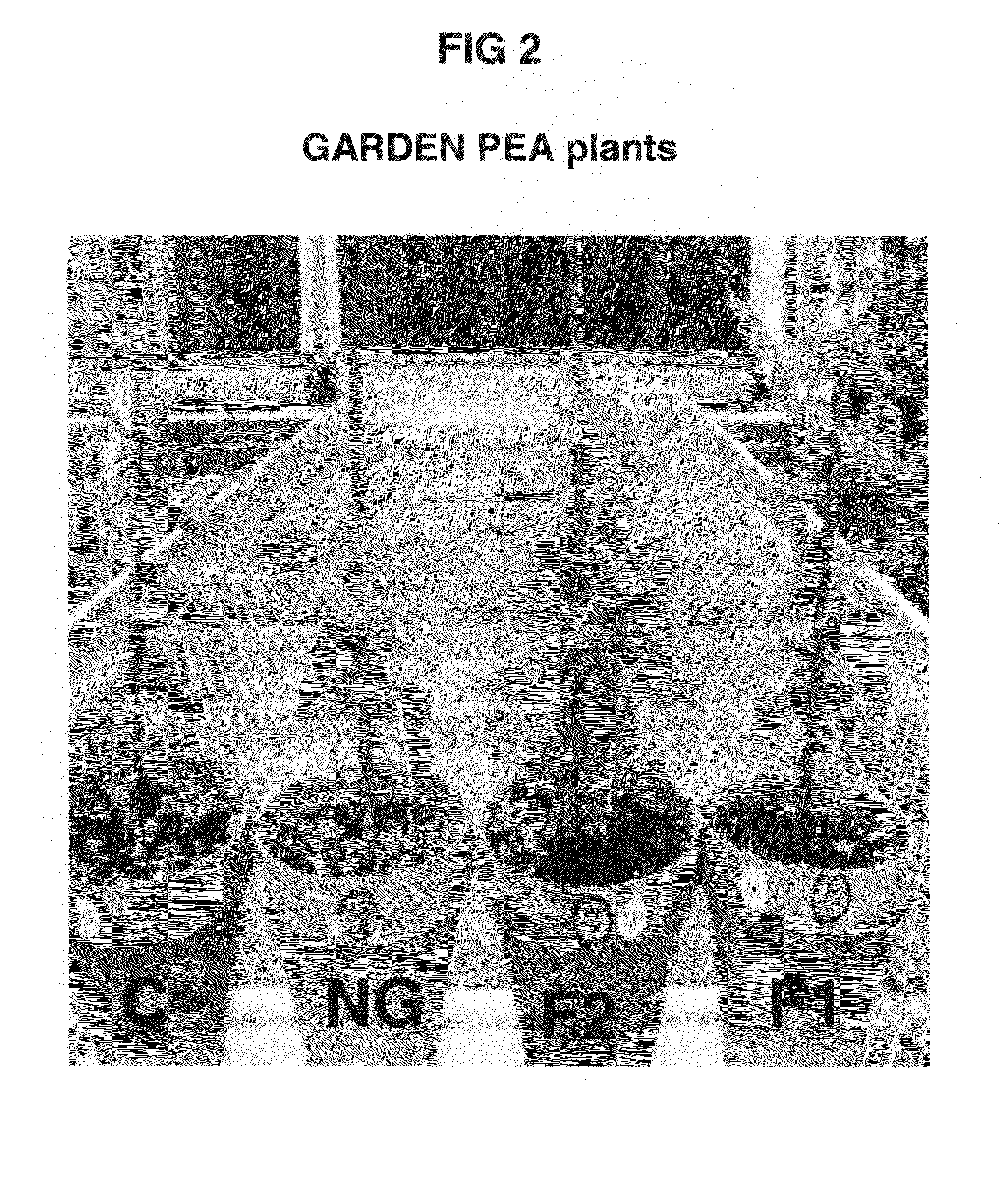
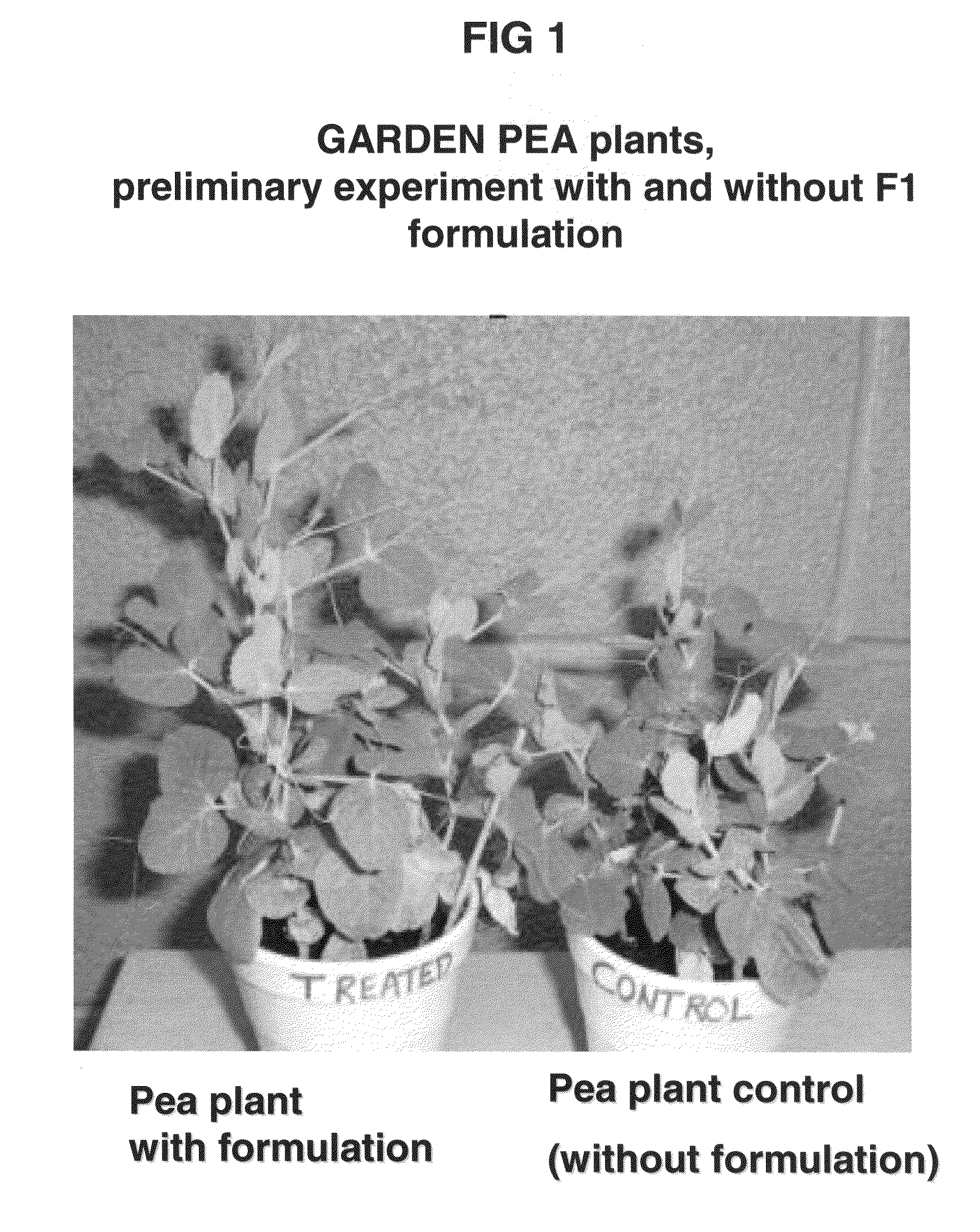
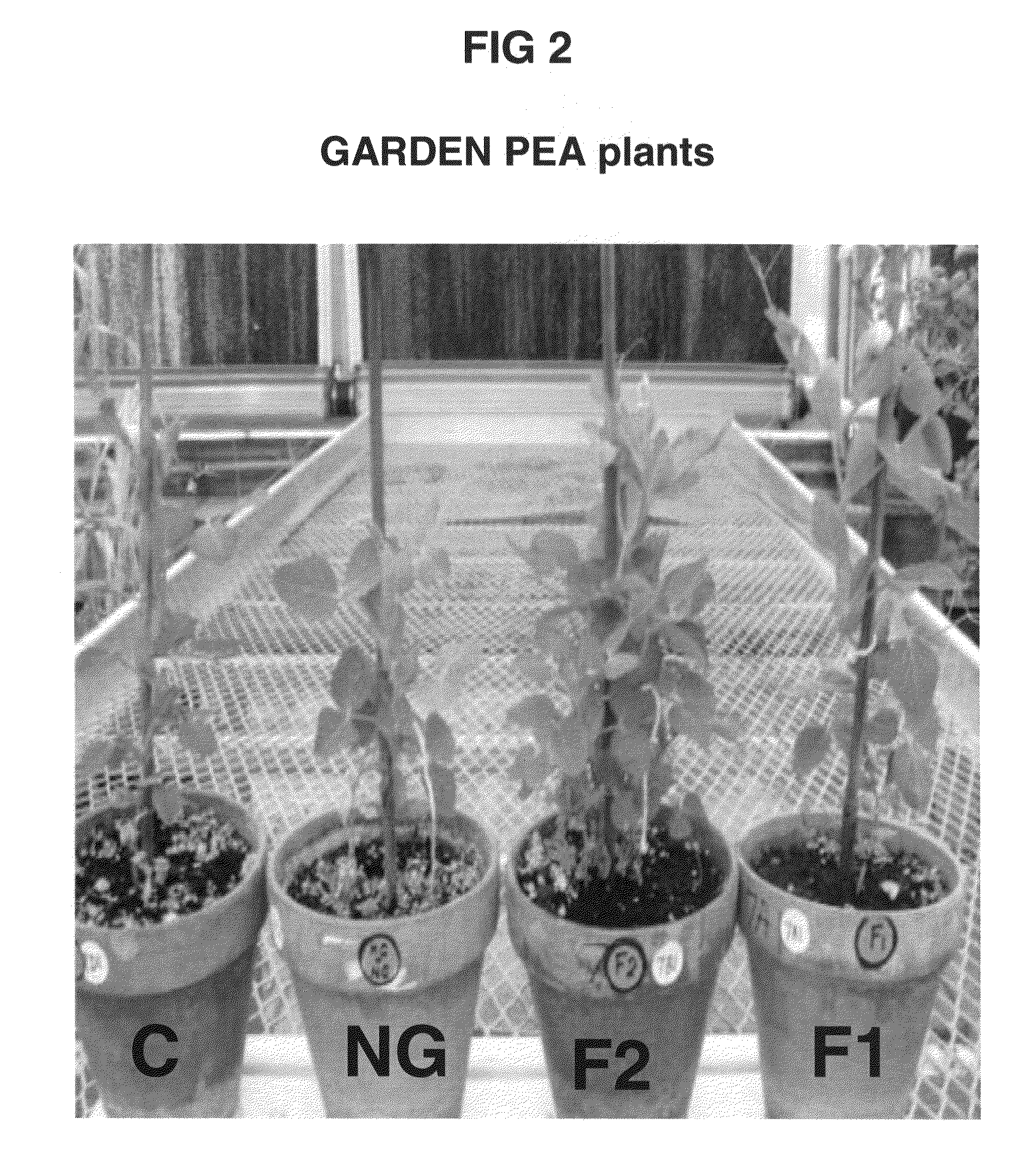
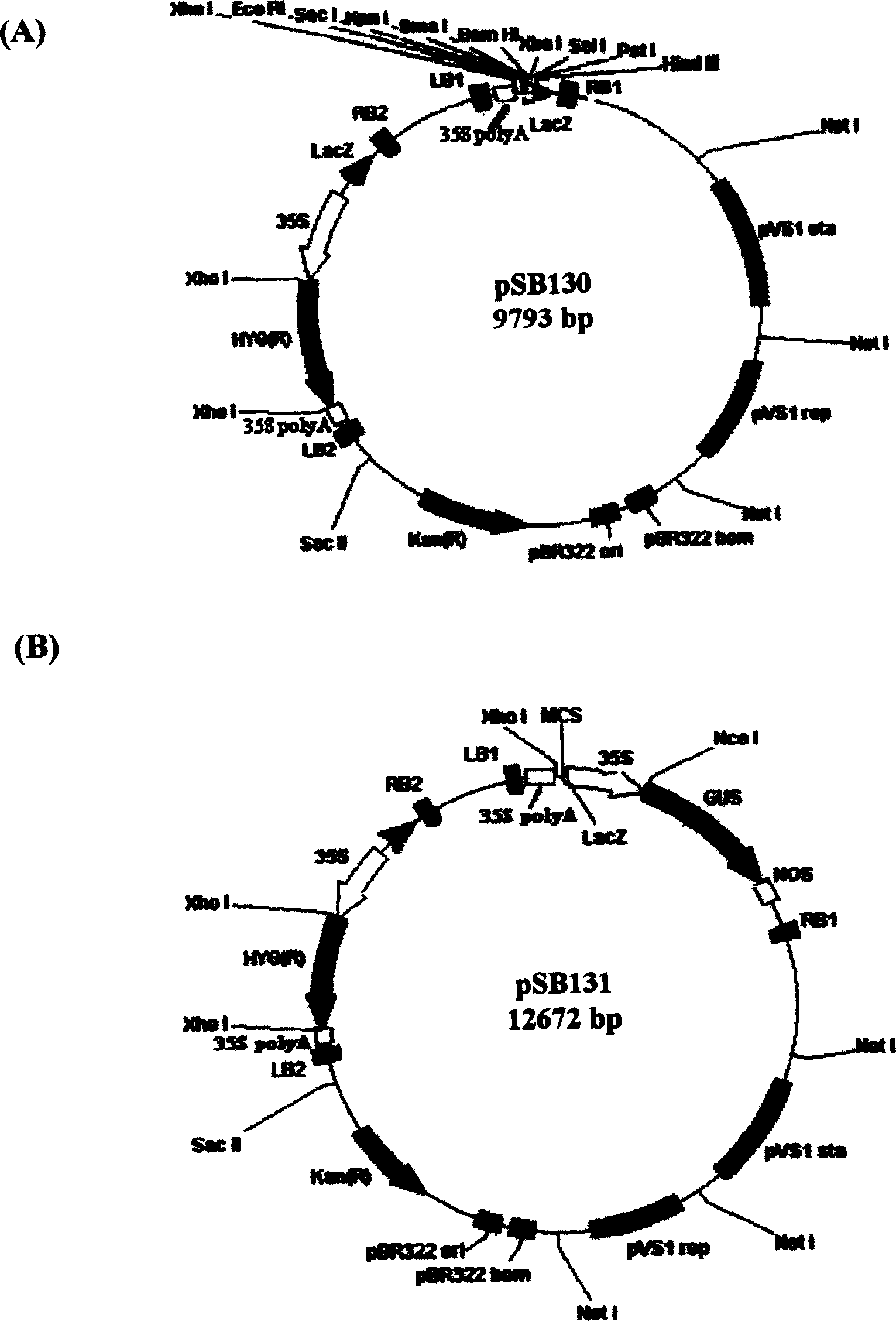
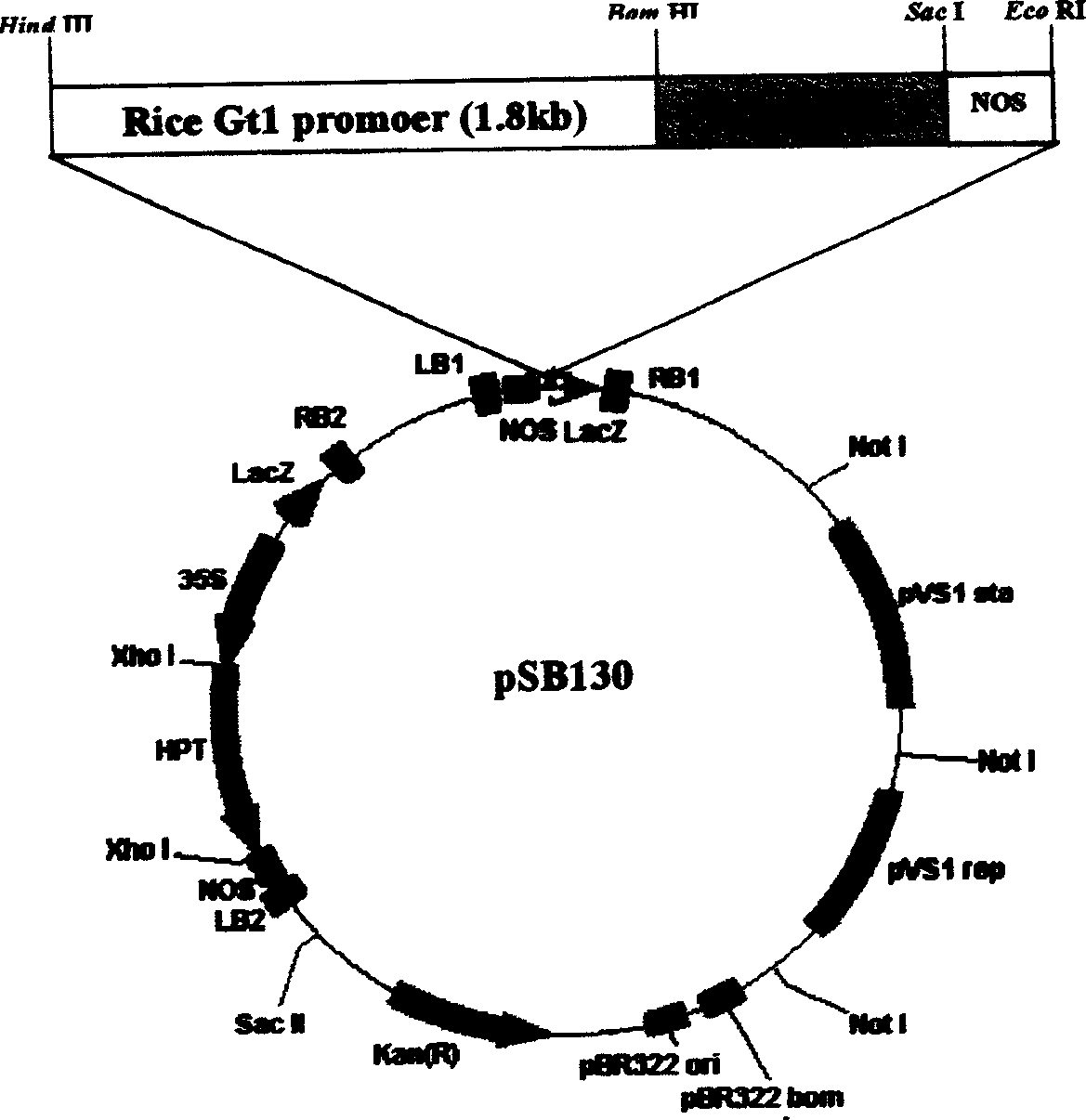
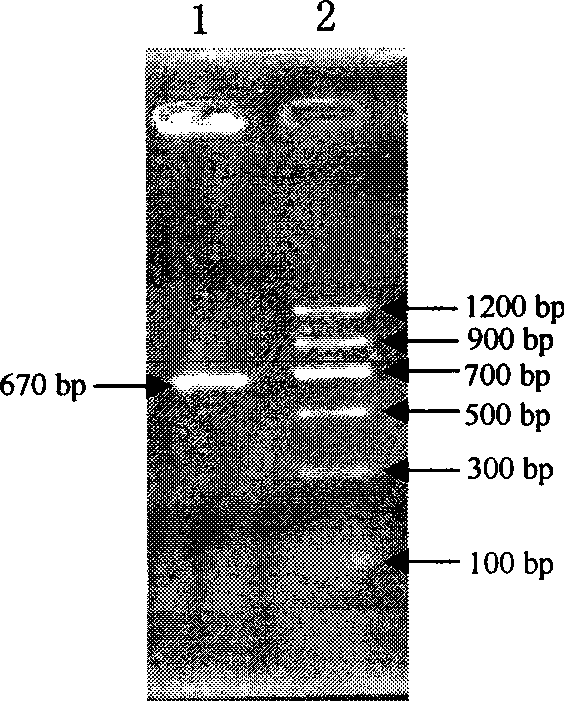
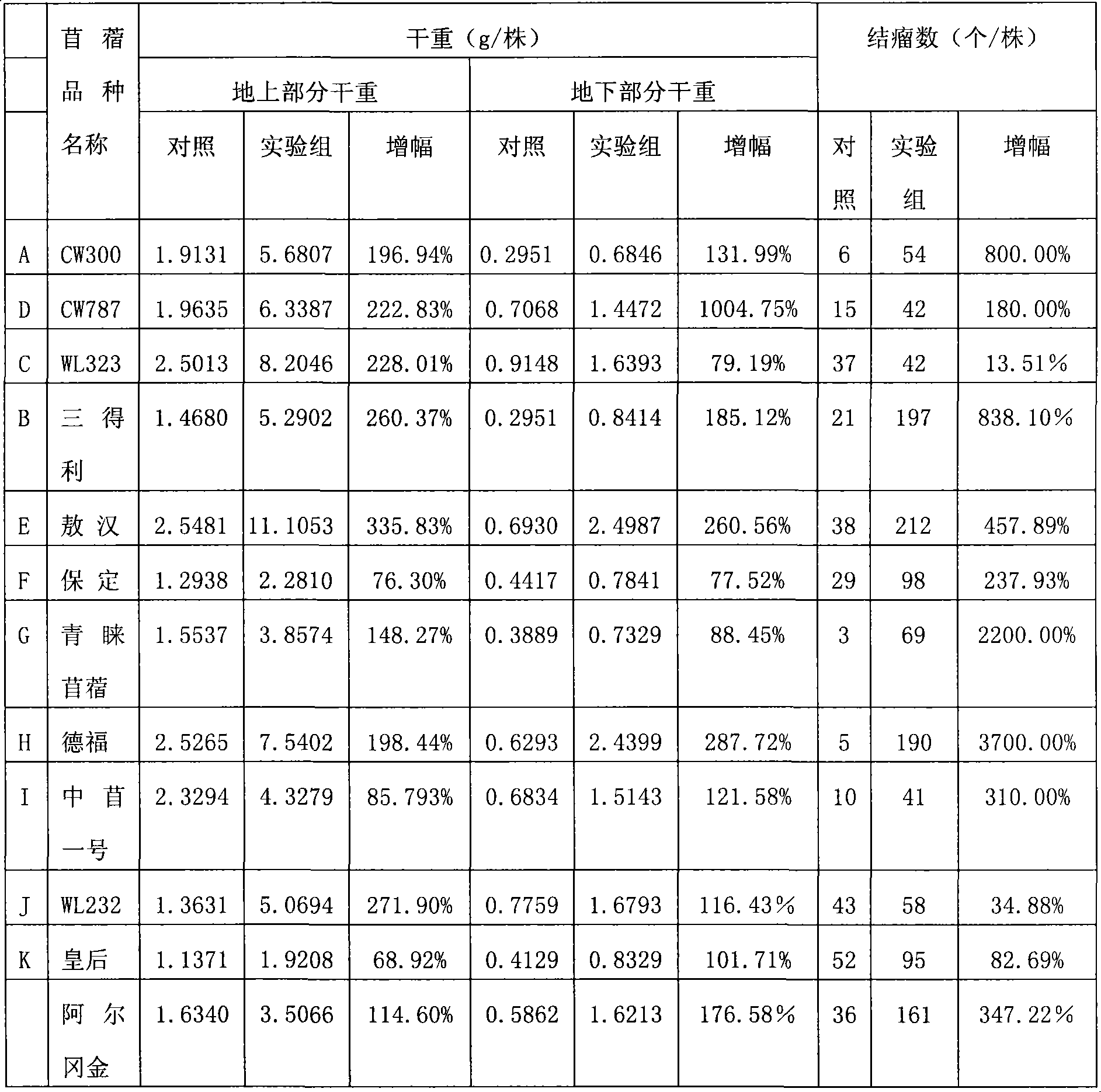
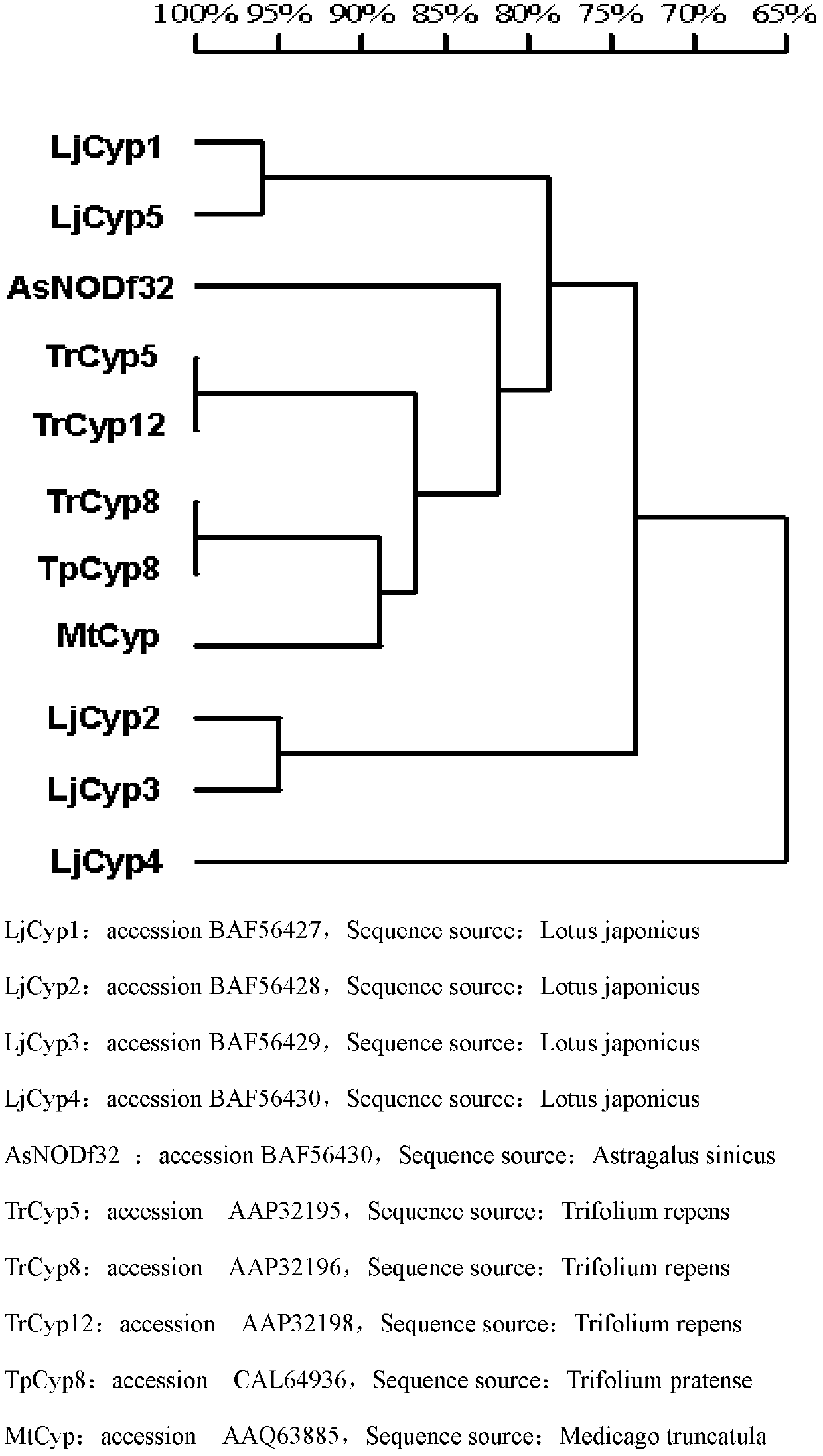
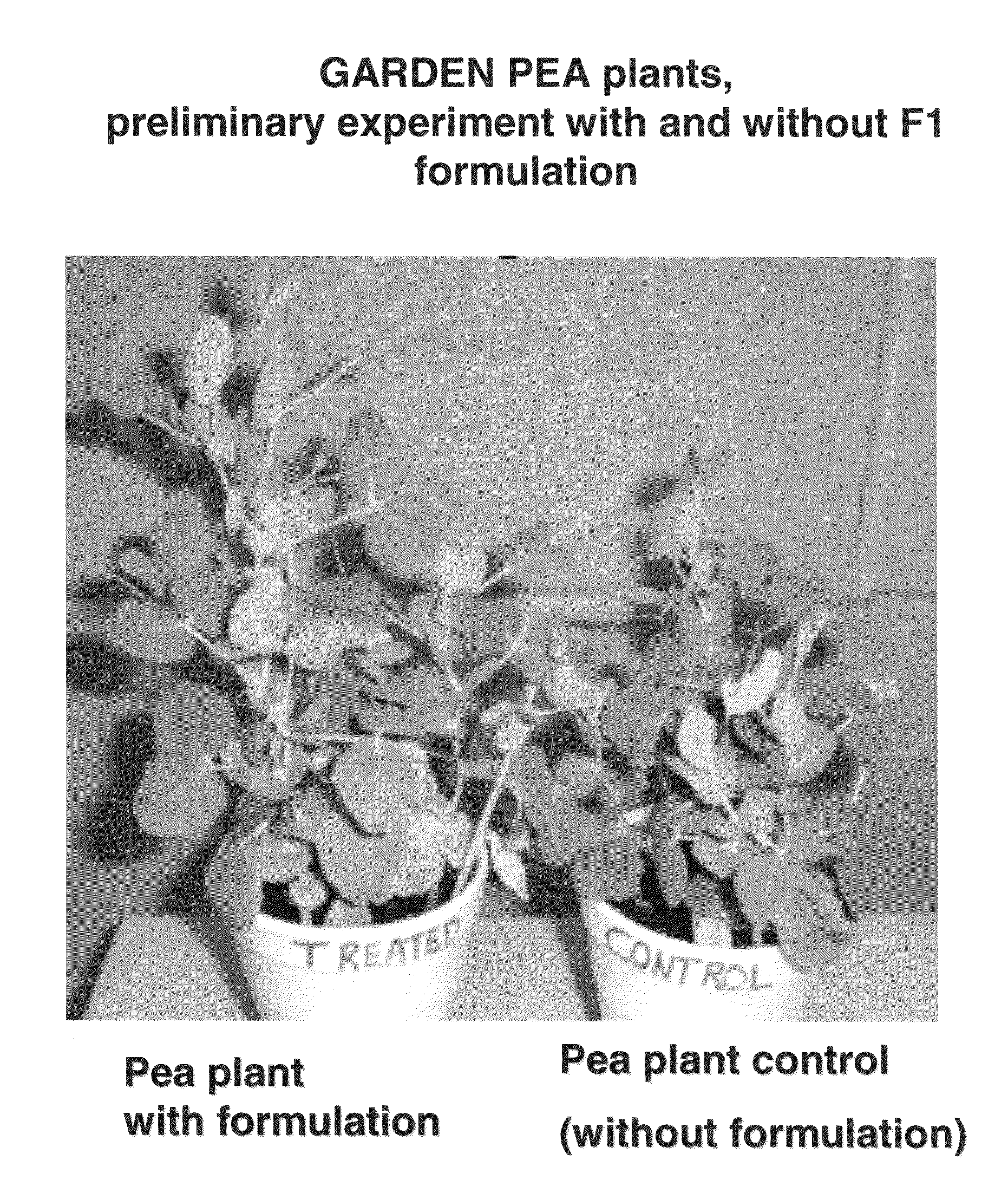
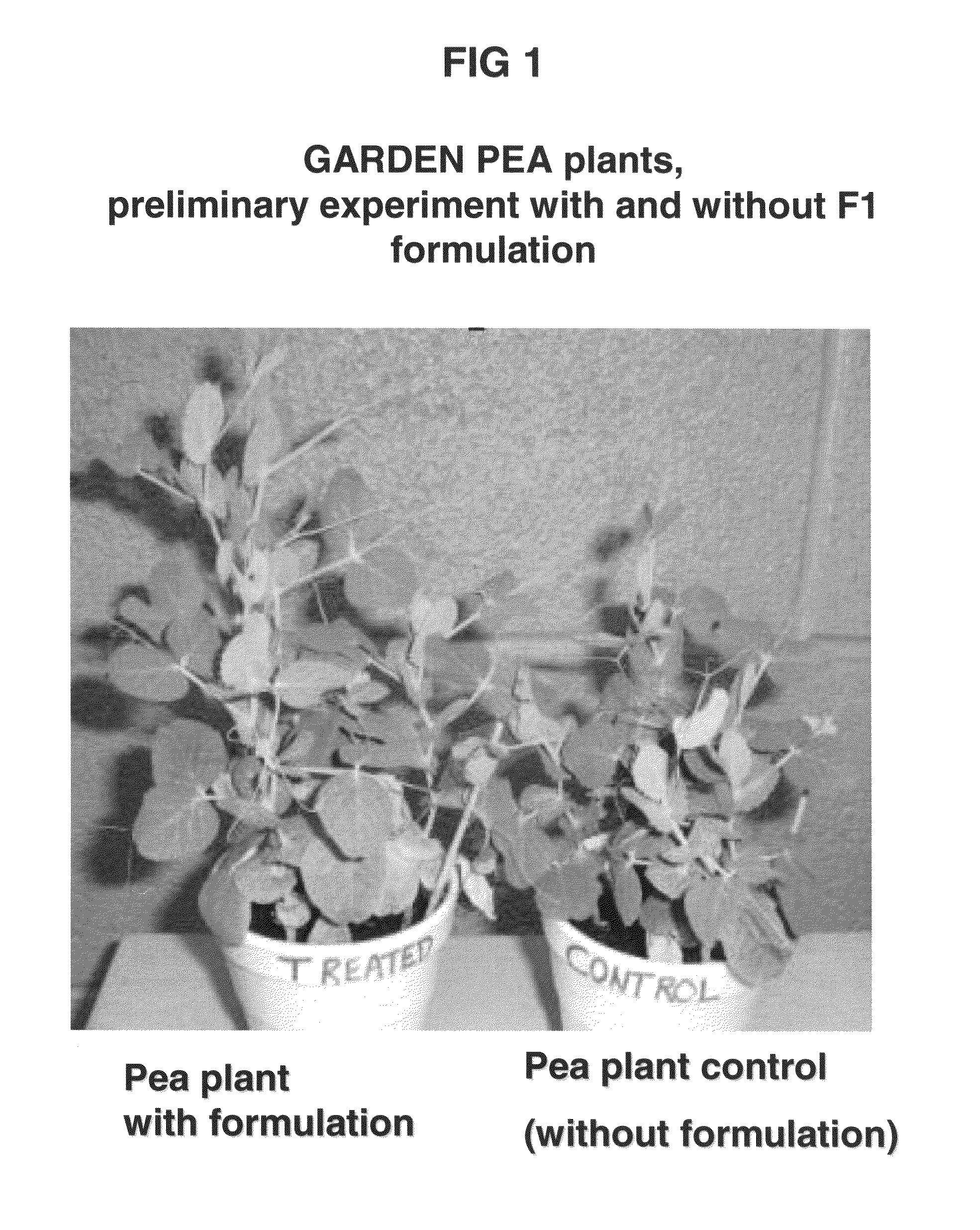
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
327 results about "Plant nodule" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Root nodules occur on the roots of plants (primarily Fabaceae) that associate with symbiotic nitrogen-fixing bacteria. Under nitrogen-limiting conditions, capable plants form a symbiotic relationship with a host-specific strain of bacteria known as rhizobia.
Polymicrobial Formulations For Enhancing Plant Productivity
ActiveUS20090308121A1Promote plant growthReduce disease incidenceBiocideFungiBiotechnologyBacteroides
The present invention relates to eco-friendly compositions and methods for providing plant growth enhancing formulations comprising mixtures of microbial isolates. In particular, numerous bacterial and fungal strains were isolated from a variety of soil types, from rhizospheres and from root nodules of leguminous plants, in designed combinations, for providing plant growth and plant productivity enhancing formulations. These specifically designed polymicrobial formulations would further provide protection against plant pathogens lowering the need for nitrogen containing fertilizers, solubilize minerals, protect plants against pathogens, and make available to the plant valuable nutrients, such as phosphate, thus reducing and eliminating the need for using chemical fertilizers and chemical pesticides.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Double T-DNA carrier and its application in cultivating of non selecting sign transgene rice
InactiveCN1597969ASmall molecular weightHigh co-transformation efficiencyFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionGenetically modified ricePlant nodule
The invention provides a simple and convenient Agrobacterium Tumefacies dual carrier containing double T-DNA structural regions, and a method of using the carrier system to cultivate transgenic rice without resistance selection label. With the help of the principle of co-conversion mediated by root nodule Agrobacterium Tumefacies, the system contains two separate T-DNA structural sections, where the first T-DNA region contains antibiotic resistance selection label gene and the second one contains a universal polyclonal site able to be arbitrarily inserted with destination gene. The double-T-DNA carrier has small molecular weight, easy to clone and after the destination gene and necessary regulation and control series are cloned in the T-DNA region containing the polyclonal site, it realizes rice co-conversion; by selfing, it selects transgenic individual with destination gene but without selectin label gene from the self-bred progeny, thus eliminating the negative effect on transgenic plant commercialized production, etc, possibly caused by selection label gene.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
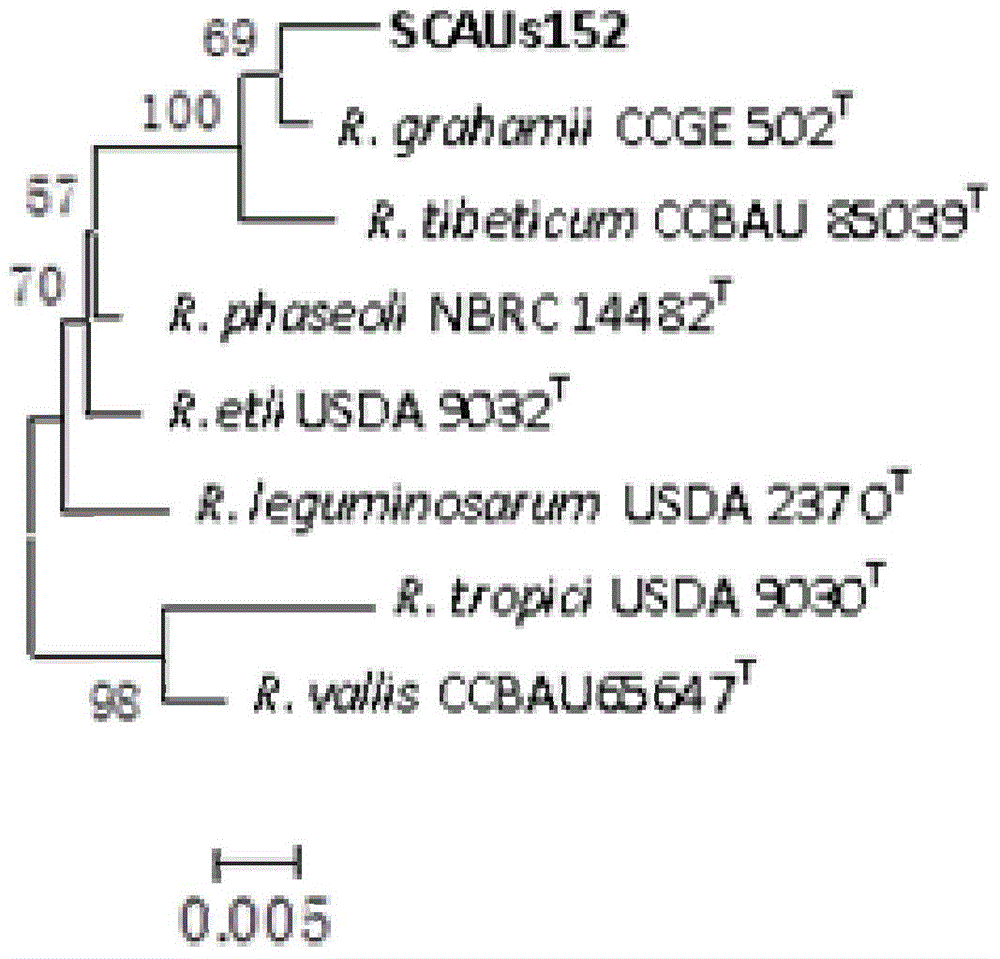
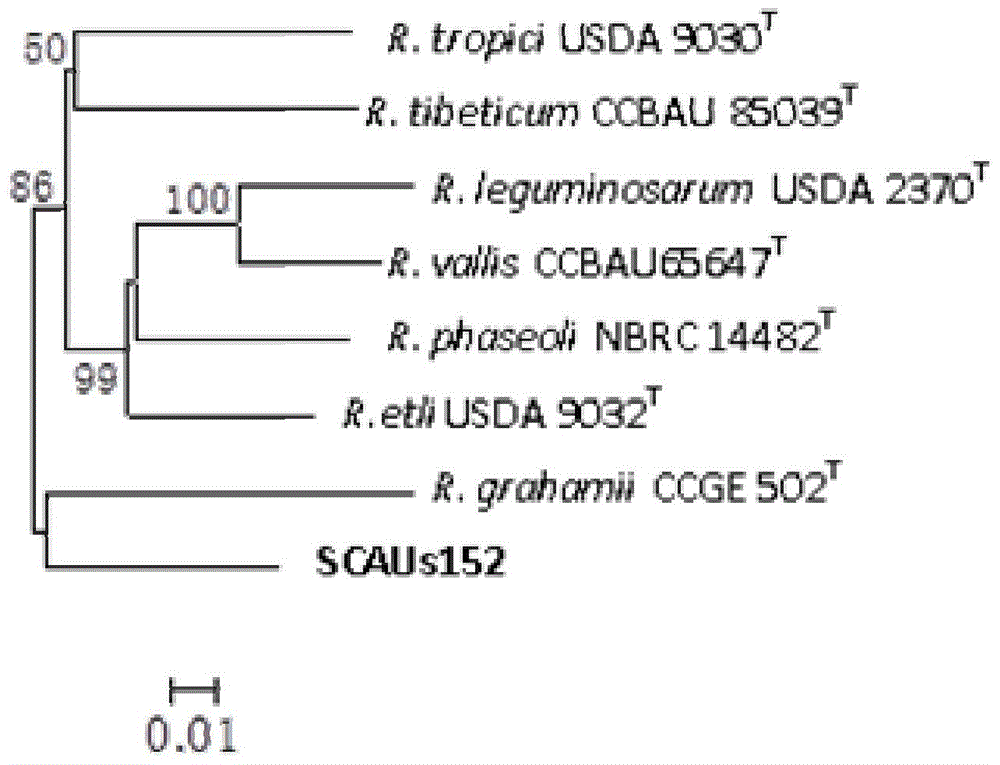
Azorhizobium strain SCAUs152 and application thereof
InactiveCN103952341AStrong stress resistanceHas the ability to secrete IAABiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyPlant nodule
The invention discloses an Azorhizobium strain SCAUs152 and application thereof. The strain is a new strain which is separated and purified from fresh soybean root nodules and belongs to Rhizobium. The strain is collected to China Center for Type Culture Collection of Wuhan University on March 14th, 2014, and the collection number is CCTCC NO.M2014085. The strain is applied to production of Sichuan soybeans. The Azorhizobium strain SCAUs152 is a favorable broad-spectrum Rhizobium japonicum strain with high symbiotic fixation capacity, wide application range of Sichuan soybean species, IAA (indoleacetic acid) secretion capacity, capacities for dissolving inorganic phosphorus, organic phosphorus and potassium and high stress tolerance. The strain has favorable matching affinity with Sichuan dominant bean species, and can enhance the soybean yield by more than 23% in different ecological regions where no nitrogen fertilizer is applied and the Azorhizobium strain SCAUs152 is inoculated, which is much different from the regions where the Azorhizobium strain SCAUs152 is not inoculated.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Functional bactericide for preventing and treating root-knot nematode
ActiveCN105724438AIncrease richnessWith nitrogen fixation functionBiocideAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserDiseaseVerticillium species
The invention provides a functional bactericide for preventing and treating root-knot nematode.The functional bactericide comprises an azotobacter bactericide, a biocontrol bacterium bactericide and a carrier, and the mass ratio of the azotobacter bactericide to the biocontrol bacterium bactericide to the carrier is (1-2.5):(1.5-5):1.The azotobacter bacterium bactericide contains nodule bacteria and azotobacter chroococcum, and the living bacterium count ratio of nodule bacteria to azotobacter chroococcum is (1-100):(1-200).The biocontrol bacterium bactericide contains paecilomyces lilacinus, verticillium chamydosporium, bacillus subtilis and bacillus cereus, and the living bacterium count ratio of paecilomyces lilacinus to verticillium chamydosporium to bacillus subtilis to bacillus cereus is (1-100):(1-100):(1-100):(1-100).The living bacteria count of the functional bactericide is larger than 0.2 billion / g.When applied to fertilizer, the functional bactericide can improve the disease preventing effect and the growth promoting effect of microbial fertilizer, guarantee nutrition supply of microbial fertilizer in the applying process, achieve the effects of preventing and treating root-knot nematode, forming healthy root nodules and promoting plant growth, increase the yield of crops and improve the quality of crops.
Owner:SHENZHEN BATIAN ECOTYPIC ENG
Fertilizer special for soybean
InactiveCN1508097AMeet nutritional needsNitrogen fixationHorticultureFertilizer mixturesSulfate radicalsPlant nodule
The present invention relates to a special-purpose fertilizer for soyabean. It is characterized by that it comprises nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium, also includes additive with slow-releasing action and special-purpose microfertilizer. The weight percentage of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium is 0.4-1:0.1-0.3:0.2-0.4. Said invention is complete in nutrients and reasonable in formula, can fully meet nutrient requirement for soyabean growth and development process, also contains the nutrient components of nitrate nitrogen, sulfate radical, boron and molybdenum, so that it is favorable for soyabean nitrogen-fixing root nodule.
Owner:中国石油化工股份有限公司巴陵分公司
A novel method for controlling soybean root disease by using rhizobia
The invention relates to a method for using soybean root nodule and endotrophic mycorrhiza to prevent soybean root disease. Wherein, the inventive bacteria seed has been stored in national microbe storage manager center, whose storage number is sinorhizobium sp; the seed L396 storage number is CGMCC No. 1851; the bacillus subtilis seed Snb2 storage number is CGMCC No.1850. And the invention uses general liquid to ferment and cultivate, uses itself or metabolite as effective active component; mixing the ferment solutions at different ratios, with effective restrain function on soybean cyst nematization and root pathogenic fungi; the density ratio between Snb2 and L392 is 8:3, and the dead ratio of young bacteria can reach 98.92%, and the relative restrain rate on cyst cultivation can reach 99.66%; the invention prepares the metabolite into water agent, to reach 78.6% prevent rate on the soybean cyst nematization. The inventive nodule bacteria can fix nitrogen and accelerate growth.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
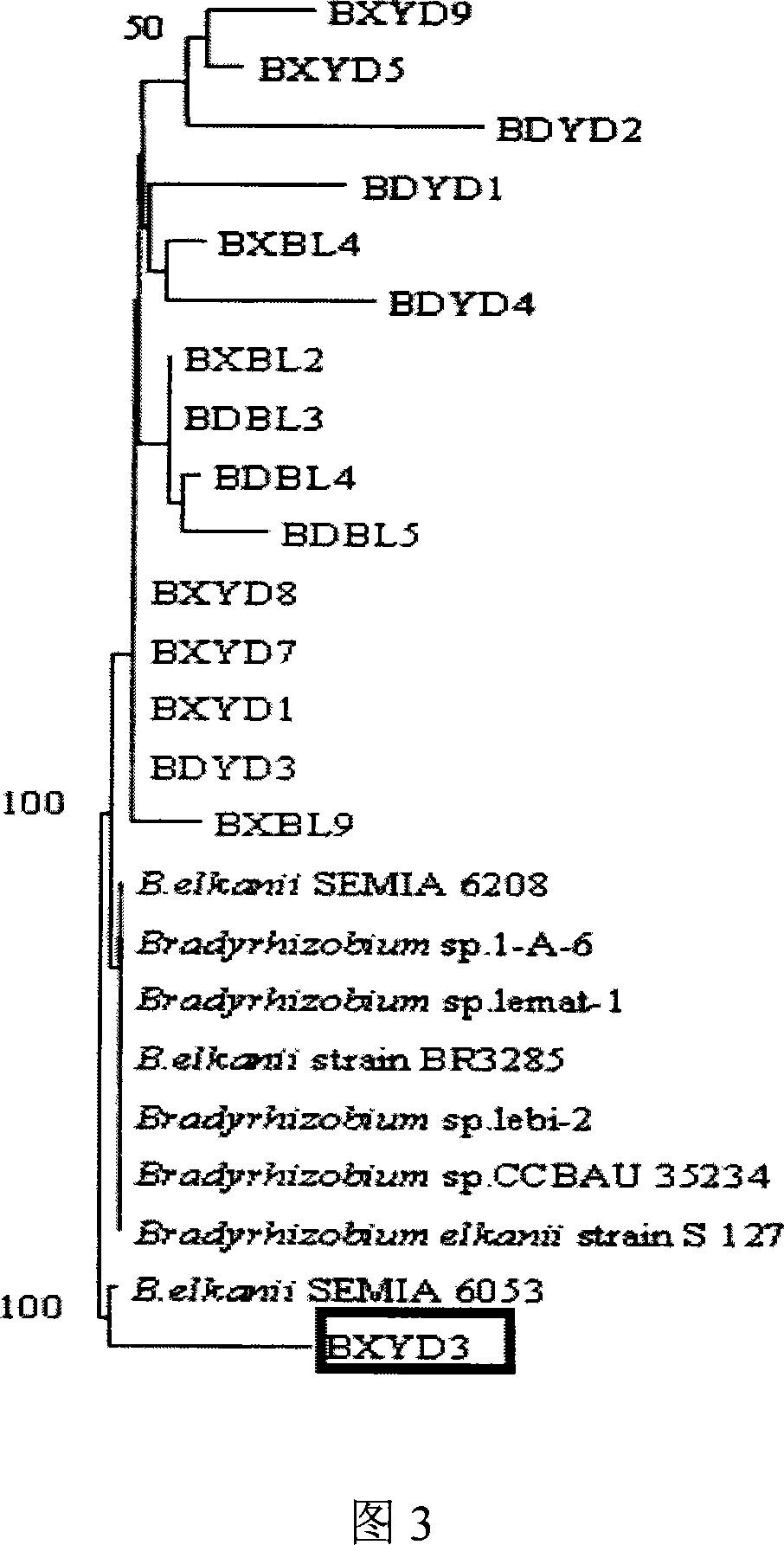
Root nodule azotobacter strain BXYD3 and uses thereof
The invention discloses a Nodule Azotobacter strain BXYD3 and the application. The strain is obtained by a way that the Rhizobia strains in the soil are respectively captured through different soybean varieties; the Rhizobia strains are separated and purified in fresh root nodules; part 16S rDNA of the strain is sequenced; the phylogenetic analysis determines that the strain is a novel Bradyrhizobium strain, which is named as Huagu 3. The Nodule Azotobacter strain BXYD3 of the invention has the characteristics of acid and aluminum tolerance and high level of nodules, which are proved by laboratory pot culture and field experiment. The inoculation of the Rhizobia strain can improve the yield of soybean more than 20 percent to 30 percent. The invention suits for the acid soil area in South China, which can be used as one of the measures for the conventional cultivation of soybean.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
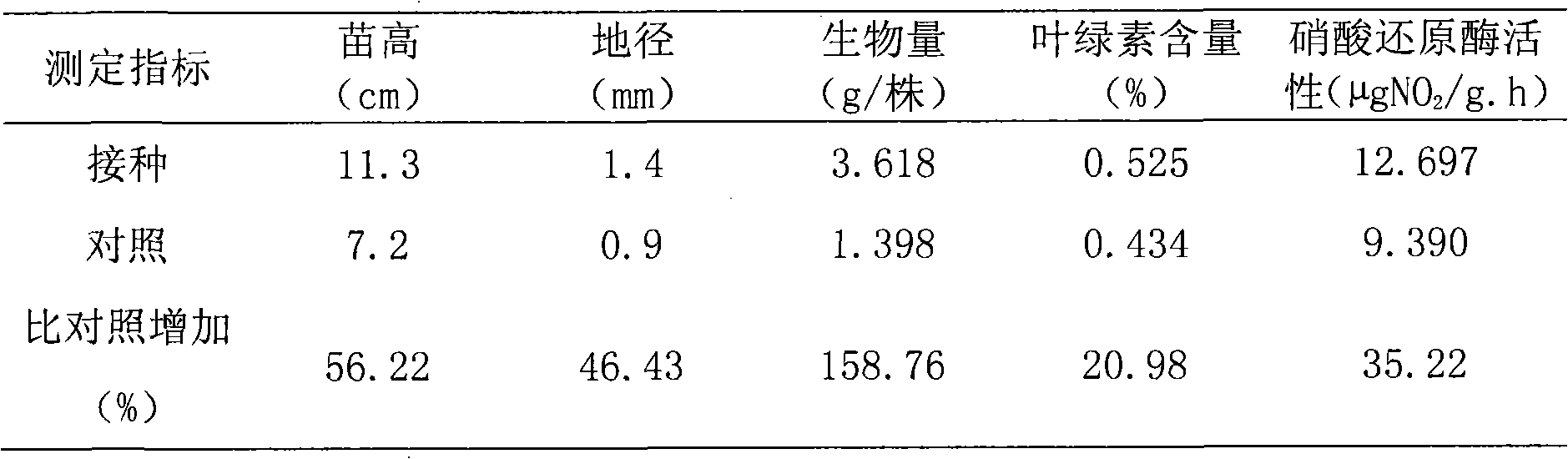
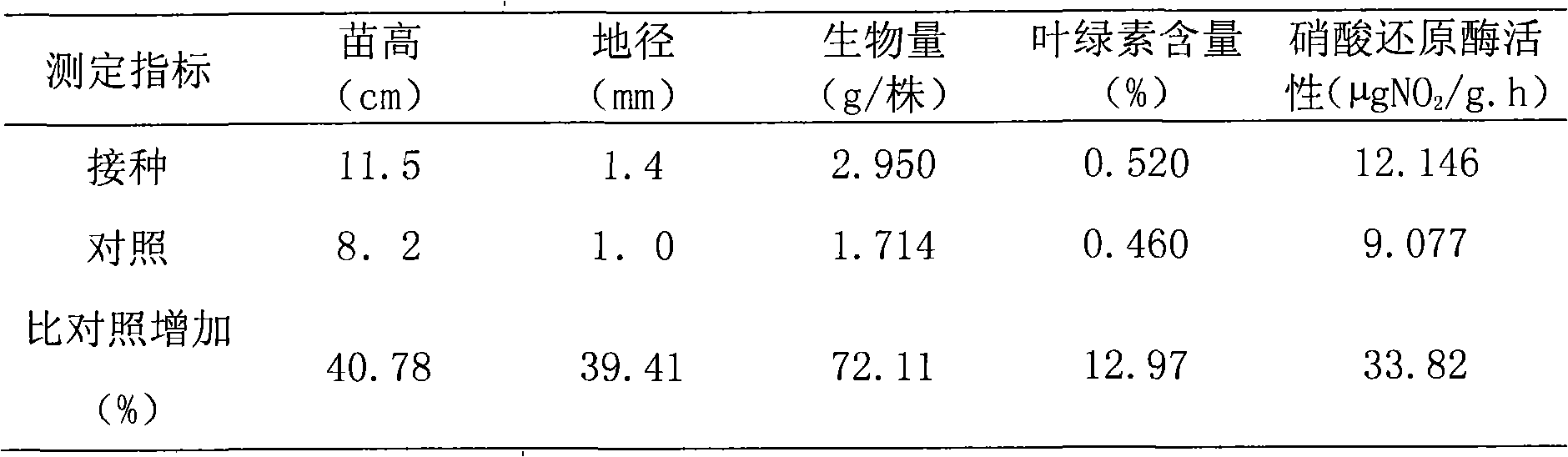
Nitrogen-fixing bacillus megaterium strain DL7 and application thereof
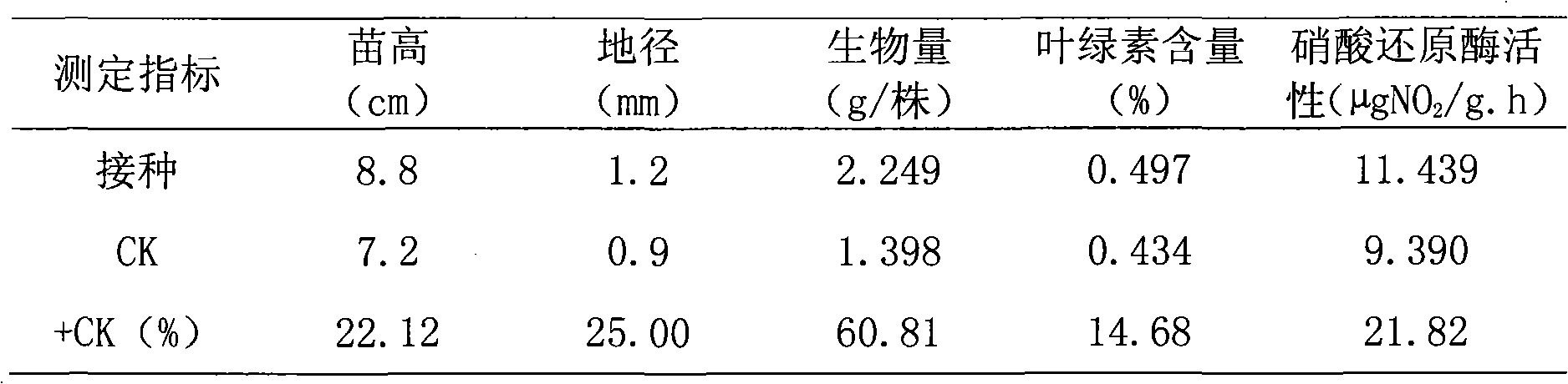
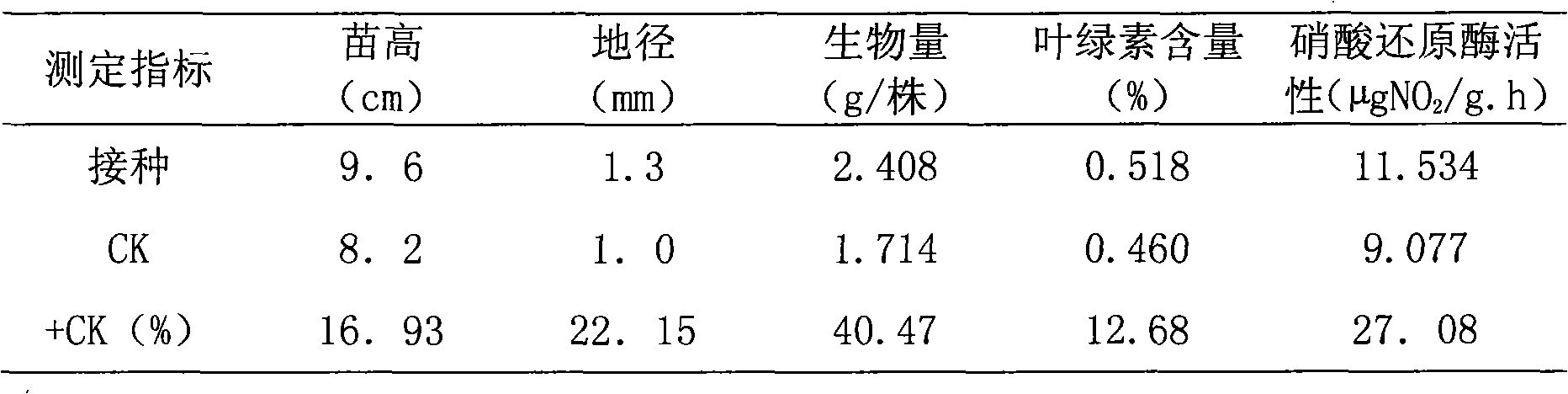
The invention relates to a nitrogen-fixing bacillus megaterium strain DL7 and application thereof. The strain is preserved in the General Microbiological Center of the China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms in June 7, 2010 and has a preserving number as CGMCC NO.3914. The strain is a new nitrogen-fixing strain obtained by using the conventional microorganism separation and purification method for Chinese podocarpus root nodules. In the strain, the nitrogenase activity is 1.5632nmol.g<-1>.h<-1>; after an eucalyptus seedling is planted, the seedling height increases 40.78-56.22 percent, the ground diameter increases 39.41-46.43 percent, the average biomass increases 72.11-158.76 percent, the chlorophyll content increases 12.97-20.98 percent, and the nitrate reductase activity increases 33.82-35.22 percent. The strain can be applied to a biological bacterial fertilizer for promoting eucalyptus seedling growth.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Special peanut film-coating slow-release fertilizer and preparation process thereof
InactiveCN101885633APlay a role in reducing costsPerfection and improvement of fertilization technologyOrganic fertilisersFertilizer mixturesCross-linkContinuous cropping
The invention discloses a special peanut film-coating slow-release fertilizer and a preparation process thereof. The special peanut film-coating slow-release fertilizer utilizes the effects of exchange, adsorption, combination and chelation of humic acid, and a reactant, a cross-linking agent and a film-forming agent are added to the humic acid to prepare a special peanut slow-release film-coating agent; then special peanut slow-release film-coating agent is mixed with a proportioned special peanut fertilizer; and an obtained mixture is subjected to granulating, film coating, dehumidifying, cooling and screening to prepare the special peanut film-coating slow-release fertilizer. The humic acid contained in the special peanut film-coating slow-release fertilizer is a high-quality organic fertilizer, and not only can be decomposed to provide nutrients, but also can stimulate the activity of root nodules, enhance the nitrogen fixing capacity and improve the disease resistance and the continuous cropping resistance. The special peanut film-coating slow-release fertilizer and the preparation process not only are a break of a slow-release technology of the fertilizer industry, but also are the perfection and the improvement of a peanut fertilizing technology, and achieve the purposes of increasing the yield, reducing the cost and realizing high efficiency on peanut production.
Owner:李振永
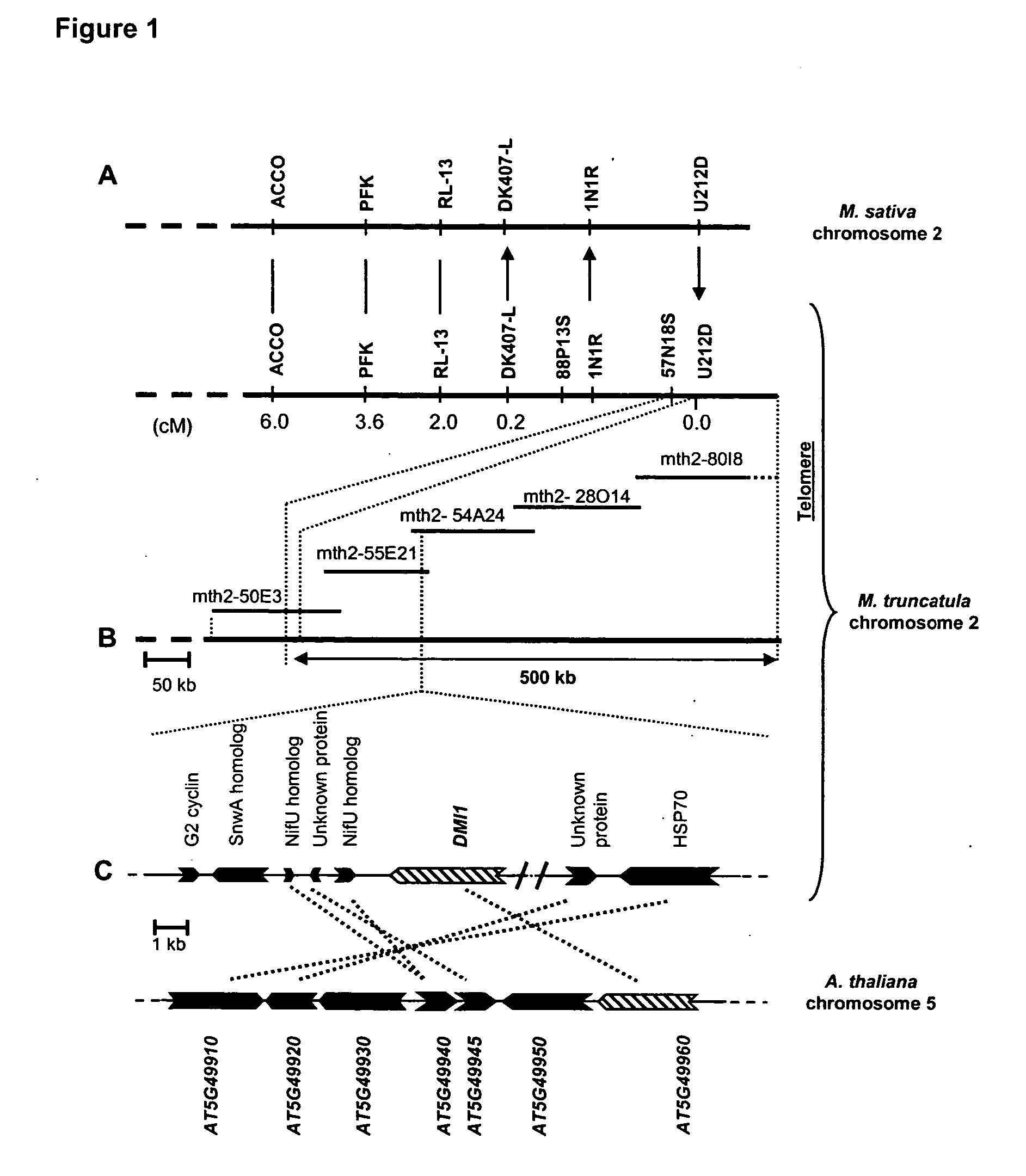
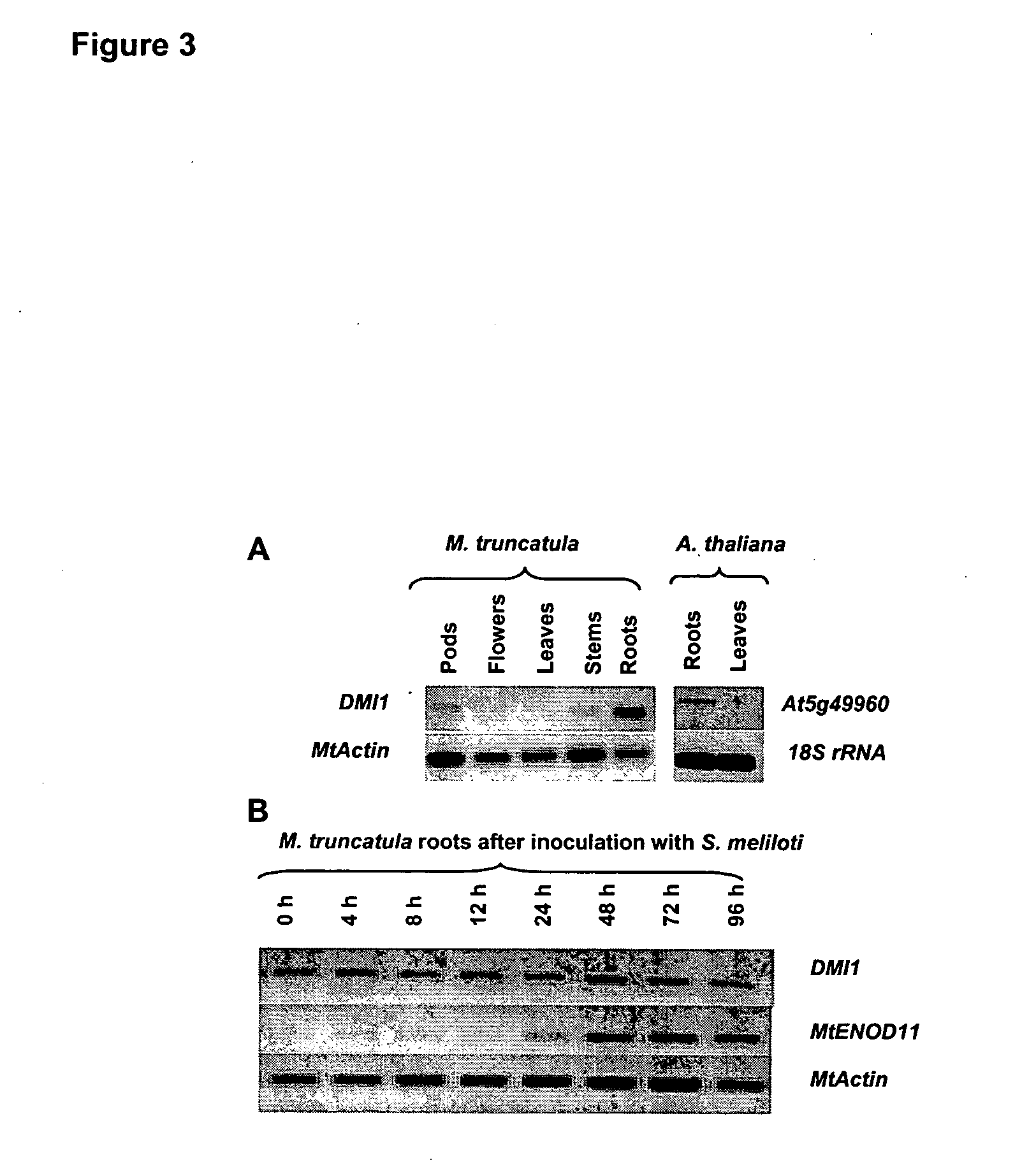
The DMI1 gene encodes a protein that is required for the early steps of bacterial and fungal symbioses
InactiveUS20050081262A1Enhanced nitrogenEnhanced phosphorous acquisitionBryophytesSugar derivativesBacteroidesPlant nodule
Mycorrhizal and rhizobial associations represent the two most important symbiotic relationships between higher plants and microorganisms, providing access to otherwise limiting supplies of phosphate and nitrogen, respectively. Although many higher plants are able to establish a symbiotic relationship with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, legumes are unusual among plants because they also form associations with nitrogen fixing soil bacteria called rhizobia. This symbiosis requires the production of bacterial signals, “Nod factors” that trigger several key developmental responses in the host plant (Dénarié et al., 1996). The DMI1 gene of the model legume M. truncatula plays a major role both in the early steps of Nod factor signaling and in the establishment of mycorrhizal symbiosis. Dmi1 mutants do not exhibit many of the early responses to Nod factors and are incapable of forming nitrogen fixing root nodules. Here we describe the cloning and preliminary characterization of DMI1. The DMI1 gene encodes a novel protein with low global similarity to ligand-gated cation channels of archaea. The protein is highly conserved in angiosperms and ancestral to land plants. Interestingly a putative A. thaliana DMI1 orthologous gene is expressed in roots. As A. thaliana is unable to establish a mycorrhizal symbiosis, this finding suggests that DMI1 may also exhibit a function that is independent of symbiotic interactions.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL DE LA RECHERCHE AGRONOMIQUE +1
Planting method for interplanting rhizoma polygonate under pear trees
InactiveCN108040724AAvoid sun exposureImprove survival rateCultivating equipmentsRoot crop cultivationPlant nodulePear tree
The invention discloses a planting method for interplanting rhizoma polygonate under pear trees and relates to the technical filed of planting. The method comprises the steps of land selection, soil loosening, pear tree transplantation, rhizoma polygonate treatment and planting, weeding, fertilization and the like. By adopting the planting method, rhizoma polygonate can be prevented from being insolated, the survival rate of rhizoma polygonate is increased, and accordingly the yield of rhizoma polygonate is increased; the root systems of the pear trees are developed and have root nodule or mycorrhiza, the soil fertility is improved, and the appropriate growth environment can be provided for rhizoma polygonate for a long time; overground parts of pear leaves and rhizoma polygonate plants are treated and can be applied to organic fertilizer for improving the soil quality, waste is sufficiently used, and the yield of the pear trees and rhizoma polygonate is increased; through interplanting of the pear trees and rhizoma polygonate, weed infestation is avoided, the use amount of the weed killer is effectively reduced, and the labor cost is saved.
Owner:渠县新市贡和中草药农民专业合作社
Nitrogen fixation stenotrophomonas maltophilia C4Y41 strain and application thereof
InactiveCN101781628APromote growthLarge biomassBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismPodocarpus
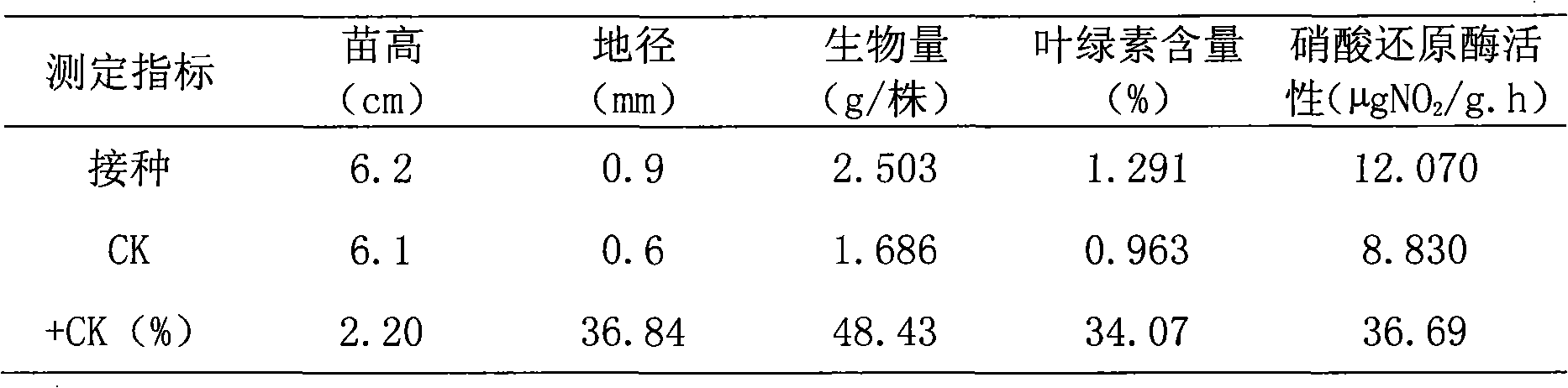
The invention relates to a nitrogen fixation stenotrophomonas maltophilia C4Y41 strain and an application thereof. The strain is stored in the common microorganism center of China microorganism strain management committee and has a storage number of CGMCC No.3349. The strain is a new nitrogen fixation strain obtained by applying a general microorganism-separating and purifying method on podocarpus root nodules, has the nitrogen fixation enzyme activity of 0.019-0.030nmol*g-1*h-1 and enables the height of inoculated eucalyptus seedlings to increase by 2.20-22.12 percent, the ground diameter to increase by 22.15-36.84 percent, the average biomass to increase by 40.47-60.81 percent, the chlorophyll content to increase by 12.68-34.07 percent and the nitrate reductase activity to increase by 21.82-36.69 percent. The strain can be applied as a biological fertilizer for stimulating the growth of the eucalyptus seedlings.
Owner:广西绿满地农资有限公司
Rhizobium for promoting growth of vicia sativa L. and application of rhizobium
ActiveCN106967652AThe effect of increasing production is obviousImprove practicalityBiocidePlant growth regulatorsRhizobium leguminosarumMicroorganism
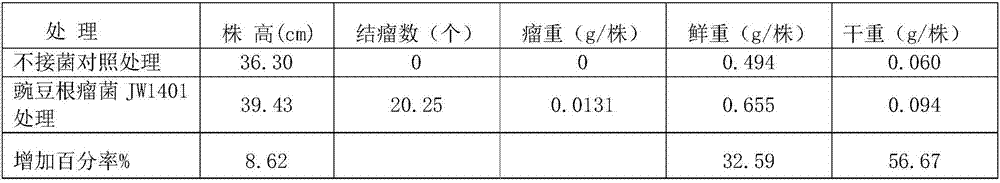
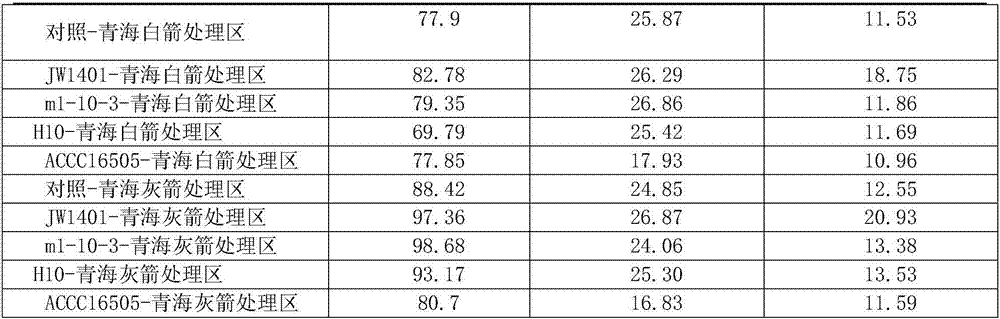
The invention discloses a rhizobium for promoting growth of vicia sativa L. and an application thereof. The rhizobium is a rhizobium leguminosarum, has a strain number of JW1401, and has a preservation number of CGMCCNo.11876 in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center. A test proves that the inoculation combination of the rhizobium leguminosarumJW1401CGMCC 11876 and the vicia sativa L. has a significant effect of increasing the production of the vicia sativa L., has relatively high practicability and generalizability, and is expected to become a novel excellent combination technology in the field of application of the rhizobium for the vicia sativa L.. The rhizobium provided by the invention has a broad application prospect in the planting industry of the vicia sativa L..
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Materials and methods for the enhancement of effective root nodulation in legumes
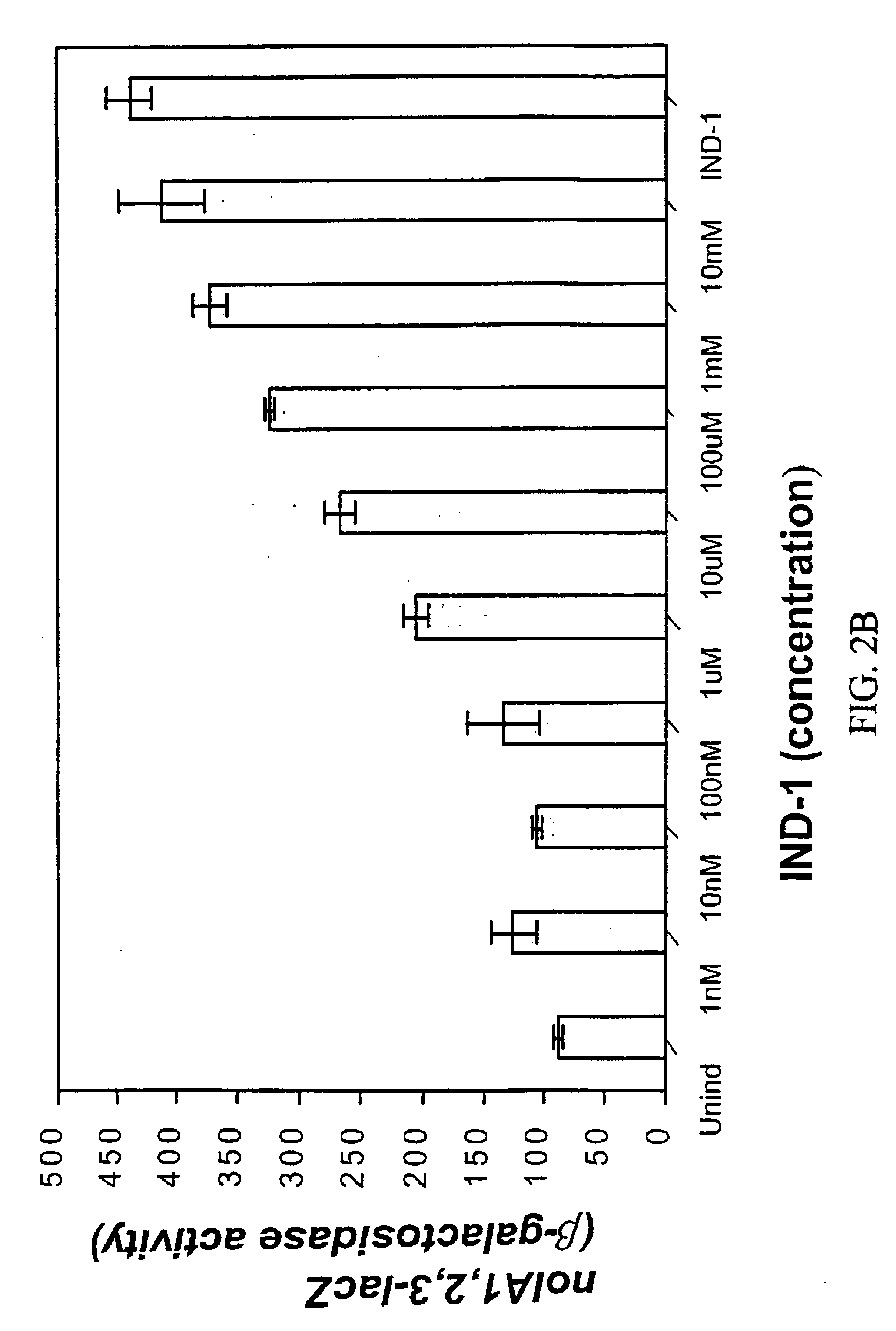
InactiveUS6855536B2Reduced nodY-lacZ inductionReduced nodulation efficiencyBiocideBacteriaBacteroidesPlant nodule
The subject invention relates to compounds and compositions which induce transcripts of the nolA gene in nitrogen-fixing bacteria, such as Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Novel bacterial strains which are insensitive too NolA, soil inoculants comprising NolA insensitive bacteria and / or nolA inducers, and methods of increasing nitrogen fixation in legumes are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
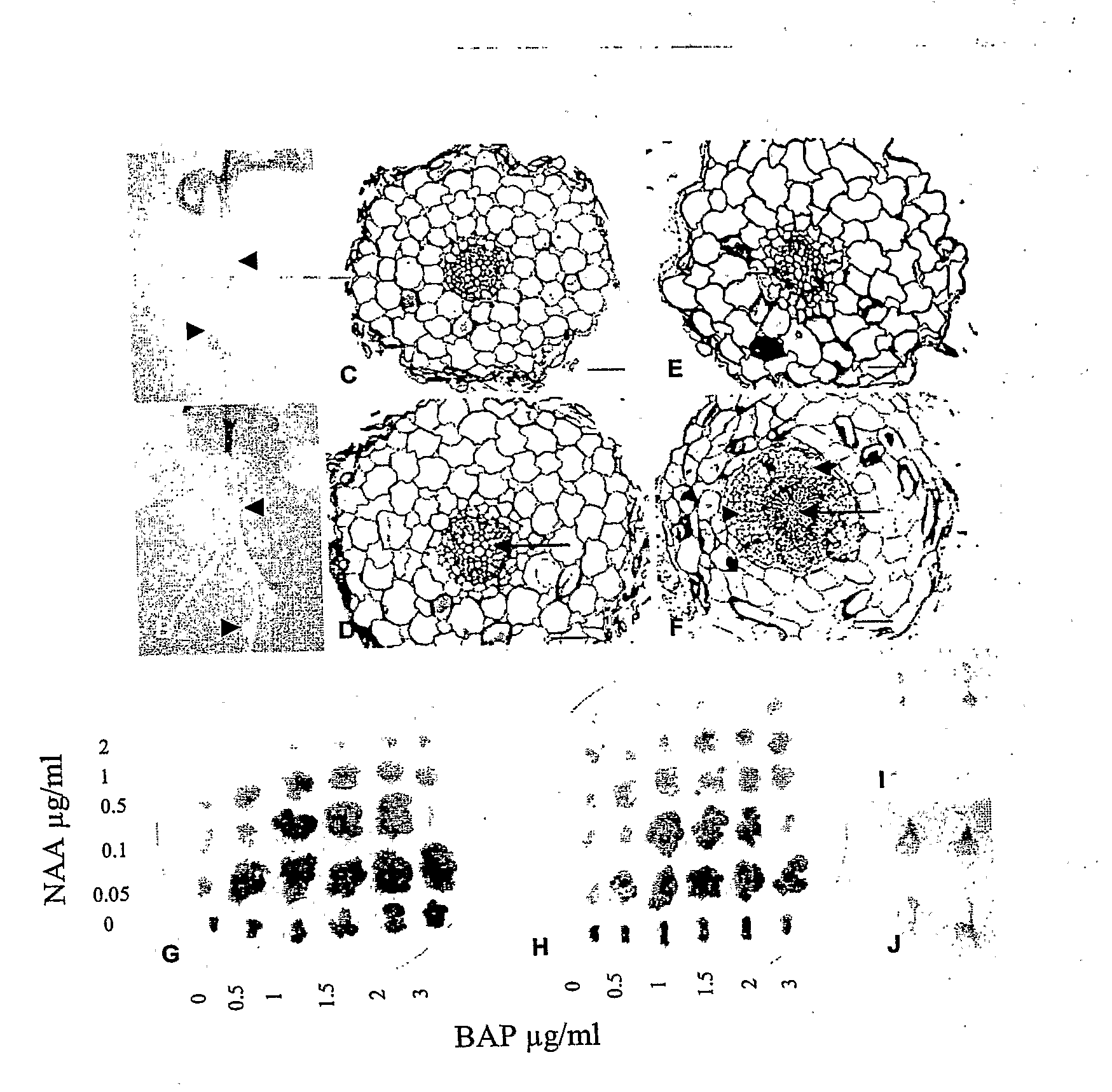
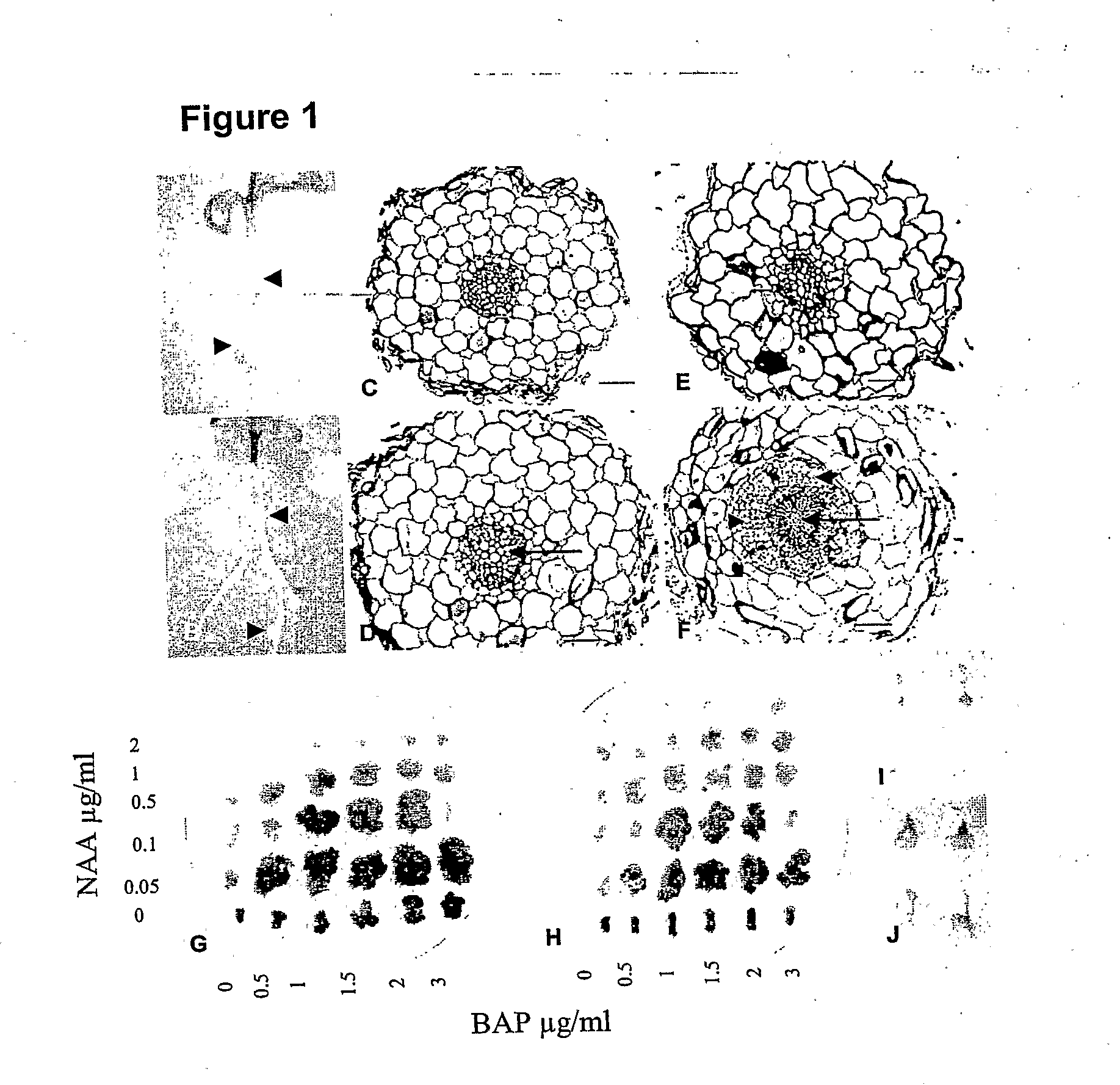
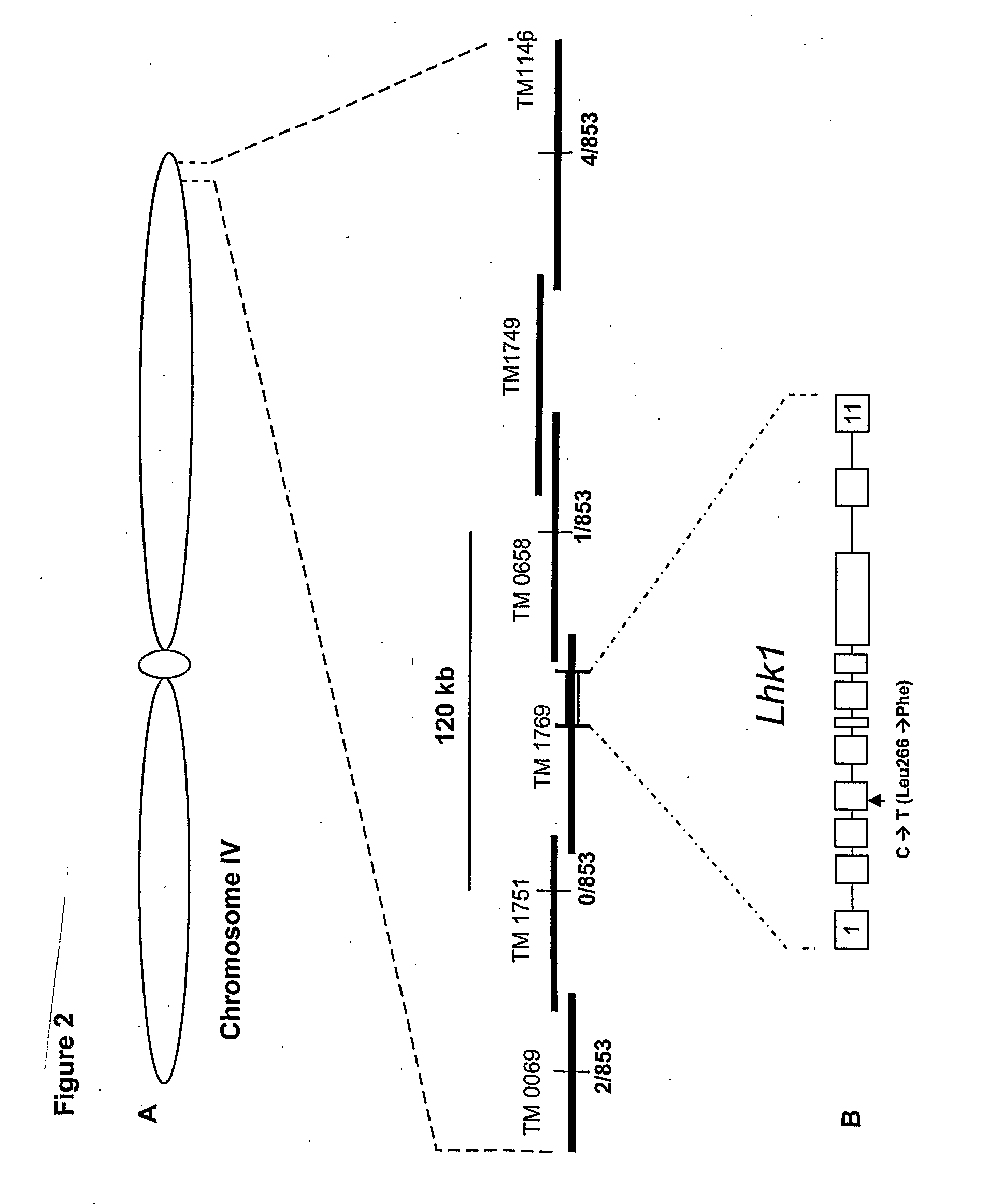
Mutant histidine kinase that confers spontaneous nodulation in plants
Formation of nitrogen fixing root nodules in legumes is induced by perception of lipochitin-oligosaccharide signal molecules secreted by compatible Rhizobium bacteria, which triggers a common symbiotic pathway. The present invention provides a spontaneous nodule formation (snf2) mutant, in which the formation of symbiotic nodules is spontaneous, leading to nodule development in the absence as well as in the presence of Rhizobium bacteria and / or exogenous rhizobial signals. The invention further provides an isolated DNA sequence encoding a mutant cytokinin-independent histidine kinase whose activity results in this ‘gain of function’ dominant phenotype of spontaneous nodule formation. Furthermore the snf2 gene is shown to confer a phenotype, characterised by regulated organogenesis of spontaneous nodules, to plants having a nodulation deficient genetic background. A gene of the invention, that confers this spontaneous nodulation phenotype, has 15 utility for the transfer and establishment of nitrogen fixing capability in non-nodulating plants, and thereby reducing the nitrogen fertiliser dependence of non-nodulating crop plants.
Owner:STOUGAARD JENS +5
Cuttage seedling culture method of liquidambar styraciflua
InactiveCN104585007APromote growthImprove breathabilityGrowth substratesCulture mediaPlant noduleNutrient solution
The invention belongs to the technical field of seedling breeding, and relates to a cuttage seedling culture method of liquidambar styraciflua. According to the method, parent semi-lignified current-year branches are selected to be sheared into cuttage branches with the length being 8 to 10cm, 2 to 3 buds and 2 to 4 leaves are reserved, the upper ends of the cuttage branches are flatly sheared, the shearing position is 1 to 1.5cm from the upper part buds, the lower part is sheared in the inclined direction, the shearing openings are flat and smooth, the cuttage branches are placed into a nutrition solution to be soaked for 1 to 2 hours and are then inserted into a mixed substrate of perlite and turfy soil subjected to sterilization treatment, and the bare-root transplanting can be carried out after the culture for 40 to 45 days in the mixed substrate of the perlite and the turfy soil. The cuttage substrate adopts the mixed substrate formed by the perlite and the turfy soil according to the weight ratio being 5:1, the ventilation performance and the moisture absorption performance are good, the cost is low, the conditions are favorable for root system growth, and the rooting rate is high; a soaking process is adopted, and cutting slips are soaked for 1 to 2 hours in the nutrition solution, so that the roots of the cutting slips have the sufficient time to absorb nutrients in the nutrition solution, then, the cutting slips are subjected to cuttage into the prepared mixed substrate, root nodules are formed after 5 to 7 days, the rooting is realized after 13 to 15 days, the bare-root transplanting can be carried out after 40 to 45 days, the root system is developed, the survival rate is high, and can reach more than 95 percent, and the seedling forming period is short.
Owner:青岛彩盛农业科技有限公司
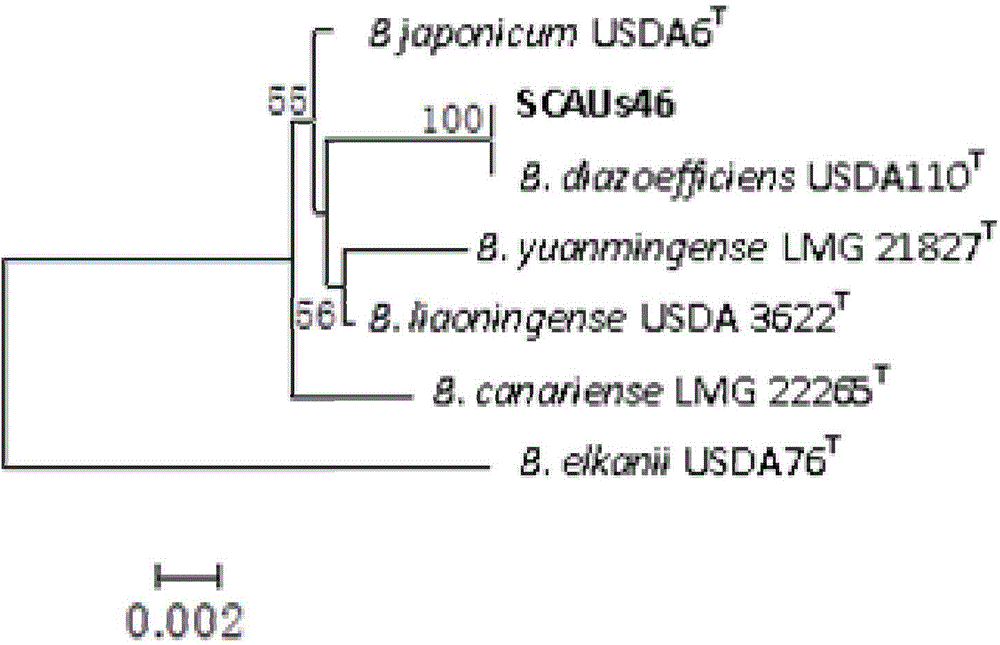
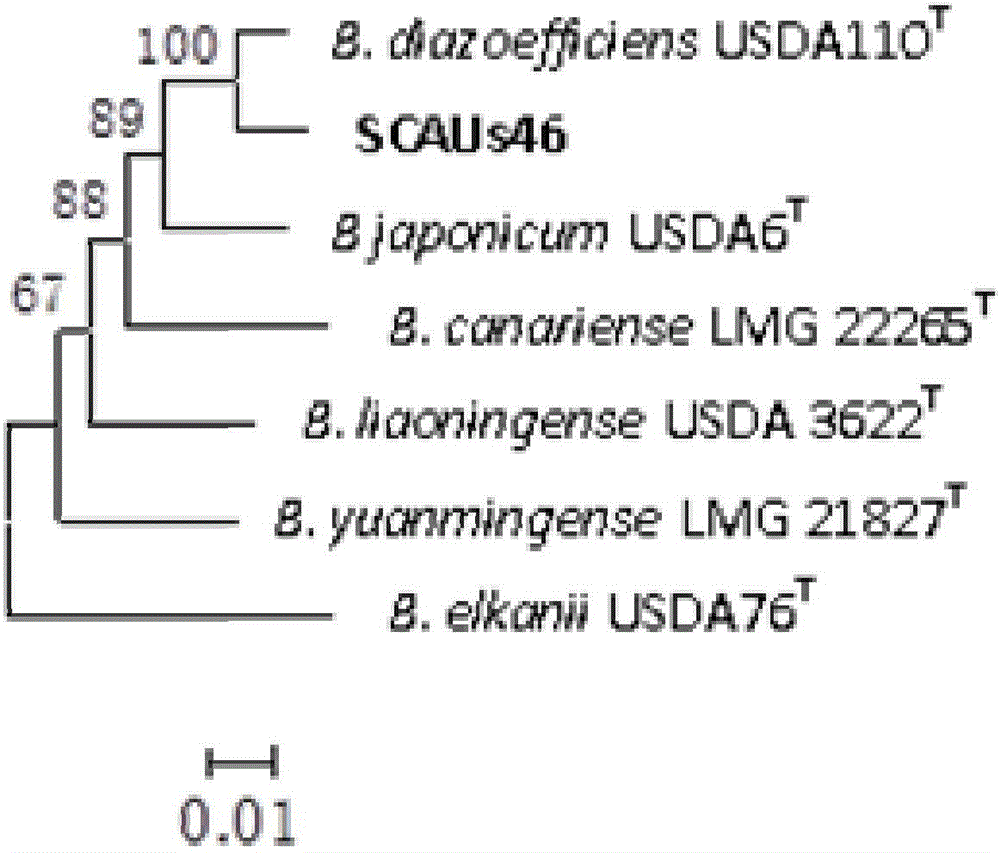
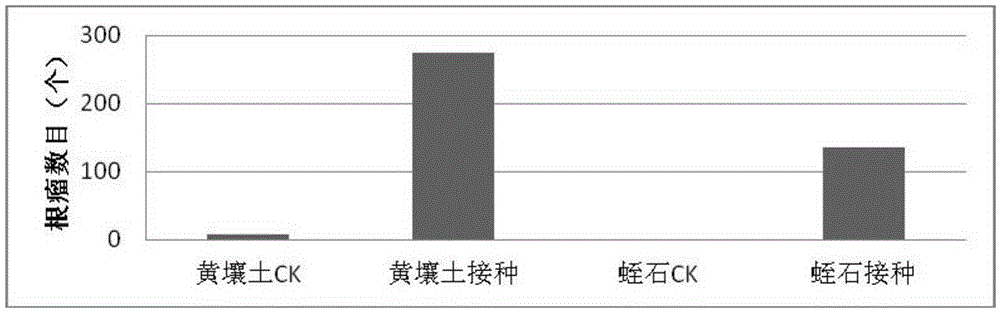
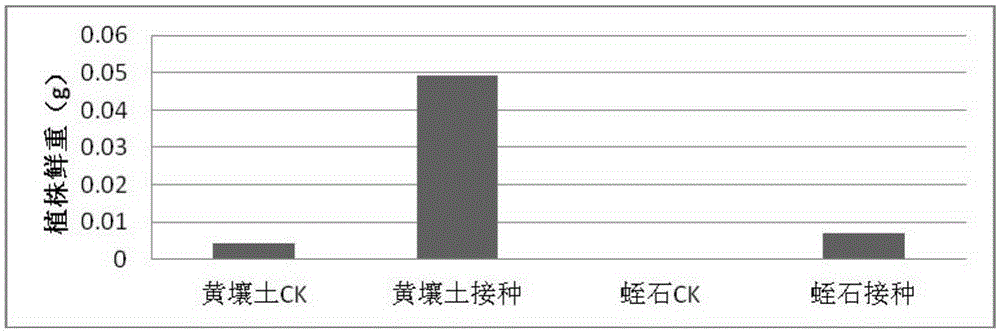
Bradyrhizobium diazoefficiens strain SCAUs46 and application thereof
InactiveCN103952344AStrong stress resistanceHas the ability to secrete IAABacteriaMicroorganism based processesPlant noduleRhizobium japonicum
The invention discloses a Bradyrhizobium diazoefficiens SCAUs46 and application thereof. The strain is separated and purified from fresh soybean root nodules, and is collected to China Center for Type Culture Collection of Wuhan University on March 14th, 2014; and the collection number is CCTCC NO.M2014083, and the classification designation is Bradyrhizobium diazoefficiens. The strain is applied to production of Sichuan soybeans. The Bradyrhizobium diazoefficiens SCAUs46is a favorable broad-spectrum Rhizobium japonicum strain with high symbiotic fixation capacity, wide application range of Sichuan soybean species, IAA (indoleacetic acid) secretion capacity, capacities for dissolving inorganic phosphorus, organic phosphorus and potassium and high stress tolerance. The strain has favorable matching affinity with Sichuan dominant bean species, and can enhance the soybean yield by more than 22% in different ecological regions where no nitrogen fertilizer is applied and the SCAUs46 is inoculated, which is much different from the regions where the SCAUs46 is not inoculated.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Rhizobium and application thereof
ActiveCN105274030ANodulation rate is highImprove survival rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPlant noduleDry weight
The invention relates to a (Bradyrhizobium sp.) LX-JX01 and application thereof. A preparation method of an inoculant for the (Bradyrhizobium sp.) LX-JX01 includes the steps of preparing a liquid DM culture medium, preparing a solid DM culture medium, activating a strain and culturing the rhizobium. The strain can be in nodulation and symbiosis with Dalbergia odorifera. When the inoculant for the Dalbergia odorifera rhizobium LX-JX01 is used for planting Dalbergia odorifera seedlings, nodulation number root nodules is increased by 3823% than a control group, fresh weight of the root nodules is increased by 1038%, dry weight of portions, above the ground, of plants is increased by 47.22%, and seedling height and plant stem diameter are increased by 1030% and 42.3% respectively, so that the inoculant can promote growing of Dalbergia odorifera. Consequently, the inoculant has wide application prospect in planting of artificial forest of Dalbergia odorifera.
Owner:领先生物农业股份有限公司
Bacterial strain of root nodule nitrogen-fixing strain series RY3 and application thereof
InactiveCN101748088AFresh heavyDry weightBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPlant noduleDry weight
The invention discloses a bacterial strain of a root nodule nitrogen-fixing strain series RY3 and application thereof. The bacterial strain (Bradyrhizobium sp. RY3) is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection on November 13th, 2009, and the collection number of the bacterial strain is CCTCC No: M 209267. The root nodule nitrogen-fixing strain series RY3 of the invention is grafted back to Stylosanthes guianensis TPRC2 and TPRC5 so that the fresh weight and dry weight of the Stylosanthes guianensis are increased by over triple. The RY3 is a highly-efficient bacterial strain which can ensure that the high yield of both the fresh weight and dry weight of the Stylosanthes guianensis can be achieved and the dissemination capacity of the Stylosanthes guianensis is stronger after the Stylosanthes guianensis is grafted with rhizobia; and after being released to the natural environment, the RY3 has no harm to human, animals and plants and does not pollute the environment.
Owner:TROPICAL CORP STRAIN RESOURCE INST CHINESE ACAD OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI +2
Bradyrhizobium sp.RY4 strain and application thereof
InactiveCN101735969AIncrease productionEffectively increase productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPlant noduleDry weight
The invention discloses a Bradyrhizobium sp.RY4 strain and application thereof. The Bradyrhizobium sp.RY4 strain is preserved at the China center for type culture collection and the preservation number is CCTCC NO:M209268. When the Bradyrhizobium sp.RY4 is back-jointed to stylosanthes guianensis TPRC2 and TPRC5, the number of root nodules, the dry weight of the root nodule, the height of the strain, the fresh weight of the plant and the nitrogenase activity are greatly increased and obviously higher than those in a control group; and the effect of the RY4 back jointed to the stylosanthes guianensis TPRC2 is better. Thalli are released to the natural environment, the thalli increase the number of the groups of nodule bacteria in soil, contribute to the nodulation and nitrogen fixation of the stylosanthes guianensis, are harmless for human beings, animals and plants, and do not pollute the environment.
Owner:TROPICAL CORP STRAIN RESOURCE INST CHINESE ACAD OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI +2
Method for planting sea-buckthorn in gobi of alpine regions
ActiveCN103283437AAdaptablePromote growth and developmentClimate change adaptationHorticultureAridPlant nodule
The invention discloses a method for planting or cultivating sea-buckthorn, particularly to a method for planting the sea-buckthorn in gobi of alpine regions, which comprises oil preparation and watering before the planting, irrigation, fertilizing, height determination, trimming and the like during the planting. Compared with the prior art, the sea-buckthorn cultivated through the method disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of high adaptability, excellent growth and development, developed root systems, more root nodules, thicker aerial stems and flourishing growth vigor, and has a survival rate more than 91% by experimental statistics, so the method is more suitable for being applied in alpine regions, particularly in areas similar to the gobi of the alpine regions of northern Sinkiang, and can promote the large-scale development of the sea-buckthorn planting industry. As the flourishing branches and leaves and huge root systems of the sea-buckthorn have multiple effects of keeping out the wind, stabilizing sands and protecting farmlands, the sea-buckthorn plays a positive role in reducing sand storms and improving the ecological environment of arid desert regions, provides sustainable resources for the northern desert regions, and promotes the development of provincial economy.
Owner:XINJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI & RECLAMATION SCI
Sinorhizobium sp. and application thereof
InactiveCN101519644AImprove nitrogen fixationEnhance colonization abilityBiocidePlant growth regulatorsSinorhizobium sp.Plant nodule
The invention discloses Sinorhizobium sp. and application thereof. The Sinorhizobium sp. NX2004062 has a storage number of CGMCC No.2883. The Sinorhizobium sp. NX2004062 can lead clover plants to safely grow, establish an effective syntaxial system with the clover plants to promote the growth of clover roots, strengthen the photosynthesis of the clover plants, increase the output of clovers on the ground and under the ground and further improve the output and the quality of the clovers; moreover, the Sinorhizobium sp. NX2004062 reduces the fertilizer application in clover production and further reduces the pollution of fertilizers to the environment.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Nitragin controlled release fertilizer special for alfalfa, and preparation and application of nitragin controlled release fertilizer
The invention relates to a nitragin controlled release fertilizer special for alfalfa, and preparation and application of the nitragin controlled release fertilizer. The fertilizer comprises the following raw materials: urea coated nitragin composition, 5 percent humic acid coated urea, sulfur and high polymer coated urea, 5 percent recycling thermoplastic resin coated urea, 6 percent recycling thermoplastic resin coated urea, 8 percent recycling thermoplastic resin coated urea, 5 percent modified epoxy resin coated diammonium phosphate on a urea base coat, 5 percent modified epoxy resin coated potassium nitrate on the urea base coat, diammonium phosphate and potassium chloride. The invention also provides a method for preparing the controlled release fertilizer special for the alfalfa. According to the controlled release fertilizer and the preparation method, trace elements required by a nitragin, root nodule growth and nitrogen fixation are coated in a urea hull together, and coatednitrogen fertilizers in release periods of phosphorus and potassium fertilizers and different nutrients are allocated reasonably according to a fertilizer requiring rule of the alfalfa, so that the controlled release fertilizer special for the alfalfa, which has double functions of inoculation and fertilization, is formed. The controlled release fertilizer is valid for two years after being applied at a time, so that labor force can be saved, and the yield of the alfalfa can be increased.
Owner:KINGENTA ECOLOGICAL ENG GRP
RY2 strain of root nodule nitrogen-fixing bacterial strain system and application thereof
InactiveCN101824390AIncrease nitrogenase activityIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPlant noduleBradyrhizobium yuanmingense
The invention discloses a RY2 strain of a root nodule nitrogen-fixing bacterial strain system and application thereof. The strain (Bradyrhizobium yuanmingense RY2) is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) on 13th November in 2009. The preservation number is CCTCC NO:M 209266. The RY2 strain of the root module nitrogen-fixing bacterial strain system can exclusively greatly improve the nitrogenase activity of TPRC2, so that the nitrogenase activity of the TPRC2 is over three times higher than that of TPRC5 and can achieve higher nitrogenase activity by using a few root nodules. The yield of stylosanthes guianensis can be improved by over 30 to 40 percent by inoculating the root nodule bacteria, and the root nodule bacteria can be suitable for intercropping of stylosanthes guianensis TPRC2 and provides a large number of nitrogen for the stylosanthes guianensis, crops and soil. Meanwhile, the RY2 has strong salt tolerance, can grow in the environment that the NaCl concentration is higher than 0.25mol / L, can be planted in the salinized soil and has better effects of improving the yield of the stylosanthes guianensis and utilizing and improving the salinized soil.
Owner:TROPICAL CORP STRAIN RESOURCE INST CHINESE ACAD OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI +2
Cysteine protease gene for regulating and controlling root nodule senescence, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103290040ARegulation of agingShort lifeHydrolasesFermentationSequence analysisPlant nodule
The invention discloses a cysteine protease gene for regulating and controlling root nodule senescence, and a preparation method and application thereof. According to the preparation method disclosed by the invention, a Japan lotaustralin genomic sequence library is compared by utilizing the known cysteine protease gene of astragalus smicus; after the Japan lotaustralin genomic sequence library is analyzed and compared on the internet in a detailed manner, a primer having strong specificity is designed to carry out gene cloning by taking initiation codon as the starting point and termination codon as the finishing point; in addition, due to sequencing analysis and comparing analysis, a cloned fragment proves that the cysteine protease gene for regulating and controlling root nodule senescence is successfully cloned from the lotaustralin genomic sequence and cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid). The invention discloses application of the cysteine protease gene on leguminous plants; the expression mode of a gene promoter and the functions of the gene in the root nodule senescence process are researched by utilizing a histochemical localization technology. Compared with contrast plants, the results show that the root nodule of an RNAi (ribonucleic acid interference) plant is enlarged; the nitrogen fixation enzyme activity is increased; senescence of the root nodule is delayed; the effective nitrogen fixation time of the root nodule is prolonged; growth of the plant is more vigorous; the cysteine protease gene disclosed by the invention has application prospect on leguminous crops.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Method for rotation of alfalfa and awnless brome
The invention relates to the technical field of agricultural planting, and particularly relates to a method for rotation of alfalfa and awnless brome. The method for rotation of alfalfa and awnless brome comprises the following steps: turning over and planting alfalfa for 5-6 years after planting the awnless brome for 5-6 years, and then turning over and planting the awnless brome, and carrying out crop rotation repeatedly. The method has the beneficial effects that the yield and the soil fertility of high-quality forage per unit area are improved in a crop rotation manner, the physical and chemical properties of soil are improved, nitrogen in atmosphere also can be fixed by root nodules of alfalfa, and the soil fertility is improved. Thus, the fertilizing amount can be correspondingly reduced, investment in manpower and chemical fertilizer is reduced, the investment in fertilizer in the next round of awnless brome planting process also can be reduced, the yield of the awnless brome is increased, the land utilization rate and the acre yield are further improved, and the economic benefits are increased.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Peanut continuous cropping high-yielding agent
InactiveCN103787755AImprove the nutritional environmentStrong plantFertilizer mixturesContinuous croppingPlant nodule
The invention discloses a peanut continuous cropping high-yielding agent, relating to a peanut continuous cropping disease-resistant high-yielding technology. The peanut continuous cropping high-yielding agent comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 30-40 percent of humic acid, 25-35 percent of grass carbon, 10-20 percent of calcium sulfate, 5-8 percent of magnesium sulfate, 3-5 percent of zinc sulfate, 3-5 percent of manganese sulfate, 5-8 percent of ferrous sulfate, 3-5 percent of borax, 1-2 percent of rare earth nitrate, 0.1-1.5 percent of ammonium molybdate, 0.5-3 percent of Chinese azalea flower, 0.5-3 percent of marigold, 0.3-1.5 percent of ningnanmycin (8 percent in concentration), 1-2 percent of verticillium chlamydosporium and 1-2 percent of bacillus subtilis. The peanut continuous cropping high-yielding agent has the advantages that by comprehensively applying organic matters, cellulose, humic acid, trace elements, soil conditioners and root nodule growth nitrogen fixation agents, soil is improved, nutrients are balanced, the fertilizer effect is improved, the soil environment is improved, and a good soil-fertilizer condition is provided for the healthy growth of peanuts. Meanwhile, by applying the Chinese azalea flower and the marigold serving organic insecticides, the ningnanmycin serving as a bactericide, the verticillium chlamydosporium agent serving as a buster of threadworms and the bacillus subtilis serving as a microbial agent, insect pests are killed, diseases are eliminated, a growing and breeding environment for soil beneficial bacteria is established, the flora advantage of the soil is improved, peanut plants are robust, and high continuous cropping yield is achieved.
Owner:山东省雅尚名品家居有限公司
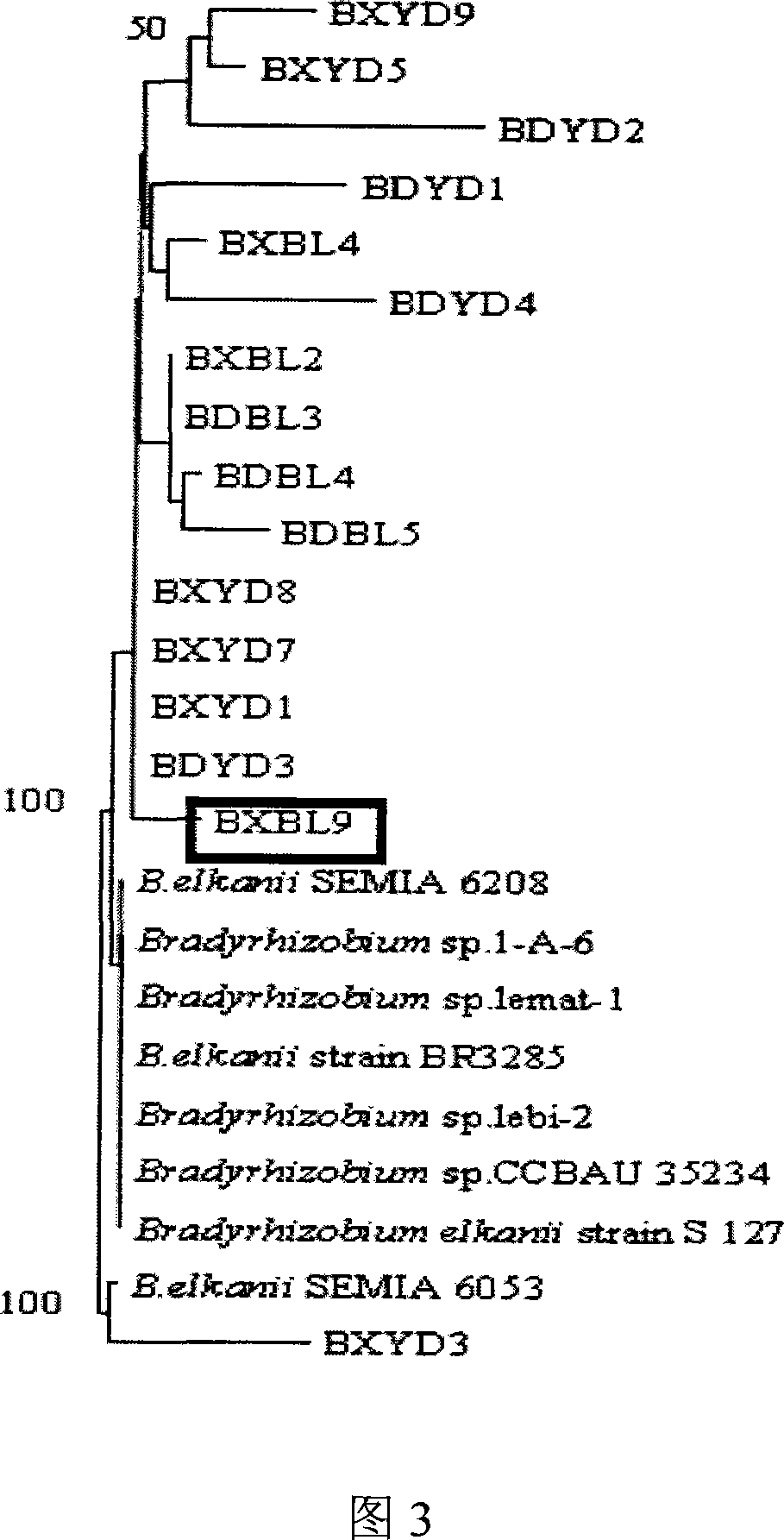
Root nodule azotobacter strain BXBL9 and uses thereof
The invention discloses a Nodule Azotobacter strain BXBL9 and the application. The strain is obtained by a way that the Rhizobia strains in the soil are respectively captured through different soybean varieties; the Rhizobia strains are separated and purified in fresh root nodules; part 16S rDNA of the strain is sequenced; the phylogenetic analysis determines that the strain is a novel Bradyrhizobium strain, which is named as Huagu 2. The Nodule Azotobacter strain BXBL9 of the invention has the characteristics of acid and aluminum tolerance and high level of nodules, which are proved by laboratory pot culture and field experiment. The inoculation of the Rhizobia strain can improve the yield of soybean more than 20 percent to 30 percent. The invention suits for the acid soil area in South China, which can be used as one of the measures for the conventional cultivation of soybean.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Treatment method of continuous cropping soil
InactiveCN107360750AImprove buffering effectAlleviate salinizationContaminated soil reclamationOrganic fertilisersContinuous croppingPlant nodule
The invention relates to a treatment method of continuous cropping soil, and belongs to the technical field of soil improvement. Harmful bacteria in the continuous cropping soil are killed by high-temperature steam treatment, then struvite, mushroom spawn culture medium waste materials, sawdust, soybean root nodule and the like are used for fermentation, nutrients are activated in the growth process of soybean rhizobia, rhizobium fertilizer is prepared, and chemical elements of N and P accumulated in the soil are activated and balanced; then activated carbon in rice husks, silicon dioxide composite dolomite, fly ash and the like are used, so that the physical properties of the fertilizer are improved, the loss of fertilizer nutrients is reduced, the utilization rate of the fertilizer is improved, the buffering performance of the soil is enhanced, harmful elements in the soil are adsorbed, heavy metal pollution of the soil is treated, soil salinity and acidification are reduced, and soil continuous cropping obstacles are overcome.
Owner:胡果青
Polymicrobial formulations for enhancing plant productivity
The present invention relates to eco-friendly compositions and methods for providing plant growth enhancing formulations comprising mixtures of microbial isolates. In particular, numerous bacterial and fungal strains were isolated from a variety of soil types, from rhizospheres and from root nodules of leguminous plants, in designed combinations, for providing plant growth and plant productivity enhancing formulations. These specifically designed polymicrobial formulations would further provide protection against plant pathogens lowering the need for nitrogen containing fertilizers, solubilize minerals, protect plants against pathogens, and make available to the plant valuable nutrients, such as phosphate, thus reducing and eliminating the need for using chemical fertilizers and chemical pesticides.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com