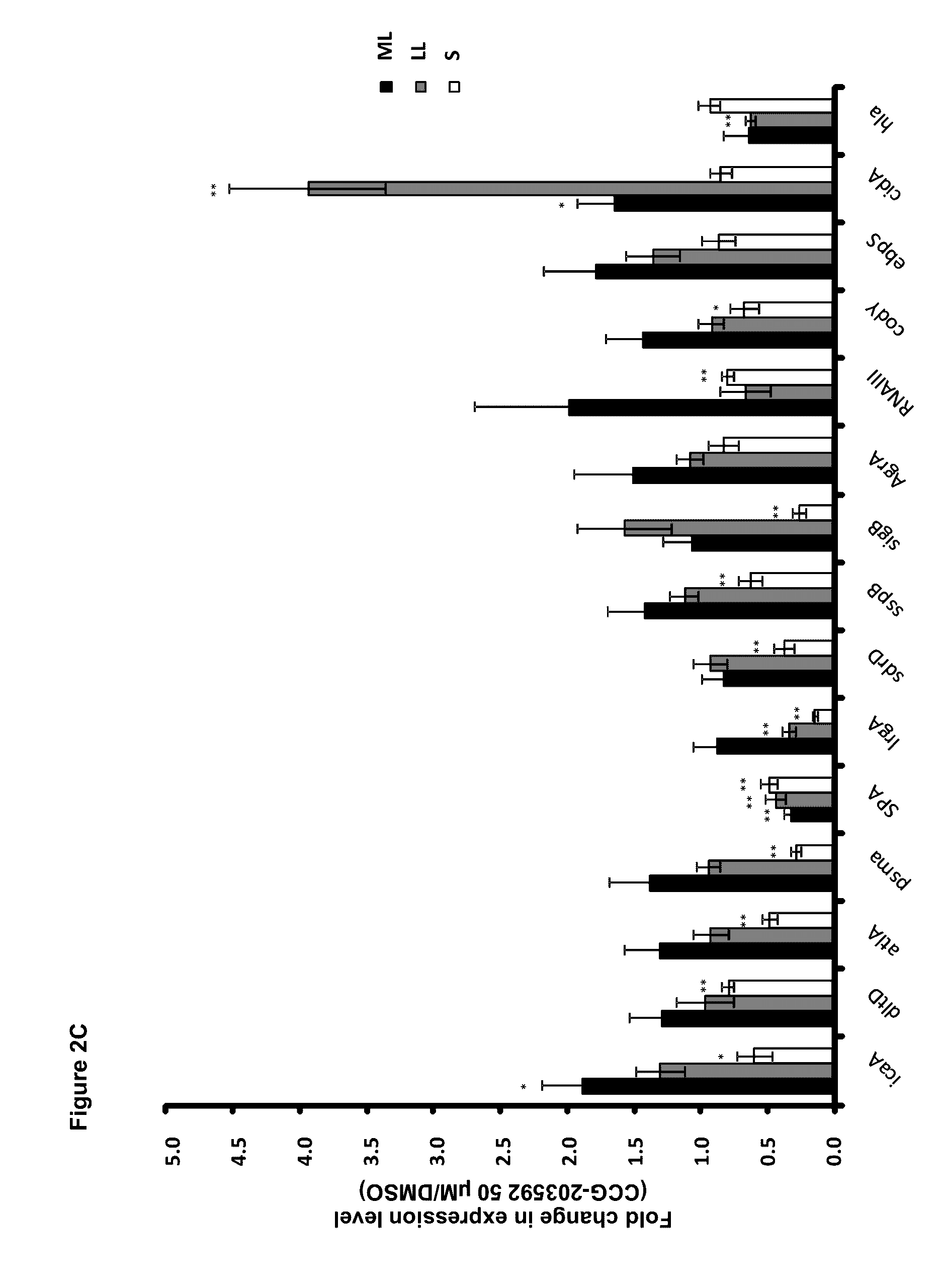
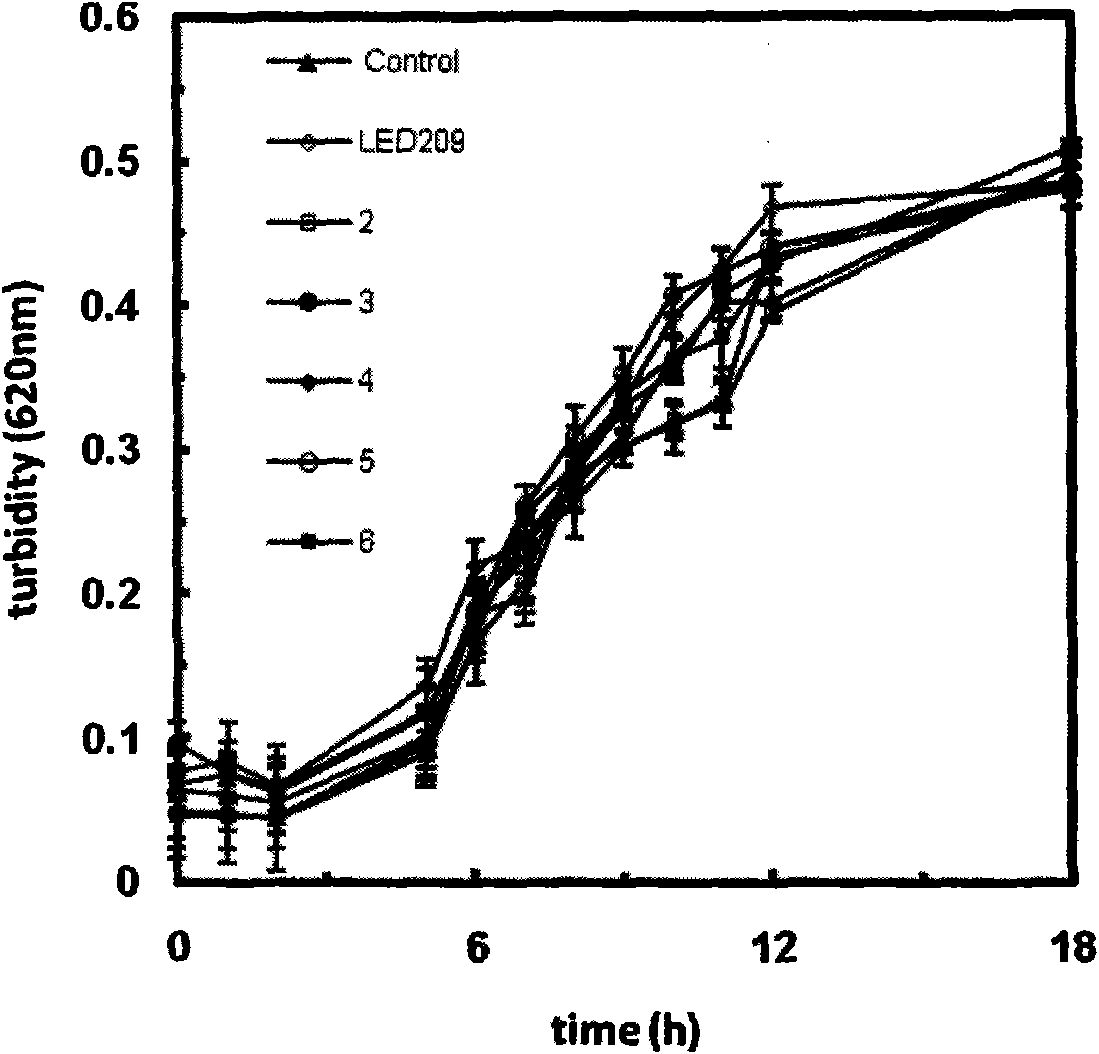
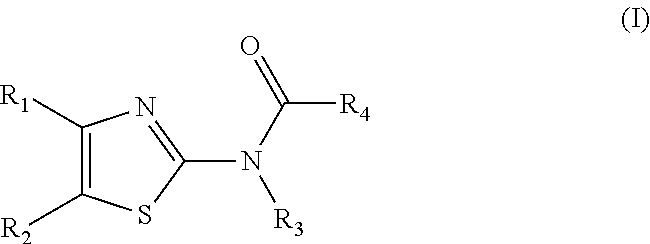
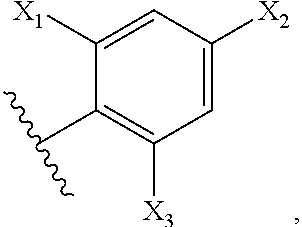
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
59 results about "Bacterial virulence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bacterial Virulence Factors are molecules synthesized by certain bacteria that increases their capacity to infect or damage human tissues.
Bacterial virulence factors and uses thereof
InactiveUS20070041997A1Reduce sheddingReduce colonizationAntibacterial agentsCompound screeningSecretory proteinScreening tool
The invention relates to, in part, secreted proteins of bacterial pathogens and methods for their use. More specifically, the invention provides in part several new common secreted proteins for A / E pathogens. In some embodiments of the invention, these polypeptides and nucleic acid molecules encoding these polypeptides, or portions thereof, are useful as vaccines, diagnostics, or drug screening tools for A / E pathogenic infections, or as reagents.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA +1
Chip for gene detection of multiple vibrios at the same time, and detection and use thereof
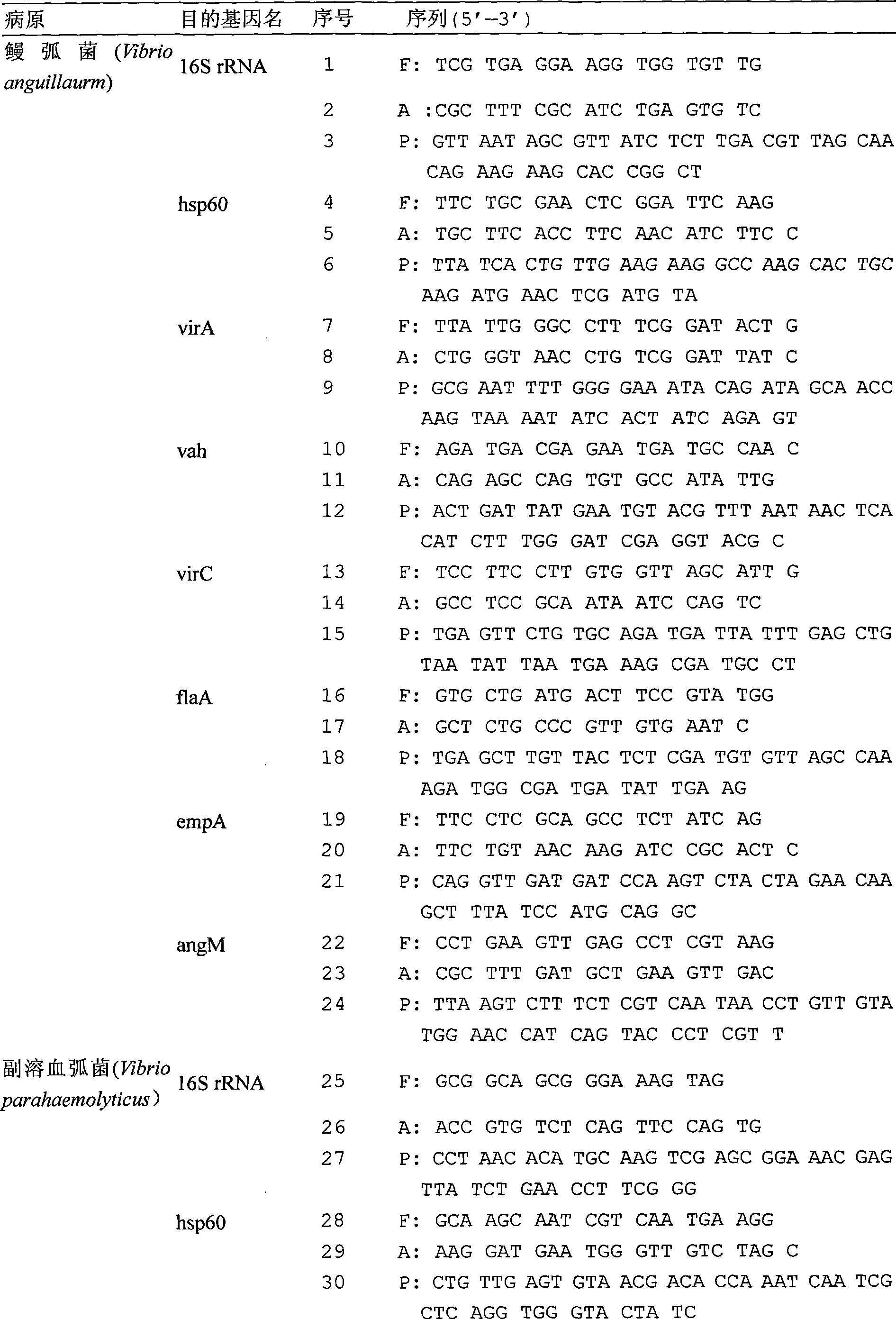
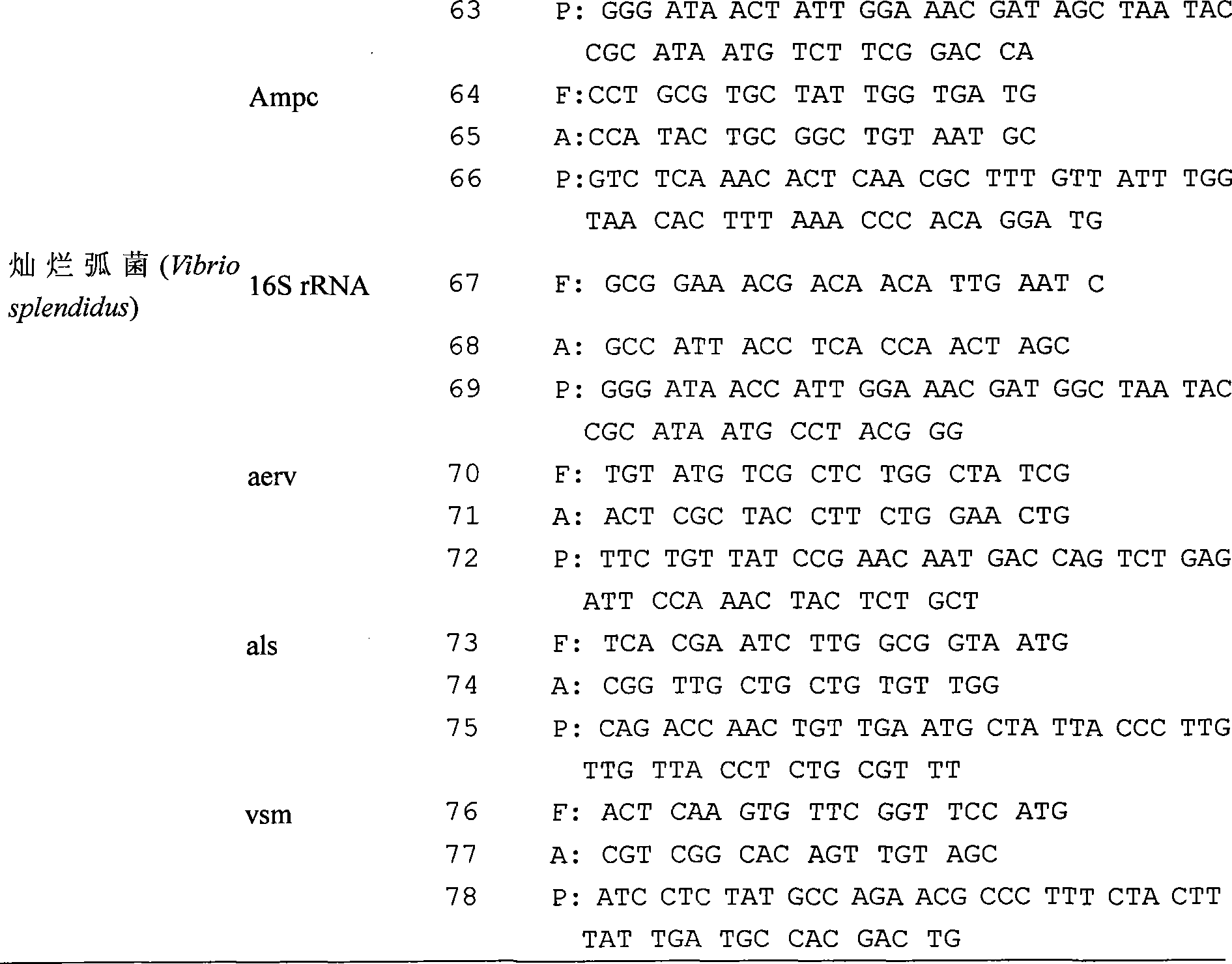
ActiveCN101475986AEffective guidanceEffectively guide productionMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesForward primerVirulent characteristics
The present invention relates to a detection chip for performing gene detection to various vibrio and its detection and applications. The invention provides 16S rRNA sequences corresponding to each vibrio of vibrio anguillarum, vibrio harveyi, vibrio alginolyticus, vibrio parahaemolyticus, brilliant vibrio and Fisher vibrio; heat shock protein hsp60 probe sequence; virulence gene probe sequence; 16S rRNA forward primer sequence; 16S rRNA reverse primer sequence; heat shock protein hsp60 forward primer sequence; heat shock protein hsp60 reverse primer sequence; virulence gene forward primer sequence and virulence gene reverse primer sequence. The present invention has specific, sensitive and high-throughput features, can simultaneously detect six kinds of bacteria virulence genes, and the invention will effectively guide the production as an important disease early-warning detection method used in clinical diagnosis of aquatic animals.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Antisense antibacterial compounds and methods
ActiveUS20150361425A1Increase antibiotic susceptibilityReduce capacityAntibacterial agentsSugar derivativesAntibiotic resistanceMorpholine
Provided are antisense morpholino oligomers targeted against bacterial virulence factors such as genes that contribute to antibiotic resistance or biofilm formation, or genes associated with fatty acid biosynthesis, and related compositions and methods of using the oligomers and compositions, for instance, in the treatment of an infected mammalian subject.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
Bacterial Virulence Factors And Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20120064572A1Reduce colonizationReduce sheddingAntibacterial agentsBacteriaBacteroidesSecretory protein
The invention relates to, in part, secreted proteins of bacterial pathogens and methods for their use. More specifically, the invention provides in part several new common secreted proteins for A / E pathogens. In some embodiments of the invention, these polypeptides and nucleic acid molecules encoding these polypeptides, or portions thereof, are useful as vaccines, diagnostics, or drug screening tools for A / E pathogenic infections, or as reagents.
Owner:UNIV NAT AUTONOMA DE MEXICO +1
Bacterial signaling molecules that down-regulate pathogenic bacterial virulence properties
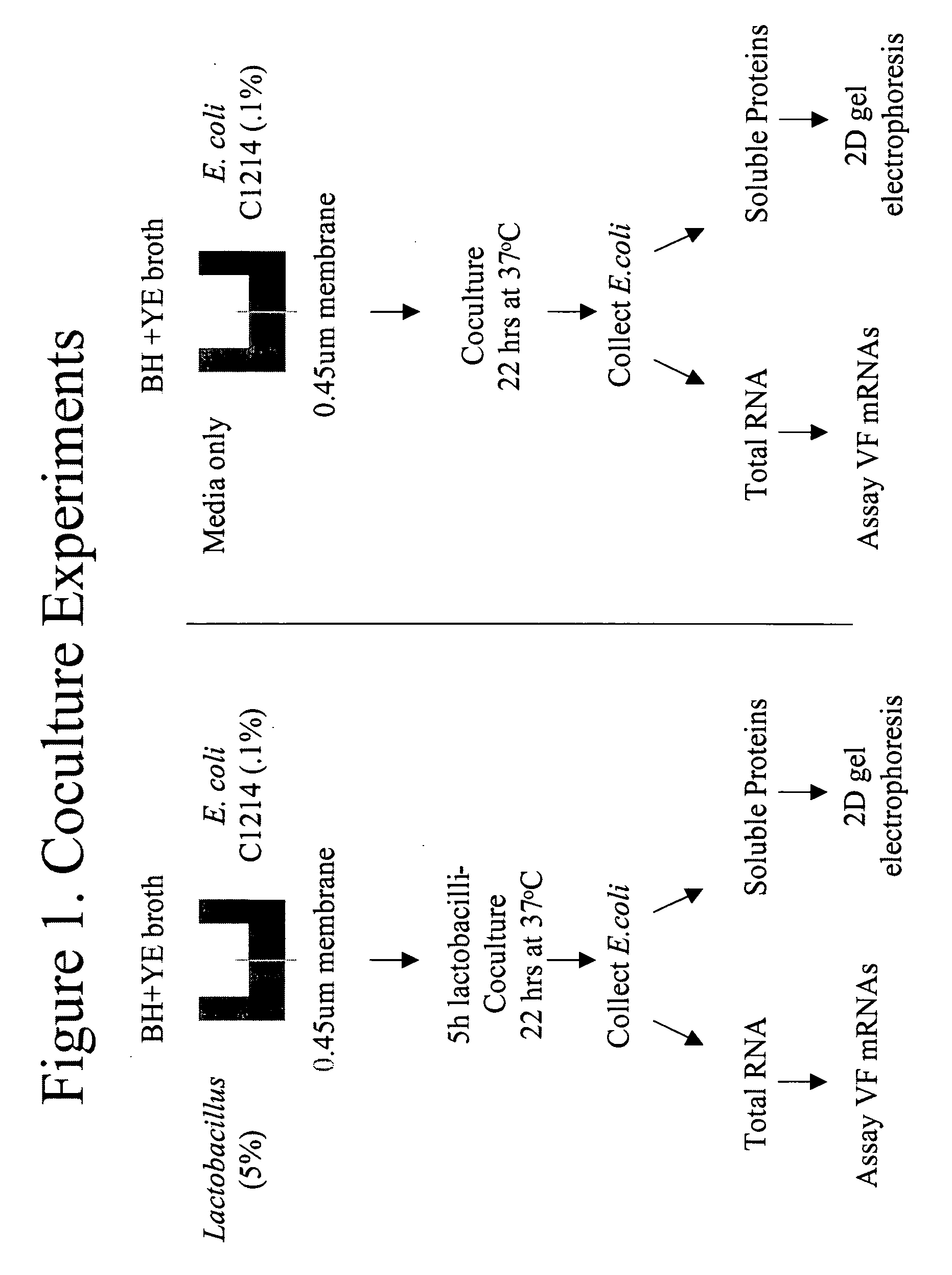
InactiveUS20070036776A1High proliferation rateReduce riskAntibacterial agentsBiocideMicroorganismVirulent characteristics
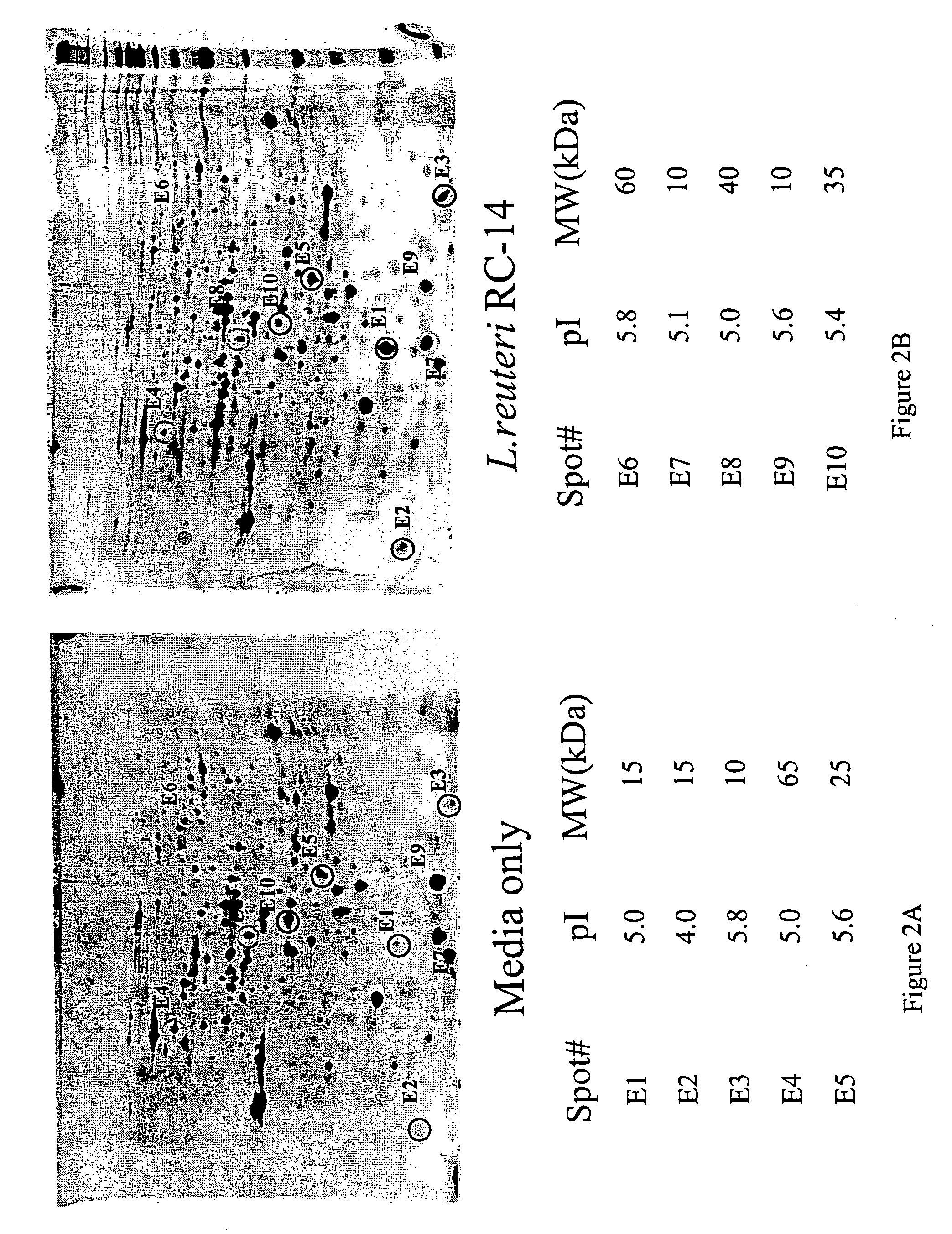
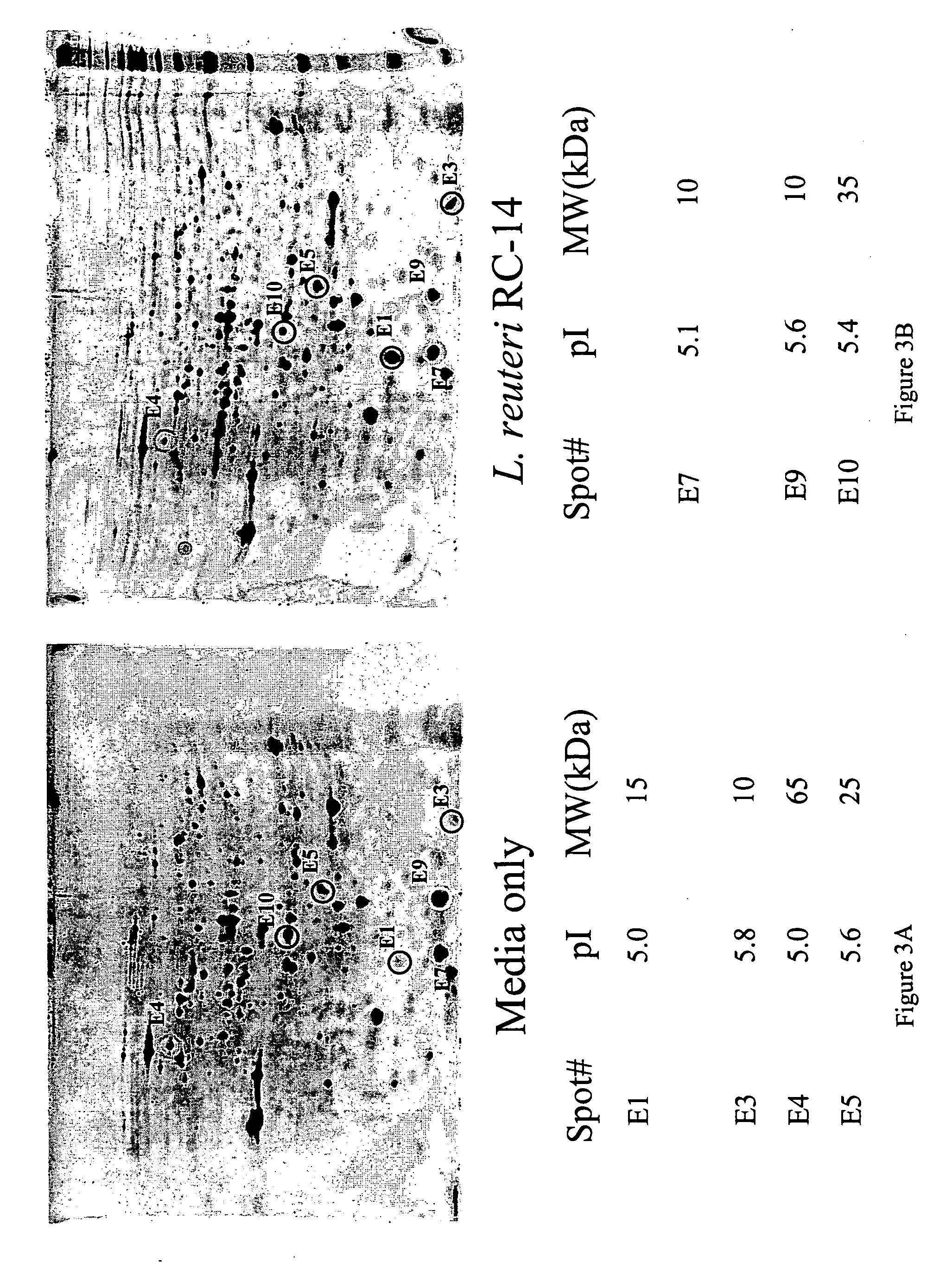
This invention relates to composition and methods of employing said composition for treating or preventing microbial associated infections and diseases. More particularly the present invention relates to bacterial proteins, peptides and amino acids which are by-products of bacteria, in particular Lactobacillus and more specifically Lactobacillus strains GR-1 and RC-14, in compositions that can treat and prevent microbial-associated infections and diseases, by altering, for example, down-regulating, virulence properties of pathogenic organisms.
Owner:CHR HANSEN AS
Treatment of bacterial infection with elastase
InactiveUS20050069532A1Reducing bacterial virulencePrevent escapePeptide/protein ingredientsAgainst vector-borne diseasesMicrobiologyNeutrophil granulocyte
The present invention relates to methods of treating bacterial infection in a subject, degrading bacterial virulence factors, preventing bacteria from escaping phagosomes of neutrophils, and preventing bacteria from invading host cells, by use of an elastase.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Reducing bacterial virulence
InactiveUS20020077272A1Many symptomMinimize consequencesBiocideBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteroidesVirulent characteristics
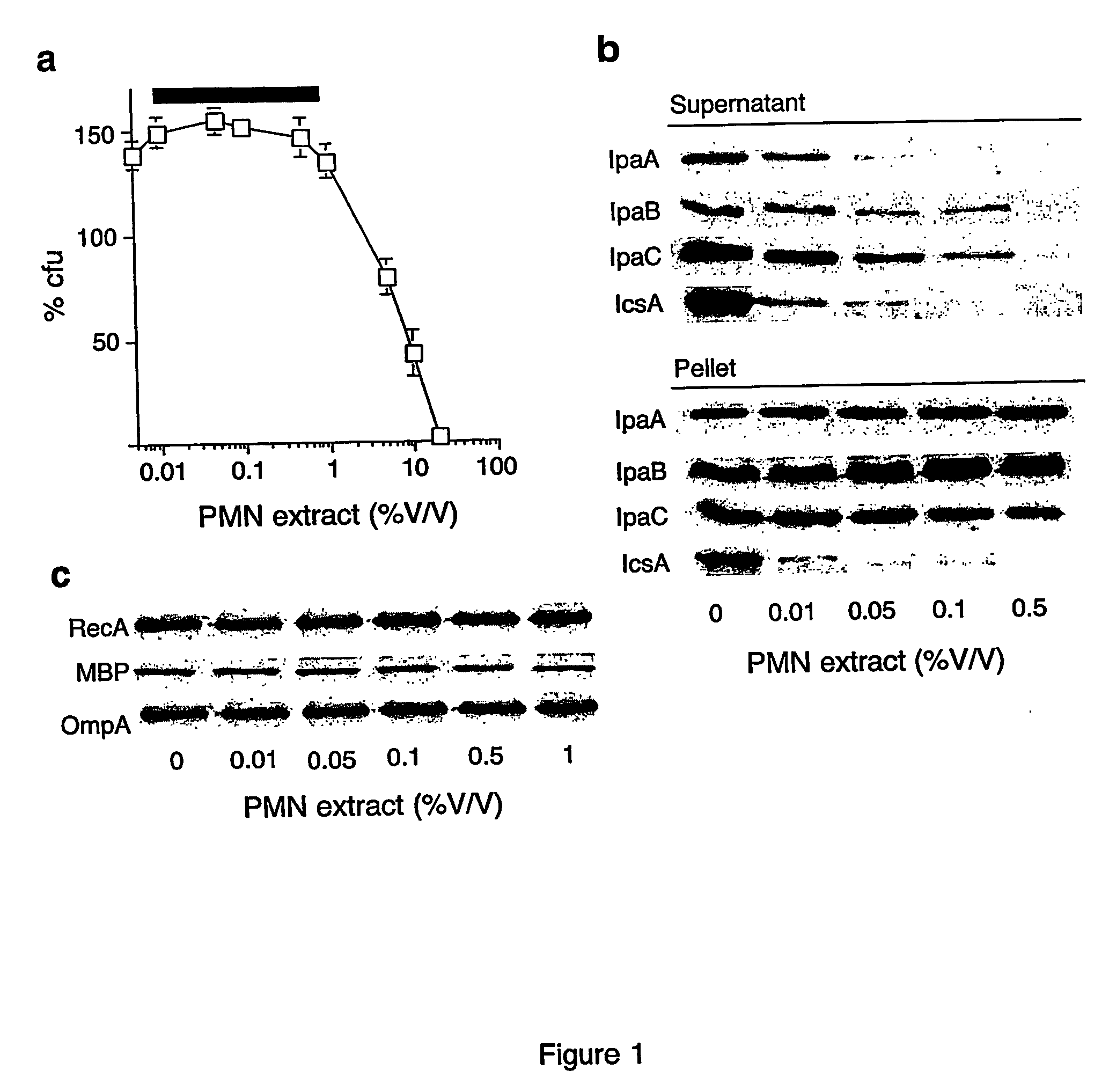
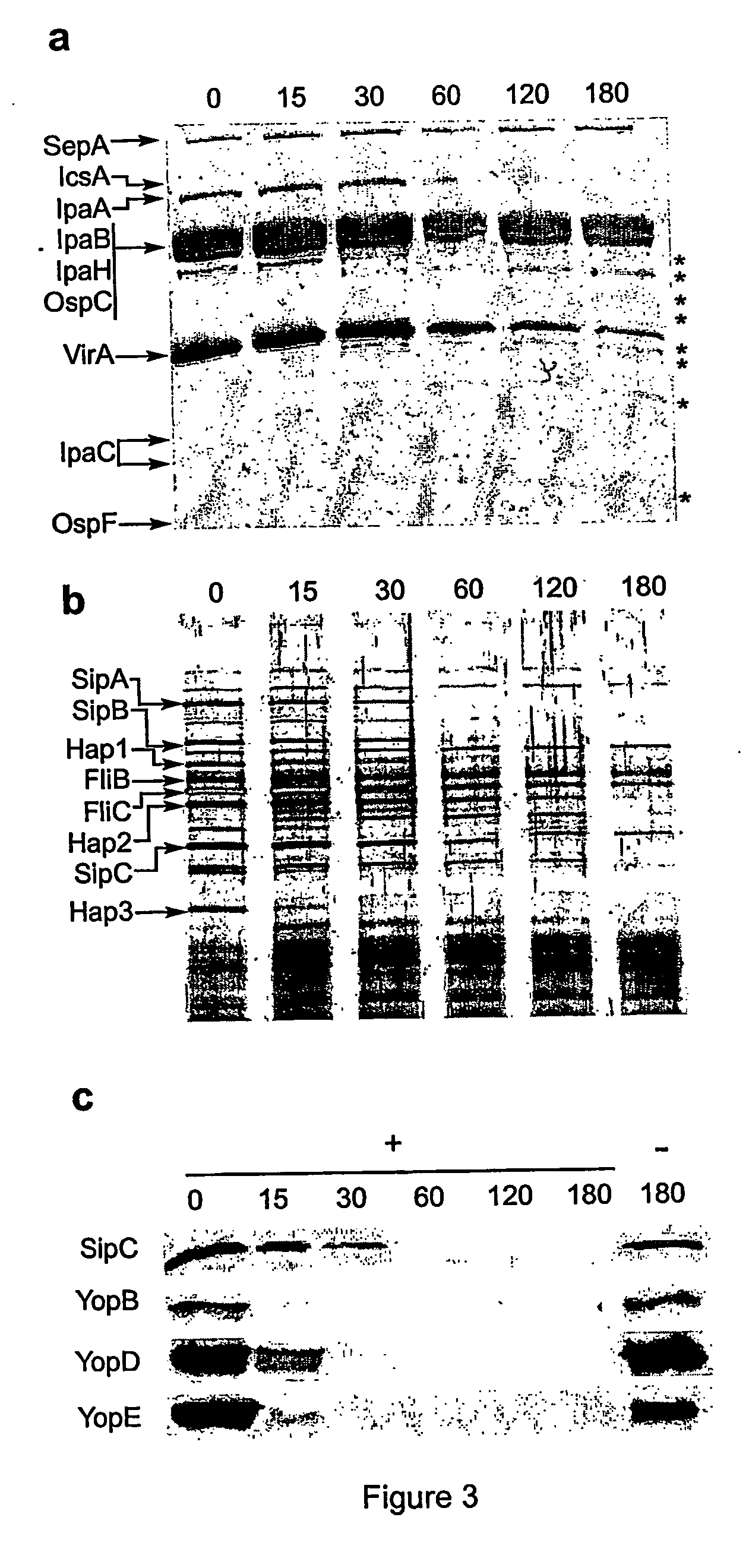
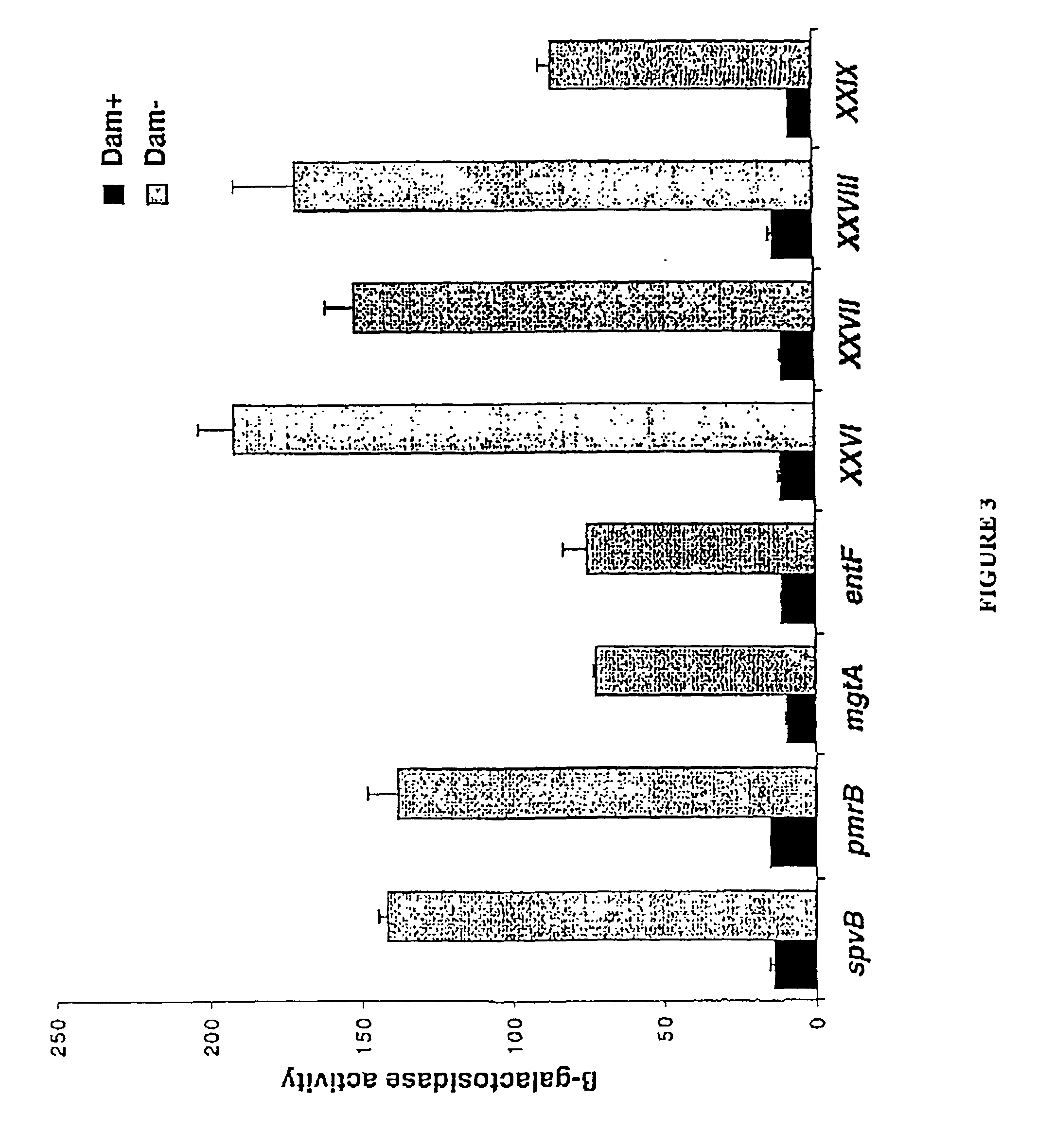
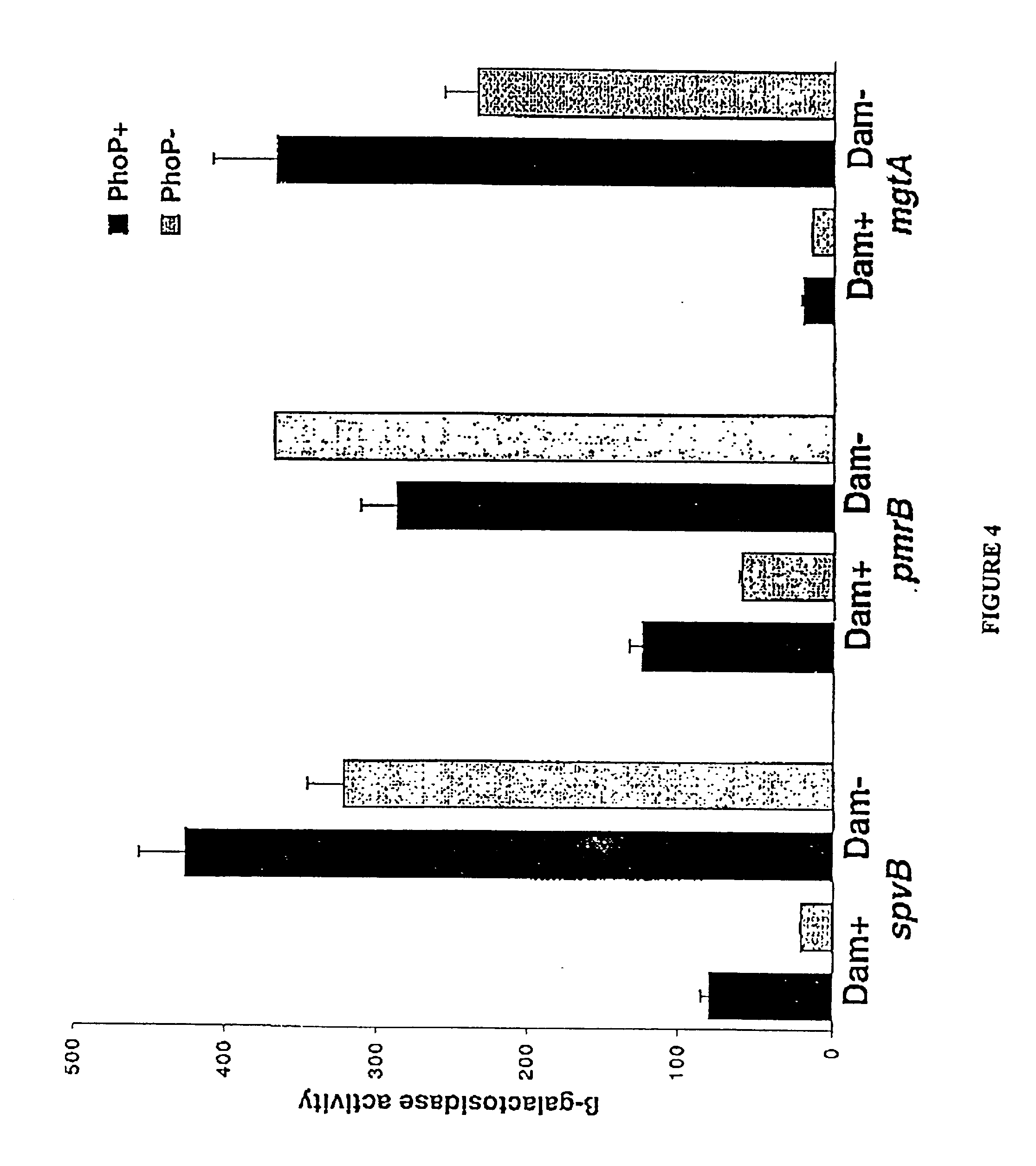
The virulence of bacterial strains and in particular pathogenic bacteria which infect human is reduced by an agent which alters the bacteria's native level or activity of DNA methyltransferase (Dam). The agent causes an alteration in the bacteria's native level of methylation of adenine in a GATC tetranucleotide which inhibits virulence of the bacteria. Thus, compounds and formulations thereof which reduce bacterial virulence inhibit proliferation of bacteria and are useful in treating bacterial infections, particularly in humans.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods of Inhibiting Bacterial Virulence and Compounds Relating Thereto
InactiveUS20100048573A1Inhibit bacterial virulenceWide applicabilityAntibacterial agentsUrea derivatives preparationMechanism of actionDrug resistance
The present invention relates to compounds and methods for the treatment of bacterial infections. Because their mechanism of action does not involve killing of bacteria or inhibiting their growth, the potential for these compounds to induce drug resistance in bacteria is minimized. Through inhibiting bacterial virulence, the present invention provides a novel means of treating bacterial infections.
Owner:OMM SCI +1
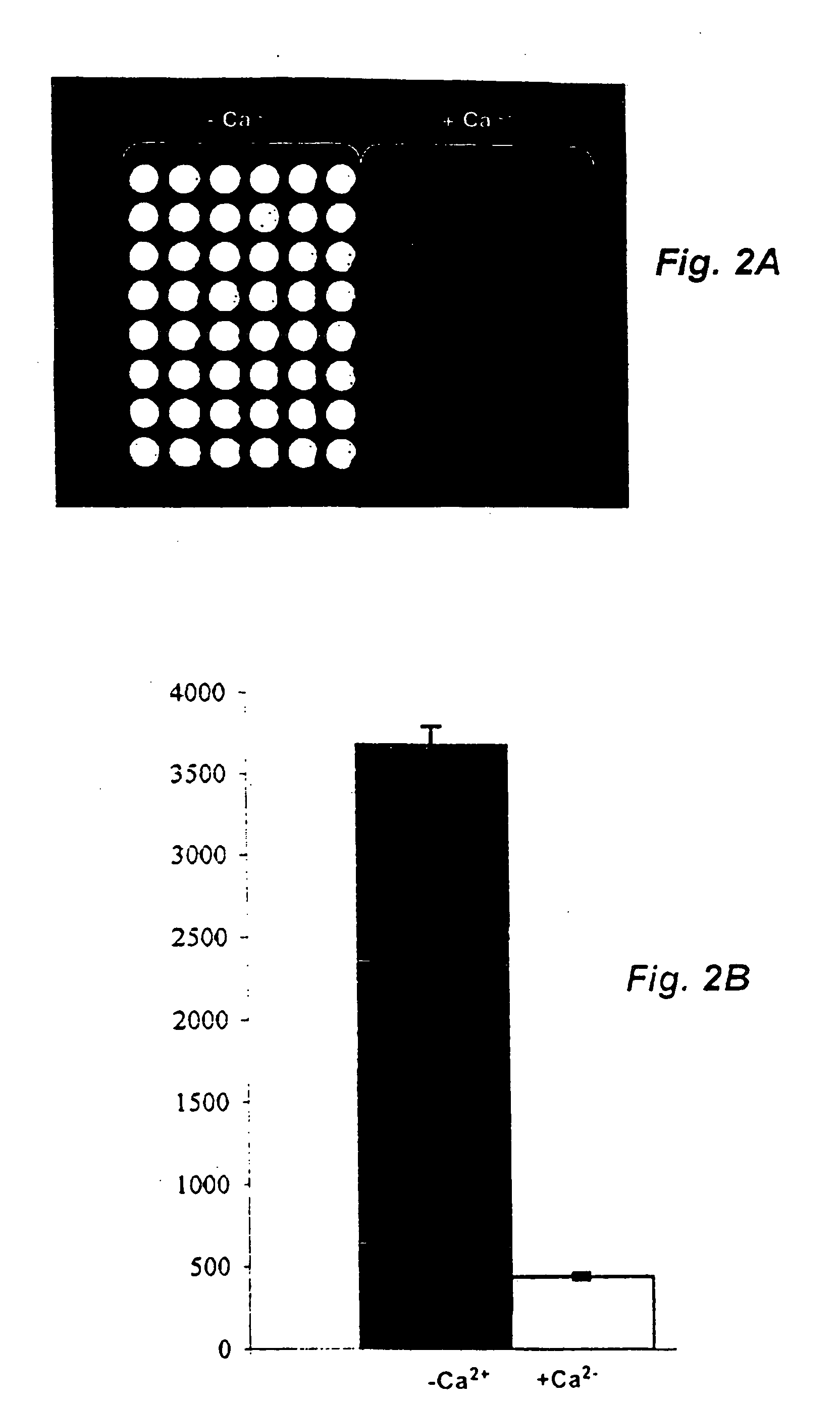
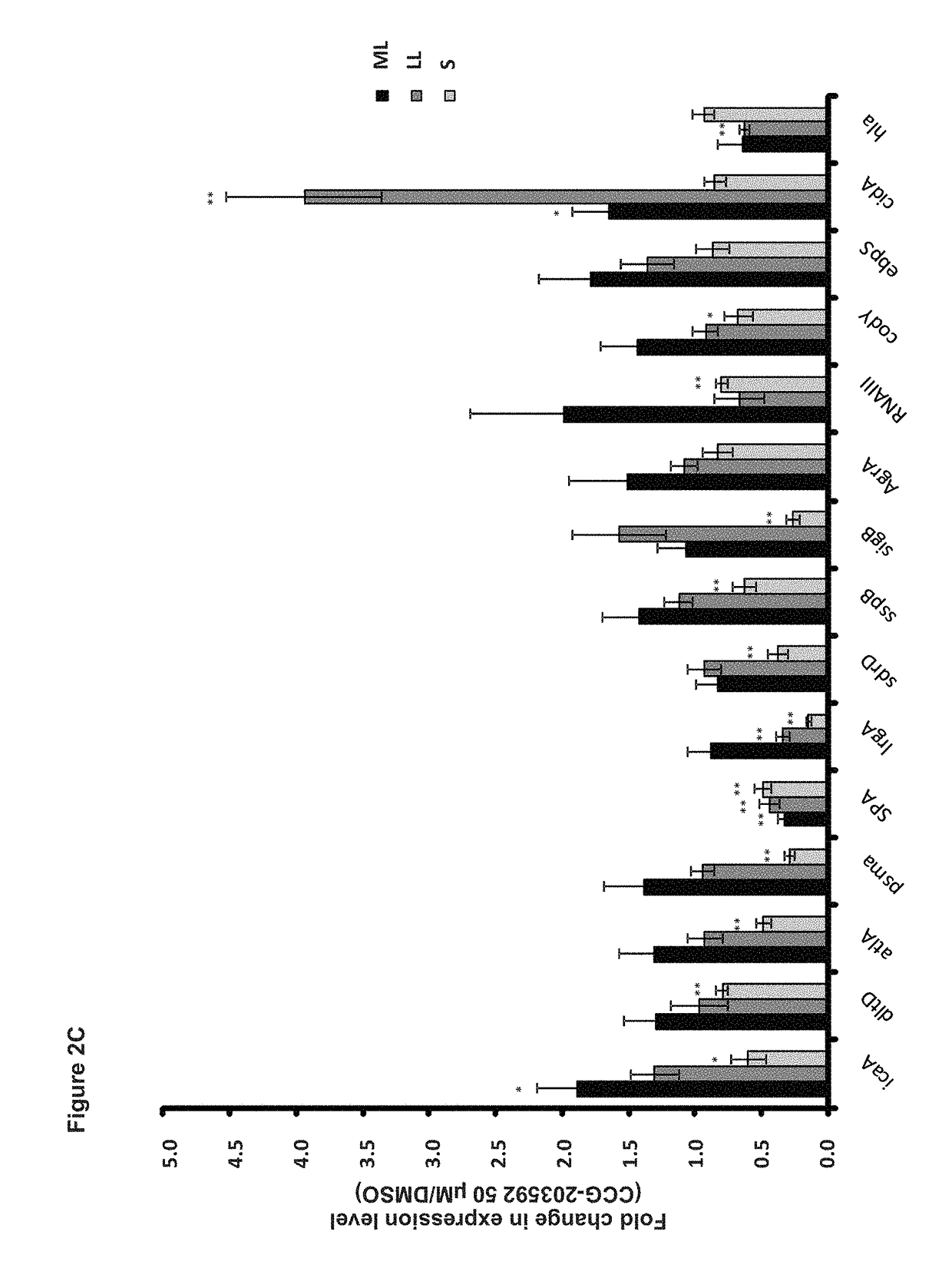
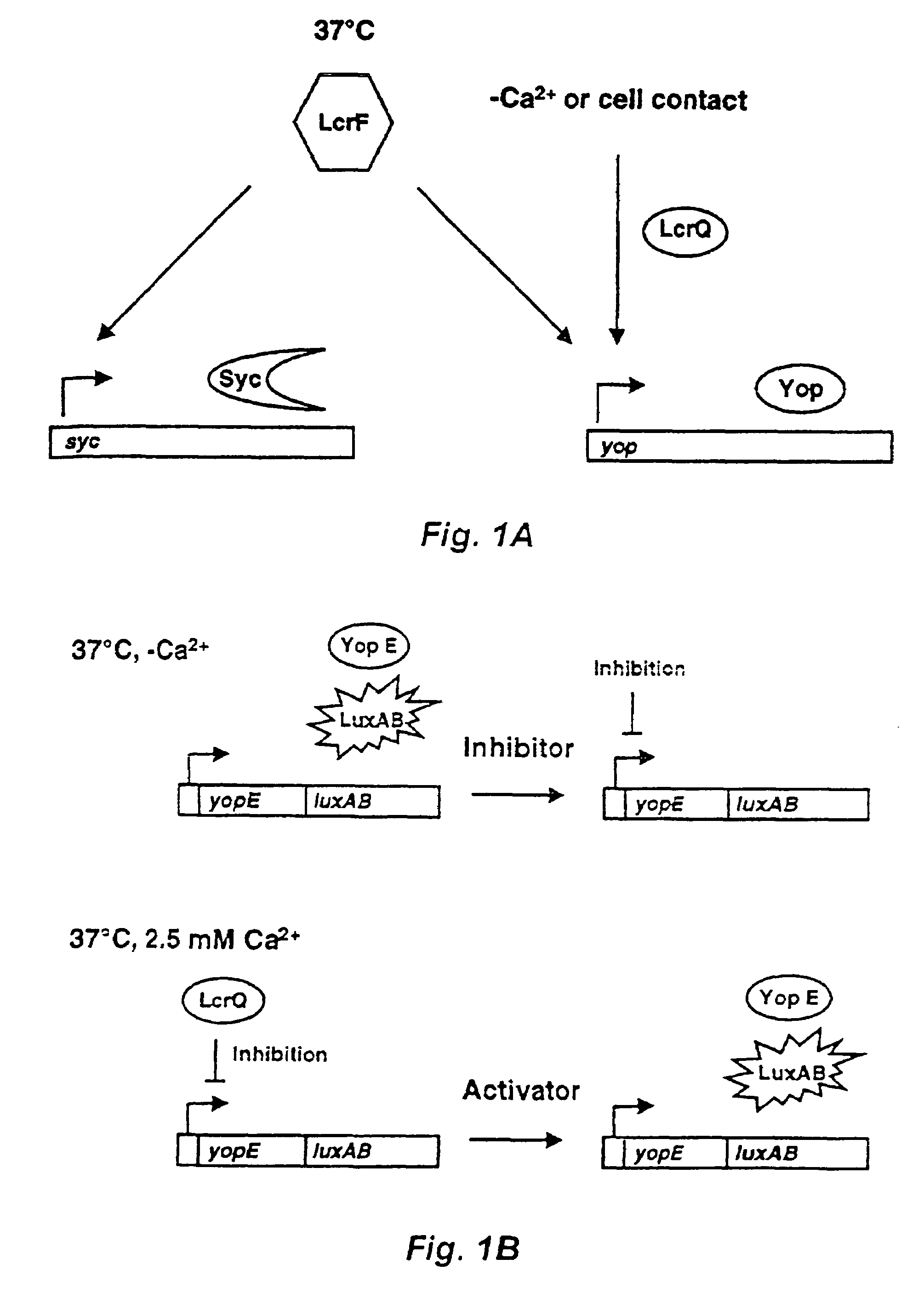
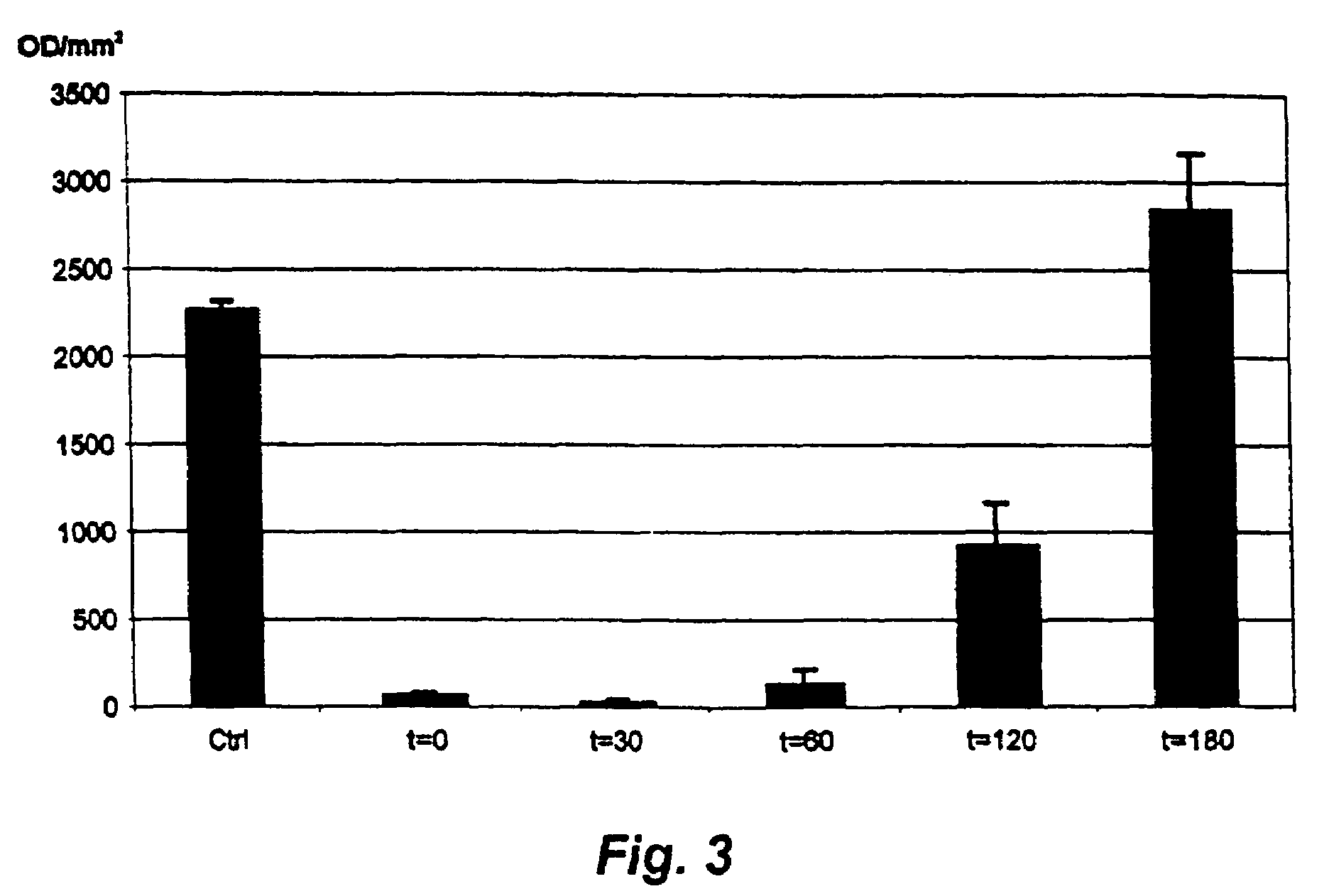
Method and probe for identifying bacterial virulence modifying agents, agents thus identifed, and their use
InactiveUS20060134724A1Stable growthSufficient DMSO toleranceOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrobiologyAntibacterial agent
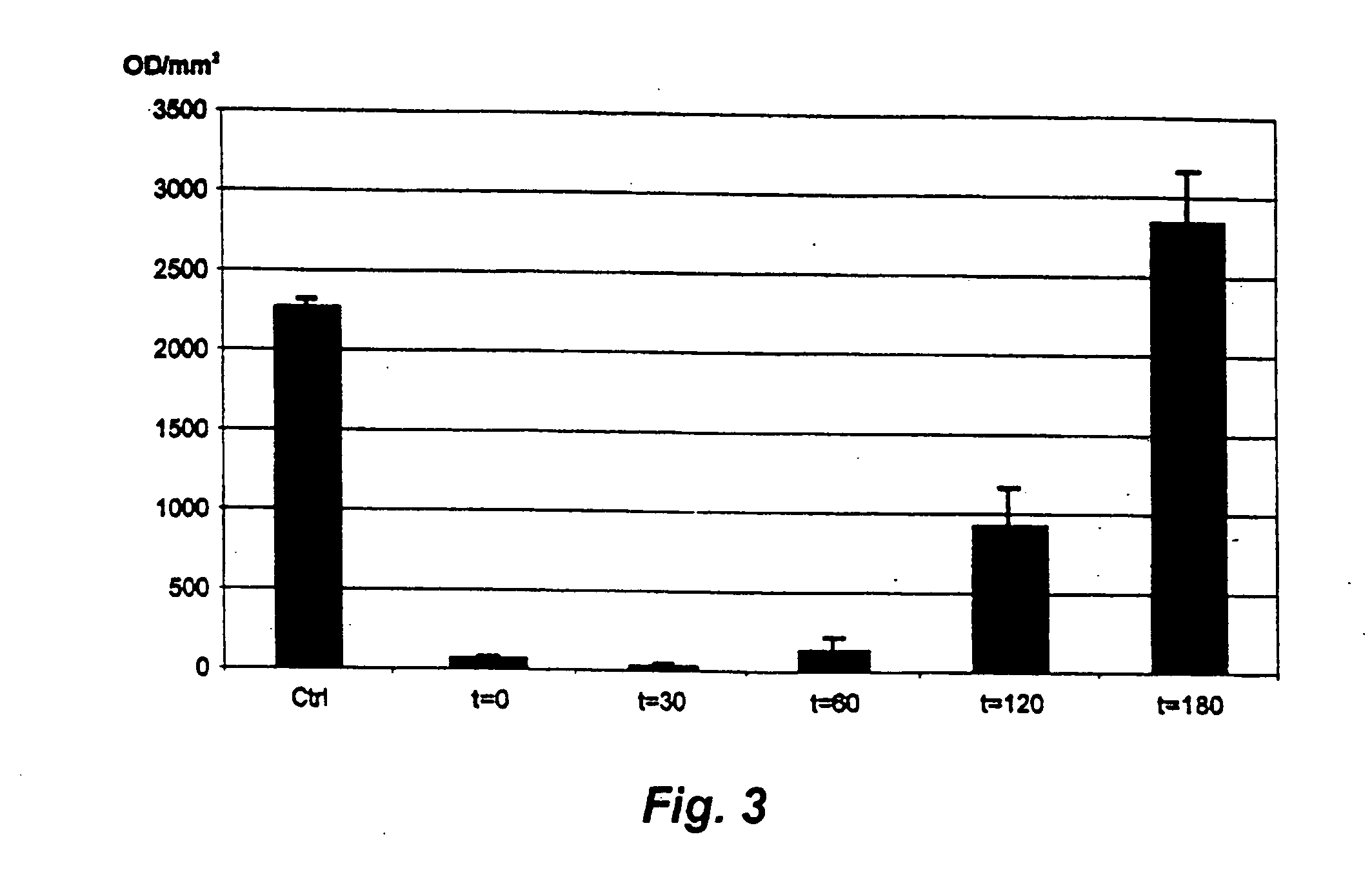
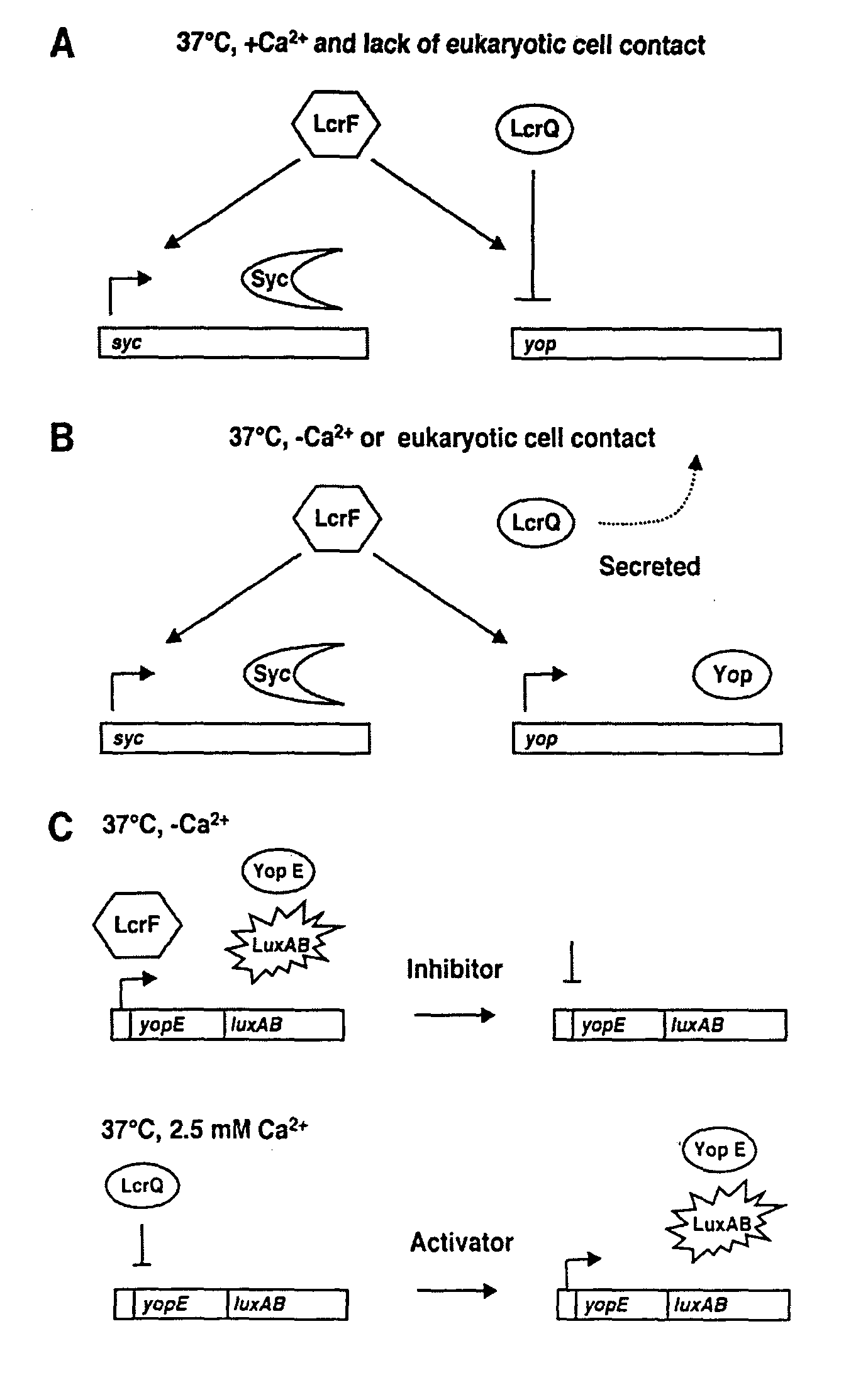
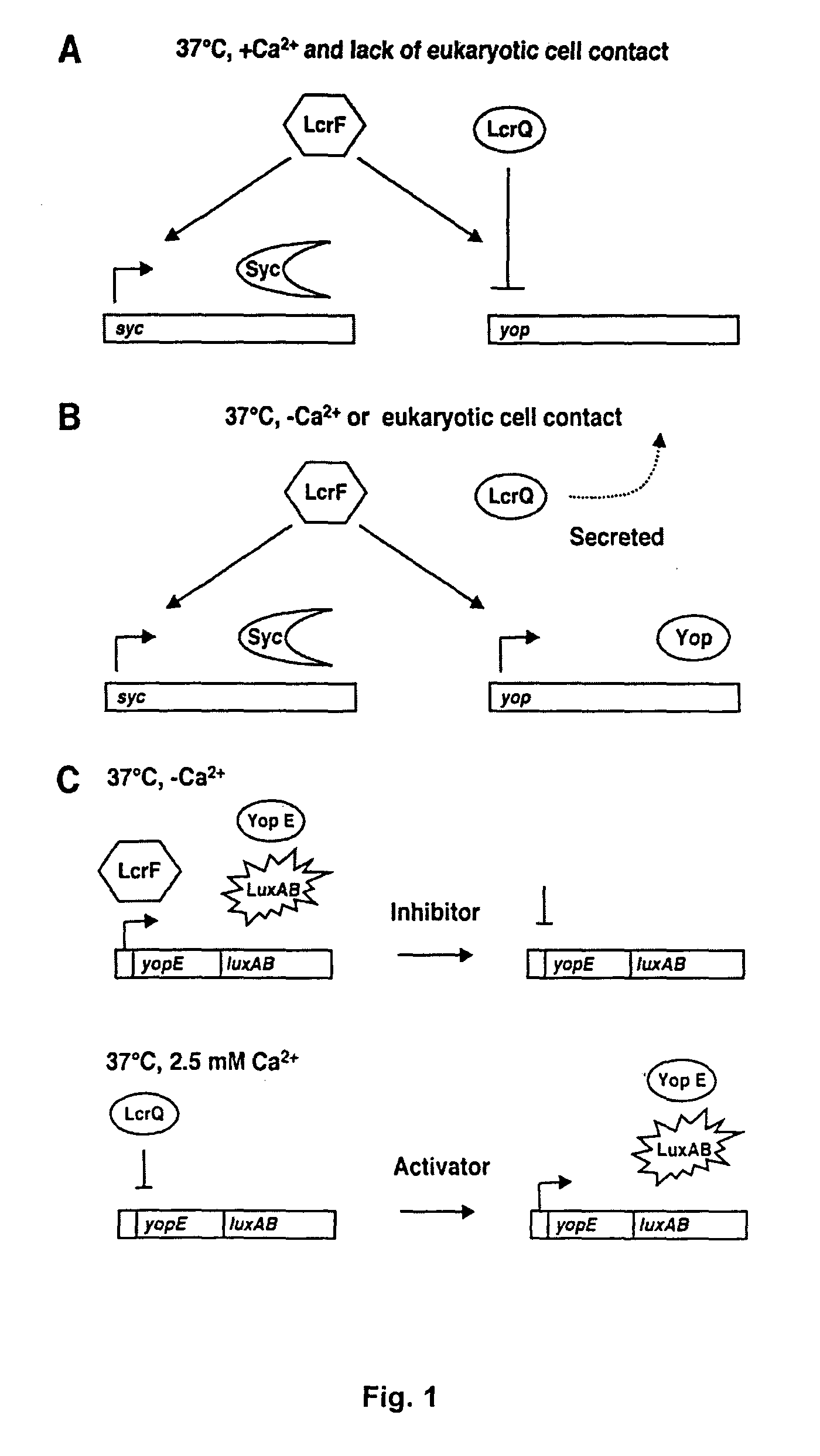
A method for identifying antibacterial agents comprises depleting bacteria of a strain comprising a luxAB construct of Ca2+, incubating the Ca2+ depleted bacteria with an agent the antibacterial effect of which shall be determined, recording the light emitted by the bacteria upon addition of an aldehyde, the incubation being carried out at a temperature which is at least 10° C. higher than the temperature at which the light is emitted by the bacteria. Also disclosed are corresponding probes and antibacterial agents identified by the method.
Owner:INNOVATIVE ANTIBIOTICS SWEDEN AB
A test kit for detecting periodontal disease
InactiveCN1906486AEasy to useBiological material analysisBiological testingWhite blood cellBacterial virulence
Test kit for diagnosing periodontal disease in a patient by analysing a sample from the oral cavity of the patient. The test kit comprises at least a first detection assay for detection of a first substance originating from bacteria and at least a second detection assay for detection of a second substance originating from the immune or inflammatory system of the patient. Most preferably, said first substance is a bacterial virulence product such as e.g. arg-gingipain from Prophyromonas gingivalis, and said second substance is human neutrophil elastase.
Owner:TENDERA
Bacterial quorum sensing inhibitor and antibacterial application thereof
InactiveCN104784160AImprove securitySeparation and purification are simple and easy to controlAntibacterial agentsBiocideBiotechnologyMinimum inhibitory concentration
The invention relates to antibacterial application of small molecular bacterial quorum sensing inhibitor Falcarindiol in the condition of no inhibition on bacteria growth concentration (subinhibitory concentration). The active compound has a broad-spectrum bacterial quorum sensing resistant activity, can inhibit bacterial virulence in subinhibitory concentration, reduces the harm of bacteria to the host, and can prevent and treat quorum sensing bacterial infections. The compound can play the role of inhibition of bacterial virulence in subinhibitory concentration, so that pressure for survival of pathogenic bacteria is not brought, drug resistance is not easy to produce, the antibacterial application of the small molecular bacterial quorum sensing inhibitor Falcarindiol in the condition of no inhibition on bacteria growth concentration (subinhibitory concentration) is different from application of killing bacteria and bacteria growth inhibition of other antibacterial agent, is also is different from the antibacterial application of bacteria growth inhibition of Falcarindiol with the bacteria concentration (the use final concentration is greater than the minimum bacteriostasis concentration), and is a new antibacterial application. The antibacterial application of the small molecular bacterial quorum sensing inhibitor Falcarindiol in the condition of no inhibition on bacteria growth concentration (subinhibitory concentration) has the advantages that: raw materials are easy to get, compound separation and purification are simple and easy to control, security is high, use concentration is low, and drug resistance is easy to produce, and the like, so that the Falcarindiol can be used in preparation of a new antibacterial agent.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Method and means for preventing and inhibiting type iii secretion in infections caused by gram-negative bacteria
A means for decreasing bacterial virulence in a mammal including man or in a plant by inhibition of the Type III secretion system at concentrations that do not prevent or substantially reduce bacterial growth comprises an N-substituted 7-quinolylmethyl amine, in particular one that is further substituted in 5- and 8-position on the quinoline ring. A corresponding therapeutic method and a pharmaceutical composition are also disclosed.
Owner:INNOVATIVE ANTIBIOTICS SWEDEN AB
Novel application of lotus plumule extracts
InactiveCN107951928ALow toxicityReduce pathogenicityAntibacterial agentsPlant ingredientsBacteroidesEthyl acetate
The application belongs to the field of medicine and discloses novel application of lotus plumule extracts, in particular to application of lotus plumule extracts in the preparation of inhibitory drugs for the quorum-sensing system. Experiments show that the lotus plumule extracts can inhibit the biological membrane of each of three species of Pseudomonas aeruginosa; that the lotus plumule extracts can inhibit the quorum-sensing system so as to decrease bacterial virulence and pathogenicity without inhibiting growth of bacteria, while bacterial drug resistance is rarely caused. Particularly all lotus plumule chloroform layer extract, lotus plumule ethyl acetate layer extract, lotus plumule total alkaloids extract and lotus plumule total flavones extract is as effective as or more effectivethan the positive drugs, furanone compounds, in inhibiting the biological membranes of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa; it is indicated that the lotus plumule extracts provide good inhibition for both Pseudomonas aeruginosa and drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Construction method and application of attenuated Listeria monocytogenes
PendingCN111269868ALow toxicityImproving immunogenicityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsMononucleosisImmunogenicity
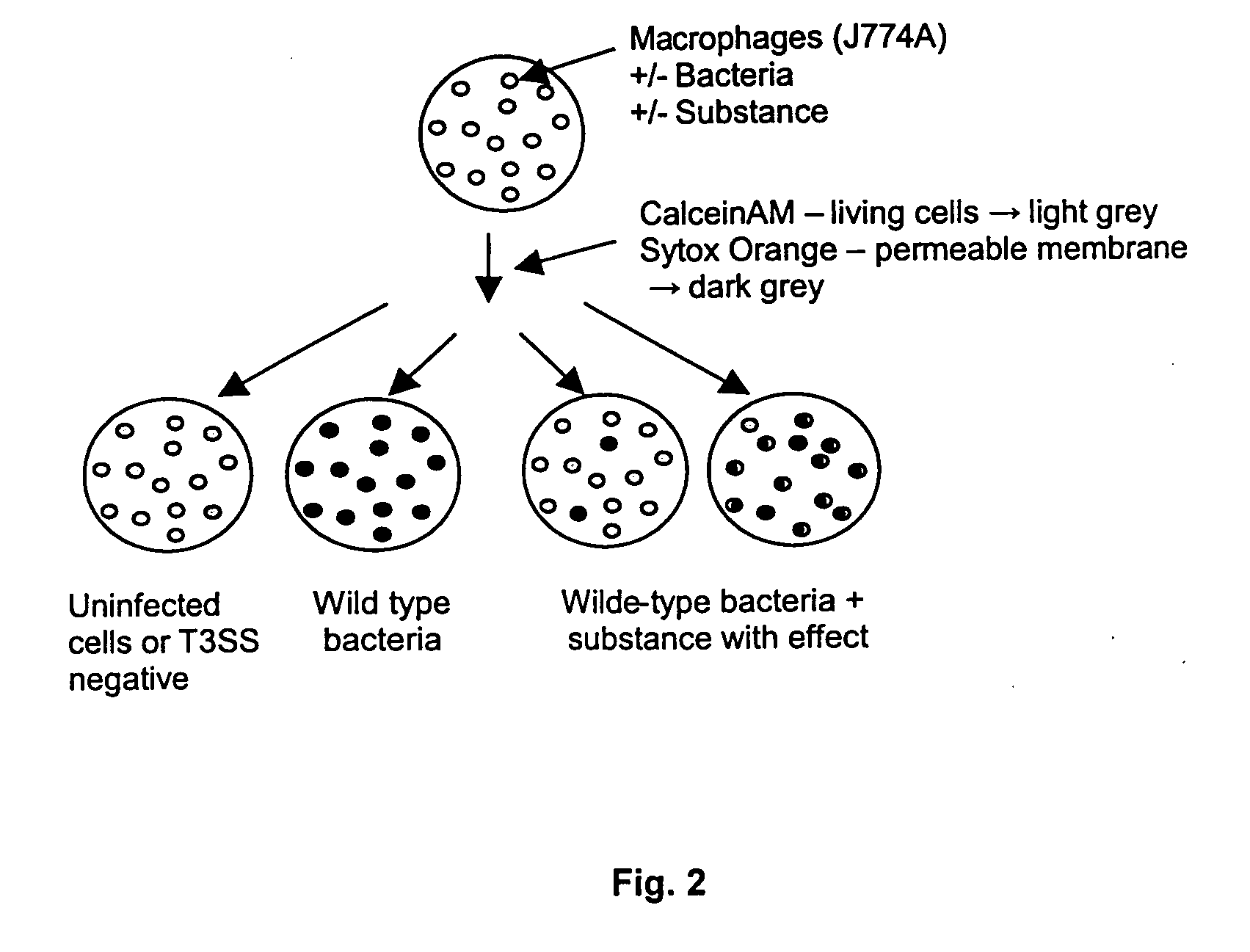
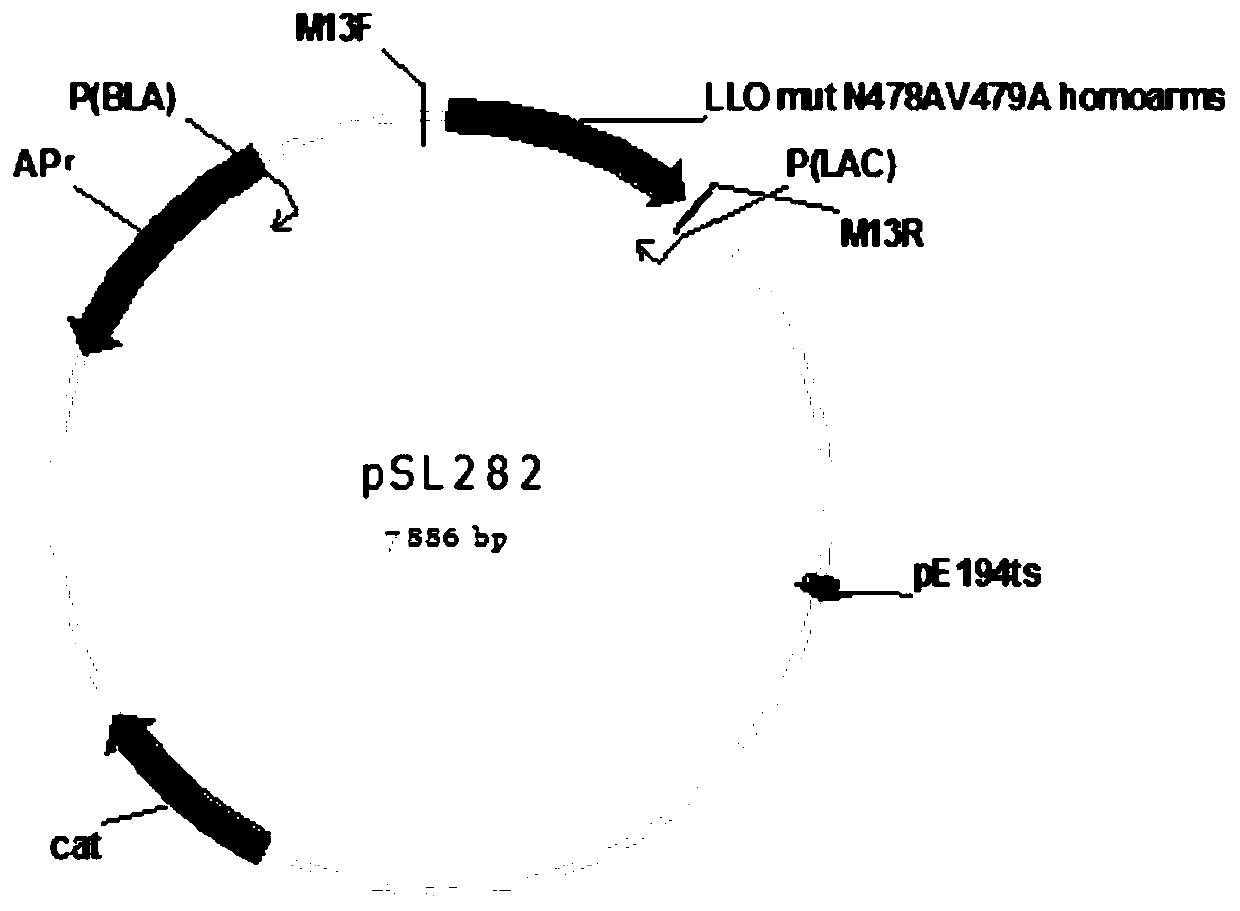
The invention relates to the field of gene engineering, and aims to provide a construction method and application of attenuated Listeria monocytogenes. A Listeria monocytogenes wild strain EGD-e is used as a construction parent, and asparagine at the 478th site and valine at the 479th site of an hly gene are respectively mutated into alanine without containing plasmids; the finally obtained attenuated strain is named as Lemo-C07, the preservation number of the attenuated strain is CGMCC 18647, and the preservation institution is China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center. The attenuated strain of Listeria monocytogenes can be used as a live vaccine treatment carrier or an immunologic adjuvant; after amino acid site-specific mutagenesis of the key sites N478 and V479 of the Listeria monocytogenes virulence gene hly, the toxicity of the Listeria monocytogenes is greatly reduced (reaching a safety level), but very good immunogenicity is still retained. As direct mutation is carried out on the Listeria monocytogenes genome, the Listeria monocytogenes does not contain resistance plasmids, the biosafety is met, and the growth of the Listeria monocytogenes is not influenced by the loss of the plasmids.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Virulence Associated Nucleic Acid Sequences and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20070105167A1Easy to produceInhibition of virulenceAntibacterial agentsCompounds screening/testingVirulent characteristicsNucleic acid sequencing
Disclosed are bacterial virulence polypeptides and nucleic acid sequences (e.g., DNA) encoding such polypeptides, and methods for producing such polypeptides by recombinant techniques. Also provided are methods for utilizing such polypeptides to screen for antibacterial or bacteriostatic compounds.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
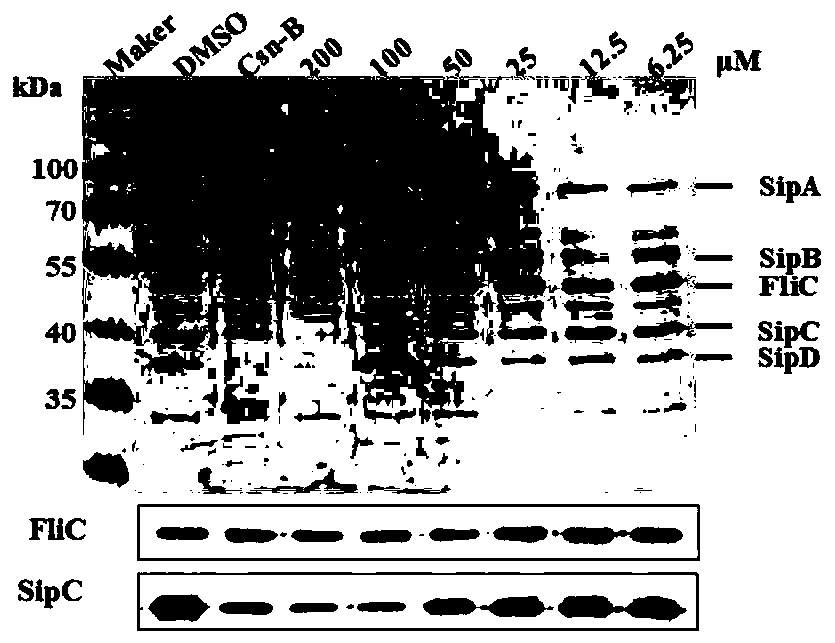
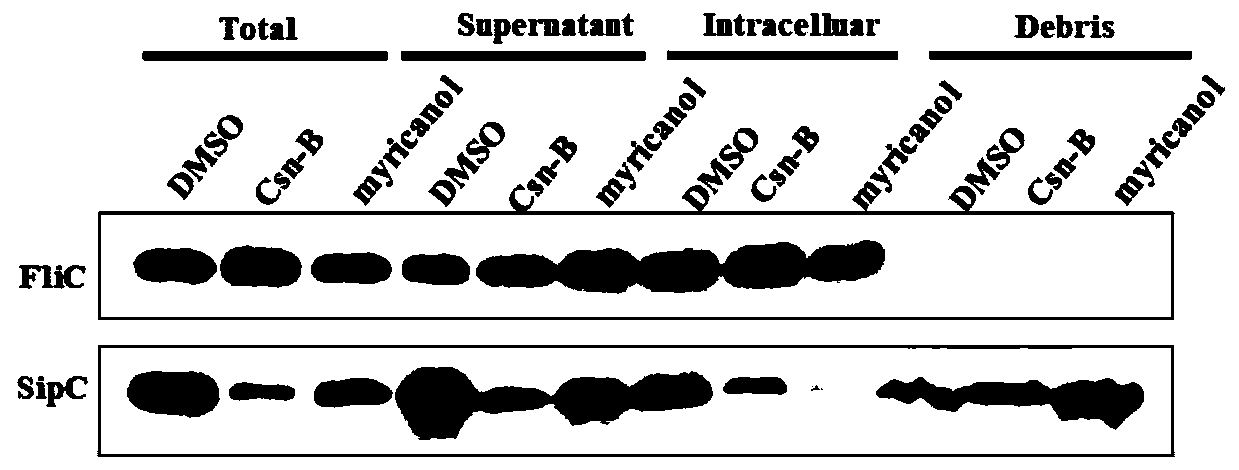
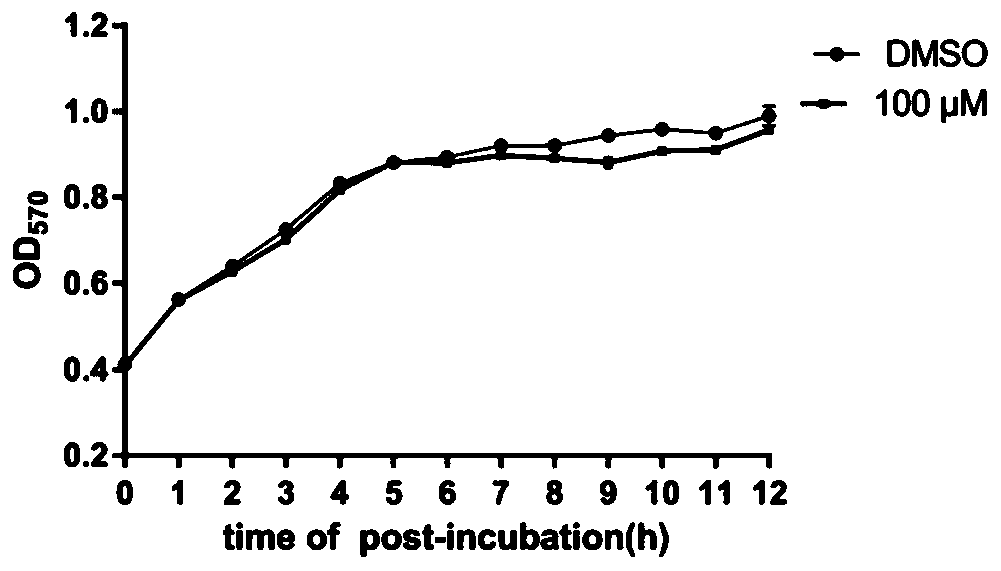
Application of myricanol in preparing drug for resisting virulence of Gram-negative bacteria
ActiveCN109985027AReduce invasionAntibacterial agentsEther separation/purificationBacteroidesVirulent characteristics
The invention relates to application of myricanol in preparing a drug for resisting bacterial virulence. The structural formula of a compound 1 is shown in the description. The myricanol is a diarylheptanoids compound, and has a function of significantly inhibiting the secretion of virulence proteins of a salmonella type III secretion system (T3SS). The inhibitor does not inhibit the growth of salmonella, but inhibits the invasion of host cells by the salmonella, and therefore the compound can be used for preparing the drug for resisting the virulence of Gram-negative bacteria.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Methods and compositions for treating bacterial infection
InactiveUS20170056405A1Reducing bacterial virulenceLow efficacyOrganic active ingredientsSurgeryResistant bacteriaBiofilm
The present disclosure relates to chemical compounds, methods for their discovery, and their therapeutic and research use. In particular, the present disclosure provides compounds as therapeutic agents against bacterial infections (e.g., biofilms). The present disclosure also provides compounds as therapeutic agents in methods for treating pneumonia, methods for reducing bacterial virulence, methods for treating a bacterial wound infection, and methods for treating a urinary tract infection. The present disclosure also provides methods for treating a bacterial infection, wherein the bacterial infection has or is suspected of having an antibiotic-resistant bacteria. The present disclosure also provides surfaces coated with the chemical compounds disclosed herein.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI +1
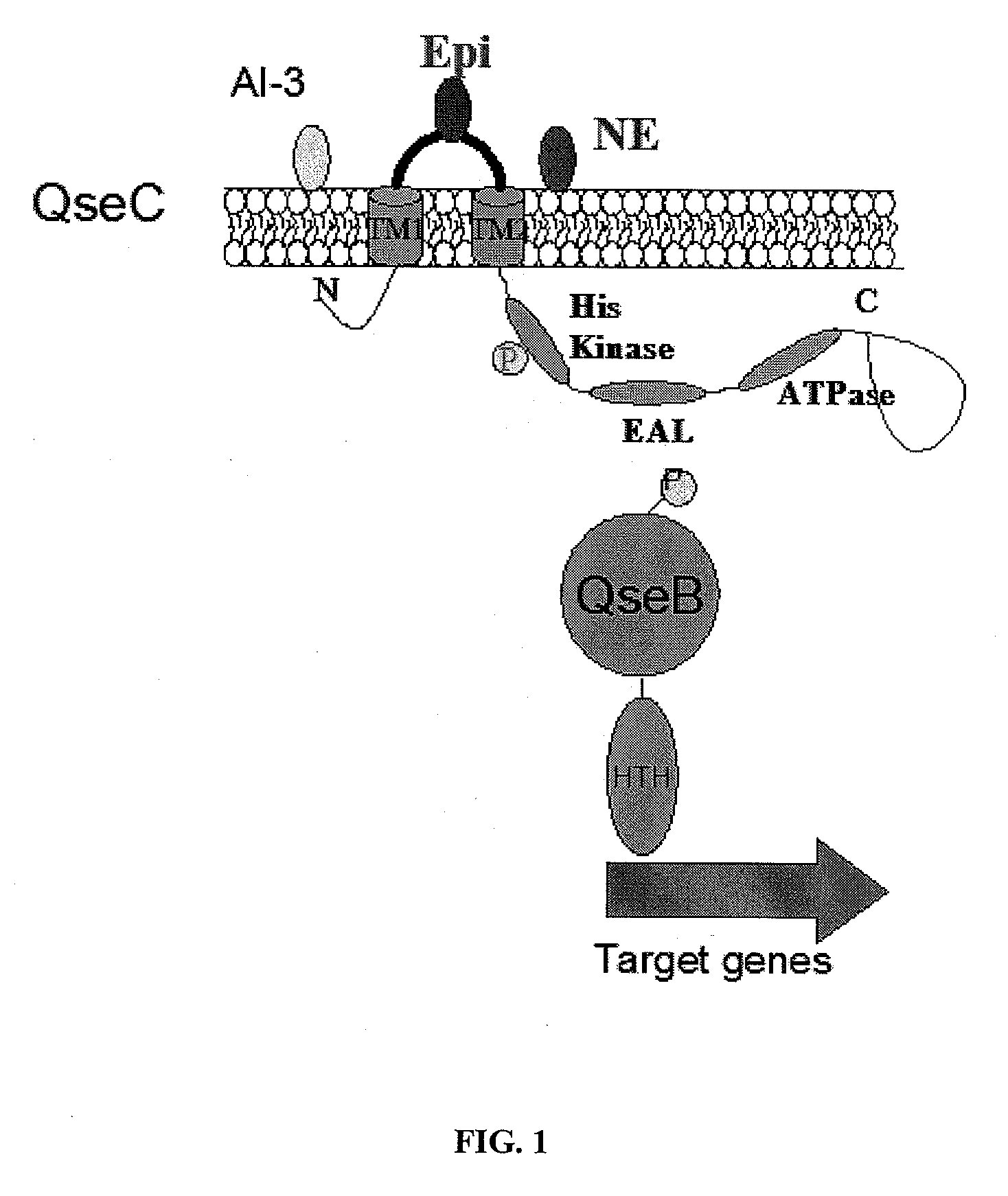
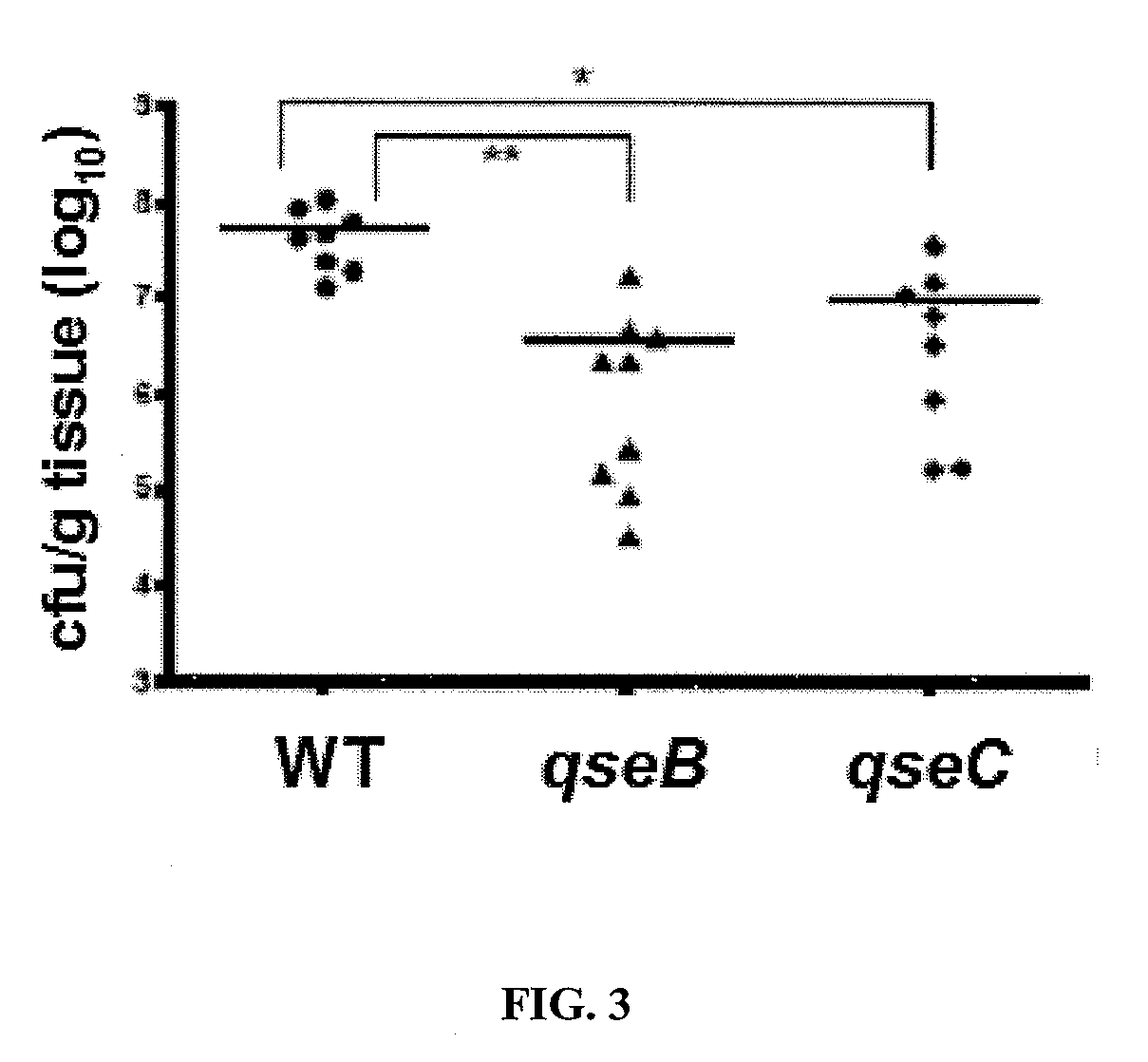
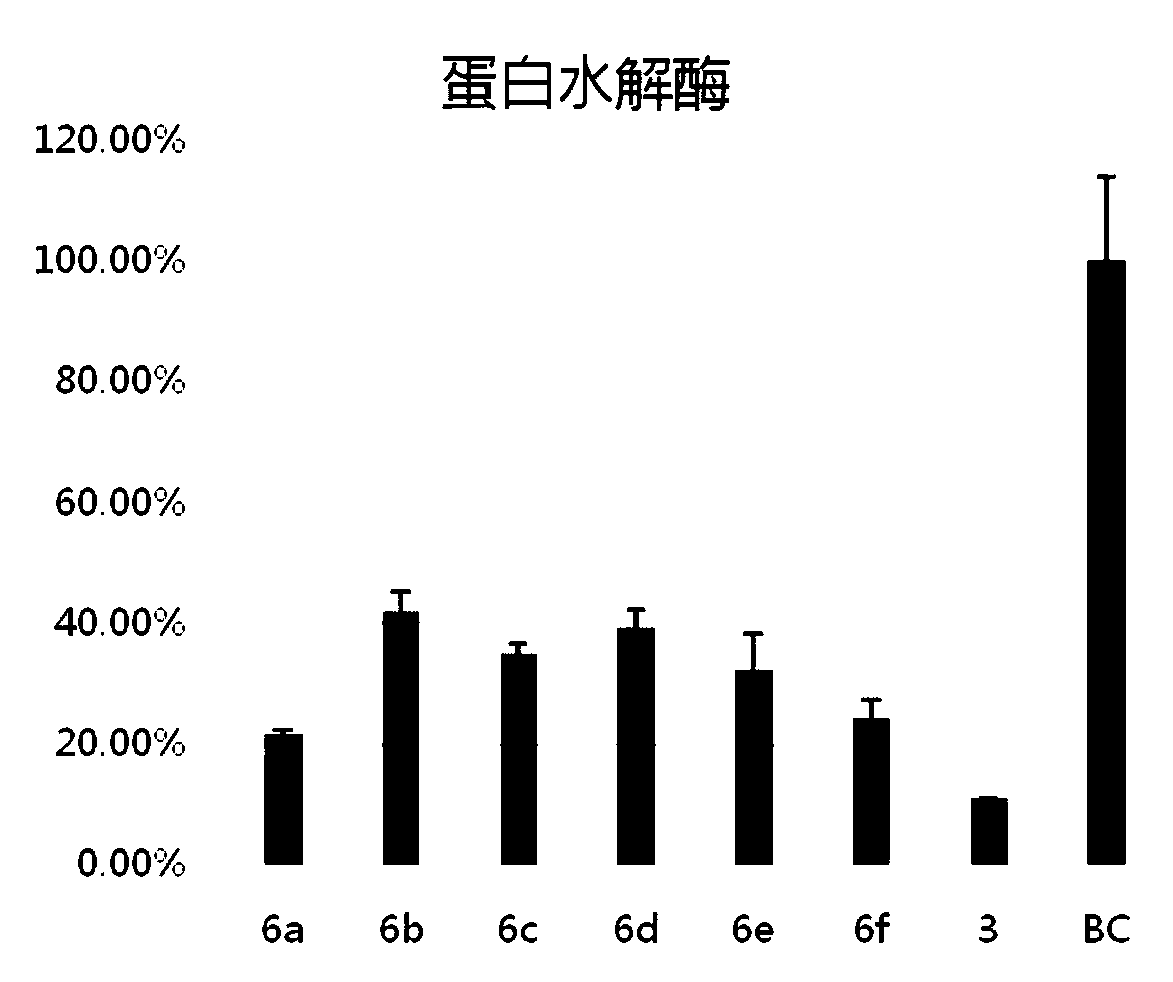
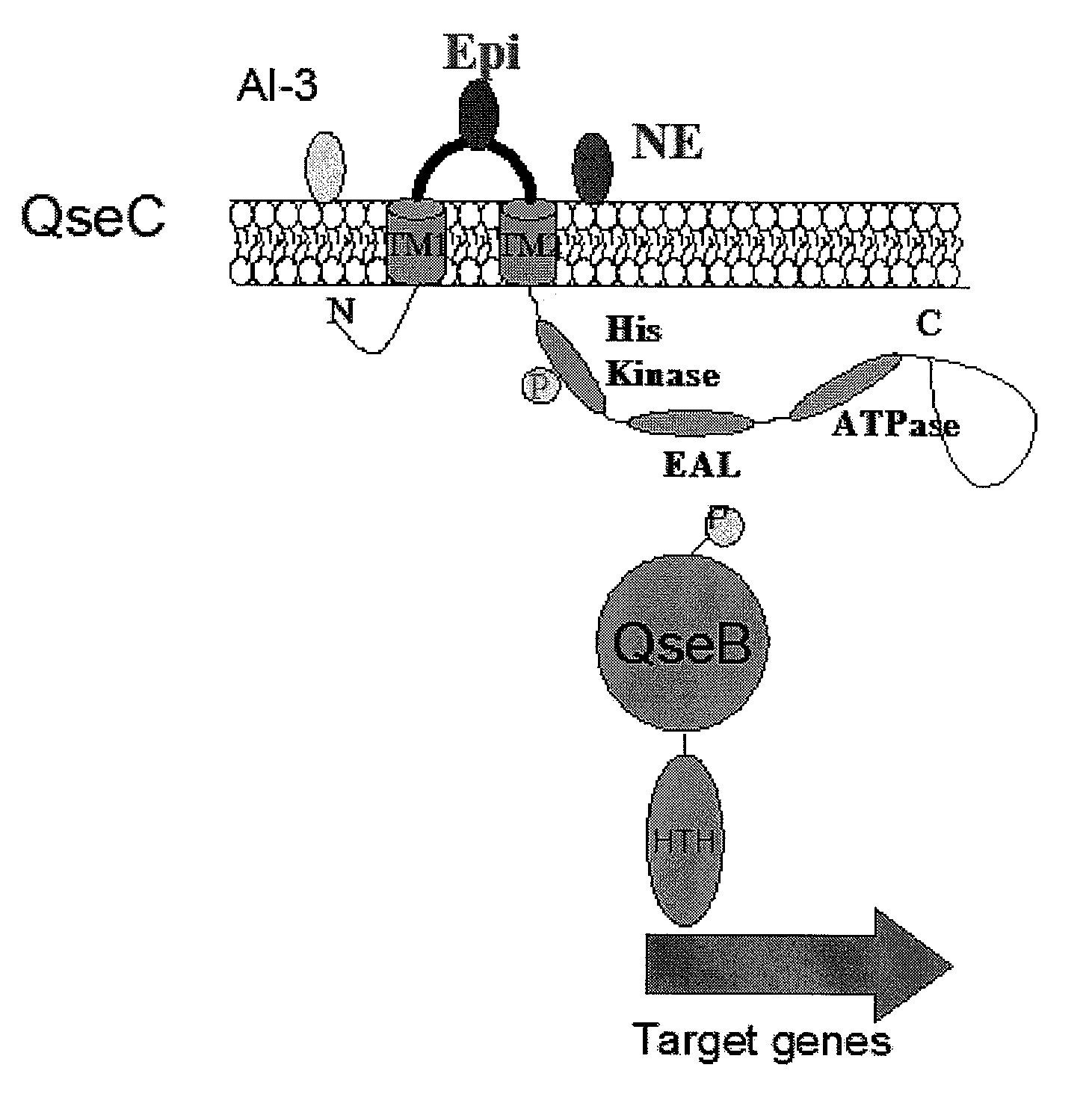
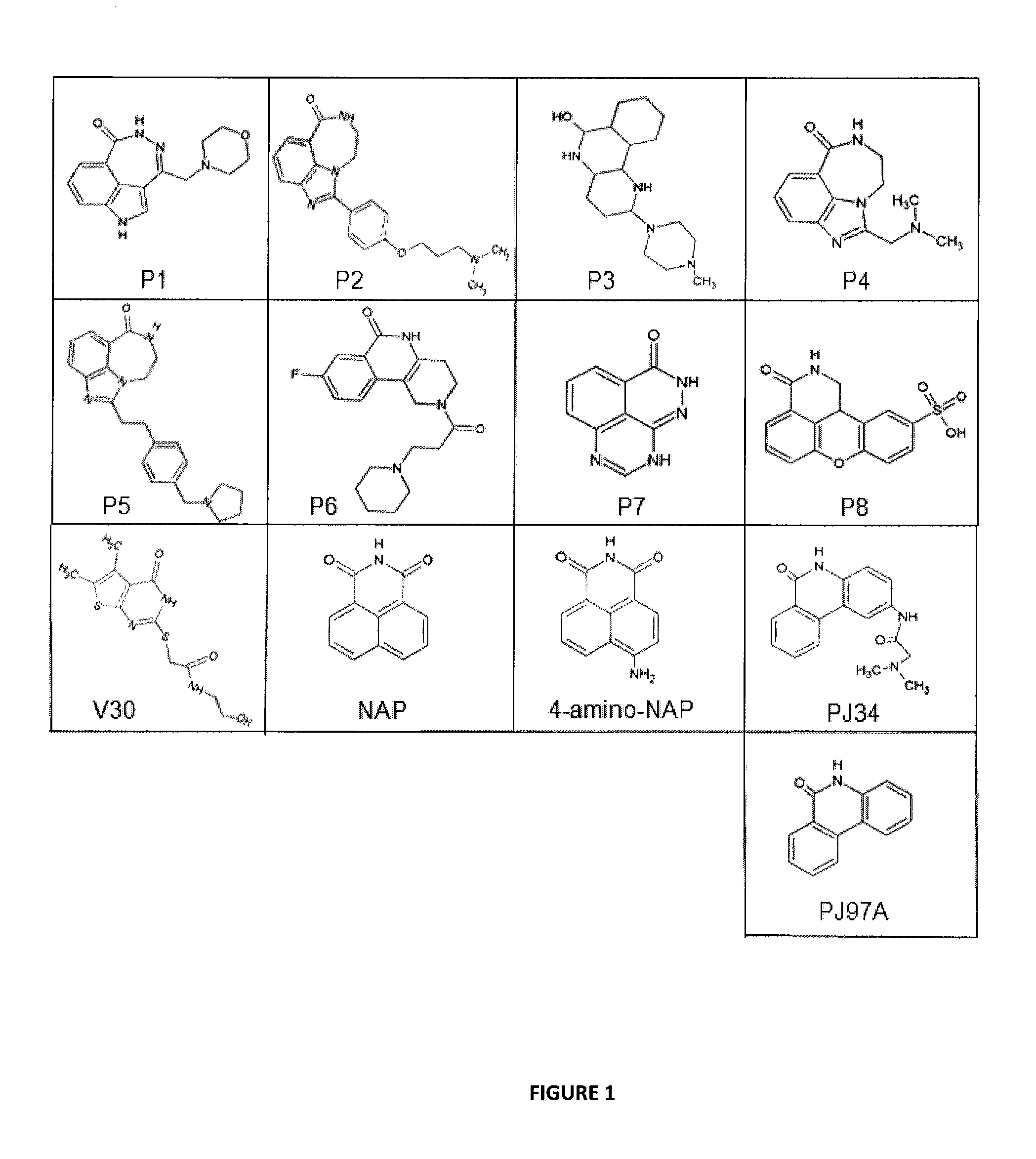
Synthetic method of QseC ligand derivatives with role of inhibiting bacterial virulence
InactiveCN101857562AAntibacterial agentsOrganic chemistryChemical synthesisMulti drug resistant bacteria
The invention discloses a synthetic method of QseC ligand derivatives capable of inhibiting bacterial virulence and an application. The QseC ligand derivatives are bacterial membrane surface protein QseC ligands and can be specifically combined with the QseC ligands and be used for retroregulation of a qseC-qseB-fliC-flhD gene pathway, thereby inhibiting the release of bacterial pathogenic virulence factors, reducing the bacterial virulence and the invasiveness during the bacterial infection and further achieving the role of controlling the harm of the bacterial infection; however, the QseC ligand derivatives do not affect normal growth and reproduction of bacteria, thereby avoiding the initiation of bacterial drug resistance pressure. The QseC ligand derivatives have the advantages of good anti-bacterial effect, low toxicity, good stability and difficult drug resistance. The QseC ligand derivatives synthesized by the optimized synthetic method of the QseC ligands and the chemical synthetic method of the derivatives thereof can be used for preparing novel broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs with resistance to multi-drug-resistant bacteria infection.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Methods for Modulating Bacterial Virulence and Related Compounds
InactiveUS20140275189A1Inhibit bacterial virulenceWide applicabilityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsBacteroidesMicrobiology
The present invention relates to compounds and methods for the treatment of bacterial infections. The compounds and methods involve the disruption of the QseC signaling pathway which modulates the virulence of some bacteria. This methodology for treatment of bacterial infections reduces evolutionary pressure to develop resistance because the bacteria are not killed in the process.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Anti-bacterial Vaccine Compositions
Gram negative bacterial virulence genes are identified, thereby allowing the identification of novel anti-bacterial agents that target these virulence genes and their products, and the provision of novel gram negative bacterial mutants useful in vaccines.
Owner:ZOETIS SERVICE LLC
Attenuating bacterial virulence by attenuating bacterial folate transport
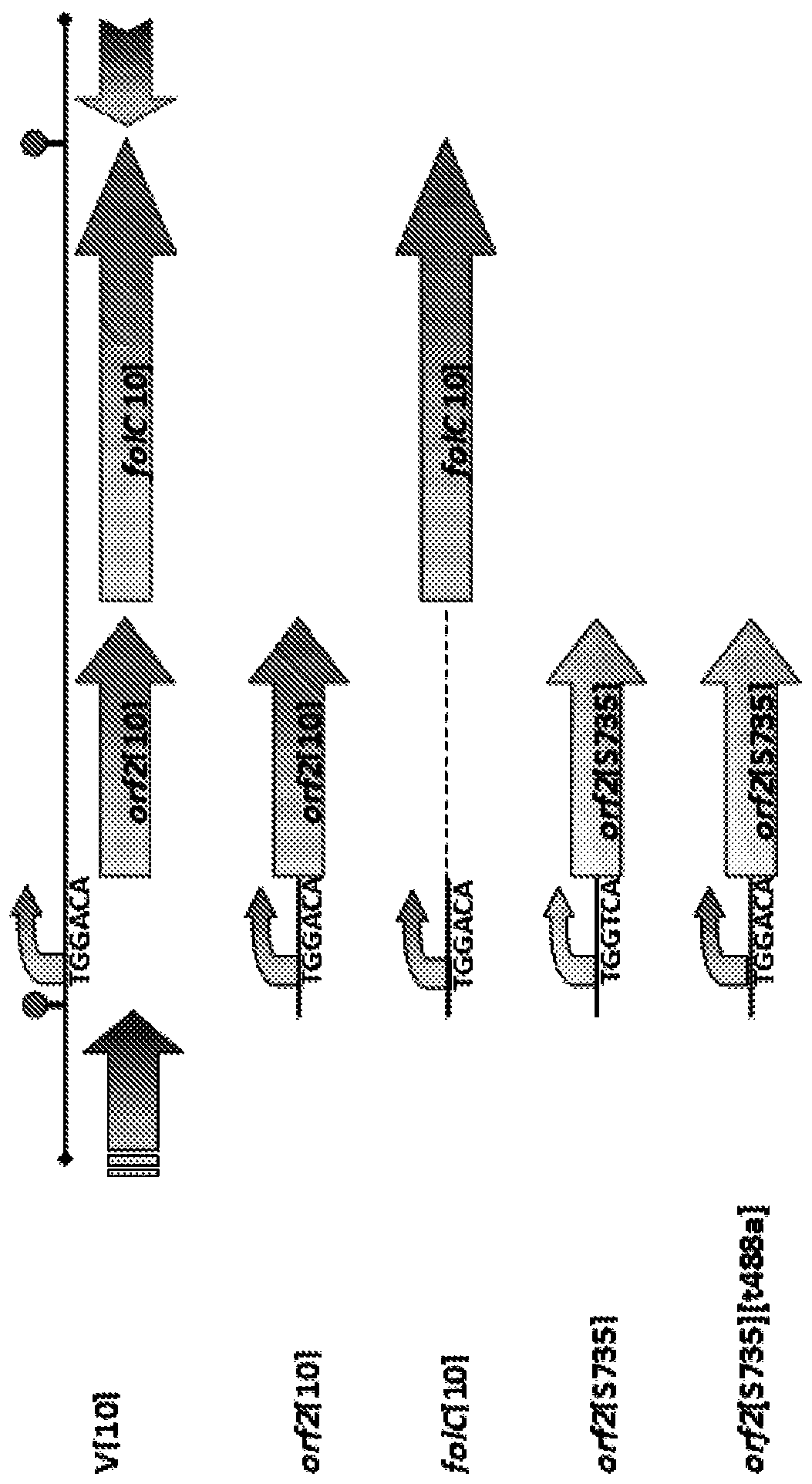
PendingCN110582296ALow toxicityEnhance immune responseAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsStreptococcus infectionMicrobiology
The invention relates to bacterial infections, vaccines directed against those infections and bacterial vaccines. More particularly, the invention relates to vaccines directed against Streptococcus infections in pigs. Provided is a [Delta]FolT mutant of a bacterium having reduced capacity to transport folate, wherein the capacity has been reduced by functionally deleting folate transporter (FolT)function. The present invention provides a method to reduce virulence of a bacterium comprising reducing the capacity of the bacterium to transport folate.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM VETMEDICA GMBH
Antisense antibacterial compounds and methods
ActiveUS9790495B2Increased susceptibilityReduce capacityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsFatty acid biosynthesisPhleic acids
Provided are antisense morpholino oligomers targeted against bacterial virulence factors such as genes that contribute to antibiotic resistance or biofilm formation, or genes associated with fatty acid biosynthesis, and related compositions and methods of using the oligomers and compositions, for instance, in the treatment of an infected mammalian subject.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
Methods and compositions for treating bacterial infection
InactiveUS9814719B2Reducing bacterial virulenceLow efficacyOrganic active ingredientsSurgeryResistant bacteriaBiofilm
The present disclosure relates to chemical compounds, methods for their discovery, and their therapeutic and research use. In particular, the present disclosure provides compounds as therapeutic agents against bacterial infections (e.g., biofilms). The present disclosure also provides compounds as therapeutic agents in methods for treating pneumonia, methods for reducing bacterial virulence, methods for treating a bacterial wound infection, and methods for treating a urinary tract infection. The present disclosure also provides methods for treating a bacterial infection, wherein the bacterial infection has or is suspected of having an antibiotic-resistant bacteria. The present disclosure also provides surfaces coated with the chemical compounds disclosed herein.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI +1
Method and probe for identifying bacterial virulence modifying agents, agents thus identified, and their use
InactiveUS7351861B2Improve the level ofCounteract inhibitionOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrobiologyAntibacterial agent
A method for identifying antibacterial agents comprises depleting bacteria of a strain comprising a luxAB construct of Ca2+, incubating the Ca2+ depleted bacteria with an agent the antibacterial effect of which shall be determined, recording the light emitted by the bacteria upon addition of an aldehyde, the incubation being carried out at a temperature which is at least 10° C. higher than the temperature at which the light is emitted by the bacteria. Also disclosed are corresponding probes and antibacterial agents identified by the method.
Owner:INNOVATIVE ANTIBIOTICS SWEDEN AB
Bacterial quorum sensing inhibitors as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109503453ANovel structureAvoid infectionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiologyPathogenic bacteria
The invention provides bacterial quorum sensing inhibitors as well as a preparation method and an application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of medical chemistry. The bacterial quorum sensing inhibitors mainly comprise alpha-pyridoin derivatives with novel structures; research proves that the derivatives can remarkably reduce expression of related pathogenic factors and bacterial virulence in a range of not inhibiting growth of pathogenic bacteria, so that the derivatives can be used as the bacterial quorum sensing inhibitors for preventing and controlling bacterial infection of aquorum sensing system. Meanwhile, the preparation method of the compounds is simple, reaction conditions are mild, raw materials are cheap and easily available, the various compounds with brand-new structure can be prepared and obtained rapidly on a large scale, and the method has good economy and large-scale industrial production value.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Methods of inhibiting bacterial virulence and compounds relating thereto
The present invention relates to compounds and methods for the treatment of bacterial infections. Because their mechanism of action does not involve killing of bacteria or inhibiting their growth, the potential for these compounds to induce drug resistance in bacteria is minimized. Through inhibiting bacterial virulence, the present invention provides a novel means of treating bacterial infections.
Owner:OMM SCI +1
Antivirulence compounds inhibiting bacterial mono-adp-ribosyltransferase toxins
InactiveUS20120142682A1Reduce adverse effectsNeutralizing the cytotoxic properties of virulence factorsAntibacterial agentsBiocideAntivirulenceToxin
Compounds that inhibit bacterial virulence factors from the mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase (mART) family of toxins have been identified that are not toxic to cells or the producing bacterial pathogen. These compounds have great potential as antivirulence agents for treating many bacterial infections and disease states.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GUELPH
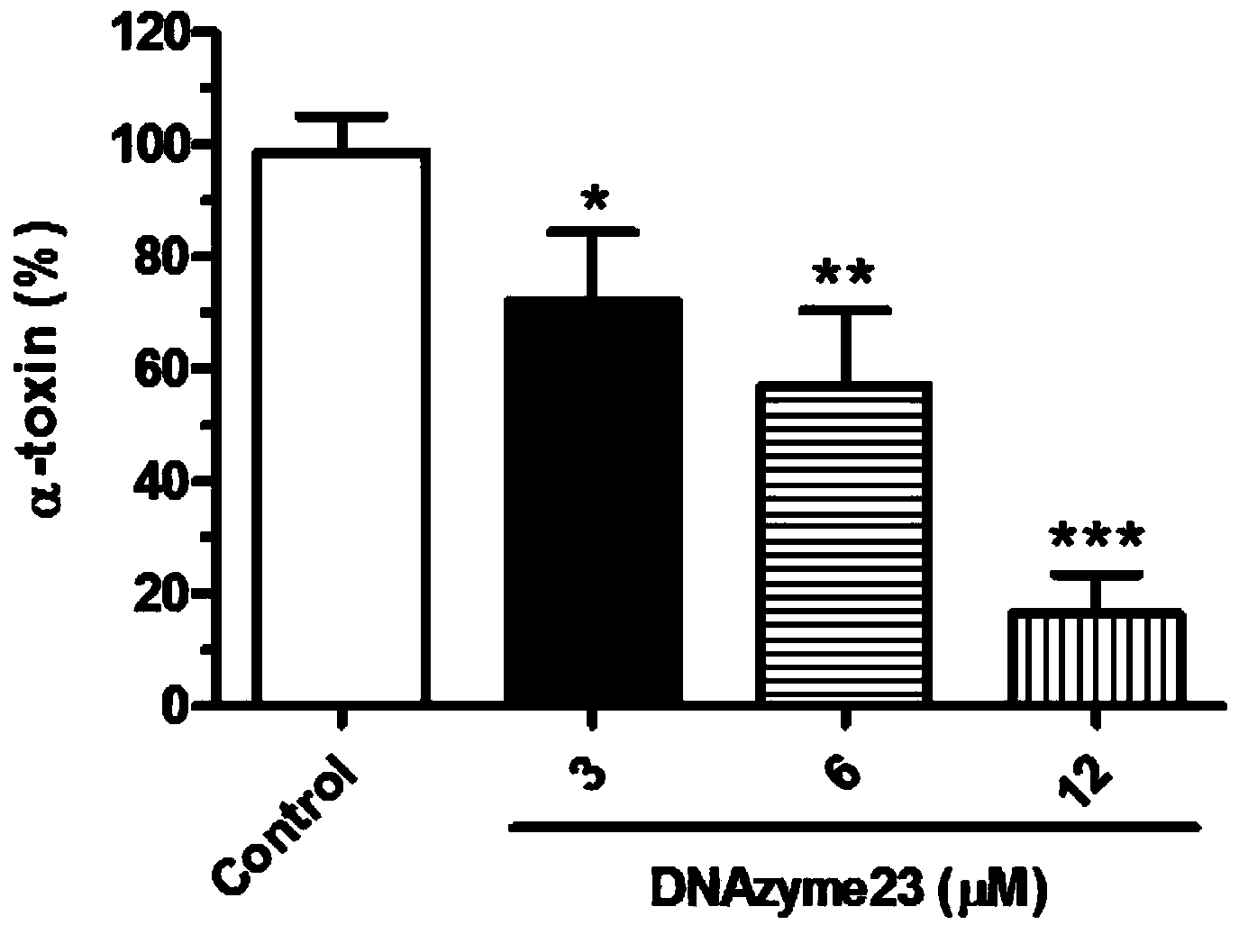
Application of antisense deoxyribozyme capable of resisting agr quorum-sensing system in MRSA (Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus)
InactiveCN104293790AReduce secretionStrong specificityAntibacterial agentsGenetic material ingredientsBacteroidesStaphylococcus cohnii
The invention discloses an antisense deoxyribozyme-DNAzyme23. The antisense deoxyribozyme disclosed by the invention adopts an effector molecule RNAIII in the staphylococcus aureus agr quorum-sensing system as a target spot, does not affect the growth state of the bacterium, can effectively block an agr signaling pathway, can significantly weaken the bacterial virulence and particularly can significantly reduce the pathogenicity of methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus. The antisense deoxyribozyme has the advantages of high specificity, low toxicity, safety and difficulty in inducing the increase of bacterial drug resistance and the like.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Rapamycin analogues and their pharmaceutical use
Novel rapamycin analogues and methods for their production with FKBP and / or MIP inhibitory activity with reduced mTOR inhibitory activity with therapeutic potential e.g. as bacterial virulence inhibitors.
Owner:ISOMERASE THERAPEUTICS
Method for evaluating the virulence of pathogenic biphasic bacteria
InactiveCN102105602ALow costMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesBacteroidesVirulent characteristics
A method for evaluating relative bacterial virulence of a biphasic bacteria in environmental systems includes measuring the concentration of DNA in the bacteria, measuring the concentration of RNA in the bacteria, determining a ratio of the concentration of RNA to the concentration of DNA and correlating the concentration ratio with a level of relative pathogenicity, wherein the bacteria is preferentially Legionella pneumophila, Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Listeria.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com