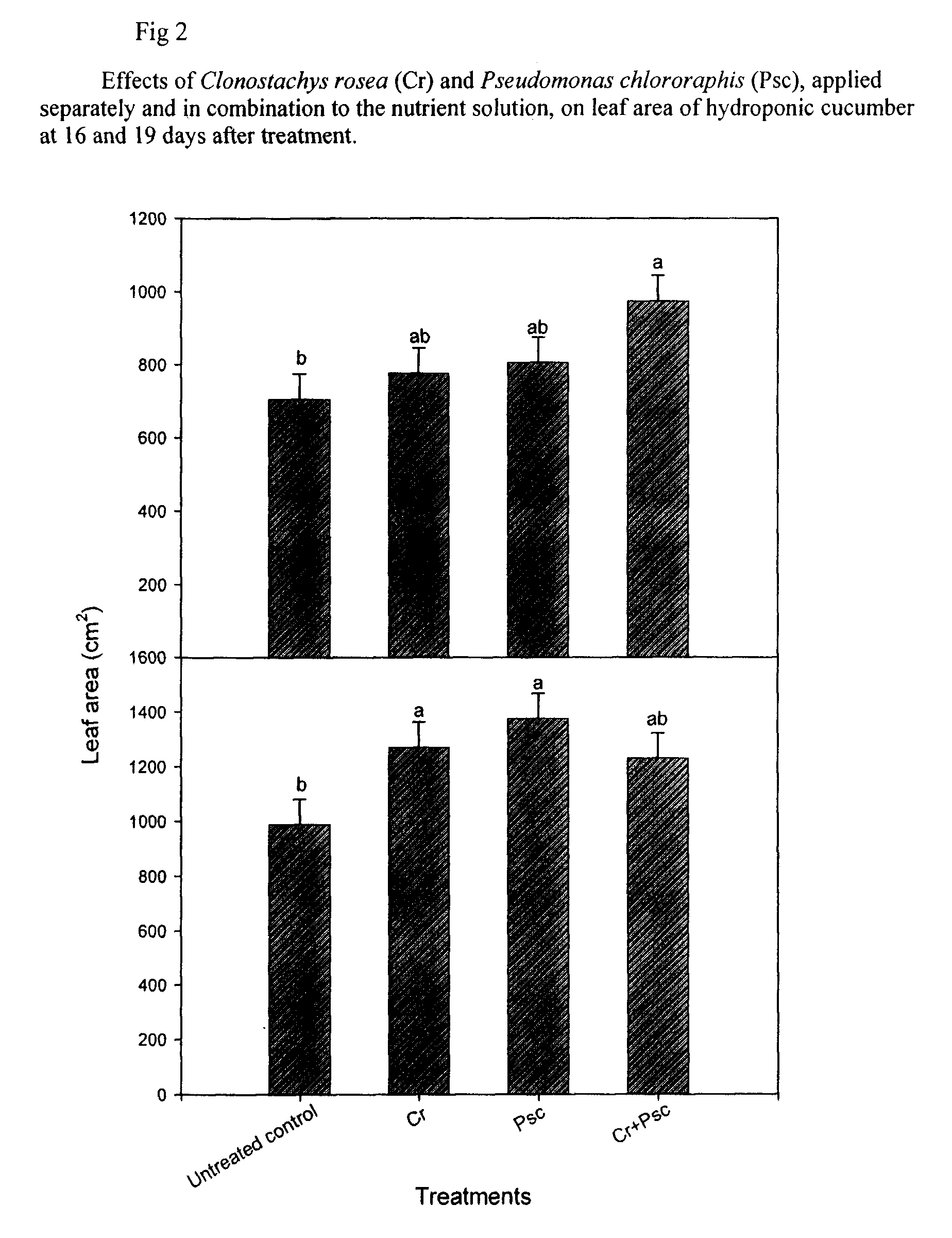
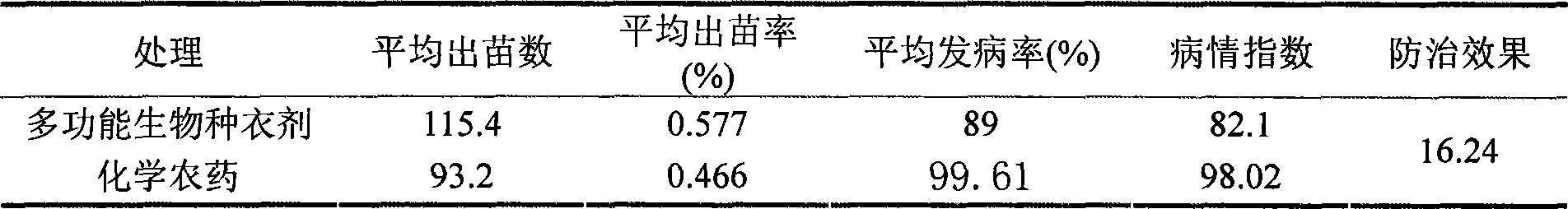
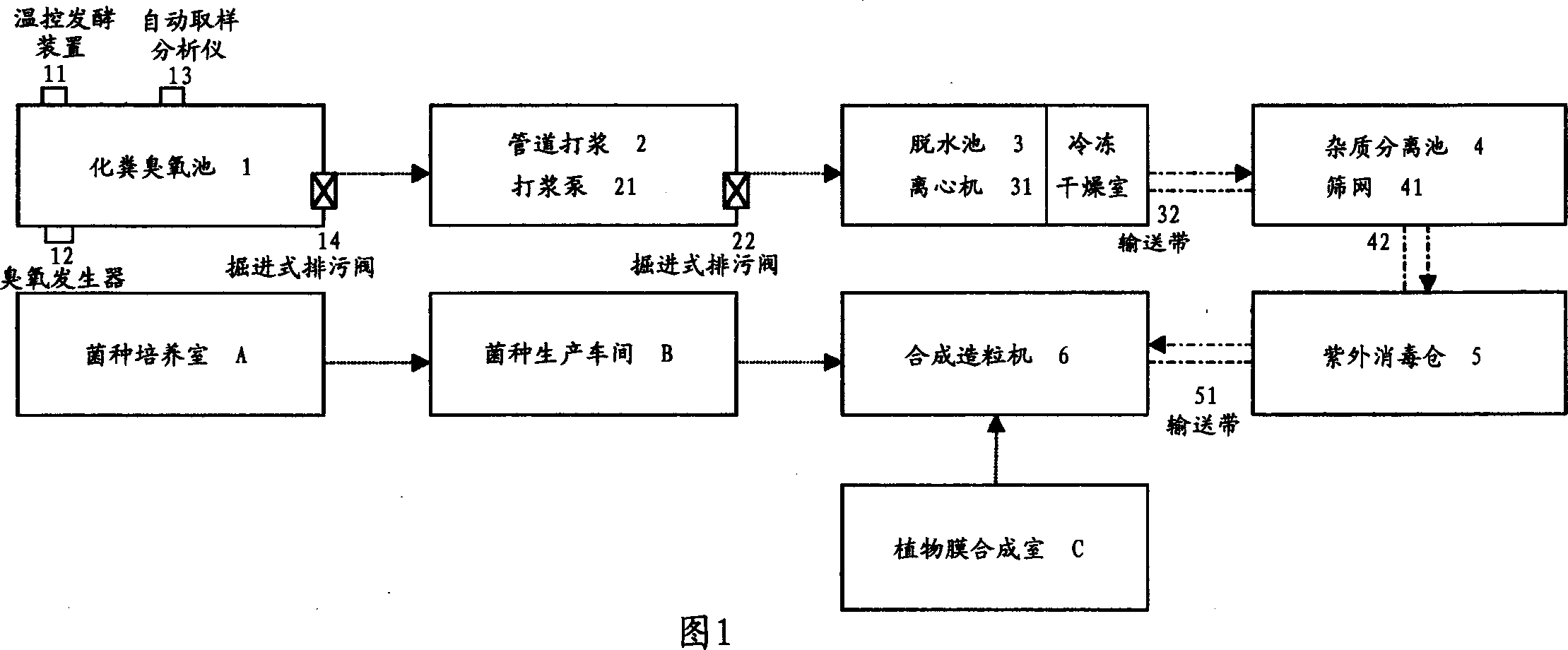
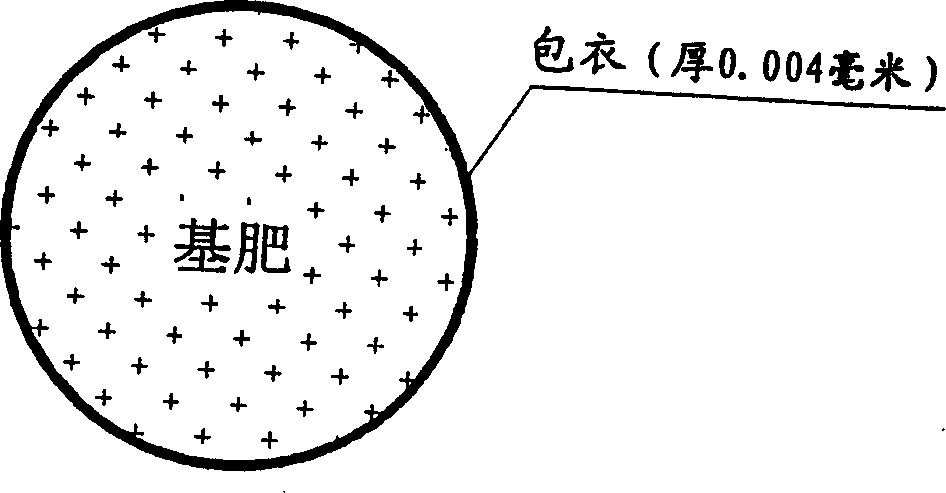
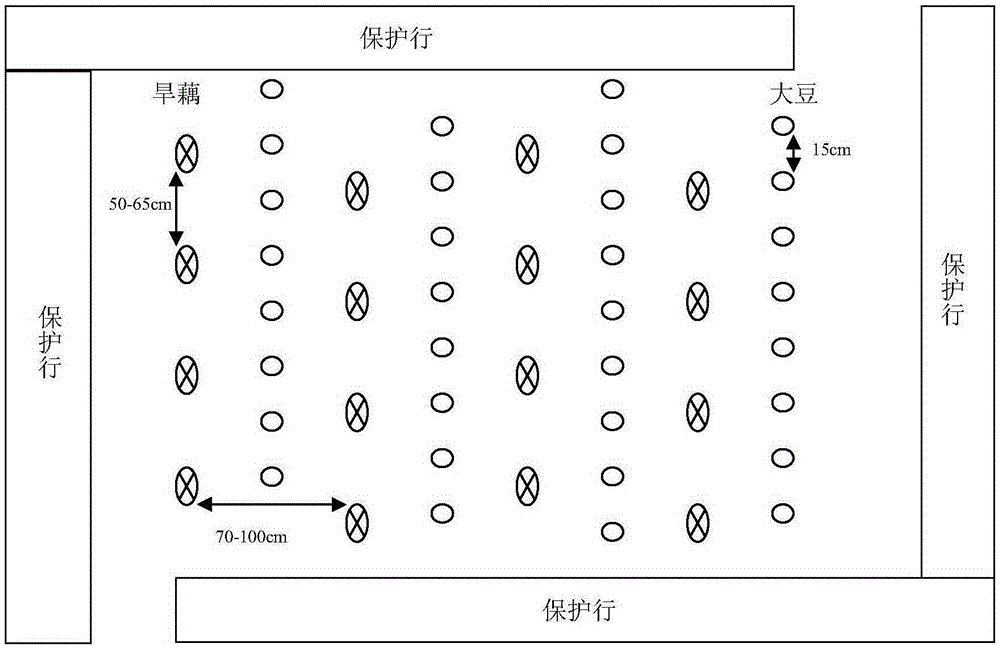
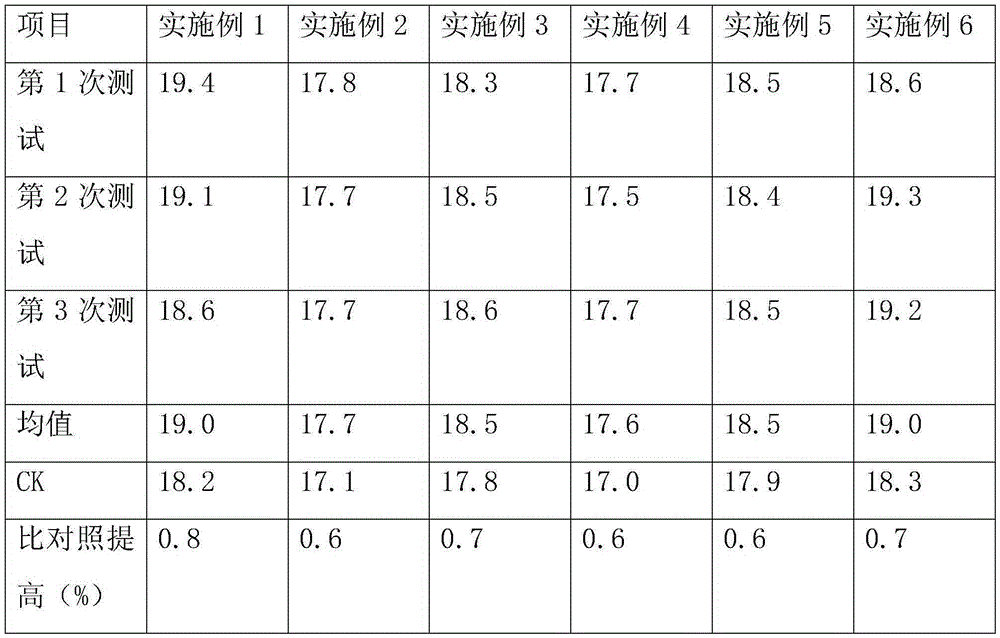
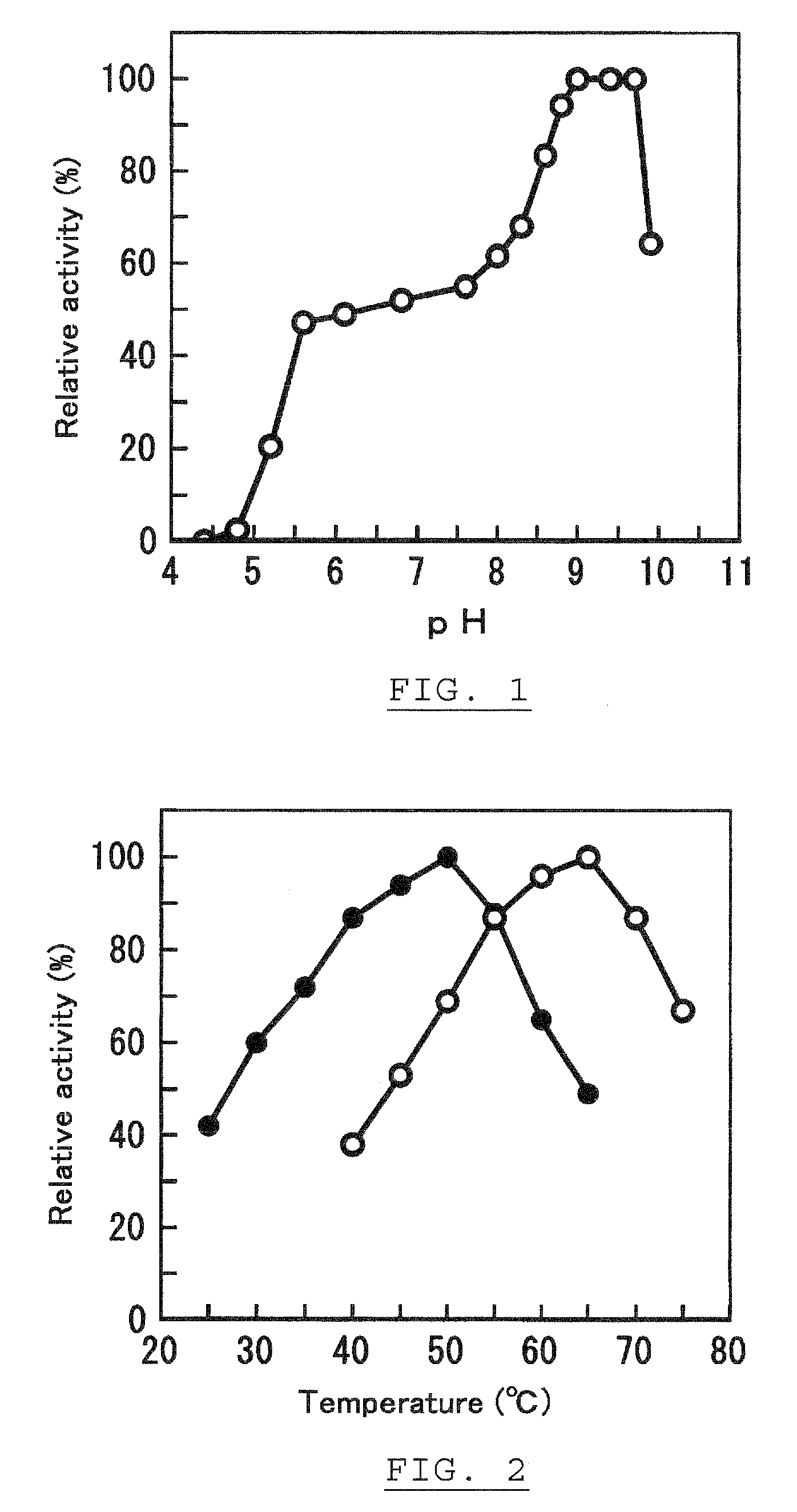
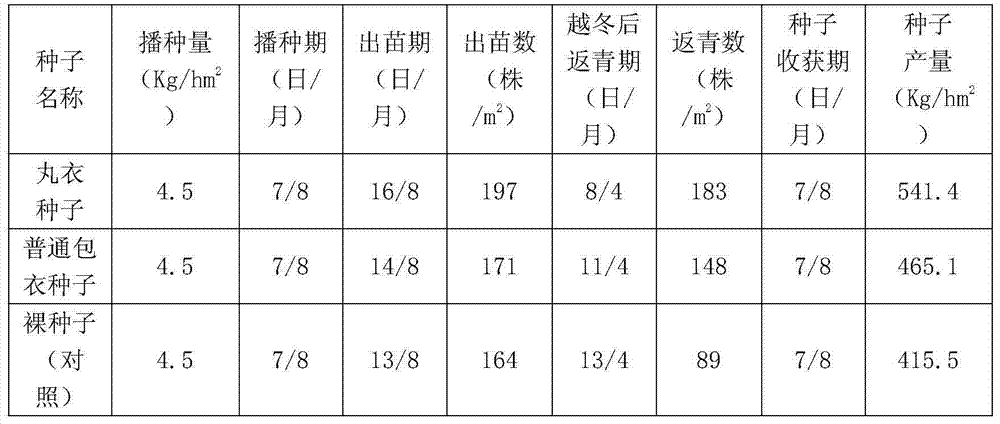
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
462 results about "Rhizobium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Rhizobium is a genus of Gram-negative soil bacteria that fix nitrogen. Rhizobium species form an endosymbiotic nitrogen-fixing association with roots of legumes and Parasponia. The bacteria colonize plant cells within root nodules, where they convert atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia using the enzyme nitrogenase and then provide organic nitrogenous compounds such as glutamine or ureides to the plant. The plant, in turn, provides the bacteria with organic compounds made by photosynthesis. This mutually beneficial relationship is true of all of the rhizobia, of which the genus Rhizobium is a typical example.
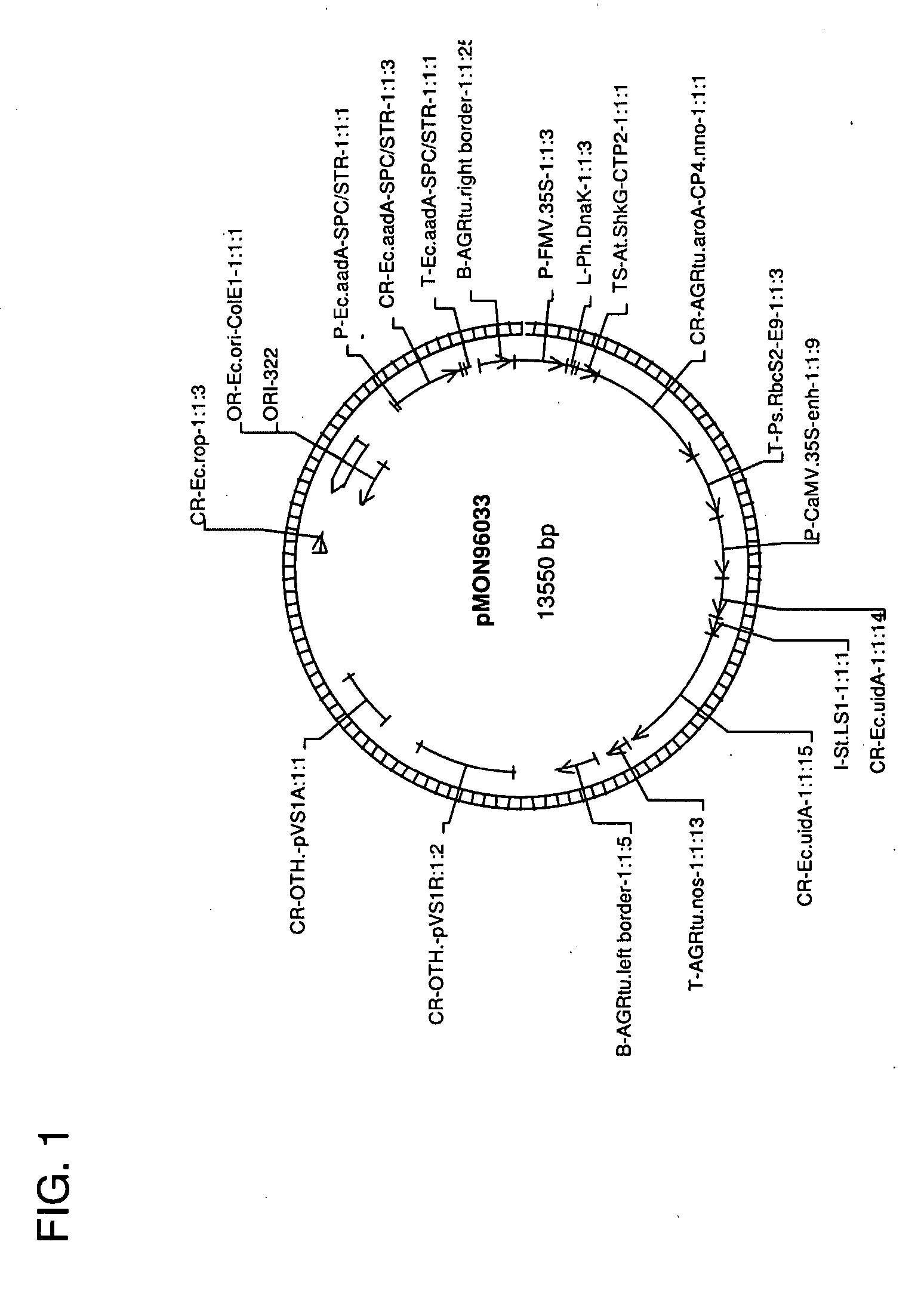
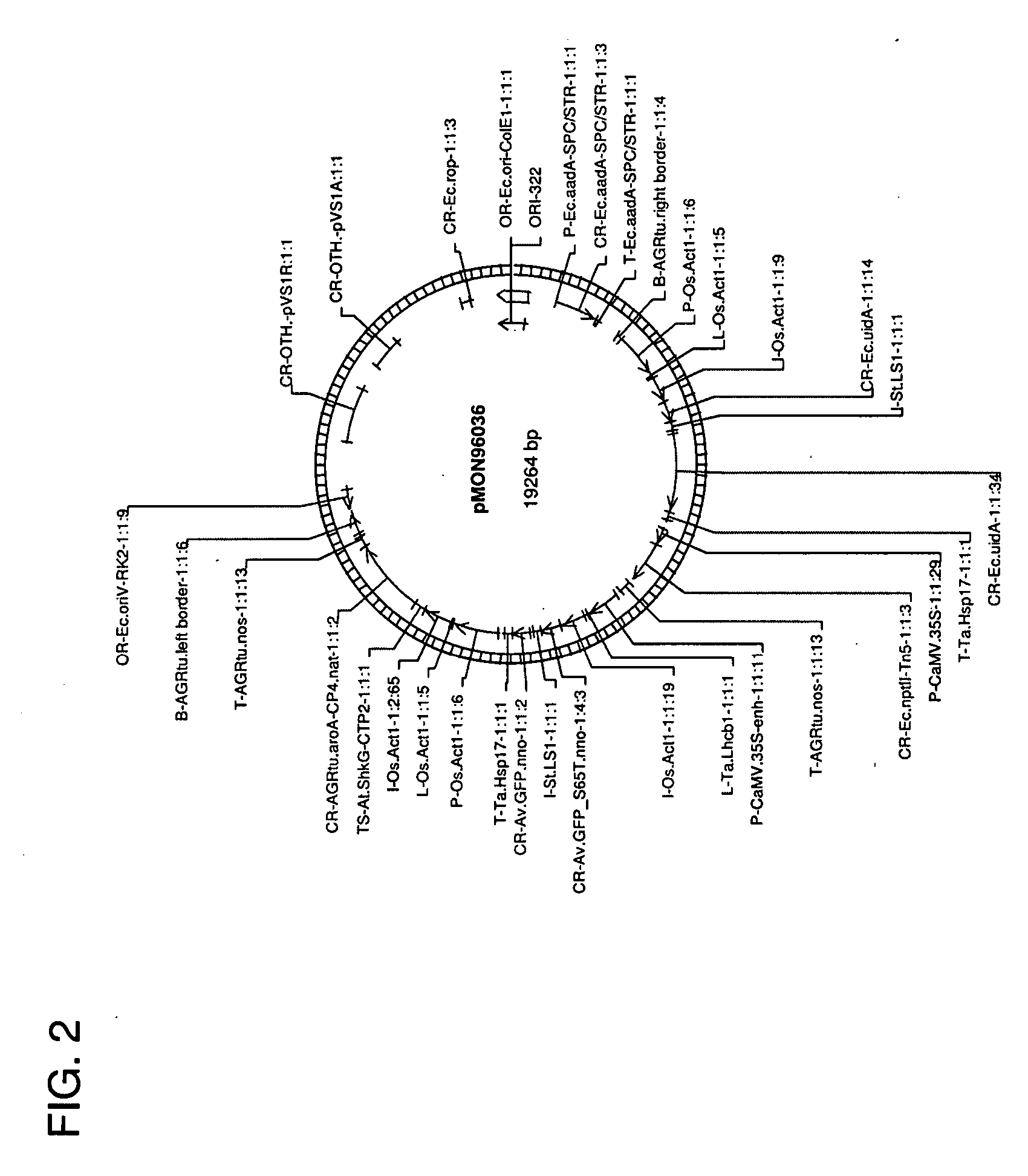
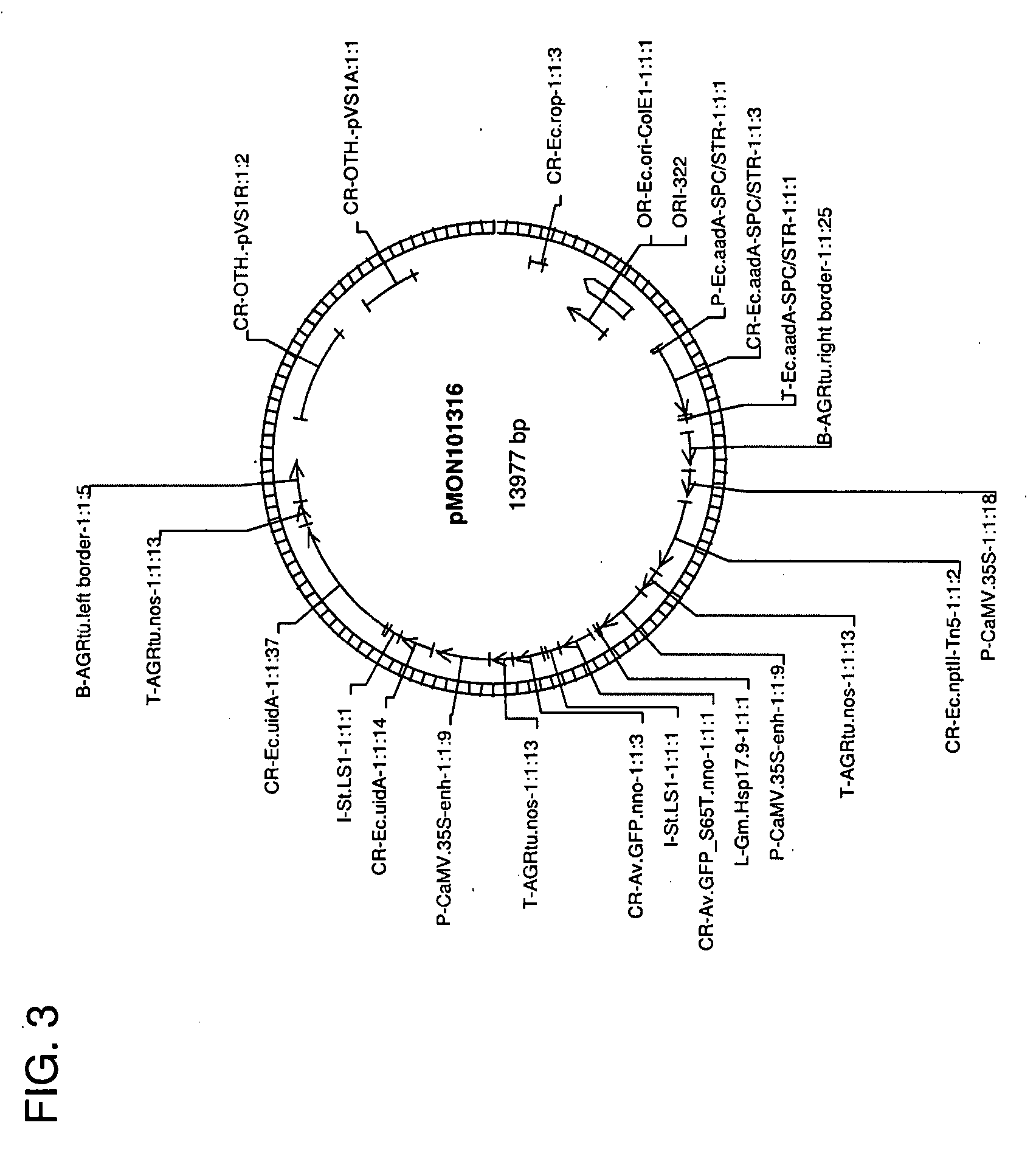
Use of non-agrobacterium bacterial species for plant transformation
The invention relates to methods for Rhizobia-mediated genetic transformation of plant cells, including soybean, canola, corn, and cotton cells. These include both VirD2-dependent and VirD2-independent methods. Bacterial species utilized include strains of Rhizobium sp., Sinorhizobium sp., and Mesorhizobium sp. Vectors for use in such transformation are also disclosed.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Biochar base soil modifier and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102660291AReduce leaching wasteGood sustained release effectAgriculture tools and machinesOrganic fertilisersDecompositionCarbonization
The invention discloses a biochar base soil modifier and a preparation method thereof. The biochar base soil modifier comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 95.5-98.5% of biomass carbon black and 1.5-4.5% of probiotics agent. Agricultural waste serves as a biomass raw material to carry out low-temperature carbonization to form the porous biomass carbon black; beneficial microorganism is enlarged and cultivated and is fermented into probiotics liquid; after mixing, solid and liquid separation, flash evaporation and drying are carried out to obtain the probiotics agent; the beneficial microorganism is selected from one or more of paenibacillus polymyxa, trichoderma strains, nitrogen-fixing bacteria, rhizobium, phosphate solubilizing bacteria, potassium bacteria, cellulose decomposition bacteria, antibiotic generation bacteria and photosynthetic bacteria. The biochar base soil modifier disclosed by the invention adopts the microporous biomass carbon which has strong adsorption capability and good light absorption and temperature-increasing effect. The probiotics agent has a high survival rate and can be stored for a long time at the normal temperature, the fertilizer synergy action is obvious, and the soil borne disease can be effectively prevented and cured.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +2
Microbial inoculum and organic fertilizers fermented by same
ActiveCN101643718AImprove adaptabilityImprove qualityFungiBio-organic fraction processingPenicilliumRhizobium
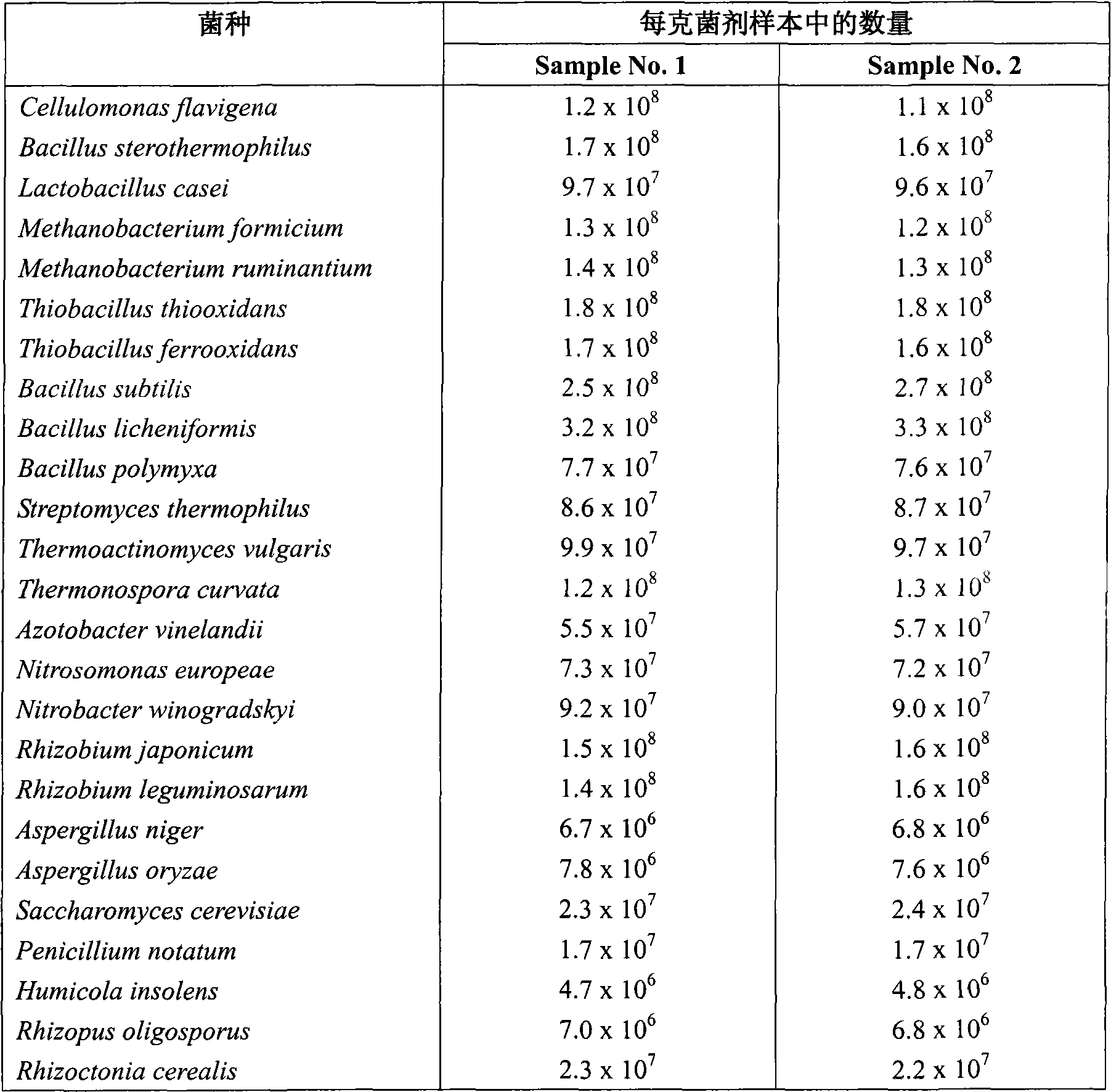
The invention relates to a microbial inoculum for fermenting and producing organic fertilizers, comprising cellulomonas, bacillus, lactobacillus, methagen, thiobacillus, streptomyces, thermoactinomyces, thermomonospora, azotobacter, nitrosomonas, nitrobacter, rhizobium, aspergillus, yeast, penicillium, humicola, rhizopus and mycorrhizal fungi. In addition, the invention also relates to organic fertilizers fermented and produced by using the microbial inoculum and a method for fermentation and production.
Owner:宋彦耕
Compound probiotics preparation for biological organic fertilizers and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102229900APromote growthImprove firmnessBio-organic fraction processingFungiAureobasidium sp.Streptomyces variabilis
The invention discloses a compound probiotics preparation for biological organic fertilizers and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: performing activated culture of 14 kinds of probiotics, including Pseudomona putida, Streptomyces violovariabilis, Rhizobium sp., Azotobacter chroococcum, Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, Bacillus cereus, Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus weihenstephanensis, Bacillus mucilaginosus, Bacillus thuringiensis, Saccharomyces rouxii, Streptomyces griseus var. ferrugineus, and Streptomyces microflavus; performing mixed inoculation at a proportion of 1% to 5% to a 500 mL liquid seed culture medium; then performing amplification culture; and finally delivering the strains to a 500 mL fermentor and fermenting for 3 to 5 days under such conditions that the temperature ranges from 28 DEG C to 30 DEG C and the rotational speed is 200 rpm, to obtain a liquid-state compound probiotics preparation. The compound probiotics preparation for biological organic fertilizers, provided by the invention, plays important roles of taking advantage of microbial ecology, improving soil, promoting plant growth, improving the yield and disease resistance of crops and reducing the consumption of fertilizers.
Owner:周剑平 +1
Microbial agent and soil modifying agent produced by fermentation thereof
ActiveCN101629156AImprove adaptabilityImprove fertilityAgriculture tools and machinesFungiFiberMicrobial agent
The invention relates to a microbial agent used for producing a soil modifying agent by fermentation, consisting of fiber monad, bacillus, lactobacillus, methanobacteria, thiobacillus, streptomycete, high-temperature actinomyces, high-temperature monad, azotobacteria, nitration monad, nitration bacilus, rhizobium, koji mold, leaven, blue mold, detritus mold, rhizopus as well as mycorrhizal fungi and substrate. In addition, the invention also relates to a soil modifying agent produced by the fermentation of the microbial agent, application thereof and the like.
Owner:宋彦耕
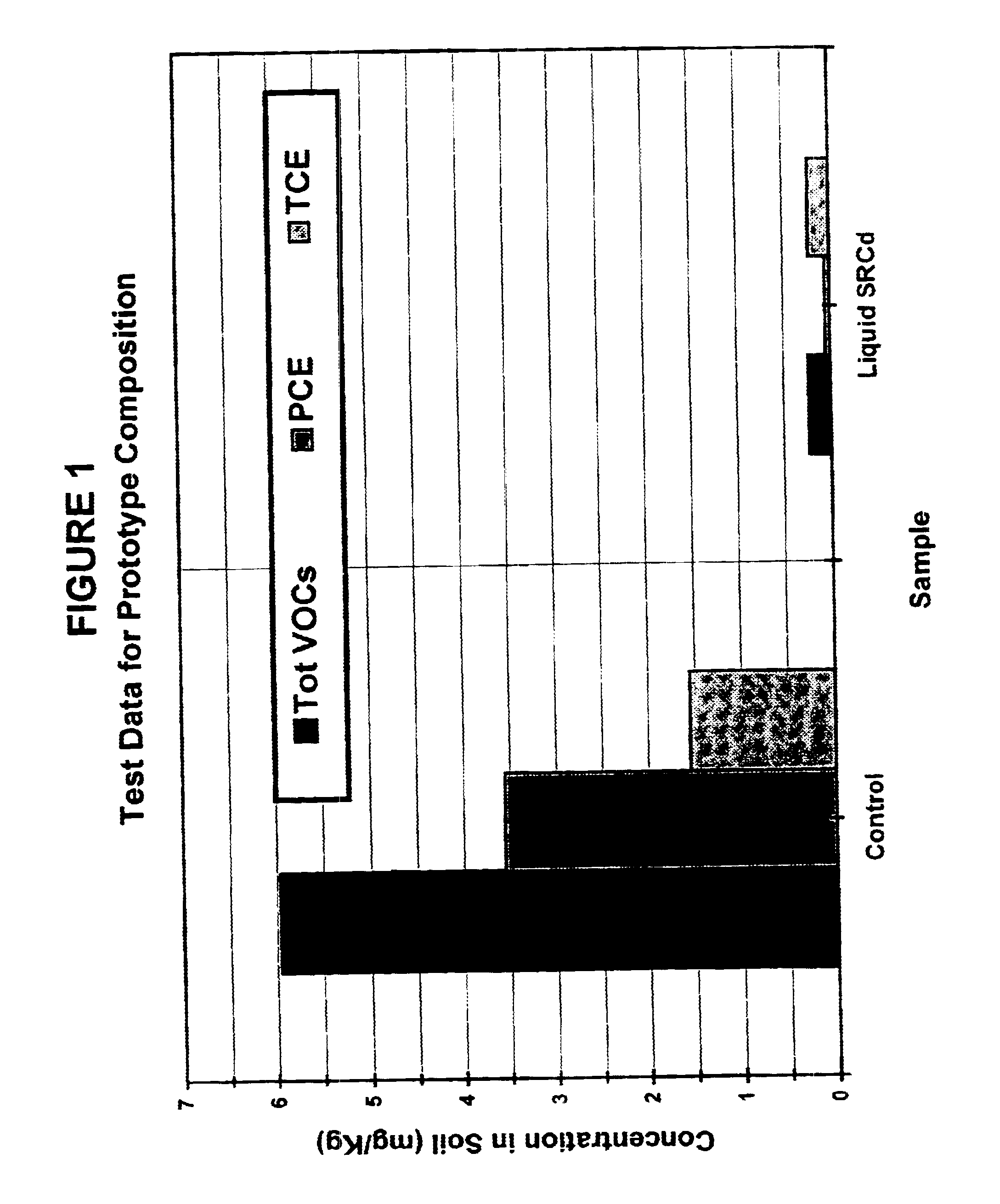
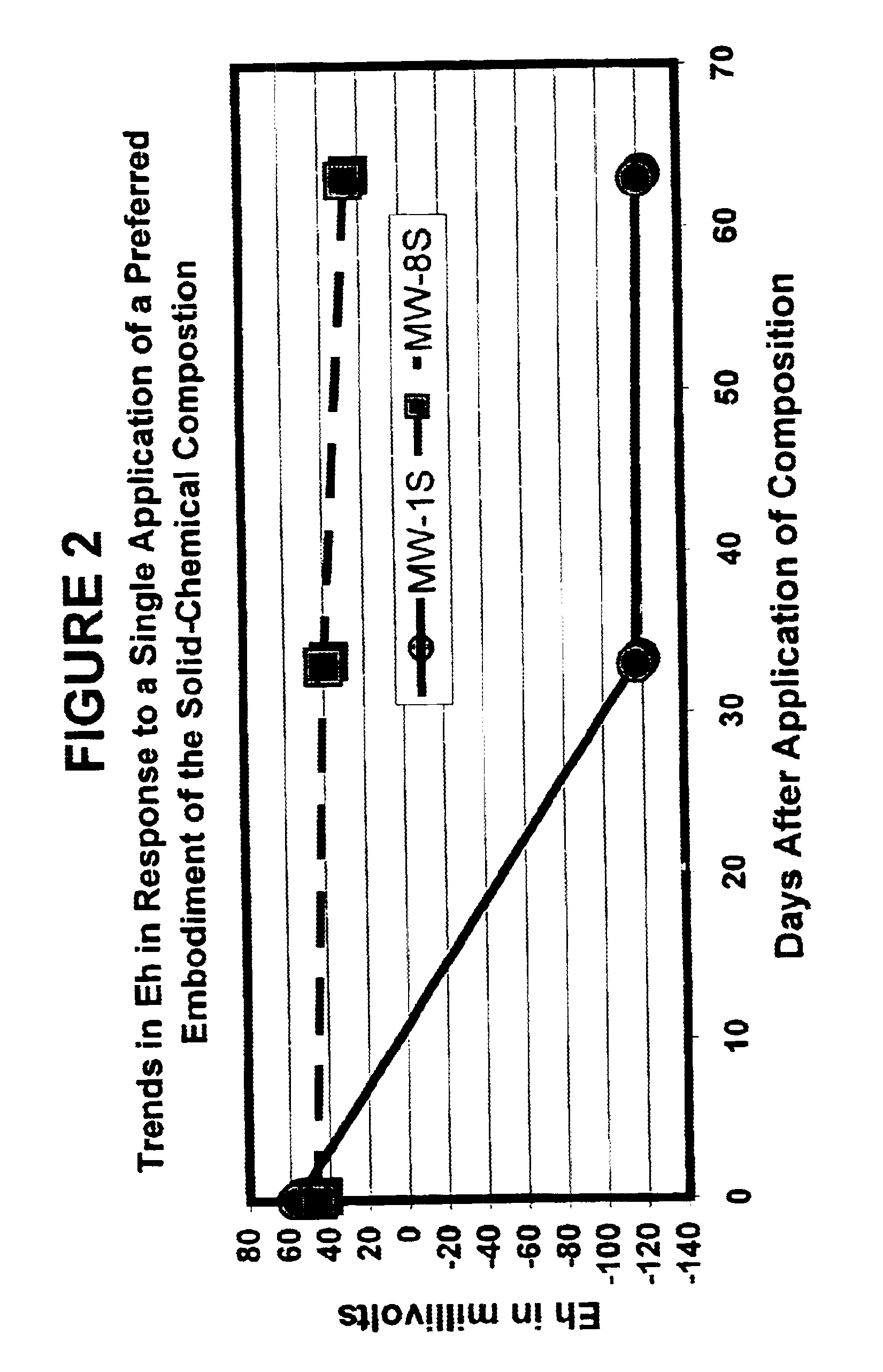
Solid-chemical composition for sustained release of organic substrates and complex inorganic phosphates for bioremediation
InactiveUS6620611B2Improve solubilityIncreasing speed and effectivenessBacteriaWater treatment compoundsPseudomonasTrichoderma spp
A slow-release solid chemical composition for environmental bioremediation is provided. The composition comprises a source of soluble organic substrates which include sugars, soluble organic polymers and mixtures of them in an amount of 7% to 90%, insoluble organic substrates an amount of 10% to 70%, complex inorganic phosphates in an amount of 0.5% to 7% and soluble organic salts in an amount of 2% to 70%. The insoluble organic substrates include fibrous plant materials, starches, cellulosic materials and mixtures of these substrates. The complex inorganic phosphates include ringed metaphosphates, linear polyphosphates and mixtures. The organic salts include lactates, formates, acetates, citrates, etc. Also the composition further comprises microorganisms which include Bacillus spp., Rhizobium spp., Bradyrhibzobium spp., Fibrobacter spp., Clostridium spp., Pseudomonas. spp., Geobacter spp., Arthrobacter spp., Nocardia, spp., aspergillus spp., Trichoderma spp., Candida spp., Yarrowia spp. and combinations of these microorganisms. The composition can be prepared in various forms, including granules, briquettes, pellets, tablets or capsules.
Owner:HINCE ERIC CHRISTIAN MR
Biomass charcoal based probiotic preparation and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102701834AReduce leaching wasteGood sustained release effectClimate change adaptationAgriculture gas emission reductionAbsorption capacityDecomposition
The invention discloses a biomass charcoal based probiotic preparation, which is composed of biomass carbon black and concentrated probiotic preparation based on a weight ratio of (8.85-9.15): (0.85-1.15). The preparation is prepared by using agricultural wastes as biomass raw materials, conducting low-temperature carbonization to form porous biomass carbon black; conducting amplification culture to beneficial microorganism, and fermenting to produce probiotic solution; mixing above materials and separating solid from liquid; and drying by flash evaporation to obtain concentrated probiotic preparation, wherein the beneficial microorganism is one or more of paenibacillus polymyxa, trichoderma, nitrogen-fixing bacteria, rhizobium, phosphate dissolving bacteria, potassium dissolving bacteria, cellulose decomposition bacteria, antibiotic producing bacteria, and photosynthetic bacteria. In addition, the invention also discloses a preparation method for the biomass charcoal based probiotic preparation. The biomass charcoal based probiotic preparation provided by the invention uses microporous biomass charcoal, which has very strong absorption capacity and very good light absorption and warming effect. The probiotic preparation is high in survival rate of live bacteria, can be preserved for a long time at normal temperature and has evident synegistic effect for fertilizer.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +2
Multifunctional additive for greening seedling growth substrate
InactiveCN101429062AIncrease vitalitySimple structureOrganic fertilisersFertilizer mixturesPotassiumPhotosynthetic bacteria
The invention discloses a green nursery stock planting substrate multifunctional additive, which is characterized in that the additive comprises the following components in weight portion: 1)150 to 200 portions of vegetable carbide; 2) 5 to 10 portions of polyacrylamide type high absorbent resin;3) 0.5 to 1 portion of inorganic fertilizer or compound fertilizer containing nitrogen, phosphorous, kalium elements and the like; 4) 0.05 to 0.1 portion of encapsulated type slow / controlled release fertilizer; 5) 10 to 20 portions of organic fertilizer; and 6) 0.03 to 0.05 portion of compound microbial inoculum comprising photosynthetic bacteria, actinomycete, microzyme, lactobacillus, rhizobium, bacillus and thiobacillus. By the additive, the planting survival rate of nursery stock is more than 98 percent, and the additive also has the advantages of quick seedling recovery, vigorous rooting, vigorous growth and obvious effects.
Owner:浙江城建房地产集团股份有限公司
Compound microbial agents, bacterial manure, preparation methods thereof and application thereof to restoration of saline alkali soil
ActiveCN105838644AStrong decompositionStrong transformationBio-organic fraction processingFungiAlkali soilBacillus megaterium
The invention relates to compound microbial agents, bacterial manure, preparation methods thereof and application thereof to restoration of saline alkali soil .In particular, the compound microbial agents comprises the bacillus megaterium microbial agent, the pseudomonas stutzeri microbial agent, the rhizobium radiobacter microbial agent, the candida tropicalis microbial agent and the lactobacillus delbrueckii microbial agent .The invention further comprises the bacterial manure containing the microbial agents, the preparation methods thereof and application thereof to restoration of the saline alkali soil .By means of the compound microbial agents, the bacterial manure, the preparation methods thereof and application thereof to restoration of the saline alkali soil, raw materials which pollute the environment easily or need to be disposed such as straw, excrements of livestocks, household garbage and sludge can be utilized sufficiently, in addition, the compound microbial bacterial manure capable of restoring the saline alkali soil can be prepared, thus the immune function and stress resistance of plants can be improved, the land salinization degree can be improved, and the purpose of achieving second ploughing of salinized soil is achieved.
Owner:陈五岭
Micro-organisms for the treatment of soil and process for obtaining them
InactiveUS20050060930A1Favorable effectBiocideAgriculture tools and machinesAzospira sp.Azospirillum brasilense
The present invention relates to product(s) containing living microorganism(s) suitable for soil treatment, microorganisms multiplying under different climatic and natural circumstances, as well as procedures for the production of the products, and procedures for the treatment of the soil and plants with the products. More particularly, the invention relates to a procedure for preparing the products from any of the microorganisms specified below, or from the mixture thereof. Furthermore, the invention relates to a procedure for the creation of the cultures of the microorganisms to be used. The subject invention also pertains to the microorganisms themselves. More particularly, the invention relates to a procedure for the treatment of the soil and the plants with a product containing at least one of the microorganisms selected from Azospirillum brasilense ssp. SW51 (NCAIM / P / B 001293), Azotobacter vinelandii ssp. M657 (NCAIM / P / B 001292), Pseudomonas fluorescens var. SW11 (NCAIM / P / B 001296), Bacillus polymyxa var. SW17 (NCAIM / P / B 001295), Bacillus megaterium var. M326 (NCAIM / P / B 001291), Micrococcus roseus ssp. A21 (NCAIM / P / B 001294), Bradyrhizobium japonicum var. PH25 (NCAIM / P / B 001302), and Streptomyces albus var. 0003 LP (NCAIM / P / B 001301), and furthermore the products multiplying and existing in the environment of the plant in question, containing the listed microorganisms and their production.
Owner:AGRO BIO HUNGARY KFT
Biomass charcoal soil conditioner and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105237294AHigh in nutrientsImprove physical and chemical propertiesFertilizer mixturesAlkali soilMicrobial agent
The invention discloses a biomass charcoal soil conditioner. The soil conditioner comprises the following raw materials by weight: 40% to 50% of biomass charcoal, 20% to 30% of a functional microbial agent, 10% to 15% of desulfurized gypsum, 5% to 10% of calcium nitrate, 5% to 10% of ground phosphate rock and 1% to 2% of amino acid, wherein the functional microbial agent contains any two selected from the group consisting of bacillus subtilis, bacillus mucilaginosus, bacillus amyloliquefaciens, azotobacter, rhizobia and bacillus megatherium. The biomass charcoal soil conditioner provided by the invention can increase the water-retention rate and air permeability of soil, improve the content of organic matters in the soil, and regulate the pH value of the soil; meanwhile, the adoption of biological means to improve microbial environment of the soil is beneficial for promoting crop growth and high-efficiency nutrient utilization, increases the yield of crops, and improves the quality of the crops. The biomass charcoal soil conditioner provided by the invention effectively utilizes wastes, can improve the soil and enhance soil fertility, and specifically has significant improvement effect on saline alkali land.
Owner:北京世纪阿姆斯生物工程有限公司
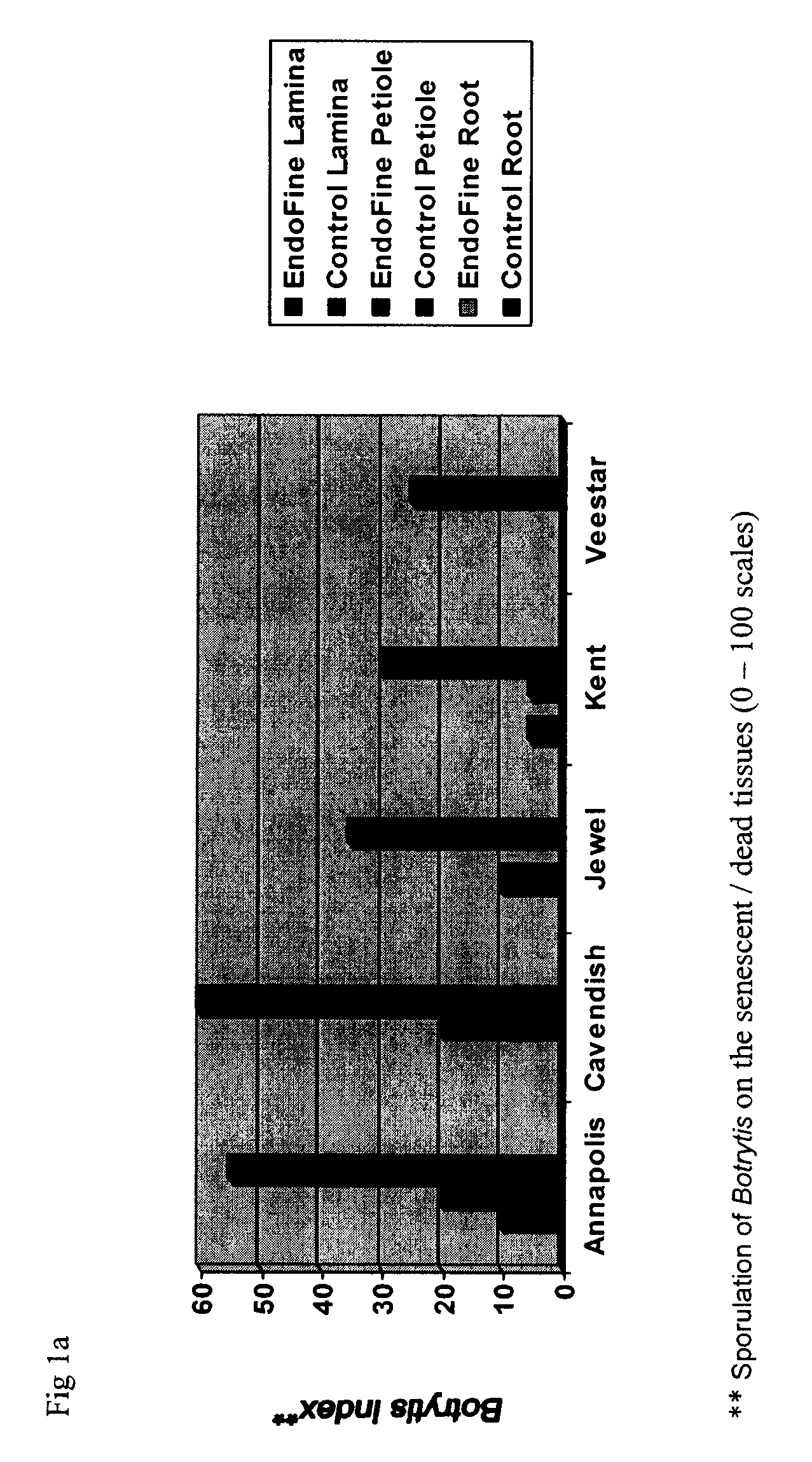
Production and use of endophytes as novel inoculants for promoting enhanced plant vigor, health, growth, yield reducing environmental stress and for reducing dependency on chemical pesticides for pest control
InactiveUS20090105076A1Improve scalabilityPrevent degradationBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyFungal endophyte
A process and method for the production of endophytes as plant inoculant products, specifically Clonostachys rosea strain 88-710, for the promotion of plant vigor, health, growth and yield are disclosed. The endophyte, Clonostachys rosea strain 88-710 produces a fungal conidial preparation by utilizing a discrete solid substrate fermentation system, namely Potato Dextrose Agar or Malt Extract Agar. Additionally, the endophyte, Clonostachys rosea strain 88-710, can act as an inoculant to stimulate and have an additive effect with rhizobium bacteria on the production of nitrogen fixing nodules on legumes and growth enhancement e.g. beans, soybeans, peas and alfalfa. As well, Clonostachys rosea strain 88-710, can combine with rooting hormones, e.g. indole-3-butyric acid (IBA) to provide inoculant and rooting benefits to cuttings / transplants of plants.
Owner:ADJUVANTS PLUS INC
Multifunctional biological seed coating agent and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a multifunctional biological seed coating agent and a preparation method thereof. The multifunctional biological seed coating agent comprises auxiliary agents and beneficial microorganism, volume ratio thereof is 1:1-5, and effective bacterium content is not less than or equal to 10<8>cfu / ml. The auxiliary agent comprises one or various auxiliary agents in film former, dispersant, adhesion agent, protectant, nutritient, anti-freeze agent, preservative and colourant. The beneficial microorganism is selected from one or various rhizobium, azotobacter, pseudomonad, bacillus, K pneumoniae, Enterobacter cloacae and Raoulterlla planticola. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving the polyvinyl alcohol and natural substance with water in a reaction kettle, mixing with the water dispersion liquid of the adhesion agent to prepare a film forming agent, and finally mixing and stirring mechanically with the beneficial microorganism fermentation liquor to obtain the finished product. The invention has the advantages of no residue, high efficiency, low toxicity, strong specificity, good film forming effect and convenient application, therefore, the multifunctional biological seed coating agent plays an significant role of preventing and controlling cotton seedling diseases as well as enhancing the cotton seedling growth under salt stress.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Biological phosphatic fertilizer as well as preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104016795AAvoid fixationImprove phosphorus dissolution rateFertilizer mixturesSoil sciencePhosphate solubilizing bacteria
The invention discloses a biological phosphatic fertilizer. The preparation method of the phosphatic fertilizer comprises the following steps: culturing AM mycorrhiza, phosphate solubilizing bacteria and rhizobium respectively, mixing with a phosphatic fertilizer to react, then adding various nutritional elements required for plants, and mixing and granulating to obtain porous fertilizer particles, so that the contact area between the fertilizer and water is increased, and the dissolving velocity of the fertilizer in water is accelerated. The biological phosphatic fertilizer can activate the phosphatic fertilizer, and can improve the absorption of the phosphatic fertilizer by plants, increase the utilization ratio of the phosphatic fertilizer, reduce the using quantity of the fertilizer and reduce the pollution to the environment; the fertilizer can be rapidly dissolved in water for irrigation and fertilization together with water, and is suitable for modern agricultural water and fertilization integration.
Owner:内蒙古和盛生态科技研究院有限公司
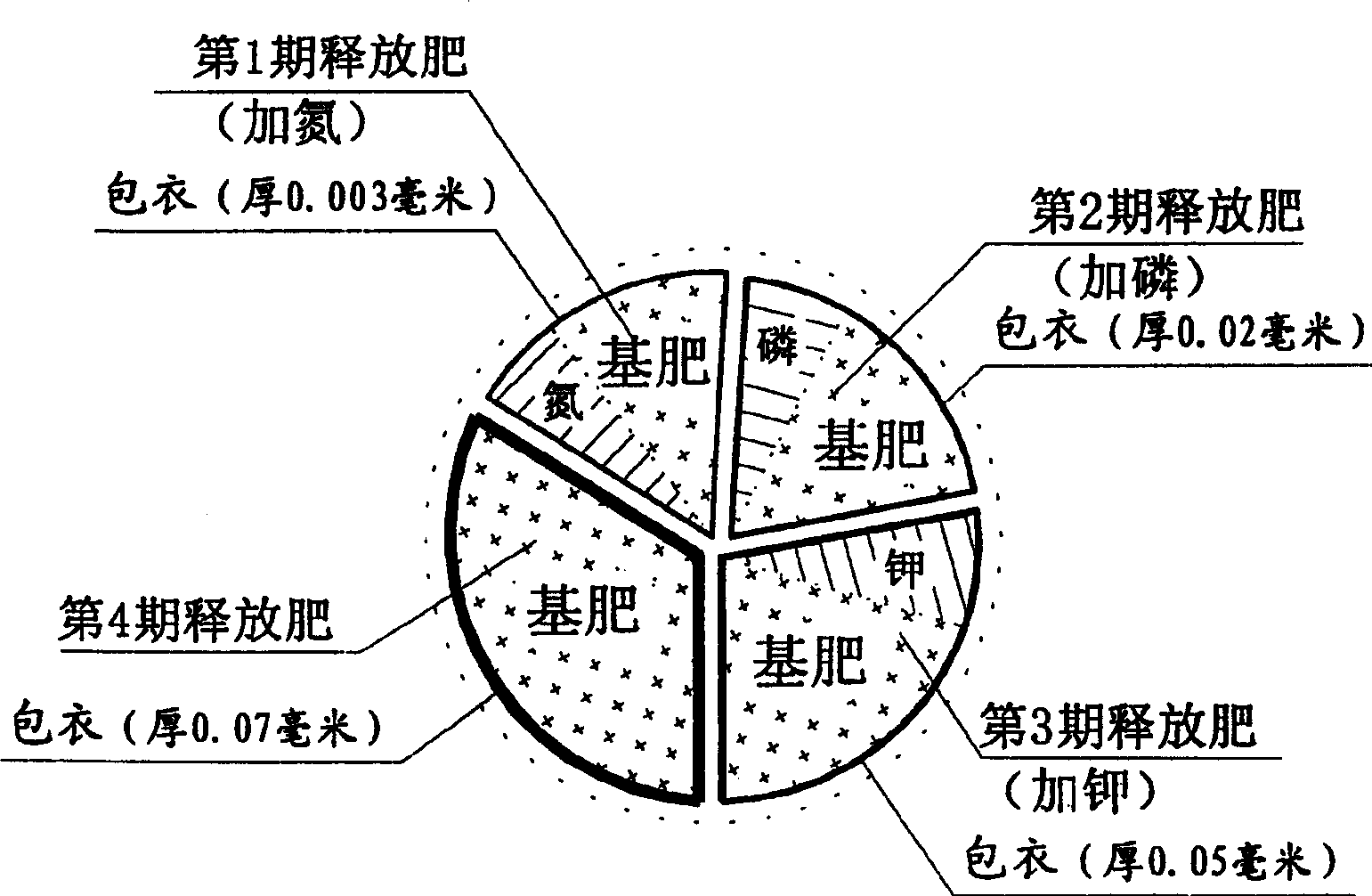
Regularly released granular organic fertilizer and its production process
InactiveCN1357520AAntioxidantWill not affect the ecological environmentBio-organic fraction processingClimate change adaptationFreeze-dryingUv disinfection
The regularly released granular organic fertilizer has manure as basic material and added nitrogen fertilizer, phosphate fertilizer, potash fertilizer, rhizobium and plant growth promoter and is produced into 0.0001-0.15 mm size coated agent. It is produced through a computerized control process, including disinfection with bacteriophage, disinfection with ozone generator, deodorizing, decoloring, centrifugal dewatering, freeze drying, sieving to eliminate impurity, mixing, coating with one layer of degradable plant casing, etc.
Owner:褚世伟 +2
Bioflocculant fermentation method with mycelium pellet as vector
InactiveCN102260729AReduce preparation timeReduce demandMicroorganism based processesFermentationHigh energyHypha
The invention relates to a bioflocculant fermentation method, in particular to a bioflocculant fermentation method with a mycelium pellet as a vector. The method solves the problems of high energy consumption, high production cost and unsuitability for large-scale industrialized fermentation production and the like existing in the existing bioflocculant fermentation method and comprises the following steps of: 1, mixing rhizobium radiobacter with bacillus sphaericus and then culturing so as to obtain flocculant-producing bacteria seed liquid; 2, culturing aspergillus niger to be a mature mycelium pellet; 3, mixing the mature mycelium pellet with the flocculant-producing bacteria seed liquid and then culturing so as to obtain a mixed mycelium pellet; 4, taking 24-hour as a fermentation period, and drawing out the mixed mycelium pellet after each fermentation period is finished and pouring the mixed mycelium pellet into fresh culture mediums for culturing; and 5, repetitively operating the step 4 for 30-35 times and namely completing. According to the bioflocculant fermentation method provided by the invention, on the premise of guaranteeing stable flocculating rate, seed liquid demand is reduced, production efficiency is increased and production energy consumption is reduced; moreover, the invention has great significance on large-scale industrialized production of bioflocculant.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Efficient cultivation method for increasing yield and starch content of canna edulis
ActiveCN105340514AInterplanting effect is goodReduce the amount of applicationFertilising methodsPlant cultivationDiseaseNitrogen
The invention discloses an efficient cultivation method for increasing the yield and starch content of canna edulis. The method comprises steps of land selection, soil preparation, sowing, field management, pest disease and weed control, maturation, harvest, and seed reservation. The method comprises following operation steps: (1) land selection and soil preparation; (2) sowing including variety selection, sowing time selection, potato seed processing, base fertilizer application and planting mode selection; (3) filed management including seedling stage management, intertillage weeding and hilling, top application of fertilizer, water management and florescence management; (4) disease and pest control including disease control and pest control; (5) maturation and harvest; and (6) seed reservation. By employing the method, the canna edulis is high in yield and starch content, and problems that the canna edulis is low in mu yield and starch content are effectively solved. Through the interplanting of canna edulis and soybeans, the growth of weeds can be effectively controlled, soil is loosened, nitrogen is fixed through soybean rhizobium, the application amount of fertilizer can be reduced, green leaves and stems of the harvested soybeans can be returned to the field, the soil productivity can be increased, and finally the income of farmers can be increased.
Owner:广西壮族自治区农业科学院经济作物研究所
Ketose 3-epimerase, its preparation and uses
An object of the present invention is to provide a novel ketose 3-epimerase, a process for producing the same, a DNA encoding the enzyme, a recombinant DNA and transformant comprising the DNA, and a process for producing a ketose by using the enzyme. The present invention solves the above objects by providing a ketose 3-epimerase which is obtainable from a microorganism of the genus Rhizobium, a process for producing the same, a DNA encoding the enzyme, a recombinant DNA and transformant comprising the DNA, and a process for converting D- or L-ketohexose into corresponding D- or L-ketohexose by epimerizing the hydroxyl group at the C-3 position of the D- or L-ketohexose; and D- or L-ketopentose into corresponding D- or L-ketopentose by epimerizing the hydroxyl group at the C-3 position of the D- or L-ketopentose; by using the enzyme.
Owner:HAYASHIBARA BIOCHEMICAL LAB INC
Alfalfa seed obducens agent and production process thereof
InactiveCN104496662AThe production application effect is remarkableReduce applicationsAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserAmmonium orthophosphate fertilisersMonopotassium phosphateGibberellin
The invention discloses an alfalfa seed obducens agent which is prepared from the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 1.5-5% of carboxymethylcellulose, 0.5-3% of rhizobium of alfalfa, 0.5-7% of biological humic acid, 0.2-3% of urea, 0.2-3% of monopotassium phosphate, 0.1-0.7% of ammonium molybdate, 0.1-0.5% of borax, 2-6% of sulfur powder, 0.15-0.7% of ferrous sulfate, 5-8% of sodium polyacrylate, 0.01-0.05% of indolebutyric acid, 0.01-0.05% of gibberellin, 0.01-0.05% of lysine acetate, 1.0-8.0% of thiram, 2.0-8.5% of thiophanate-methyl and the balance of alfalfa seeds. Aiming to the characteristics that alfalfa in the seedling stage is not saline-alkaline tolerant, draught tolerant, susceptible to diseases and the like, anti-salt and alkali, anti-drought and soil sterilizing factors are respectively added into the obducens agent disclosed by the invention, and moreover, the alfalfa seed obducens agent is obvious in production and application effects and is deeply welcomed by farmer households.
Owner:酒泉大业种业有限责任公司
Facultatively autotrophic sulfur oxidation denitrification rhizobium F43b and application thereof
The invention discloses a facultatively autotrophic sulfur oxidation denitrification rhizobium F43b and an application thereof. The Rhizobium sp. F43b<T> is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) Wuhan University in Wuhan in China on March 30, 2016 with the preservation number of CCTCC NO:M 2016158. The Rhizobium sp. F43b<T> is facultatively autotrophic rhizobium with sulfur oxidation and denitrification functions, can remove COD, nitrates and sulfides from polluted water or deposits, realizes simultaneous removal of carbon, nitrogen and sulfur from the polluted water or deposits, and provides bacterial strains and microbial preparations for river restoration and carbon, nitrogen and sulfur wastewater treatment, and researches of the rhizobium provide theoretic guidance for river restoration and removal of carbon, nitrogen and sulfur.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
Rhizobium capable of efficiently solubilizing phosphorus and application of rhizobium
ActiveCN105950520APhosphate dissolving ability enhancedHigh affinityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFungicideRoot nodule
The invention discloses a rhizobium capable of efficiently solubilizing phosphorus and application of the rhizobium. The phosphorus solubilizing rhizobium is named as Rhizobium sp.P-1 and preserved in China Center For Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) on June 16, 2016, and the preservation number is CCTCC M 2016333. The rhizobium can convert difficultly-soluble inorganic phorphorus into a high-quality phosphorus compound which can be directly absorbed and utilized by plants. By using the screened rhizobium in a lettuce pot culture experiment, the content of effective phosphorus in soil can be obviously increased, it is guaranteed that the lettuce yield is not decreased on the condition that the application amount of phosphate fertilizer is decreased by 50%, and the nutritional quality of lettuce is improved. The rhizobium can be used for preparing a phosphorus solubilizing fungicide, be widely applied to agricultural production, improve the bio-availability of difficultly-soluble phosphorus in the soil, increase the phosphate fertilizer utilization efficiency, save fertilizer and increase the yield and has the important significance and application value on the aspect of keeping agricultural ecological balance.
Owner:武汉一禾生态环境检测中心 +1
Sinorhizobium SCAUs65 and application thereof
InactiveCN104277994AStrong stress resistanceStrong symbiotic nitrogen fixationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPotassiumMicrobiology
The invention discloses sinorhizobium SCAUs65 and application thereof. The strain is separated and purified from a fresh soybean nodulation; the strain is collected in the China center for type culture collection on March 14, 2014, the collection number of the strain is CCTCC NO: M2014084, and the strain is classified and named as sinorhizobium fredii. The strain is applied to the production of szechuan soybeans. The sinorhizobium SCAUs65 disclosed by the invention is an excellent broad-spectrum soybean rhizobium strain which has the advantages of high symbiotic nitrogen-fixing capacity, wide applicable range on szechuan soybean variety, inorganic phosphorus dissolving capacity, organic phosphorus dissolving capacity and potassium dissolving capacity and high stress resistance and has good matching affinity with szechuan main planted soybean variety. A soybean is increased in yield more than 38.9% by being inoculated with the sinorhizobium SCAUs65 without applying a nitrogen fertilizer in different ecological regions and achieves the difference to a significance level compared with a soybean which is not inoculated with the sinorhizobium SCAUs65.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Purification compound bacterium and purification compound probiotic preparation as well as preparation method of compound probiotic preparation
InactiveCN103881929AImprove processing efficiencyNo secondary pollutionFungiBacteriaYeastIndustrial fermentation
The invention relates to a purification compound bacterium. The compound bacterium consists of 10-30% of beer yeast, 10-30% of plant lactic bacillus, 10-30% of lactobacillus acidophilus, 10-30% of bacillus subtilis, 5-15% of bacillus cereus and 5-15% of rhizobium radiobacter. Furthermore, the invention relates to a purification compound probiotic preparation and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of inoculating the purification compound bacterium on a comprehensive liquid culture medium, and implementing multi-strain compound fermentation within a temperature range of 28-35 DEG C. By combining various aerobic, facultative and anaerobic strains, the purification compound probiotic preparation is prepared through an advanced industrial fermentation technology. The compound probiotic preparation has such advantages as being wide in application scope, high in treatment efficiency, free from secondary pollution, simple in equipment required, convenient for operation, low in operation cost, low in environmental load, and simple and convenient maintenance and management.
Owner:ZHANJIANG DEYUE BIOENG CO LTD
Rapeseed cake multi-effect fertilizer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104261970AHighlight substantiveImprove ventilationCalcareous fertilisersBio-organic fraction processingMonopotassium phosphateRapeseed
The invention relates to a rapeseed cake multi-effect fertilizer and a preparation method thereof. The fertilizer is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 200-250 parts of rapeseed cakes, 30-40 parts of pig manure, 30-40 parts of chicken manure, 30-40 parts of corn stalks, 30-40 parts of rice straws, 10-20 parts of calcium superphosphate, 10-20 parts of urea, 10-15 parts of monopotassium phosphate, 8-10 parts of ammonium phosphate, 8-10 parts of ferrous sulfite, 3-5 parts of zinc sulfate, 3-5 parts of boric acid, 10-20 parts of rhizobium powder, 8-15 parts of EM fungus, 3-4 parts of brown sugar and a proper amount of water. By adopting organic matter fermentation technology, the prepared rapeseed cake multi-effect fertilizer is not only rich in abundant organic matters and nutritional elements needed during growth of crops, is beneficial to the growth and fruiting of crops and improvement of yield of crops and content of nutritional substances, but also can effectively improve the morbidity resistance of crops, improve the structure, water retention and fertilizer retention and the like of soil, thus being a non-toxic multi-effect fertilizer with good ventilation property.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
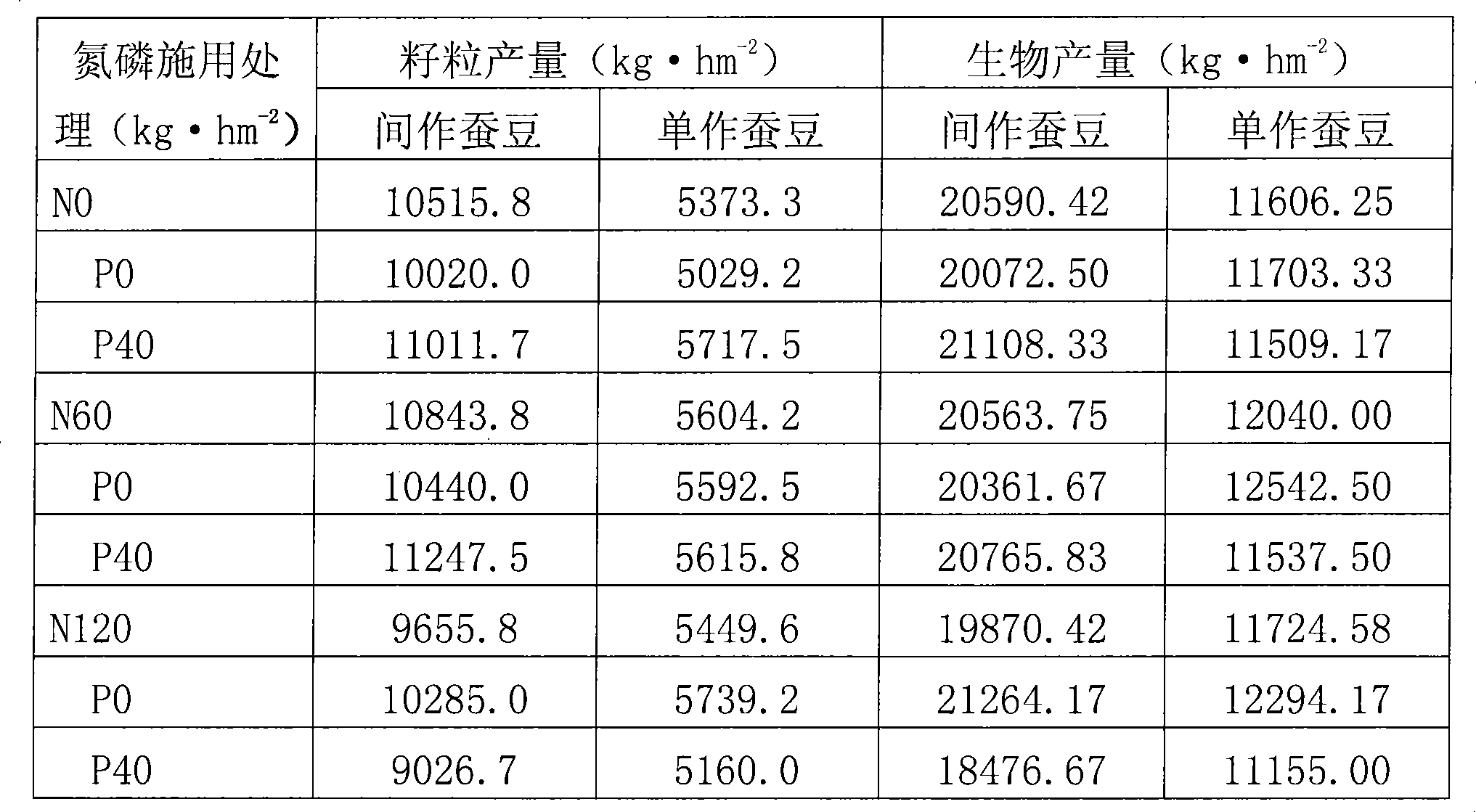
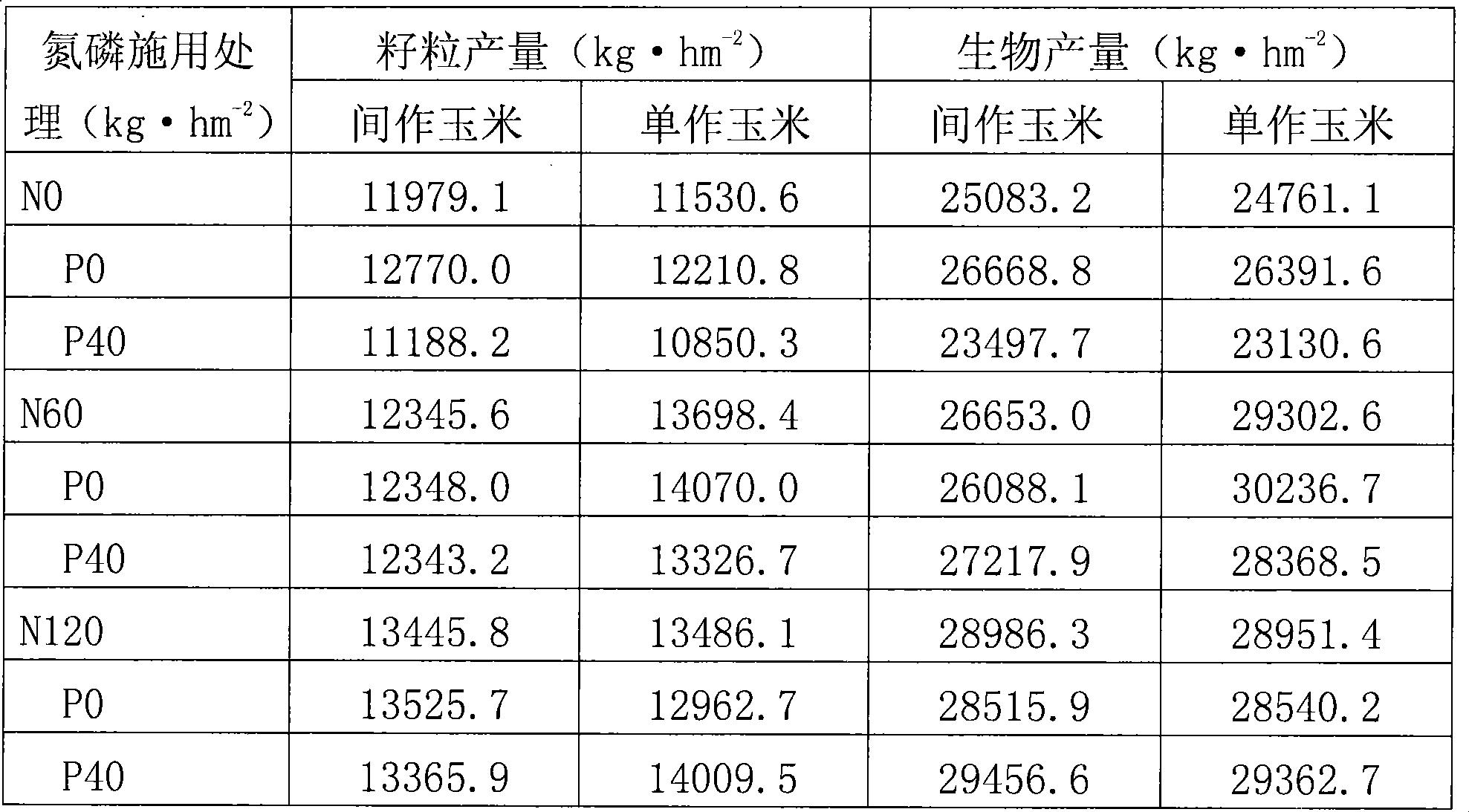
Method for planting horsebean intercropped with corn
InactiveCN101438664AIncrease productionIncrease biological nitrogen fixationFertilising methodsHorticultureAgricultural scienceCrop cultivation
The invention discloses a broad bean and corn intercropping method and belongs to the field of crop cultivation methods. The method mainly relates to intercropping of the broad bean and the corn, wherein, emergence of seedlings of the broad bean is 10-20 days earlier than that of the corn, the broad bean and the corn are intercropped at a row ratio of 2:2 and at a row spacing from 28cm to 32cm. The method can help realize the purpose of simultaneously improving yield of the broad bean and biological nitrogen fixation amount, avoid the disadvantages of low yield of a leguminous crop which is cropped separately; secondly, the method can greatly reduce manually applied nitrogen fertilizer to save the plantation cost, and relieve the pressure on the environment due to nitrogen fertilizer abuse; furthermore, the method can adequately utilize indigenous rhizobium to avoid a degeneration problem of artificially inoculated strains, reduce operation steps such as inoculation and the like and save the inoculation cost.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
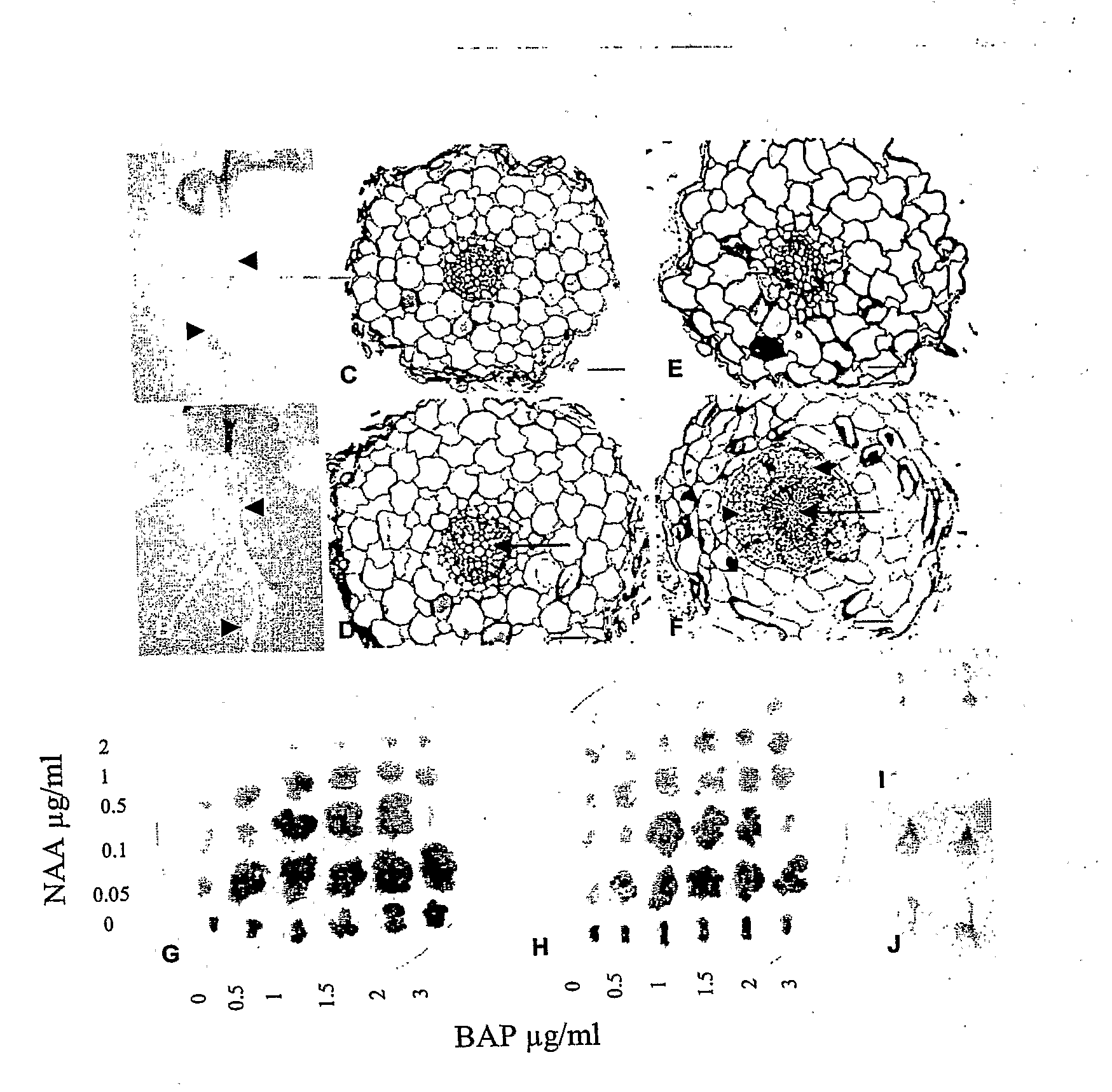
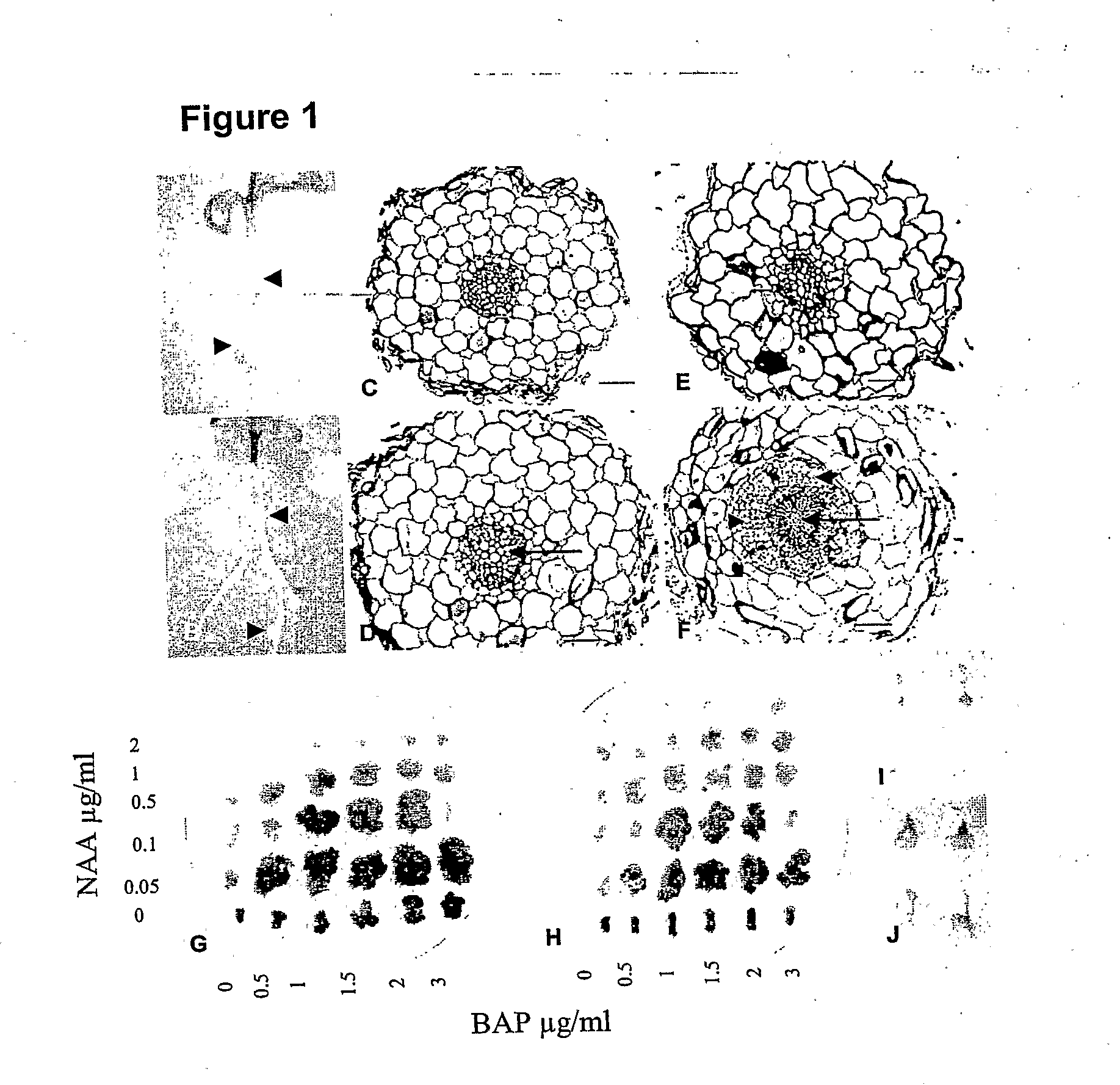
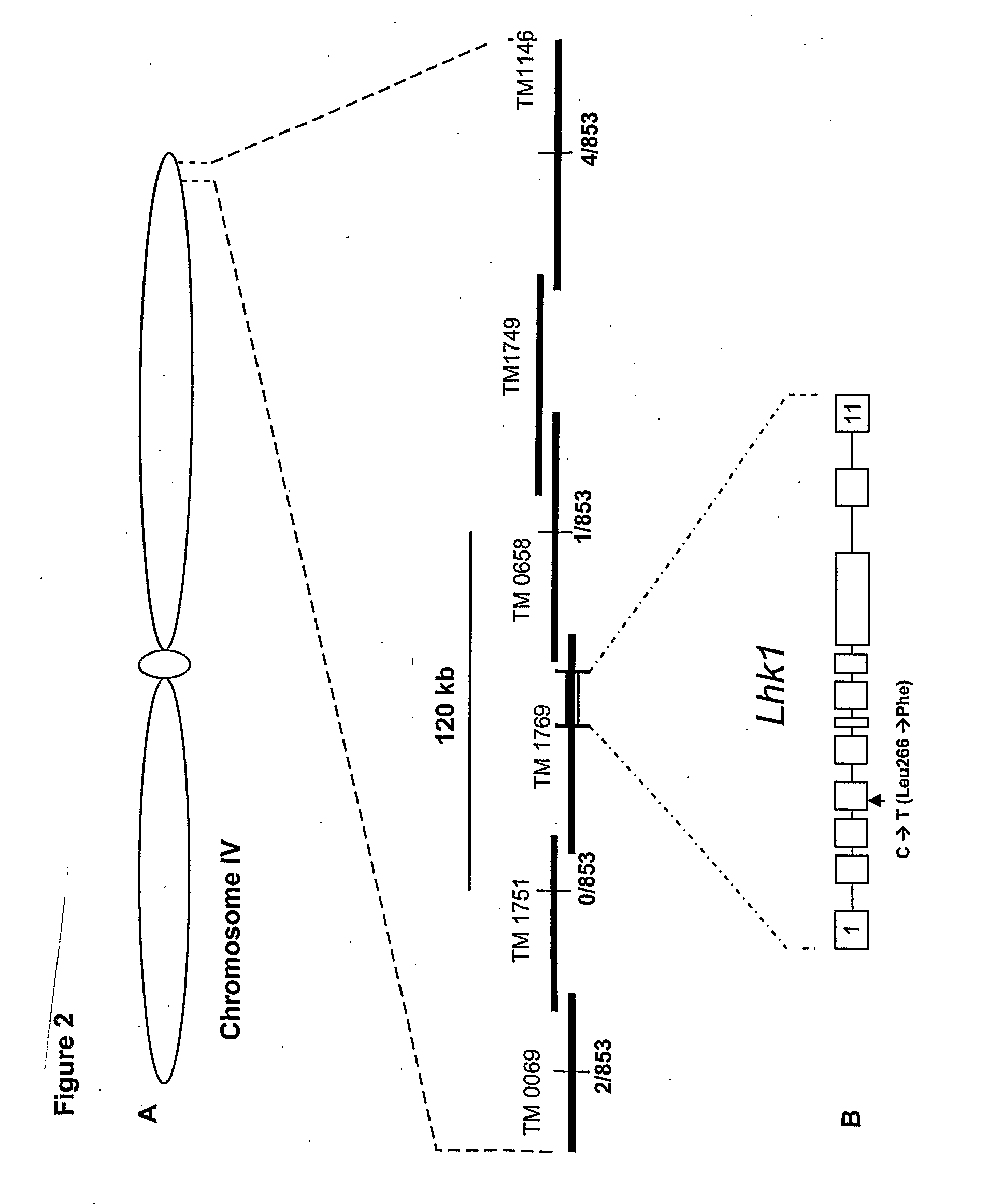
Mutant histidine kinase that confers spontaneous nodulation in plants
Formation of nitrogen fixing root nodules in legumes is induced by perception of lipochitin-oligosaccharide signal molecules secreted by compatible Rhizobium bacteria, which triggers a common symbiotic pathway. The present invention provides a spontaneous nodule formation (snf2) mutant, in which the formation of symbiotic nodules is spontaneous, leading to nodule development in the absence as well as in the presence of Rhizobium bacteria and / or exogenous rhizobial signals. The invention further provides an isolated DNA sequence encoding a mutant cytokinin-independent histidine kinase whose activity results in this ‘gain of function’ dominant phenotype of spontaneous nodule formation. Furthermore the snf2 gene is shown to confer a phenotype, characterised by regulated organogenesis of spontaneous nodules, to plants having a nodulation deficient genetic background. A gene of the invention, that confers this spontaneous nodulation phenotype, has 15 utility for the transfer and establishment of nitrogen fixing capability in non-nodulating plants, and thereby reducing the nitrogen fertiliser dependence of non-nodulating crop plants.
Owner:STOUGAARD JENS +5
Rhizobium radiata and method for producing curdlan gum fermentation liquid using the bacterium
ActiveCN102277319AImprove conversion rateReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyCulture fluid
The invention belongs to microbial fermentation, and particularly discloses Rhizobium radiobacter and a method for producing curdian fermentation liquor by using the strain. The method for producing the curdian fermentation liquor by using the strain comprises the following steps of: inoculating seed liquid which contains Rhizobium radiobacter CGMCC No.5031 serving as the strain after amplification culture into culture solution of a fermentation tank according to the inoculation amount of between 5 and 10 mass percent, wherein the fermentation culture solution contains a carbon source, an essential nitrogen source and nutrient substances; regulating the pH value of the fermentation culture solution, and performing ventilation fermentation; and supplementing a carbon source, a nitrogen source, nutrient substances and water in the fermentation process, and performing ventilation fermentation for not less than 90 hours to obtain fermentation liquid containing curdian. By the method, the defect that the content of solid matter in the curdian fermentation liquor is low in the prior art is overcome; and the method has the advantages that: the carbon source in the fermentation liquor can be better utilized by the strain, the transformation rate is high in the fermentation process, the content of the solid matter in the fermentation liquor is high, the production cost is greatly reduced and the like.
Owner:HEBEI XINHE BIOCHEM
Harden soil improvement method
InactiveCN104663066ASimple structureIncrease humusBio-organic fraction processingOrganic fertiliser preparationLivestock manureEvaporation
The invention discloses a harden soil improvement method. The harden soil improvement method includes that using crop straw, peat soil and livestock manure to manufacture organic compound fertilizer, using lactic acid bacteria powder, nitrobacteria powder and rhizobium powder to manufacture mixed bacterial manure, mixing the organic compound fertilizer, mixed bacterial manure and microbial water retaining agent, and applying to the harden soil after mixing uniformly. The harden soil improvement method solves the problems that the moisture evaporation of the harden soil is fast, the harden soil is lack of organic substance, and the soil fertility is weak.
Owner:朱全顺
Bacterium capable of degrading pesticides chlorimuron-ethyl and carbendazim and application thereof
The invention discloses a bacterium capable of degrading pesticides chlorimuron-ethyl and carbendazim and an application of the bacterium. The bacterium capable of degrading pesticides chlorimuron-ethyl and carbendazim is rhizobium sp. LD1616 and the preservation number of the bacterium is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.7775. The rhizobium sp. LD1616 with the preservation of CGMCC NO.7775, disclosed by the invention, has the advantages that the degradation rate of the bacterium to chlorimuron-ethyl (45mg / L) is up to 71.56% in 7 days in an inorganic salt culture medium and the degradation rate of the bacterium to carbendazim (100mg / L) is up to 24.92% in 5 days, which indicates that the bacterium is capable of efficiently degrading the chlorimuron-ethyl and the carbendazim and has a broad application prospect in the remediation of soil polluted by residual pesticides chlorimuron-ethyl and carbendazim.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Rhizobium and application thereof
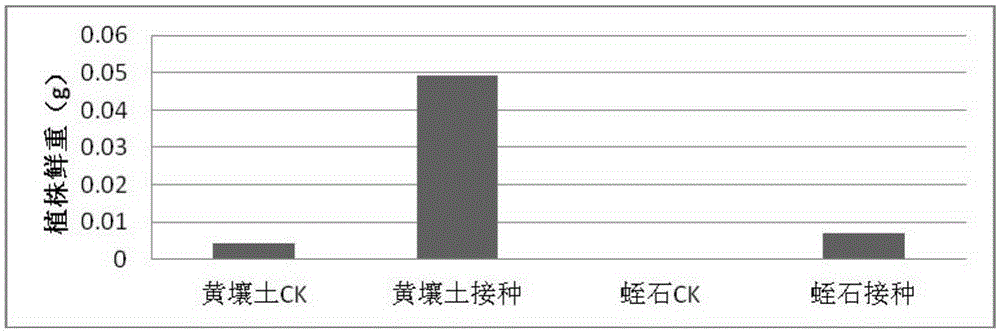
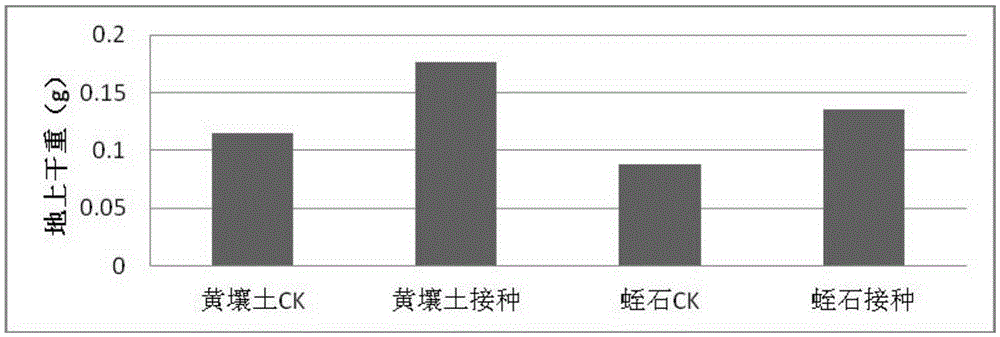
ActiveCN105274030ANodulation rate is highImprove survival rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPlant noduleDry weight
The invention relates to a (Bradyrhizobium sp.) LX-JX01 and application thereof. A preparation method of an inoculant for the (Bradyrhizobium sp.) LX-JX01 includes the steps of preparing a liquid DM culture medium, preparing a solid DM culture medium, activating a strain and culturing the rhizobium. The strain can be in nodulation and symbiosis with Dalbergia odorifera. When the inoculant for the Dalbergia odorifera rhizobium LX-JX01 is used for planting Dalbergia odorifera seedlings, nodulation number root nodules is increased by 3823% than a control group, fresh weight of the root nodules is increased by 1038%, dry weight of portions, above the ground, of plants is increased by 47.22%, and seedling height and plant stem diameter are increased by 1030% and 42.3% respectively, so that the inoculant can promote growing of Dalbergia odorifera. Consequently, the inoculant has wide application prospect in planting of artificial forest of Dalbergia odorifera.
Owner:领先生物农业股份有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com