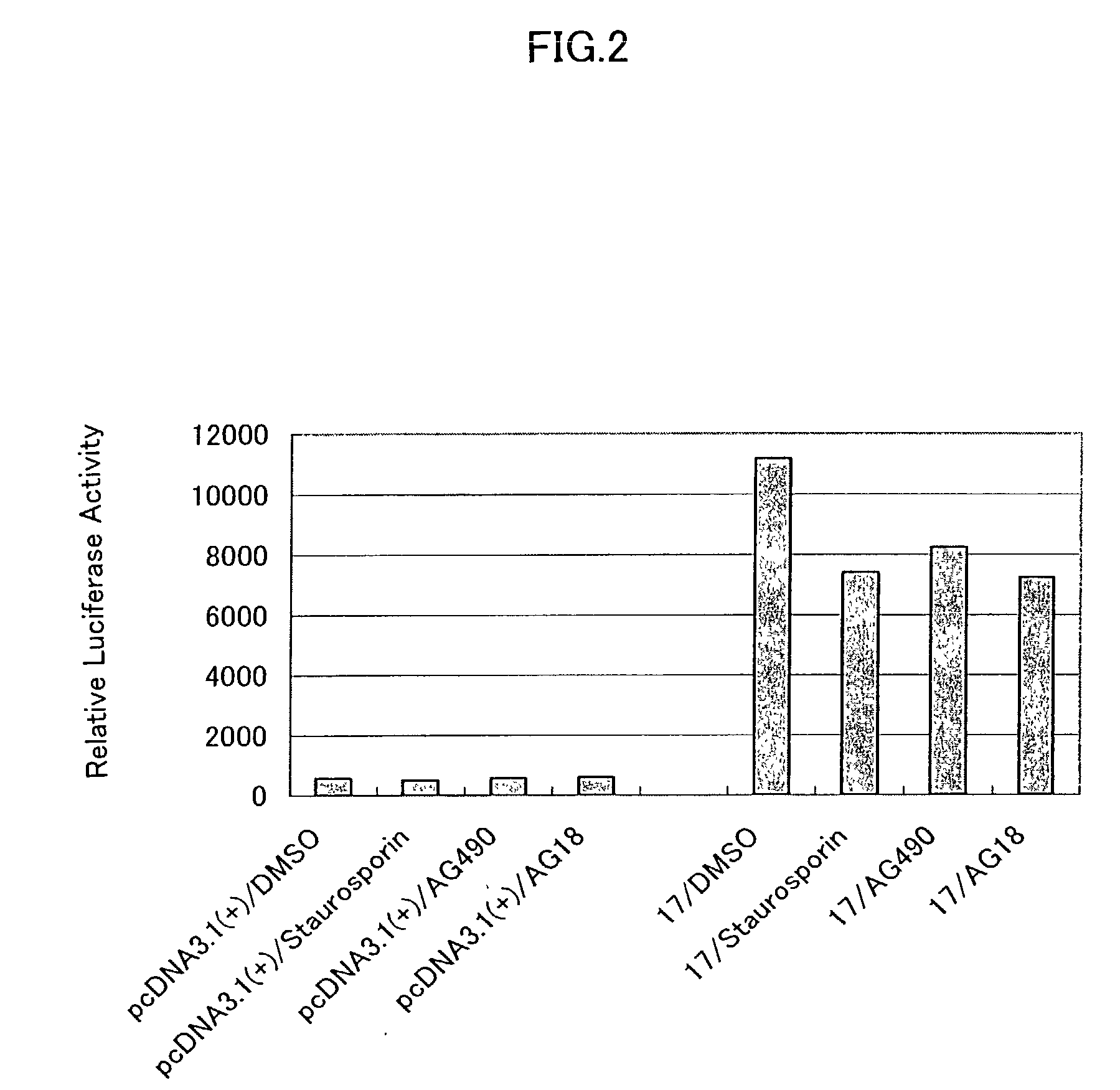
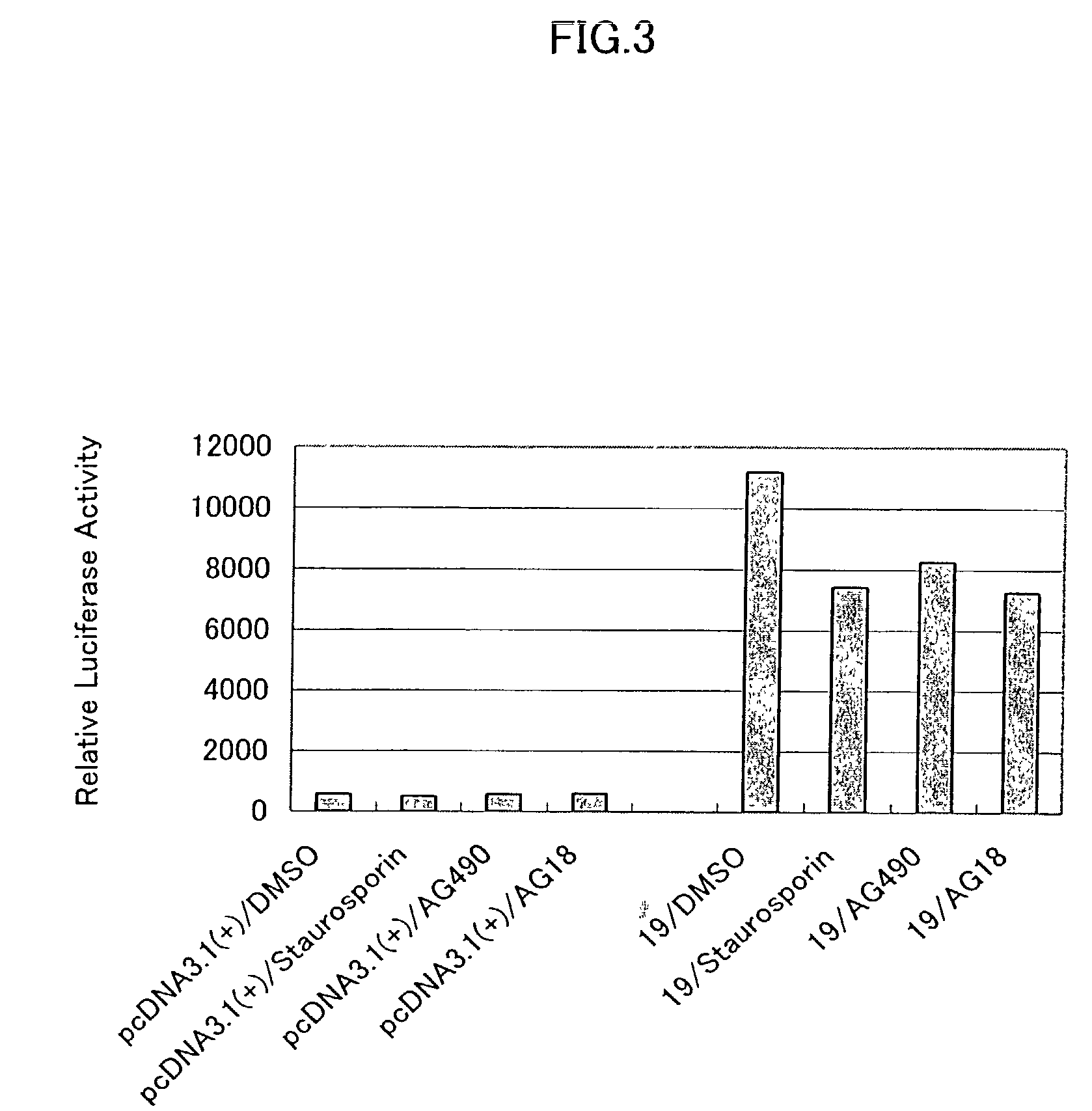
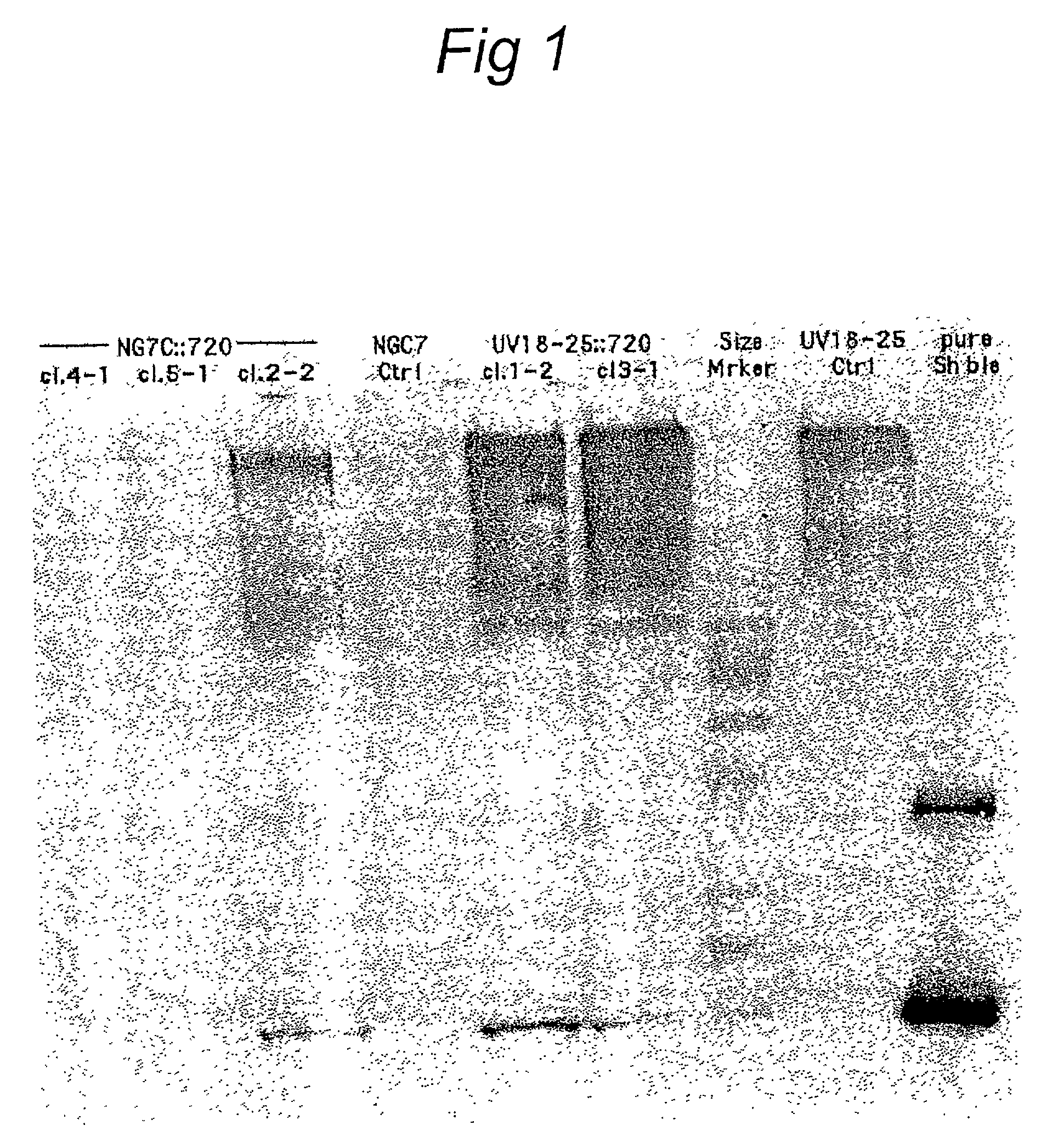
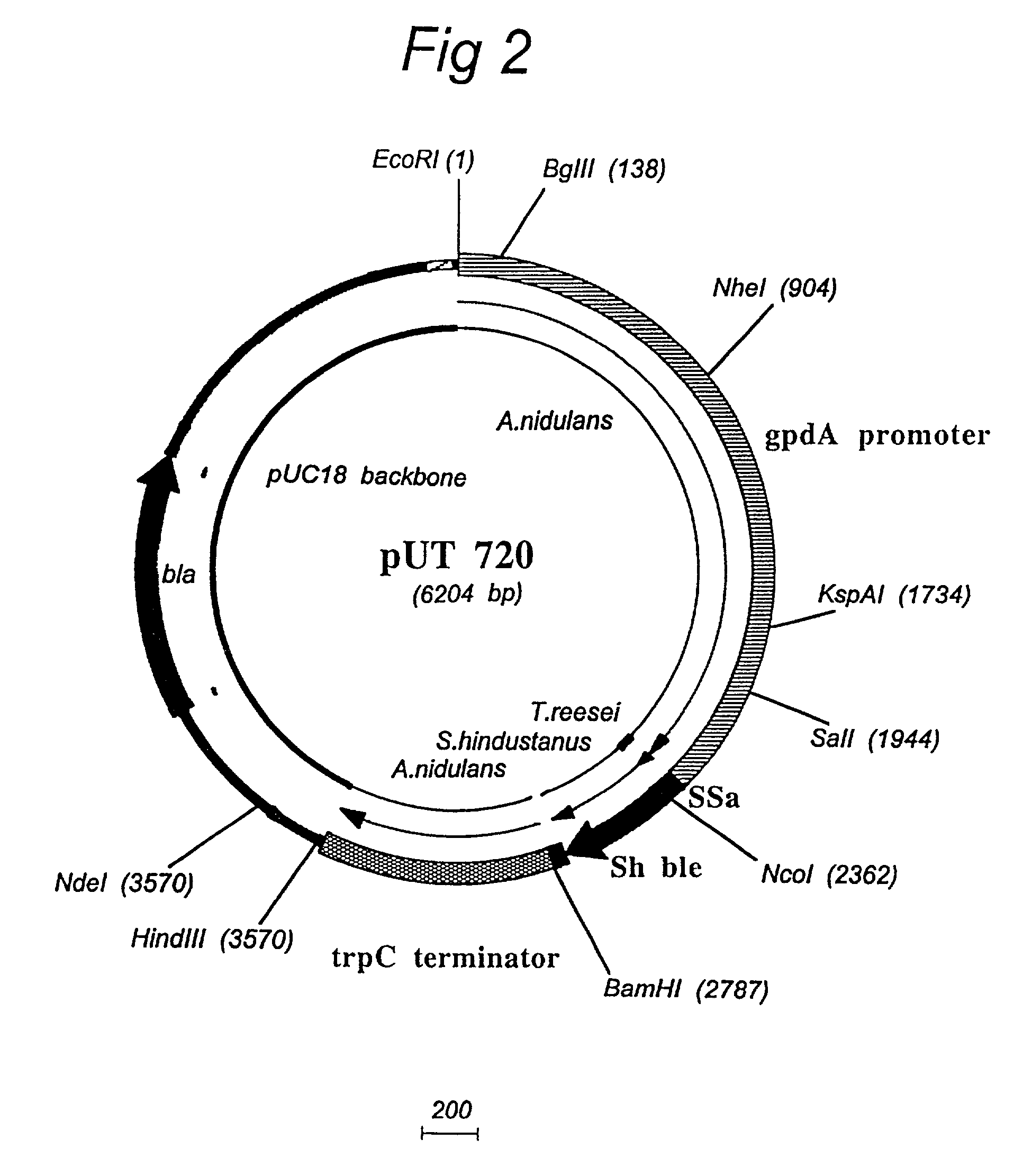
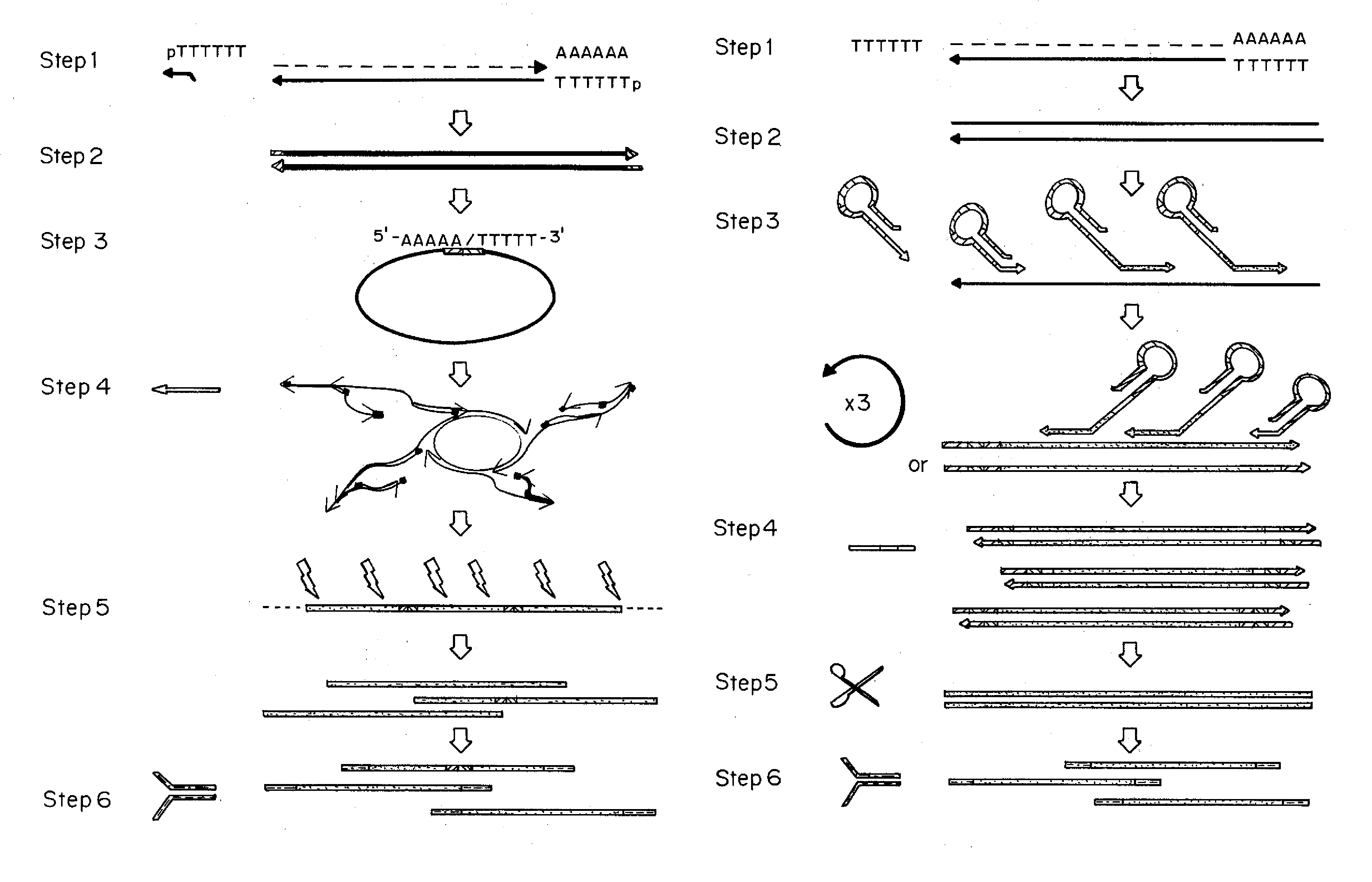
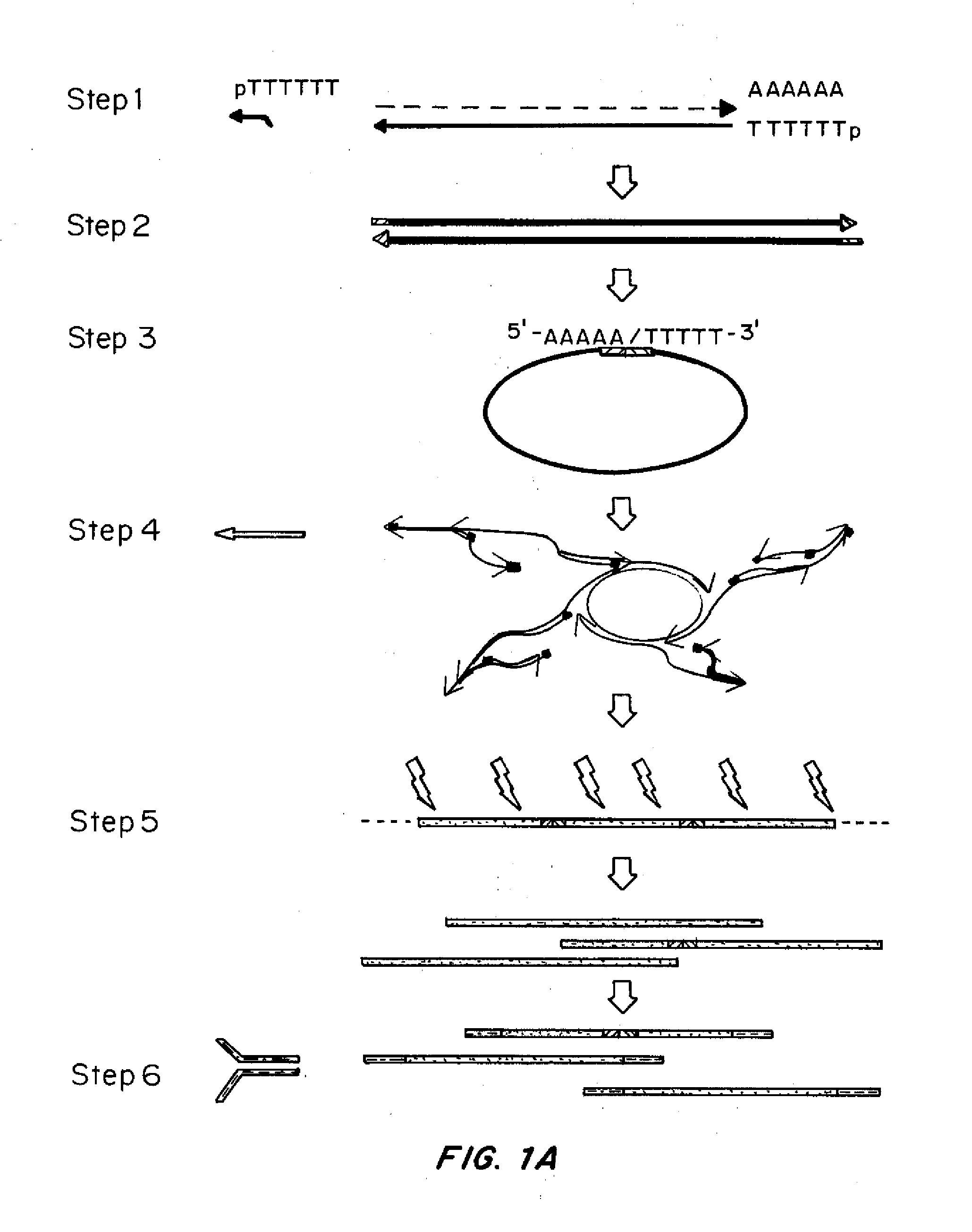
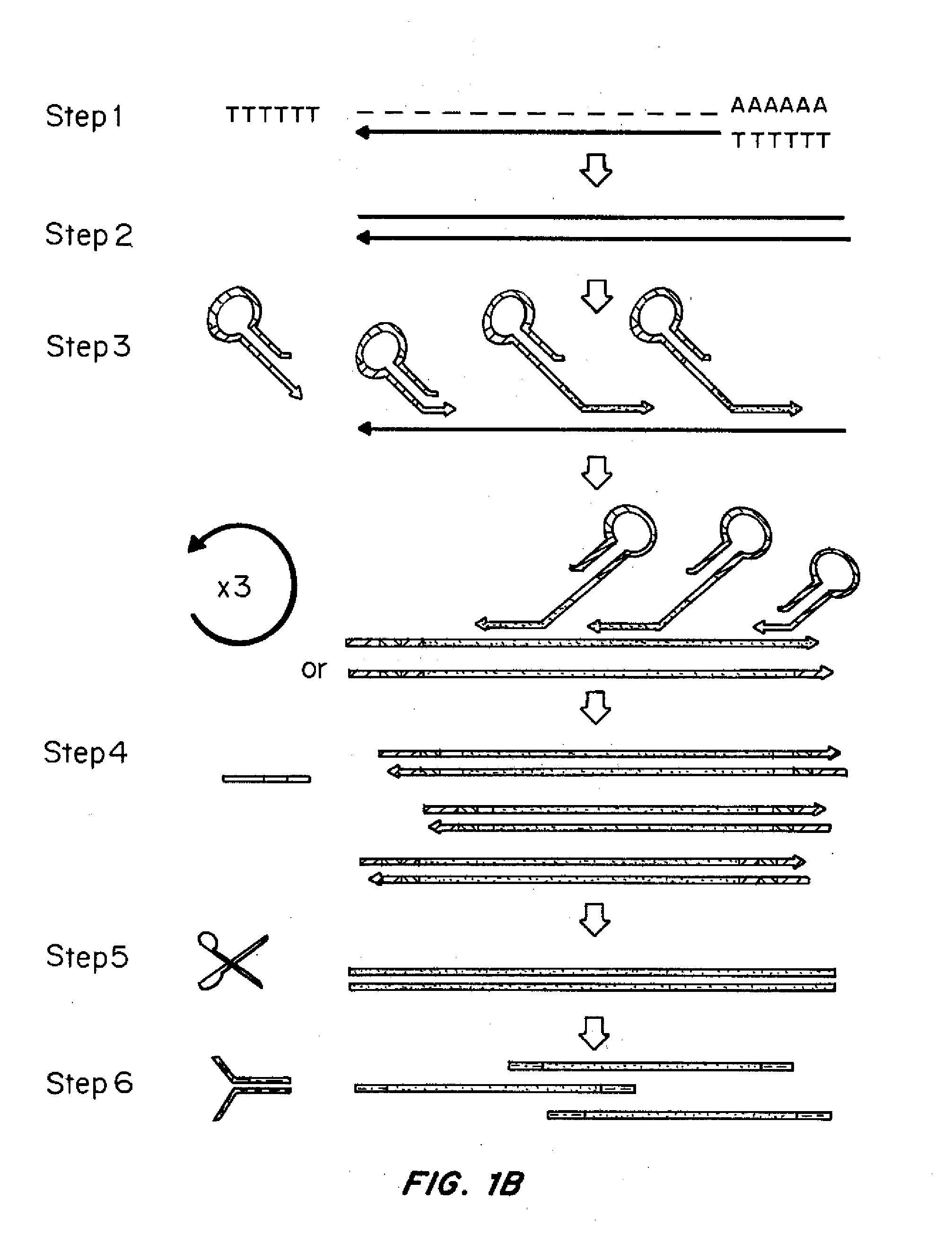
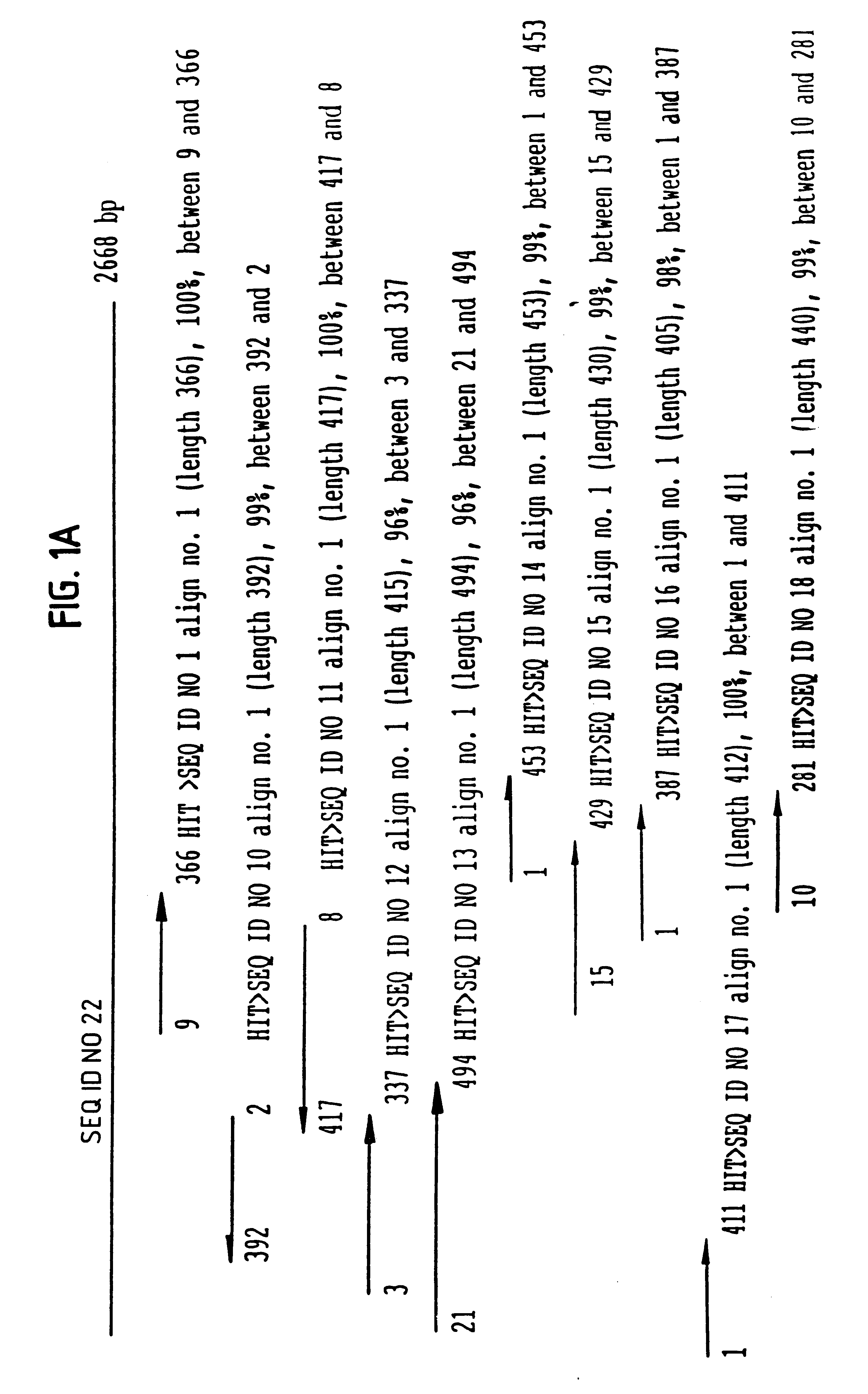
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
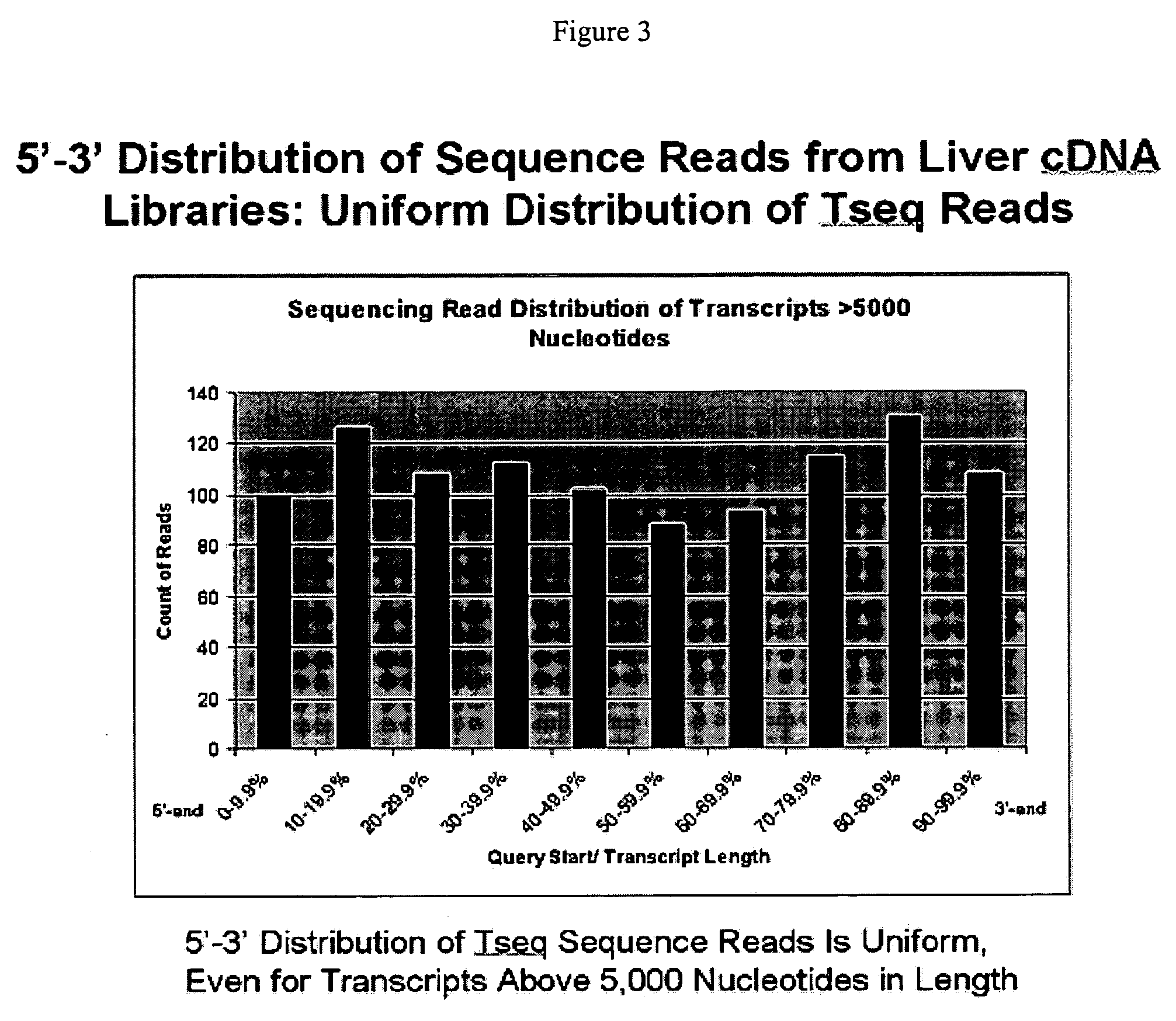
568 results about "CDNA library" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
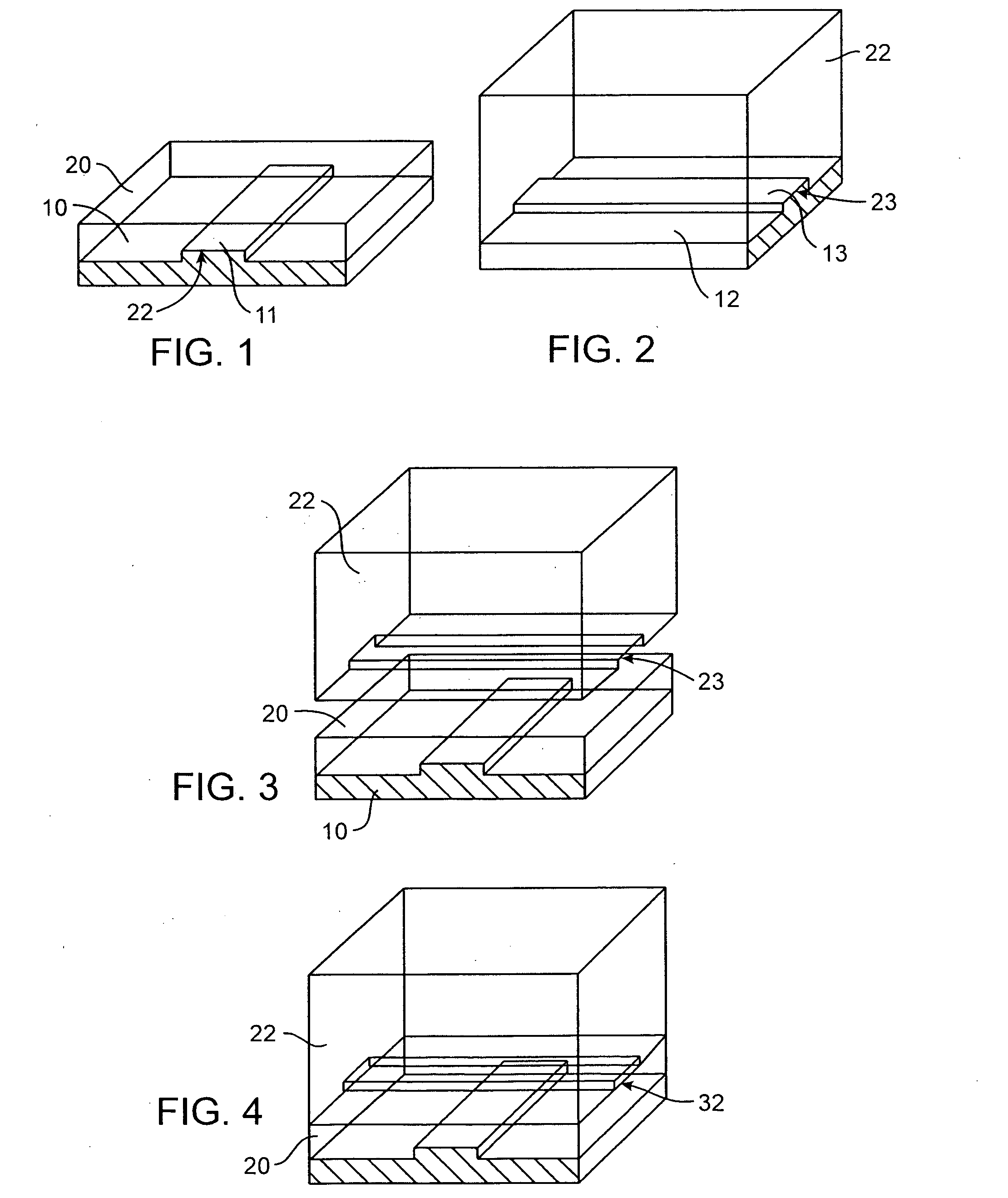
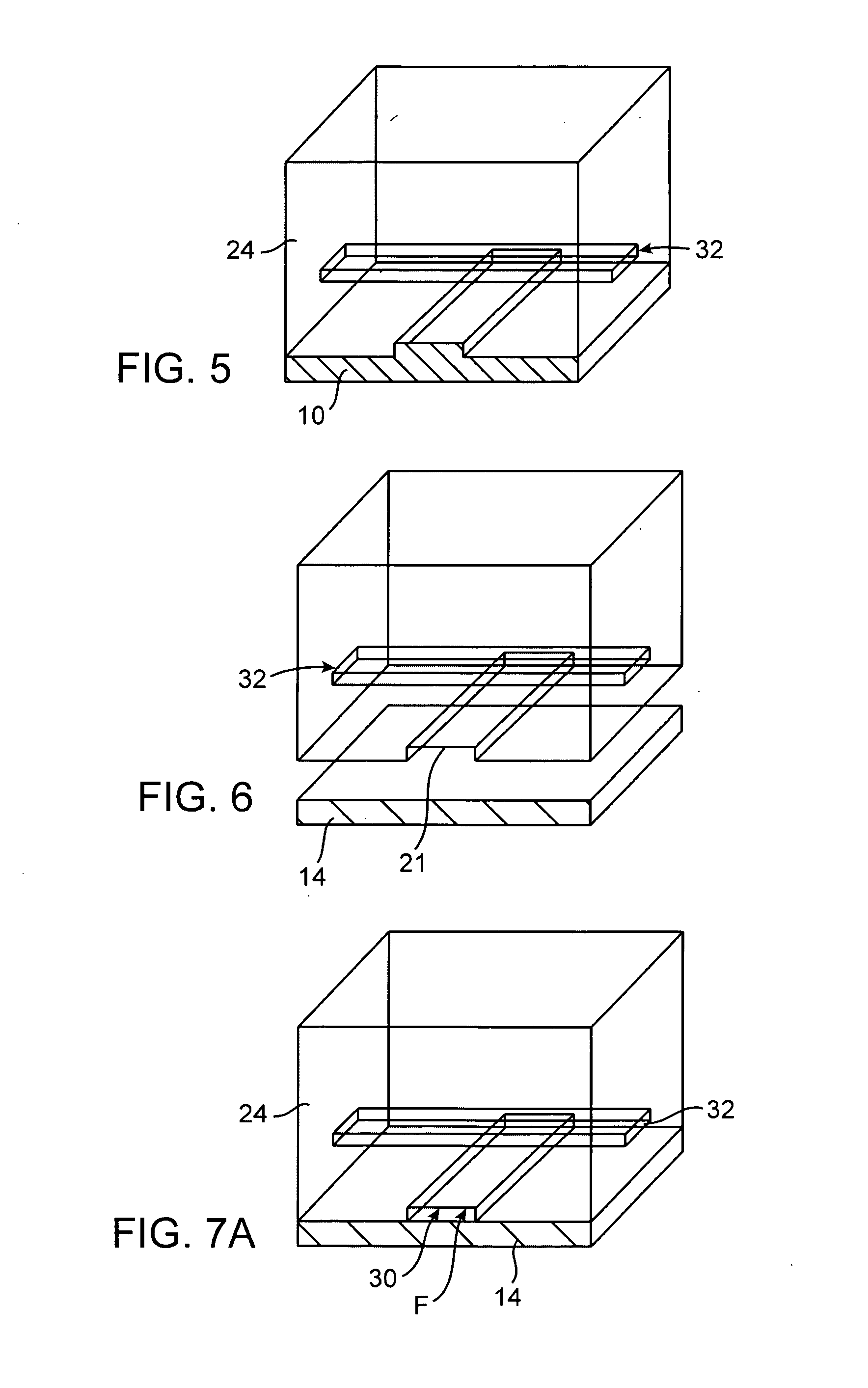
A cDNA library is a combination of cloned cDNA (complementary DNA) fragments inserted into a collection of host cells, of which constitute some portion of the transcriptome of the organism and are stored as a "library". cDNA is produced from fully transcribed mRNA found in the nucleus and therefore contains only the expressed genes of an organism. Similarly, tissue-specific cDNA libraries can be produced. In eukaryotic cells the mature mRNA is already spliced, hence the cDNA produced lacks introns and can be readily expressed in a bacterial cell. While information in cDNA libraries is a powerful and useful tool since gene products are easily identified, the libraries lack information about enhancers, introns, and other regulatory elements found in a genomic DNA library.
Microfluidic nucleic acid analysis
ActiveUS20050053952A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCDNA libraryCells isolation
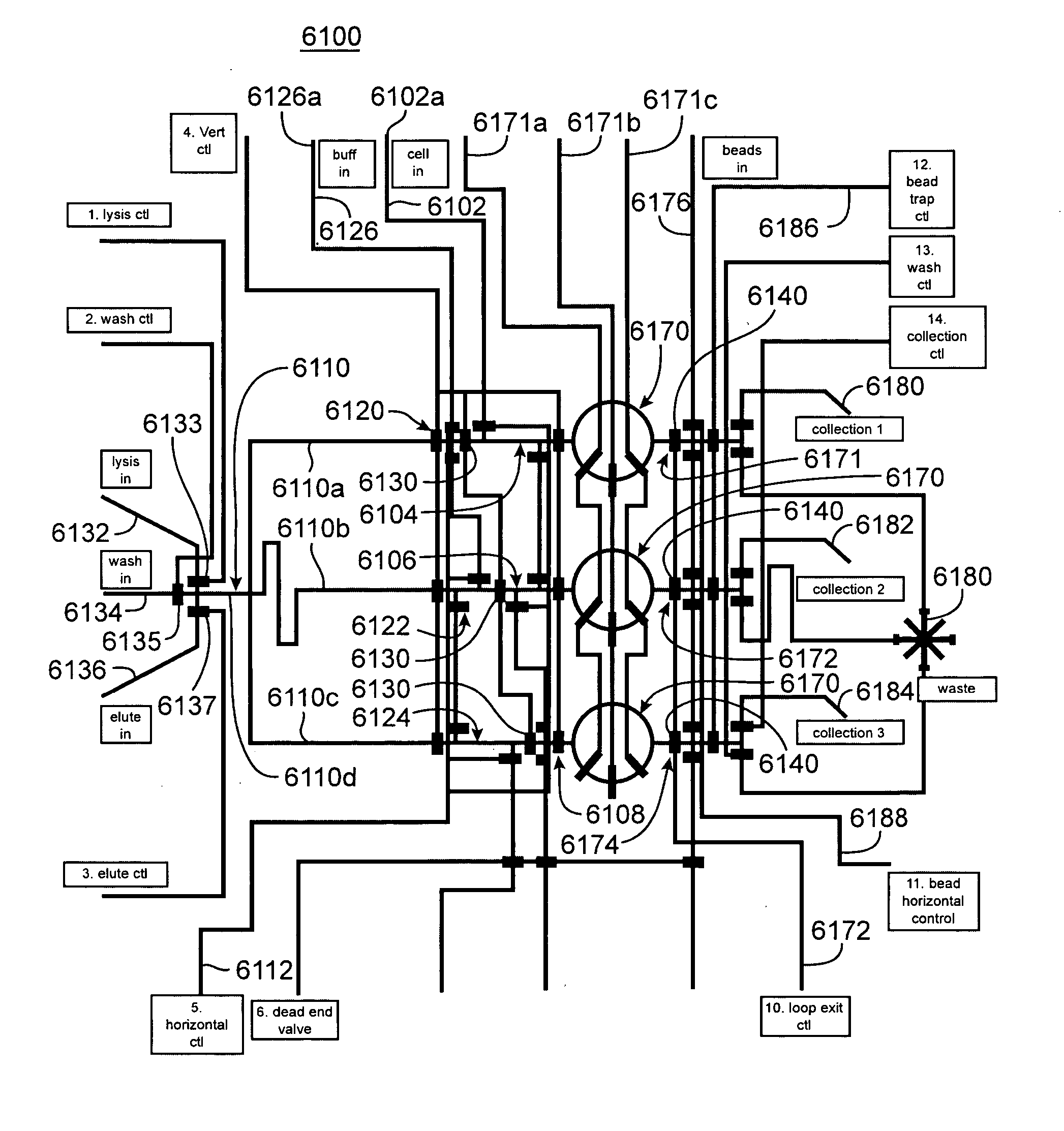
Nucleic acid from cells and viruses sampled from a variety of environments may purified and expressed utilizing microfluidic techniques. In accordance with one embodiment of the present invention, individual or small groups of cells or viruses may be isolated in microfluidic chambers by dilution, sorting, and / or segmentation. The isolated cells or viruses may be lysed directly in the microfluidic chamber, and the resulting nucleic acid purified by exposure to affinity beads. Subsequent elution of the purified nucleic acid may be followed by ligation and cell transformation, all within the same microfluidic chip. In one specific application, cell isolation, lysis, and nucleic acid purification may be performed utilizing a highly parallelized microfluidic architecture to construct gDNA and cDNA libraries.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Gene expression analysis in single cells
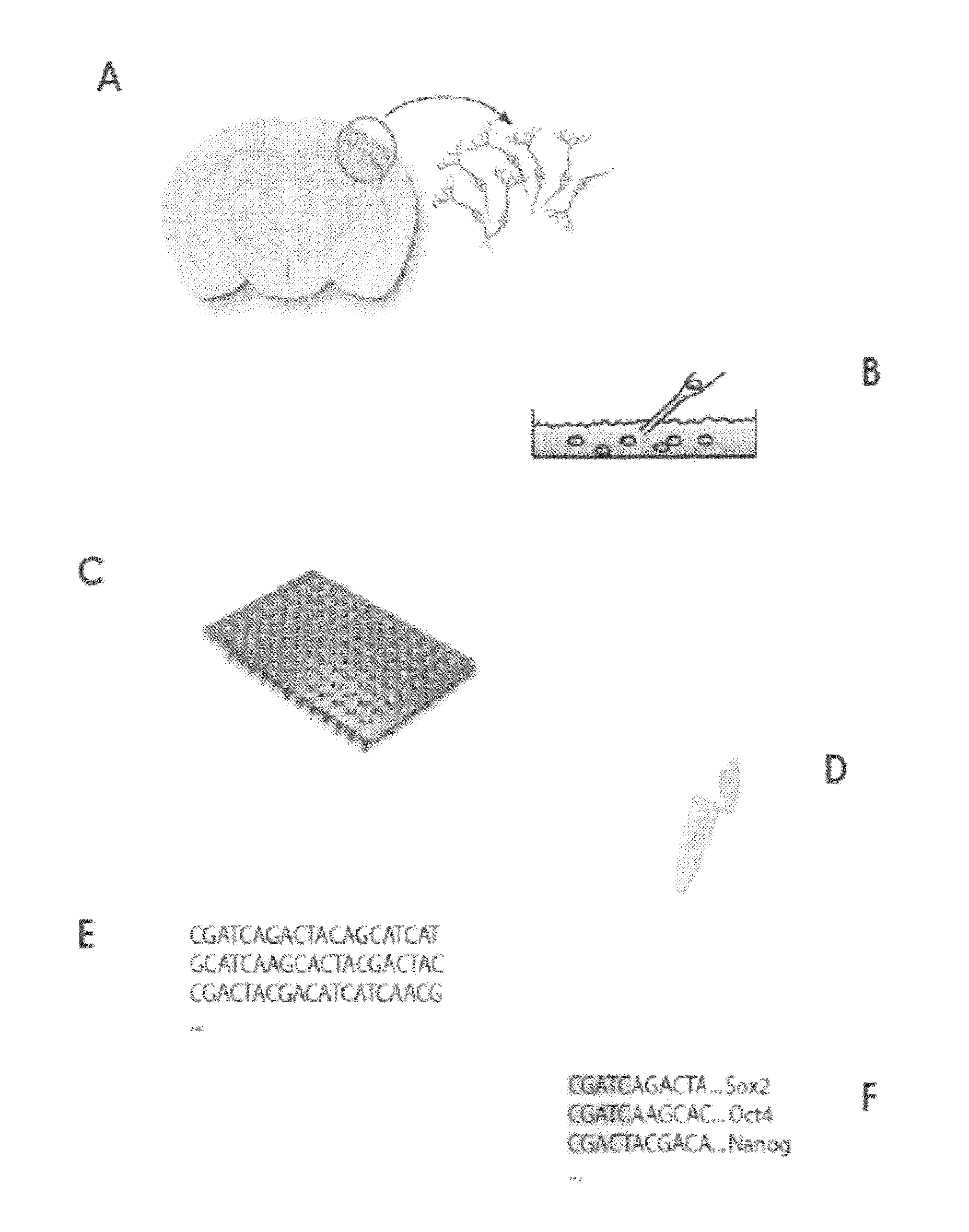
The present invention provides methods and compositions for the analysis of gene expression in single cells or in a plurality of single cells. The invention provides methods for preparing a cDNA library from individual cells by releasing mRNA from each single cell to provide a plurality of individual mRNA samples, synthesizing cDNA from the individual mRNA samples, tagging the individual cDNA, pooling the tagged cDNA samples and amplifying the pooled cDNA samples to generate a cDNA library. The invention also provides a cDNA library produced by the methods described herein. The invention farther provides methods for analyzing gene expression in a plurality of cells by preparing a cDNA library as described herein and sequencing the library.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
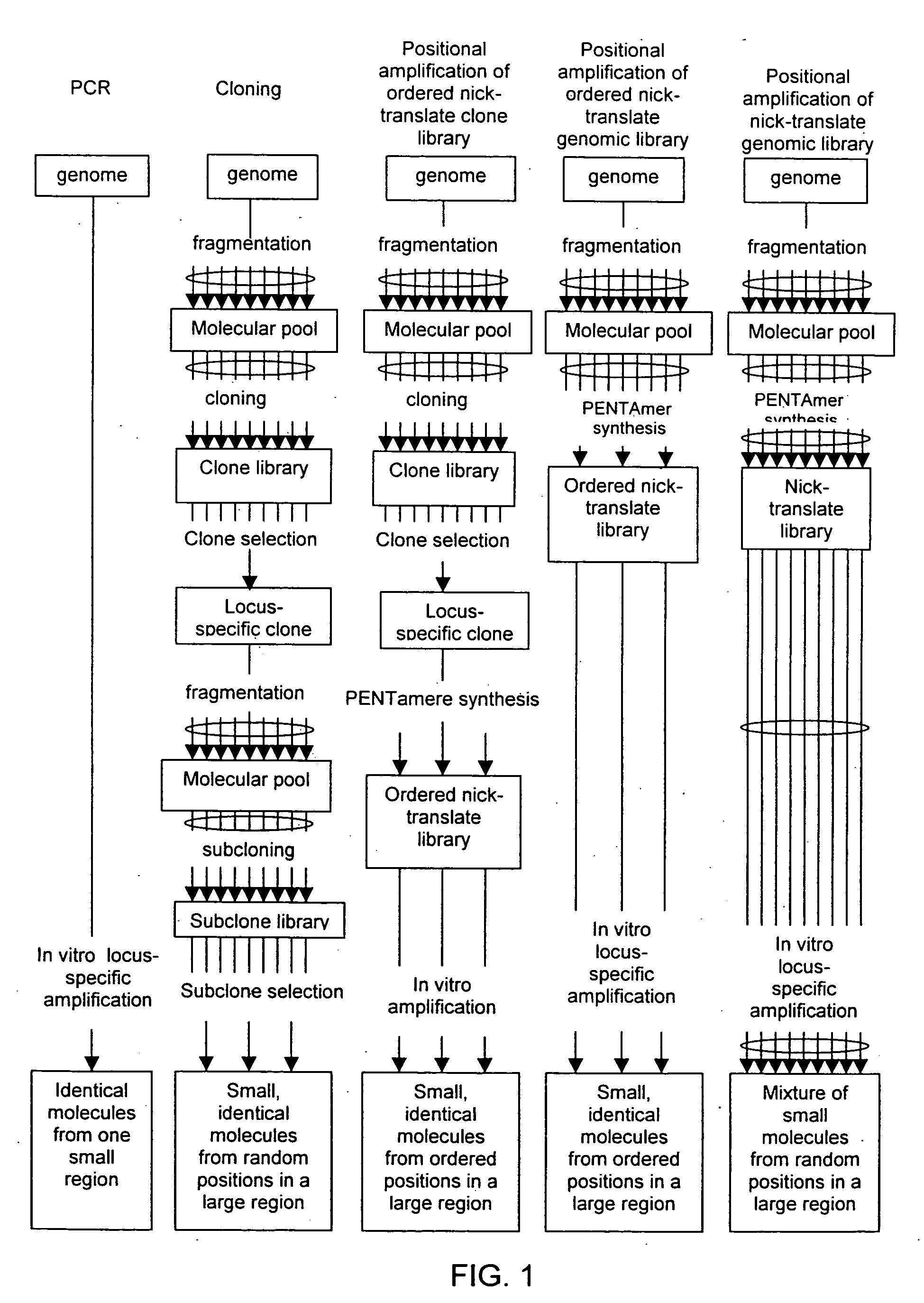
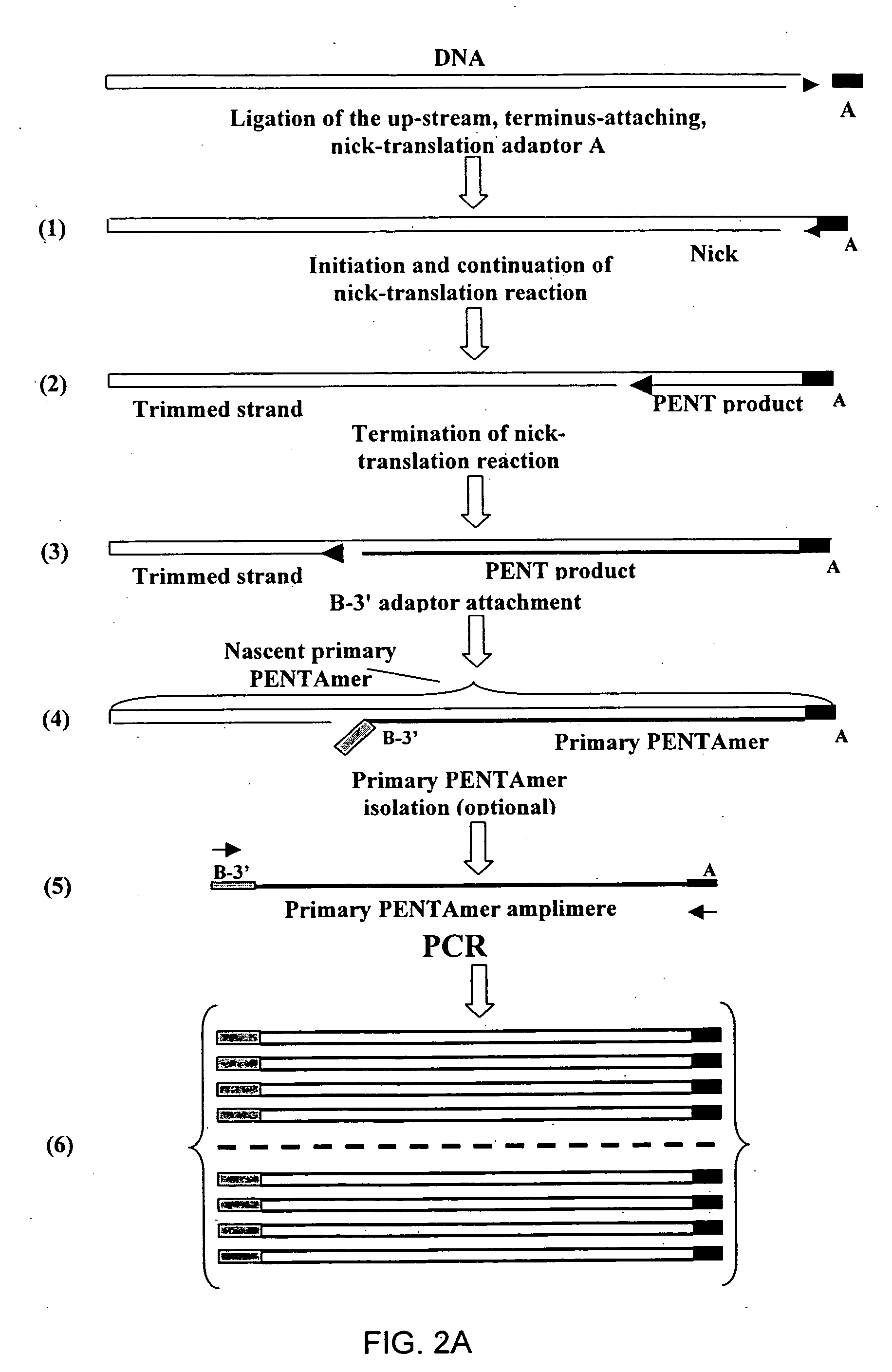
Method of producing a DNA library using positional amplification
InactiveUS20060068394A1Microbiological testing/measurementOrganic chemistry methodsCDNA libraryPentamer
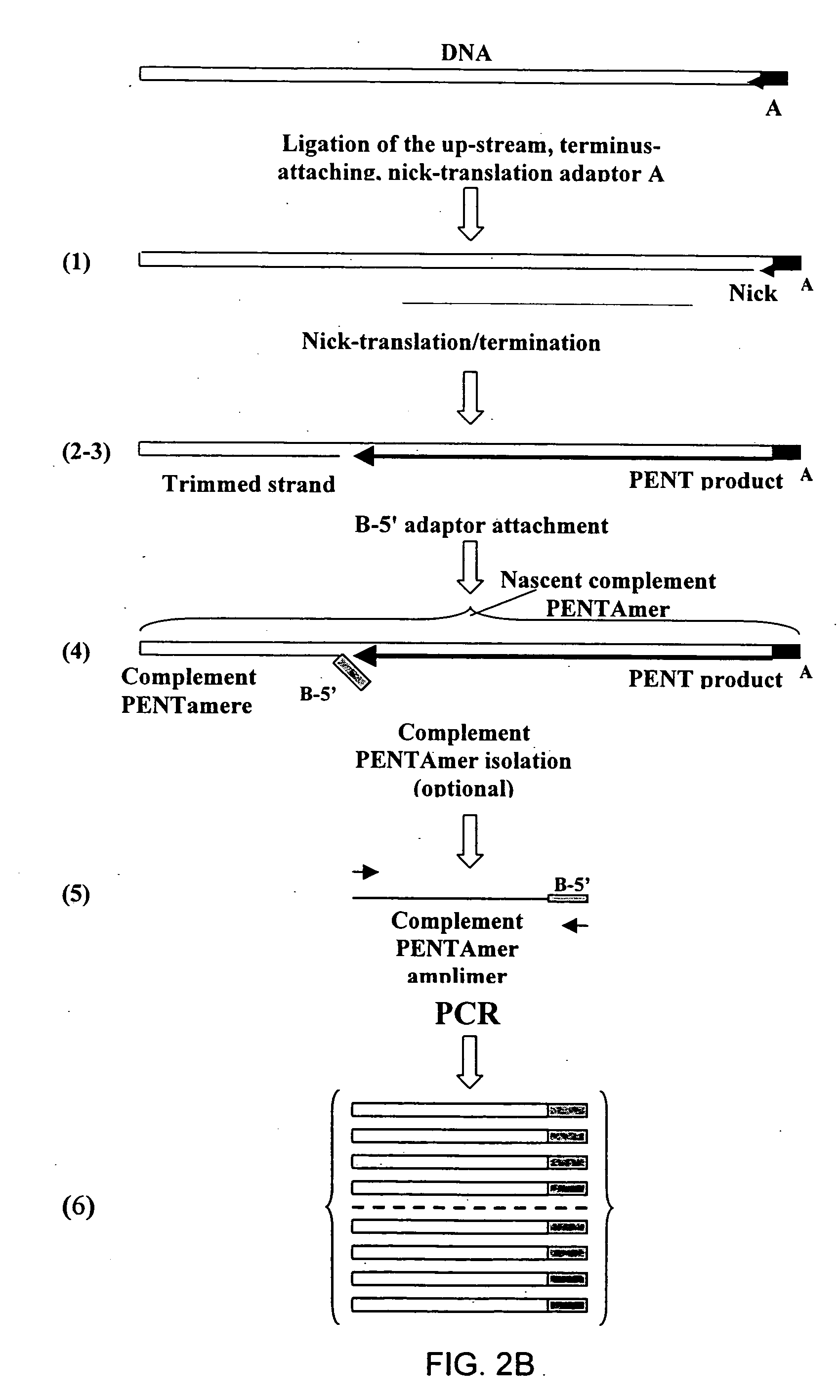
The disclosed invention relates to general and specific methods to use the Primer Extension / Nick Translation (PENT) reaction to create an amplifiable DNA strand, called a PENTAmer. A PENTAmers can be made for the purpose of amplifying a controlled length of DNA located at a controlled position within a DNA molecule, a process referred to as Positional Amplification by Nick Translation (PANT). In contrast to PCR, which amplifies DNA between two specific sequences, PANT can amplify DNA between two specific positions. PENTAmers can be created to amplify-very large regions of DNA (up to 500,000 bp) as random mixtures (unordered positional libraries), or as molecules sorted according to position (ordered positional libraries). PANT is fast and economical, because PENTAmer preparation can be multiplexed. A single PENTAmer preparation can include very complex mixtures of DNA such as hundreds of large-insert clones, complete genomes, or cDNA libraries. Subsequent PCR amplification of the preparation using a single specific primer can positionally amplify contiguous regions along a specific clone, along a specific genomic region, or along a specific expressed sequence.
Owner:LANGMORE JOHN +1
Methods for measuring relative amounts of nucleic acids in a complex mixture and retrieval of specific sequences therefrom
InactiveUS20020172965A1Poor enrichmentMultiplicative improvement in overall enrichmentMicrobiological testing/measurementOther foreign material introduction processesCDNA libraryNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention relates to a method for the comparative assessment of the level of specific nucleic acid sequences in samples derived from different sources. More specifically, the invention relates to a method using oligonucleotides covalently linked to a solid support, such as beads, to isolate specific labeled nucleic acid sequences from complex mixtures. The methods disclosed allow quantitative comparisons of the amount of nucleic acid of defined sequence in a plurality of different samples of nucleic acid, e.g., from different cells or tissues or from genetic libraries. Nucleic acids from the samples are labeled in such a fashion that the signals can be distinguished and compared following hybridization to the oligonucleotides on the beads. According to the invention, the solid supports with the hybridized nucleic acid may be retrieved, and the target nucleic acid eluted and analyzed. Furthermore, the invention provides a method for tagging individual clones from a cDNA library such that they can be identified uniquely and retrieved by hybridization to specific beads.
Owner:DELTAGEN PROTEOMICS
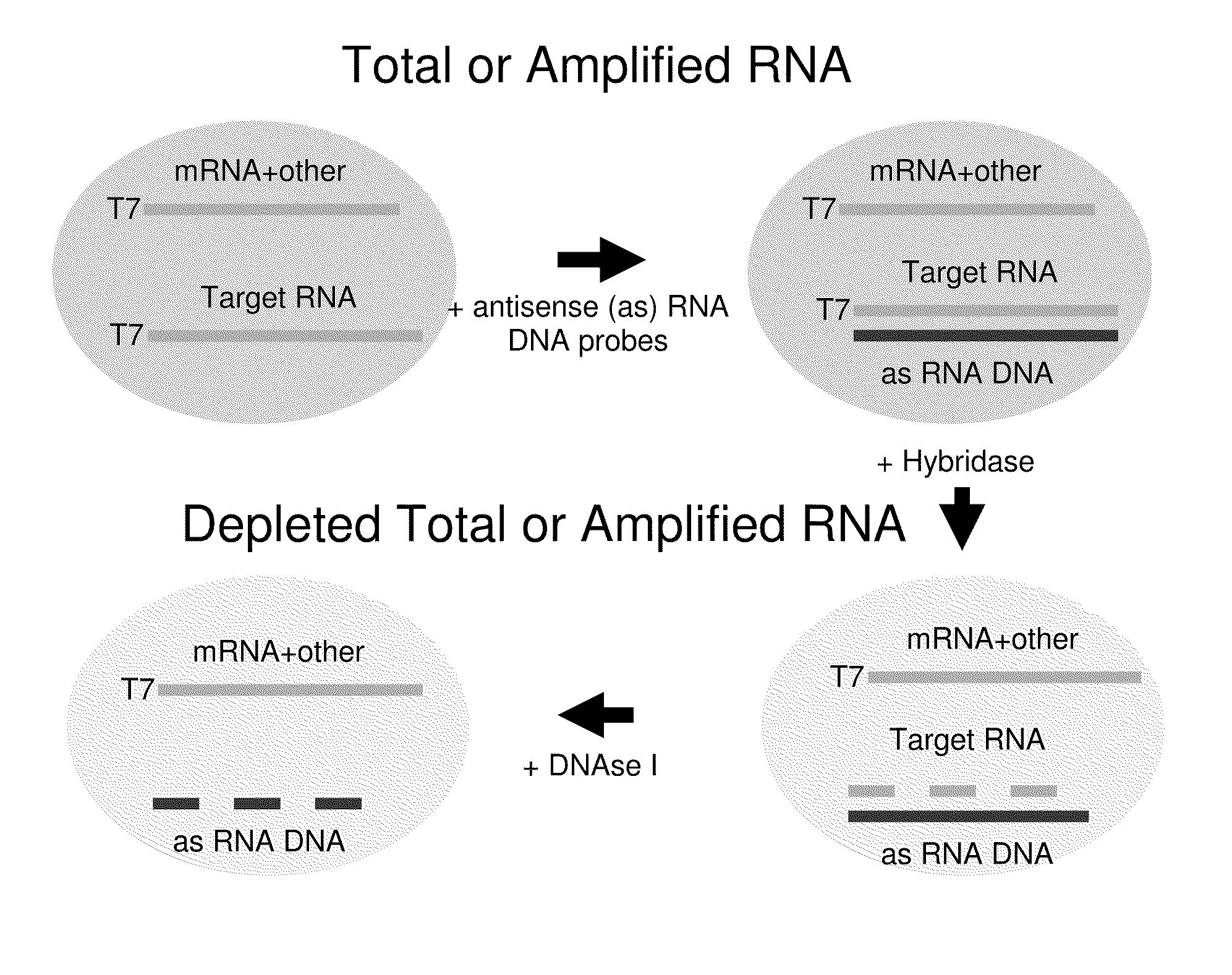
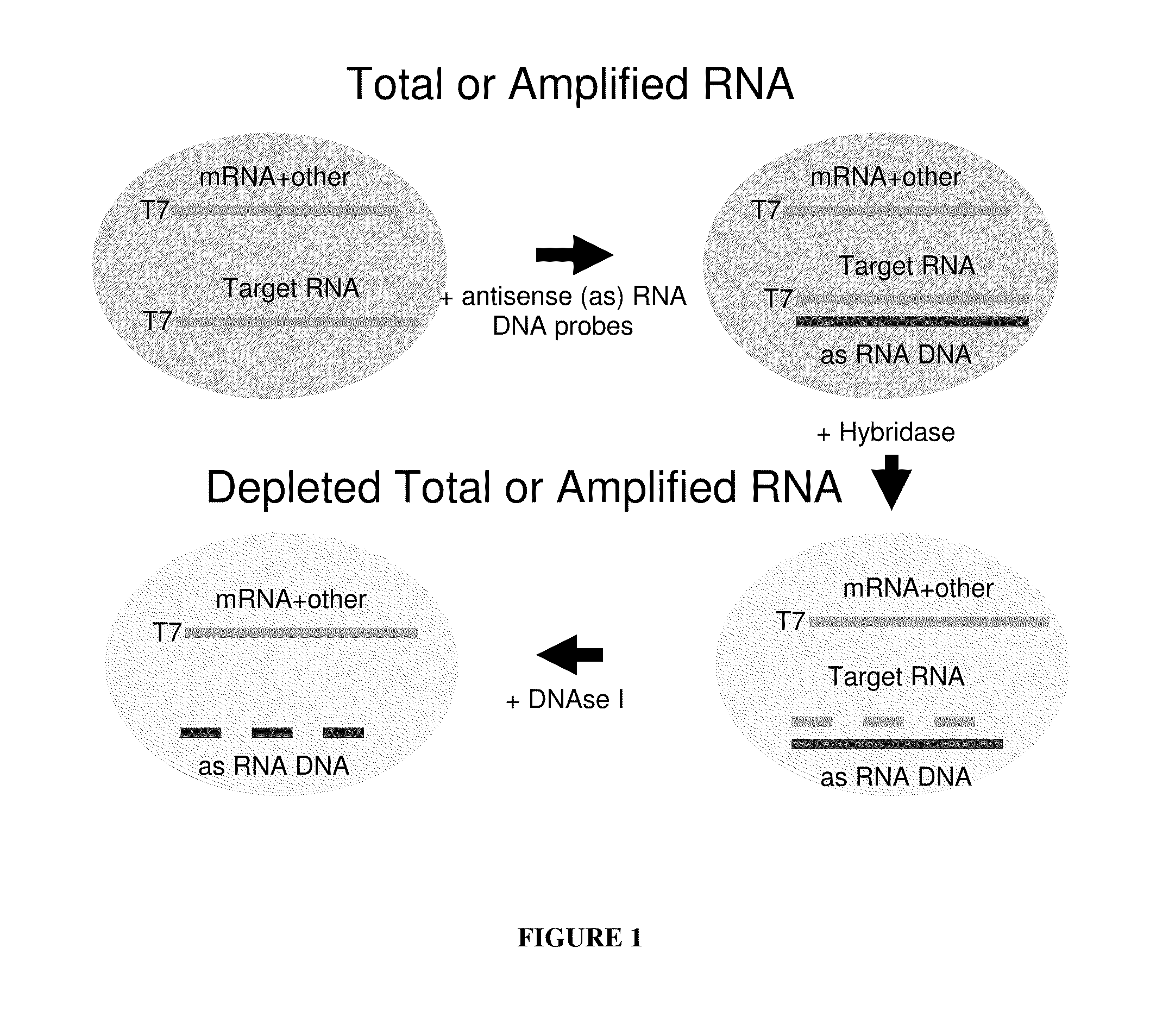
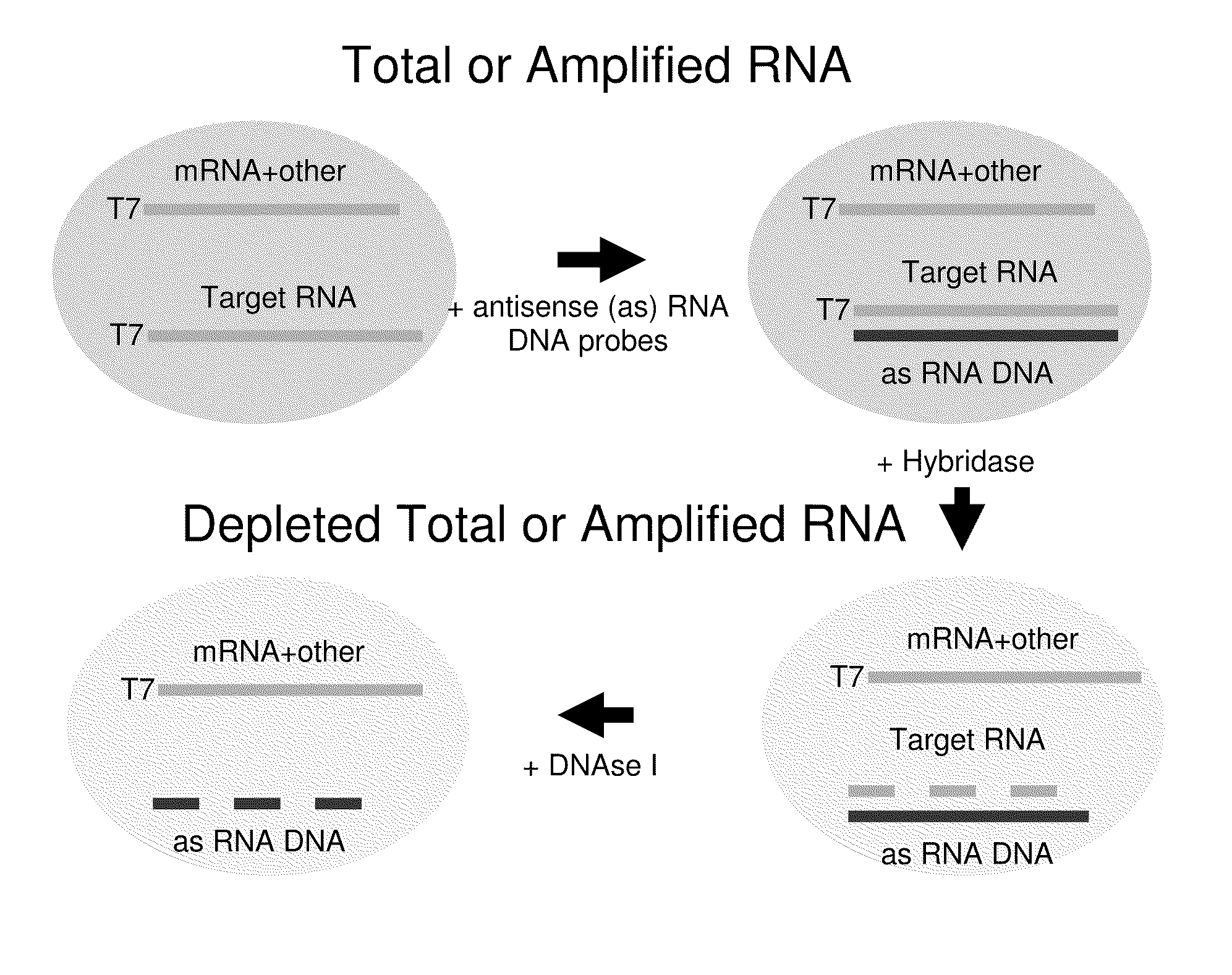
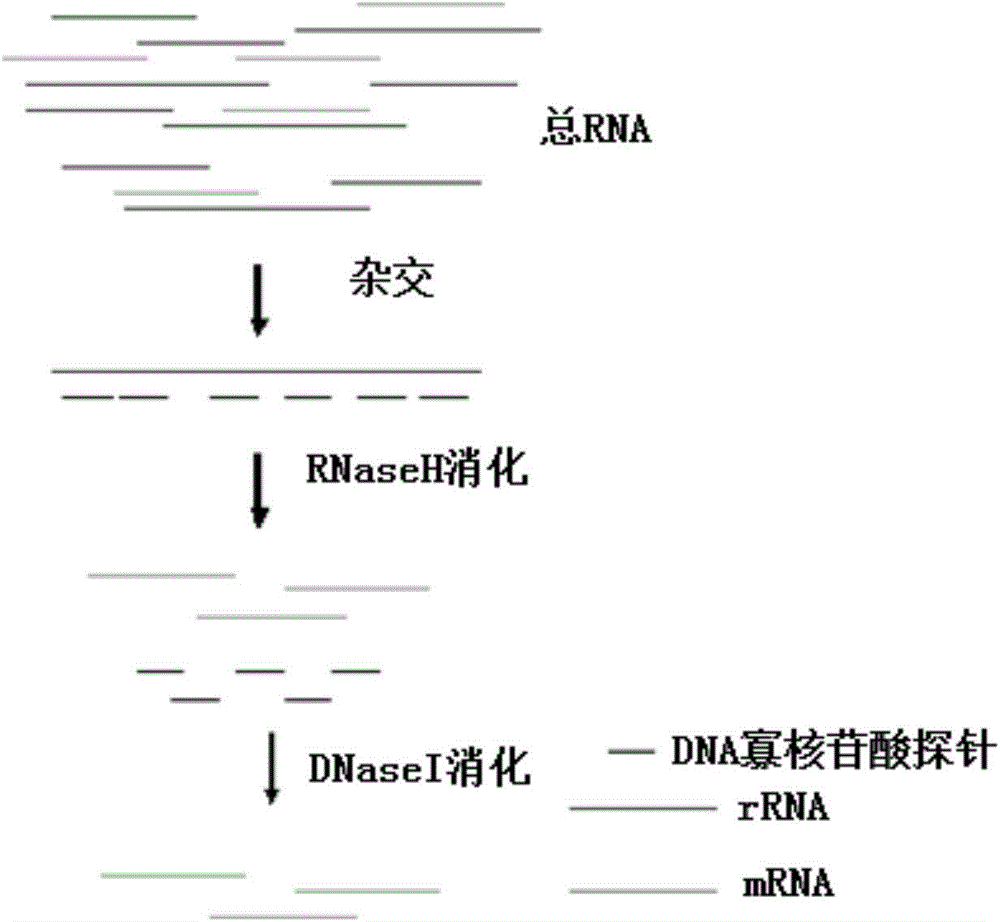
Methods for depleting RNA from nucleic acid samples
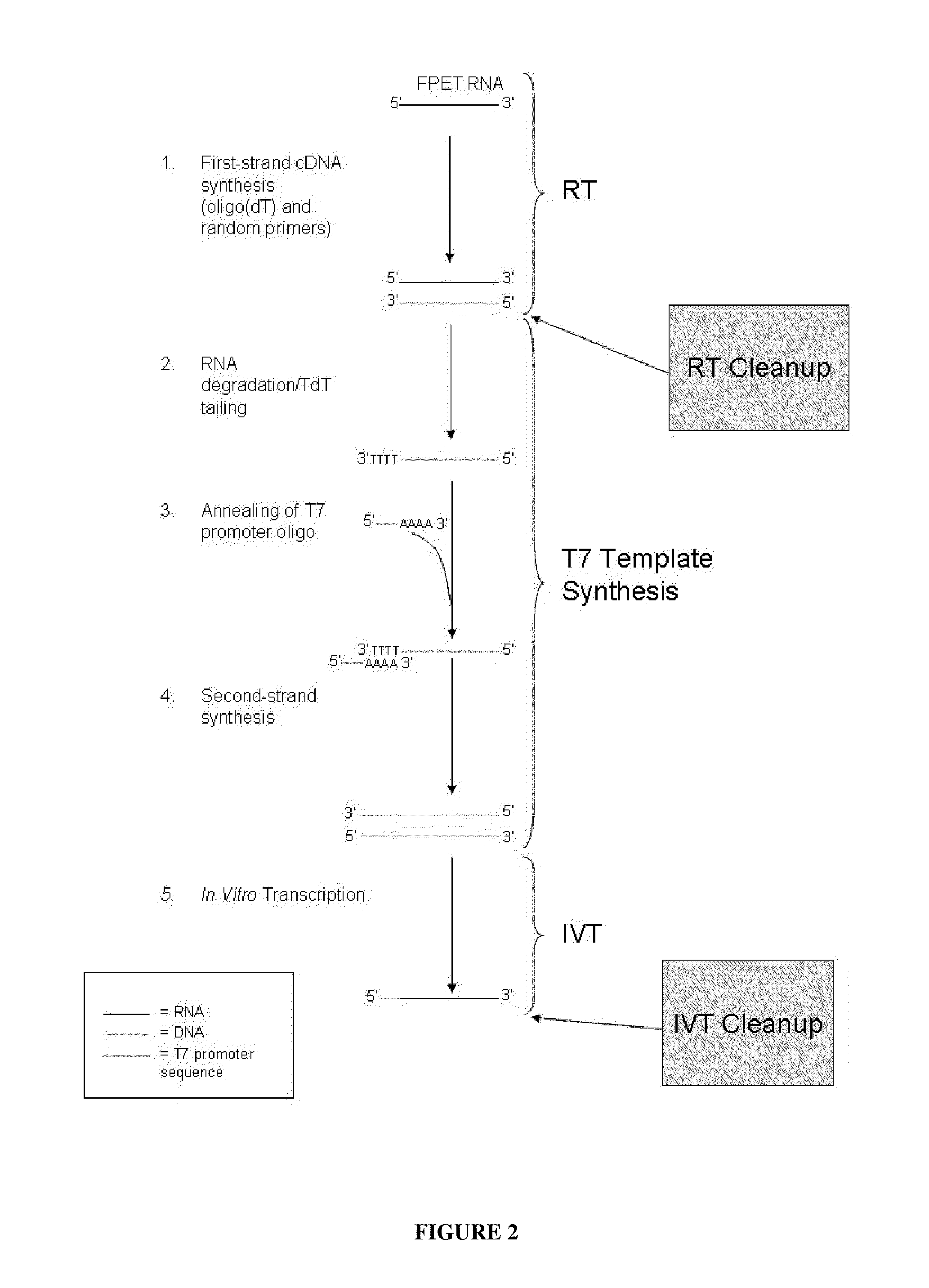
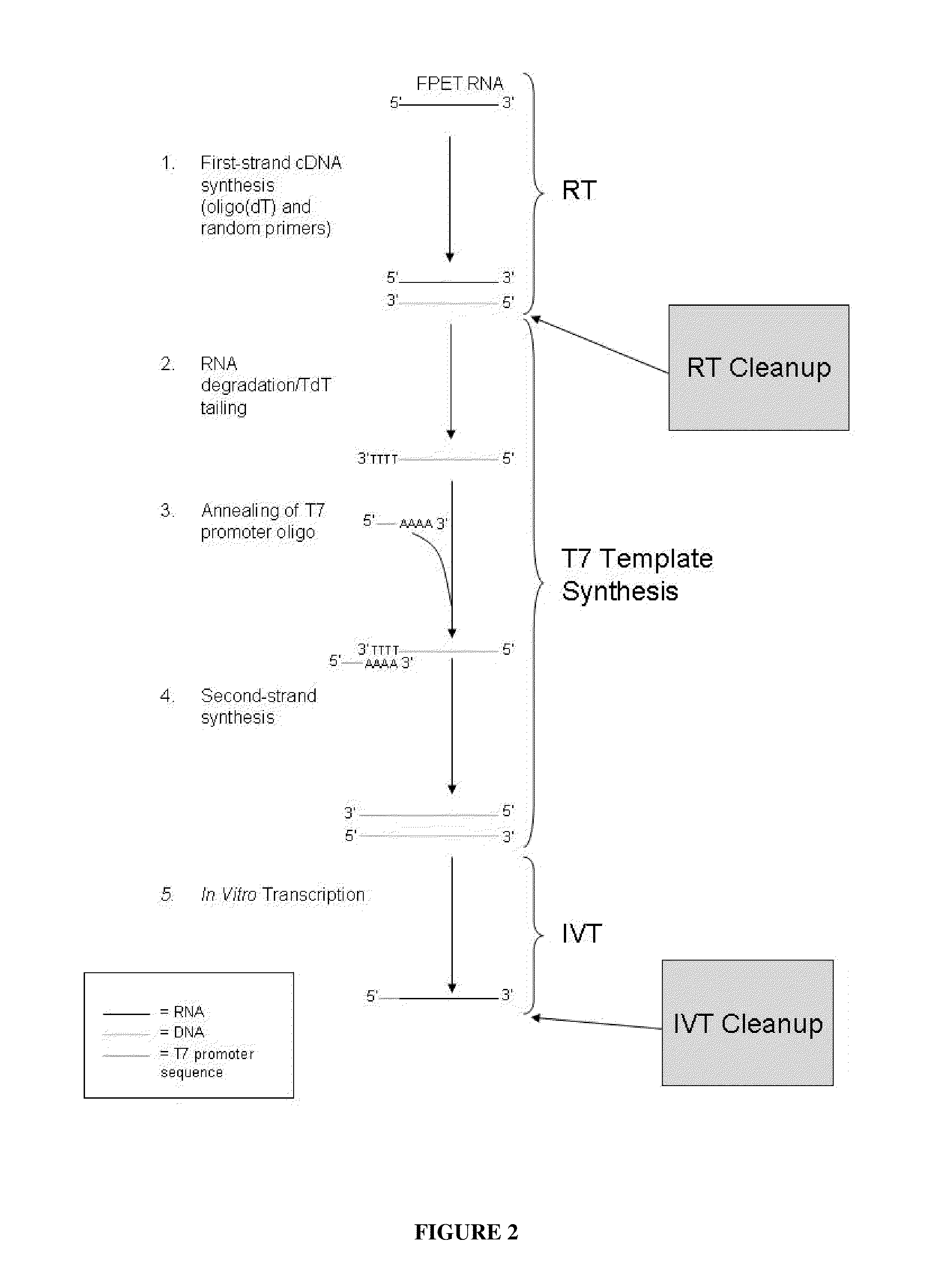
ActiveUS20110111409A1Reduce interferenceReduce unnecessary workSugar derivativesHydrolasesCDNA libraryParaffin embedded tissue
The invention relates to methods of depleting RNA from a nucleic acid sample. The RNA may be any RNA, including, but not limited to, rRNA, tRNA, and mRNA. The method is useful for depleting RNA from a nucleic acid sample obtained from a fixed paraffin-embedded tissue (FPET) sample. The method may also be used to prepare cDNA, in particular, a cDNA library for further analysis or manipulation.
Owner:GENOMIC HEALTH INC
GENE EXPRESSION ANALYSIS METHOD USING TWO DIMENSIONAL cDNA LIBRARY
InactiveUS20120245053A1Efficient detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningCDNA libraryGene expression level
The present invention provides a method and / or means for collecting and analyzing an individual cell in a tissue, and at the same time, quantitatively monitoring the expression levels of various genes while keeping two-dimensional information in the tissue. Specifically, the present invention provides a method comprising preparing a cDNA library from mRNA while keeping two-dimensional cellular distribution information and obtaining the gene expression levels at any site or all sites at a level of single cell. More specifically, the present invention provides a method comprising preparing a cDNA library in a sheet-form from mRNA while keeping two-dimensional cellular distribution information and repeatedly using the cDNA library in the detection of the gene expression, thereby allowing measurement of the expression distribution for a number of genes at a high accuracy.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
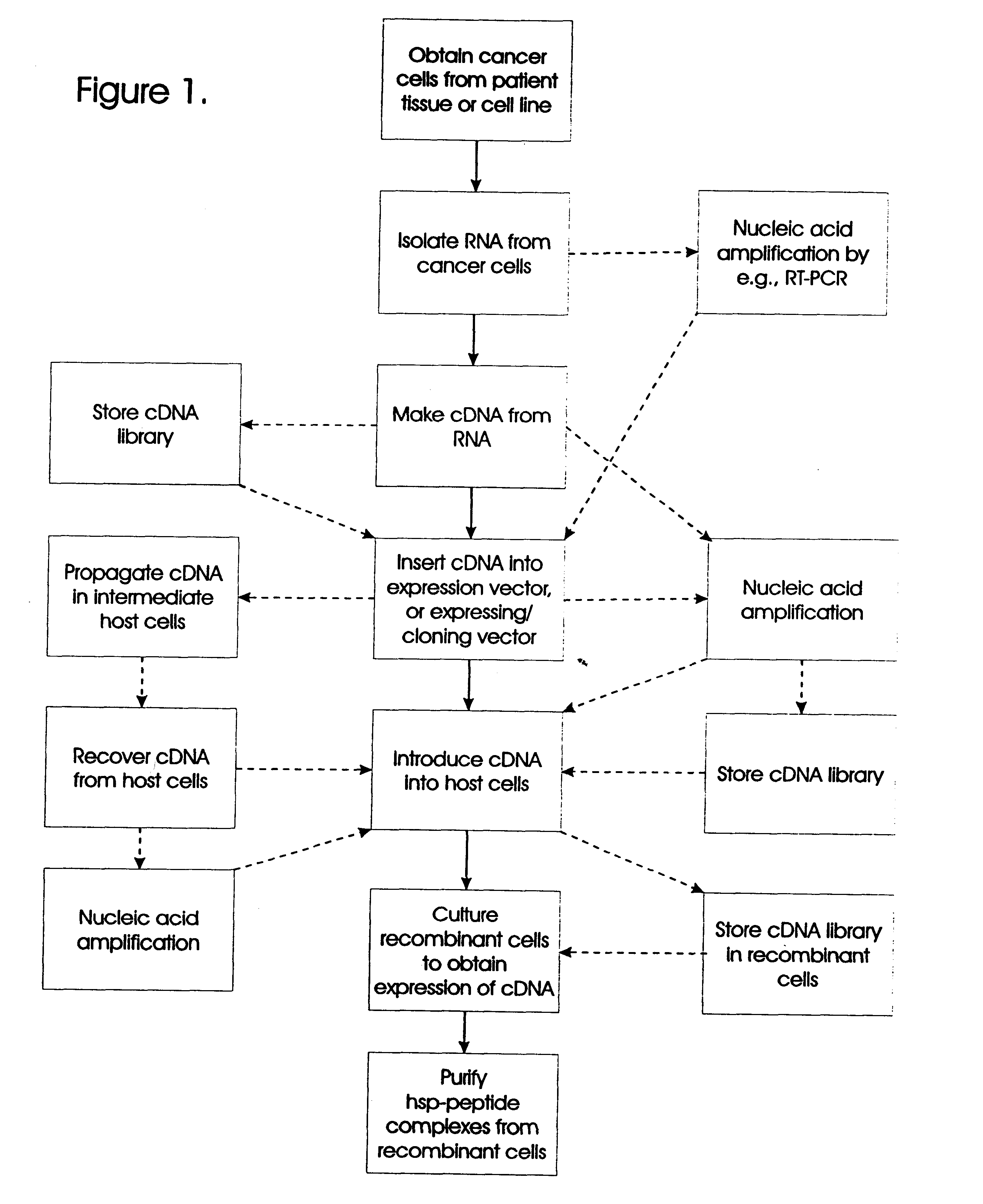
Methods for preparation of vaccines against cancer
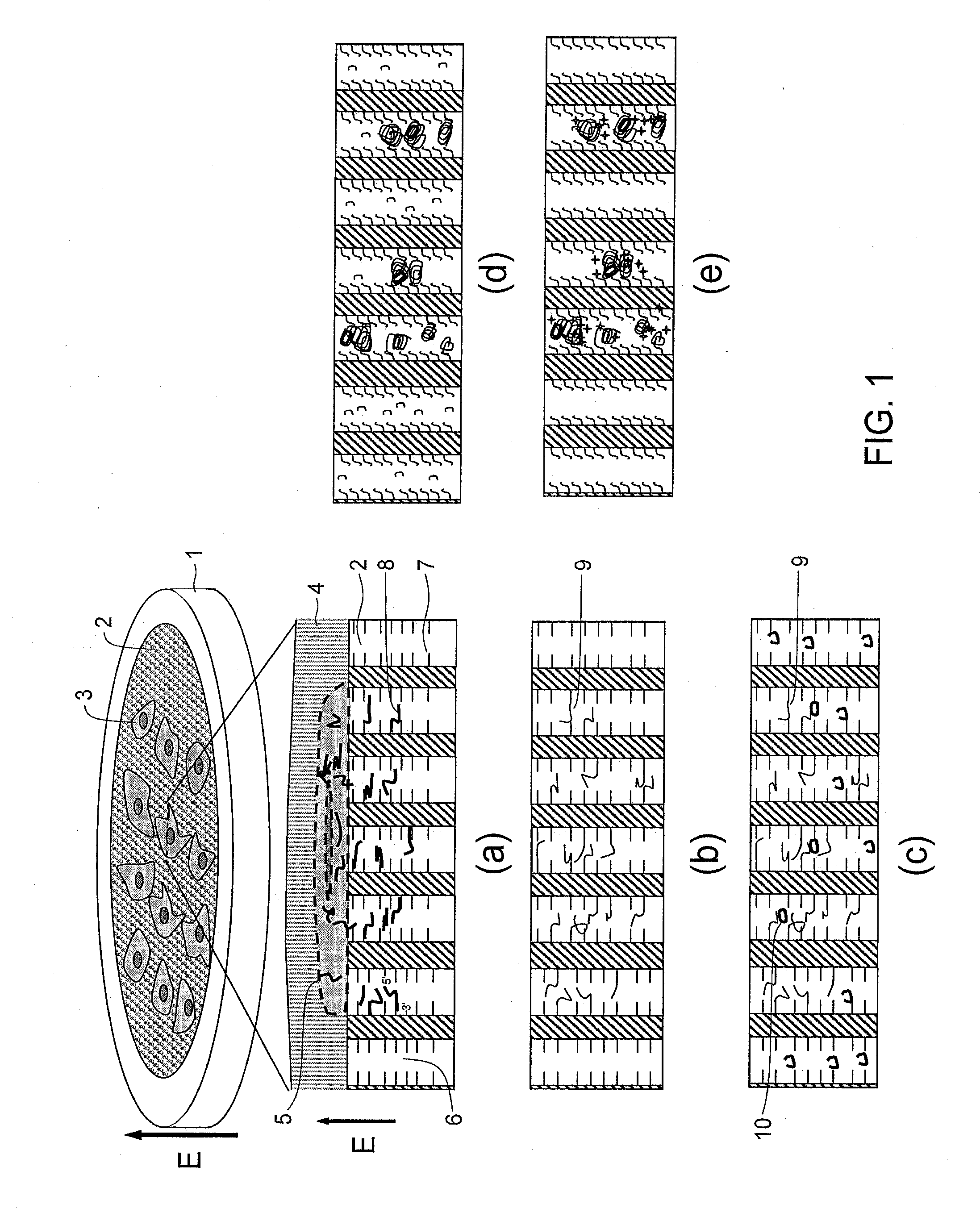
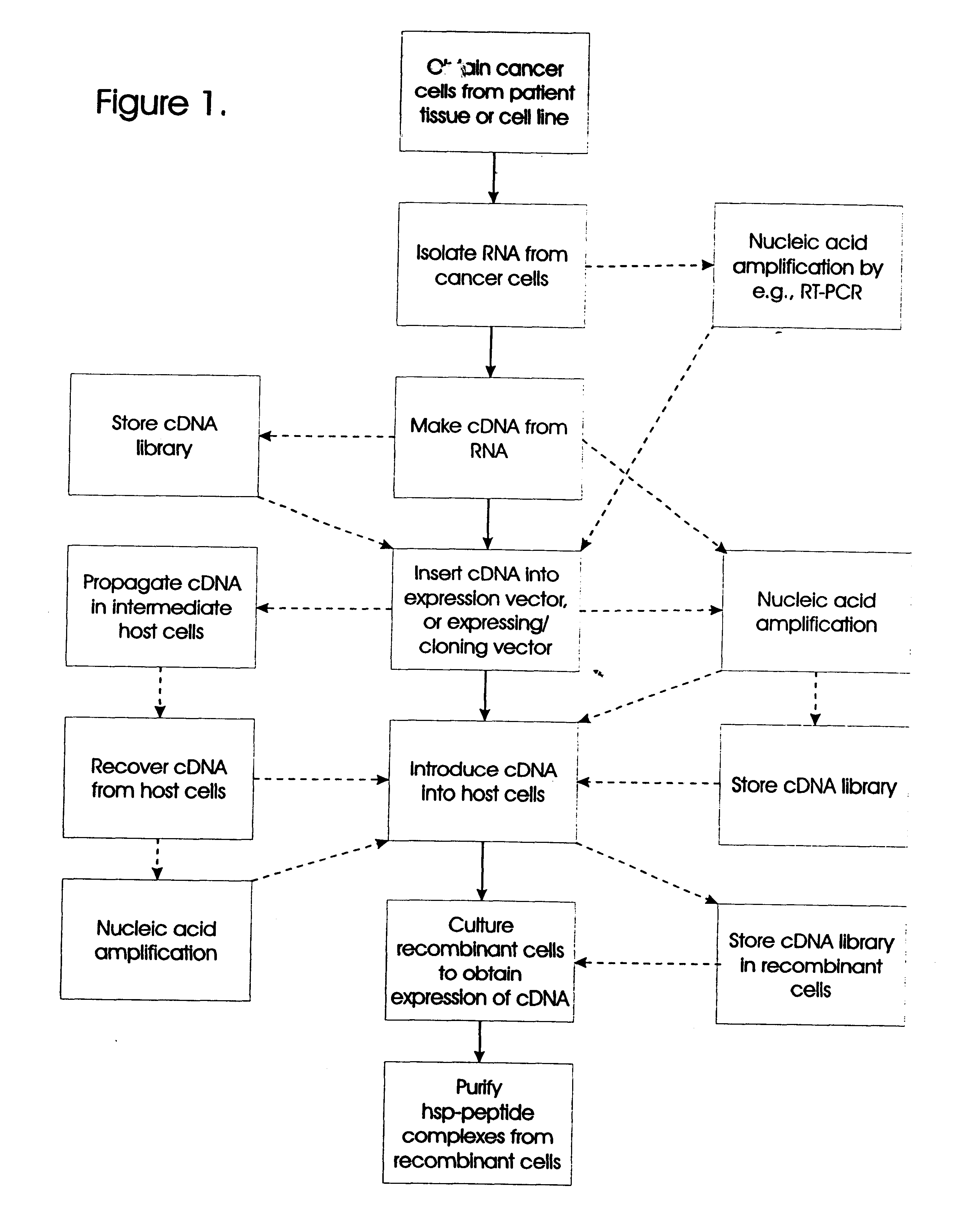
The present invention relates to methods for preparing immunogenic, prophylactically and therapeutically effective complexes of heat shock proteins noncovalently associated with antigenic peptides of cancer cells. The claimed methods comprise the constructing of a cDNA library from cancer or preneoplastic cell RNA, expressing the cDNA library in an appropriate host cell, and recovering the immunogenic complexes from the cells. Large amounts of such immunogenic complexes can be obtained by large-scale culturing of host cells containing the cDNA library. The complexes can be used as a vaccine to elicit specific immune responses against cancer or preneoplastic cells, and to treat or prevent cancer.
Owner:FORDHAM UNIVERSITY
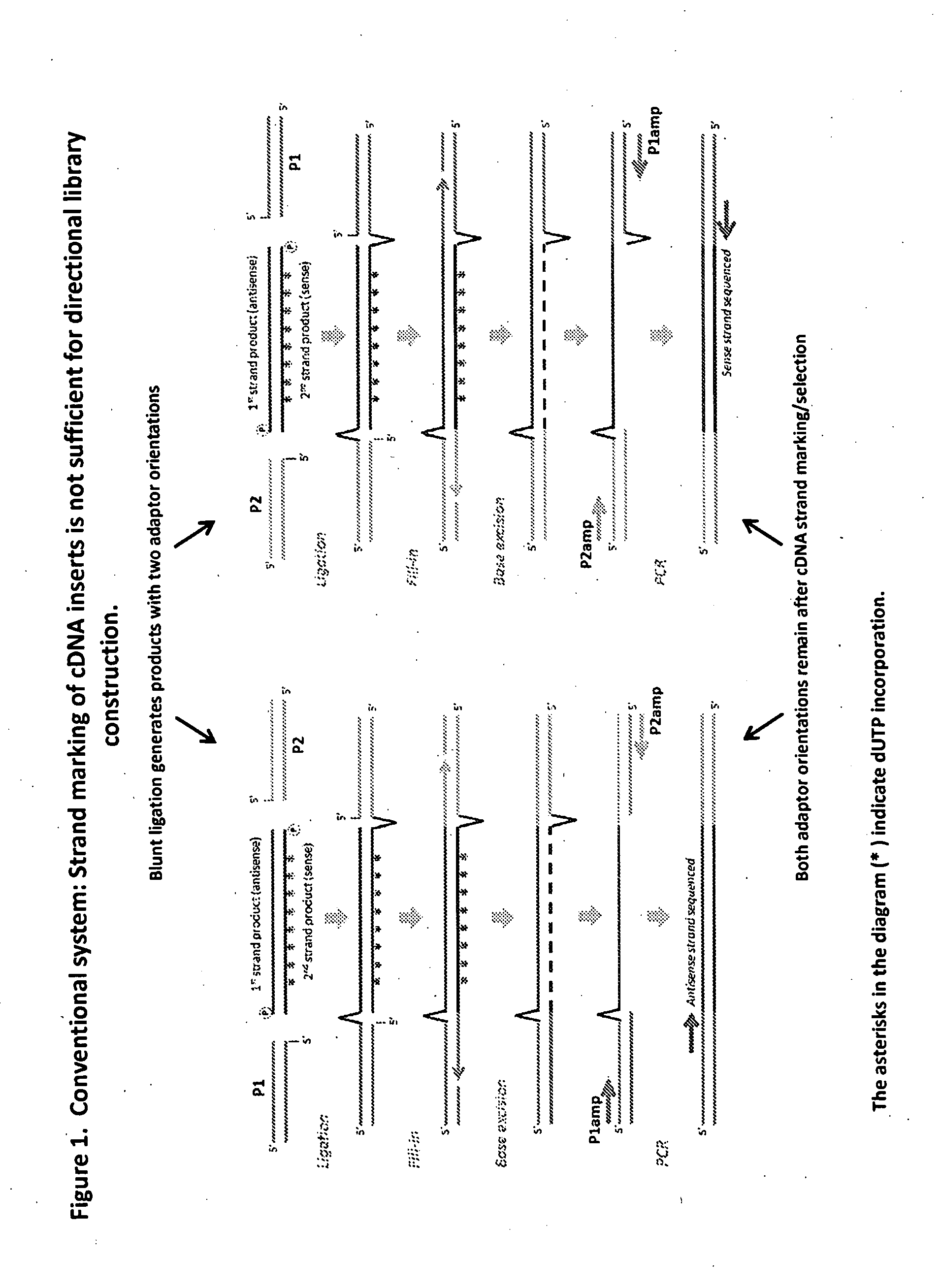
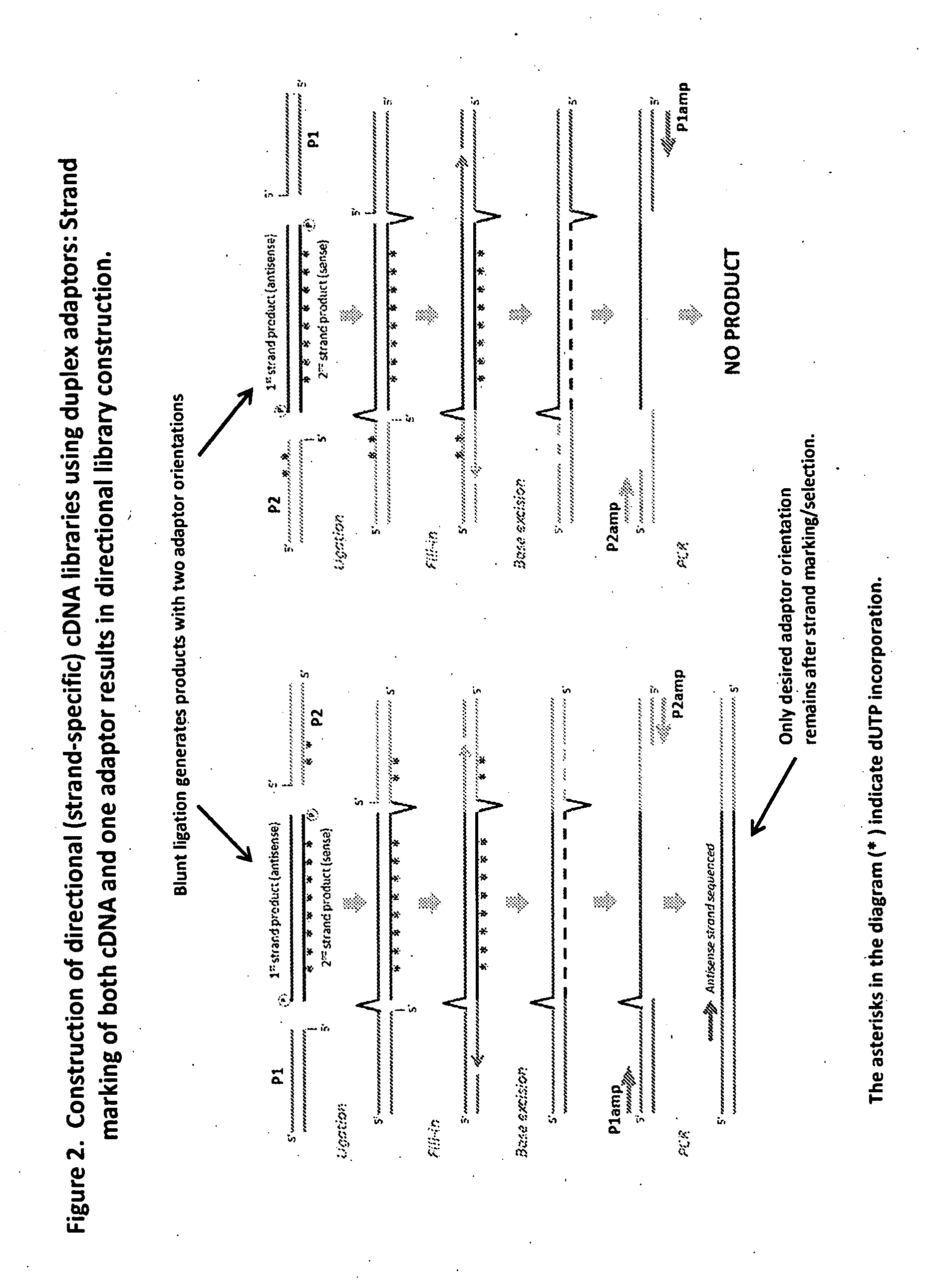
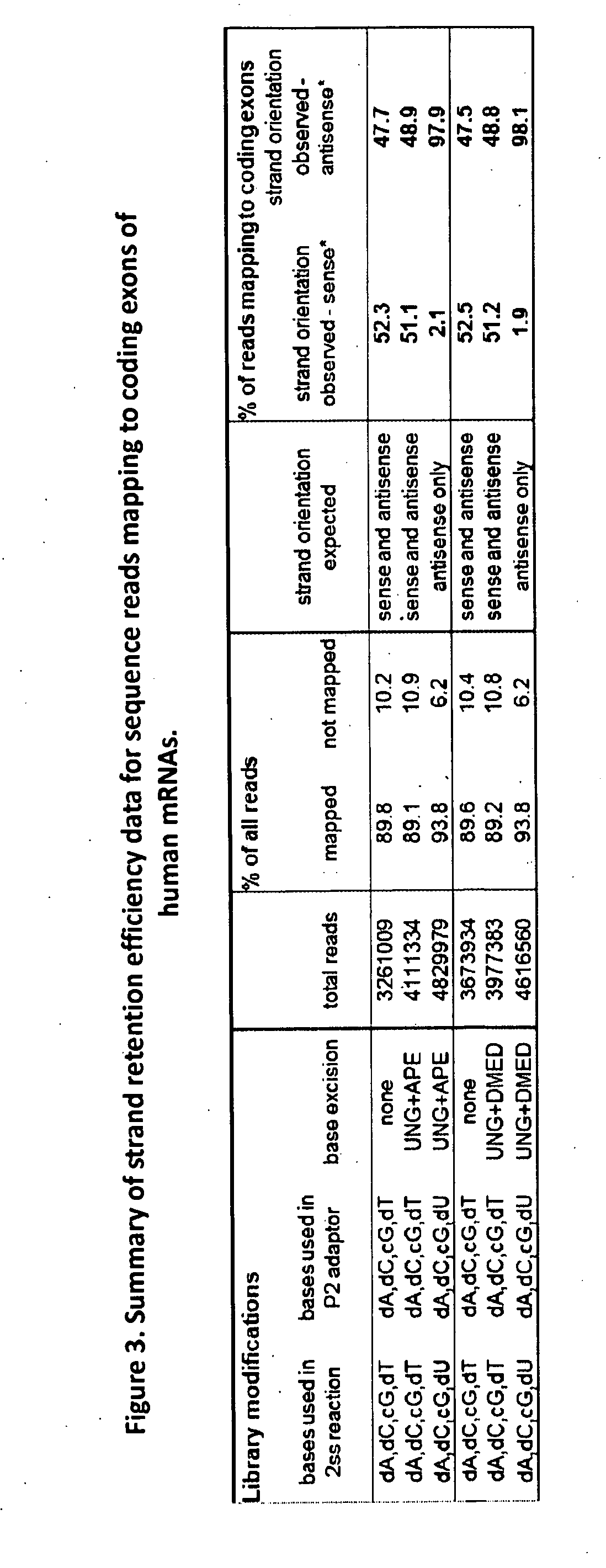
Compositions and methods for directional nucleic acid amplification and sequencing
ActiveUS20140303000A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationCDNA libraryNucleic acid
The invention provides methods and compositions, including kits, for directional nucleic acid amplification and sequencing. The invention further provides methods and compositions for the construction of directional cDNA libraries.
Owner:NUGEN TECH
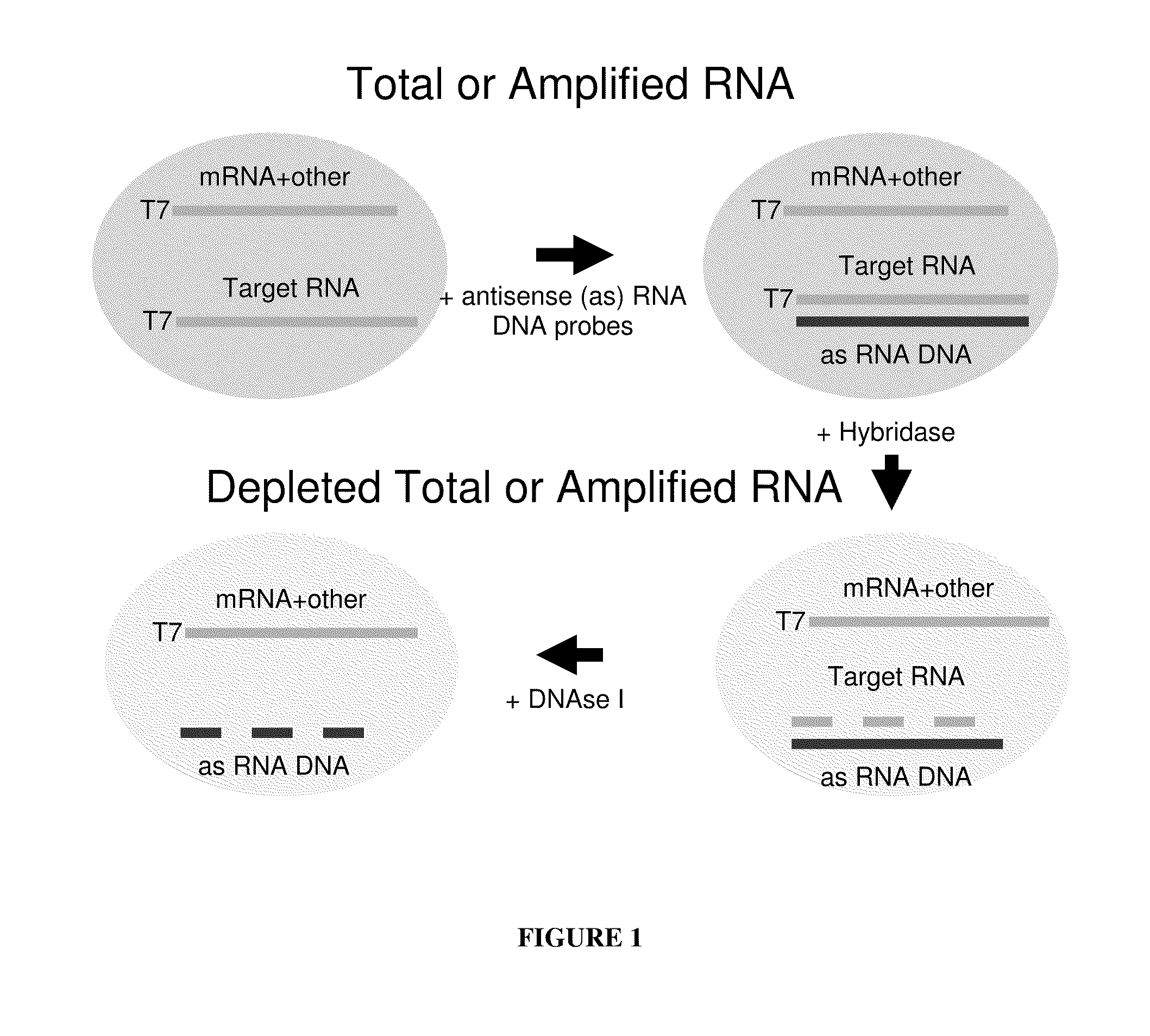
Methods for depleting RNA from nucleic acid samples
ActiveUS9005891B2Reduce interferenceWork lessSugar derivativesHydrolasesCDNA libraryParaffin embedded tissue
The invention relates to methods of depleting RNA from a nucleic acid sample. The RNA may be any RNA, including, but not limited to, rRNA, tRNA, and mRNA. The method is useful for depleting RNA from a nucleic acid sample obtained from a fixed paraffin-embedded tissue (FPET) sample. The method may also be used to prepare cDNA, in particular, a cDNA library for further analysis or manipulation.
Owner:GENOMIC HEALTH INC
Methods and reagents to detect and characterize norwalk and related viruses
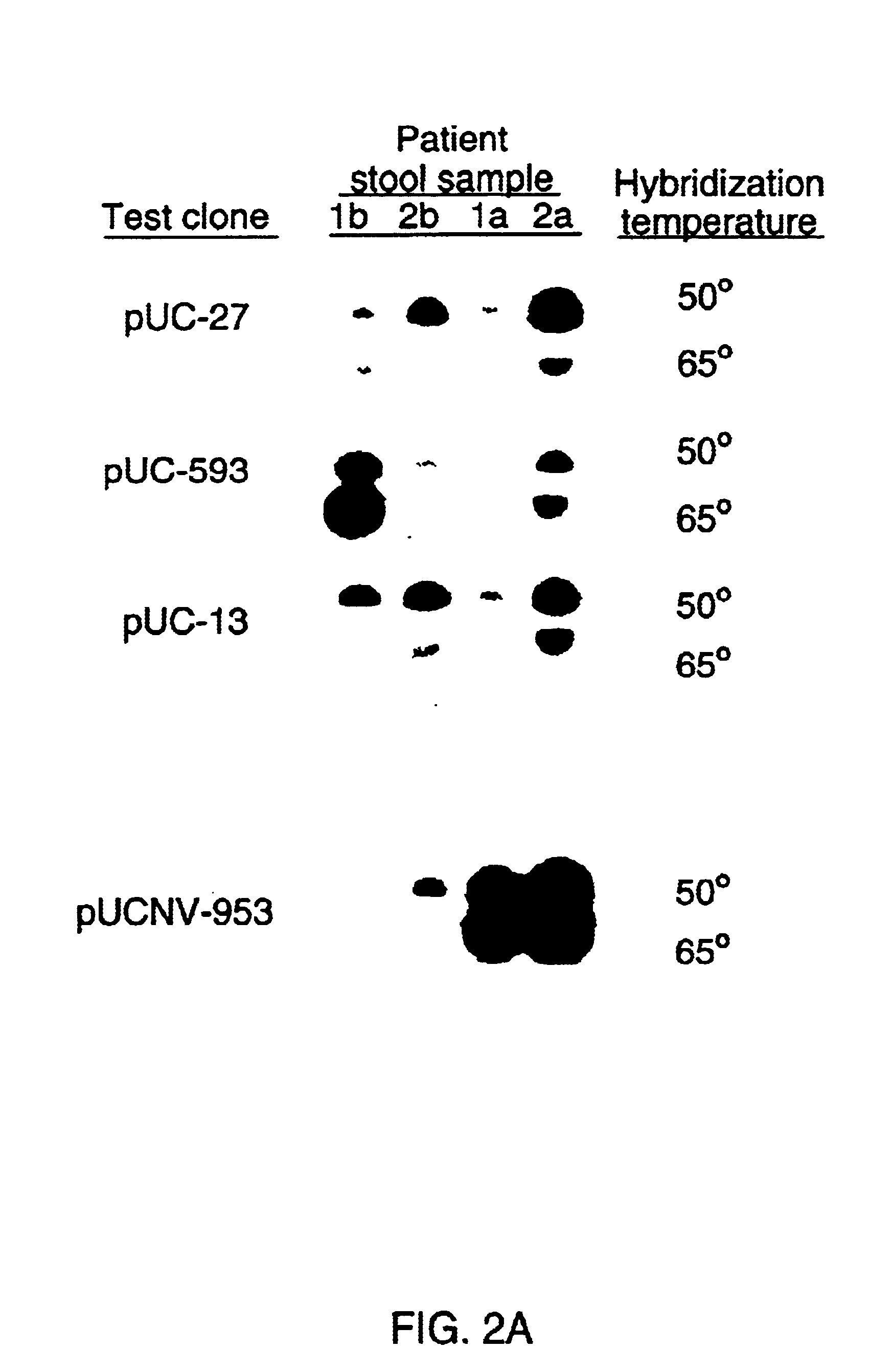
Double-stranded cDNA was synthesized from nucleic acid extracted from Norwalk virus purified from stool specimens of volunteers. One clone was isolated from a cDNA library constructed in a pUC-13 vector after amplification of the cDNA. The specificity of this cDNA (pUCNV-953) was shown by hybridization assays. The cDNA reacted with post (but not pre-) infection stool samples from Norwalk volunteers and with highly purified Norwalk virus, but not with other common enteric viruses such as hepatitis A virus and rotavirus. Finally, the probe detected virus in the same fractions of CsCl gradients in which viral antigen was detected using a specific Norwalk virus radioimmunoassay, and particles were detected by immune electron microscopy. Single-stranded RNA probes derived from the DNA clone after subcloning into an in vitro transcription vector were also used to show that the Norwalk virus contains a ssRNA genome of about 8 kb in size. The original clone was also used to detect additional cDNAs which represent at least 7 kb of nucleic acid of the Norwalk genome. The availability of a Norwalk-specific cDNA and the first partial genome sequence information allow rapid cloning of the entire genome and of establishment of sensitive diagnostic assays. Such assays can be based on detection of Norwalk virus nucleic acid or Norwalk viral antigen using polyclonal or monoclonal antibodies to proteins expressed from the cDNA or to synthetic peptides made based on the knowledge of the genome sequence. Assays using proteins deduced from the Norwlk virus genome and produced in expression systmes can measure antibody responses. Vaccines made by recombinant DNA technology are now feasible.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
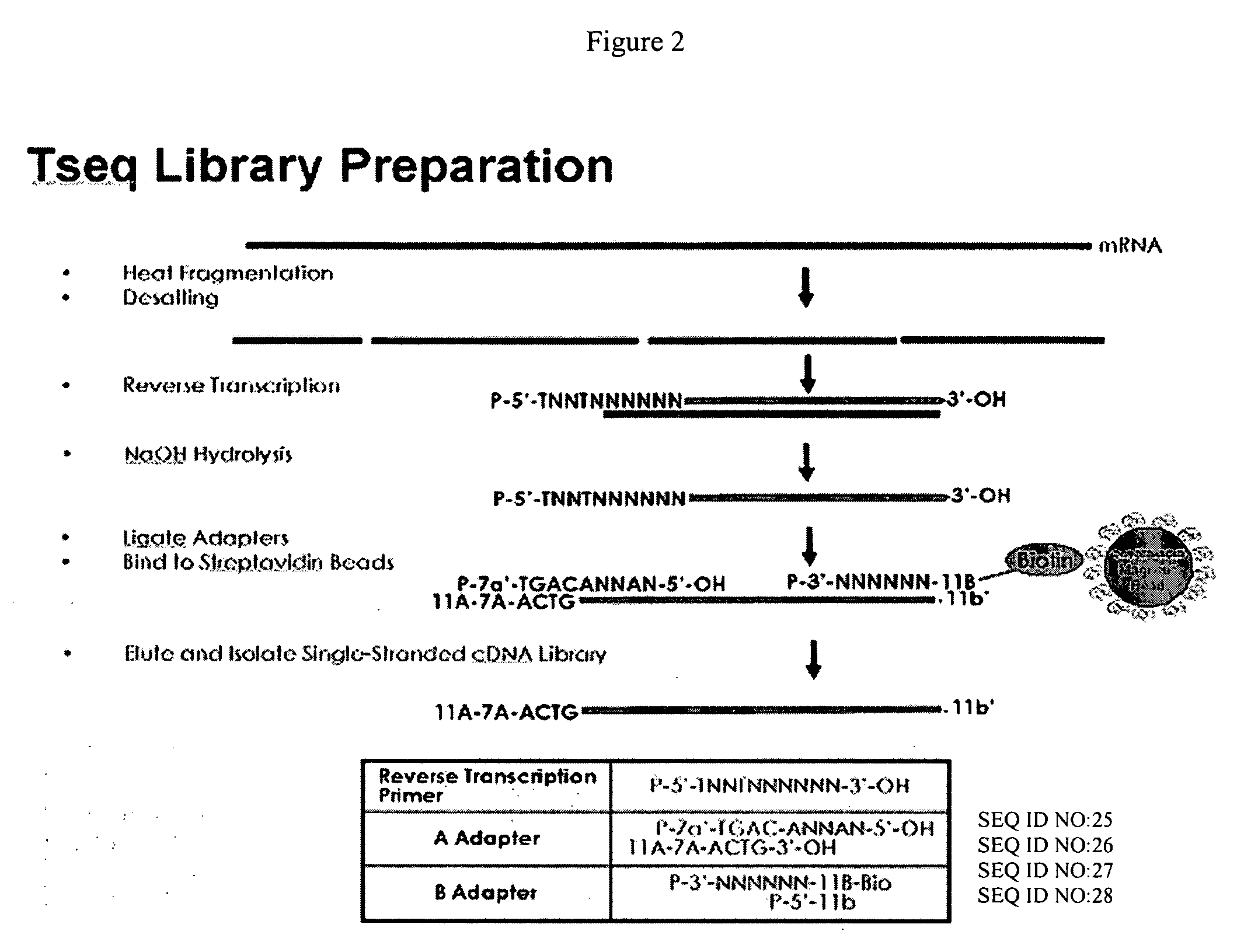
cDNA library preparation
InactiveUS20070117121A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningCDNA libraryAutomated sequencing
New biochemical protocols for high throughput processing of mRNA samples into cDNA libraries with adaptor sequences compatible with automated sequencing systems are provided. The provided methods produces cDNA libraries which do not have 3′ bias associated with current cDNA library production methods. New methods for the production of DNA libraries from DNA are also provided.
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
Methods for quantitative cDNA analysis in single-cell
ActiveUS20070281313A1High sensitivityPurification of smallMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationCDNA libraryLysis
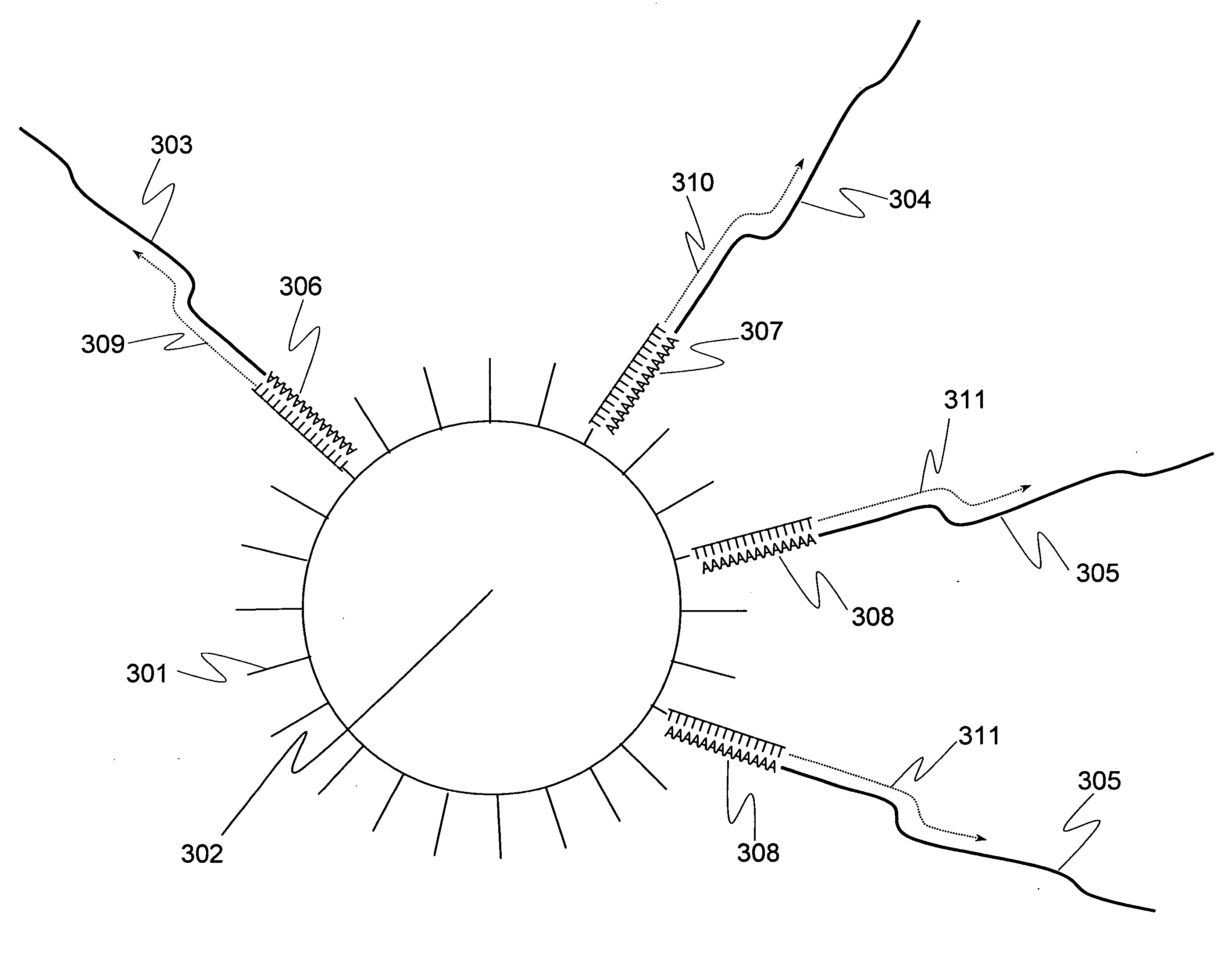
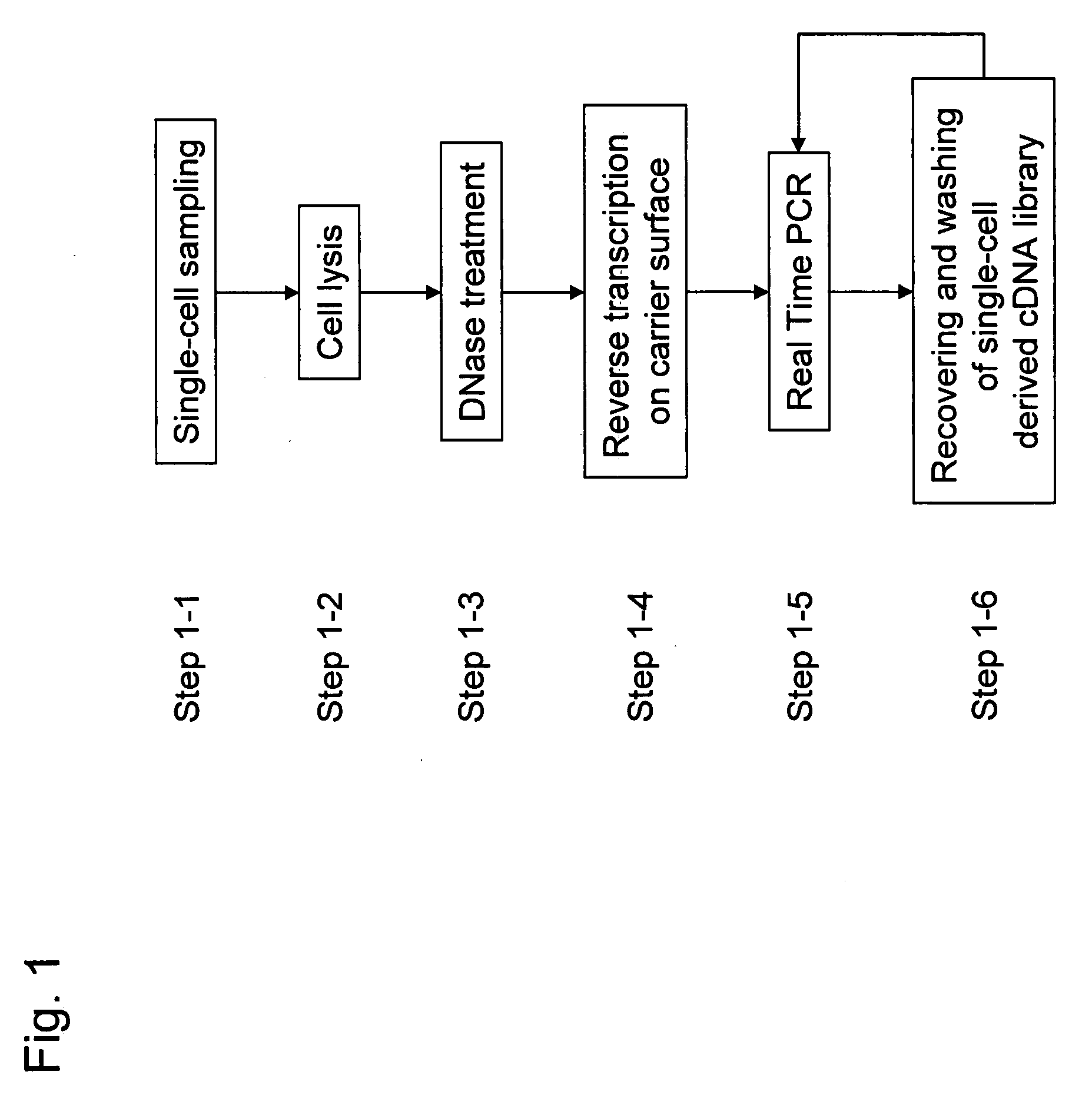
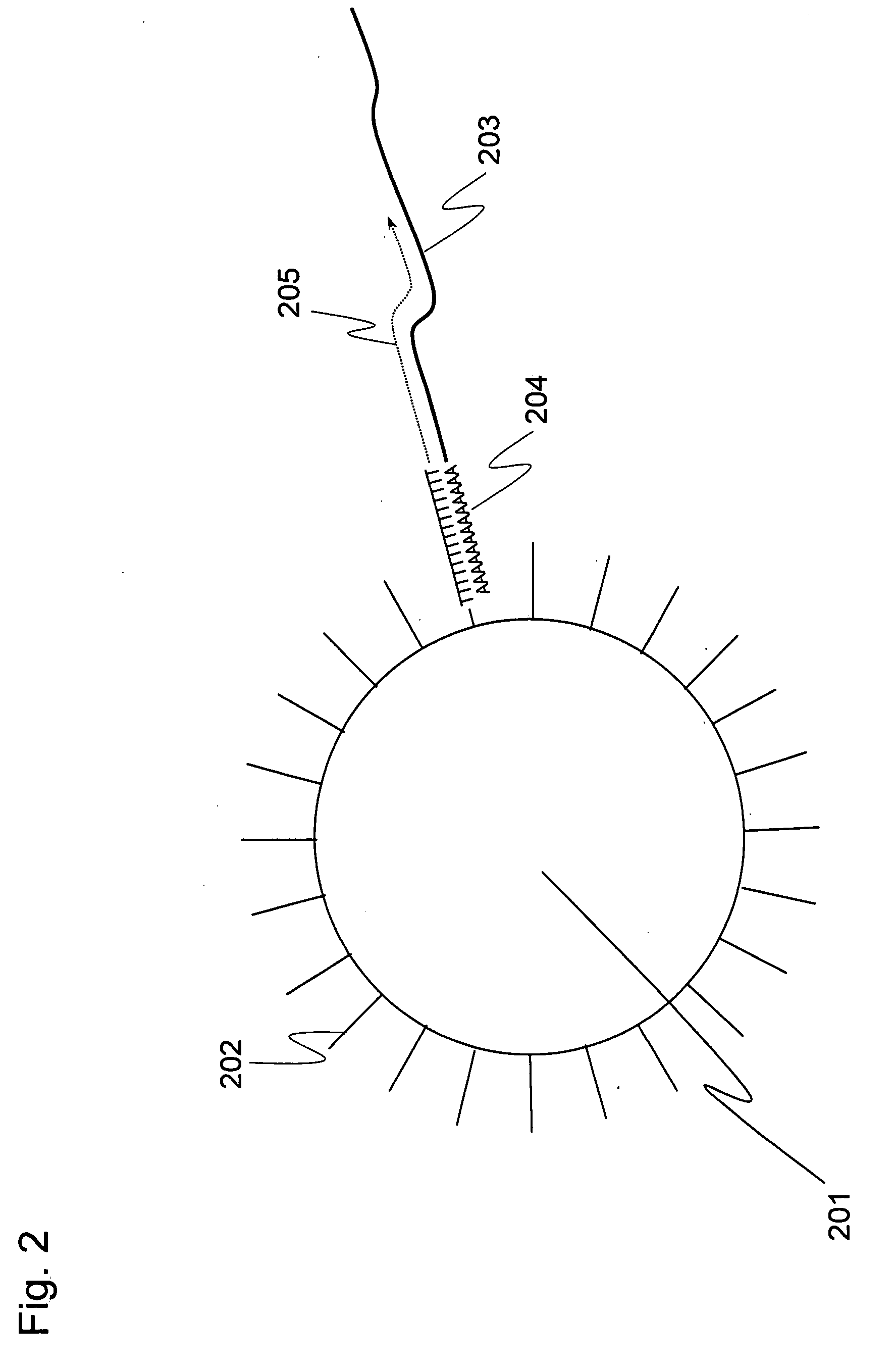
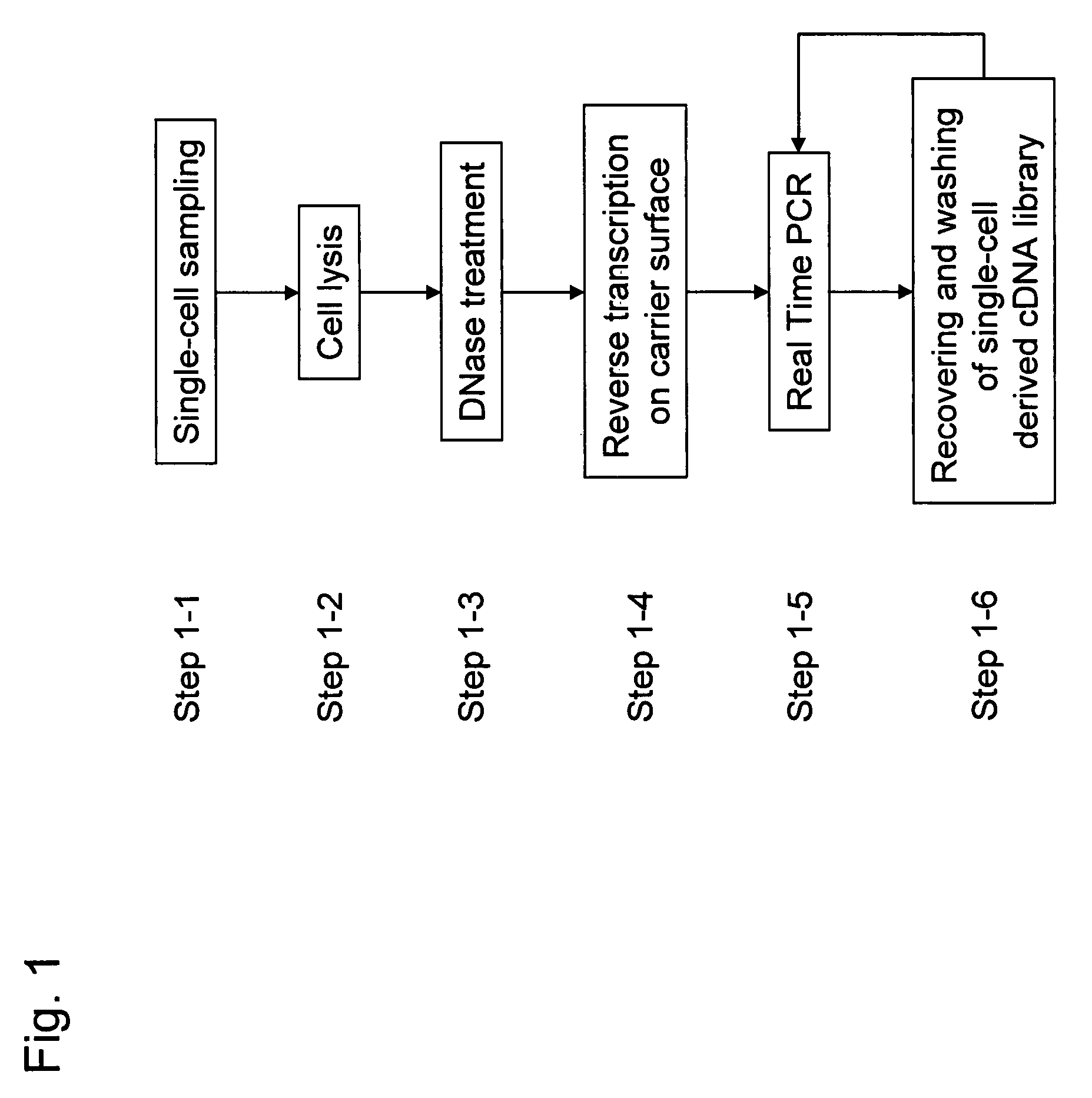
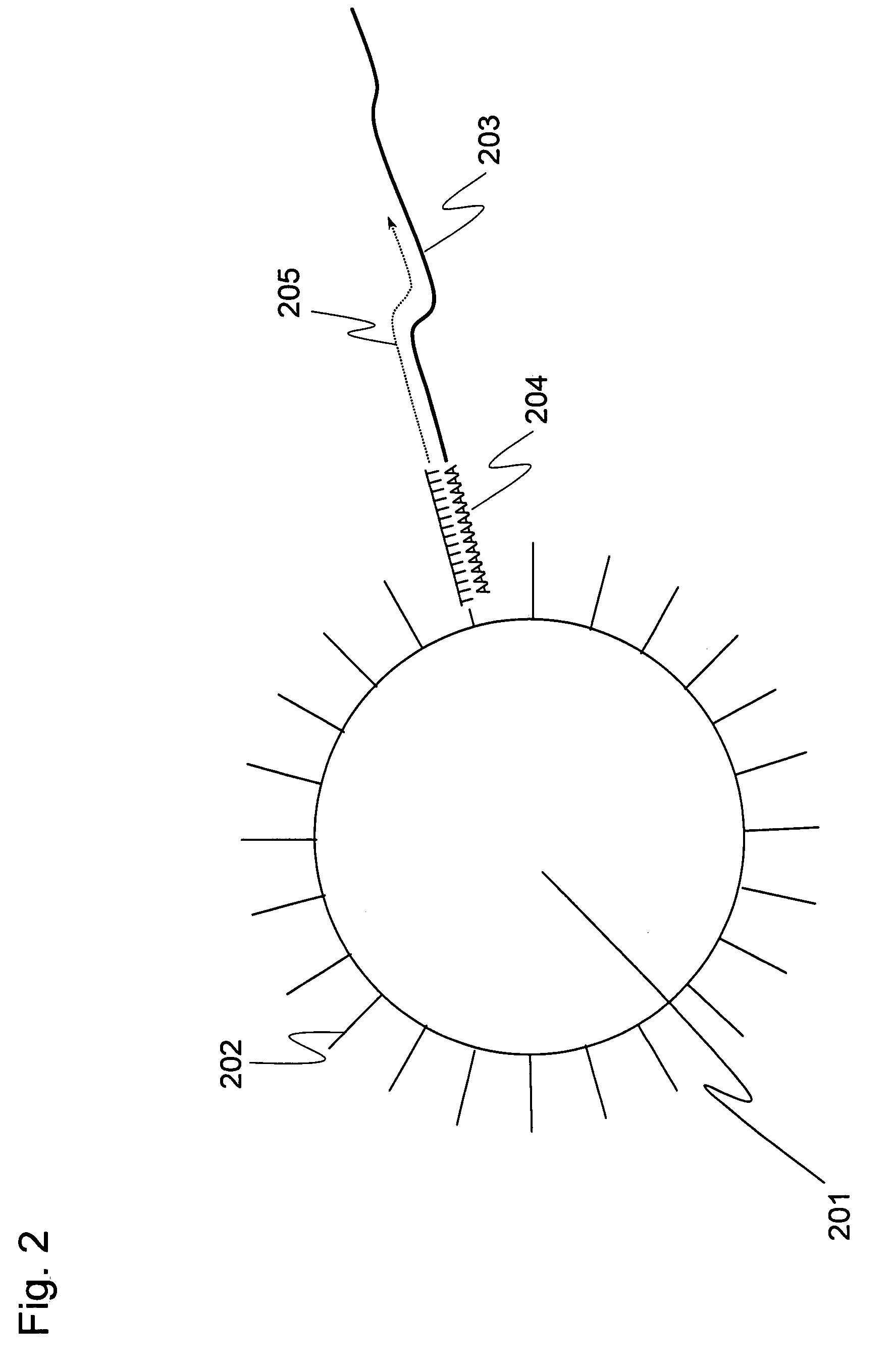
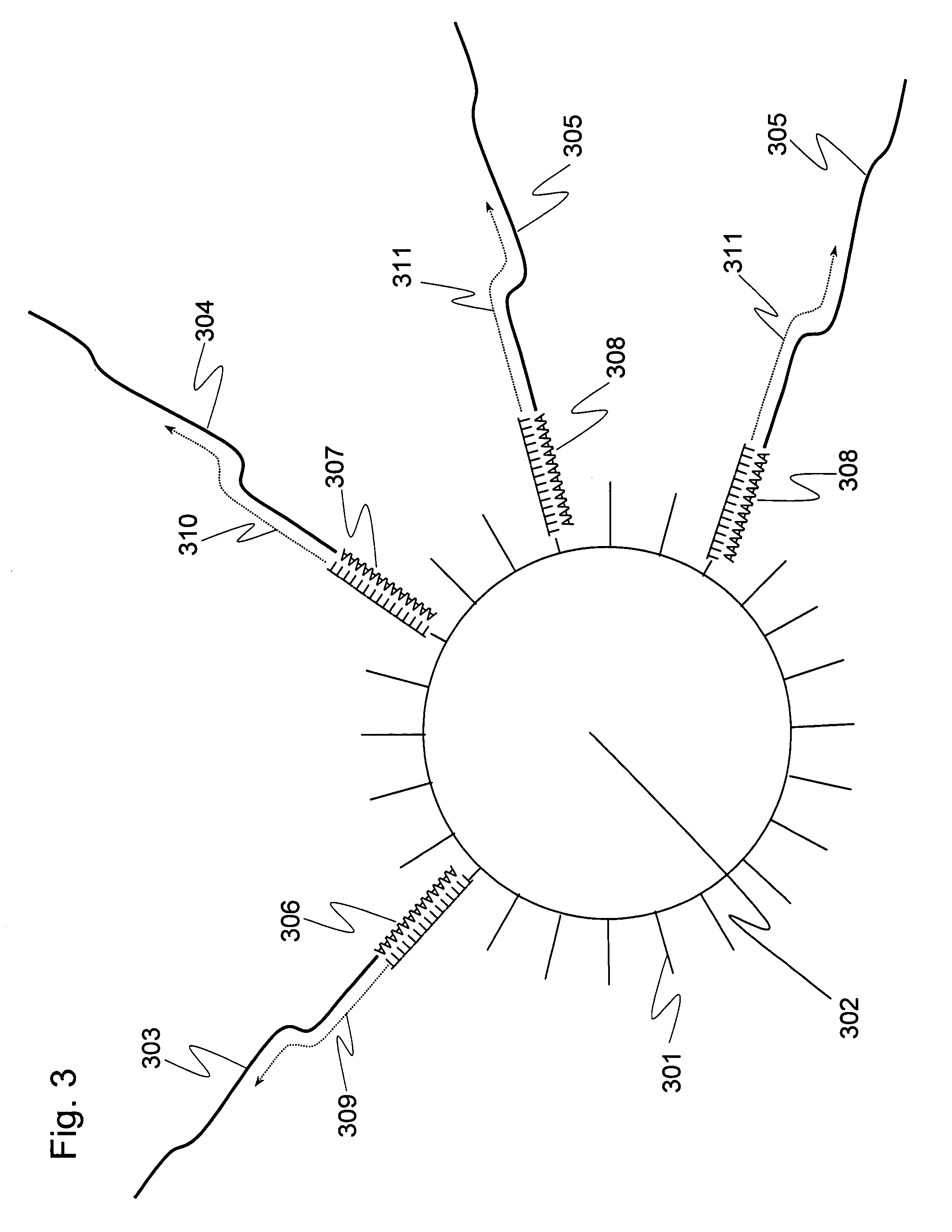
It is an object to provide a method of suitably analyzing the amount of gene expression of a single-cell.A method of detecting a nucleic acid comprisinga step of sampling a single-cell from a sample containing at least a single-cell,a cell lysis step of lysing cell membrane of the sampled single-cell and extracting nucleic acids from the cell,a DNase treatment step of degrading DNA of the extracted nucleic acids with DNase,a step of hybridizing mRNA of the total RNA contained in the single-cell with oligo (dT) fixed onto a carrier,a step of performing reverse transcription of the mRNA hybridized with the oligo (dT) to fix cDNA derived from the single-cell onto the carrier, thereby preparing a single-cell derived cDNA library fixed onto a carrier, anda step of amplifying cDNA fixed onto the carrier and simultaneously detecting an amplification amount of the cDNA.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Methods for quantitative cDNA analysis in single-cell
ActiveUS8802367B2Purification of smallSmall recoverySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCDNA libraryLysis
It is an object to provide a method of suitably analyzing the amount of gene expression of a single-cell.A method of detecting a nucleic acid comprisinga step of sampling a single-cell from a sample containing at least a single-cell,a cell lysis step of lysing cell membrane of the sampled single-cell and extracting nucleic acids from the cell,a DNase treatment step of degrading DNA of the extracted nucleic acids with DNase,a step of hybridizing mRNA of the total RNA contained in the single-cell with oligo (dT) fixed onto a carrier,a step of performing reverse transcription of the mRNA hybridized with the oligo (dT) to fix cDNA derived from the single-cell onto the carrier, thereby preparing a single-cell derived cDNA library fixed onto a carrier, anda step of amplifying cDNA fixed onto the carrier and simultaneously detecting an amplification amount of the cDNA.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
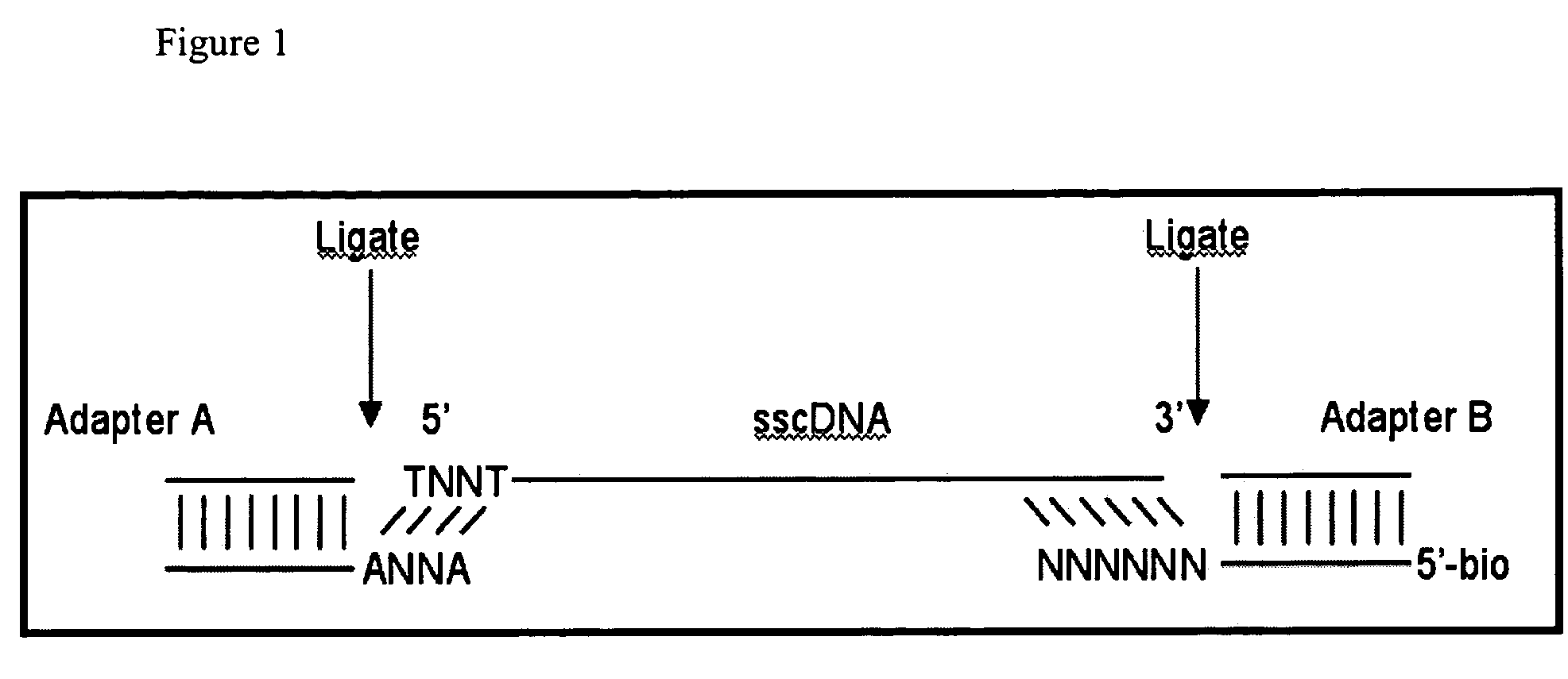
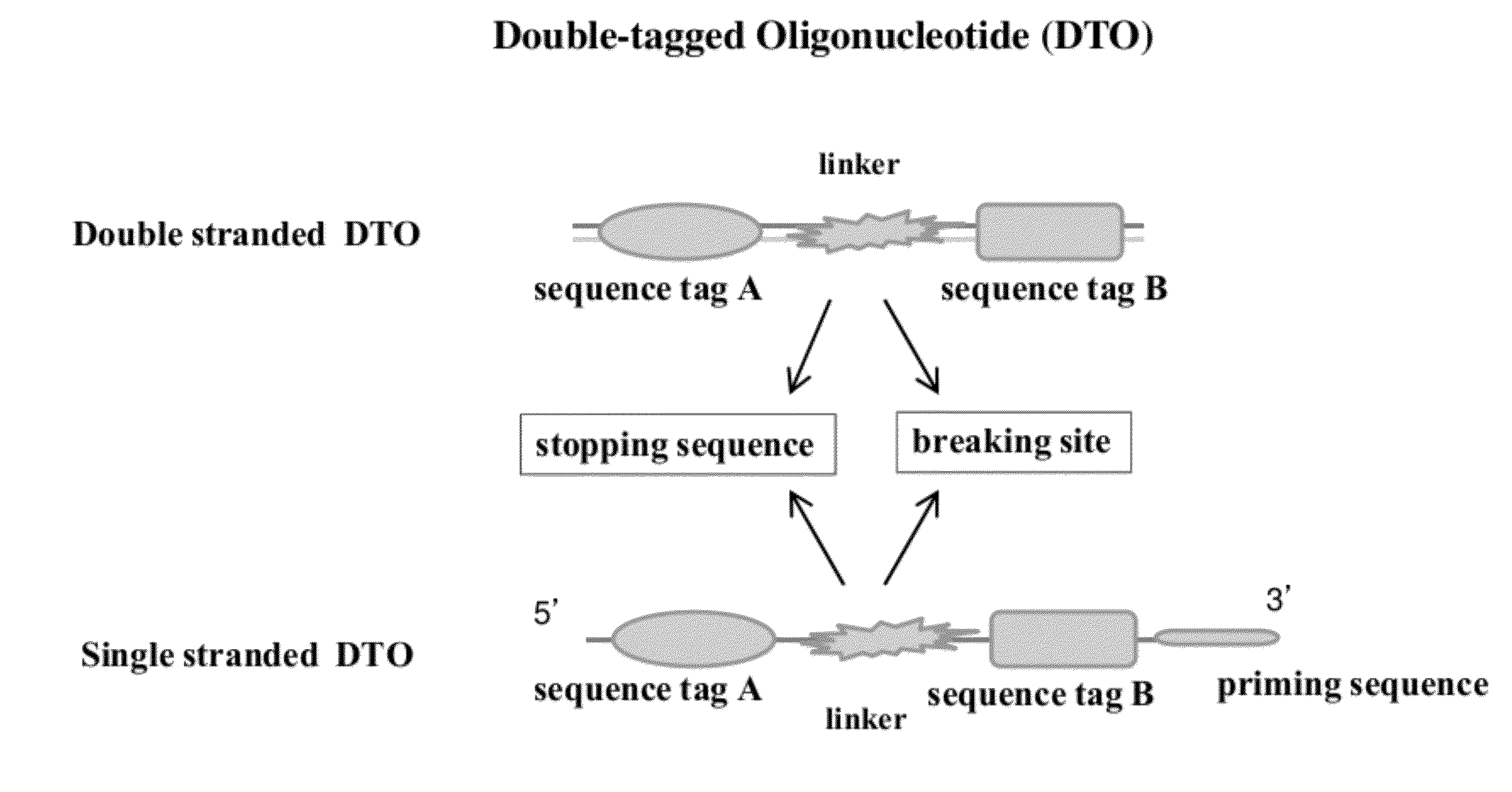
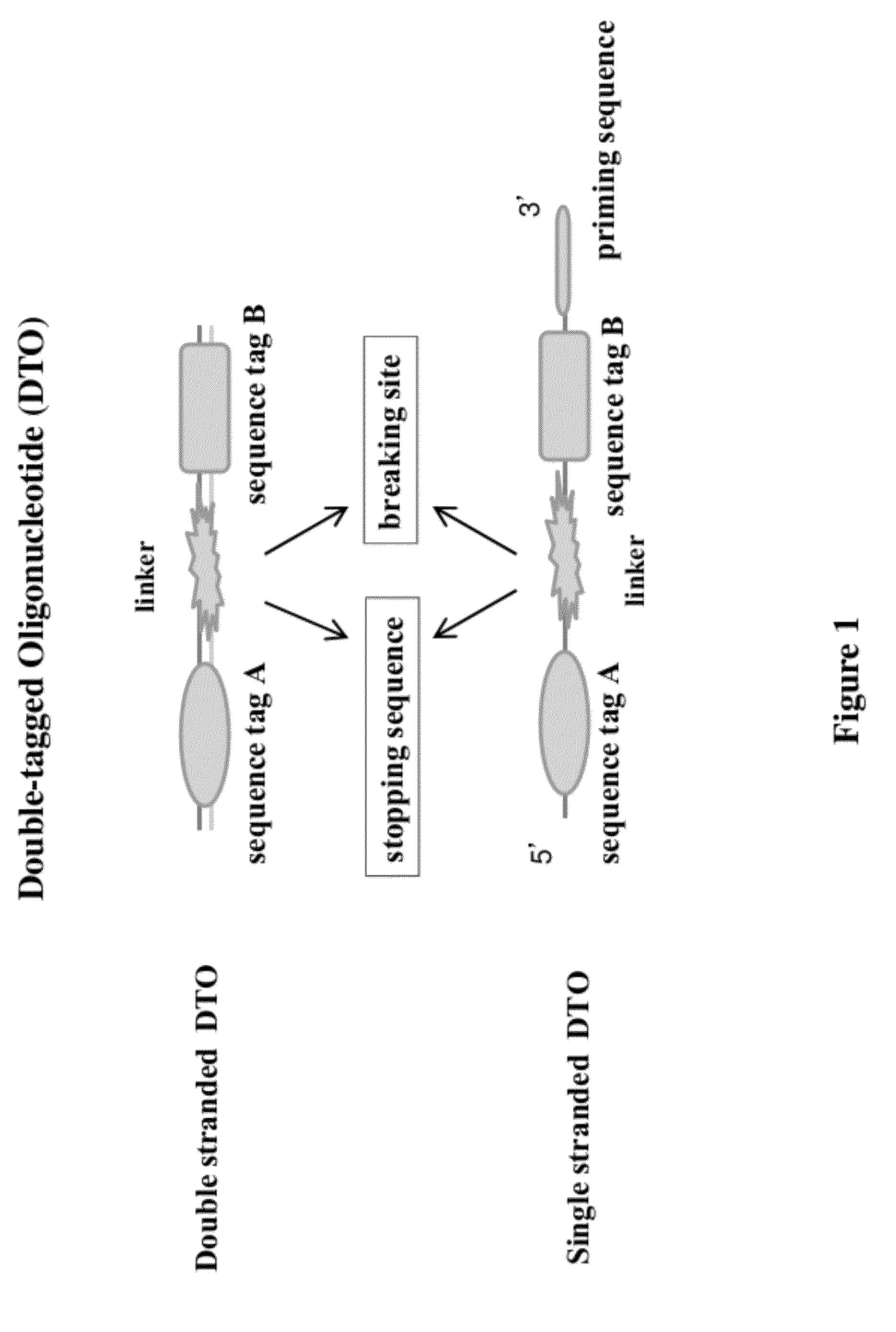
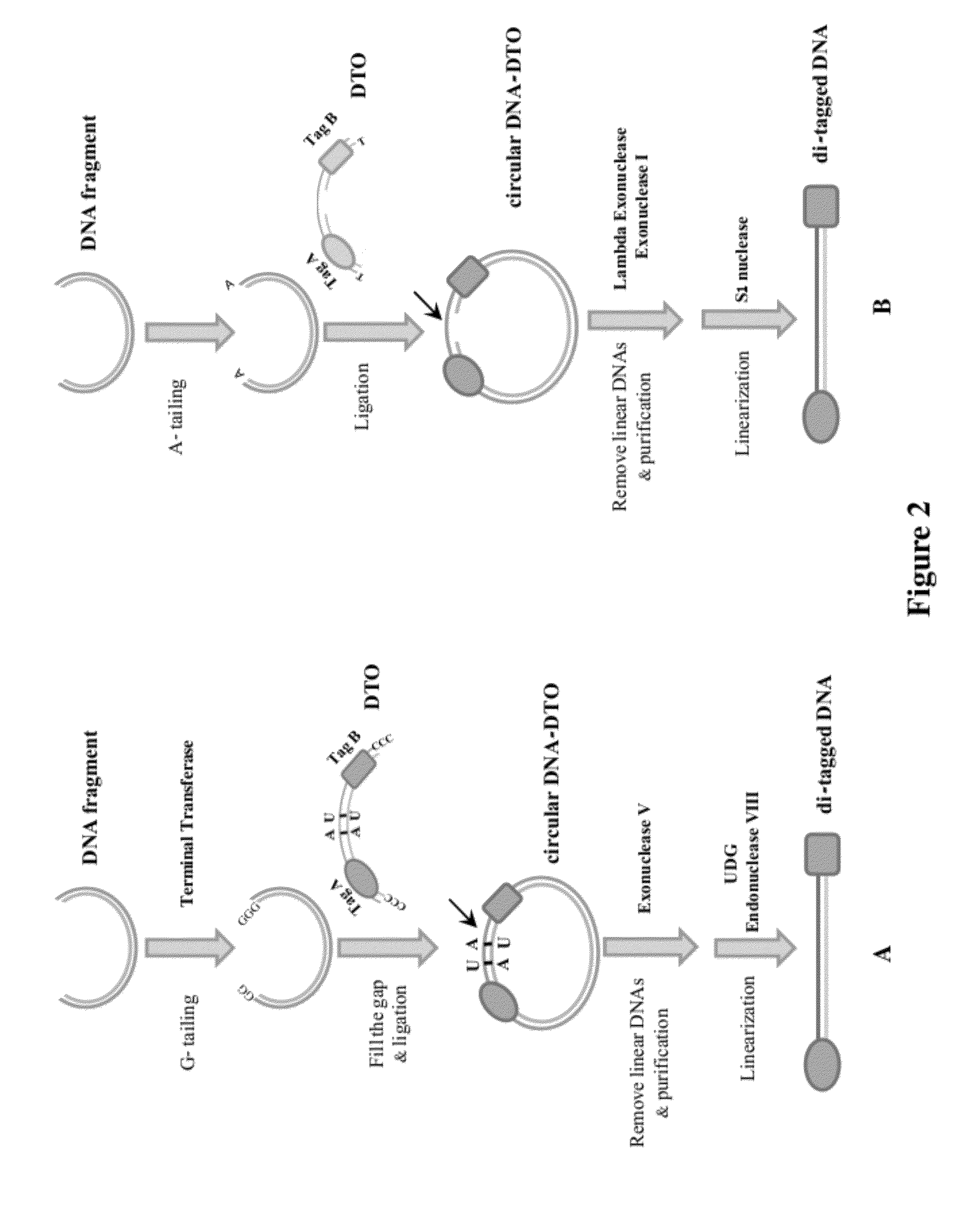
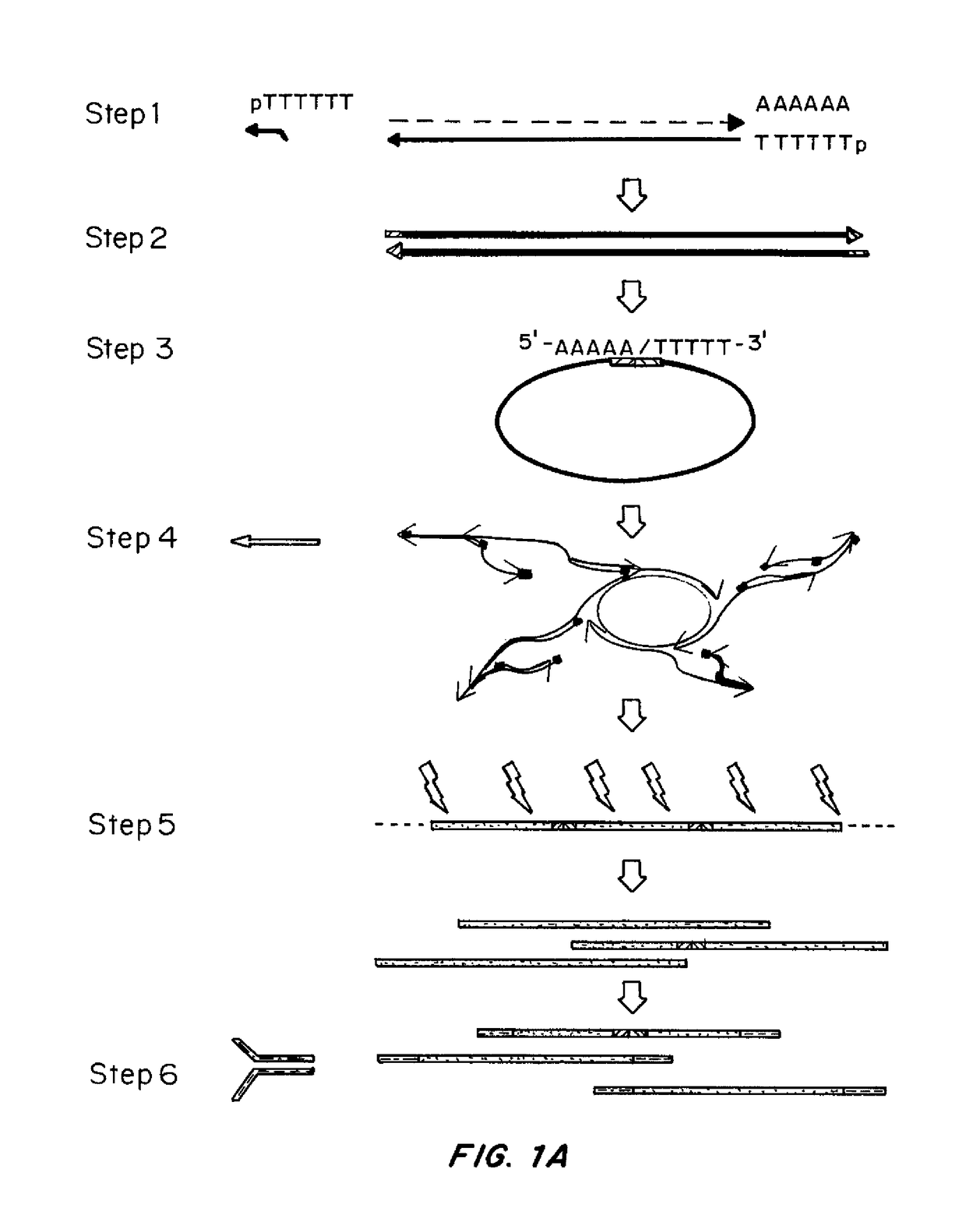
Methods of Making Di-Tagged DNA Libraries from DNA or RNA Using Double-tagged Oligonucleotides
ActiveUS20120283145A1Avoid it happening againEasy to separateMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationCDNA librarySingle strand dna
Disclosed are methods, compositions and kits related to making double-tagged DNA libraries from RNA / DNA samples. A double-tagged oligonucleotide (DTO) is employed to efficiently add two different tags to ends of DNAs to make a double-tagged DNA libraries. Also disclosed are methods to make mate pair libraries using the double-tagged oligonucleotide, and methods to make double-tagged single stranded DNA. The double-tagged DNA libraries of the invention are ready to be used on next generation sequencing machines.
Owner:GNOMEGEN
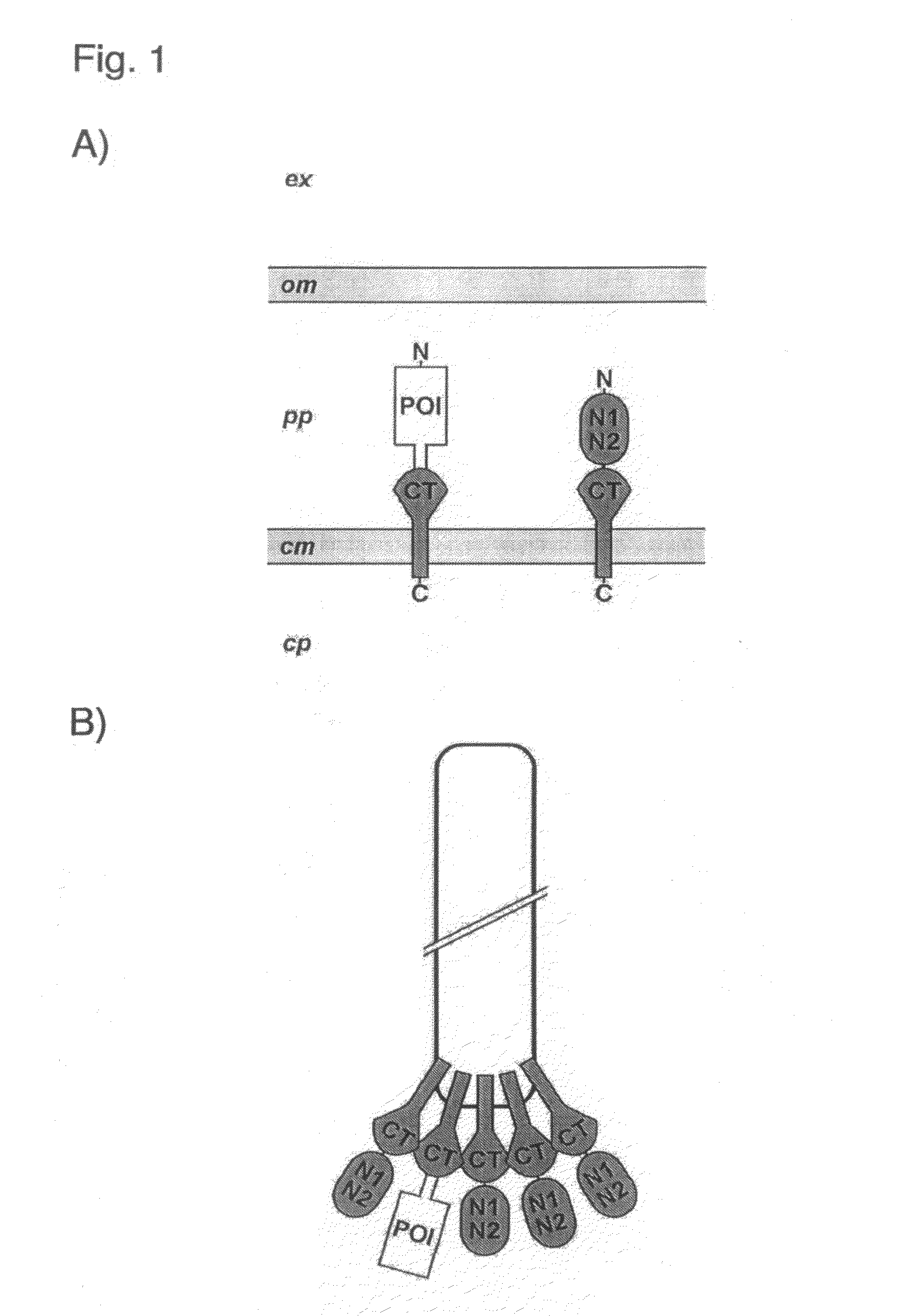
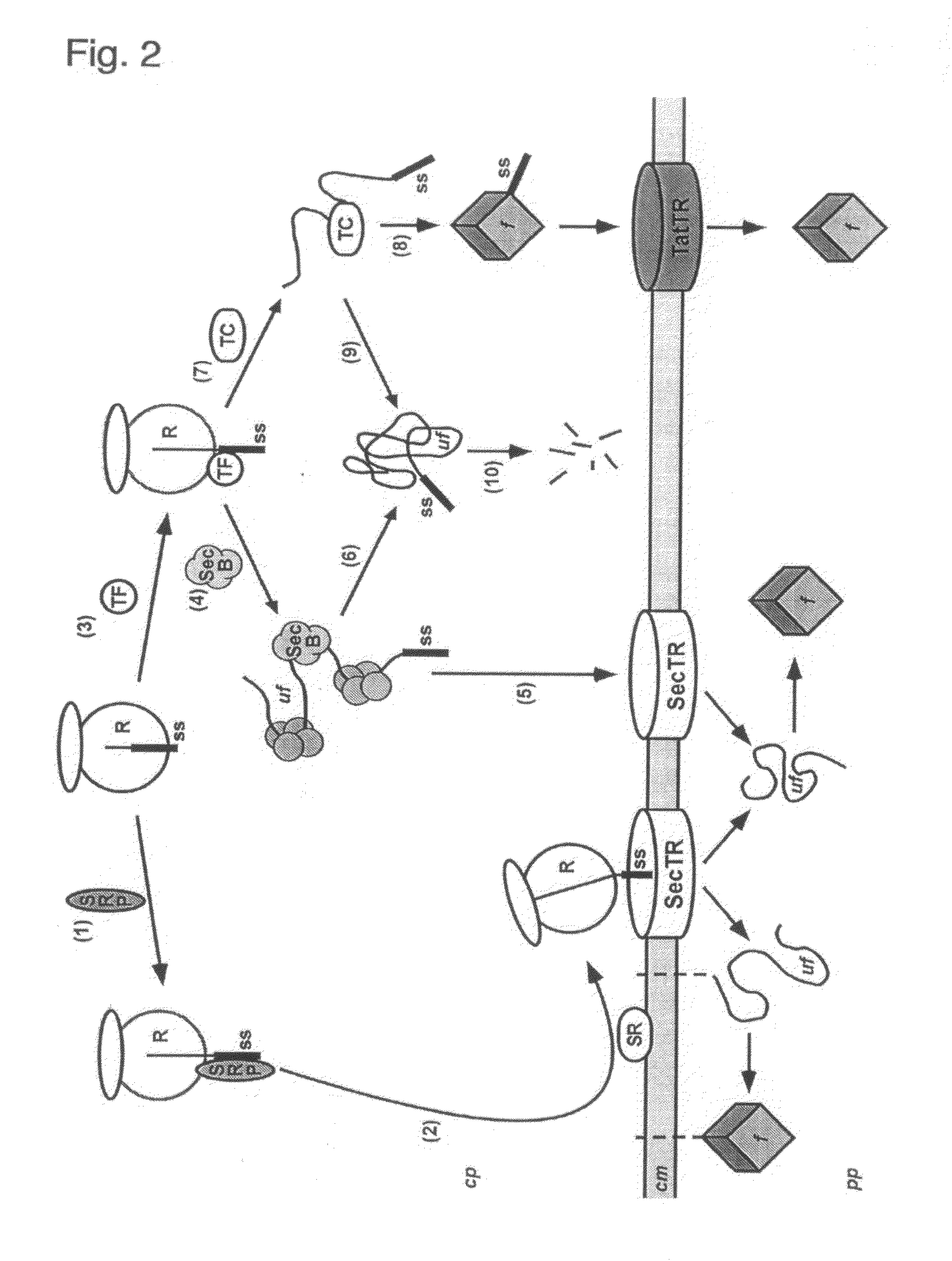
Phage Display Using Cotranslational Translocation of Fusion Polypeptides
ActiveUS20110118146A1Difficult to displayAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMicroorganism librariesSignal recognition particleCDNA library
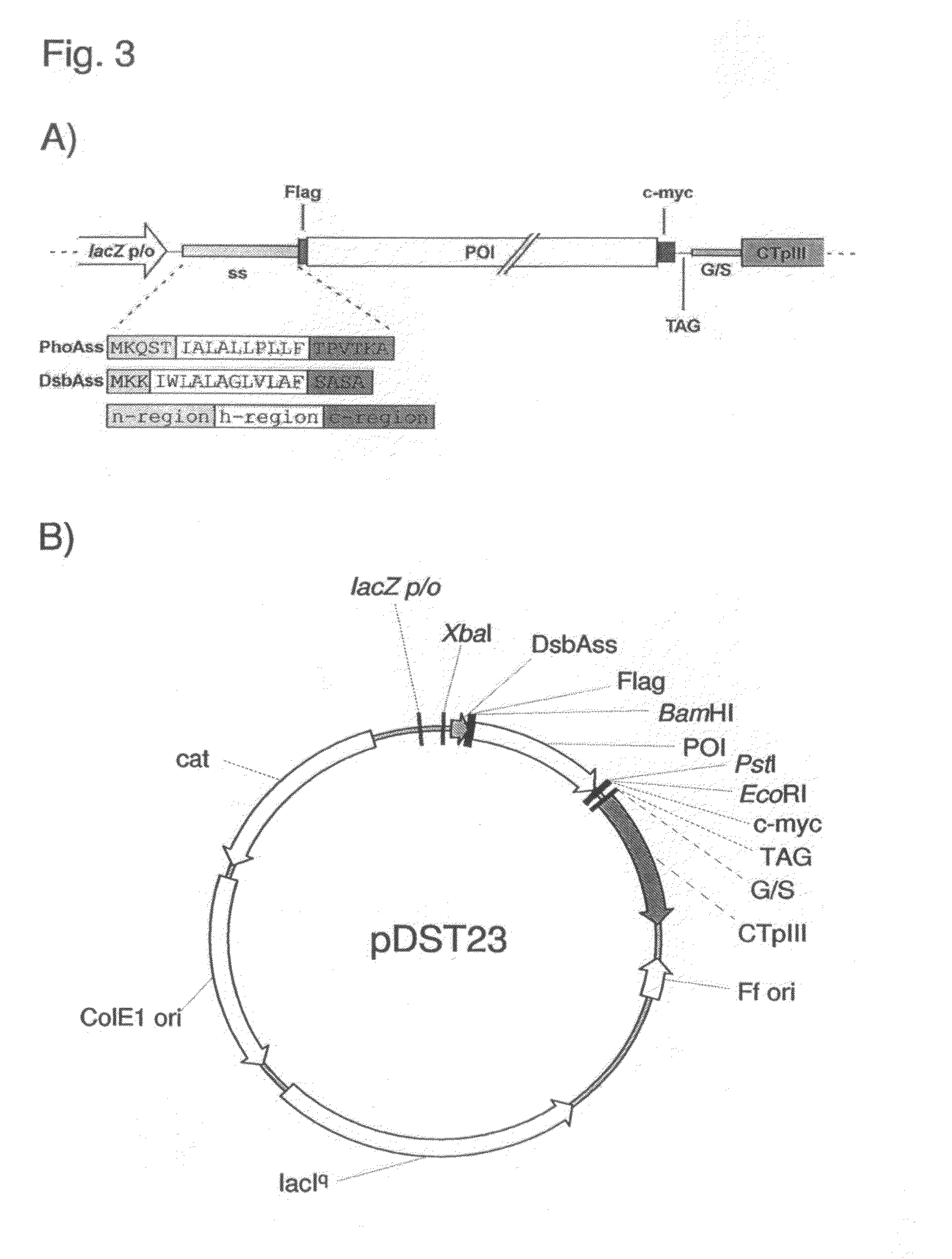
The present invention relates to a filamentous phage display method wherein the polypeptides of interest displayed on the phage particle are cotranslationally translocated across the cytoplasmic membrane of Gram-negative bacteria based on the signal recognition particle pathway. This method is particularly suitable for polypeptides, which are known to be difficult to display on phages, and for proteins of cDNA libraries and other combinatorial libraries, in particular when derived from very fast folding, stable protein scaffolds. The invention further relates to phage or phagemid vectors useful in the method comprising a gene construct coding for a fusion polypeptide comprising the polypeptide to be displayed on the phage particle and an N-terminal signal sequence promoting cotranslational translocation.
Owner:UNIV ZURICH
Methods of screening biological agents
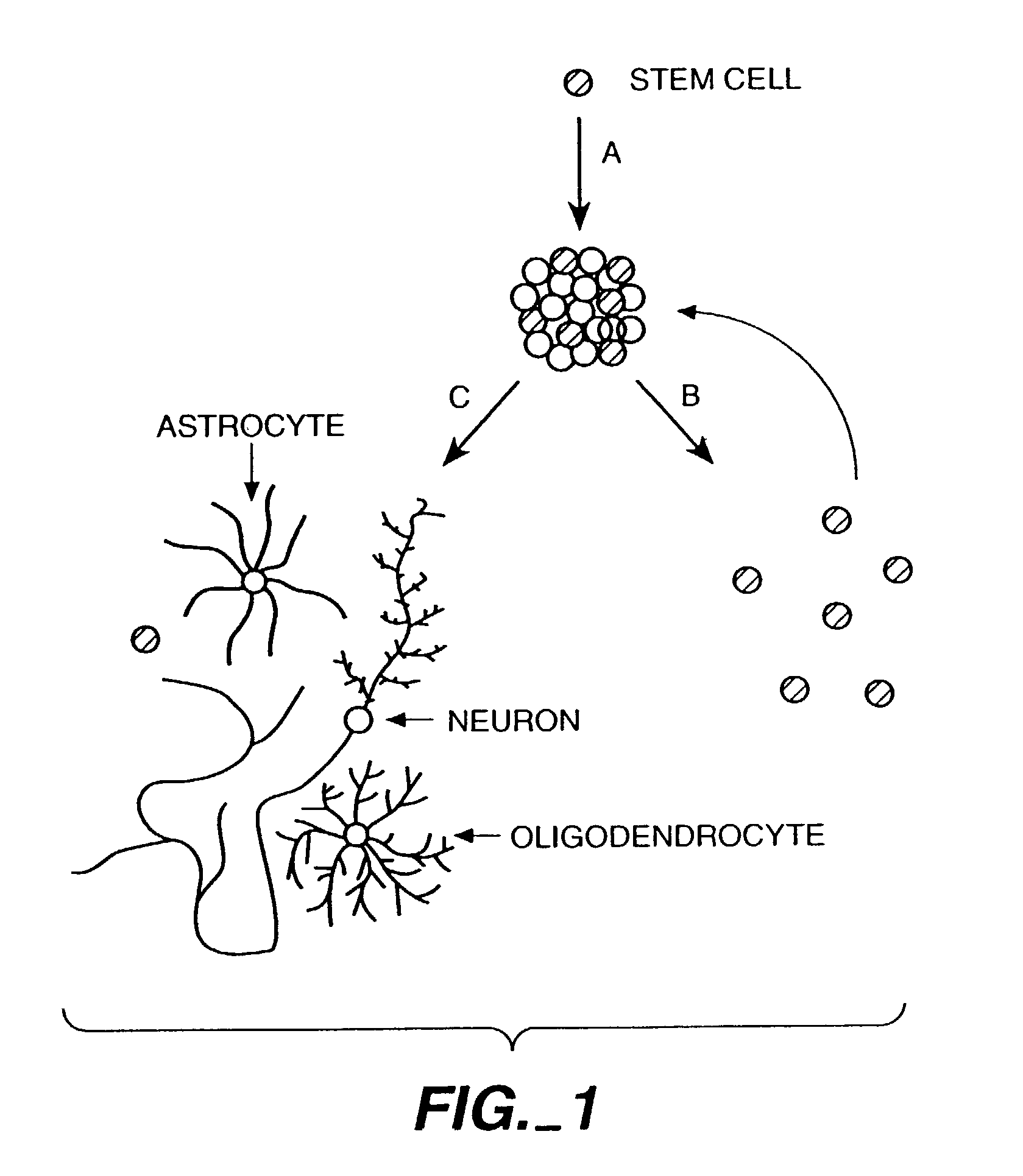
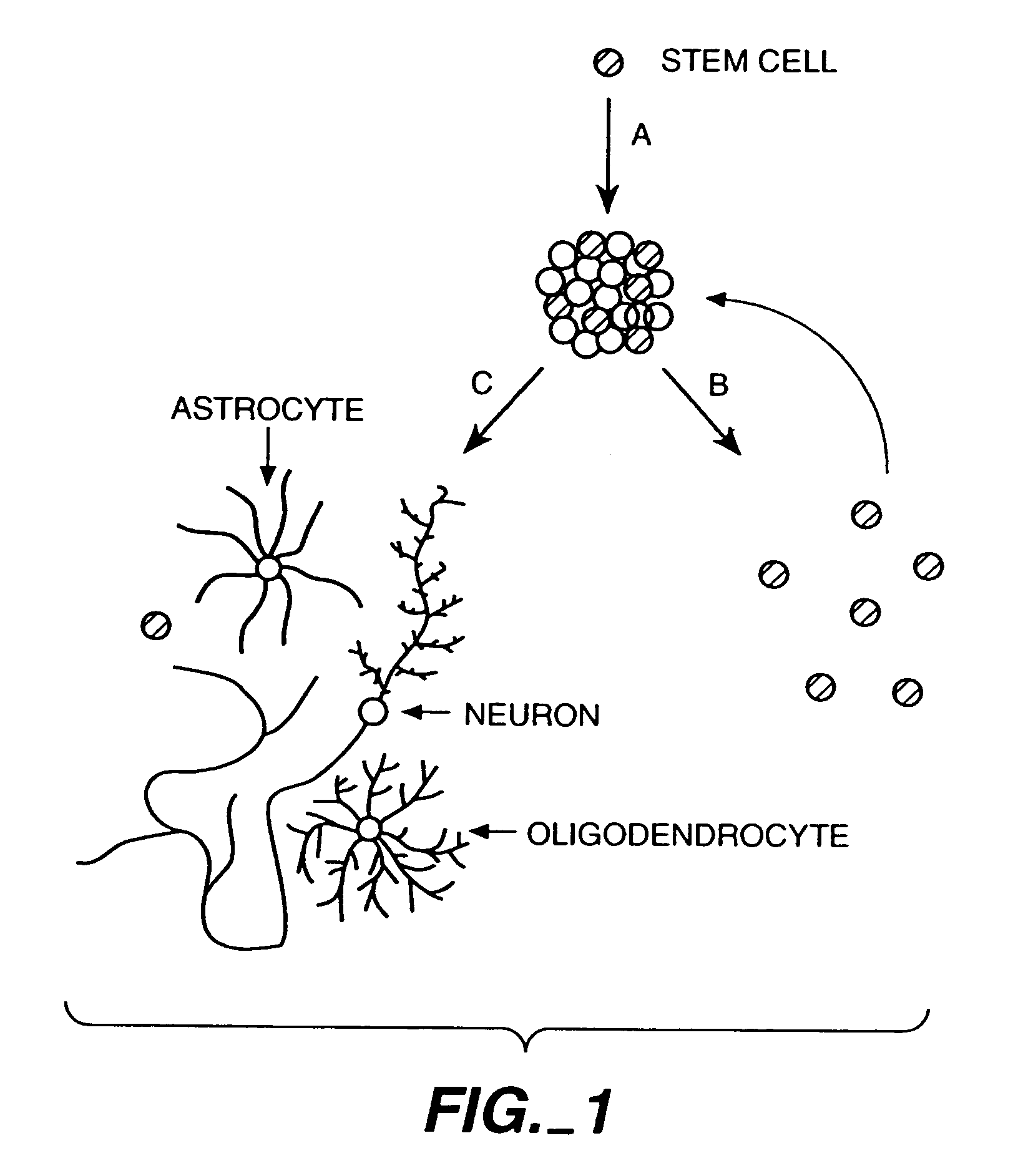
The invention discloses methods of proliferation and differentiation of multipotent neural stem cells. Also provided are methods of making cDNA libraries and methods of screening biological agents which affect proliferation differentiation survival phenotype or function of CNS cells.
Owner:STEMCELLS CALIFORNIA
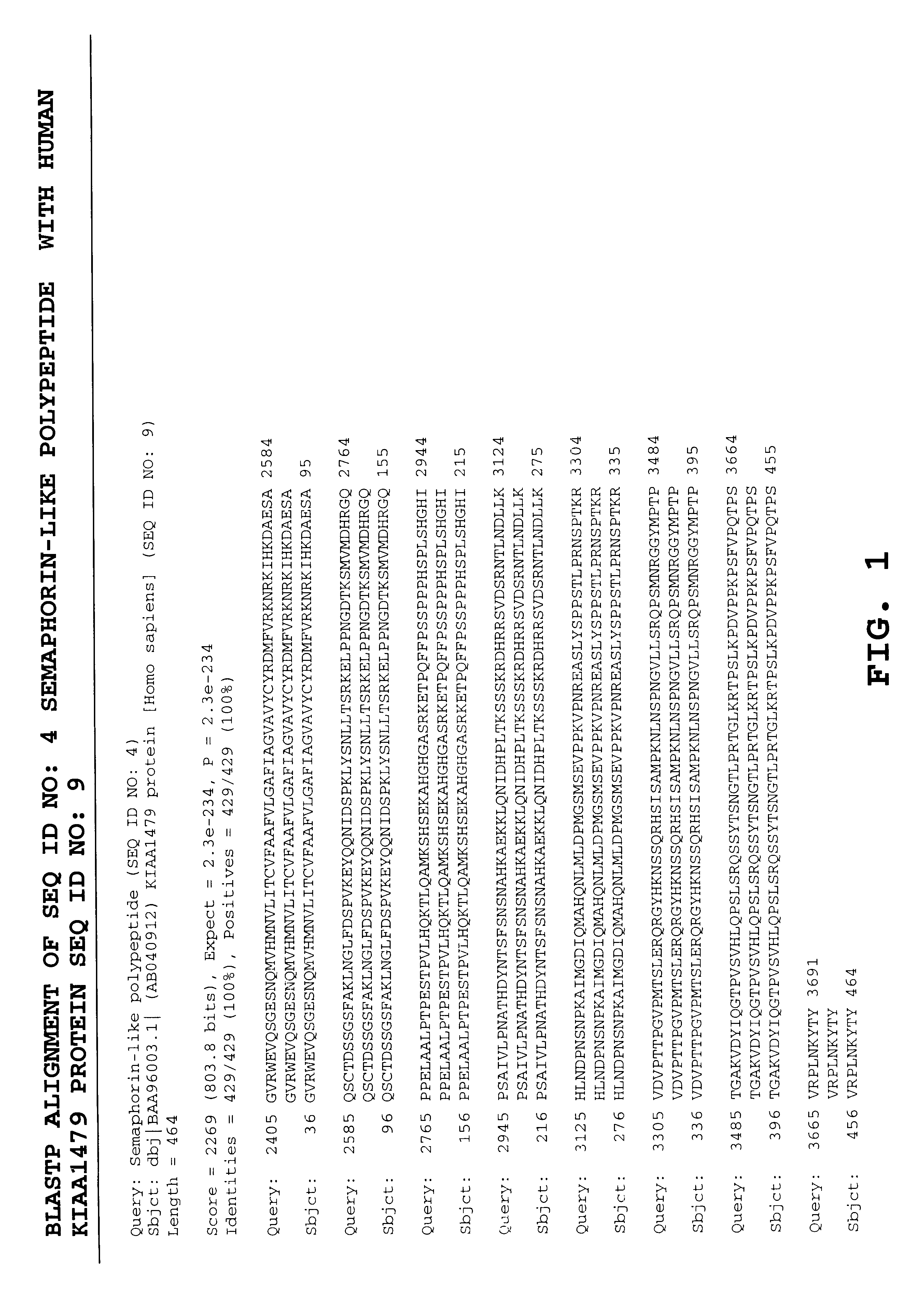
Antibodies specific for semaphorin-like polypeptides
The invention provides novel polynucleotides and polypeptides encoded by such polynucleotides and mutants or variants thereof that correspond to a novel human secreted semaphorin-like polypeptide. These polynucleotides comprise nucleic acid sequences isolated from cDNA library from fetal liver-spleen (Hyseq clone identification numbers 5688868 (SEQ ID NO: 1)). Other aspects of the invention include vectors containing processes for producing novel human secreted semaphorin-like polypeptides, and antibodies specific for such polypeptides.
Owner:NUVELO INC
Methods for preparation of vaccines against cancer
The present invention relates to methods for preparing immunogenic, prophylactically and therapeutically effective complexes of heat shock proteins noncovalently associated with antigenic peptides of cancer cells. The claimed methods comprise the constructing of a cDNA library from cancer or preneoplastic cell RNA, expressing the cDNA library in an appropriate host cell, and recovering the immunogenic complexes from the cells. Large amounts of such immunogenic complexes can be obtained by large-scale culturing of host cells containing the cDNA library. The complexes can be used as a vaccine to elicit specific immune responses against cancer or preneoplastic cells, and to treat or prevent cancer.
Owner:FORDHAM UNIVERSITY
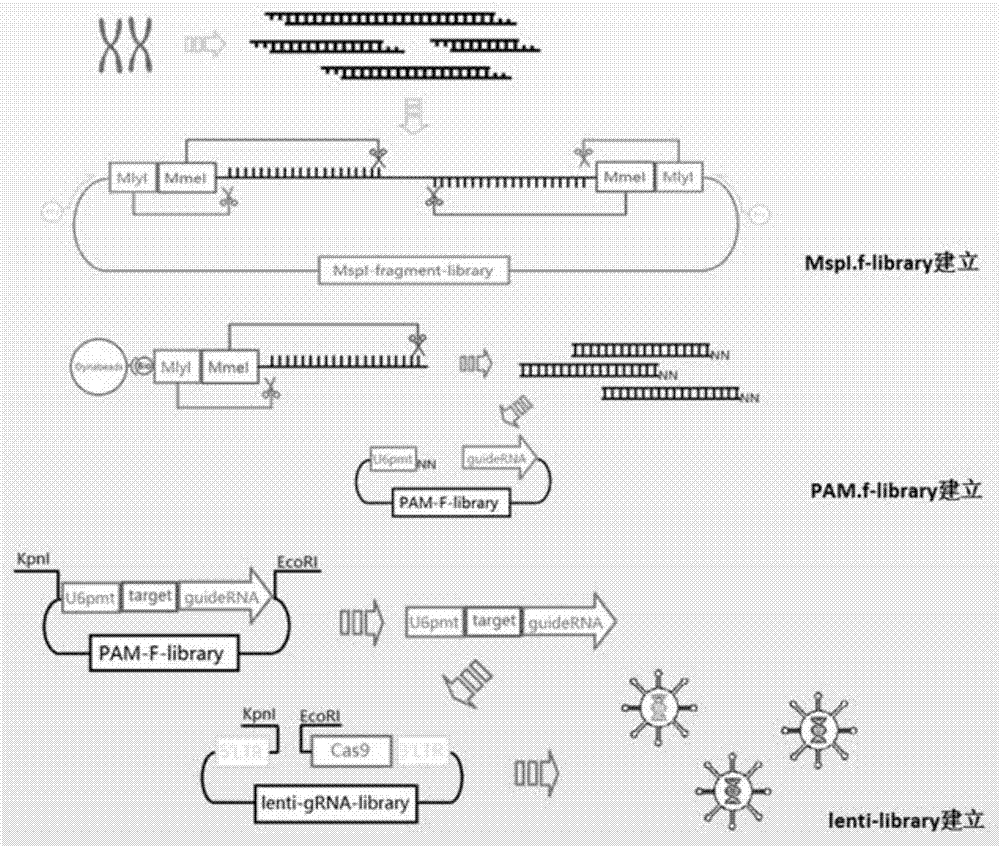
Method used for construction of CRISPR/Cas9 genome knockout library with enzymatically digested genome
ActiveCN107099850AReduce manufacturing costEasy to operateLibrary creationDNA preparationCDNA libraryBiology
The invention relates to a construction method of a genome knockout library, and more specifically discloses a method used for construction of a CRISPR / Cas9 genome knockout library with an enzymatically digested genome. The method is used for solving problems in the prior art that species gene information is incomplete, artificial design coverage is low, and both time and labor are consumed. The method comprises following steps: 1, construction of a Mspl.f-library library; 2, obtaining of 20bp gRNA target sequence fragments; 3, construction of a PAM-f.library library; and 4, construction of a Lenti-gRNA-library library. The method used for obtaining gRNA libraries is independent of any known species genome sequence information, so that the problem in the prior art that species gene information is incomplete, artificial design coverage is low, and both time and labor are consumed are solved, and the knockout library coverage rate is increased greatly. The method is used for construction of a CRISPR / Cas9 genome knockout library.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Antibody of fucosylated Golgi protein GP73 and use thereof
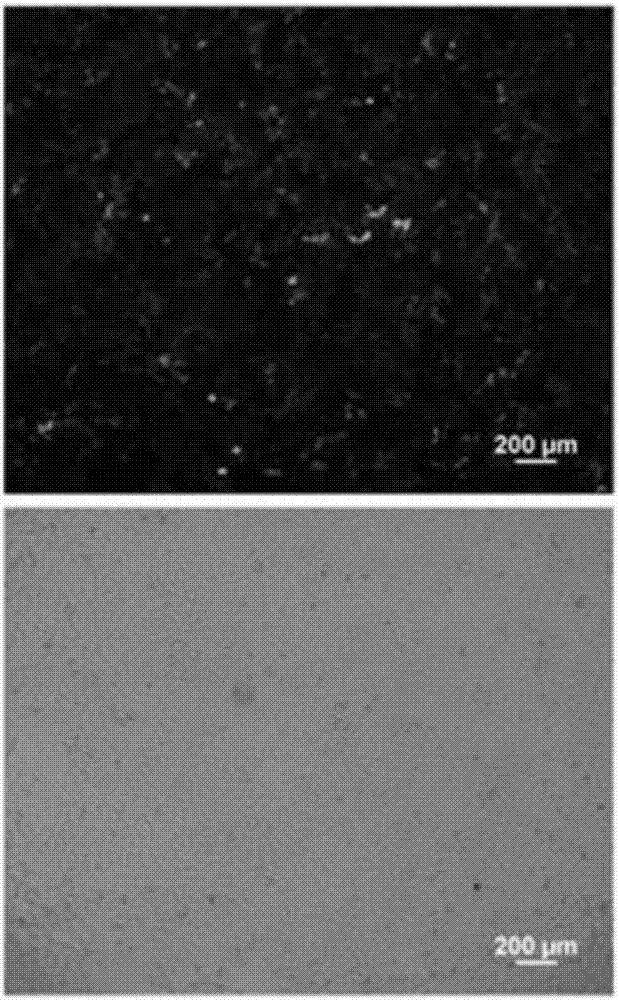
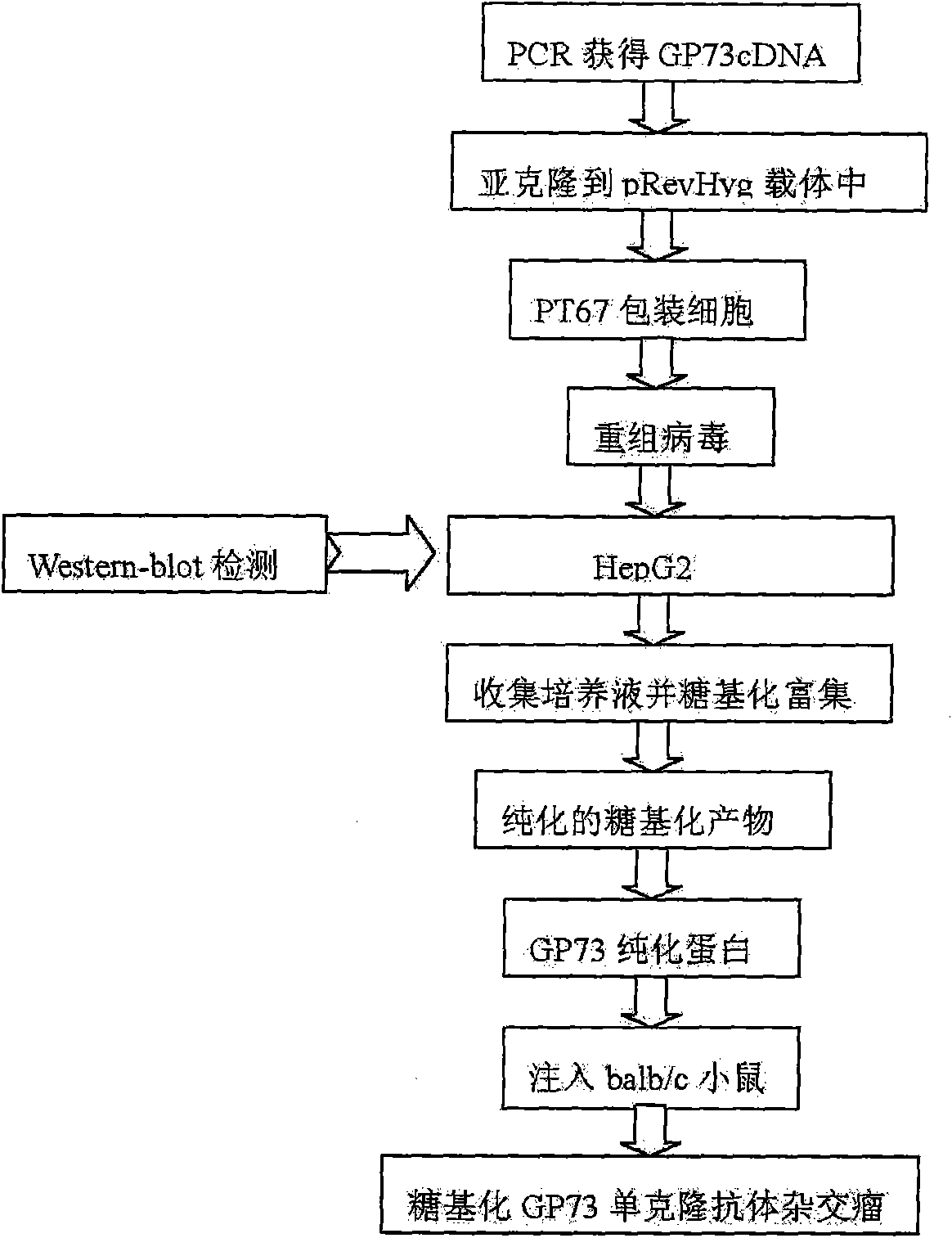
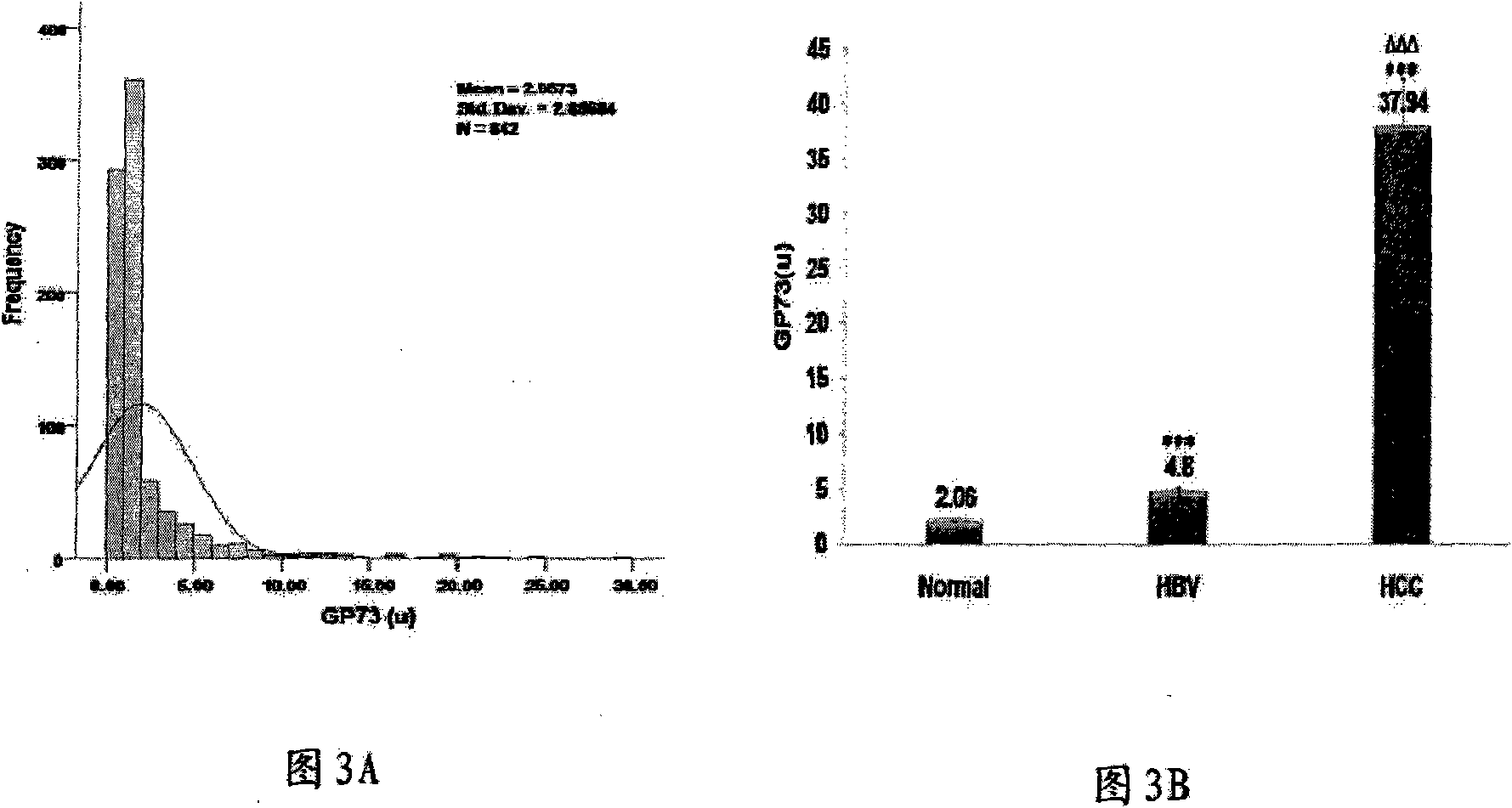
InactiveCN101555282AFast detection methodReduce testing costsTissue cultureImmunoglobulins against fungi/algae/lichensCDNA libraryDisease
The invention relates to an antibody against fucosylated protein GP73, a method for preparing the antibody against the fucosylated protein GP73, a reagent for diagnosing liver cancers, a kit for diagnosing the liver cancers, application of the reagent and / or the kit to preparing products for diagnosing liver diseases and a method for preparing purified fucosylated protein GP73. Occurrence, development and metastasis of liver cancers are diagnosed by detecting the fucosylated protein GP73 or the antibody. The antibody against the fucosylated protein GP73 can be more widely used for affinity chromatography, cDNA library screening, immunologic diagnosis or pharmaceutical preparation.
Owner:THE INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
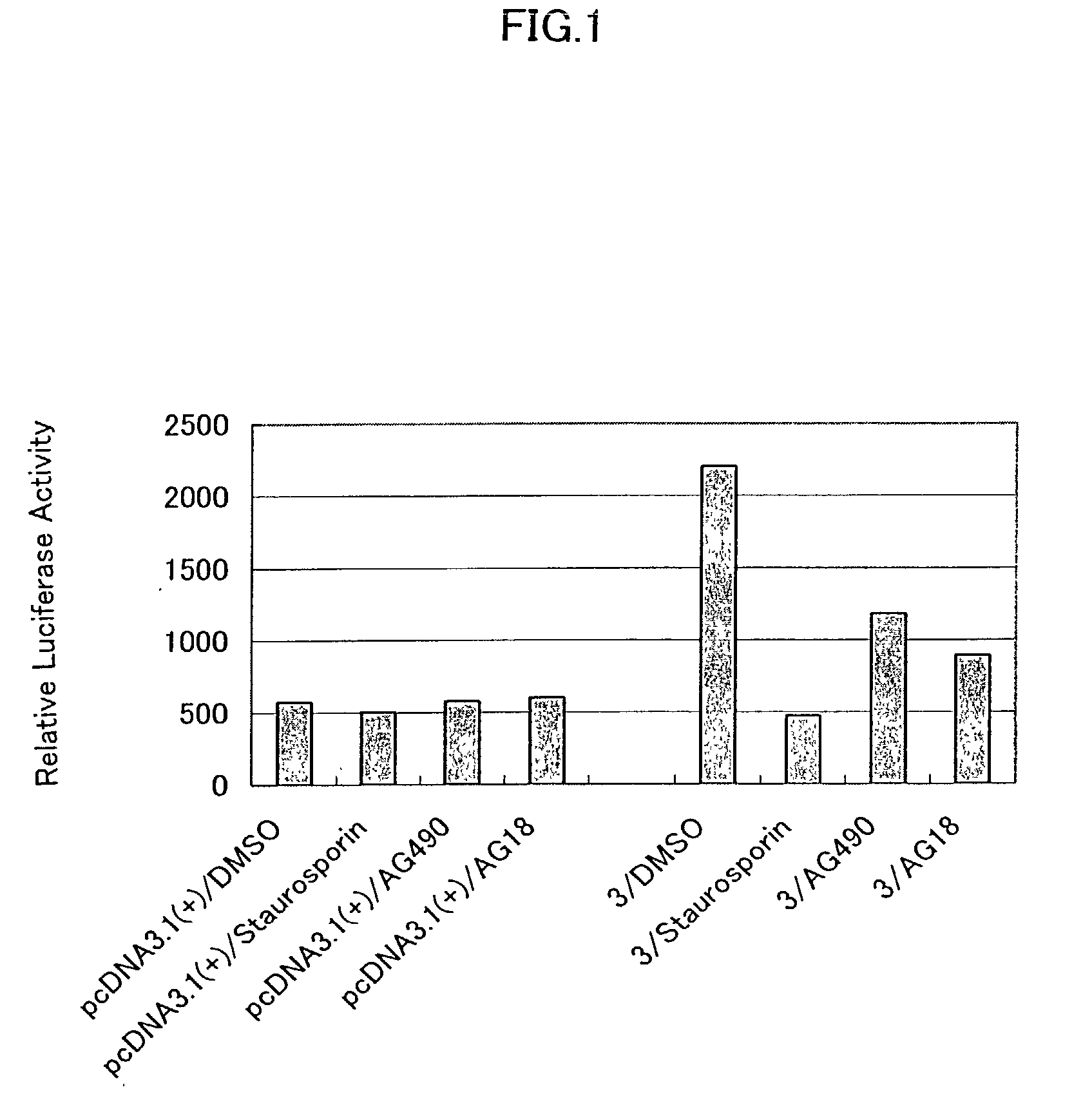
STAT6 activation gene
Proteins having activity that promotes STAT6 activation, which are used for diagnosing, treating or preventing diseases associated with the excessive activation or inhibition of STAT6 are provided. Using a STAT6 response reporter plasmid, cDNA encoding a protein capable of promoting STAT6 activation was cloned from the cDNA library constructed from human lung fibroblasts, and the DNA sequence and the deduced amino acid sequence are determined. The protein, the DNA encoding the protein, a recombinant vector containing the DNA, and a transformant containing the recombinant vector are useful for screening a substance inhibiting or promoting STAT6 activation.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI KK
High-throughput screening of expressed DNA libraries in filamentous fungi
InactiveUS7122330B2Minimizes and eliminates formationLow culture viscosityHydrolasesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBiotechnologyCDNA library
The invention provides a method for the expression of exogenous DNA libraries in filamentous fungi. The fungi are capable of processing intron-containing eukaryotic genes, and also can carry out post-translational processing steps such as glyclosylation and protein folding. The invention provides for the use of fungi with altered morphology, which permits high-throughput screening and directed molecular evolution of expressed proteins. The same transformed fungi may be used to produce larger quantities of protein for isolation, characterization, and application testing, and may be suitable for commercial production of the protein as well.
Owner:DANISCO US INC +1
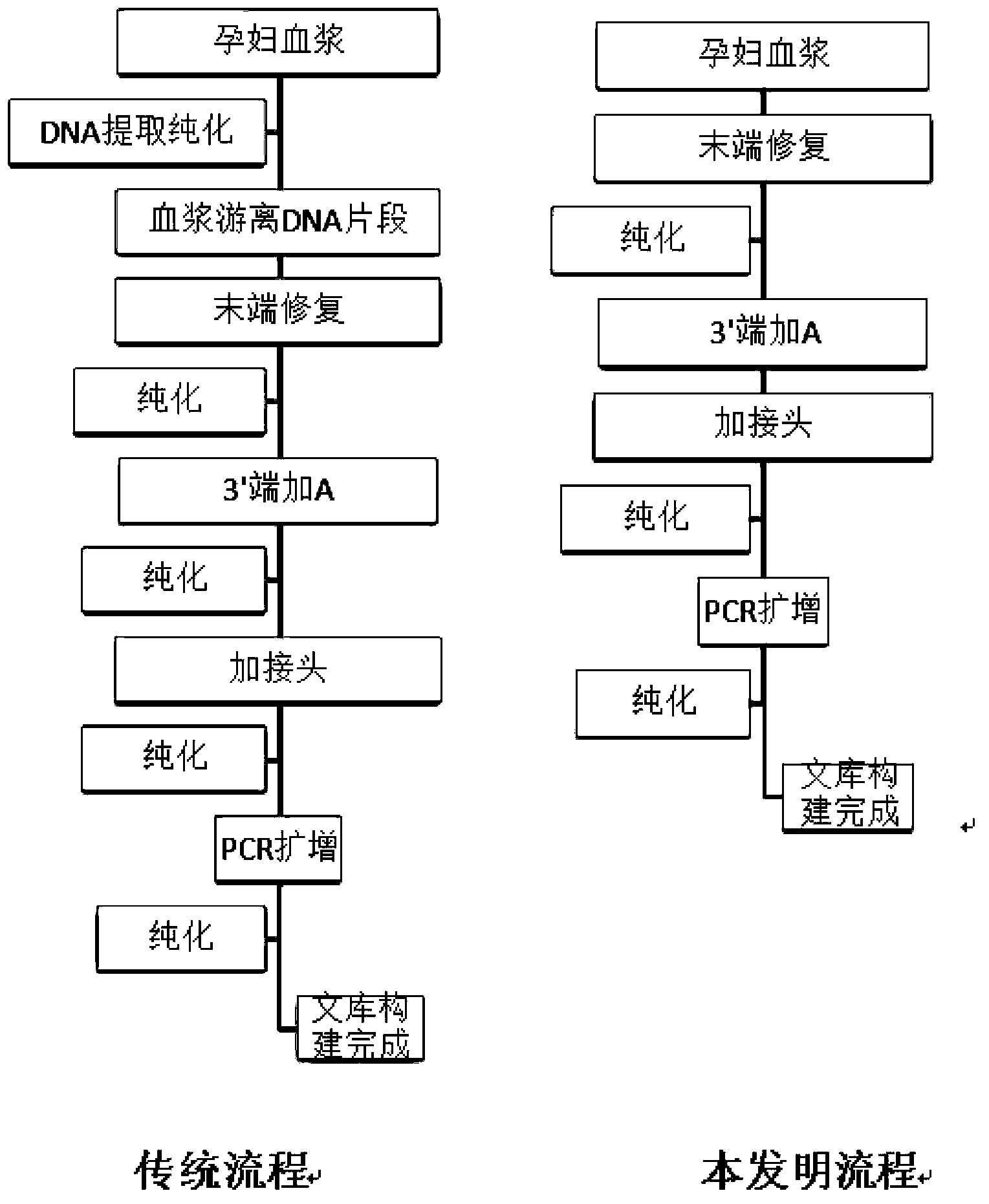
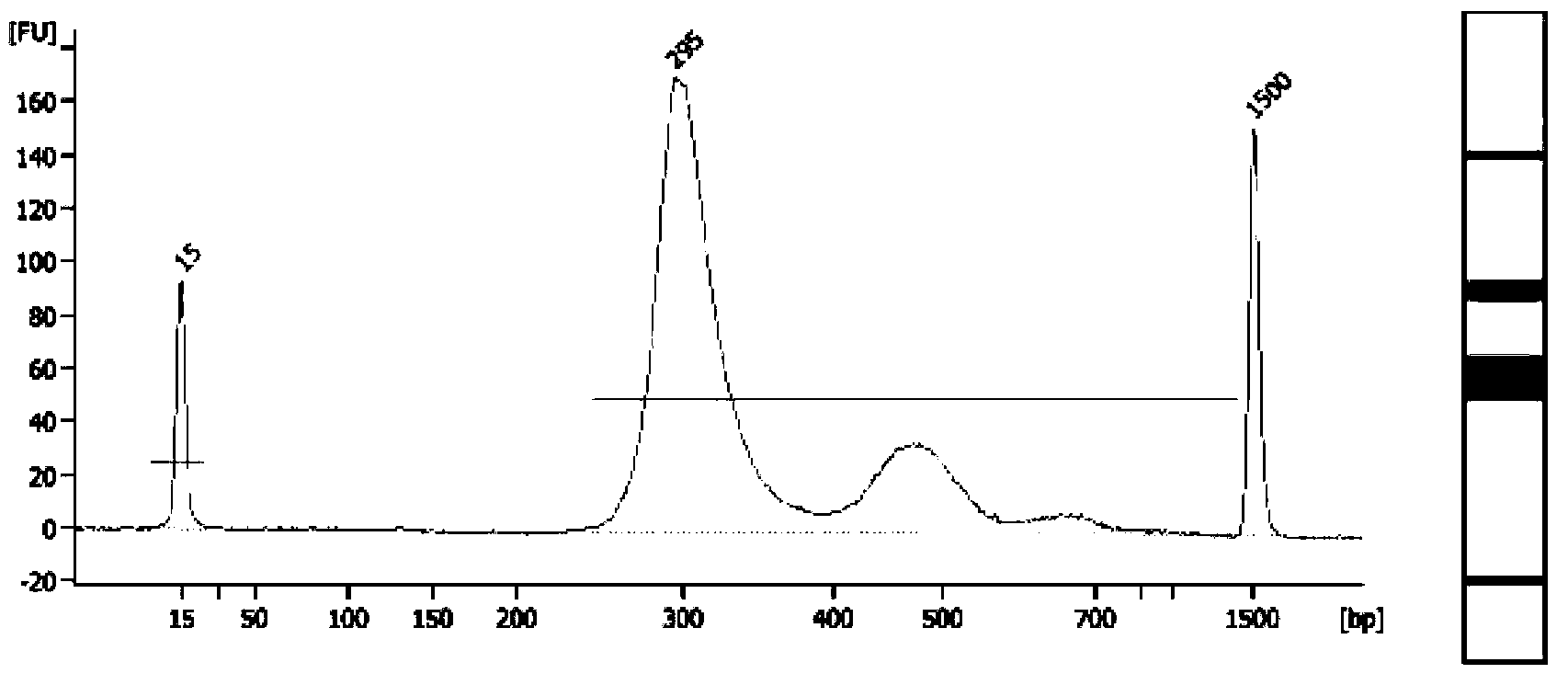
DNA library construction method for prenatal diagnosis
InactiveCN103361743AQuality improvementLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationCDNA libraryDNA extraction
The invention provides a DNA library construction method for prenatal diagnosis. According to the DNA library construction method for the prenatal diagnosis, pregnant woman blood plasma is directly used for library construction, and a DNA extraction step is omitted, so that use amount of the pregnant woman blood plasma can be reduced, at the same time, possibility of deviation of fetal DNA content can be reduced, and cost and time for the DNA library construction are greatly reduced. Another aspect of the invention relates to DNA libraries prepared by any of above preparation methods. The third aspect of the invention relates to a DNA sequencing method. The DNA library construction method has good application prospect.
Owner:ANNOROAD GENE TECH BEIJING
Compositions and methods for cDNA synthesis
InactiveUS7470515B2Increase total outputReduce RNA sequence biasSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyCDNA library
Methods for making cDNA molecules, for amplification of RNA by PCR and for preparation of cDNA libraries are provided. Kits for making cDNA molecules also are provided. Compositions are also provided comprising mixtures of reagents, including reverse transcriptases, buffers, cofactors and other components, suitable for immediate use in conversion of RNA into cDNA and RT PCR without dilution or addition of further components. These compositions are useful, alone or in the form of kits, for cDNA synthesis or nucleic acid amplification (e.g., by the Polymerase Chain Reaction) or for any procedure utilizing reverse transcriptases in a variety of research, medical, diagnostic, forensic and agricultural applications.
Owner:QUANTA BIOSCI
Methods for preparing cDNA from low quantities of cells
ActiveUS10017761B2Easy to collectMinimize contaminationDNA preparationCDNA libraryMicroarray profiling
Methods for preparing cDNA libraries from single and low quantities of cells are disclosed. The methods are based on the principles of multi-strand displacement amplification or semi-random primed polymerase chain reaction. The methods typically include a step of reverse transcription and subsequent amplification of cDNA. The methods can be adapted for preparation of cDNA libraries that are representative of mRNA or whole RNA expressed by the cell or cells. The cDNA is suitable for sequencing or microarray analysis.
Owner:YALE UNIV
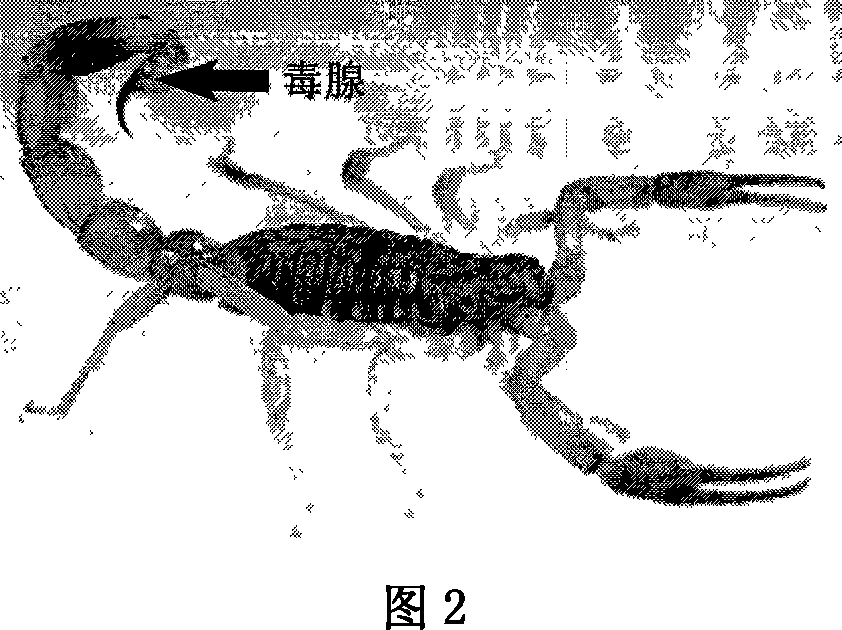
East-Asia scorpion antibiotic peptide gene and preparation method and application
ActiveCN101063102AHigh antibacterial activitySimple and efficient approach to molecular designAntibacterial agentsBacteriaChemical synthesisCDNA library
The invention discloses a preparing method of east Asia Tityus antibiotic peptide gene and appliance, which comprises the following steps: restructuring bacillus coli Escherichia coli DH5a / BmKAMP1, CCTCC NO: M207036; constructing east Asia Tityus ioterium cell cDNA library; choosing PCR method; sieving positive colony of scorpion antibiotic peptide gene from ioterium cDNA library; sequence-analyzing coding trait of antibiotic peptide gene; assuring amino acid sequence of the antibiotic peptide gene; adopting chemosynthesis antibiotic peptide; possessing inhibition of diverse density for Gram's bacterium. This antibiotic peptide possesses specificity and high active, which can be used as antibacterial drugs.
Owner:唐克煌
Methods of proliferating undifferentiated neural cells
The invention discloses methods of proliferation and differentiation of multipotent neural stem cells. Also provided are methods of making cDNA libraries and methods of screening biological agents which affect proliferation differentiation survival phenotype or function of CNS cells.
Owner:BOCO SILICON VALLEY INC
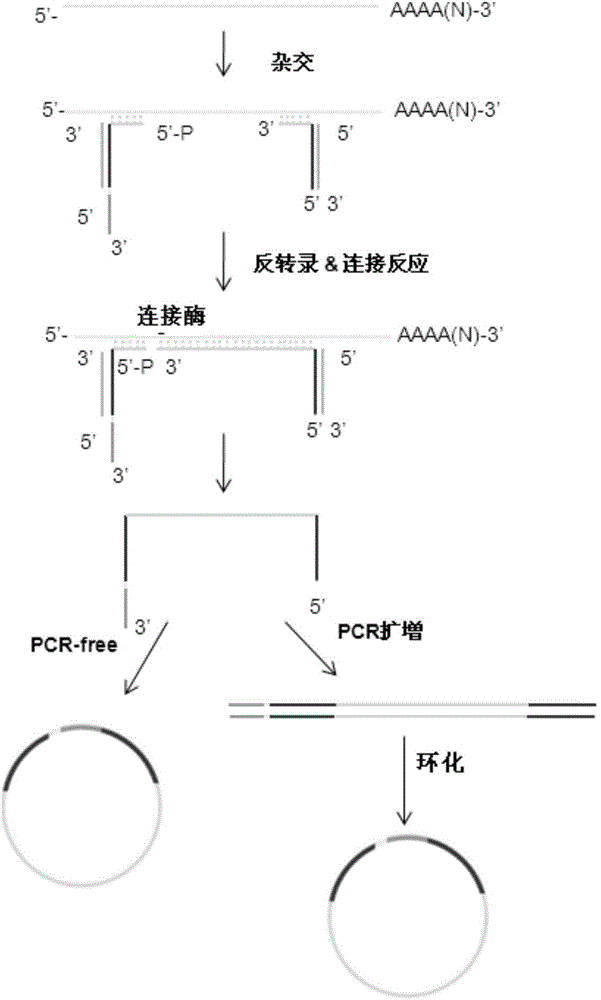
mRNA fragmentation method and method for constructing sequencing library based on same
ActiveCN105985945AReduce cumbersome stepsImprove real reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationCDNA libraryBridge type
The invention relates to an mRNA fragmentation method and a method for constructing a sequencing library based on the mRNA fragmentation method. The mRNA fragmentation method provided by the invention employs forward and reverse bridge-type probes, realizes breakage of an mRNA sample through one-step reverse transcription and connection reaction, and introduces two terminal linkers during reverse transcription so as to obtain a cDNA library with linkers at two terminals. The cDNA library with the linkers at the two terminals can directly undergo cyclization reaction or undergo PCR amplification before cyclization reaction, so a sequencing library for single-stranded cyclic nucleic acids can be obtained; or a sequencing library for single-stranded nucleic acids can be obtained by directly subjecting the cDNA library to amplification. When the mRNA fragmentation method is applied to construction of the sequencing library, tedious steps like restoration of a tail terminal and arrangement of a linker on one end at first and another linker on the other end next in traditional construction of libraries can be omitted; experimental flow is greatly simplified; a library construction period is shortened; and library construction cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:MGI TECH CO LTD
Methods For Preparing cDNA From Low Quantities of Cells
ActiveUS20140213485A1Minimize contaminationEasy to collectNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementCDNA libraryMicroarray profiling
Methods for preparing cDNA libraries from single and low quantities of cells are disclosed. The methods are based on the principles of multi-strand displacement amplification or semi-random primed polymerase chain reaction. The methods typically include a step of reverse transcription and subsequent amplification of cDNA. The methods can be adapted for preparation of cDNA libraries that are representative of mRNA or whole RNA expressed by the cell or cells. The cDNA is suitable for sequencing or microarray analysis.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Stem cell growth factor-like polypeptides
The invention provides novel polynucleotides and polypeptides encoded by such polynucleotides and mutants or variants thereof that correspond to a novel human and mouse secreted stem cell growth factor-like polypeptide. These polynucleotides comprise nucleic acid sequences isolated from cDNA libraries prepared from mouse bone marrow and human fetal liver spleen, ovary, adult brain, lung tumor, spinal cord, cervix, ovary, endothelial cells, umbilical cord, placental, lymphocyte, lung fibroblast, fetal brain, and testis. Other aspects of the invention include vectors containing processes for producing novel human secreted stem cell growth factor-like polypeptides, and antibodies specific for such polypeptides.
Owner:KIRIN PHARMA +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com