Method for removing bacteria from blood using high flow rate
a high-flow rate, bacteria technology, applied in other blood circulation devices, other chemical processes, medical devices, etc., can solve the problems of bacterial infection, septic shock, bacteremia quickly, etc., to shorten the duration of bacteremia and quick reduce the load of bacteria
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Removal of Bacteria with Low or Undetectable Affinity for Heparan Sulfate
[0104]This example illustrates the use of heparin coated beads to remove bacterial pathogens with low affinity or undetectable affinity for heparan sulfate from whole blood.
[0105]It has been reported in the literature that over 50 different pathogens target heparan sulfate proteoglycans found on syndecans as an initial attachment site during their pathogenesis. Surprisingly, surface bound heparin can function as a surrogate to heparan sulfate binding organisms.
[0106]Our studies have shown that heparinized adsorption media can remove high concentration of S. aureus and MRSA from whole blood. Also, the study showed that the bacteria attached to the heparinized surface were not killed, and thus did not release potential inflammatory toxins and their byproducts into the blood. Thus, the heparin-bound media can be used in an extracorporeal device to effectively and safely remove circulating bacteria including drug-r...
example 2
Adsorption Media with a Hydrophilic Surface
[0126]This example shows the adsorption media comprising a hydrophilic surface which can be used to removed bacteria from whole blood or serum.
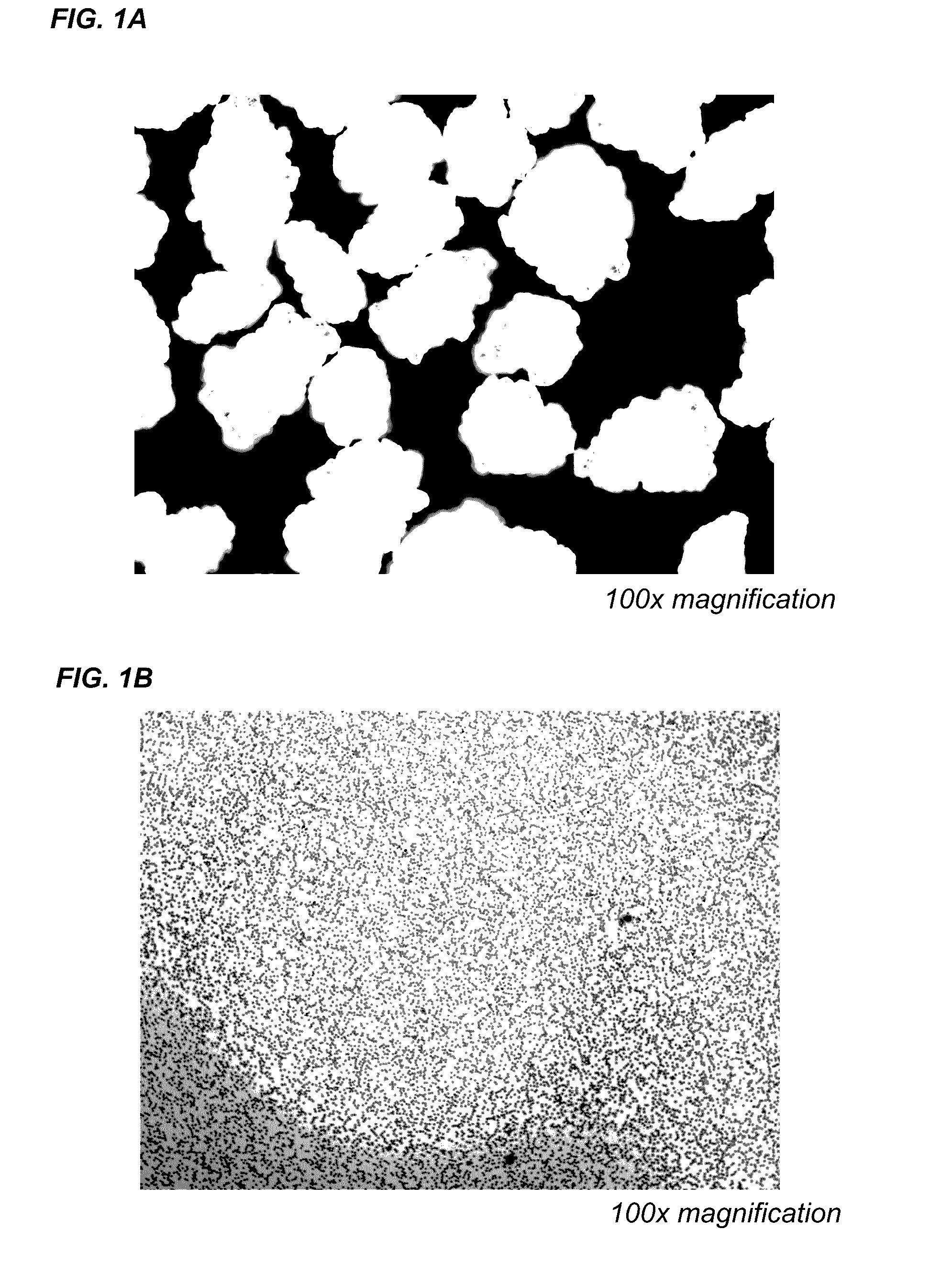
[0127]The adsorption media described herein contains a surface topography that enables its binding to pathogens, such as those with no affinity or low affinity to heparin (FIG. 1A). Without being bound by any particular theory, it is believed that a rough, uneven or ungulating surface may contribute to the affinity of the bacteria to the adsorption media.
[0128]FIG. 1B shows an image of a human blood smear for comparison. FIG. 2 shows a size comparison of bacteria, e.g., Staphylococcus aureus and Chlamydia, and viruses, e.g., pox virus, herpes virus, influenza virus, and picornavirus (polio).
example 3
Blood Filters for Use in High Linear Flow Rate Extracorporeal Therapies
[0129]This example provides an exemplary design of an extracorporeal filter cartridge that is used to accommodate high linear flow rates.
[0130]An extracorporeal blood filter can be designed to operate safely at specific flow rates used with common pump systems. If the pressure drop across a blood filter is too high, hemolysis can occur. Typically, dialysis systems operate with pressures below 34 kPa to avoid the risk of hemolysis.
[0131]For a cartridge filled with packed adsorbent media, the pressure drop across the cartridge depends on the flow rate, particle size, particle modulus, height of the packed media, and viscosity of blood. If a filter media is not sufficiently rigid, then compression of the media can occur with increased blood flow resulting in a reduced porosity that can lead to unsafe pressures.
[0132]The first variable to determine is the minimum particle size allowable for specific column heights an...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| water contact angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| linear flow velocity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com