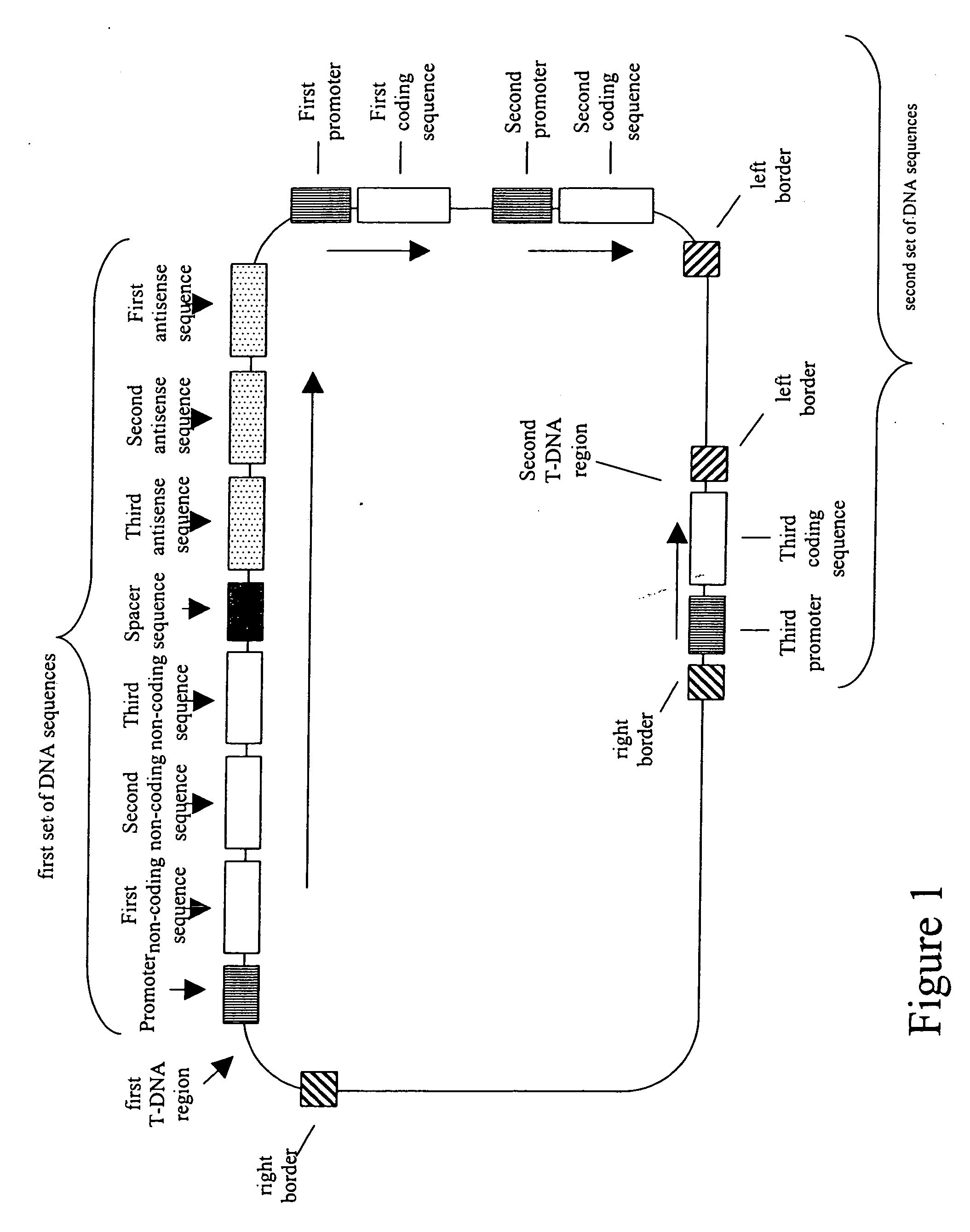
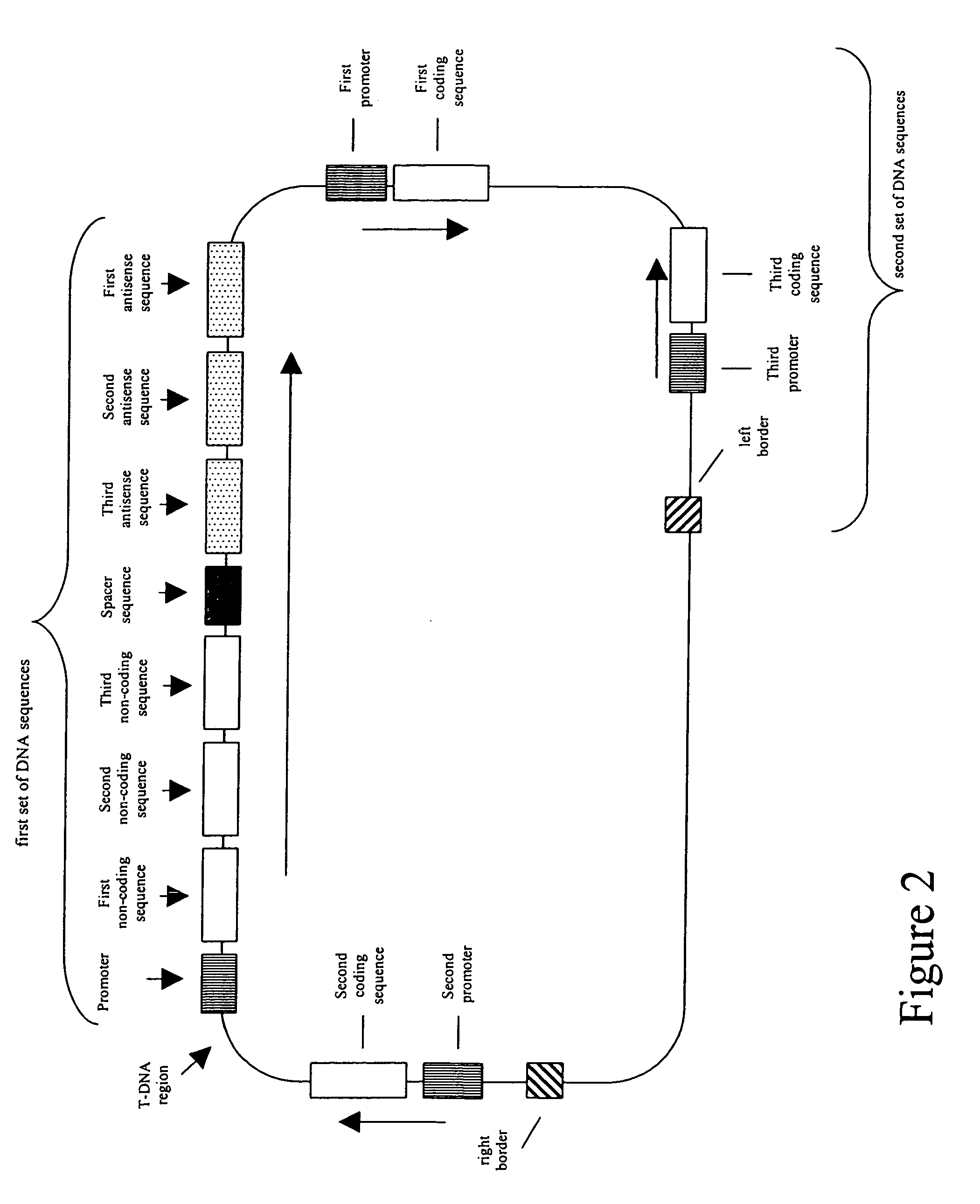
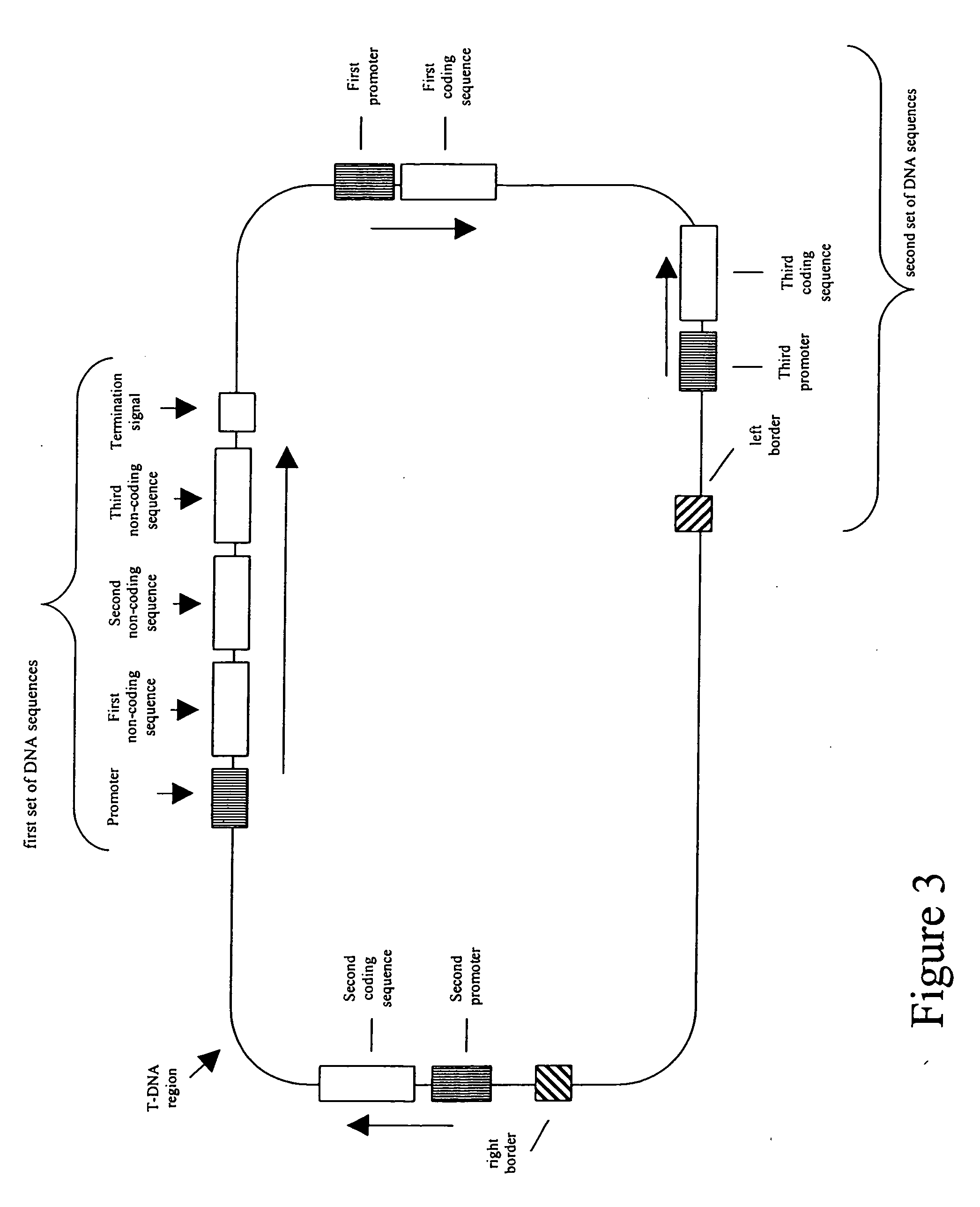
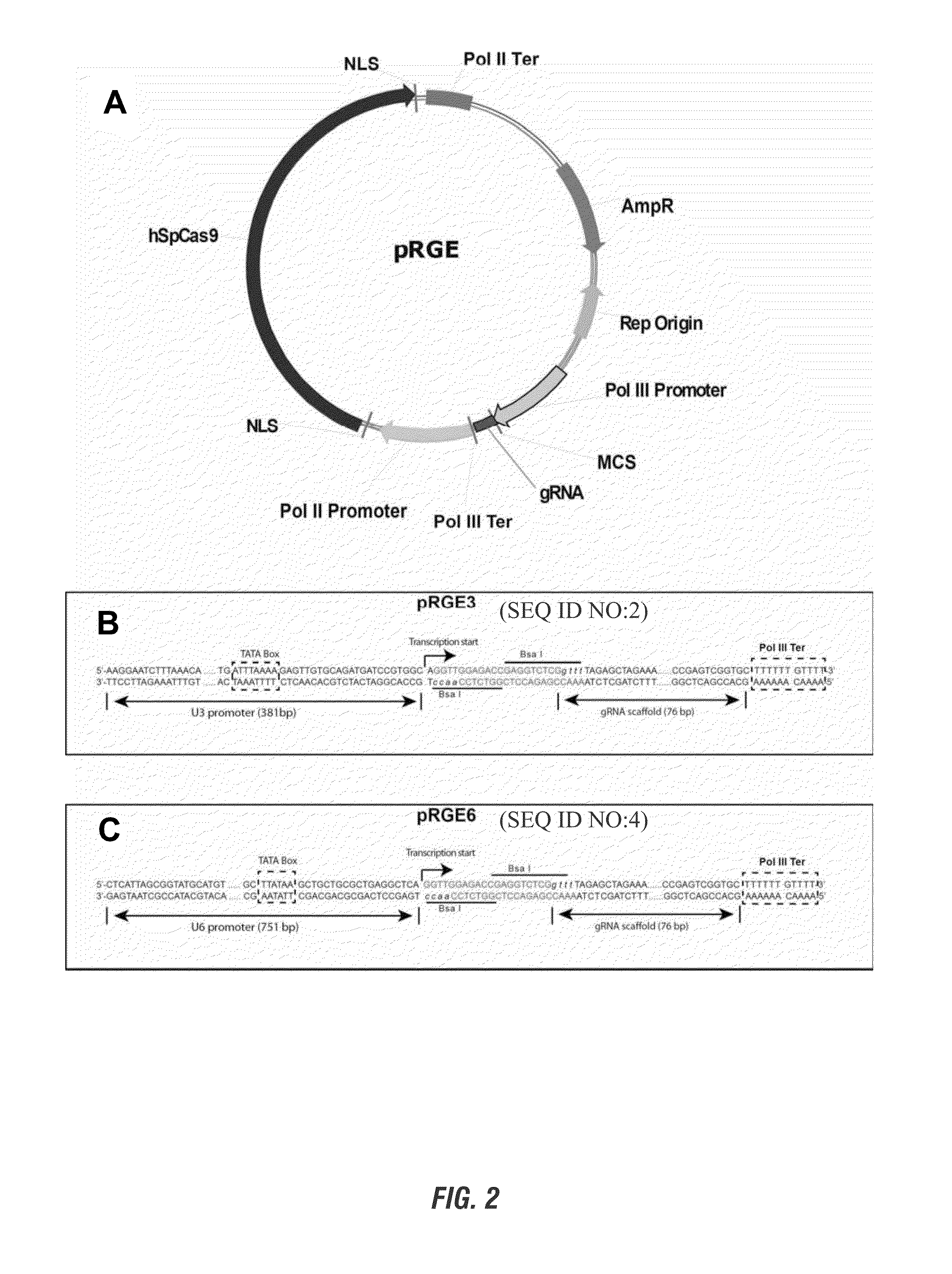
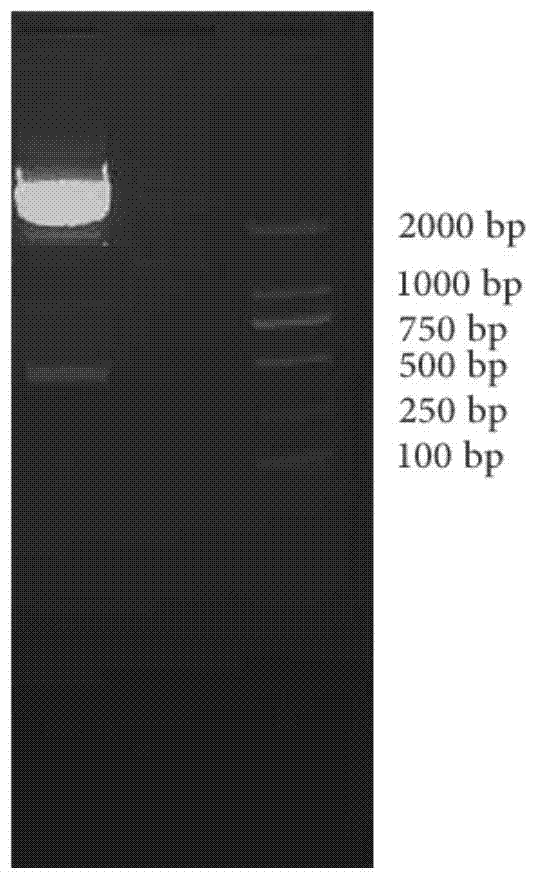
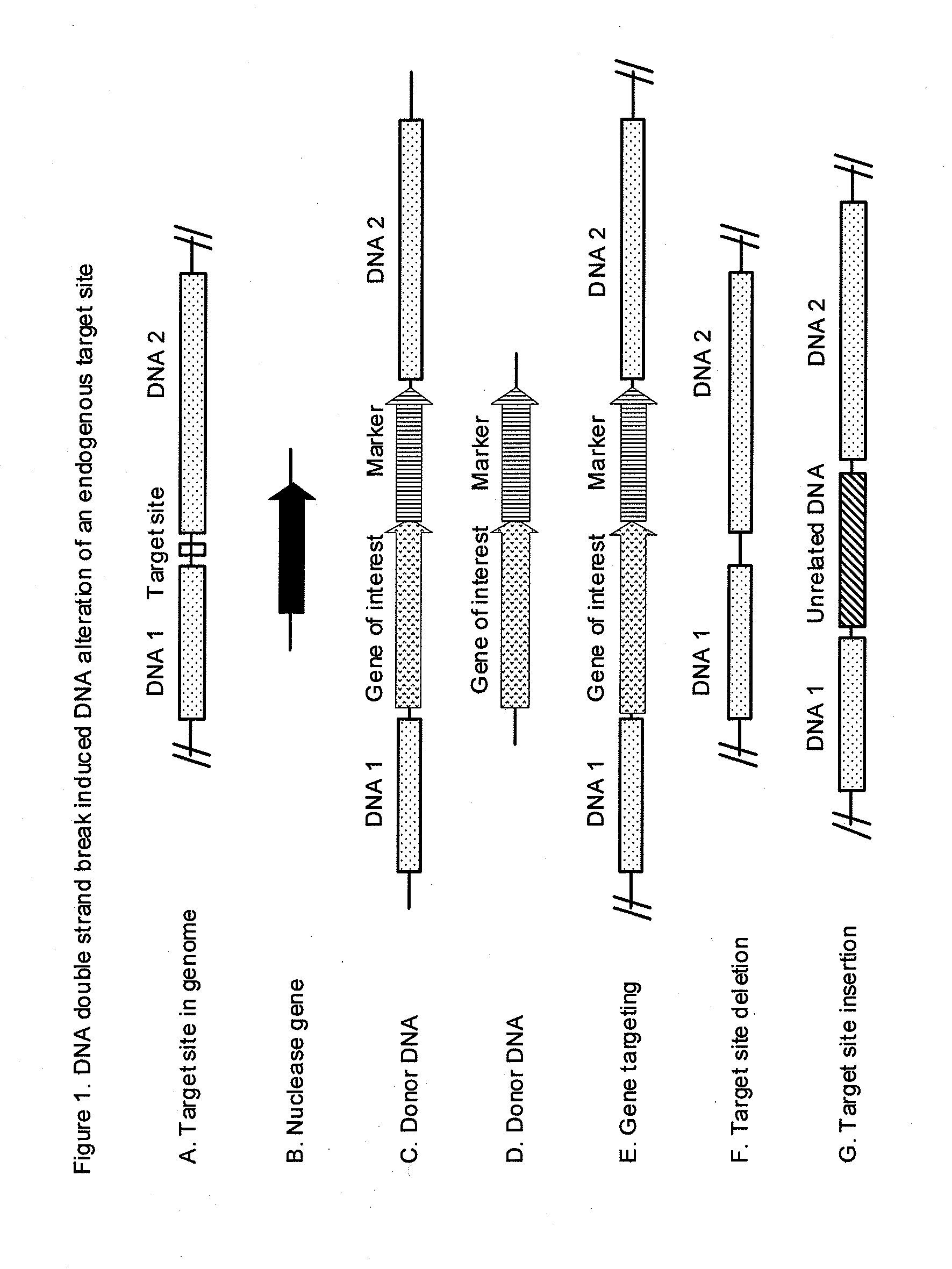
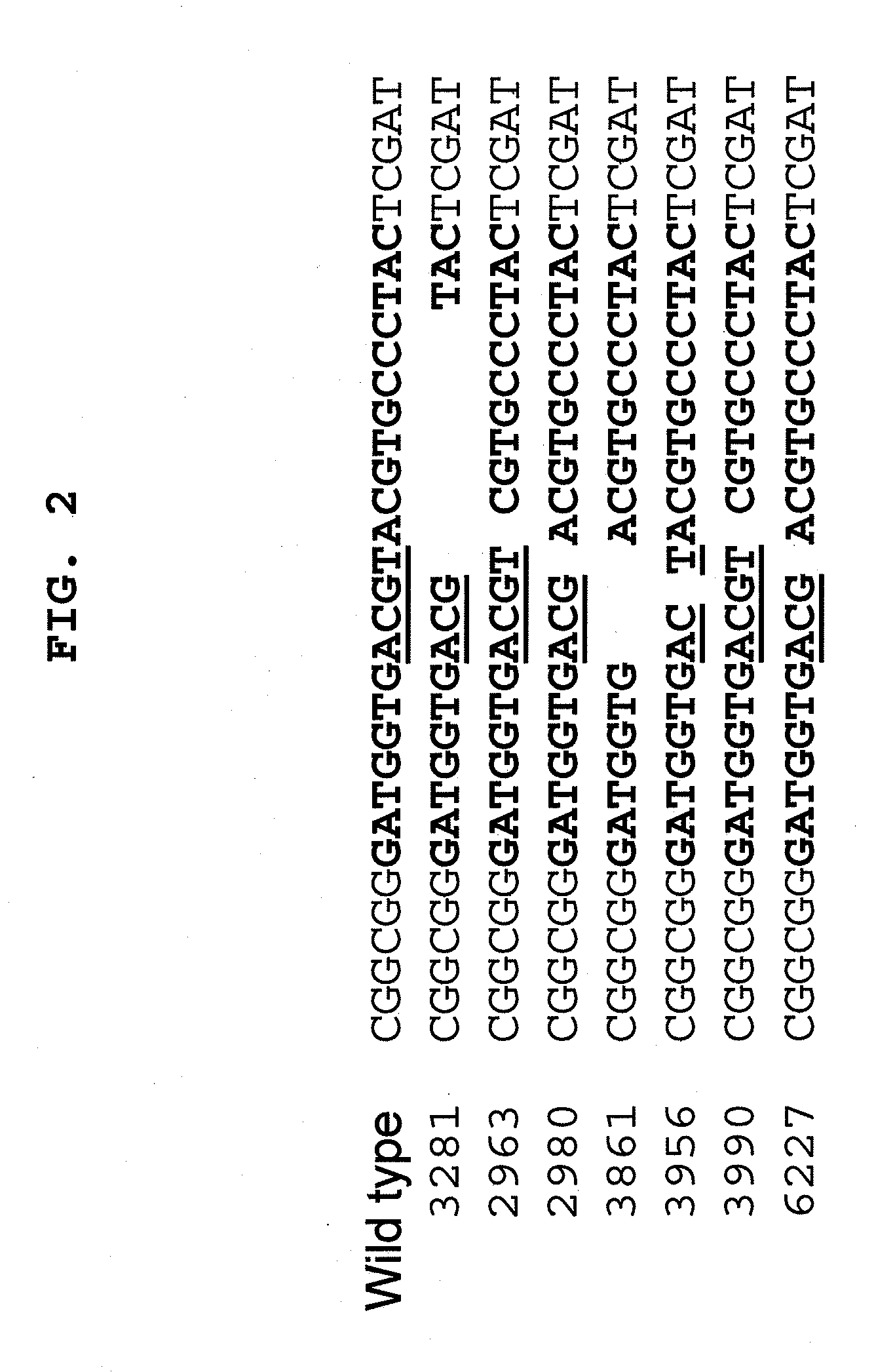
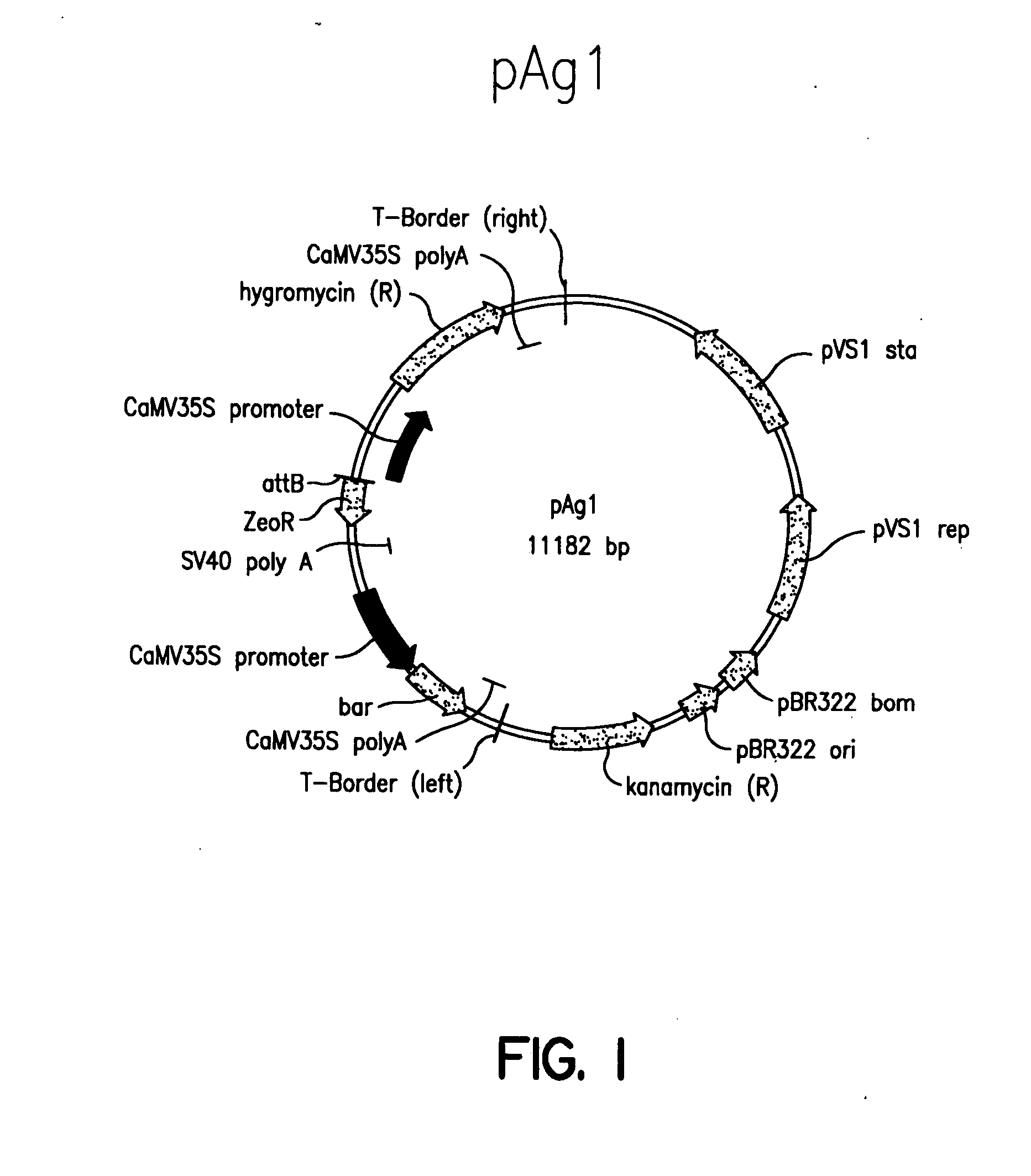
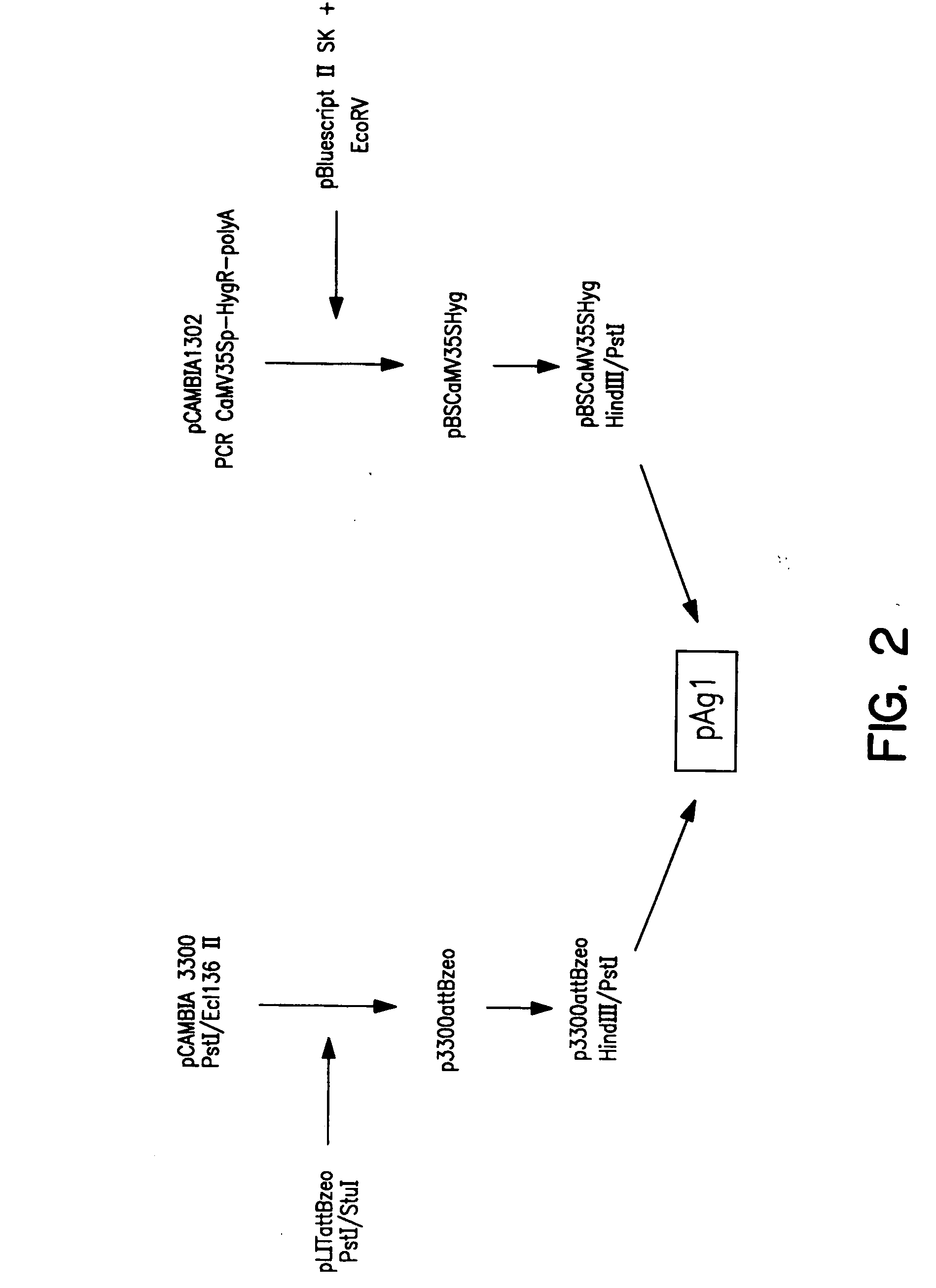
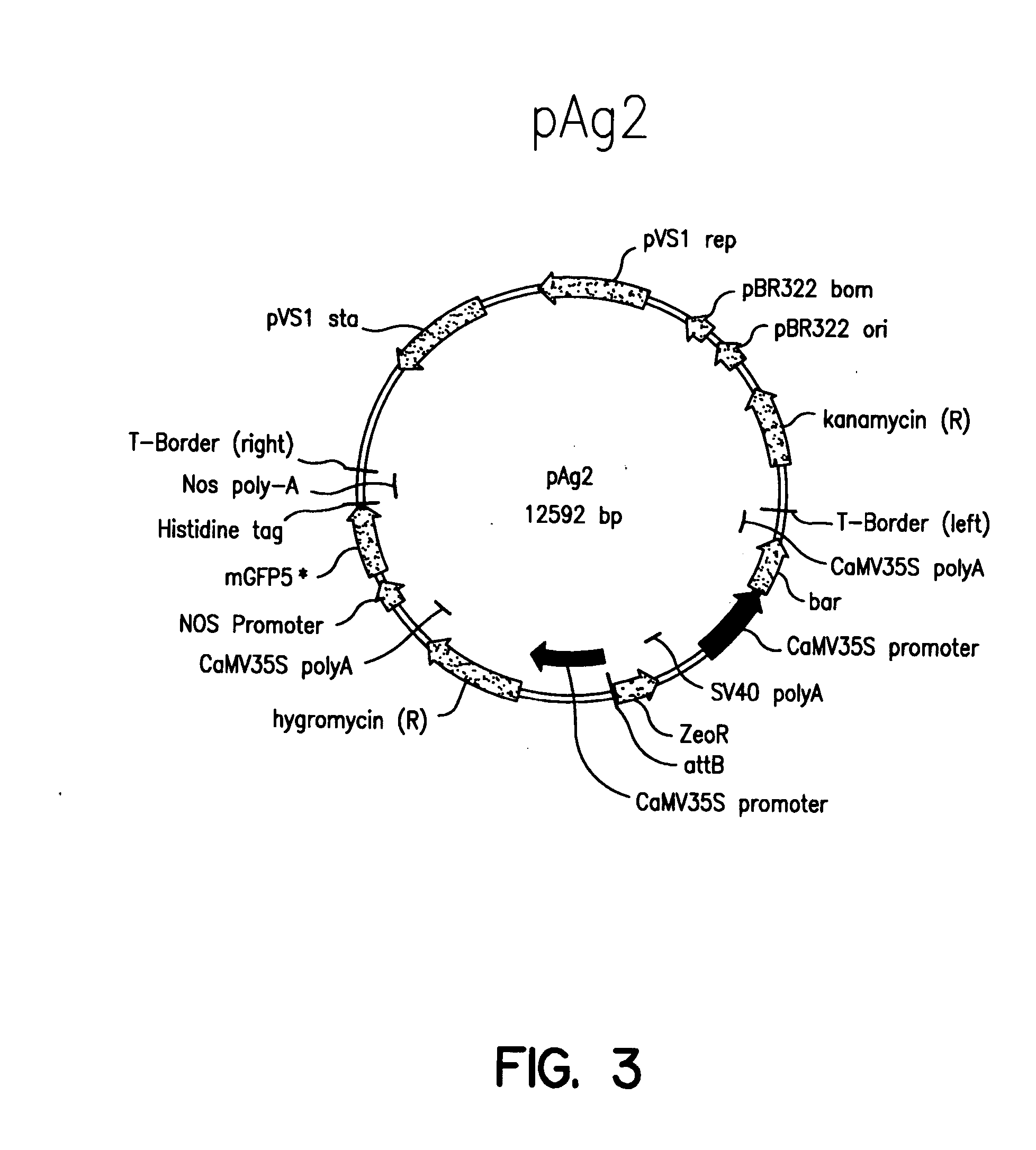
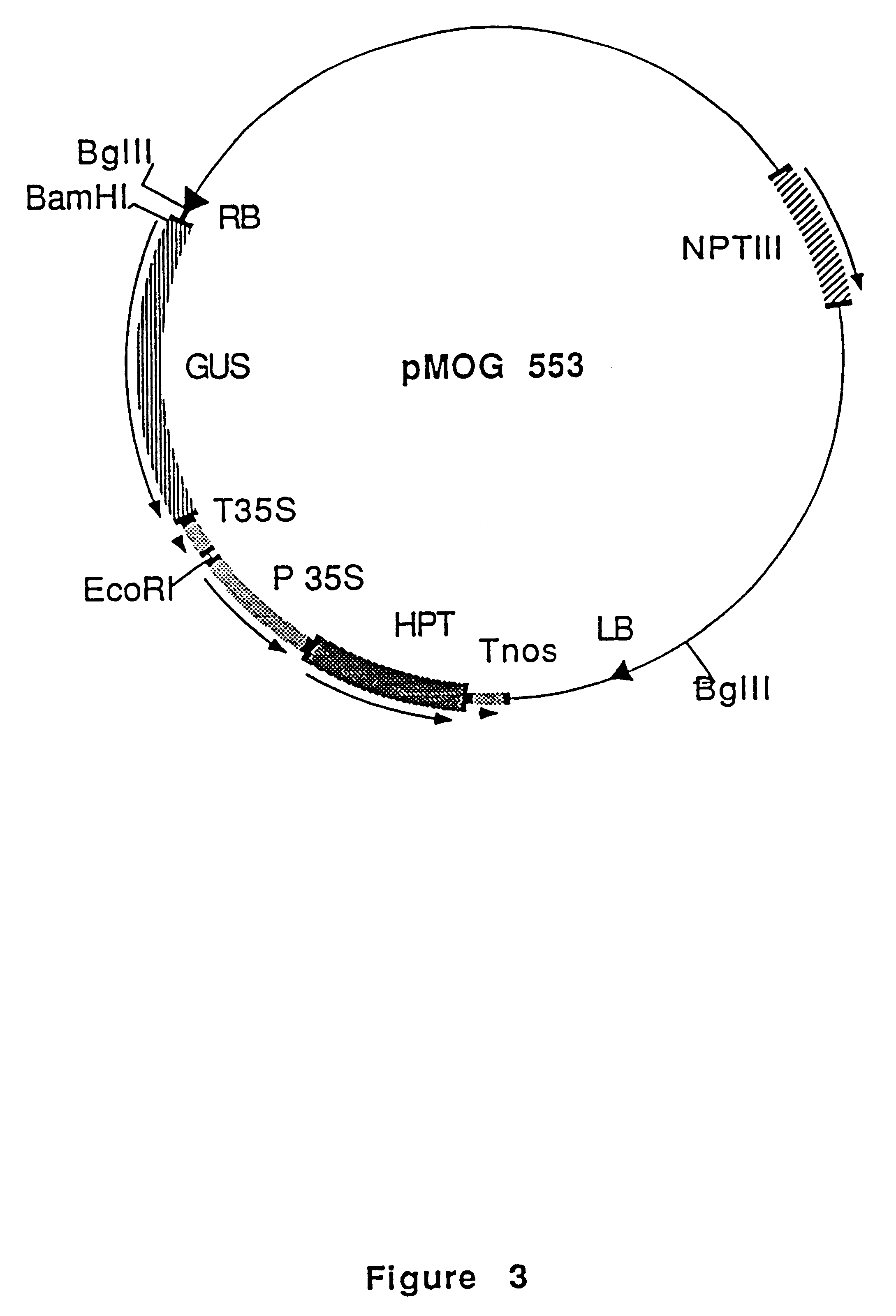
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1293 results about "Plant genes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Plant Specific Genetics. Plants, like all other known living organisms, pass on their traits using DNA. Plants however are unique from other living organisms in the fact that they have Chloroplasts. Like mitochondria, chloroplasts have their own DNA.
Plant genome sequence and uses thereof
InactiveUS7868149B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementADAMTS ProteinsPlant biochemistry
The present invention is in the field of plant biochemistry and genetics. More specifically the invention relates to nucleic acid molecules from plant cells, in particular, genomic DNA sequences from rice plants and nucleic acid molecules that contain markers, in particular, single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and repetitive element markers. In addition, the present invention provides nucleic acid molecules having regulatory elements or encoding proteins or fragments thereof. The invention also relates to proteins and fragments of proteins so encoded and antibodies capable of binding the proteins. The invention also relates to methods of using the nucleic acid molecules, markers, repetitive elements and fragments of repetitive elements, regulatory elements, proteins and fragments of proteins, and antibodies, for example for genome mapping, gene identification and analysis, plant breeding, preparation of constructs for use in plant gene expression, and transgenic plants.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Genomic plant sequences and uses thereof
The present invention discloses rice genomic promoter sequences. The promoters are particularly suited for use in rice and other cereal crops. Methods of modifying, producing, and using the promoters are also disclosed. The invention further discloses compositions, transformed host cells, transgenic plants, and seeds containing the rice genomic promoter sequences, and methods for preparing and using the same.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Chimeric gene for the transformation of plants
InactiveUSRE37287E1Most efficientPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSugar derivativesPolyadenylationIncreased tolerance
Chimeric gene for conferring to plants an increased tolerance to a herbicide having as its target EPSPS comprises, in the direction of transcription, a promoter region, a transit peptide region, a coding sequence for glyphosate tolerance and a polyandenylation signal region, wherein the transit peptide region comprises, in the direction of translation, at least one transit peptide of a plant gene encoding a plastid-localized enzyme and then a second transit peptide of a plant gene encoding, a plastid-localized enzyme. Production of glyphosate-tolerant plants is disclosed.
Owner:BAYER SAS
Nucleic acid constructs and methods for producing altered seed oil compositions
InactiveUS20060206963A1Increased oleic acid contentReduce saturated fatty acid contentTransferasesBiofuelsFatty acid biosynthesisAdemetionine
The present invention is in the field of plant genetics and provides recombinant nucleic acid molecules, constructs, and other agents associated with the coordinate manipulation of multiple genes in the fatty acid synthesis pathway. In particular, the agents of the present invention are associated with the simultaneous enhanced expression of certain genes in the fatty acid synthesis pathway and suppressed expression of certain other genes in the same pathway. Also provided are plants incorporating such agents, and in particular plants incorporating such constructs where the plants exhibit altered seed oil compositions.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Plant genome sequence and uses thereof
InactiveUS20070039076A1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesRice plantsGenomic DNA
The present invention is in the field of plant biochemistry and genetics. More specifically the invention relates to nucleic acid molecules from plant cells, in particular, genomic DNA sequences from rice plants and nucleic acid molecules that contain markers, in particular, single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and repetitive element markers. In addition, the present invention provides nucleic acid molecules having regulatory elements or encoding proteins or fragments thereof. The invention also relates to proteins and fragments of proteins so encoded and antibodies capable of binding the proteins. The invention also relates to methods of using the nucleic acid molecules, markers, repetitive elements and fragments of repetitive elements, regulatory elements, proteins and fragments of proteins, and antibodies, for example for genome mapping, gene identification and analysis, plant breeding, preparation of constructs for use in plant gene expression, and transgenic plants.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
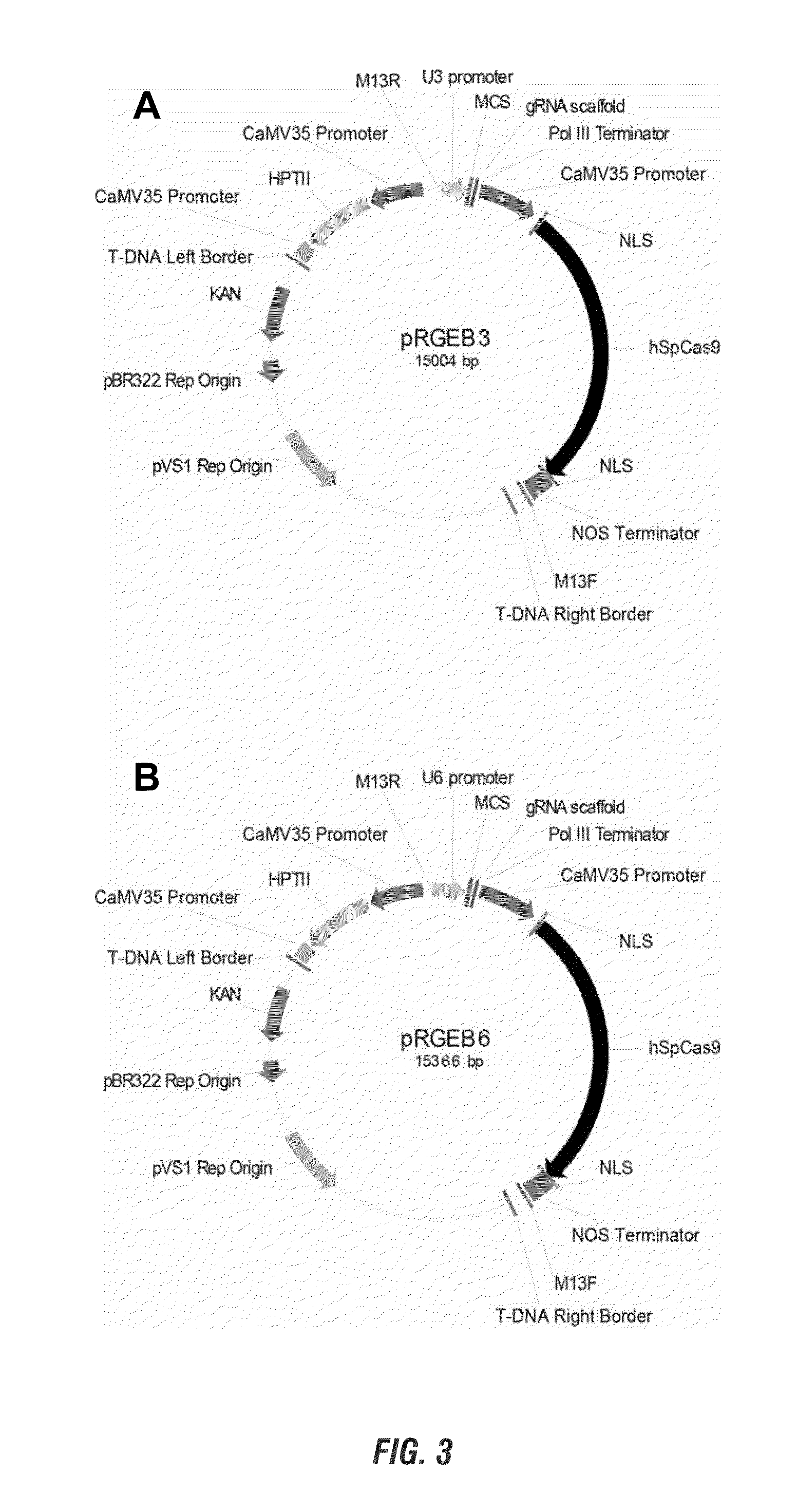
Gene targeting and genetic modification of plants via rna-guided genome editing
InactiveUS20150067922A1Improve stateFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionGenome editingGenetically modified crops
The present invention provides compositions and methods for specific gene targeting and precise editing of DNA sequences in plant genomes using the CRISPR (cluster regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) associated nuclease. Non-transgenic, genetically modified crops can be produced using these compositions and methods.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Plant genes involved in defense against pathogens
InactiveUS20070016976A1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesCancer researchPlant genes
Methods to identify genes, the expression of which are altered in response to pathogen infection, are provided, as well as the genes identified thereby and their corresponding promoters.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
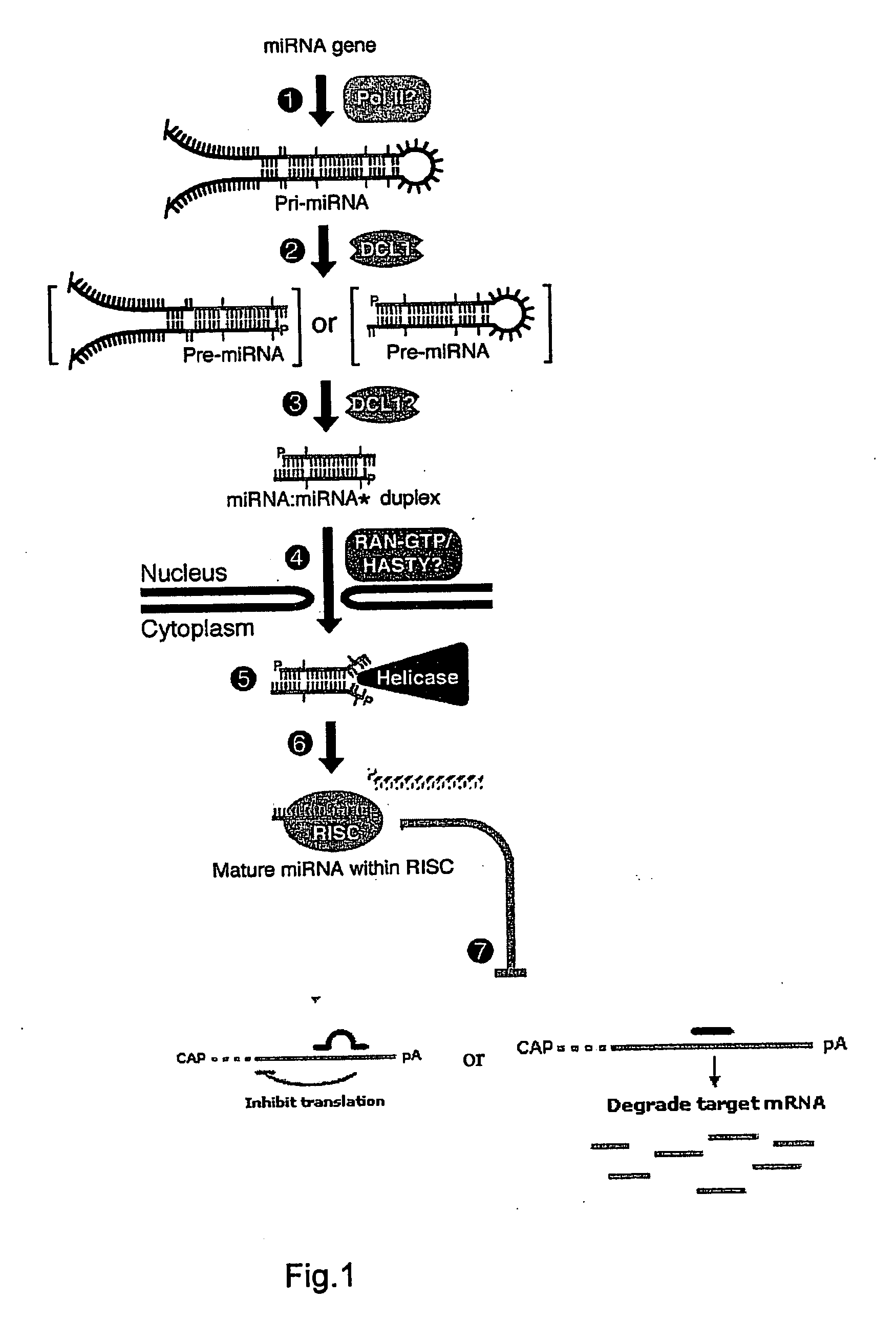
Improved Methods Controlling Gene Expression
The present invention is in the field of genetics, especially plant genetics, and provides agents capable of controlling gene expression. The present invention specifically provides sequences of naturally occurring, tissue-specifically expressed microRNAs. The invention further provides for transgenic expression constructs comprising sequences encoding said microRNAs. By incorporation of the microRNA encoding sequence the expression from said expression construct is specifically silenced in the tissue where the naturally occurring microRNA is naturally expressed. Thereby the expression profile resulting from the promoter is modulated and leakiness is reduced. The invention further provides for a method for modulating transgenic expression by incorporating sequences encoding said microRNAs into transgenic expression constructs. The compositions and methods of the invention can be used to enhance performance of agricultural relevant crops and for therapy, prophylaxis, research and diagnostics in diseases and disorders, which afflict mammalian species.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
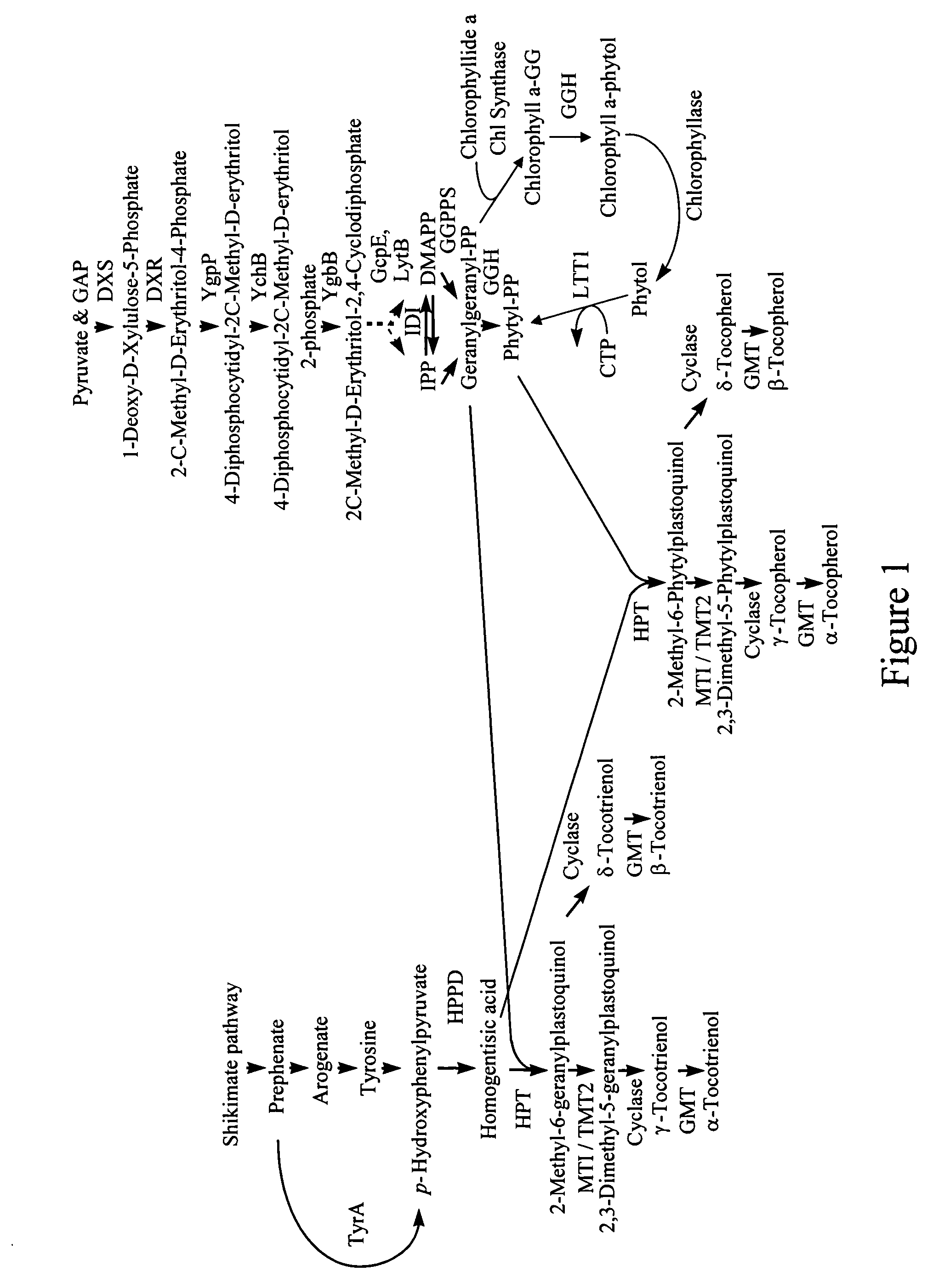
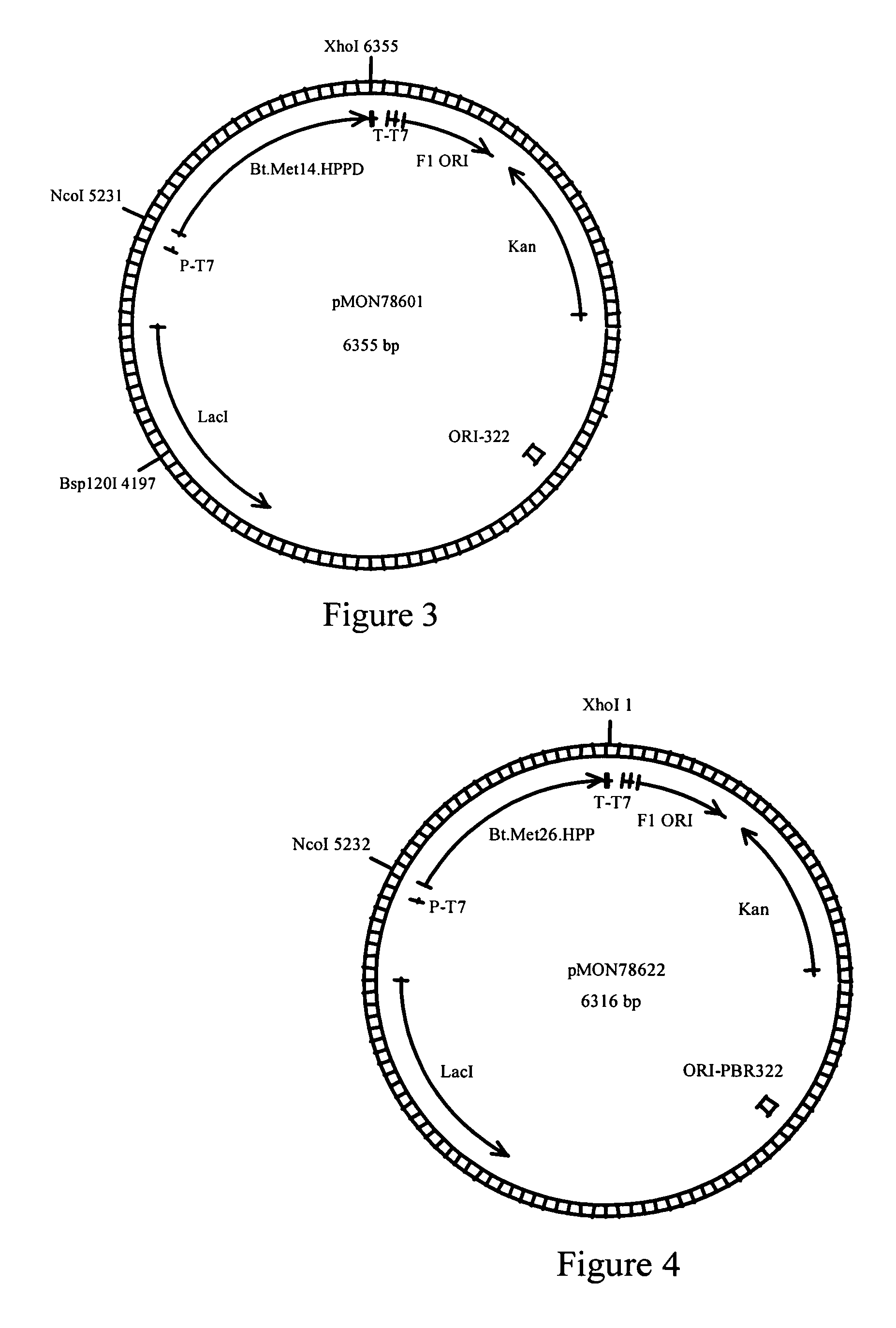
Genes encoding 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase (HPPD) enzymes for plant metabolic engineering
ActiveUS7297541B2Reduce riskAid in immune functionSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnology4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase activity
The present invention is in the field of plant genetics and biochemistry. More specifically, the present invention relates to genes and polypeptides associated with the tocopherol biosynthesis pathway, namely those encoding 4-Hydroxyphenylpyruvate Dioxygenase activity, and uses thereof.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Nucleic acid molecules and other molecules associated with plants
The present invention is in the field of plant genetics. More specifically the invention relates to nucleic acid molecules and nucleic acid molecules that contain markers, in particular, single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and repetitive element markers. In addition, the present invention provides nucleic acid molecules having regulatory elements or encoding proteins or fragments thereof. The invention also relates to proteins and fragments of proteins so encoded and antibodies capable of binding the proteins. The invention also relates to methods of using the nucleic acid molecules, markers, repetitive elements and fragments of repetitive elements, regulatory elements, proteins and fragments of proteins.
Owner:BYRUM JOSEPH +2
Promoter, promoter control elements, and combinations, and uses thereof
ActiveUS20120084885A1Enhancing and reducing regionImmunoglobulinsFermentationGene productSynthetic DNA
The present invention provides DNA molecules that constitute fragments of the genome of a plant, and polypeptides encoded thereby. The DNA molecules are useful for specifying a gene product in cells, either as a promoter or as a protein coding sequence or as an UTR or as a 3′ termination sequence, and are also useful in controlling the behavior of a gene in the chromosome, in controlling the expression of a gene or as tools for genetic mapping, recognizing or isolating identical or related DNA fragments, or identification of a particular individual organism, or for clustering of a group of organisms with a common trait. One of ordinary skill in the art, having this data, can obtain cloned DNA fragments, synthetic DNA fragments or polypeptides constituting desired sequences by recombinant methodology known in the art or described herein
Owner:CERES INC
Plant Genes Associated With Seed Oil Content And Methods Of Their Use
InactiveUS20110191904A1High oil contentRaise the ratioOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationBiotechnologyReticulum cell
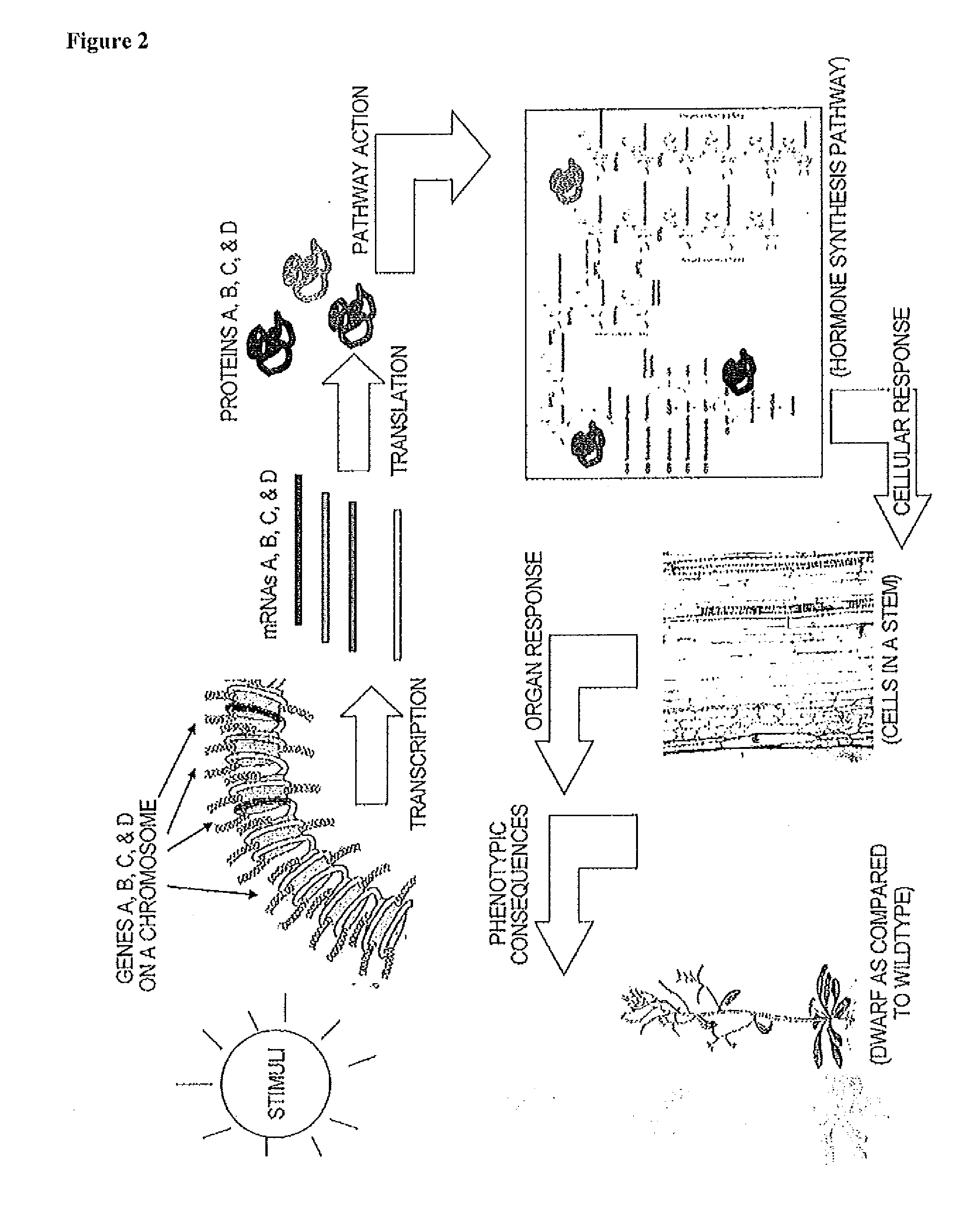
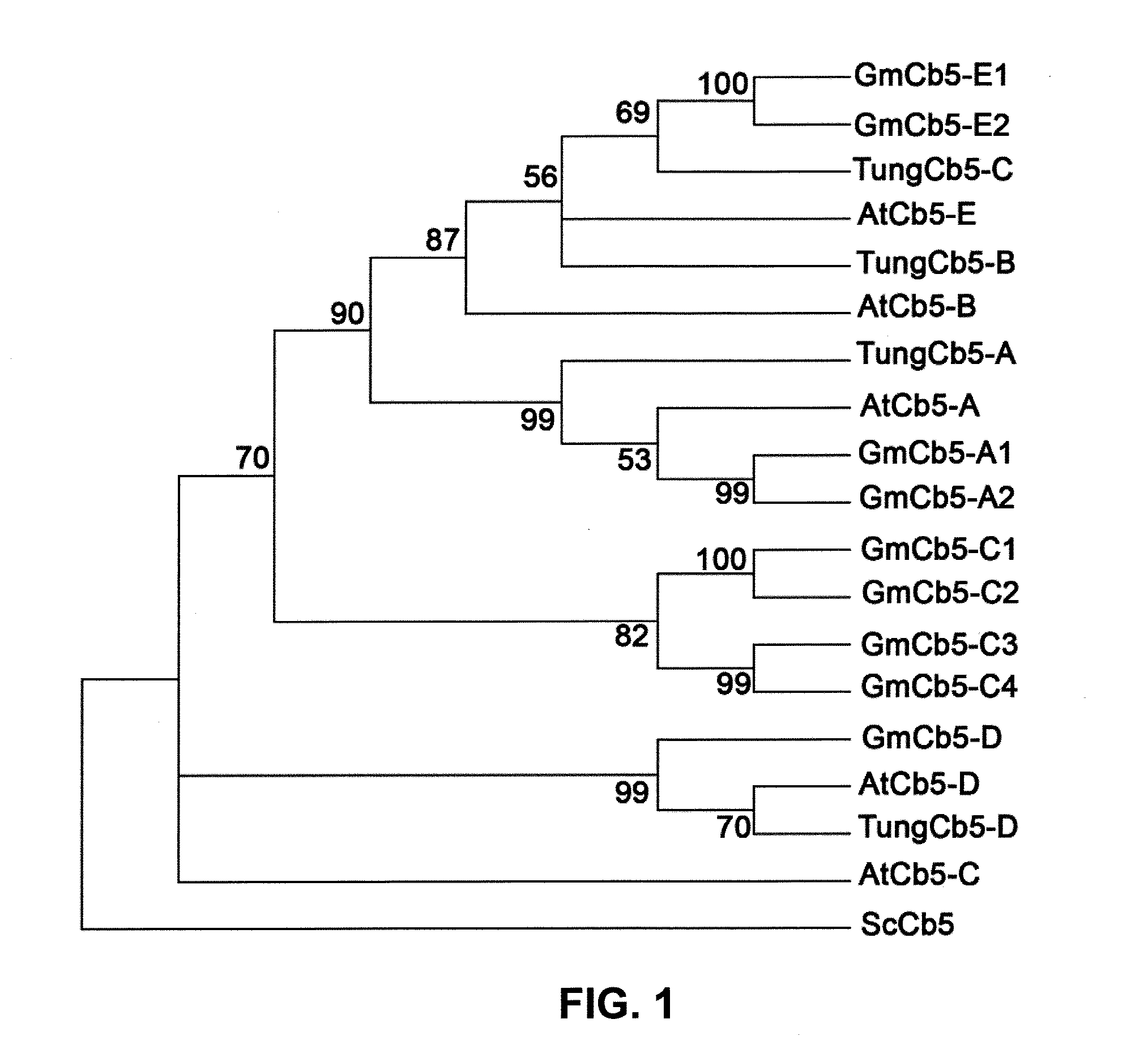
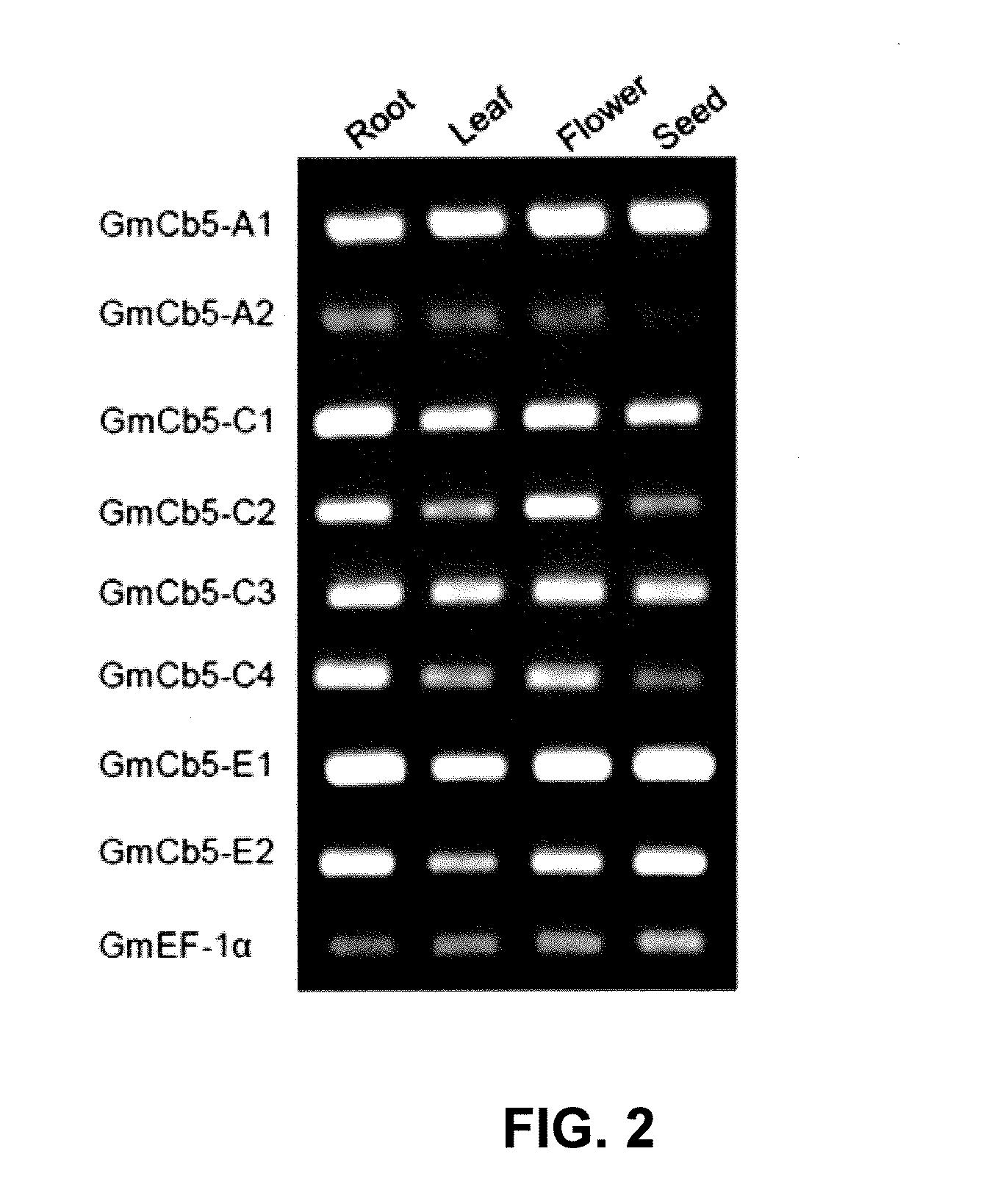
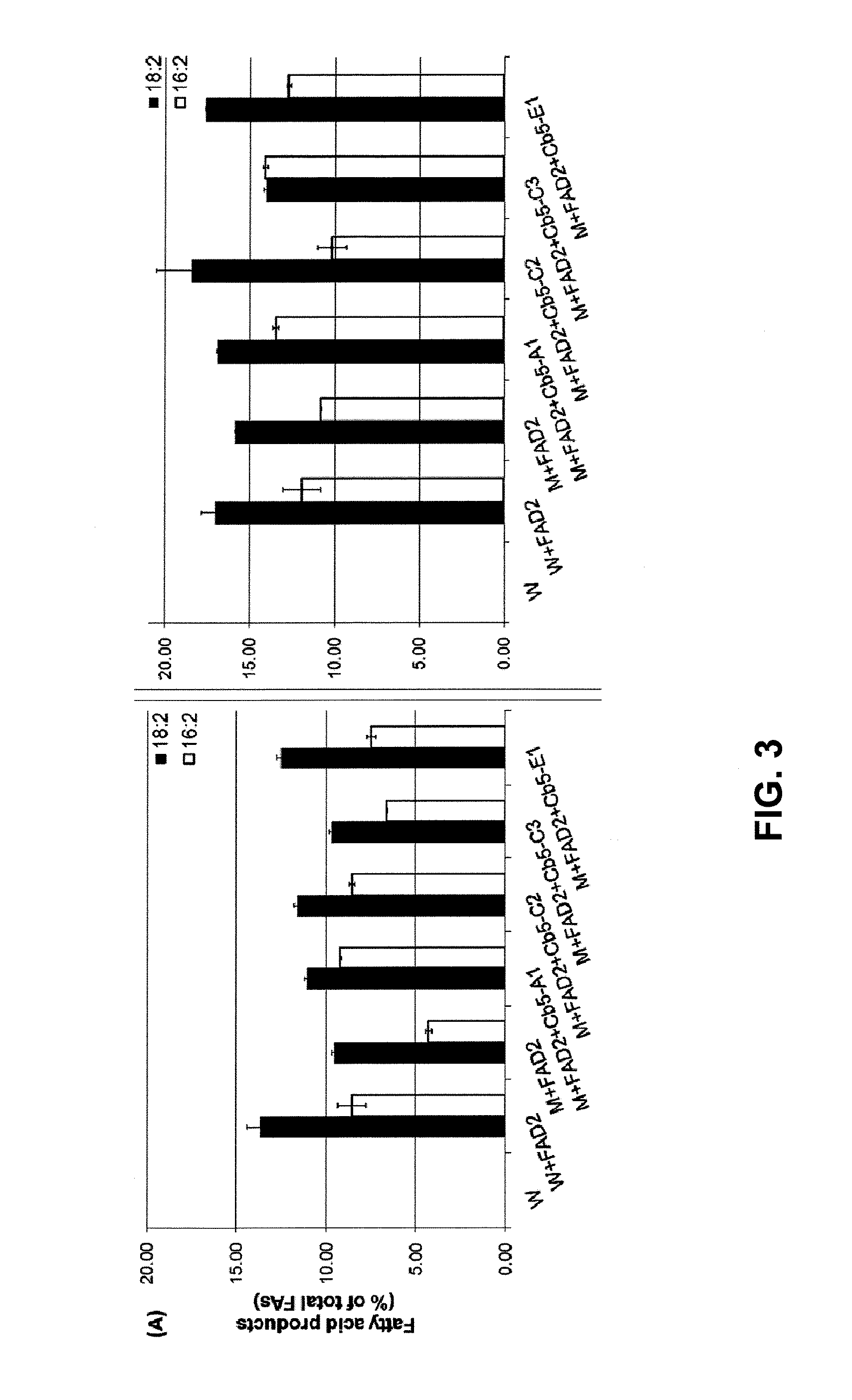
Cytochrome b5 (Cb5) is a haem-binding protein located in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and the outer mitochondrial membranes of higher eukaryotes. In higher plants, animals, and fungi, the ER resident Cb5 has been shown to play a role in desaturation of acyl CoA fatty acids. Higher plants Cb5 isoforms from plants such as soybean or Arabidopsis are capable of modulating omega-3 desaturation. Co-expression of certain Cb5 isoforms with FAD3 in a host plant results in increased production of seed oil content as well as altered ratio between different fatty acids. It is also disclosed here that overexpression of Yarrowia ACL enzymes in the plastids of a host plant helps boost the synthesis of acetyl CoA, which in turn, may lead to increased synthesis of fatty acids and enhanced oil accumulation in the seeds.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Cotton plant promoters
InactiveUS6259003B1Process can be usedImprove featuresSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesFiberFibers tissue
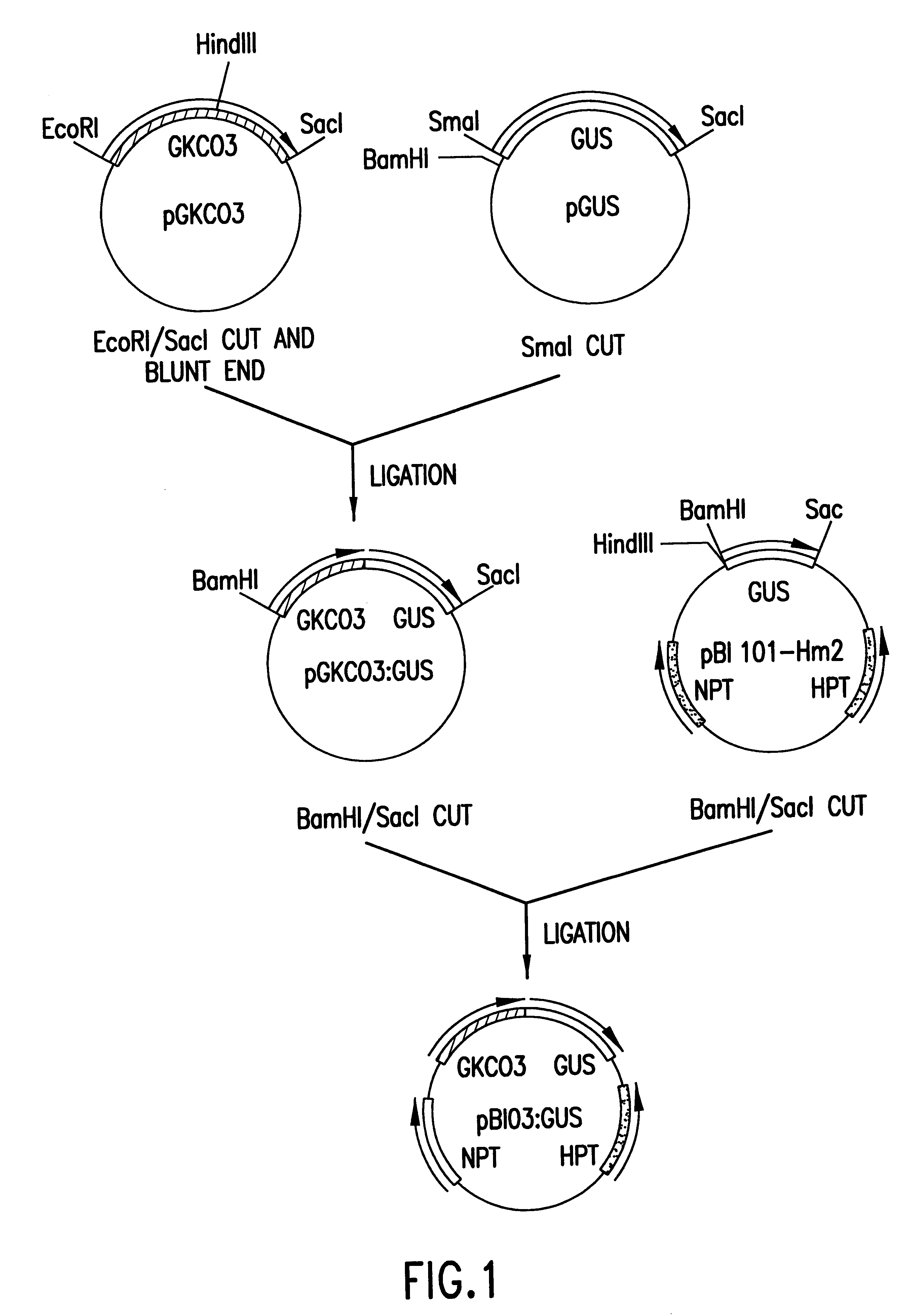
Novel plant promoters isolated from cotton fiber tissues are provided. The plant promoters are located upstream cotton plant genes KC03, KC18, KC22, and Gh3, all of which are expressed in cotton fibers, and contain (a) DNA having the nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID NO:1, 6, 11, or 16. Also provided are plant expression vectors prepared by introducing the plant promoters into appropriate vectors; transformed plant cells prepared by introducing the plant expression vectors into host plant cells; transformed plants regenerated from the transformed plant cells; transformed plant seeds obtained from the transformed plants; and processes for producing transformed plants from the plant seeds.
Owner:TOVO BOSEKI +1
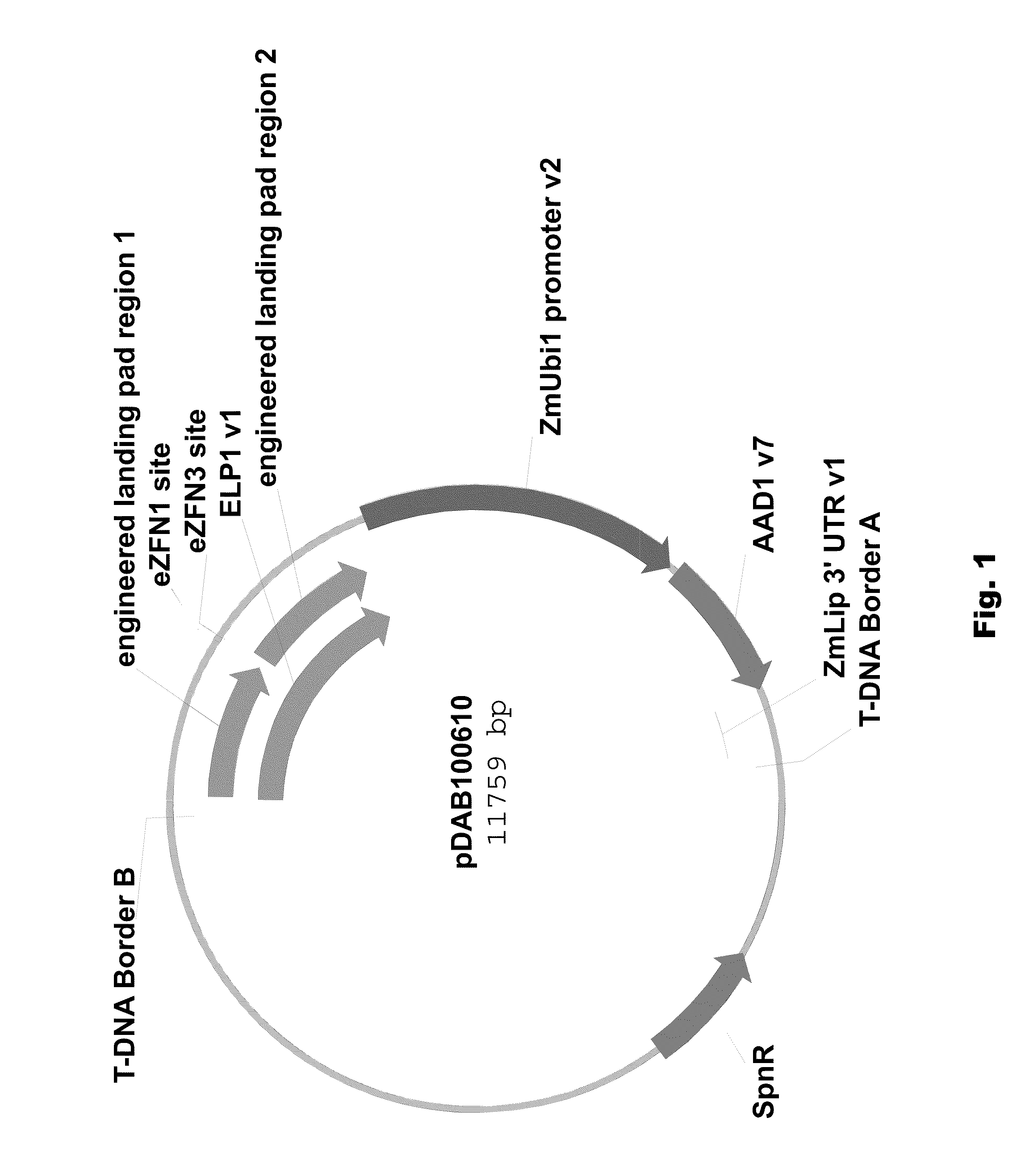
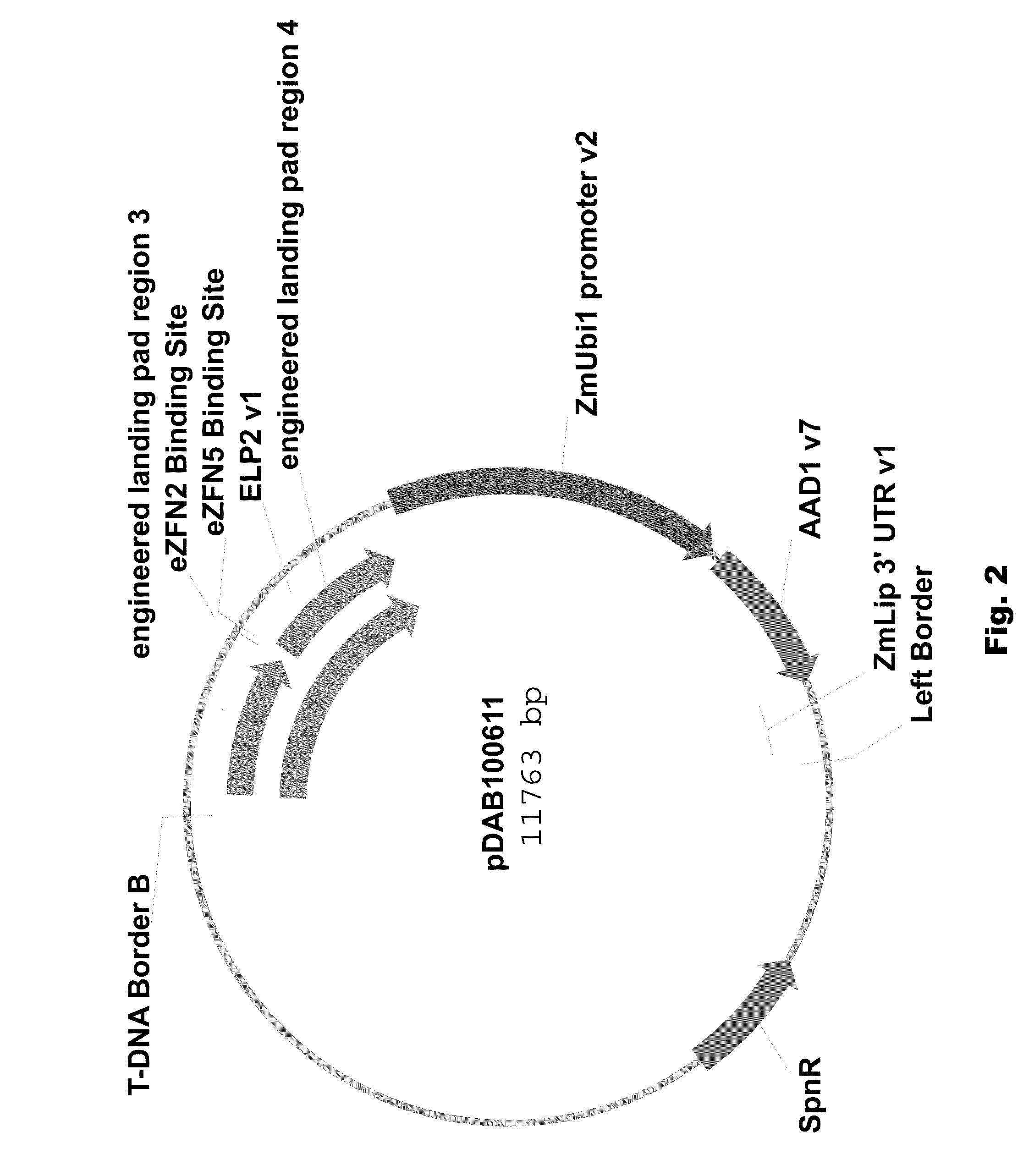
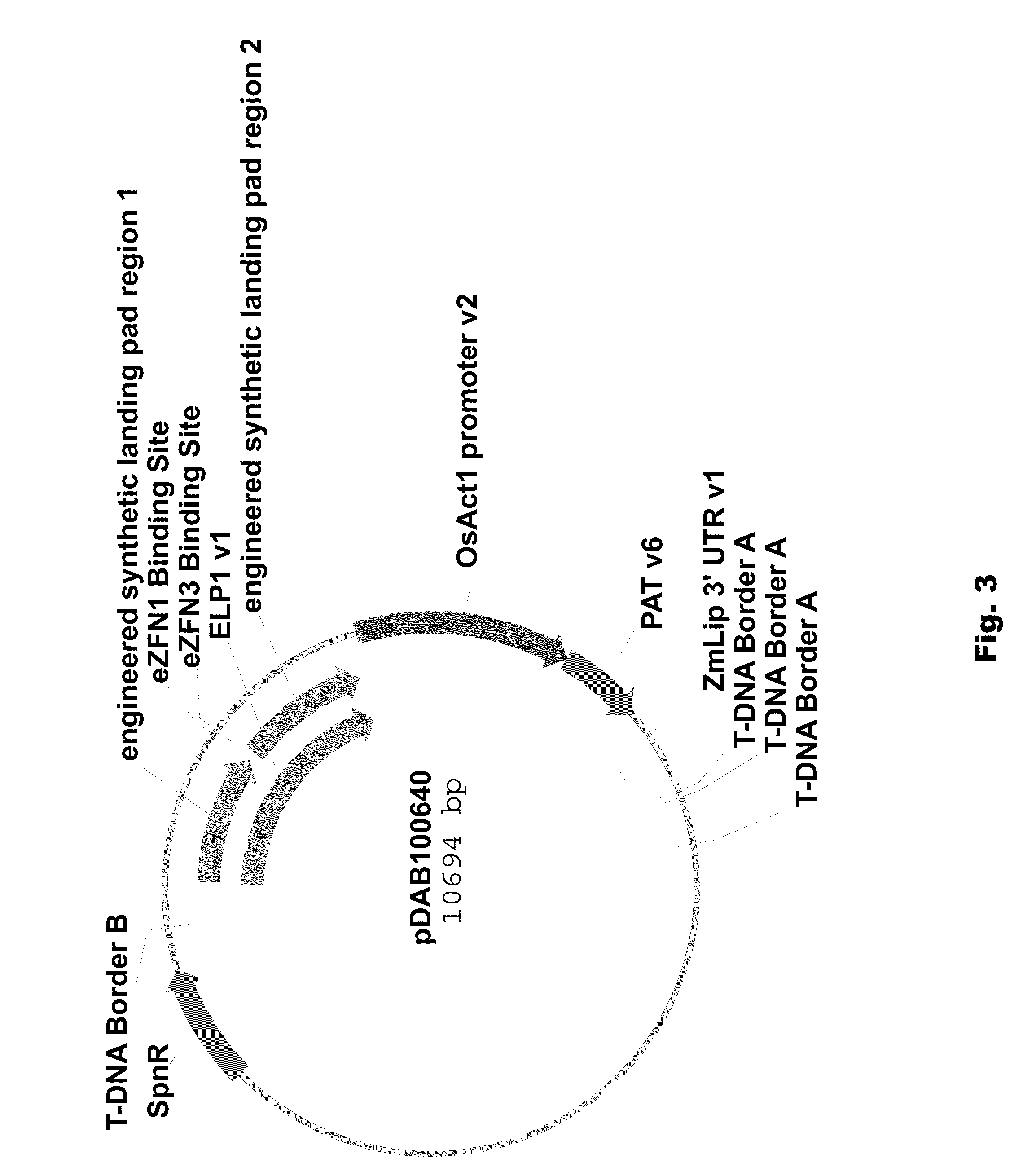
Engineered landing pads for gene targeting in plants
InactiveUS20110191899A1Reduce and eliminate needEasy to reorganizeOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationZinc finger nucleaseGene targets
A method for producing a transgenic plant includes providing a nucleic acid molecule comprising at least two regions of nucleic acid sequence that lack sequence homology with genomic DNA of the plant cell, and at least two zinc finger nuclease recognition sites, wherein the at least two regions of nucleic acid sequence that lack sequence homology with genomic DNA of the plant cell flank the at least two zinc finger nuclease recognition sites. A plant cell or tissue having the nucleic acid molecule stably integrated into the genome of the plant cell is transformed. A plant is regenerated from the plant cell. Transgenic plants are produced by the method. Seeds are produced by the transgenic plants.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
DNA encoding a plant deoxyhypusine synthase, a plant eukaryotic initiation factor 5A, transgenic plants and a method for controlling senescence programmed and cell death in plants
InactiveUS6538182B1Lower Level RequirementsExtended shelf lifeBacteriaOxidoreductasesAntisense OrientationApoptotic programmed cell death
Regulation of expression of programmed cell death, including senescence, in plants is achieved by integration of a gene or gene fragment encoding senescence-induced deoxyhypusine synthase, senescence-induced eIF-5A or both into the plant genome in antisense orientation. Plant genes encoding senescence-induced deoxyhypusine synthase and senescence-induced eIF-5A are identified and the nucleotide sequences of each, alone and in combination are used to modify senescence in transgenic plants.
Owner:SENESCO TECHNOLOGIES INC
Application of CRISPR/nCas9 mediated site-directed base substitution in plant
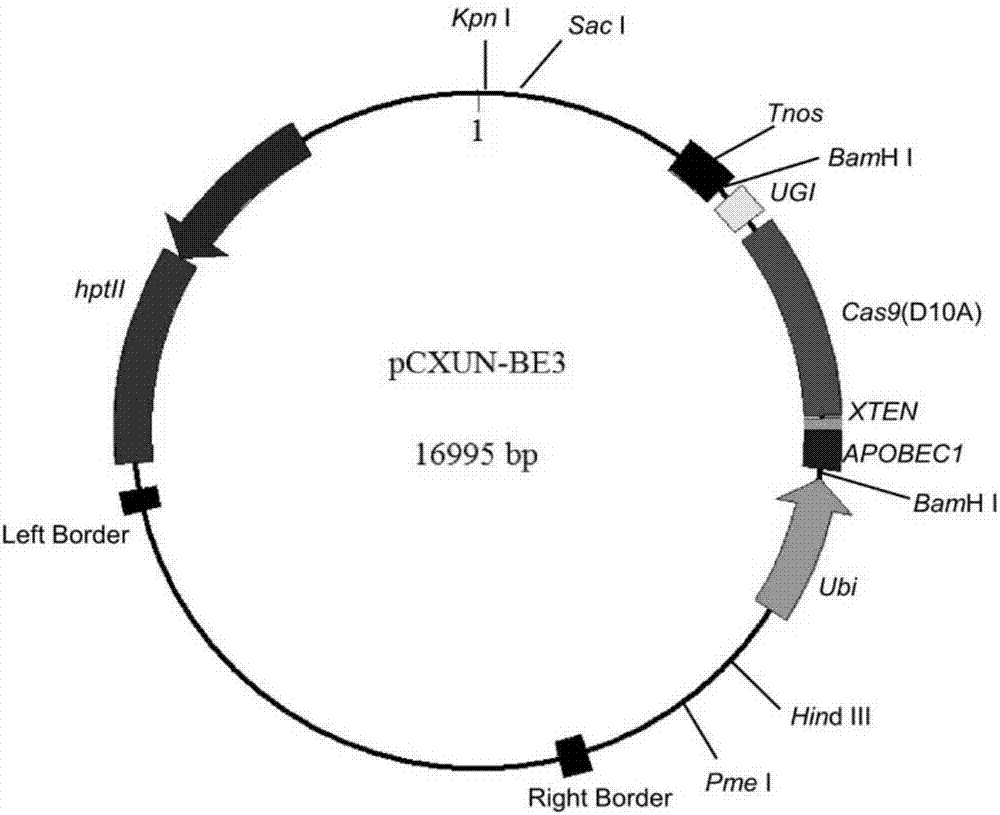
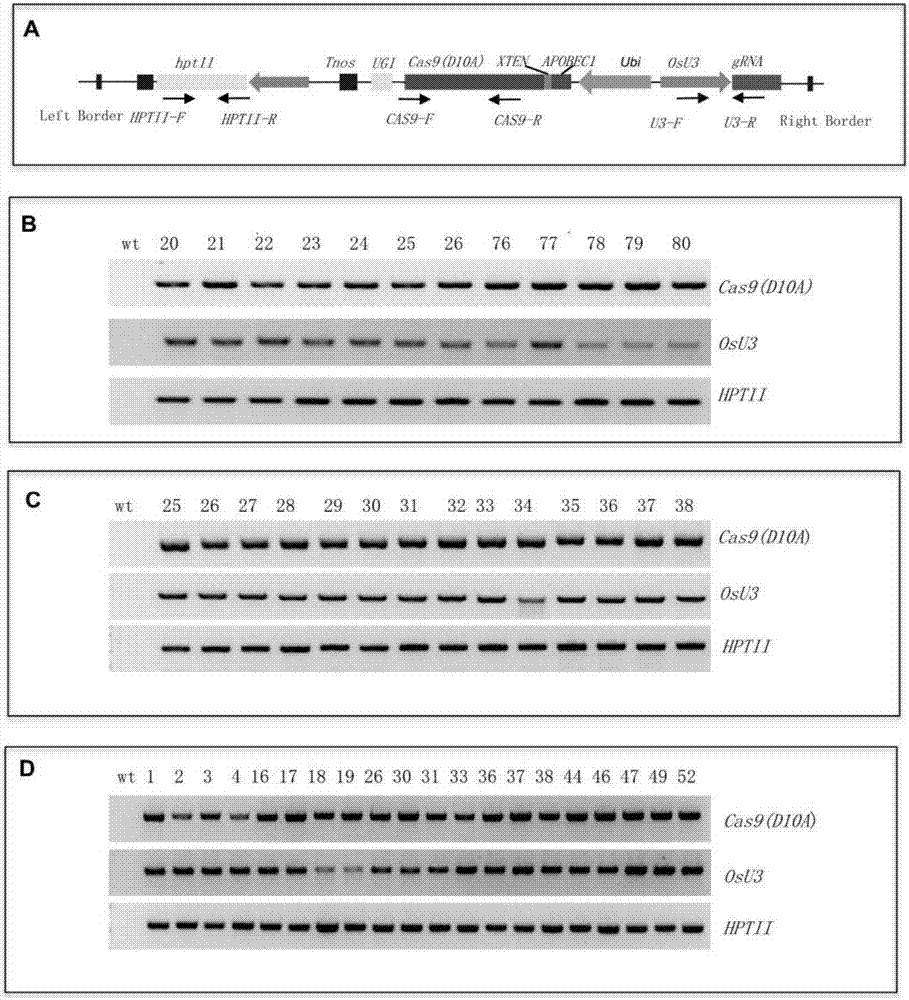
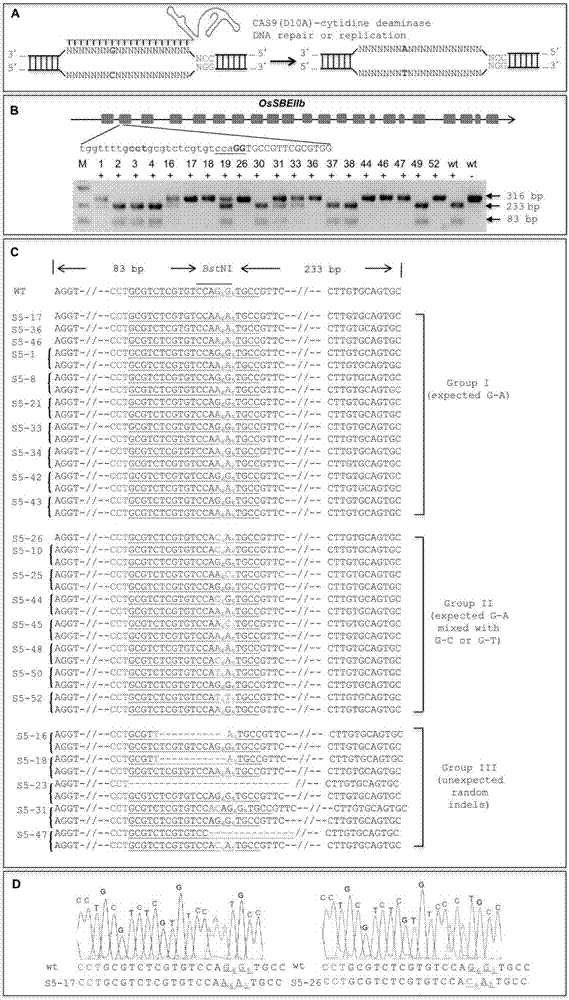
ActiveCN107043779ARapid improvement of agronomic traitsImproved agronomic traitsVectorsVector-based foreign material introductionUracil-DNA glycosylaseSubstitution method
The invention discloses application of CRISPR / nCas9 mediated site-directed base substitution in a plant. The invention provides a plant genome site-directed edition system. The system comprises a BE3 plant expression carrier (expressing a fusion protein composed of nCas9(D10A), deaminase and a uracil DNA glycosylase inhibitory protein), and rice OsPDS and OsSBEIIb are taken as target genes for verifying the system. Results show that an expected site-directed mutant plant is respectively obtained in the three selected target spots, accurate site mutation of a base is realized in rice, and the highest efficiency reaches about 20%, so that a feasible and effective base substitution method is provided for crop breeding, the method has strong application potential in the aspect of agricultural breeding, and a foundation is provided for rapidly improving important agronomic traits of crops.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
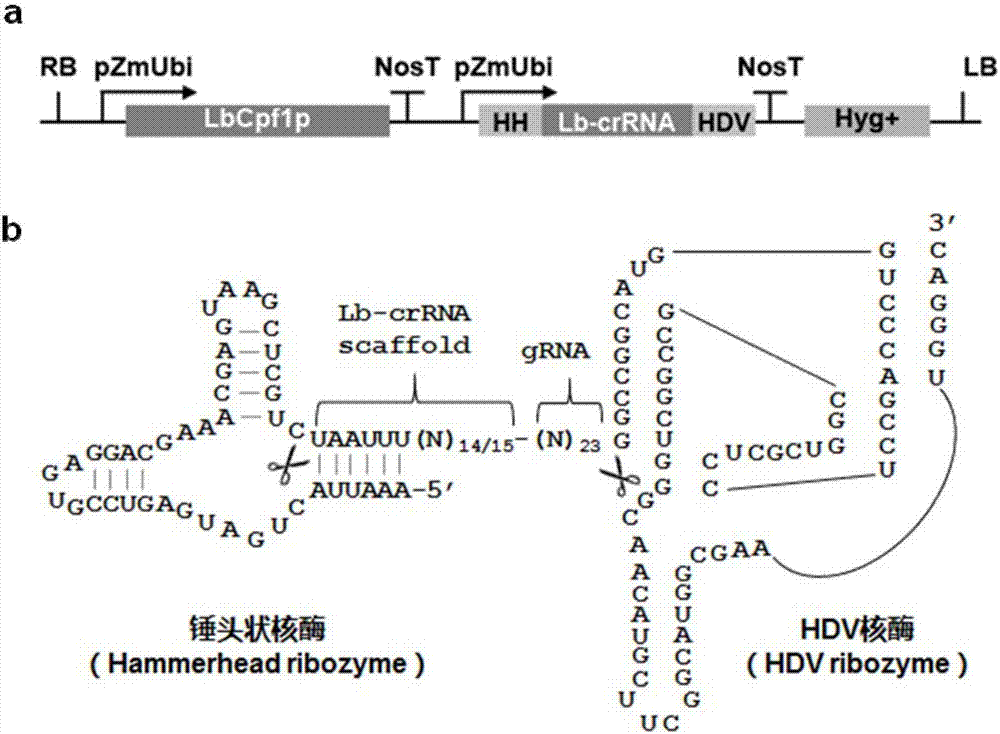
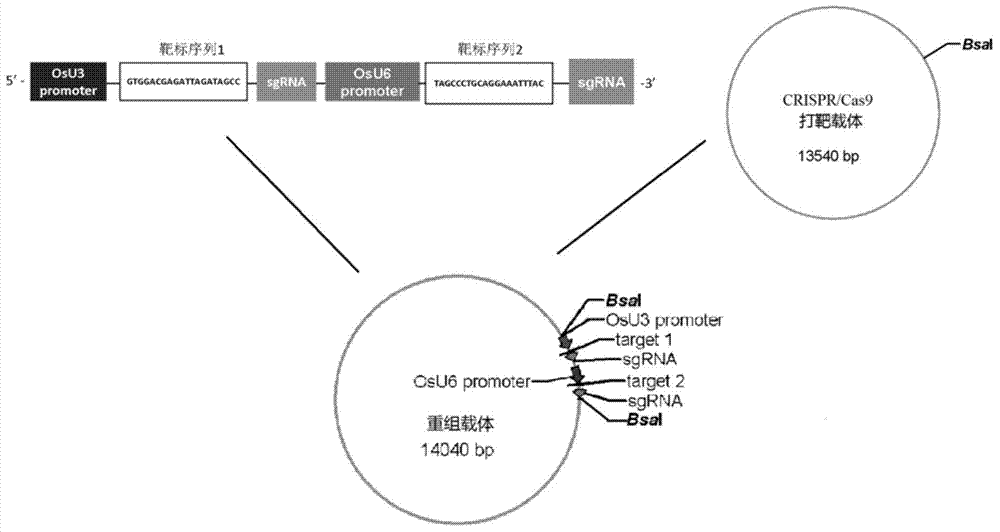
CRISPR/Cpf1 plant genome directional modification function unit, carrier comprising function unit, and application thereof
ActiveCN107012164AEfficient constructionDirectional modification shortcutVector-based foreign material introductionGene expressionNuclease
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene engineering, and concretely relates to a CRISPR / Cpf1 plant genome directional modification function unit, a carrier comprising the function unit, and application thereof. The invention aims to build an effective plant genome CRISPR / Cpf1 directional modification framework carrier according to an action principle of a CRISPR / Cpf1 system and a vegetable cell gene expression characteristic, and realize high-efficient application thereof in plant genome directional modification. The technical scheme provided by the invention is characterized by building the CRISPR / Cpf1 plant genome directional modification framework carrier formed by lachnospiraceae bacterium Cpf1 nuclease protein (LbCpf1) expression unit and a guiding crRNA transcription expression unit. The invention also provides a method for designing specificity-guided crRNA and building a CRISPR / Cpf1 recombinant expression vector aiming at rice genome target loci by adopting the CRISPR / Cpf1 plant genome directional modification framework carrier. The invention provides the high-efficient CRISPR / Cpf1 plant directional modification framework carrier, which can effectively realize simple, fast and high-efficient directional modification based on the CRISPR / Cpf1 system aiming at a plant genome target sequence.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method for improved plant breeding
InactiveUS20110167721A1Quick analysisAvoid prolonged exposureGrain huskingGrain polishingGenotypeBreeding program
The invention relates generally to an improved plant breeding system. More particularly, this invention relates to a method for automated, high throughput analysis of plant phenotype and plant genotype in a breeding program.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI
Plant Expression Constructs and Methods of Utilizing Same
InactiveUS20100071088A1Improve protectionSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesWhole bodyGene silencing
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREW UNIV OF JERUSALEM LTD +1
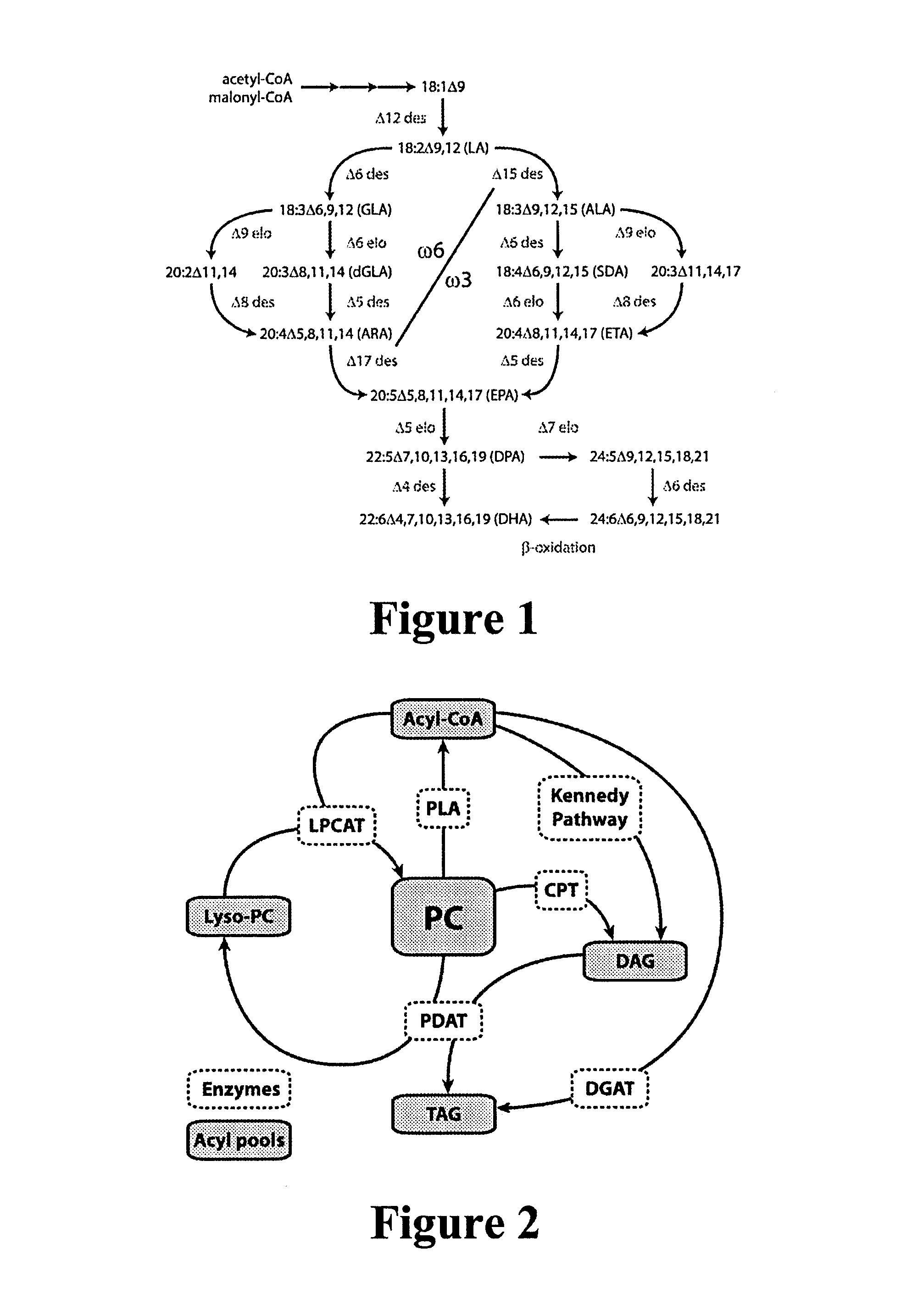
Enzymes and methods for producing omega-3 fatty acids
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG +1
CRISPR/Cas9 system for efficiently editing plant gene groups in fixed-point mode
ActiveCN105177038AClimate change adaptationVector-based foreign material introductionAgricultural scienceNucleotide
The invention discloses a first expression cassette containing a promoter pYAO. In the expression cassette, the promoter pYAO promotes a coding gene expression of Cas9 nuclease; the promoter pYAO is shown in the following steps that (a1), the promoter pYAO is a DNA molecule at the 1-1012 position from the 5' tail end in a sequence table first sequence; (a2), the promoter pYAO is a DNA molecule which has 75% or more of identity with a nucleotide sequence which is defined by (a1) and has a promoter function; (a3), the promoter pYAO is a DNA molecule which hybridizes with the nucleotide sequence defined by (a1) or (a2) under strict conditions and has a promoter function. Experiments prove that YAO genes of high-expression genes at a plant gametophte or / and embryonic development early-stage are utilized for driving the expression of Cas9 genes, and the plant gene groups can be efficiently edited.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
DNA encoding a plant deoxyhypusine synthase, a plant eukaryotic initiation factor 5A, transgenic plants and a method for controlling senescence programmed and cell death in plants
InactiveUS6878860B1Lower Level RequirementsReduce and prevent expression of geneBacteriaOxidoreductasesAntisense OrientationApoptotic programmed cell death
Regulation of expression of programmed cell death, including senescence, in plants is achieved by integration of a gene or gene fragment encoding senescence-induced deoxyhypusine synthase, senescence-induced elF-5A or both into the plant genome in antisense orientation. Plant genes encoding senescence-induced deoxyhypusine synthase and senescence-induced elF-5A are identified and the nucleotide sequences of each, alone and in combination are used to modify senescence in transgenic plants.
Owner:AGRIBODY TECH INC
Method for deleting selection marker gene of transgenic rice
ActiveCN104846010AHigh distribution frequencyEasy to operateVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsGenetically modified ricePlant genetic engineering
The invention provides a method for deleting a selection marker gene of transgenic rice and belongs to the field of plant gene engineering. The method for efficiently deleting the marker gene of the transgenic rice in a plant level is established by utilizing a genome fixed-point editing technology mediated by a CRISPR / Cas9 system. The whole segment of the marker gene can be effectively deleted by utilizing the method, and only an expression frame of the marker gene is deleted pointedly without change of the expression of other components in the transgenic rice. Thus, the transgenic rice without the selection marker gene can be efficiently bred by utilizing the method, so that the safety doubt of people about the selection marker gene can be completely removed.
Owner:RICE RES ISTITUTE ANHUI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Promoter, promoter control elements, and combinations, and uses thereof
ActiveUS20110191912A1Enhancing and reducing regionPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsGene productSynthetic DNA
The present invention provides DNA molecules that constitute fragments of the genome of a plant, and polypeptides encoded thereby. The DNA molecules are useful for specifying a gene product in cells, either as a promoter or as a protein coding sequence or as an UTR or as a 3′ termination sequence, and are also useful in controlling the behavior of a gene in the chromosome, in controlling the expression of a gene or as tools for genetic mapping, recognizing or isolating identical or related DNA fragments, or identification of a particular individual organism, or for clustering of a group of organisms with a common trait. One of ordinary skill in the art, having this data, can obtain cloned DNA fragments, synthetic DNA fragments or polypeptides constituting desired sequences by recombinant methodology known in the art or described herein.
Owner:CERES INC
Methods and compositions for producing male sterile plants
Methods of making a targeted modification in a male fertility gene in the genome of a plant are disclosed. The methods involve contacting a plant cell with an engineered double-strand-break-inducing agent capable of inducing a double-strand break in a target sequence in the male fertility gene and identifying a cell comprising an alteration in the target sequence. Also disclosed are plants, plant cells, plant parts, and seeds comprising a male fertility gene with an alteration in a male fertility gene. Nucleic acid molecules comprising male fertility genes with at least one targeted modification therein, optimized nucleic acid molecules encoding endonucleases that are engineered double-strand-break-inducing agents and expression cassettes, host cells, and plants comprising one or more of the nucleic acid molecules are further disclosed.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Plant artificial chromosomes, uses thereof and methods of preparing plant artificial chromosomes
InactiveUS20060143732A1Easy to zoom inSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsHeterologousEuchromatin
Methods for preparing cell lines that contain plant artificial chromosomes, methods for preparation of plant artificial chromosomes, methods for targeted insertion of heterologous DNA into plant artificial chromosomes, and methods for delivery of plant chromosomes to selected cells and tissues are provided. In particular, plant artificial chromosomes that are substantially composed of repeated nucleic acid units of varying amounts of heterochromafin and euchromatin are provided. Also provided are methods of using plant and animal artificial chromosomes in the production of valuable transgenic plants. Methods for identifying plant genes encoding particular traits using artificial chromosomes and for producing an acrocentric plant chromosome also are provided.
Owner:CALYX BIO VENTURES +1
Nucleic acid constructs and methods for producing altered seed oil compositions
ActiveUS20050034190A9Suppressing endogenous expressionIncreasing endogenous expressionTransferasesBiofuelsFatty acid biosynthesisAdemetionine
The present invention is in the field of plant genetics and provides recombinant nucleic acid molecules, constructs, and other agents associated with the coordinate manipulation of multiple genes in the fatty acid synthesis pathway. In particular, the agents of the present invention are associated with the simultaneous enhanced expression of certain genes in the fatty acid synthesis pathway and suppressed expression of certain other genes in the same pathway. Also provided are plants incorporating such agents, and in particular plants incorporating such constructs where the plants exhibit altered seed oil compositions.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Nematode-inducible plant gene promoter
An isolated DNA fragment that promotes root knot or cyst nematode indcuible transcription of a coding sequence downstream of and operably linked to the fragment in at least an Arabidopsis thaliana plant and a chimeric DNA sequence including the DNA fragment. Also, methods for the use of the DNA fragment.
Owner:SYNGENTA MOGEN BV
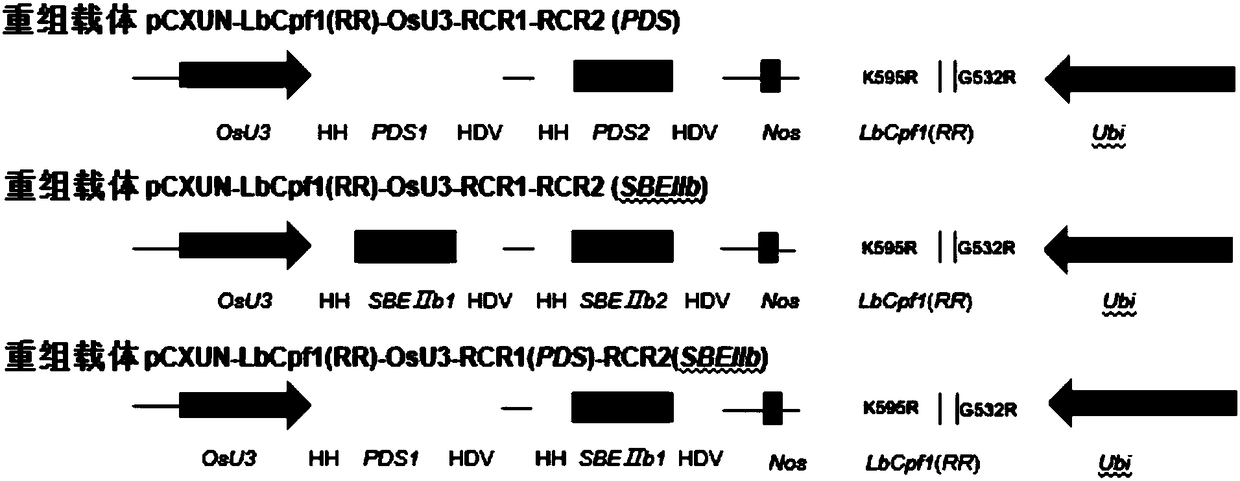
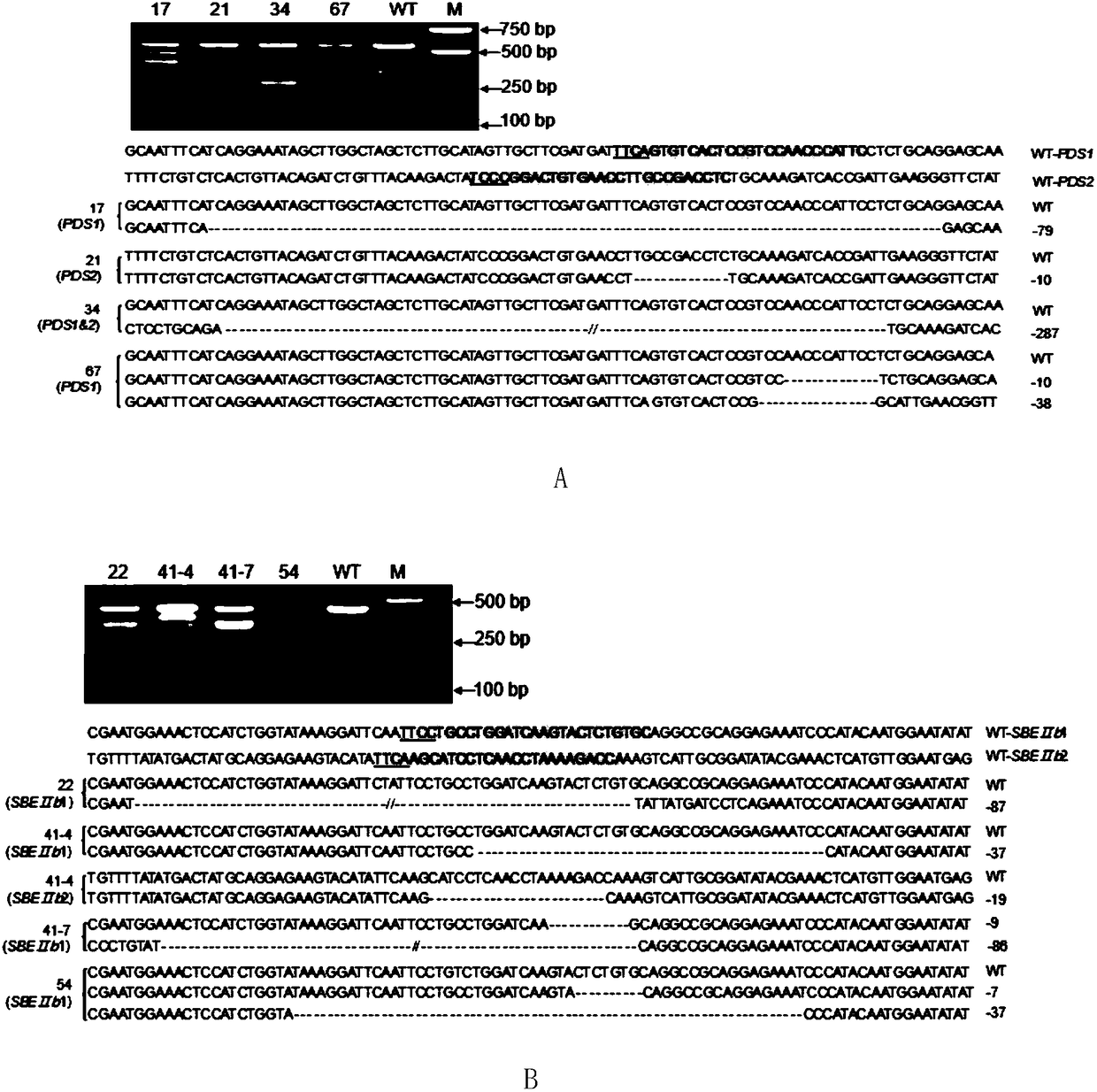
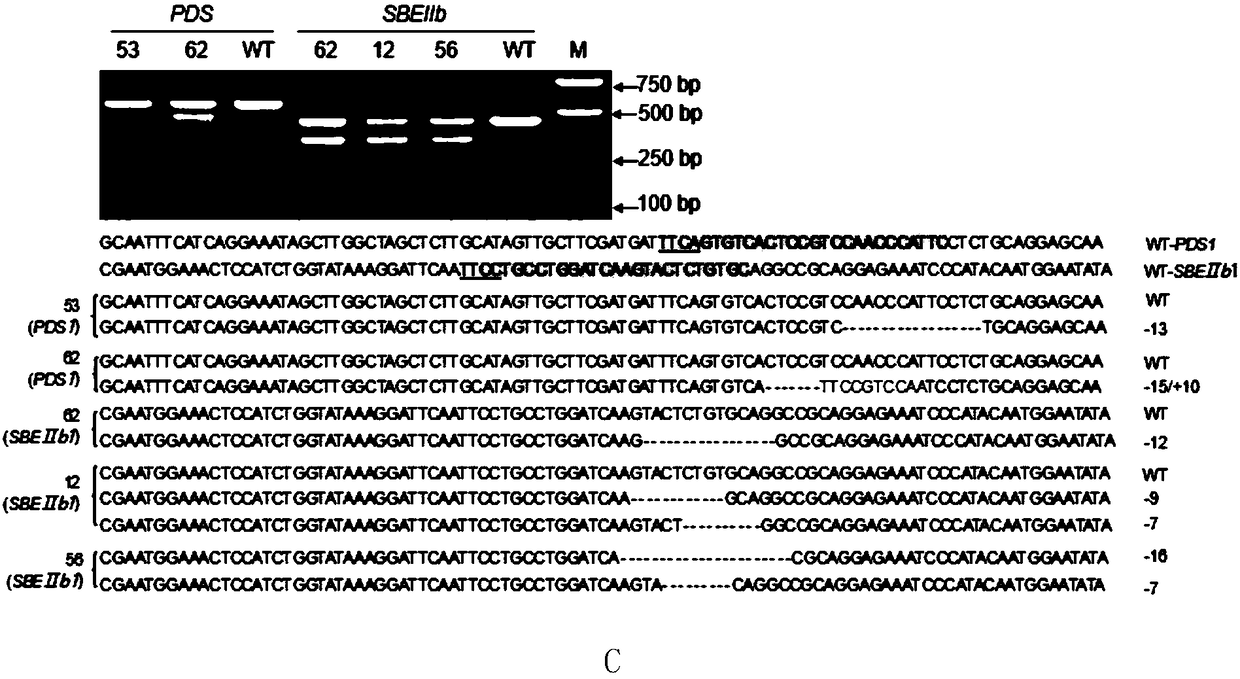
Application for using LbCpf1-RR mutant in CRISPR/Cpf1 system in plant gene editing
ActiveCN108486146AExpand the scope of editingAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNucleic acid vectorRice plantsMutant
The invention discloses application for using an LbCpf1 - RR mutant in a CRISPR / Cpf1 system in plant gene editing. The application for using the LbCpf1 - RR mutant in the CRISPR / Cpf1 system in plant gene editing uses an OsPDS gene and an OsSBEIIb gene as target genes, constructs a target double loci of one gene and a series of vectors of two genes, and utilizes an agrobacterium-mediated transformation method to import the vectors into rice callus, and rice plants with the target gene knockout are successfully obtained by using the LbCpf1-RR mutant. The only difference between the LbCpf1-RR mutant and the protein LbCpf1 is that the 532nd amino acid changes from G to R, and the 595th amino acid changes from K to R. The LbCpf1-RR mutant provided by the application for using the LbCpf1 - RR mutant in the CRISPR / Cpf1 system in plant gene editing expands the PAM site sequence identified by the LbCpf1-RR mutant, so that the editing range of the CRISPR / Cpf1 system in rice genome is expanded, great significance for promoting the application of the system in the field of plant genome editing is achieved. The application for using the LbCpf1 - RR mutant in the CRISPR / Cpf1 system in plant geneediting has great application value.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Recombinant vector and non-GMO gene editing plant screening method
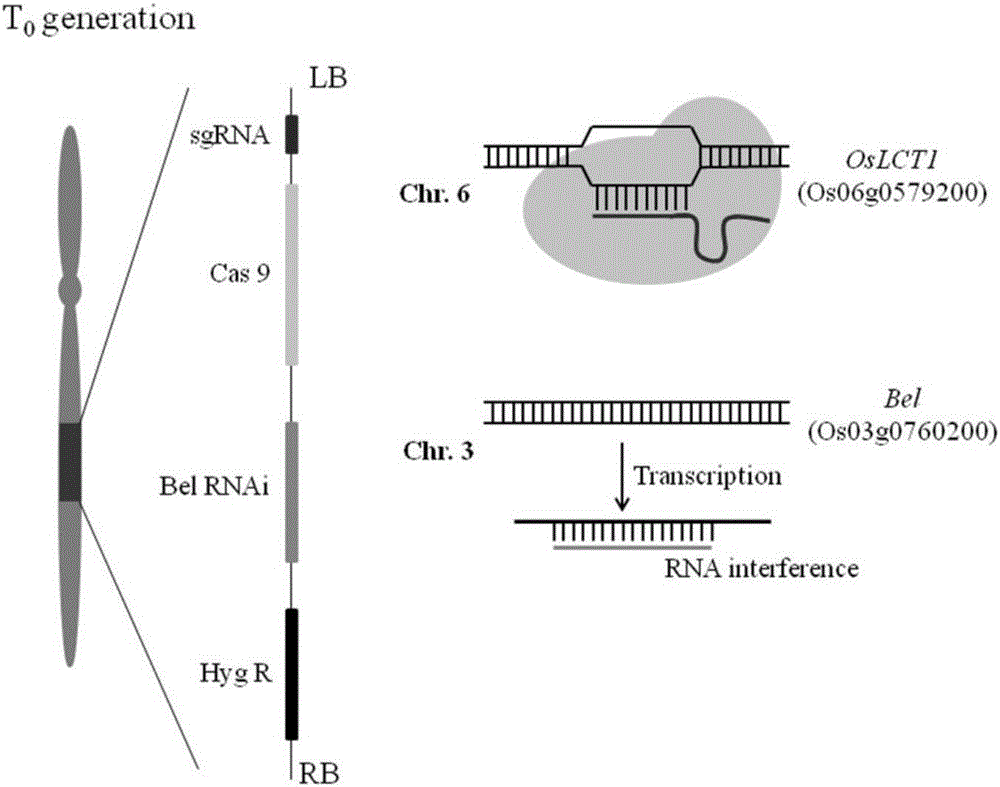
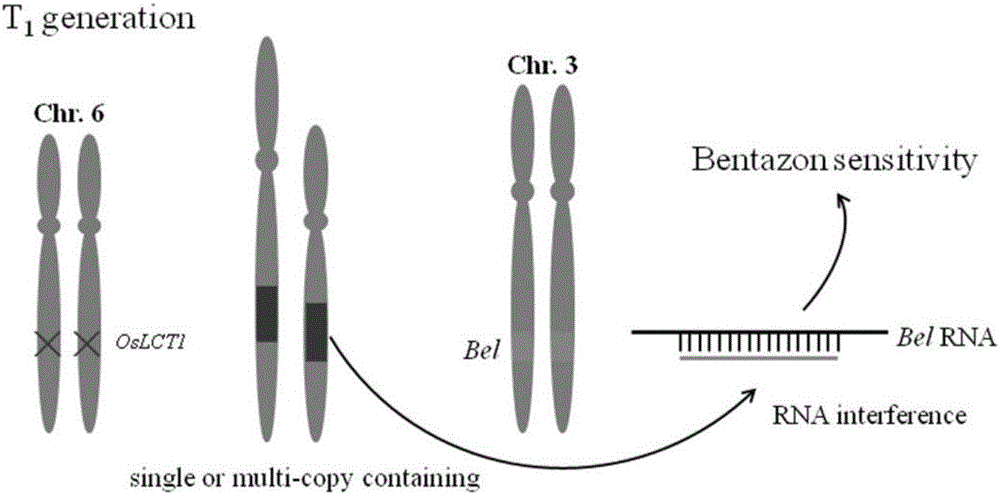
ActiveCN106222193AInexpensive screening methodSimple screening methodVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsResistant genesHerbicide screen
The invention discloses a recombinant vector and a non-GMO gene editing plant screening method. An initial carrier in the recombinant vector is a CRISPR / Cas9 carrier which contains sgRNA gene, Cas9 gene and screening label gene and is used for plant gene editing, the recombinant vector carries a BelRNAi expression element, and a hairpin RNA interference fragment interfering with bentazone resistance gene is generated through transcription of the BelRNAi expression element. By introducing the BelRNAi expression element to the initial carrier and conducting bentazone herbicide screening on future generation plants, offspring with target gene mutated are reserved, and it is also ensured that the mutated offspring do not contain transgenic fragments; screening method is cheaper, simpler and more effective.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com