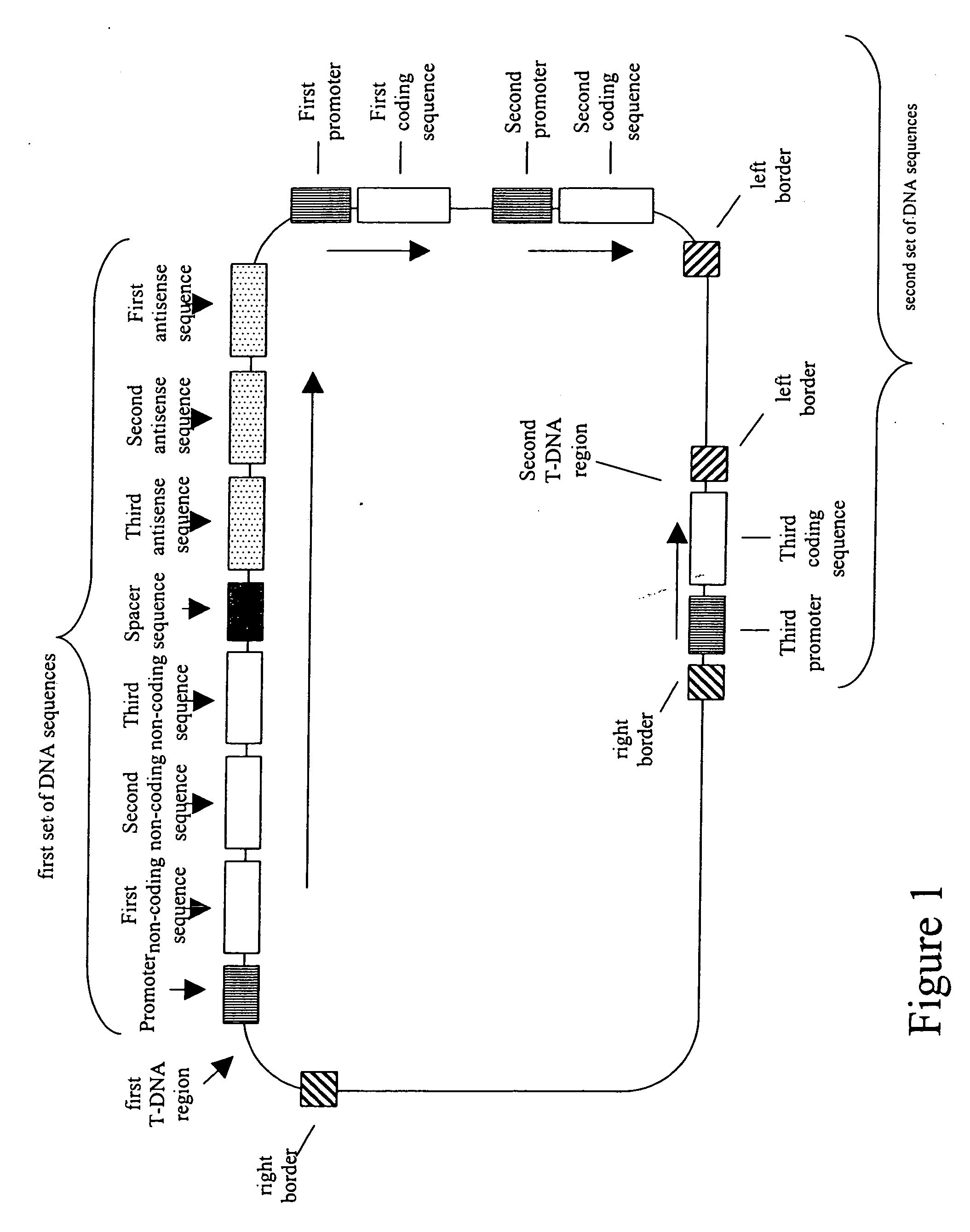
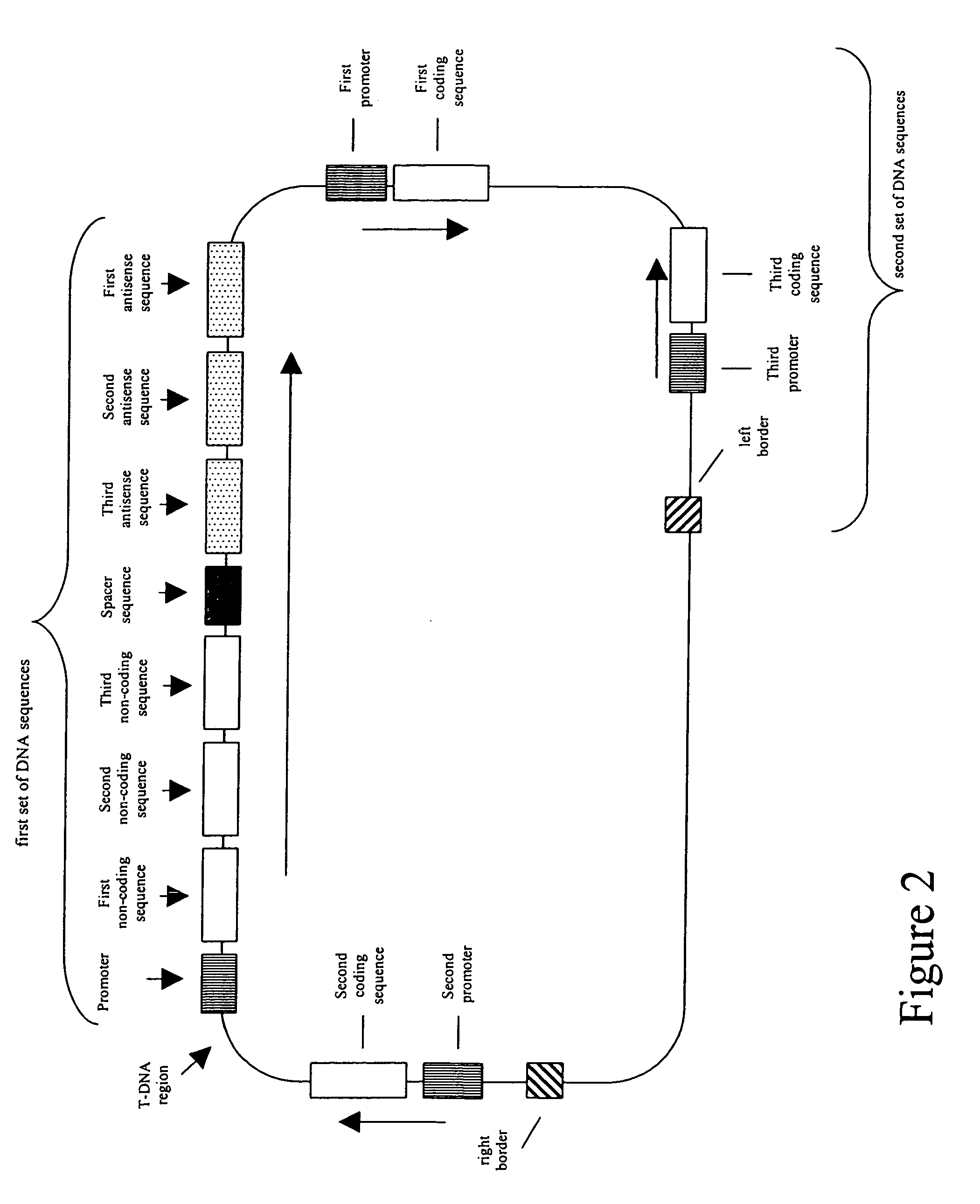
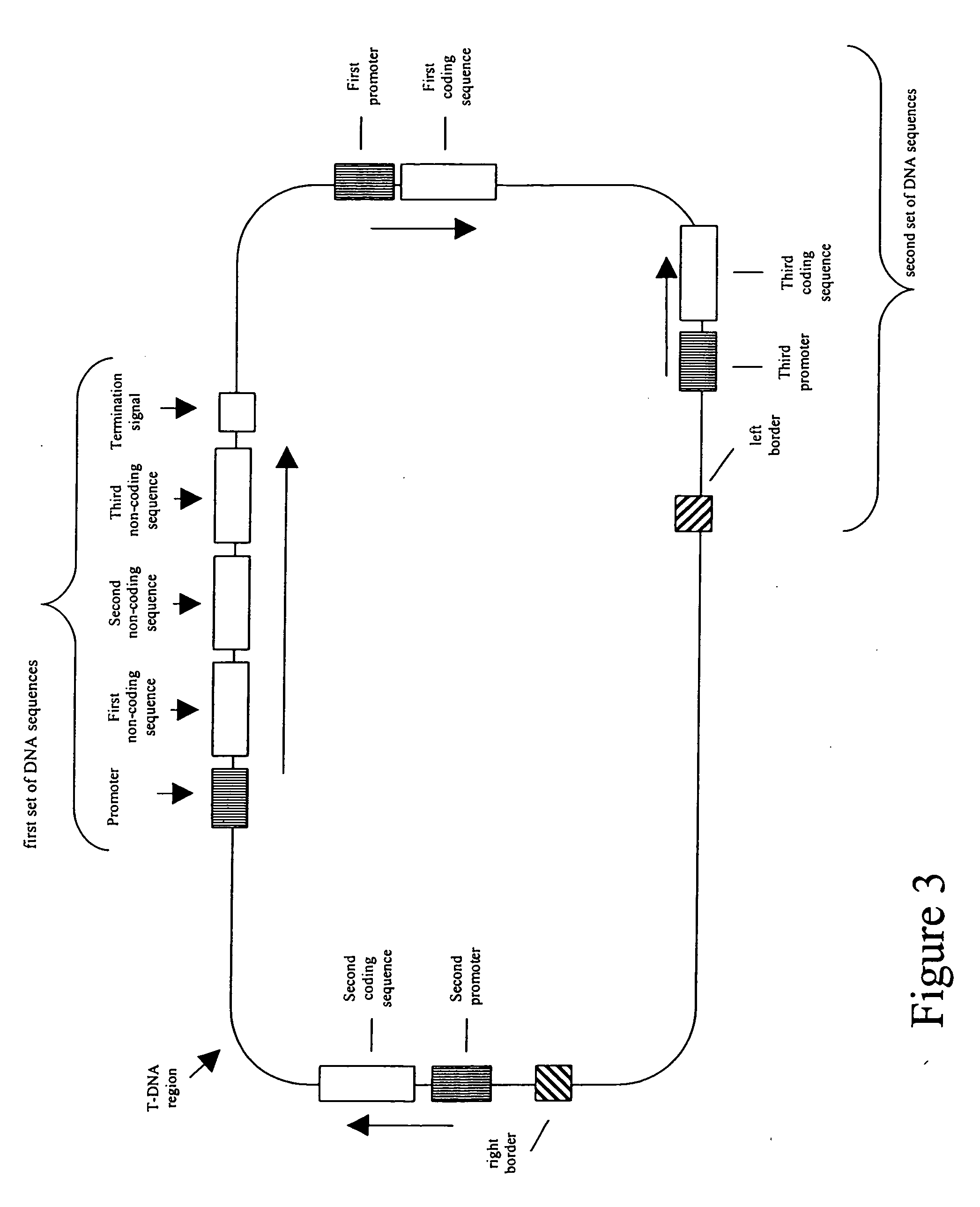
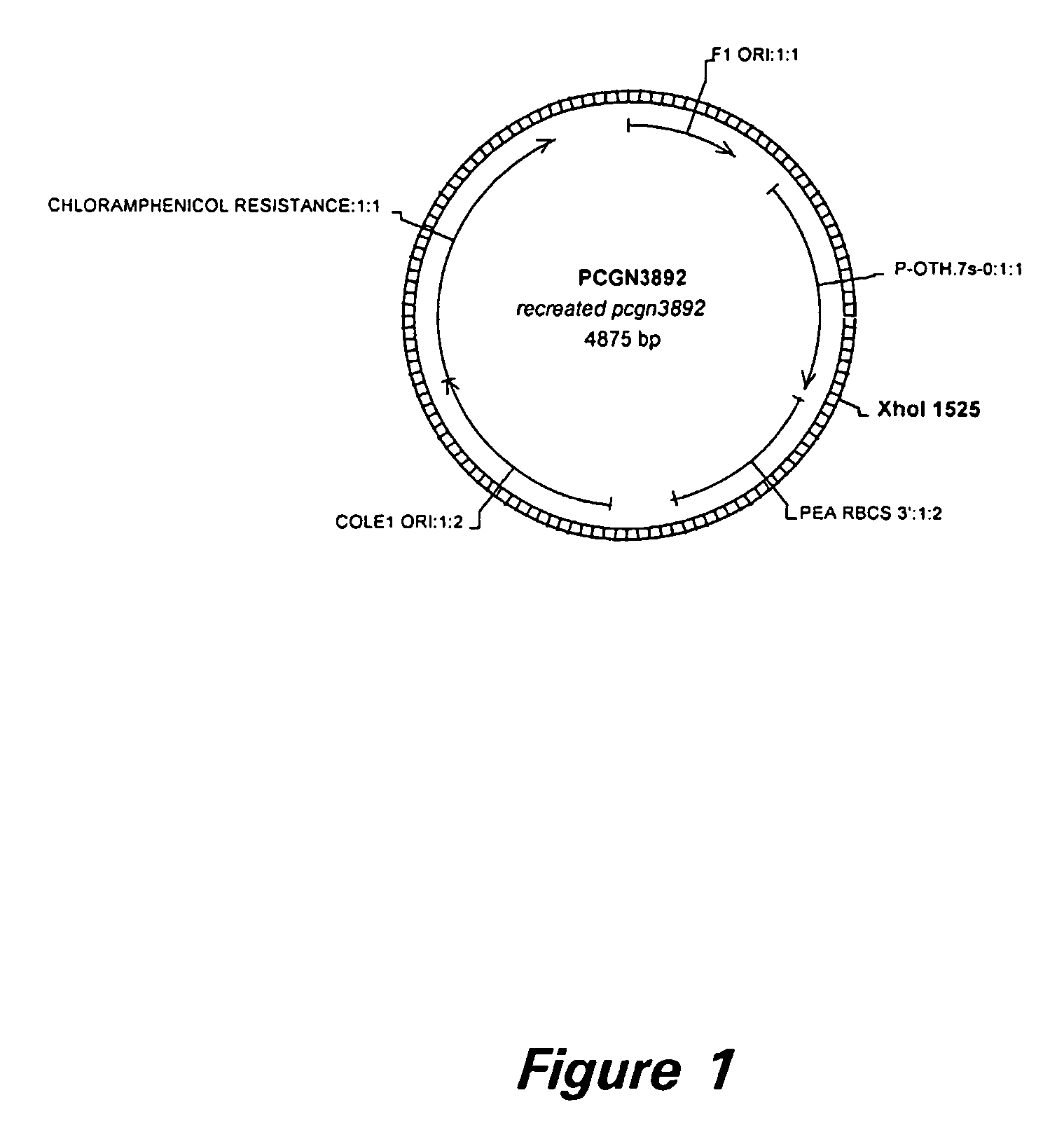
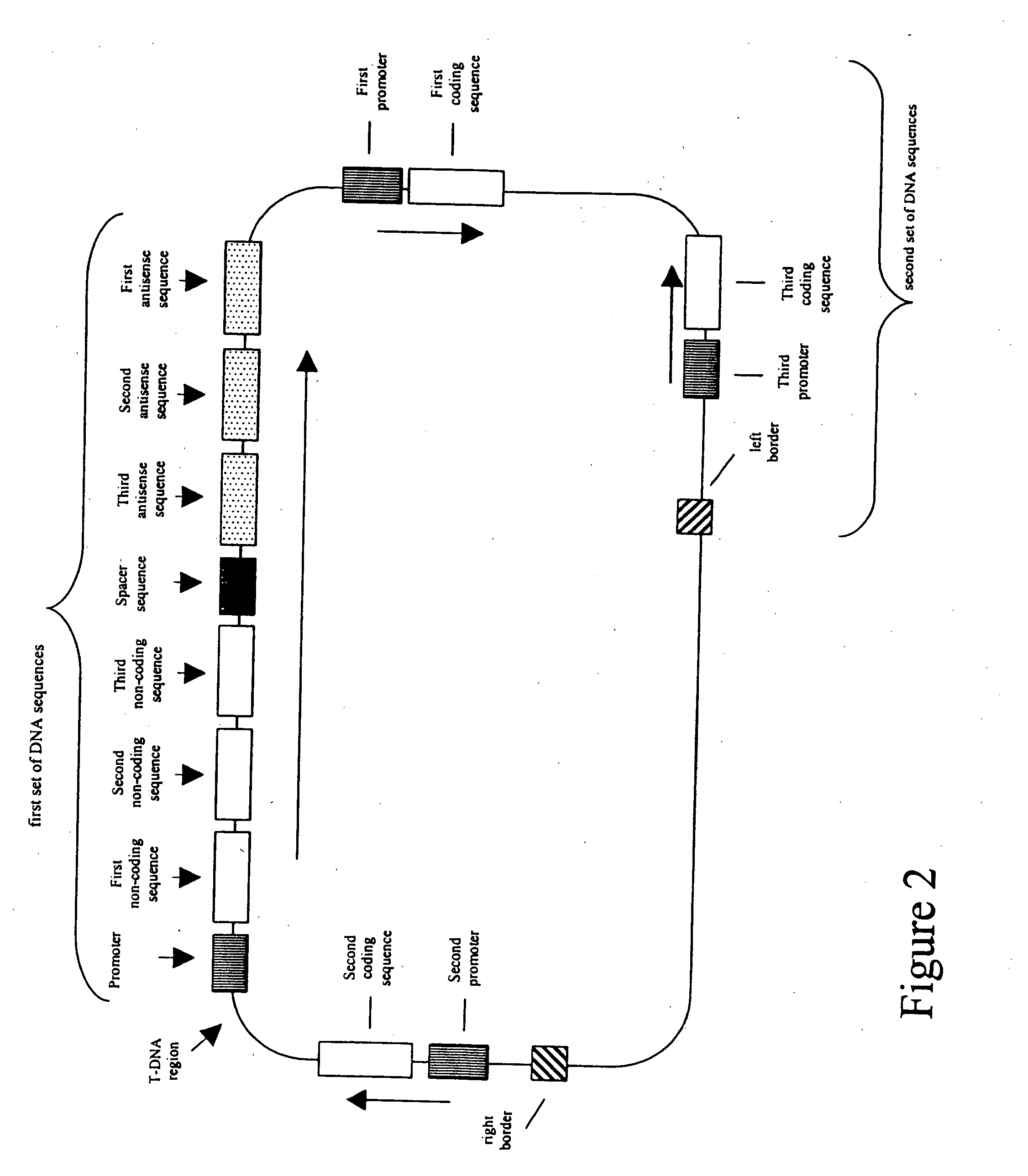
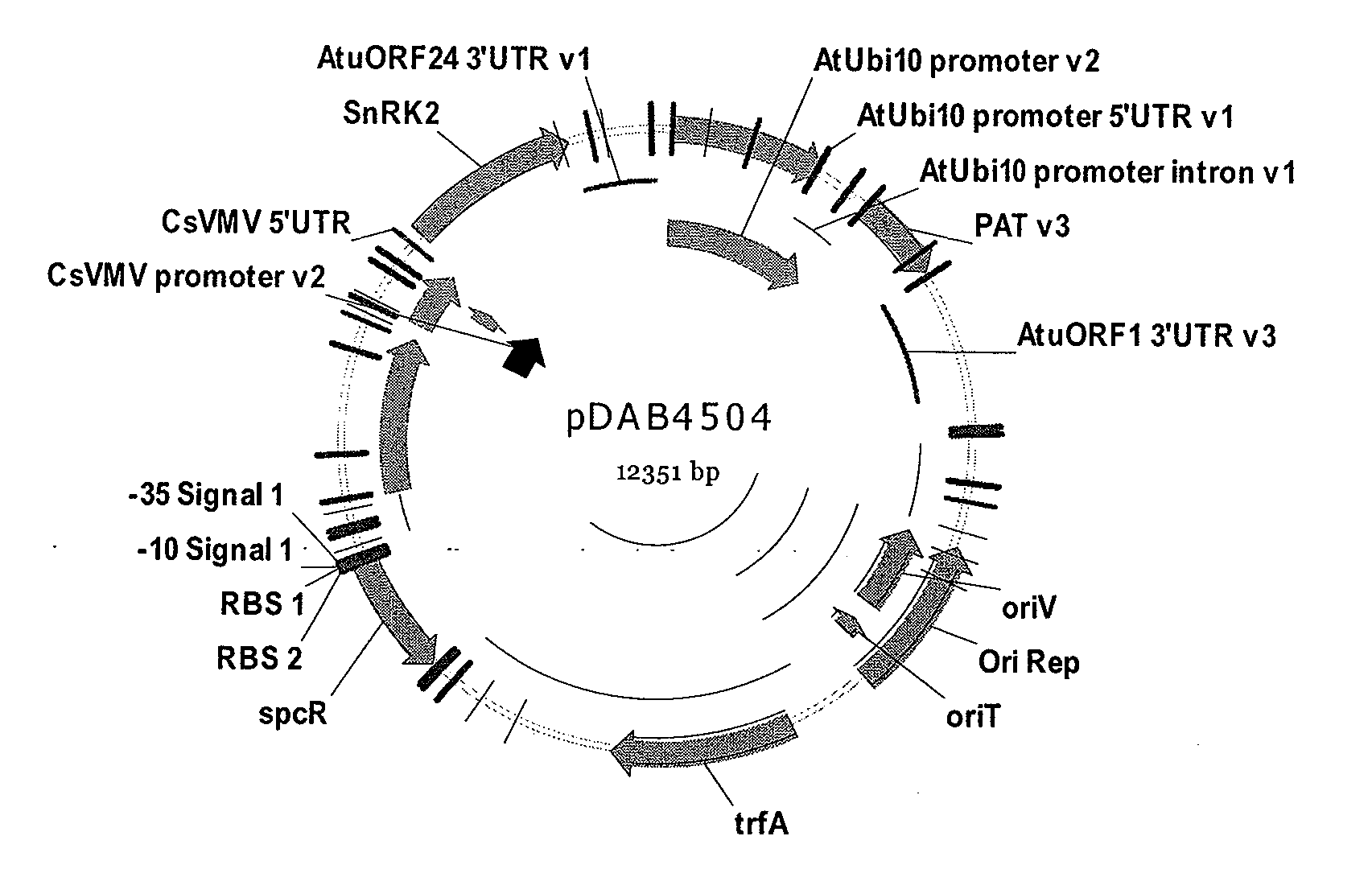
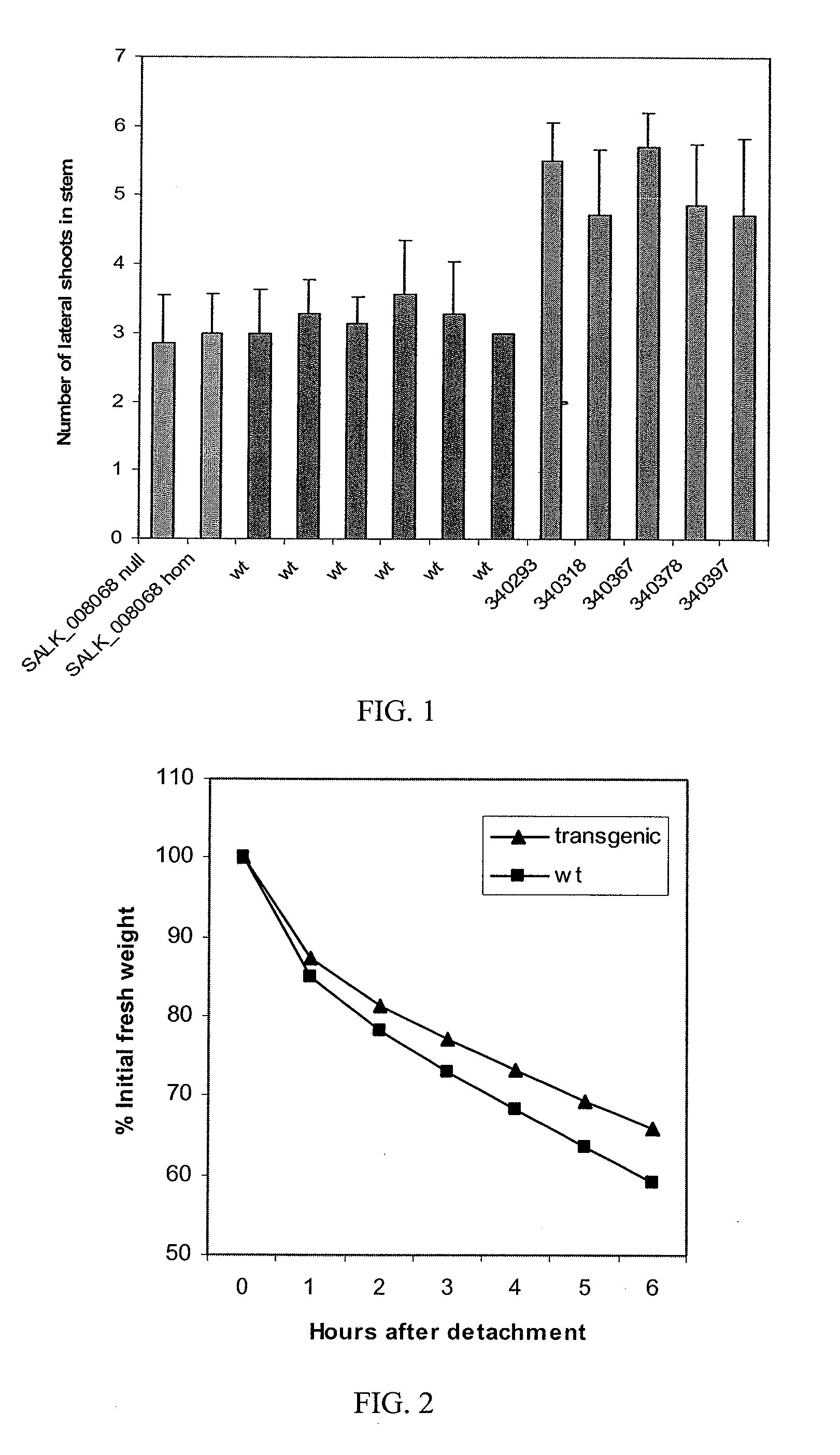
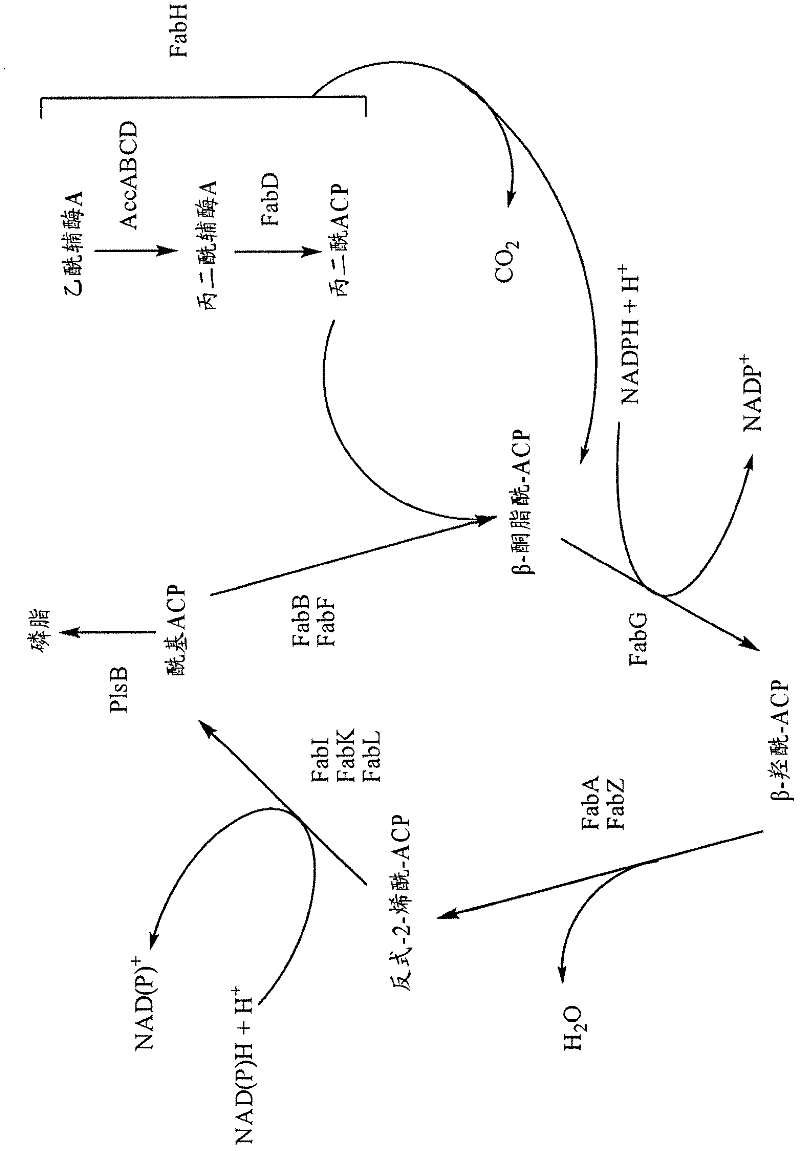
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
113 results about "Fatty acid biosynthesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
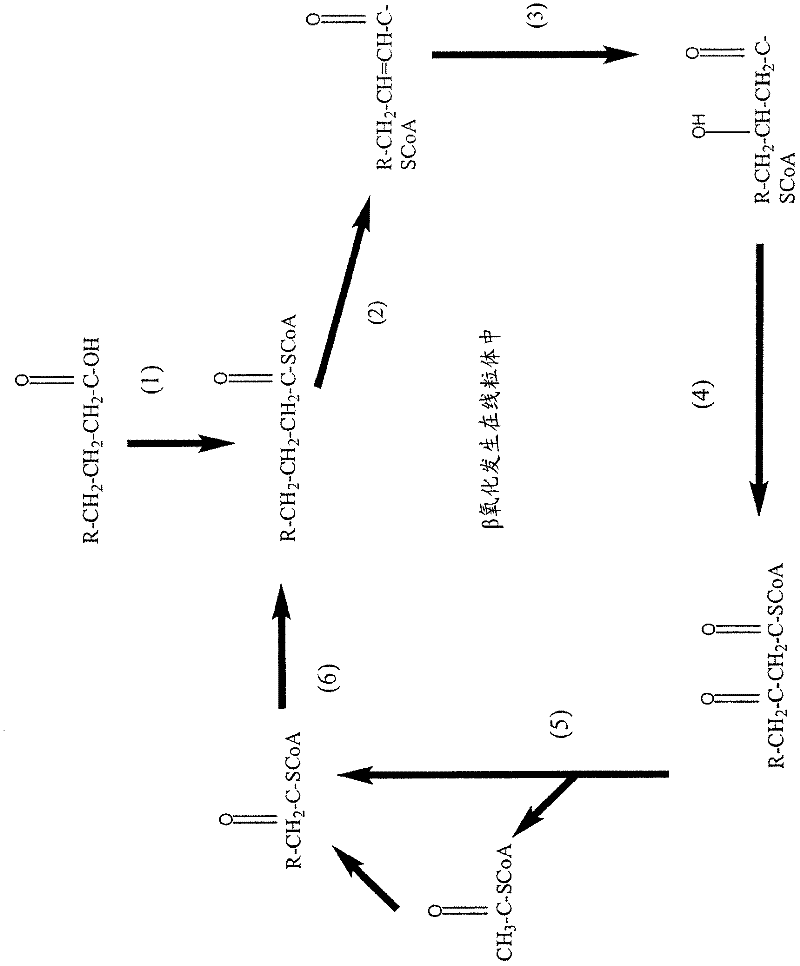
Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and NADPH through the action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. This process takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell.
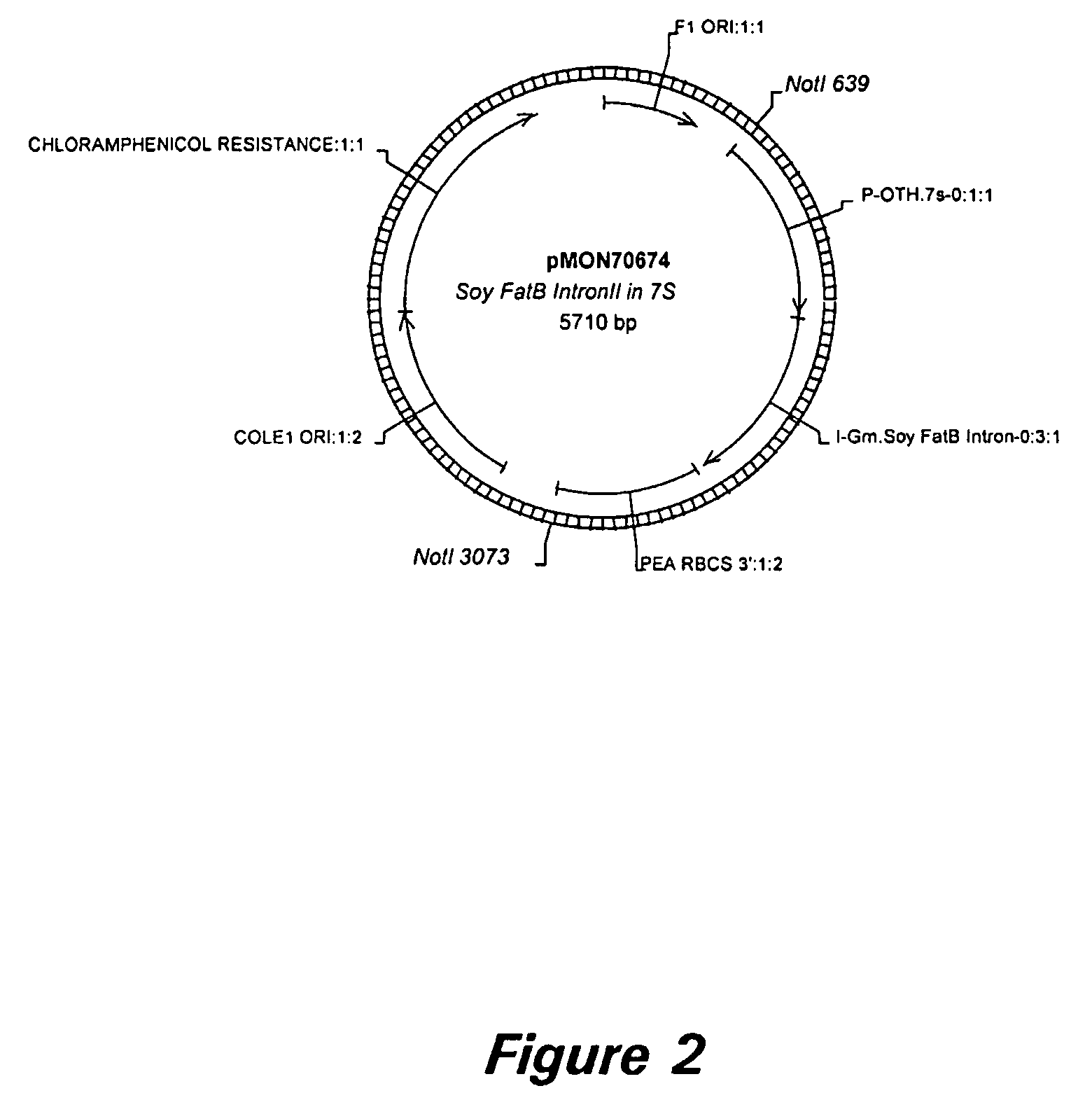
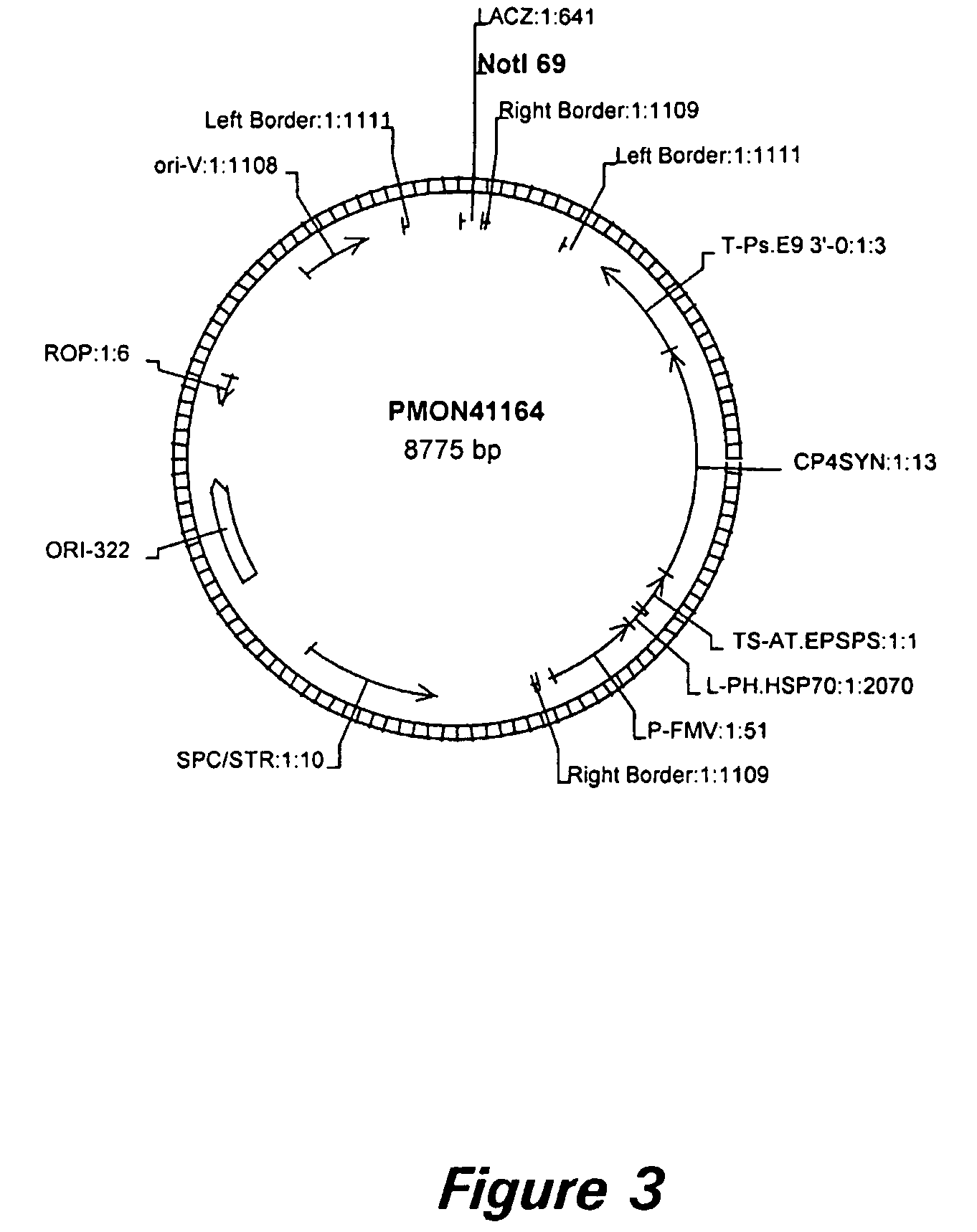
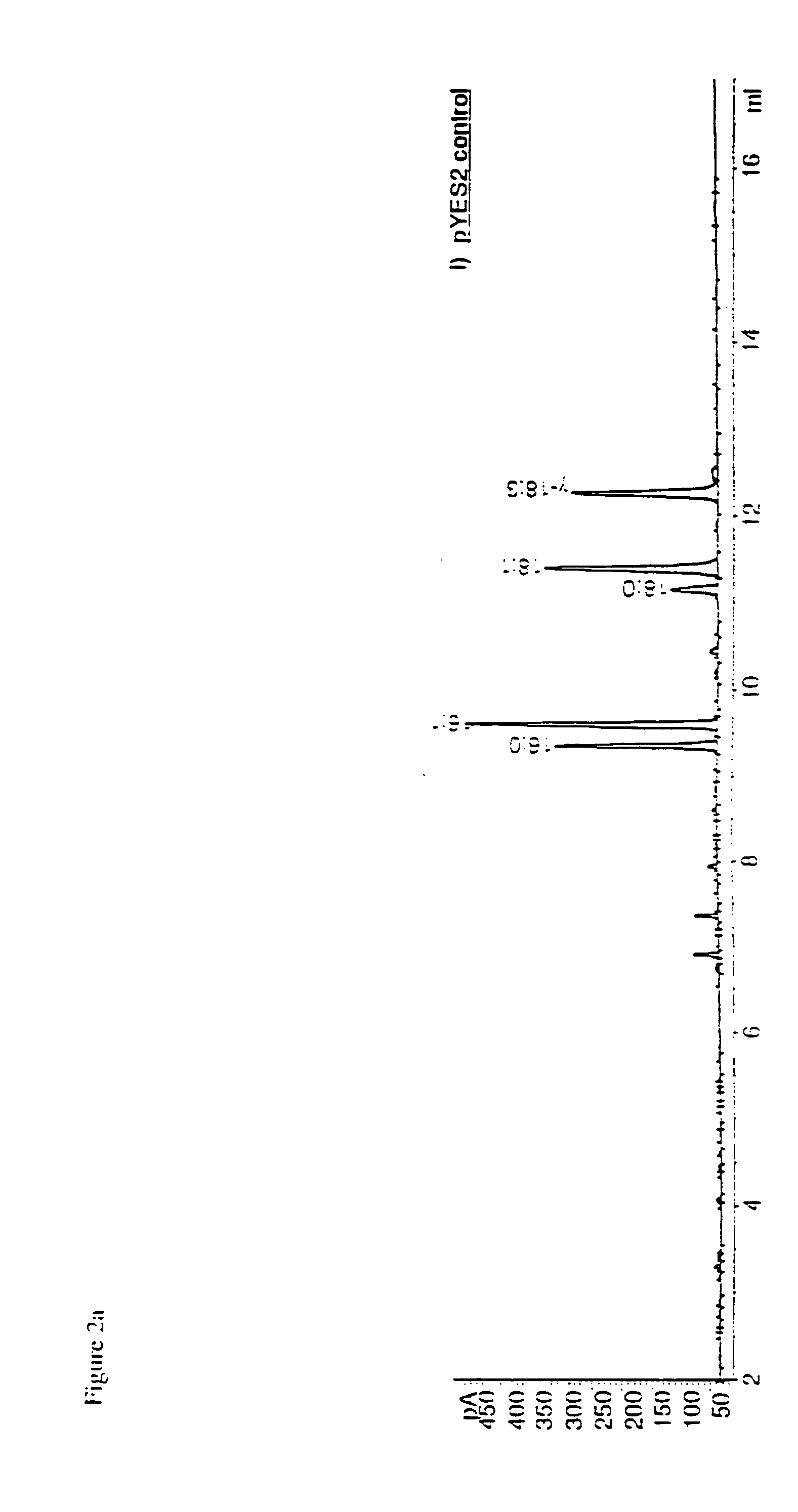
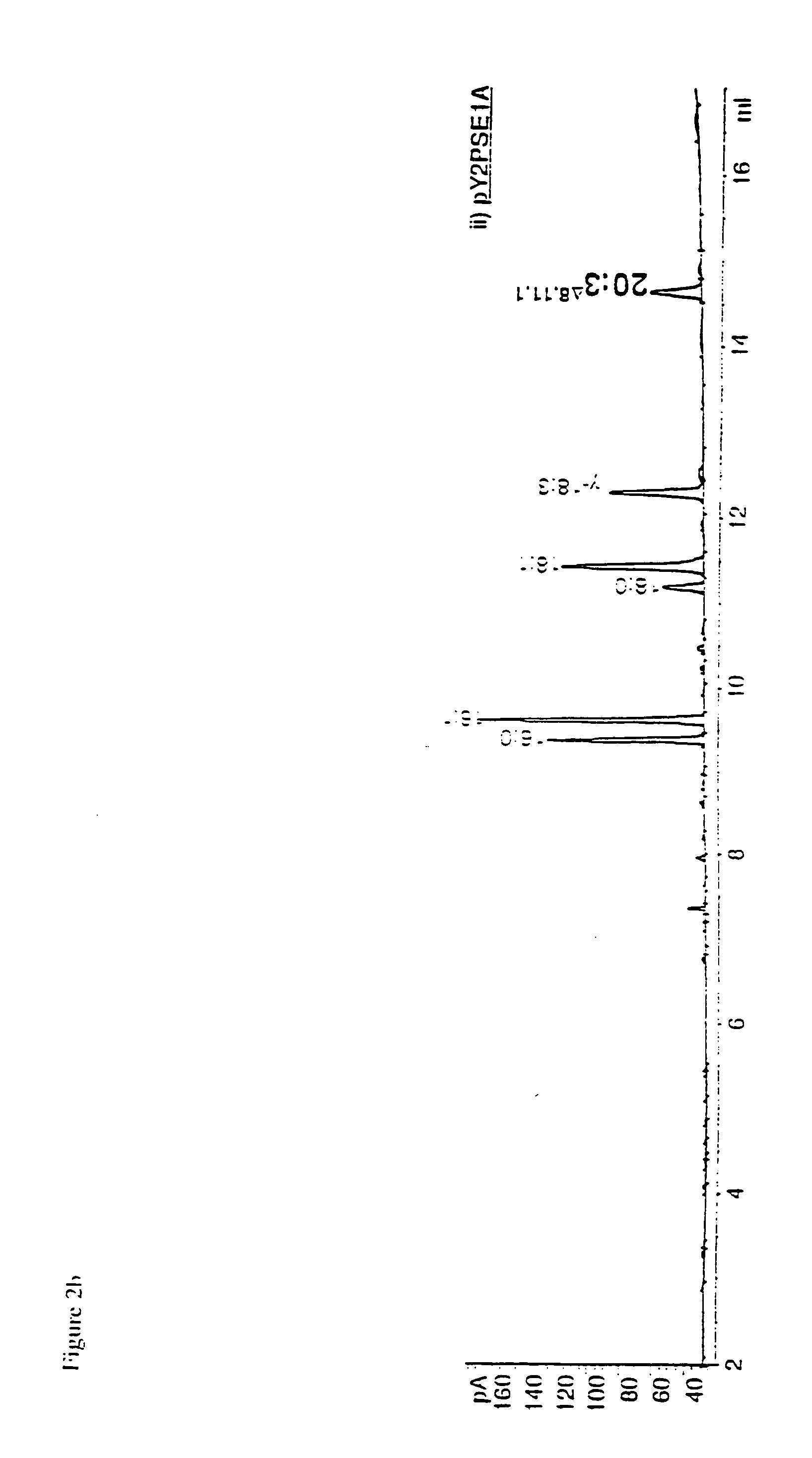
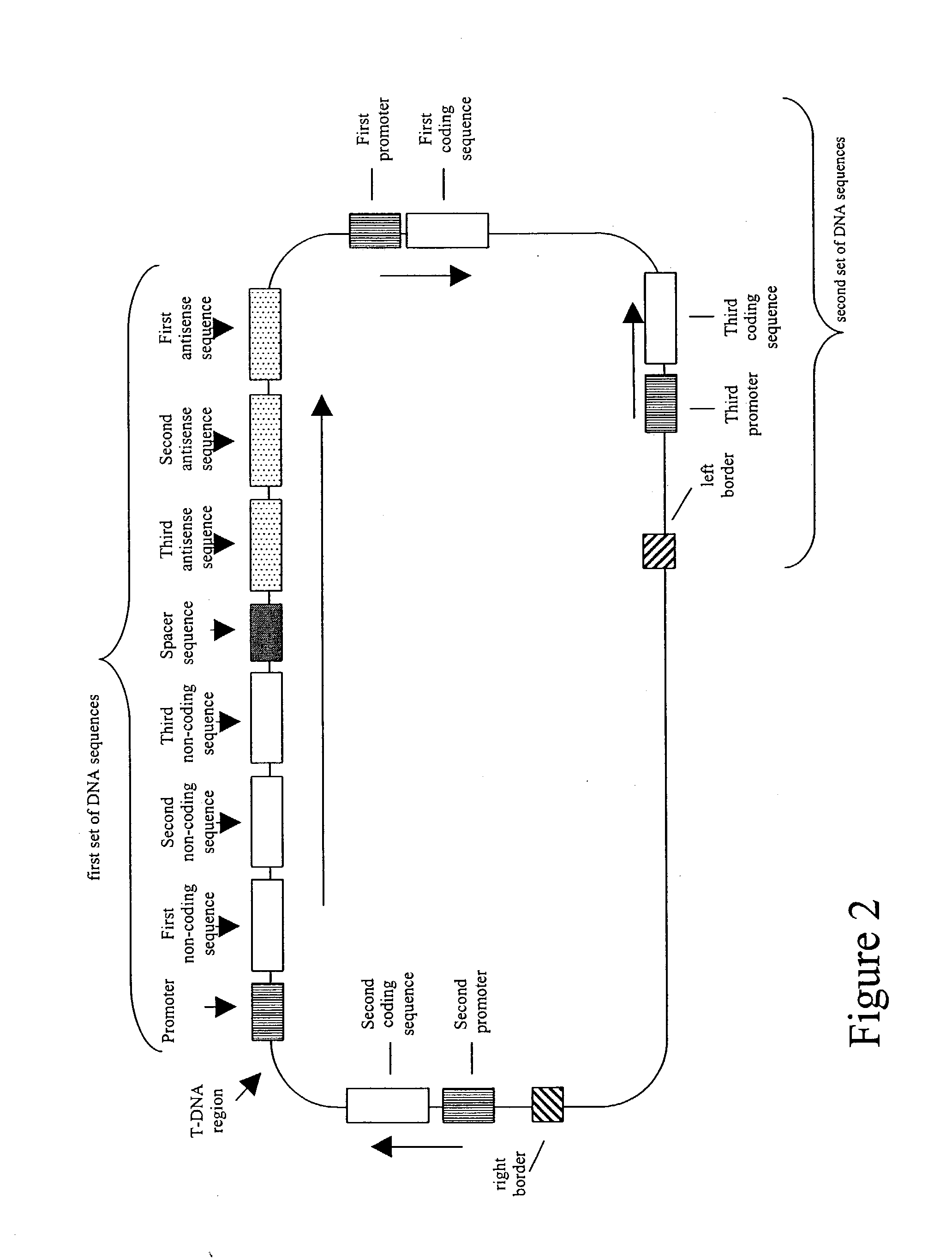
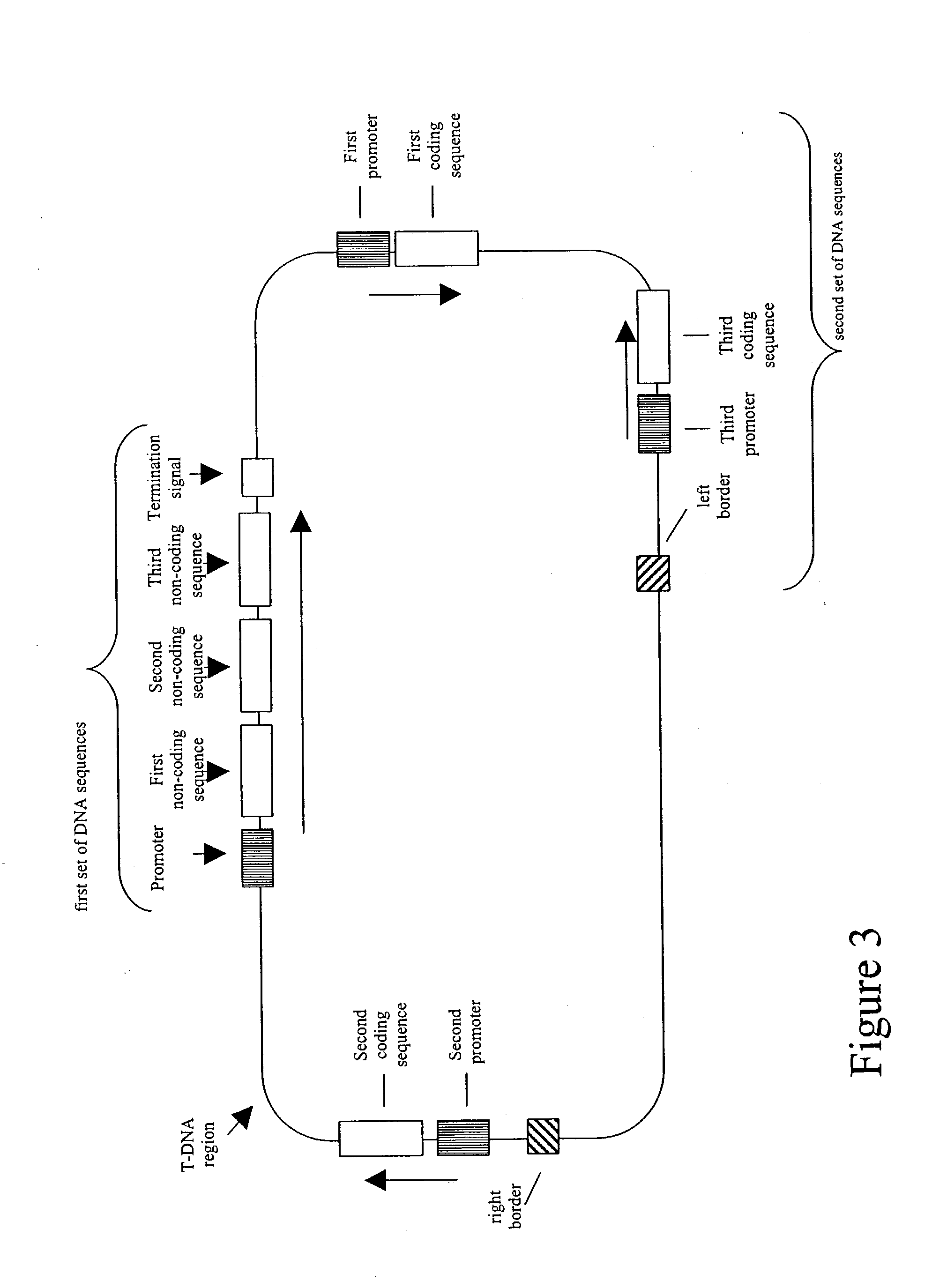
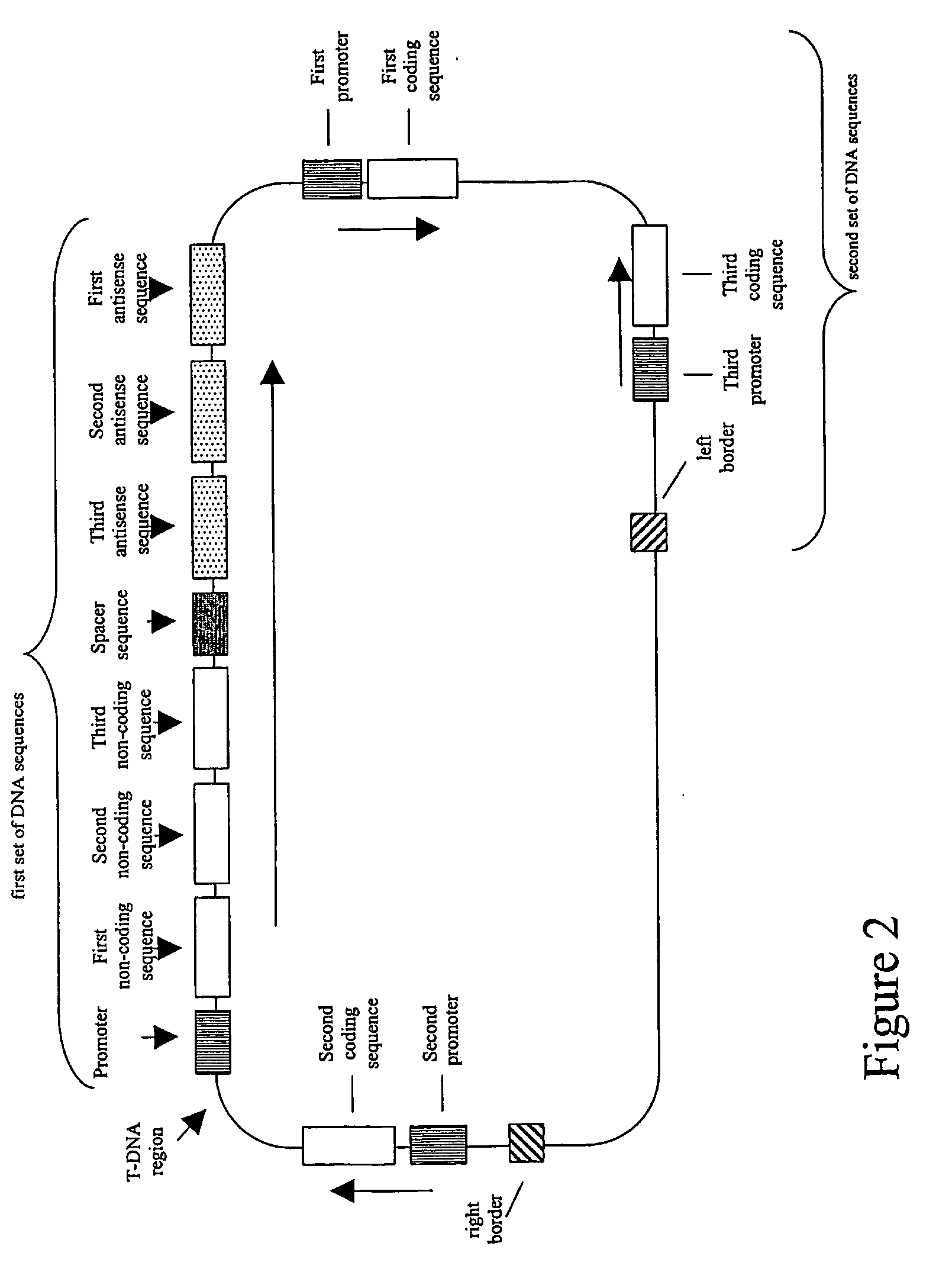
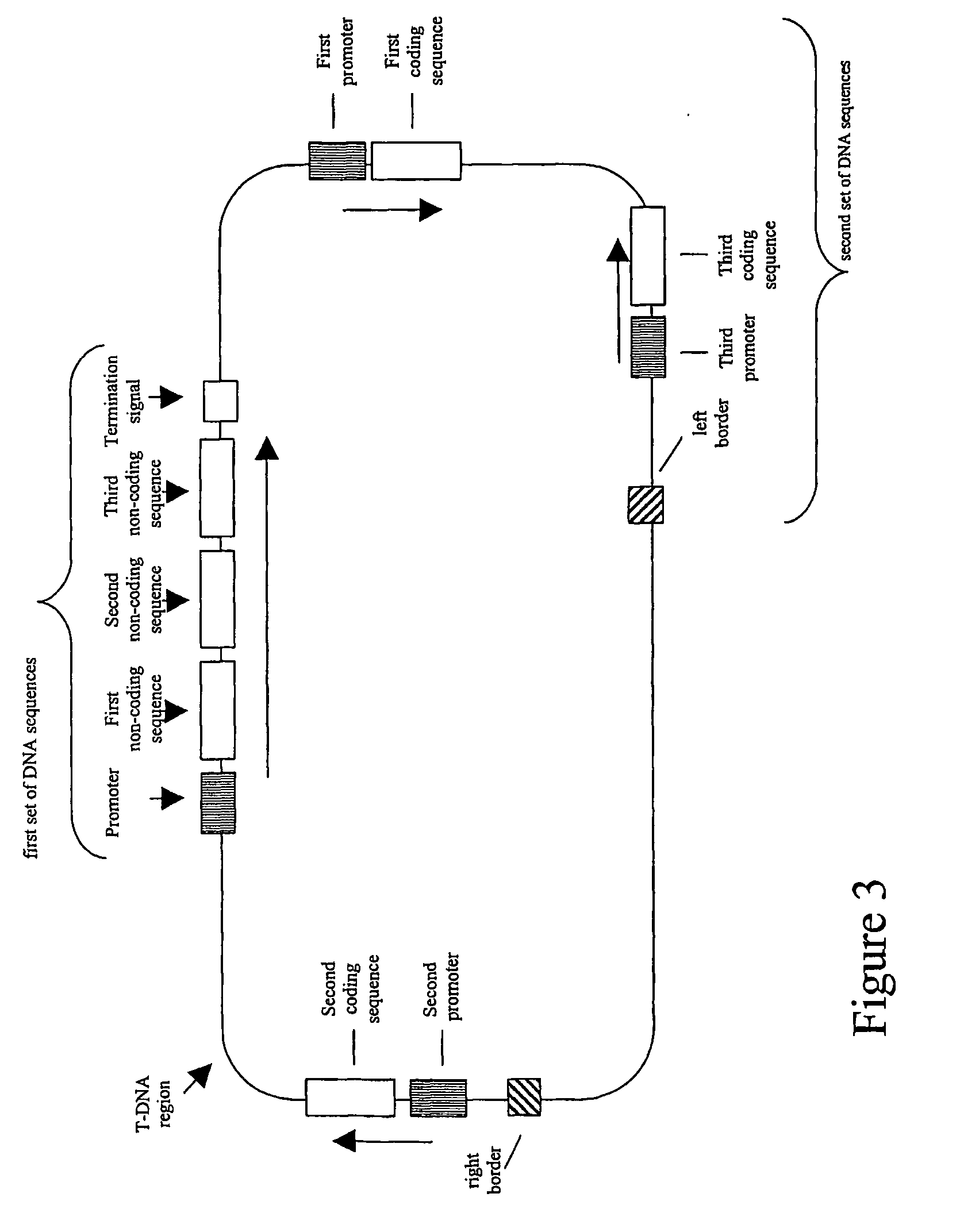
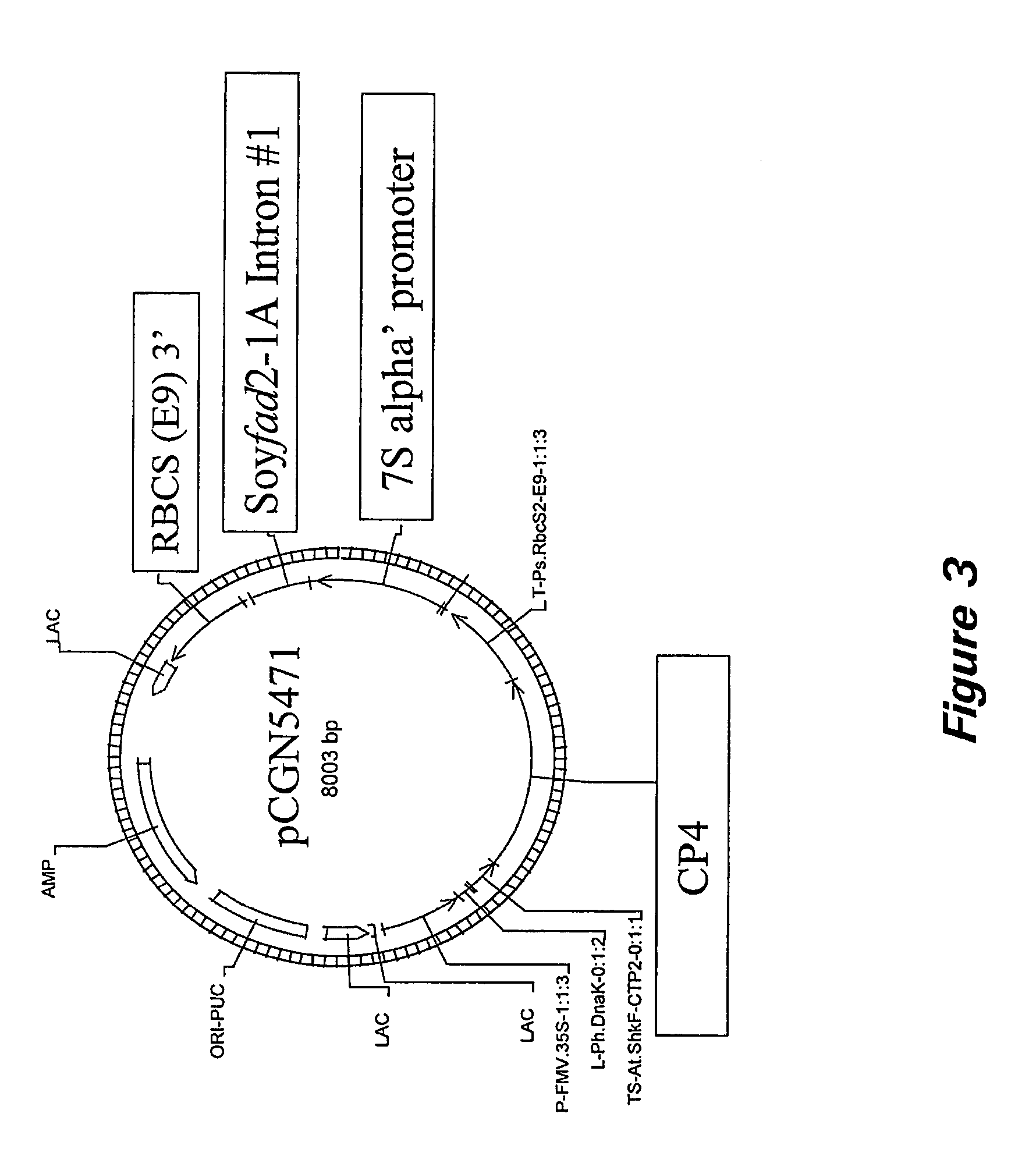
Nucleic acid constructs and methods for producing altered seed oil compositions
InactiveUS20060206963A1Increased oleic acid contentReduce saturated fatty acid contentTransferasesBiofuelsFatty acid biosynthesisAdemetionine
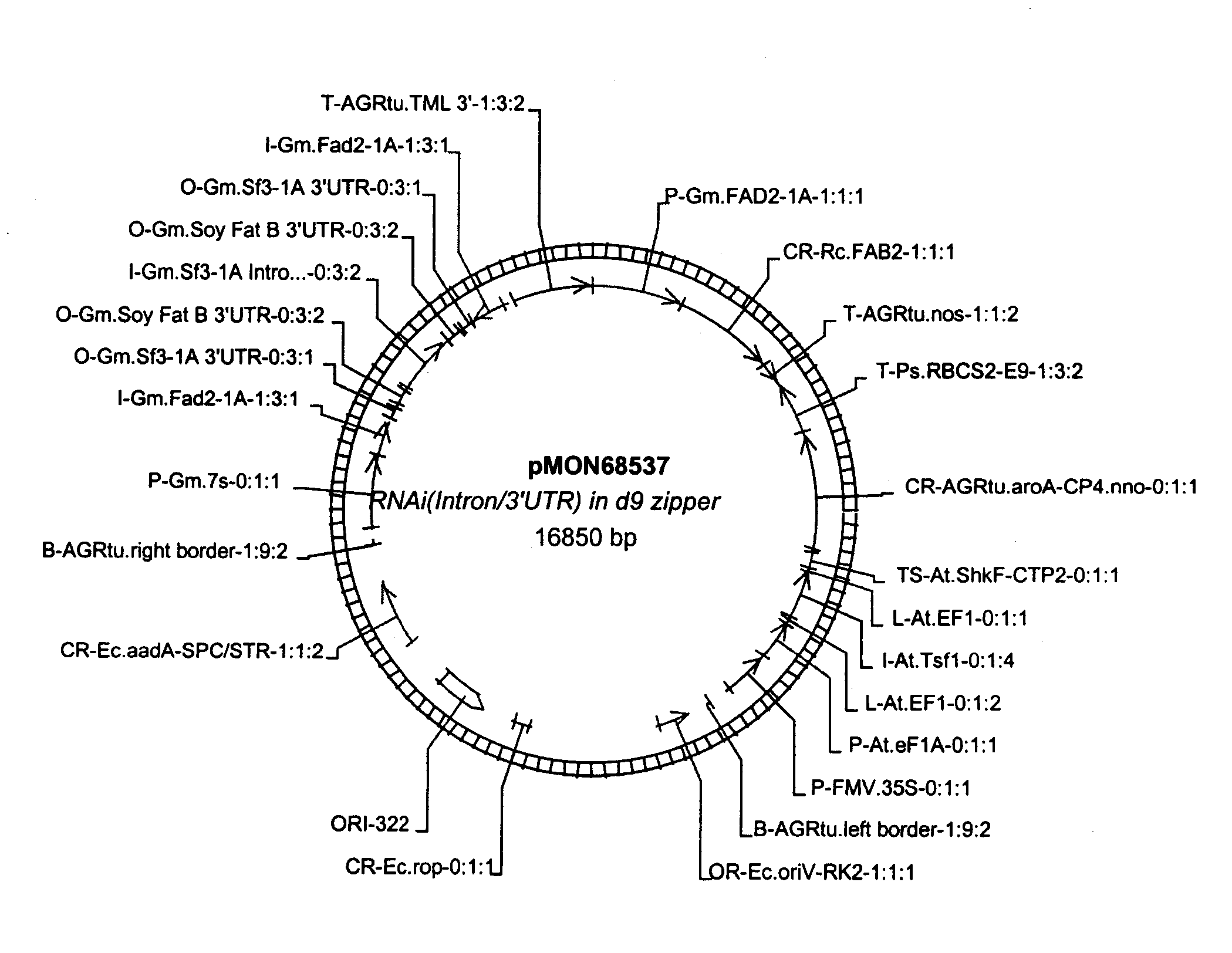
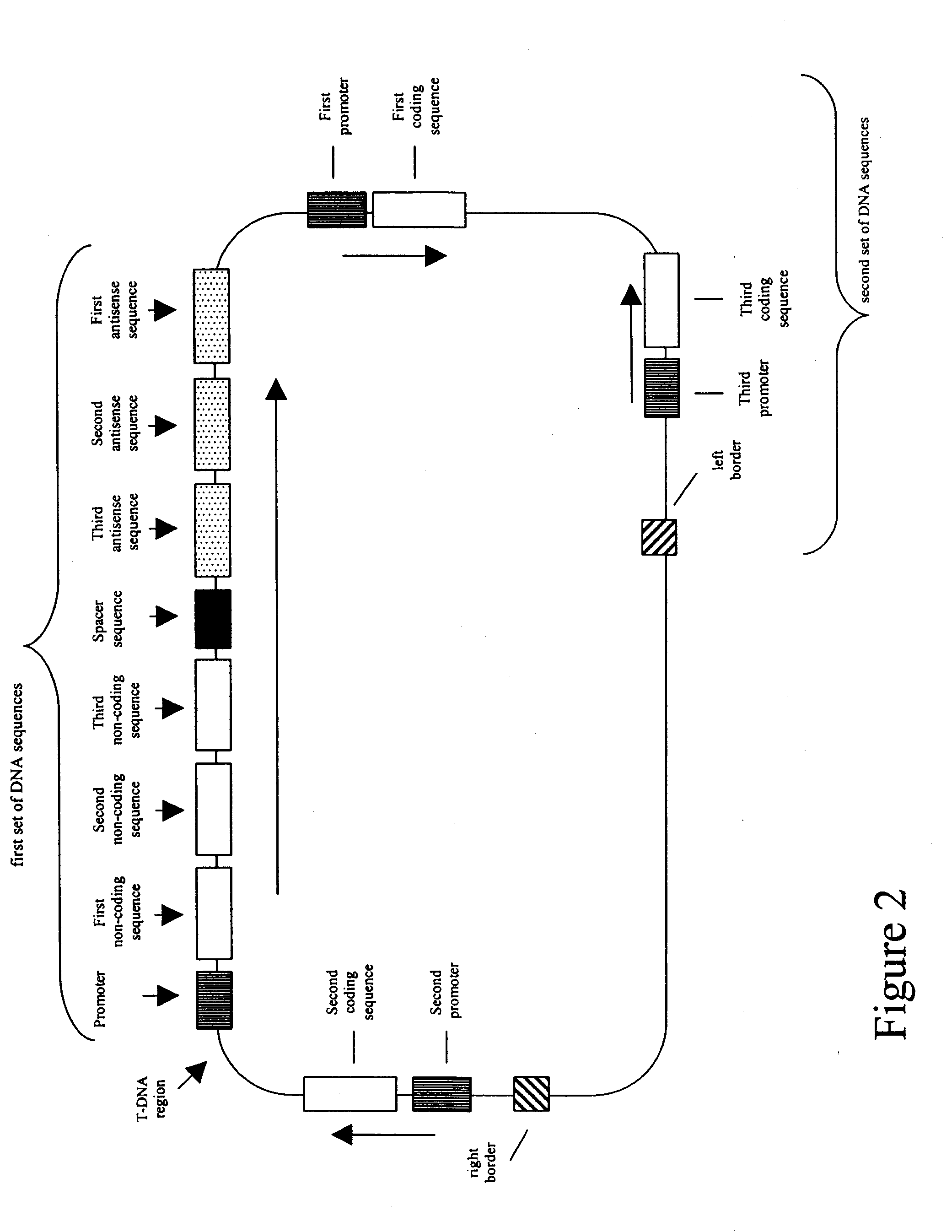
The present invention is in the field of plant genetics and provides recombinant nucleic acid molecules, constructs, and other agents associated with the coordinate manipulation of multiple genes in the fatty acid synthesis pathway. In particular, the agents of the present invention are associated with the simultaneous enhanced expression of certain genes in the fatty acid synthesis pathway and suppressed expression of certain other genes in the same pathway. Also provided are plants incorporating such agents, and in particular plants incorporating such constructs where the plants exhibit altered seed oil compositions.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Thioesterase-related nucleic acid sequences and methods of use for the production of plants with modified fatty acid composition
InactiveUS20050262588A1HydrolasesOther foreign material introduction processesFatty acid biosynthesisNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention is directed to nucleic acid molecules and nucleic acid constructs, and other agents associated with fatty acid synthesis, particularly the ratios of saturated and unsaturated fats. Moreover, the present invention is directed to plants incorporating such agents where the plants exhibit altered ratios of saturated and unsaturated fats. In particular, the present invention is directed to plants incorporating such agents where the plants exhibit altered levels of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Novel elongase gene and method for producing multiple-unsaturated fatty acids
InactiveUS20040111763A1Improve efficiencyIncrease productionCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsElongaseTriacylglycerol VLDL
The invention relates to a novel elongase gene with the sequences stated in sequence SEQ ID NO:1, SEQ ID NO: 3, SEQ ID NO: 5 and SEQ ID NO: 7 or their homologs, derivatives or analogs, to a gene construct comprising this gene or its homologs, derivatives and analogs, and to its use. The invention also relates to vectors or transgenic organisms comprising an elongase gene with the sequence SEQ ID NO:1, SEQ ID NO: 3, SEQ ID NO: 5 and SEQ ID NO: 7 or its homologs, derivatives and analogs. The invention furthermore relates to the use of the elongase gene sequences alone or in combination with further elongases and / or further fatty acid biosynthesis genes. The present invention relates to a novel elongase gene with the sequence SEQ ID NO:1 or its homologs, derivatives and analogs. Furthermore, the invention relates to a process for the preparation of polyunsaturated fatty acids and to a process for introducing DNA into organisms which produce large amounts of oils and, in particular, oils with a high content of unsaturated fatty acids. Moreover, the invention relates to an oil and / or a fatty acid preparation with a higher content of polyunsaturated fatty acids with at least two double bonds and / or a triacylglycerol preparation with a higher content of polyunsaturated fatty acids with at least two double bonds.
Owner:BASF AG
Nucleic acid sequences and methods of use for the production of plants with modified polyunsaturated fatty acids
InactiveUS7067722B2Change ratioSugar derivativesTransferasesFatty acid biosynthesisNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention is directed to nucleic acid molecules and nucleic acid constructs, and other agents associated with fatty acid synthesis, particularly the ratios of saturated and unsaturated fats. Moreover, the present invention is directed to plants incorporating such agents where the plants exhibit altered ratios of saturated and unsaturated fats. In particular, the present invention is directed to plants incorporating such agents where the plants exhibit altered ratios of monounsaturated to polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Nucleic acid sequences and methods of use for the production of plants with modified polyunsaturated fatty acids
InactiveUS20050262589A1Change ratioSugar derivativesTransferasesFatty acid biosynthesisUnsaturated fatty acid
The present invention is directed to nucleic acid molecules and nucleic acid constructs, and other agents associated with fatty acid synthesis, particularly the ratios of saturated and unsaturated fats. Moreover, the present invention is directed to plants incorporating such agents where the plants exhibit altered ratios of saturated and unsaturated fats. In particular, the present invention is directed to plants incorporating such agents where the plants exhibit altered ratios of monounsaturated to polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Owner:CALGENE LLC
Enzymes and methods for producing omega-3 fatty acids
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG +1
Novel elongase gene, and process for the preparation of polyunsaturated fatty acids
InactiveUS20080160054A1Improve efficiencyIncrease productionOrganic active ingredientsFatty acid chemical modificationBiotechnologyFatty acid biosynthesis
The invention relates to a novel elongase gene with the sequences stated in sequence SEQ ID NO:1, SEQ ID NO: 3, SEQ ID NO: 5 and SEQ ID NO: 7 or their homologs, derivatives or analogs, to a gene construct comprising this gene or its homologs, derivatives and analogs, and to its use. The invention also relates to vectors or transgenic organisms comprising an elongase gene with the sequence SEQ ID NO:1, SEQ ID NO: 3, SEQ ID NO: 5 and SEQ ID NO: 7 or its homologs, derivatives and analogs. The invention furthermore relates to the use of the elongase gene sequences alone or in combination with further elongases and / or further fatty acid biosynthesis genes. The present invention relates to a novel elongase gene with the sequence SEQ ID NO:1 or its homologs, derivatives and analogs.Furthermore, the invention relates to a process for the preparation of polyunsaturated fatty acids and to a process for introducing DNA into organisms which produce large amounts of oils and, in particular, oils with a high content of unsaturated fatty acids. Moreover, the invention relates to an oil and / or a fatty acid preparation with a higher content of polyunsaturated fatty acids with at least two double bonds and / or a triacylglycerol preparation with a higher content of polyunsaturated fatty acids with at least two double bonds.
Owner:BASF AG
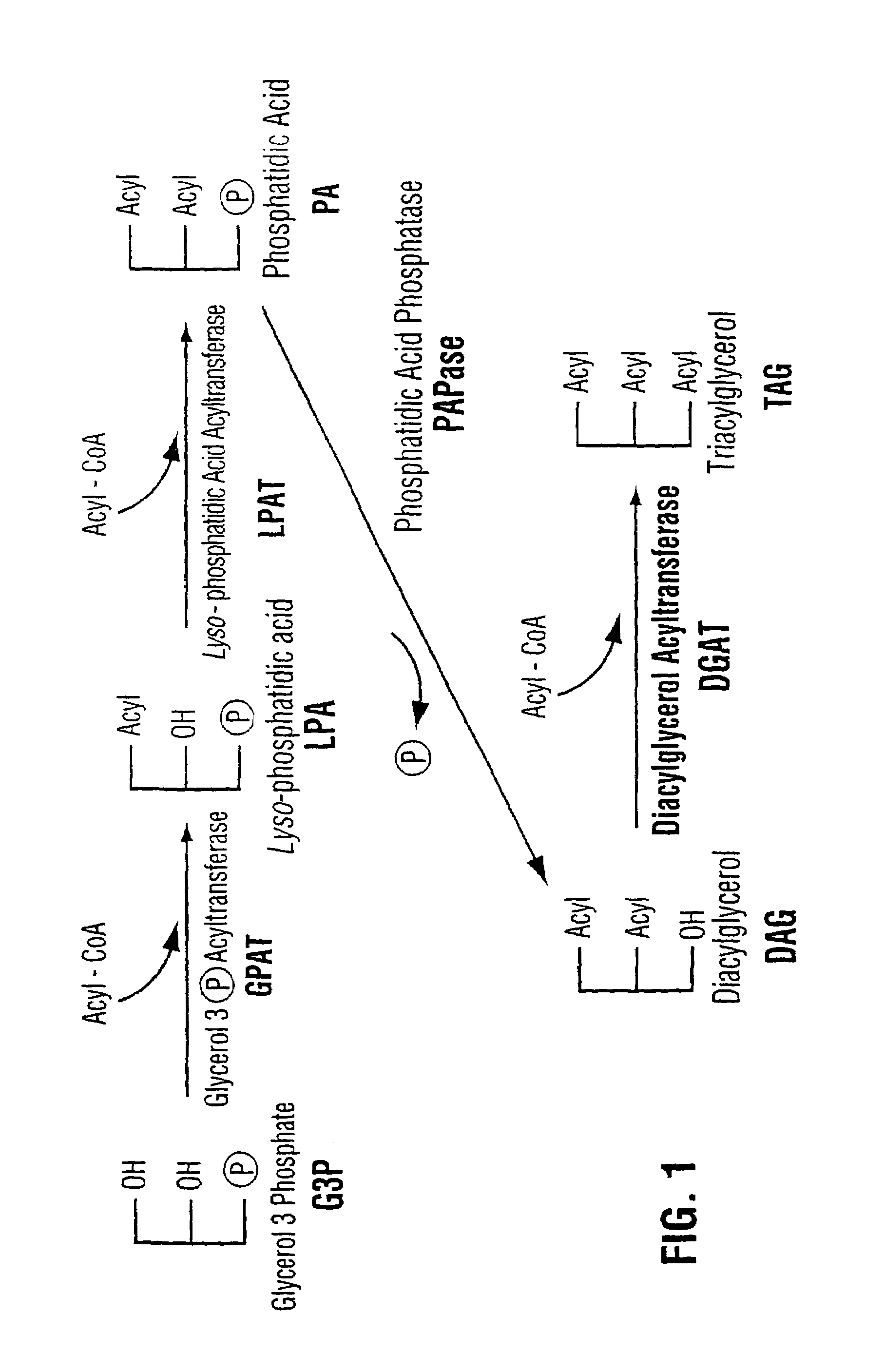
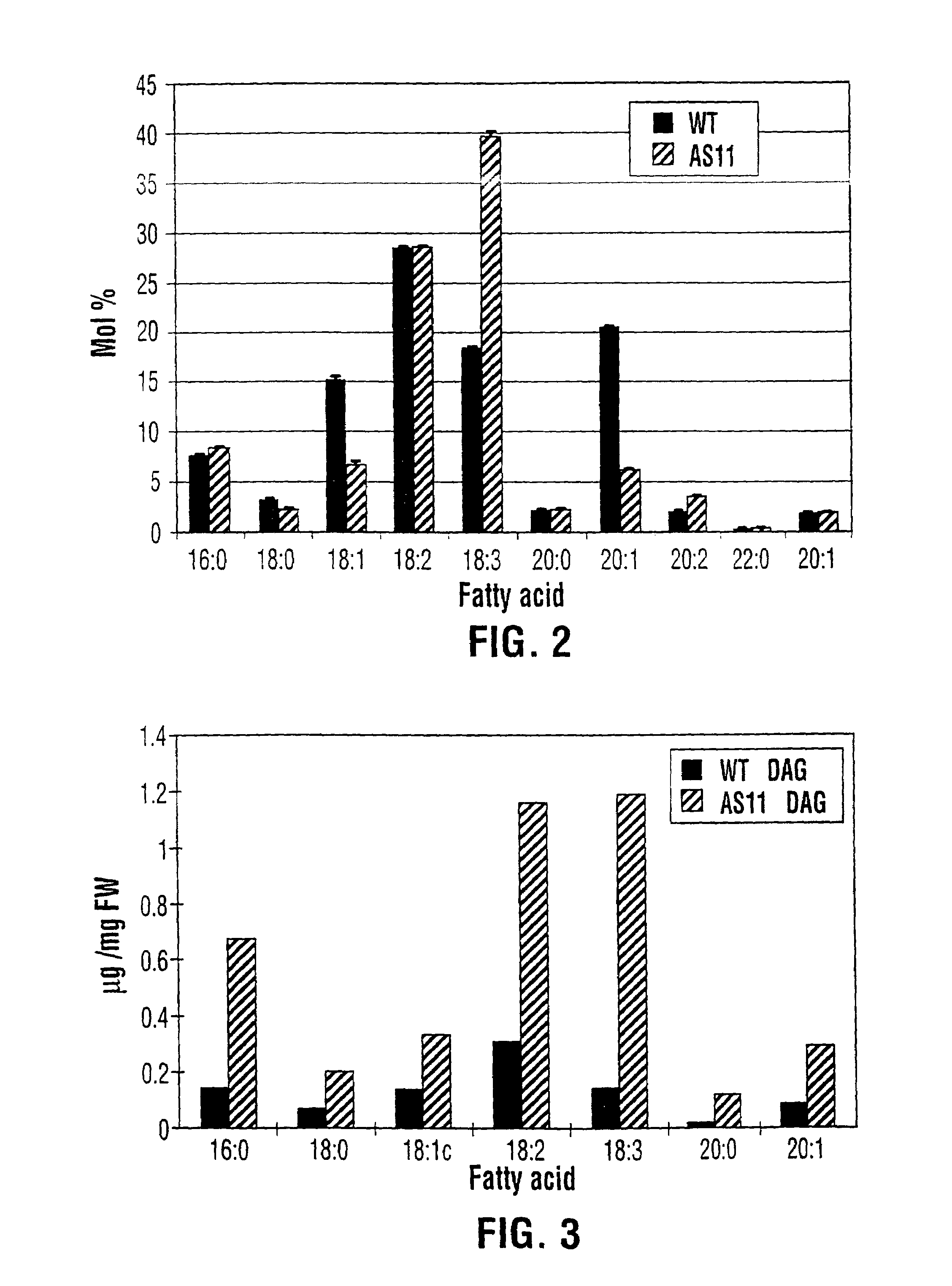
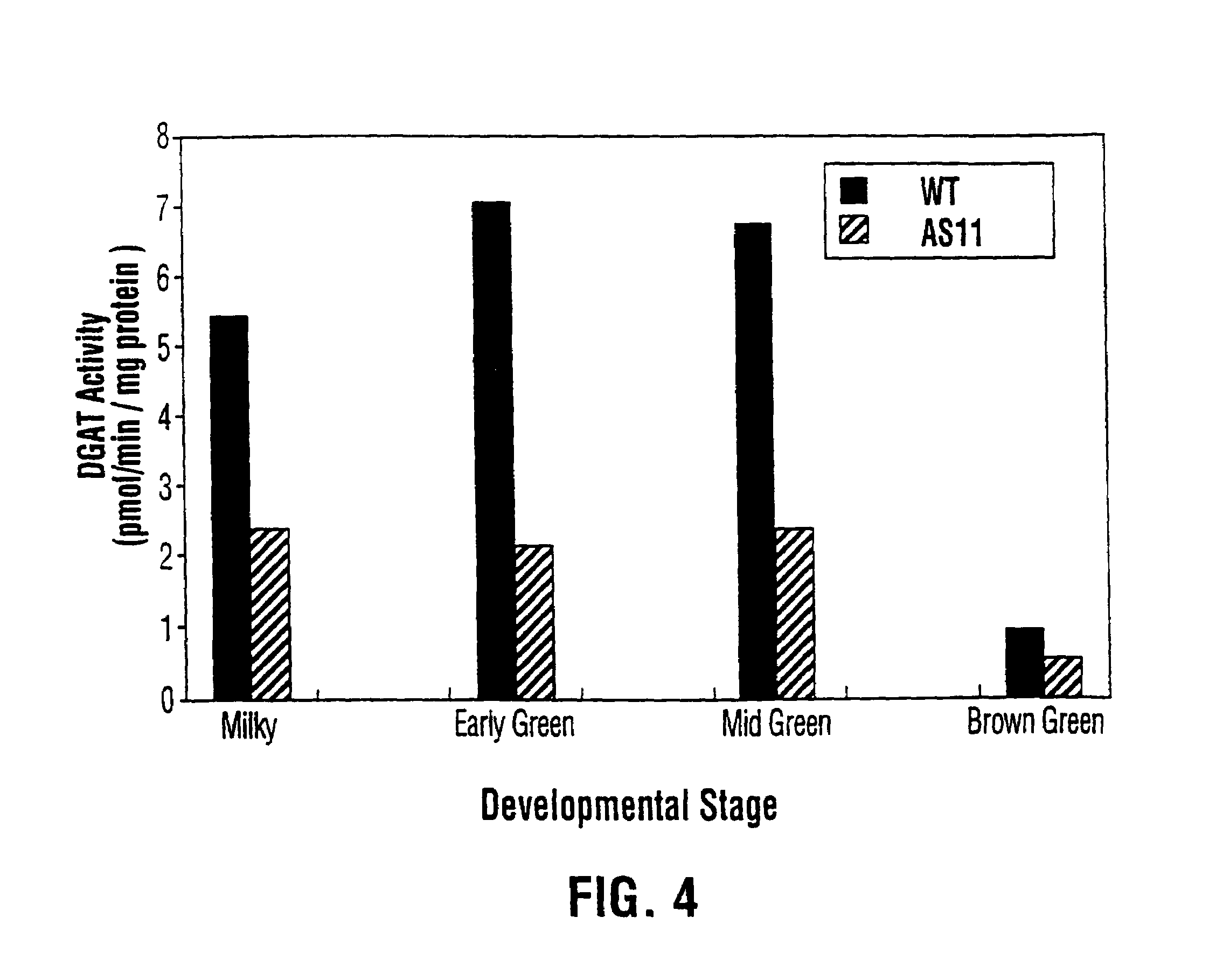
Diacylglycerol acyltransferase gene from plants
InactiveUS7015373B1Reduced DGAT activityReduce rateSugar derivativesTransferasesBrassicaceaePlanting seed
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Nucleic acid constructs and methods for producing altered seed oil compositions
ActiveUS20050034190A9Suppressing endogenous expressionIncreasing endogenous expressionTransferasesBiofuelsFatty acid biosynthesisAdemetionine
The present invention is in the field of plant genetics and provides recombinant nucleic acid molecules, constructs, and other agents associated with the coordinate manipulation of multiple genes in the fatty acid synthesis pathway. In particular, the agents of the present invention are associated with the simultaneous enhanced expression of certain genes in the fatty acid synthesis pathway and suppressed expression of certain other genes in the same pathway. Also provided are plants incorporating such agents, and in particular plants incorporating such constructs where the plants exhibit altered seed oil compositions.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
High throughput screening method for biological agents affecting fatty acid biosynthesis
InactiveUS6951729B1Reduce NADH consumptionReduce consumptionCompound screeningApoptosis detectionHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsScreening method
Provided is a screening method for compounds affecting fatty acid biosynthesis, the method comprising: providing a reaction mixture comprising: an acyl carrier moiety or enzymes and precursors sufficient to generate the acyl carrier moiety; a bacterial enzymatic pathway comprising at least two consecutively acting enzymes selected from the group consisting of: malonyl-CoA:ACP transacylase, beta-ketoacyl-ACP synthase III, NADPH dependent beta-ketoacyl-ACP reductase, beta-hydroxylacyl-ACP dehydrase and enoyl-ACP reductase; and substrates and cofactors required for the operation of the enzymes; contacting the reaction mixture with a prospective bioactive agent; conducting a high throughput measurement of the activity of the enzymatic pathway; and determining if the contacting altered the activity of the enzymatic pathway.
Owner:DEBIOPHARM INTERNATIONAL SA
Nucleic acid constructs and methods for producing altered seed oil compositions
The present invention is in the field of plant genetics and provides recombinant nucleic acid molecules, constructs, and other agents associated with the coordinate manipulation of multiple genes in the fatty acid synthesis pathway. In particular, the agents of the present invention are associated with the simultaneous enhanced expression of certain genes in the fatty acid synthesis pathway and suppressed expression of certain other genes in the same pathway. Also provided are plants incorporating such agents, and in particular plants incorporating such constructs where the plants exhibit altered seed oil compositions.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Nucleic acid constructs and methods for producing altered seed oil compositions
The present invention is in the field of plant genetics and provides recombinant nucleic acid molecules, constructs, and other agents associated with the coordinate manipulation of multiple genes in the fatty acid synthesis pathway. In particular, the agents of the present invention are associated with the simultaneous enhanced expression of certain genes in the fatty acid synthesis pathway and suppressed expression of certain other genes in the same pathway. Also provided are plants incorporating such agents, and in particular plants incorporating such constructs where the plants exhibit altered seed oil compositions.
Owner:FILLATTI JOANNE J +2
Nucleic acid sequences and methods of use for the production of plants with modified polyunsaturated fatty acids
The present invention is directed to nucleic acid molecules and nucleic acid constructs, and other agents associated with fatty acid synthesis, particularly the ratios of saturated and unsaturated fats. Moreover, the present invention is directed to plants incorporating such agents where the plants exhibit altered ratios of saturated and unsaturated fats. In particular, the present invention is directed to plants incorporating such agents where the plants exhibit altered ratios of monounsaturated to polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Owner:CALGENE LLC
Antisense antibacterial compounds and methods
ActiveUS20150361425A1Increase antibiotic susceptibilityReduce capacityAntibacterial agentsSugar derivativesAntibiotic resistanceMorpholine
Provided are antisense morpholino oligomers targeted against bacterial virulence factors such as genes that contribute to antibiotic resistance or biofilm formation, or genes associated with fatty acid biosynthesis, and related compositions and methods of using the oligomers and compositions, for instance, in the treatment of an infected mammalian subject.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
Method for preparing resistant starch of corn
InactiveCN101427741AGood physical and chemical propertiesDelicate tasteFood preparationFatty acidFermentation
The invention relates to a preparation method of corn resistant starch, which uses common corn starch as raw material to produce corn resistant starch with multiple physiological functions and characteristics by combined treatment of microbial fermentation and hot pressing and cooling. The resistant starch has physiologic functions of effectively controlling body weight, preventing constipation, appendicitis, hemorrhoids and colon cancer, controlling diabetes, increasing lipid discharge, improving lipid composition, promoting absorption of zinc, calcium and magnesium ions, increasing removal of cholesterol and cholic acid, and reducing cholesterol biosynthesis, lipid absorption and fatty acid biosynthesis. The resistant starch used in food processing industry has better physicochemical properties than those of dietary fiber, low water retention capacity, good mouthfeel, no influence on food, and improve food texture. The invention solves the problems in production of resistant starch, including low yield and lack of high amylase starch in China.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Diacylglycerol acyltransferase gene from plants
InactiveUS20050193446A1Increase TAG contentChange ratioTransferasesOther foreign material introduction processesPlanting seedAdemetionine
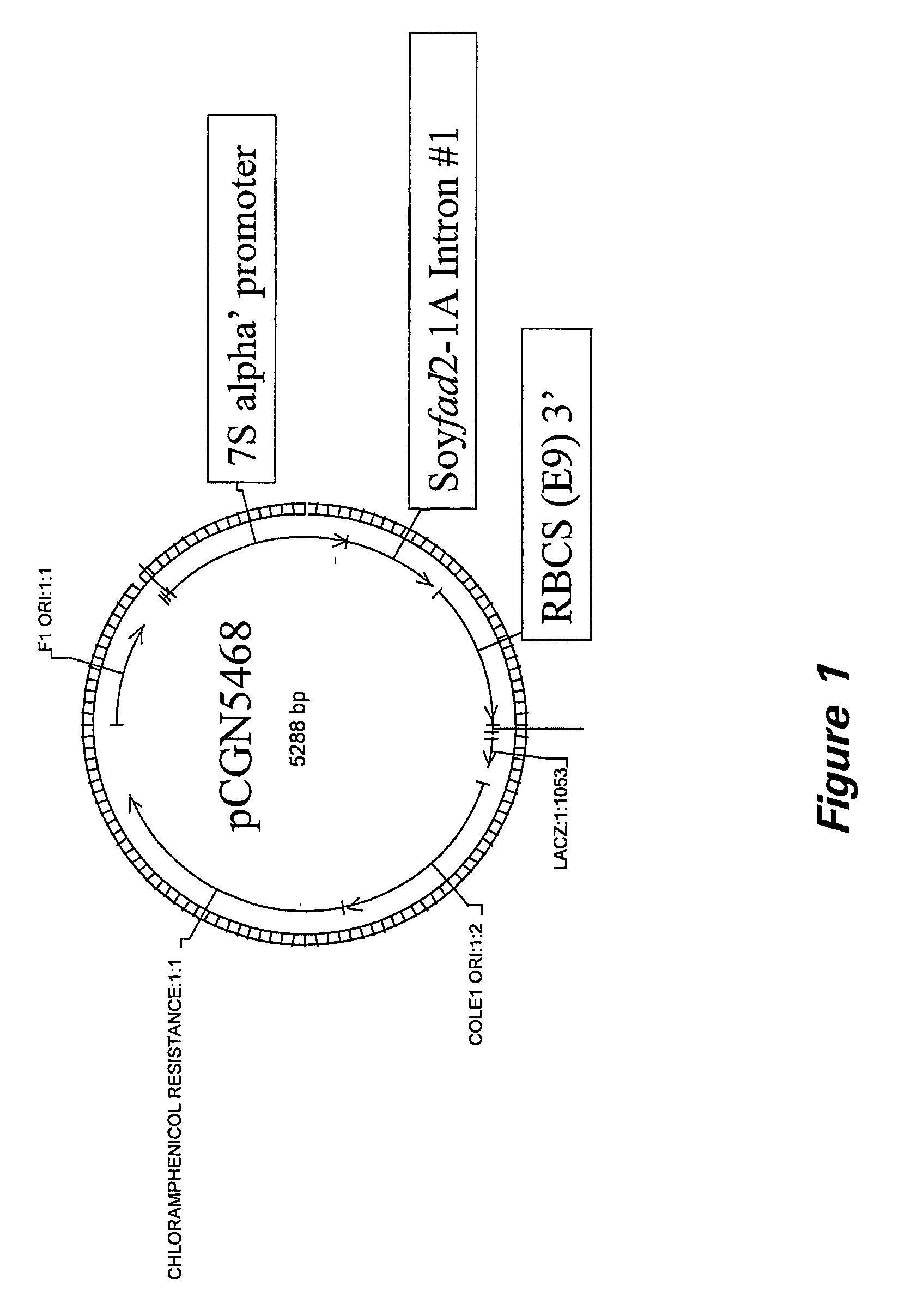
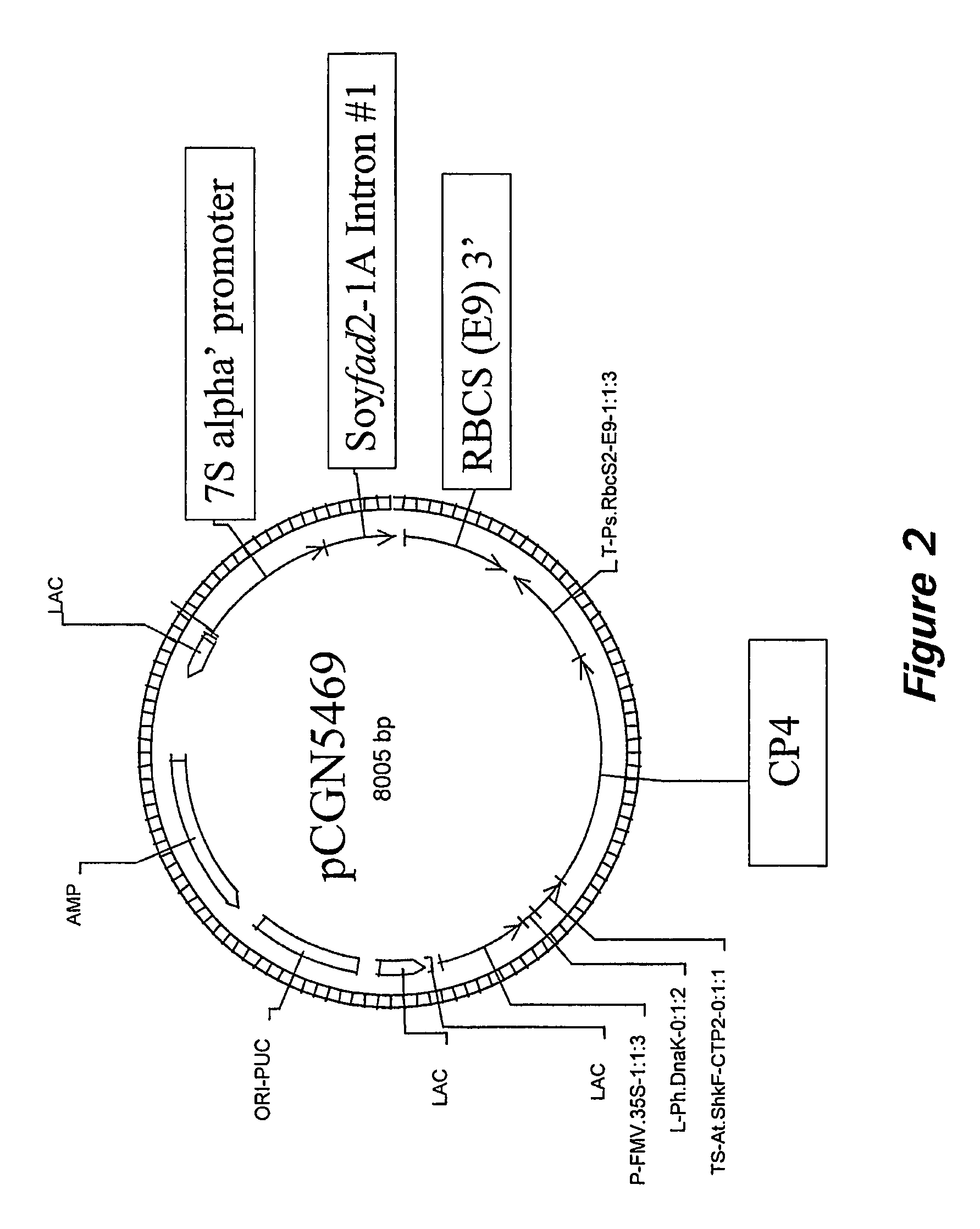
The present invention relates to the isolation, purification, characterization and use of the plant diacylglycerol acyltransferase (DGAT) gene and genetic products. The invention includes isolated and purified DGAT DNA and relates to methods of regulating seed oil content, the ratio of diacylglycerol / triacylglycerol proportions in the seed oil, fatty acid synthesis, seed oil acyl composition, seed size / weight and carbon flux into other seed components, using the gene, and to tissues and plants transformed with the gene. The invention also relates to transgenic plants, plant tissues and plant seeds having a genome containing an introduced DNA sequence of the invention, and a method of producing such plants and plant seeds.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Plant pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase gene
InactiveUS6500670B1High activityImprove availabilitySugar derivativesClimate change adaptationBrassicaceaePlanting seed
The present invention relates to the isolation, purification, characterization and use of a mitochondrial pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase (PDHK) gene [SEQ ID NO:1](pYA5; ATCC No 209562) from the Brassicaceae (specifically Arabidopsis thaliana). The invention includes isolated and purified DNA of the stated sequence and relates to methods of regulating fatty acid synthesis, seed oil content, seed size / weight, flowering time, vegetative growth, respiration rate and generation time using the gene and to tissues and plants transformed with the gene. The invention also relates to transgenic plants, plant tissues and plant seeds having a genome containing an introduced DNA sequence of SEQ ID NO:1; or a part of SEQ ID NO:1 characterized in that said sequence has been introduced into an antisense or sense orientation, and a method of producing such plants and plant seeds. The invention also relates to substantially homologous DNA sequences from plants encoding proteins with deduced amino acid sequences of 25% or greater identity, and 50% or greater similarity, isolated and / or characterized by known methods using the sequence information of SEQ ID NO:1, and to parts of reduced length that are still able to function as inhibitors of gene expression by use in an anti-sense, co-suppression or other gene silencing technologies.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Cotton alpha-globulin promoter for seed-specific expression of transgenes
ActiveUS7626081B2Improve seed qualityInhibit seed germinationSugar derivativesStable introduction of DNAHeterologousFatty acid biosynthesis
The present invention is directed to 5′ regulatory regions of a cotton seed-specific gene, α-globulin. The 5′ regulatory region, or parts thereof, when operably linked to either the coding sequence of a native gene, heterologous gene or a sequence complementary to a native plant gene, direct expression of the coding sequence or complementary sequence in a plant seed. The regulatory regions are useful in expression cassettes and expression vectors for the transformation of plants. Also provided are methods of modulating the levels of a native or heterologous gene such as a fatty acid synthesis or lipid metabolism gene by transforming a plant with the subject expression cassettes and expression vectors.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
Cell systems and methods for improving fatty acid synthesis by expression of dehydrogenases
ActiveUS20130280793A1Increased propagation rateIncreased proliferationSugar derivativesUnicellular algaeFatty acid biosynthesisMicroorganism
The invention relates to methods for producing lipids such as fatty acid products in recombinant host cells engineered to express a non-native gene encoding a dehydrogenase. The recombinant microorganisms are able to proliferate at a higher rate as compared with microorganisms that do not express a non-native dehydrogenase gene, and cultures of microorganisms that are engineered for lipid production and that express a non-native dehydrogenase produce more lipid than cultures of control microorganisms that do not include a non-native dehydrogenase gene.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Nucleic acid constructs and methods for producing altered seed oil compositions
ActiveUS20090151029A1Reduce decreaseEffectively eliminating the expressionTransferasesBiofuelsFatty acid biosynthesisFatty acid
The present invention is in the field of plant genetics and provides recombinant nucleic acid molecules, constructs, and other agents associated with the coordinate manipulation of multiple genes in the fatty acid synthesis pathway. In particular, the agents of the present invention are associated with the simultaneous enhanced expression of certain genes in the fatty acid synthesis pathway and suppressed expression of certain other genes in the same pathway. Also provided are plants incorporating such agents, and in particular plants incorporating such constructs where the plants exhibit altered seed oil compositions.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Plant snf1-related protein kinase gene
ActiveUS20100281574A1Altered respiration rateIncrease biomassClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesSucrosePlanting seed
The present invention relates to the isolation, purification, characterization and use of the plant Snf1-related protein kinase (SnRK) gene and genetic products. The invention includes isolated and purified SnRK DNA and relates to methods of regulating water loss and plant drought tolerance, sucrose content, starch content, seed oil content, fatty acid synthesis, seed oil acyl composition, seed size / weight, resistance / tolerance to biotic stresses, increased root biomass, and / or carbon flux into other seed components, plant, using the gene, and to tissues and plants transformed with the gene. The invention also relates to transgenic plants, plant tissues and plant seeds having a genome containing an introduced DNA sequence of the invention, and a method of producing such plants and plant seeds.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Production of fatty acid esters
Methods of producing fatty acid esters, such as fatty acid ethyl esters, from microorganisms genetically engineered to alter the expression of genes involved in fatty acid synthesis and / or ethanol production, such that a microorganism is obtained that can produce an alcohol, a fatty acid and an ester synthase in the absence of exogenously added alcohols.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
Regulation and control method for improving EPA (Eicosapentaenoic Acid) content in schizochytrium and application
InactiveCN108707630AIncrease EPA contentIncrease the content of EPAMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyFatty acid biosynthesis
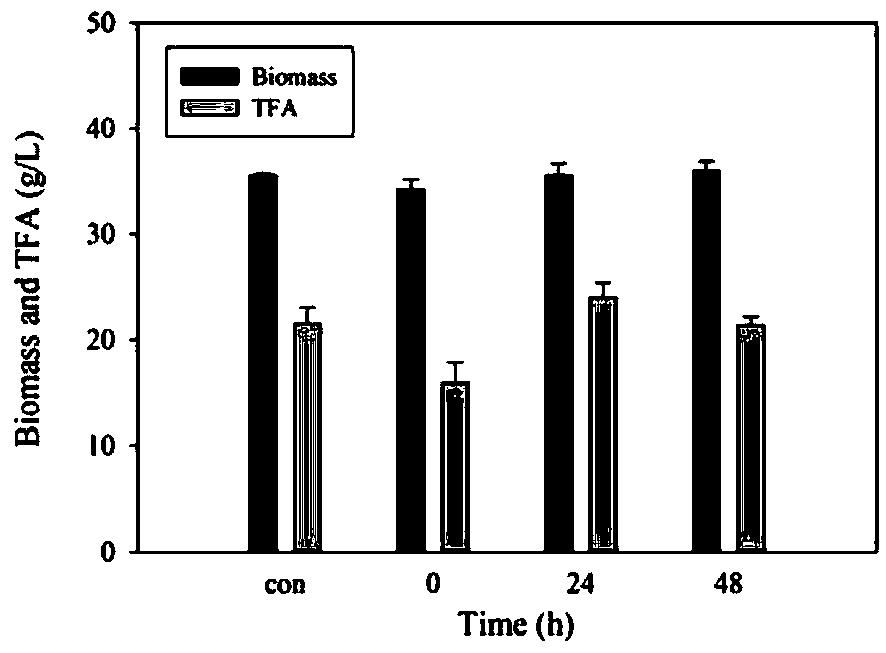
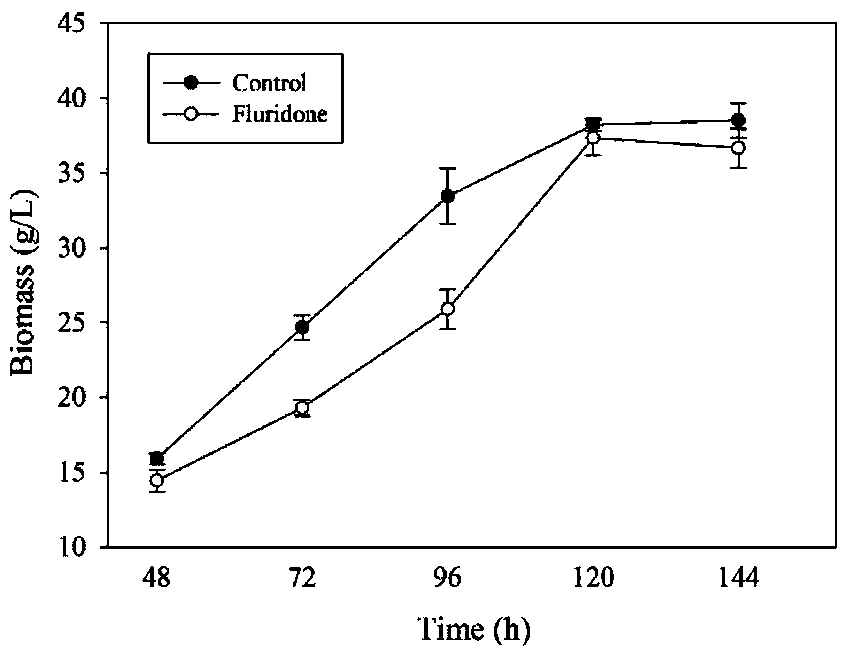
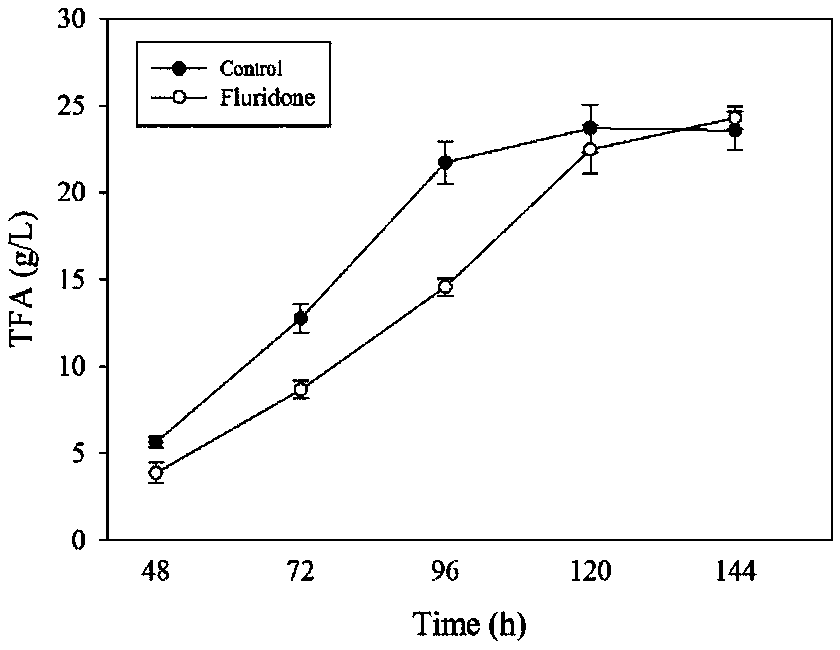
The invention provides a regulation and control method for improving the EPA (Eicosapentaenoic Acid) content in schizochytrium and application and relates to marine microorganisms. A strain schizochytrium sp. MYA1381 is subjected to flat plate and second-grade seed activation to prepare a seed solution; then the strain is inoculated to a fermentation culture medium; fluridone is added at differentphases of the growth of the schizochytrium. The fluridone can be applied to improvement of the EPA content in the schizochytrium. The fluridone is applied to regulation and control of a fatty acid synthesis way for the first time and a new thought is provided for improving the EPA content in the schizochytrium. The fluridone is added and the content of EPA in schizochytrium grease is remarkably improved and is improved by 42.31 percent when being compared with a manner without the fluridone. A foundation is provided for improving the EPA content in the schizochytrium by utilizing the fluridone.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Heterocyclic modulators of lipid synthesis
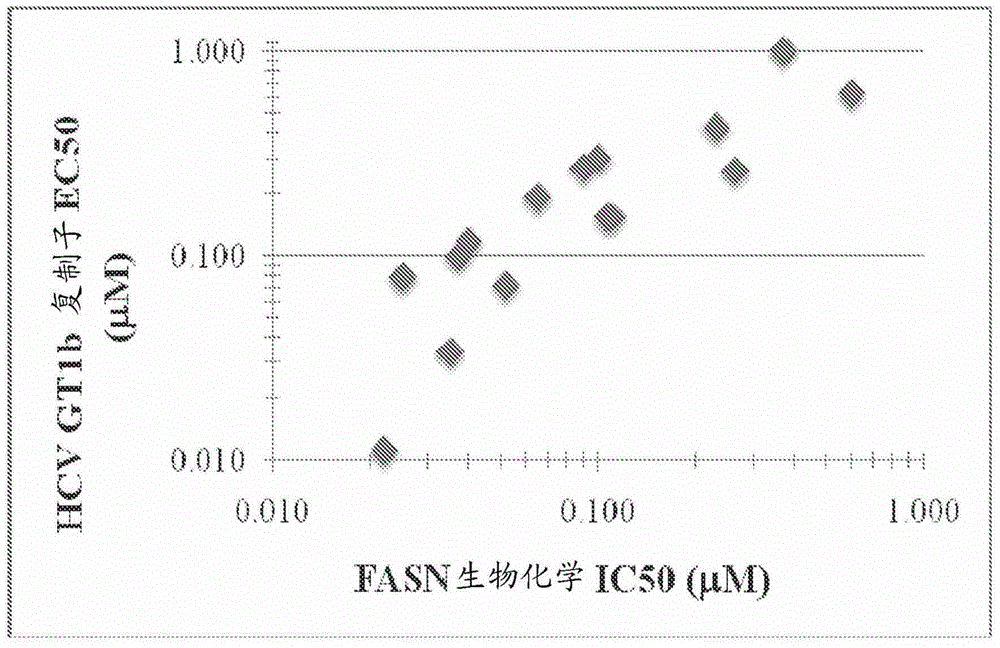
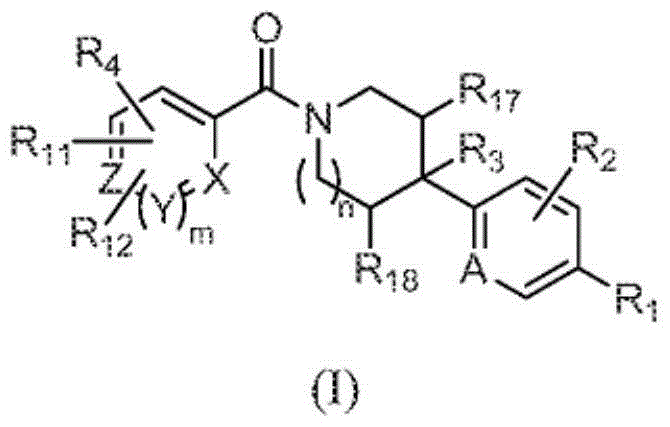
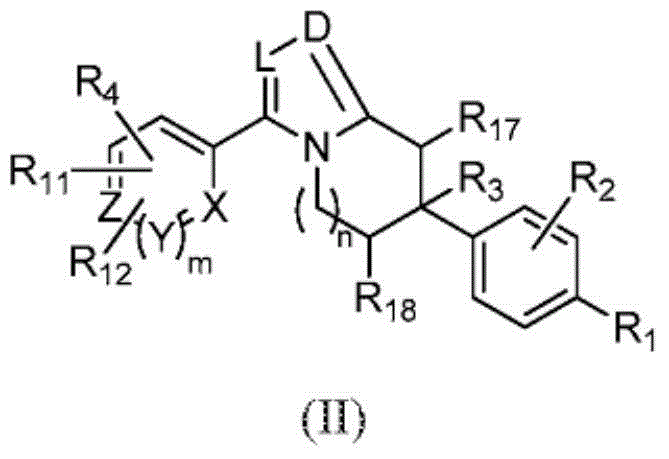
ActiveCN103561576AImproved antiviral activityHigh anticancer activityBiocideSenses disorderFatty acid biosynthesisMembrane lipid metabolism
Compounds that are fatty acid synthesis modulators are provided. The compounds may be used to treat disorders characterized by disregulation of the fatty acid synthase function by modulating the function and / or the fatty acid synthase pathway. Methods are provided for treating such disorders including viral infections, such as hepatits C infection, cancer and metabolic disorders.
Owner:GANNEX PHARM CO LTD
Application of corytuberine in preparing medicament for resisting Eimeria tenella
InactiveCN101474181AInhibitory activityInhibitionPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsFatty acid biosynthesisDrug
The invention provides new uses of corytuberine in the preparation of anti-eimeria tenella medicines. The corytuberine can efficiently prohibit activity of malonyl monoacyl coenzyme A: ACP transacylase represented by amino acid sequences like SEQ NO.1. The enzyme is a key enzyme in the process of type II fatty acid synthesis of the eimeria tenella, the activity of the enzyme can be prohibited to disorder of the fatty acid metabolism of the eimeria tenella while having no influence on the fatty acid metabolism of hosts of the eimeria tenella, so as to realize the aim of prohibiting the eimeria tenella from invading chicken intestine epithelial cells.
Owner:广东省农业科学院兽医研究所
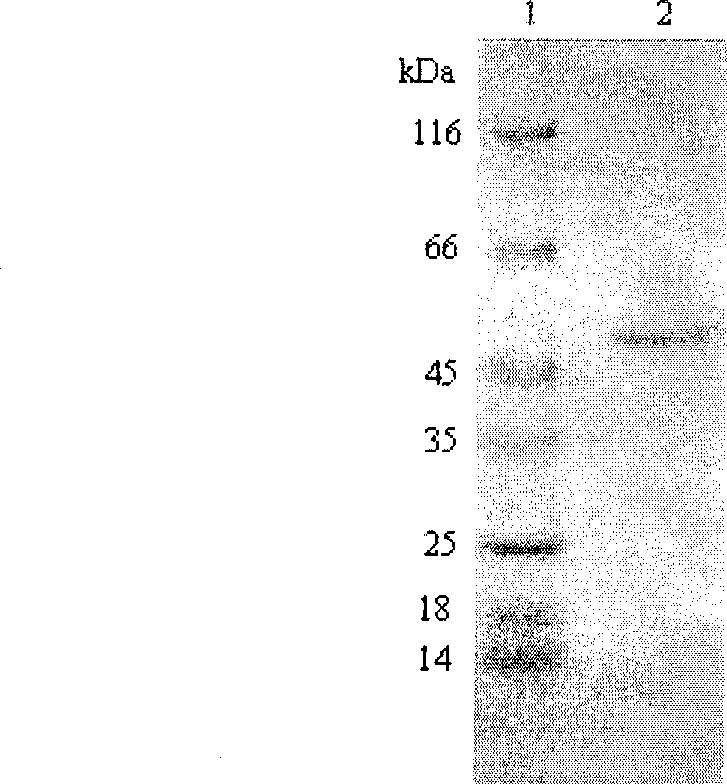
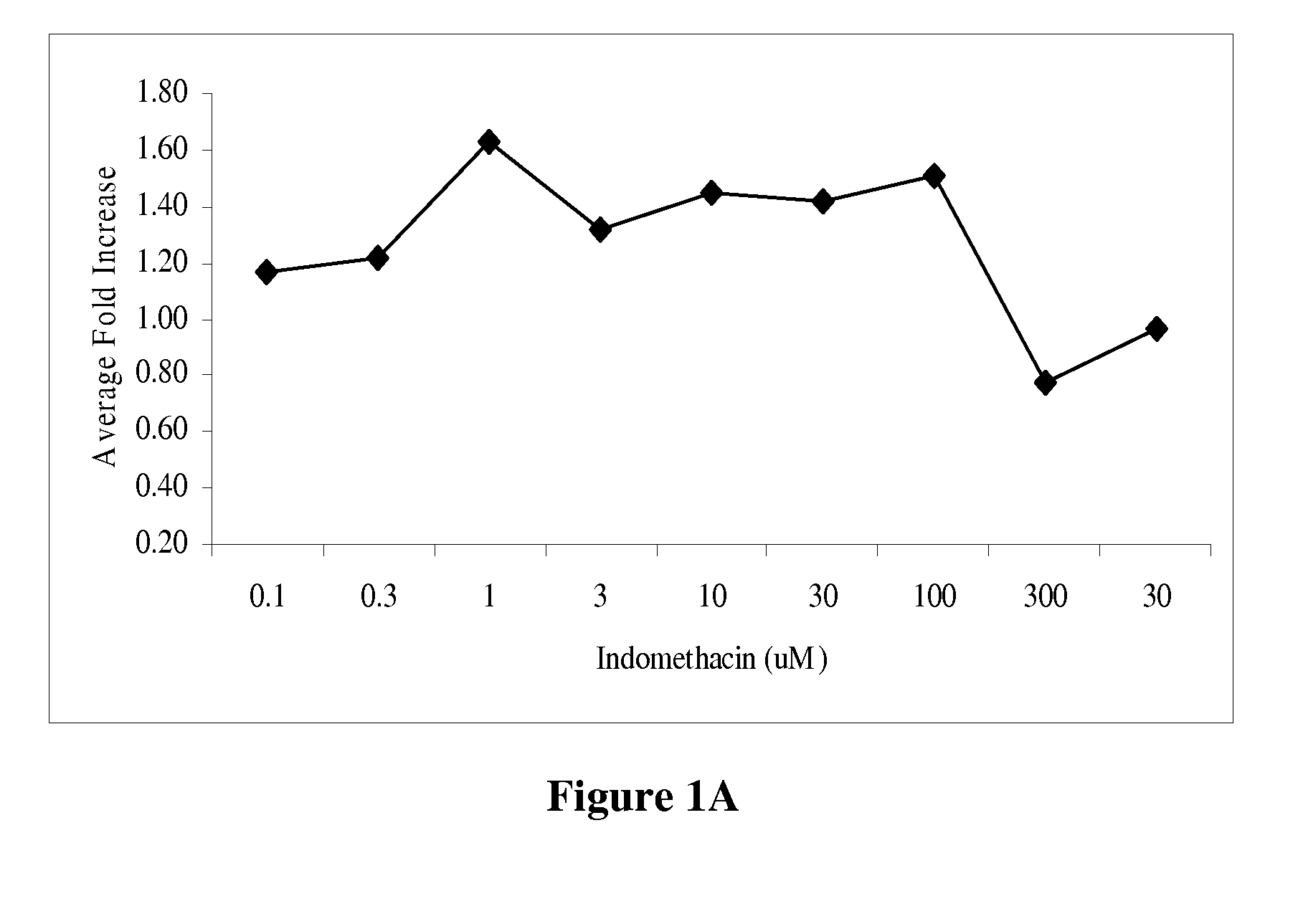
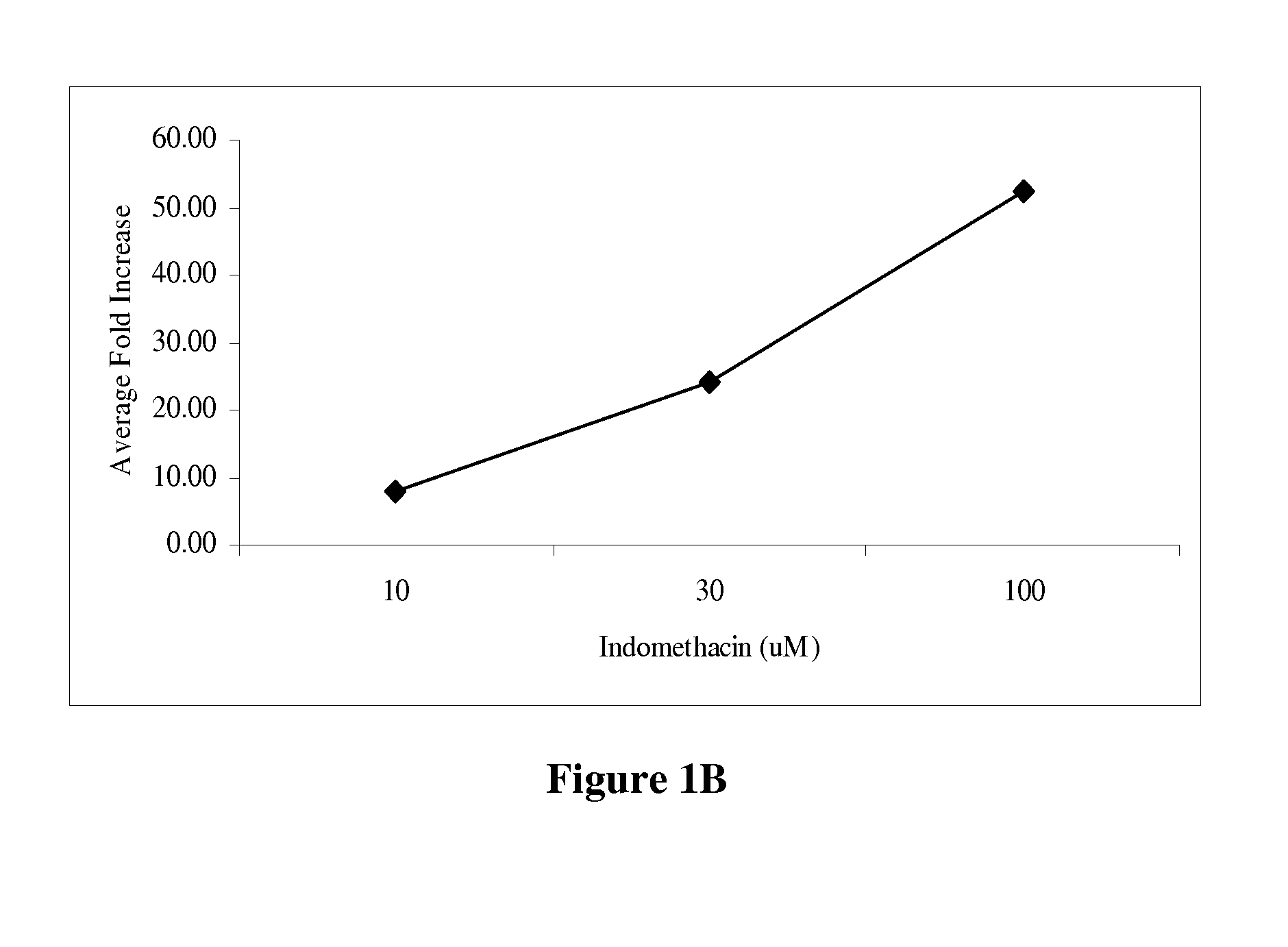
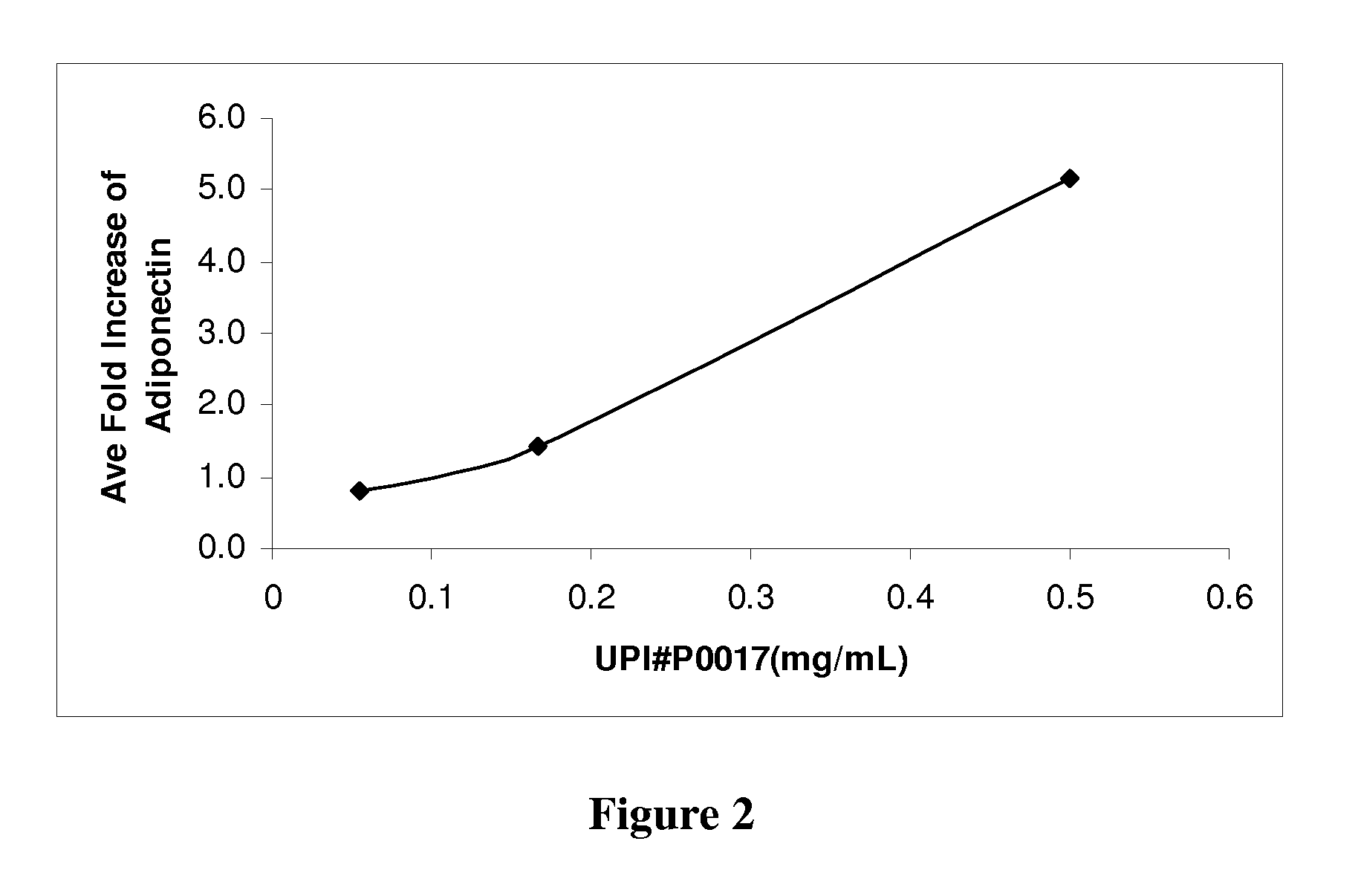
Chromones As Therapeutic Agents
ActiveUS20080166438A1Increase productionIncrease insulin sensitivityBiocideMetabolism disorderTG - TriglycerideSteroid biosynthesis
The present invention describes the identification and isolation of chromones and novel chromone compositions from plant sources that exhibit up-regulation of adiponectin production by adipocytes and the normalization of virtually hundreds of genes related to glucose and fatty acid metabolic and signaling pathways. The chromone compositions are effective in enhancing adiponectin production by adipocytes and regulating genes involved in fatty acid biosynthesis, mitochondrial β-oxidation of fatty acids, steroid biosynthesis, gluconeogenesis, fat transport, PPARα / RXRα liver signaling and xenobiotic metabolism. The chromone compositions can be used to increase insulin sensitivity, improve glucose tolerance, lower triglyceride levels and balance glucose levels in mammals. Included in the present invention are methods for the prevention and treatment of a variety of diseases and conditions including, but not limited to insulin resistance, glucose intolerance, hyperglycemia, metabolic syndromes, dyslipidemia, and hypertriglyceridemia.
Owner:UNIGEN
Breeding method for high-growing-capability crypthecodium cohnii mutant algal strain
ActiveCN106754862AThe effect of directional domestication is obviousEfficient and rapid breeding methodUnicellular algaeElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentFatty acid biosynthesisBiotechnology
The invention discloses a crypthecodium cohnii mutant algal strain breeding method taking an inhibitor (including but not limited to sethoxydim) of a key enzyme (Acetyl CoA carboxylase) for fatty acid synthesis as selective pressure. The method comprises atmospheric and room temperature plasma (ARTP) mutation of a crypthecodium cohnii algal strain and mutant algal strain screening under the selective pressure of the inhibitor (including but not limited to sethoxydim) of Acetyl CoA carboxylase, as well as crypthecodium cohnii algal strain acclimation under the selective pressure of the inhibitor (including but not limited to sethoxydim) of Acetyl CoA carboxylase. The method is characterized in that the ARTP mutation technique and the algal strain screening method based on the inhibitor (including but not limited to sethoxydim) of Acetyl CoA carboxylase are combined together, and also the algal strain acclimation method based on the inhibitor (including but not limited to sethoxydim) of Acetyl CoA carboxylase is used. Compared with a conventional crypthecodium cohnii algal strain breeding method, the breeding method provided by the invention has the characteristic that the high-growing-capability algal strain can be efficiently and quickly obtained.
Owner:KUNMING ZAONENG BIOTECH CO LTD
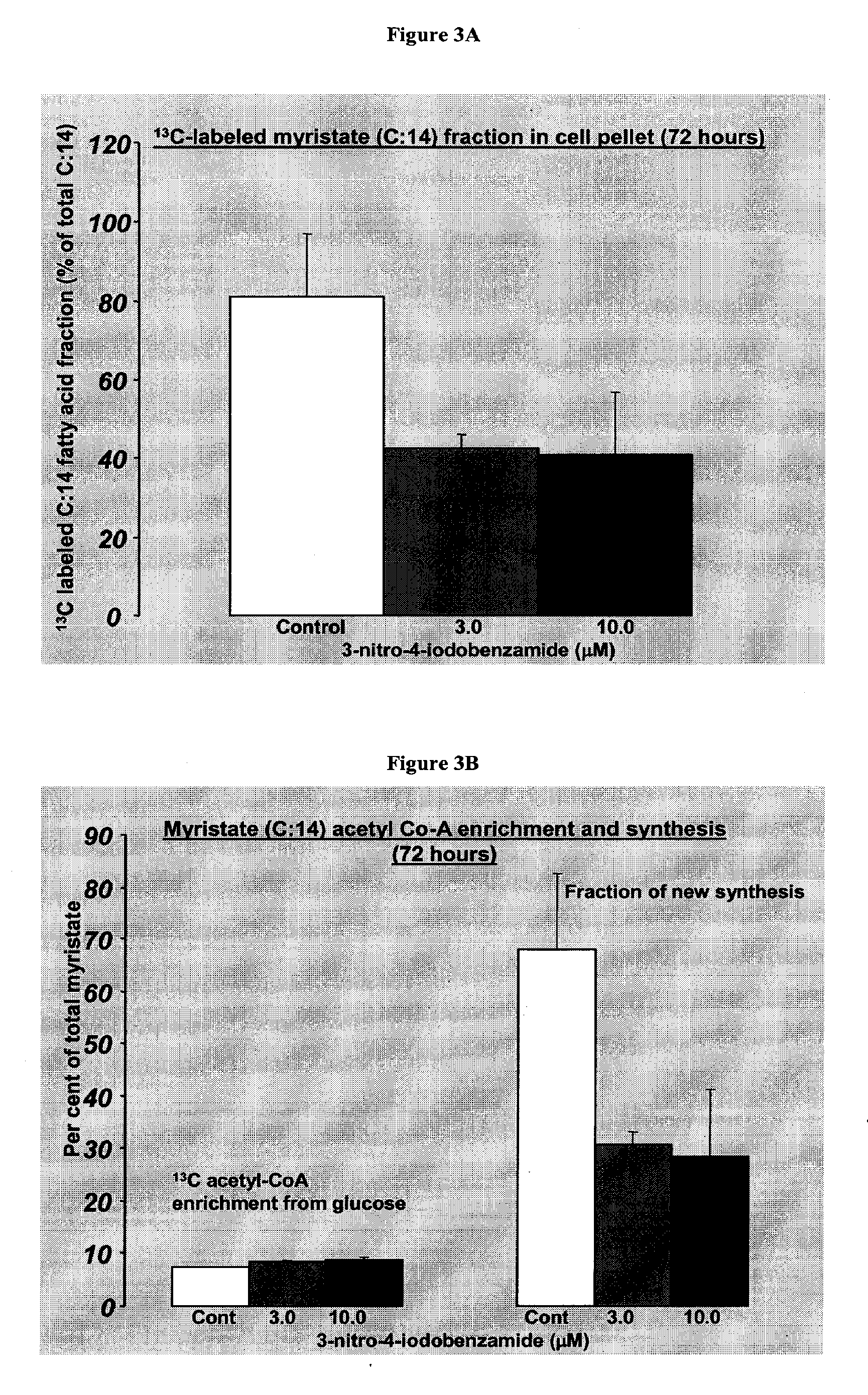
Monitoring of the inhibition of fatty acid synthesis by iodo-nitrobenzamide compounds
The present invention relates to a method of treating a fatty acid synthesis related disease comprising administering to a patient in need thereof an effective amount of a PARP inhibitor or metabolite thereof to inhibit fatty acid synthesis, wherein the fatty acid synthesis related disease is obesity, diabetes, or cardiovascular disease. The present invention also relates to a method of treating a cancer in a subject comprising: (i) identifying a level of fatty acid in a sample from the subject, and (ii) administering an effective amount of a PARP inhibitor or metabolite thereof to inhibit fatty acid synthesis in the subject, wherein the administration is based on the level of fatty acid, thereby treating the cancer in the subject. The present invention further relates to a method of treating Her-2 related cancers by administering to a patient in need thereof an effective amount of a PARP inhibitor or metabolite thereof to inhibit fatty acid synthesis.
Owner:BIPAR SCI INC
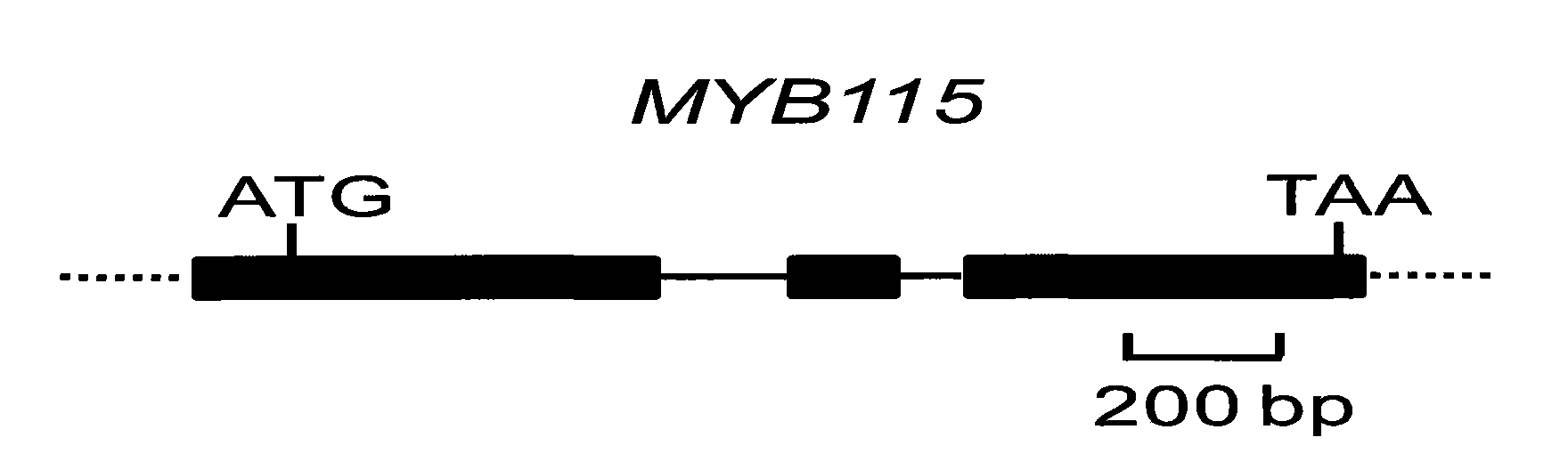
Transcription factor for enhancing embryogenesis of plant cell and synthesis of fatty acid as well as encoding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a transcription factor for enhancing the embryogenesis of a plant cell and the synthesis of fatty acid as well as an encoding gene and an application thereof. The transcription factor is the following proteins: (a) a protein formed by an amino acid sequence disclosed by the sequence 3 in a sequence table; (b) relevant proteins derived from (a), enhancing the embryogenesis of the plant cell and obtained through replacing and / or losing and / or adding one or a plurality of amino acids in the amino acid sequence disclosed by the sequence 3 in the sequence table. The invention also discloses the encoding gene of the transcription factor and a recombined expression vector containing the gene, a transgene clone or a recombined germ. The transcription factor for enhancing the embryogenesis of a plant cell and the synthesis of fatty acid and the encoding gene thereof have great application values, such as enhancing the embryogenesis of the plant cell, culturing transgene plants with improved fatty acid content, being used as screening marks of the transgene plates, enabling plants to have asexual reproduction capacity and producing synthetic seed.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
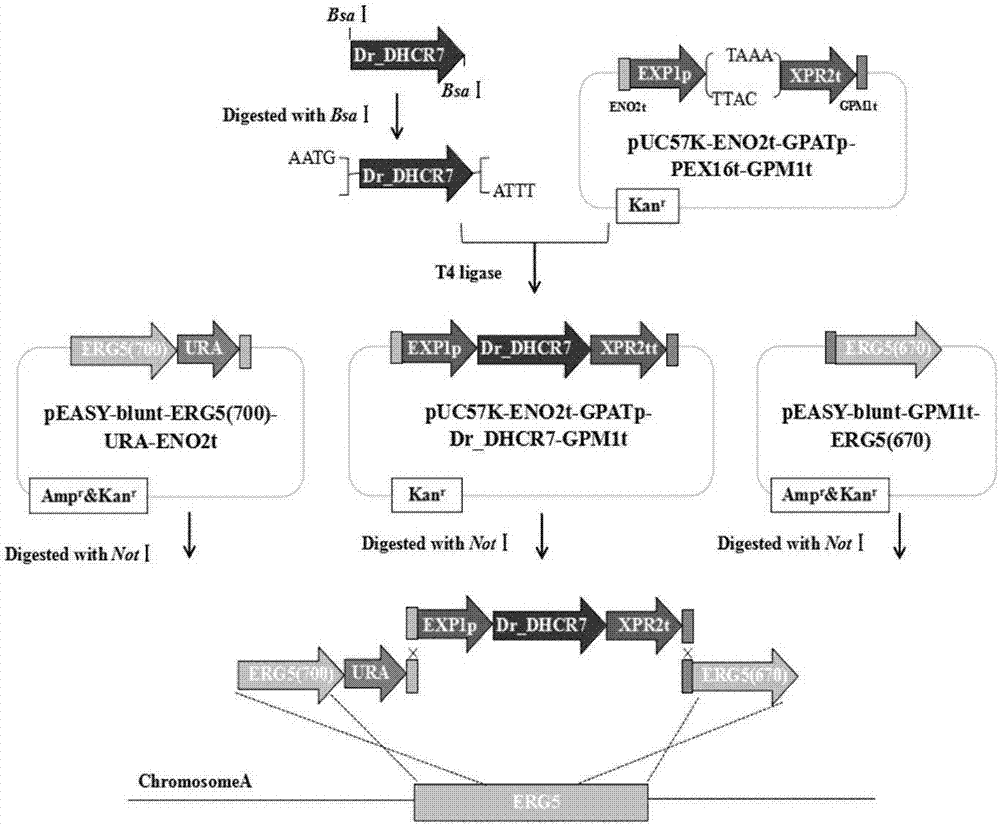
Recombinant strain as well as construction method and application in producing campesterol thereof
The invention relates to the technical field of genetic engineering, in particular to a recombinant strain as well as a construction method and application in producing campesterol thereof. The invention constructs a recombinant strain expressing a DHCR7 gene and an ERG5 gene with inactivation. The strain also over-expresses an acetyl-CoA metabolism-related gene, the recombinant yarrowia lipolytica chassis strain increases the yield of the campesterol by regulating the metabolic flow of the acetyl-CoA synthesis and fatty acid synthesis in the cytoplasm, and the experiments show that the yield of campesterol of the recombinant strain can reach 941.5mg / L after process optimization.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com