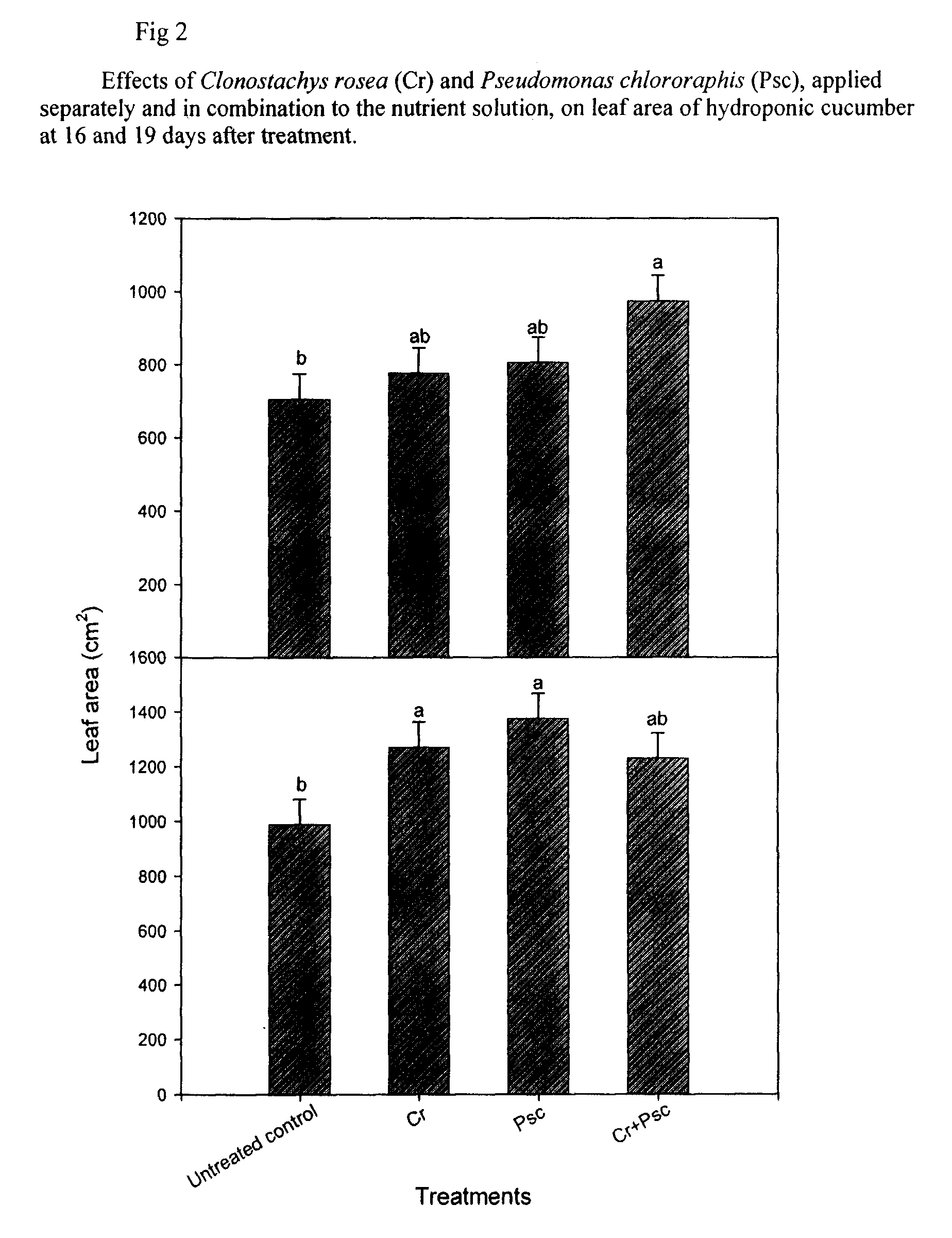
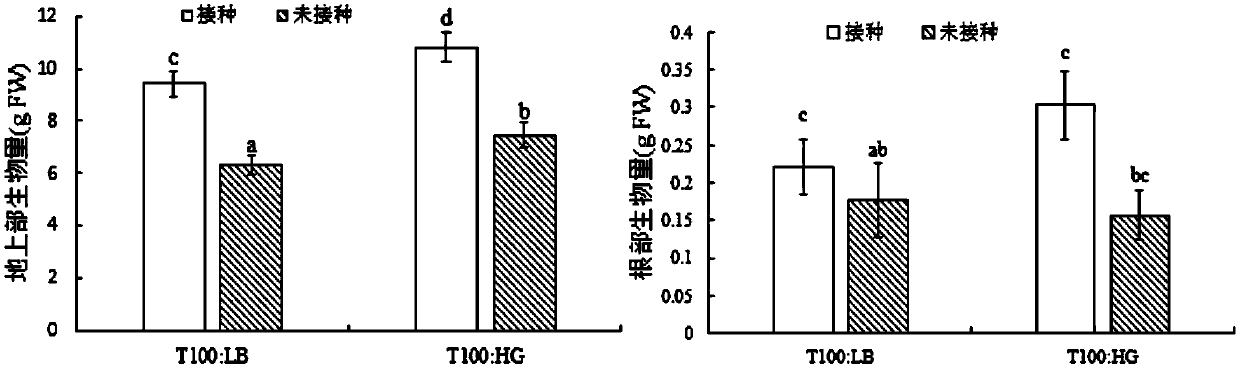
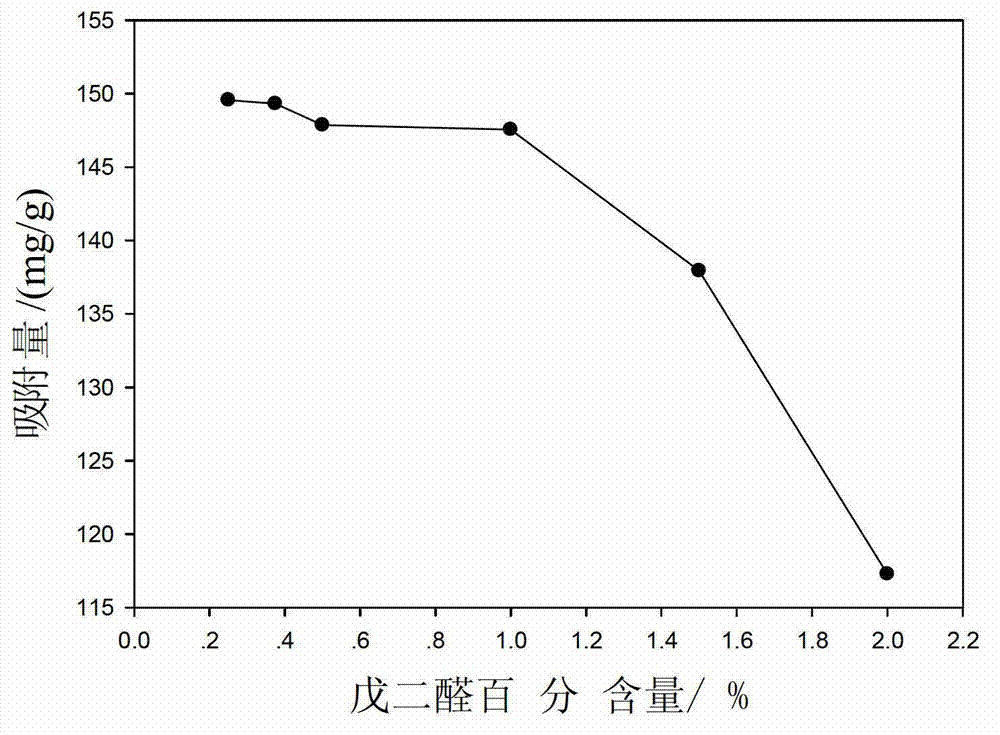
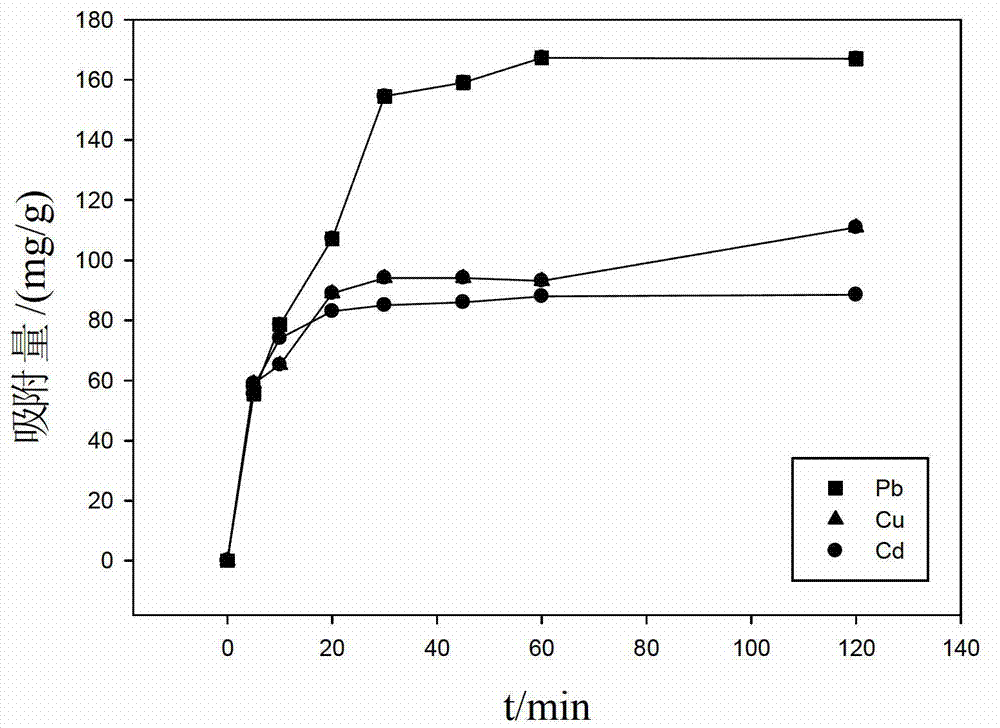
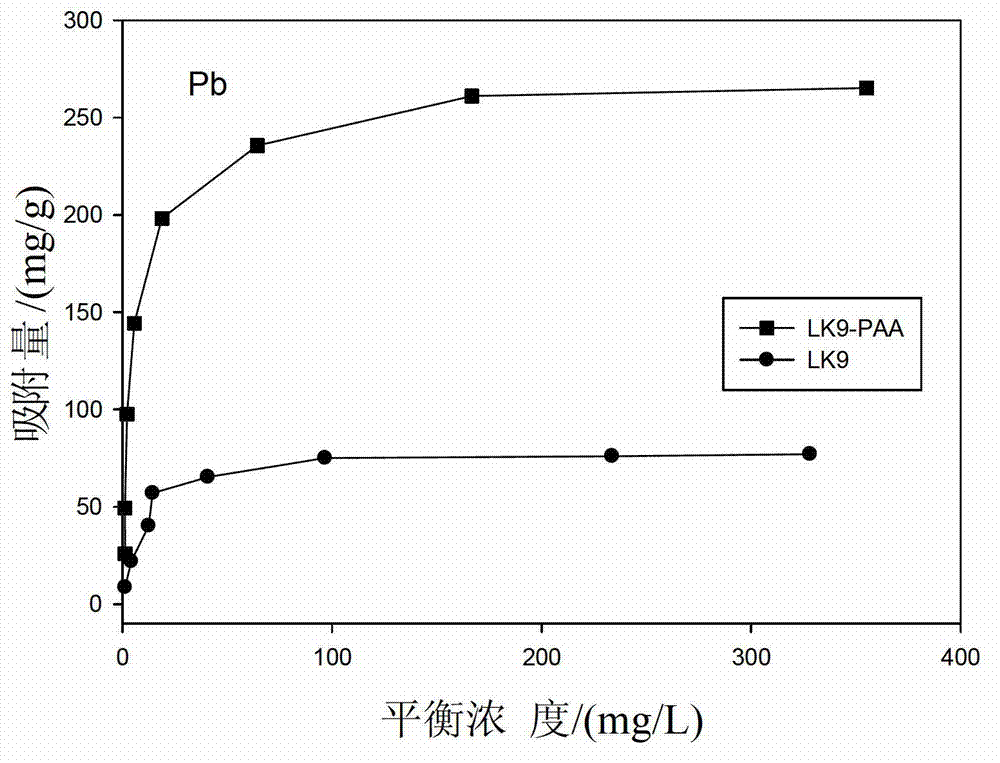
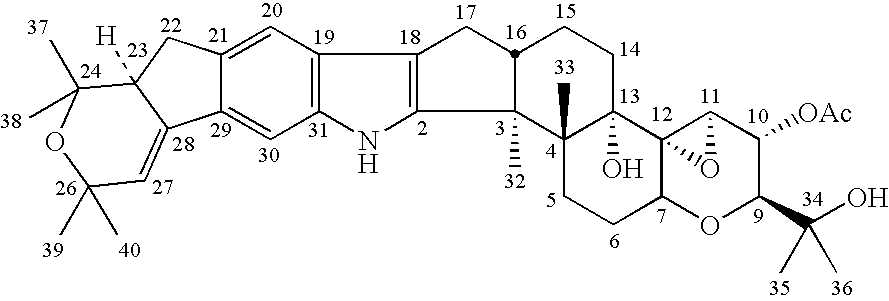
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
307 results about "Endophyte" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An endophyte is an endosymbiont, often a bacterium or fungus, that lives within a plant for at least part of its life cycle without causing apparent disease. Endophytes are ubiquitous and have been found in all species of plants studied to date; however, most of the endophyte/plant relationships are not well understood. Some endophytes may enhance host growth, nutrient acquisition and improve the plant's ability to tolerate abiotic stresses, such as drought, and decrease biotic stresses by enhancing plant resistance to insects, pathogens and herbivores.
Modulated nutritional quality traits in seeds
This invention relates to methods and materials for modulating seed nutritional quality traits of seeds produced by a wheat, cotton, soybean, or maize plant, said plant having been heterologously disposed to, or grown from, a plant element treated with an endophyte.
Owner:INDIGO AG INC
Production and use of endophytes as novel inoculants for promoting enhanced plant vigor, health, growth, yield reducing environmental stress and for reducing dependency on chemical pesticides for pest control
InactiveUS20090105076A1Improve scalabilityPrevent degradationBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyFungal endophyte
A process and method for the production of endophytes as plant inoculant products, specifically Clonostachys rosea strain 88-710, for the promotion of plant vigor, health, growth and yield are disclosed. The endophyte, Clonostachys rosea strain 88-710 produces a fungal conidial preparation by utilizing a discrete solid substrate fermentation system, namely Potato Dextrose Agar or Malt Extract Agar. Additionally, the endophyte, Clonostachys rosea strain 88-710, can act as an inoculant to stimulate and have an additive effect with rhizobium bacteria on the production of nitrogen fixing nodules on legumes and growth enhancement e.g. beans, soybeans, peas and alfalfa. As well, Clonostachys rosea strain 88-710, can combine with rooting hormones, e.g. indole-3-butyric acid (IBA) to provide inoculant and rooting benefits to cuttings / transplants of plants.
Owner:ADJUVANTS PLUS INC
Eucalyptus endophyte and application thereof
InactiveCN101974438APromote absorptionPromote growthBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyEndophyte
The invention provides a penicilliums p. strain and application thereof. Eucalyptus endophyte is a penicilliums p. strain 1, and the collection number is CGMCC No.4297. The eucalyptus endophyte inoculated to eucalyptuses can improve the low phosphorus stress resistance of the eucalyptuses and promote phosphorus absorption of the eucalyptuses. Because the eucalyptus endophyte is used for promoting the phosphorus absorption of the eucalyptuses, and when the strains are inoculated to the eucalyptus plants, the activities of the plant phosphatase and the soil phosphatase can be improved, the pH value of the soil rhizosphere can be reduced, and the plant P utilization rate is greatly improved; therefore, the purpose of promoting normal growth of the plants in the low phosphorus soil is fulfilled, and the utilization rate of the soil phosphate fertilizer is greatly reduced.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Burkholderia pyrrocinia and application thereof in control of dothiorella gregaria
ActiveCN101555458ARapid identificationAccurate identificationBiocidePlant growth regulatorsFungal endophyteMicrobiology
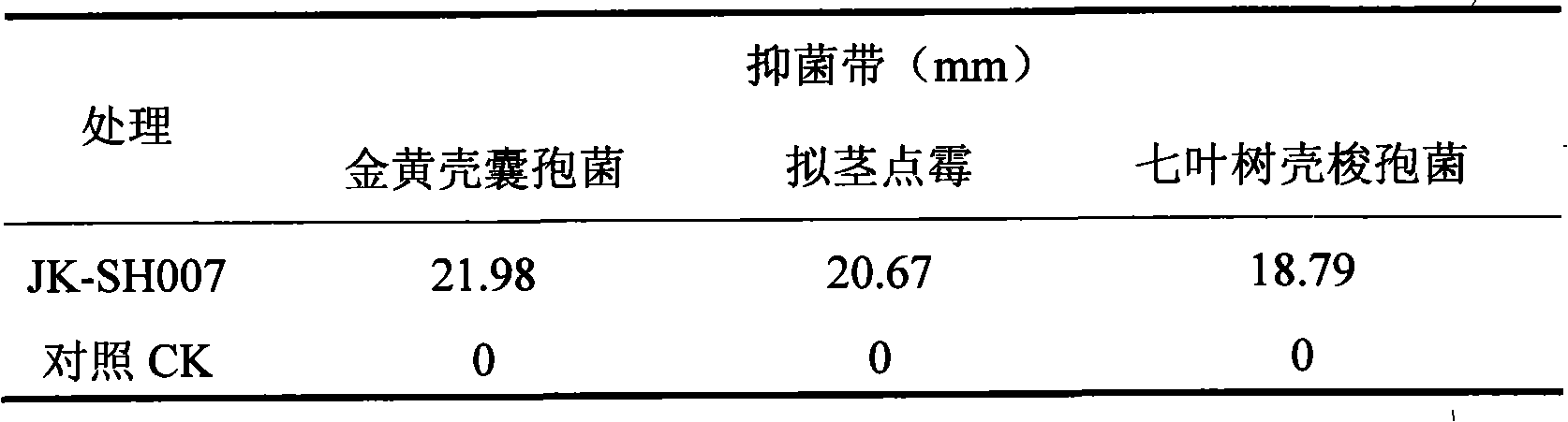
The invention discloses a burkholderia pyrrocinia JK-SH007 which is classified and named as burkholderia pyrrocinia and preserved in China center for type culture collection (CCTCC) with the preservation number of M 209028 and the preservation date of February 18th, 2009. The invention also discloses the application of the burkholderia pyrrocinia in controlling dothiorella gregaria and promoting poplar to grow. The invention further provides a bactericide for controlling dothiorella gregaria, which is obtained by inoculating the JK-SH007 in a culture medium to be fermented and cultured. The JK-SH007 is plant endophyte which has strong inhibiting effect for botryosphaeria dothidea of the poplar and antagonism for various pathogenic fungis, and has the advantages of simple culture condition, easy storage and commercial process as well as good developing and applying prospect.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
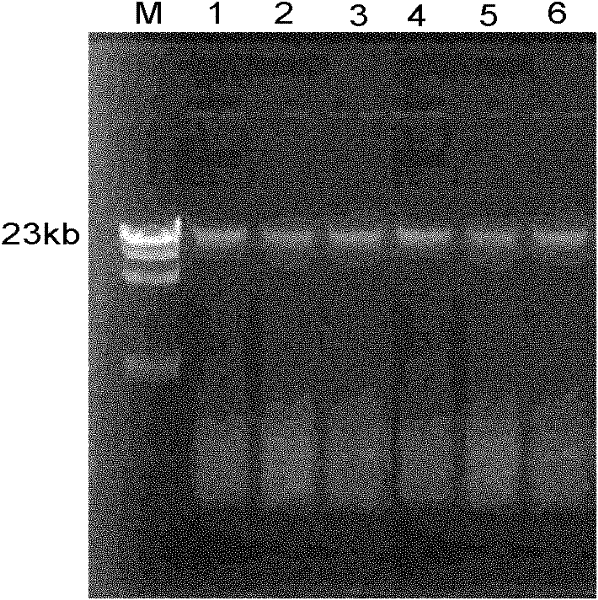
Extraction and purification method of total plant endophyte genome DNA for colony analysis
InactiveCN102174509AQuality improvementIncrease credibilityFermentationPlant genotype modificationPurification methodsPhosphate
The invention discloses an extraction and purification method of total plant endophyte genome DNA for colony analysis. The method comprises the following steps of: shearing and grinding the surface bacteria removed fresh plant tissues into paste, soaking the plant tissues into sterilized phosphate buffer solution, performing thermostatic shaking for 1 hour in a table concentrator to separate out microbial cells from the plant tissues, standing, transferring the suspension to a centrifuge tube, performing centrifugal collection on microbial bacteria, then adding lysing solution, shaking and uniformly mixing the solution to release DNA from the cells, repeatedly extracting protein by chloroform-isoamylol, performing centrifugal sedimentation with isopropanol and washing with 70 percent ice ethanol, performing purification by using a DNA specific centrifugal adsorption column to obtain total crude extracted genome DNA, and finally, performing polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplificationby using special primers to obtain high-quality plant endophyte specific DNA fragments for subsequent analysis. The invention has the advantages that: the method is simple and effective, high in quality, low in pollution and the like, and provides high-quality guarantee for comprehensively and completely researching a plant endophyte colony structure.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Bacillus pumilus and application in preventing and treating dothiorella gregaria
ActiveCN101643711ASimple cultivation conditionsEasy to storeBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBacillus pumilusFungal endophyte
The invention discloses a bacillus pumilus JK-SX001 which is classified and named bacillus pumilus and collected in a China center for type culture collection (CCTCC) and has the collection number ofM 209026 on February 18th, 2009. The invention also discloses applications of the bacillus pumilus in preventing and treating dothiorella gregaria and promoting the growth of a poplar. The invention also provides a bactericide for preventing and treating the dothiorella gregaria, which is obtained by vaccinating the JK-SX001 in a culture medium to ferment and culture. The JK-SX001 is a plant endophyte, has obvious inhibiting effect on dothiorella gregaria, simple culture condition, easy storage and favorable development and application prospect and is easy for industrialized production.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
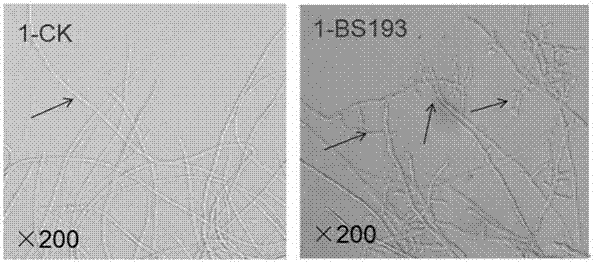
Bacillus subtilis BS193 for preventing and controlling potato late blight and application of bacillus subtilis BS193
InactiveCN106995791AGrowth inhibitionReduce pollutionBiocideBacteriaFungal endophyteMicrobiological culture
The invention provides bacillus subtilis BS193 for preventing and controlling a potato late blight and application of bacillus subtilis BS193 and belongs to the technical field of crop disease prevention and control. A strain is Bacillus subtilis BS193 and has been recorded and preserved by China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center at March 27, 2017 with a preservation number being CGMCC No. 13936. The strain inhibits growth of germs of the potato late blight by generating active substances and expresses better preventing and controlling effect to the potato late blight. The fungicide can be used for atomizing or root irrigation of a potato plant when being applied and can also be used by being mixed with an organic fertilizer to prepare a bacterial fertilizer. The bacillus subtilis BS193 provided by the invention is obtained by being extracted from a tomato plant body, belongs to endophyte, is nontoxic, does not have pathogenicity, and thus having a good application prospect in biological prevention and control of the potato late blight.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION FAAS
Rapid propagation method for dendrobii officmalis caulis
InactiveCN105052753AStrong plantWell developed root systemHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureEndophyteHigh survival rate
The invention discloses a rapid propagation method for dendrobii officmalis caulis. The rapid propagation method comprises the following steps: sterilizing the surfaces of seed capsules, sowing the sterilized seeds in a germination culture medium, grafting seedlings germinated by seeds to a protocorm differential medium, transferring differentiated seedlings to a strong seedling rooting medium to finally obtain the tissue culture seedlings of dendrobii officmalis caulis. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that uncracked capsules of dendrobii officmalis caulis are adopted so as to effectively prevent endophytes of dendrobii officmalis caulis from bringing troubles to tissue culture and lower pollution rate; a tri-generation culturing method including seed germination, subculture and strong seedling rooting is adopted, so that the seedling period is greatly shortened and the production cost is lowered; and the cultured tissue culture seedlings are robust, and have developed roots and high survival rate.
Owner:JIANGSU POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE OF AGRI & FORESTRY
Pennisetum purpureum Schum-derived bacillus megaterium and use thereof
ActiveCN104762228AHas nitrogen fixationPossess siderophore capacityBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyBacillus megaterium
The invention relates to Pennisetum purpureum Schum-derived bacillus megaterium and a use thereof and belongs to the technical field of microbes. The Pennisetum purpureum Schum-derived bacillus megaterium pp02 has a class name of Bacillus megaterium pp02, is preserved in the China general microbiological culture collection center (CGMCC) and has a preservation number of CGMCC 9415. The Pennisetum purpureum Schum-derived bacillus megaterium has iron-producing carrier, azotification and IAA production characteristics, has an IAA yield of 10.57 microgrammes per milliliter, has a strong plant root colonization ability and good salt resistance, can grow in a culture medium containing 5% of NaCl (50g / L) and is an excellent plant growth promoting endophyte strain. Through infection of hybrid pennisetum with the Pennisetum purpureum Schum-derived bacillus megaterium, plant salt resistance is substantially improved, plant growth is promoted, and fresh weight, dry weight and height of the plant above the ground are substantially improved. The Pennisetum purpureum Schum-derived bacillus megaterium has important development and application prospects in study of hybrid pennisetum microbial fertilizer and promotion of growth and development of plants in saline marginal land.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
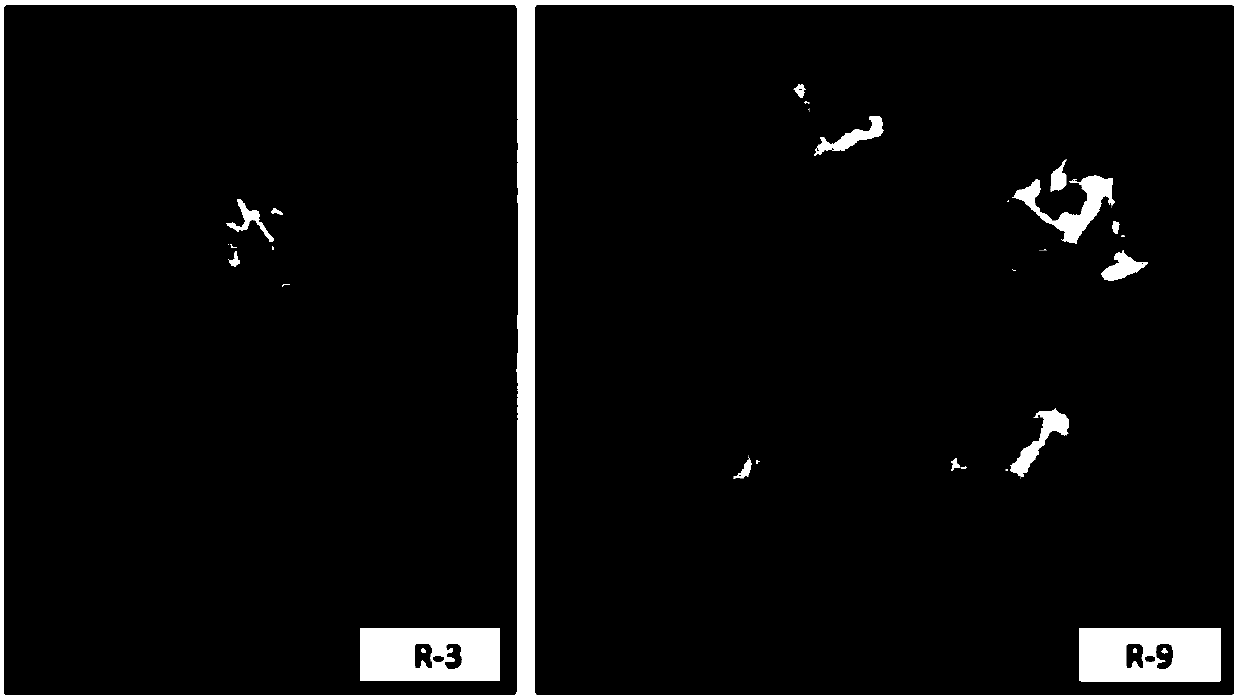
Two ralstonia-solanacearum-resistant endophytic bacillus velezensis strains and application thereof
ActiveCN107779420AExcellent field control effectStrong colonization abilityBiocideBacteriaNicotiana tabacumPlant roots
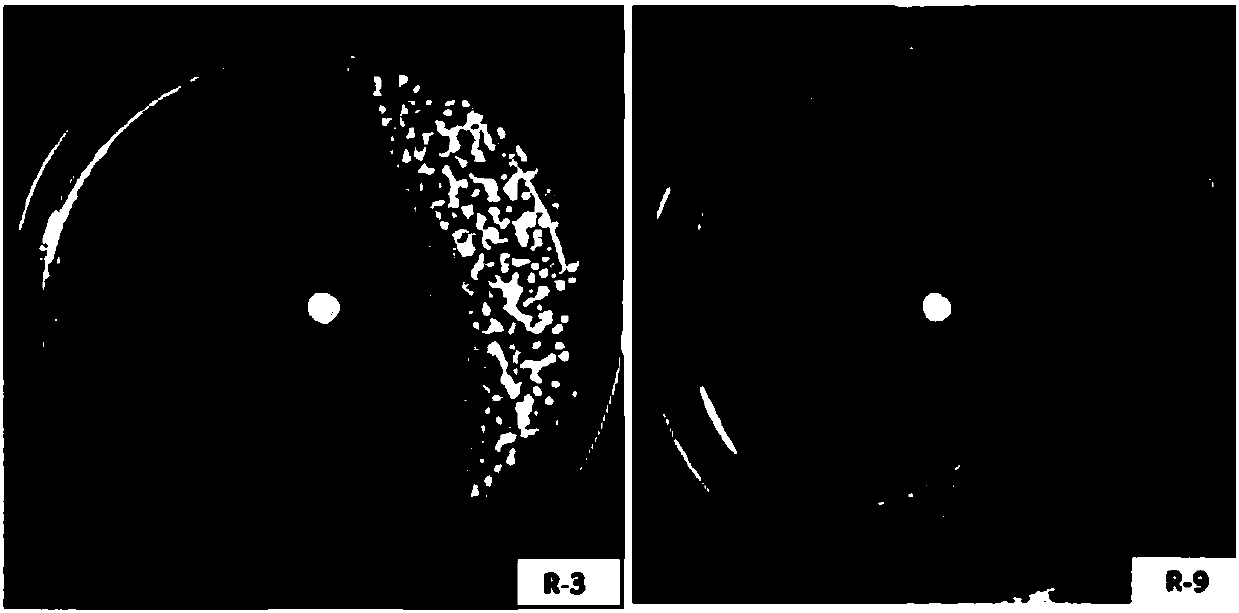
The invention relates to two ralstonia-solanacearum-resistant endophytic bacillus velezensis strains and application thereof. By separation, screening and purification in roots of healthy tobacco plants in a ralstonia solanacearum occurrence area of the Enshi Prefecture, two biocontrol bacillus endophyticus strains R-3 and R-9 are obtained, have evident resistance effects on ralstonia solanacearumand are both capable of generating high-temperature-resistant ralstonia-solanacearum-resistant substances. By gyrB gene sequence identification and phylogenetic tree construction, results show that the R-3 and R-9 are both bacillus velezensis; by potted plant root irrigation experimental verification, the bacilli R-3 and R-9 have great colonization performance in tobacco roots and can enter stemsthrough root transmission; by field experimental verification, bacillus velezensis R-3 and R-9 are effective in ralstonia solanacearum prevention and treatment, remarkably superior to chemical agentkasugamycin and free of pollution. The biocontrol endophyte research field is further enriched by researching on the bacilli R-3 and R-9, and a guiding significance to ralstonia solanacearum prevention and treatment is achieved.
Owner:湖北省烟草公司恩施州公司
Garlic endophyte for accelerating black garlic fermentation process and application thereof in black garlic fermentation
ActiveCN102936573AEasy to operateQuality improvementBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismEndophyte
The invention provides garlic endophyte for accelerating a black garlic fermentation process and an application thereof in the black garlic fermentation, relates to the garlic endophyte and the application thereof in the black garlic fermentation, and belongs to the field of black garlic fermentation from garlic endophyte. The garlic endophyte for accelerating the black garlic fermentation process is Bacillus subtilis S<8nyzx-1> which is preserved in the common microorganism center of China general microbiological culture collection center (CGMCC) with a preservation number of CGMCC No. 6647.
Owner:DAQING BRANCH OF HEILONGJIANG ACAD OF SCI
Separation method for plant endophyte
The invention discloses a separation method for plant endophyte. The separation method comprises the steps of: sampling, surface sterilization, tissue grinding, separation and pure cultivation, and particularly comprises sampling health plants, storing in classification, soaking in an ethanol solution, soaking again in an sodium hypochlorite solution, washing by sterile water, weighing 0.3-0.3 g, adding the sterile water and grinding. The separation method further comprises the steps of: diluting the ground slurry in gradients, plate cultivating after coating, repeating each processing for 3-5 times, selecting single colonies according to eight phenotypic characteristics of bacterial colonies, consisting of shape, size, humidity, color, texture, surface, edge and transparency, for pure cultivation, and moving the pure cultivated single colonies into the test tube slants for preservation. Through the application of the separation method for plant endophyte, the diversity separation result of the plant endophyte is effectively prevented from being manually enlarged or lost; and the separation method for plant endophyte plays a very important role in researching the composition characteristics of plant endophyte colonies and enriching the gene resources of the endophyte.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
Seed endophytes across cultivars and species, associated compositions, and methods of use thereof
Owner:靛蓝股份公司
Endophyte compositions and methods for improvement of plant traits
Owner:INDIGO AG INC
Endophyte compositions and the methods for improvement of plant traits
This invention relates to methods and materials for modulating the characteristics of a plant, said plant having been heterologously disposed to an endophyte or a plurality of endophytes, or derived from a plant reproductive element heterologously disposed to an endophyte or a plurality of endophytes.
Owner:INDIGO AG INC
Plant endophyte and application thereof
ActiveCN103224900APromote rice growthIncreased available zinc contentBiocidePlant growth regulatorsSedum alfrediiFertilizer
The invention discloses a plant endophyte with a category name of Enterobacter sp. and a complete name of Enterobacter sp. SaCS20. The strain is preserved at China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on March 28th, 2013, and has a preservation number of CGMCC NO: 7381. The invention also discloses the application of the plant endophyte in promoting paddy rice growth, improving paddy rice yield, or promoting trace element zinc accumulation in paddy rice. The Enterobacter sp. CGMCC 7381 provided by the invention is separated from the root system of a zinc hyperaccumulator sedum alfredii. The plant endophyte has no pathogenicity upon paddy rice, and can be successfully colonized into paddy rice root systems. With the plant endophyte, paddy rice growth can be promoted, rhizosphere soil available zinc content can be increased, and grain zinc enrichment can be promoted. The application provided by the invention is simple to operate, and is safe and economical. With the plant endophyte and the application, soil micronutrient fertilizer investment can be reduced, and crop yield can be increased.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
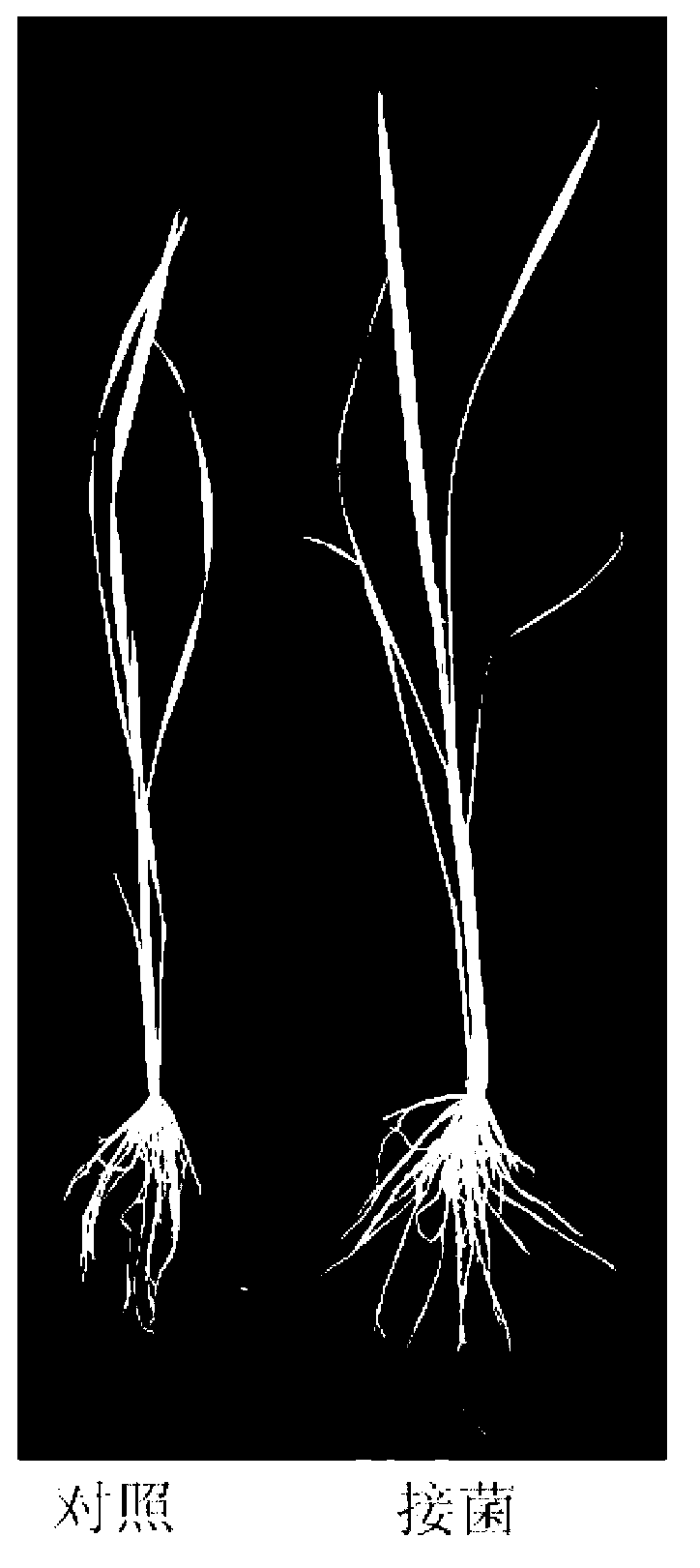
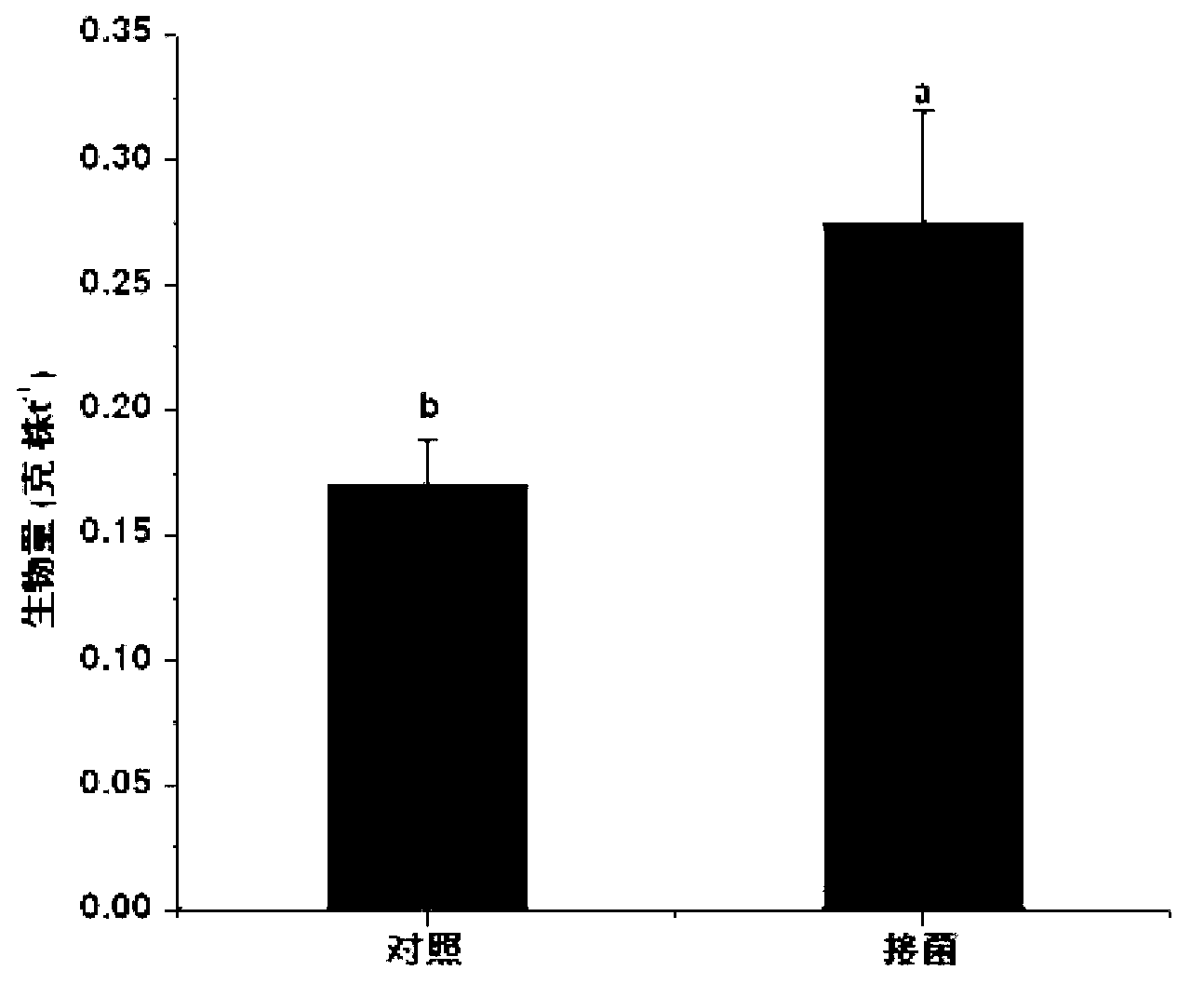
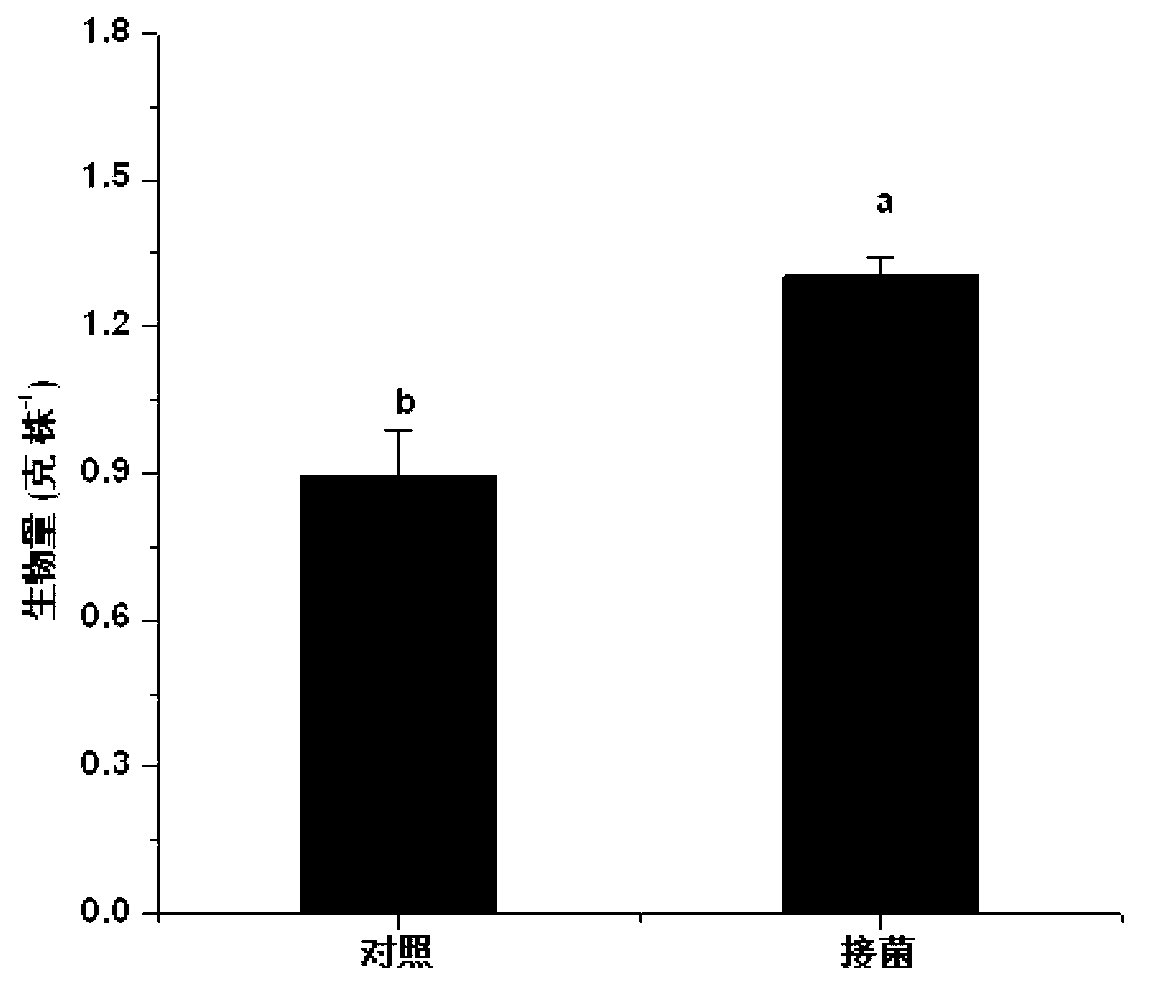
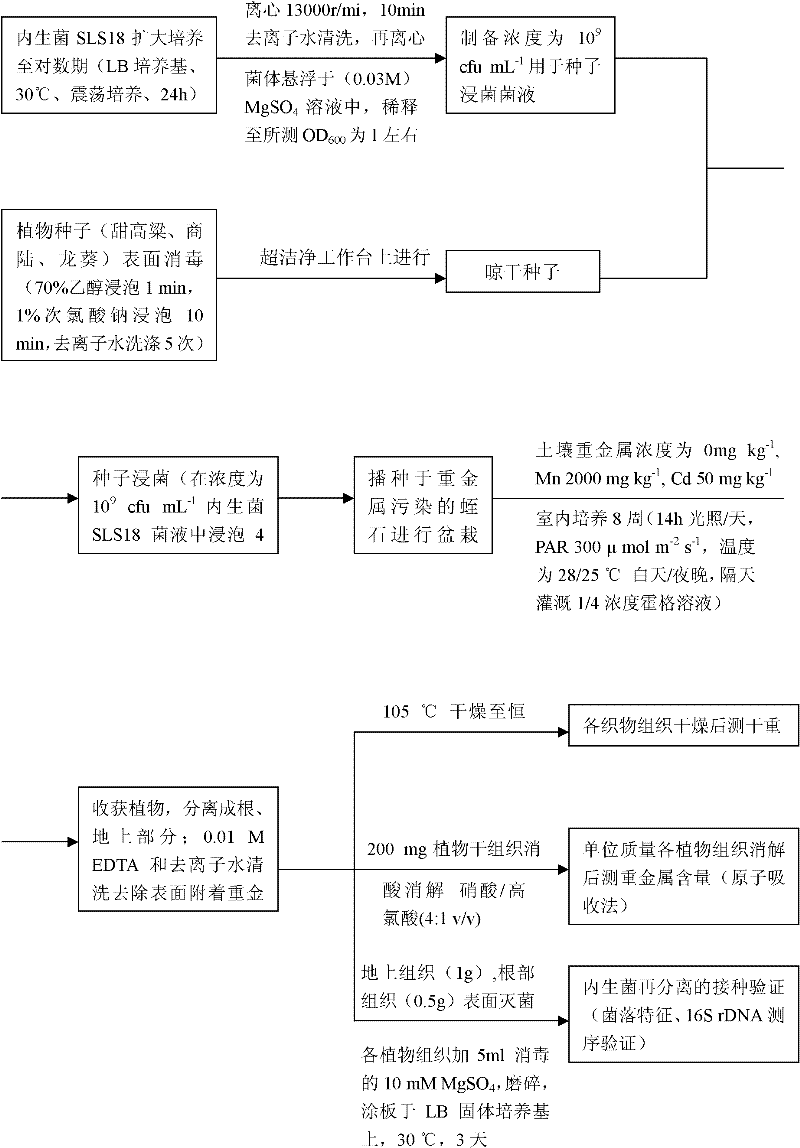
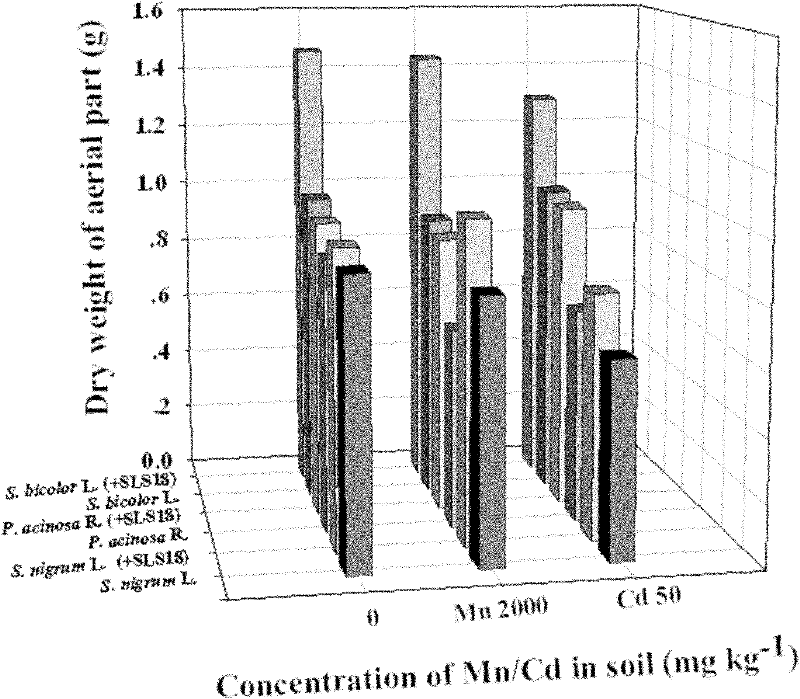
Endophyte for promoting growth of plants and remediation of heavy metal-contaminated soil and application
InactiveCN102161976AAvoid competitionHigh pollution efficiencyPlant growth regulatorsBiocideFungal endophytePlant growth
The invention provides an endophyte for promoting the growth of plants and the remediation of heavy metal-contaminated soil and application thereof. Bacterial liquid of endophyte SLS18 is utilized to dip-dye Sorghum bicolor L. in a mode of seed bacteria dipping to colonize the endophyte SLS18 into the Sorghum bicolor L. to accompany each stage of the growth of the Sorghum bicolor L., so that the growth of the Sorghum bicolor L. on heavy metal-contaminated marginal land and the remediation of soil are promoted. The endophyte SLS18 is separated from the stem of a hyperaccumulator, namely pokeberry root, is obtained through screening, and is an endophyte which can be successfully colonized in the Sorghum bicolor L., has a remarkable effect of promoting the growth of the Sorghum bicolor L. and has the heavy metal resistance. A method is easy to operate, and is safe and economic, no new pollution is introduced into soil environment, heavy metal-contaminated marginal land resources can be effectively utilized so as to avoid the rival of energy crops and food crops against finite cultivated land, and heavy metal-contaminated land can also be effectively remediated.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Production and use of endophytes as novel inoculants for promoting enhanced plant vigor, health, growth, yield reducing environmental stress and for reducing dependency on chemical pesticides for pest control
InactiveUS8101551B2Prevent degradationRapid site occupationBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyMyriophyllum
Owner:ADJUVANTS PLUS INC
Application of Bacillus megaterium YJB3 in plant growth promotion and bio-control
ActiveCN107593769APromote growthLarge biomassBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBacillus megateriumEcological environment
The invention discloses an application of Bacillus megaterium YJB3 in plant growth promotion and bio-control, and belongs to the field of plant protection. The Bacillus megaterium YJB3 has phosphorusdissolving, nitrogen fixing, ferritin producing and other plant growth promoting functions, and also has a plant pathogen inhibiting bio-control effect. Endophytes are colonized in plants or rhizospheres in a rhizosphere inoculation, blade spray or smear treatment or seed or root soaking manner by using a plant endophyte YJB3 bacterium liquid, so the nutrient level of inoculated plants is improved, the disease resistance is improved, the plant biomass is increased, and the plant growth is promoted. The Bacillus megaterium YJB3 is simple, safe and economic to operate, can reduce the use amountsof pesticides and chemical fertilizers in agricultural production and reduce agricultural non-point source pollution, and is of great significance to improving the ecological environment of farmlandsoil and improving the quality of agricultural products.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Salvia miltiorrhiza endophyte with danshinolic acid B accumulation inducing effect, and use thereof
The invention relates to a Salvia miltiorrhiza endophyte and its use in the improvement of danshinolic acid B accumulation in the Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root culturing process. The Salvia miltiorrhiza endophyte is Pseudomonas psychrotolerans LG4 concretely, and has a preservation number of CCTCC NO:M2015085. The Salvia miltiorrhiza endophytec an promote the accumulation of a phenolic acid substance (danshinolic acid B) in Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Method for producing taxol by utilizing Chinese yew seed endophyte
The invention provides a method for producing taxol by utilizing Chinese yew seed endophyte. The method for producing the taxol by utilizing the Chinese yew seed endophyte comprises the following steps: sterilizing and inoculating while Chinese yew seeds are taken as explants, then carrying out secondary sterilization, culturing for a period of time, picking endophytic fungi at the periphery of the Chinese yew seeds, placing the endophytic fungi into a PDA solid culture medium, culturing, then picking part of bacterial plaque, placing the picked bacterial plaque into PDA liquid and culturing; filtering ferment with gauze, and extracting filtrate with ethyl acetate; carrying out reduced-pressure distillation at the temperature of 35 DEG C after filtering by adopting a rotary evaporator, and dissolving in a small amount of methyl alcohol, so that a methanol solution containing taxol is obtained. The method for producing the taxol by utilizing the Chinese yew seed endophyte has the advantages that the problems that Chinese yew plants grow slowly and chemical synthesis of the taxol is complex while a fungus culturing technique is applied can be solved, a foundation is provided for industrial production of the taxol by fungal fermentation, the method for producing the taxol by utilizing the Chinese yew seed endophyte is environment-friendly, raw materials are rich, and the problem of high supply shortage of the taxol can be well relieved.
Owner:LIAOCHENG UNIV
Method for removing endophytes from pistacia chinensis bunge seeds and quickly germinating pistacia chinensis bunge seeds
ActiveCN102498793AImprove germination rateGrow vigorouslySeed immunisationGerminating apparatusChinese pistachioEndophyte
The invention discloses a method for removing endophytes from pistacia chinensis bunge seeds and quickly germinating the pistacia chinensis bunge seeds. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: sterilizing the pistacia chinensis bunge seeds, of which the shells are removed by using ethanol and sodium hypochlorite; soaking the seeds in water to perform ultrasonic processing; and flushing the seeds, and then inoculating the seeds to a seed germination culture medium to obtain aseptic robust seedlings. By adoption of the method, the difficulty that the germination rate of the seeds is influenced by pollution caused by inexhaustive sterilization and long sterilization time is solved, and more importantly, the germination rate of the seeds is increased, the seedlings grow robustly, and a basis is provided for tissue culture and genetic transformation of pistacia chinensis bunge.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of preparing enzymes in biomimetic manner and the enzymes capable of eliminating atherosclerosis
InactiveCN107897895AReduce the difficulty of productionShorten the production cycleFood ingredient functionsBiotechnologyMetabolic waste
The present invention discloses a method of preparing enzymes in a biomimetic manner and the enzymes capable of eliminating atherosclerosis. A first contribution is as follows: cognitive limitations of probiotics and enzymes in the existing technology are broken through, plant own endophytes and endogenous enzymes are used in the biomimetic manner to produce the enzymes, and active ingredients invarious plants are fully released; a second contribution is as follows: in classifications of plant phyla, classes, orders, families, tribes, genera and species, due to the close endophytes and endogenous enzymes, the plants within the same families can be constrainedly fermented together, or plant characteristic components in the fermentation processes are seriously affected; a third contributionis as follows: based on academic points of eliminating pathogens to strengthen vital qi in ''Confucians' Duties to Their Parents'' and macroscopic thoughts that all the pathogen eliminating methods can be achieved by three methods of sweating, emesis and purgation, food enzymes with functions of the sweating, emesis and purgation are used to replace medicines, and purposes of clearing body metabolic waste are achieved by the three ways of the sweating, emesis and purgation; and a fourth contribution is as follows: the method merges modern technology, reduces production difficulties, shortensproduction cycles, and improves product quality.
Owner:丛繁滋
Modification method for improving bacteria heavy metal adsorption capacity, adsorbent and application thereof
InactiveCN102965312AEasy to handleEasy to operateBacteriaWater contaminantsCross-linkEnvironmental resistance
The invention provides a modification method for improving bacteria heavy metal adsorption capacity, an adsorbent and the application of the method. The method takes glutaraldehyde as a cross-linking agent, and comprises the step of: connecting poly allyamine hydrochloride (PAA / HCl) to the surface of plant endophyte Pseudom onas sp. LK9 thallus so as to cause the surface of the thallus to have a great deal of amino groups and further improve the adsorption effect of the thallus for heavy metals. The maximum adsorbing capacities of the obtained adsorbent for the heavy metals Pb<2+>, Cd<2+> and Cu<2+> are respectively 269.9mg / g, 145.0mg / g and 148.0mg / g; and compared with an LK9 adsorbent which is not modified, the adsorbing capacities are respectively increased by 192.98mg / g, 121.85mg / g and 128.35mg / g. The invention has the characteristics of being simple in method, simple and convenient to operate, remarkable and rapid in adsorption effect, environment-friendly and the like, thus having great application potential in the aspect of heavy metal pollution water treatment.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Screening method of endophyte of dioscorea zingiberensis for producing diosgenin
The invention obtains an endophyte of a dioscorea zingiberensis by steps of field sampling, sample surface sterilization, isolation of microorganism, liquid culture and the like; the strain is identified as bacillus licheniformis, which can produce diosgenin of the dioscorea zingiberensis and can be used as production strain for fermentation.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Strain of antagonistic poplar colletotrichumgloeosporioides and application thereof
The invention discloses a strain of antagonistic bacteria for preventing and controlling poplar colletotrichumgloeosporioides and application thereof. The antagonistic bacteria are bacillus atrophaeus XW2, and the microbial collection number is CGMCC NO. 7689. The bacillus atrophaeus XW2 is obtained through plate face-to-face culturing and screening of poplar endophytes via a flat plate, has an obvious antagonistic effect on the poplar colletotrichumgloeosporioides, can be used for effectively inhibiting the growth of poplar colletotrichumgloeosporioides hypha and germination of spores and preventing and controlling plant diseases caused by the poplar colletotrichumgloeosporioides, is a biological prevention and control potential strain with high protection effect and good environmental safety and has good development and application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY +1
Peltate yam rhizome endophyte for generating saponinase and application
InactiveCN105779306AIncrease productionTo satisfy the market's needsFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyIndustrial fermentation
The invention discloses peltate yam rhizome endophyte for generating saponinase and application. The peltate yam rhizome endophyte is Aspergillus flavus strain SYfx213.2 and preserved in CGMCC, and the preservation number of the peltate yam rhizome endophyte is CGMCC 11517. The peltate yam rhizome endophyte can be used for industrial fermentation and production of peltate yam rhizome saponinase, the yield of saponinase can be improved, and the market requirement is met.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Grass endophytes
An endophyte or endophyte culture of N. lolii species is described that, in combination with a host grass does not cause typical symptoms of ryegrass toxicosis in grazing animals and also contains levels of compounds from the class of janthitrems epoxides to individually or in combination protect the host grass from pests or abiotic stresses or both. Uses and methods are also described to produce and characterise the combination as well as alternative uses for compounds from the class of janthitrem epoxide compounds.
Owner:GRASSLANZ TECH
Flavonoid glycoside and isoquinoline alkaloid complex for inhibiting multi-drug-resistant staphylococcus aureus and preparation of carrier-free nano-drug of flavonoid glycoside and isoquinoline alkaloid complex
InactiveCN112010849AHigh antibacterial activitySensitiveAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsQuinolineFlavonoid glycosides
The invention provides a novel flavonoid glycoside and isoquinoline alkaloid complex structure, preparation, antibacterial application and three complex carrier-free nano-drugs with self-assembly performance. The structural general formula of the complex is shown in the specification, the complex has excellent selective antibacterial ability, and the activity of endophyte escherichia coli and probiotics bacillus subtilis and enterococcus faecium is not influenced while pathogenic bacteria staphylococcus aureus is killed; meanwhile, the compound has a good inhibition effect on multiple drug-resistant staphylococcus aureus, and is superior to norfloxacin, oxacillin, tetracycline and ciprofloxacin. The nano-drug formed by self-assembling the three complexes is uniform in form and good in dispersity and stability, gel or fiber is formed under the condition that auxiliary materials are not needed, and support is provided for development of a carrier-free pure drug delivery preparation.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
A method for screening endophytic fungi that can improve the ability of crops to resist fungal diseases
InactiveCN102283118AImprove resistance to fungal diseasesHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureBiotechnologySporeling
The invention discloses a method for screening endophytic fungi capable of improving the ability of crops to resist fungal diseases. The steps include: 1) collecting plant materials to obtain plant-free transplanted seedlings without any disease; 2) separating endophytic fungi from plants fungi; 3) Prepare endophyte spore suspensions from the isolated endophytic fungi, and mycelial suspensions from endophytic fungi that do not produce spores; 4) Inoculate endophytic fungal spores or mycelial suspensions until the 5) Infect the transplanted seedlings inoculated with endophytic fungi and the transplanted seedlings not inoculated with endophytic fungi with pathogenic fungi, and observe the control after one month Effect, the endophytic fungi with a control effect greater than 80% are endophytic fungi that can improve the ability of the crops to resist fungal diseases.
Owner:XIAN UNVERSITY OF ARTS & SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com