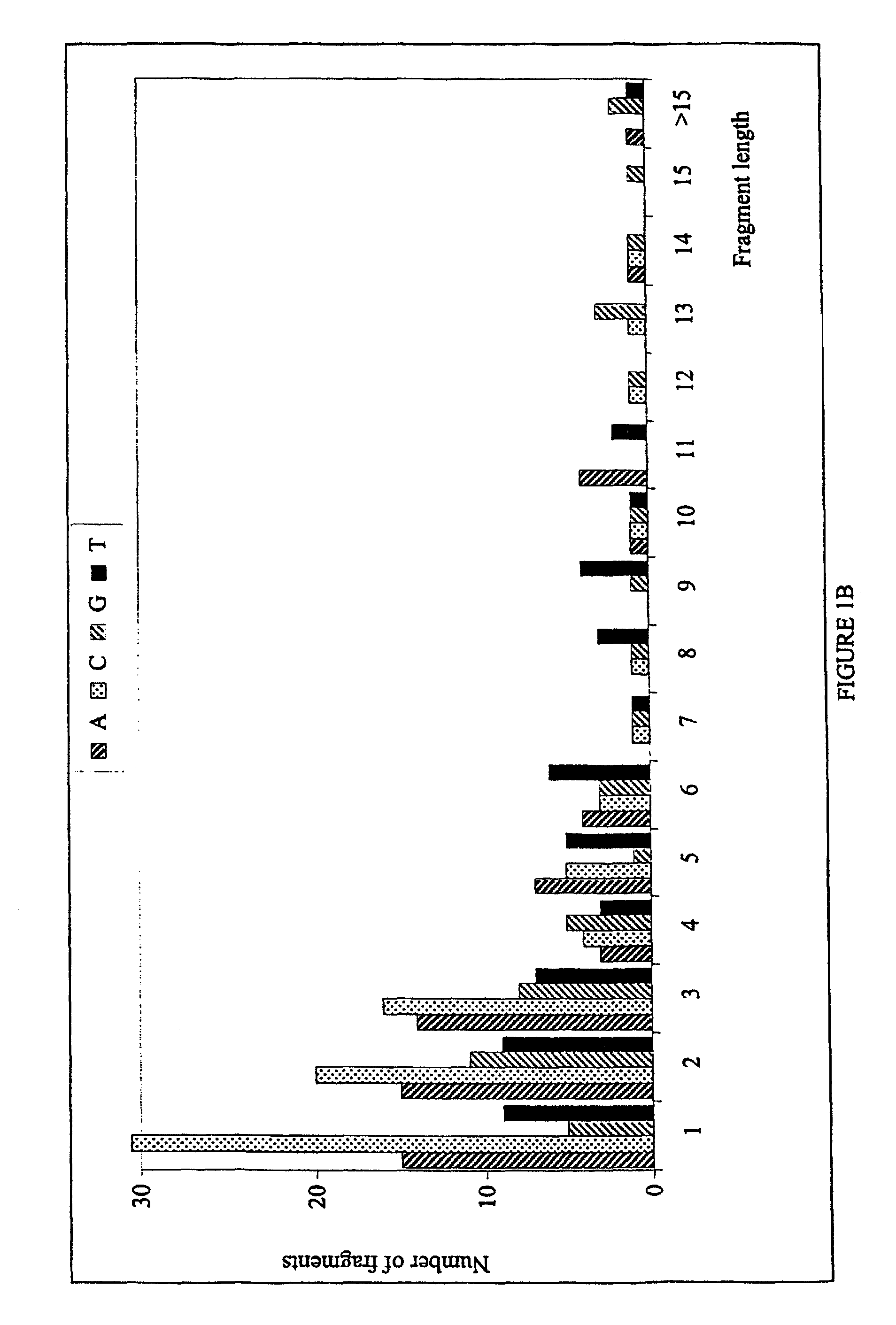
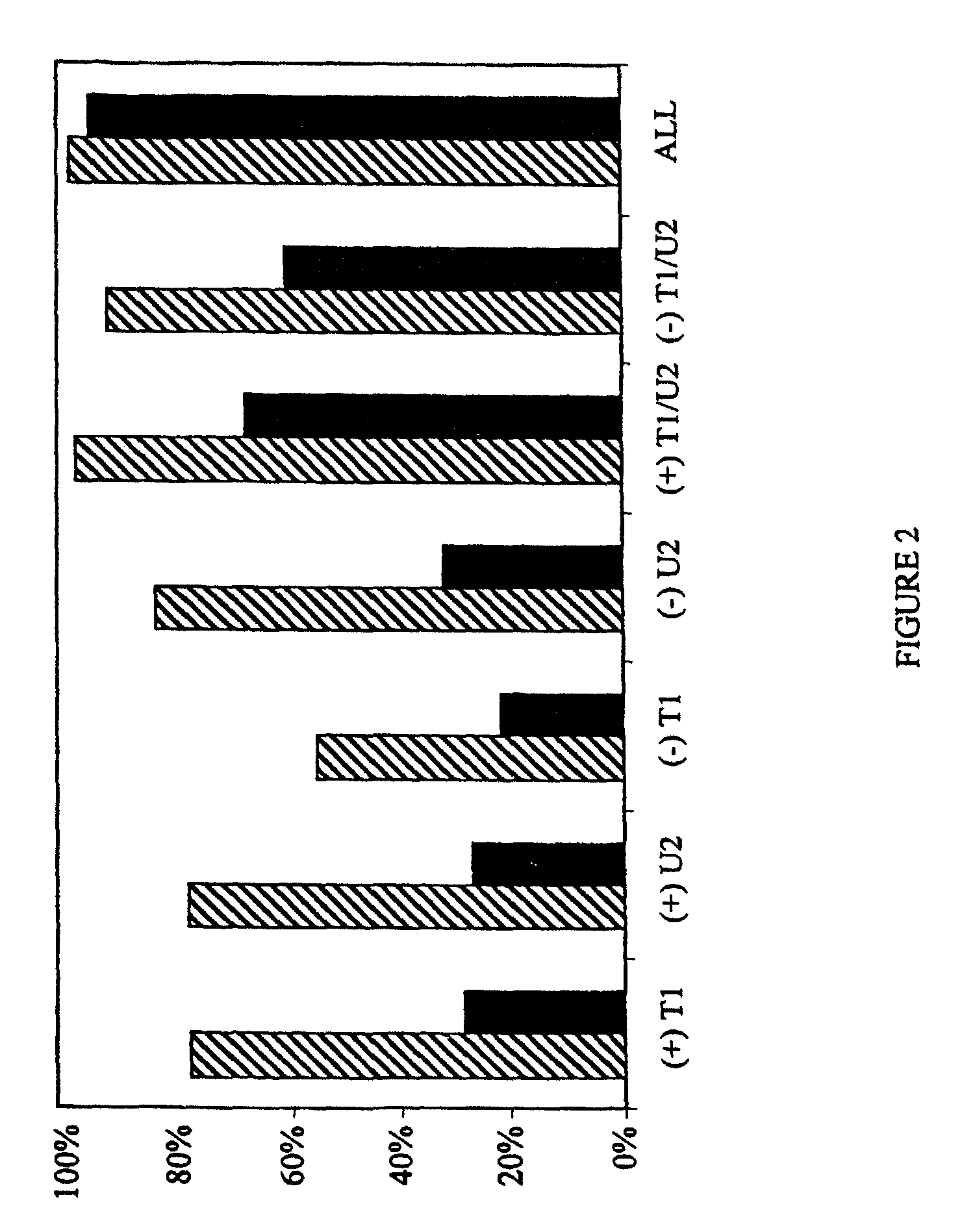
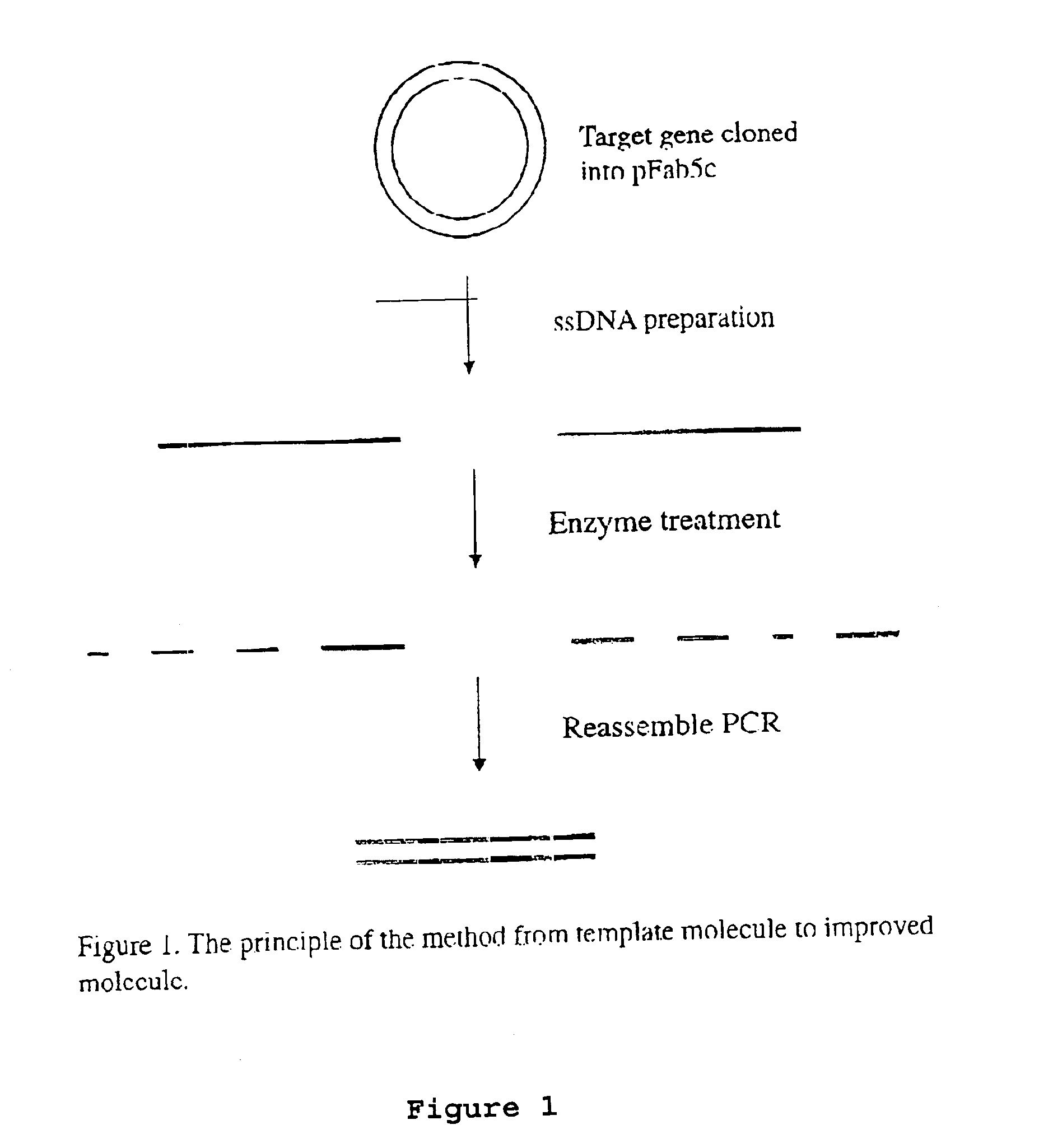
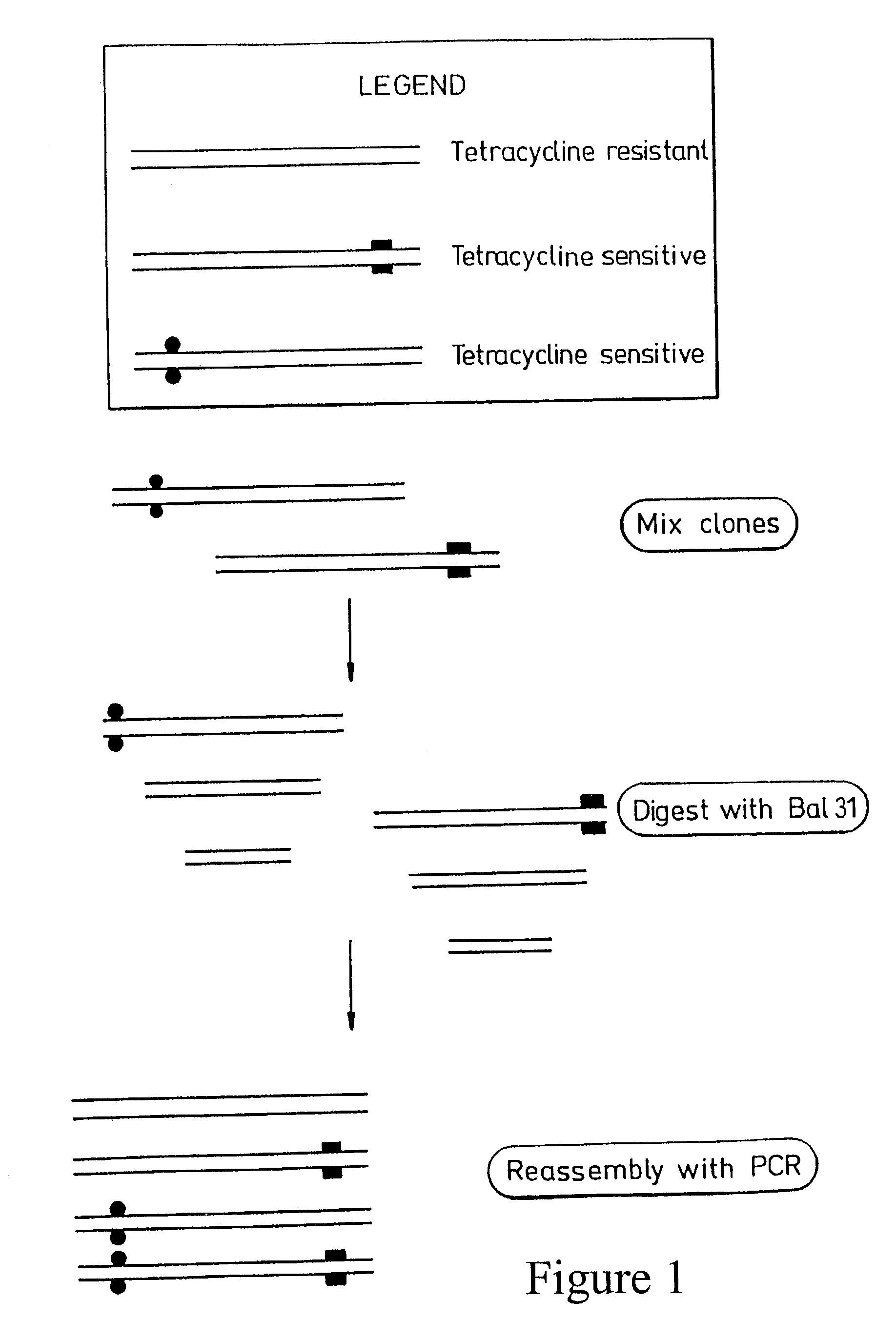
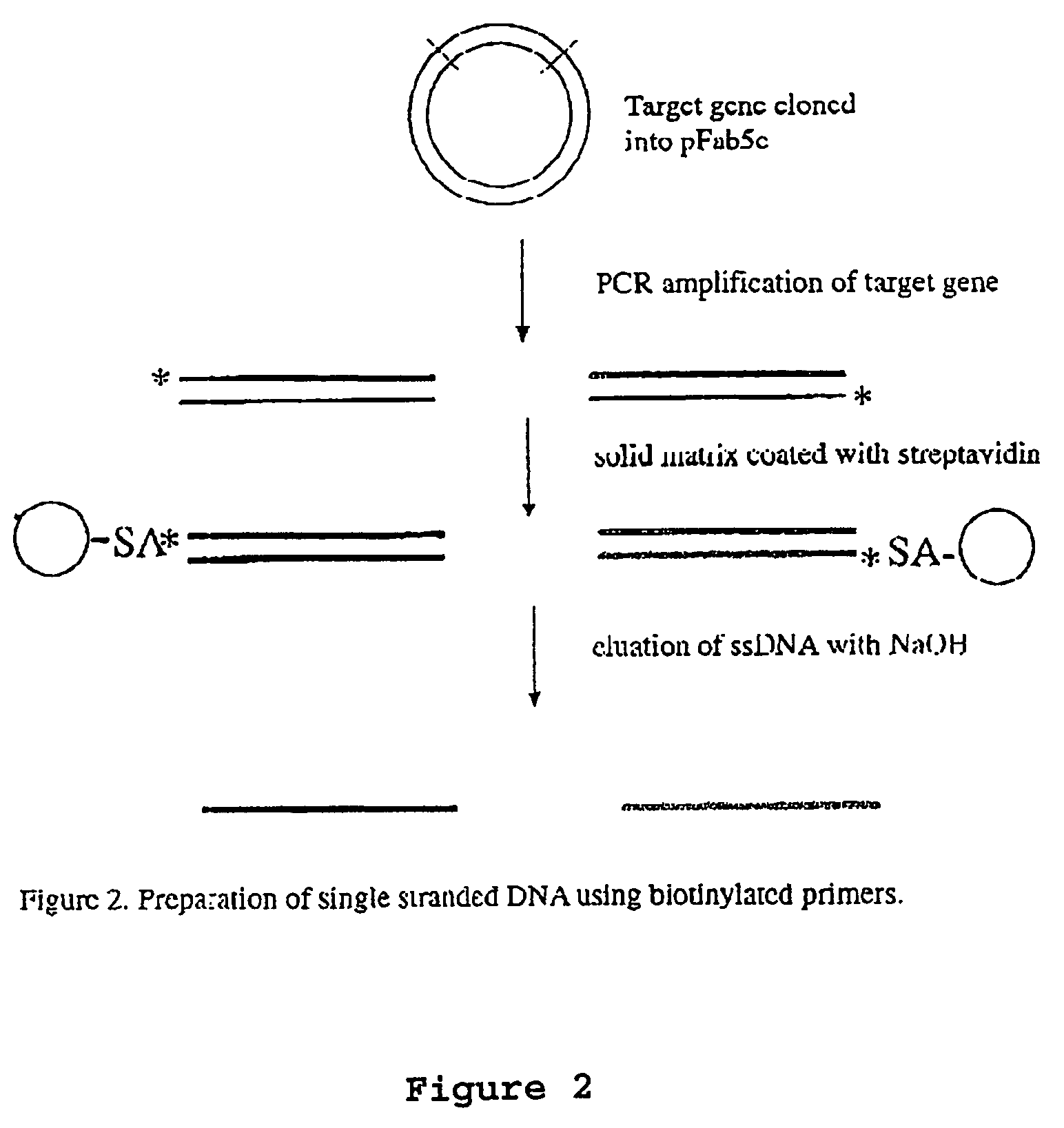
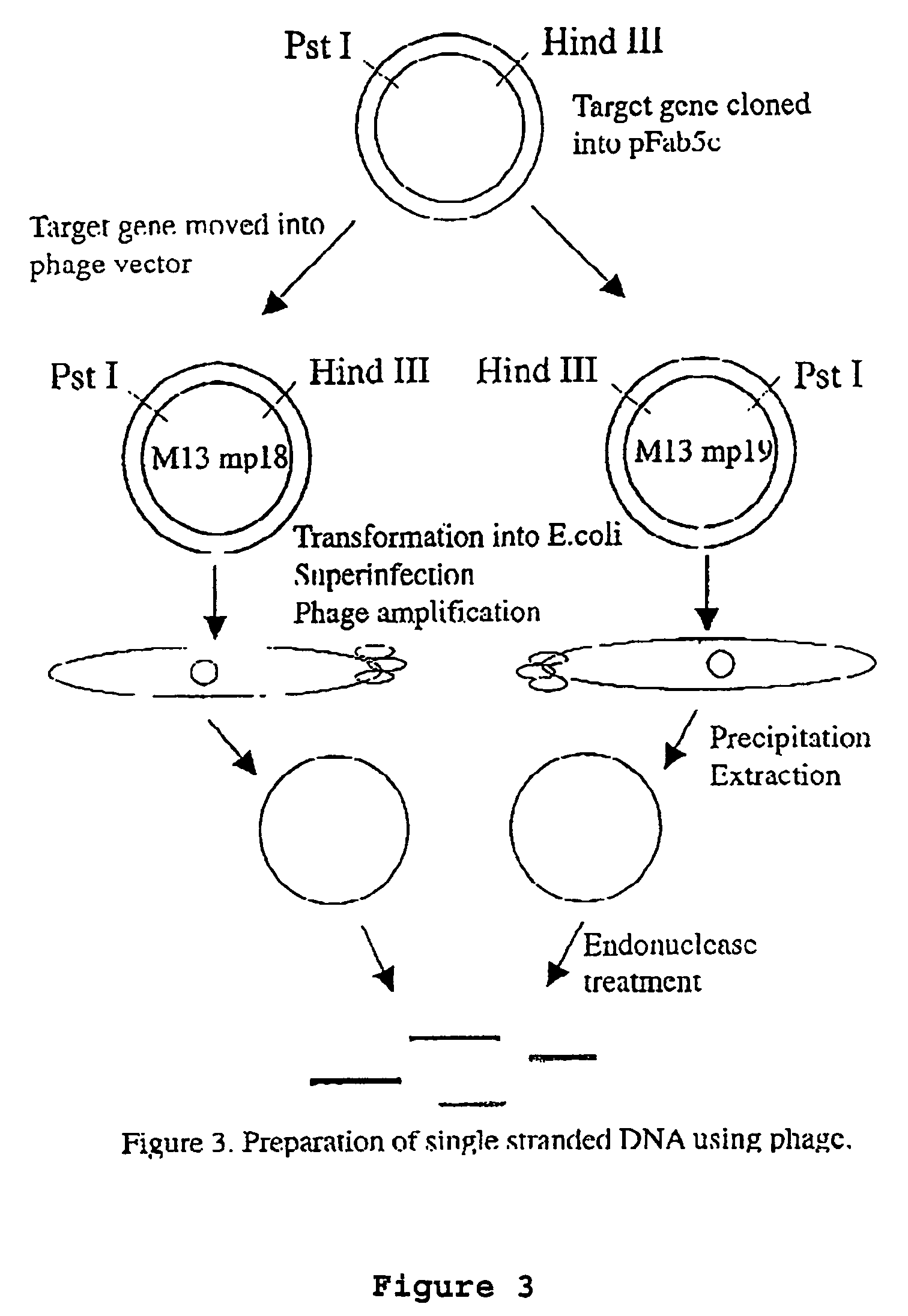
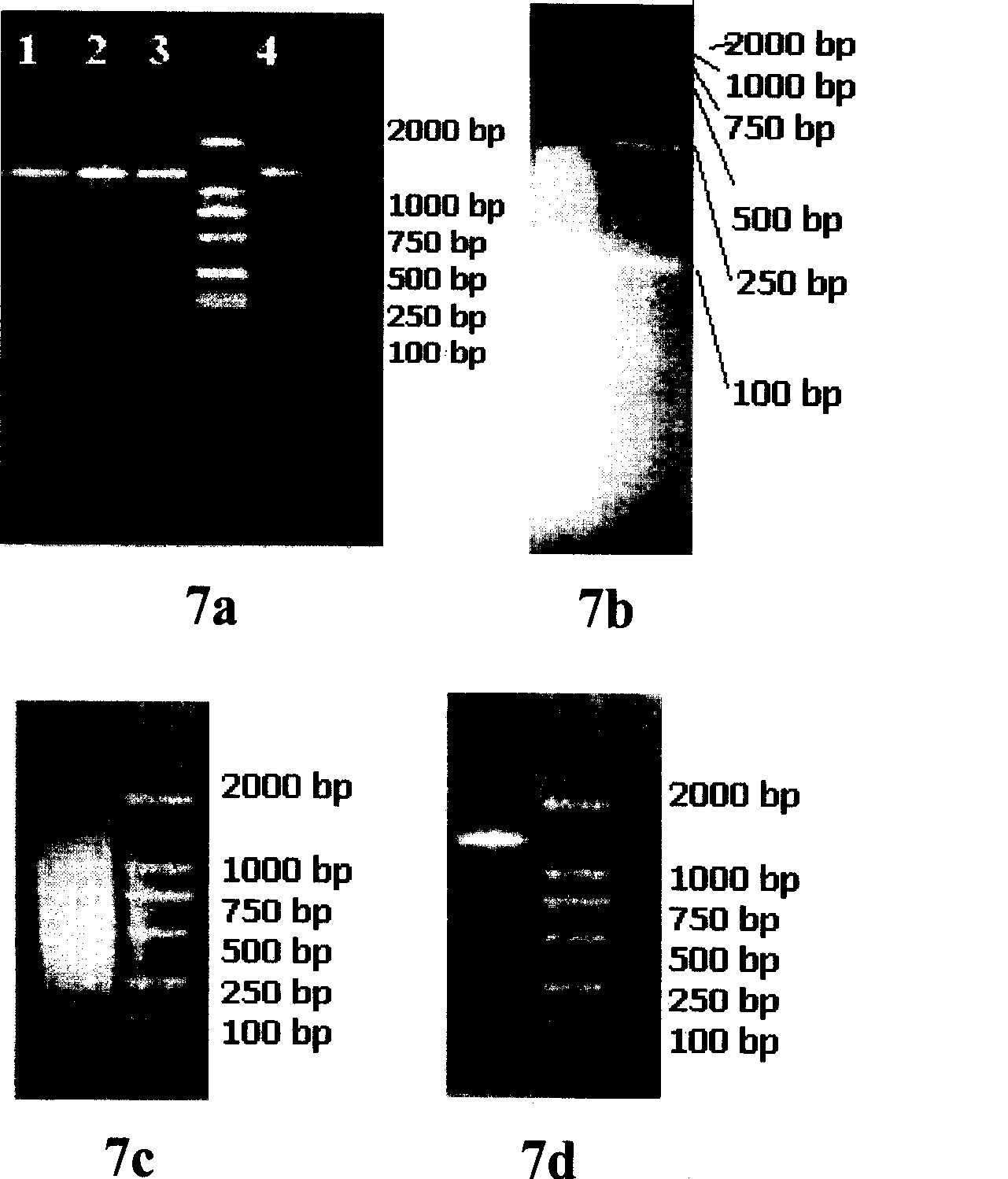
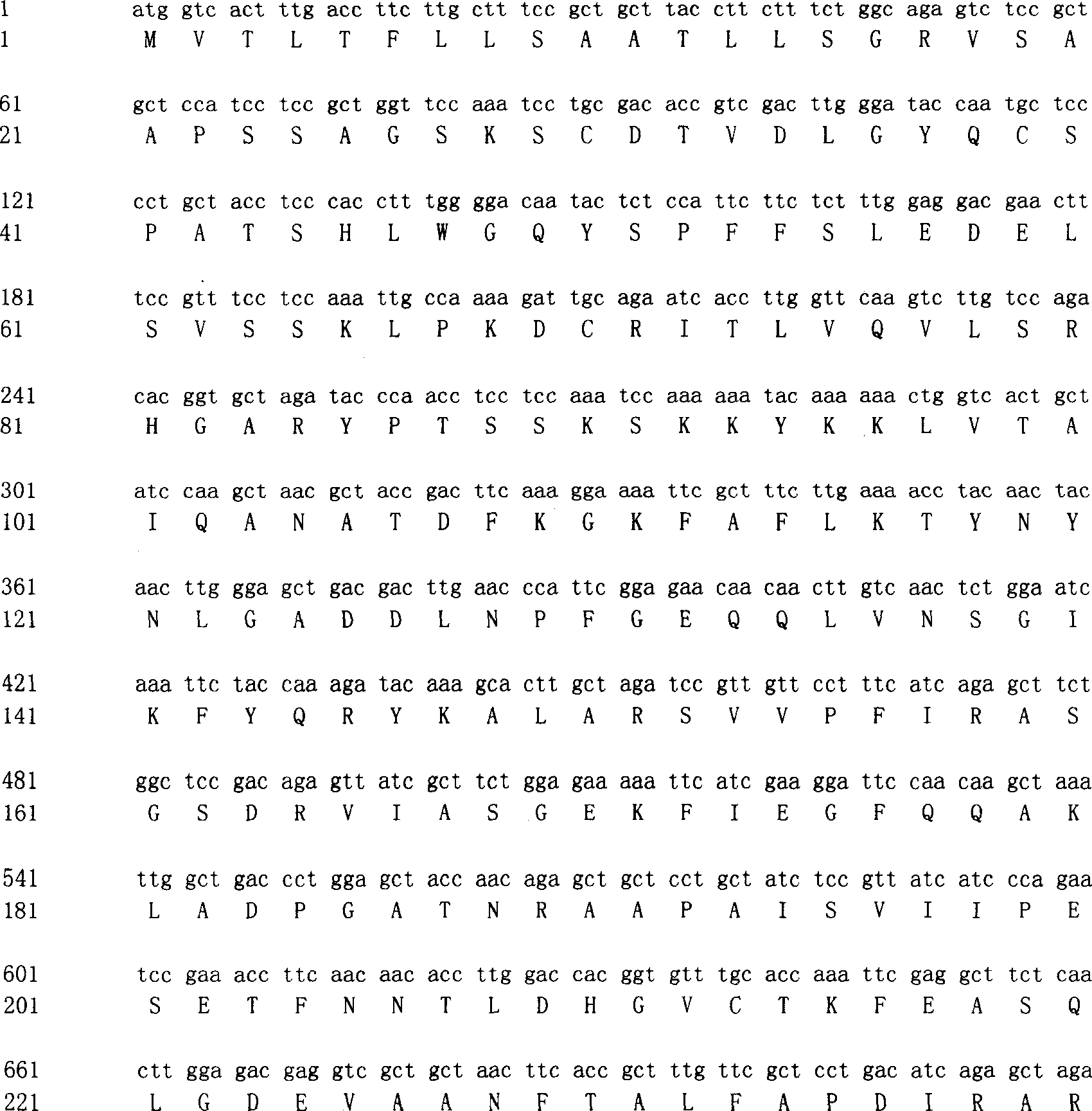
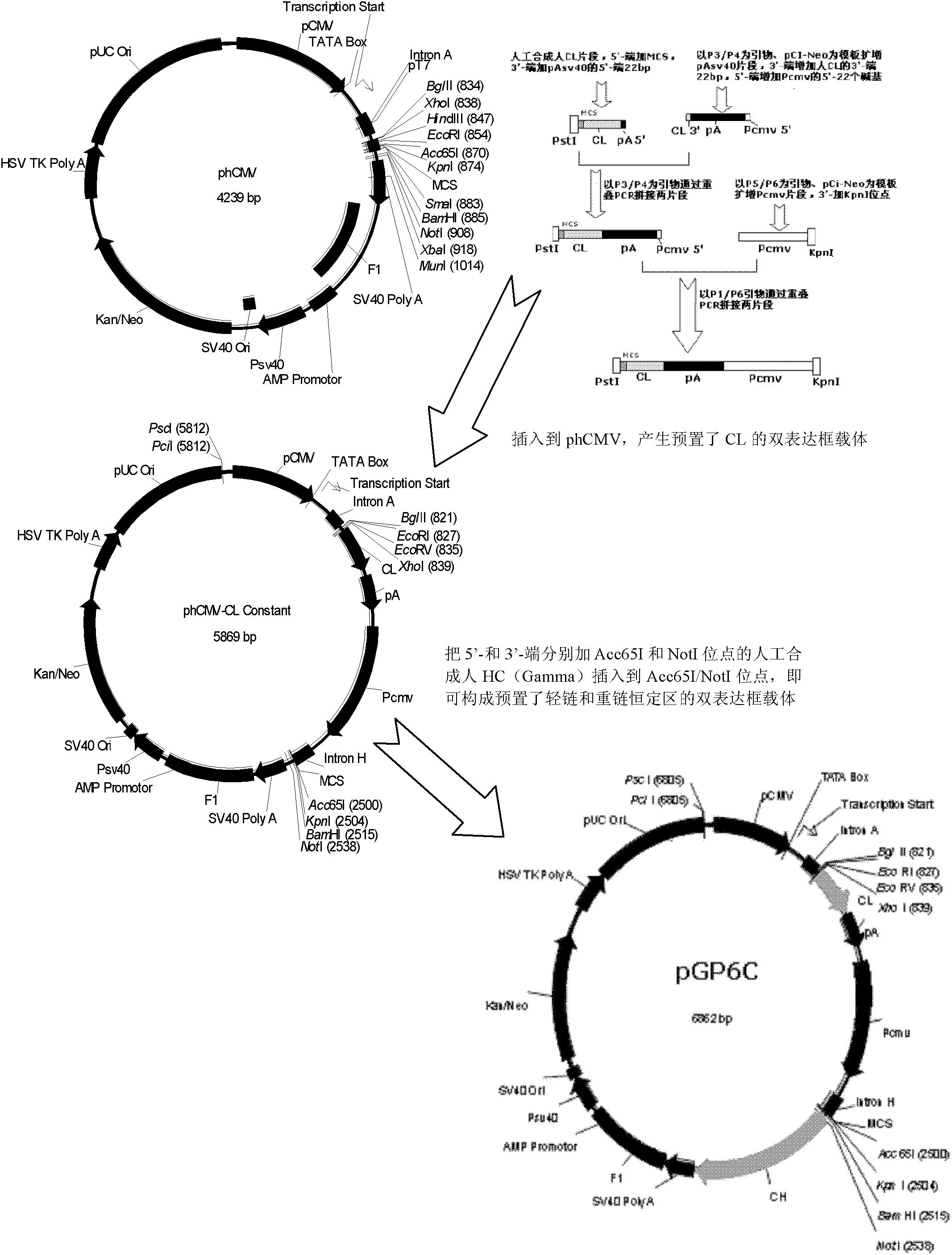
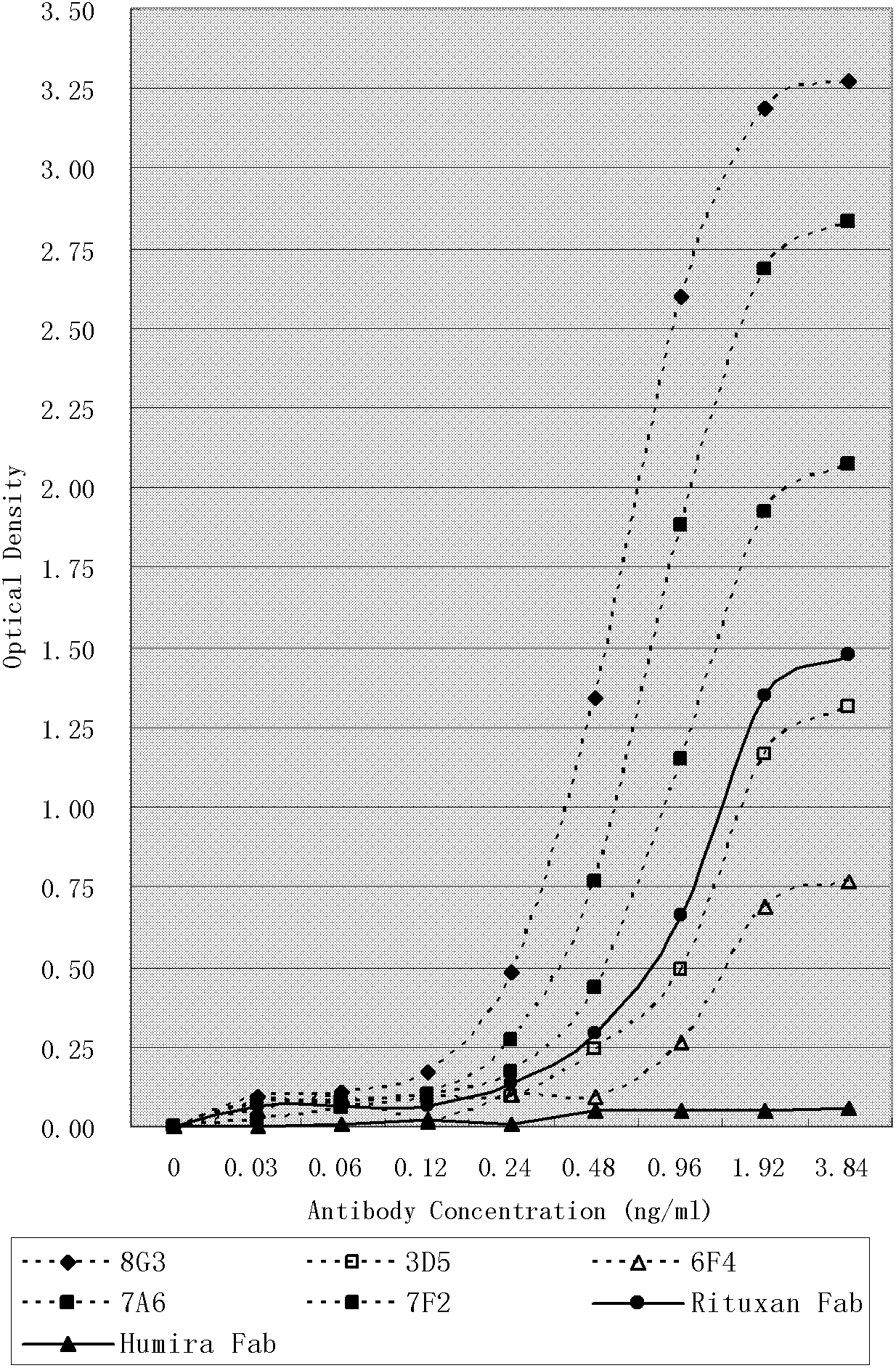
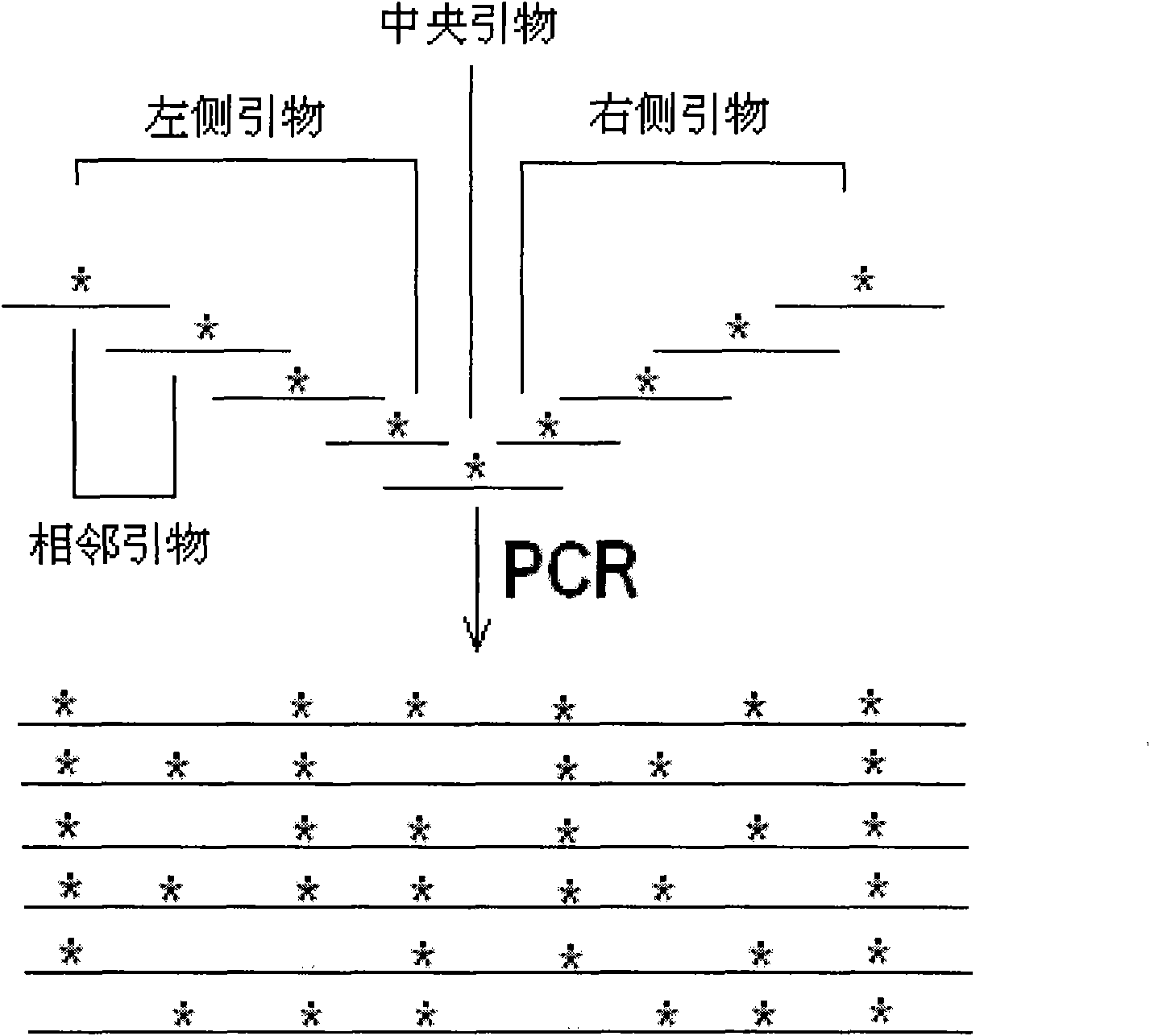
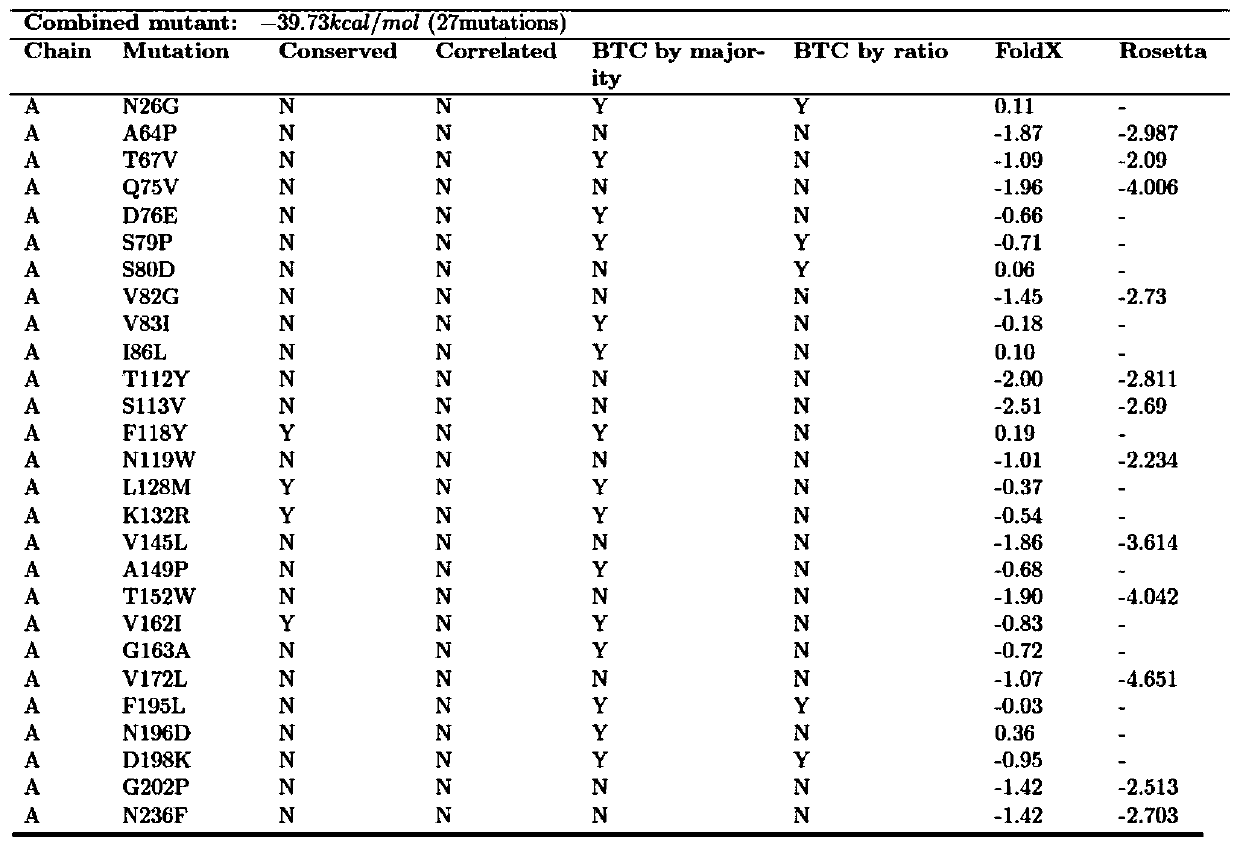
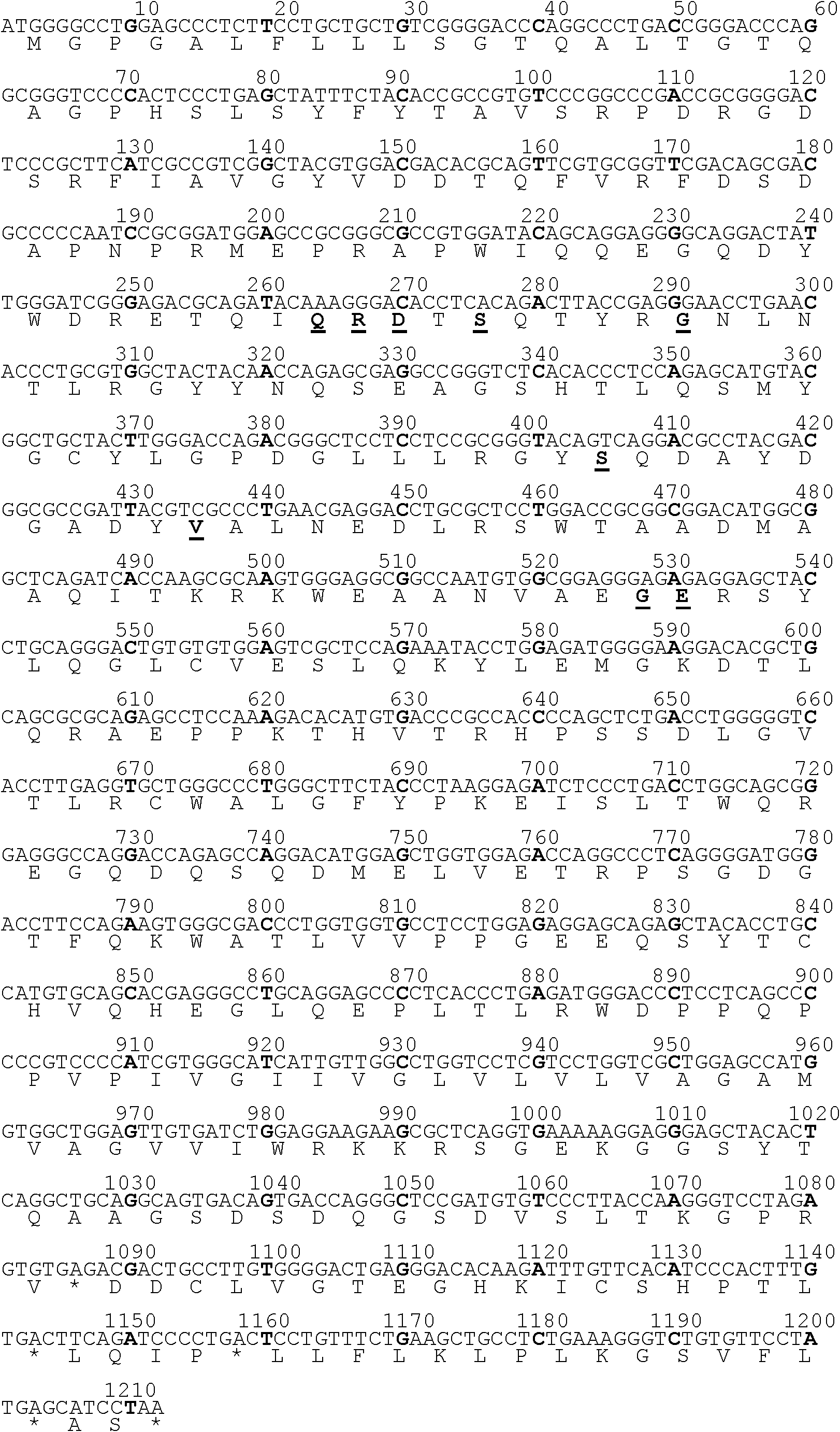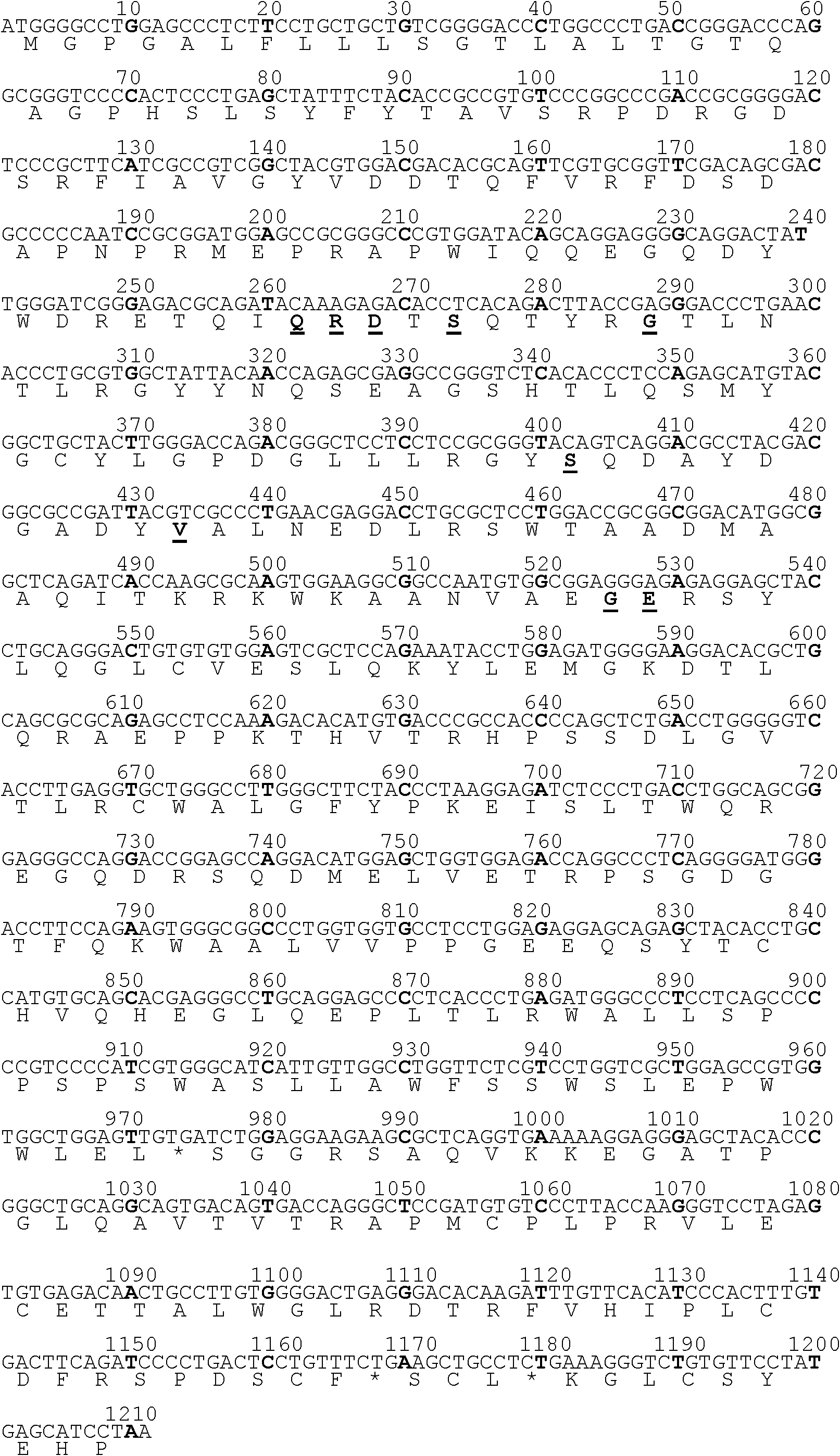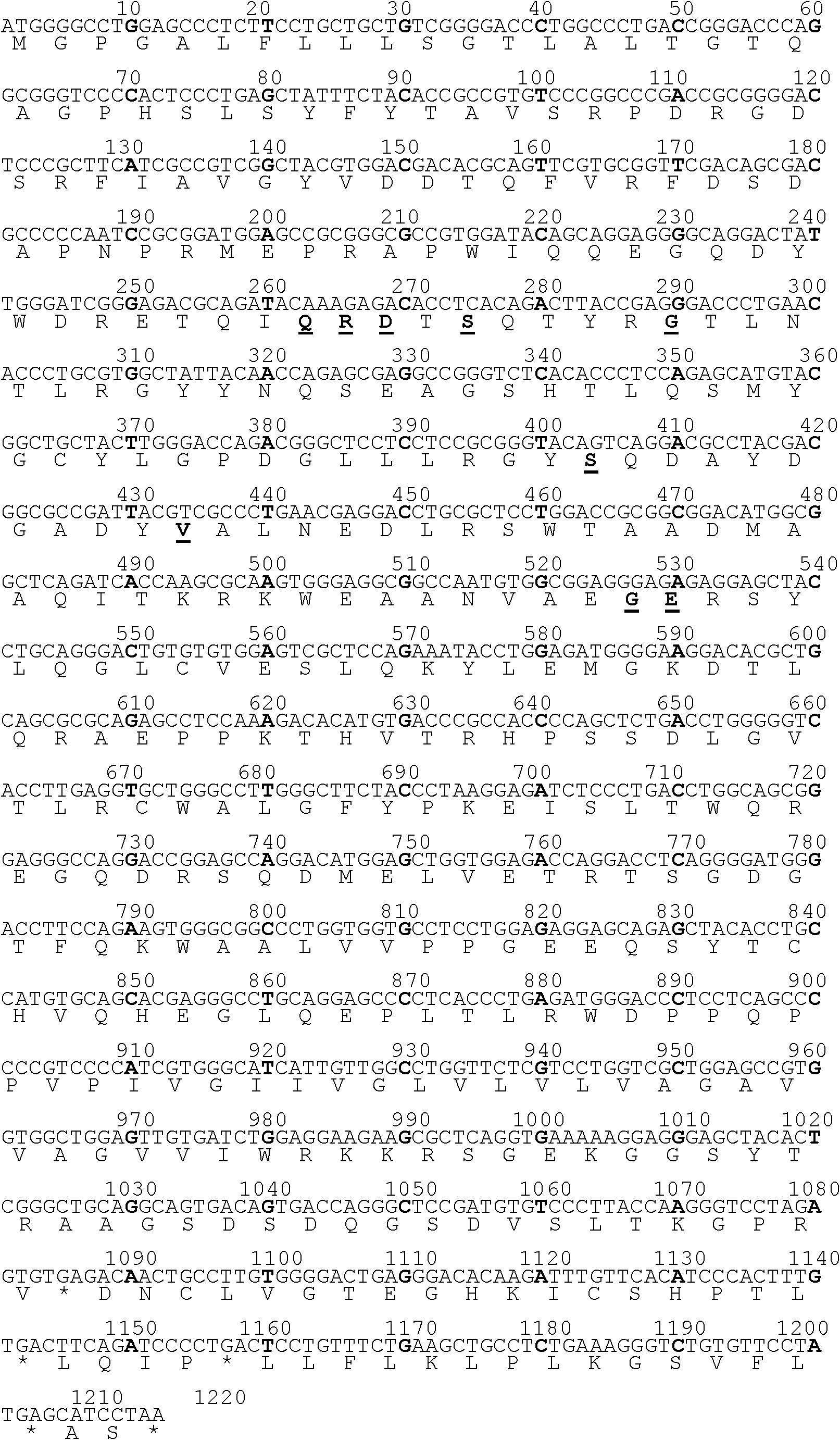Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
75 results about "Molecular evolution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Molecular evolution is the process of change in the sequence composition of cellular molecules such as DNA, RNA, and proteins across generations. The field of molecular evolution uses principles of evolutionary biology and population genetics to explain patterns in these changes. Major topics in molecular evolution concern the rates and impacts of single nucleotide changes, neutral evolution vs. natural selection, origins of new genes, the genetic nature of complex traits, the genetic basis of speciation, evolution of development, and ways that evolutionary forces influence genomic and phenotypic changes.
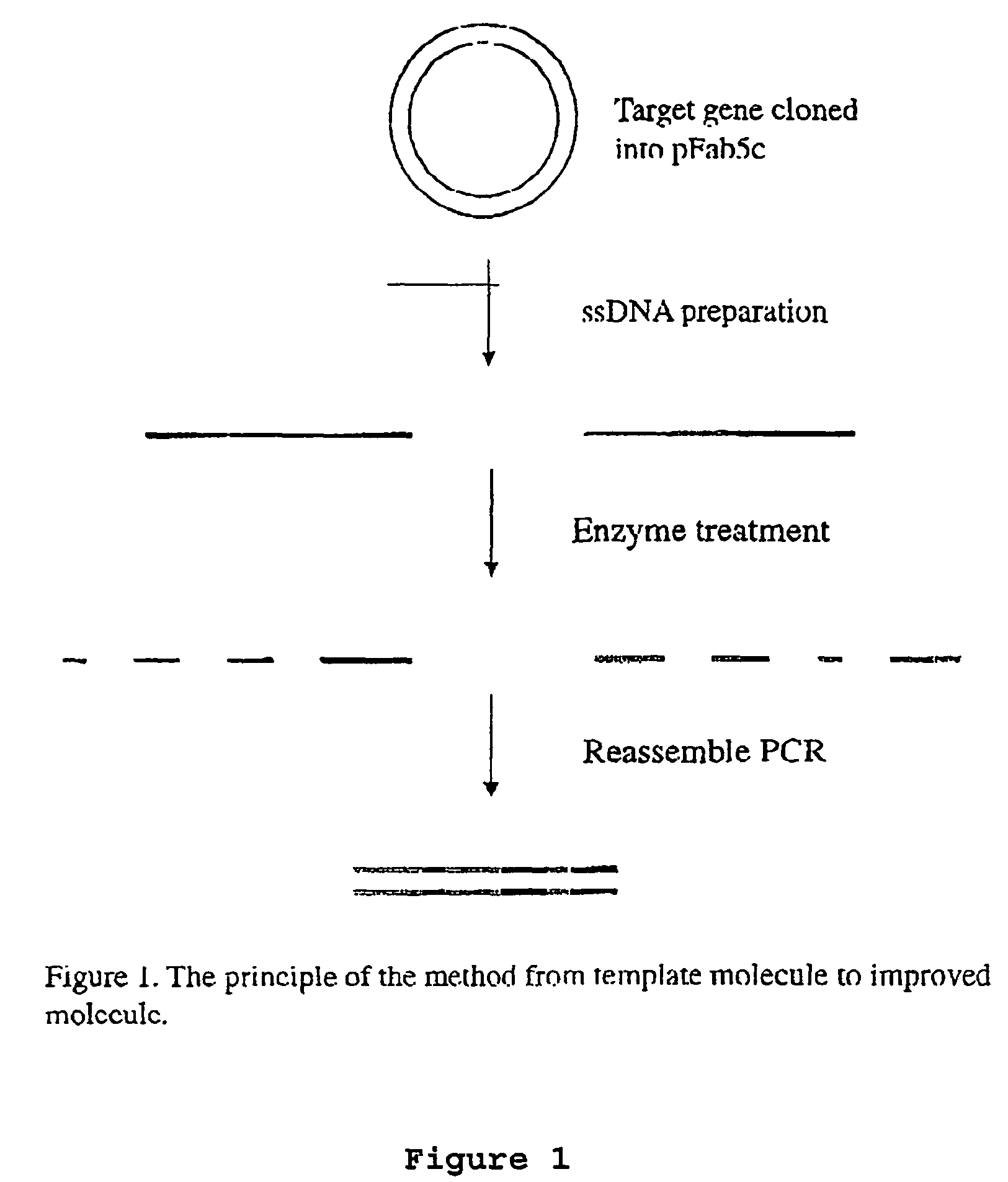
Method for in vitro molecular evolution of protein function
InactiveUS6989250B2Altered propertyIncreased complexitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideIn vivo
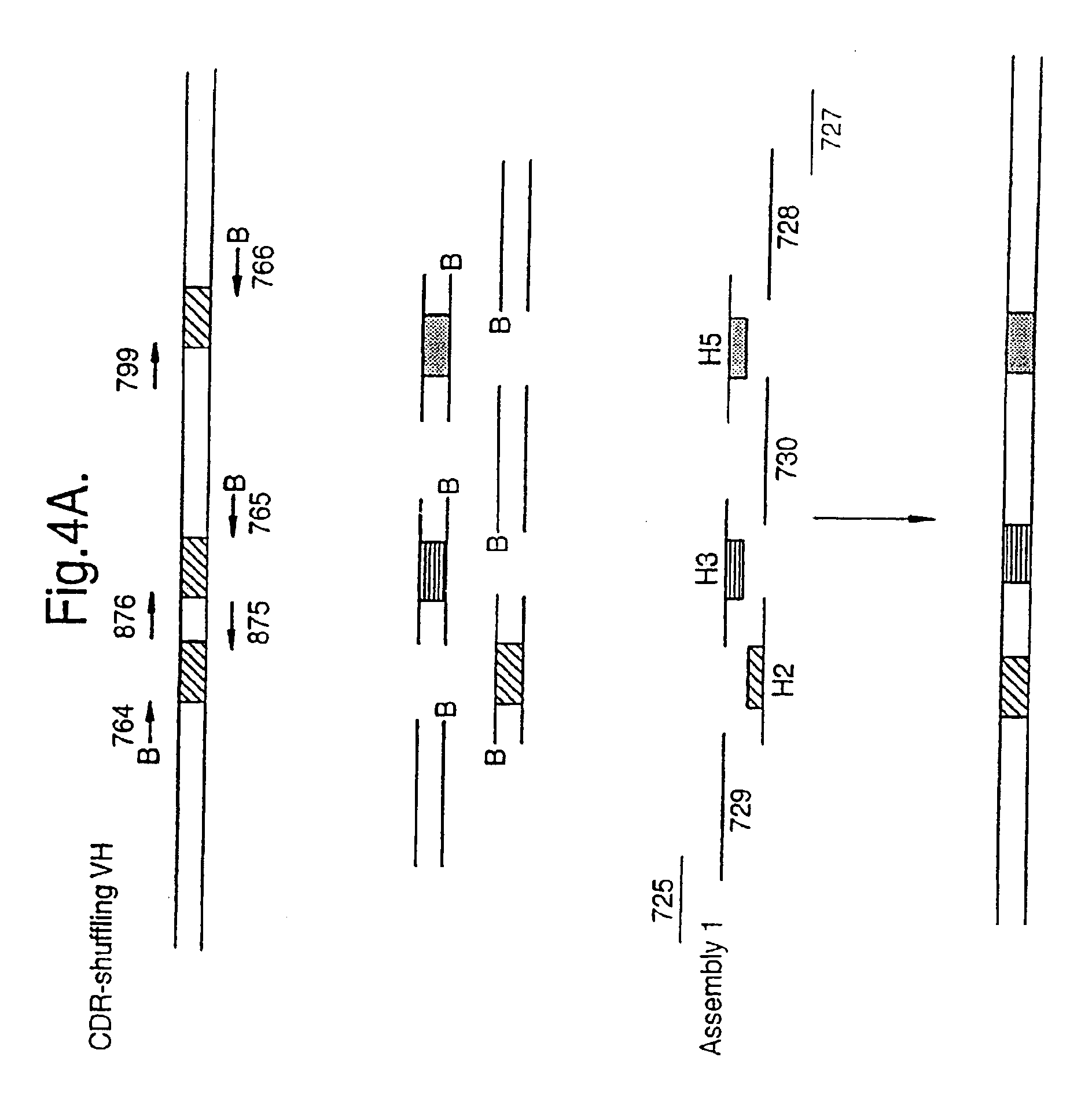
The present invention relates to a method for in vitro creation of molecular libraries evolution of protein function. Particularly, it relates to variability and modification of protein function by shuffling polynucleotide sequence segments. A protein of desired characteristics can be obtained by incorporating variant peptide regions (variant motifs) into defined peptide regions (scaffold sequence). The variant motifs can be obtained from parent DNA which has been subjected to mutagenesis to create a plurality of differently mutated derivatives thereof or they can be obtained from in vivo sequences. These variant motifs can then be incorporated into a scaffold sequence and the resulting coded protein screened for desired characteristics. This method is ideally used for obtaining antibodies with desired characteristics by isolating individual CDR DNA sequences and incorporating them into a scaffold which may, for example, be from a totally different antibody.
Owner:BIOINVENT INT AB
Diagnostic sequencing by a combination of specific cleavage and mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20060252061A1Rapid and reliableQuick fixMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseSomatic cell
The present invention is in the field of nucleic acid-based diagnostic assays. More particularly, it relates to methods useful for the "diagnostic sequencing" of regions of sample nucleic acids for which a prototypic or reference sequence is already available (also referred to as "re-sequencing"), or which may be determined using the methods described herein. This diagnostic technology is useful in areas that require such re-sequencing in a rapid and reliable way: (i) the identification of the various allelic sequences of a certain region / gene, (ii) the scoring of disease-associated mutations. (iii) the detection of somatic variations, (iv) studies in the field of molecular evolution, (v) the determination of the nucleic acid sequences of prokaryotic and eukaryotic genomes; (vi) identifying one or more nucleic acids in one or more biological samples; (vii) and determining the expression profile of genes in a biological sample and other areas.
Owner:AGENA BIOSCI
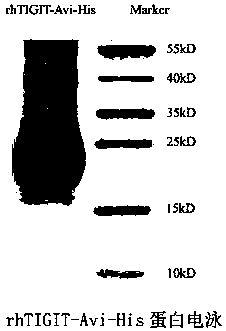
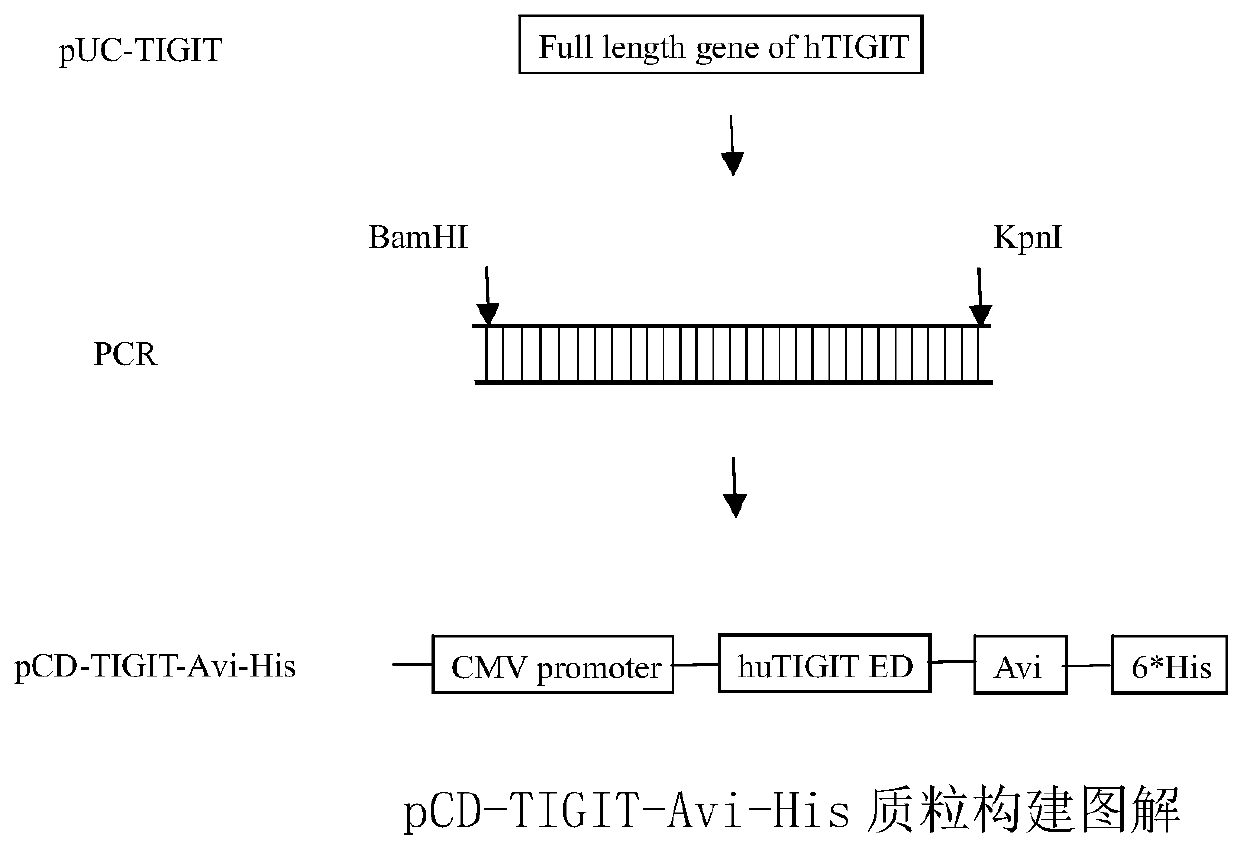
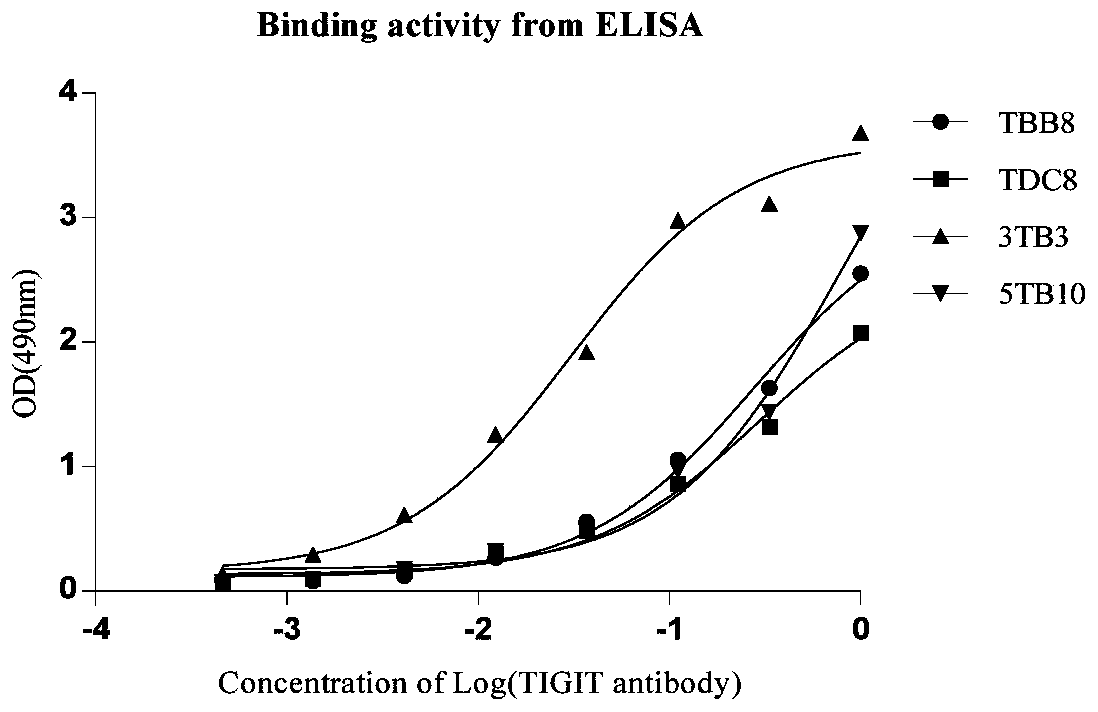
Full-human huTIGIT monoclonal antibody and application thereof
The invention relates to an anti-human TIGIT monoclonal antibody which is particularly related to high-affinity anti-human TIGIT monoclonal antibody with blocking activity. A large-capacity fully-synthetic human phage antibody library is constructed, the specific anti-human TIGIT monoclonal antibody and the high-affinity anti-human TIGIT monoclonal antibody which is optimized after molecular evolution are screened from the human phage antibody library, and the monoclonal antibody comprises a full-human frame region and variable regions of a full-human light chain and a heavy chain.
Owner:ANHUI ANKE BIOTECHNOLOGY (GRP) CO LTD
Separation identification and purification process for chicken source H9N2 avian influenza virus strain and uses thereof
The invention relates to the field of animal virology, and provides separation identification and purification methods, biological characteristics and applications in biology of a recombinant fowl H9N2 avian influenza virus strain with preservation number being CCTCC NO:V200811; the differences between the virus and other separation strains are explained in term of molecular level; and the virus strain is proved to be capable of being used as candidate strain of avian influenza vaccines and as antigen of H9 subtype AIV hemoagglutination and hemoagglutination inhibition test (HA-HI). The strain has significance in knowing the molecular evolution and antigenic variation of fowl H9N2 avian influenza virus in China.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY MEDICINE SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Separation identification and purification process for chicken source H9N2 avian influenza virus strain and uses thereof
The invention relates to the field of animal virology, and provides separation identification and purification methods, biological characteristics and applications in biology of a recombinant fowl H9N2 avian influenza virus strain with preservation number being CCTCC NO:V200812; the differences between the virus and other separation strains are explained in term of molecular level; and the virus strain is proved to be capable of being used as candidate strain of avian influenza vaccines and as antigen of H9 subtype AIV hemoagglutination and hemoagglutination inhibition test (HA-HI). The strain has significance in knowing the molecular evolution and antigenic variation of fowl H9N2 avian influenza virus in China.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY MEDICINE SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
7beta-hydroxysterol dehydrogenase mutant and application of 7beta-hydroxysterol dehydrogenase mutant in ursodeoxycholic acid synthesis
ActiveCN107099516AEasy to separate and extractOvercoming the problem of inactivation processingOxidoreductasesGenetic engineeringChenodeoxycholic acidSubstrate concentration
The invention discloses a 7beta-hydroxysterol dehydrogenase mutant with increased activity and stability which is obtained through molecular evolution, recombinant expression plasmid containing the 7beta-hydroxysterol dehydrogenase mutant gene and a recombinant expression transformant and a preparation method of a recombinant mutant enzyme preparation, and the invention also provides an application of the recombinant mutant enzyme preparation in ursodeoxycholic acid synthesis. The 7beta-hydroxysterol dehydrogenase has excellent activity and heat stability, can efficiently catalyze asymmetric reduction of 7-carbonyl lithocholic acid to prepare the ursodeoxycholic acid; the 7beta-hydroxysterol dehydrogenase is subjected to immobilization and then is subjected to couple by an enzyme method with the immobilized 7beta-hydroxysterol dehydrogenase, epimerization of a substrate chenodeoxycholic acid with low cost can be directly catalyzed, ursodeoxycholic acid can be prepared through continuous conversion, and the operation is simple. Compared with the prior art reported currently, ursodeoxycholic acid prepared by hydroxysterol dehydrogenase through catalysis has the advantages of high substrate concentration, short reaction time, complete reaction, and high product purity, and has strong industrial application prospect.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Reagent kit for extracting DNA in Chinese alligator chorion film and use method thereof
InactiveCN101368179AHigh purityIncrease concentrationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationHigh concentrationChinese alligator
The invention discloses a kit for extracting DNA in the egg shell membrane of Yangtze alligator and a use method thereof, and the kit comprises the following reagents: a reagent A, a reagent B, a reagent C, a reagent D, a reagent E and a reagent F. The template DNA which is extracted by the kit has good purity, and the kit can be used for gene amplification sequencing and typing. In the amplification of the 12S rRNA gene, the mitochondrial D-loop region and the Cyt b gene, all the extracted shell membrane DNA templates can be successfully amplified to obtain the fragment products with expected identical sizes, high concentration and high specificity. Microsatellite DNA marker specificity primers are utilized to obtain typing data through the PCR amplification to be used for the identification in disputed paternity of Yangtze alligator. In addition, the method also can be applied to the extraction of other ovipara such as the turtles, the birds and the like. The obtained template DNA can be widely applied to the studies of the ovipara on the fields such as population genetic analysis, molecular evolution, evolution of relationship among individuals and the like.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
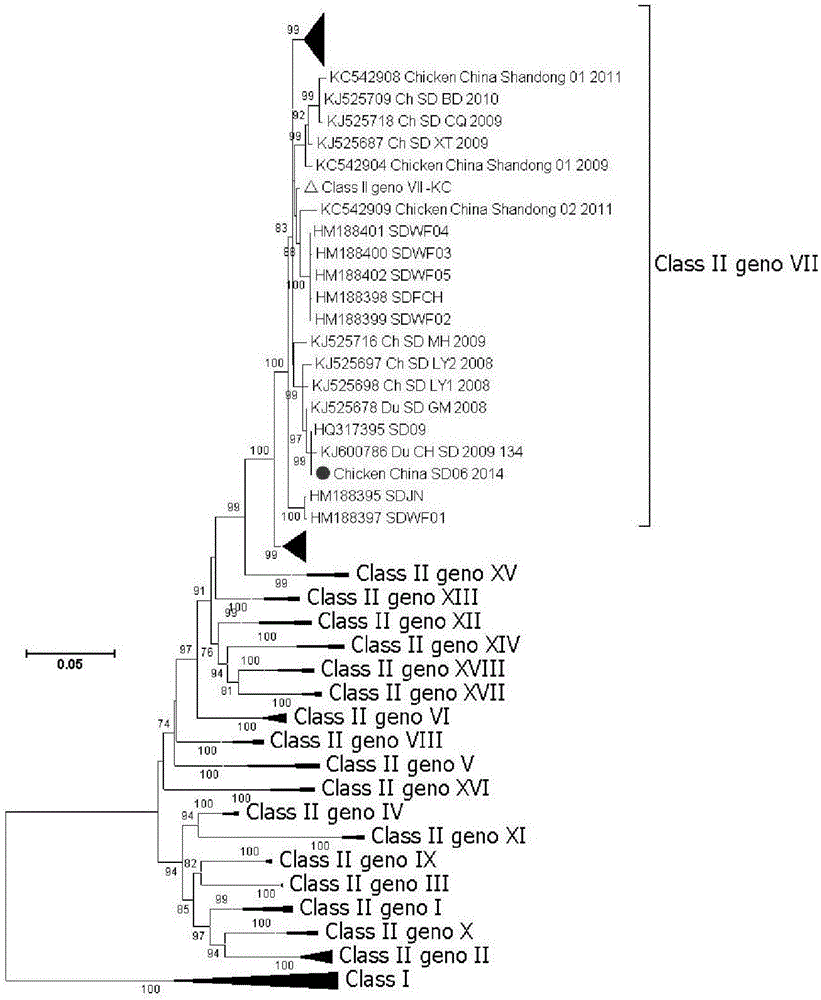
Isolation, identification and purification method and application of gene VII type Newcastle disease virus strain
InactiveCN105543180ASsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsMolecular evolutionAntibody
The invention relates to the field of animal virology, provides an isolation, identification and purification method and application of a gene VII type Newcastle disease virus strain, and particularly provides a gene VII type (Class II) Newcastle disease virus strain Chicken / China / SD06 / 2014, an isolation, identification and purification method of the strain and part of biological properties of the strain. The preservation number of the strain is CCTCC NO: V201544. The phyletic evolution and protein variation conditions of the strain are analyzed so as to confirm the feasibility that the strain serves as a candidate Newcastle disease vaccine strain and an HA-HI experiment antibody, and thus data is provided for molecular evolution and epidemiologic study of the Newcastle disease virus.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY MEDICINE SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Diagnostic sequencing by a combination of specific cleavage and mass spectrometry
InactiveUS6994969B1Rapid and reliableQuick fixSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseMass spectrometry imaging
The present invention is in the field of nucleic acid-based diagnostic assays. More particularly, it relates to methods useful for the “diagnostic sequencing” of regions of sample nucleic acids for which a prototypic or reference sequence is already available (also referred to as “re-sequencing”), or which may be determined using the methods described herein. This diagnostic technology is useful in areas that require such re-sequencing in a rapid and reliable way: (i) the identification of the various allelic sequences of a certain region / gene, (ii) the scoring of disease-associated mutations, (iii) the detection of somatic variations, (iv) studies in the field of molecular evolution, (v) the determination of the nucleic acid sequences of prokaryotic and eukaryotic genomes, (vi) identifying one or more nucleic acids in one or more biological samples', (vii) and determining the expression profile of genes in a biological sample and other areas.
Owner:AGENA BIOSCI
Method for in vitro molecular evolution of protein function
InactiveUS6958213B2Provide effectSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNegative strandNucleotide
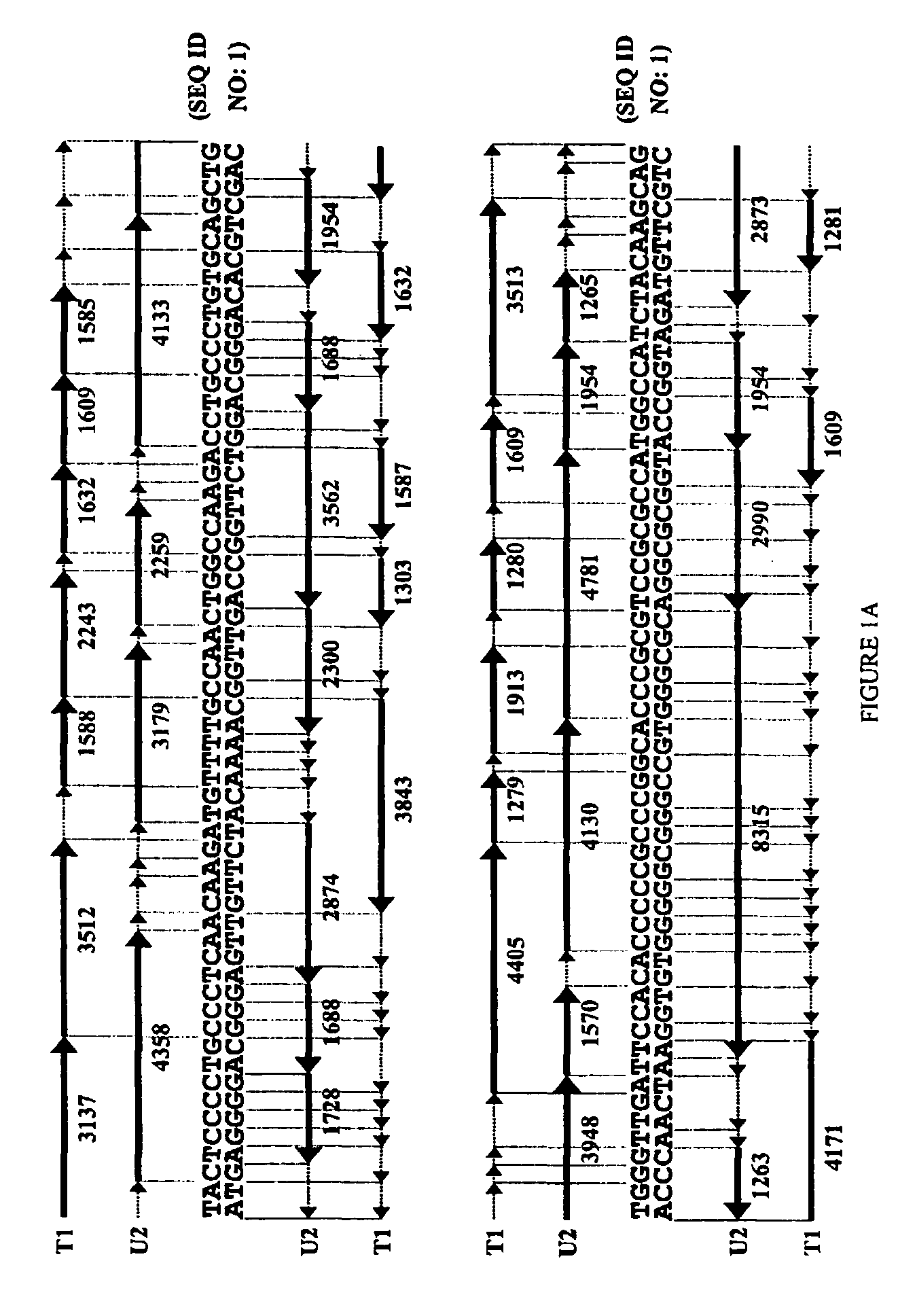
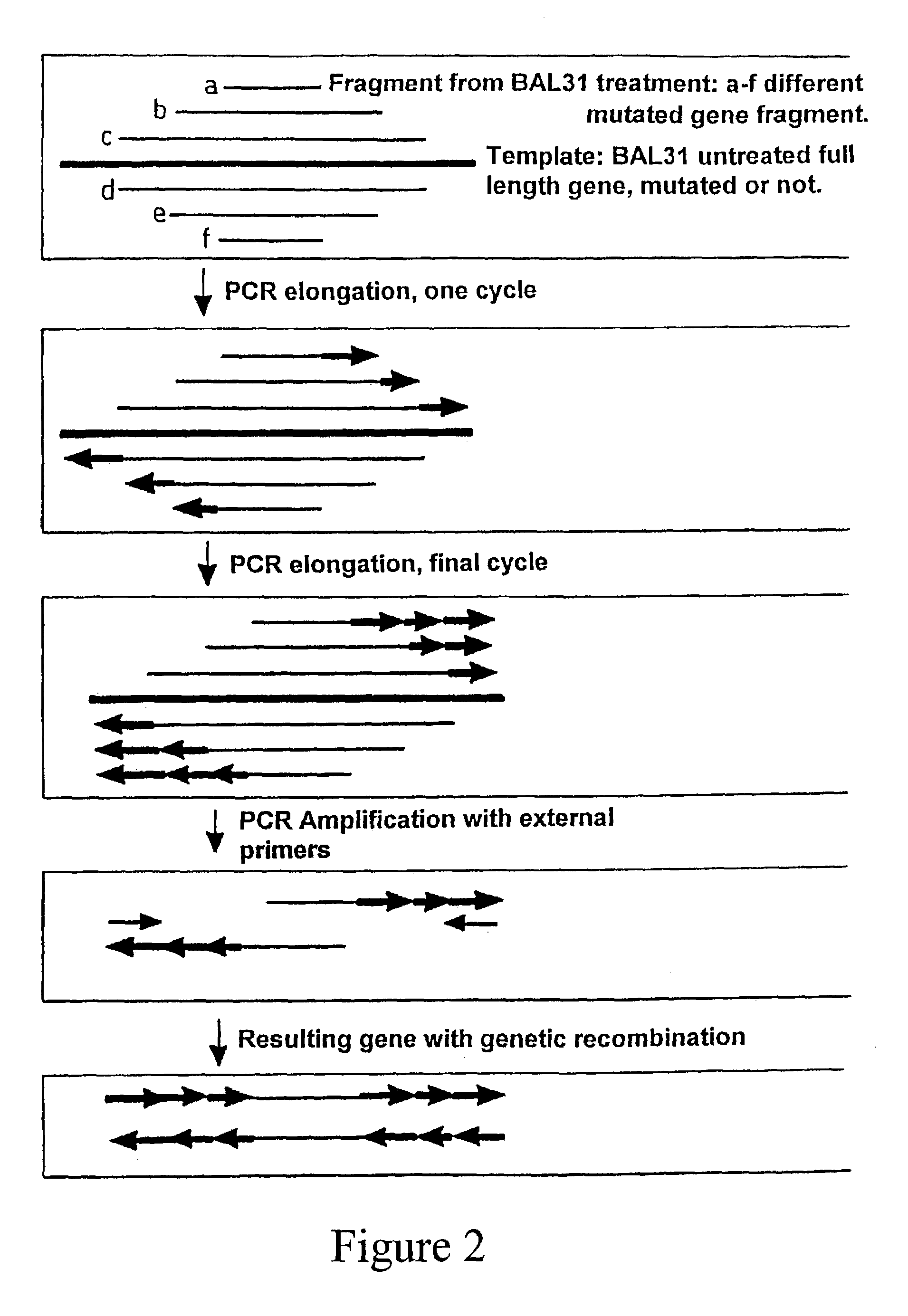
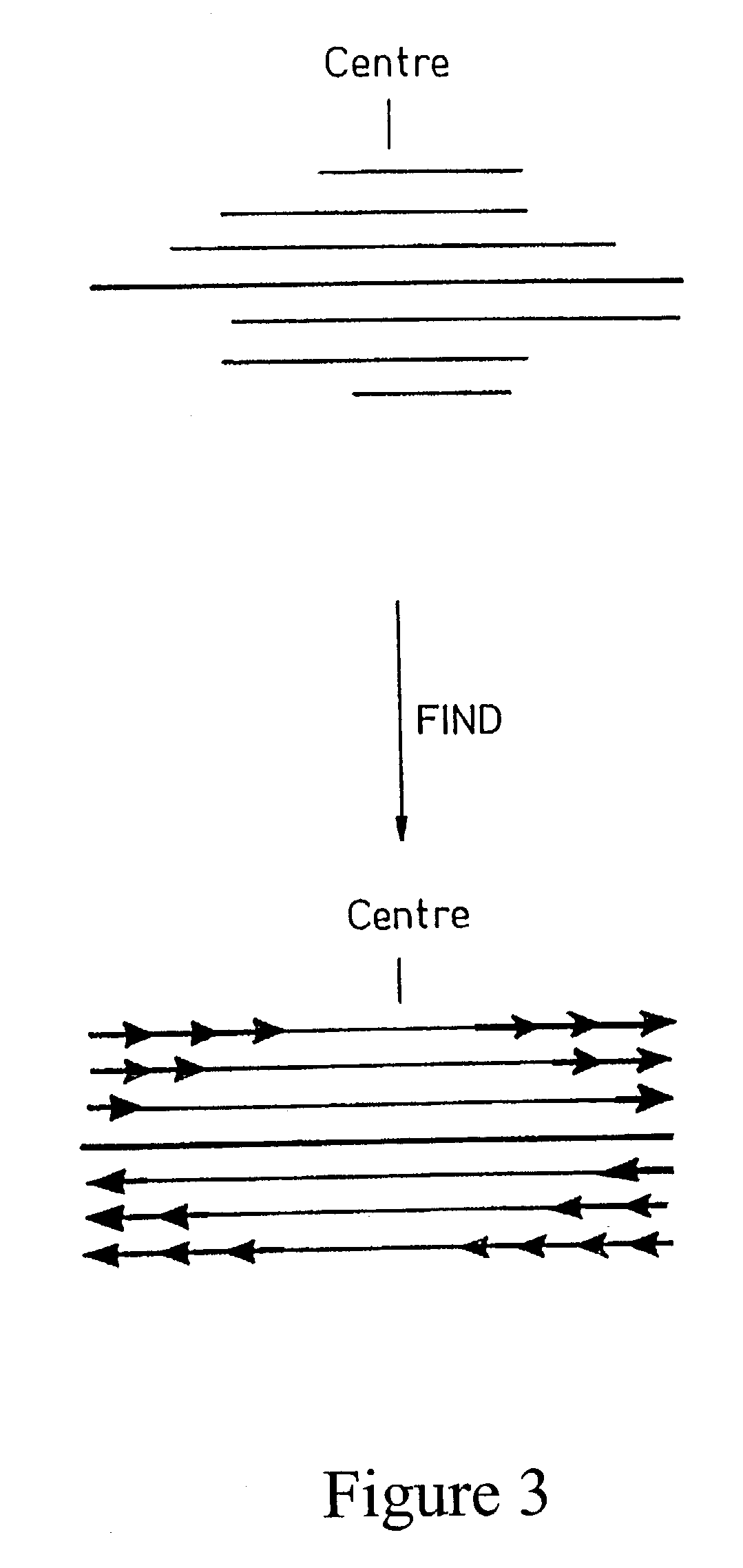
The invention provides a method for generating a polynucleotide sequence or population of sequences from parent single stranded polynucleotide sequences encoding one or more protein motifs, comprising the steps of(a) providing single stranded DNA constituting plus and minus strands of parent polynucleotide sequences;(b) digesting the single stranded polynucleotide sequences with a nuclease other than DNase I to generate populations of single stranded fragments;(c) contacting said fragments generated from the plus strands with fragments generated from the minus strands and optionally, adding primer sequences that anneal to the 3′ and 5′ ends of at least one of the parent polynucleotides under annealing conditions;(d) amplifying the fragments that anneal to each other to generate at least one polynucleotide sequence encoding one or more protein motifs having altered characteristics as compared to the one or more protein motifs encoded by said parent polynucleotides.
Owner:ALLIGATOR BIOSCI
Method for in vitro molecular evolution of protein function involving the use of exonuclease enzyme and two populations of parent polynucleotide sequence
InactiveUS7153655B2Good effectLonger effectMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleotideADAMTS Proteins
The present invention relates to a method for in vitro evolution of protein function. In particular, the method relates to the shuffling of nucleotide segments obtained from exonuclease digestion. The present inventors have shown that polynucleotide fragments derived from a parent polynucleotide sequence digested with an exonuclease can be combined to generate a polynucleotide sequence which encodes for a polypeptide having desired characteristics. This method may be usefully applied to the generation of new proteins (e.g., antibodies and enzymes) or parts thereof having modified characteristics as compared to the parent protein.
Owner:ALLIGATOR BIOSCI
Kit used for paternity test of giant pandas
InactiveCN101948919AAccurate Paternity TestAccurate Genetic MonitoringMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologySpecies groups
The invention discloses a kit used for a paternity test of giant pandas. 68 allelic genes of 11 STR gene loci, obtained by microsatellite study, of the giant pandas are taken as typing standard substances, and parameters of annealing temperature and magnesium ion concentration in a PCR process of the STR gene loci are optimized, wherein the typing standard substances correspond to the allelic genes of the gene loci one by one, so that the microsatellite typing can be performed accurately. The kit of the invention can perform the paternity test and genetic monitoring accurately on species groups of captive giant pandas, complete genealogy, reorganize blood relationship and provide very useful molecular markers for the study in the aspects such as the molecular evolution of the giant pandas, the population migration and the behavioral ecology of wild giant pandas and the like in future, and has very significant theoretical and practical significance on the formulation and implementation of the conservation and breeding plans of rare species.
Owner:CHENGDU RES BASE OF GIANT PANDA BREEDING
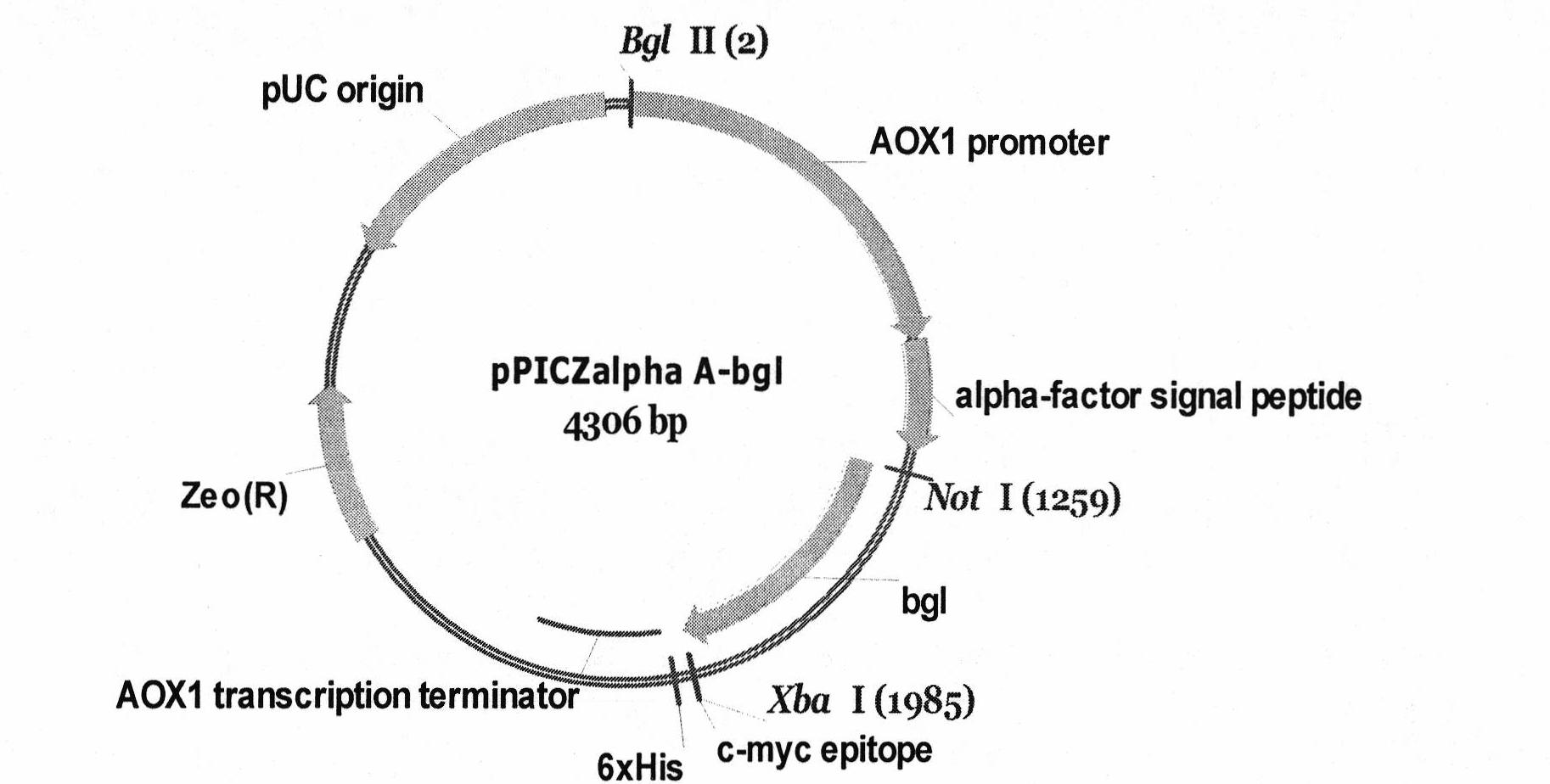
High-yield and temperature-resistant beta-dextranase pichia pastoris and construction thereof
The invention discloses a pichia pastoris recombinant strain and application thereof in the field of gene engineering. The research room performs directed evolution with improved thermal stability on bacillus amyloliquefaciens producing beta-1,3-1,4-glucanase gene by in-vitro molecular evolution technology to obtain a plurality of mutants with improved thermal stability. In the invention, a beta-1,3-1,4-glucanase gene bg1 with most obviously improved thermal stability is expressed in a pichia pastoris system for the first time. The gene is cloned to a pichia pastoris expression vector pPICZalphaA and constructed to AOX I methanol inducible promoter downstream to obtain recombinant plasmid pPICZalphaA-his6-bg1; the recombinant plasmid is subjected to Pme I linearization to transform pichia pastoris GS115; and the bg1 gene is integrated on the pichia pastoris chromosome through homologous recombination and positioned on the downstream of yeast alpha-factor to realize heterogenous secretion expression. By optimizing the culture condition of the recombinant strain, the optimal expression conditions of the beta-1,3-1,4-glucanase are that the pH is 7.0, OD600 is 2.5, the daily induced addition amount of methanol is 1 percent and the culture time of the strain after the methanol induction is 2.5 to 3 days. The protein expression level for secreting the beta-glucanase to a culture medium under the condition is 190mg / L, and the specific activity of one milligram of protein reaches 4,312U. SDS-PAGE result shows that the size of the expressed protein is about 27KDa and matches with the size of theoretical molecular weight.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Rapid detection card for detecting pesticide residues, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102399850AHigh activityImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementPesticide residueAcetylcholinesterase
The invention relates to a rapid detection card for detecting pesticide residues, a preparation method and application thereof. The fast detection card comprises a coverage film, a first plastic board, sample loading holes, an enzyme tablet, a plastic film, a second plastic board and a substrate sheet, wherein the coverage film is adhered to the surface of the first plastic board; at least two sample loading holes are formed in the first plastic board; the enzyme tablet fixed with housefly acetylcholinesterase is adhered to the reverse sides of the sample loading holes and is opposite to the sample loading holes; the substrate sheet, which is fixed with acetyl indophenol and is adhered to the position corresponding to the enzyme tablet, is arranged on the second plastic board; and the plastic film is arranged in the middles of the first plastic board and the second plastic board. In the rapid detection card, enzyme is the housefly acetylcholinesterase which is subjected to molecular evolution, so the rapid detection card has the advantages of high activity, high sensitivity, high stability and the like and can be applied to the rapid detection of organophosphorus and carbamic acid ester pesticide residues in agricultural products, food and soil and particularly vegetables, fruits.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Human anti-human VEGF monoclonal antibody molecule and application thereof
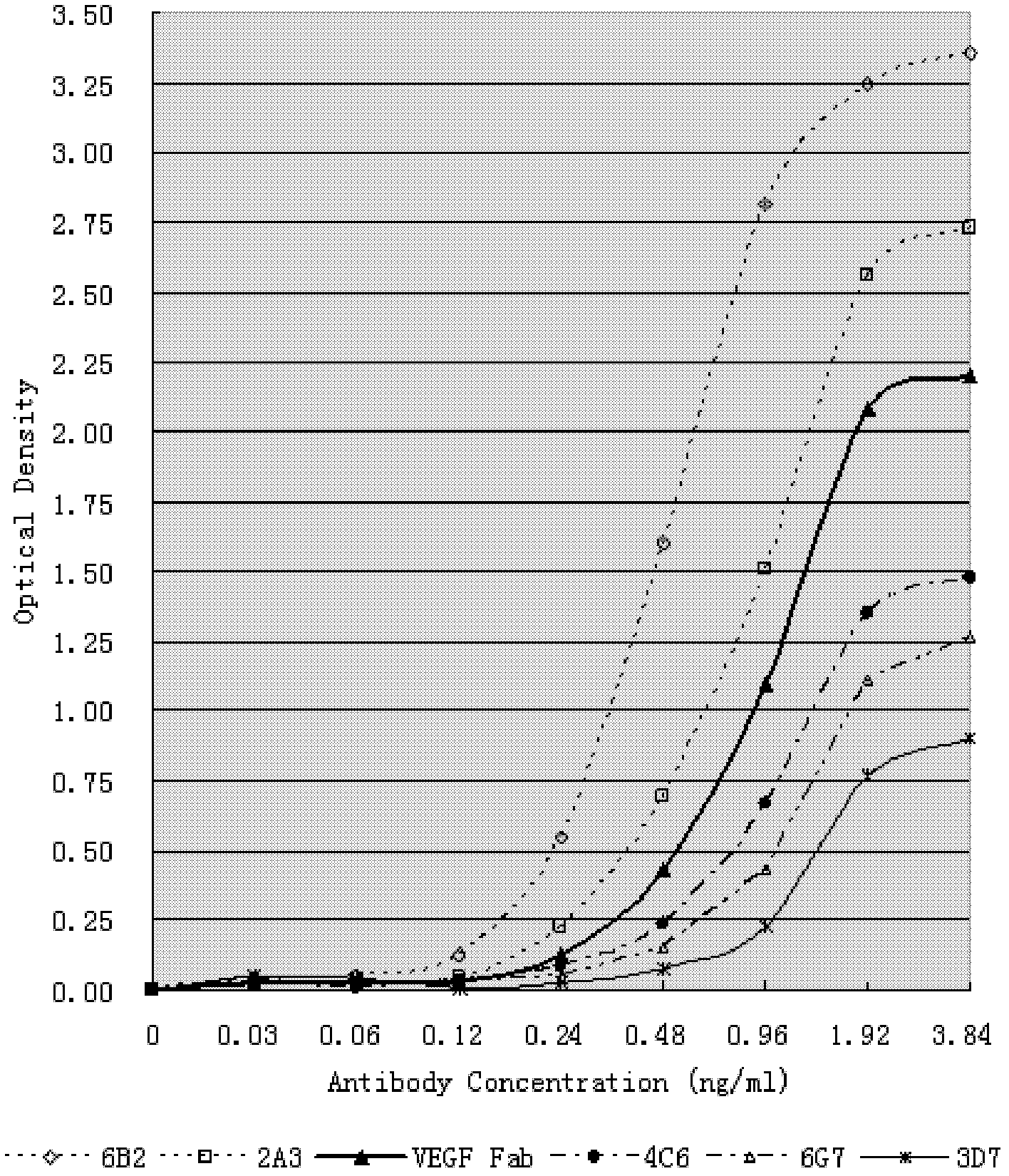
The invention relates to an anti-human VEGF monoclonal antibody and a coding nucleic acid sequence thereof, and especially relates to an anti-human VEGF monoclonal antibody having a high affinity and a low dissociation rate. The preferable anti-human VEGF monoclonal antibody comprises a human Fc region, a framework region, and a human light-chain and / or heavy-chain variable region obtained through molecular evolution. The invention also discloses medicinal compositions composed of the human antibody, an application of the human antibody in human disease treatment, and a method for using the human antibody in the treatment.
Owner:DANYANG ZHENGYUAN BIOTECH
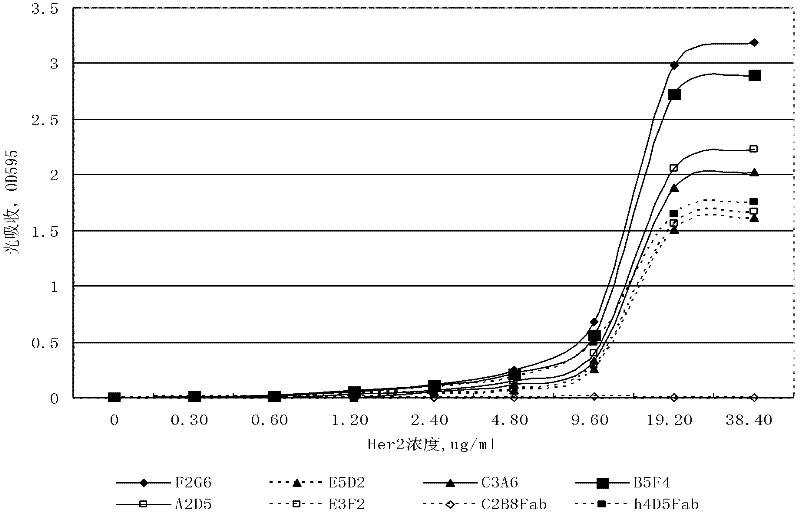
Fully humanized antihuman HER2 monoclonal antibody
The invention relates to a fully humanized antihuman HER2 monoclonal antibody, particularly an antihuman HER2 monoclonal antibody having high affinity and low dissociation rate. The antihuman HER2 monoclonal antibody preferred by the invention comprises a fully humanized Fc region, a framework region, and a CDR region of a fully humanized light chain and / or heavy chain, wherein the CDR region is obtained by molecular evolution. The invention also discloses an application of a medicine composition consisting of the antihuman HER2 monoclonal antibody in treating human diseases and a method for using the antihuman HER2 monoclonal antibody in treatment.
Owner:广州誉嘉生物科技有限公司
Method for screening and quantifying various enzyme activities using a genetic enzyme screening system
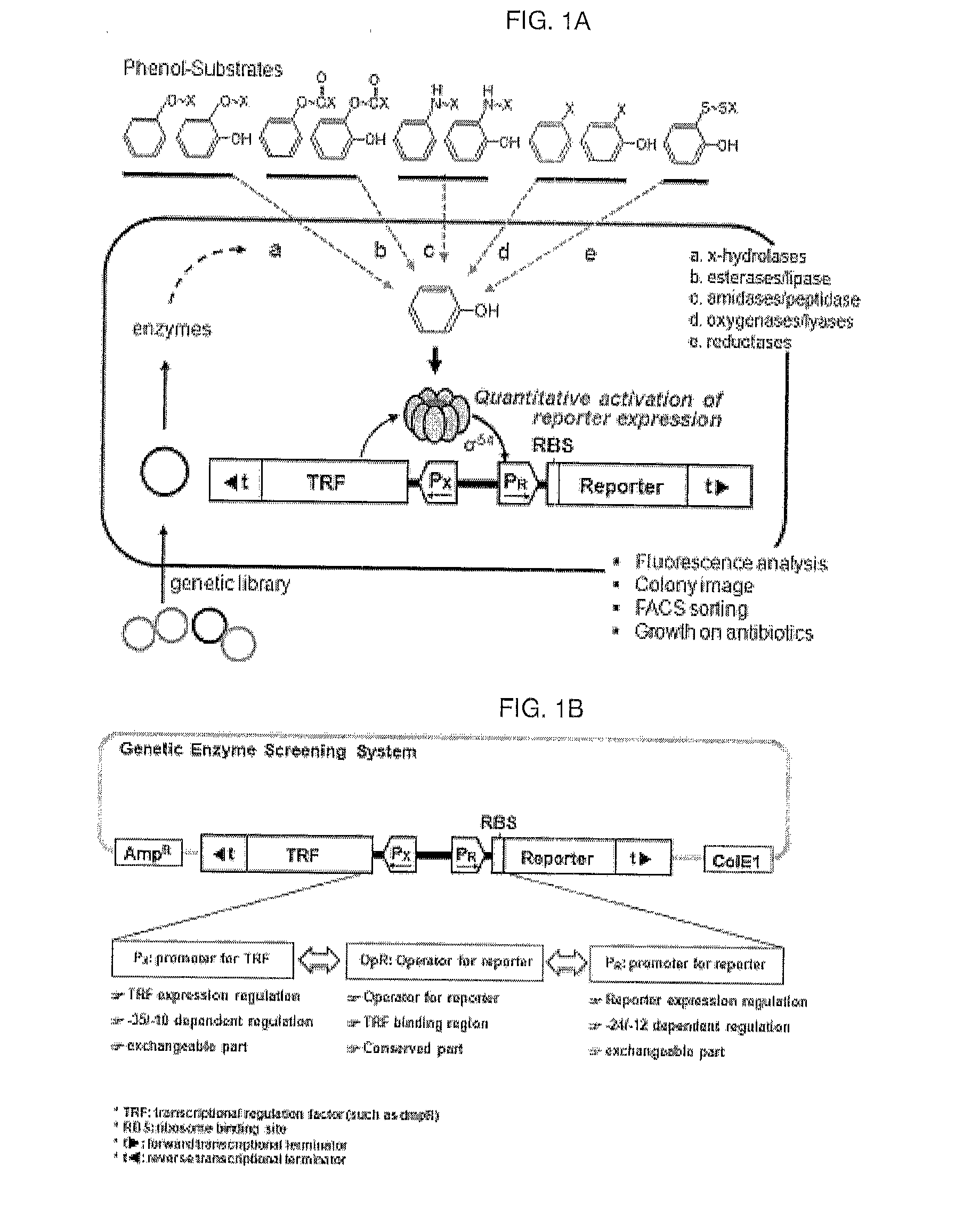
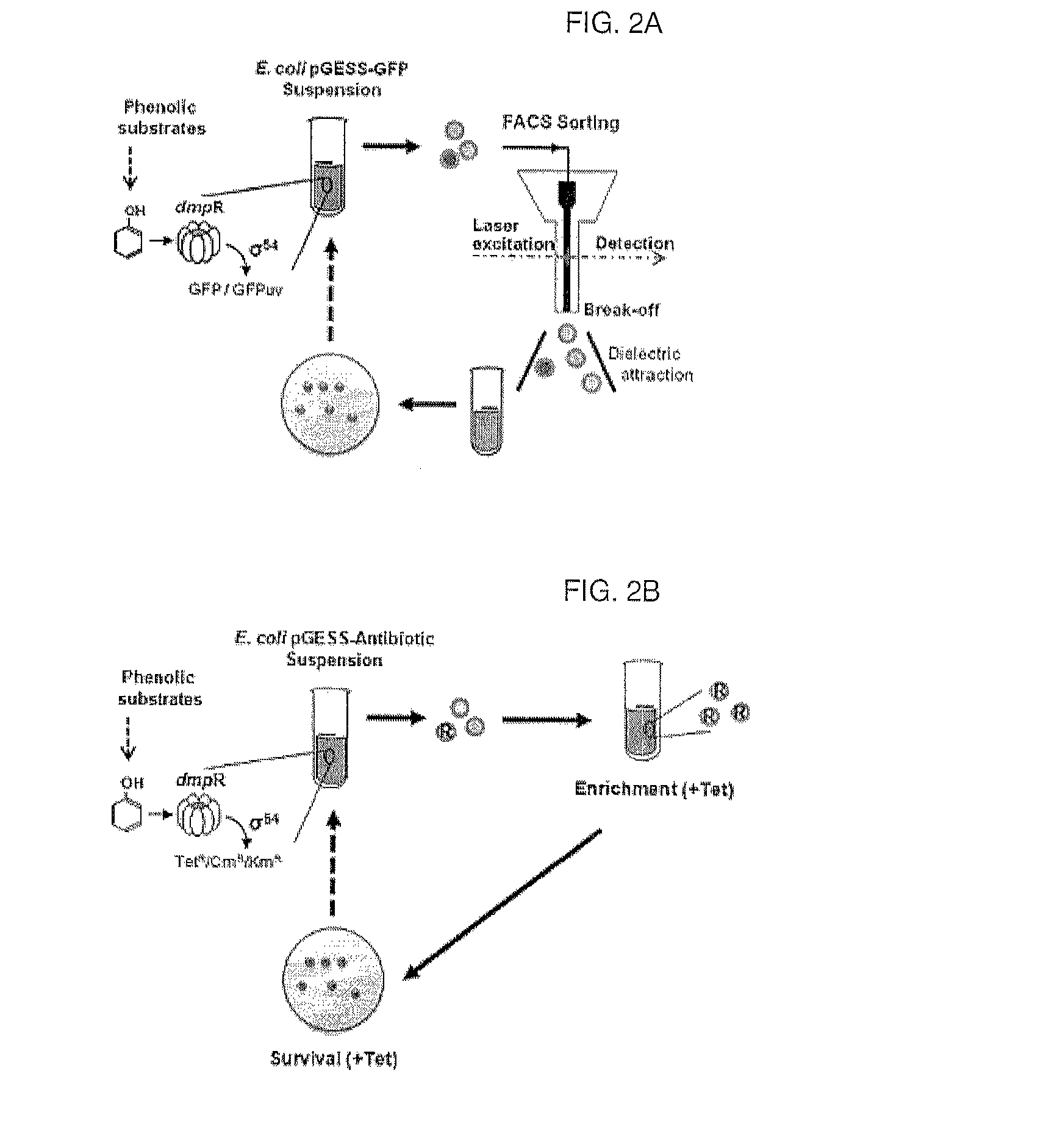
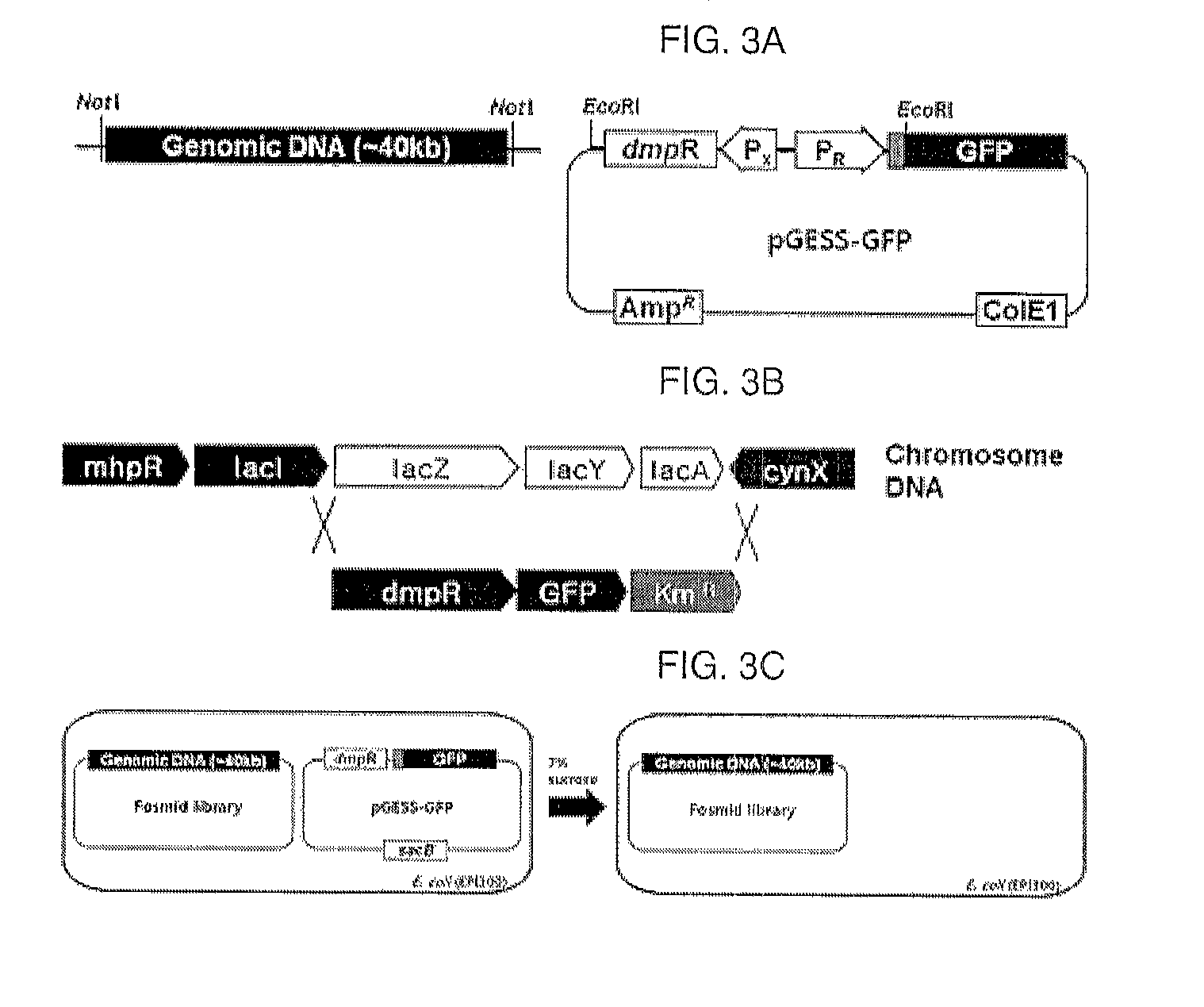
A method of detecting and quantifying various enzymatic activities using a constructed artificial genetic circuit GESS (genetic enzyme screening system) for sensing phenolic compounds and a method of screening a trace of activities of target enzymes from a metagenome using the artificial genetic circuit, thereby securing target enzyme genes. When the method for screening and quantifying target enzymatic activity is used, useful genes can be screened from various genetic communities, including environmental or metagenomic libraries, at a single cell level in high throughput (million / day). Further, the sensitivity of the genetic circuit to phenol derivatives and the expression thereof can be controlled, and thus the genetic circuit can rapidly sense and quantify various enzymatic activities. Thus, the method can be advantageously used in the protein engineering technology for enzyme modification. Particularly, it can quantitatively investigate enzymatic activity, and thus can be applied to molecular evolution technology.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF BIOSCI & BIOTECH
Method for in vitro molecular evolution of protein function
Owner:ALLIGATOR BIOSCI
Family shuffling technology system for improvement of multiple genes related to phytase
The invention relates to a system for modifying phytase through synthesis of a plurality of related phytase genes and combination of in vitro oriented molecular evolution. In the system, four different types of phytase genes are designed and synthesized according to methanol yeast favored codon, and a plurality of genes participate in family shuffling, so the system can obtain mutation potential which is larger than single-gene shuffling and mutation, and develops oriented molecular evolution research of the phytase and promotes the marketization process of the phytase in China through gene family shuffling and a high-flux screening system. The phytase can promote utilization of animal nutritive materials and reduce phosphorus emission, and has large potential in reducing environmental pollution, and large ecological benefit.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Pfu DNA polymerase and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106011100AHigh sensitivityImprove anti-interference abilityTransferasesFermentationInterference resistanceProkaryotic expression
The invention provides a Pfu DNA polymerase and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises constructing a Fast Pfu DNA polymerase prokaryotic expression vector, constructing an expression strain, inoculating a medium with the strain, carrying out induced expression, collecting bacteria, breaking the bacteria and carrying out purification to obtain the Pfu DNA polymerase. The preparation method utilizes a molecular evolution technology to reconstruct a common Pfu enzyme, prepares the novel Fast Pfu polymerase, has the characteristics of fast rate, high sensitivity and high interference resistance and is a novel high-fidelity DNA polymerase.
Owner:NOVOPROTEIN SCI INC
Human anti-human CD20 monoclonal antibody molecule and application thereof
The invention relates to an anti-human monoclonal antibody and a coding nucleic acid sequence thereof, and especially relates to an anti-human CD20 monoclonal antibody having a high affinity and a low dissociation rate. The preferable anti-human CD20 monoclonal antibody comprises a human Fc region, a framework region, and a human light-chain and / or heavy-chain variable region obtained through molecular evolution. The invention also discloses medicinal compositions composed of the human antibody, an application of the human antibody in human disease treatment, and a method for using the human antibody in the treatment.
Owner:广州市流式生物科技有限公司
Goose-array type localized random mutation method and application thereof in monoclonal antibody molecular evolution technology
InactiveCN102051396AAchieve evolutionAvoid the difficult problem of complex PCRImmunoglobulinsFermentationRandom mutationMonoclonal antibody
The invention discloses a goose-array type localized random mutation method and an application thereof in the monoclonal antibody molecular evolution technology. The goose-array type localized random mutation method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: designing a goose-array type primer of a target sequence of random mutation polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification, synthesizing the primer, mixing, and performing overlapping PCR to obtain the amplified sequence with random mutation in a designated area. The goose-array type localized random mutation method provided by the invention can be used in the monoclonal antibody molecular evolution. The invention further combines the key amino acid (KA) scanning, the goose-array type localized random mutation method and the phage display technology to provide a monoclonal antibody molecular evolution method. The mutation method provided by the invention is used in molecular evolution and has high speed, high success rate and wide application range.
Owner:DANYANG ZHENGYUAN BIOTECH
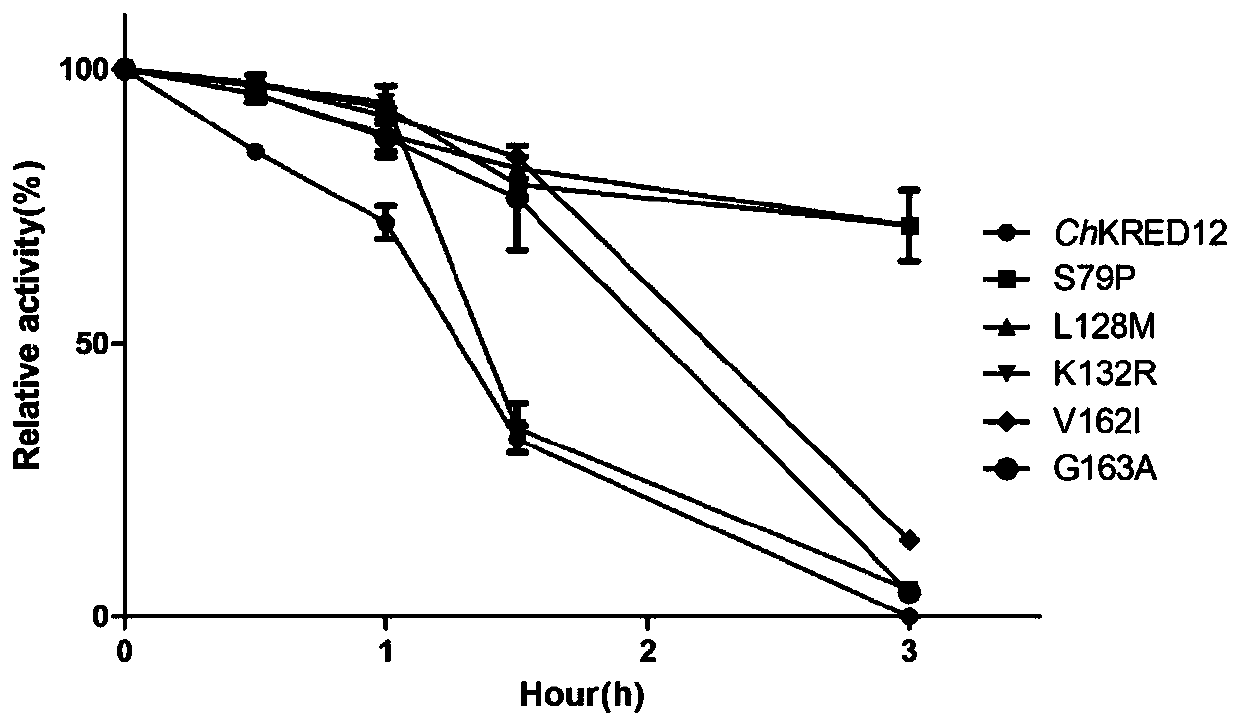
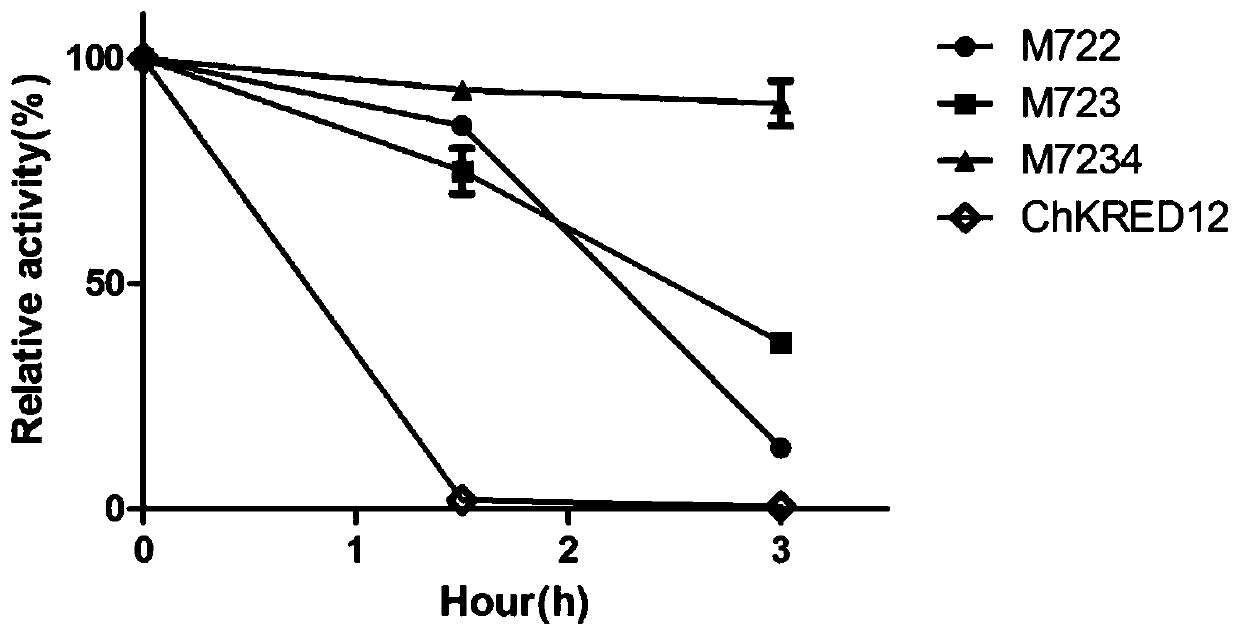
Carbonyl reductase mutant with improved thermal stability
ActiveCN109837254AActivity was not affectedIncrease flexibilityOxidoreductasesVector-based foreign material introductionAlcoholHeat resistance
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering, and particularly relates to a carbonyl reductase ChKRED12 heat-resistant mutant. The carbonyl reductase ChKRED12 can be used for efficiently catalytically preparing duloxetine chiral alcohol and other intermediates, but has relatively poor heat stability. By utilizing the rationally designed scheme, the enzyme can be subjected to molecular evolution, heat resistance of the mutant can be greatly improved, and industrial application can be favored.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Pouch pig SLA-1 gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a pouch pig SLA-1 gene and application thereof. The invention comprises cDNA amplification, sequencing and analysis of a pouch pig in characteristic species in China which comprises four SLA-1 alleles, wherein the four SLA-1 alleles have the following base sequences shown as SEQ ID NO: 1, SEQ ID NO: 2, SEQ ID NO: 3 and SEQ ID NO: 4. The gene sequences and gene molecular characteristics and a molecular evolution map obtained on the basis can be used for constructing a gene library of the pouch pig, identifying species of the pouch pig and guiding inheritance breeding of the pouch pig.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
Mutant human epidermal growth factor gene, protein, preparation methods for mutant human epidermal growth factor gene and protein, and application of mutant human epidermal growth factor gene and protein
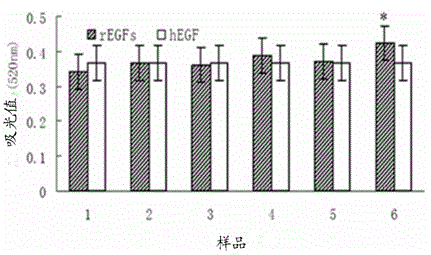
InactiveCN102719439AHigh activityReduce dosageCosmetic preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsMutated proteinNucleotide
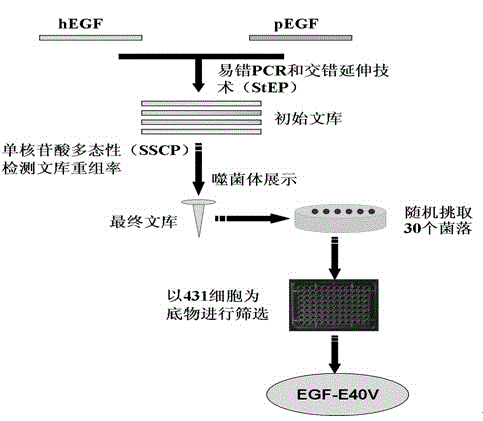
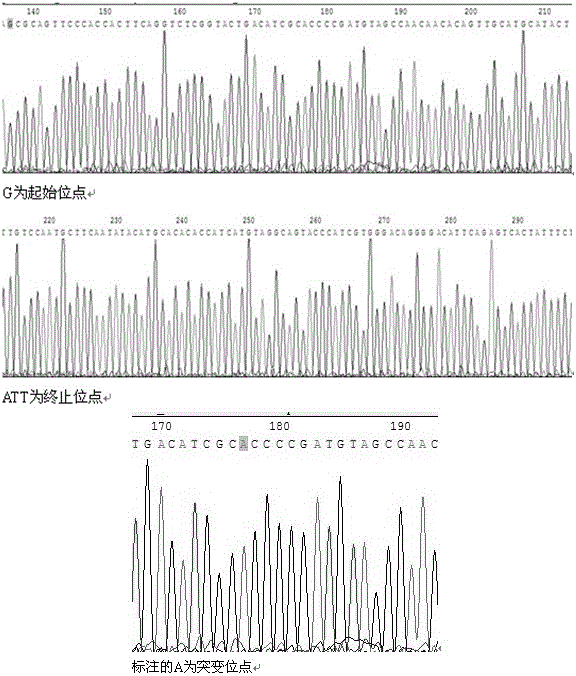
The invention discloses a mutant human epidermal growth factor (hEGF) gene, protein, preparation methods for the mutant human epidermal growth factor gene and the protein, and application of the mutant human epidermal growth factor gene and the protein, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The sequences of the mutant human epidermal growth factor gene and the protein are shown as SEQ ID NO:1 and SEQ ID NO:2 respectively. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) of an hEGF and a porcine epidermal growth factor (pEGF) are subjected to directed molecular evolution to construct an EGF directed evolution library by a method of the combination of error-prone polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and stagger extension process-PCR, and then the mutant human epidermal growth factor gene is screened. According to the sequence, A at 119th position of a nucleotide sequence of a wild EGF is mutated into T; Glu at 40th position of amino acid encoded by the wild EGF is mutated into Val; and the function of mutated protein is the same as that of wild EGF protein, the specific activity of the mutated protein is 20 percent higher than that of the wild EGF protein, the mutated protein can be used for preparing a medicine or a diagnostic reagent for preventing epidermal growth factor-related diseases, the using amount is reduced, and the side effect of the mutated protein is reduced.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Gene directed molecular evolution system in vitro based on half-rational evolutionary design
InactiveCN101311185ACombined screening system is simpleSimple and efficientSugar derivativesDNADNA shuffling
The invention relates to a simple and efficient gene in vitro directed evolution system based on half-reasoning design; the system can achieve larger mutation potential and more definite mutation region compared with the conventional reshuffle mutation by combining DNA reshuffle mutation and the half-reasoning design and can provide more diversified mutant population for the modification of gene and protein, wherein, the mutant sites of the diversified mutant population are positioned in critical area.. With the combination of a screening system, reliable improved gene or protein can be obtained more easily; moreover, the system of the invention has effectiveness as well as simple and convenient operation.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
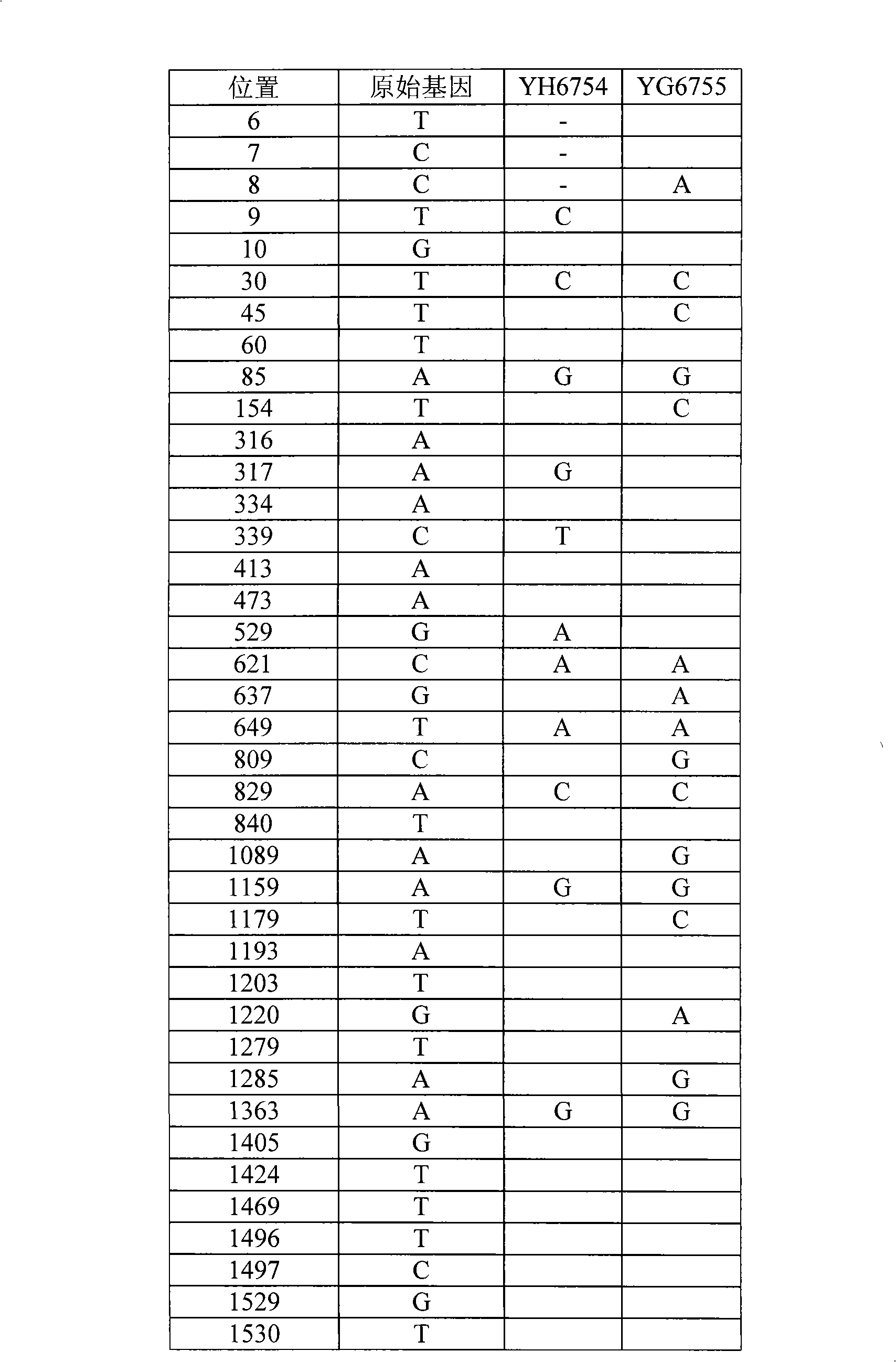
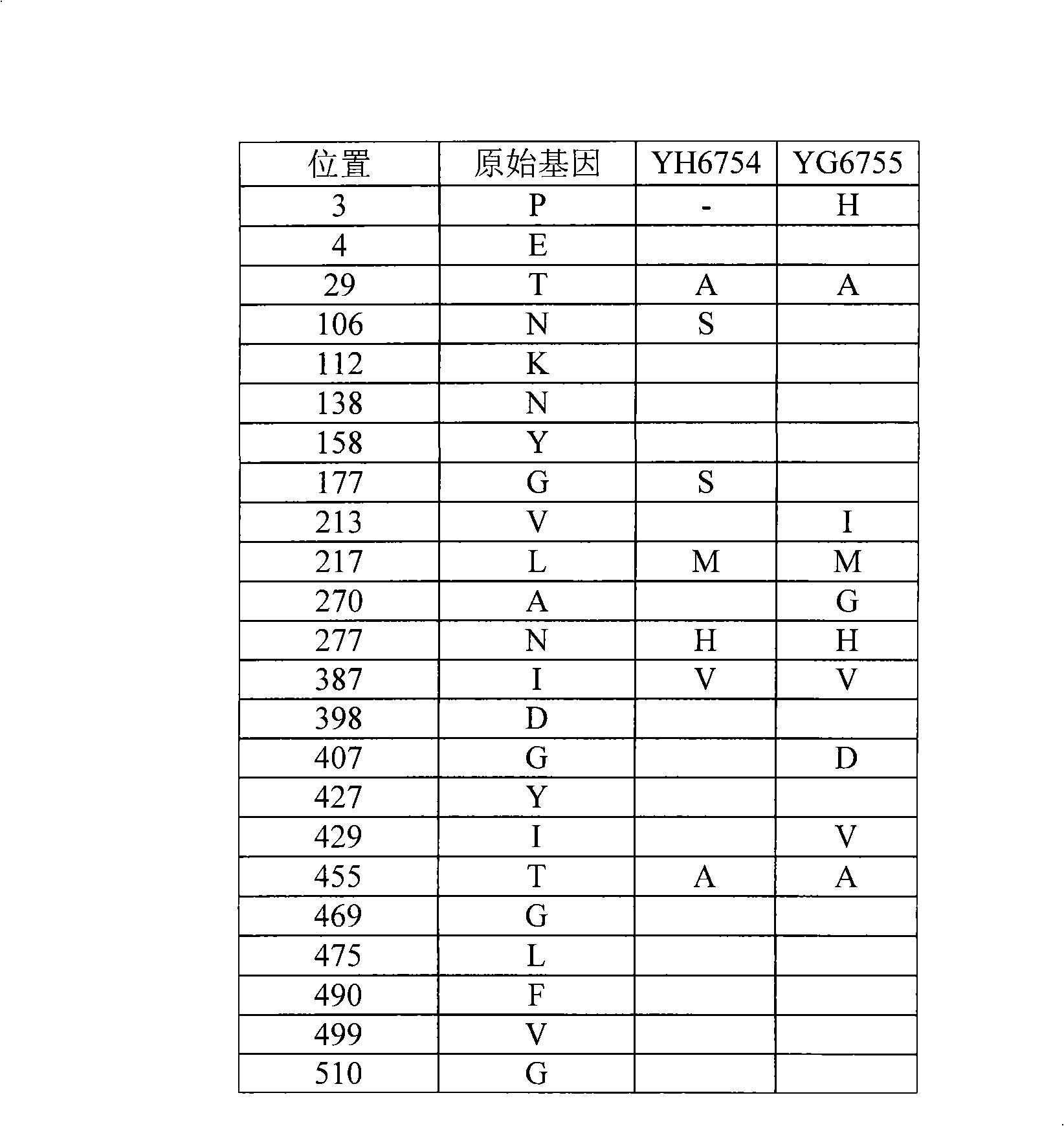
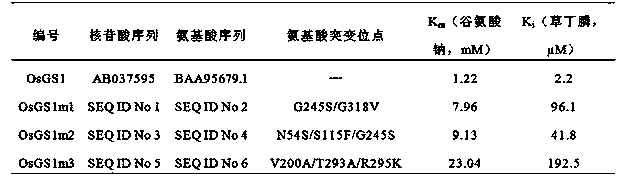
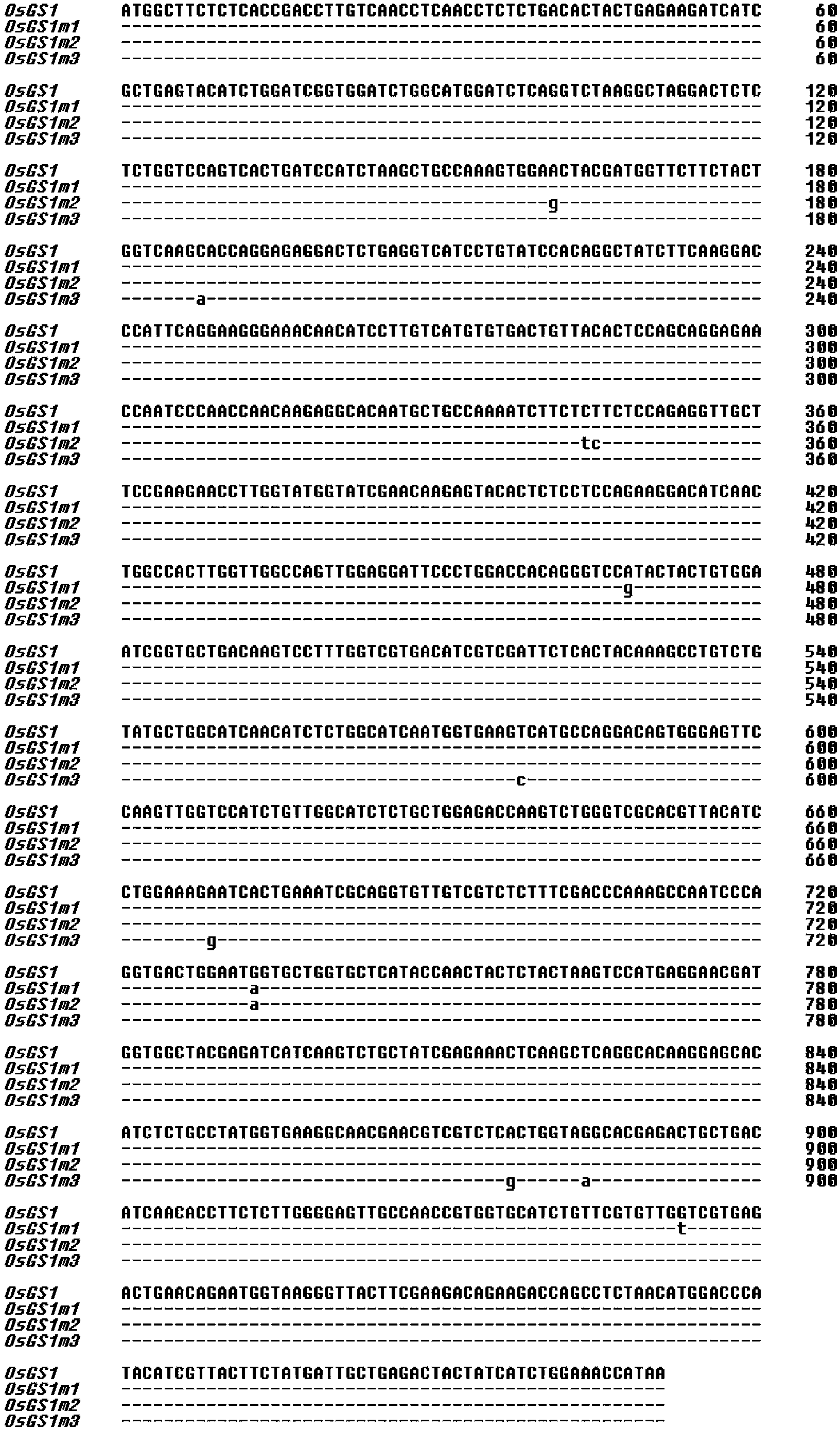
Three glufosinate-resistant rice cytoplasm type glutamine synthetase mutants
InactiveCN104164441AIncrease resistanceImprove screening efficiencyFungiMicroorganism based processesWild typeBiology
The invention relates to glutamine synthetases with substantially enhanced glufosinate resistance. The glutamine synthetases with substantially enhanced glufosinate resistance are mutants obtained through in vitro directed molecular evolution of wild rice cytoplasm type glutamine synthetase. The numbers, the amino acid sequences and corresponding amino acid mutation sites of the mutants are OsGS1m1, SEQIDNo2 and G245S / G318V; OsGS1m2, SEQIDNo4 and N54S / S115F / G245S; and OsGS1m3, SEQIDNo6 and V200A / T293A / R295K respectively. The glufosinate enzyme activity inhibition constants Ki of the mutants OsGS1m1, OsGS1m2 and OsGS1m3 are 43.7, 19 and 87.5 times higher than the resistance of the wild glutamine glutamine synthetase. Verification of the functions of the three mutation genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae further proves that the expression in the three genes can improve the glufosinate tolerance of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae from 10mM to above 100mM. The expression mode of the above yeast is very similar to the expression mode of a plant, so the verification result of the functions in the yeast proves that the three mutants have a very good application potential in the cultivation of glufosinate-resistant plants.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Whole genome sequencing method of influenza B virus
PendingCN107488742AEasy to purifyEasy to recycleMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenomic sequencingOpen reading frame
The invention discloses a whole genome sequencing method of an influenza B virus. By the whole genome sequencing method, in allusion to conserved regions of PB2, PB1, PA, HA, NP, NA, MP and NS genes of the influenza B virus, 14 pairs of oligonucleotide primer sequences covering the full gene length (an open reading frame), altogether 28 oligonucleotide primer sequences shown as SEQ ID No. 1 to SEQ ID No. 28, are designed, M13 forward and reverse primer sequences are added to both ends of forward and reverse amplification primers, and a sequencing reaction step after gene amplification is simplified. The invention also discloses treatment to a sample to be detected, an RT-PCR reaction system, an RT-PCR reaction condition, a sequencing reaction system and a sequencing reaction condition. According to the whole genome sequencing method, whole genome amplification of the influenza B virus which is epidemic in China mainland can be achieved so as to obtain whole genome sequencing information of the influenza B virus; the whole genome sequencing method is easy to operate and convenient to apply; and according to the whole genome sequencing method, a feasible technical method is provided for the etiological research and molecular evolution analysis of the influenza B virus in China.
Owner:SHANGHAI BIOGERM MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Engineering strain for efficiently expressing MccJ25 and fermentation process of engineering strain
ActiveCN113774006AEfficient expressionThe post-processing purification process is simpleBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
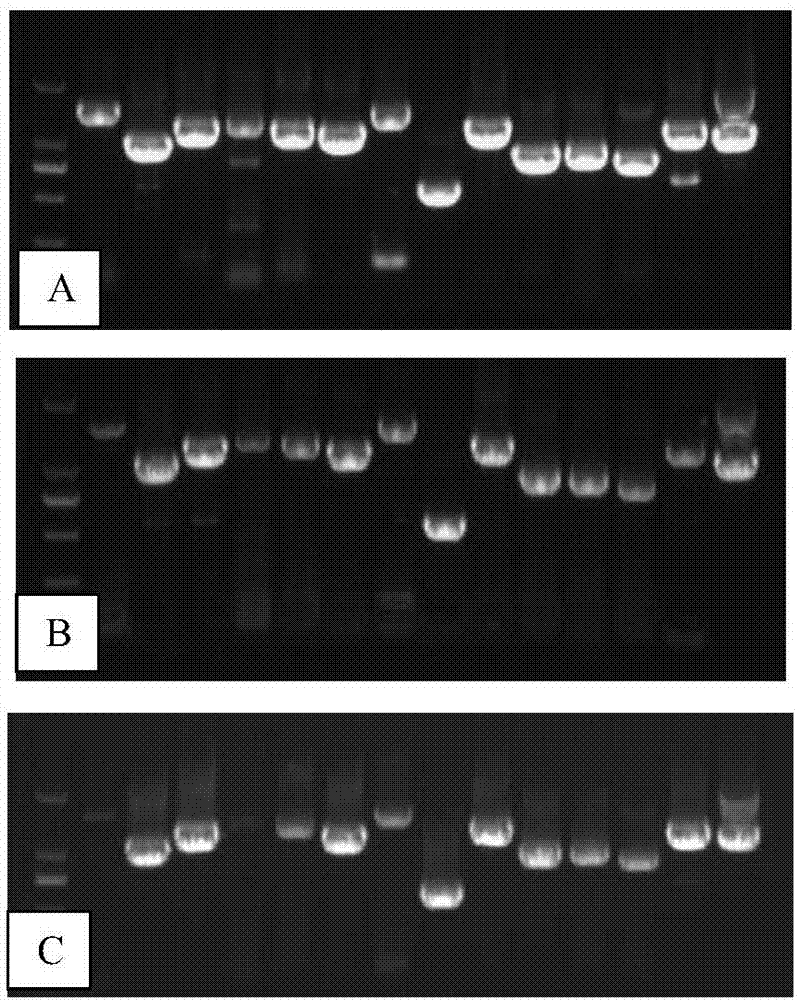
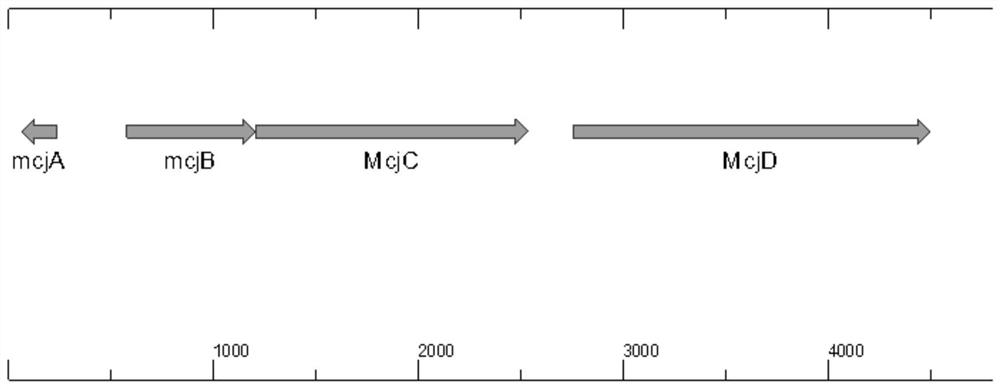
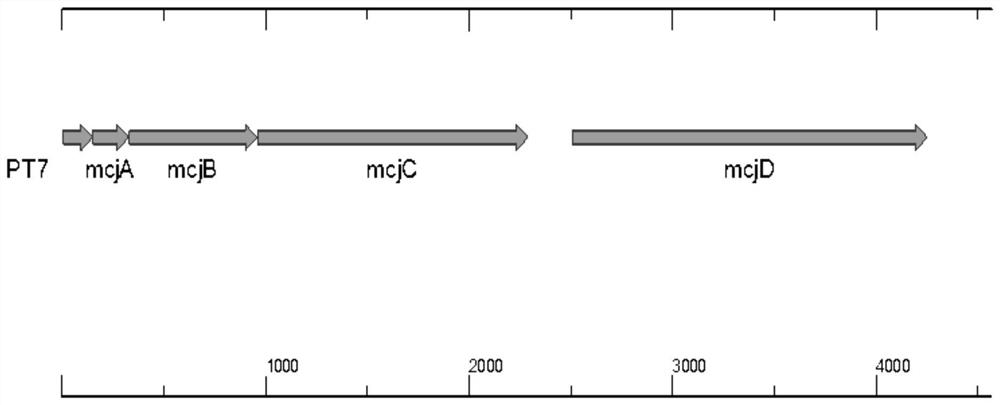
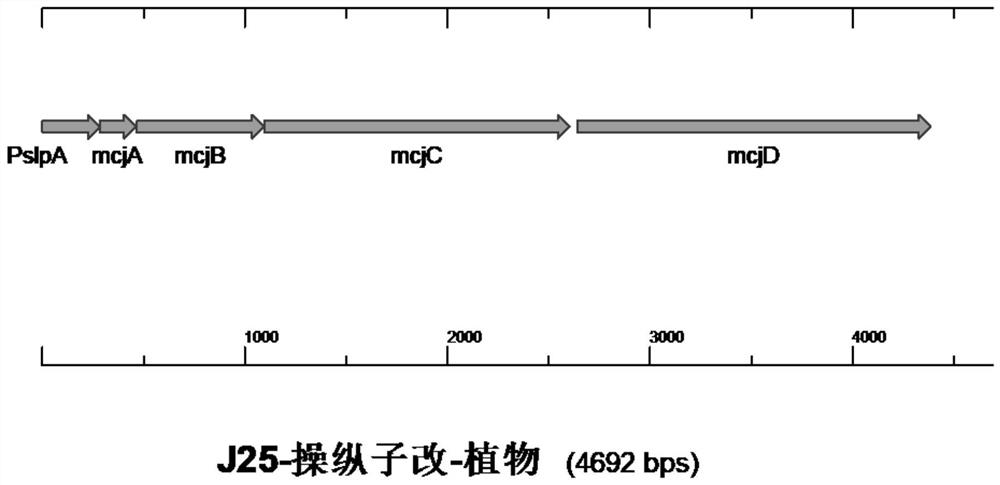
The invention provides an engineering strain for efficiently expressing MccJ25. The engineering strain is used for solving the problem of low expression level of Microcin J25 in the prior art. The engineering strain is constructed by the following method: genetic operation is separately carried out on mcjABCD to become a direction, a promoter T7 is shared in Escherichia coli and is cloned on a vector pBR322, high-efficiency expression in the Escherichia coli is realized, and the expression level is 2.4 g / L. According to the scheme, new expression vectors are constructed, an Escherichia coli expression vector and a lactobacillus plantarum expression vector are separately constructed to efficiently express the MccJ25, meanwhile, a directed evolution technology is adopted, molecular evolution is performed on an MccJ25 gene cluster, and efficient expression of the MccJ25 is realized. Extracellular expression is carried out on the Escherichia coli, intracellular expression is carried out on lactobacillus plantarum, the expression levels reach 4.1g / L and 2.3g / L separately, an industrialization level is achieved, and a foundation is laid for further application of biological veterinary drugs and feed additives.
Owner:安杰利(重庆)生物科技有限公司
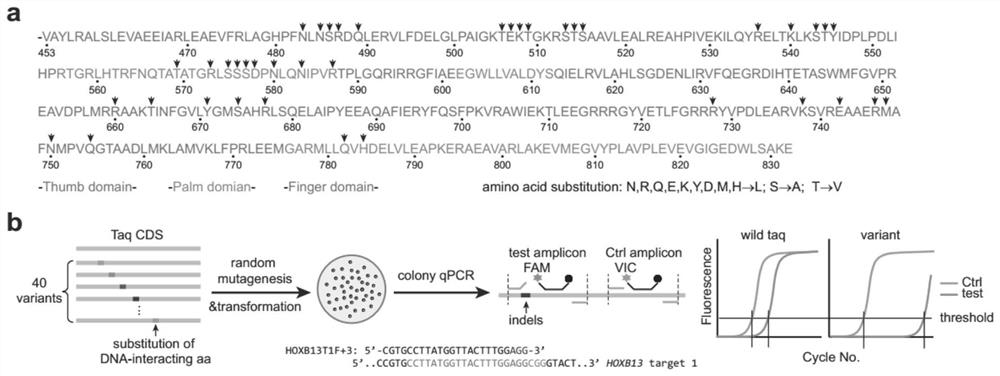
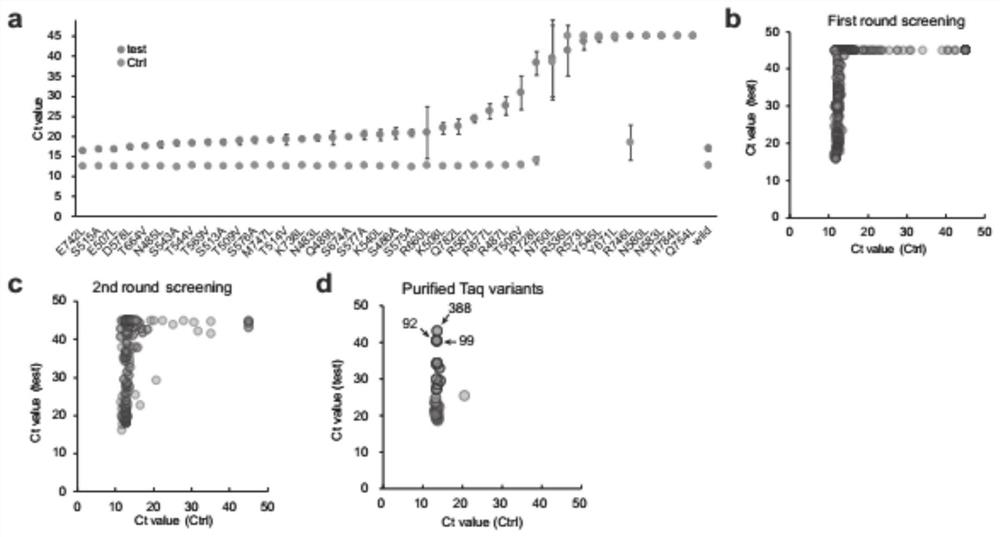
High-specificity Taq DNA polymerase variantS and application thereof in genome editing and gene mutation detection
ActiveCN112921015AImprove performanceStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesWild typeVariome
The invention provides high-specificity Taq DNA polymerase variants and application thereof in genome editing and gene mutation detection, and belongs to the technical field of biology. Semi-rational directed molecular evolution is carried out on A wild type full-length Taq DNA polymerase, so that the specificity of the polymerase is improved. All polar amino acids, directly interacting with a primer / template compound, on Taq enzyme are selected to be mutated one by one to obtain 40 Taq variants, and then extensive random mutagenesis is performed on the basis of the variants and wild type sequences to generate a Taq mutant library. A series of Taq mutants with high specificity are screened on a qPCR screening system by taking genome editing indels plasmid as a template, and the Taq mutants show great advantages in CRISPR / Cas9 editing efficiency evaluation and single cell cloning genotyping, so that the Taq mutants have good practical application value.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com