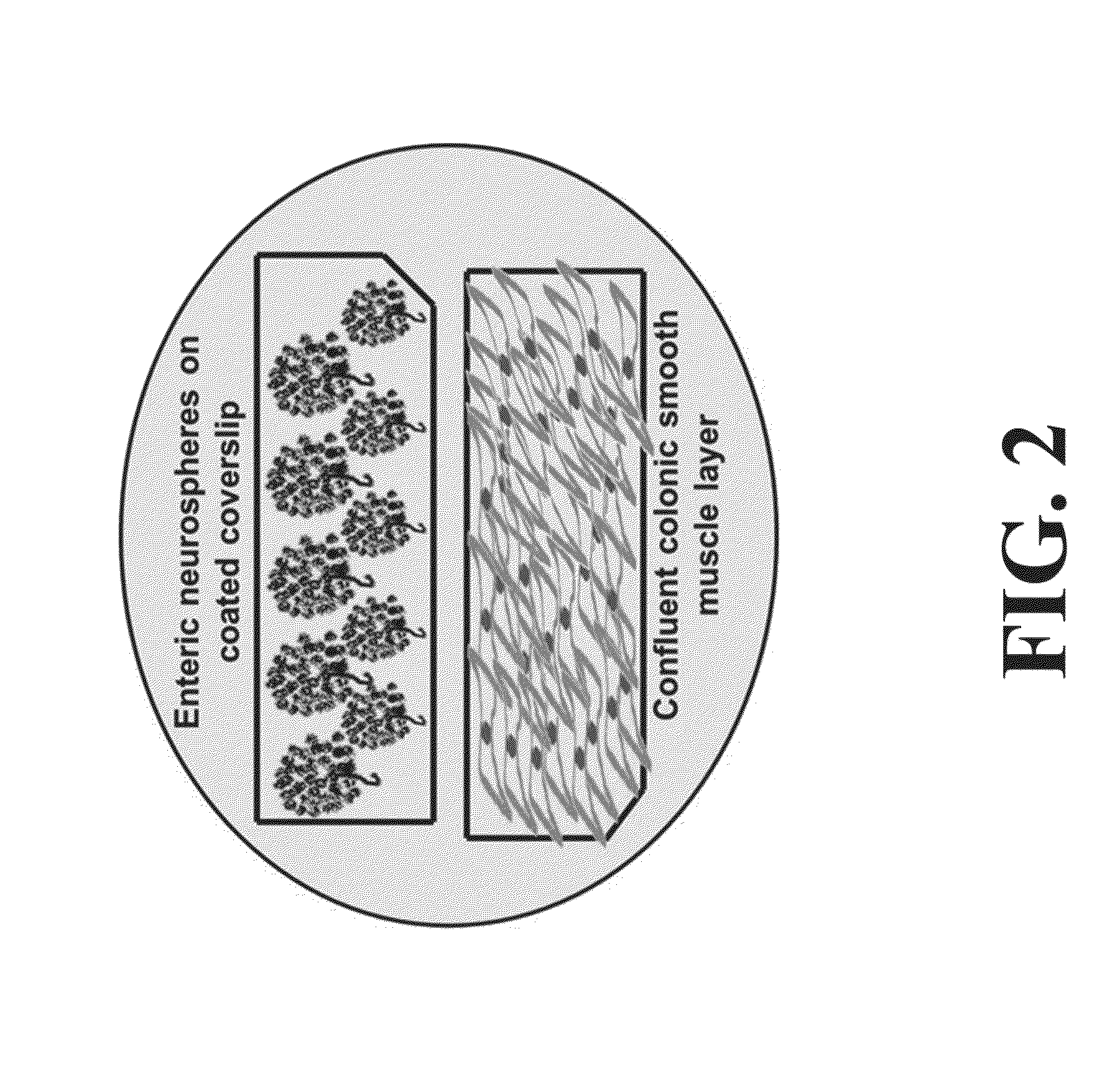
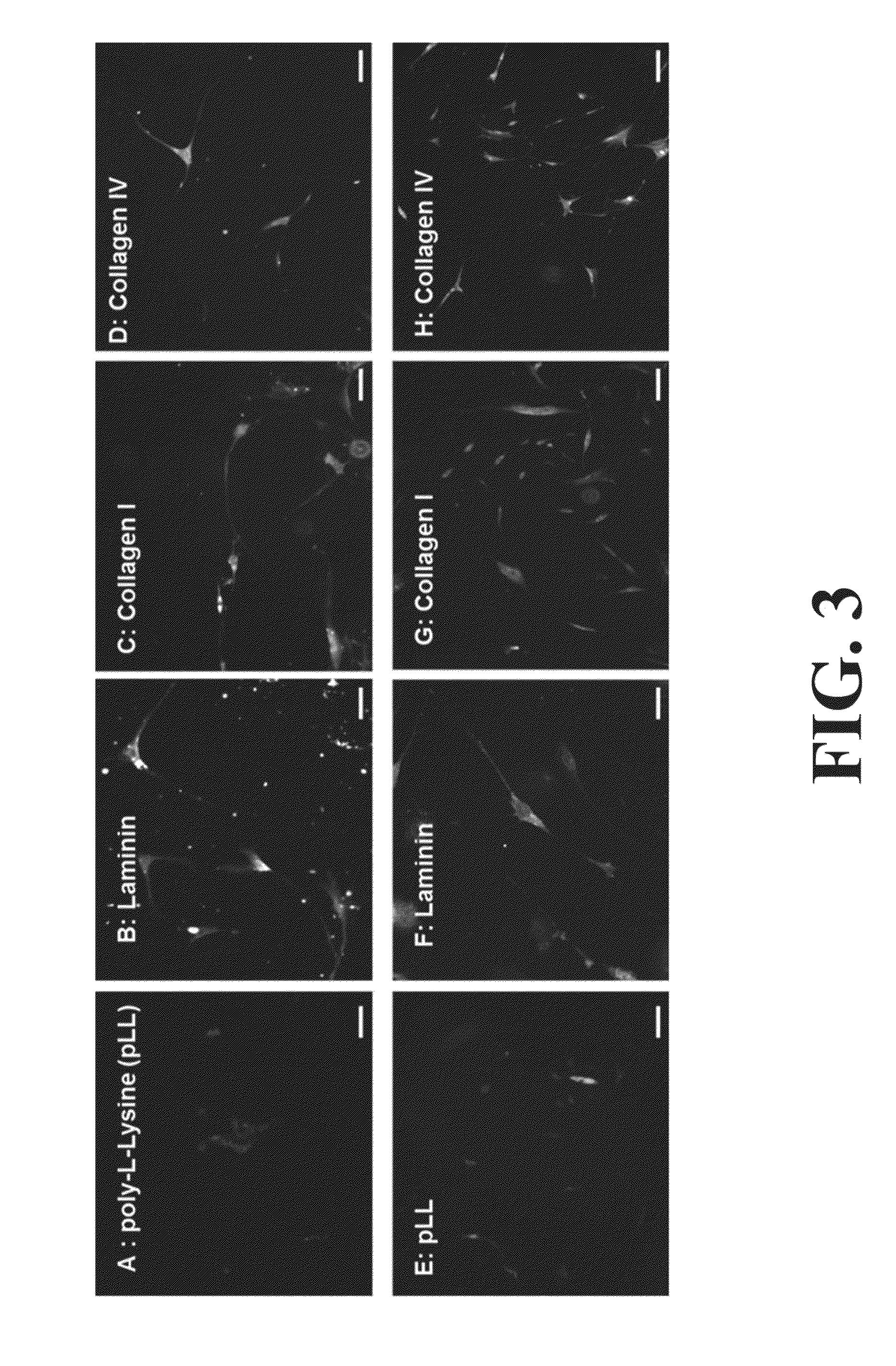
Differentiation and stability of neural stem cells can be enhanced by in vitro or in vivo culturing with one or more extracellular matrix (ECM) compositions, such as collagen I, IV, laminin and / or a heparan sulfate proteoglycan. In one aspect of the invention, adult mammalian enteric neuronal progenitor cells can be induced to differentiate on various substrates derived from components or combinations of neural ECM compositions. Collagen I and IV supported neuronal differentiation and extensive glial differentiation individually and in combination. Addition of laminin or heparan sulfate to collagen substrates unexpectedly improved neuronal differentiation, increasing neuron number, branching of neuronal processes, and initiation of neuronal network formation. In another aspect, neuronal subtype differentiation was affected by varying ECM compositions in hydrogels overlaid on intestinal smooth muscle sheets. The matrix compositions of the present invention can be used to tissue engineer transplantable innervated GI smooth muscle constructs to remedy aganglionic disorders.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
Small molecules for neuronal differentiation of embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS20110046092A1Increasing neuronal differentiationEnhance cell viabilityBiocideNervous disorderPluripotential stem cellDifferentiation Agents
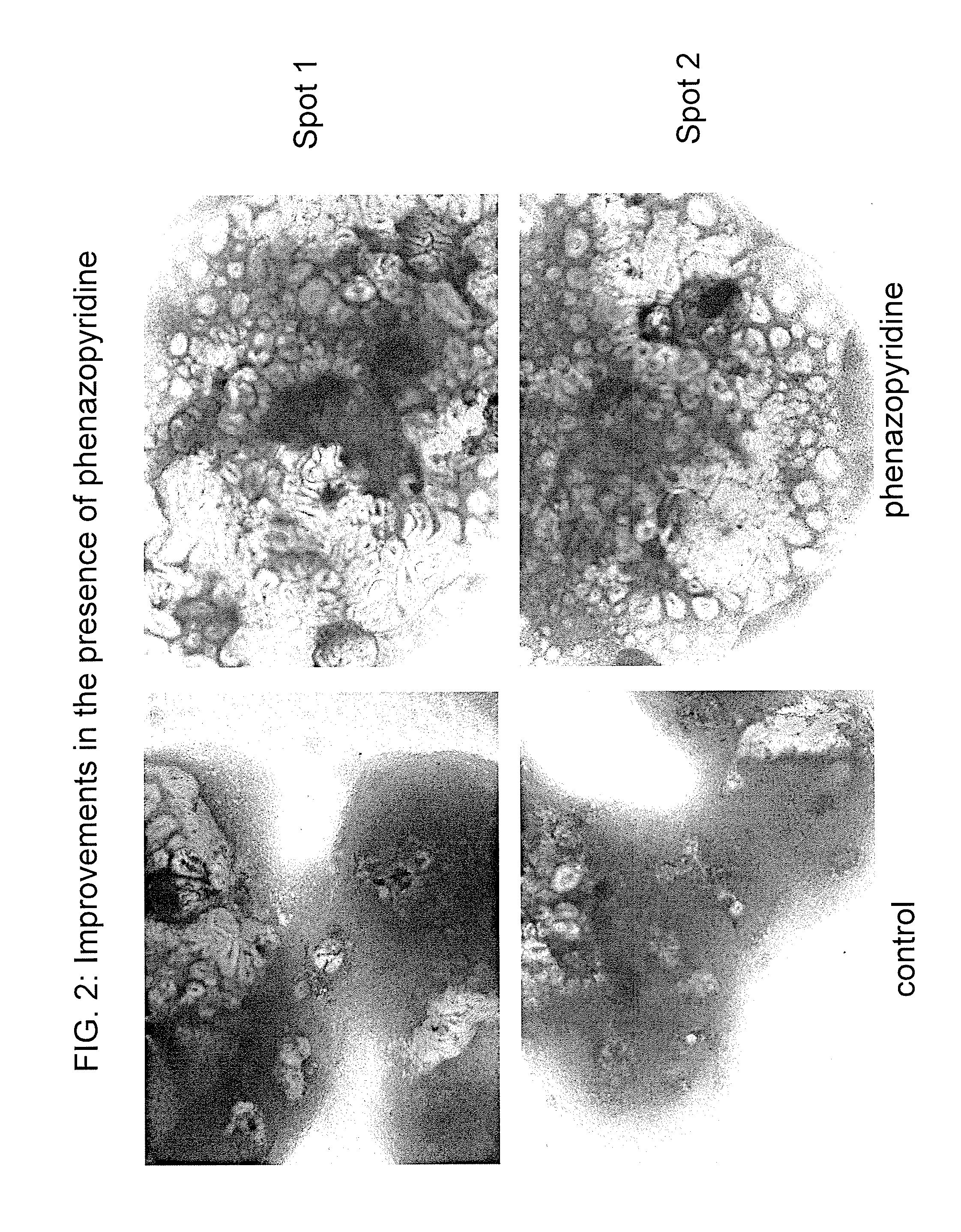
A method of preparing neural precursor cells by exposing pluripotent stem cells or neural stem cells to a differentiation agent. The agent is a pyridine analog, which in preferred embodiments is a phenylethynyl-substituted or phenylazo-substituted pyridine. In other embodiments, a method of enhancing neural precursor cell survival is provided in which the survival is enhanced by exposure to the pyridine analog. In further embodiments, a method of preparing neuronal cells is provided in which pluripotent or neural stem cells exposed to the pyridine analog are then incubated without the pyridine analog, resulting in differentiation into neurons, astrocytes and oligodendrocytes. These methods may be used in toxicological screens, e.g., to evaluate the neurotoxicity of a test compound.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
Novel serum-free medium for inducing neural stem cells and application of novel serum-free medium
ActiveCN108315301AEasy to useSolve the problems restricting the clinical use of neural stem cellsGenetically modified cellsCulture processSerum free mediaMultipotential stem cell
The invention provides a novel serum-free medium for inducing neural stem cells. The medium comprises a neural stem cell-induced medium, a neural stem cell proliferation culture medium and a neuronaldifferentiation medium, wherein the neural stem cell-induced medium consists of an animal basal culture medium N2G21 and neural induction compounds PD98059 and JW55; the neural stem cell proliferationculture medium consists of the animal basal culture medium N2G21 and a growth factor OsrbFGF; the neuronal differentiation medium is an N2G21 basal culture medium. The culture medium adopts a scientific design and a simple formula; compared with the prior art, the novel serum-free medium disclosed by the invention has the advantages that pure chemical molecules replace a protein signal antagonist; a non-animal original growth factor is used to replace a traditional animal original growth factor; neural stem cells which can self update and are differentiated into neuronal cells are obtained byhuman multipotential stem cell culture; in addition, the neural stem cells prepared by using the culture medium have higher clinical safety.
Owner:IREGENE THERAPEUTICS LTD
Lactobacillus Reuteri DSM 17938 for the Development of the Enteric Nervous System
InactiveUS20140363409A1Promotes normalPromotes healthy neuronalBiocideBacteria material medical ingredientsNervous systemEnteric nervous system
The invention relates to Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938, and compositions comprising Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938, for promoting the healthy development and / or repair of the enteric nervous system in mammals. Humans or animals and, in particular, a foetus, pre-term or term-born infant, toddler or child may benefit from the invention. The invention may be especially beneficial to those infants having experienced IUGR, or having a low, or very low birth weight, and / or suffered from enteric nervous system growth retardation either in utero or, during or after birth. The administration of to Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 promotes normal and healthy neuronal and glial development. It also ensures healthy neuronal differentiation in the peripheral nervous system.
Owner:BIOGAIA AB
Method for 3D culture of autologous fat MSCs derived neural precursor cells
ActiveCN107164326AImprove adhesionGuaranteed adhesionCulture processNervous system cellsNeurulationCell adhesion
The invention discloses a method for 3D culture of autologous fat MSCs (mesenchymal stem cells) derived neural precursor cells. The method includes the steps of: S1. preparing a collagen 3D scaffold; S2. collecting adipose tissue and separating adipose cells, using an MSCs medium for culture to harvest P0 generation MSCs, resuspending the P0 generation MSCs with the MSCs medium, and performing culture to harvest P1 generation MSCs; S3. pretreating the collagen 3D scaffold; S4. using the MSCs medium to resuspend the P1 generation MSCs, conducting inoculation into a tissue culture dish containing the collagen 3D scaffold, and using an NPCs (neural precursor cells) medium to conduct further culture for 6 days, thus harvesting NPCs. The method provided by the invention employs laminin and vitronectin to coat collagen sponge so as to construct the collagen 3D scaffold, can promote MSCs adhesion and inhibit neuronal differentiation, then uses the MSCs medium for pretreatment of the collagen 3D scaffold so as to prevent agglomeration of MSCs during adhesion, and maximumly guarantees single cell adhesion. According to the invention, abdominal adipose tissue is collected and separated, MSCs is amplified, and the collagen 3D scaffold is employed to culture NPCs, and the obtained NPCs can meet the purity and preparation demands of autologous fat MSCs derived NPCs.
Owner:北京再生生物科技研究院有限公司
Use of nibp polypeptides
InactiveUS20120258539A1Inhibition of activationPromote cell deathPeptidesFermentationCancer cellNF-kappaB activation
Methods for regulating NF-κB activation in cells comprising introducing into the cell a vector comprising a nucleic acid sequence encoding a NIK and IKK2 Binding Protein (NIBP) polypeptide, wherein the NIBP polypeptide is expressed in the cell, are provided. Also provided are methods for reversing the cancerous phenotype of a cancer cell and for modulating neuronal differentiation.
Owner:TEMPLE UNIVERSITY
Pigment epithelium-derived factor: characterization, genomic organization and sequence of the PEDF gene
InactiveUS20060008900A1Senses disorderNervous disorderPIGMENT EPITHELIUM-DERIVED FACTORNeuron survival
Nucleic acids encoding the neurotrophic protein known as pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF), a truncated version of PEDF referred to as rPEDF, and equivalent proteins, vectors comprising such nucleic acids, host cells into which such vectors have been introduced, recombinant methods for producing PEDF, rPEDF, and equivalent proteins, the rPEDF protein and equivalent proteins of rPEDF and PEDF-BP, -BX and BA, and the PEDF protein produced by recombinant methods. Effects and uses of these variants on 1) neuronal differentiation (neurotrophic effect) 2) neuron survival (neuronotrophic effect) and 3) glial inhibition (gliastatic effect) are described.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
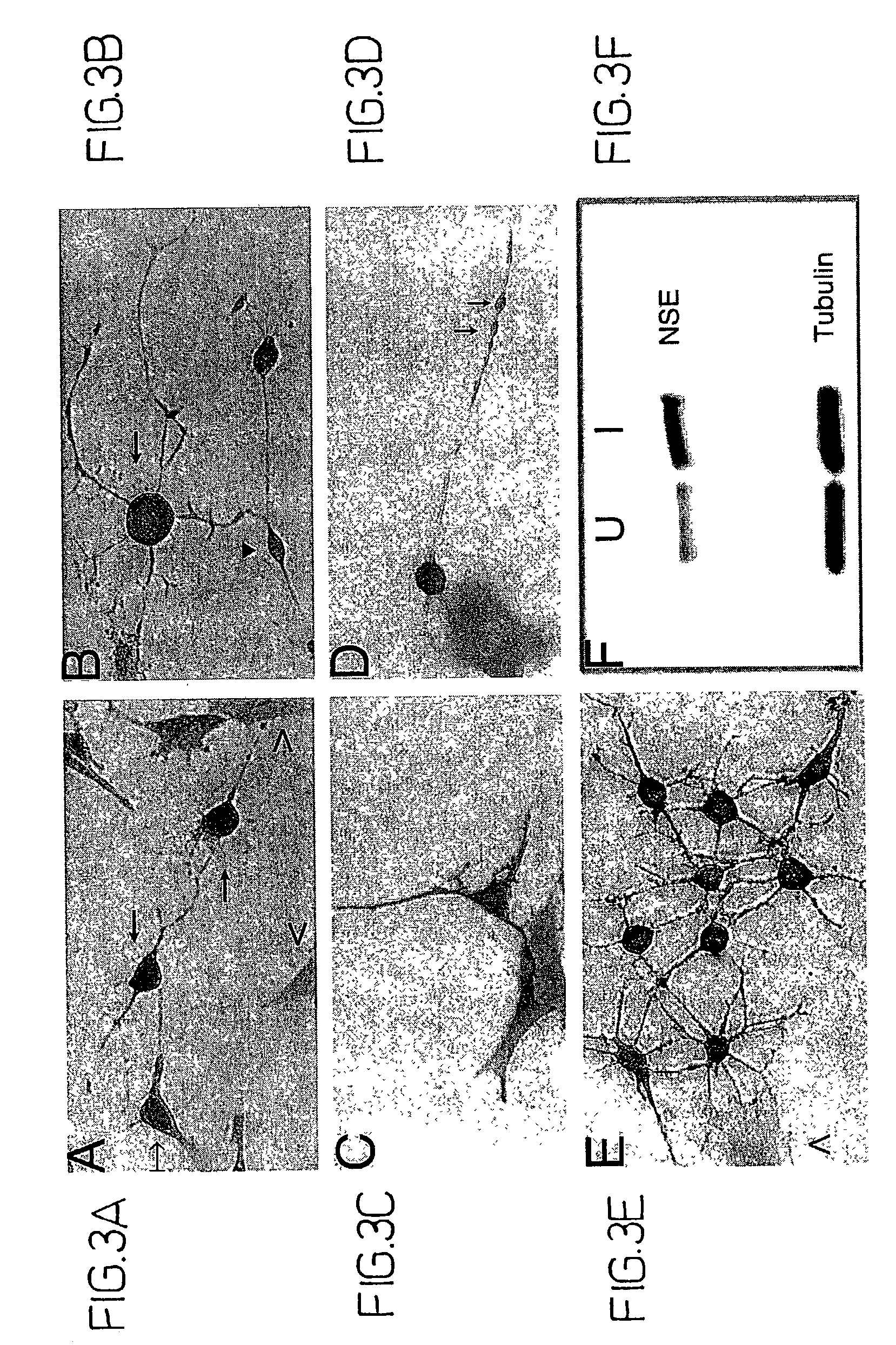
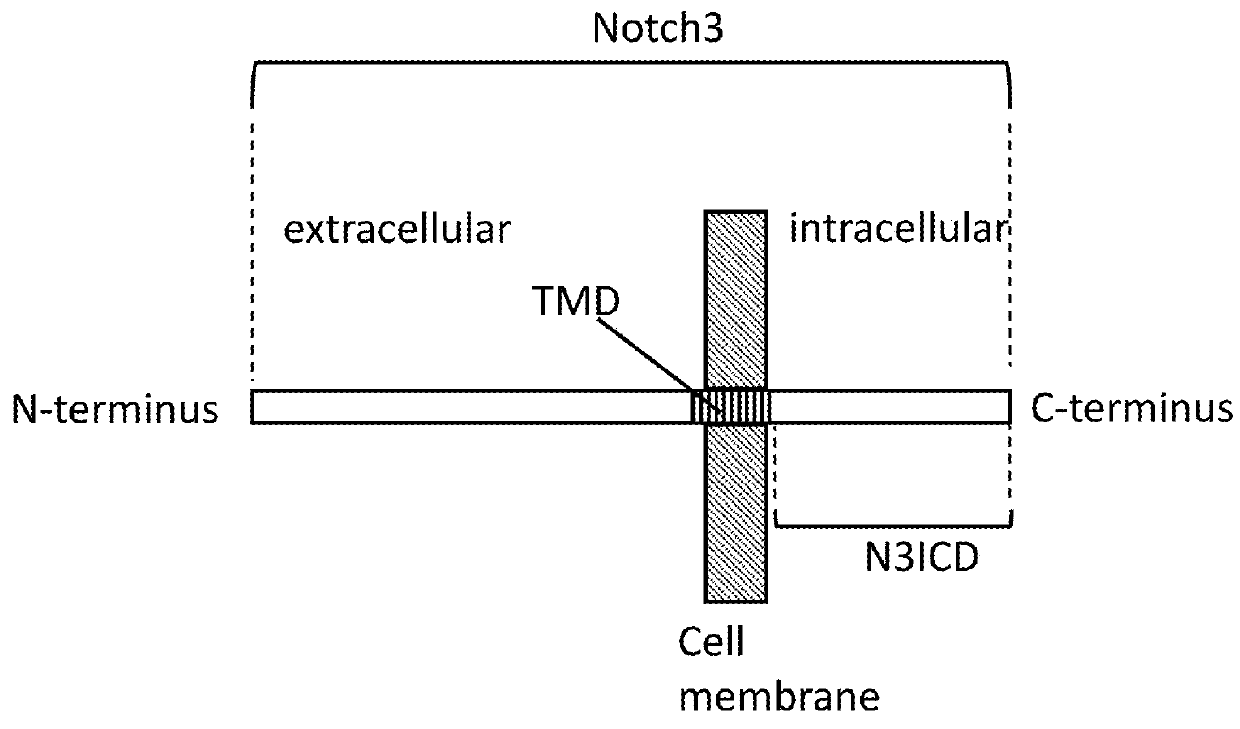
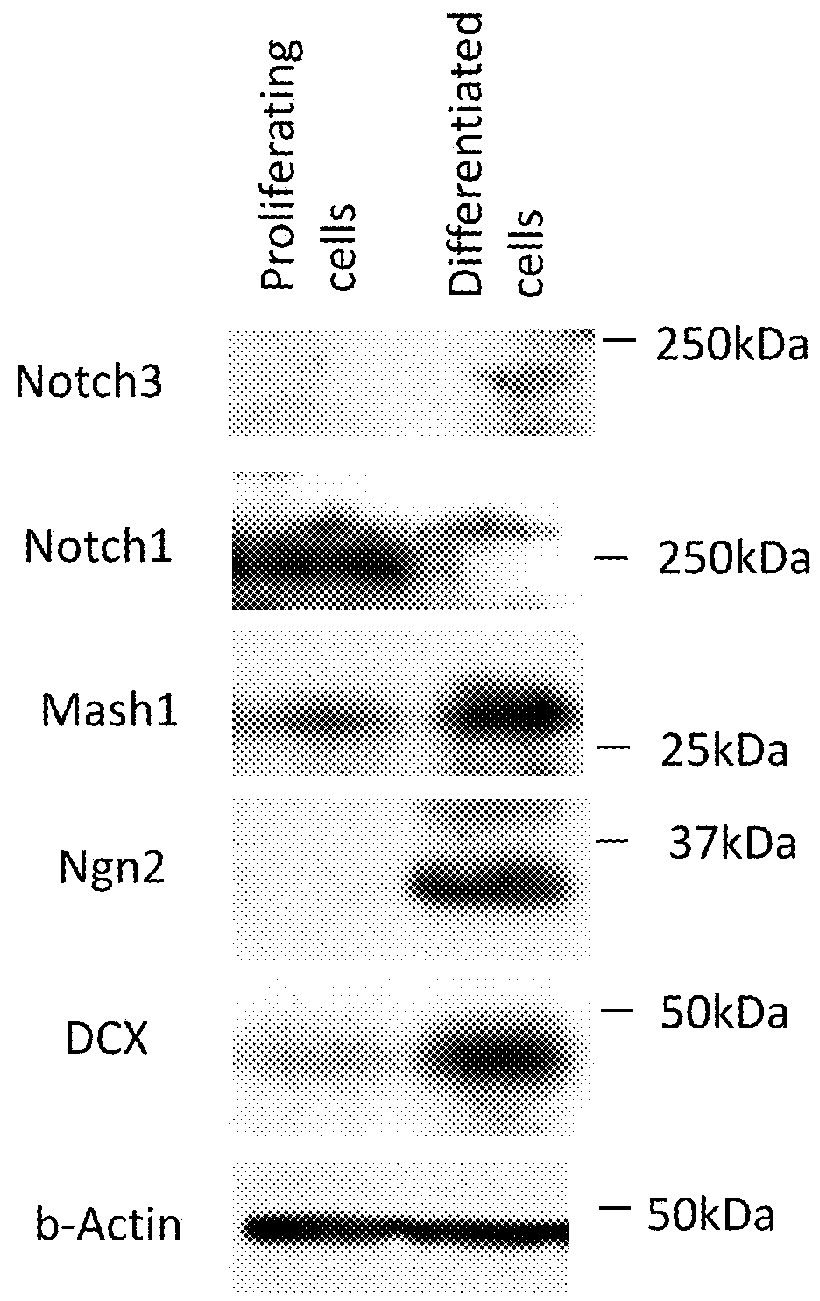
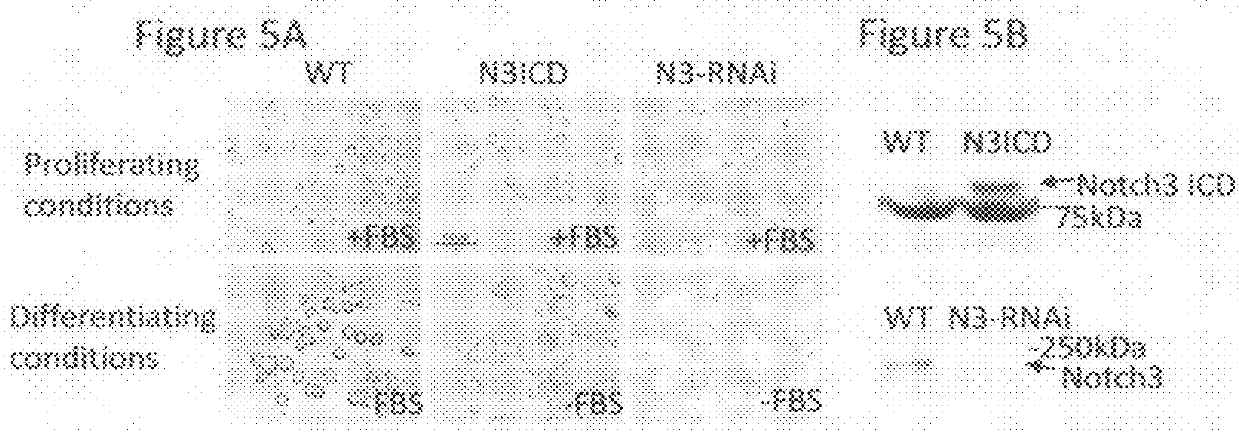
Method of inducing cellular differentiation using the Notch3 receptor intracellular domain
The present invention relates to the intracellular domain of Notch3 that can activate signaling and initiate transcription, thereby initiating cellular differentiation in general, and neuronal differentiation in particular. The present invention includes the use of polynucleotide sequences that code, entirely or partially, for the intracellular domain of Notch3, for the purpose of inducing cellular differentiation. The present invention includes the use of Notch3 intracellular domain polynucleotide or polypeptide sequences for the purpose of treating diseases or disorders, by inducing cellular differentiation.
Owner:RUSANESCU GABRIEL
Biomarker specific to brain/nerve or specific to neuronal differentiation
The invention provides a polypeptide and a specific partial peptide thereof, as well as a polynucleotide and a specific partial nucleotide thereof, that can be used as a biomarker specific for the brain / nerves or specific for nerve differentiation; an expression vector for such a polynucleotide and a specific partial peptide thereof; a transformant incorporating such an expression vector; an antisense molecule, RNAi-inducing nucleic acid (e.g., siRNA), aptamer, or antibody for such a biomarker, and a composition comprising the same; a mammalian cell or non-human mammal wherein the expression or a function of such a biomarker is regulated; a measuring means (e.g., primer set, nucleic acid probe, antibody, aptamer) for such a biomarker, and a reagent comprising the same and the like.
Owner:REVERSE PROTEOMICS RES INST
Potential protein capable of serving as Alzheimer's disease drug action target and application thereof
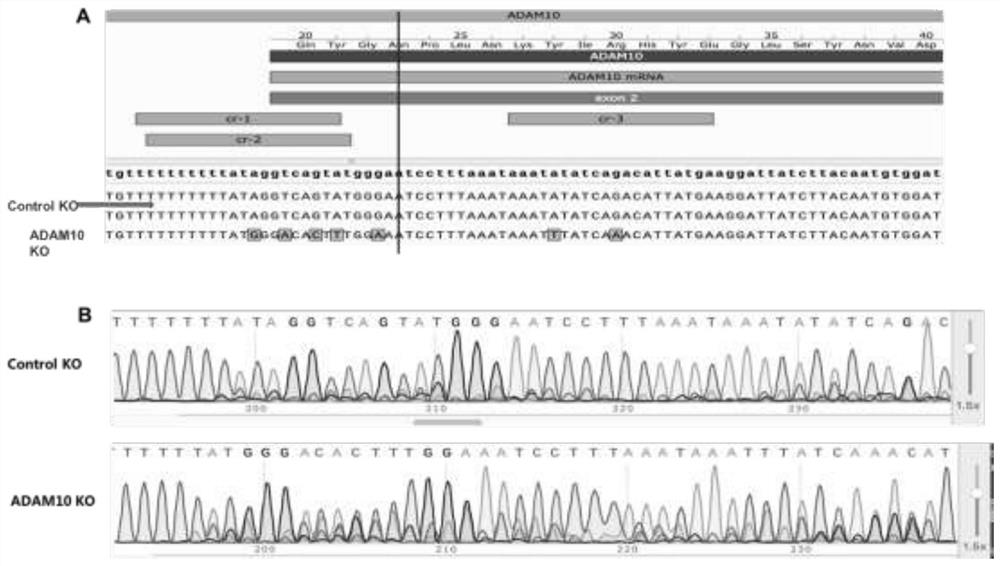
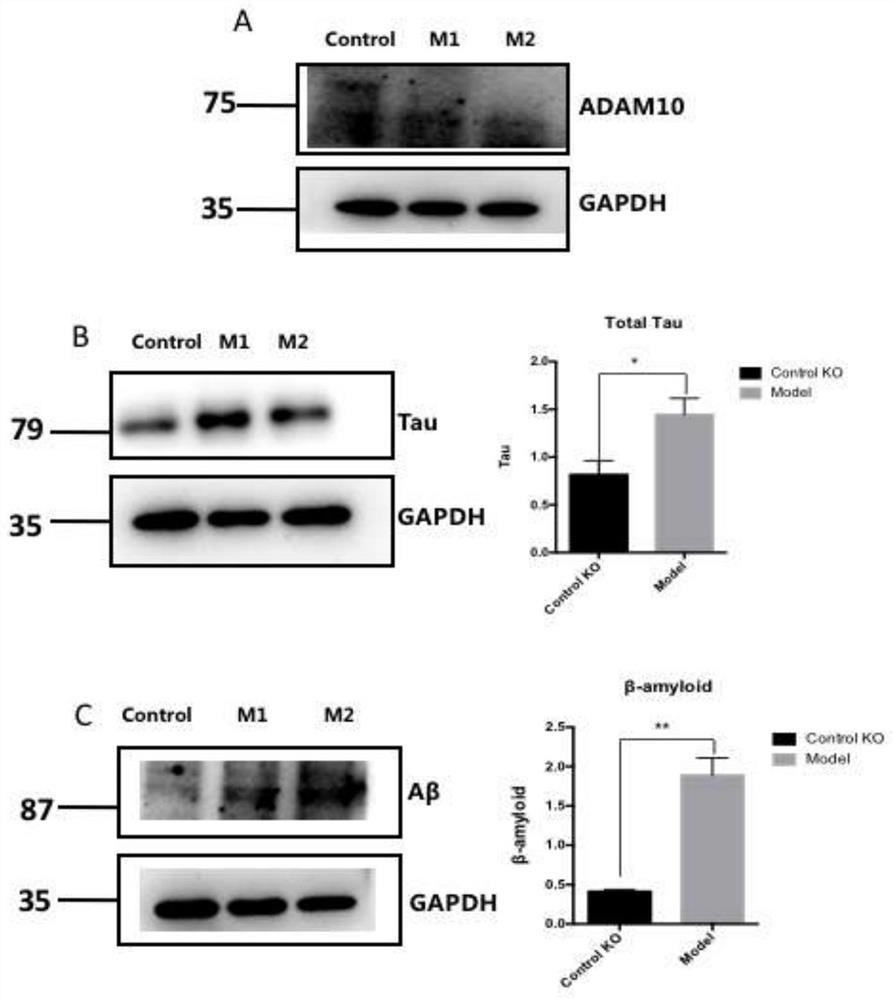
PendingCN113151290AImpaired neural differentiationSignificantly slowed growth rateNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsPTBP1Pharmaceutical drug
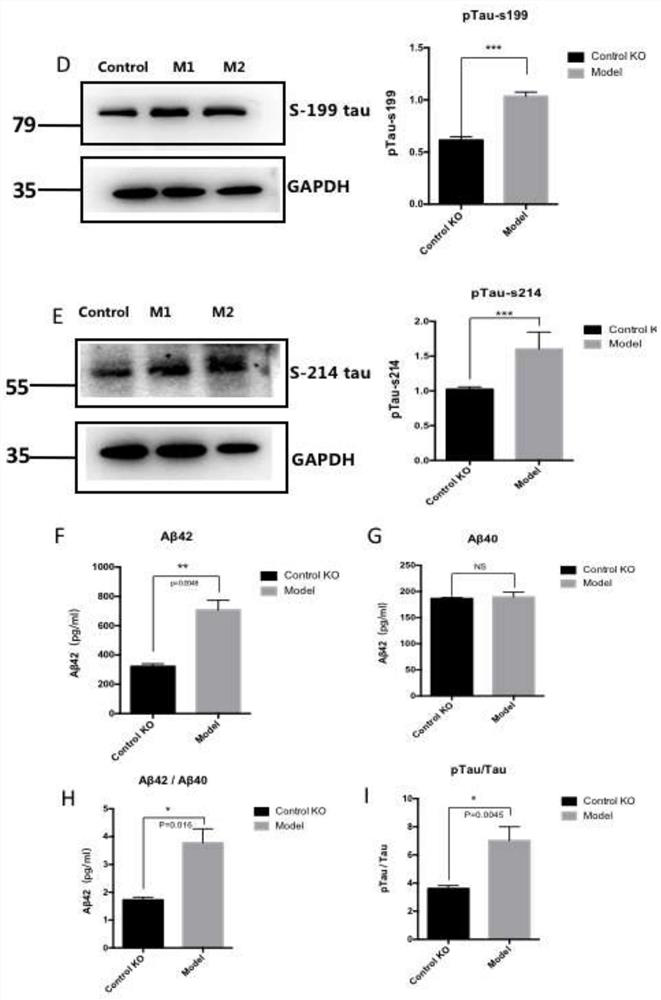
The invention discloses a potential protein capable of serving as an action target of an Alzheimer's disease drug and application of the potential protein. The invention discloses application of a substance for inhibiting PTBP1 gene expression in preparation of a medicine for treating Alzheimer's disease. According to the invention, ADAM10 is successfully knocked out from SH-SY5Y cells to construct an AD cell model, in the model, it is found for the first time that PTBP1 protein is significantly increased in ADAM10KO cells, and the interaction between PTBP1 and Tau is significantly enhanced. After the PTBP1 gene of the ADAM10KO cell is knocked out and the PTBP1 protein is knocked down, Abeta42 and Tau protein can be remarkably reduced, the cell neuronal differentiation capacity is enhanced, the neuronal length is remarkably increased, and meanwhile information exchange between cells is remarkably increased. The data shows that the PTBP1 protein can be a novel target spot in AD.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Nanotopography-mediated reverse uptake platform for nucleic acid delivery and applications thereof
ActiveUS9114092B2Non-toxicHighly effectiveOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesNanotopographyMammalian cell
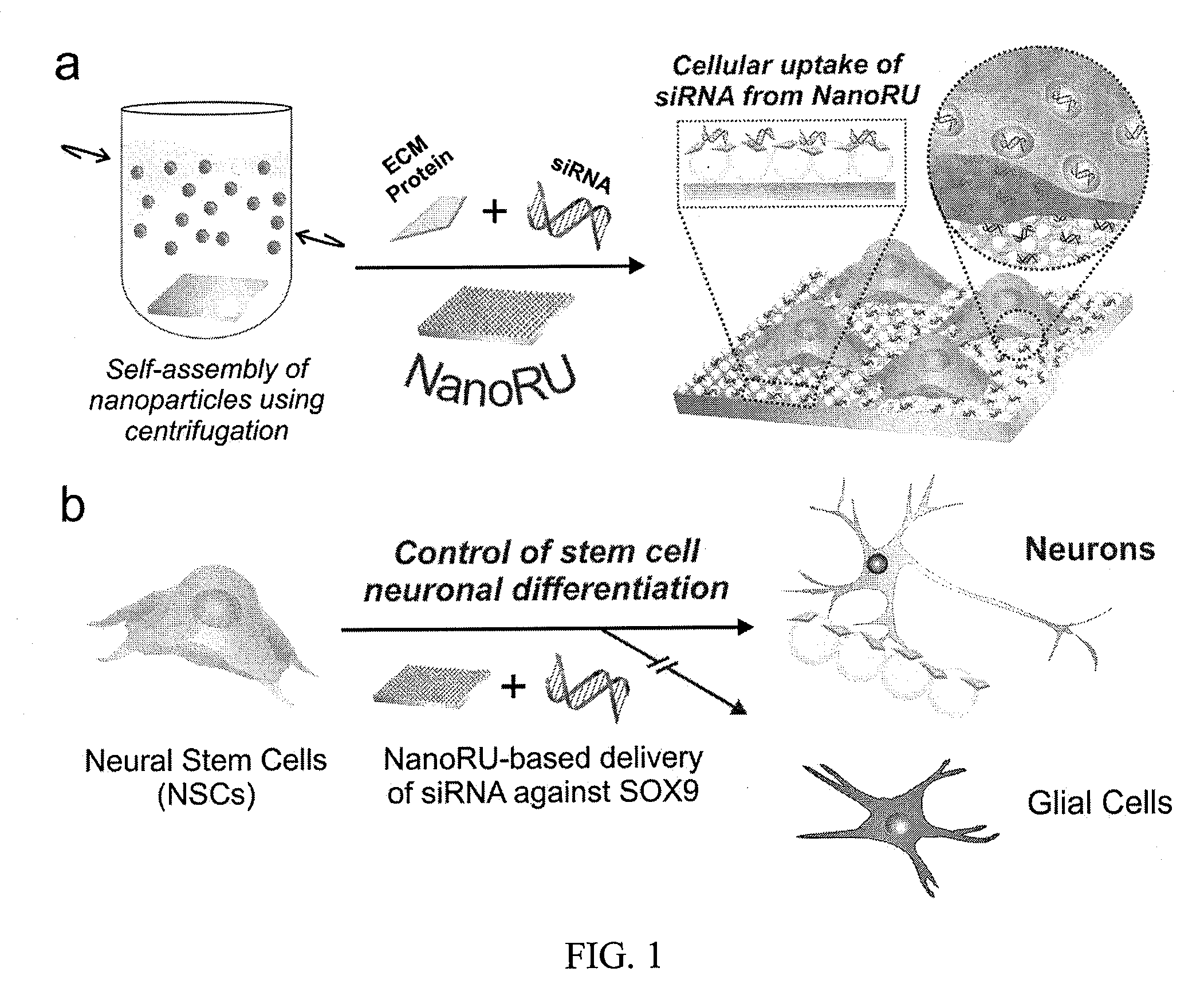
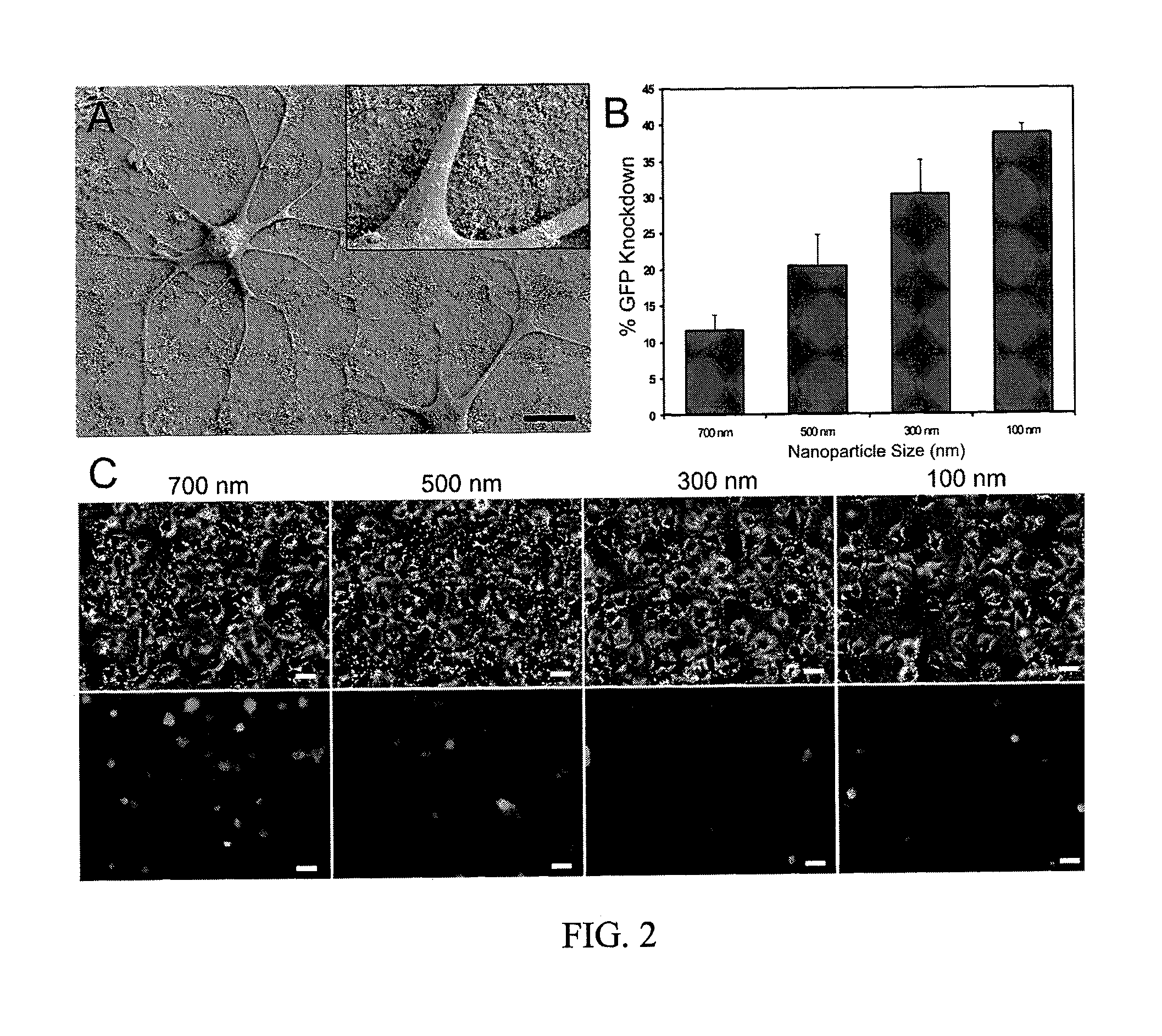
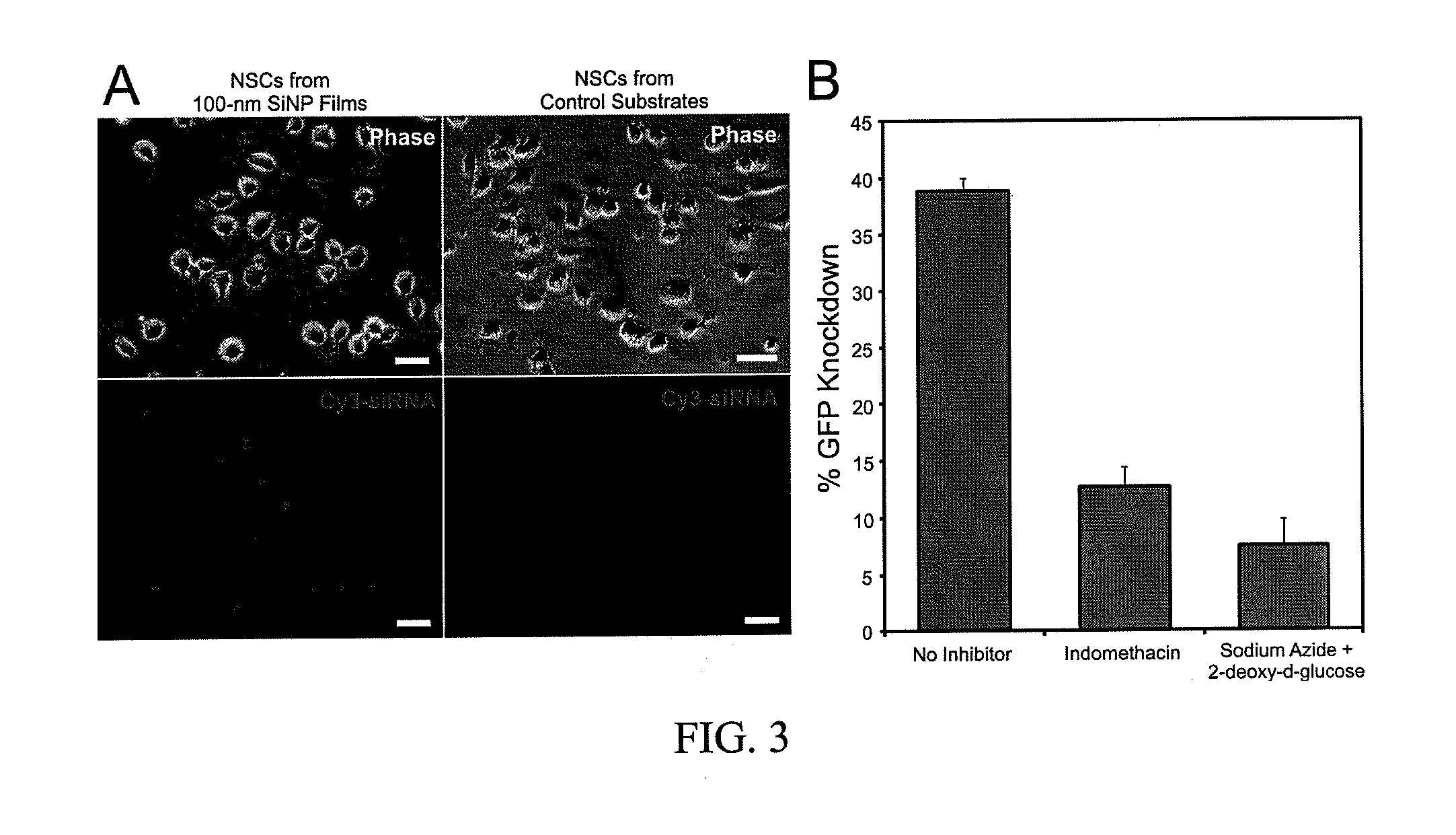
This application discloses a nanotopography-mediated reverse uptake (NanoRU) platform useful for intracellular delivery of nucleic acids into mammalian cells, in particular stem cells, as well as methods of preparation and applications thereof. In particular, this system can be used to deliver small interfering ribonucleic acids (siRNAs) into neural stem cells and enhance neuronal differentiation of the stem cells.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
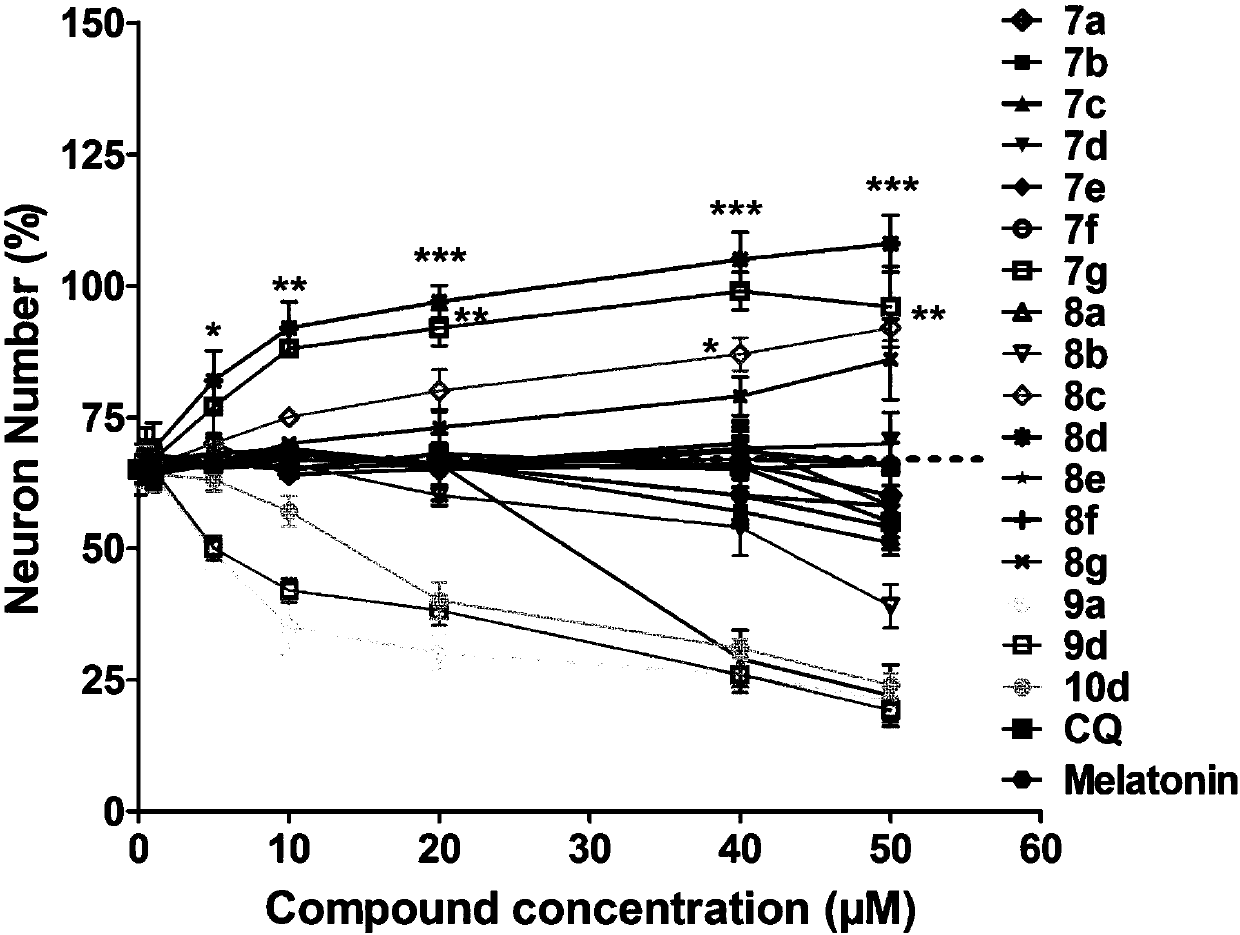
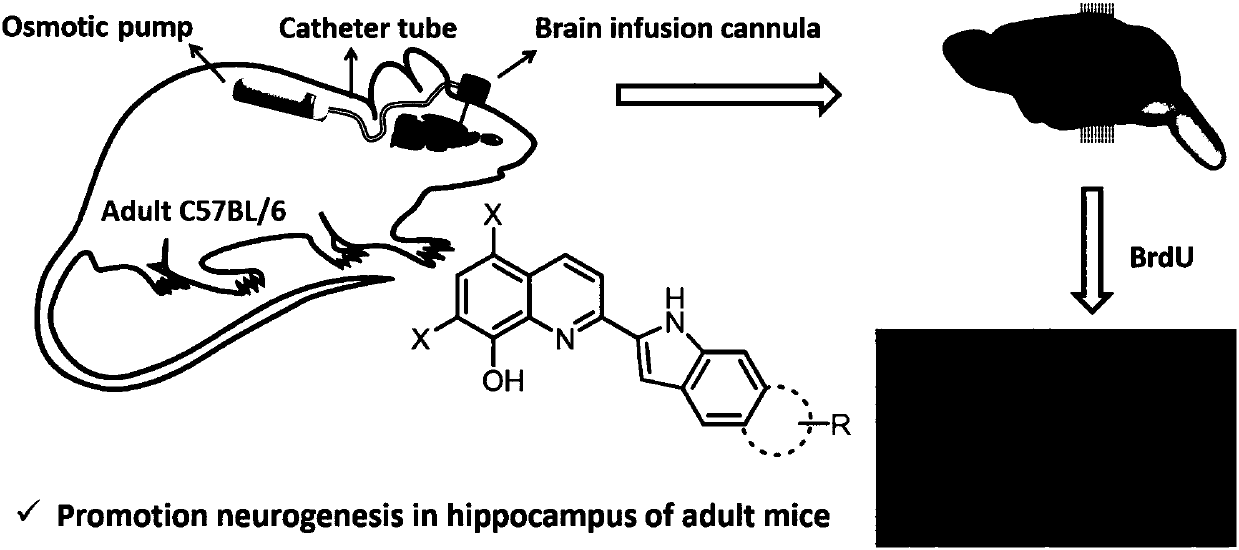
Quinoline-indole derivative and application thereof in preparation of drug used for treating alzheimer disease
InactiveCN107778282AOptimize spaceImprove cognitive abilityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDepolymerizationCognitive capability
The invention discloses a quinoline-indole derivative and application thereof in preparation of a drug used for treating, improving and / or preventing alzheimer disease. The quinoline-indole derivativedisclosed by the invention is a multi-target anti-alzheimer disease active molecule, has the effects of inducing increase of number of neure of nerve cells PC12, neuronal differentiation and antioxidation and inhibiting Abeta aggregation and depolymerization, can promote formation of cerebral hippocampal neuron of an adult mouse and can improve APP / PS1 cognitive capability and spatial memory of an alzheimer disease mouse.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Neuronal differentiation promoter
The present invention provides an agent for promoting neuronal differentiation of neural stem cells, which contains a p38 inhibitor. In addition, the present invention provides a method of promoting neuronal differentiation of neural stem cells, which includes cultivating neural stem cells in the presence of a p38 inhibitor. Neural stem cells are gliogenic or neurogenic. The p38 inhibitor is a nucleic acid which hybridizes to DNA or mRNA encoding p38 under physiological conditions, thereby inhibiting the transcription and / or translation thereof, an expression vector of the nucleic acid, a low molecular p38 inhibitor and the like.
Owner:KEIO UNIV
Preparation method for tissue engineering nerves of compound seed cells
InactiveCN103446628ARetain structural advantagesReduced effects of axon regenerationSkeletal/connective tissue cellsProsthesisCell-Extracellular MatrixECM Protein
The invention discloses a preparation method for tissue engineering nerves of mesenchymal stem cells induced by compound nerves. The preparation method for tissue engineering nerves of mesenchymal stem cells induced by compound nerves comprises the steps of extracting nerves with an improved enzyme-hypotension-chemical detergent in a trigeminy manner based on a Sondell preparation method, constructing tissue engineering peripheral nerves with biological activity in vitro, and then compounding mesenchymal stem cells which are subjected to in-vitro cultivation, amplification and neuronal differentiation induction. According to the preparation method provided by the invention, the destructive effect caused by an existing acceptable chemical preparation method, namely the Sondell method, on a nerve basal membrane tube and an extracellular matrix structure to a certain extent is overcome; the influence on axonal regeneration is alleviated. The tissue engineering nerves of the mesenchymal stem cells induced by the compound nerves, which are prepared by the method disclosed by the invention, can be applied to the preparation of nerve grafts and have good effects in restoring peripheral nerve defect.
Owner:居李生物科技(北京)有限公司
Method of treating pain using agents that promote neuronal differentiation
ActiveUS20180000897A1High sensitivitySensitivity to painOrganic active ingredientsDipeptide ingredientsMedicineNeuron
The present invention is based on the seminal concept of treating pain by promoting neuronal differentiation. The invention provides a method of treating pain utilizing agents that induce neuronal differentiation by activating specific receptors. The invention also provides a method of screening of agents for the purpose of use in treating pain, based on their neuronal differentiation activity.
Owner:RUSANESCU GABRIEL
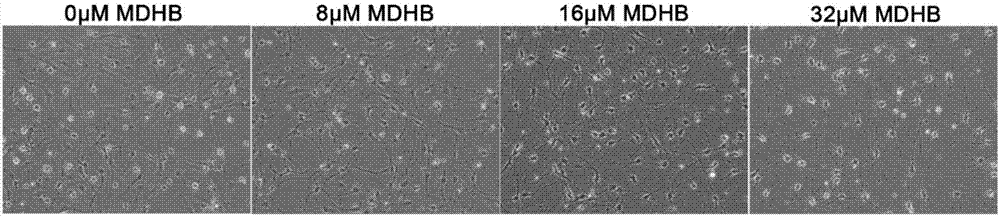
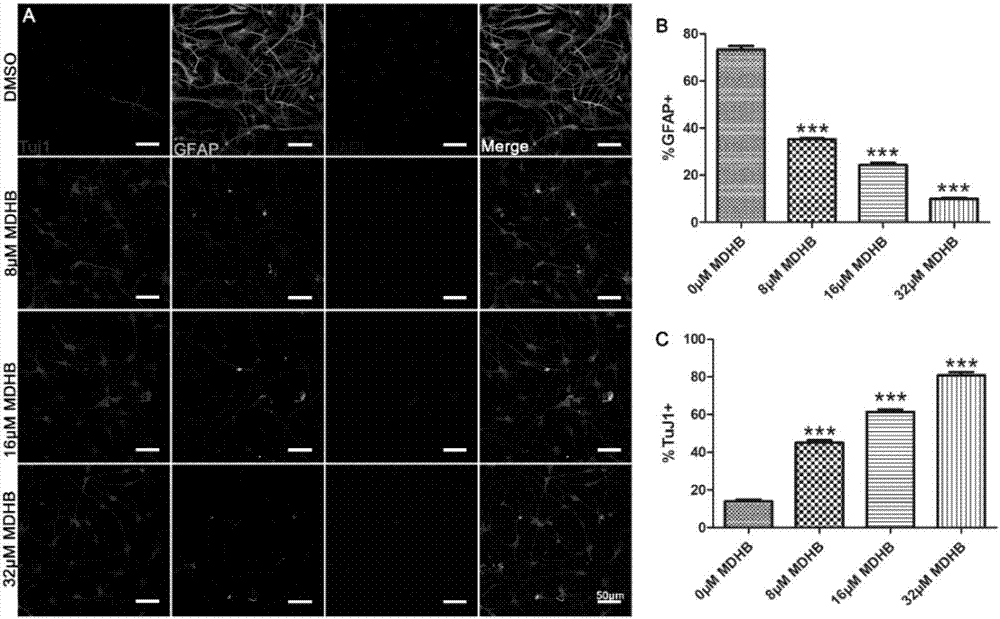
Application of 3,4-methyl dihydroxybenzoate in preparation of drugs for inducing directional differentiation of neural stem cells or neural precursor cells
ActiveCN107365744AHigh purityHigh activityNervous disorderNervous system cellsDiseaseCholinergic cells
The invention discloses application of 3,4-methyl dihydroxybenzoate (MDHB) in preparation of drugs for inducing directional differentiation of neural stem cells or neural precursor cells. The invention discovers that MDHB has the effect of directionally inducing differentiation of neural stem cells or neural precursor cells to cholinergic neurons, can be used for developing drugs for curing related diseases (SCI, AD and the like) of cholinergic neuron damage and loss, can be used for cell transplantation therapy of related diseases (SCI, AD and the like) of cholinergic neuron damage and loss, and can be used for developing directional inducers and the like of neural stem cells or neural precursor cells. The new pharmacological activity of MDHB is determined, the illumination of a pesticide effect mechanism provides reference for developing new drugs with proprietary intellectual property rights, MDHB is applied to basic experiments in the field of neurosciences, and a novel method is provided for searching models of cholinergic neurons.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com