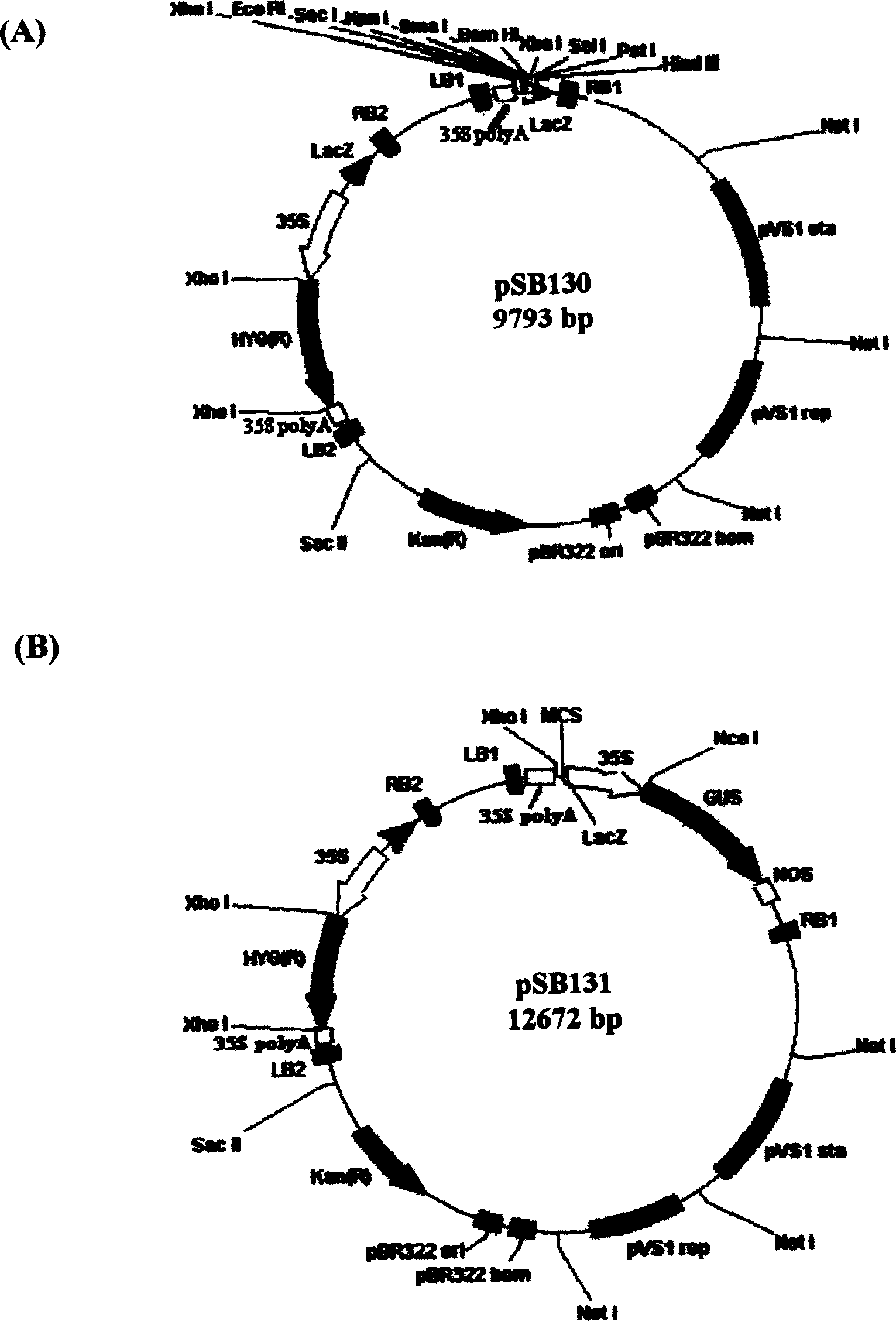
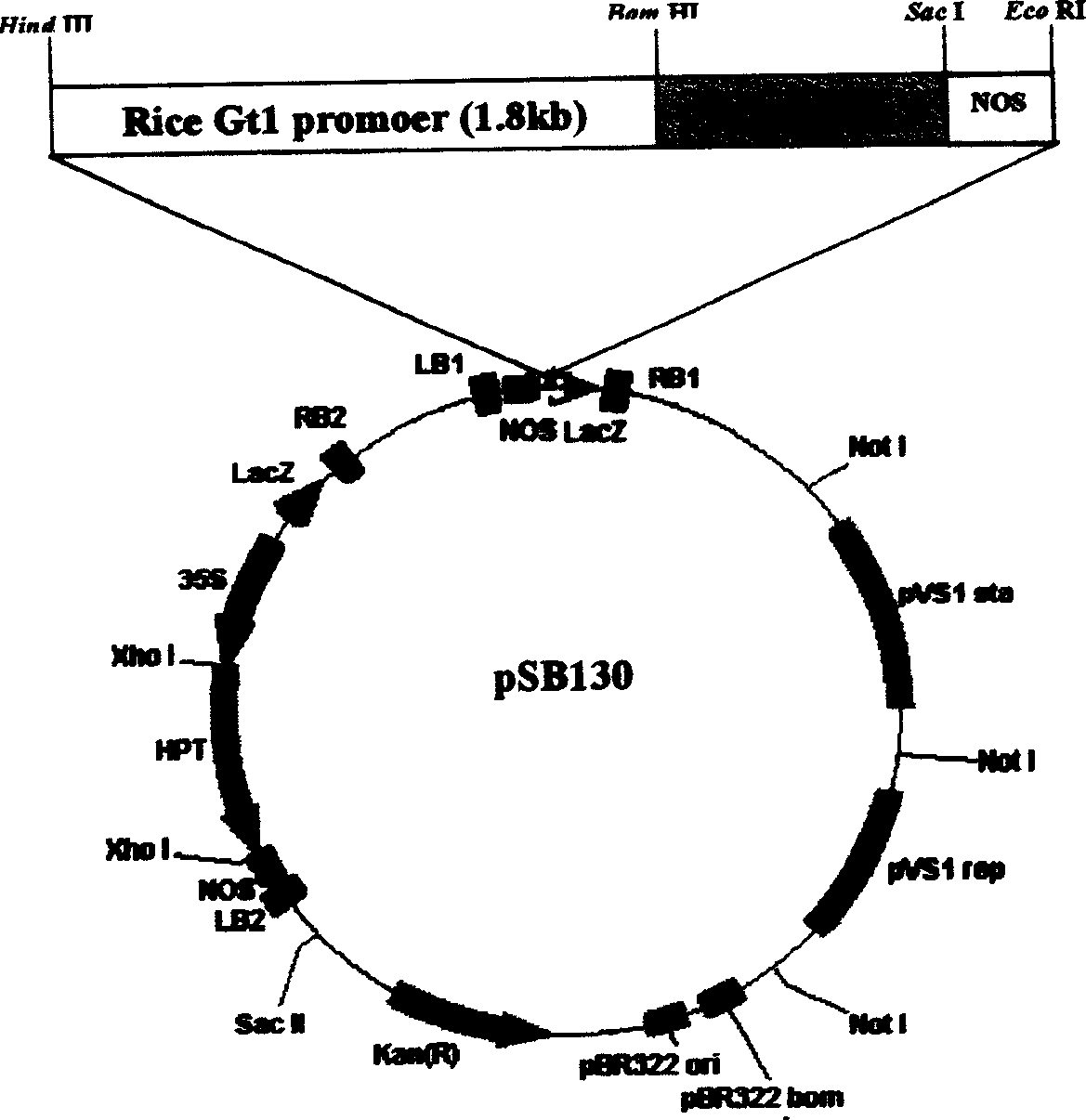
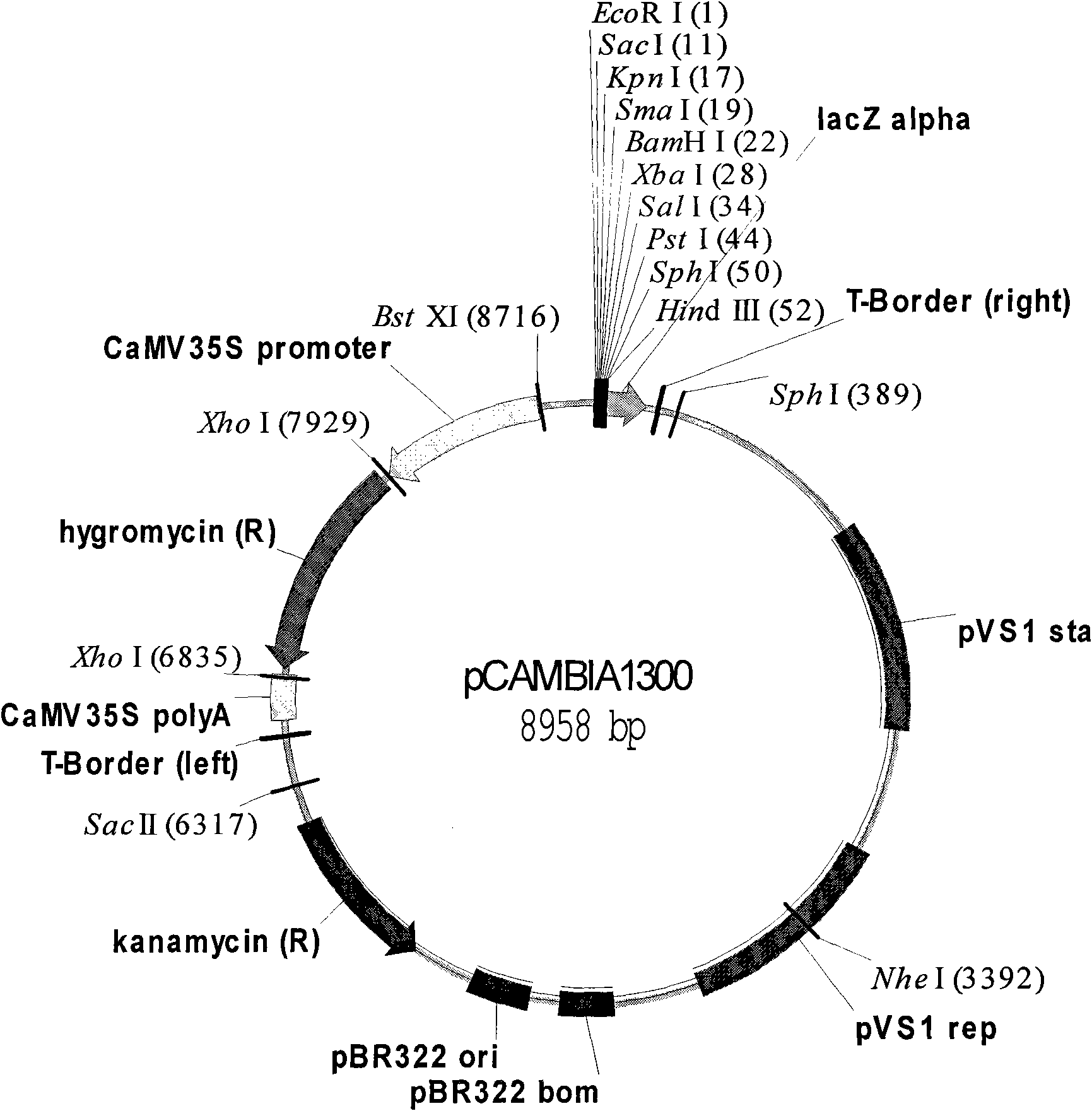
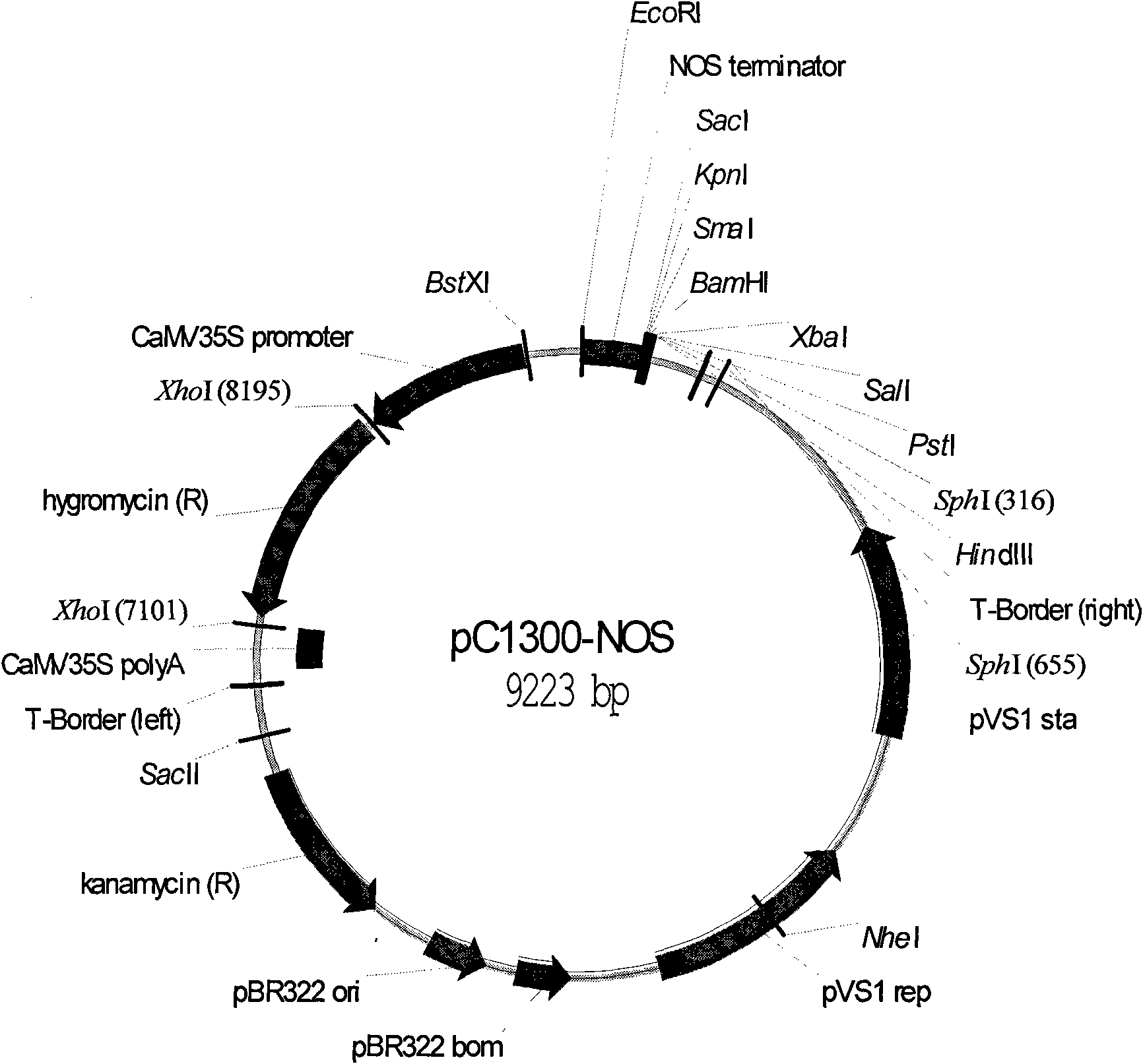
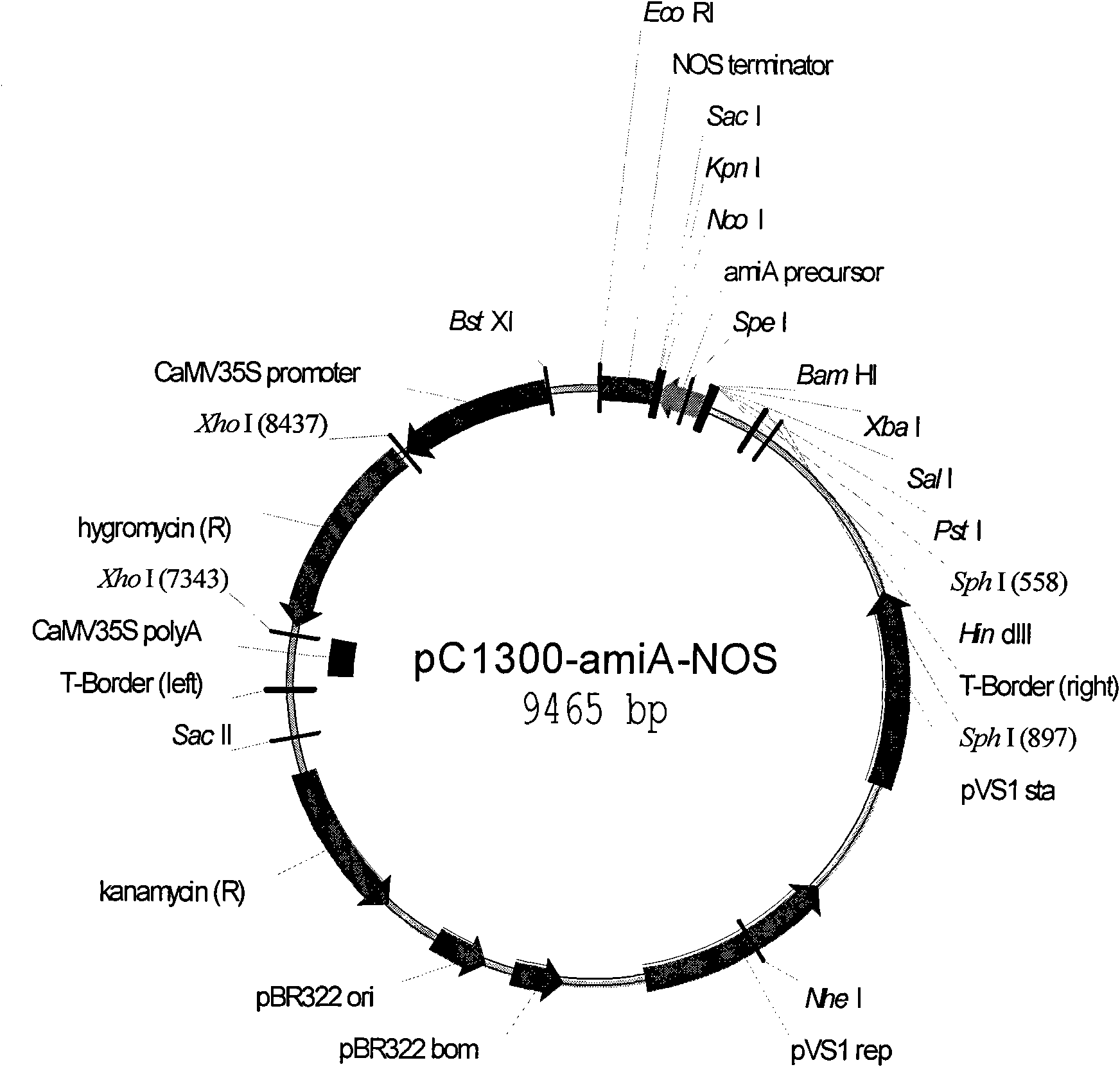
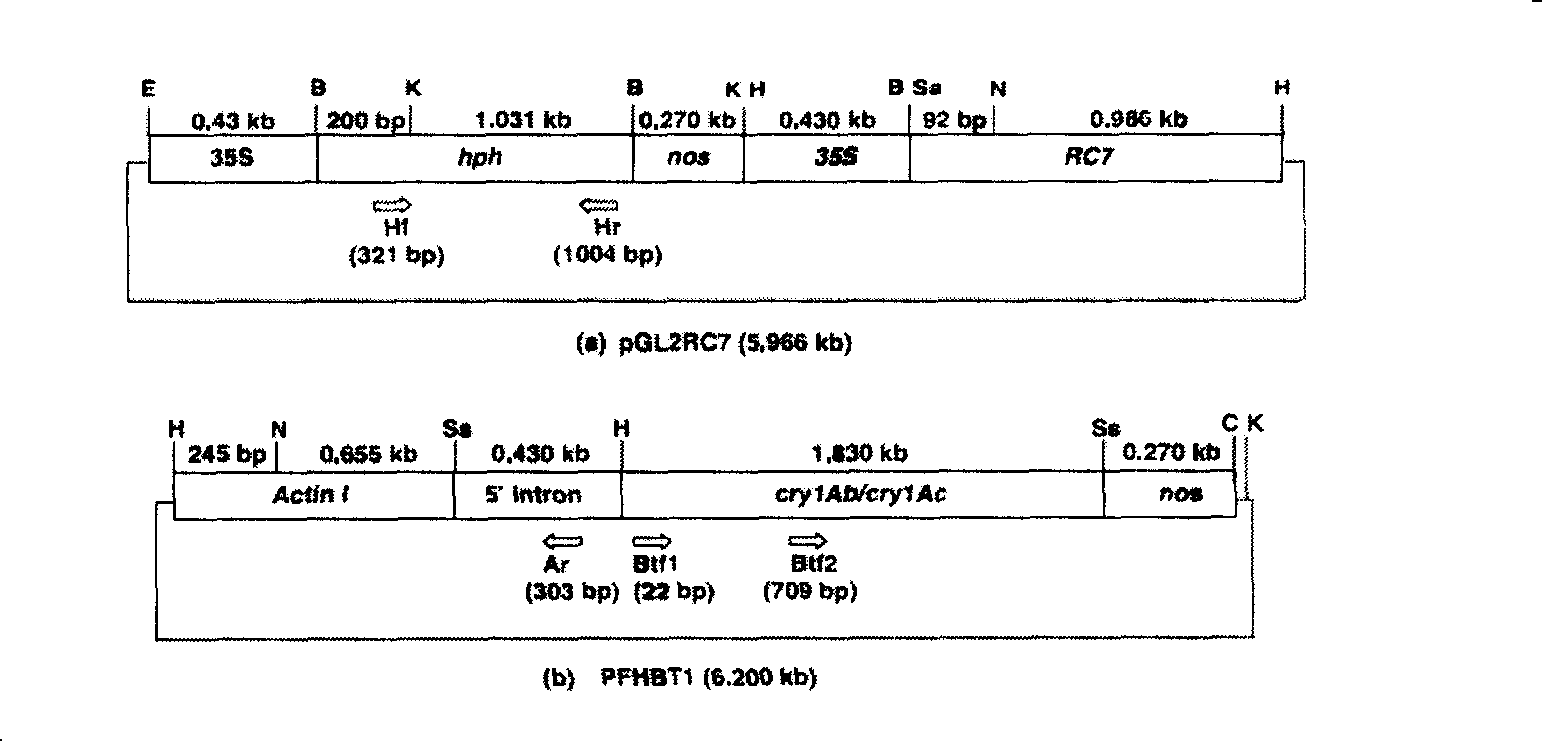
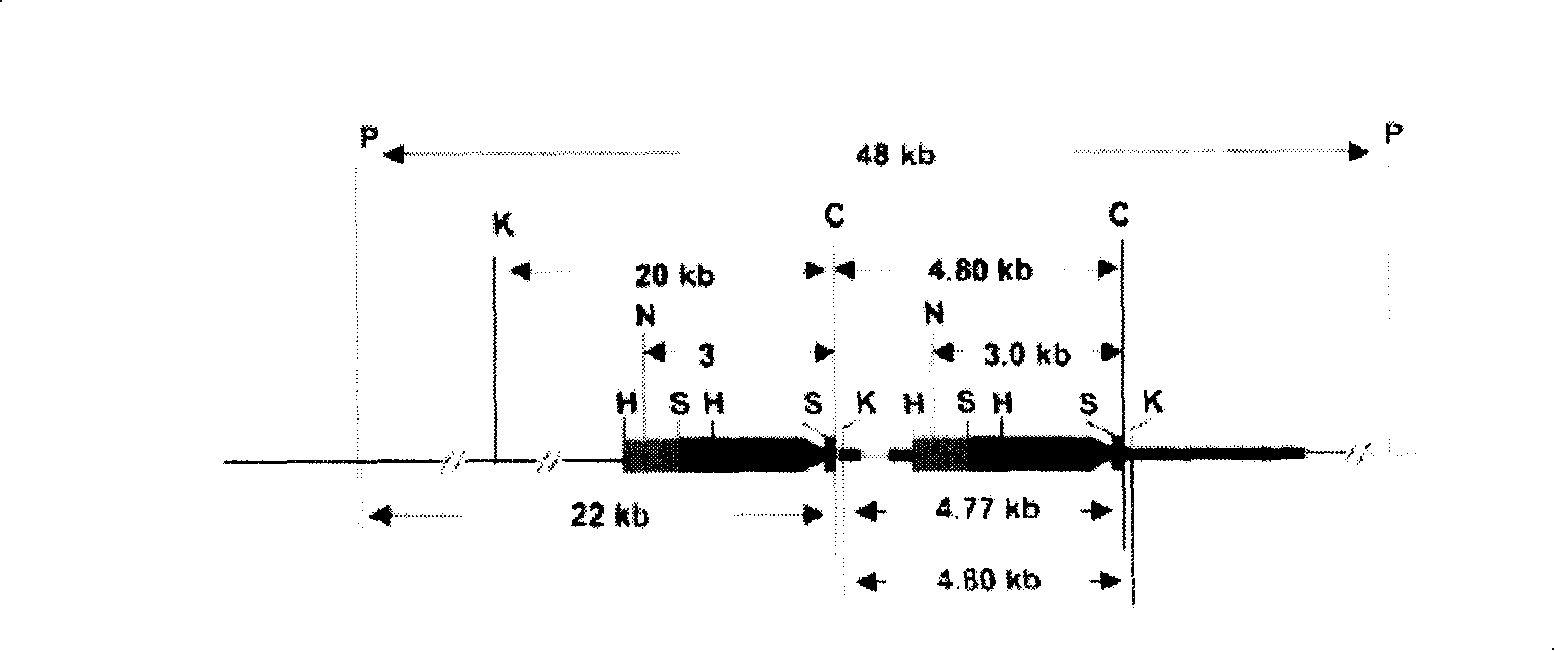
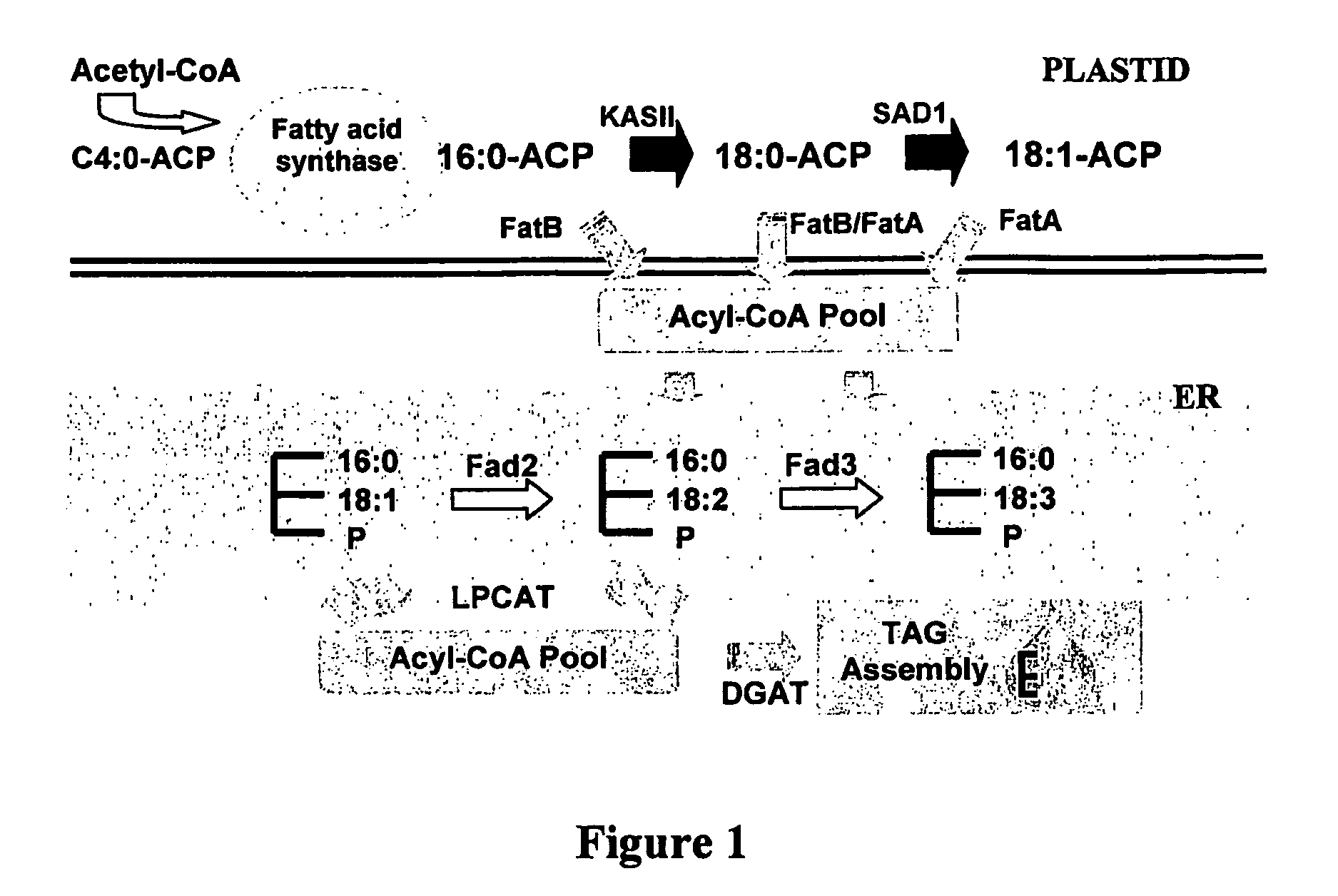
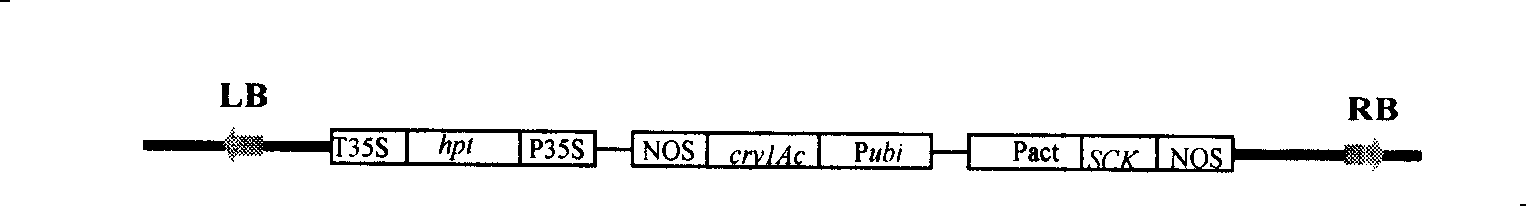
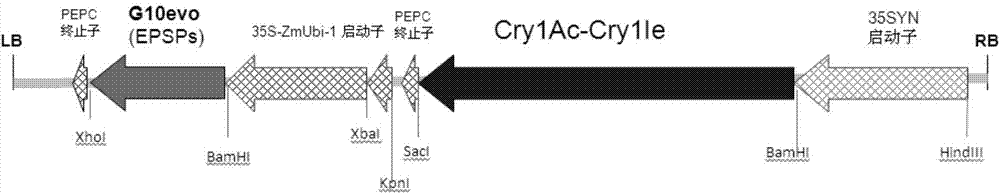
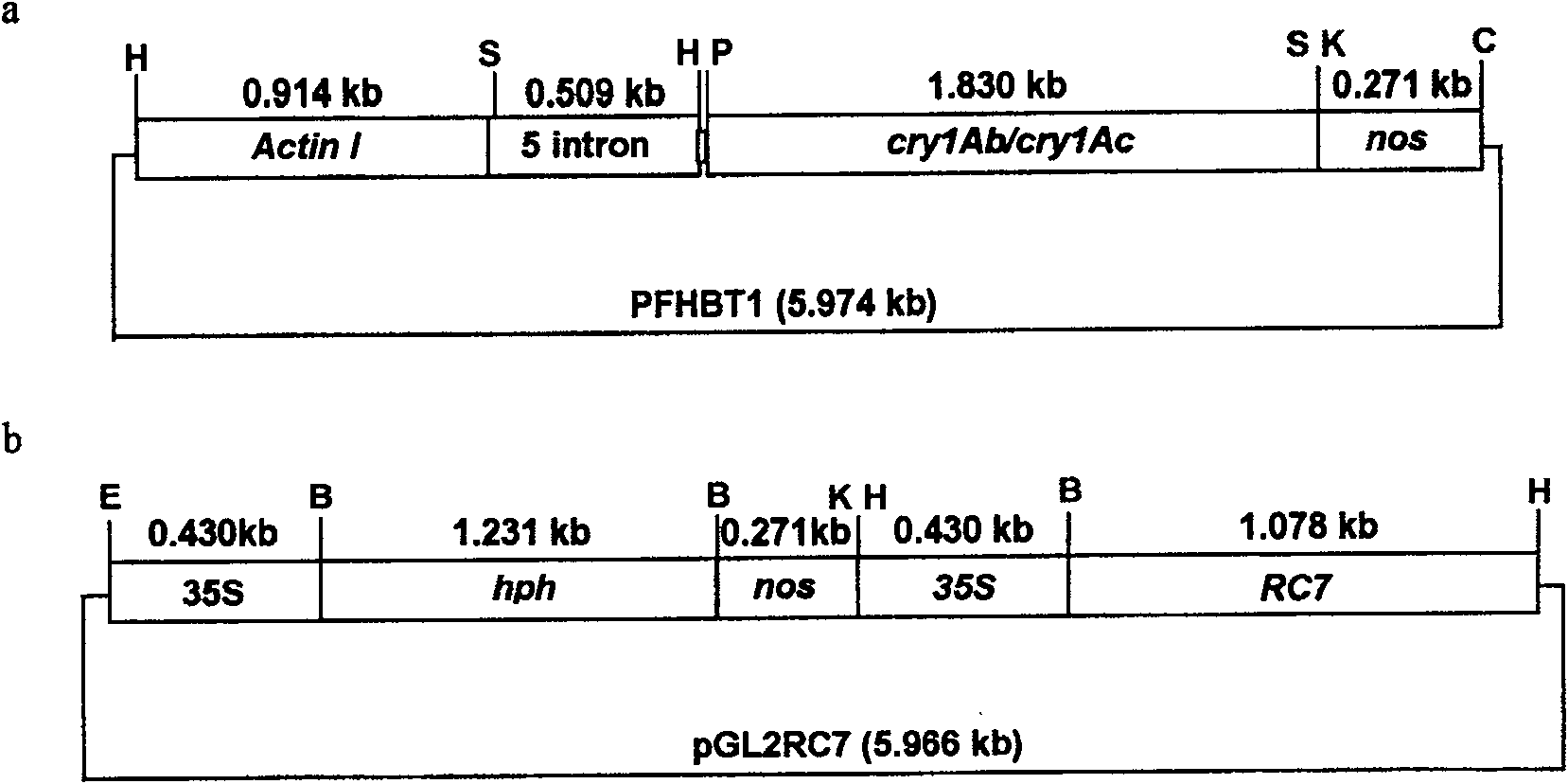
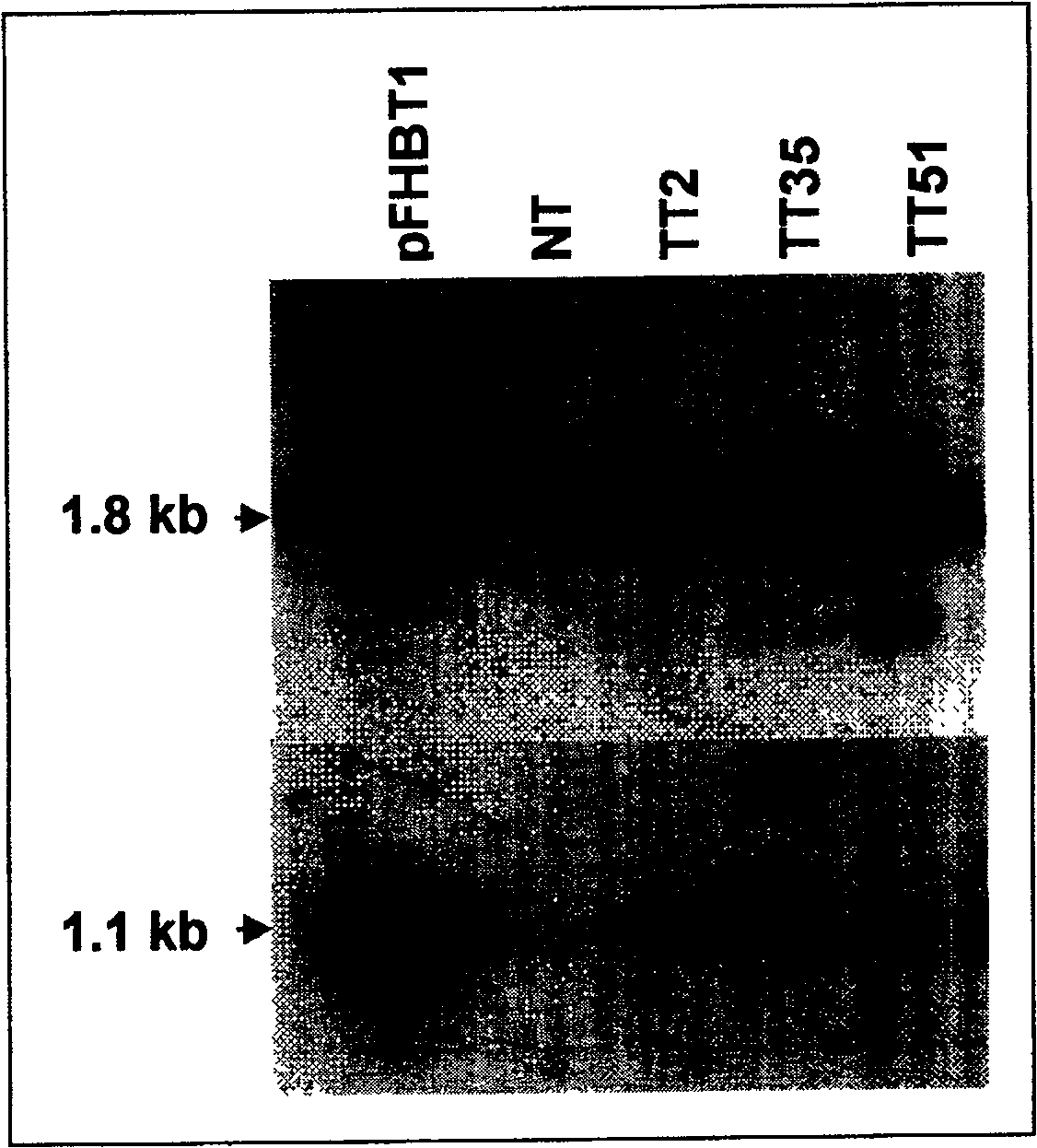
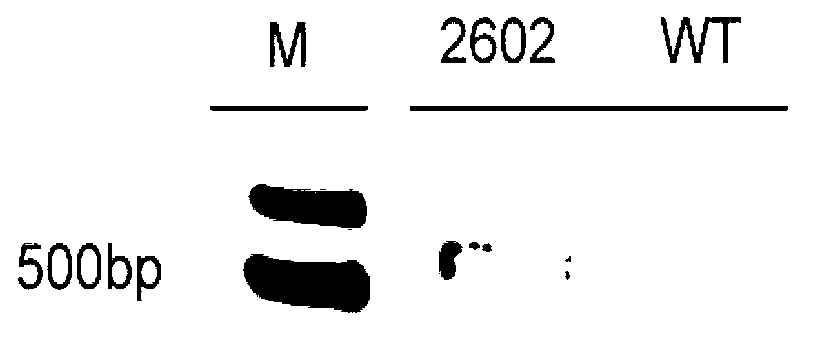Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
797 results about "Genetically modified rice" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Genetically modified rice are rice strains that have been genetically modified (also called genetic engineering). Rice plants have been modified to increase micronutrients such as vitamin A, accelerate photosynthesis, tolerate herbicides, resist pests, increase grain size, generate nutrients, flavours or produce human proteins.
Herbicide tolerant rice plants and methods for identifying same
ActiveUS20080289060A1Superior agronomic phenotypeImprove scalabilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementRice plantsGenetically modified rice
The invention provides specific transgenic rice plants, plant material and seeds, characterized in that these products harbor a specific transformation event at a specific location in the rice genome. Tools are also provided which allow rapid and unequivocal identification of the event in biological samples.
Owner:BAYER CROPSCIENCE NV
Method for deleting selection marker gene of transgenic rice
ActiveCN104846010AHigh distribution frequencyEasy to operateVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsGenetically modified ricePlant genetic engineering
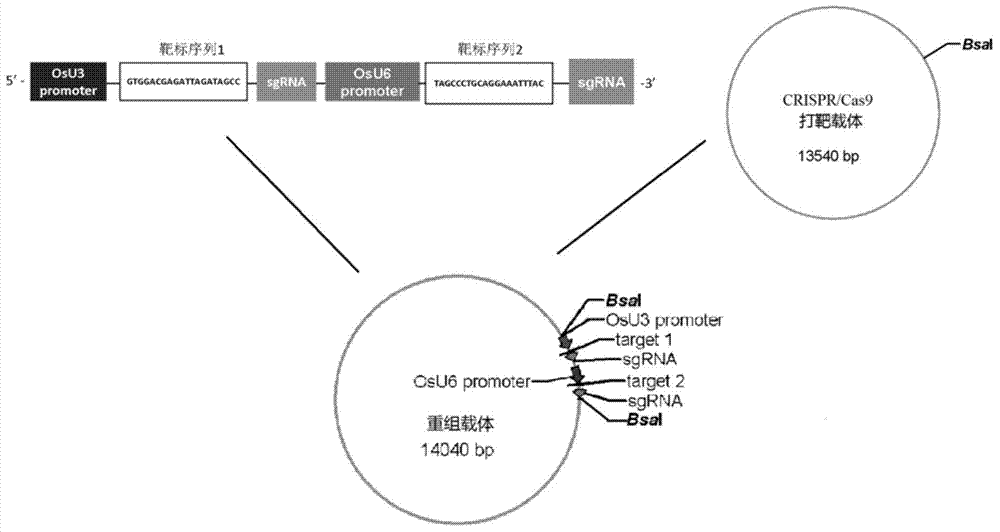
The invention provides a method for deleting a selection marker gene of transgenic rice and belongs to the field of plant gene engineering. The method for efficiently deleting the marker gene of the transgenic rice in a plant level is established by utilizing a genome fixed-point editing technology mediated by a CRISPR / Cas9 system. The whole segment of the marker gene can be effectively deleted by utilizing the method, and only an expression frame of the marker gene is deleted pointedly without change of the expression of other components in the transgenic rice. Thus, the transgenic rice without the selection marker gene can be efficiently bred by utilizing the method, so that the safety doubt of people about the selection marker gene can be completely removed.
Owner:RICE RES ISTITUTE ANHUI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Transgenic rice culture method
InactiveCN1840655APlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsGenetically modified riceAgricultural science
The provided specific site can integrates exogenous gene to stable express and affect little to the acceptor. Besides, it also provides a composite gene structure, which can be integrated by rice gene DNA sequence near specific site and DNA sequence of exogenous gene, and be used to culture new rice series by sexual hybridization and somatic hybridization.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Double T-DNA carrier and its application in cultivating of non selecting sign transgene rice
InactiveCN1597969ASmall molecular weightHigh co-transformation efficiencyFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionGenetically modified ricePlant nodule
The invention provides a simple and convenient Agrobacterium Tumefacies dual carrier containing double T-DNA structural regions, and a method of using the carrier system to cultivate transgenic rice without resistance selection label. With the help of the principle of co-conversion mediated by root nodule Agrobacterium Tumefacies, the system contains two separate T-DNA structural sections, where the first T-DNA region contains antibiotic resistance selection label gene and the second one contains a universal polyclonal site able to be arbitrarily inserted with destination gene. The double-T-DNA carrier has small molecular weight, easy to clone and after the destination gene and necessary regulation and control series are cloned in the T-DNA region containing the polyclonal site, it realizes rice co-conversion; by selfing, it selects transgenic individual with destination gene but without selectin label gene from the self-bred progeny, thus eliminating the negative effect on transgenic plant commercialized production, etc, possibly caused by selection label gene.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Method for improving rice resistance to bacterial leaf blight by using leaf specific expression artificial microRNA
InactiveCN101979548AReduce other adverse outcomesVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsGenetically modified riceDisease
The invention relates to the technical field of plant gene engineering, in particular to design, verification and application of a rice disease resistance related DNA molecule of 21nt. An artificial microRNA sequence of the 21nt is artificially designed, and an artificial microRNA precursor is constructed by using a natural microRNAosa-mi528 precursor as a skeleton. In transgenic rice, the artificial microRNA precursor is specifically expressed by using a leaf specific promoter of a rice or arabidopsis thaliana source so that the resistance of the transgenic rice to bacterial leaf blight can be enhanced and important agronomic traits of the transgenic rice such as fertility and the like is not affected at the same time.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Side sequence of exogenous insert of transgene paddy strain Bt Shanyou 63
InactiveCN101240277AMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationGenetically modified riceBiotechnology
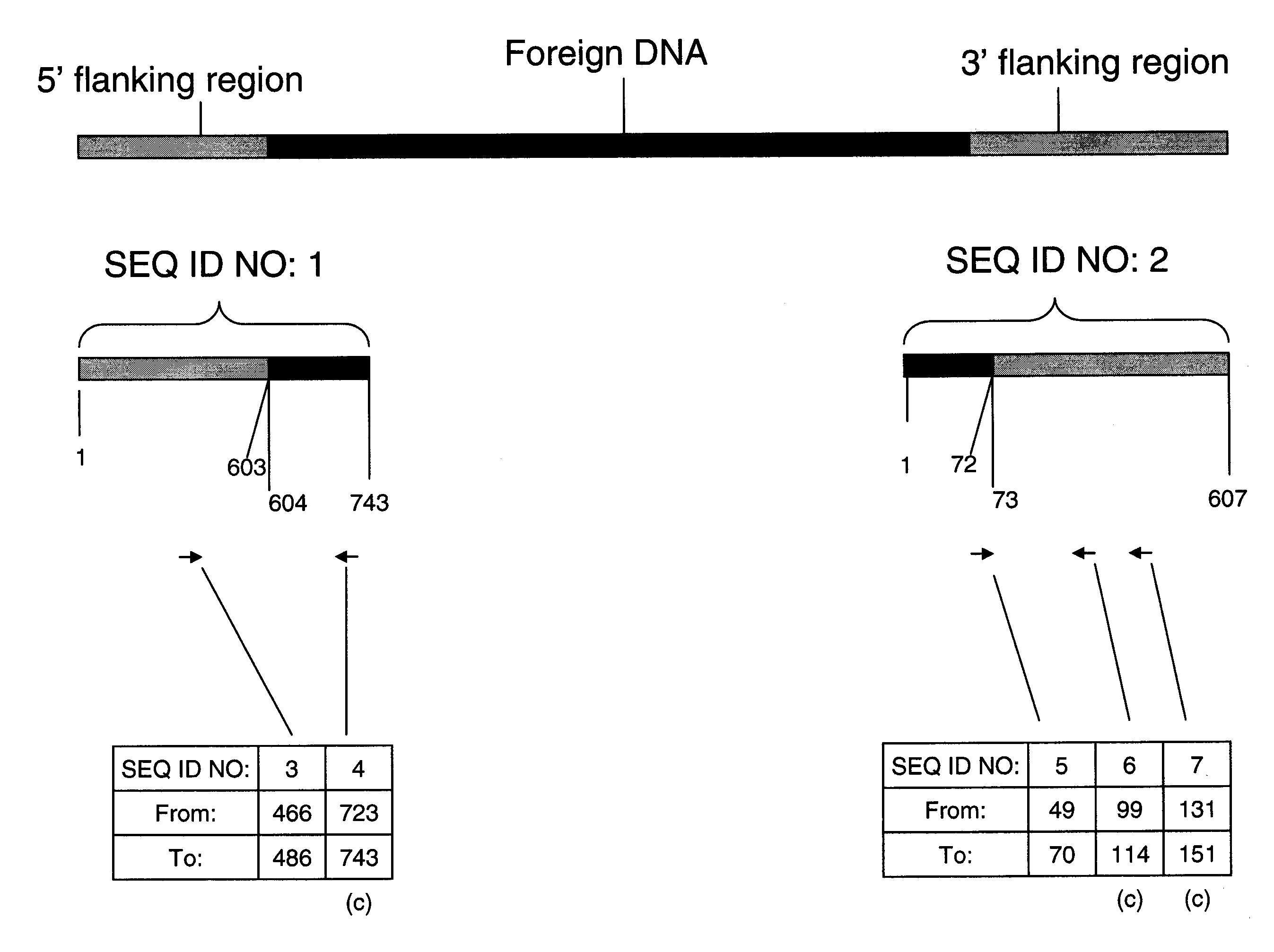
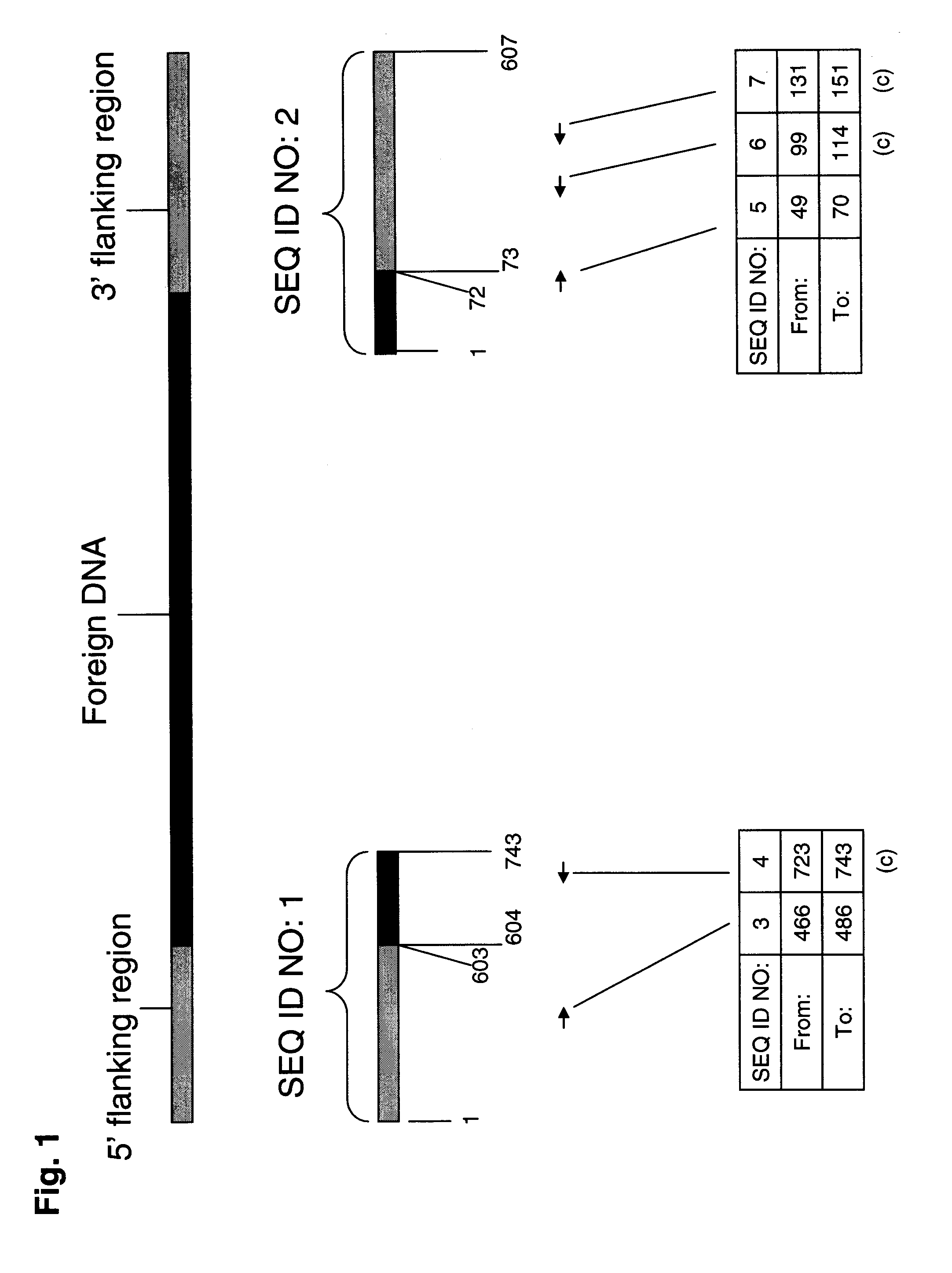
The invention relates to a side sequence of exogenous interpose fragments of transgene paddy rice line Bt SHANYOU 63. its 5' side sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO1 and its 3' side sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO2. The line specificity determine the nature and definite quantity PCR detection of sensitive idiosyncratic transgene paddy rice line Bt SHANYOU 63 is constructed by using side sequence as aim DNA amplification fragments.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Altering the fatty acid composition of rice
ActiveUS8530724B2Extended shelf lifeReduced activitySolid waste disposalMowersGenetically modified riceRice plants
The present invention relates to rice oil, rice bran and rice seeds which have altered levels of oleic acid, palmitic acid and / or linoleic acid. The present invention also provides methods for genetically modifying rice plants such that rice oil, rice bran and rice seeds produced therefrom have altered levels of oleic acid, palmitic acid and / or linoleic acid. Specifically this is achieved through modulation of Fad2 and / or FatB expression.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
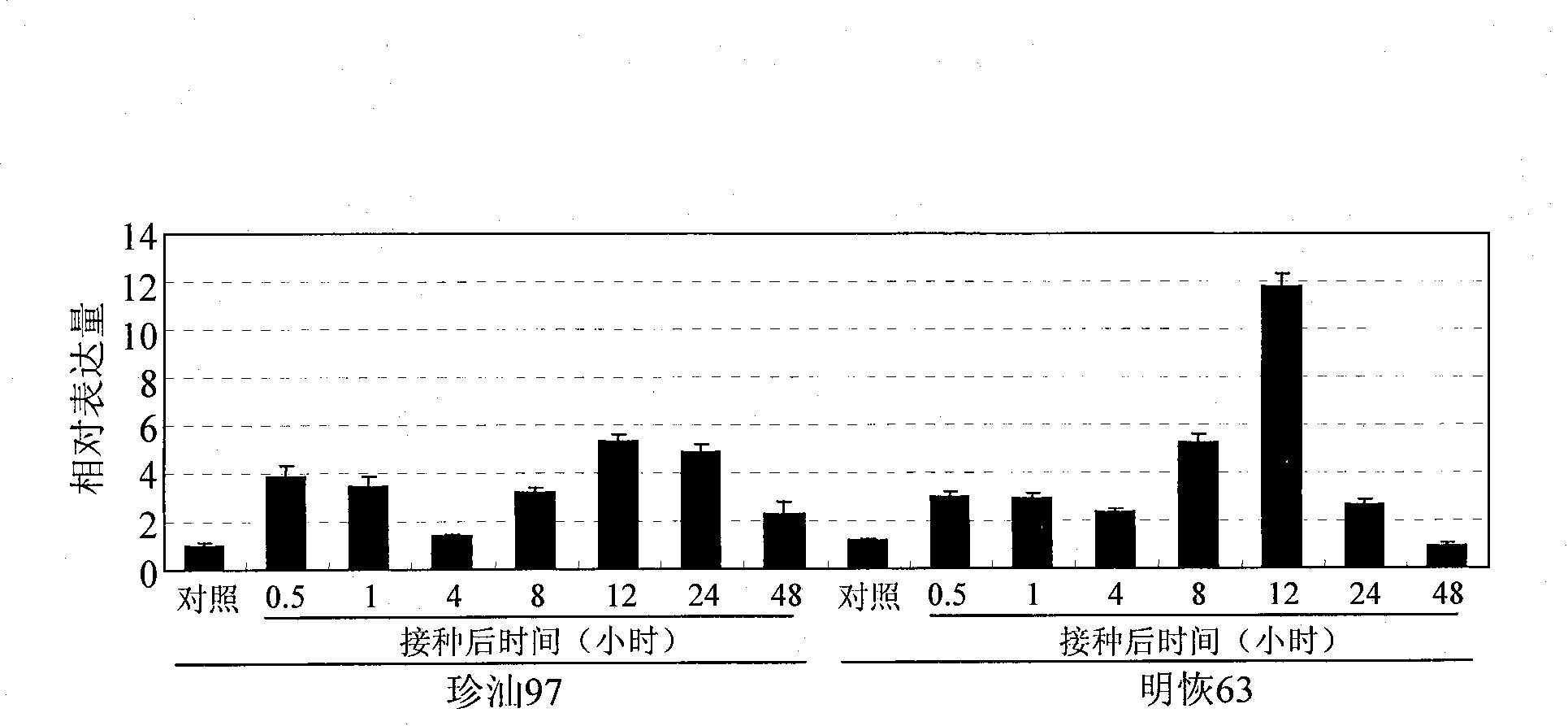
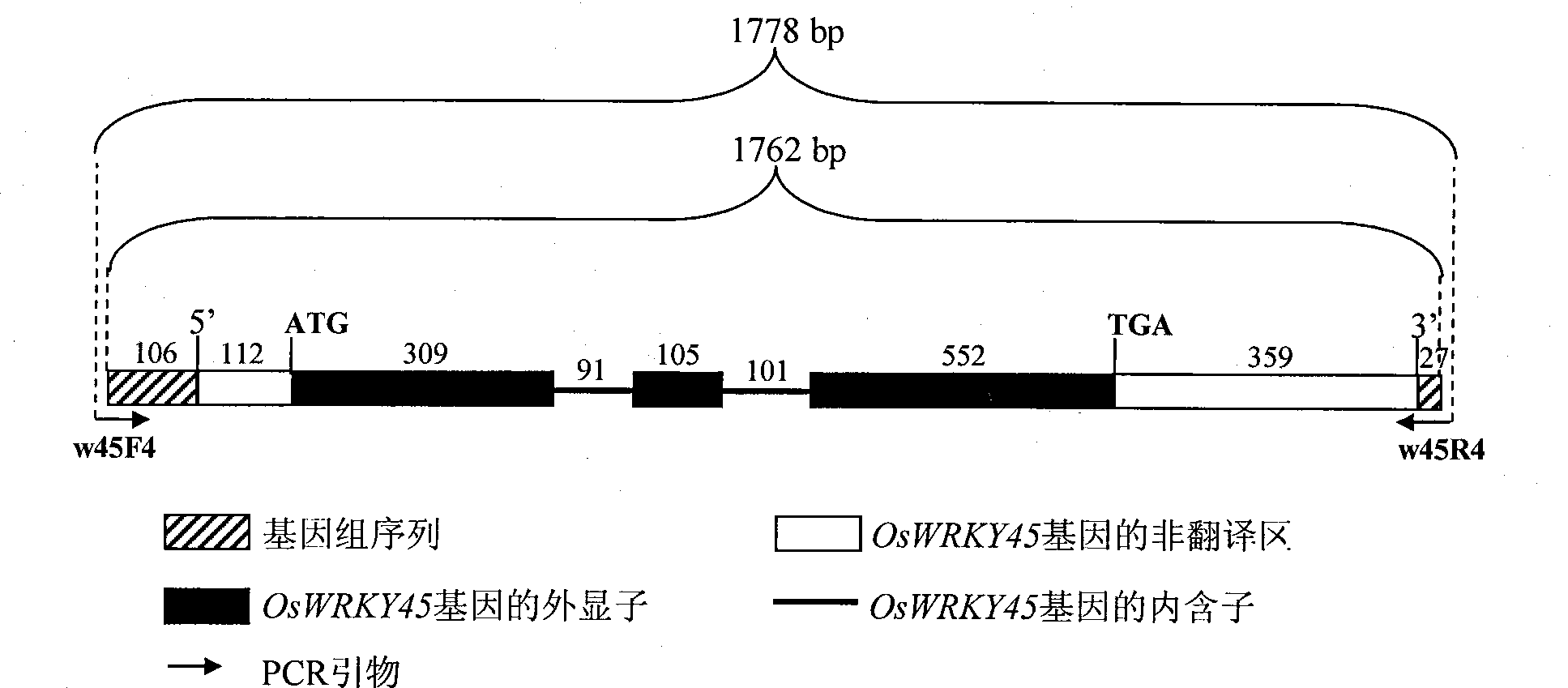
Rice disease resistance relevant gene OsWRKY45-2 and application thereof in improving rice disease resistance
InactiveCN101386856AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionGenetically modified ricePlant genetic engineering
The invention relates to the technical field of plant genetic engineering, in particular relates to isolating clone and functional verification of a DAN fragment containing a gene OsWRKY45-2 related to rice disease resistance. The gene OsWRKY45-2 codes WRKY proteinoids and can endow rice with resistance to the diseases caused by bacterial pathogenic bacteria, namely the leaf blight bacteria (Xanthomonas oryzae pv.oryzae) and fungal pathogenic bacteria, namely the rice blast bacteria (Magnaporthe grisea). The fragment and the exogenous regulatory sequence thereof are directly transferred into rice, thus the resistance capability of transgenic rice with over-expression OsWRKY45-2 against bacterial blight in and rice blast is improved remarkably.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Flanking sequence of transgenic rice Kefeng No. 6 and qualitative PCR detection method
InactiveCN101824411AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenetically modified riceAgricultural science
Owner:CHINA NAT RICE RES INST
Side sequence of exogenous insert of transgene paddy strain Kefeng 6
InactiveCN101240279AMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationGenetically modified riceBiotechnology
The invention relates to a side sequence of exogenous interpose fragments of transgene paddy rice line kefeng No.6 rice. its 5' side sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO1 and its 3' side sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO2. The line specificity determine the nature and definite quantity PCR detection of sensitive idiosyncratic transgene paddy rice line kefeng No.6 rice is constructed by using side sequence as aim DNA amplification fragments.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Exogenous insertion element flanking sequences of transgenic rice strain 223F-S21 and application thereof
InactiveCN103773759AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationGenetically modified riceBiotechnology
The invention discloses an exogenous insertion element flanking sequence of a transgenic rice strain 223F-S21, wherein the flanking sequence is a 3-end flanking sequence and is shown as SEQ ID NO. 1. The invention further discloses an exogenous insertion element flanking sequence of another transgenic rice strain 223F-S21, wherein the flanking sequence is a 5-end flanking sequence and is shown as SEQ ID NO. 2. According to the invention, the exogenous insertion element flanking sequences of the transgenic rice strain 223F-S21 are cloned for the first time, and the situation that the exogenous insertion element flanking sequences of the transgenic rice strain 223F-S21 can be used as targeted DNA amplified fragments to establish sensitive and specific the strain specific qualitative PCR of the transgenic rice strain 223F-S21 is definite. By adopting the exogenous insertion element flanking sequences cloned and separated by the invention, a transgenic-strain specific PCR detection method can be further established.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Side sequence of exogenous insert of transgene paddy strain Kemingdao 1
InactiveCN101240278AMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationGenetically modified riceBiotechnology
The invention relates to a side sequence of exogenous interpose fragments of transgene paddy rice line snout moth's larva-subduing rice. its 5' side sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO1 and its 3' side sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO2. The line specificity determine the nature and definite quantity PCR detection of sensitive idiosyncratic transgene paddy rice line snout moth's larva-subduing rice is constructed by using side sequence as aim DNA amplification fragments.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for studying metabolic difference of transgenic rice and non-transgenic rice
InactiveCN102478563AThe pre-processing process is simpleImprove reliabilityComponent separationBiotechnologyGenetically modified rice
The invention discloses a method for studying metabolic difference of transgenic rice and non-transgenic rice. The method analyzes rice seed extract with liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) technology to obtain metabolic profiling of rice, studies integral difference of metabolic profiling data between transgenic rice and non-transgenic rice by multivariate statistics method, and finds out compound with significant contribution to metabolic phenotype difference, to provide a basis for evaluation of unintended effect and safety of transgenic rice. The simple and rapid analysis method with good repeatability is suitable for batch analysis of practical samples.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Rice Cultivar Templeton
InactiveUS20110072534A1Improve nutritional qualityIndustrial useOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationGenetically modified riceOryza
A rice cultivar designated Templeton is disclosed. The invention relates to the seeds of rice cultivar Templeton, to the plants of rice cultivar Templeton, to plant parts of rice cultivar Templeton, and to methods for producing a rice plant produced by crossing rice cultivar Templeton with itself or with another rice variety. The invention also relates to methods for producing a rice plant containing in its genetic material one or more transgenes and to the transgenic rice plants and plant parts produced by those methods. This invention also relates to rice cultivars, or breeding cultivars, and plant parts derived from rice cultivar Templeton, to methods for producing other rice cultivars, lines or plant parts derived from rice cultivar Templeton, and to the rice plants, varieties, and their parts derived from use of those methods. The invention further relates to hybrid rice seeds, plants, and plant parts produced by crossing rice cultivar Templeton with another rice cultivar.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
Method of Controlling Plant Growth and Architecture by Controlling Expression of Gibberellin 2-Oxidase
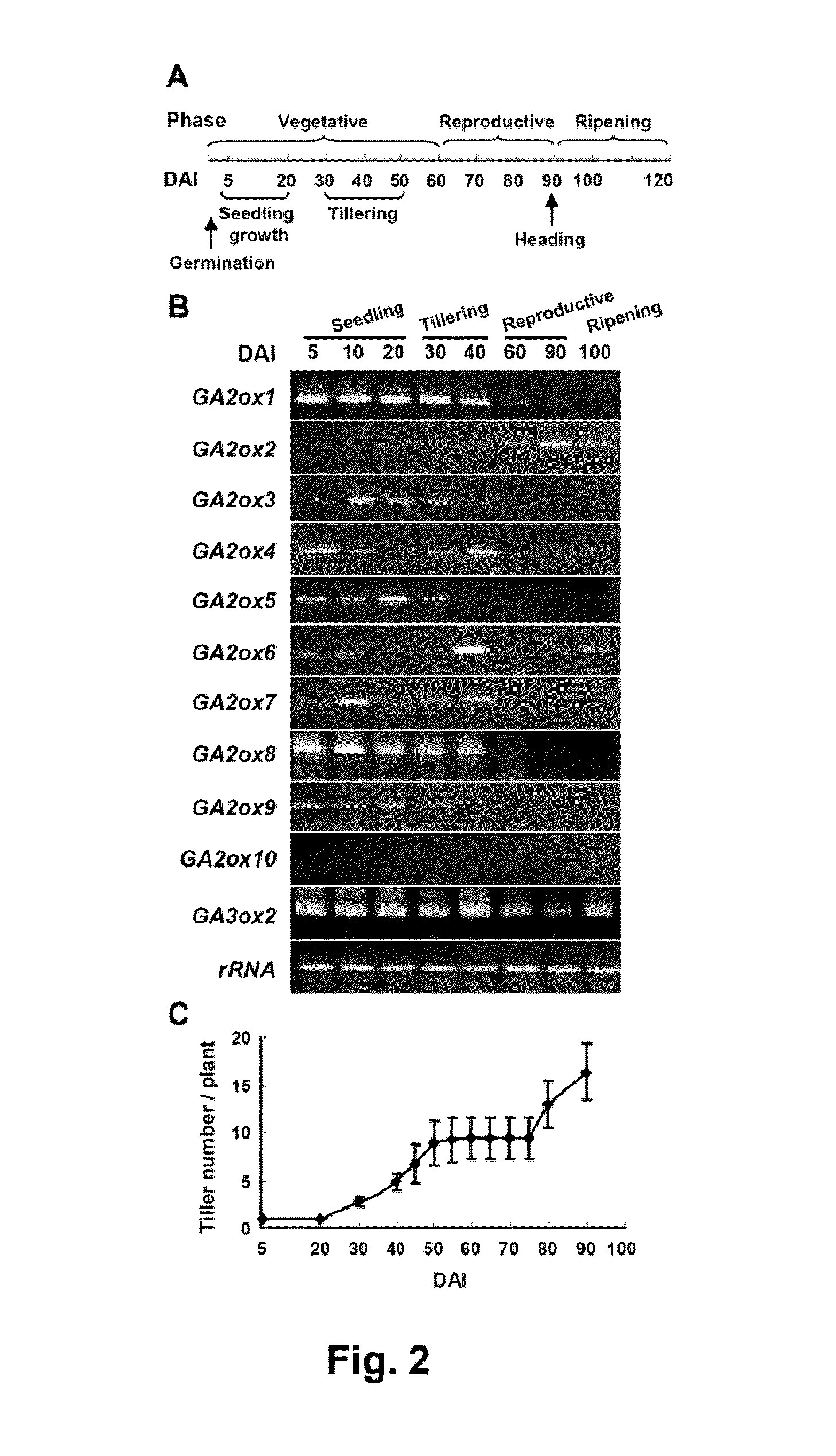
InactiveUS20100095406A1Reduce the overall heightIncrease the number ofBacteriaSugar derivativesGenetically modified riceMutant phenotype
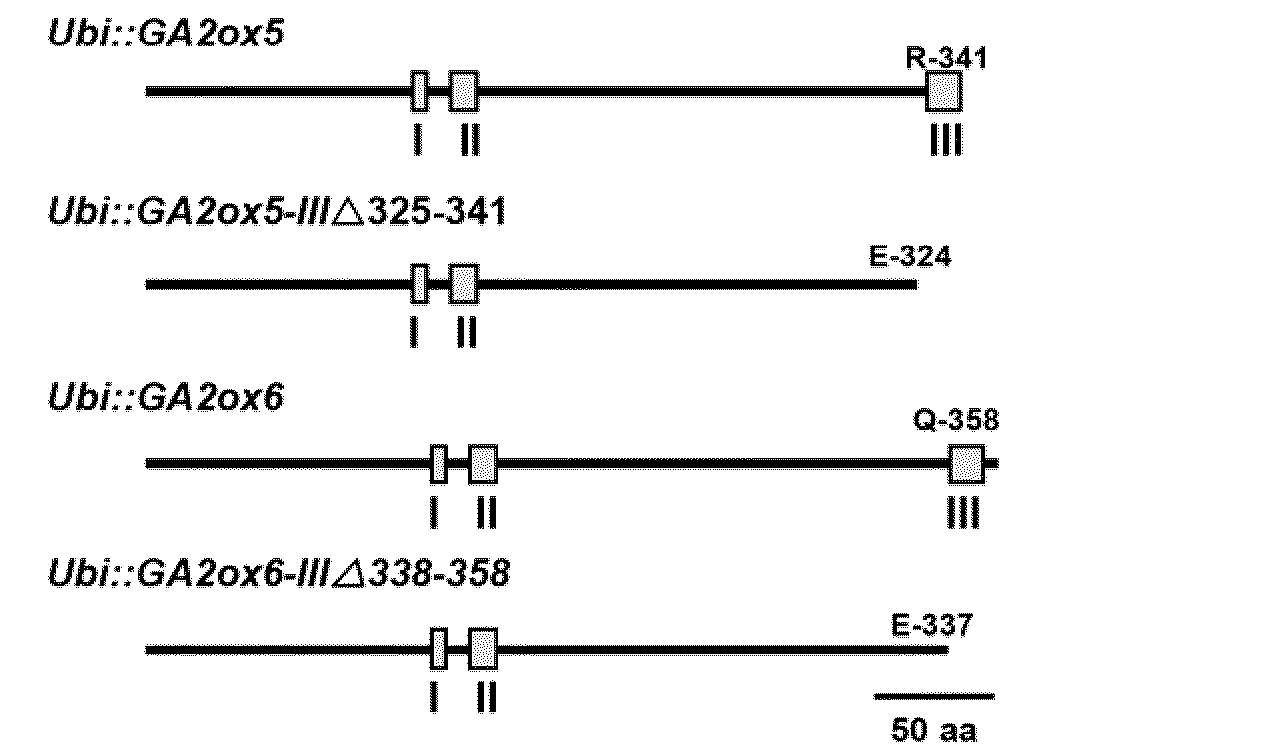
Novel gibberellin 2-oxidase (GA2ox) genes were identified. Differential expression of GA2ox genes correlated with flower development, seed germination, tiller growth and other developmental processes. In addition, the early and increased growth of tiller and adventitious root and altered root architecture caused by overexpression of GA2oxs further suggest the pleiotropic role of GA2oxs in controlling growth and architecture in plants such as rice. GA2ox5, GA2ox6 and GA2ox9 were three genes encoding class C20 GA2oxs in rice. Mutants or transgenic rice overexpressing class C20 GA2oxs exhibited a broad range of mutant phenotypes, including semi-dwarfism, increased root system and higher tiller numbers that may favor grain yield. Mutations in the conserved domain III were found to affect the physiological activity of class C20 GA2oxs. Methods are described for controlling plant growth and architecture by controlling gene expression of gibberellin 2-oxidase in the plant.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
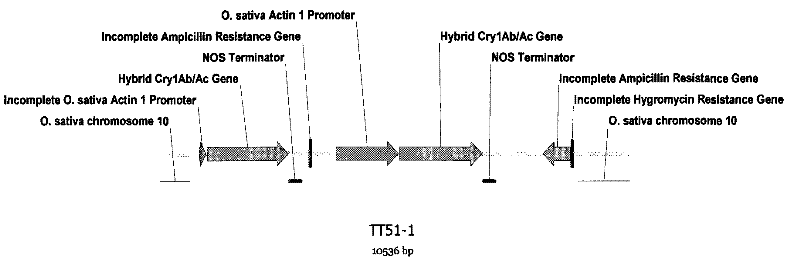
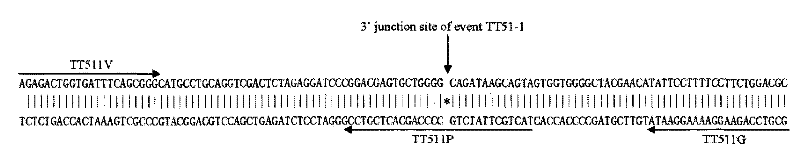
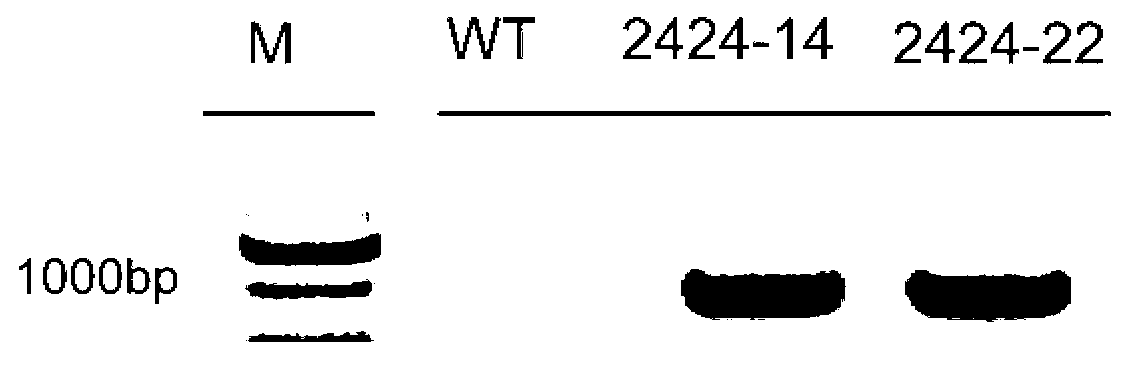
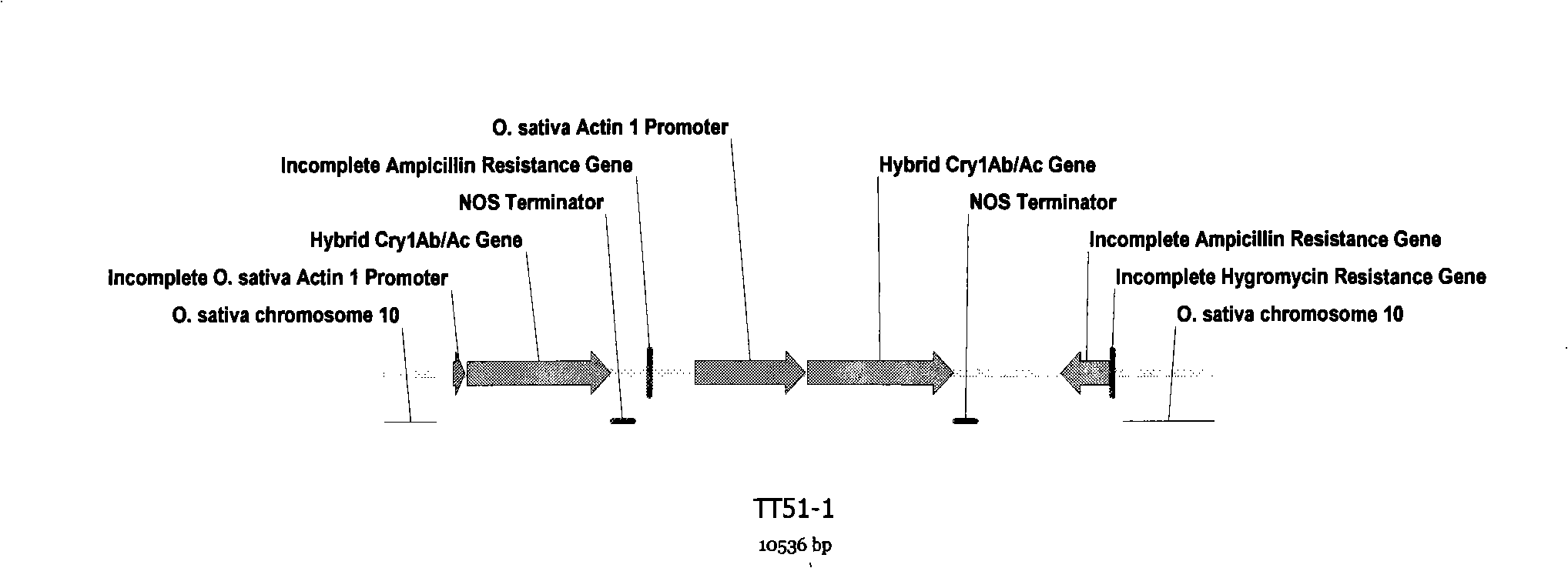
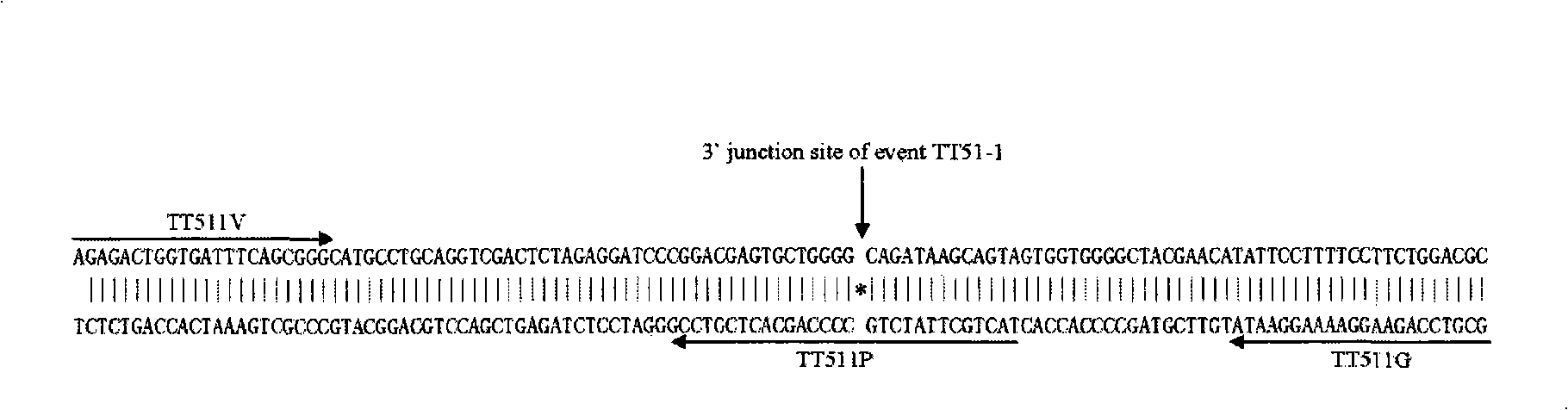
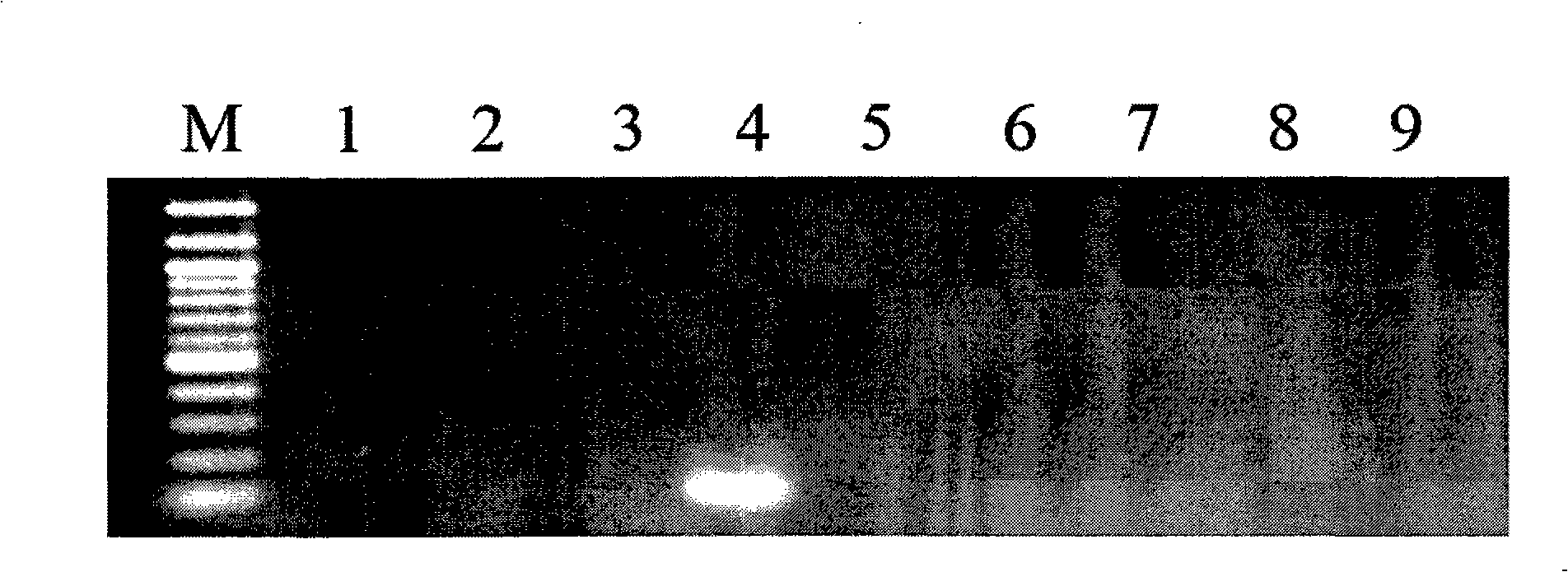
Transgenic rice TT51-1 transformation event foreign vector integration site complete sequence and use thereof
InactiveCN101302520BMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationGenetically modified riceAgricultural science
The invention discloses an event whole sequence with an integration site of a foreign vector transferred by transgenic paddy rice TT51-1 and application of the event whole sequence, relating to safety evaluation and detection of transgenic paddy rice in the biological engineering technical field. The invention uses transgenic insect-resistant rice variety TT51-1 as a material, extracts a gene group DNA as a template, and divides into four sections to enlarge TT51-1 event whole sequence containing a side paddy rice gene group sequence which is shown in SEQ NO.1, and the whole sequence is formed commonly by a basic group of between first and 673rd from the paddy rice gene group, a basic group of between 674th and 9364th from a vector sequence and a basic group of between 9365th and 10536th from the paddy rice gene group; the whole sequence is applicable to carrying out detection, monitoring and safety management of the transgenic paddy rice TT51-1(including parent strain, hybridism F1 and later generation) and products (including plant, tissue, paddy, rice and products thereof).
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Modified glyphosate-resistant gene and glyphosate-resistant rice cultivation method
InactiveCN107129993AIncrease resistanceAgronomic traits do not changeMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesGenetically modified riceAgricultural science
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant gene engineering, in particular to a modified glyphosate-resistant gene and a glyphosate-resistant rice cultivation method and comprises modification of glyphosate genes, building of plant expression vectors of the glyphosate-resistant gene and a glyphosate-resistant transgenosis rice cultivation method. Artificially-synthesized modified glyphosate-resistant gene serves as a target gene, the sequence of the gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, and the target gene is led into rice receptors by an agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated transformation method to obtain high glyphosate-resistant transgenosis rice GT28. the glyphosate-resistant gene of GT28 is recombined by the aid of sexual hybridization and somatic hybridization technique to obtain new rice germplasm, and new glyphosate-resistant varieties (strains) of rice are cultivated.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Application of synthetic transcription factor VP64-Os03g57670
ActiveCN103214581AChange traitsEnhanced coercion capabilitiesBacteriaHybrid peptidesGenetically modified riceSequence motif
The invention provides an application of a synthetic transcription factor VP64-Os03g57670. The synthetic transcription factor is constructed by fusing a transcription factor activated sequence motif VP64 (namely four transcription factor activated sequence motifs VP16) and paddy transcription factor Os03g57670 gene, and is converted to the paddy, so as to change the grain characteristic of paddy, so that the transgenic paddy seed is remarkably shorter, wider, and lighter in thousand seed weight, and paddy blade is crimped, therefore, the paddy has a better market application prospect.
Owner:CROPEDIT BIOTECHNOLOGY INC
Transgenic rice culture method
InactiveCN100582223CHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureGenetically modified riceAgricultural science
The provided specific site can integrates exogenous gene to stable express and affect little to the acceptor. Besides, it also provides a composite gene structure, which can be integrated by rice gene DNA sequence near specific site and DNA sequence of exogenous gene, and be used to culture new rice series by sexual hybridization and somatic hybridization.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
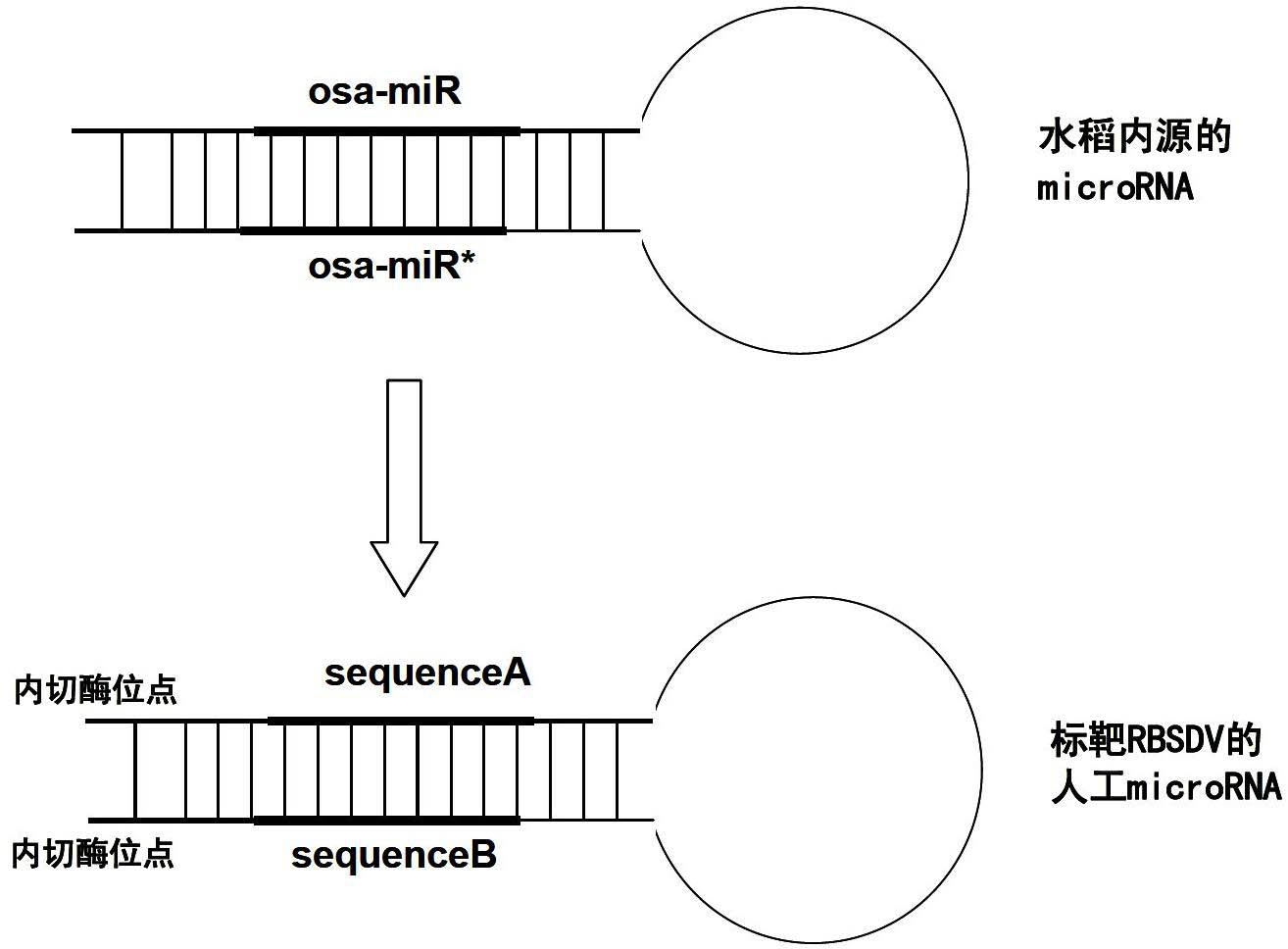
Method for enhancing black streaked dwarf resistance of paddy rice by using artificial microRNA (micro Ribonucleic Acid) and special double chain RNA thereof
InactiveCN102676510AIncrease resistancePopular fastVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsGenetically modified riceDisease
The invention discloses a method for enhancing black streaked dwarf resistance of paddy rice by using an artificial microRNA (micro Ribonucleic Acid) and a special double chain RNA thereof. The double chain RNA consists of a sequence A and a sequence B. The method comprises the following steps of: replacing a mature body sequence of an entogenous microRNA of paddy rice and an inverse complementary sequence of a mature body thereof respectively by the sequence A and the sequence B; simultaneously, designing a restriction enzyme cutting site and a protecting basic group on 5' and 3' of the microRNA, and obtaining an artificial microRNA vector through artificial synthesis; and transferring the vector into a plant expression vector with a strong promoter through restriction enzyme ligation, and introducing the plant expression vector into paddy rice to obtain transgenic paddy rice which is resistant to black streaked dwarf. The disease resistance of paddy rice is enhanced through an artificial microRNA technology, target missing is prevented, high safety is achieved, and the disease-resistant property can be inherited stably.
Owner:山东省农业科学院高新技术研究中心
Oryza officinalis anti-Xanthomonas oryzae major gene Xa3/Xa26-2 and application for improving disease resistance of rice thereof
The invention relates to the technical field of the plant genetic engineering, in particular to the isolation and cloning and functional verification of the DNA fragment of oryza officinalis anti-Xanthomonas oryzae major gene Xa3 / Xa26-2. The Xa3 / Xa26-2 gene is used to code the leucine-rich protein kinase protein. The Xa3 / Xa26-2 gene ensures that rice can resist diseases caused by bacterial pathogen-Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. The DNA fragment and the regulatory sequence thereof are directly transferred in rice, and the resistance capability to Xanthomonas oryzae of the transgenic rice carrying Xa3 / Xa26-2 is significantly enhanced.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
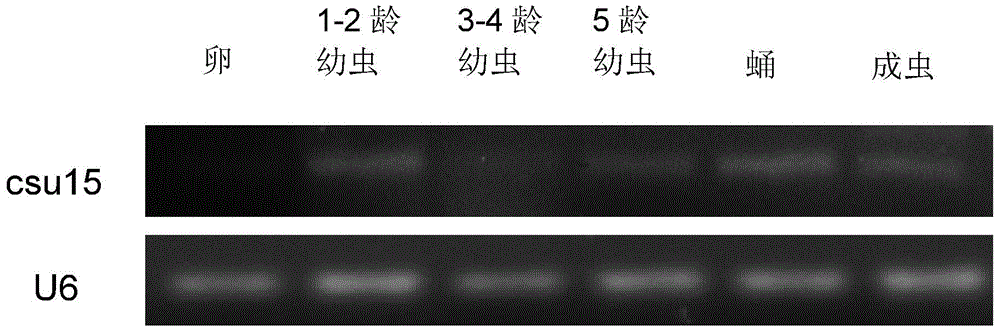
Application of Chilo suppressalis endogenesis small RNA in rice inset resistance improvement
InactiveCN104673827AIncreased metabolic burdenSmall gene fragmentFermentationPlant genotype modificationGenetically modified riceA-DNA
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene engineering, in particular relates to application of Chilo suppressalis (Walker) endogenesis small RNA in rice inset resistance improvement, and aims to verify the function and study the application of an obtained Chilo suppressalis endogenesis small RNA sequence. By means of high-flux small RNA sequencing and bioinformatics analysis, a DNA sequence of Chilo suppressalis endogenesis small RNA csu-15, and the nucleotide sequence of the DNA sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO:1. The sequence of csu-15 is adopted to establish an artificial microRNA (amiRNA) expression carrier and convert rice. The in-vitro stalk insect inoculation experiment shows that Chilo suppressalis growth can be remarkably inhibited in transgenic rice.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Corn CCCH-type zinc finger protein, and encoding gene ZmC3H54 and application thereof
InactiveCN104829700AIncreased sensitivityIncreased ability to tolerate droughtFungiBacteriaGenetically modified riceNucleotide
The invention discloses a corn CCCH-type zinc finger protein, and an encoding gene ZmC3H54 and an application thereof. An amino acid sequence of the corn CCCH-type zinc finger protein is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 in a sequence table. The nucleotide acid sequence of the encoding gene ZmC3H54 of the corn CCCH-type zinc finger protein disclosed by the invention is as shown in SEQ ID NO.2 in the sequence table. The invention further discloses a recombinant carrier, a recombinant bacterium, a transgenic cell line or an expression cassette containing the encoding gene ZmC3H54. The ZmC3H54 gene disclosed by the invention participates into stress response, so that the resistance to abiotic adversity stress of a plant can be improved; a transgenic plant has relatively high sensitivity on ABA; the tolerance of transgenic rice on drought is improved; the family gene is separated and cloned from corn; and the developing function of the family gene in the aspect of improving the stress resistance of a target plant is identified.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Use of UDPG pyrophosphorylase in rice
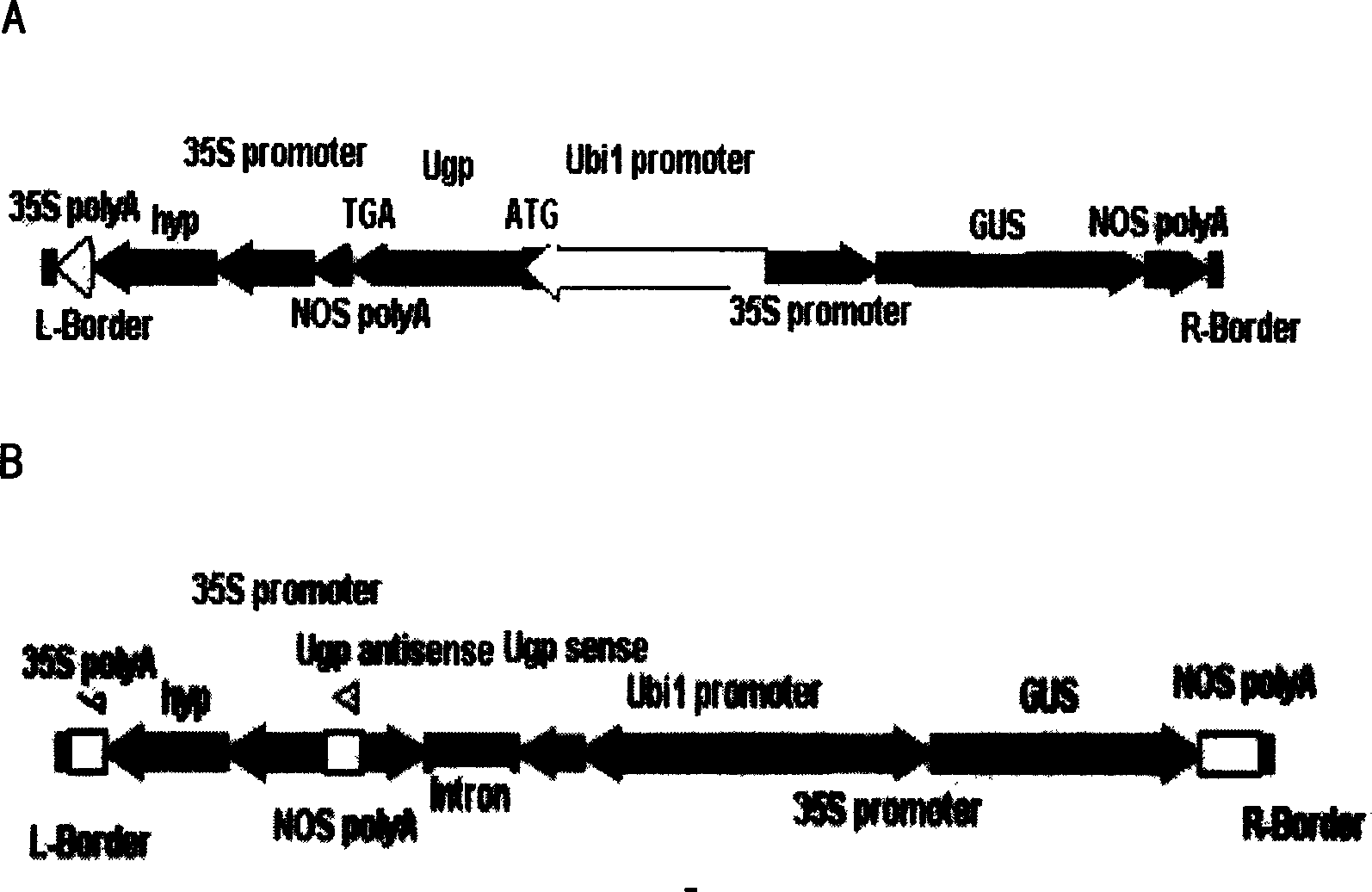
InactiveCN1614023APromote growthGrow moreFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionGenetically modified riceUridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase
The invention was involved in the application of uridine 5'diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase gene in the rice field. Uridine 5'diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase gene was connected with intensified or inhibited expression vector, which was intensified or, inhibited and transferred expression vector into rice, then, uridine 5'diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase gene in rice was intensified or inhibited. The rice that was intensified by uridine 5'diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase gene had rapid growth, long ears, many seeds and high yields per plant, while the rice that was inhibited by uridine 5'diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase gene showed that male sterility was barren and its pollen was with 100% sterility. It was with self-sterility while cross was normal. The invention was found to provide a new path for improving rice species applying uridine 5'diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase gene.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Preparation method of glyphosate resistant transgenic rice
InactiveCN104004781AReduce the number of copiesShort processPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsMolecular identificationGenetically modified rice
The invention provides a preparation method of glyphosate resistant transgenic rice. The method comprises the following steps: converting an expression vector containing glyphosate resistant gene into Agrobacterium tumefaciens, invading rice calluses by the Agrobacterium tumefaciens, transferring the calluses to a selective aluminum containing glyphosate for screening, choosing resistant calluses, differentiating, rooting, hardening-seedling, and transplanting to obtain glyphosate resistant transgenic rice. A molecular identification result shows that an exogenous gene is stably expressed. The obtained glyphosate resistant transgenic rice contains glyphosate herbicide resistant gene, contains no other screening marker genes, and can be used as a commercial herbicide resistant rice kind to reduce the reduce the later process and accelerate the breeding pace. The method has the advantages of simple operation, low copy number of transgenic plants, stable heredity properties, and good market application prospect.
Owner:CHINA NAT SEED GRP
Method and uses for expressing polypeptide in endosperm using cereal non-storage protein as fusion vector
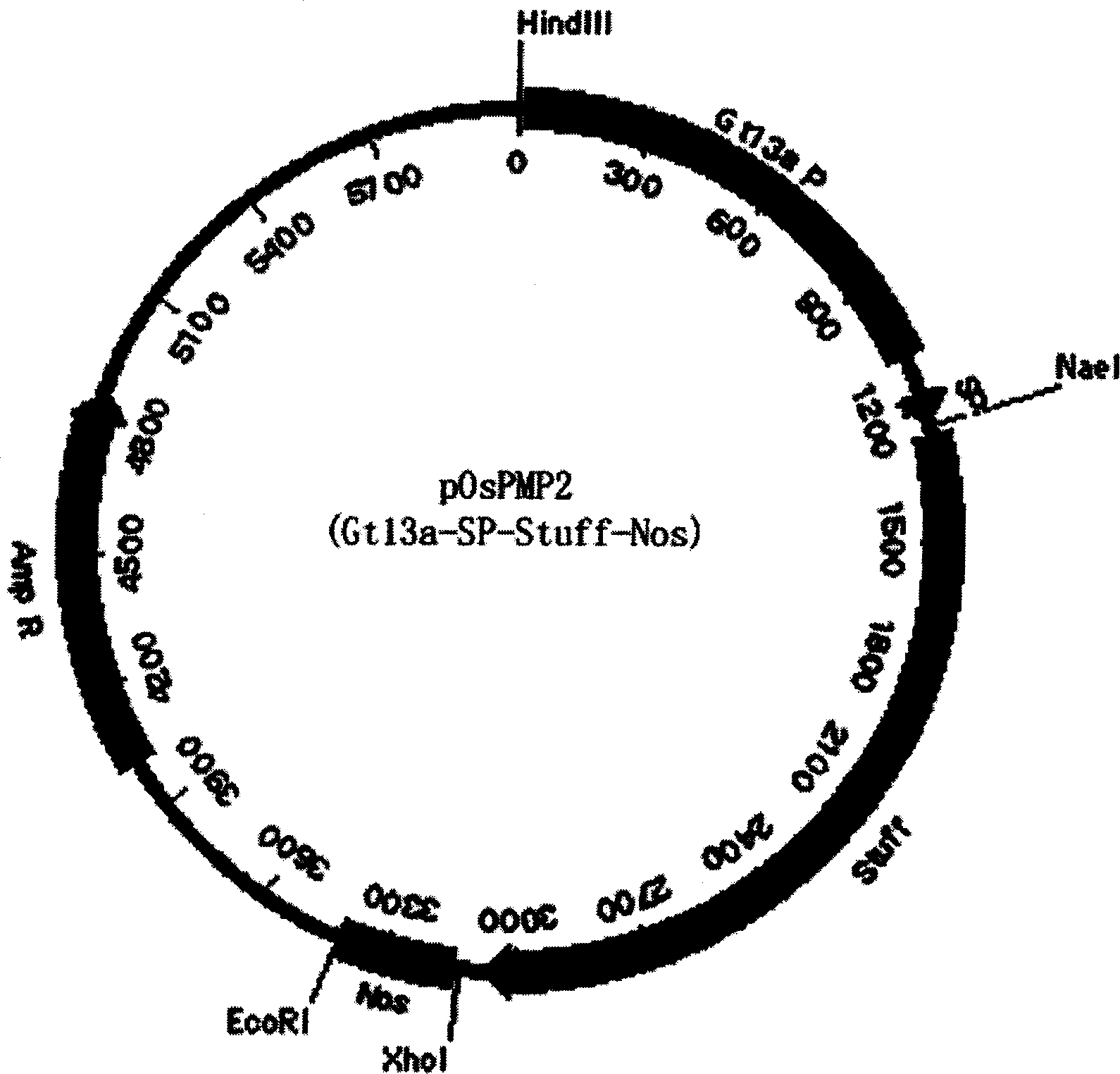
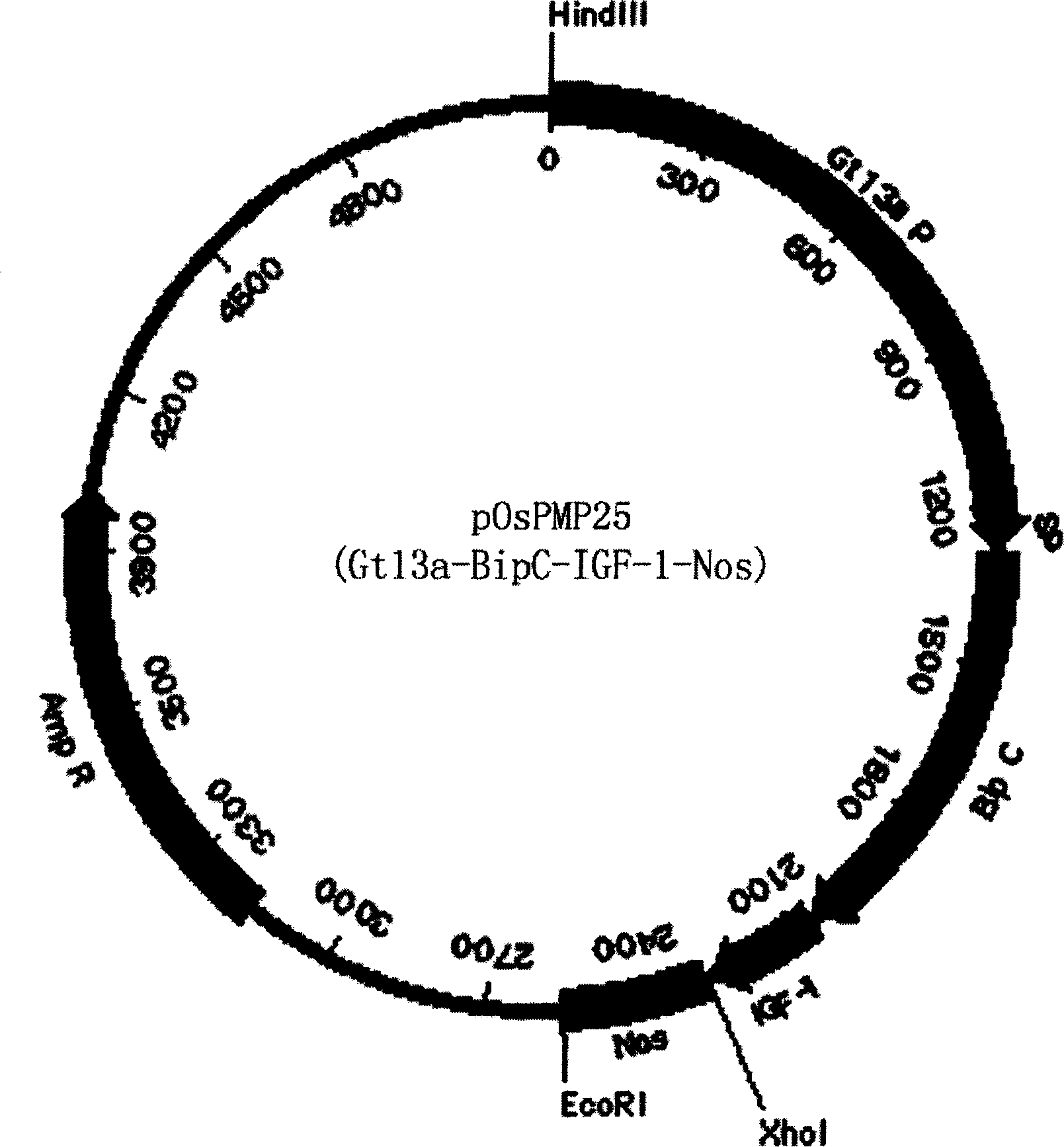
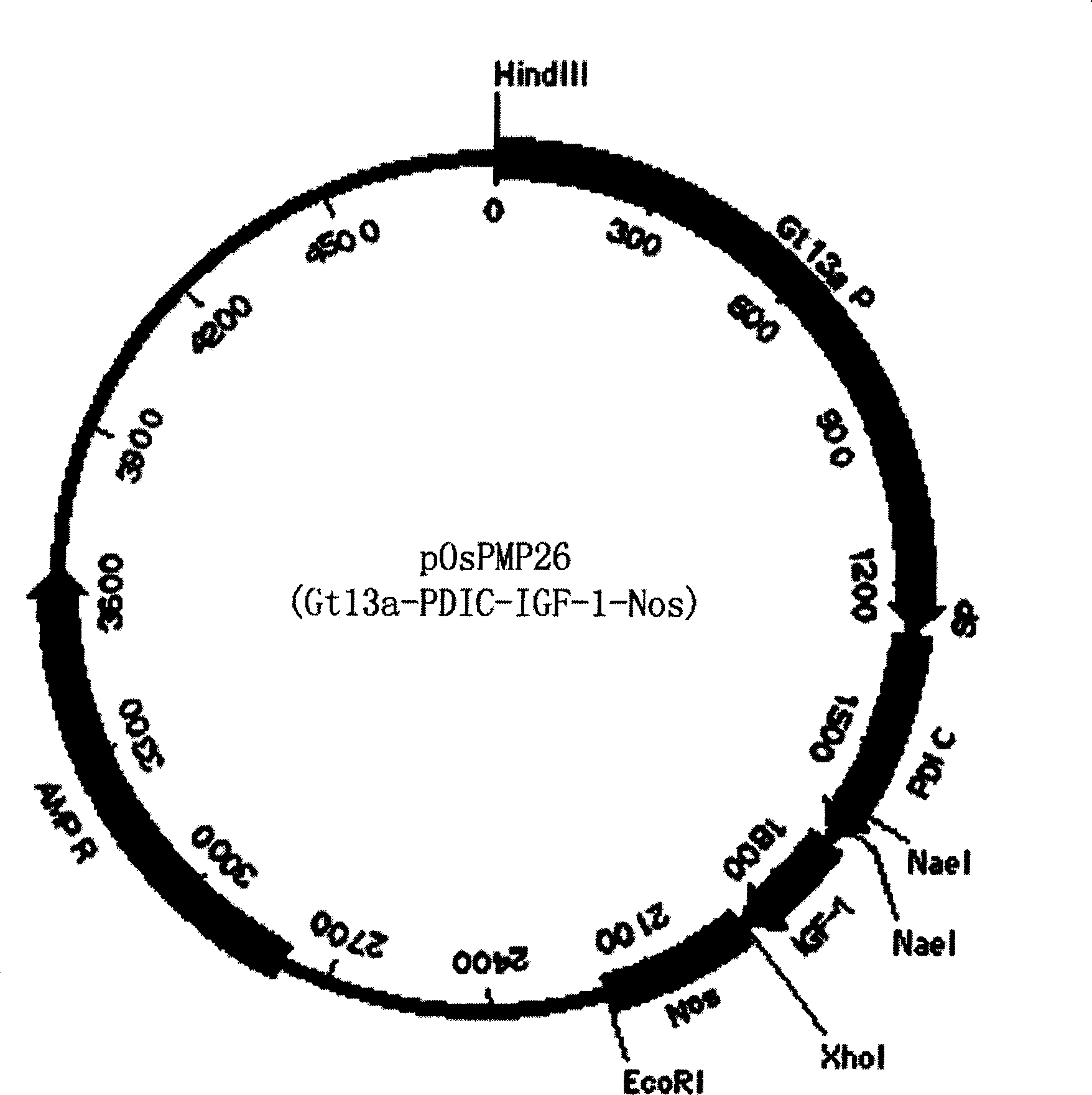
ActiveCN1884517AImprove solubilityBiologically activeInsulin-like growth factorsFermentationGenetically modified riceFusion Protein Expression
The invention discloses a method of using corn non-storage protein as molten carrier in endosperm expression polypeptide and its application, which includes: first obtaining rice astopic promoter and signal peptide; secondarily constructing rice albuminous cell specific expression carrier; thirdly using rice preference codon to prepare rice non-storage protein Bip gene C-end which is used as molten carrier, wheat PD1 gene C end and para-insulin growth factor-1 gene; fourthly constructing expression fusion protein carrier; fifthly obtaining genetically modified rice and barley plant with more than 0.3 % seed dry weight of their fusion protein expression. The invention is of simple process, convenient operation and low cost, and can be used in corn endosperm to express various polypeptides.
Owner:WUHAN HEALTHGEN BIOTECHNOLOGY CORP
Method for identifying transgenic rice and non-transgenic rice based on NIR (Near Infrared Spectrum)
InactiveCN102841072AEasy to operateImprove identification accuracyColor/spectral properties measurementsGenetically modified riceInfrared
The invention discloses a method for identifying transgenic rice and non-transgenic rice based on NIR (Near Infrared Spectrum), which comprises the following steps of: (1) transmitting the NIR to the rice seed samples, and collecting the diffuse reflection spectrum information of all the rice samples; (2) respectively preprocessing the diffuse reflection spectrum information for all the rice seed samples, extracting the spectrum information in characteristic spectrum regions after preprocessing through a principal component analysis method, selecting principal components, and acquiring the scores of the principal components; (3) building a model by the principal component scores corresponding to the rice seed sample spectrum information as an input and the rice seed type set values corresponding to the rice seed samples as an output; and (4) acquiring the scores of the principal components of the spectrum of rice seeds to be detected, taking the scores into the model in the step (3), and obtaining the types of the rice seeds to be detected. The invention is high in identification precision, simple to operate, low in cost, and is capable of realizing quickly and losslessly identifying the transgenic rice and the non-transgenic rice.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
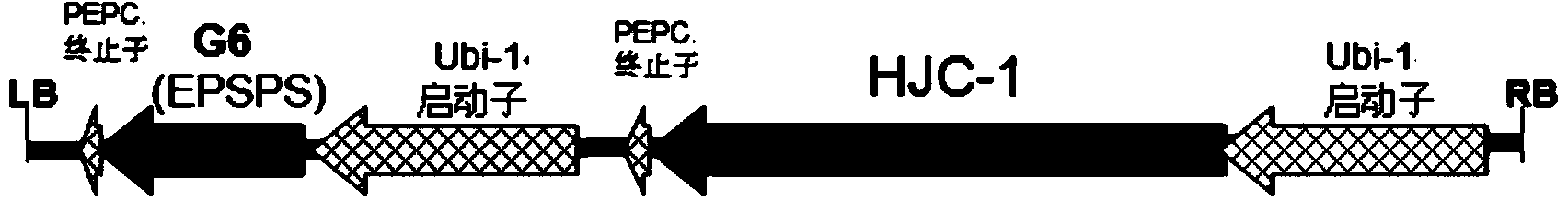
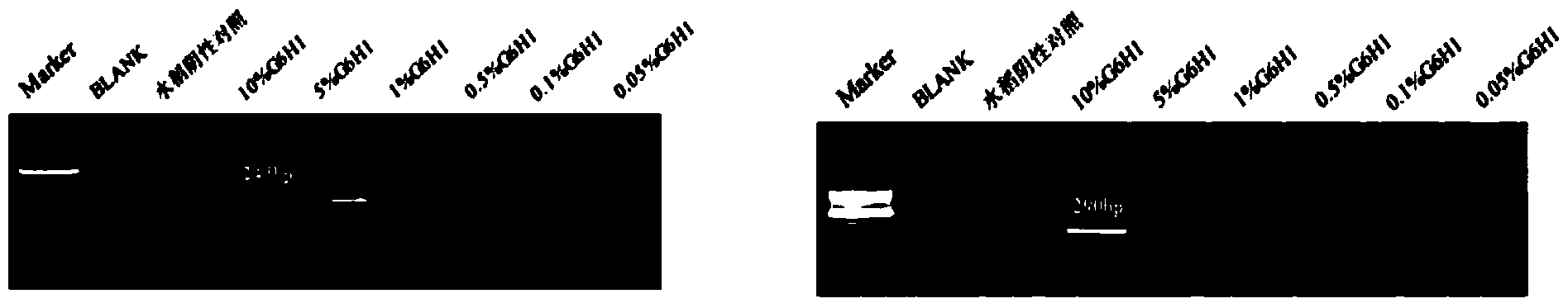
Qualitative PCR detecting method for transgenic insect-resistant herbicide-tolerant rice G6H1 and derived varieties thereof
InactiveCN103923999AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenetically modified riceAgricultural science
The invention discloses a qualitative PCR detecting method for transgenic insect-resistant herbicide-tolerant rice G6H1 and derived varieties thereof, and belongs to the qualitative detecting field of transgenic rice varieties. The invention firstly discloses 8 pairs of specific PCR detecting primer pairs for detecting the transgenic insect-resistant herbicide-tolerant rice G6H1 and derived varieties thereof. Based on this, the invention establishes a qualitative PCR detecting method for the transgenic insect-resistant herbicide-tolerant rice G6H1 and derived varieties thereof, which is strong in specificity and high in sensitivity. The invention further discloses a qualitative PCR detecting kit for the transgenic insect-resistant herbicide-tolerant rice G6H1 and derived varieties thereof. An experiment for specificity, sensitivity and detection limit proves that the qualitative PCR detecting method for the transgenic insect-resistant herbicide-tolerant rice G6H1 variety is strong in specificity, high in sensitivity and good in detection limit, and applicable to qualitative detection of the transgenic G6H1 rice and derived varieties thereof.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Application of synthetic transcription factor VP64-Os01g63510
ActiveCN103224563AIncrease thousand kernel weightGood market application valueBacteriaHybrid peptidesGenetically modified riceAgricultural science
The invention provides application of a synthetic transcription factor VP64-Os01g63510. Transcription factor activation motifs VP64 (namely the four transcription factor activation motifs VP16) and paddy rice transcription factors Os01g63510 are constructed to obtain the synthetic transcription factor in a gene fusion mode. The synthetic transcription factor VP64-Os01g63510 is transformed into paddy rice to improve characters of paddy rice seeds. Therefore, the genetically modified paddy rice seeds are obviously lengthened and widened, the thousand seed weight is obviously increased, and the market application prospects are good.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Transgenic rice TT51-1 transformation event foreign vector integration site complete sequence and use thereof
InactiveCN101302520AMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringGenetically modified riceAgricultural science
The invention discloses an event whole sequence with an integration site of a foreign vector transferred by transgenic paddy rice TT51-1 and application of the event whole sequence, relating to safety evaluation and detection of transgenic paddy rice in the biological engineering technical field. The invention uses transgenic insect-resistant rice variety TT51-1 as a material, extracts a gene group DNA as a template, and divides into four sections to enlarge TT51-1 event whole sequence containing a side paddy rice gene group sequence which is shown in SEQ NO.1, and the whole sequence is formed commonly by a basic group of between first and 673rd from the paddy rice gene group, a basic group of between 674th and 9364th from a vector sequence and a basic group of between 9365th and 10536th from the paddy rice gene group; the whole sequence is applicable to carrying out detection, monitoring and safety management of the transgenic paddy rice TT51-1(including parent strain, hybridism F1 and later generation) and products (including plant, tissue, paddy, rice and products thereof).
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com