Sinorhizobium sp. and application thereof
A rhizobia and bacterial agent technology, applied in the direction of application, bacteria, and chemicals for biological control, etc., can solve the problems affecting alfalfa production, stress resistance, colonization ability, competition for nodulation ability, nitrogen fixation activity, symbiotic synergistic nitrogen fixation Unsatisfactory effect and other problems, to achieve good nitrogen fixation effect, enhance light and effect, and reduce pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Embodiment 1, isolation and identification of bacterial strain
[0035] 1. Isolation of strains
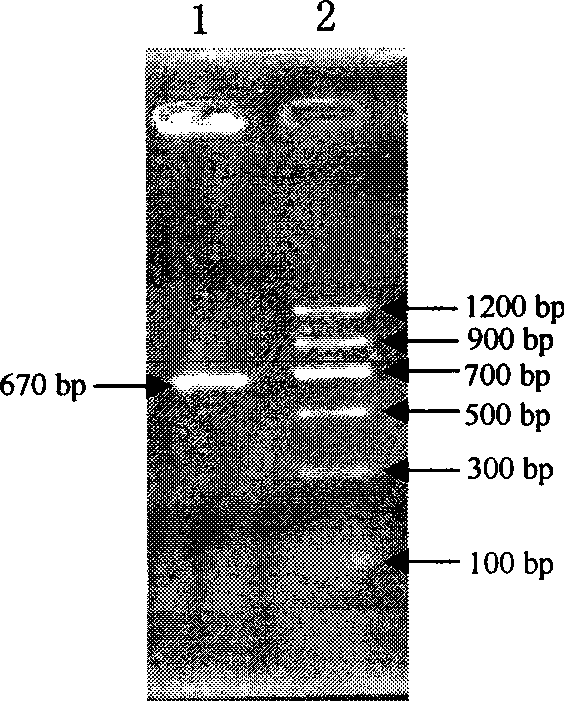
[0036] Method: From the alfalfa experimental field in Beibao, Luhua Town, Xixia District, Ningxia City, alfalfa plants growing vigorously above the ground were collected, and the nodules on the roots were observed. The pink nodules were picked and placed in small sampling bottles. Anhydrous sodium sulfate was placed at the bottom as a desiccant. After taking the root nodules back indoors, wash them three times with sterile water, disinfect the surface with 3% sodium hypochlorite for 5 minutes, and then wash them once with sterile water, then transfer the root nodules to sterilized absorbent paper, and absorb the water. Put the root nodule in a sterilized mortar and smash it, use the inoculation loop to dip its juice, and use the method of bacterial streaking to put it on the YMA crystal violet selection medium (that is, add 100,000 points on the basis of the YMA solid medi...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Embodiment 2, utilizing bacterial strain NX2004062 to cultivate 12 alfalfa varieties
[0057] 1. Preparation of bacterial agent of bacterial strain NX2004062
[0058] 1. Culture of bacteria
[0059] Streak inoculation of the cryopreserved strain NX2004062 on the slant of YMA medium, culture at 30°C for 48 hours to activate the strain; then inoculate the strain NX2004062 into a 1000ml Erlenmeyer flask containing 300ml of YMA liquid medium with 1-2% inoculation amount Medium (that is, the filling volume of the culture medium YMA is 30%), culture on a shaker, wherein the culture temperature is 28° C., the initial pH is 6.0, the speed of the shaker is 200 rpm, and the shaker culture time is 48 hours to obtain a bacterial solution.
[0060] 2. Prepare bacterial agents according to the following methods:
[0061] (1) Mix the bacterial solution obtained from the above cultivation with peat, and then absorb the bacterial solution with peat to make a powder-type bacterial agen...
Embodiment 3
[0074] Embodiment 3, utilizing bacterial strain NX2004062 to cultivate 12 alfalfa varieties
[0075] 1. Preparation of bacterial agent of bacterial strain NX2004062
[0076] 1. Culture of bacteria
[0077] Same as described in Example 2.
[0078] 2. Prepare bacterial agents according to the following methods:
[0079] (1) Mix the bacterial solution obtained from the above culture with peat, and absorb the bacterial solution with peat to make a powdered bacterial agent, and detect the effective number of viable bacteria, pH value and miscellaneous bacteria rate in the bacterial agent by plate counting. The experiment was repeated 3 times, and the results were averaged. The amount of viable bacteria in the bacterial agent was measured to be equal to 1×10 8 cfu / g peat, pH 6.8.
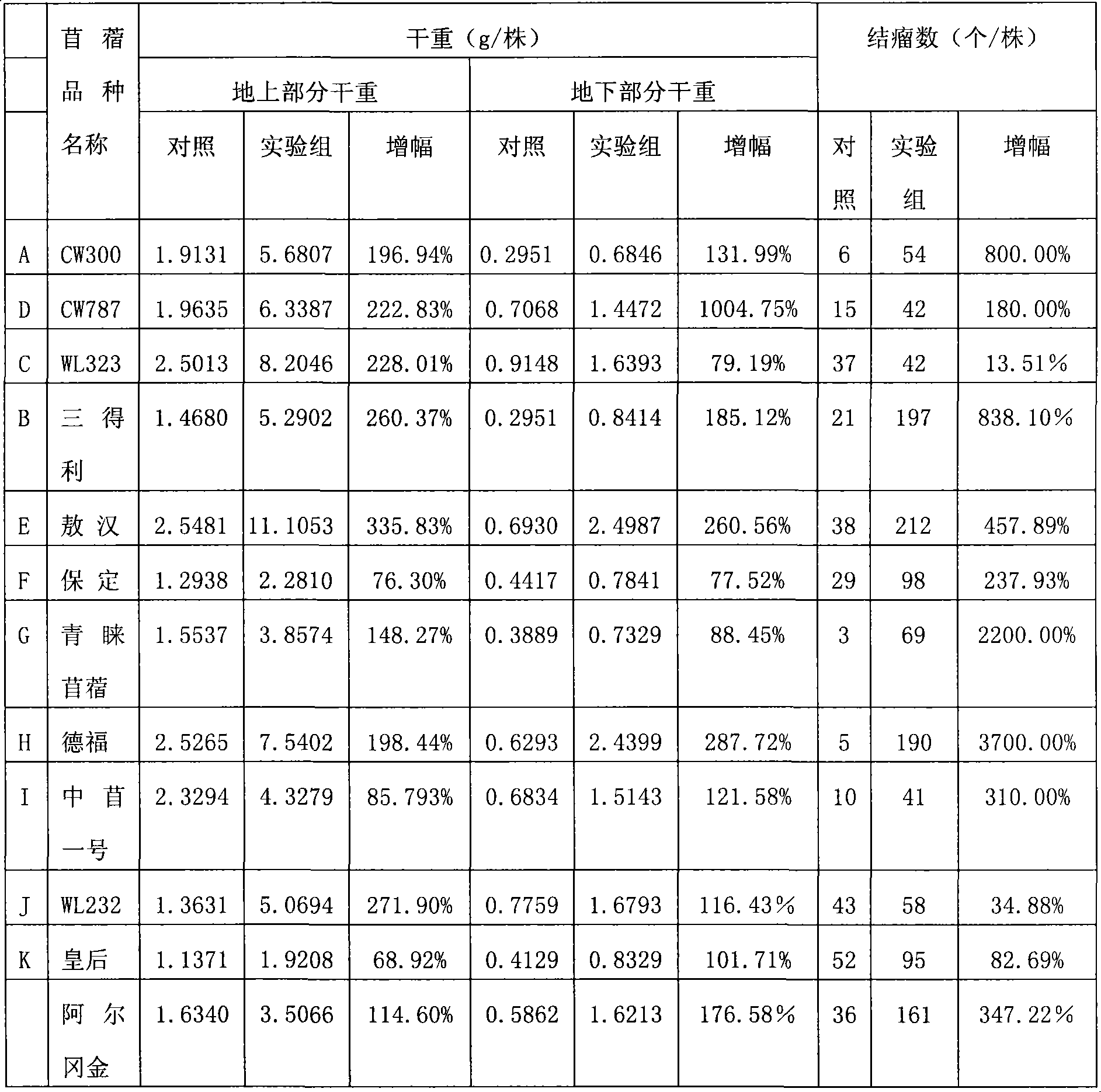
[0080] Two, utilize the bacterium agent that step 1 obtains to cultivate 12 alfalfa varieties
[0081] The names and sources of the 12 alfalfa varieties (lines) used in this experiment are the same ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com