Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
150 results about "Glutamine synthetase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Glutamine synthetase (GS) (EC 6.3.1.2) is an enzyme that plays an essential role in the metabolism of nitrogen by catalyzing the condensation of glutamate and ammonia to form glutamine...
Bacterial glutamine synthetases and methods of use
ActiveUS20090018016A1Improve nitrogen utilizationIncrease productionBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyDNA construct
Compositions and methods for conferring herbicide resistance to and improving nitrogen utilization of bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions comprising a coding sequence for a polypeptide that confers resistance or tolerance to herbicidal glutamine synthetase inhibitors are provided. The coding sequences can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in plants. Compositions also comprise transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, isolated polynucleotides corresponding to herbicidal glutamine synthetase inhibitor-resistant polynucleotides are provided. Additionally, polypeptides corresponding to the polynucleotides are encompassed. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated polynucleotides comprising a variant of SEQ ID NO:1, wherein the variant polynucleotide encodes a polypeptide that is resistant to inhibition by herbicidal glutamine synthetase inhibitor.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Bacterial glutamine synthetases and methods of use
Compositions and methods for conferring herbicide resistance to and improving nitrogen utilization of bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions comprising a coding sequence for a polypeptide that confers resistance or tolerance to herbicidal glutamine synthetase inhibitors are provided. The coding sequences can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in plants. Compositions also comprise transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, isolated polynucleotides corresponding to herbicidal glutamine synthetase inhibitor-resistant polynucleotides are provided. Additionally, polypeptides corresponding to the polynucleotides are encompassed. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated polynucleotides comprising a variant of SEQ ID NO:1, wherein the variant polynucleotide encodes a polypeptide that is resistant to inhibition by herbicidal glutamine synthetase inhibitor.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
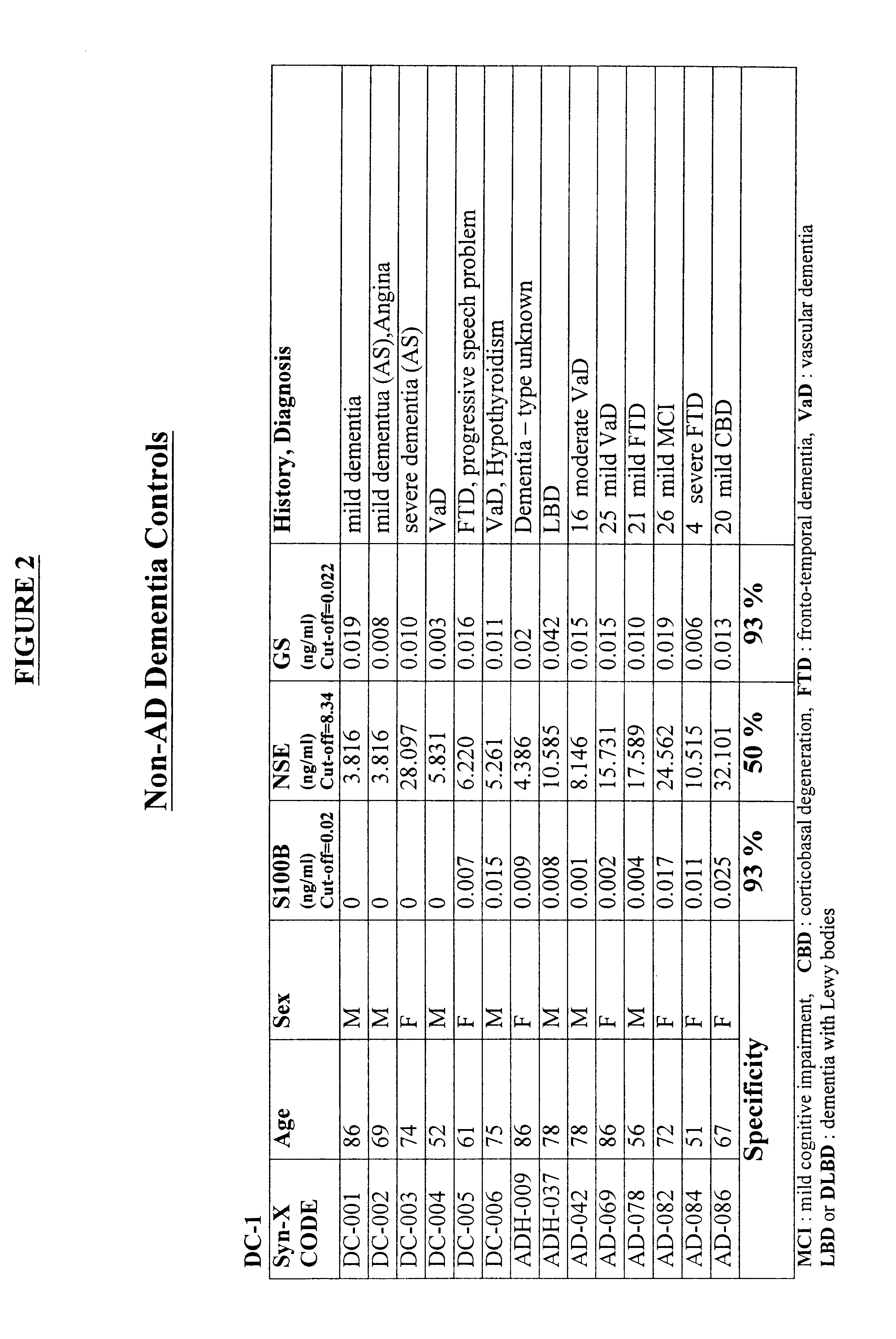
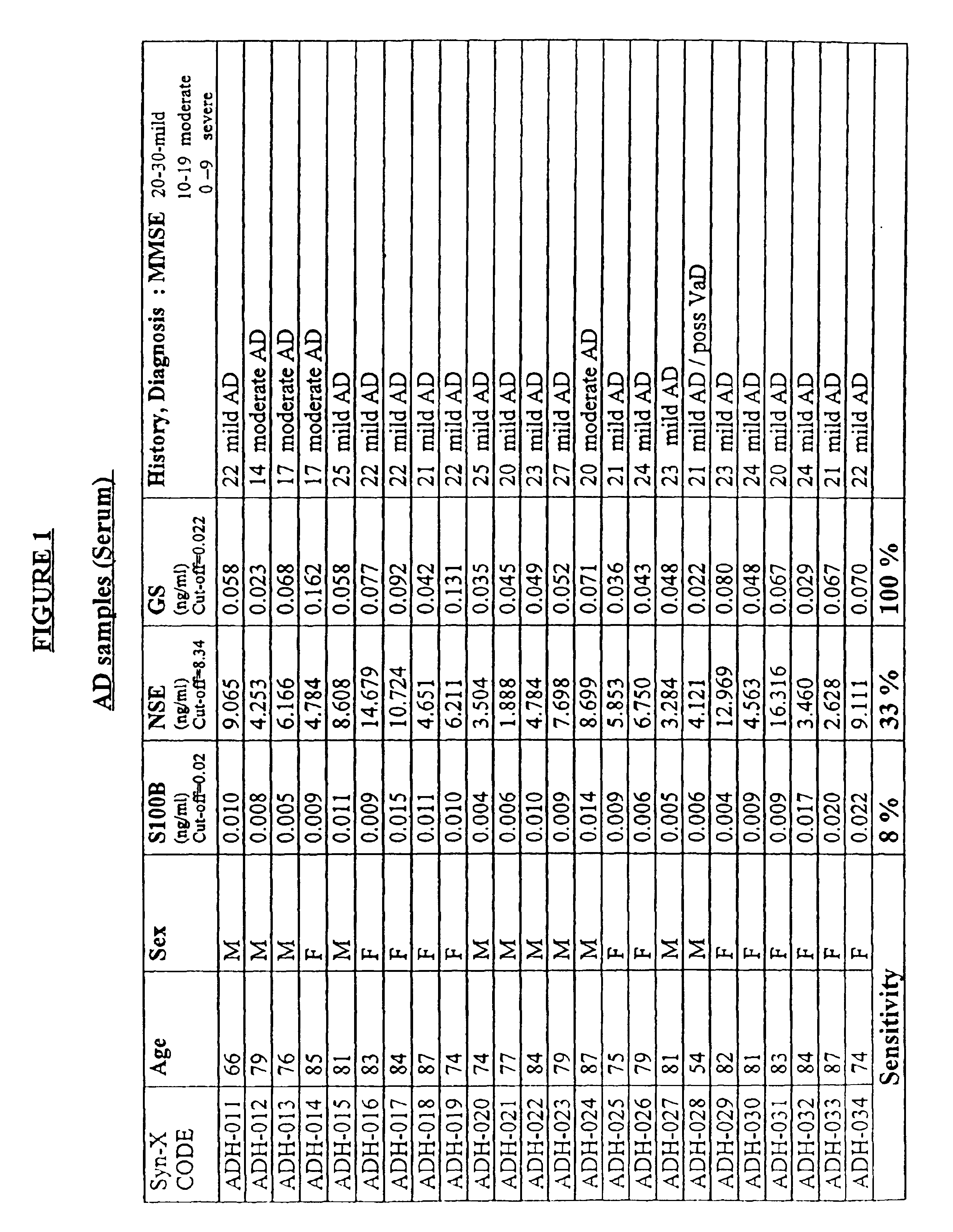
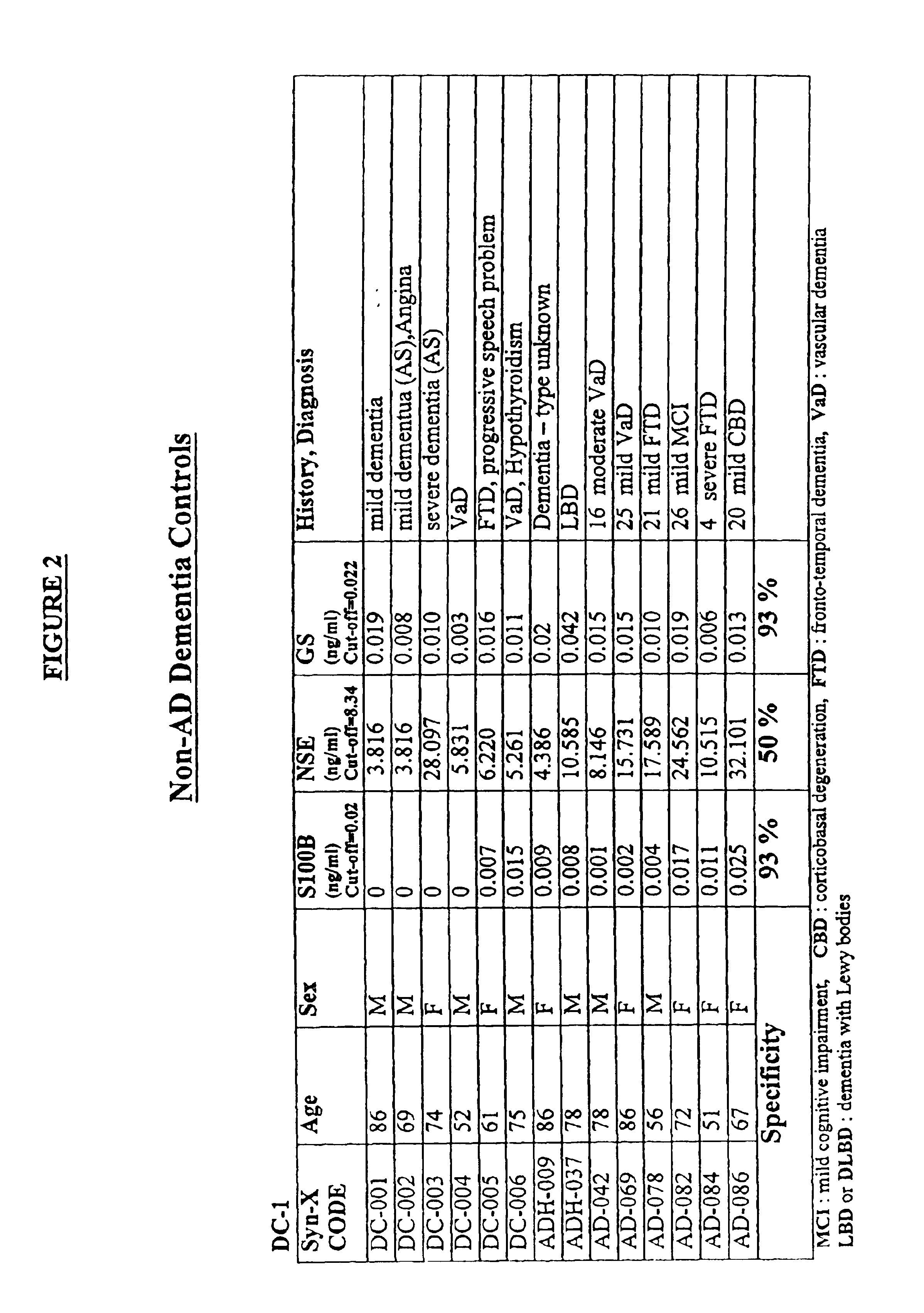
Process for differential diagnosis of Alzheimer's dementia and device therefor
InactiveUS6451547B1Efficient identificationImmunoglobulins against animals/humansDisease diagnosisWhole blood productBiochemical markers
A method for diagnosing Alzheimer's disease(AD) is disclosed. The method involves directly detecting the presence of a biochemical marker, specifically human glutamine synthetase, in bodily fluid, preferably blood or a blood product. The detection is by an immunoassay incorporating an antibody specific to human glutamine synthetase. In addition, a method for distinguishing between AD and non-AD dementia is disclosed.
Owner:NANOGEN INC
Method for detecting blood ammonia content and blood ammonia diagnostic reagent kit
InactiveCN1749756AStrong specificityImprove test accuracyColor/spectral properties measurementsBiological testingAdenosinePeroxidase
The present invention belongs to the field of medical detection technology. The reagent kit for blood ammonia diagnosis includes buffering solution, adenosine triphophate, glutamic acid, pyruvic acid, alcohol, oxidized coenzyme, glutamine synthetase, pyruvate oxidase, hydrogen peroxidase, aldehyde dehydrogenase and stabilizer. Through mixing the sample and reagent in certain volume ratio to produce enzyme coupling reaction, and detecting in biochemical analyzer the main wavelength absorbency change speed, the blood ammonia content is measured. The present invention can obtain the measurement result in biochemical analyzer in high sensitivity, high precision and no contamination of various foreign and internal matters.
Owner:王尔中
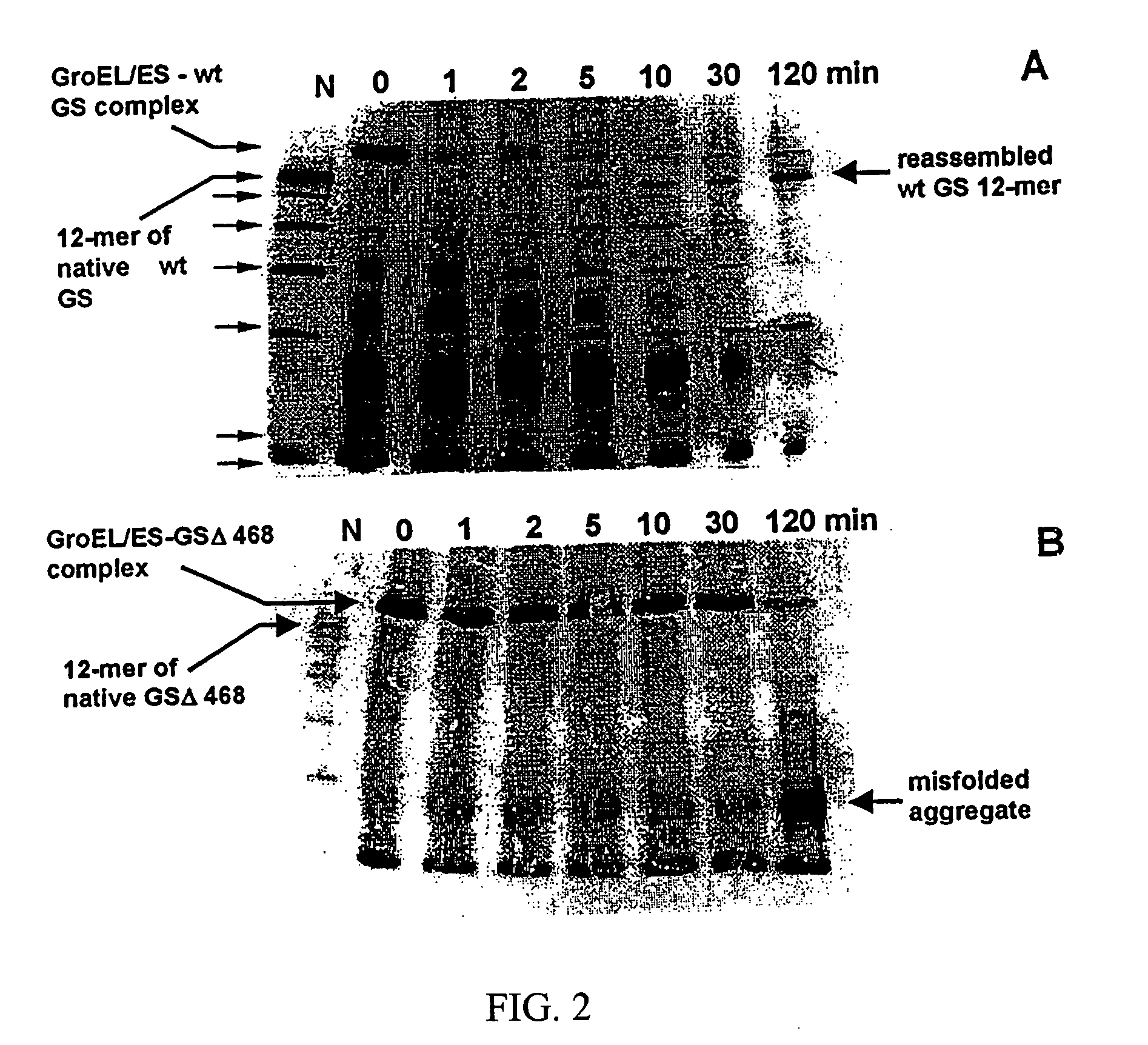
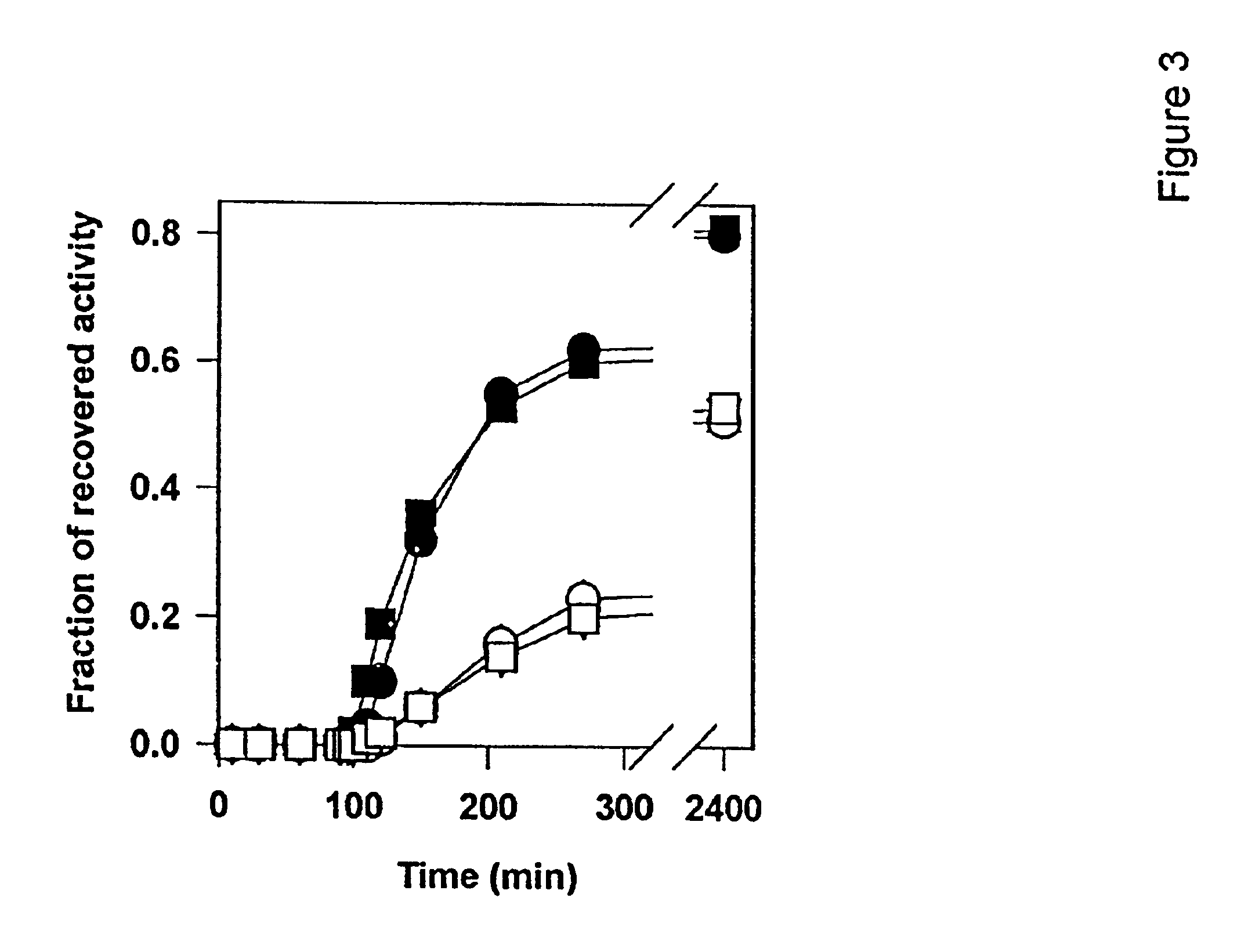
Chaperonin and osmolyte protein folding and related screening methods
InactiveUS20050196824A1Microbiological testing/measurementPeptide preparation methodsIonic strengthOsmolyte
The invention describes an inexpensive in vitro protein folding process for preventing large scale protein misfolding and aggregation, for concentrating aggregation prone chaperonin-protein folding intermediates in a stable non-aggregating form, and for rapidly screening these stable concentrates for the best folding solution conditions. The process comprises: (1) the formation of a chaperone-substrate complex and (2) the release of the substrate using a broad array of folding solutions containing different osmolyte ions, detergents, gradients of ionic strength and pH or other commonly used folding additives. Specifically, when the chaperonin / osmolyte protein process was applied to identify and optimize GSΔ468 bacterial glutamine synthetase mutant refolding conditions that otherwise cannot be folded in vitro by commonly used techniques, 67% of the enzymatic activity was recovered.
Owner:UNIV KANSAS MEDICAL CENT
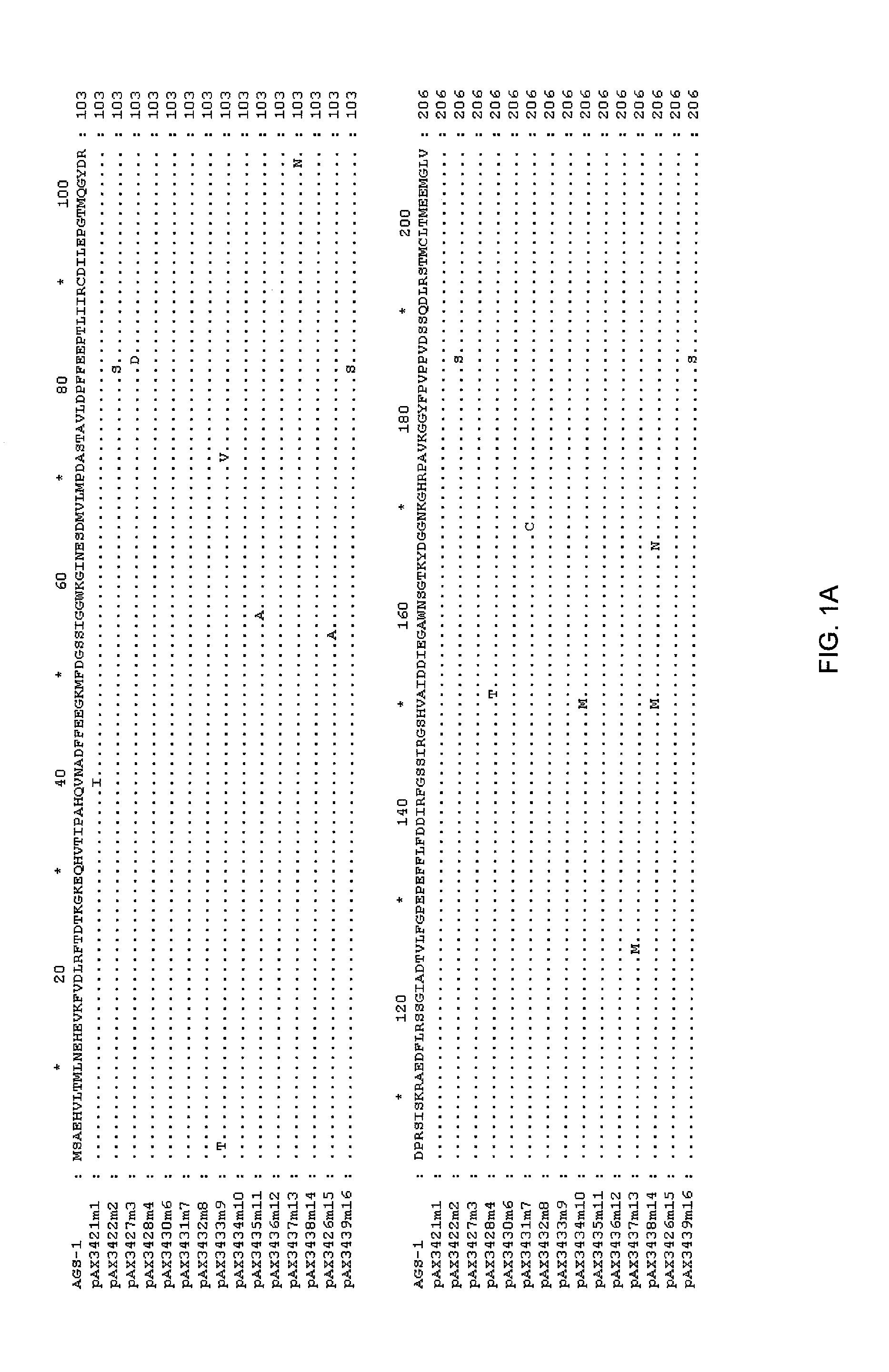
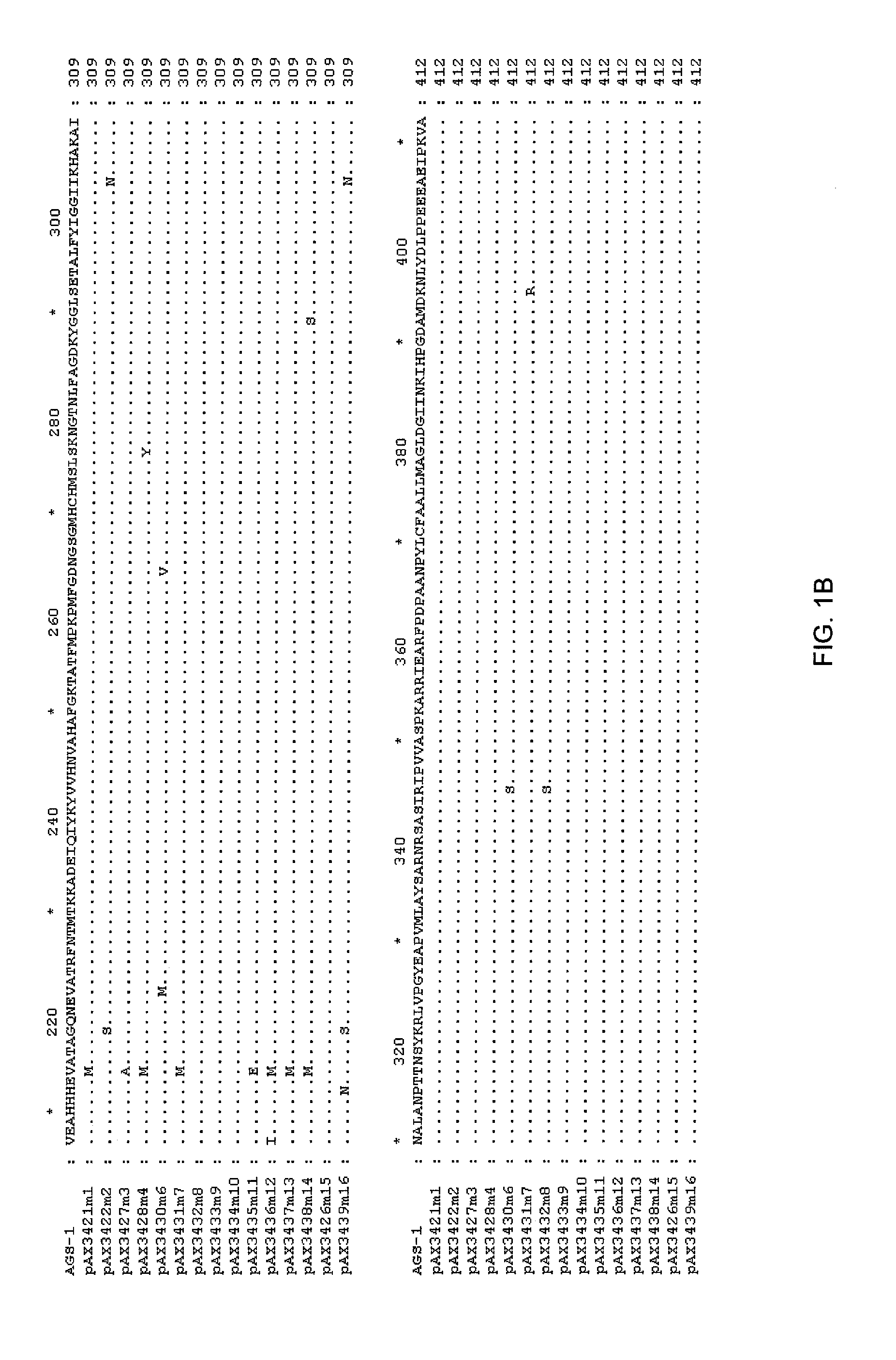
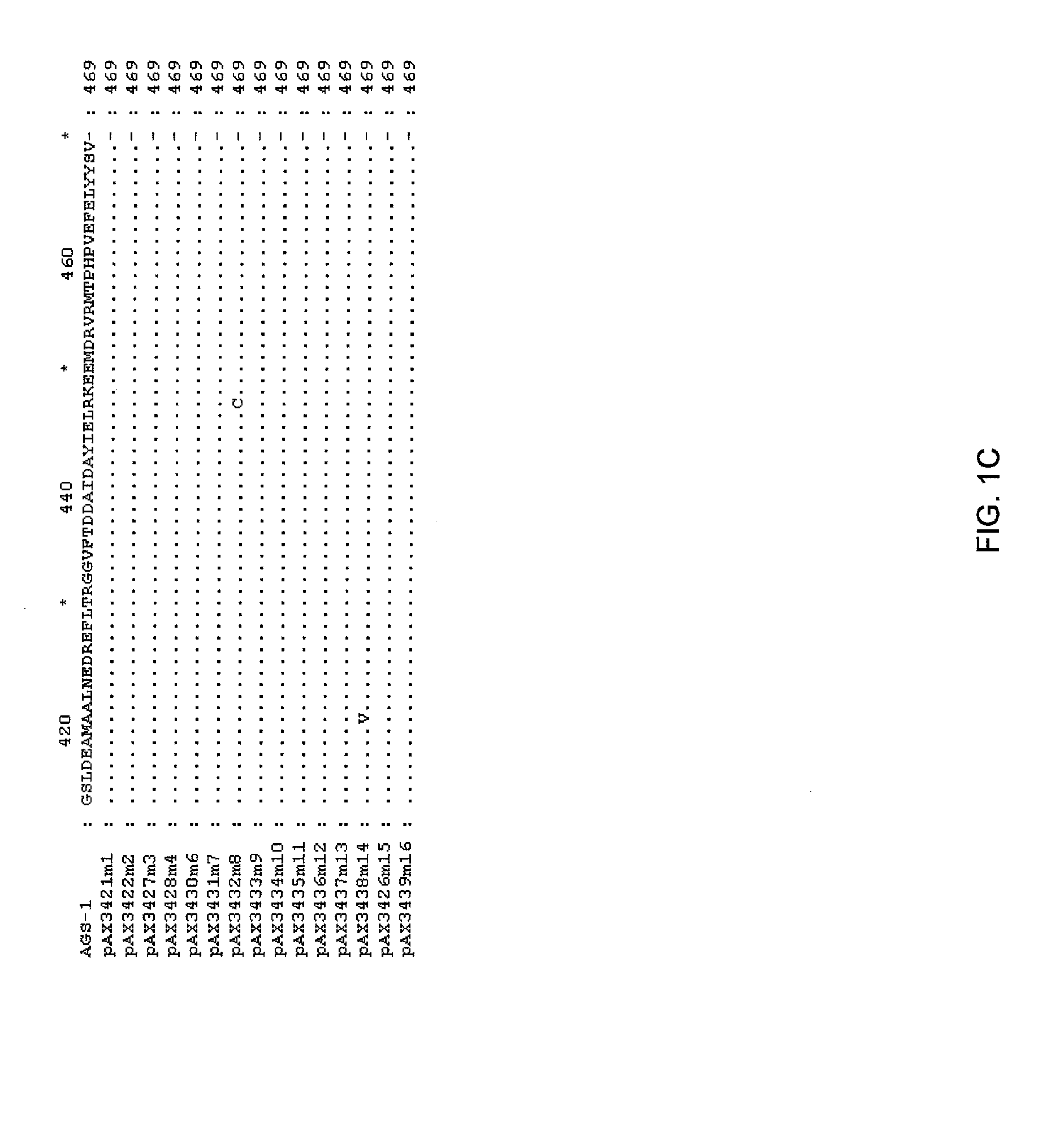
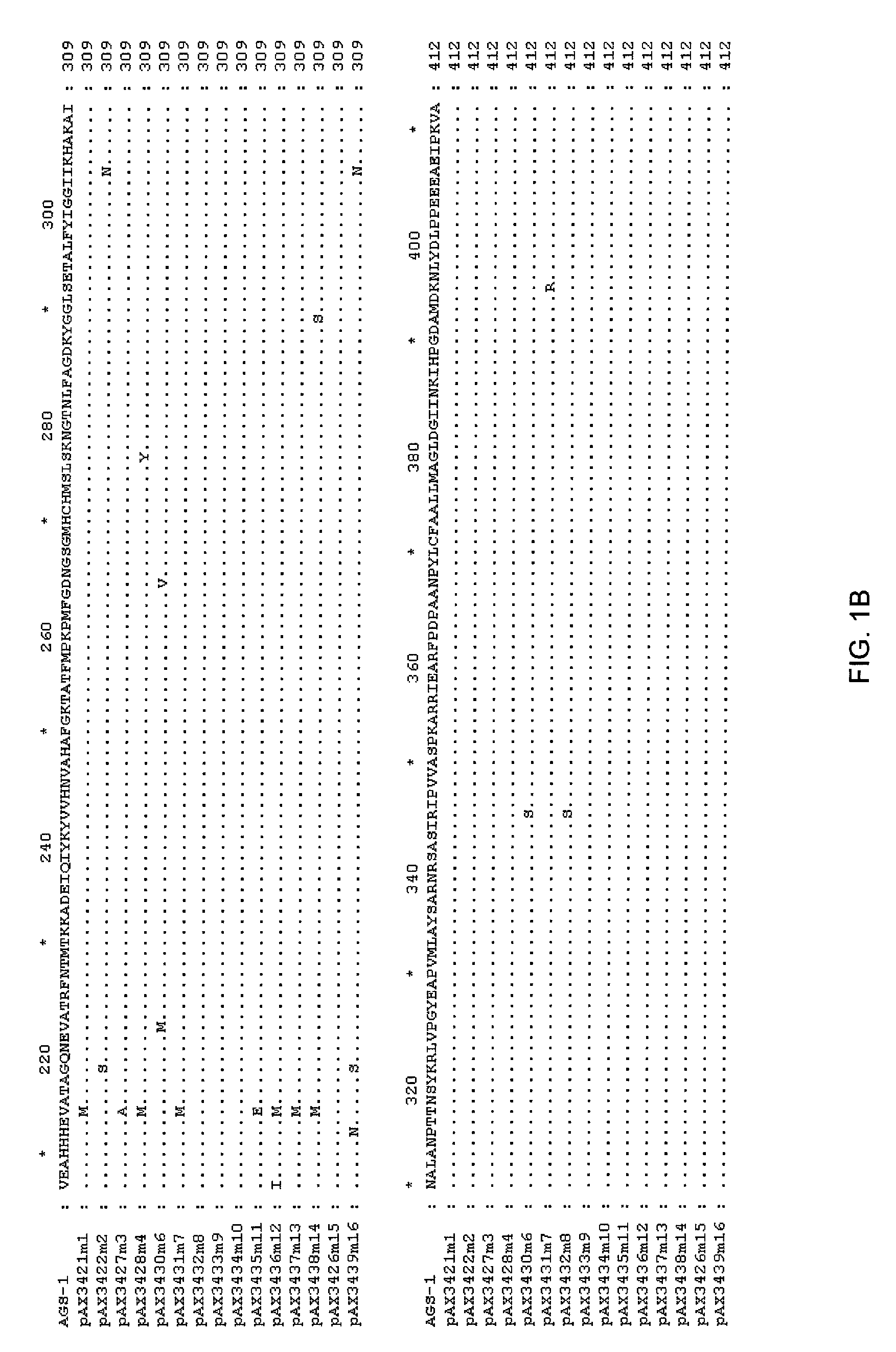
Glutamine synthetase mutant with glufosinate resistance and application and cultivation method of glutamine synthese mutant
The invention discloses a glutamine synthetase mutant with glufosinate resistance and application and a cultivation method of the glutamine sythetase mutant, and relates to the field of biotechnology.Compared the amino acid sequence of the glutamine synthetase mutant with the reference sequence, the glutamine synthetase mutant with glufosinate resistance disclosed in the present invention has oneor two combinations of the following mutations that: (1) the mutation of the glutamine sythetase mutant corresponding to the 59th amino acid site of the reference sequence is X1, wherein X1=A, C, D,E, F, G, H, I, K, P, T, V or Y; and (2) the mutation of the glutamine sythetase mutant corresponding to the 296th amino acid site of the reference sequence is X2, and X2=A, D, E, G, I, K, M, P, Q, R,S, T or V. The glutamine synthetase mutant has the characteristic of glufosinate resistance, and can be used to cultivate new varieties of plants with glufosinate resistance.
Owner:SICHUAN GEVOTO BIOTECH CO LTD
Novel uses for drugs targeting glutamine synthetase
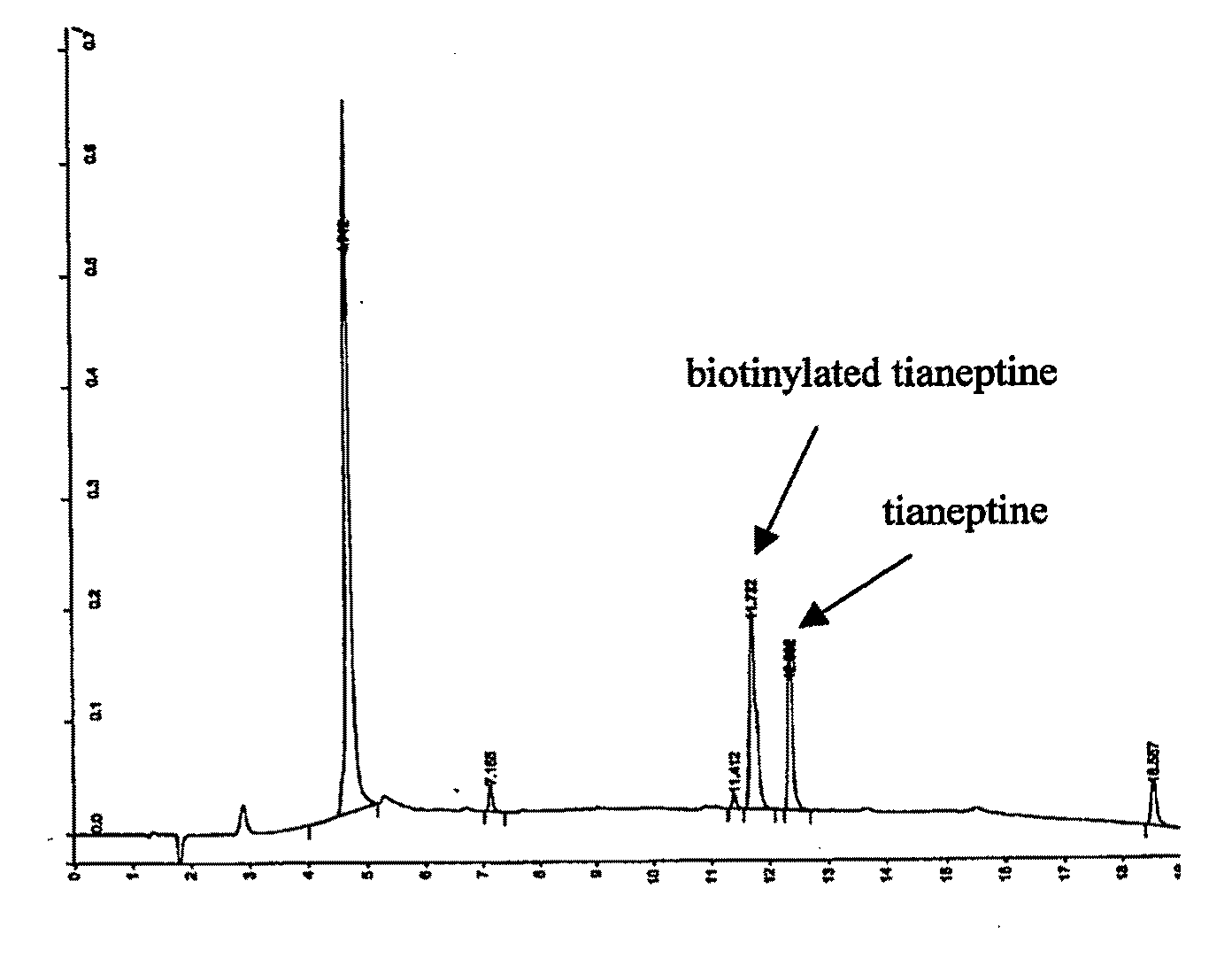
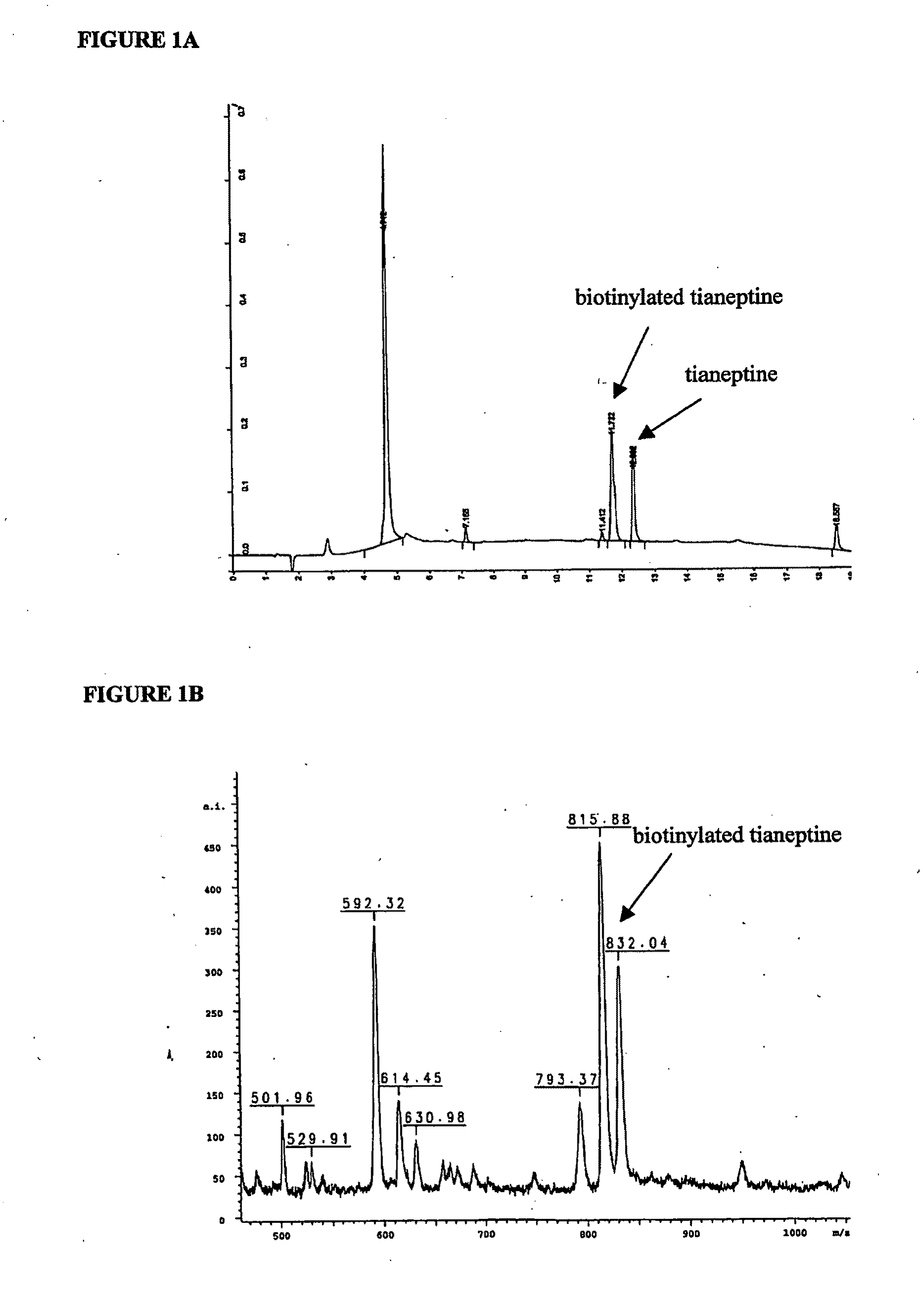
InactiveUS20090209474A1Cut surfaceLess side effectsBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementMetaboliteTianeptine
The present invention relates to novel therapeutic uses of tianeptine, salts, isomers, pro-drugs, metabolites and structural analogs thereof. Furthermore, the present invention relates to the use of tianeptine, salts, isomers, pro-drugs, metabolites and structural analogs thereof, in obtaining methods of screening and of developing drugs. Finally, the present invention relates to the novel therapeutic use of other glutamine synthetase (GS) ligands and to the use of these ligands in obtaining methods for screening and developing drugs.
Owner:NEWTHERA
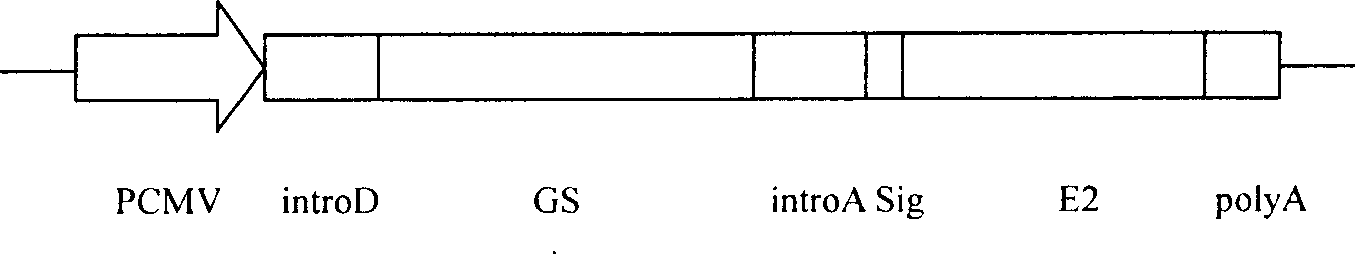
Method for expressing hepatitis C virus envelope protein E2 by mammal cell with high efficient secretion
The present invention relates to biomedicine technology. HCV envelope protein E2 mediates the combination between HCV and target cell and is key protein relates to HCV infection and one kind of low expression protein hard to obtain in gene recombination process. The present invention aims at provides high efficiency secretion method for mammal to express HCV envelope protein E2. The method constitutes one new type of mammal cell expressing plasmid, which expresses target gene E2 protein in high level while expressing glutamine synthetase as the screening marker in low level. The present invention makes it possible to batch prepare recombinant HCV envelope protein E2 with the natural biological function and antigenicity of HCV envelope protein, lays the foundation for development of serological HCV infection detecting reagent and HCV vaccine, and provides HCV molecular virological research with important material.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Construction of escherichia coli genetically engineered bacterium and application of escherichia coli genetically engineered bacterium to production of L-tryptophan
ActiveCN108753860AClear genetic backgroundEfficient accumulationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliTryptophan synthesis
The invention relates to an escherichia coli genetically engineered bacterium and a method for efficiently producing L-tryptophan by utilizing the escherichia coli genetically engineered bacterium. The genetically engineered bacterium is obtained by correspondingly transforming and combining L-tryptophan synthesis-related genes in escherichia coli through a metabolic engineering method (includinggene integration, point mutation and promoter substitution) and introducing a glutamine synthetase coding gene glnA from lactobacillus acidophilus on genome of the escherichia coli. The strain is usedfor carrying out shake-flask fermentation; 10 to 12g / L of L-tryptophan can be accumulated within 24 hours, reaches the maximum value reported in China and is improved by 15.1 percent compared with that of an existing L-tryptophan industrial strain carrying plasmid, which shows that the strain has good potential for industrially producing the L-tryptophan.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Systems and methods for making hepatocytes from extrahepatic somatic stem cells and use thereof
Owner:NATIONAL YANG MING UNIVERSITY
Genetically engineered bacterium over-expressing heterogenous glutamine synthetase and construction method thereof
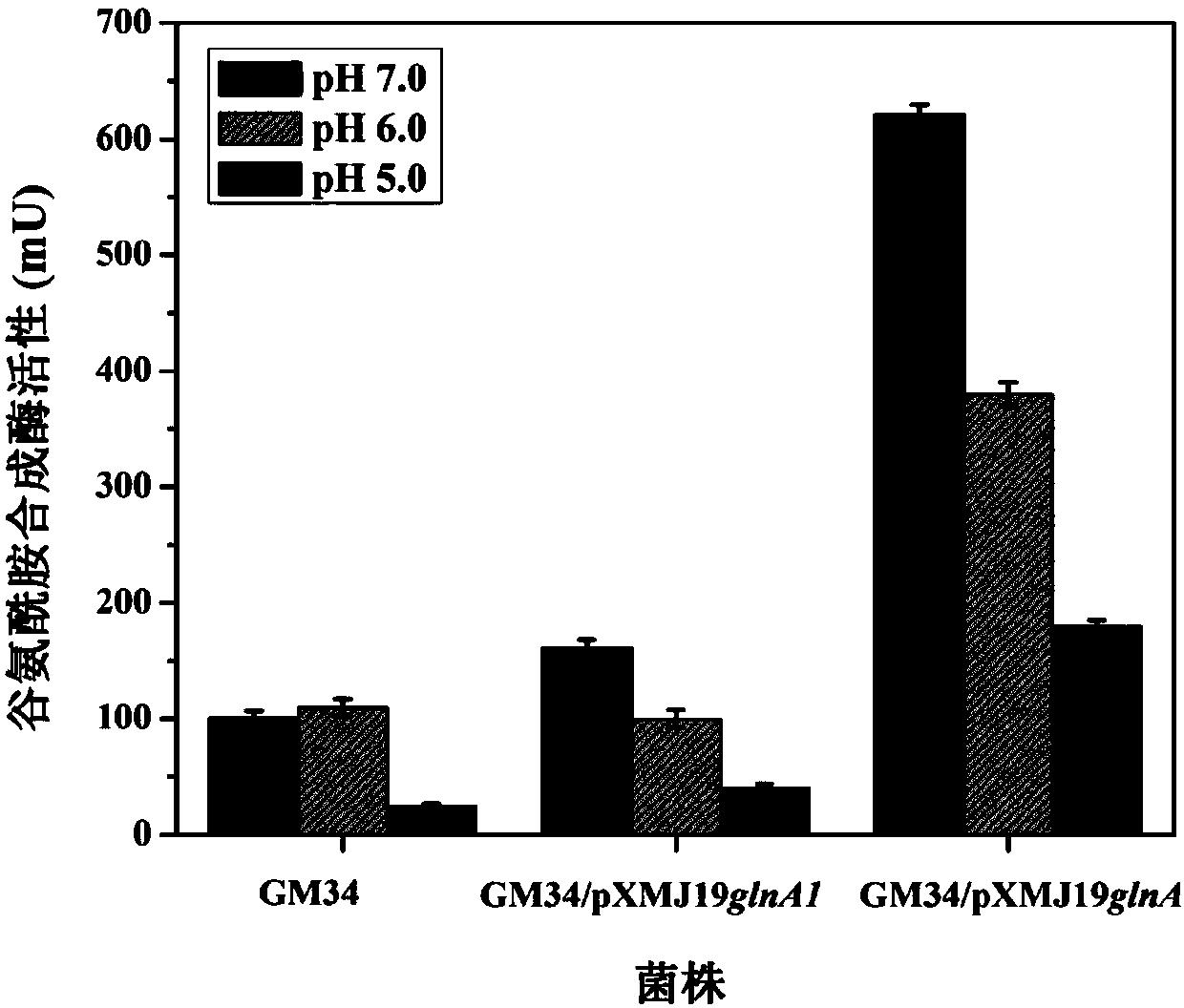
The invention provides a corynebacterium glutamicum genetically engineered bacterium over-expressing heterogenous glutamine synthetase and a construction method thereof. The construction method comprises the following steps: synthesizing and optimizing a glutamine synthetase glnA derived from lactobacillus acidophilus; by virtue of a restriction enzyme ligation method, connecting the gene glnA onto an escherichia coli-corynebacterium glutamicum shuttle type expression carrier pXMJ19, so that an expression carrier pXMJ19glnA is constructed; and introducing the expression carrier pXMJ19glnA intoa corynebacterium glutamicum GM34 or a corynebacterium glutamicum TP607, so that a genetically engineered bacterium GM34 / pXMJ19glnA or TP607 / pXMJ19glnA is constructed. The genetically engineered bacterium provided by the invention has the advantages that exogenous glutamine synthetase is over-expressed, so that yield of L-glutamine is obviously improved; meanwhile, the synthetase is over-expressed in an L-tryptophan producing strain, so that yield of L-tryptophan is obviously improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Application of GMFB (glia maturation factor beta), GMFB disrupter and application of GMFB disrupter
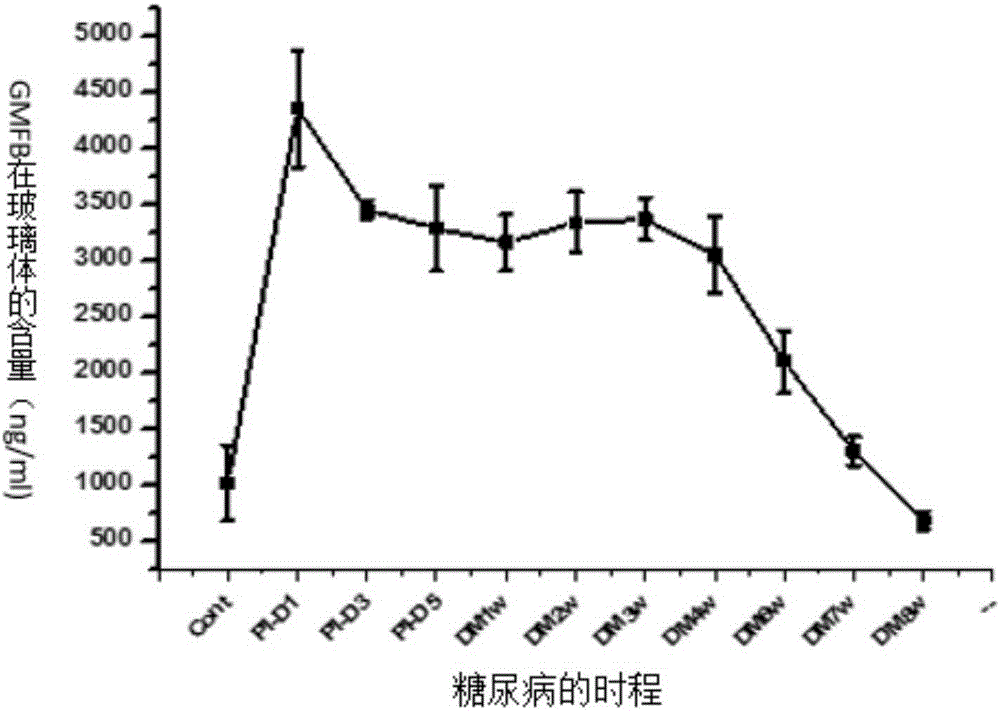
ActiveCN105154527AElevated GMFB contentDecreased glutamine synthaseMetabolism disorderGenetic material ingredientsDiabetes retinopathyDisease course
The invention relates to application of GMFB (glia maturation factor beta) as a biomarker for early diagnosis of diabetic retinopathy and for diabetes progression, application of GMFB as a therapeutic target of diabetic retinopathy, a GMFB disrupter and application of the GMFB disrupter. Compared with the prior art, the invention proves that the GMFB content in vitreous body is significantly improved in early period of diabetes in rats of STZ-induced I type diabetes (TIDM). The invention is the first to prove that GMFB content gradually drops with the development of DR (diabetic retinopathy), therefore the GMFB is applicable to dynamic detection of DR progress; the invention is the first to prove that by interfering GMFB expression in rats of DR, visual function can be protected; and the invention is the first to prove that GMFB mediates retinopathy mechanism, including causing decrease of glutamine synthetase of Muller cell, death of ganglion cells and inducing autophagy of photoreceptor cells.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Ammonia diagnosis/determination reagent kit and ammonia concentration determination method
InactiveCN101169411AFast measurementImprove accuracyMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementWavelengthGlyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
The invention relates to an ammonia diagnosing / measuring reagent box which utilizes the technique of the enzyme contrasting color method and the enzyme jointing method, and belongs to the technical field of the medicine / food / environment test. The main components of the reagent box of the invention mainly include cushion liquid, coenzyme, glutamic acid, adentosine triphosphoric acid, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, glutamine synthetase, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and stabilizing agent; the reagent box generates a series of enzymic reactions through the mixing of the samples and the reagent at a certain cubage rate, and then the reactants are positioned under an ultraviolet / visible light analyzer which tests the reducing speed of the absorbency at the main wave length of 340nm, thereby measuring the concentration size of the enzyme. The invention can absolutely get needed measuring result through the ultraviolet / visible light analyzer.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
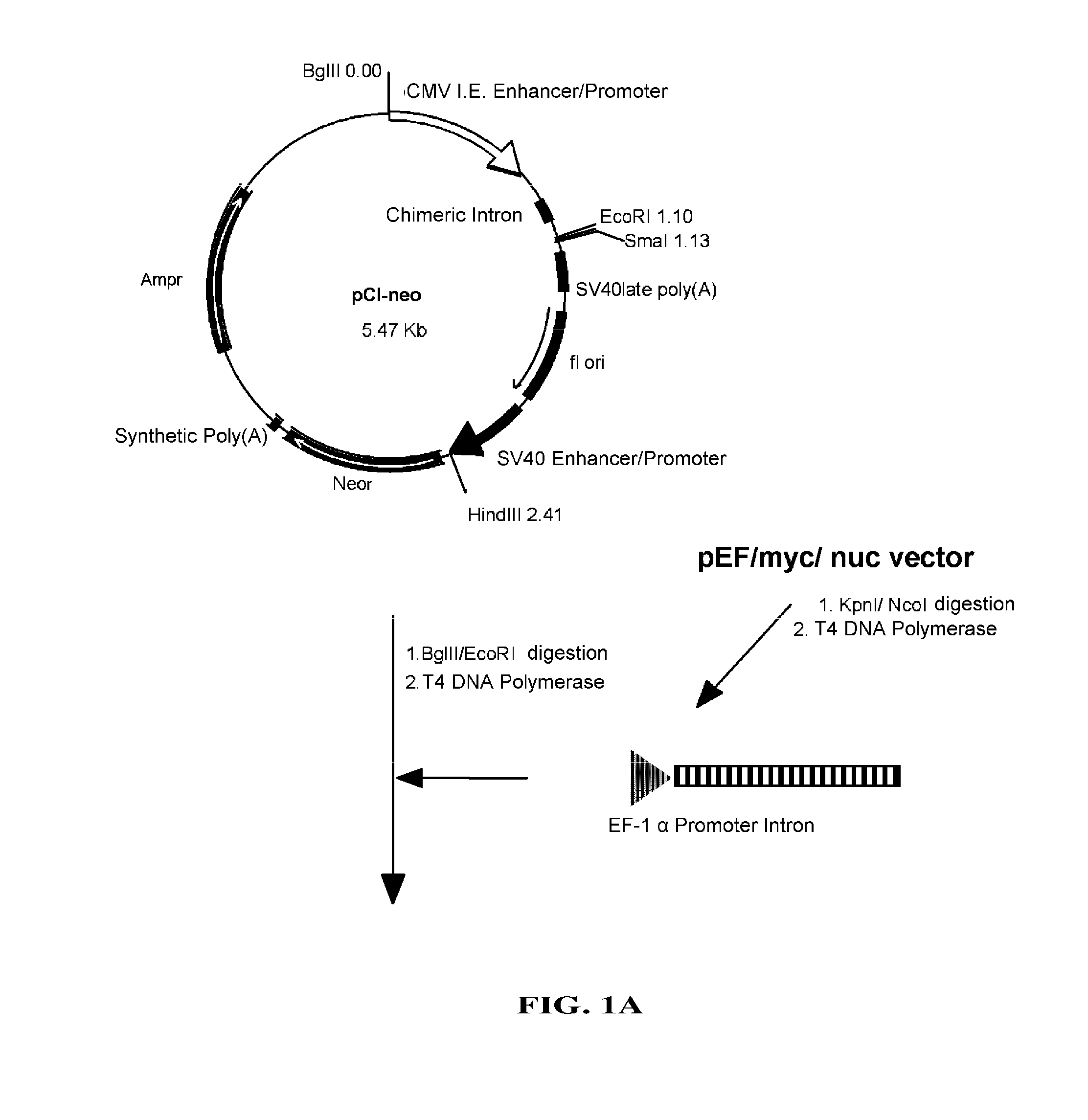
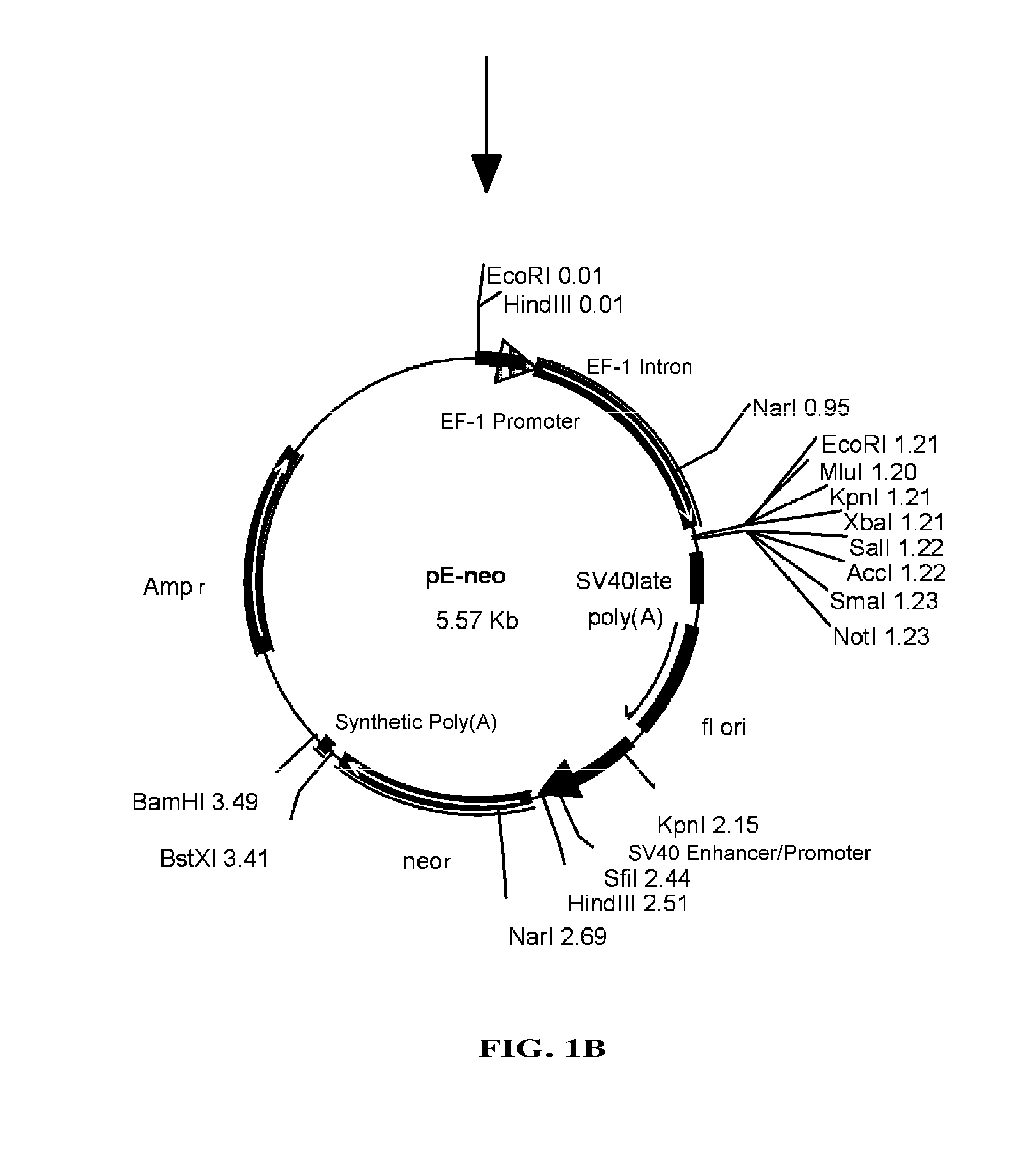
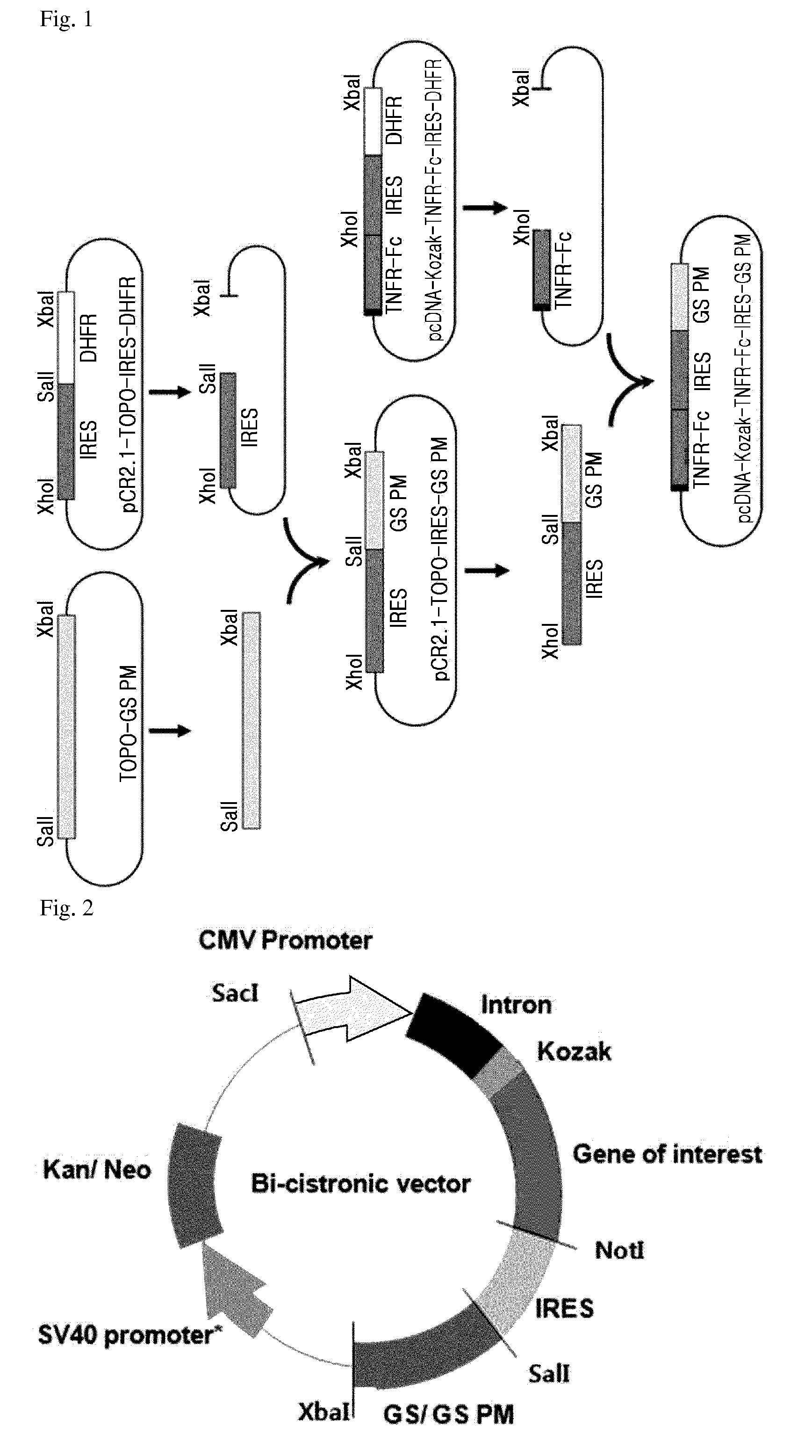
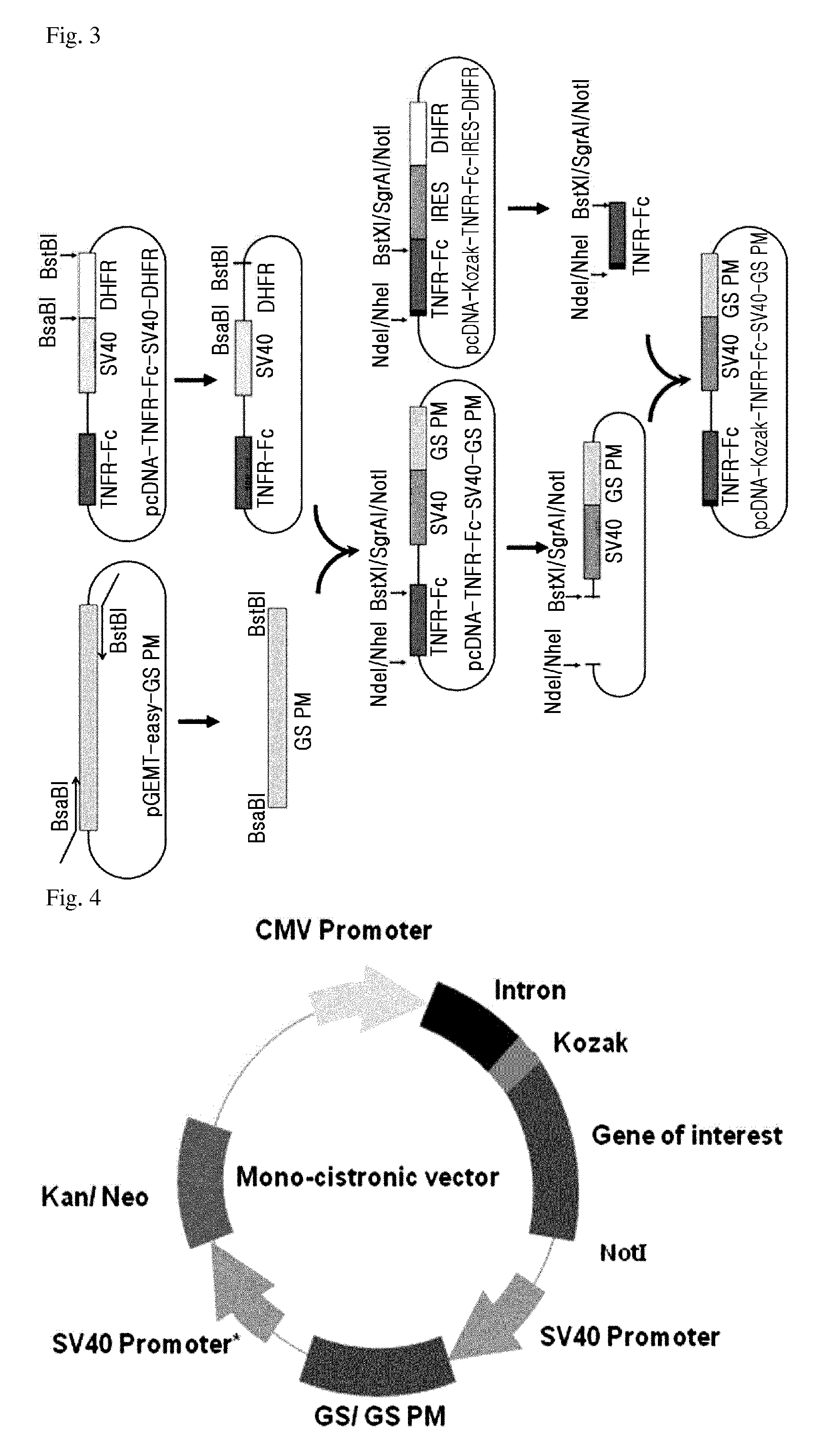
Glutamine synthetase high-efficiency expression vector with dual expression cassettes
ActiveCN104195173BHigh expressionEasy to filterVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationCloning SiteHydrolysis
The invention relates to a glutamine synthetase expression vector which can be amplified and have two expression cassettes. The main components of the glutamine synthetase expression vector include the following six parts: a first expression cassette component, a second expression cassette component, an f1 replicon, a glutamine synthetase expression cassette component, an ampicillin beta lactamase hydrolysis expression cassette component and a ColE1 replicon, wherein a strong enhancer / promotor CMV (Cytomegalovirus) and an immediate early enhancer / promotor are adopted to the first expression cassette component and the second expression cassette component; a weak promotor / enhancer SV40 is adopted to the glutamine synthetase expression cassette component, so that the expression of glutamine synthetase is reduced, and the screening of high-expression cloning is facilitated; and expression protein coding genes are respectively cloned to the expression vector through a multiple cloning site A and a multiple cloning site B. The glutamine synthetase expression vector disclosed by the invention is suitable for simultaneously expressing 1-2 proteins efficiently in mammalian cells and especially suitable for expressing antibody proteins.
Owner:BEIJING BIYANG BIOTECH
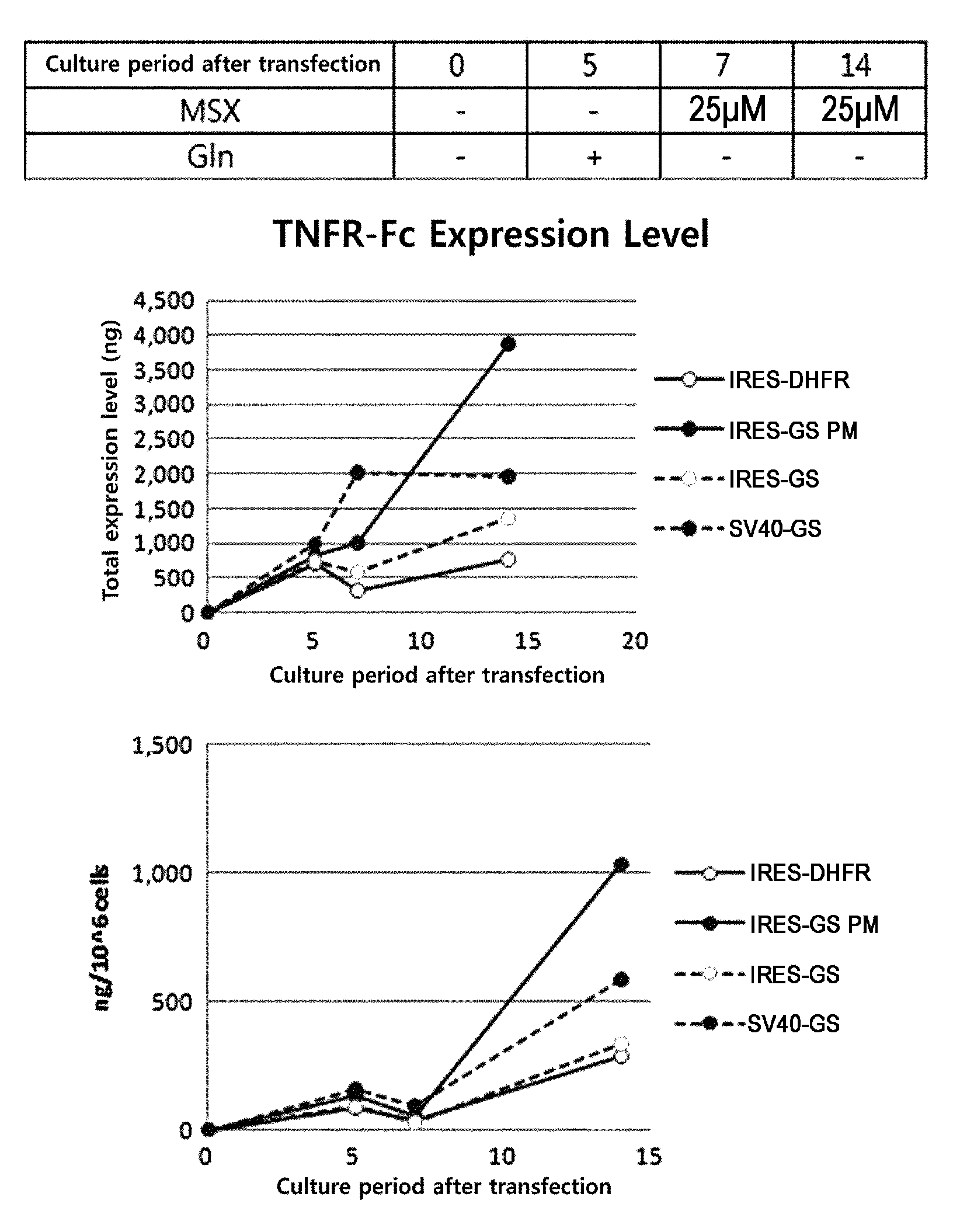
Novel expression vector
InactiveUS20130244231A1Low costEfficient expressionAnimal cellsVectorsInternal ribosome entry siteRegulatory site
Disclosed are a novel expression vector for efficient expression of recombinant proteins in mammalian cells, a mammalian cell transformed with the vector, and a method for production of the mammalian cell. The expression vector includes a gene expression regulatory site, and a gene encoding the protein downstream thereof, and an internal ribosome entry site further downstream thereof, and a gene encoding a glutamine synthetase further downstream thereof.
Owner:JCR PHARMA
Recombinant microorganism for producing sialic acid and application of recombinant microorganism
ActiveCN112175893AEfficient conversionReduce manufacturing costBacteriaHydrolasesPhosphoric Acid EstersGlucosamine Synthetase
The invention relates to the technical field of microbial fermentation, and in particular relates to a recombinant microorganism for producing sialic acid and application of the recombinant microorganism. Compared with a starting strain capable of synthesizing sialic acid, the recombinant microorganism provided by the invention has increased expression of 6-phosphoglucosamine synthetase or a mutant thereof and increased expression of fructose-1,6-diphosphate esterase and / or glutamine synthetase. According to the invention, the recombinant microorganism capable of producing sialic acid by taking cheap carbon sources, such as glucose and glycerol, as raw materials through fermentation is obtained by modifying the microorganism; the sialic acid yield of the recombinant microorganism is remarkably improved; efficient conversion from the cheap carbon sources, such as glucose and glycerol, to sialic acid is realized; the production cost of sialic acid is remarkably reduced; and the recombinant microorganism has important industrial application value.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
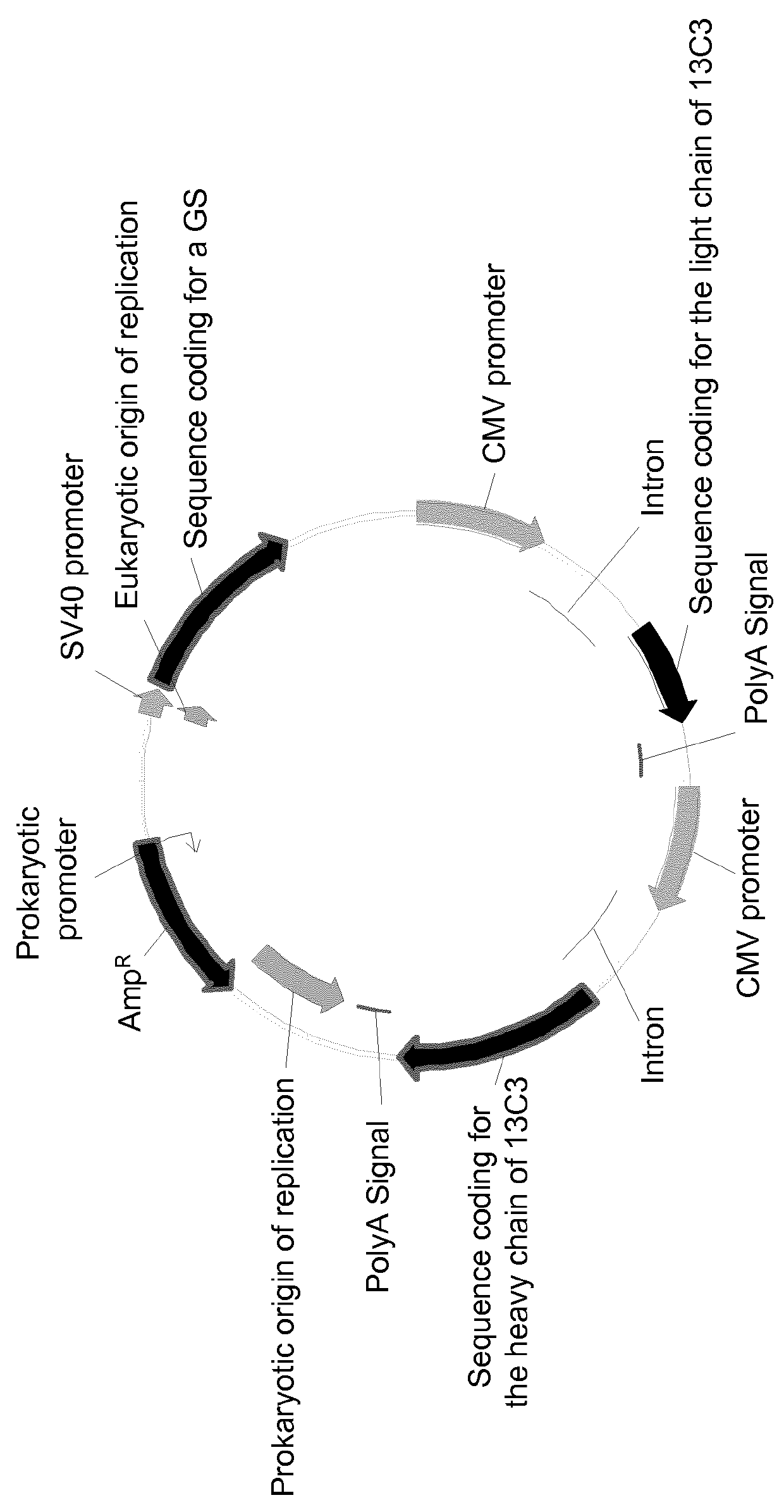
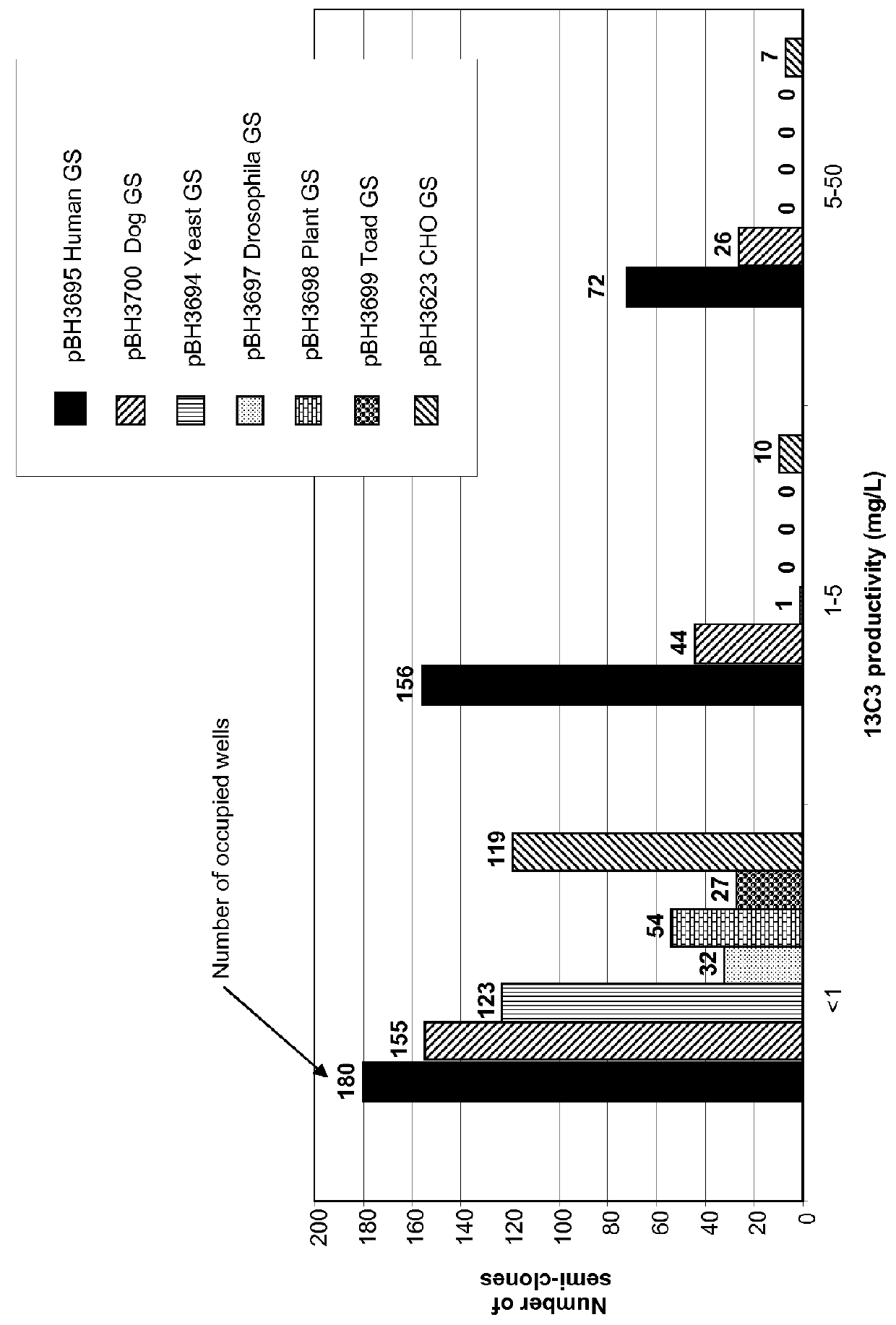
Expression vector comprising a polynucleotide encoding a modified glutamine synthetase and a method for preparing a target protein employing the same
Owner:ARES TRADING SA
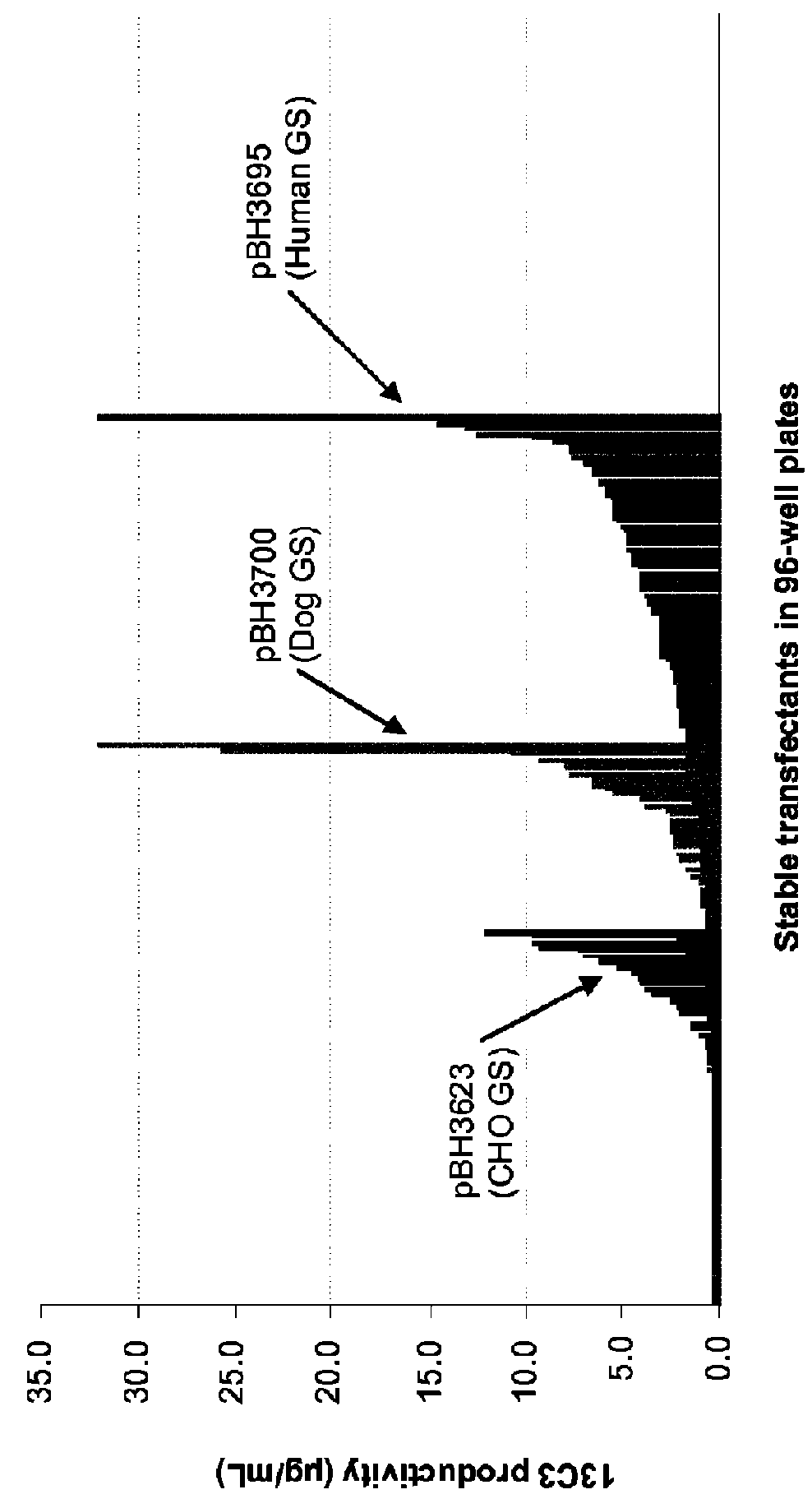
CHO expression system
The present invention is within the field of industrial protein production. The inventors have designed and constructed a new expression system comprising an expression vector coding for a glutamine synthetase of human or dog origin, and a CHO cell line. More specifically, the invention pertains to a combination of (i) a DNA vector suitable for production of a recombinant protein, wherein said vector comprises a sequence coding for a glutamine synthetase, and (ii) a Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cell line, wherein said GS comprises a sequence at least 94.5% identical to the sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1 or to the sequence of SEQ ID NO: 2.
Owner:SANOFI SA
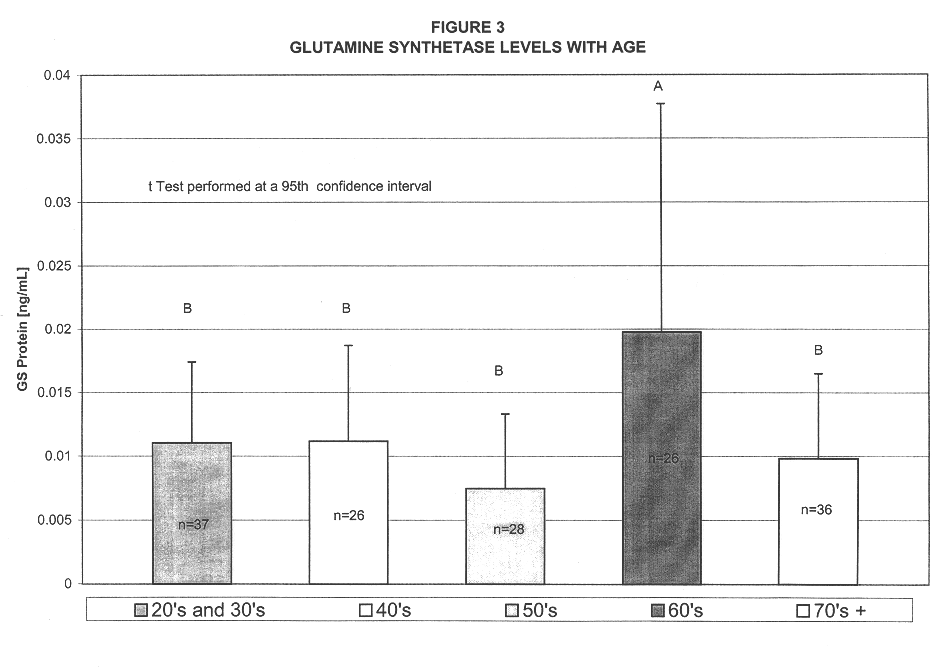
Process for determining the presence of monomeric brain associated human glutamine synthetase in patients exhibiting mild cognitive impairment
InactiveUS7070945B2Efficient identificationImprove diagnostic capabilitiesEnzymologyArtificial cell constructsWhole blood productMild cognitive impairment (MCI)
A method for determining those patients suffering from mild cognitive impairment (MCI) who have a likelihood of progressing to Alzheimer's disease (AD) is disclosed. The method involves directly detecting the presence of a biochemical marker, specifically human glutamine synthetase, in bodily fluid, preferably blood or a blood product. The detection is by an immunoassay incorporating an antibody specific to human glutamine synthetase. In addition, a method for distinguishing between AD and non-AD dementia is disclosed.
Owner:NANOGEN INC
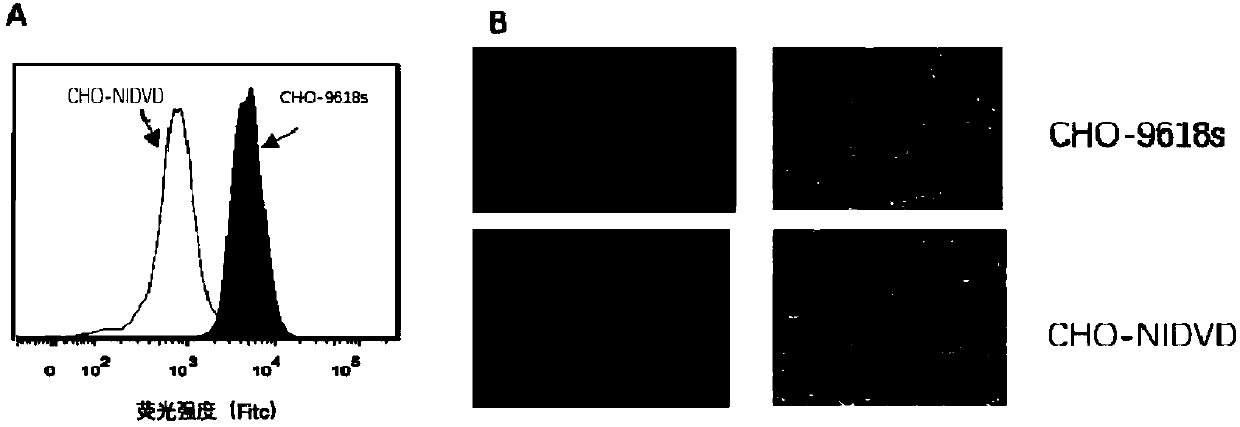
Modified Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells and application thereof
ActiveCN107760650AHigh density growthImprove efficacyMicroorganism based processesImmunoglobulinsBiotechnologyHamster
The invention relates to modified CHO cells and application thereof. The modified CHO cells can realize stable and high-density growth under condition of serum-free suspension culture, and preferably,the modified CHO cells do not express functional glutamine synthetase (GS) and fucosyltransferase 8 (FUT8). The modified CHO cells are particularly applicable to high-level eukaryotic expression of recombinant proteins (especially antibodies), and thus have good application prospects in the fields of genetic engineering and protein engineering.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV +1
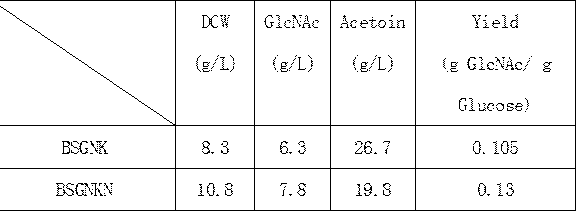
Recombinant bacillus subtilis and method for promoting synthesis of acetylglucosamine by overexpressing glutamine synthetase by virtue of recombinant bacillus subtilis
InactiveCN108570441AEasy to buildEasy to useBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliExtracellular
The invention discloses recombinant bacillus subtilis. According to the recombinant bacillus subtilis, on the basis of the recombinant bacillus subtilis BSGNK, escherichia coli glutamine synthetase (EglnA) is overexpressed so as to obtain recombinant bacteria BSGNKN; and the recombinant bacillus subtilis BSGNK takes B. subtilis 168 delta nagP delta gamP delta gamA delta nagA delta nagB delta ldh delta pta delta glck::lox72 as a host, and the recombinant expression of glms and GNA1 is controlled by promoters PxylA and P43 respectively. The invention further discloses a method for promoting thesynthesis of acetylglucosamine by overexpressing the glutamine synthetase by virtue of the recombinant bacillus subtilis. The obtained recombinant bacillus subtilis has the advantages that the extracellular accumulation efficiency of the acetylglucosamine and the conversion efficiency of a substrate can be improved, the content of the acetylglucosamine in fermentation supernate is 7.8 g / L and is increased by 23.8% compared with the content of the acetylglucosamine of control bacteria BSGNK, a foundation is laid for further metabolic engineering modification of the bacillus subtilis for production of glucosamine, and in addition, the recombinant bacillus subtilis is simple in construction method and convenient to use and has a good application prospect.
Owner:DAZIRAN BIOLOGICAL GRP CO LTD
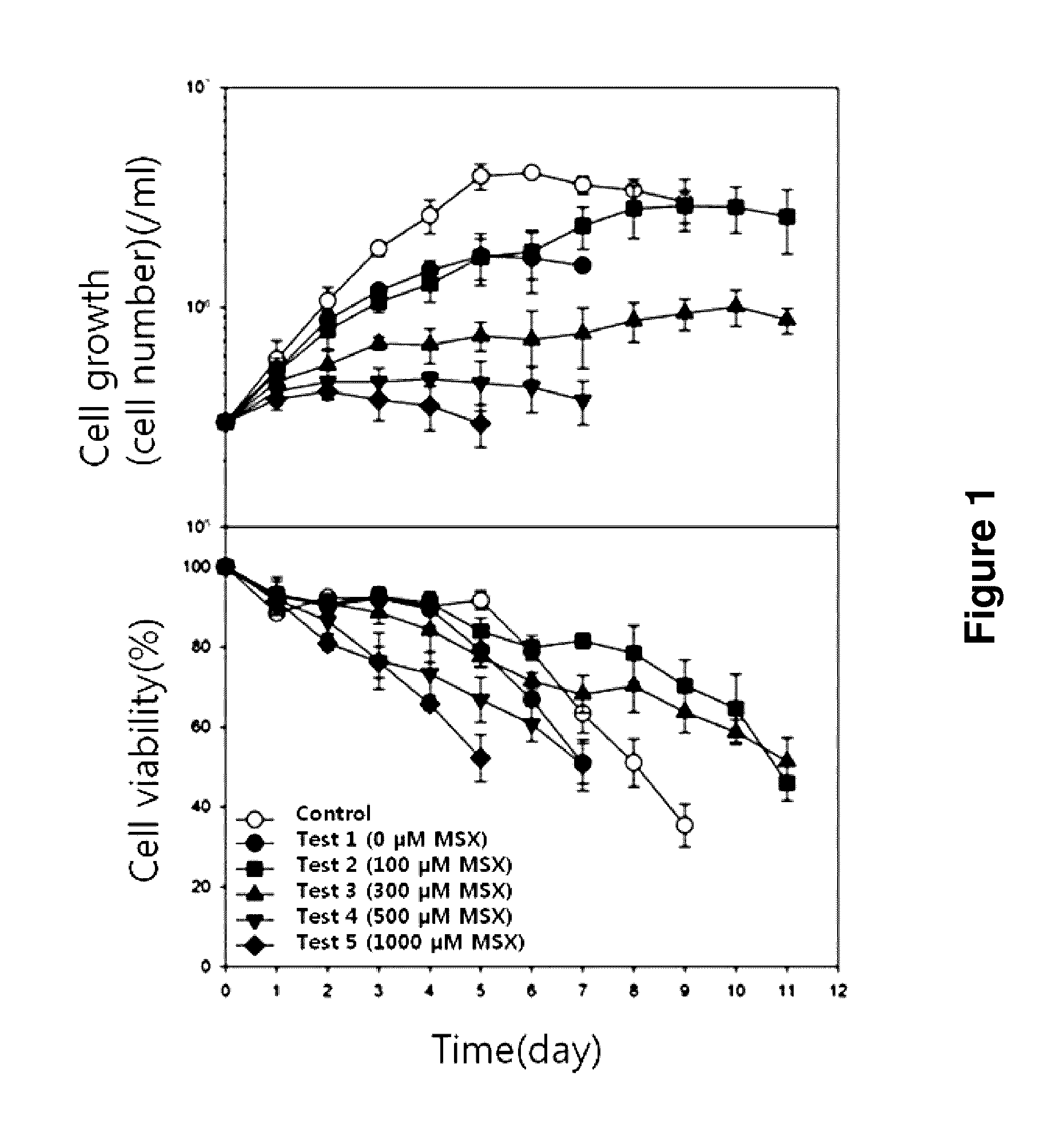
Cell line containing a knockout of the glutamine synthetase (GS) gene and a method of producing target proteins using a GS knockout HEK293 cell line
ActiveUS9567578B1Efficient cell lineLoses synthesis abilityGenetically modified cellsArtificial cell constructsProtein targetKidney
The present invention relates to a novel GS (glutamine synthetase) gene knock out transgenic HEK293 (human embryonic kidney 293) cell line and a production method of a target protein using the said transgenic HEK293 cell line. Particularly, the present inventors eliminated the expression of GS in the HEK293 cells in order to overcome a barrier of the cell line selection caused by the over-expression of GS, for producing a target protein by GS / MSX system, by which the efficiency of the cell line selection for the high production of a target protein would be increased and accordingly the protein production by the selected cell line would be increased, suggesting that the human originated transgenic HEK293 cell line could be efficiently used for the production of a target protein.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
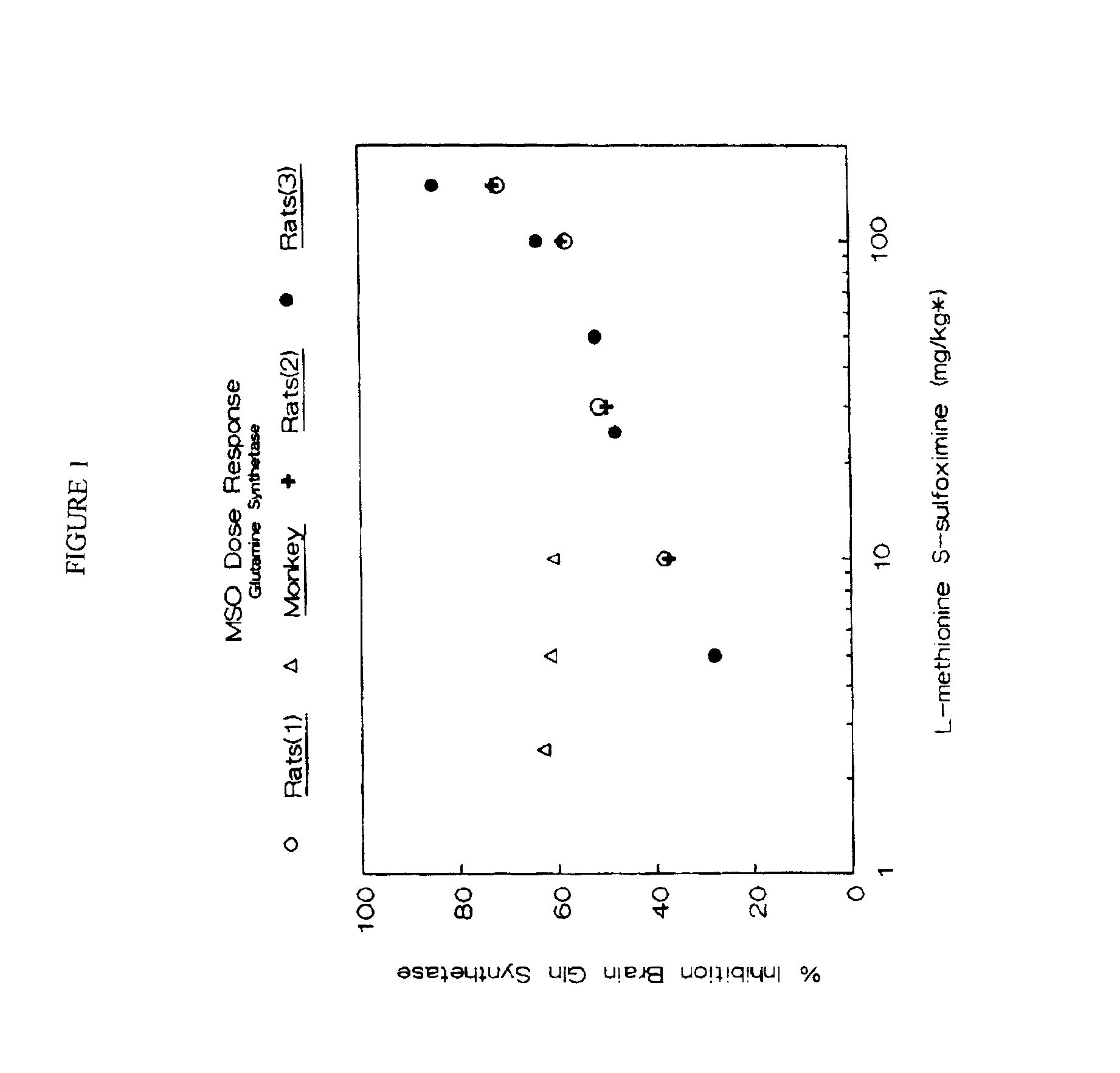
Dosage form of L-Methionine S-Sulfoximine
InactiveUS6875792B2Suppression problemLower Level RequirementsBiocideNervous disorderDiseaseHyperammonemic encephalopathy
Methods for the treatment of both diseases susceptible to the inhibition of mammalian glutamine synthetase and progressive hyperammonemic encephalopathy comprising administering L-methionine S-sulfoxime at a dose not to exceed 10 mg / kg body weight are disclosed. Preferably, the dose should not exceed 8 mg / kg; more preferably, the dose should not exceed 5 mg / kg; most preferably, the dose should not exceed 2.5 mg / kg.
Owner:BURTCH PHARMA LLC
Process for the production of plants with enhanced growth characteristics
InactiveUS6846969B2Enhance plant growthImprove growth performanceClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyAntisense Orientation
The invention is drawn to plant cell transformation with a nucleic acid construct comprising a prokaryotic ammonium-specific asparagine synthetase, type A, coding sequence, operably linked to a chloroplast transit peptide-encoding sequence, wherein said plant cells also contain a nucleic acid construct comprising a chloroplastic glutamine synthetase coding sequence in antisense orientation. Plant cells containing both nucleic acid constructs, and plants regenerated therefrom, exhibit improved growth characteristics.
Owner:BAYER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY GMBH
Chaperonin and osmolyte protein folding and related screening methods
The invention describes an inexpensive in vitro protein folding process for preventing large scale protein misfolding and aggregation, for concentrating aggregation prone chaperonin-protein folding intermediates in a stable non-aggregating form, and for rapidly screening these stable concentrates for the best folding solution conditions. The process comprises: (1) the formation of a chaperone-substrate complex and (2) the release of the substrate using a broad array of folding solutions containing different osmolyte ions, detergents, gradients of ionic strength and pH or other commonly used folding additives. Specifically, when the chaperonin / osmolyte protein process was applied to identify and optimize GSΔ468 bacterial glutamine synthetase mutant refolding conditions that otherwise cannot be folded in vitro by commonly used techniques, 67% of the enzymatic activity was recovered.
Owner:KANSAS MEDICAL CENT UNIV OF
High efficiency biological weed control bacterial and breeding selection method
InactiveCN1446465ALoose requirementsPlay the role of enriching soil microorganismsBiocideAnimal repellantsXanthomonas campestrisDepressant
An efficient bioherbiciding xanthomonas campestris pv. retroflexus is prepared through sampling the soil near the root of weeds such as crabgrass herb, caper euphorbia, cassia, etc and their stem andleaves, separating with NPC culture medium and chlorella pyrenoidosa and glutamine synthetase depressants, and screening the bacterial strains with high herbiciding activity and broad spectrum. Its advantage is high herbiciding effect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum and application thereof in production of L-glutamine
ActiveCN113684165AIncrease productionHigh glycosamine conversion rateBacteriaTransferasesBacterosiraGlutamic acid
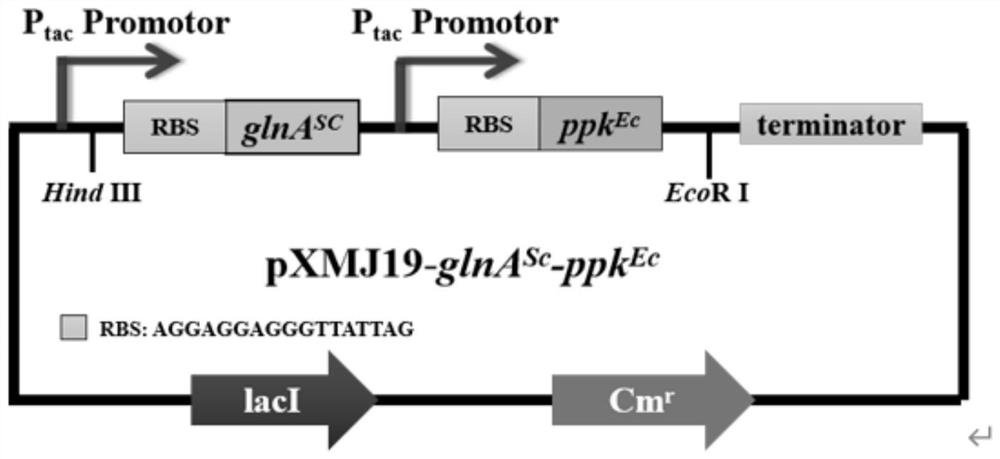
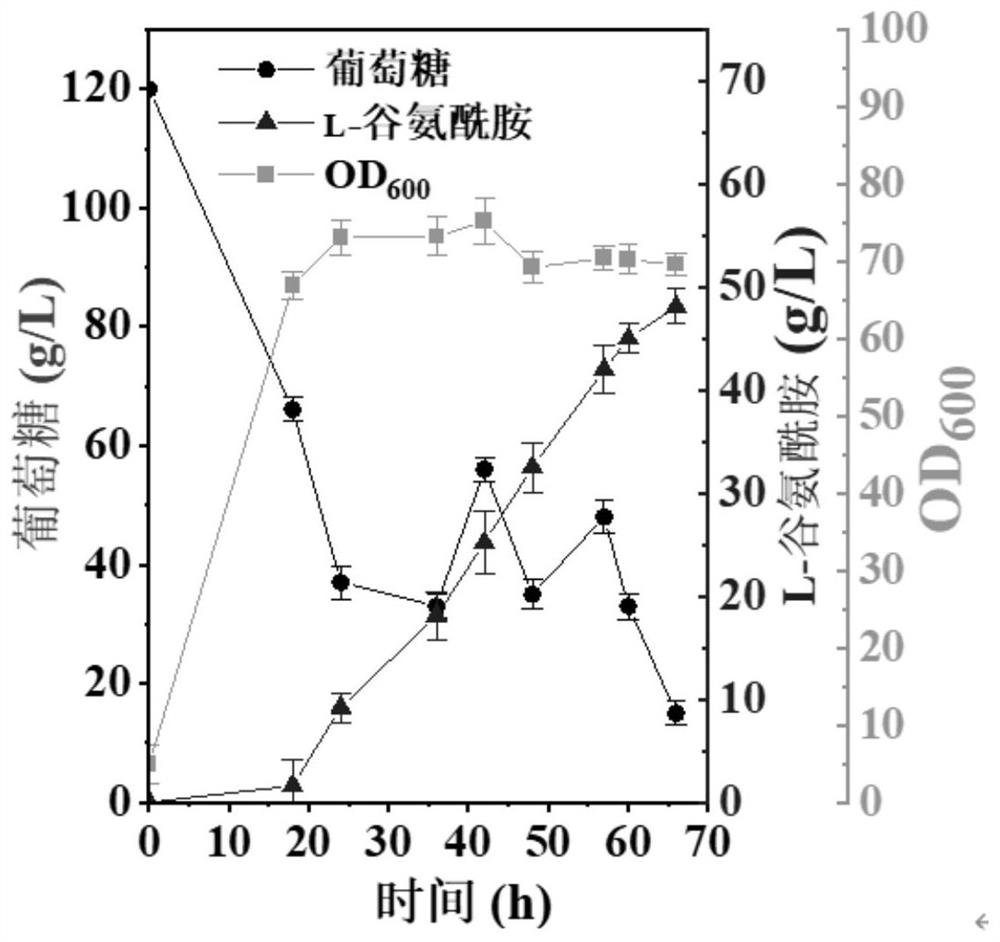
The invention discloses recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum and application thereof in production of L-glutamine, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The activity of gamma-glutamate kinase, glutamic acid secretion mechanical channel protein and adenosine acylase of glutamine synthetase in cells of the recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum is lost, and plasmid pXMJ19 is used for co-expressing the glutamine synthetase from saccharomyces cerevisiae and polyphosphate kinase from escherichia coli. The invention provides the recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum CGQ03 / pXMJ19-glnASc-ppkEc capable of producing the L-glutamine at high yield; the recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum is inoculated into a 5L fermentation tank and is fermented for 66h, so that the yield of the L-glutamine in fermentation liquid reaches 73.5 + / -3.1g / L and the conversion rate of glucosamine reaches 0.368 + / -0.034.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Corynebacterium glutamicum for high yield of L-glutamine as well as construction method and application thereof
PendingCN110951661AIncrease productionImprove conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGlutaric acidKetoglutarate dehydrogenase
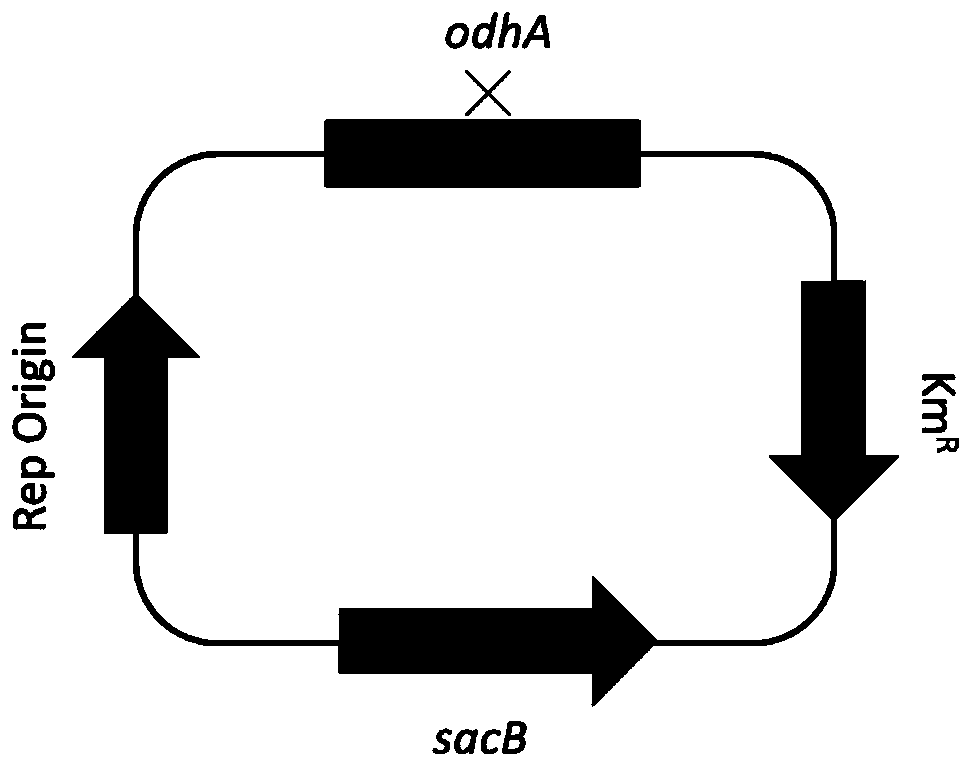
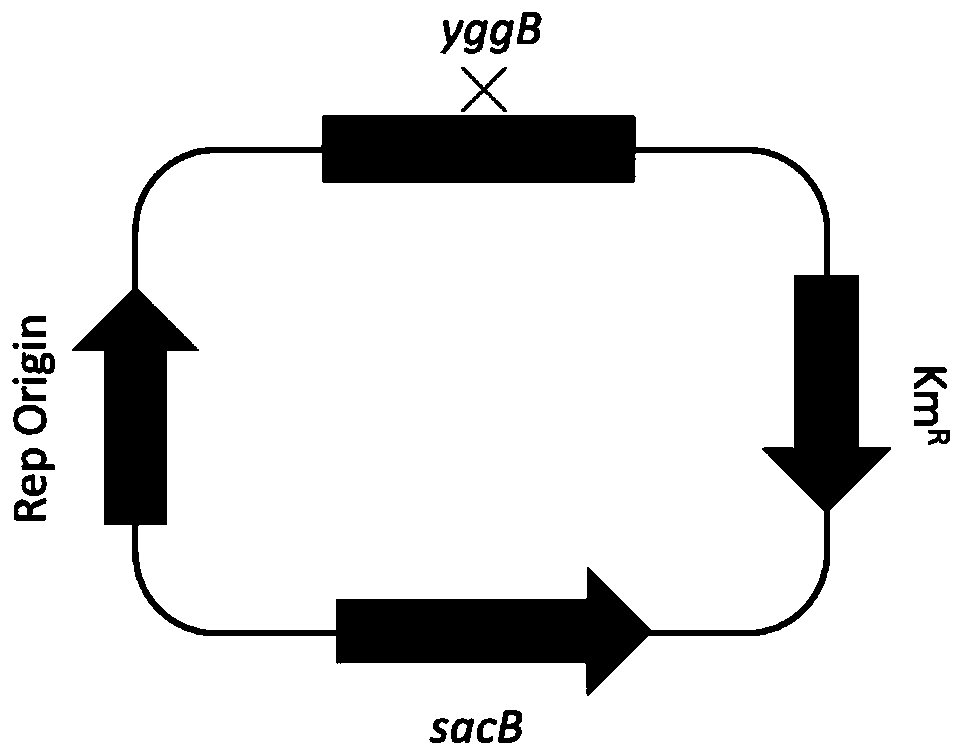
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering, and discloses corynebacterium glutamicum for high yield of L-glutamine as well as a construction method and an application of corynebacterium glutamicum. The activity of alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase and / or glutamic acid exporter protein in cells of the corynebacterium glutamicum for highly producing L-glutamine is lost, and adenylation modification of glutamine synthetase is removed. According to the corynebacterium glutamicum for highly producing L-glutamine disclosed by the invention, L-glutamine can be accumulated in a culture medium or cells, so that the yield of L-glutamine is increased to a great extent. The experiments show that the corynebacterium glutamicum disclosed by the invention is an L-glutamine high-yieldstrain; compared with an unmodified strain, the strain has the advantages that the capacity of producing L-glutamine is enhanced, L-glutamine can be effectively accumulated, the yield of L-glutamine is increased, the conversion rate is relatively high, a foundation is laid for industrial production of L-glutamine, and the strain has a wide industrial application prospect.
Owner:新疆梅花氨基酸有限责任公司
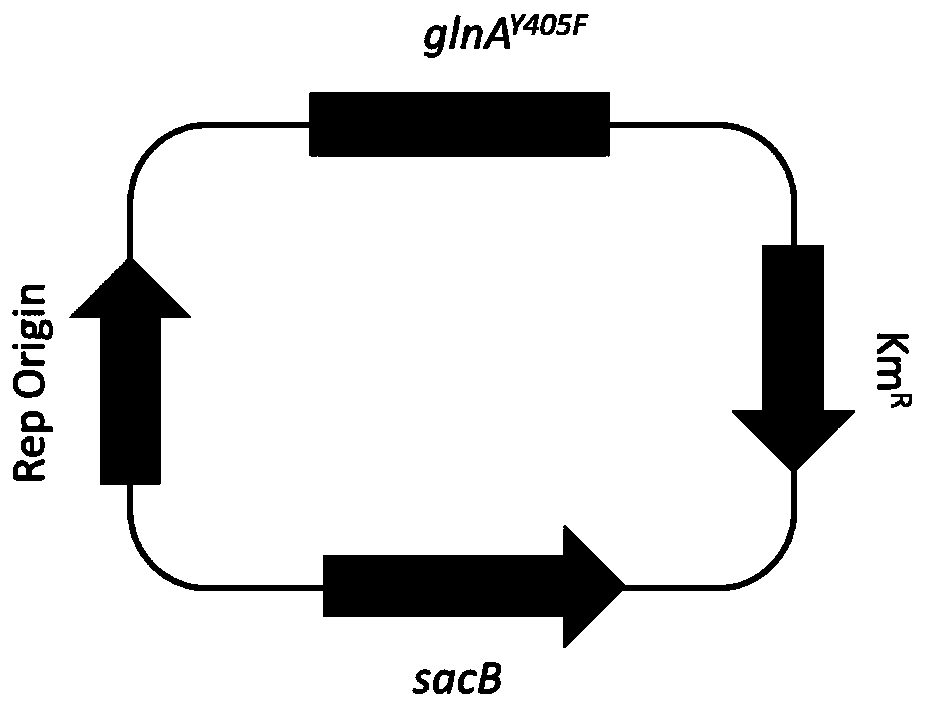
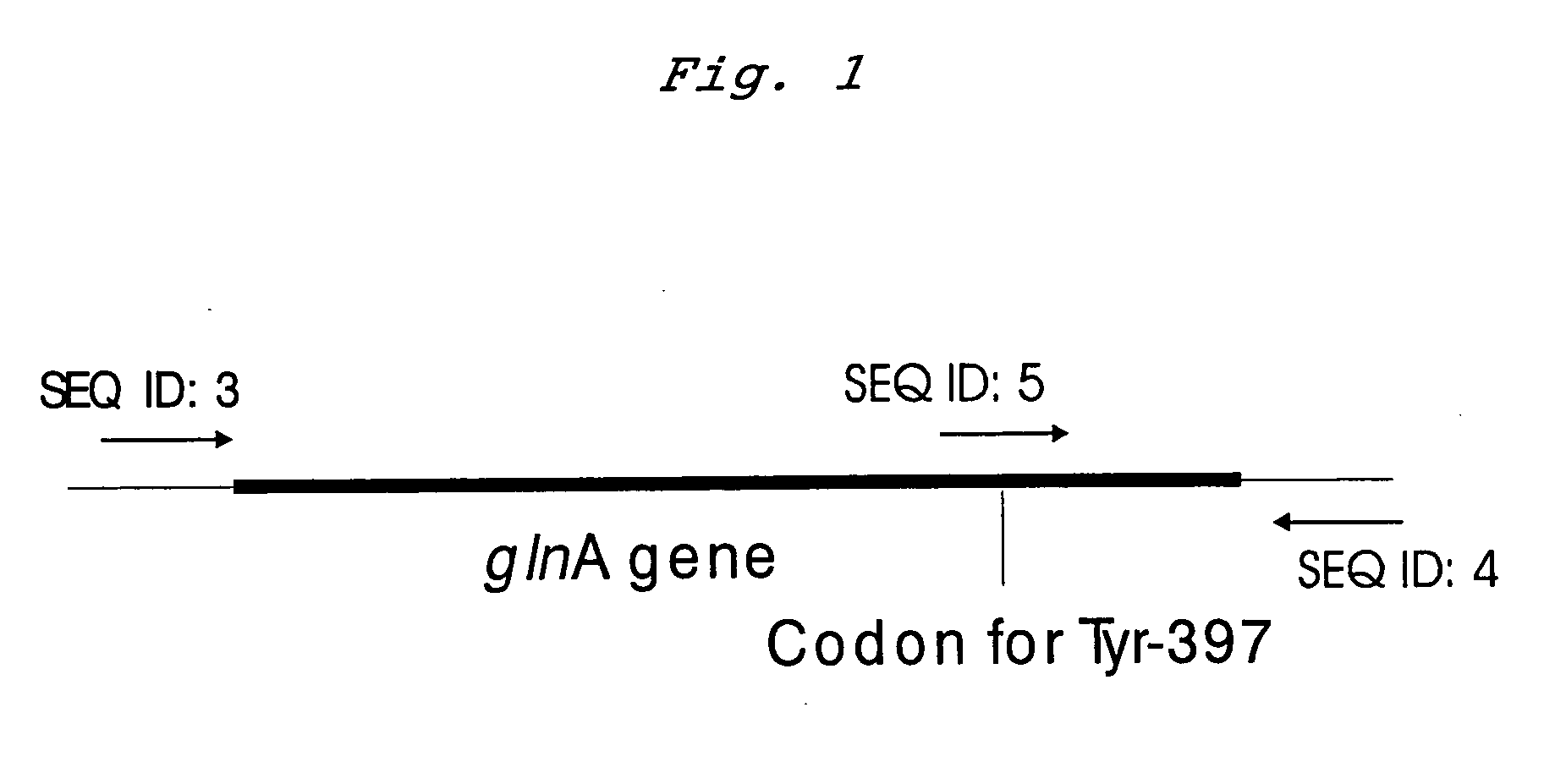
Mutant glutamine synthetase and method for producing amino acids
Amino acids, such as L-glutamine, L-arginine, L-tryptophan, L-histidine and L-glutamate are produced using a bacterium belonging to the genus Escherichia harboring a mutant glutamine synthetase in which the tyrosine amino acid residue corresponding to position 397 in a wild type glutamine synthetase is replaced with any of amino acid residues, preferably with phenylalanine.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Plant-derived glufosinate-resistant glutamine synthetase mutant, nucleic acid molecule and application
PendingCN112574967AGlufosinate-resistantMaintain biological enzyme catalytic activityLigasesVector-based foreign material introductionPlant SourcesGene engineering
The invention discloses a plant-derived glutamine synthetase mutant with glufosinate-ammonium resistance, a nucleic acid molecule and application, and relates to the technical field of gene engineering. Compared with the wild glutamine synthetase, the glutamine synthetase mutant disclosed by the invention has mutation at the nth site, wherein D, E, G, H, N, P, Q and V are formed or deleted after mutation, so that the glutamine synthetase by the mutation hasglufosinate-ammonium resistance. Thus, the glutamine synthetase mutant can be used for cultivating a new glufosinate-resistant plant variety.
Owner:SICHUAN GEVOTO BIOTECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com