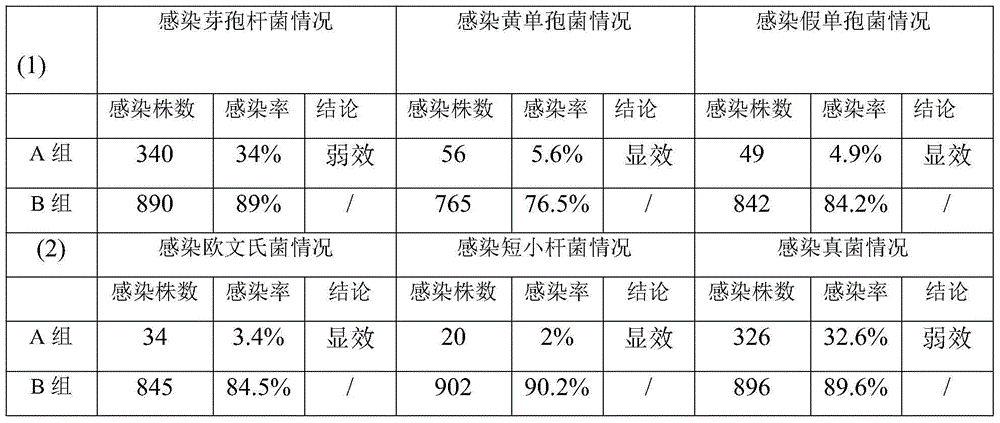
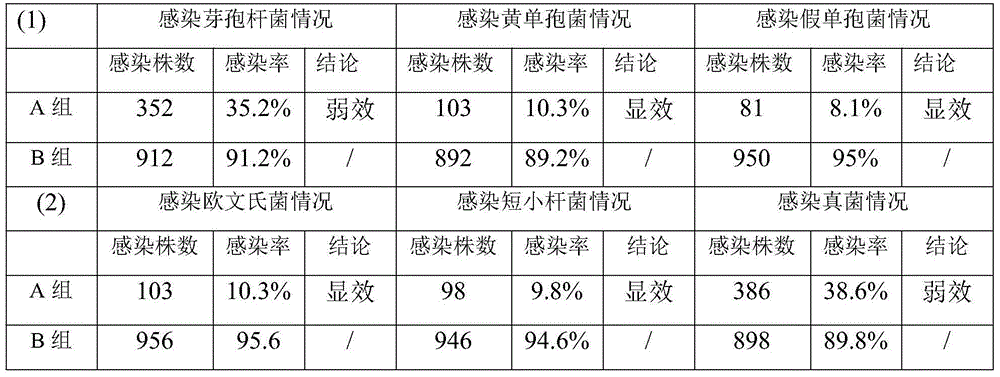
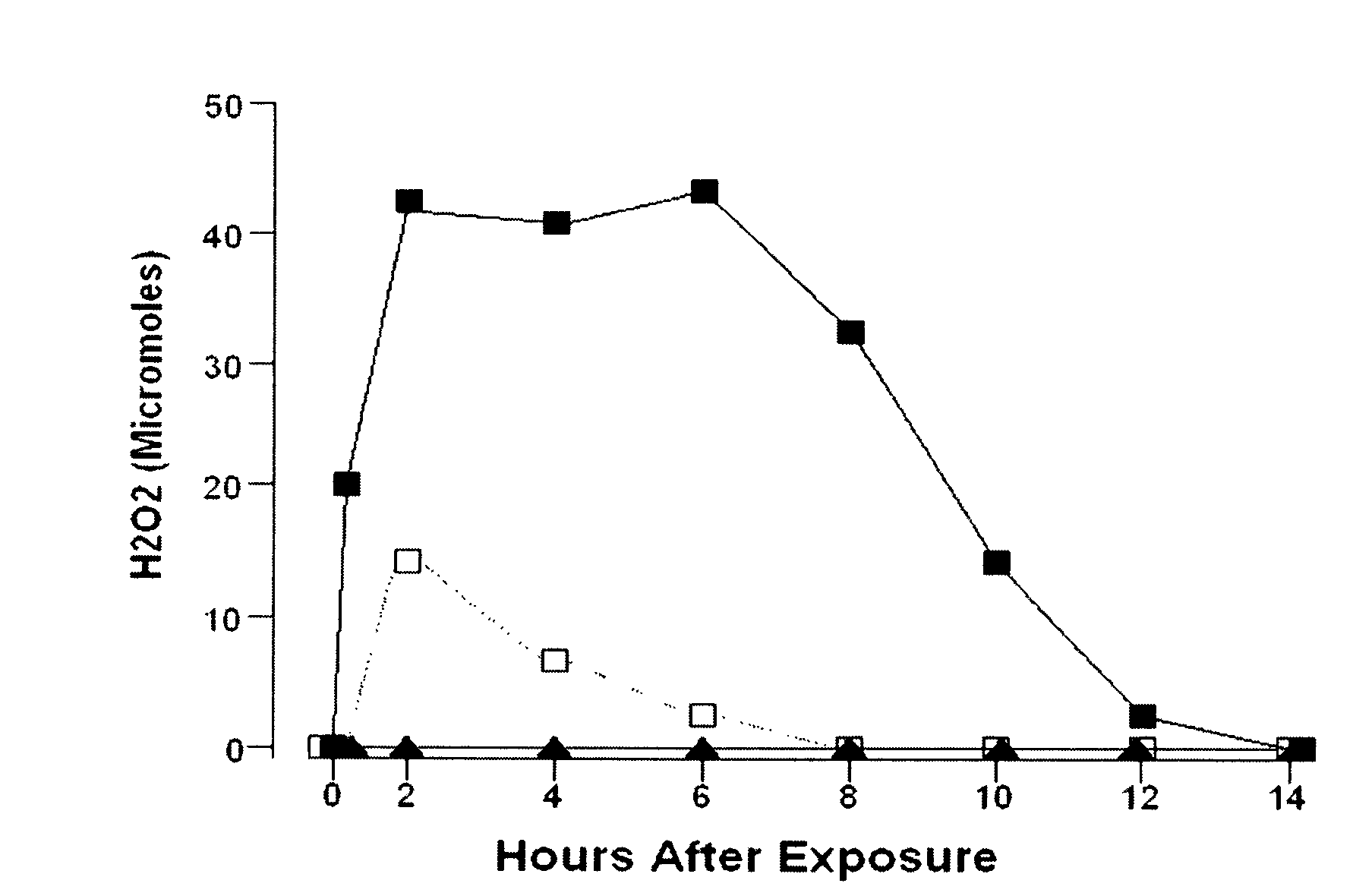
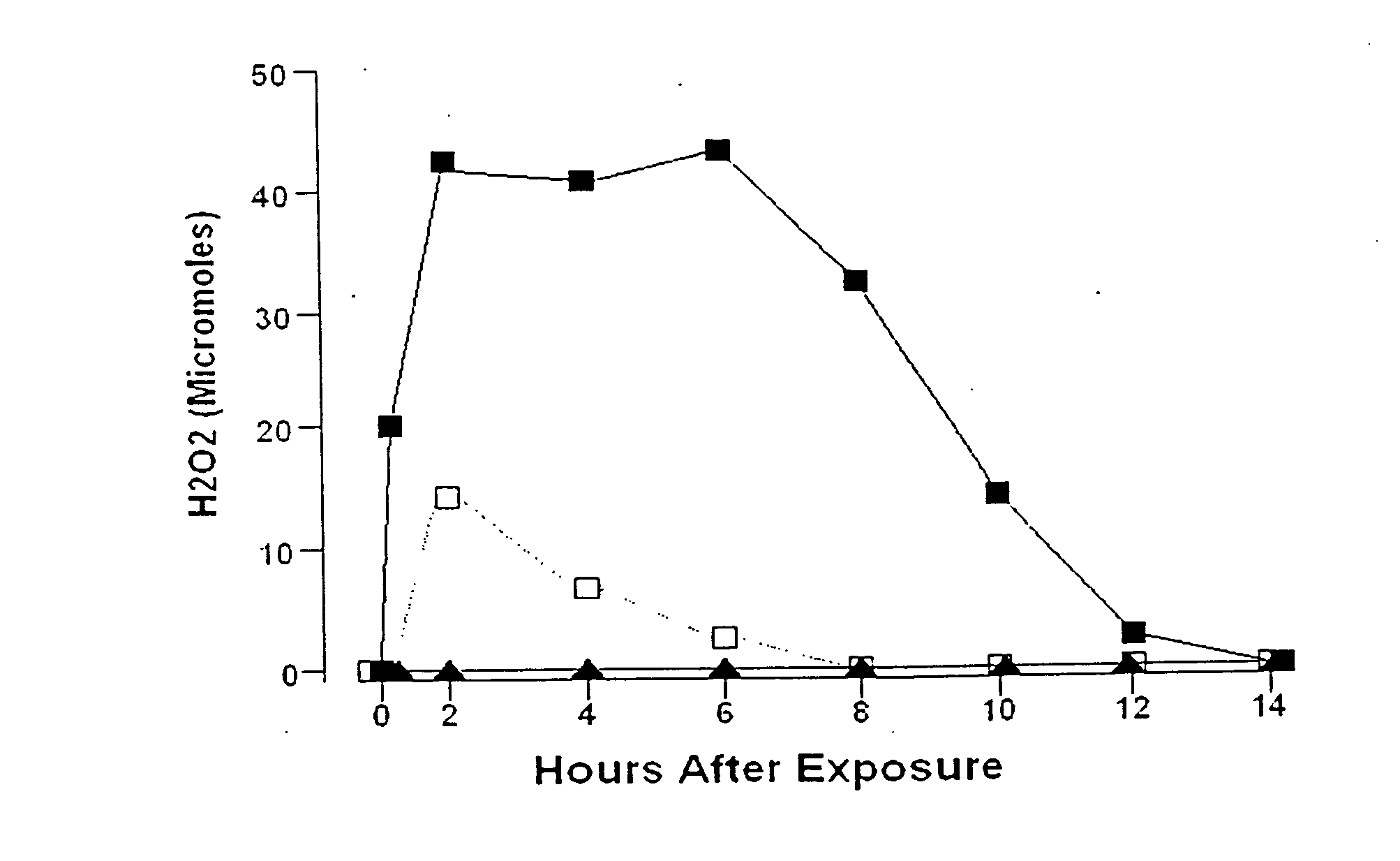
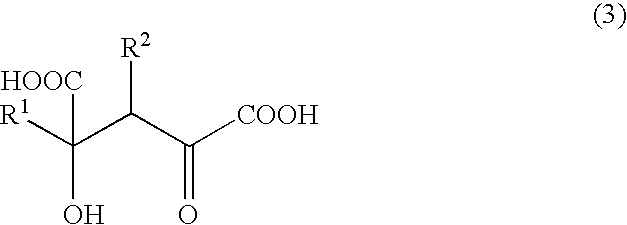Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
221 results about "Xanthomonas campestris" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Xanthomonas campestris is bacterial species that causes a variety of plant diseases, including "black rot" in cruciferous vegetables and bacterial wilt of turfgrass. It is also used in the commercial production of xanthan gum, a high-molecular-weight polysaccharide which has many important uses, especially in the food industry.
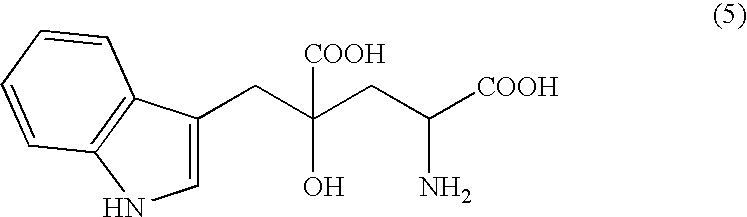
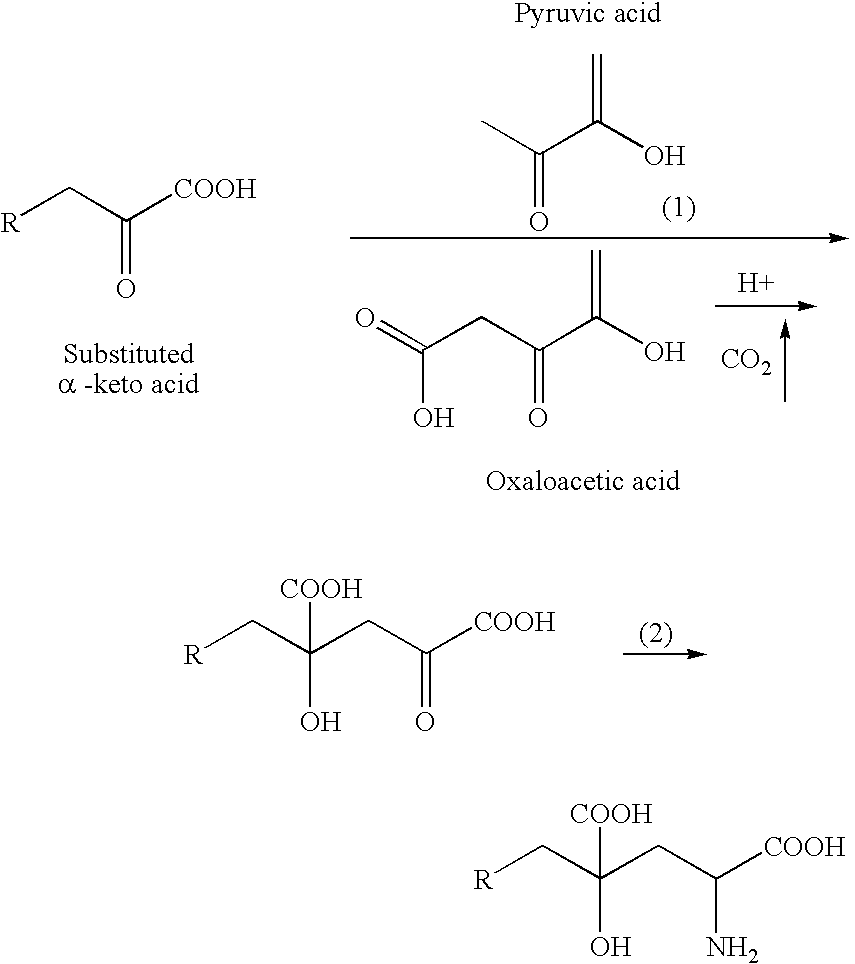
Novel aldolase and production process of substituted alpha-keto acids
4-(Indol-3-ylmethyl)-4-hydroxy-2-oxoglutarate, which is useful as an intermediate in the synthesis of monatin, may be synthesized from indole pyruvic acid and pyruvic acid (and / or oxaloacetic acid) by using a novel aldolase derived from the genus Pseudomonas, Erwinia, Flavobacterium, or Xanthomonas.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
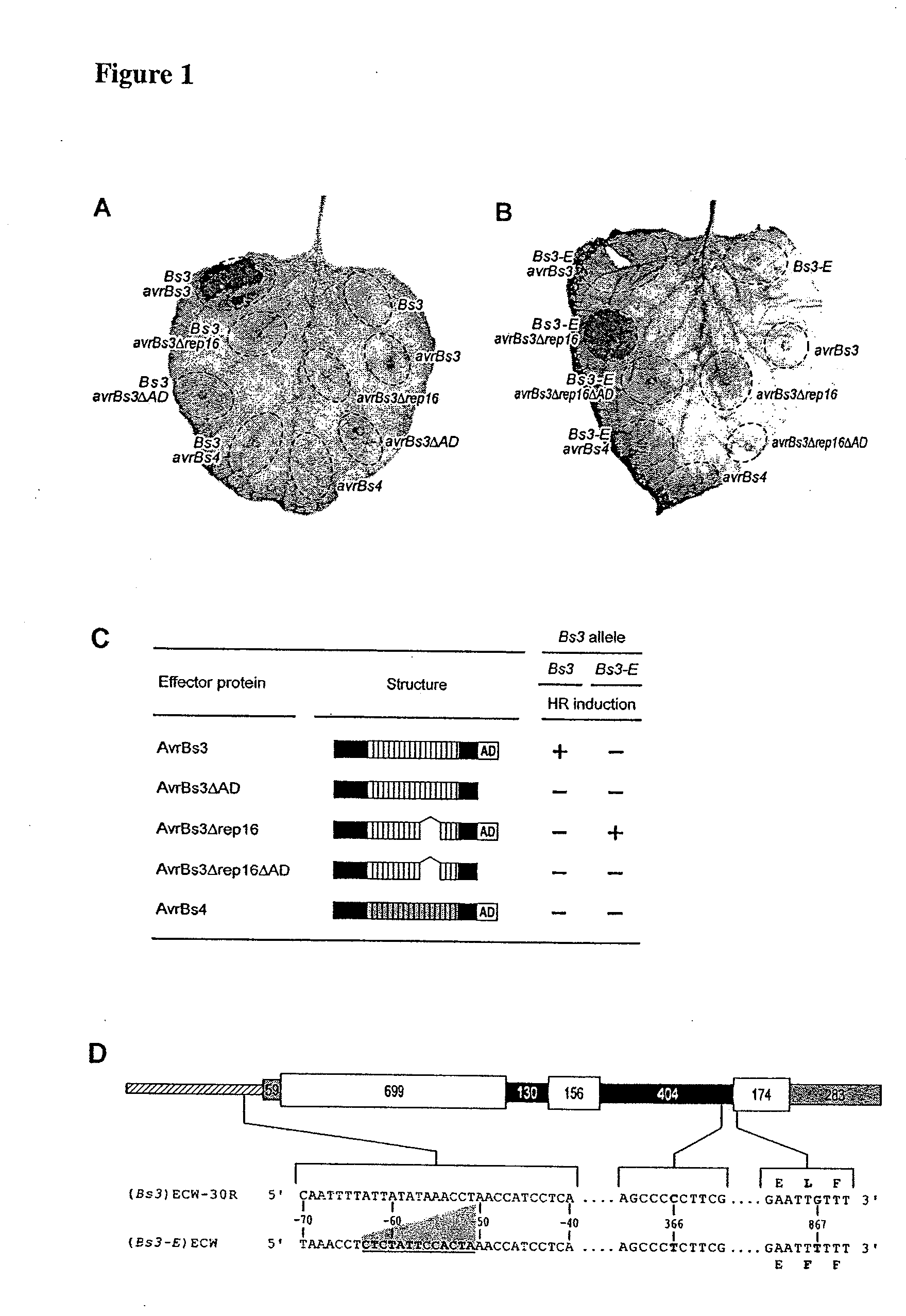
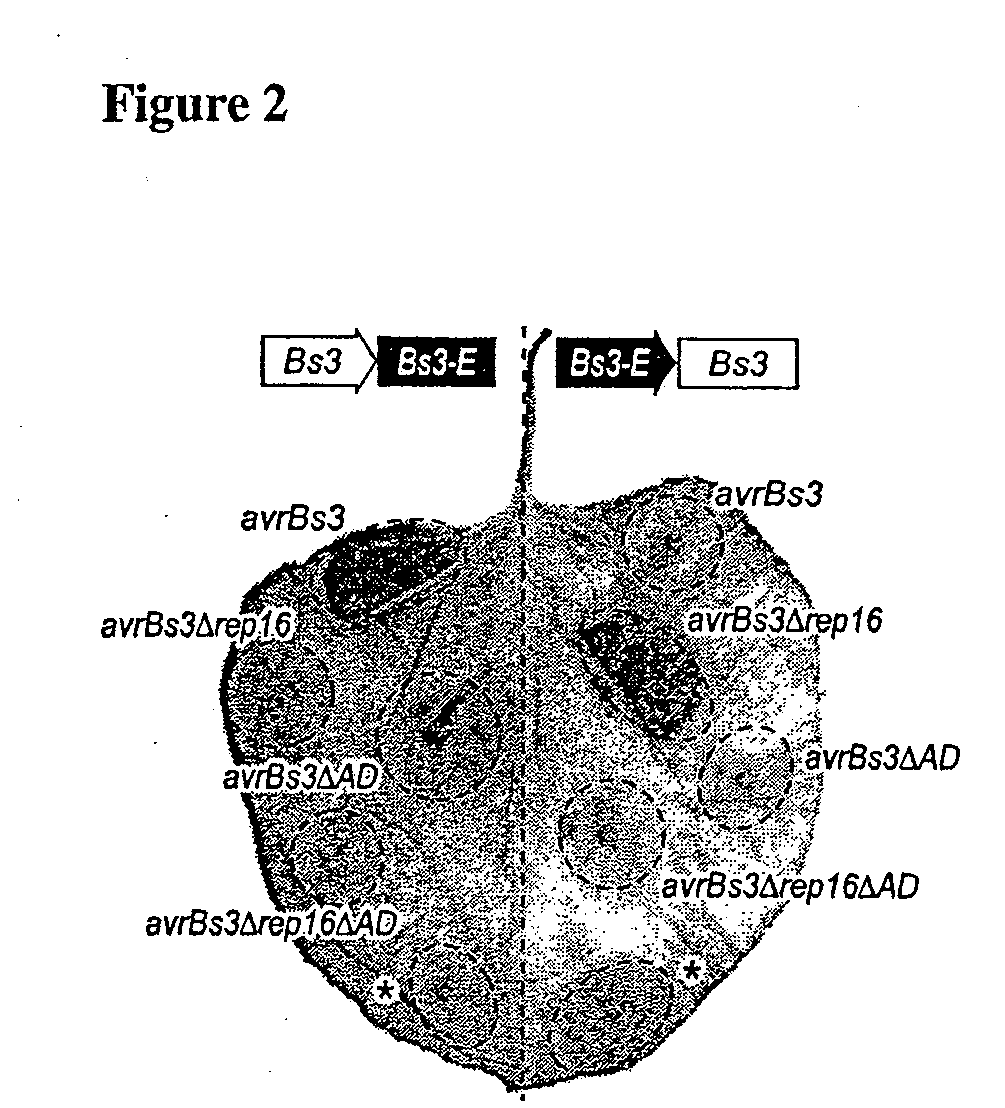
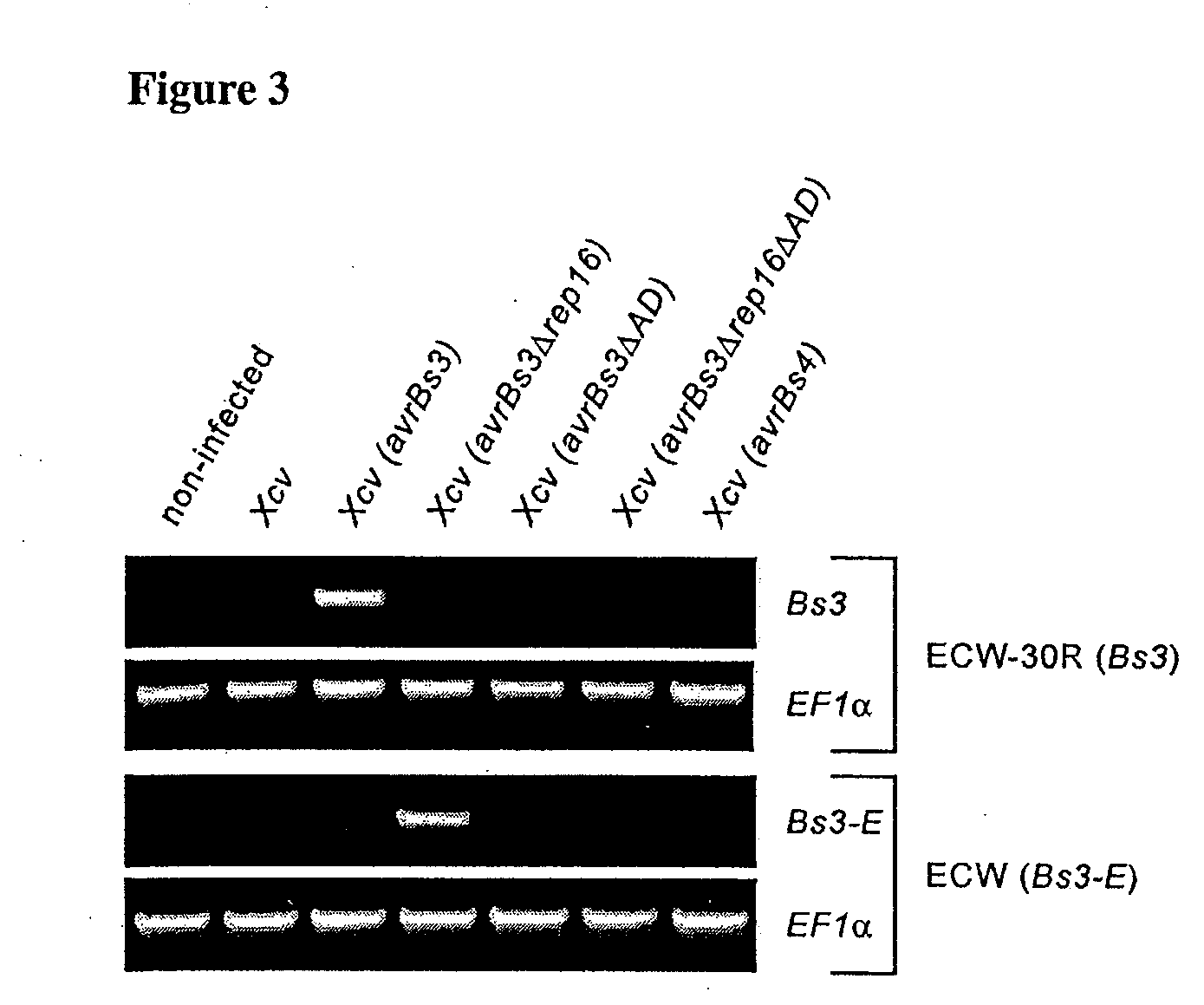
Bs3 resistance gene and methods of use
ActiveUS20090133158A1Improve plant resistanceImprove the immunityBryophytesSugar derivativesXanthomonas campestrisBacteroides
Isolated nucleic acid molecules that confer resistance to the plant pathogen Xanthomonas campestris are provided. These molecules may be introduced into plants that are otherwise susceptible to infection by this bacterium in order to enhance the resistance of the plant to this plant pathogen. Additionally provided are isolated polypeptides and isolated nucleic acid molecules comprising plant promoters. Methods of using the nucleic acid molecules to increase the resistance of plants to pathogens and to express genes of interest in plants are provided.
Owner:TWO BLADES FOUND
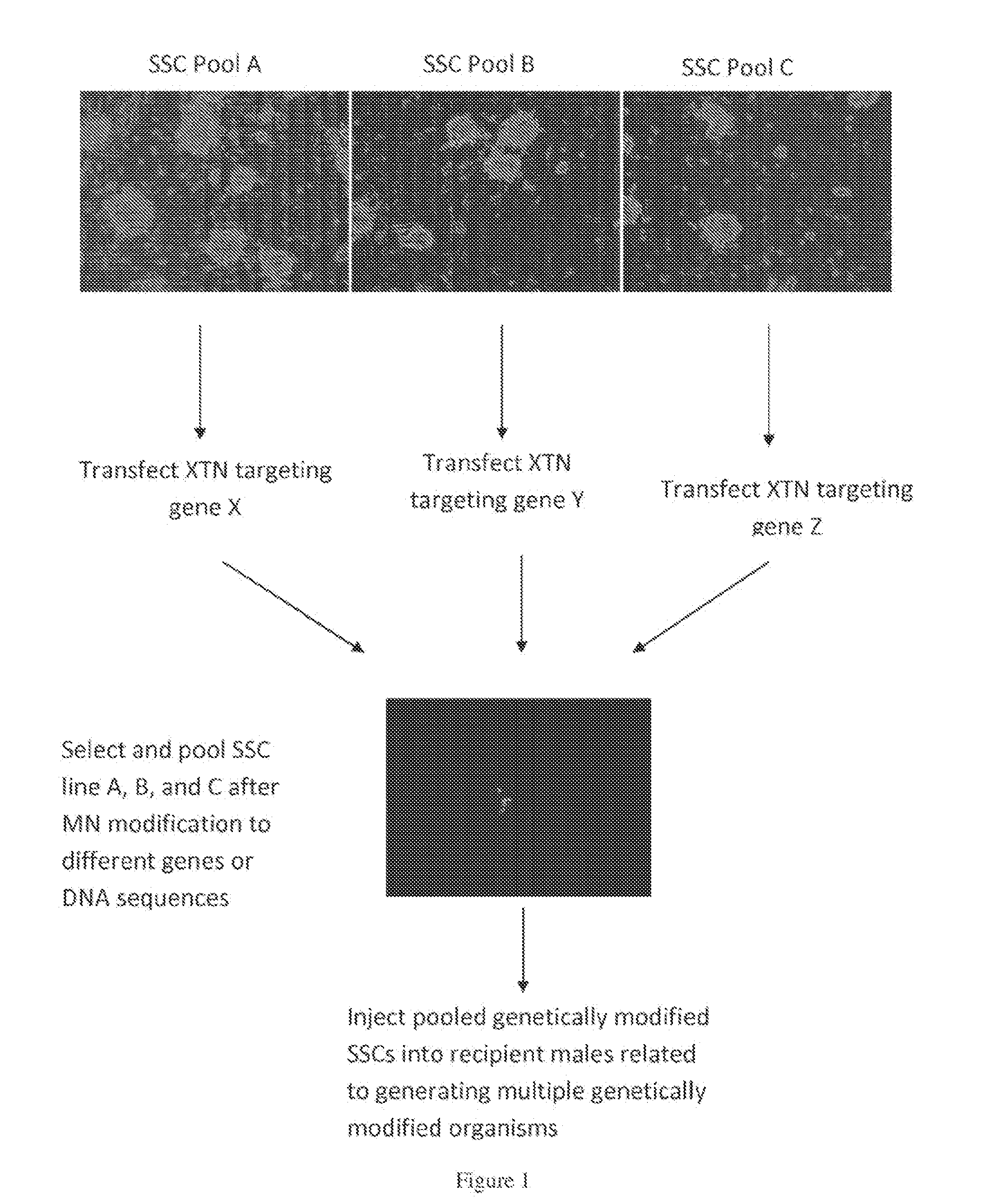
Methods for site-specific genetic modification in stem cells using xanthomonas tal nucleases (XTN) for the creation of model organisms
InactiveUS20140201858A1FermentationVector-based foreign material introductionHeterologousXanthomonas campestris
The invention relates to organisms and compositions comprising one or more stem cells or one or more embryos, wherein the one or more stem cells or one or more embryos comprise one or more of the following mutations: (i) a deletion mutation; (ii) a knockout mutation; and / or (iii) an addition of a heterologous nucleic acid sequence; wherein the one or more mutations of (i), (ii), and / or (iii) are site-specific mutations caused by a Xanthomonas TAL nuclease (XTN). The invention also relates to method of mutating an embryo, iPS cell, stem cell, or more particularly a spermatogonial stem cell by exposing the nucleic acid sequence contained within such embryos or cell with a Xanthomonas TAL nuclease.
Owner:TRANSPOSAGEN BIOPHARM +1
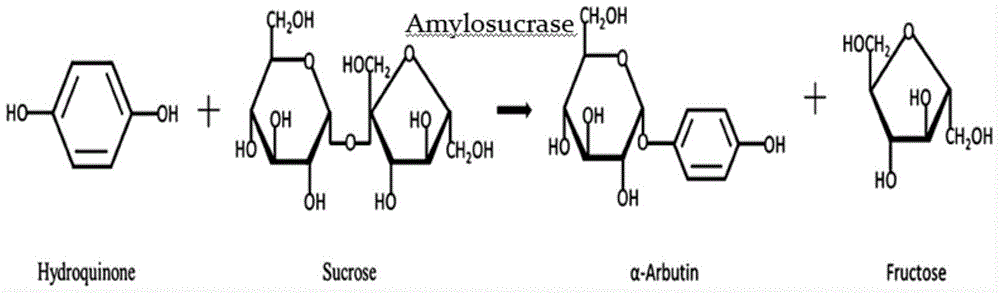
Process for preparing alpha-arbutin through fermentation
ActiveCN1635139AIncrease productionReduce manufacturing costFermentationXanthomonas campestrisALPHA-ARBUTIN
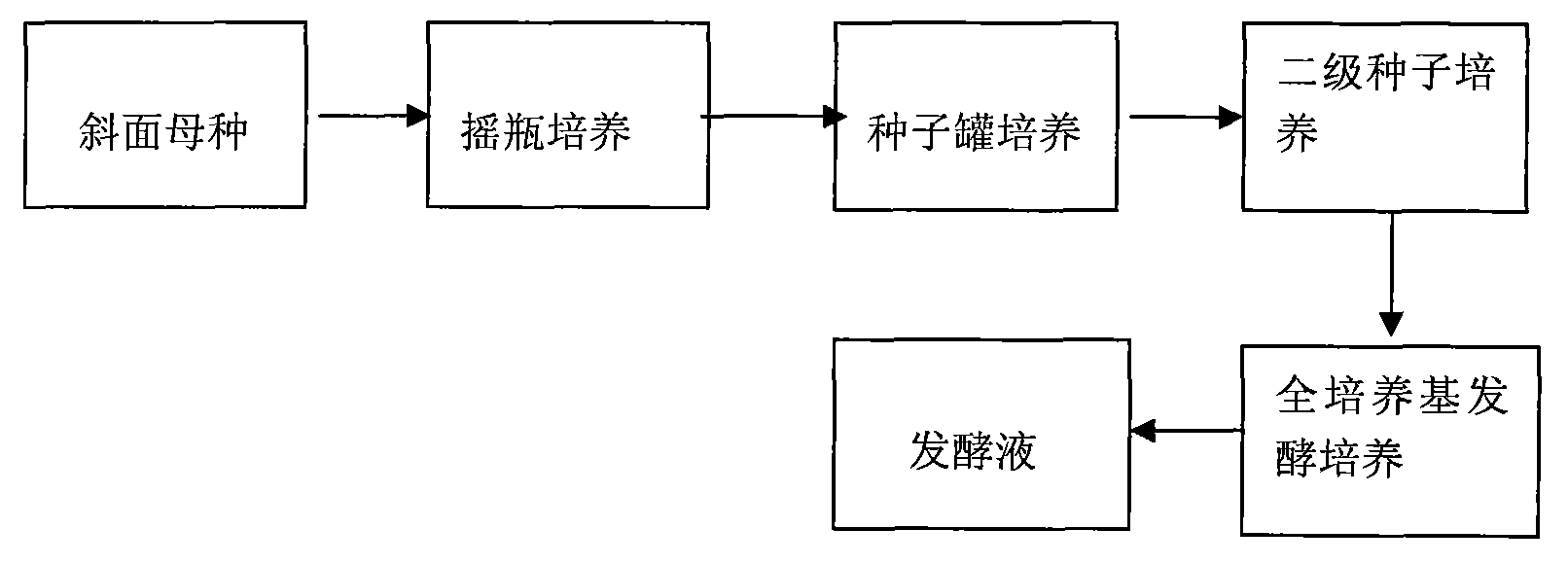
The invention relates to a method for preparing alpha-arbutin which comprises steps of preparing slope seeds, selecting culture mediums, optimizing reaction conditions and extracting products and so on. The invention employs Xanthomonas campestris to ferment to produce the alpha-arbutin without use of organic solvents during the production and generation of harmful substances during the fermentation process. The invention has advantages of low production cost, simple process, and safe operation. And the alpha-arbutin yield produced by the method is high, the alpha-arbutin content in fermentation liquor is 8-11g / L, and the conversion rate of the hydroquinone can be 91%. The alpha-arbutin can obviously inhibit activities of tyrosinase, reduce tyrosinase deposition in skins, and bleach skins, remove freckles.
Owner:CHENGZHI LIFE SCI CO LTD
High-temperature compost decay-promoting bacterial compound inoculant and applications thereof
InactiveCN103614326ASimplify the manufacturing processDecomposition function is stableBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaBiotechnologyXanthomonas campestris
The invention discloses a compost inoculant and applications thereof. The active ingredients of the composting inoculant provided by the invention include clostridium thermocellum, geobacillus stearothermophilus, Taiwan false xanthomonas, brevibacillus agri and bacillus licheniformis in a CFU (colony-forming unit) ratio of (3-5):(1-2):(1-2):(1-2):(1-2). Strains in the inoculant provided by the invention can grow in a symbiosis state well, and under the conditions of microaerobic co-culturing, lignocelluloses can be regularly proliferated and effectively decomposed in proportion. The inoculant is simple in manufacturing process due to co-culturing, stable in decomposition function, and long in quality ensured period. Experiments show that when the inoculant is adopted for fermenting composts, large gas feeding is not required, the energy is saved, and the nitrogen loss is reduced; composts can be thoroughly decomposed in advance, thereby improving the quality of fertilizers.
Owner:MOUNT EMEI GREEN LAND ECOLOGICAL AGRI DEV LIMITED
Microbial agent, and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN102250801AOvercome the disadvantage of low degradation abilityEfficient degradationBacteriaWater contaminantsXanthomonas campestrisPseudoxanthomonas japonensis
The invention provides a microbial agent which comprises a medium and thalli, wherein, the thalli comprise at least two selected from the group consisting of pseudoxanthomonas japonensis with an accession number CGMCC No.4797, pseudomonas with an accession number CGMCC No.4793, gordonia amicalis with an accession number CGMCC No.4794, rhodococcus rubber with an accession number CGMCC No. 4795 and gordonia alkanivorans with an accession number CGMCC No.4796. The invention also provides a preparation method for the microbial agent and application of the microbial agent in degradation of petroleum hydrocarbon, bioremediation of soil polluted by petroleum and bioremediation of water bodies polluted by petroleum.
Owner:宁夏中微泰克生物技术有限责任公司
Xanthomonas, preparation method thereof and method thereof for producing temperature resistant xanthan gum polysaccharide
ActiveCN101906390AImprove temperature resistanceViscosity loss is smallBacteriaMutant preparationBiotechnologyXanthomonas campestris
The invention discloses a xanthomonas Xanthomonassp. S-96#, preparation method thereof and a method thereof for producing temperature resistant xanthan gum polysaccharide, including seed selection of temperature resistant high viscosity strain, expanding culture of seed, fermentation and extraction processing steps. The strain of the invention has good temperature resistance, the produced xanthan gum polysaccharide product has stable quality, the viscosity of the product after being heated is obviously higher than similar product, application indexes are excellent, and the original production process of similar products is improved, production process is safe, thus being capable of substituting the existing xanthan gum product and being widely applied to the petroleum development industries requiring high viscosity under high temperature condition.
Owner:ORDOS ZHONGXUAN BIOCHEM
Method for catalyzed synthesizing alpha arbutin from free cells or immobilized cells
A process for catalytically synthesizing alpha-arbutoside from the free or immobilized cells of Xanthomonas campestris (CGMCC No.1243) includes such steps as preparing somatic cells, choosing reaction system, choosing immobilizing carrier, preparing immobilized cells, optimizing reaction condition, and extracting product. Said alpha-arbuto side can be used for beautifying skin.
Owner:厦门绿启源生物科技有限公司
Method for preparing transparent xanthan gum by utilizing microorganism fermentation
InactiveCN101613726AHigh light transmittanceSimple production processMicroorganism based processesFermentationXanthomonas campestrisMicroorganism
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing required compound by adopting fermentation, in particular to a method for preparing transparent xanthan gum by utilizing microorganism fermentation. The invention comprises the following steps: selecting and using xanthomonas campestris as production strain; preparing the slant strain; preparing the slant strain into seed liquid by intermediate culture; connecting the seed liquid fermentation medium into the fermentation medium for fermentation; preparing the fermentation liquid containing xanthan gum. The invention solves the problem of poor transmittance of the products existing in the prior art; the invention has the advantages that the technology is simple and reasonable, the production cost is low, and xanthan gum with higher transmittance can be extracted from the fermentation liquid prepared by the invention.
Owner:HEBEI XINHE BIOCHEM
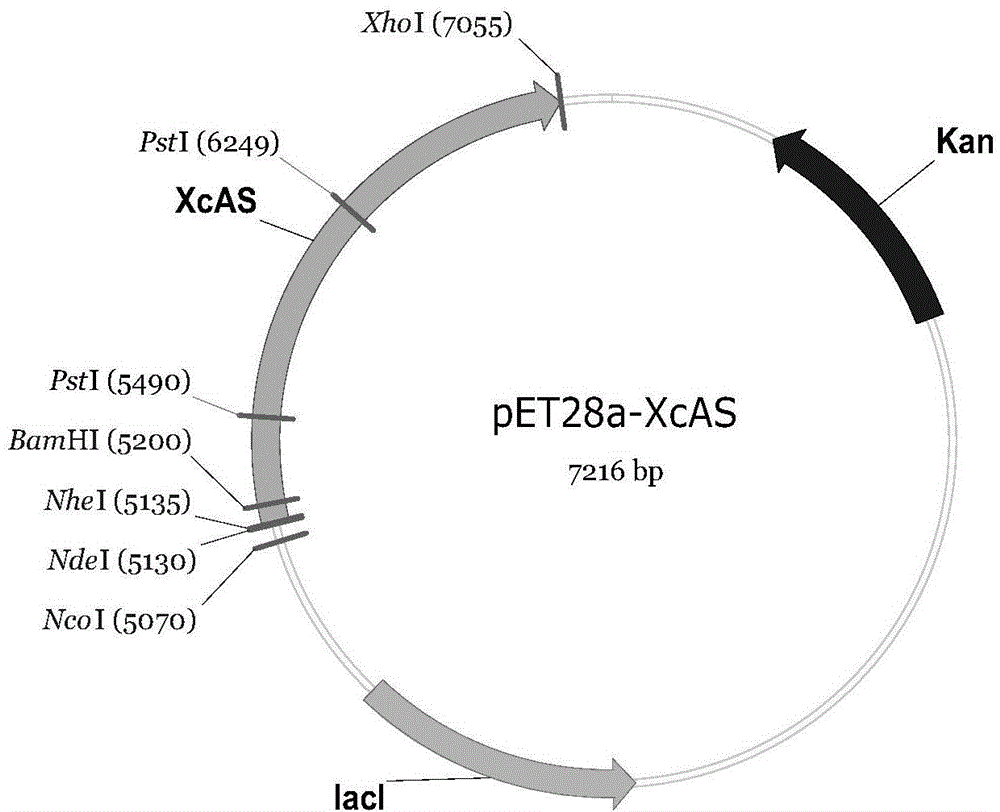
Gene engineering bacteria producing alpha-arbutin and construction method and application of gene engineering bacteria
ActiveCN106148256AReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliXanthomonas campestris
The invention discloses gene engineering bacteria producing alpha-arbutin and a construction method and application of the gene engineering bacteria. The invention provides recombinant bacteria which are obtained by a leading amylosucrase coding gene into target bacteria; amylosucrase is derived from Xanthomonas campestris. It is proved through experiments that the amylosucrase gene derived from Xanthomonas campestris CGMCC 1.3408 is led into colibacillus to construct the gene engineering bacteria, the gene engineering bacteria are used for producing alpha-arbutin, the conversion efficiency reaches 99%, the production intensity is 7.56 g / L / h, and the highest level as reported at home and abroad so far is achieved; meanwhile, maltose which is high in price is not used as donor in the production process, and enzyme purification is not needed. In this way, the production cost of alpha-arbutin is greatly reduced, and therefore the bacterial strain can have an extremely important position in alpha-arbutin production.
Owner:ANHUI HUAHENG BIOTECH
Fermentation method for producing high viscocity xanthan gum by xanthomonas campestris
InactiveCN101560537AReduce consumptionProcess fermentation time shortenedMicroorganism based processesFermentationXanthomonas campestrisFood culture
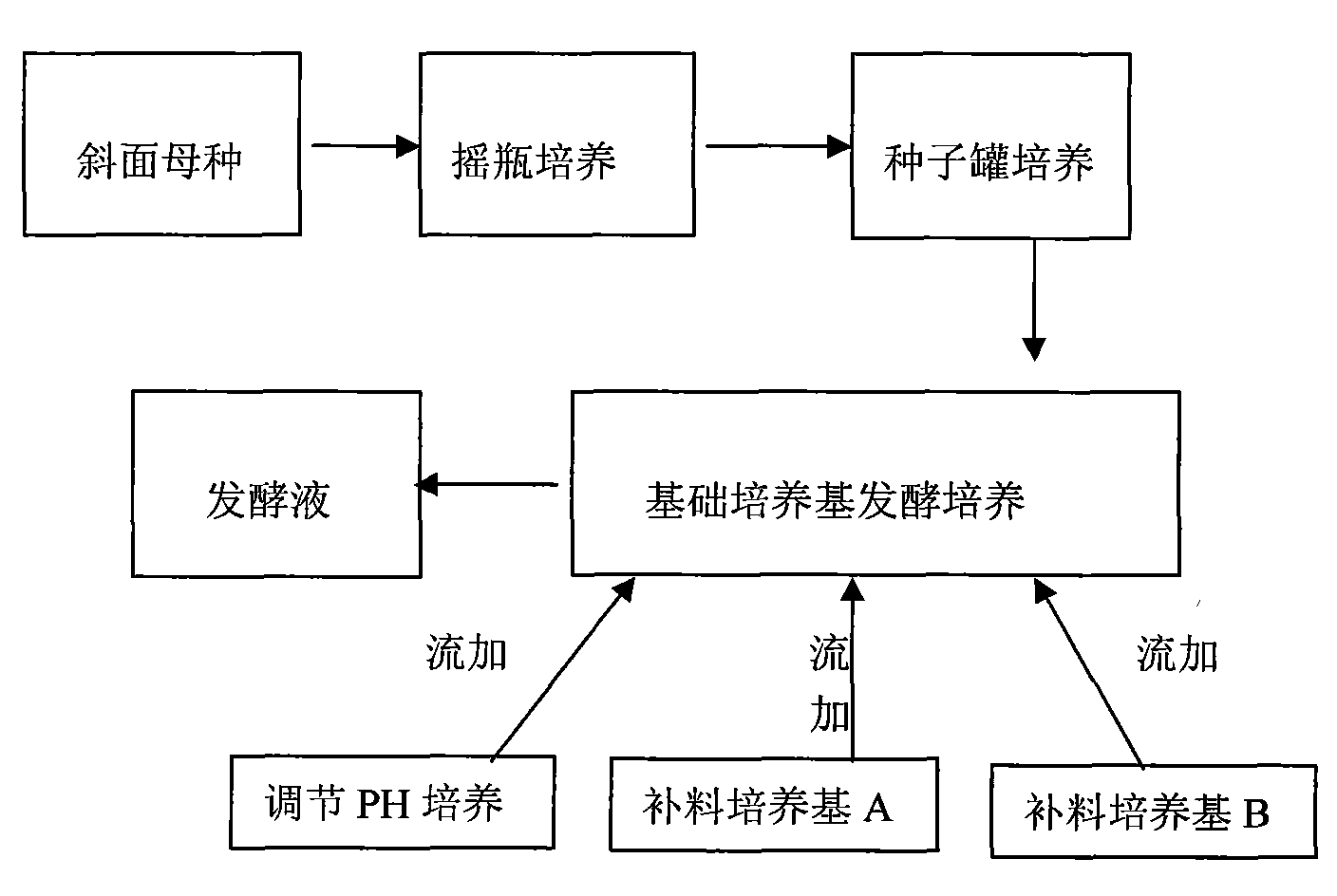
The invention discloses a fermentation method for producing high viscocity xanthan gum by xanthomonas campestris, which relates to the technical field of the production of the xanthan gum by using microorganism fermentation engineering. The prior fermentation method for producing the xanthan gum by the xanthomonas campestris comprises: slant mother seeds, shaking culture, starter can culture, total culture medium fermentation culture and fermentation liquor extracting stage; and a fermentation culture stage of the invention is designed to be a basal culture medium fermentation culture stage which comprises a supplementary food culture medium A fed-batch, a food culture medium B fed-batch and a pH regulation and control process. Starch and crude farm product containing starchiness are sequentially batch-fed in two steps under the condition of firm control of fermentation liquor photodensity to increase the carbon nitrogen ratio gradually; the ferment pH value is controlled by an acid-base neutralization solution, so that the process fermentation time is reduced from 60 to 75 hours to 40 to 48 hours; high cost industrial raw materials are replaced by the low cost primary farm products, so that the raw material cost is reduced by 15 to 20 percent; the reduction of the fermentation time reduces the energy consumption by 25 to 30 percent; and experimental data shows that the feed stock conversion reaches 85 to 90 percent and the viscocity is improved by 10 to 20 percent.
Owner:SICHUAN HENGYI TECH
Separated paddy bacterial blight bacterial phage and application thereof
ActiveCN106957825APrevent diseaseEase survivalBiocideMicroorganism based processesXanthomonas campestrisBacterial blight
The invention discloses a separated paddy bacterial blight bacterial phage and an application thereof. The phage disclosed by the invention is preserved at China Center for Type Culture Collection with the preservation No. CCTCC NO: M2015727. The separated phage disclosed by the invention is a virulent phage separated from natural soil, the phage Xoo_sp15 is utilized to prevent and control plant diseases caused by xanthomonas and the preventing and control effect is excellent. The phage is expected to be highly purified and developed into a biopesticide for avoiding the propagation of plant xanthomonas and the growth and propagation of xanthomonas in plants and can be used for effectively preventing and treating the plant diseases caused by xanthomonas.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Method for synthesizing alpha-arbutin by enzymic method through catalysis
InactiveCN102978265AImprove conversion rateIncrease productivityMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyXanthomonas campestris
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing alpha-arbutin by an enzymic method through catalysis. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, culturing a slant seed: taking a xanthomonas campestris CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) NO.1243 strain, and inoculating the xanthomonas campestris CGMCC NO.1243 strain in a slant culture medium for culturing; 2, culturing a liquid strain: selecting a ring strain, inoculating the ring strain in a basic fermentation culture medium, and placing on a table concentrator for oscillating and culturing to obtain a seed culture solution; 3, adding the seed culture solution in the basic fermentation culture medium, oscillating and culturing for 24-48h, freezing, centrifugally collecting thalli, washing the thalli with a PBS (Phosphate Buffer Solution) for 2-3 times, ultrasonically crushing at a low temperature, centrifuging, and taking supernate, namely intracellular crude enzyme; and 4, adding cane sugar and hydroquinone in the intracellular crude enzyme for reacting, and separating and purifying a reaction product to obtain the alpha-arbutin. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high production efficiency, high transformation rate of the hydroquinone, low cost, short process flow and the like.
Owner:韦慧芳 +1
Multiplexed lateral flow microarray assay for detection of citrus pathogens Xylella fastidiosa and Xanthomonas axonopodis PV citri
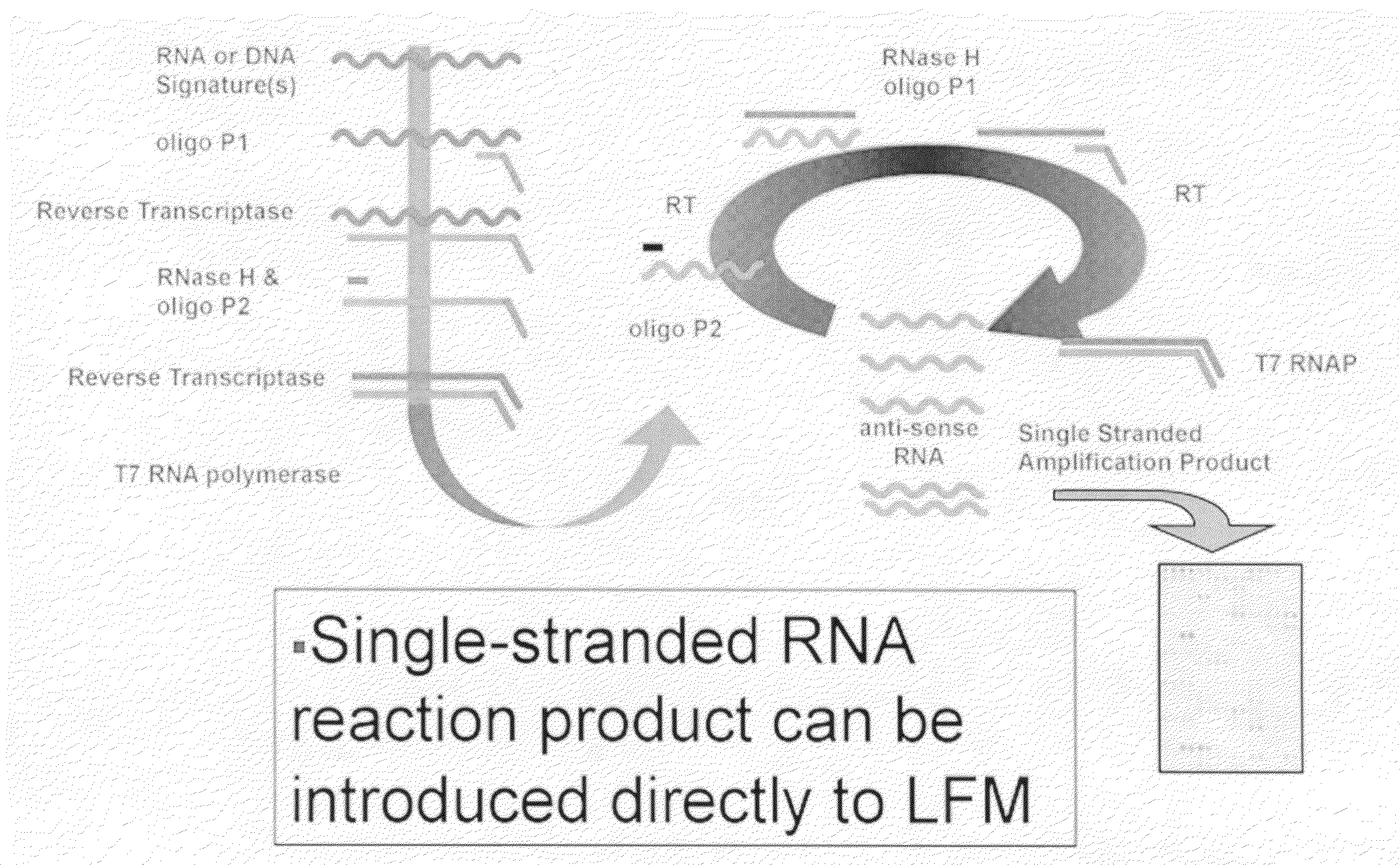
InactiveUS20100029496A1Highly efficient isothermal amplification techniqueExcellent linear dynamic rangeMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningFluorescenceGene targeting
The invention provides highly sensitive and specific assays for the major citrus pathogens Xylella fastidiosa and Xanthomonas axonopodis, including a field deployable multiplexed assay capable of rapidly assaying for both pathogens simultaneously. The assays are directed at particular gene targets derived from pathogenic strains that specifically cause the major citrus diseases of citrus variegated chlorosis (Xylella fastidiosa 9a5c) and citrus canker (Xanthomonas axonopodis pv citri). The citrus pathogen assays of the invention couple a highly efficient isothermal amplification technique with lateral flow nucleic acid hybridization detection, thereby providing an inexpensive and facile means of rapidly detecting pathogen nucleic acid targets while circumventing hardware requirements for fluorescence detection and PCR thermocycling. The citrus pathogen assays of the invention offer femtomole sensitivity, excellent linear dynamic range, and rapid and specific detection.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
Pseudoxanthomonasjaponensis and microorganism microbial inoculum as well as applications thereof
InactiveCN102250794AOvercome the disadvantage of low degradation abilityEfficient degradationBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationXanthomonas campestrisMicroorganism
The invention provides a pseudoxanthomonasjaponensis with the collection number of CGMCC No.4797 and a microorganism microbial inoculum containing the same and also provides an application of the pseudoxanthomonasjaponensis or the microorganism microbial inoculum to the degradation of petroleum hydrocarbon, an application to biological remediation of the petroleum pollution, an application to biological remediation of soil polluted by the petroleum and an application to biological remediation of water polluted by the petroleum. The pseudoxanthomonasjaponensis with the collection number of CGMCC No.4797 and the microorganism microbial inoculum containing the same have very strong capability of degrading the petroleum hydrocarbon and can be widely applied to degradation of the petroleum hydrocarbon and remediation of the petroleum pollution, such as the remediation of the soil polluted by the petroleum, the remediation of the water polluted by the petroleum and the like.
Owner:INST OF ENVIRONMENT & SUSTAINABLE DEV IN AGRI CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
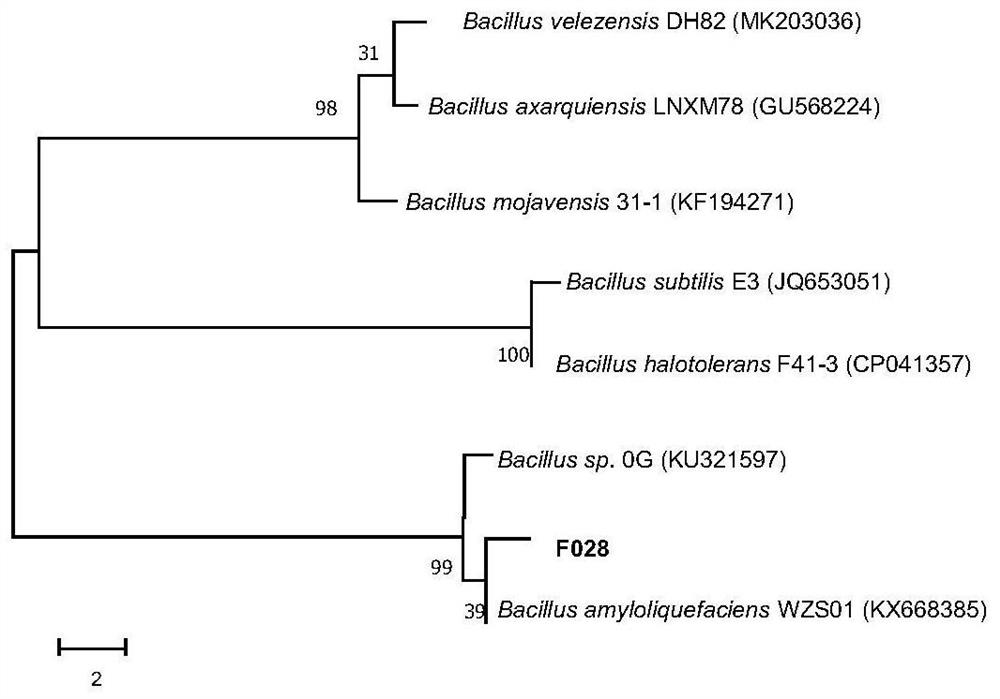
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, microbial agent as well as preparation method and application of microbial agent
ActiveCN112553122ABroad-spectrum antagonistic activityFast growthBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyMicrobial agent
The invention provides Bacillus amyloliquefaciens F028. The strain is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on April 20, 2020, and has a preservation registration number of CGMCC No.19590. A biological control preparation prepared from the strain has a broad-spectrum antibacterial effect on bacterial diseases caused by Xanthomonas campestris, Erwiniacarotovora and Ralstonia solanacearum, and fungal diseases caused by Botrytis cinerea, Rhizoctonia solani, AlternariaNees, Fusarium, Phytophthora spp, Glomerellacingulata(Stonem.)Spauld et Schrenk, Colletotrichumcapsici and Beauveria bassiana. According to the invention, a new resource is provided for replacing a chemically synthesized bactericide with microorganisms and preventing and controlling plant diseases by using a biological prevention and control method, and the Bacillus amyloliquefaciens can be developed and utilized as a biopesticide; and moreover, the Bacillus amyloliquefaciens provided by the invention has a promotion effect on the plant growth of tomatoes and tobaccos, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Acinetobacter lactucae and application thereof to degradation of quorum-sensing signal molecule DSF
ActiveCN107964516AHigh degradation activityReduce the severity of the diseaseBiocideBacteriaXanthomonas campestrisSignalling molecules
The invention discloses Acinetobacter lactucae and an application thereof to degradation of a quorum-sensing signal molecule DSF (diffusible signal factor). The invention provides a bacterial strain of Acinetobacter lactucae QL-1, the bacterial strain is preserved in a China Center for Type Culture Collection on September 11th, 2017, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M2017487. The bacterialstrain can employ the quorum-sensing signal molecule DSF as a sole carbon source for growth, and 2mM of DSF signal molecules can be completely degraded in 15 hours with high degradation activity andstable degradation performance. The bacterial strain QL-1 has substantial biocontrol effects for black rot caused by Xanthomonas campestris XC1, and the bacterial strain also has characteristics of fast growth speed, simple cultivation method, good adaptation capability without easy variation, and great application potential for promotion of control of pathogens which are pathogenic depending on DSF; and at the same time, the product can reduce the problem of abuse of pesticides, and provides a new thinking for biological control of plant diseases.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Dentifrice composition
ActiveCN1988876AGood dispersionAppropriate grinding forceCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsXanthomonas campestrisKappa-Carrageenan
A dentifrice composition which comprises (A) heavy calcium carbonate having a mean particle diameter of 5 to 15 m, (B) water-insoluble inorganic granules having a collapse strength of 10 to 200g / granule, a mean particle diameter of 50 to 150 m, and a difference of 100 m or below between 90% particle diameter and mean particle diameter, and (C) a water-soluble polymeric material comprising at least one member selected from Group (a) and at least one member selected from Group (b) at a (b) / (a) mass ratio of 0.25 to 3, Group (a): sodium alginate, sodium carboxymethylcellulose, methylcellulose, hydroxyethylcellulose, Xanthomonas campestris, lambda-carrageenan, and straight-chain sodium polyacrylate, and Group (b): gellan gum, agar, kappa-carrageenan, iota-carrageenan, gelatin, pectin, and crosslinked sodium polyacrylate, and which has a total content of (a) and (b) of 0.5 to 1.5% by mass based on the whole of the composition.
Owner:LION CORP
Herbicidal composition for the control of annual bluegrass
InactiveUS6162763AEffective herbicideImprove controlBiocideMicroorganismsXanthomonas campestrisChemical composition
A herbicidal composition for the control of annual bluegrass, comprising, as active ingredients, a microorganism belonging to the genus Xanthomonas and having control ability against annual bluegrass and paraffin is disclosed. This composition exhibits excellent herbicidal effect against annual bluegrass, but does not cause any phytotoxicity in various turfgrasses.
Owner:JAPAN TOBACCO INC
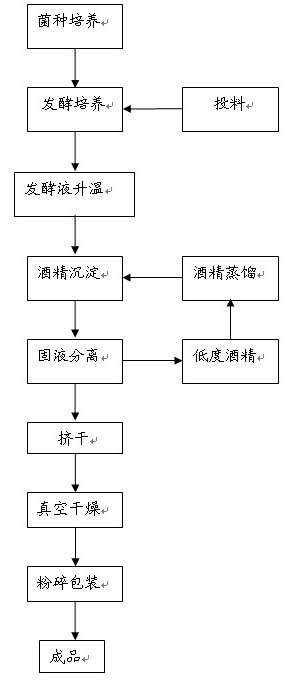
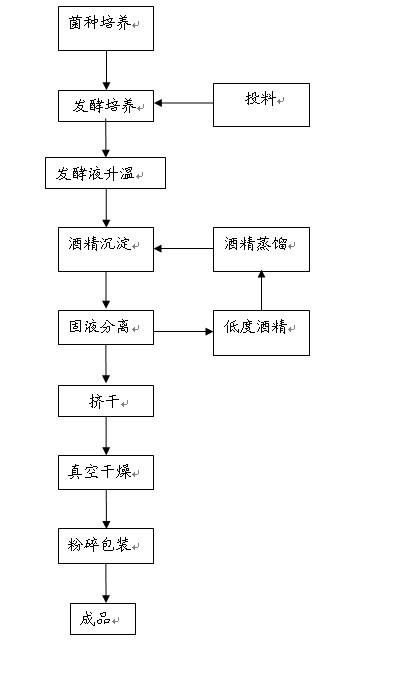
Method for fermenting and producing xanthan gum using steam-explosion straw as raw material
The invention relates to a method for preparing xanthan gum by employing airing straw as raw material, comprising following steps: disintegrating airing straw, adding them into water, adjusting pH with acid to 4.5- 5.5, adding fiber enzyme according to ratio of 10-40 units of enzyme for each gram airing straw, stirring evenly, proceeding enzymolysis at 45-55 Deg. C for 40-80 hours; decoloring hydrolyzate; adding NH4NO3, yeast paste, light calcium carbonate and Na2HPO4*12H2O into decolored hydrolyzate as culture medium; inoculating Xanthomonas campestris 1.1781 for fermentation at 25-32 Deg. C for 72-96 hours, separating and getting xanthan gum. The invention is characterized by cheap raw material and low cost.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Germ-immune type inductive agent and application thereof
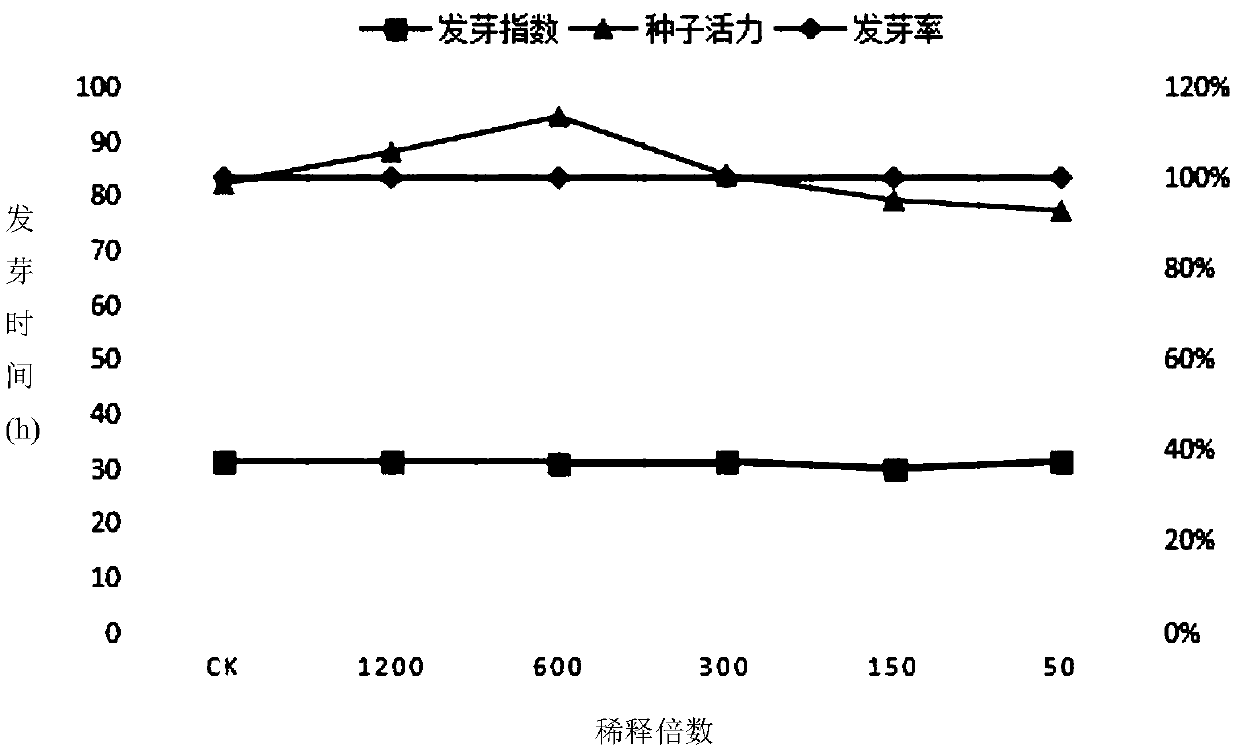
The invention discloses a germ-immune type inductive agent and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of plant immune induction. The germ-immune type inductive agent is characterized in that the germ-immune type inductive agent is prepared from uniformly mixing 34 percent of fructo-oligose, 30 percent of radix astragali polysaccharide, 16 percent of trichoderma, 12 percent of lecithin and 8 percent of bacillus subtilis according to the weight ratio, and 6% germ-immune type inductive agent water solution is sprayed for three times in the strawberry virus-free bottle seedling hardening process, wherein the time interval is 7 days. The germ-immune type inductive agent disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the resistance of strawberry virus-free seedlings to pathogenic bacteria is effectively improved, so that good congenital characters of the strawberry virus-free seedlings are guaranteed. The germ-immune type inductive agent has excellent immunity on xanthomonas campestris, pseudomonas pseudoacaligenes, bacteria erwinia and bacillus pumilus in natural planting and has weak immunity on bacillus and fungi.
Owner:湖北勤劳农夫生态农业股份有限公司
Bioimmune-aggressin composition for suppression of xanthomonad infections in agriculture crops
ActiveUS20050153005A1Reduce harmBiocideDead animal preservationXanthomonas campestrisAgriculture crops
A composition for treating Xanthomonas spp. infections in agriculture crops wherein the treatment composition is an admixture of T. harzianum, Y. schidigera root extract, Y. schidigera leaf extract, and X. spp. extract. The composition is also efficacious as a pre-infection agent for enhancing the resistance of agriculture crops to such infections. The composition is preferably applied by spraying.
Owner:BIOSYS
Bioimmune-aggressin composition for suppression of Xanthomonad infections in agriculture crops
InactiveUS20060165818A1Reduce harmBiocideDead animal preservationXanthomonas campestrisAgriculture crops
A composition for treating Xanthomonas spp. infections in agriculture crops wherein the treatment composition is an admixture of T. harzianum, Y. schidigera root extract, Y. schidigera leaf extract, and X. spp. extract. The composition is also efficacious as a pre-infection agent for enhancing the resistance of agriculture crops to such infections. The composition is preferably applied by spraying.
Owner:BIOSYS
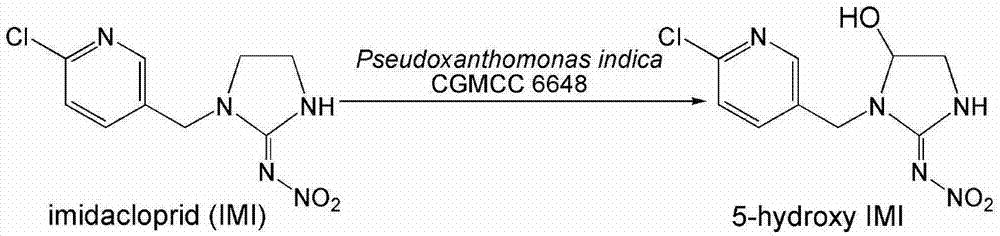
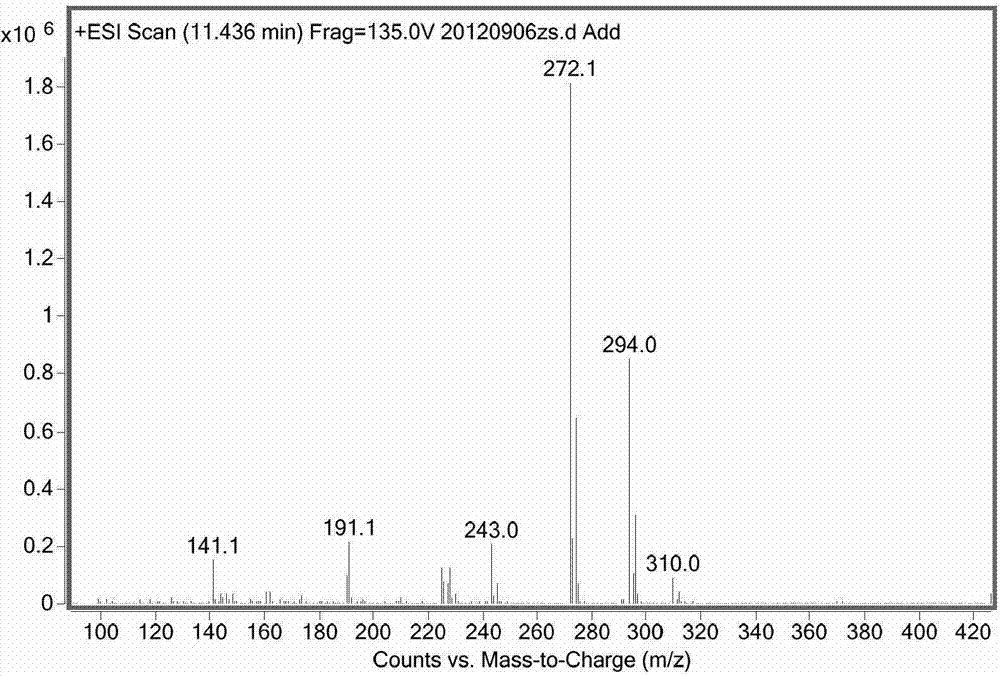
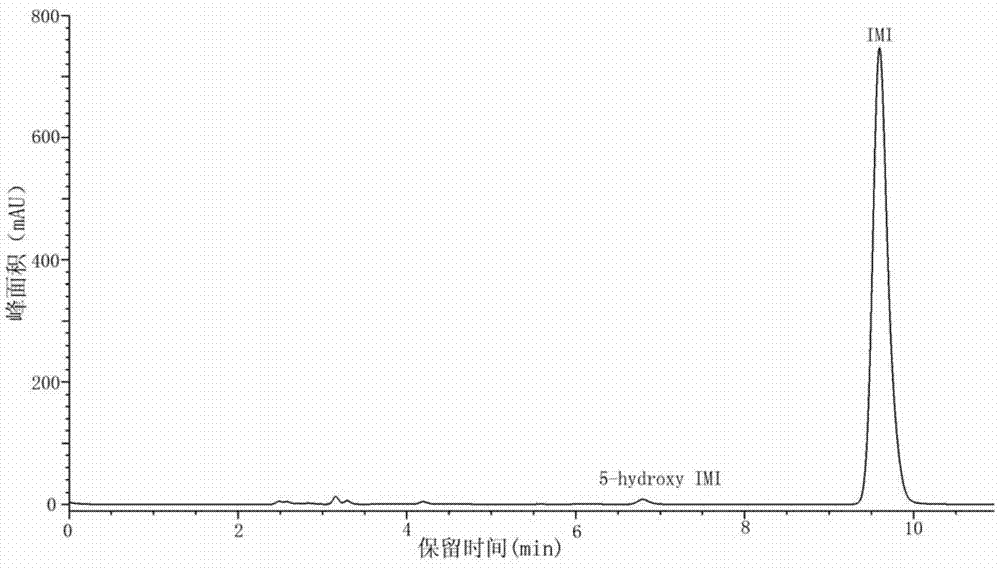
Pseudoxanthomonas indica and application thereof in degrading chloronicotinyl insecticide imidacloprid
The invention discloses a pseudoxanthomonas indica CGMCC6648 for degrading chloronicotinyl insecticide imidacloprid; the main route for reducing imidacloprid is to carry out hydroxylation on imidacloprid so as to generate 5-hydroxy imidacloprid. Sugar and organic acid are added in a resting cell transformation solution, thus the imidacloprid hydroxylation ability of the pseudoxanthomonas indica CGMCC6648 can be greatly improved.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Pectate lyases with increased thermostability and/or enzymatic activity
ActiveUS20100285569A1Improve enzymatic activityImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaPre-extraction tea treatmentXanthomonas campestrisEscherichia coli
Using site-directed mutagenesis to mutate the Xanthomonas campestris pectate lyase gene, variants of Xanthomonas campestris pectate lyase with improved thermostability and / or enzymatic activity have been expressed in Escherichia coli, and then isolated and purified. The mutant Xanthomonas campestris pectate lyases are more effective than the wild-type enzyme, also expressed in E. coli, in removing pectic compounds from natural hemp fiber.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Application of gene for coding 4-hydroxyphenylphruvic acid dioxygenase
The invention provides an application of a gene (XC_0450) for coding 4-hydroxyphenylphruvic acid dioxygenase to the production of xanthan gum. The gene is used for constructing and breeding a genetic engineering bacterium for producing the xanthan gum with high yield. A gene recombinant plasmid (pL0450) carried by the genetic engineering bacterium is obtained by introducing the pL0450 to a wild type bacterial strain (8004) of xanthomonas campestris sarson mutation (Xcc). The genetic engineering bacterium is the 8004 / PL0450 of a multi-copied pL0450 which carries the gene.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Bionectria ochroleuca Bo-1 strain, cultures thereof, and applications of the strain and the cultures thereof in resisting pathogenic bacteria
ActiveCN103232940AHighly antagonistic propertiesEnhanced inhibitory effectBiocideFungiBiotechnologyXanthomonas campestris
The present invention relates a plant endophyte Bionectria ochroleuca Bo-1 strain, cultures thereof, and applications of the strain and the cultures thereof in resisting pathogenic bacteria. The strain is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC), the address of the center is Wuhan University, Wuhan, China, the accession number is CCTCCNO: M2013027, and the preservation date is January 18, 2013. The Bionectria ochroleuca Bo-1 strain of the invention has high resisting performance for Xanthomonas campestris pv.oryzae, and a strong inhibitory effect on Monilia albicans (M.albican), Escherichia coli (E. coli), Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus ), Bacillus subtilis (B. subtilis) and other pathogenic bacteria.
Owner:郎溪品旭科技发展有限公司
Preparation method of microbial flocculant for purifying aquaculture seawater
ActiveCN106011215APromote acylationIncreased acetylationSeawater treatmentWaste water treatment from animal husbandryXanthomonas campestrisSeawater
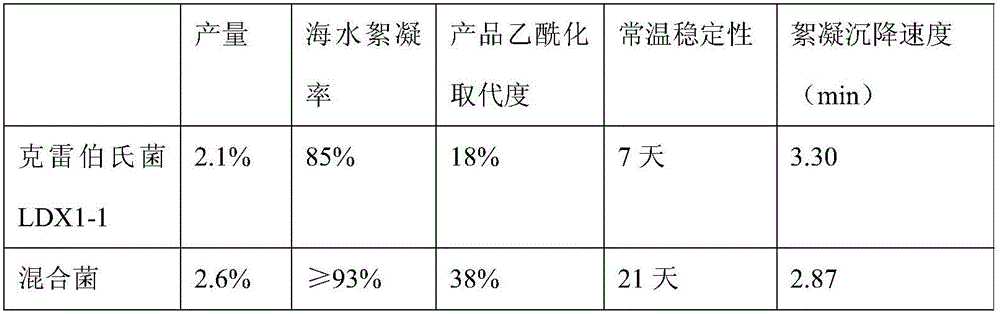
The invention discloses a preparation method of a microbial flocculant for purifying aquaculture seawater. The preparation method is characterized by carrying out synergistic fermentation on a mixed strain of klebsiella LDX1-1 and xanthomonas campestris CICC10258 with fermentation of a high-magnesium fermentation culture medium by adopting an antagonism-free compatible shake flask, and carrying out gelation strength treatment by adopting a salt mixture after the fermentation is completed. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is fast in fermentation speed, the technology can be easily operated, the fermentation concentration is high, and the production cost is low; the produced flocculant is used for treating high-salinity high-buoyancy seawater, has the characteristics of stable structure, flocculating block compactness and fast settling speed, and has an obvious effect in purifying the aquaculture seawater.
Owner:QINGDAO YAODONG GRP
Bacillus for antagonizing fusarium wilt and promoting growth and application thereof
ActiveCN110982725AEnhanced inhibitory effectEconomical and effective preventionBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyXanthomonas campestris
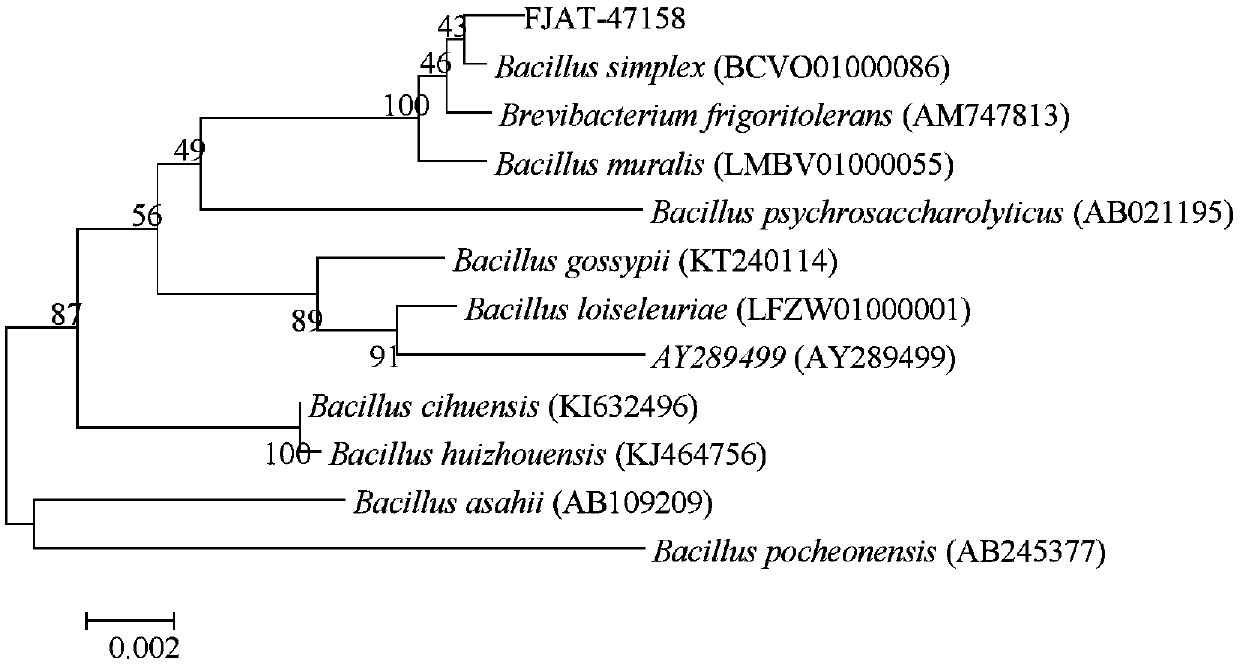
The invention provides bacillus for antagonizing fusarium wilt and promoting growth and an application of the bacillus. The bacterial strain is bacillus simplex FJAT-47158, and the chemical name of the bacterial strain is Bacillus simplex FJAT-47158. The bacterial strain is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, and the preservation number of the bacterial strainis CGMCC NO. 15946. The bacillus disclosed by the invention not only can inhibit phytopathogens such as fusarium oxysporum, xanthomonas carpetalis and the like, but also can improve the activity of plant seeds and promote the growth of the seeds, can be used for preventing and treating fusarium wilt, and is an environment-friendly, economical and effective biocontrol bacterium for preventing andtreating diseases.
Owner:福建省农业科学院农业生物资源研究所
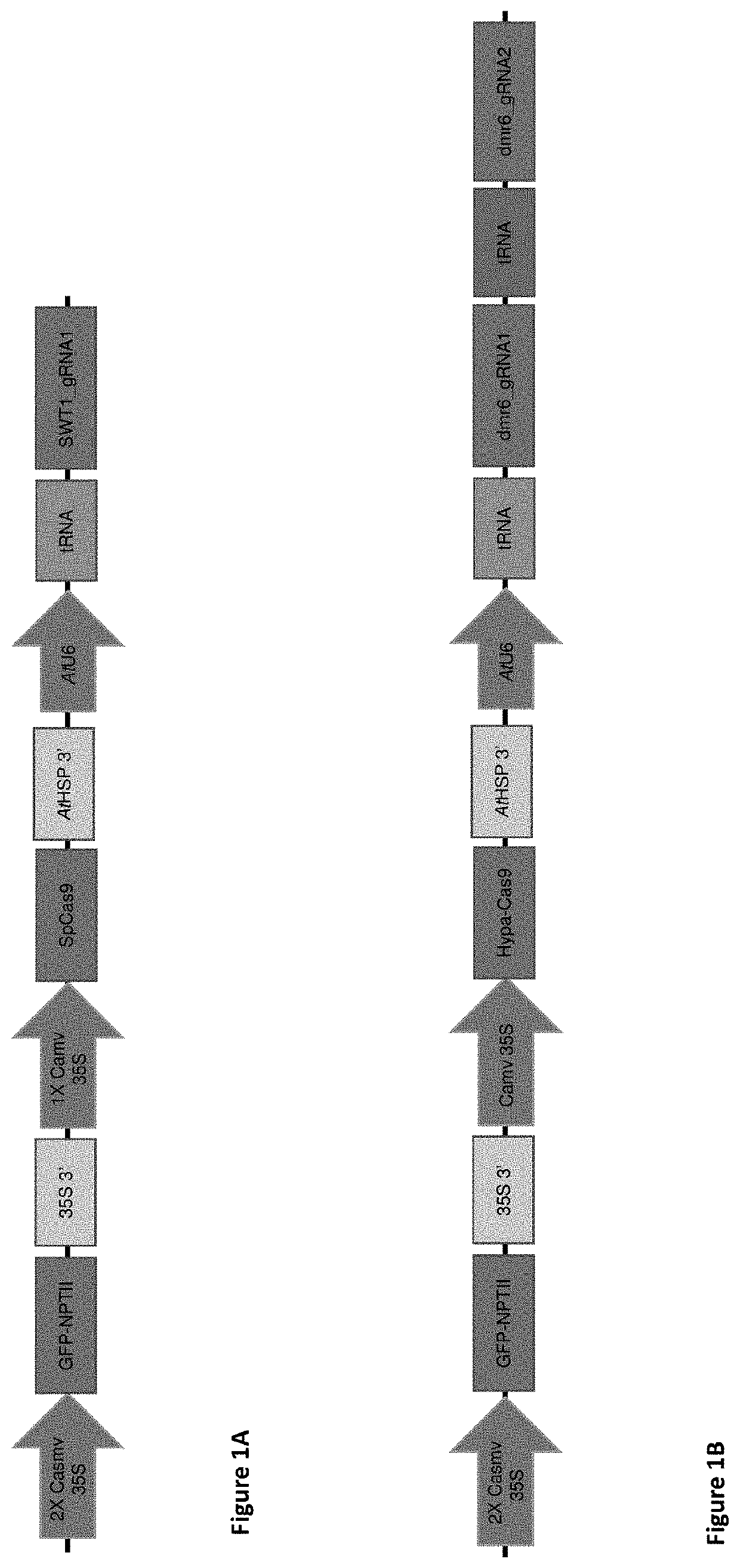
Targeted editing of citrus genes for disease resistance
PendingUS20210189410A1Reduce commercial valueCrop yield lossHydrolasesPlant peptidesBiotechnologyXanthomonas campestris
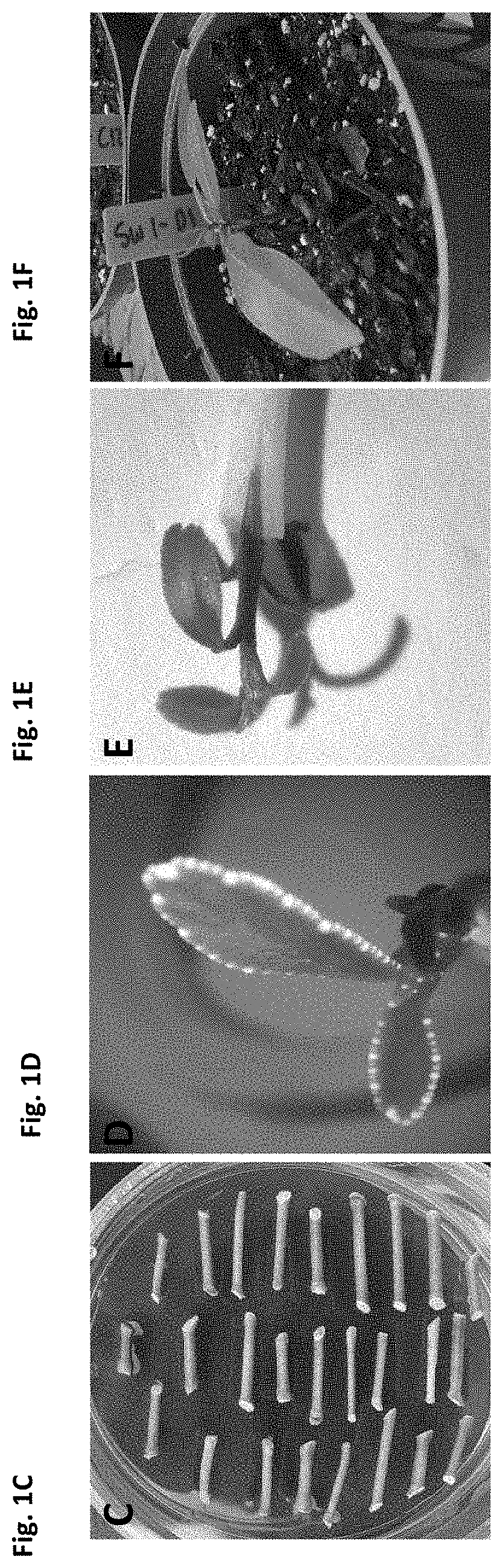
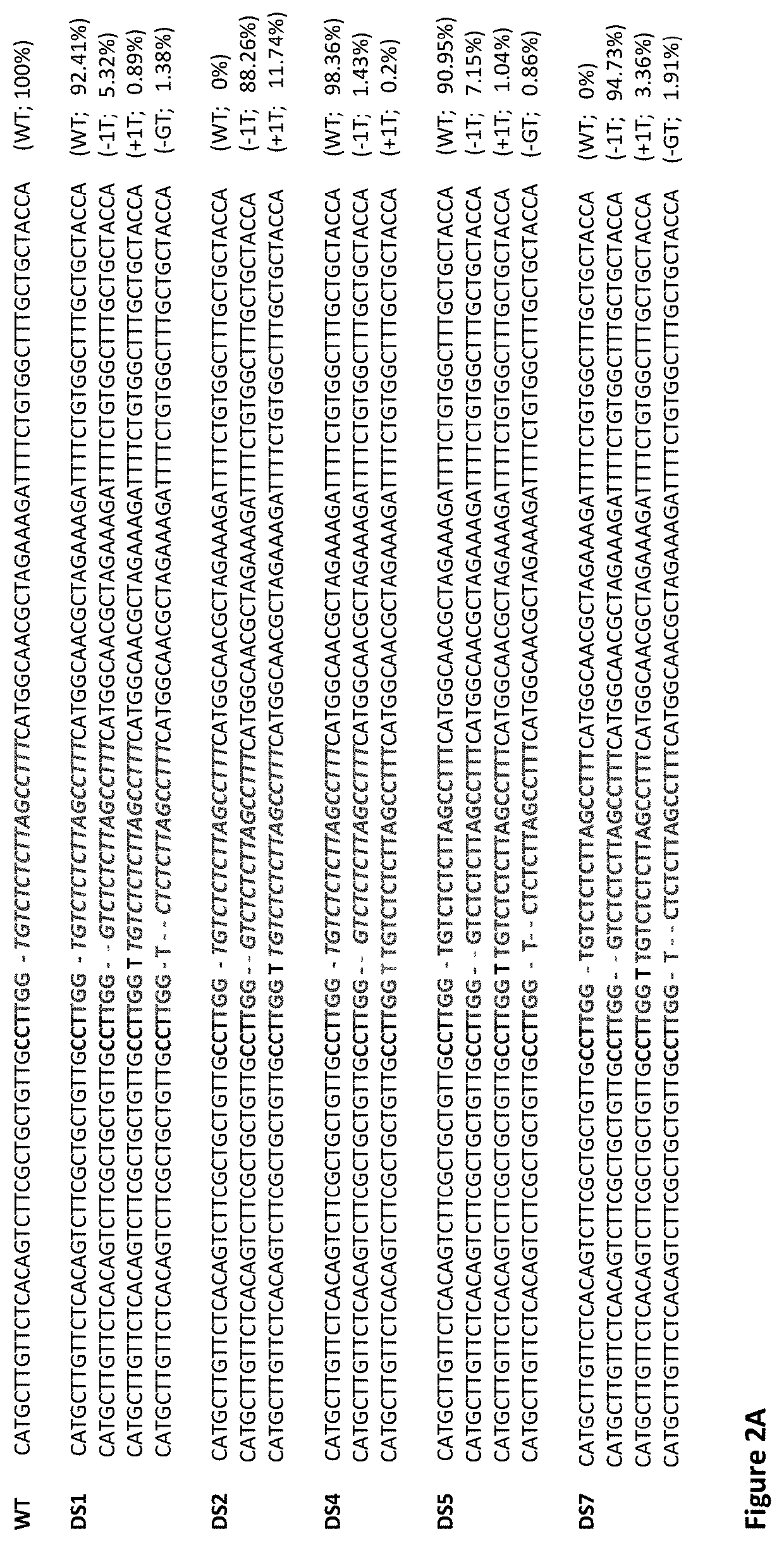
Disclosed herein our novel methods of increasing resistance of Citrus plants to diseases, in particular, citrus canker disease caused by Xanthomonas citri ssp. citri and Huanglongbing disease. Some embodiments relate to novel methods of altering gene sequence, structure and expression of certain disease susceptibility genes in the Citrus plant. Other embodiments relate to gene constructs equipped to be introduced into Citrus cells and direct modifications to target gene sequences.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com