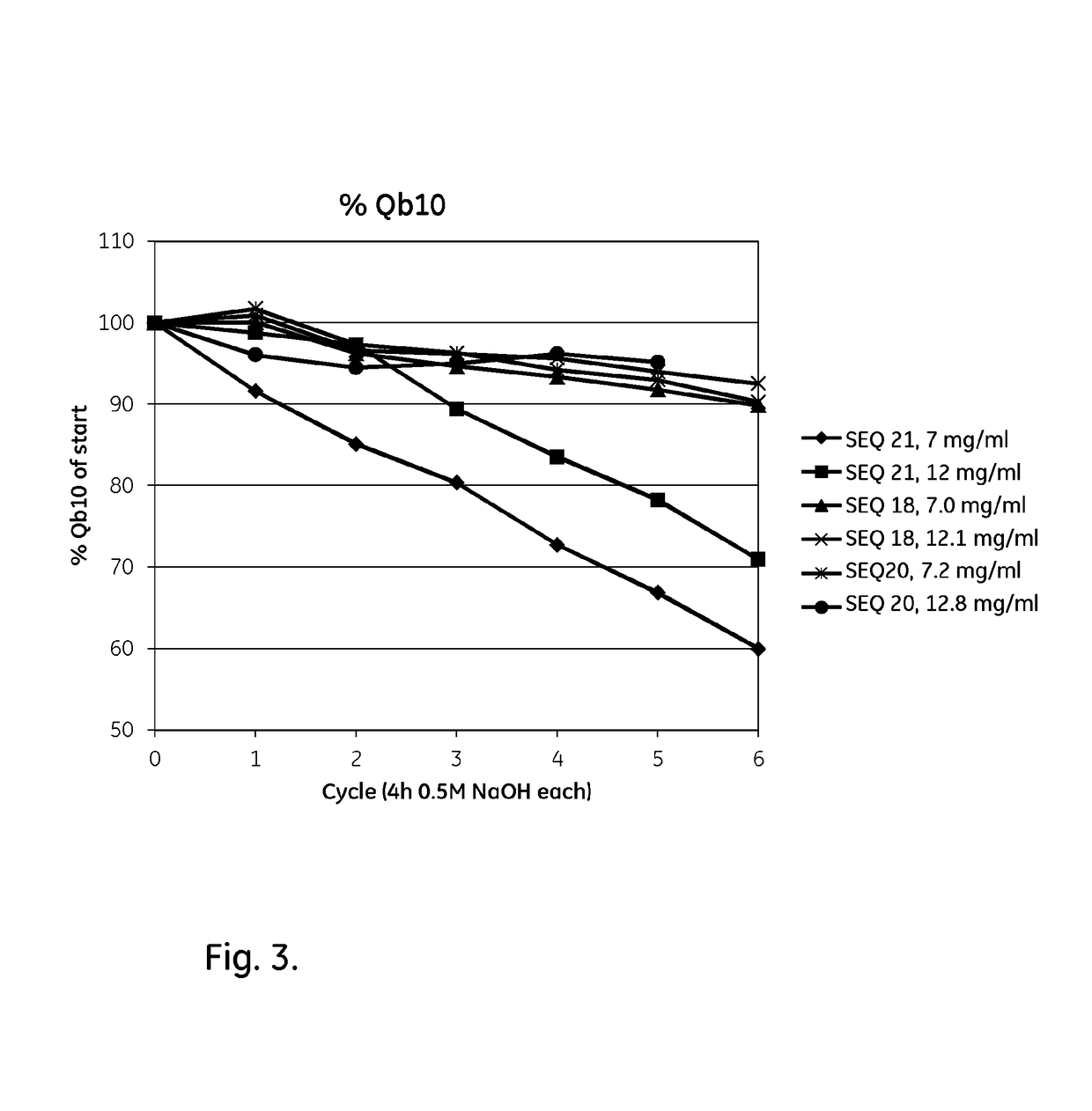
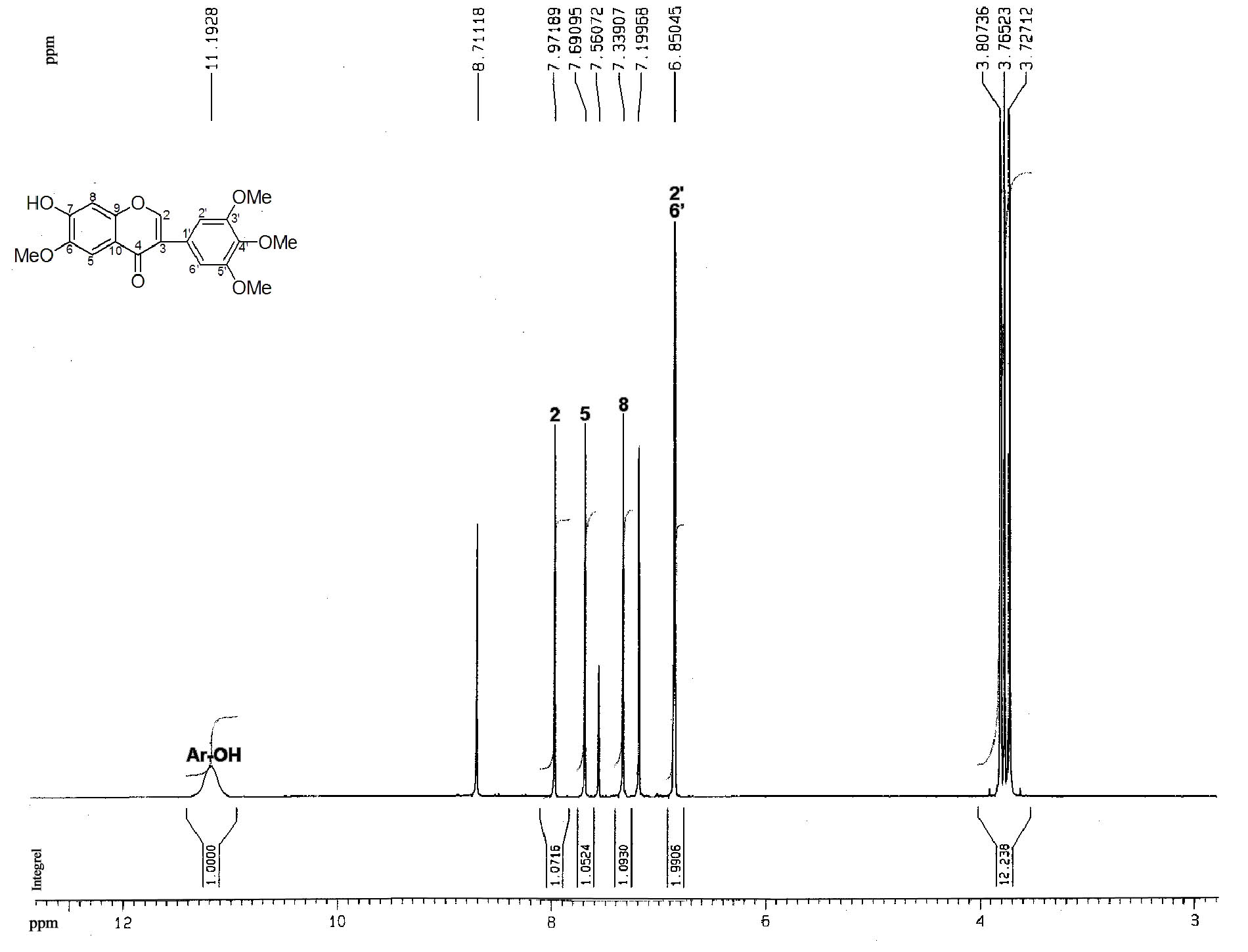
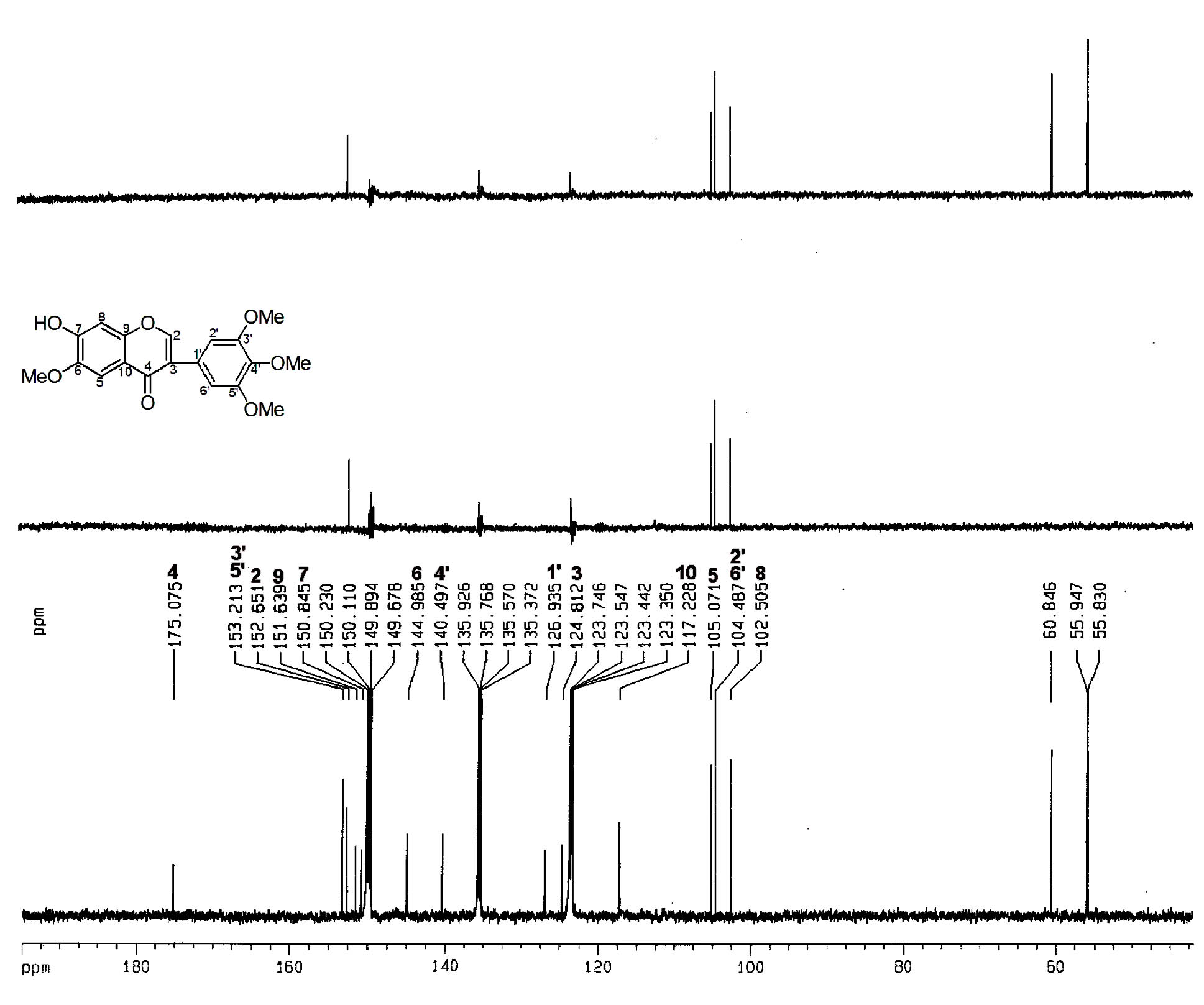
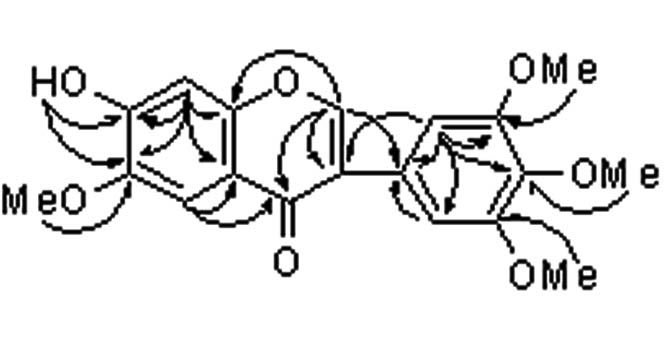
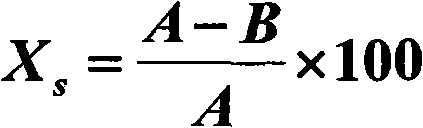Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
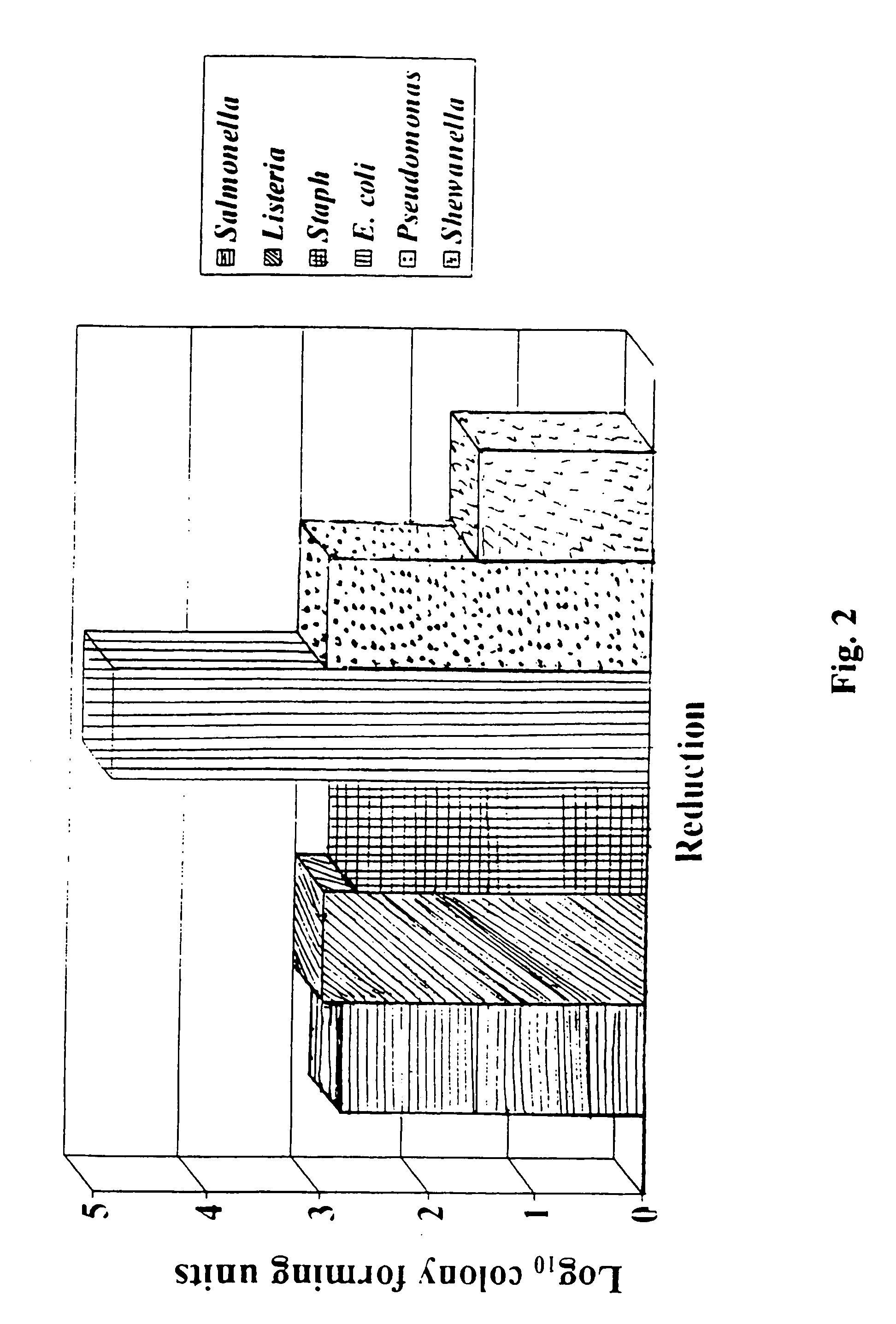
2005 results about "Staphylococcus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Staphylococcus is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria in the family Staphylococcaceae in the order Bacillales. Under the microscope, they appear spherical (cocci), and form in grape-like clusters. Staphylococcus species are facultative anaerobic organisms (capable of growth both aerobically and anaerobically).
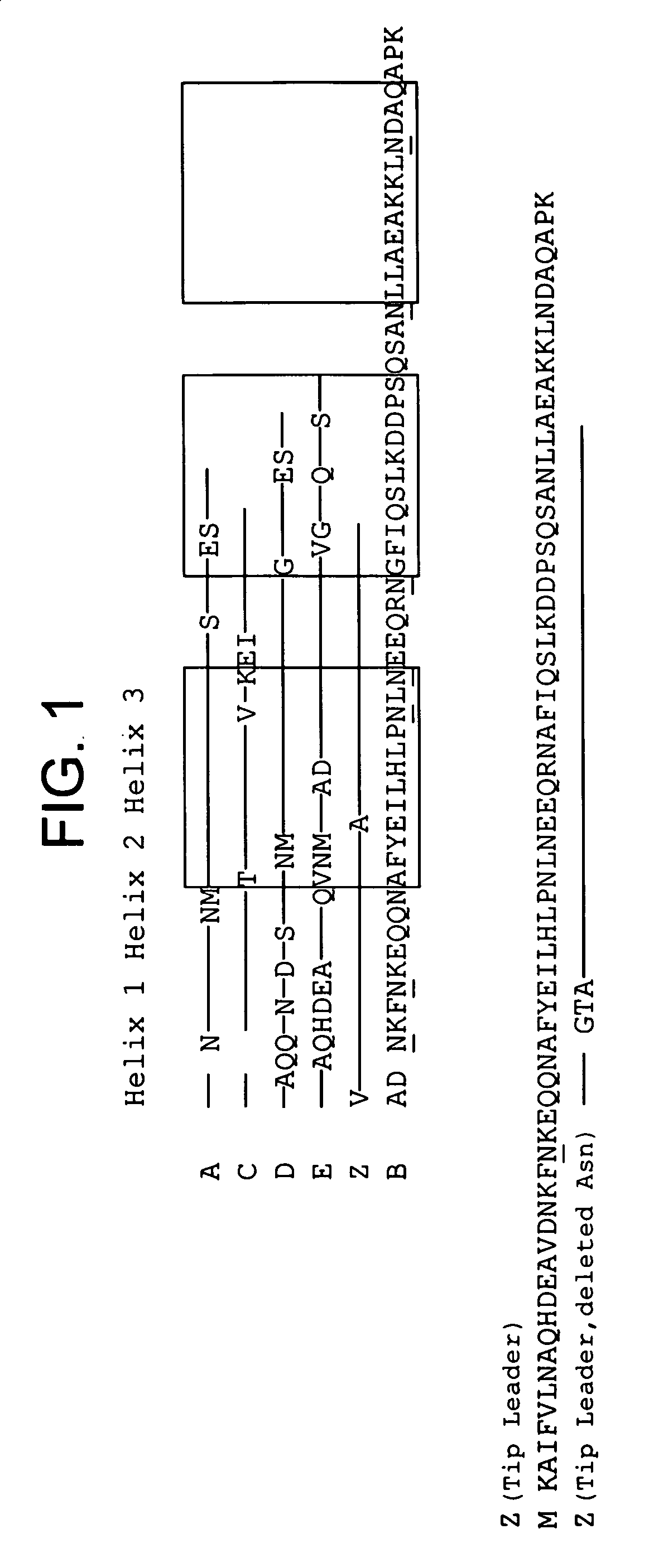
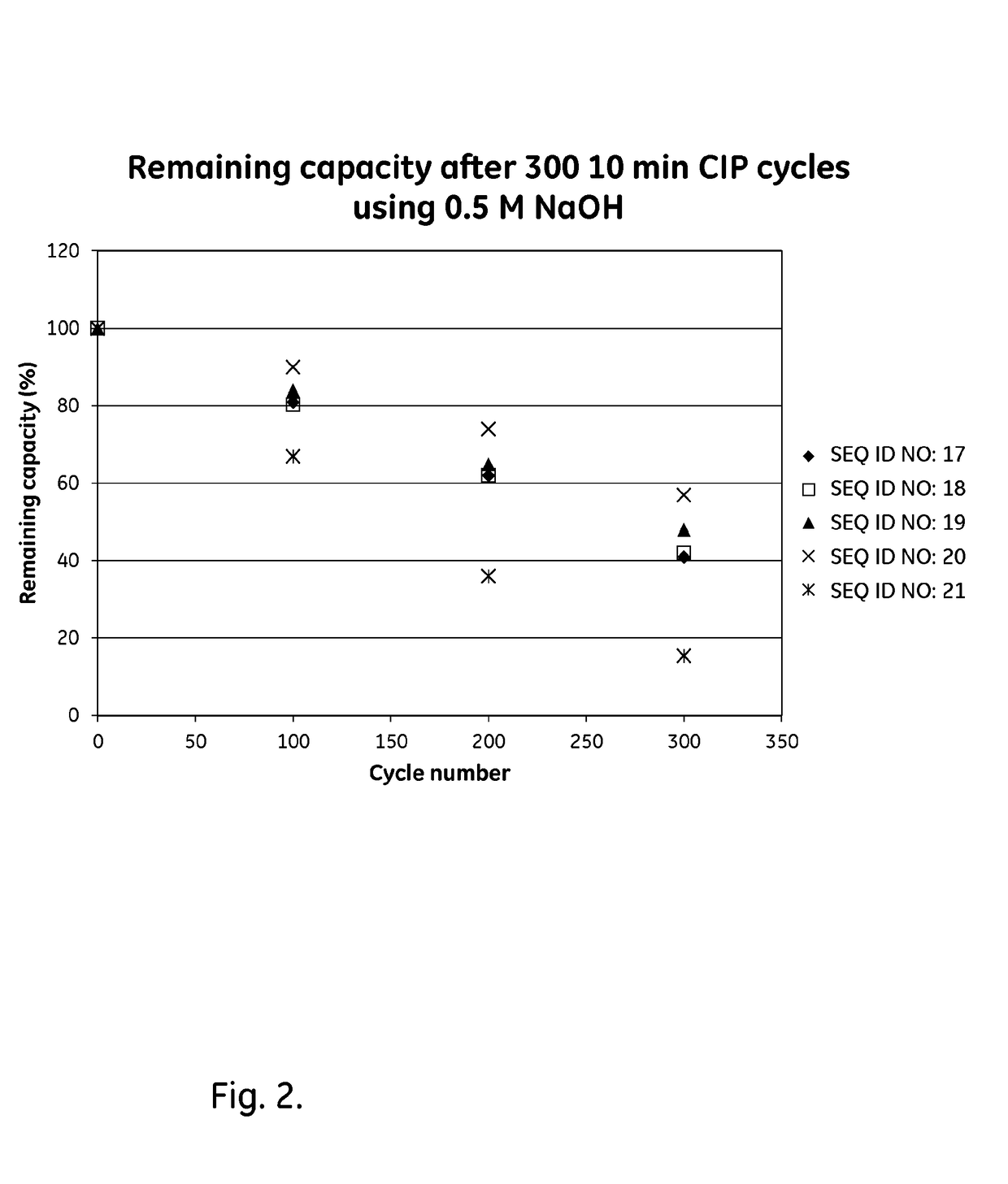
Mutant protein
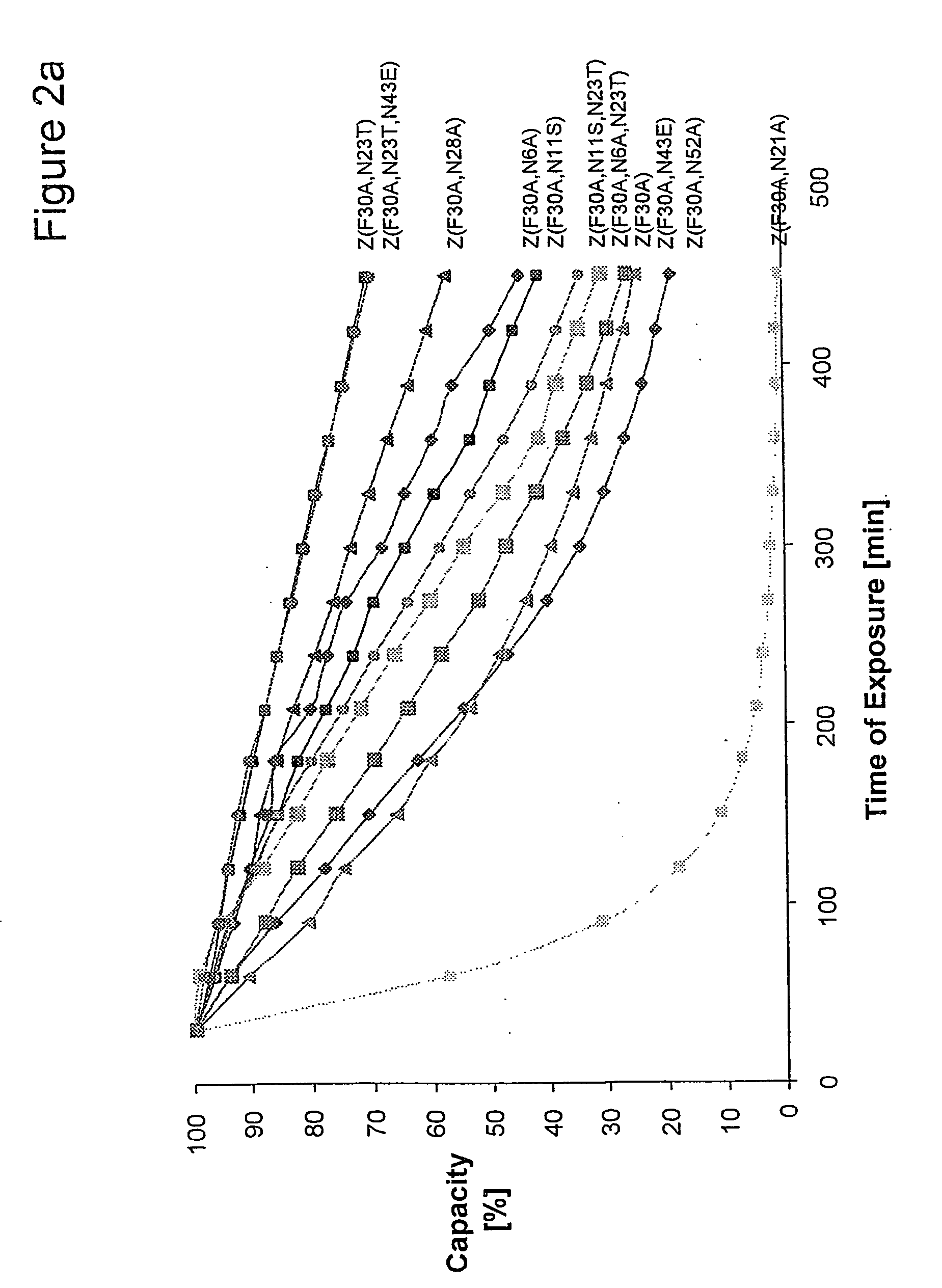
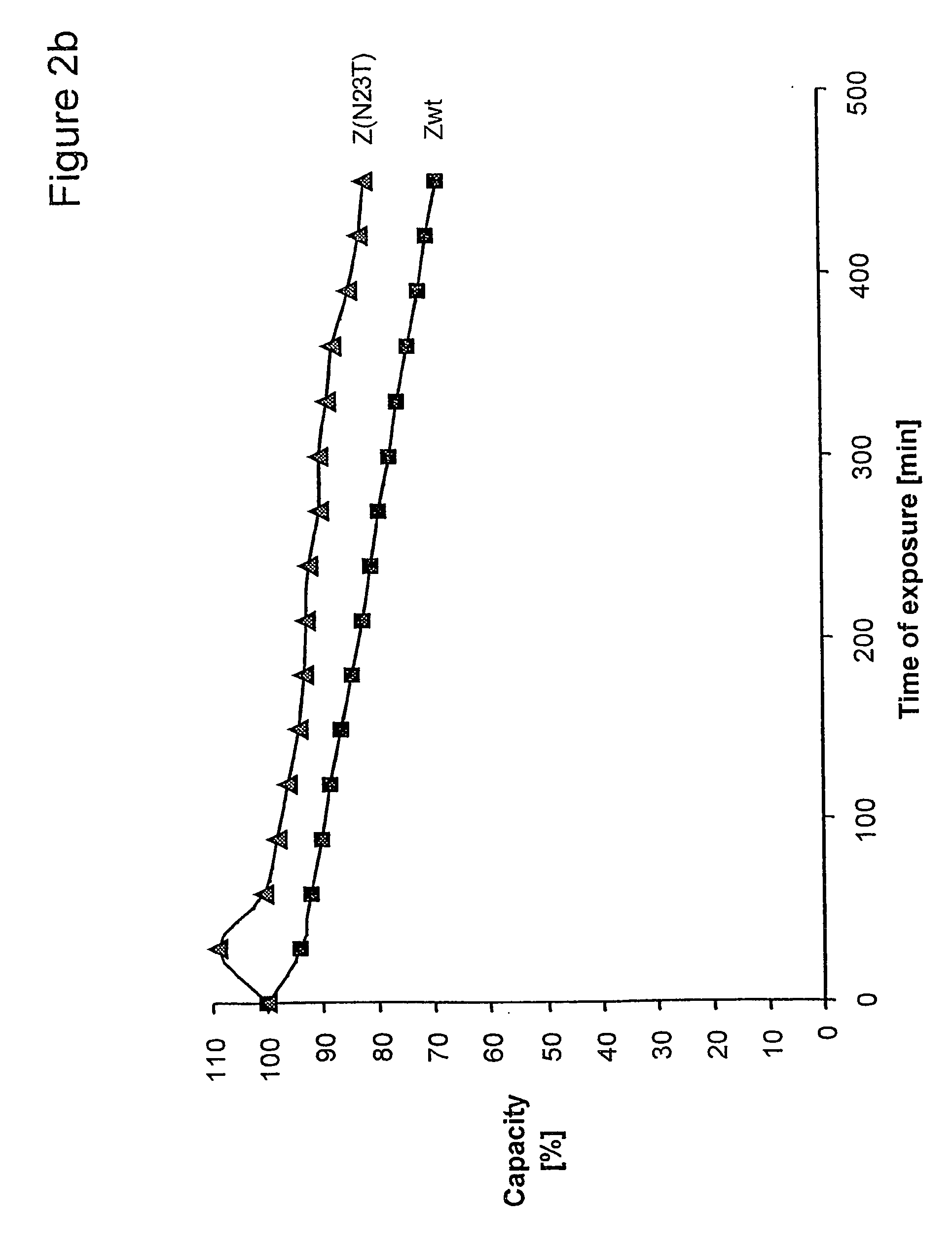
InactiveUS20060194950A1Improve stabilityIncreased pH-valuesBacteriaSerum immunoglobulinsMutated proteinComplementarity determining region
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIO SCI CORP
Mutated immunoglobulin-binding protein
ActiveUS20050143566A1Improve stabilityIncreased pH-valuesSerum immunoglobulinsComponent separationComplementarity determining regionChemical stability
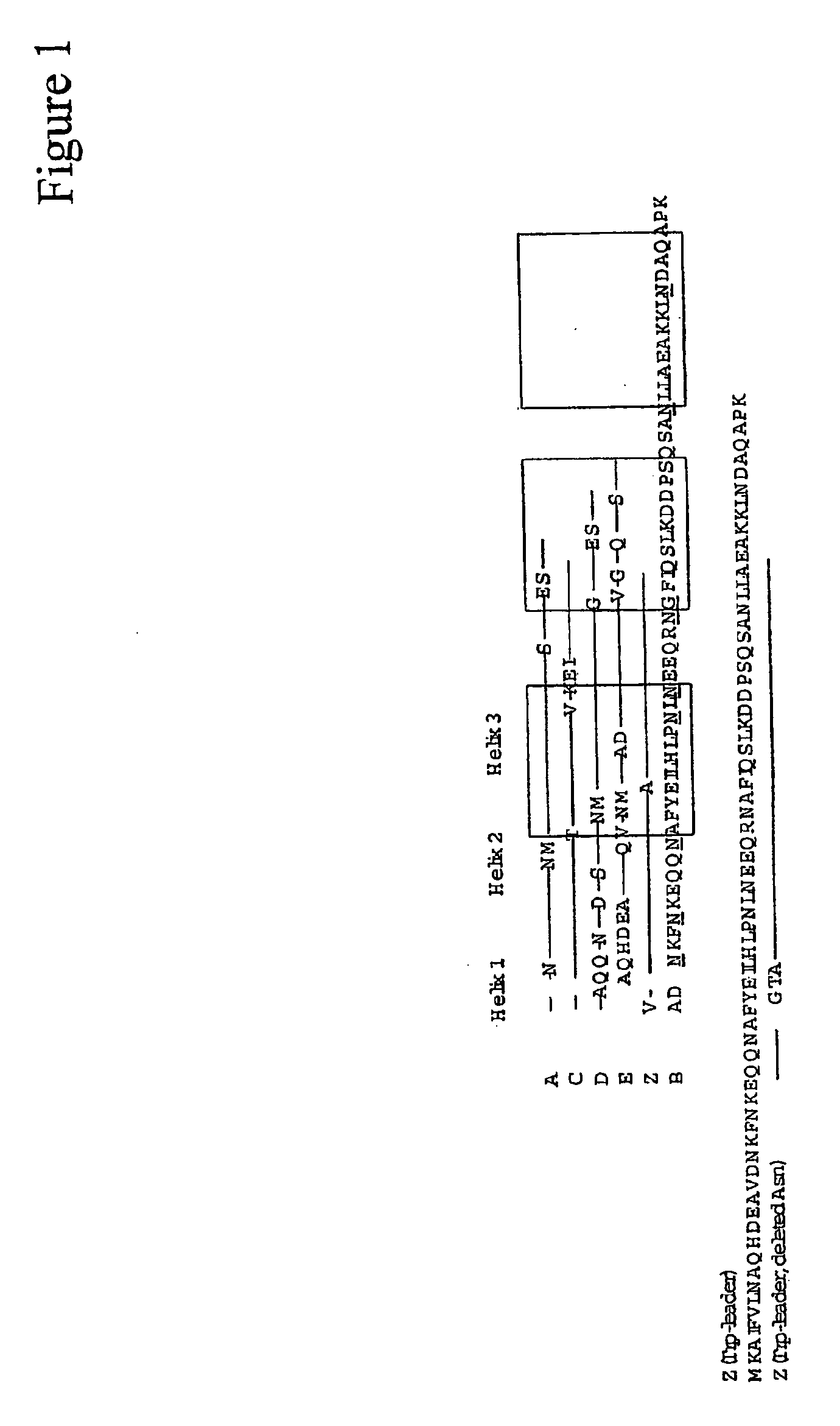
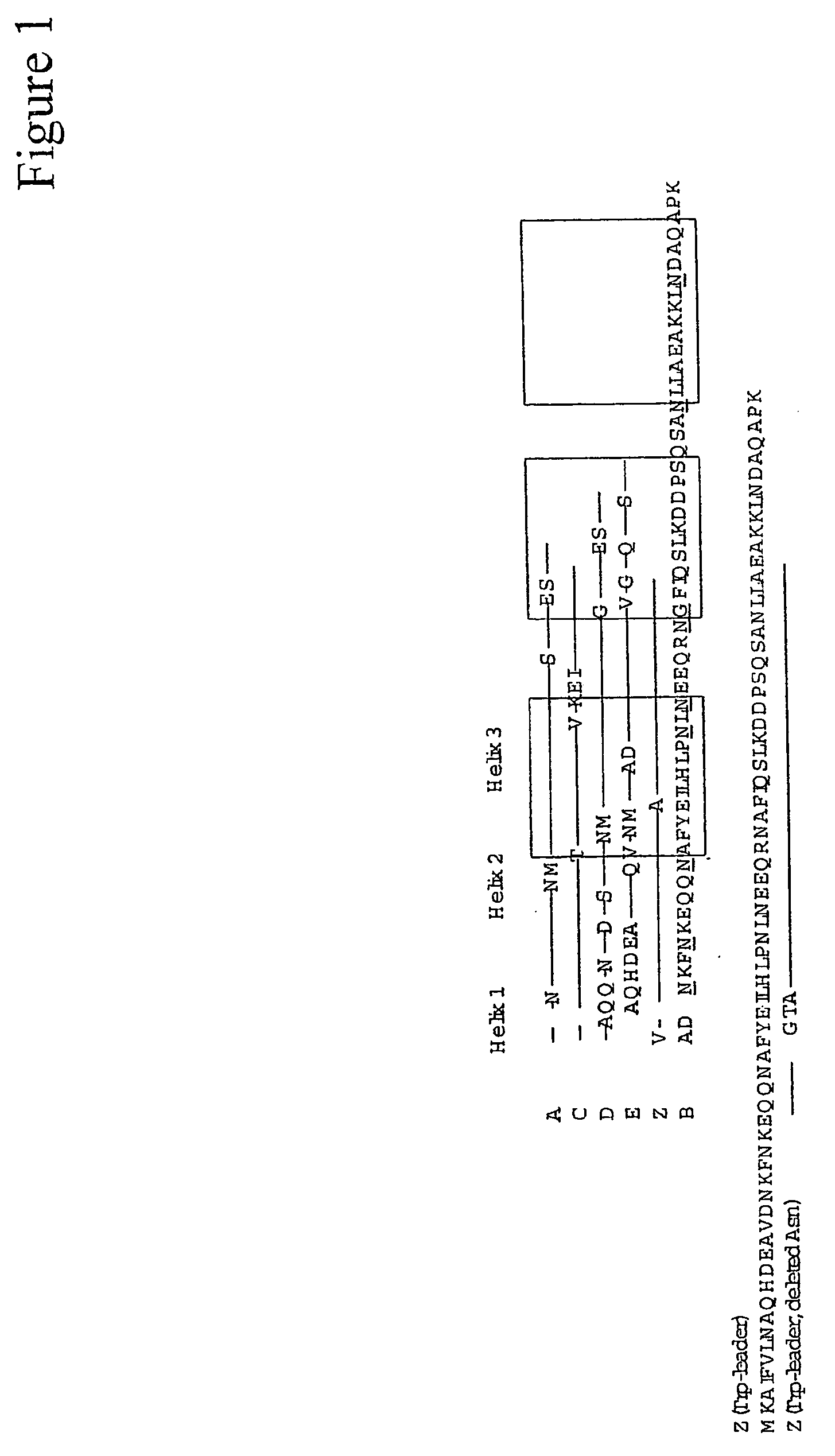
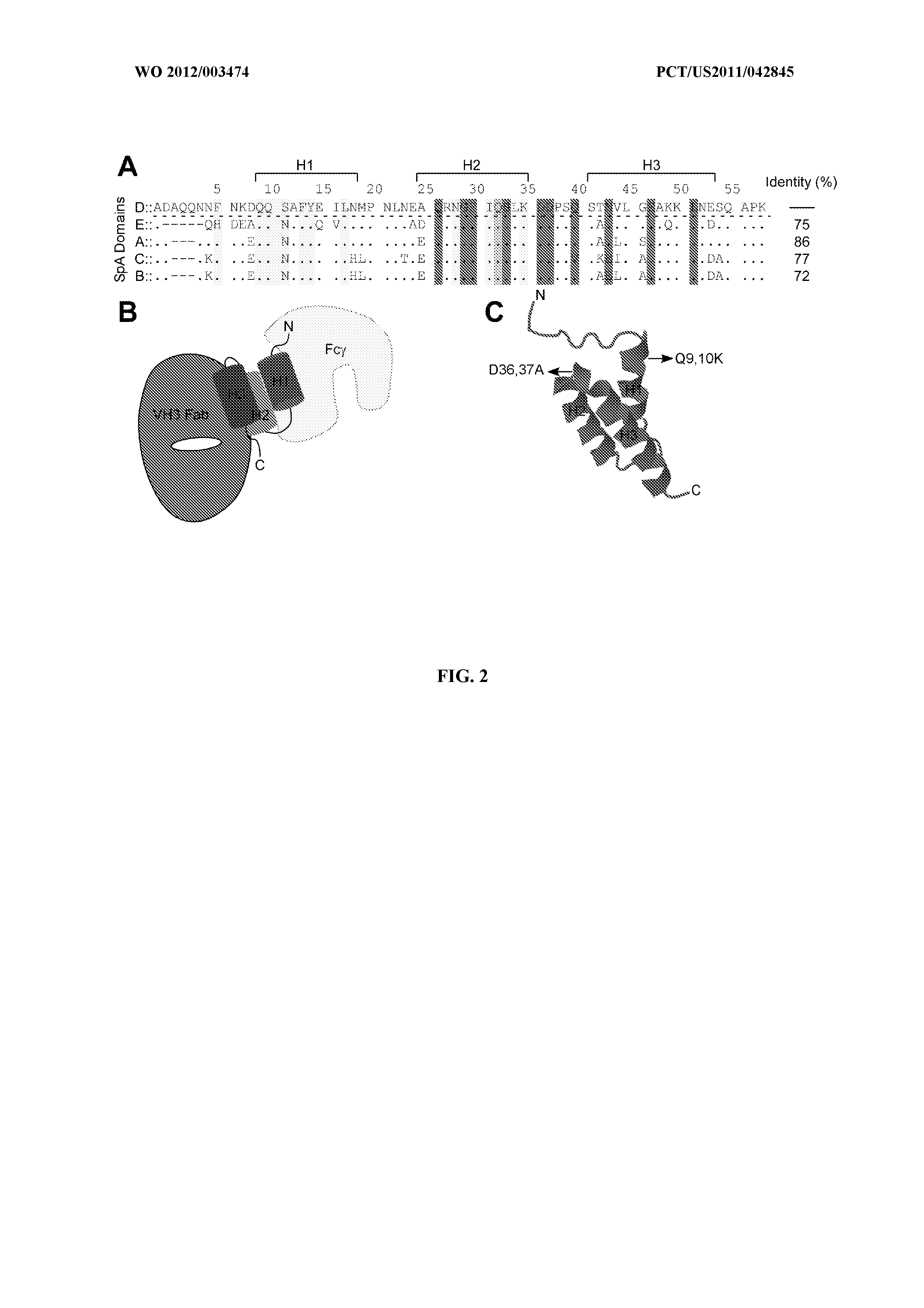
The present invention relates to an immunoglobulin-binding protein, wherein at least one asparagine residue has been mutated to an amino acid other than glutamine or aspartic acid, which mutation confers an increased chemical stability at pH-values of up to about 13-14 compared to the parental molecule. The protein can for example be derived from a protein capable of binding to other regions of the immunoglobulin molecule than the complementarity determining regions (CDR), such as protein A, and preferably the B-domain of Staphylococcal protein A. The invention also relates to a matrix for affinity separation, which comprises an immunoglobulin-binding protein as ligand coupled to a solid support, in which protein ligand at least one asparagine residue has been mutated to an amino acid other than glutamine.
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
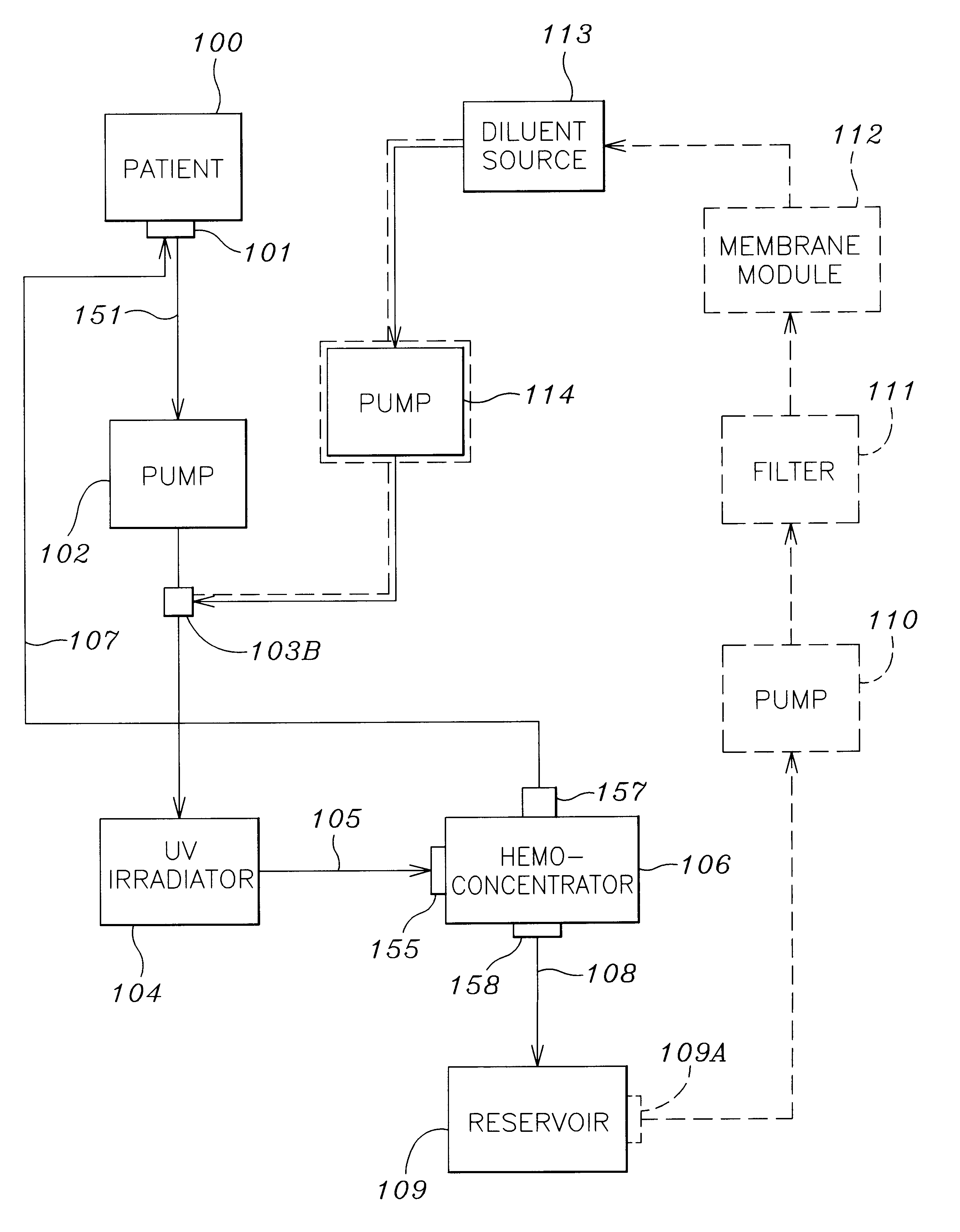
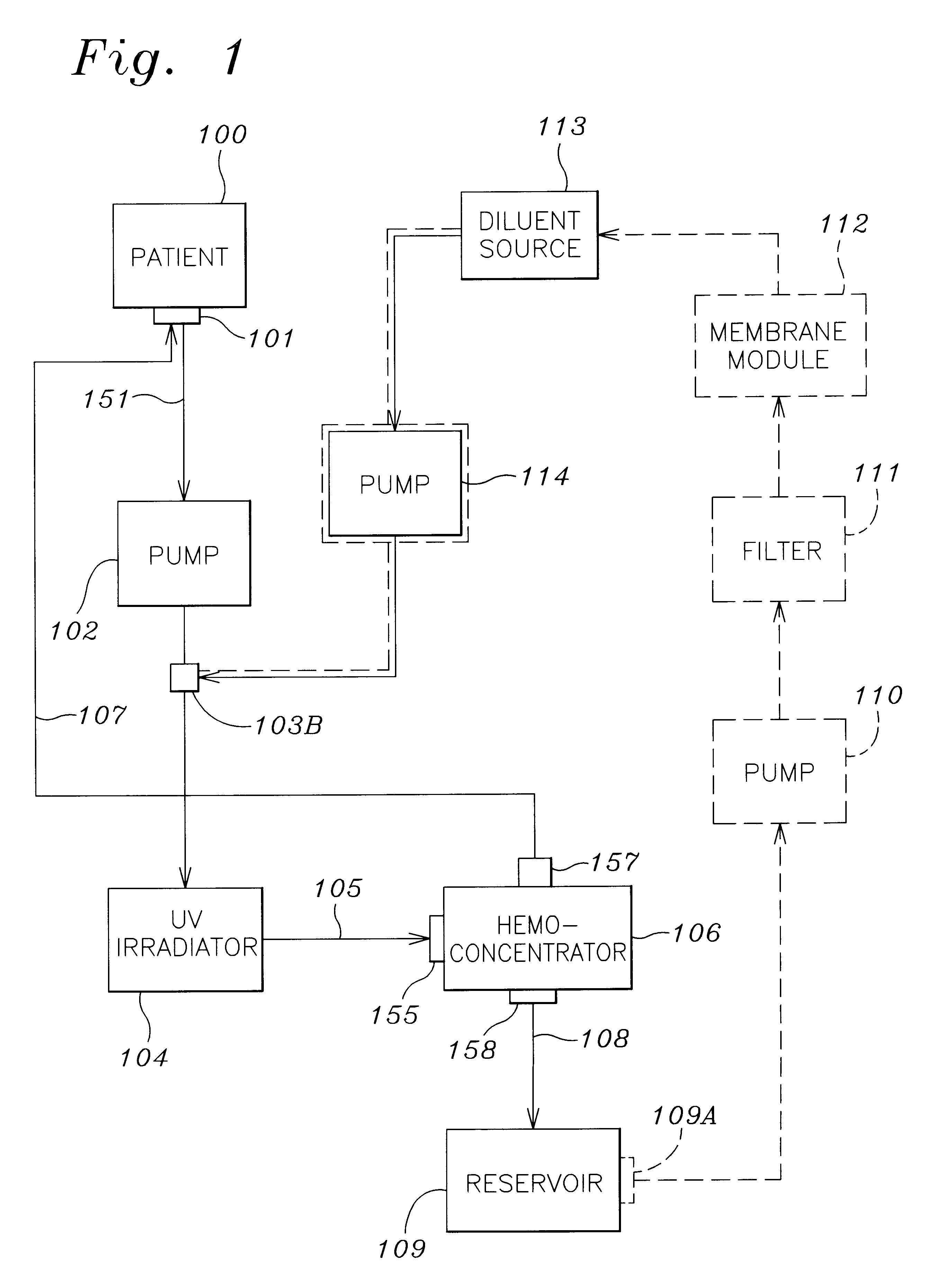
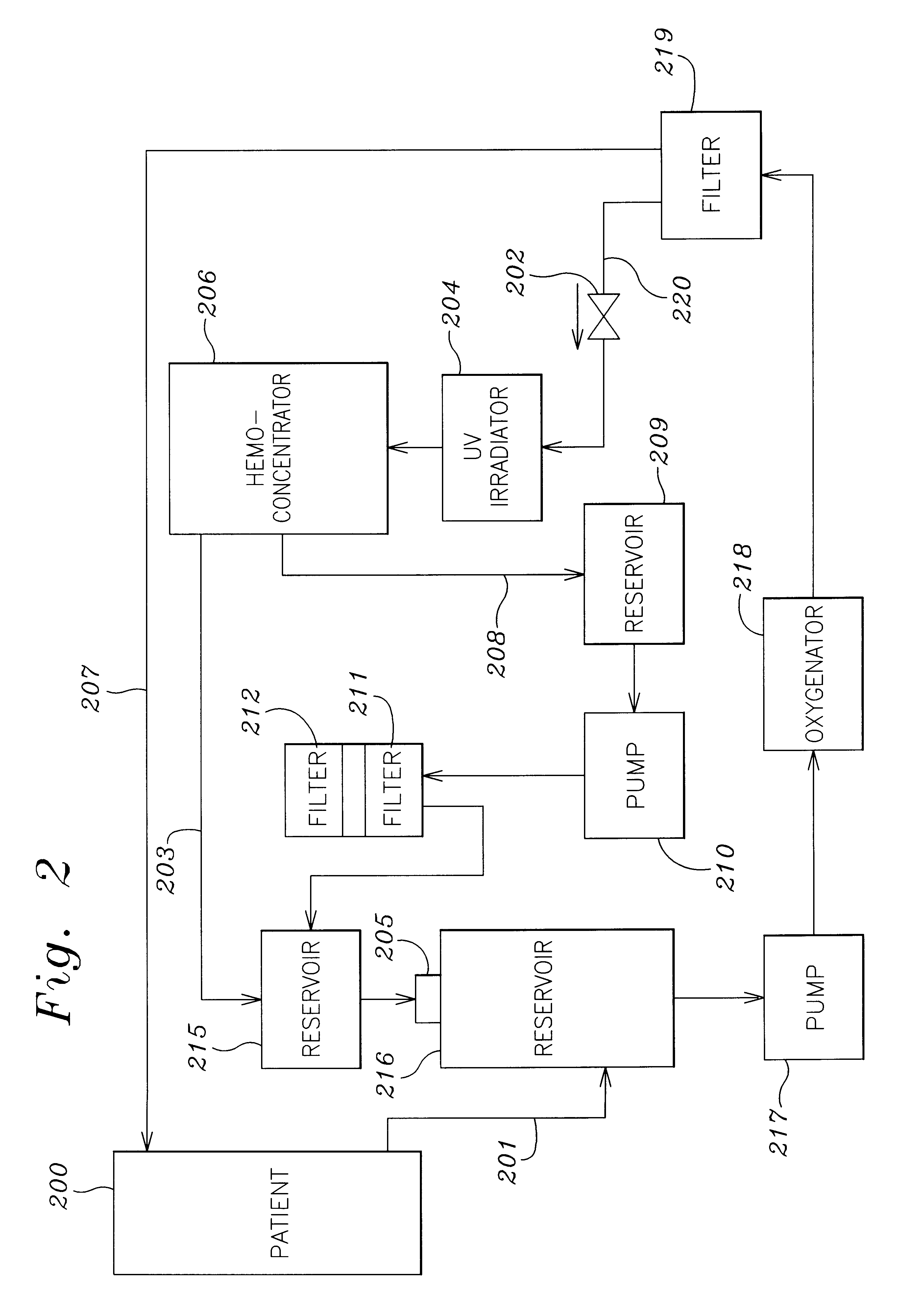
Septicemia prevention and treatment system
InactiveUS6193681B1Electrolysis componentsOther blood circulation devicesStaphylococcus cohniiFiltration
A method and apparatus for preventing and treating septicemia in patient blood. The extracorporeal system includes an anti-microbial device to kill at least 99% of bloodborne microorganisms, a hemoconcentrator / filtration unit to remove approximately 90% of target molecules from the patient blood and a filter unit to remove target molecules from patient blood from the sieved plasma filtrate. Target molecules are produced by microorganisms as well as the patient's cells and include endotoxins from gram negative bacteria, exotoxins from gram negative and gram positive bacteria, as well as RAP protein mediator from Staphylococcus aureus, and cell mediators such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and interleukin 1-beta, complement proteins C3a and C5a, and brandykinin.
Owner:HEMAVATION
Protein ligands
ActiveUS20060194955A1Retention characteristicReduce leakageImmunoglobulins against animals/humansBiological testingComplementarity determining regionStaphylococcus
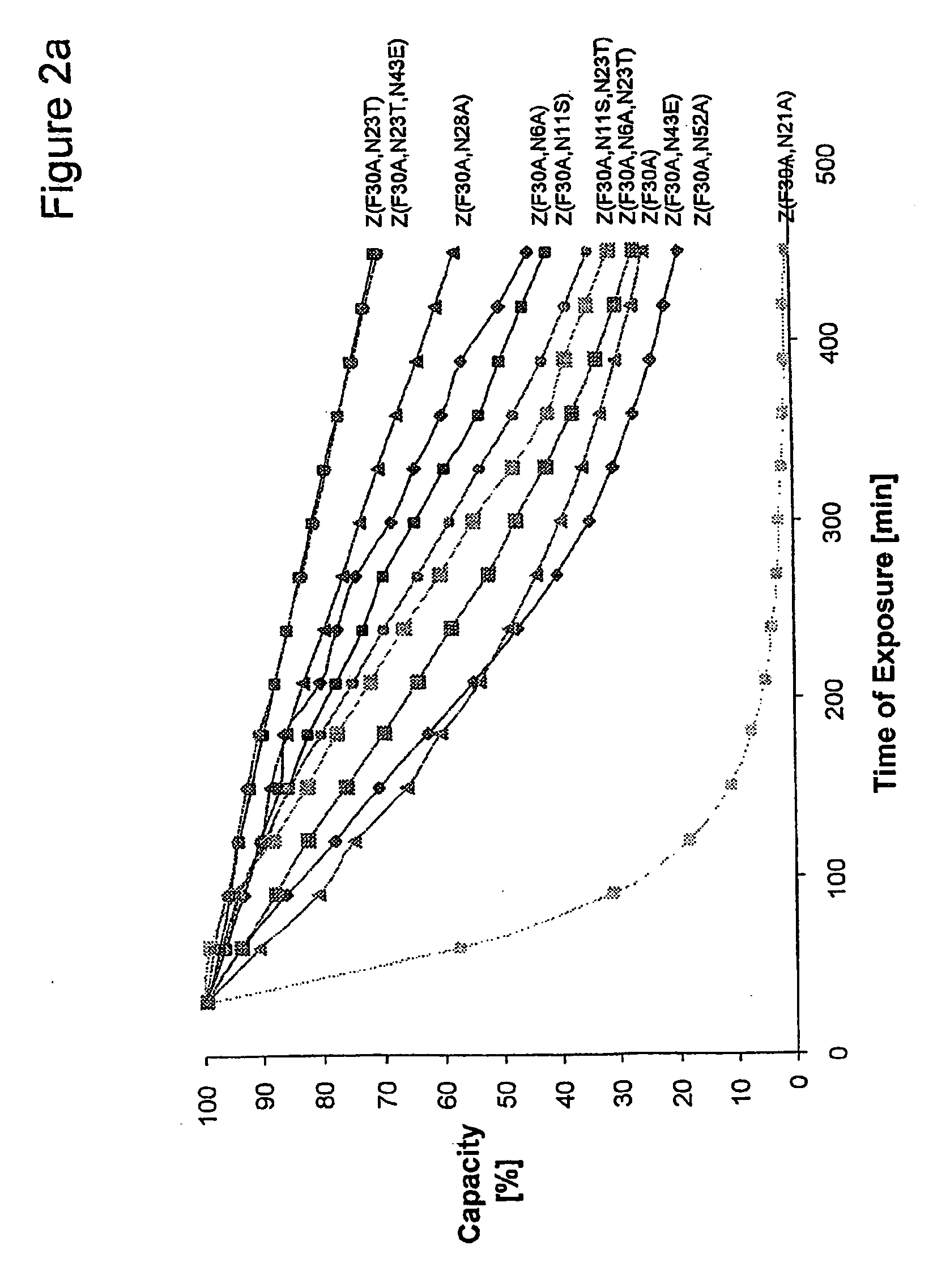
The present invention relates to the use of an alkali-stable protein, wherein at least one asparagine residue has been mutated to an amino acid other than glutamine or aspartic acid, which mutation confers an increased chemical stability at pH-values of up to about 13-14 compared to the parental molecule. The protein can for example be derived from a protein capable of binding to other regions of the immunoglobulin molecule than the complementarity determining regions (CDR), such as protein A, and preferably the B-domain of Staphylococcal protein A. The invention also relates to a matrix for affinity separation, which comprises an immunoglobulin-binding protein as ligand coupled to a solid support, in which protein ligand at least one asparagine residue has been mutated to an amino acid other than glutamine.
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
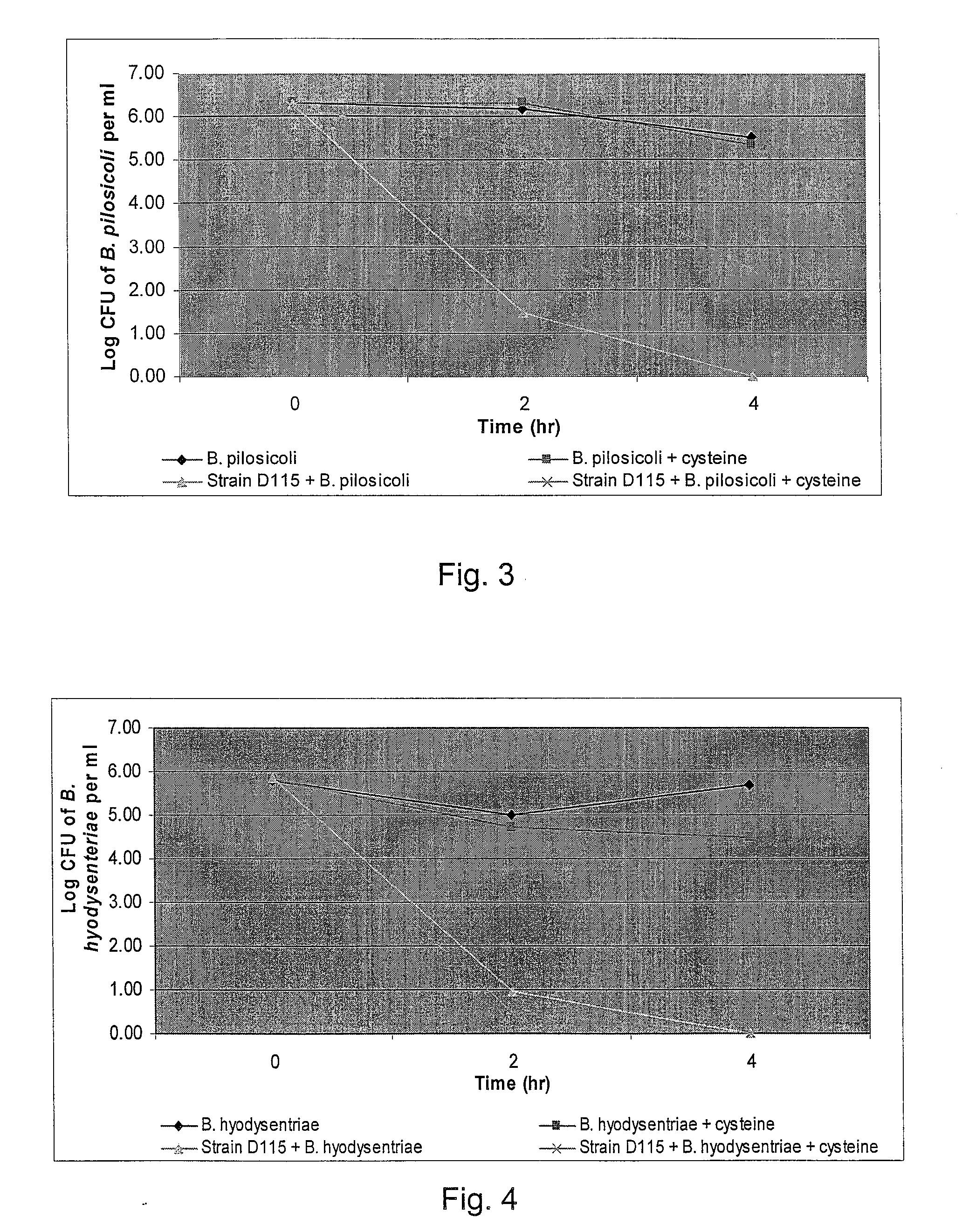
Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial and Antifungal Activity of Lactobacillus Johnsonii D115
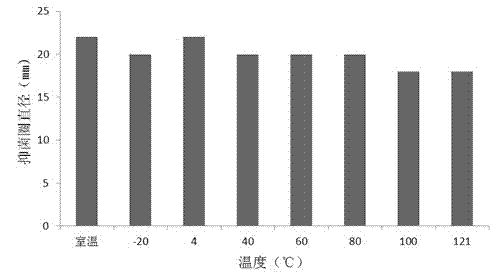
The present invention demonstrated the potential use of Lactobacillus johnsonii D115 as a probiotic, as a prophylactic agent or as a surface treatment of materials against human and animal pathogens such as Brachyspira pilosicoli, Brachyspira hyodysenteriae, Shigella sonnei, Vibrio cholera, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, Campylobacter jejuni, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Enterococcus faecalis, Enterococcus faecium, Clostridium perfringens, Yersinia enterocolitica, Escherichia coli, Klebbsiella pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella spp., Bacillus cereus, Aspergillus niger and Fusarium chlamydosporum. The proteineous antimicrobial compound was partially characterized and found to be heat tolerant up to 121° C. for 15 min, and acid tolerant up to pH1 for 30 min at 40° C. The compound is also stable to enzymatic digestion, being able to retain more than 60% antimicrobial activity when treated with pepsin and trypsin.
Owner:KEMIN IND INC
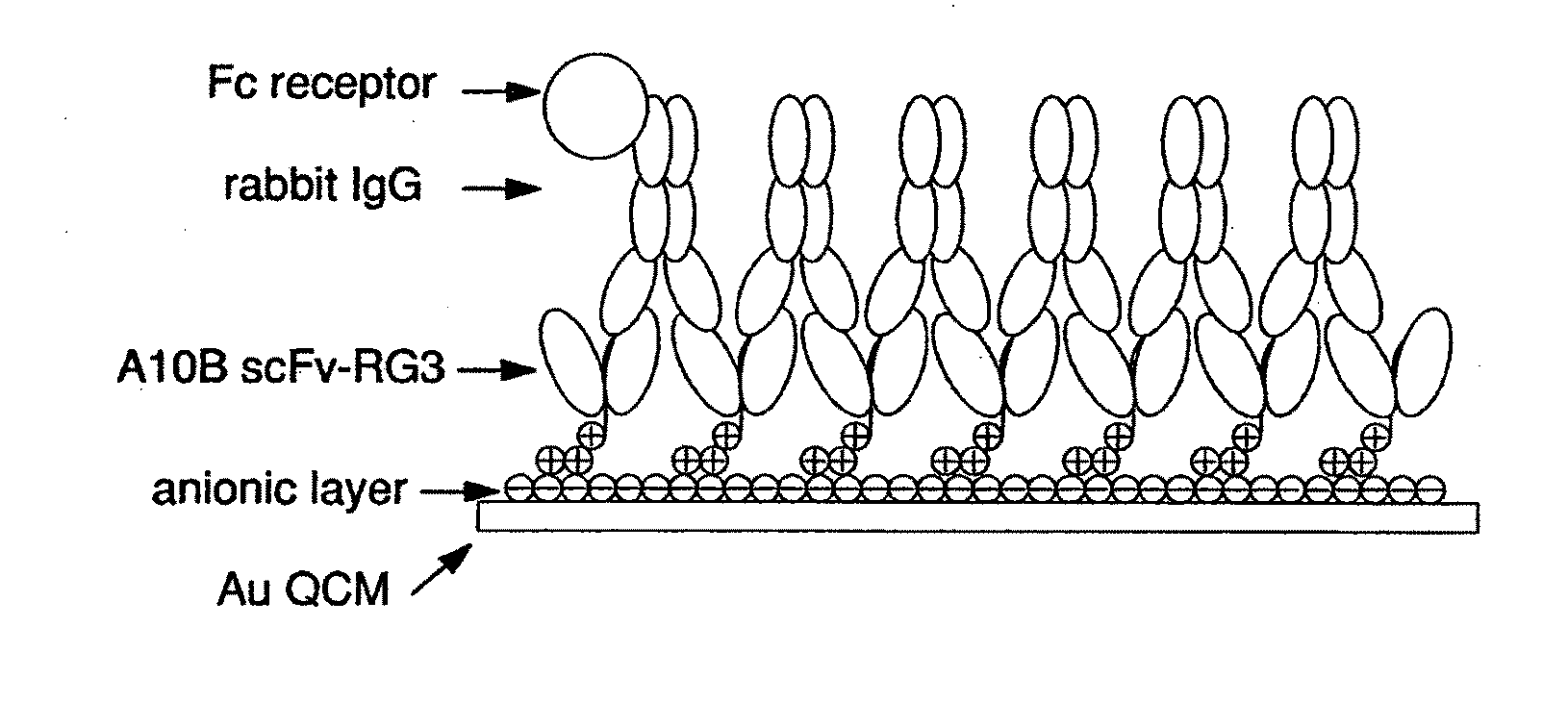
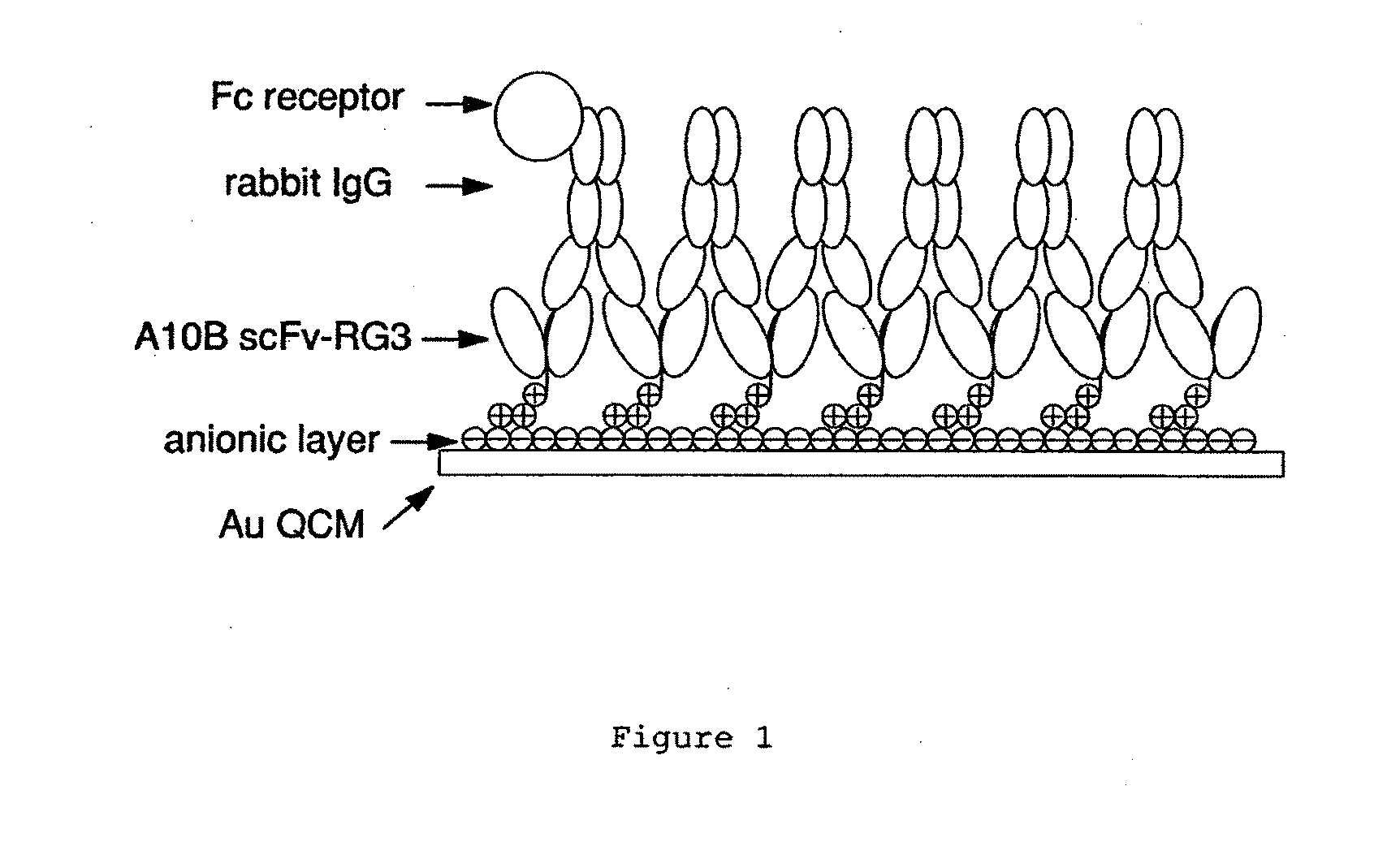
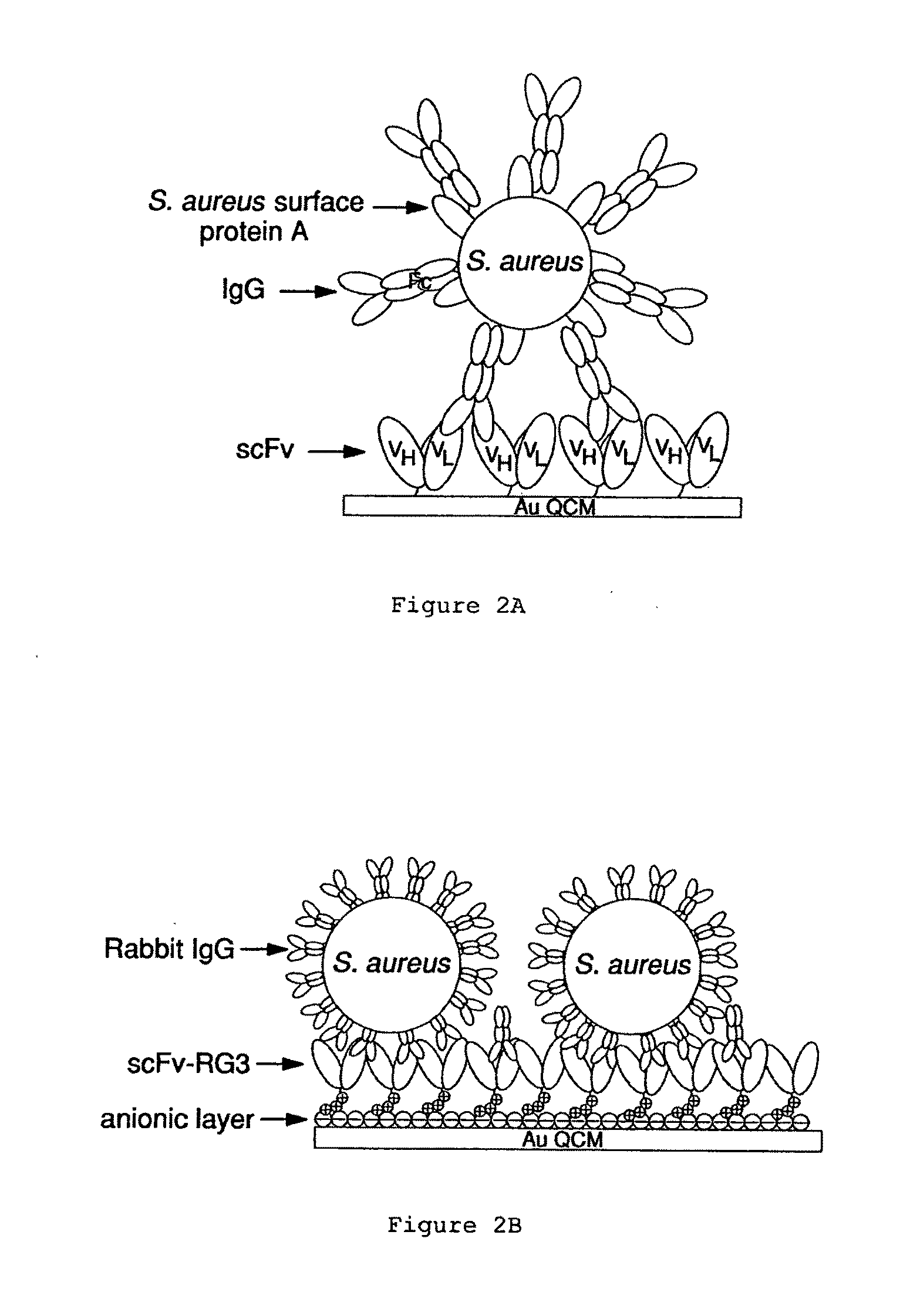
Immunosensors: scFv-linker design for surface immobilization
InactiveUS20110201032A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologySingle-Chain AntibodiesSide chain
An apparatus and methods for binding an analyte of interest in a sample are provided. The apparatus comprises a substrate with an exposed surface with an compound, that is electrostatically charged or capable of forming hydrogen bonds, provided bound to the solid substrate. A recombinant single chain antibody (scFv) molecule specific for the analyte of interest, having one or more amino acids with charged or hydrogen-bond forming sidechains in a linker polypeptide portion, is bound to the layer on the solid substrate. When the analyte of interest is present in the sample the scFv binds the analyte to the solid substrate. The apparatus can be used with an immunoglobulin layer to detect Fc receptors, so as to detect microorganisms such as Staphylococcus aureus having protein A or protein G.
Owner:OAKLAND UNIVESITY +1
Compositions and methods related to protein a (SPA) variants
ActiveUS20130171183A1Prevents alleviates ameliorates symptomImprove survivalAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsStaphylococcusVirology
The present invention concerns methods and compositions for treating or preventing a bacterial infection, particularly infection by a Staphylococcus bacterium. The invention provides methods and compositions for stimulating an immune response against the bacteria. In certain embodiments, the methods and compositions involve a non-toxigenic Protein A (SpA) variant.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Broad-spectrum antibacterial bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain and application thereof
ActiveCN103173397ASimple cultivation conditionsPromote growthBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyBacillus amylolyticus
The invention relates to bacillus amyloliquefaciens NCPSJ7 and further relates to an application of the strain in treating plant diseases, diseases before and after harvesting fruits and vegetables as well as in preventing food-borne pathogenic bacteria and putrefying bacteria. The strain is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) on March 22, 2013, wherein the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M2013098 and the strain is named as bacillus amyloliquefaciens NCPSJ7. The thallus and fermentation liquor of the strain disclosed by the invention has the effects of treating plant diseases caused by plant pathogenic fungus including antagonistic peach root rotten disease, fusarium wilt of cucumber, botrytis cinerea, jujube anthracnose, pear black spot, pear blue mould, apple brown rot, apple altermaria leaf spot, watermelon fusarium wilt and the like, as well as diseases after harvesting fruits and vegetables and food-borne pathogenic bacteria and putrefying bacteria including antagonistic staphylococcus aureus, salmonella paratyphi A, vibrio parahaemolyticus, yeast and the like; moreover, the bacillus amyloliquefaciens is broad in spectrum and antibacterial and great in potential in developing novel, efficient and natural biological control and biological preservative and fresh-keeping preparation.
Owner:INST OF AGRO FOOD SCI & TECH SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Polysaccharide-staphylococcal surface adhesin carrier protein conjugates for immunization against nosocomial infections
ActiveUS20070141077A1Prevention and reduction of severityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsCarrier proteinImmunogenicity
Immunogenic polysaccharide-protein conjugates having a polysaccharide antigen (or its oligosaccharide fragment representing one or more antigenic epitopes) derived from a nosocomial pathogen conjugated to a staphylococcal surface adhesin carrier protein are used in immunogenic compositions to elicit antibody responses to both the polysaccharide antigen and the staphylococcal surface adhesin carrier protein. Such immunogenic compositions are used to immunize against diseases caused by Staphylococcal aureus, Staphylococcal epidermidis or other nosocomial pathogens.
Owner:WYETH HOLDINGS CORP
Preparation method of composite functional fabric with antimicrobial, anti-ultraviolet, deodorization and self-cleaning functions
ActiveCN104294583ASimple methodGood antibacterial, anti-ultraviolet and deodorizing propertiesLight resistant fibresWrinkle resistant fibresStaphylococcusHydrogen
The invention discloses a preparation method of a composite functional fabric with antimicrobial, anti-ultraviolet, deodorization and self-cleaning functions. The preparation method comprises the steps of preparing an activated modified treatment liquid, preparing a nano-titania dispersion liquid, processing fabrics by virtue of the activated modified treatment liquid, processing the fabrics by virtue of the nano-titania dispersion liquid, and the like. After the composite functional fabric is processed, the UPF value is more than 100, the deodorization rate is more than 95%, the photocatalysis self-cleaning fading rate of the composite functional fabric to chili oil is 96.7%, and the antibacterial rate (to staphylococcus) is 98.6%; after the composite functional fabric is washed for ten times in families, the UPF value is more than 50, the deodorization rate of the composite functional fabric to substances (including ammonia gas, formaldehyde, acetaldehyde, sulfureted hydrogen, nicotine and trimethylamine) is more than 90%, the photocatalysis self-cleaning fading rate of the composite functional fabric to chili oil is 93.9%, and the antibacterial rate (to staphylococcus) is 95.8%.
Owner:江苏巧雅纺织科技有限公司
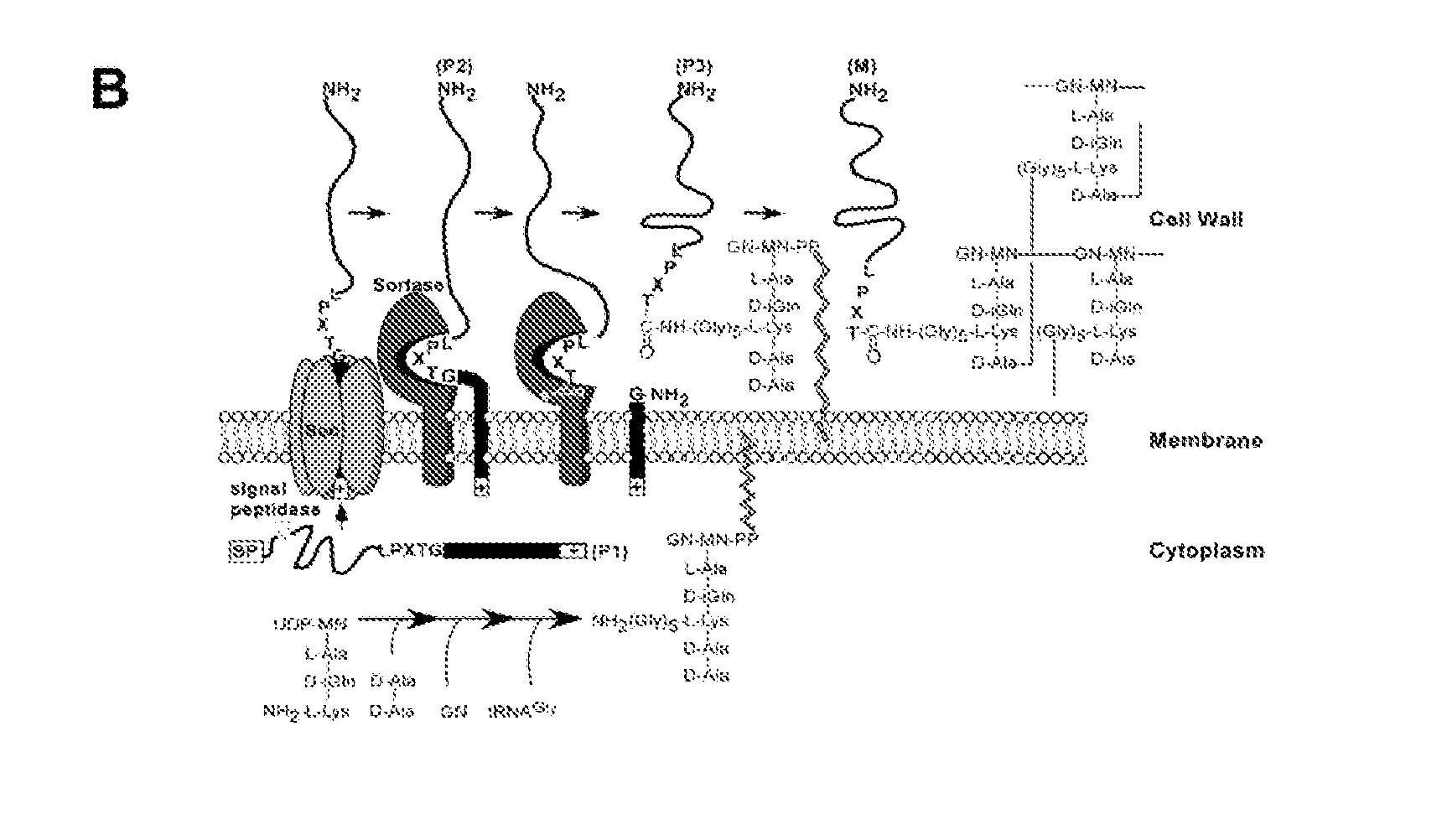
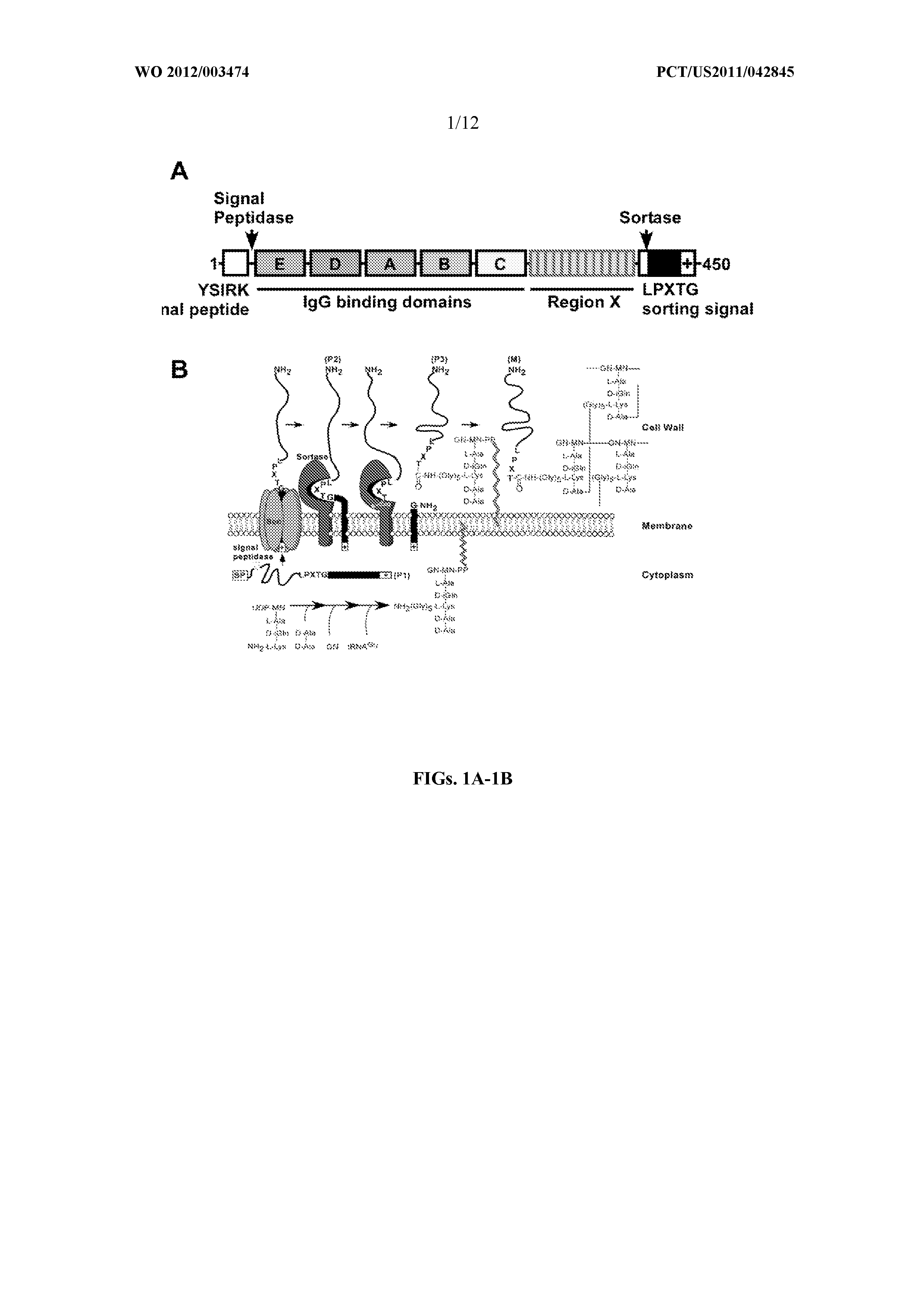
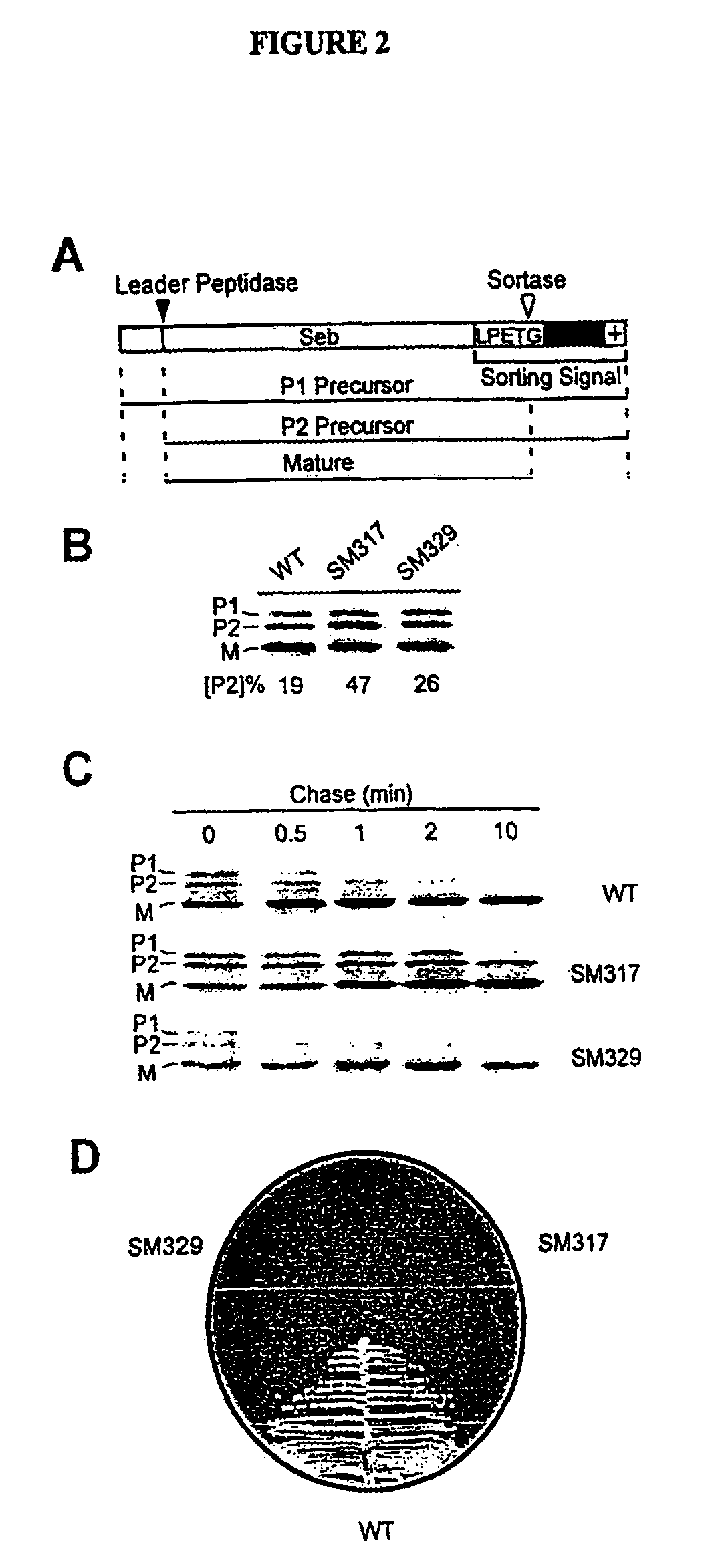
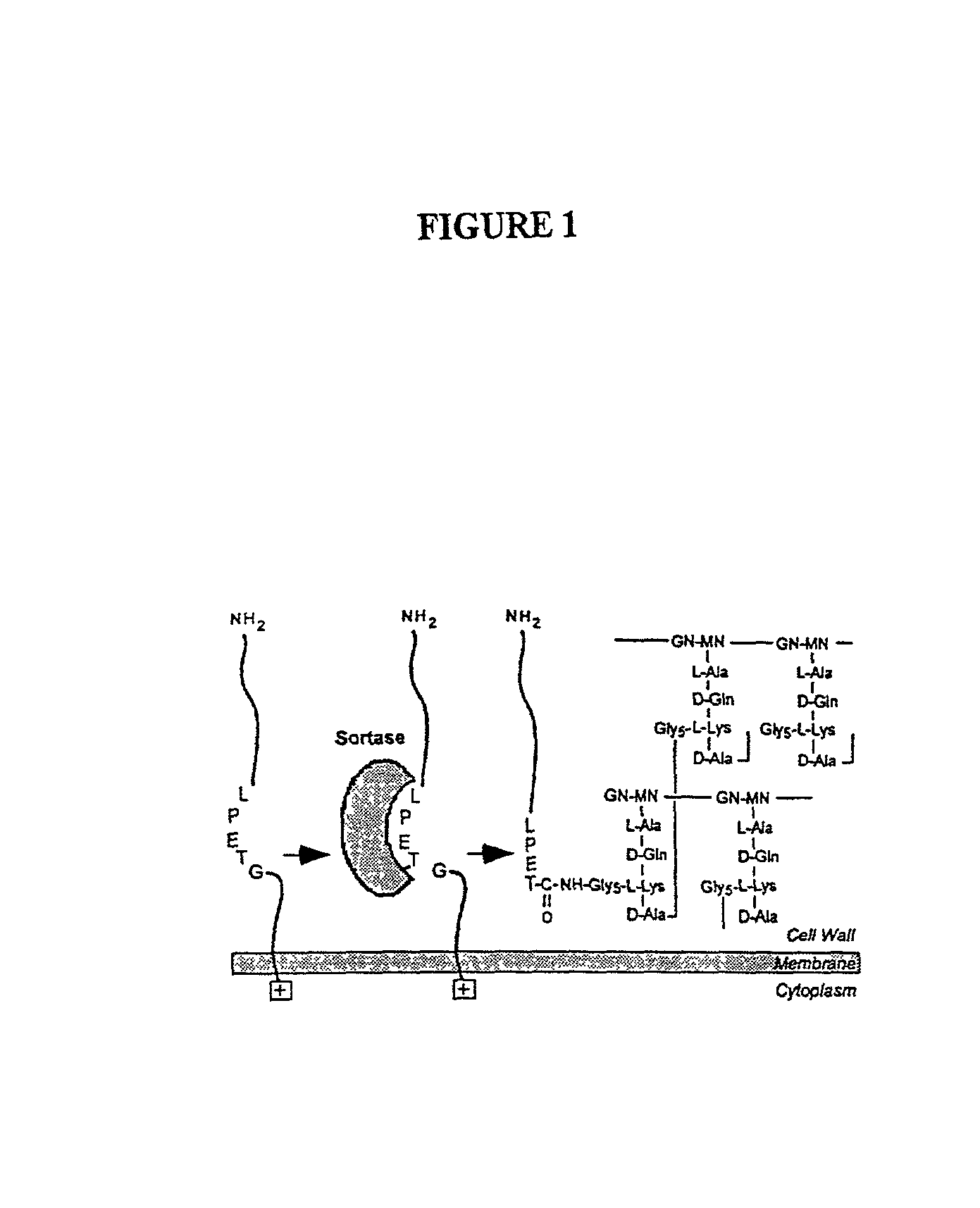
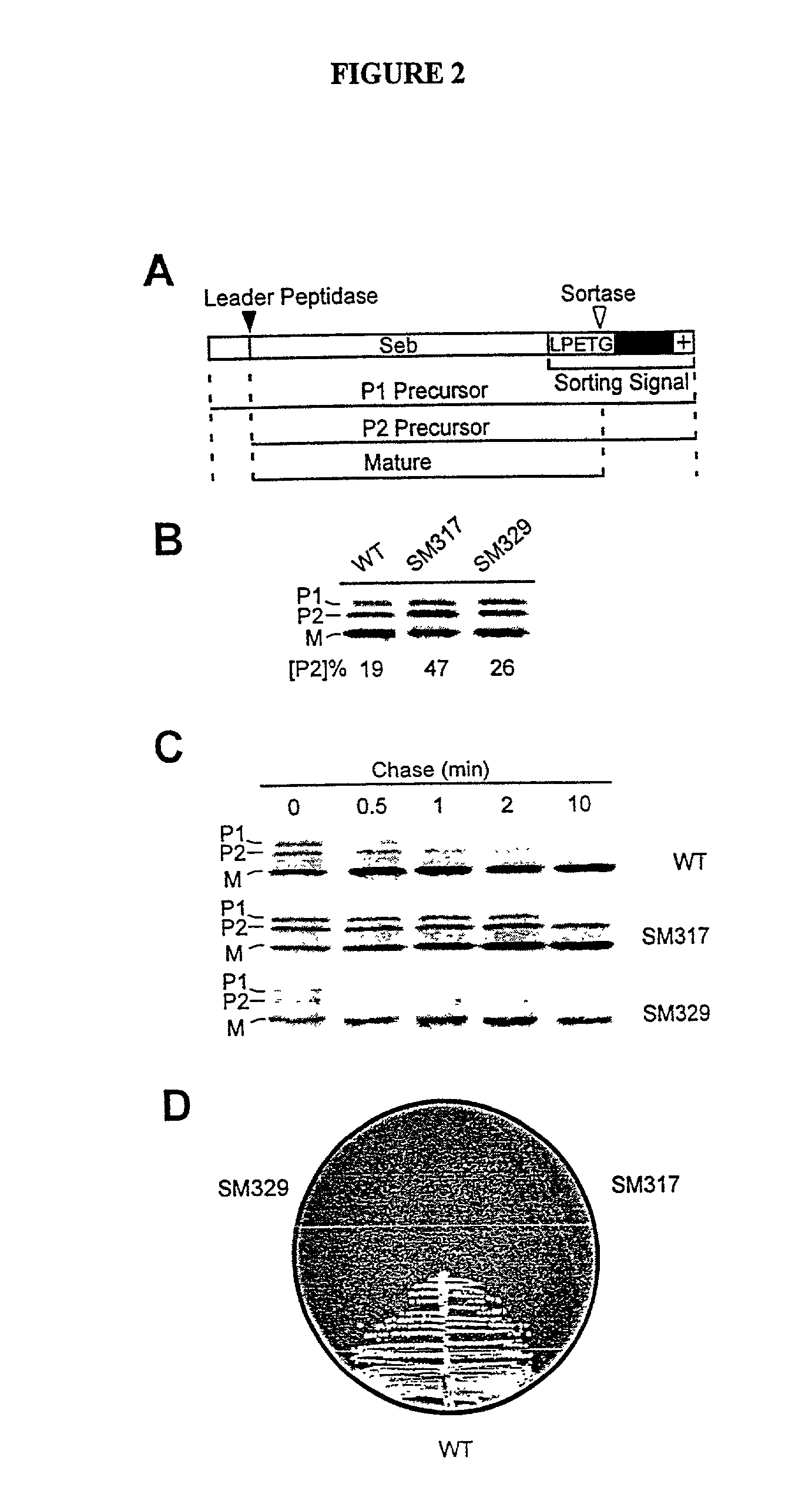
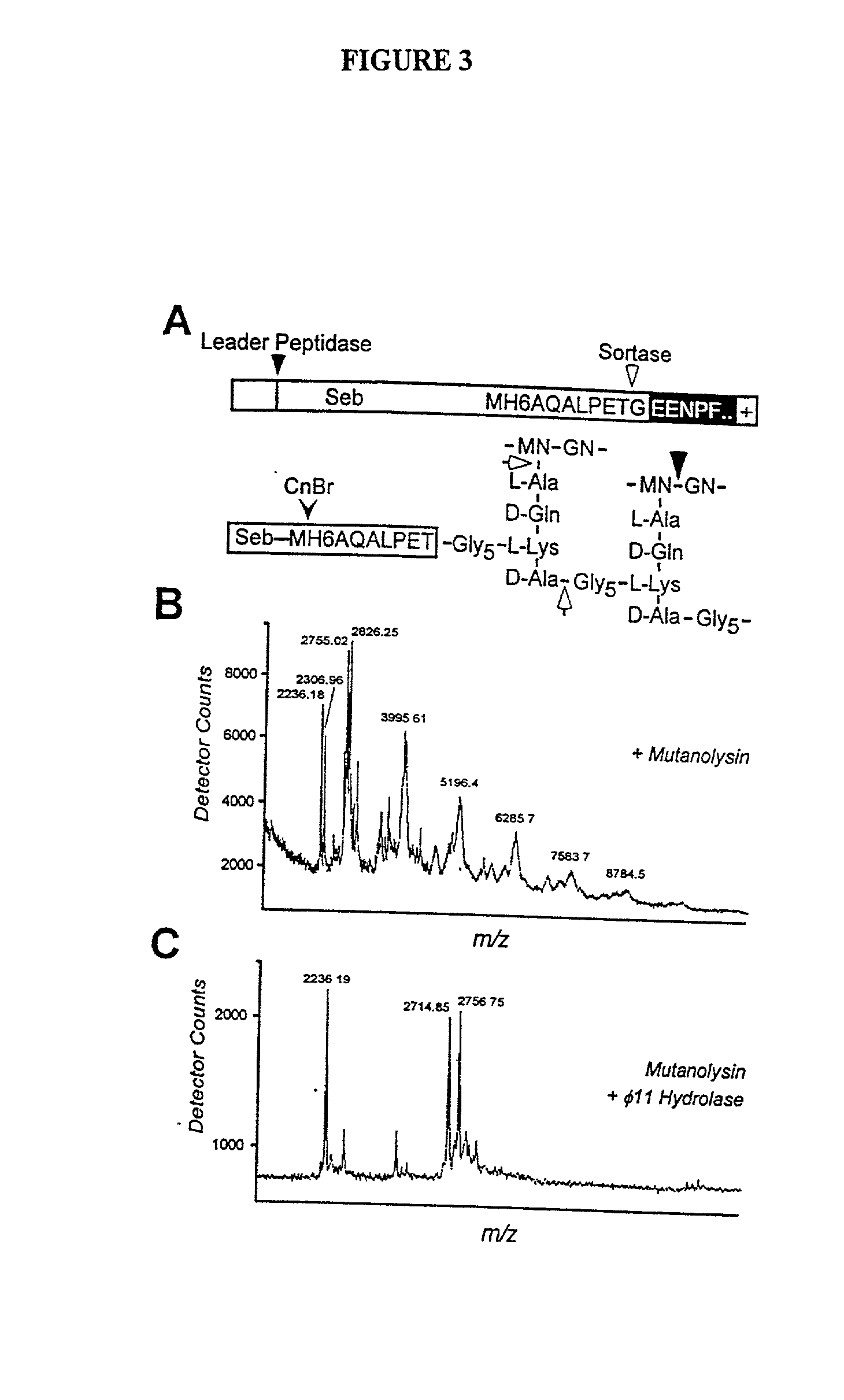
Identification of sortase gene
The present invention is a substantially purified sortase-transamidase enzyme from Gram-positive bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus. A specific sortase-transamidase enzyme disclosed has a molecular weight of about 29,076 daltons and catalyzes a reaction that covalently cross-links the carboxyl terminus of a protein having a sorting signal to the peptidoglycan of a Gram-positive bacterium, where the sorting signal has a a motif of NPQ / KTN / G therein. Variants of the enzyme, methods for cloning the gene encoding the enzyme and expressing the cloned gene, and methods of use of the enzyme, including for screening for antibiotics and for display of proteins or peptides on the surfaces of Gram-positive bacteria, are also disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
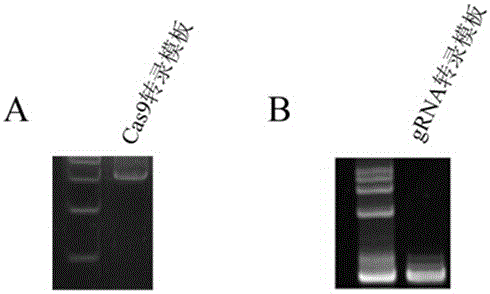
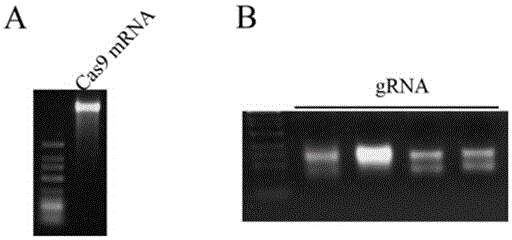
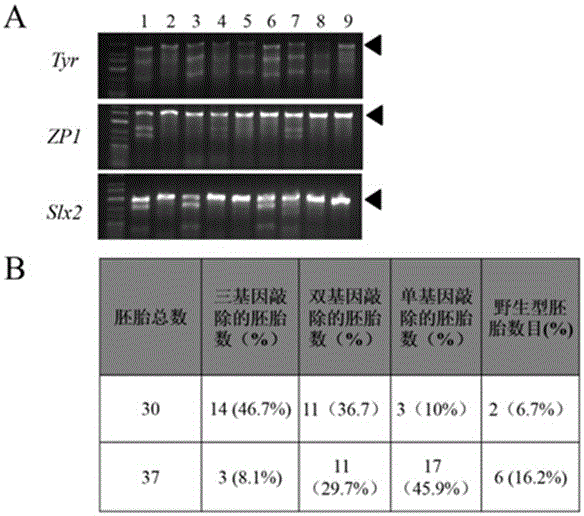
Preparation method of staphylococcus aureus CRISPR/Cas9 system and application of system in constructing mouse model
The invention discloses a preparation method of a staphylococcus aureus CRISPR / Cas9 system and an application of the system in constructing a genetically modified mouse model. The staphylococcus aureus CRISPR / Cas9 system is composed of two components, namely Cas9 mRNA and gRNA, wherein a preparation method of the Cas9 mRNA is achieved by adding a T7 promoter to the upstream region of original Cas9 coding DNA, and a preparation method of the gRNA is achieved by adding the T7 promoter to the upstream region of an original gRNA coding sequence. The staphylococcus aureus Cas9 mRNA and gRNA, which are injected to mouse fertilized embryos through micro-injection, can achieve gene editing and modification of various types, such as single-gene knockout, multi-gene knockout and / or gene knock-in and the like, on the mouse fertilized embryos; therefore, the CRISPR / Cas9 system has a good application prospect in the aspects of fertilized embryo gene editing and modification of such animals as mouse and the like as well as construction of animal models.
Owner:GUANGZHOU MAGIGEN BIOTECH
Identification of sortase gene
InactiveUS20030022178A1Fluorescence enhancementIncreased cleavageAntibacterial agentsFungiEnzyme GeneCarboxyl radical
The present invention is a substantially purified sortase-transamidase enzyme from Gram-positive bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus. The enzyme having a molecular weight of about 23,539 or about 29,076 daltons and catalyzing a reaction that covalently cross-links the carboxyl terminus of a protein having a sorting signal to the peptidoglycan of a Gram-positive bacterium, the sorting signal having: (1) a motif of LPX3X4G therein; (2) a substantially hydrophobic domain of at least 31 amino acids carboxyl to the motif; and (3) a charged tail region with at least two positively charged residues carboxyl to the substantially hydrophobic domain, at least one of the two positively charged residues being arginine, the two positively charged residues being located at residues 31-33 from the motif, wherein X3 is any of the twenty naturally-occurring L-amino acids and X4 is selected from the group consisting of alanine, serine, and threonine, and wherein sorting occurs by cleavage between the fourth and fifth residues of the LPX3X4G motif. Variants of the enzyme, methods for cloning the gene encoding the enzyme and expressing the cloned gene, and methods of use of the enzyme, including for screening for antibiotics and for display of proteins or peptides on the surfaces of Gram-positive bacteria, are also disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Staphylococcal immunotherapeutics via donor selection and donor stimulation
InactiveUS7045131B2Avoid detectionImmunoglobulins against bacteriaPharmaceutical delivery mechanismDonor selectionStaphylococcal infections
A method and composition for the passive immunization of patients infected with or susceptible to infection from Staphylococcus bacteria such as S. aureus and S. epidermidis infection is provided that includes the selection or preparation of a donor plasma pool with high antibody titers to carefully selected Staphylococcus adhesins or MSCRAMMs, or fragments or components thereof, or sequences with substantial homology thereto. The donor plasma pool can be prepared by combining individual blood or blood component samples which have higher than normal titers of antibodies to one or more of the selected adhesins or other proteins that bind to extracellular matrix proteins, or by administering carefully selected proteins or peptides to a host to induce the expression of desired antibodies, and subsequently recovering the enhanced high titer serum or plasma pool from the treated host. In either case, the donor plasma pool is preferably purified and concentrated prior to intravenous introduction into the patient, and the present invention is advantageous in that a patient can be immunized against a wide variety of potentially dangerous staphylococcal infections. Kits for identifying potential donor with high titers of the selected adhesins are also provided. The present invention thus provides methods and compositions which can be highly effective against infections associated with Staphylococcus bacteria.
Owner:INHIBITEX INC
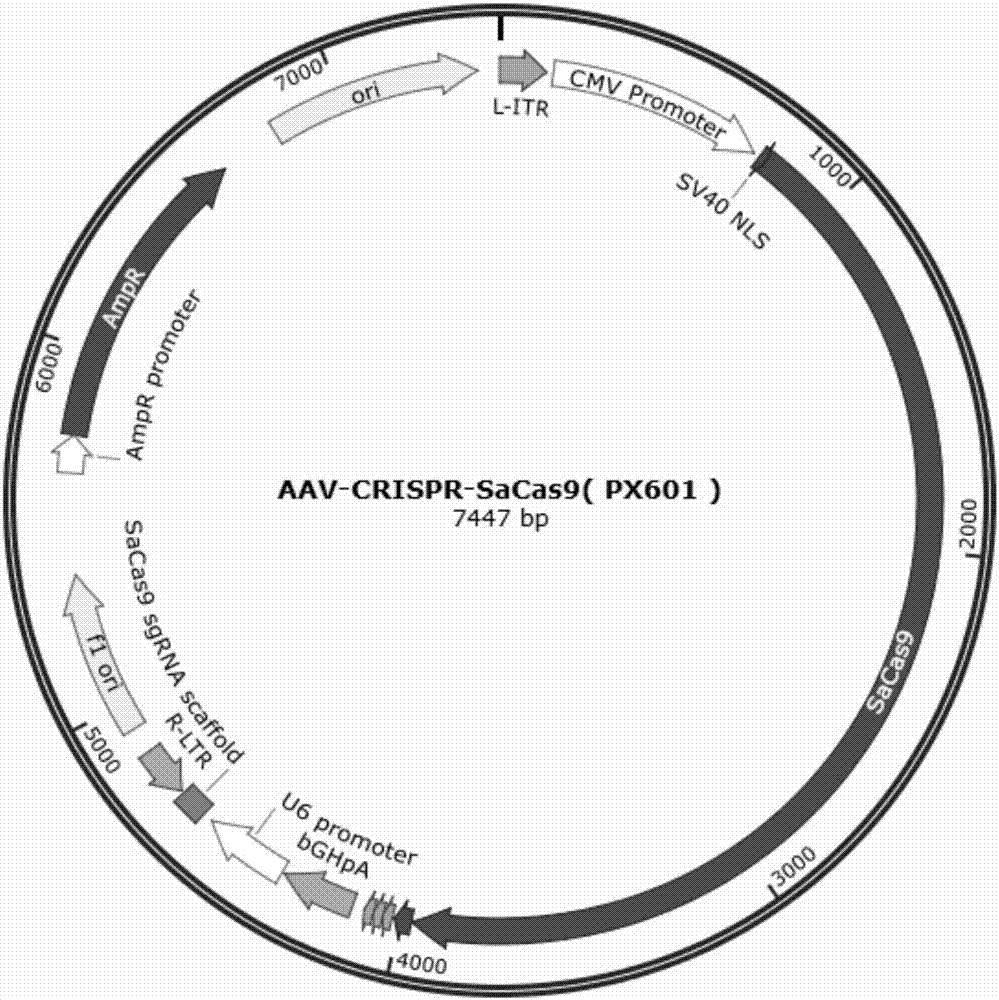
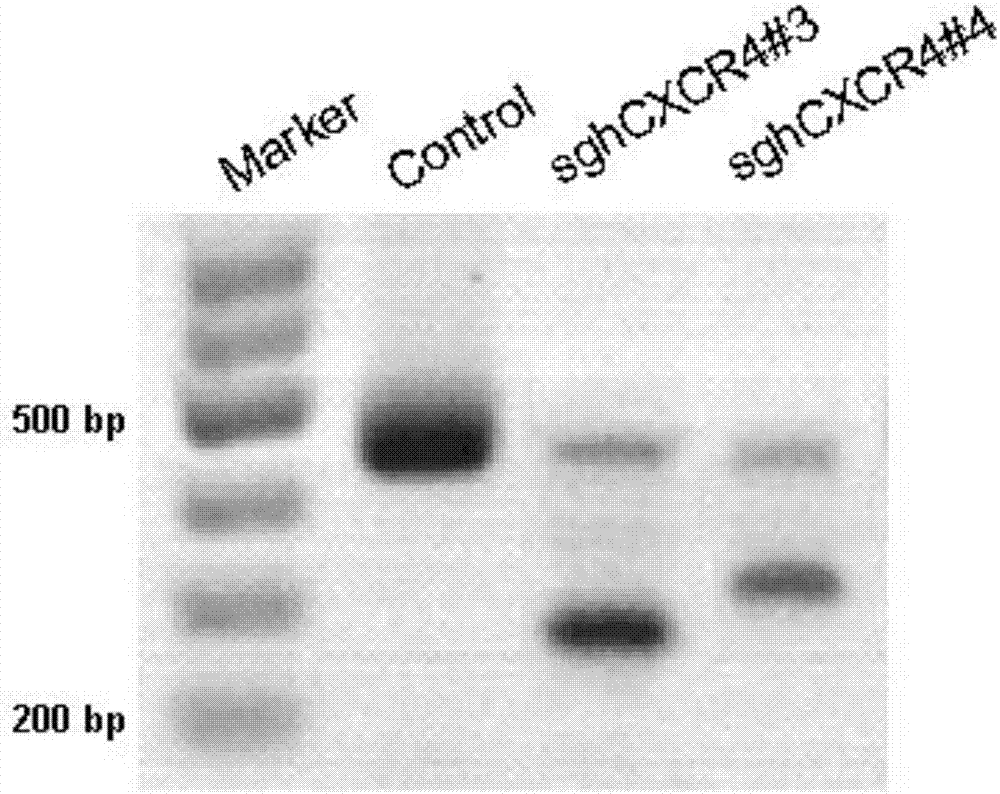
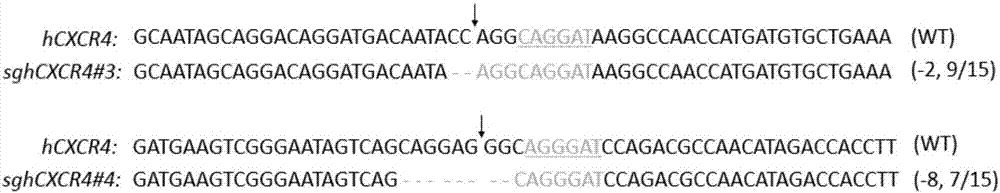
CRISPR/SaCas9 based specific human CXCR4 gene knockout method
InactiveCN107236739AAchieve knockoutSimple methodHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAImmune deficiency syndromeStaphylococcus aureus bacteria
The invention discloses sgRNA for specific targeting of a human CXCR4 gene, a sgRNA-containing staphylococcus aureus CRISPR / SaCas9 system and a method for specific human CXCR4 gene knockout by the method. A target sequence of sgRNA is shown as any one of SEQ ID NO:1-4. sgRNA for specific targeting of the human CXCR4 gene and AAV-CRISPR / SaCas9 plasmids are connected to form a carrier and packaged into AAV infection cells, simplicity, convenience, high efficiency and specificity in CXCR4 gene knockout are realized, and accordingly the problem of limitation in adoption of SpCas9 targeted CXCR4 for treatment of acquired immune deficiency syndrome is effectively solved.
Owner:上海捷易生物科技有限公司
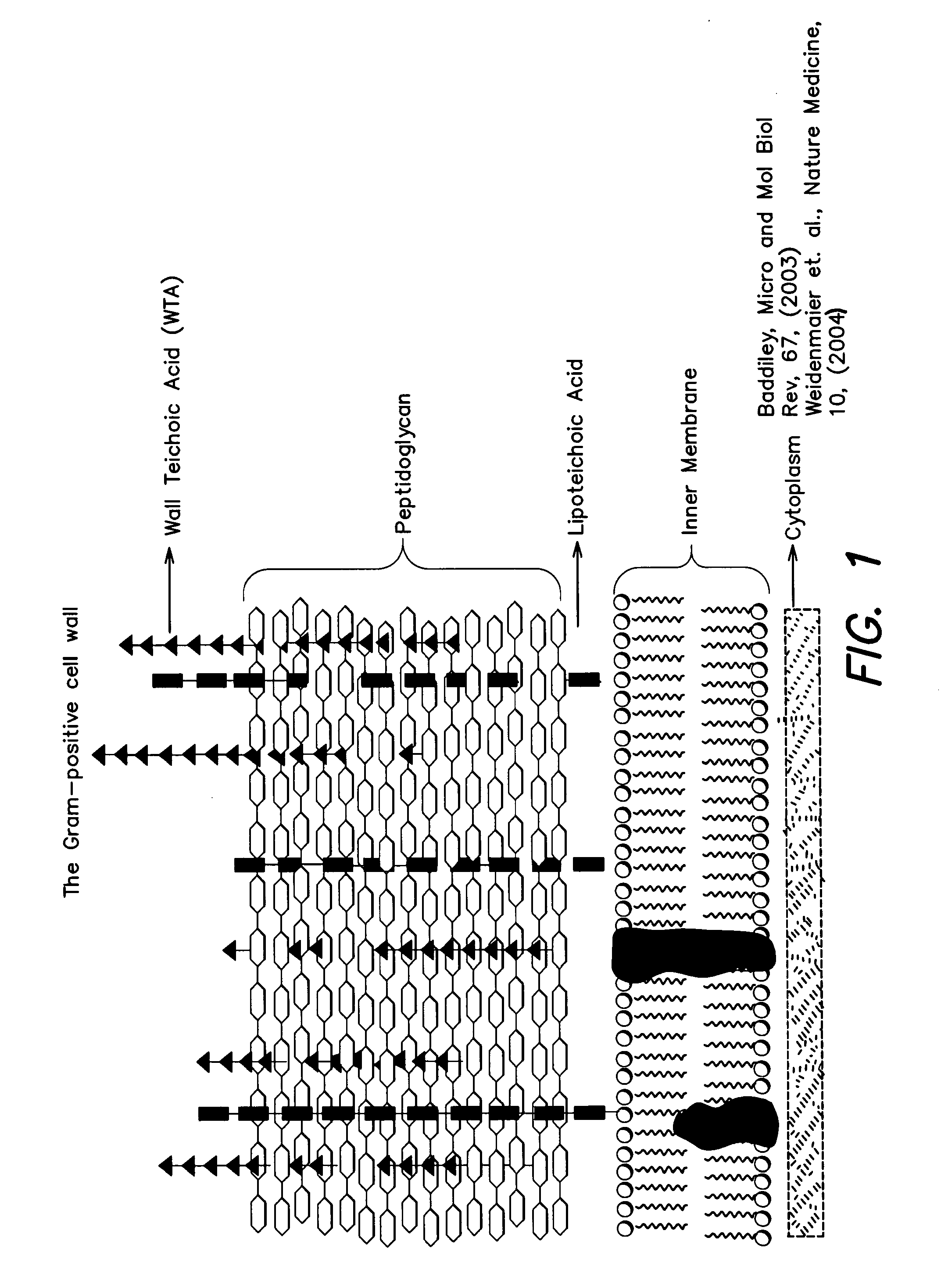
Methods and compounds for antimicrobial intervention
InactiveUS8598342B2Antibacterial agentsBiocideSynthetic analogueMethicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
The present invention provides Wall Teichoic Acid biosynthesis inhibitors such as compound 1835F03 (targocil) and related synthetic analogs. The invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions thereof and methods for treating bacterial infection and the suppression of growth of bacterial cells by administering a Wall Teichoic Acid biosynthesis inhibitor. The invention is particularly useful for the treatment of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). The invention further provides procedures for the syntheses of Wall Teichoic Acid biosynthesis inhibitors. The invention also provides methods for the identification of antibacterial therapeutic agents.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Staphylococcal immunotherapeutics via donor selection and donor stimulation
InactiveUS20060222651A1Immunoglobulins against bacteriaPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPassive ImmunizationsCell-Extracellular Matrix
A method and composition for the passive immunization of patients infected with or susceptible to infection from Staphylococcus bacteria such as S. aureus and S. epidermidis infection is provided that includes the selection or preparation of a donor plasma pool with high antibody titers to carefully selected Staphylococcus adhesins or MSCRAMMs, or fragments or components thereof, or sequences with substantial homology thereto. The donor plasma pool can be prepared by combining individual blood or blood component samples which have higher than normal titers of antibodies to one or more of the selected adhesins or other proteins that bind to extracellular matrix proteins, or by administering carefully selected proteins or peptides to a host to induce the expression of desired antibodies, and subsequently recovering the enhanced high titer serum or plasma pool from the treated host.
Owner:PATTI JOSEPH +2
Kit for quickly detecting 15 pneumonia pathogenic bacteria
ActiveCN107338315AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesStaphylococcus aureus
The invention discloses a kit for quickly detecting 15 pneumonia pathogenic bacteria. The kit can detect streptococcus pneumoniae, staphylococcus aureus, haemophilus influenzae, mycoplasma pneumoniae, pseudomonas aeruginosa, baumanii, enterococcus faecalis, enterococcus faecium, klebsiella pneumoniae, escherichia coli, enterobacter cloacae, stenotrophomonas maltophilia, burkholderia cepacia, legionella pneumophila and chlamydia pneumoniae which cover clinically common pneumonia pathogenic bacteria difficult to culture. 16S rDNA and specific gene sequences corresponding to the pneumonia pathogenic bacteria are detected by combining gene chips with multiple asymmetric PCR reactions, and the categories of the bacteria in a to-be-detected sample are identified in genus and species. The kit makes up for the defect that current clinical detection of pneumonia pathogenic bacteria is not in time or comprehensive and a novel detection means for early diagnosis and early treatment of patients suffering from pneumonia is provided.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA +1
Antimicrobial composition for pre-harvest and post-harvest treatment of plants and animals
ActiveUS7192618B2Minimize growth and spreadReduce Microbial ContaminationHeavy metal active ingredientsFatty acid chemical modificationFood additiveDisinfectant
Owner:CMS TECH INC +1
Antibacterial composition based on natural plant raw material and application of antibacterial composition
InactiveCN104688810AImprove securityEfficient bactericidal effectAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsBiotechnologyDisease
The invention relates to an antibacterial composition based on a natural plant raw material and an application of the antibacterial composition, especially prevention and treatment of skin and mucosal diseases and infection of people and animals. The medicine tolerance problem of an antibiotic is an increasingly serious problem in global attention. The invention aims at providing a safe and effective natural antibacterial composition to avoid the problem of the medicine tolerance of the antibiotic instead of the antibiotic. The natural antibacterial composition provided by the invention has a broad-spectrum efficient sterilization effect, and is effective for gram-positive bacterium, gram-negative bacterium and fungus; candida albicans, staphylococcus aureus and escherichia coli can be completely killed within one minute; and meanwhile, the antibacterial composition has good safety. In addition, the composition also has the efficacy of resisting viruses, inflammation and allergy. The composition can be used for preventing and treating skin and mucosal diseases and infection of people and animals. The problem of the medicine tolerance generated by functional antibiotics is avoided.
Owner:KUNMING BIKAI TECH
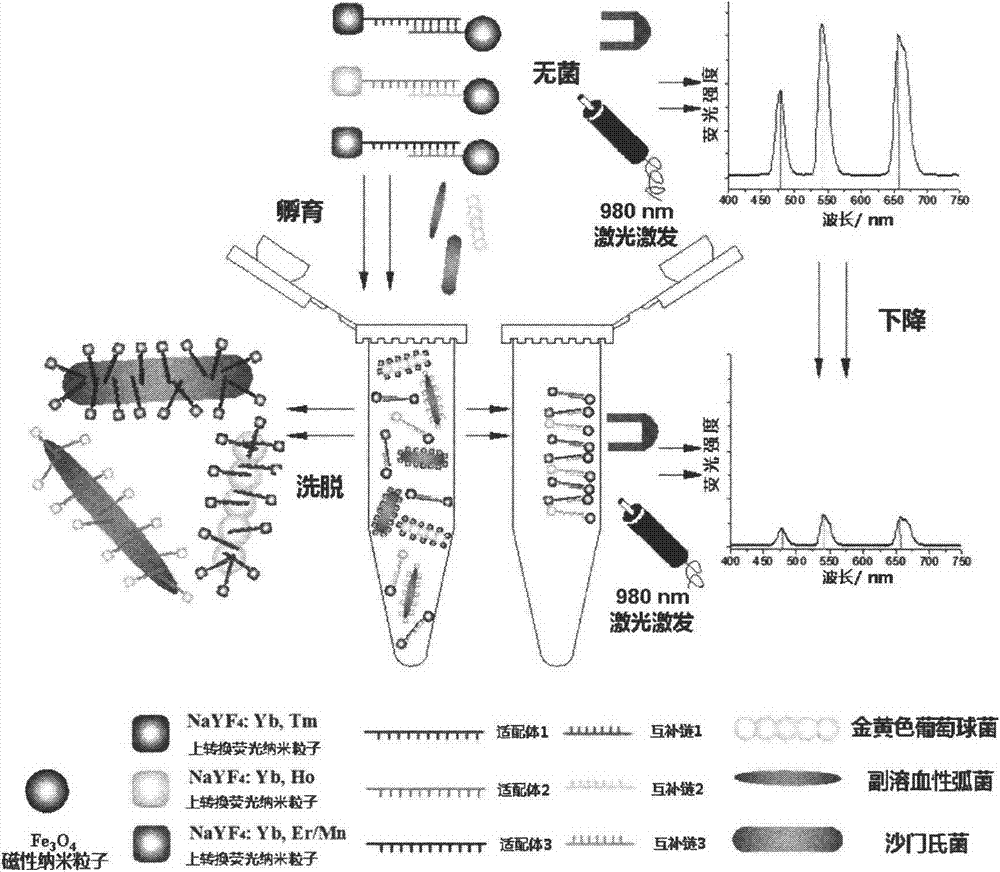
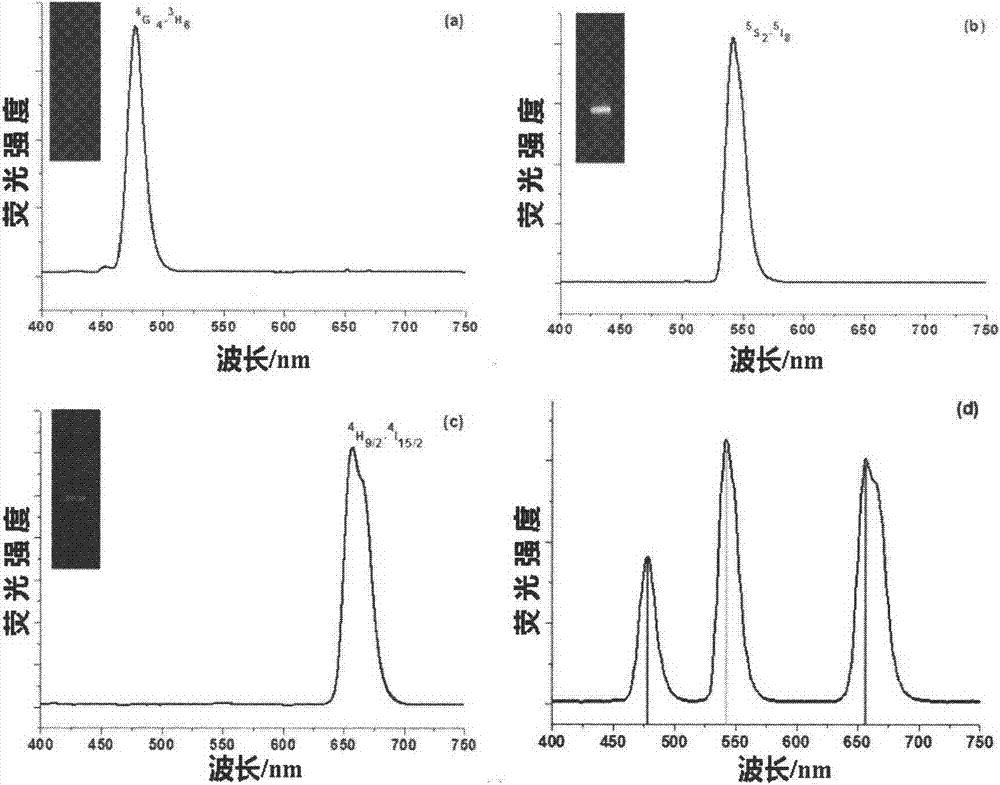
Method used for simultaneous detection of three food-borne pathogenic bacteria based on multicolor upconversion fluorescence labeling
ActiveCN103940792AImprove accuracy and stabilityHigh sensitivityFluorescence/phosphorescencePathogenic bacteriaFluorescence spectrometry
The invention provides a method used for simultaneous detection of three food-borne pathogenic bacteria based on multicolor upconversion fluorescence labeling. According to the method, three upconversion materials with differentiable fluorescence spectrums are used for forming multicolor upconversion fluorescent nanoprobes via respective connection with aptamers of staphylococcus aureus, vibrio parahaemolyticus, and salmonella, and complementary oligonucleotide single chains of the aptamers are connected with magnetic nanoparticles so as to form nano-composites. When bacteria to be tested are in a detection system, double chain unwinding is realized because of specific binding of the pathogenic bacteria with corresponding aptamers; it is possible to realize simultaneous quantitative determination of staphylococcus aureus, vibrio parahaemolyticus, and salmonella by monitoring upconversion fluorescence signal strength at 477nm, 550nm, and 660nm, detection linear range ranges from 50 to 1000000cfu / ml, and detection limits are 25cfu / ml, 10cfu / ml, and 15cfu / ml respectively. The method is used for detection of pathogenic bacteria, is high in sensitivity, is rapid and convenient, and can be used for detection of the three pathogenic bacteria in food such as milk and shrimp meat; and results are accurate and reliable.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
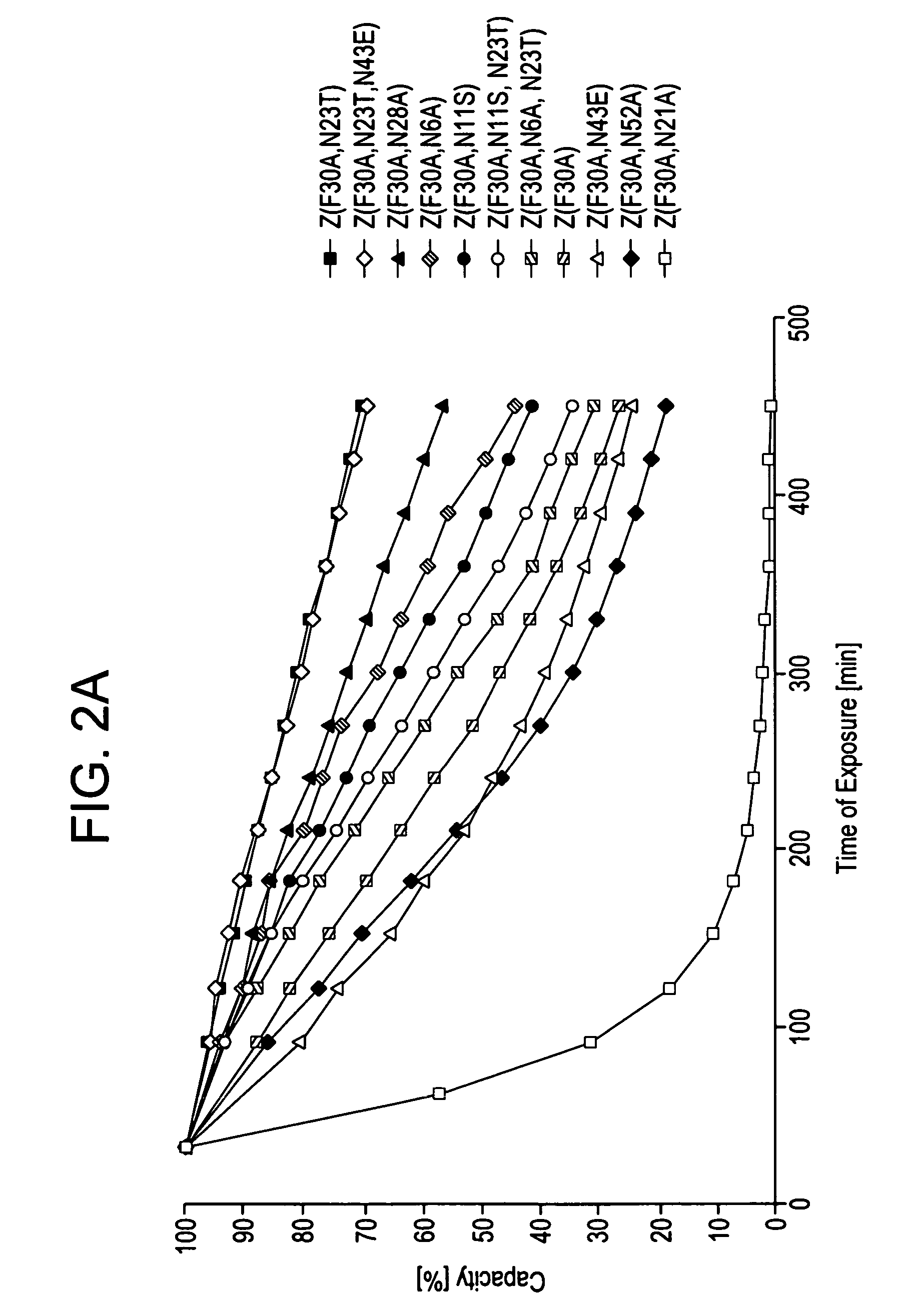
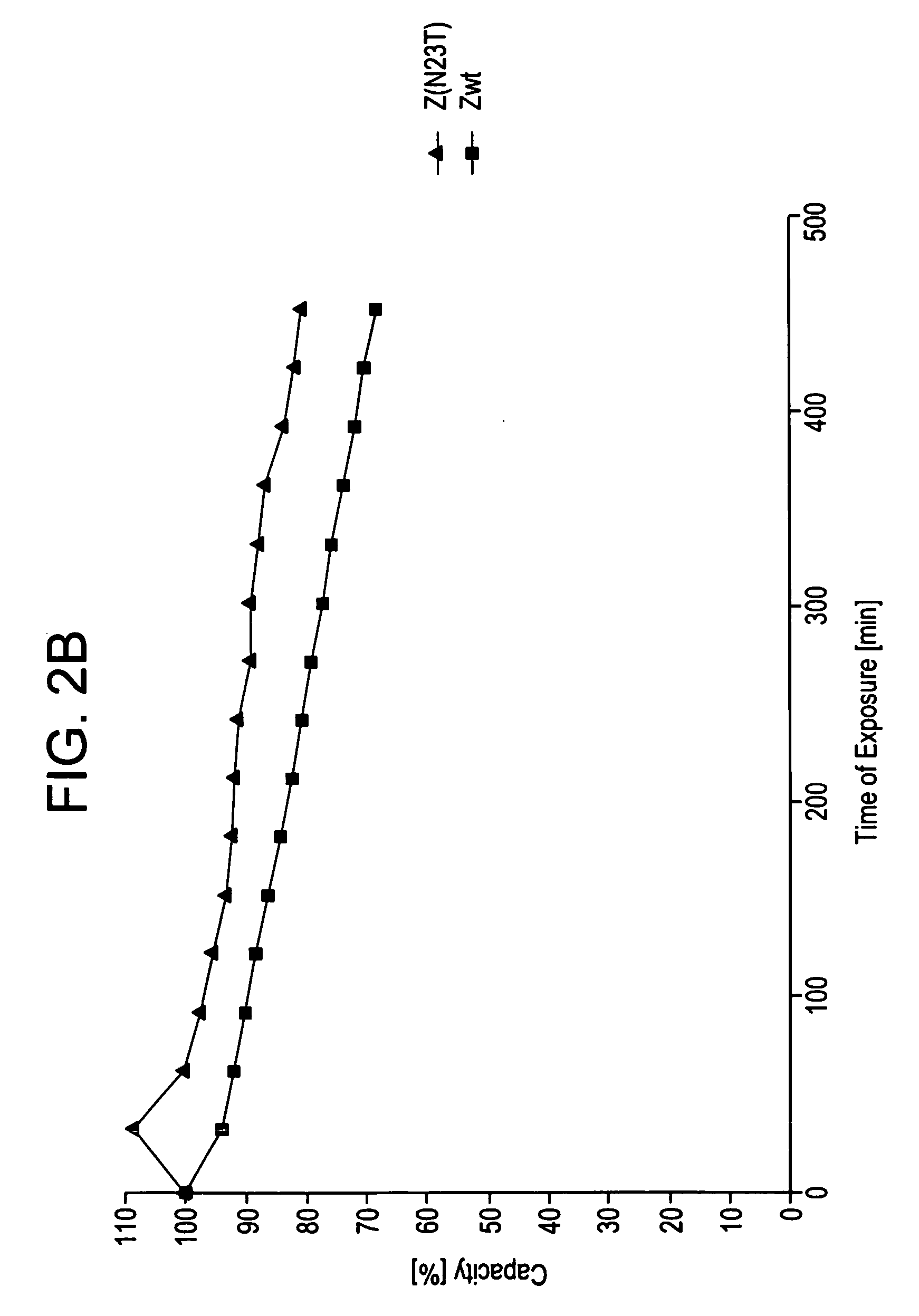
Mutated Immunoglobulin-Binding Polypeptides
ActiveUS20170334954A1Improved alkaline stabilityImprove stabilityHybrid immunoglobulinsSolid sorbent liquid separationArginineFc binding
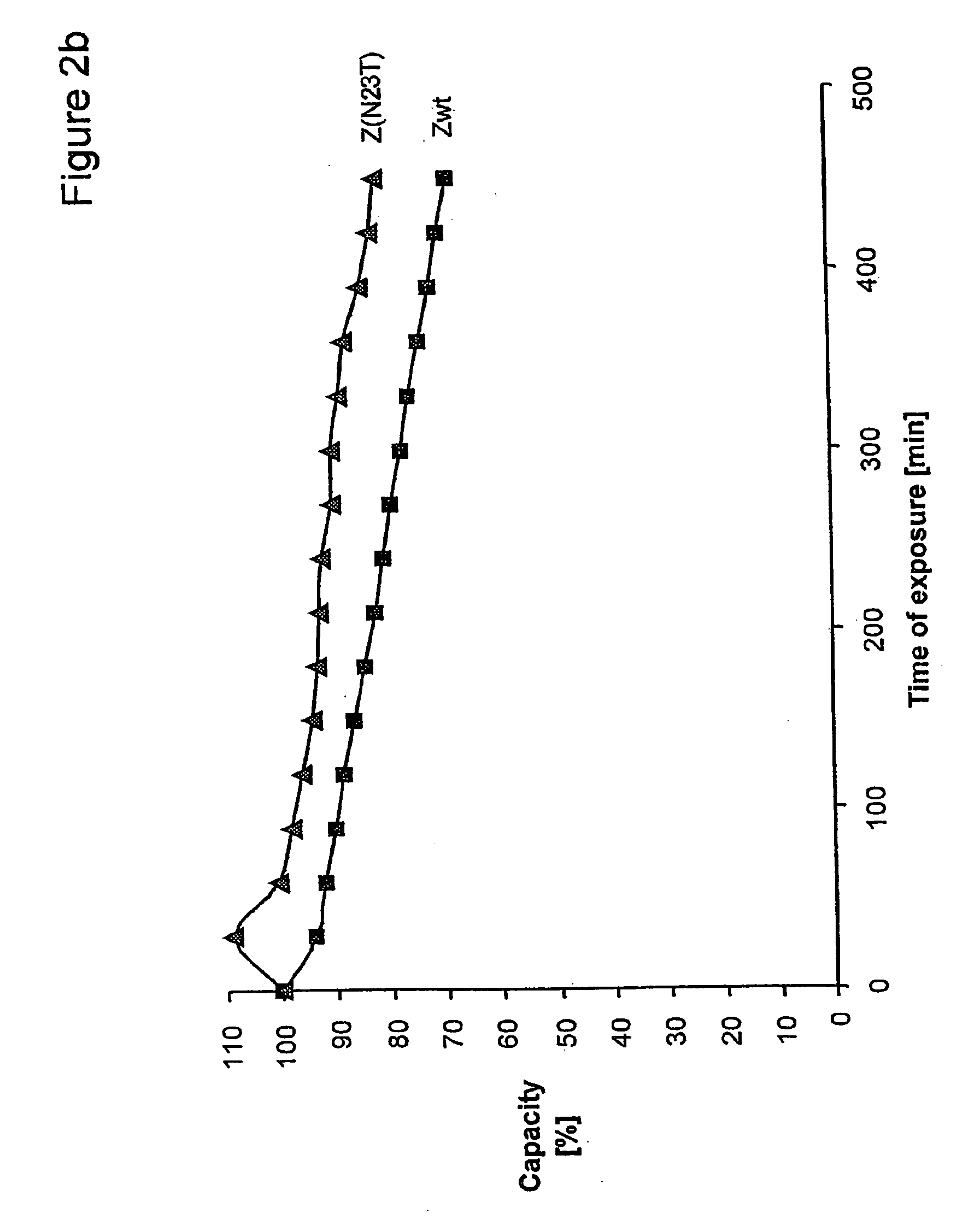
An Fc-binding polypeptide of improved alkali stability, comprising a mutant of an Fc-binding domain of Staphylococcus Protein A (SpA), as defined by SEQ ID NO: 1, SEQ ID NO: 2, SEQ ID NO:3, SEQ ID NO: 4, SEQ ID NO: 5, SEQ ID NO:6, SEQ ID NO:7, SEQ ID NO:22, SEQ ID NO 51 or SEQ ID NO 52 wherein at least the asparagine or serine residue at the position corresponding to position 11 in SEQ ID NO:4-7 has been mutated to an amino acid selected from the group consisting of glutamic acid, lysine, tyrosine, threonine, phenylalanine, leucine, isoleucine, tryptophan, methionine, valine, alanine, histidine and arginine.
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
Biological organic fertilizer prepared by aerobic fermentation of biogas residue and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103848698AWon't burnDecompose thoroughlyBio-organic fraction processingWaste based fuelMicrobial agentPseudomonas
The invention provides a biological organic fertilizer prepared by aerobic fermentation of a biogas residue and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps: mixing the biogas residue and a swelling agent to form a fermentation raw material, inoculating a compound microbial agent in the fermentation raw material, uniformly mixing for fermenting, and adding urea, diammonium phosphate, a potassium chloride inorganic salt, brown nitrogen-fixing bacteria, mycorrhiza fungi, silicate bacteria, photosynthetic bacteria acetic bacteria, bifidobacterium, and saccharomycetes after the fermentation is completed to prepare the biological organic fertilizer, wherein the compound microbial agent comprises strains of bacillus, pseudomonas, staphylococcus, streptomyces, penicillium, aspergillus and trichoderma. The compound microbial agent prepared by using the biological organic fertilizer has a pertinence to aerobic fermentation of the biogas residue, and is capable of effectively increasing the fermentation rate of the biogas residue, shortening the fermentation time and realizing high-additional value production, innocent treatment and recycling of the biogas residue; and the problem of resources and environment of villages and small towns is solved, and the rapid development of construction of new countryside and towns and cities can be promoted.
Owner:青岛福瑞斯生物能源科技开发有限公司
Isoflavone compound in tobacco rhizome and preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses an isoflavone compound in a tobacco rhizome and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: crushing a tobacco rhizome sample, performing ultrasonic extraction for 3 to 5 times by using 95 percent ethanol, combining the extracts, filtering, performing reduced pressure concentration to obtain an extract, primarily separating the extract by using silica gel column chromatography, further separating the extract by adopting high performance liquid chromatography, and thus obtaining the required new compound. Antibacterial activity screening test results show that the compound has strong antibacterial effect on common proteus species, escherichia coli, staphylococcus, bacillus subtilis and the like. The compound used for cigarette tipping paper plays an obvious role in inhibiting microbes for polluting the cigarette tipping paper.
Owner:YUNNAN RES INST OF TOBACCO SCI
Polylactic acid antibacterial nanofiber membrane and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102086565AImprove breathabilityImprove stabilityFilament/thread formingNon-woven fabricsBiotechnologySpinning
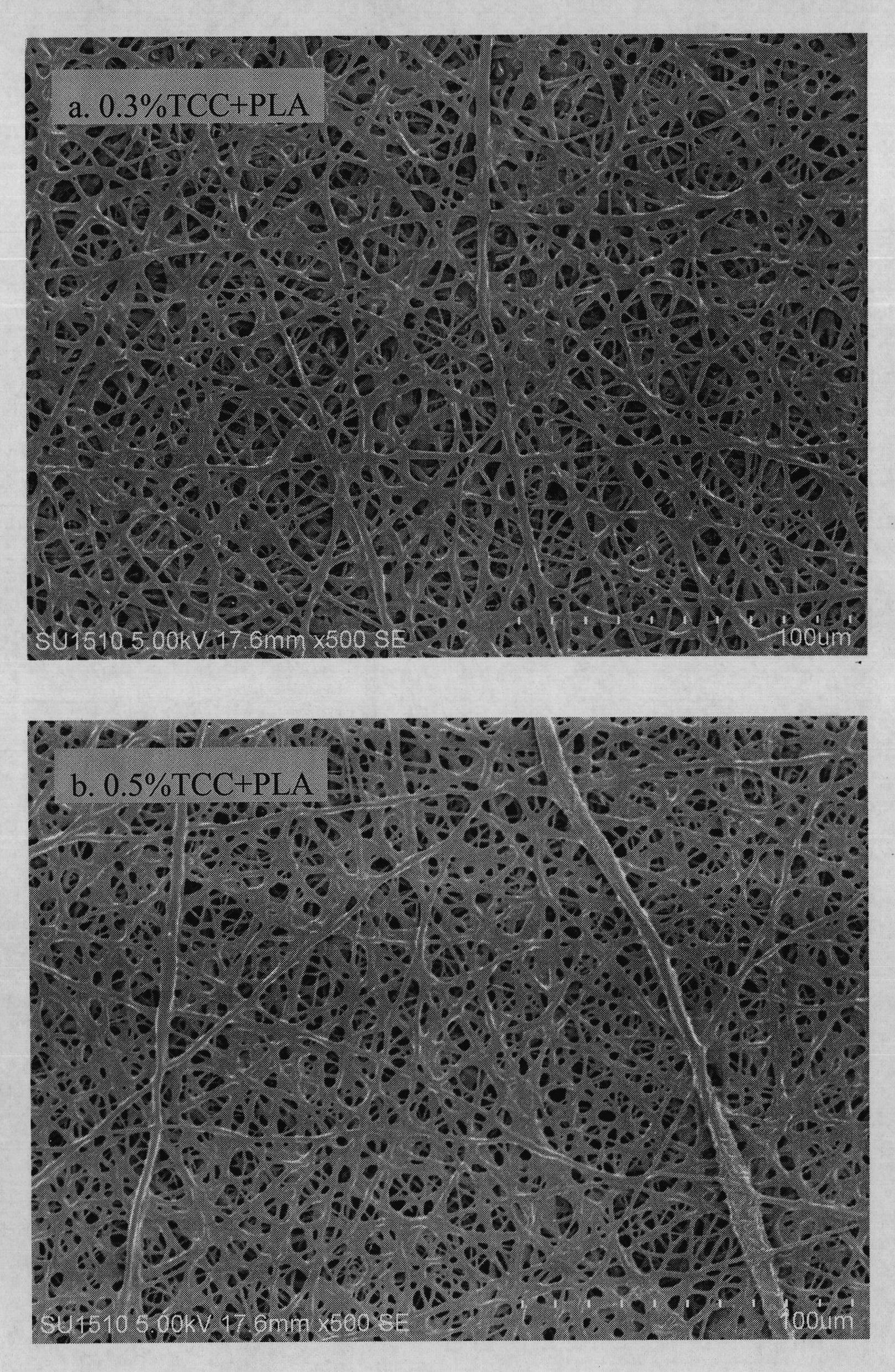
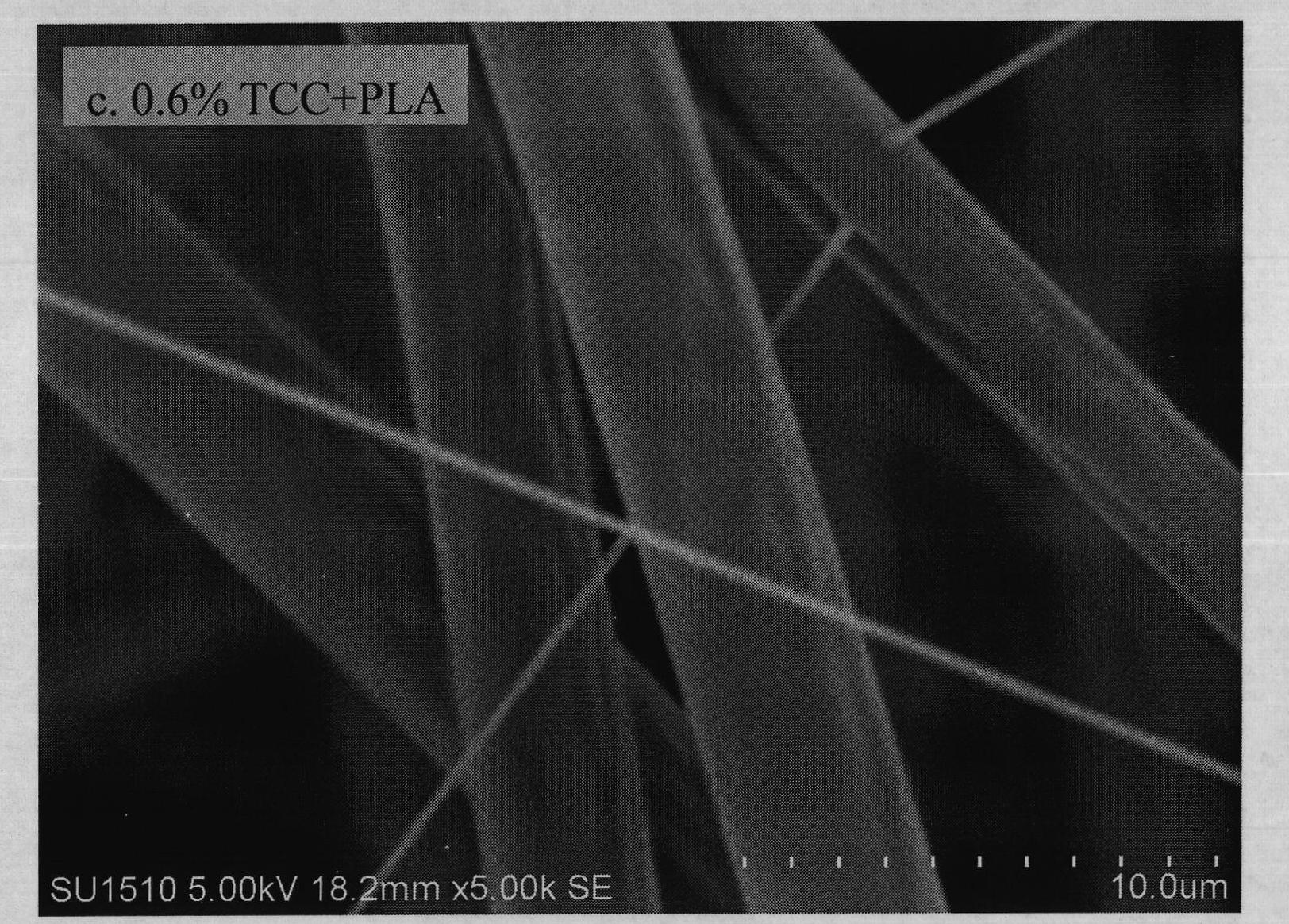
The invention discloses a polylactic acid antibacterial nanofiber membrane and a preparation method thereof, which belong to the technical field of functional spinning. An antibacterial agent is added into polylactic acid, and an electrostatic spinning technology is adopted to prepare the polylactic acid antibacterial nanofiber membrane with high antibacterial activity. The antibacterial agent in the fiber membrane is triclocarban (TCC). The nanofiber membrane comprises 95 or 94 mass percent of polylactic acid and 5 or 6 mass percent of antibacterial activity TCC. The obtained antibacterial fiber membrane can inhibit over 93 percent of staphylococcus aureus, escherichia coli and candida albicans. The antibacterial fiber membrane can be applied to the fields of daily use, spinning, industry and medicaments.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Bacillus velezensis CSQXDZ26 strain and application thereof
ActiveCN111471624AGrowth inhibitionGood biological control effectBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyConiella castaneicola
The invention discloses a bacillus velezensis strain CSQXDZ26, which is bacillus velezensis (Bacillus velezensis) with the preservation number of CGMCC NO. 17935. The bacillus velezensis CSQXDZ26 hasremarkable antagonistic activity on bacterial plant diseases such as Xanthomonas oryzae pv. Oryzae, Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola, and xanthomonasaxonopodis pv. glycines AND THE LIKE; meanwhile, the bacillus velezensis CSQXDZ26 also has antibacterial activity on fungal plant diseases such as dithiorella gregaria, Fusarium graminearum, Fusarium oxysporum f.sp.Cucumerinum, Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. momordicae, Alternaria solani or Alternaria alternate, and also has excellent inhibition effect on common food spoilage bacteria such as bacillus subtilis, proteusbacillus vulgaris and staphylococcus aureus.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
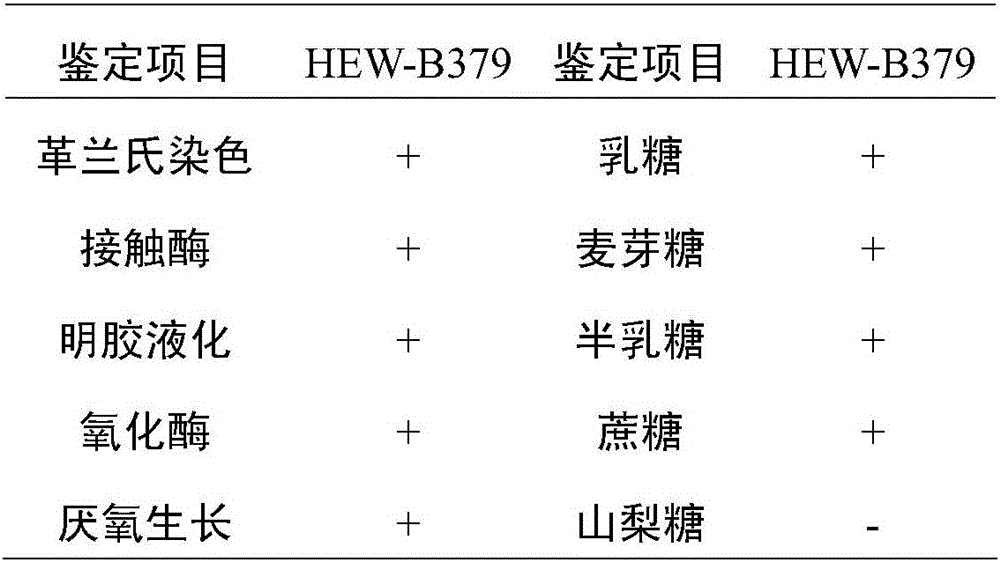
Bacillus coagulans HEW-B379 with probiotic effect, and application thereof
ActiveCN106011036AStrong heat resistanceStrong fermentation abilityAntibacterial agentsBacteriaEscherichia coliFeed conversion ratio
The invention provides a Bacillus coagulans HEW-B379 with a probiotic effect. The above strain is named as HEW-B379, and the preservation number of the strain is CGMCC No.12553. The Bacillus coagulans HEW-B379 has a substantial probiotic property, and can effectively inhibit growth breeding of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella typhi, salmonella, Shigella, Proteus species, Shewanella putrefaciens and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The Bacillus coagulans HEW-B379 has strong stress resistance, can resist high temperature and simulated gastric juice and simulate bile salt environment, can keep the survival rate of 99-100%, and can effectively adjust microbial balance of animal intestinal tracts, inhibit growth of harmful microbes, promote nutrition absorption of animals, improve the conversion rate of a feed and improve the productivity of the animals.
Owner:BEIJING HESWOF BIOTECH CO LTD
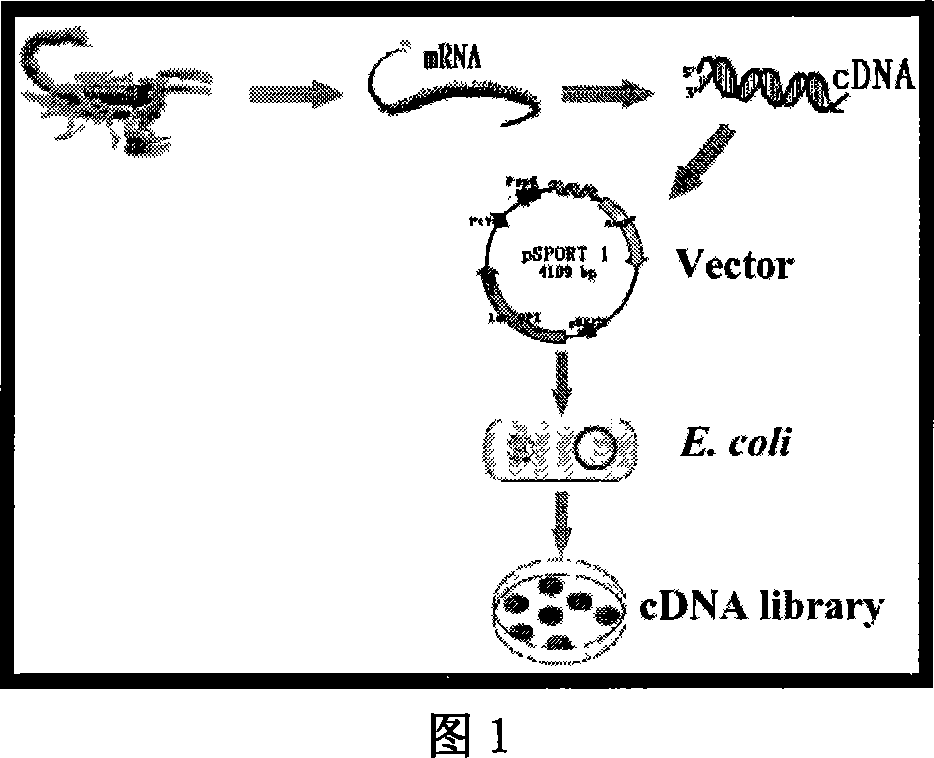
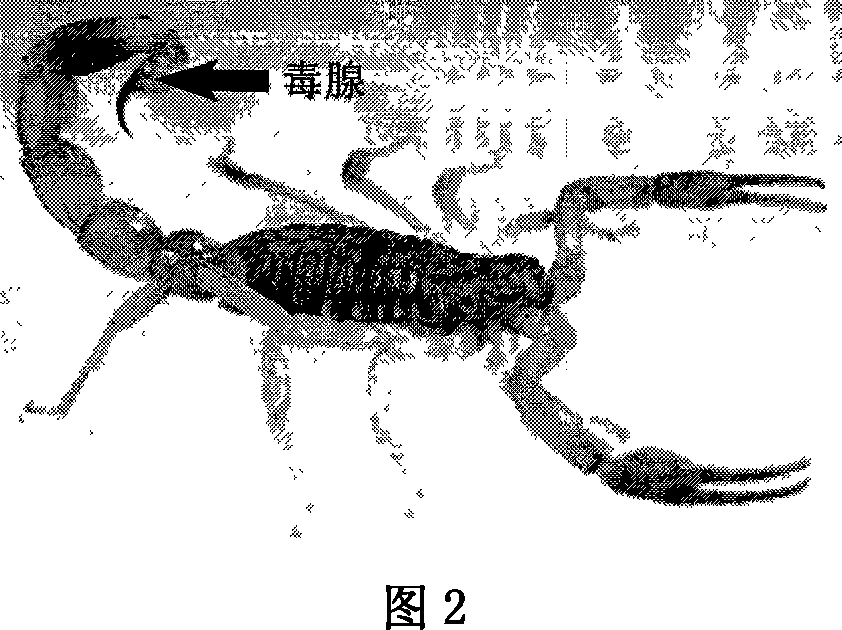
East-Asia scorpion antibiotic peptide gene and preparation method and application
ActiveCN101063102AHigh antibacterial activitySimple and efficient approach to molecular designAntibacterial agentsBacteriaChemical synthesisCDNA library
The invention discloses a preparing method of east Asia Tityus antibiotic peptide gene and appliance, which comprises the following steps: restructuring bacillus coli Escherichia coli DH5a / BmKAMP1, CCTCC NO: M207036; constructing east Asia Tityus ioterium cell cDNA library; choosing PCR method; sieving positive colony of scorpion antibiotic peptide gene from ioterium cDNA library; sequence-analyzing coding trait of antibiotic peptide gene; assuring amino acid sequence of the antibiotic peptide gene; adopting chemosynthesis antibiotic peptide; possessing inhibition of diverse density for Gram's bacterium. This antibiotic peptide possesses specificity and high active, which can be used as antibacterial drugs.
Owner:唐克煌
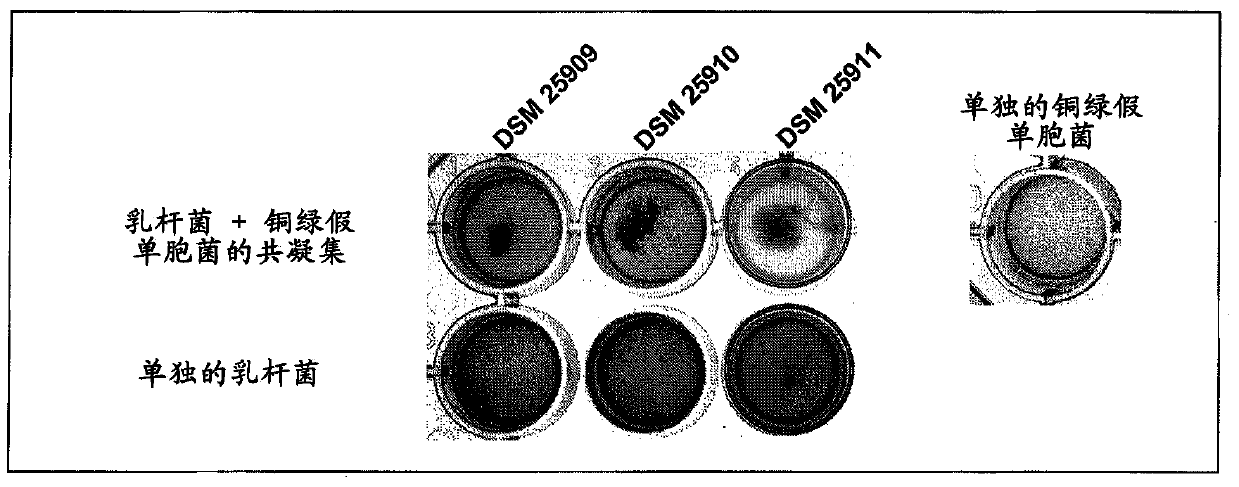
Novel lactic acid bacteria and compositions containing them
The invention relates to a microorganism, of the order of lactic acid bacteria or analog, fragment, derivative, mutant or combination thereof. Said microorganism, or analog, fragment, derivative, mutants or combination thereof can be co-aggregated with at least Staphylococcus aureus or Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Owner:ORGANOBALANCE MEDICAL AG
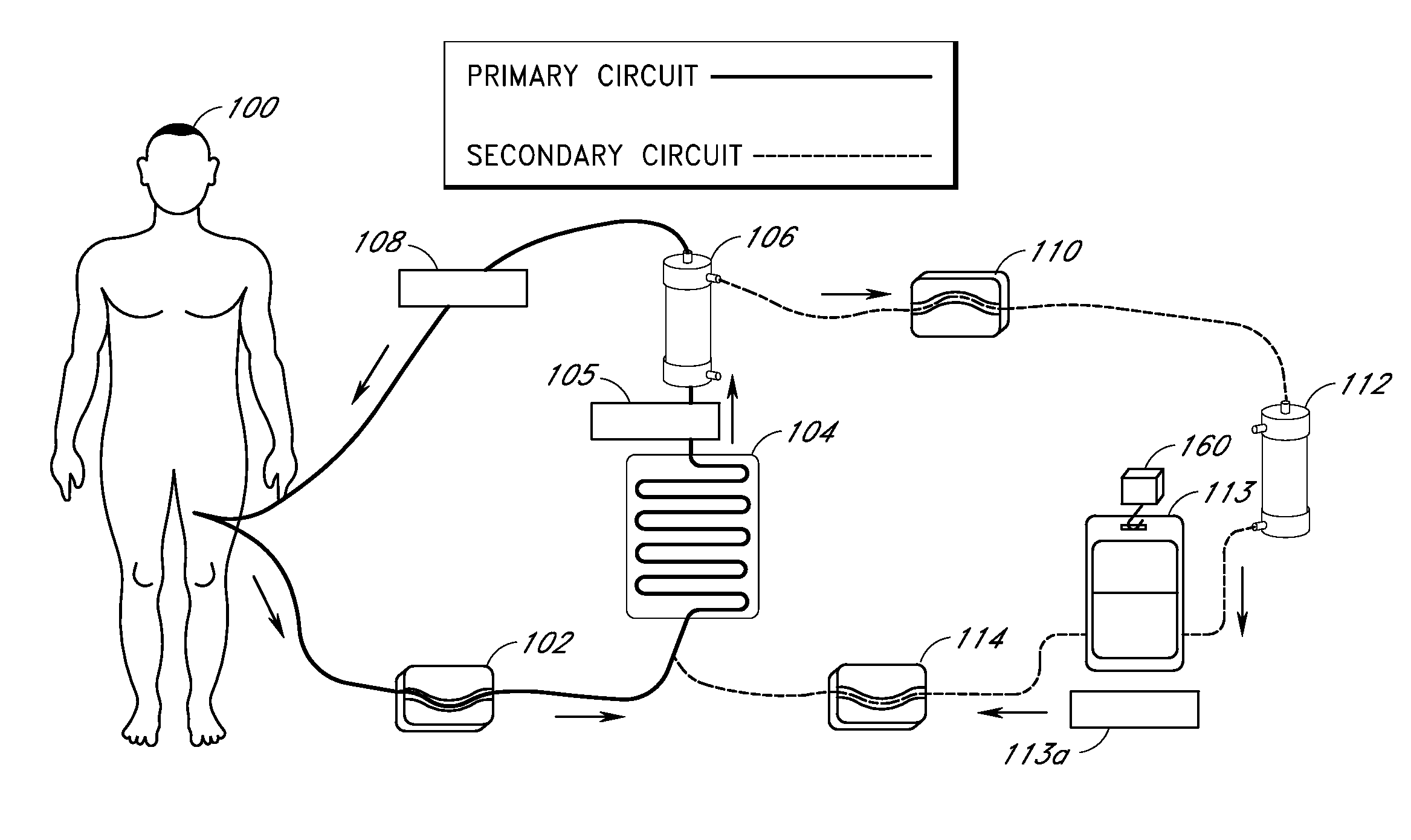
Apparatus and method for down-regulating immune system mediators in blood
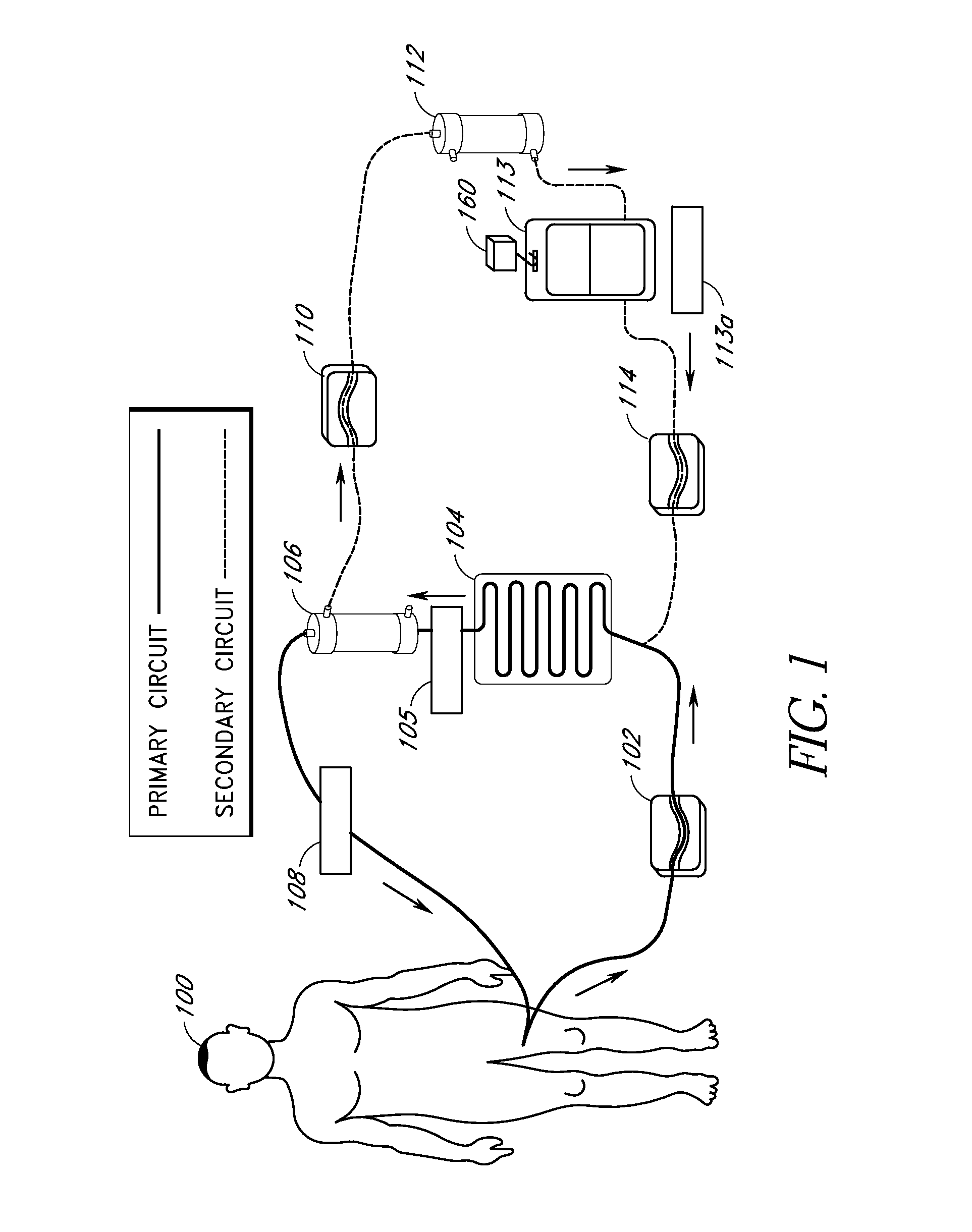
InactiveUS20070190050A1Reducing free radicals in a patient's bloodReduce concentrationSemi-permeable membranesSolvent extractionInterleukin 6White blood cell
A method and apparatus for preventing and treating septicemia in patient blood is provided. The extracorporeal system includes an antimicrobial device to inactivate at least 99% of bloodborne microorganisms, a hemoconcentrator / filtration unit to remove approximately 50-75% of target molecules from the patient blood and a filter unit to remove target molecules from patient blood from the sieved plasma filtrate. Target molecules are produced by microorganisms, as well as by the patient's cells. These molecules include endotoxins from Gram negative bacteria, exotoxins from Gram negative and Gram positive bacteria, as well as RAP protein mediator from Staphylococcus aureus, and cell mediators such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and interleukin 1-beta, interleukin 6, complement proteins C3a and C5a, and bradykinin.
Owner:HEMAVATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com