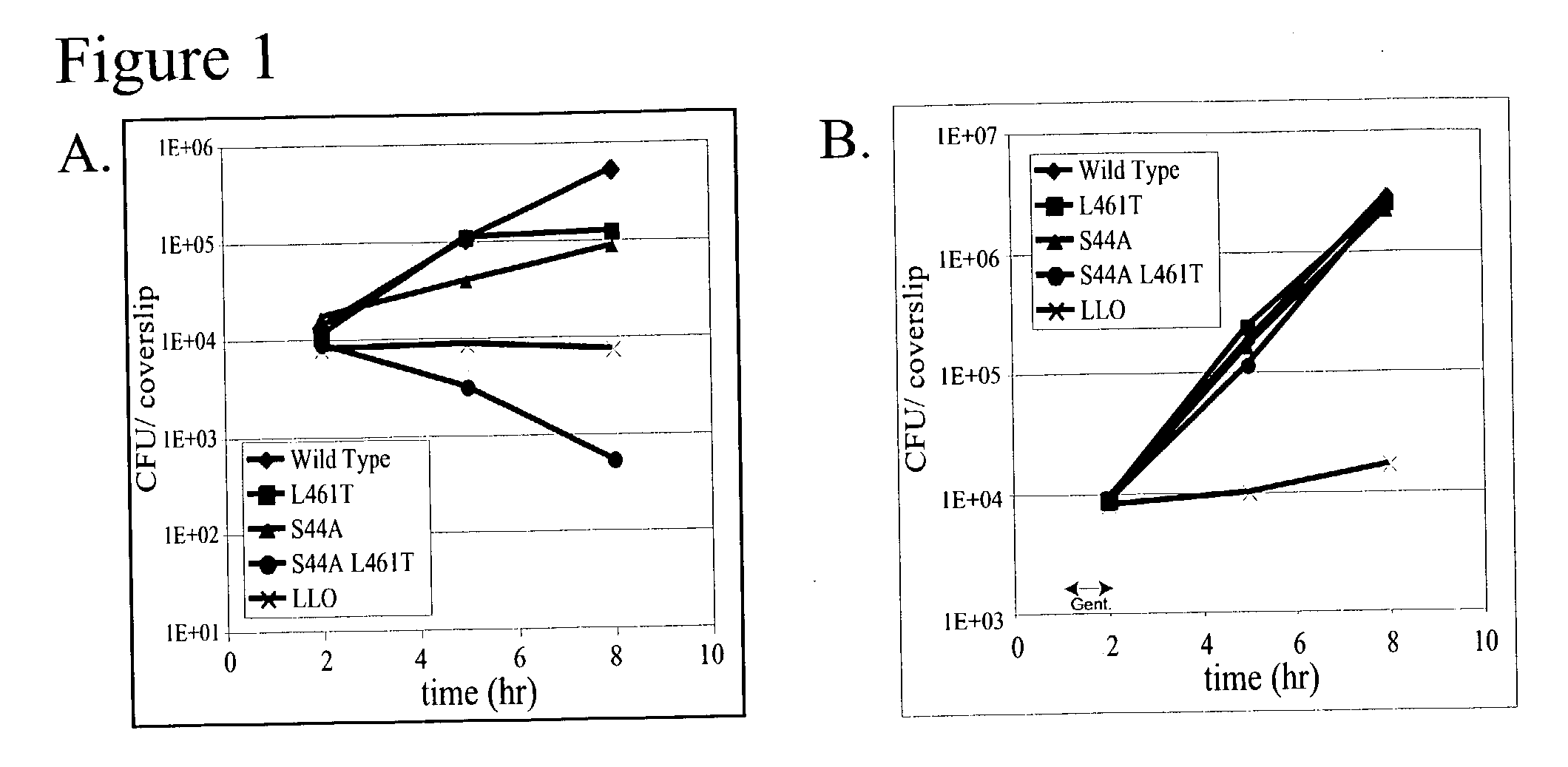
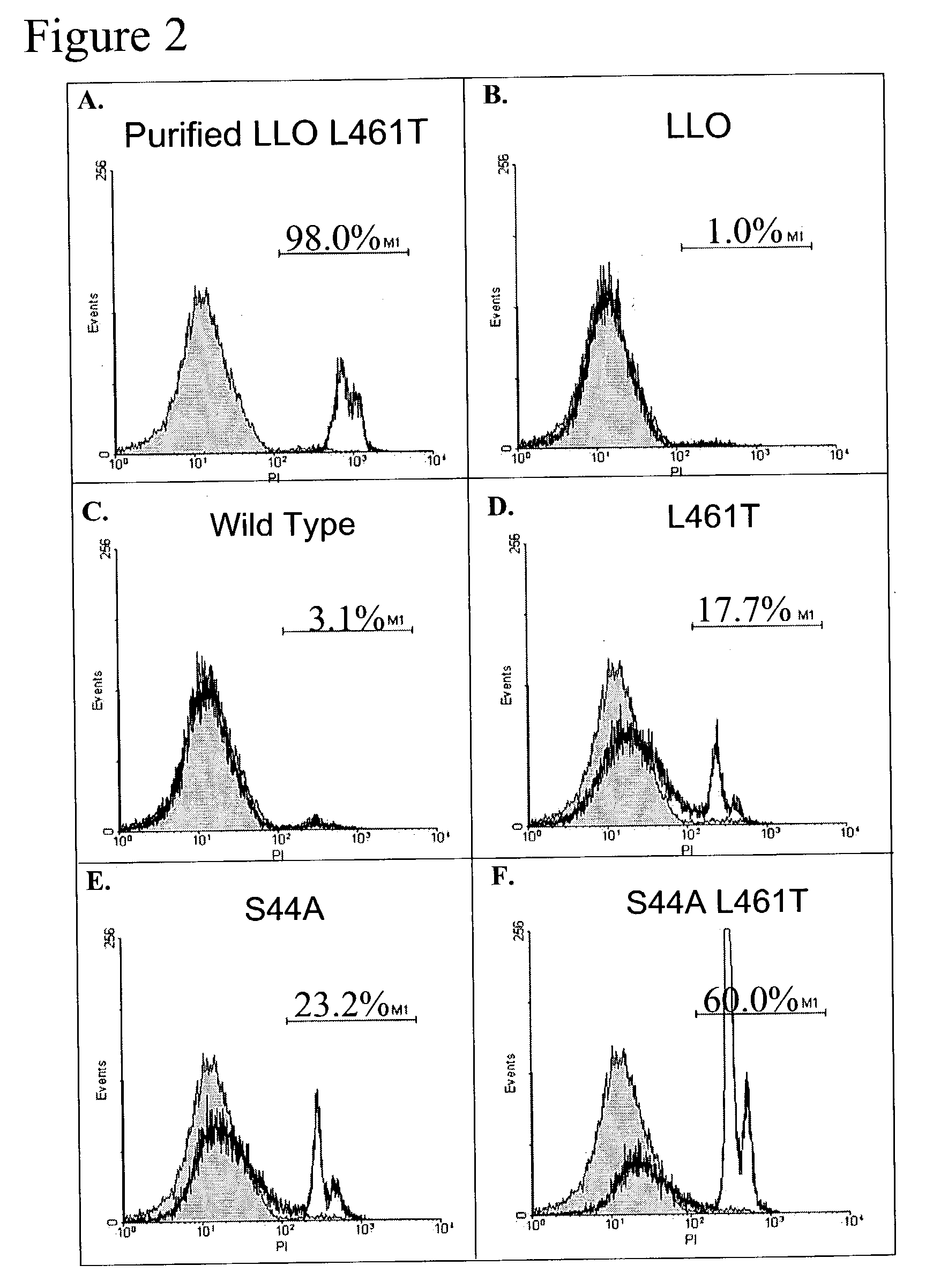
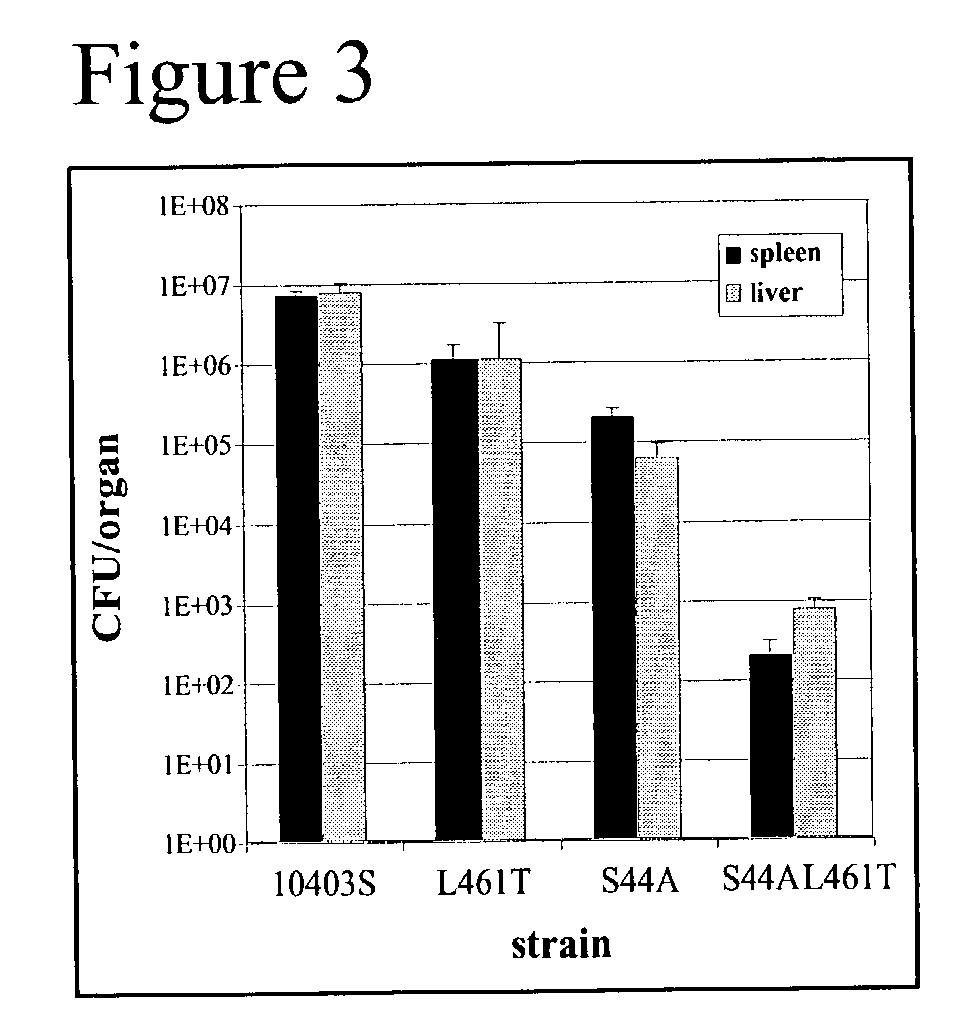
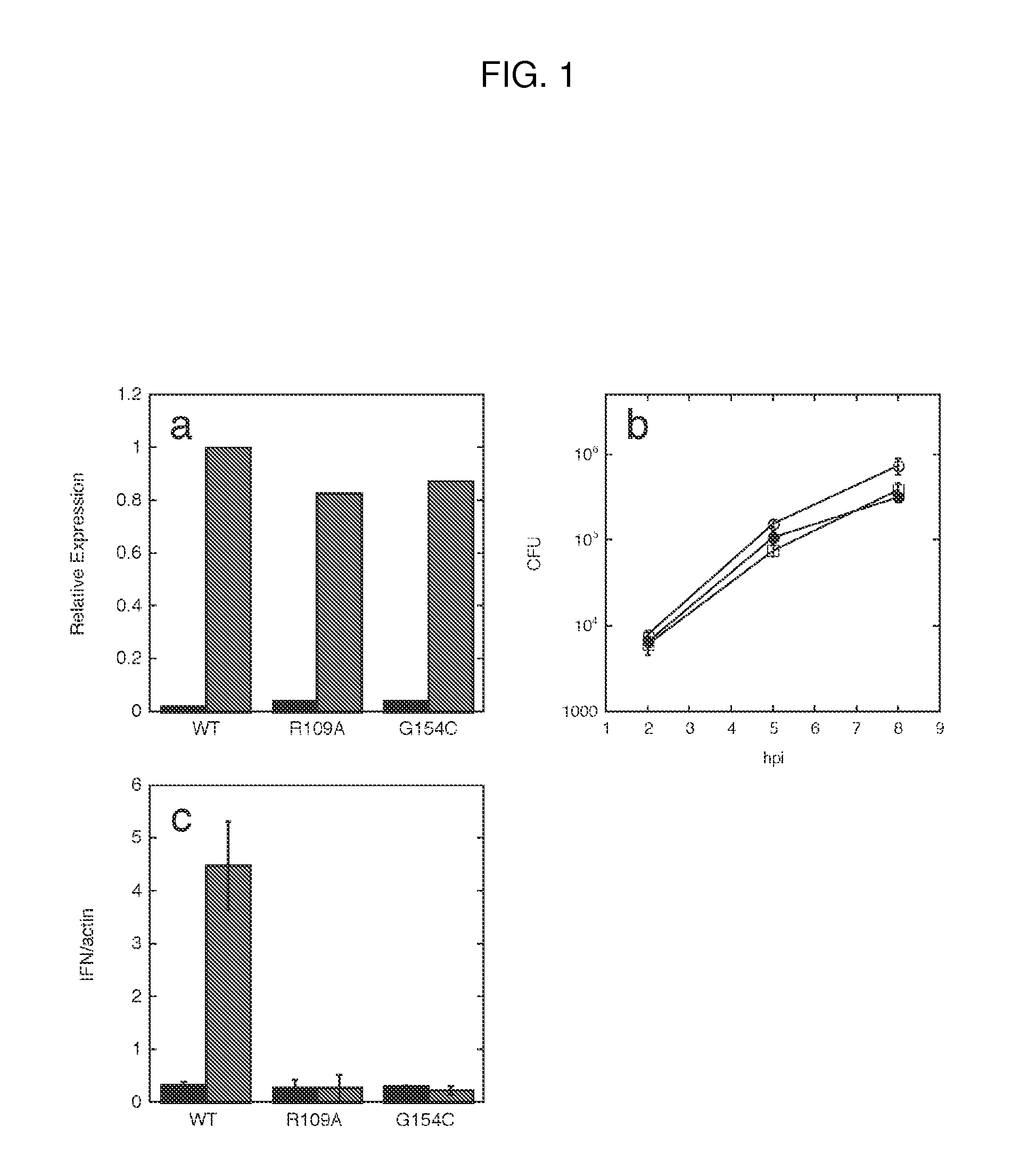
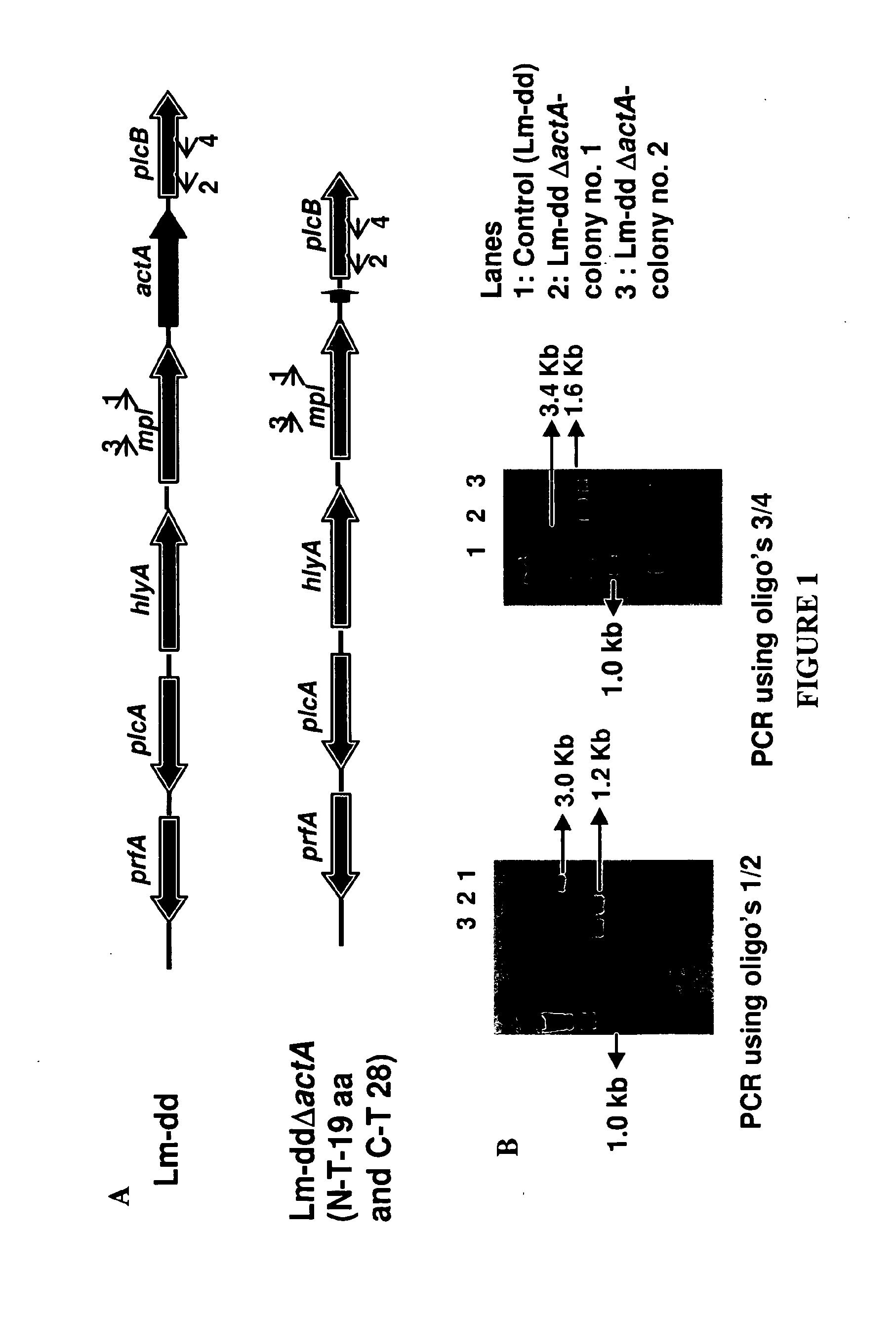
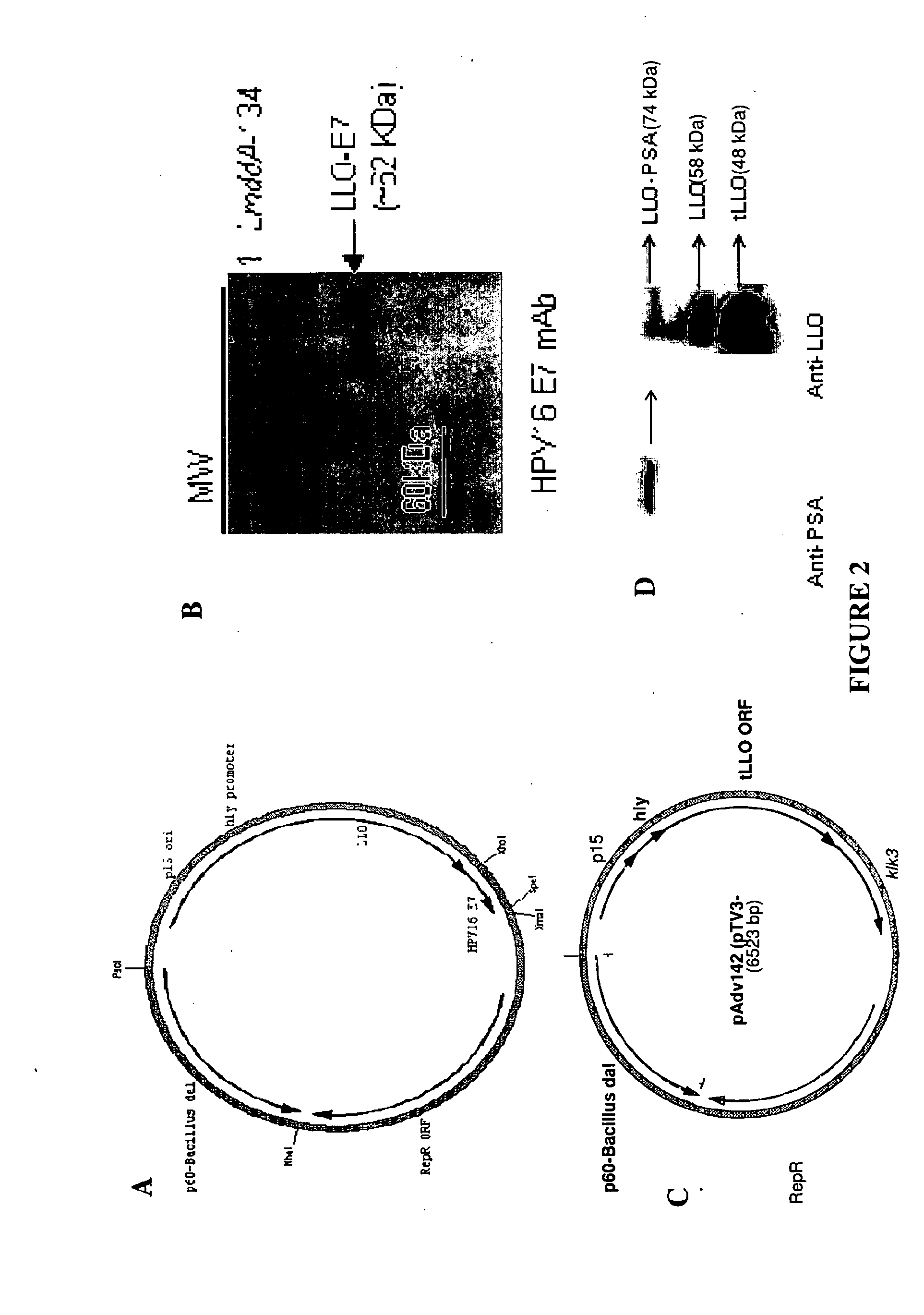
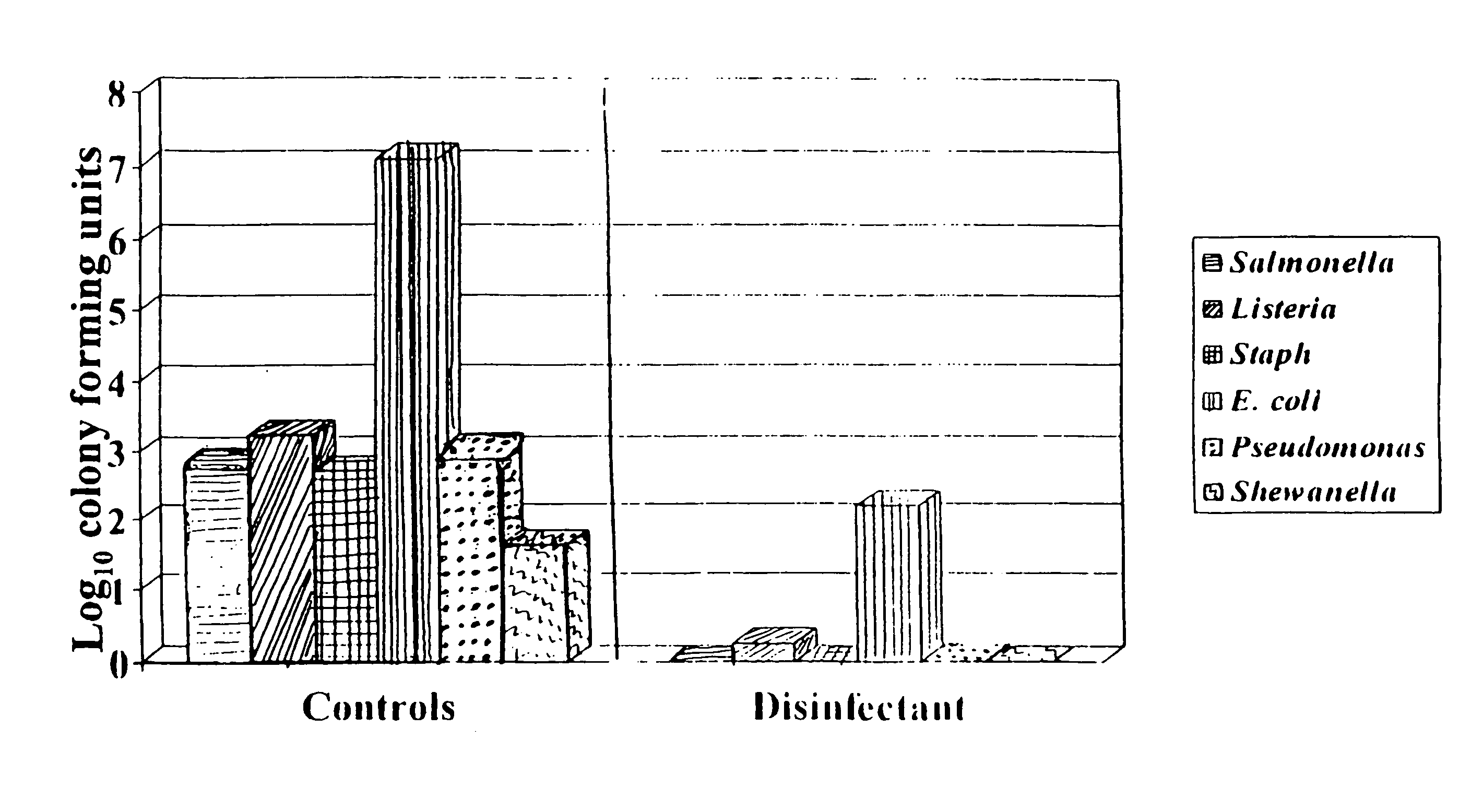
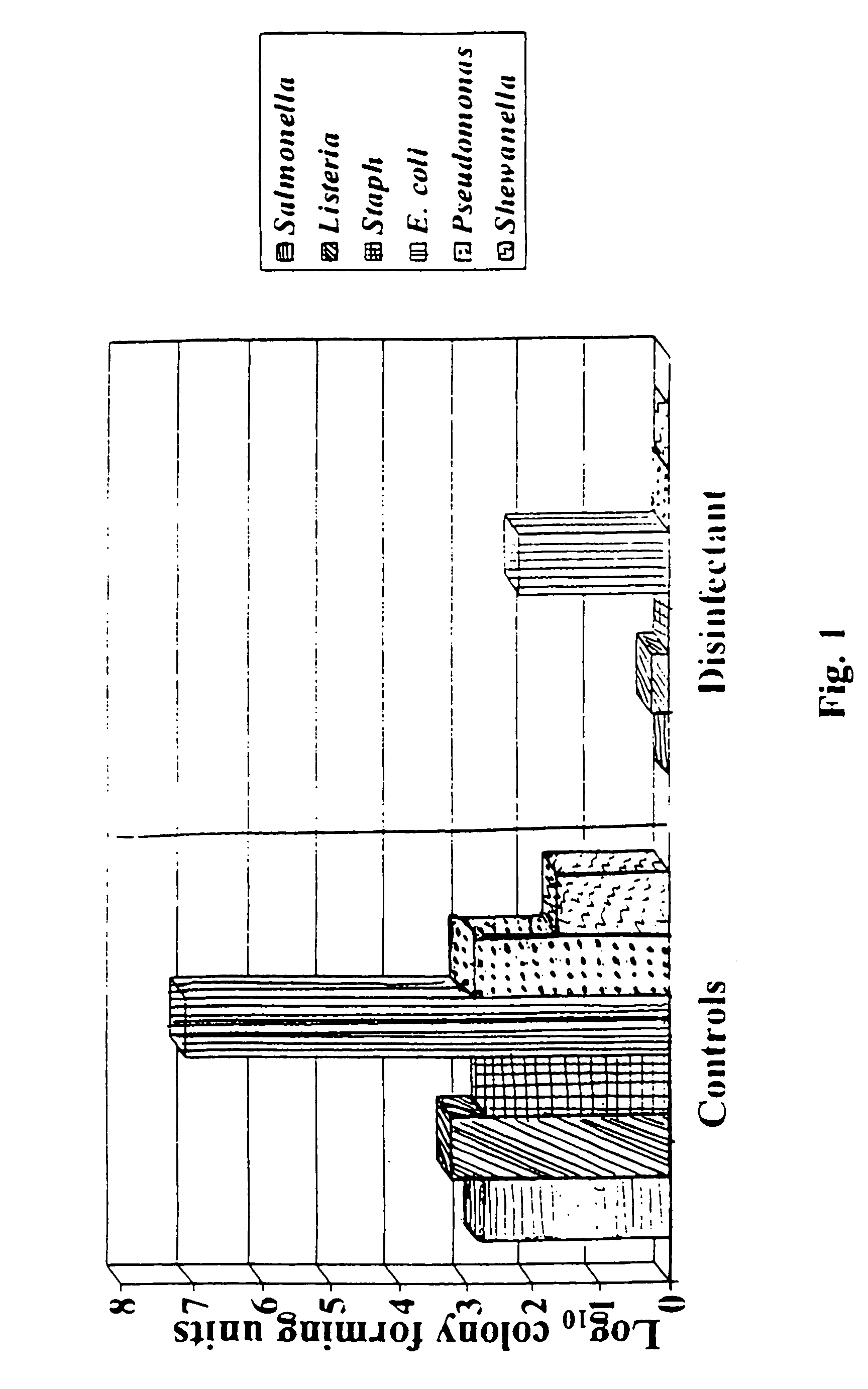
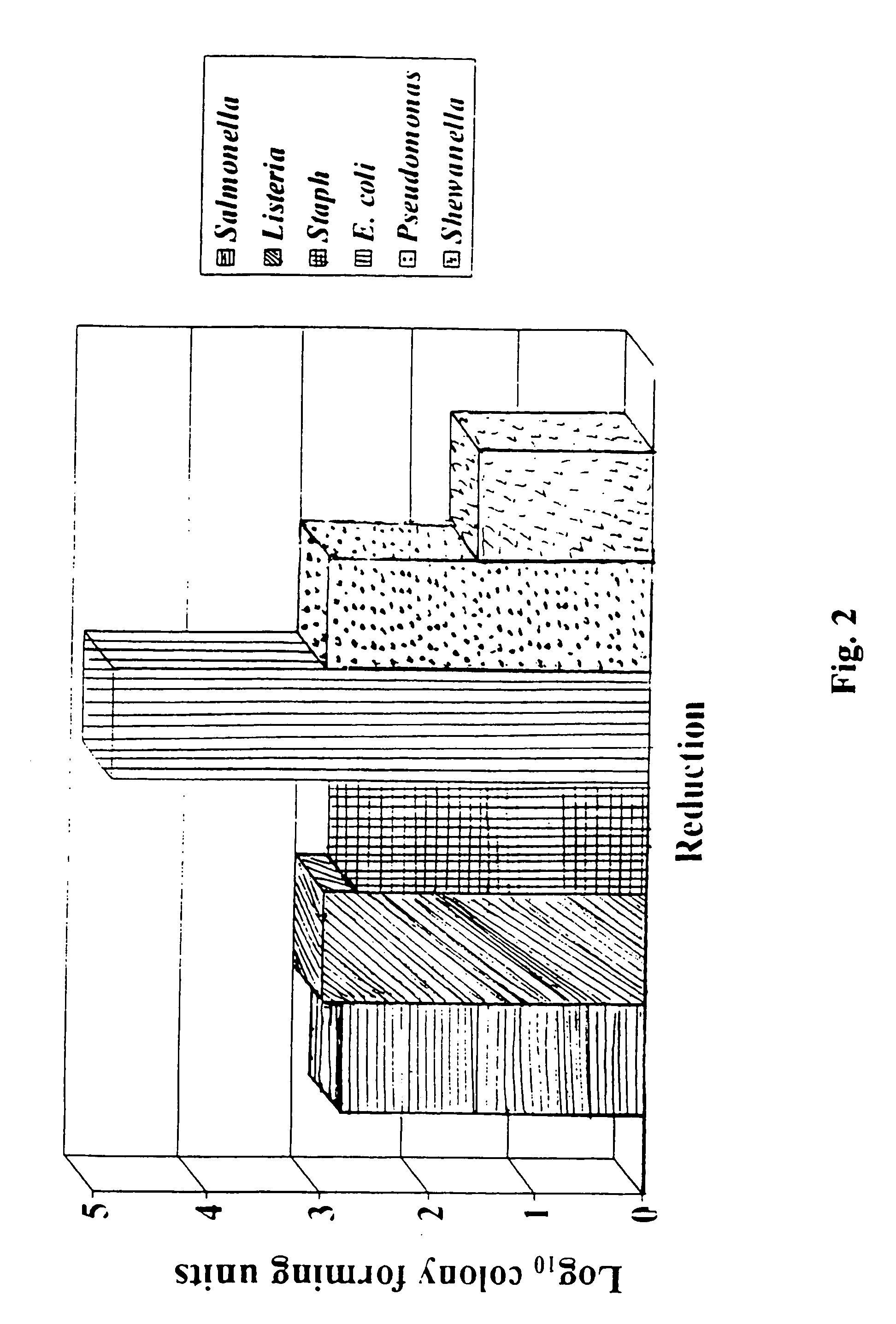
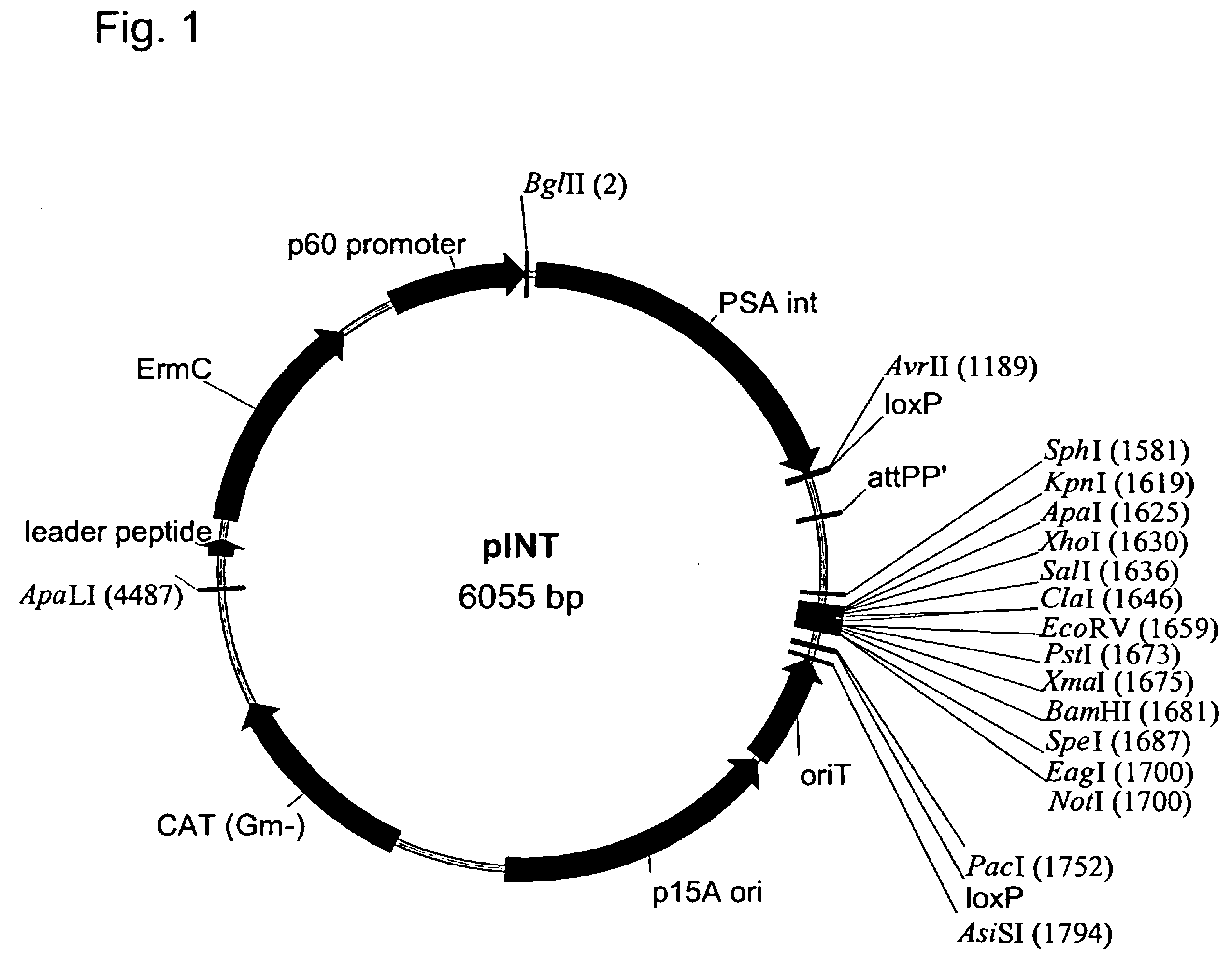
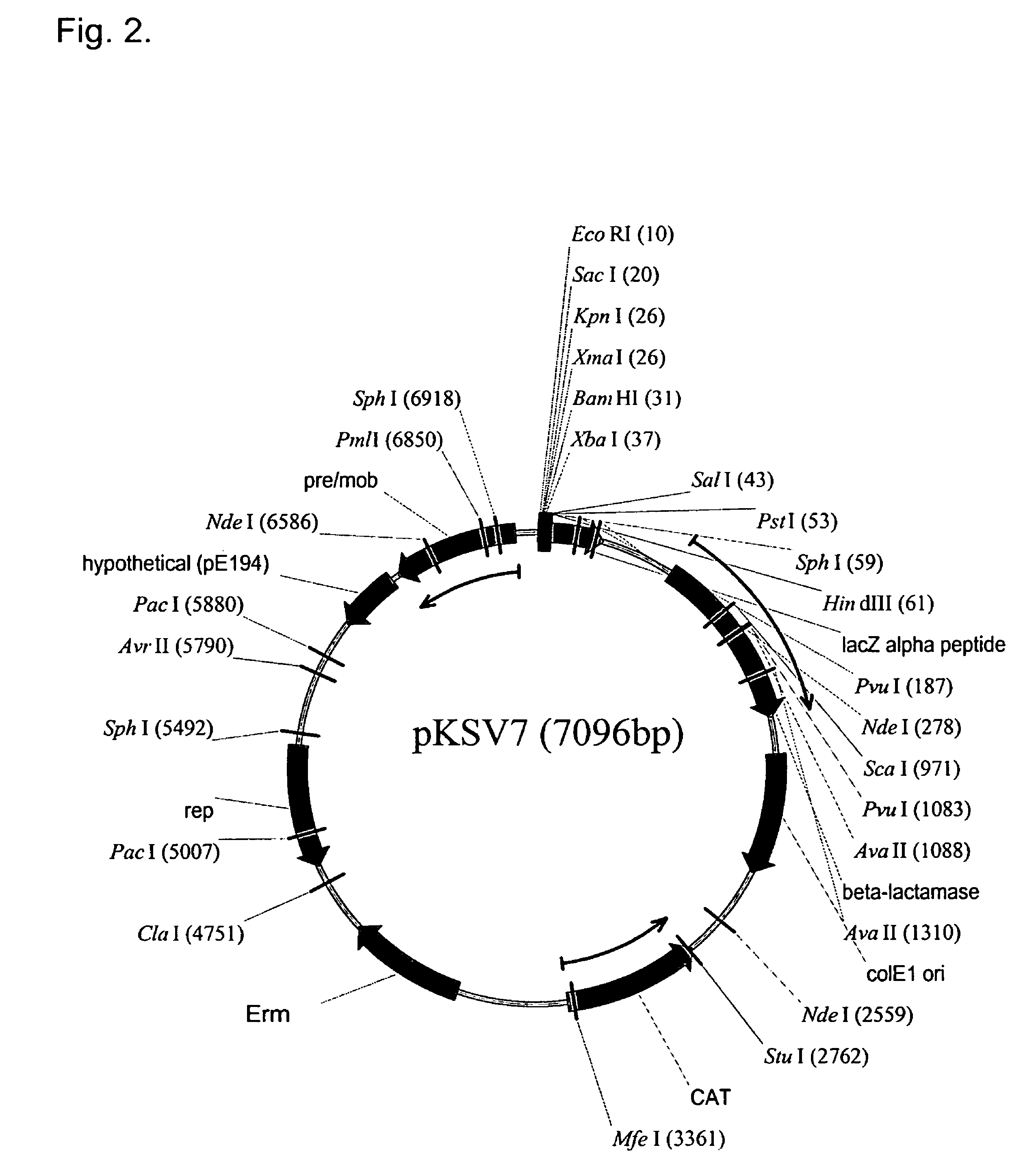
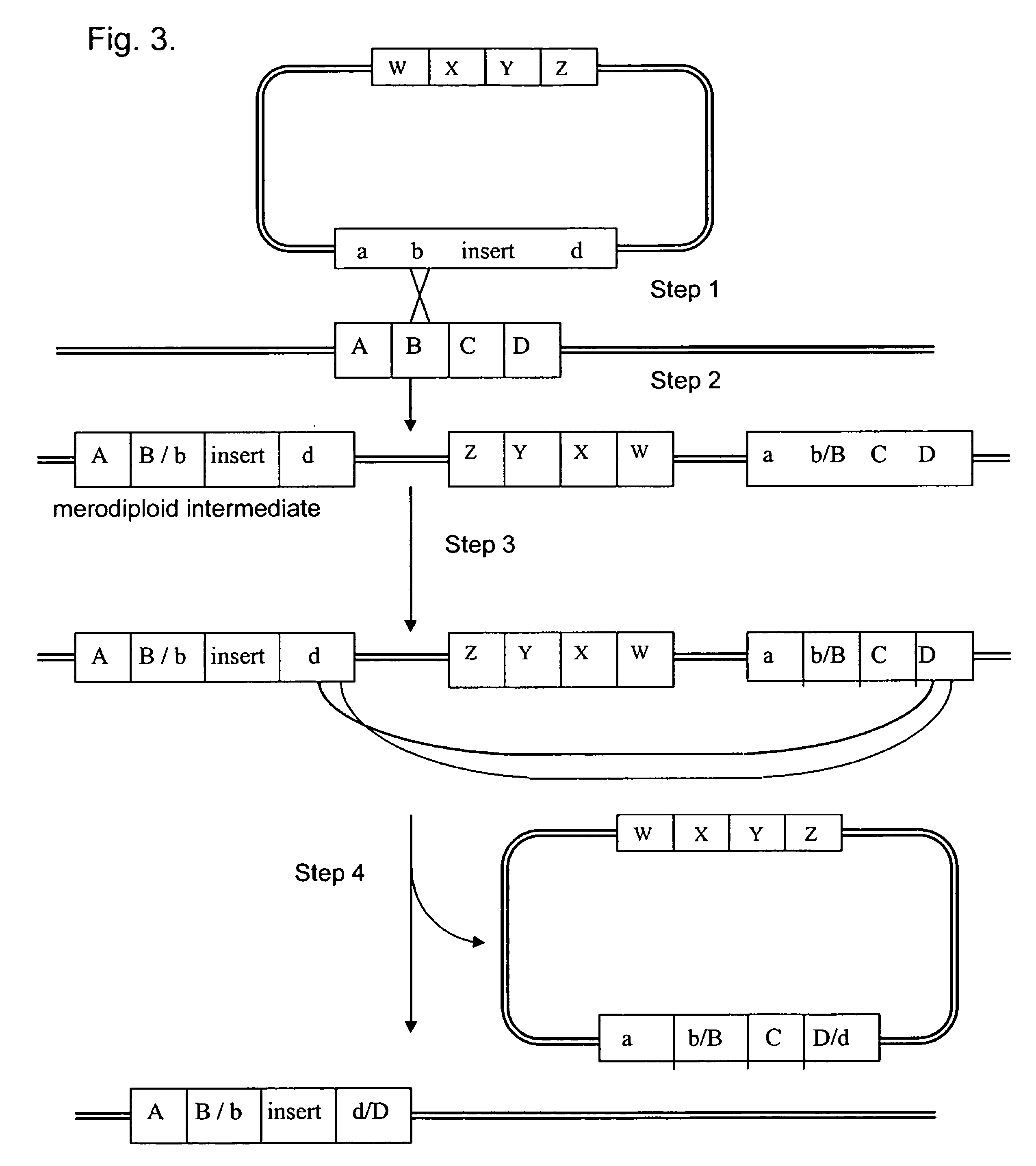
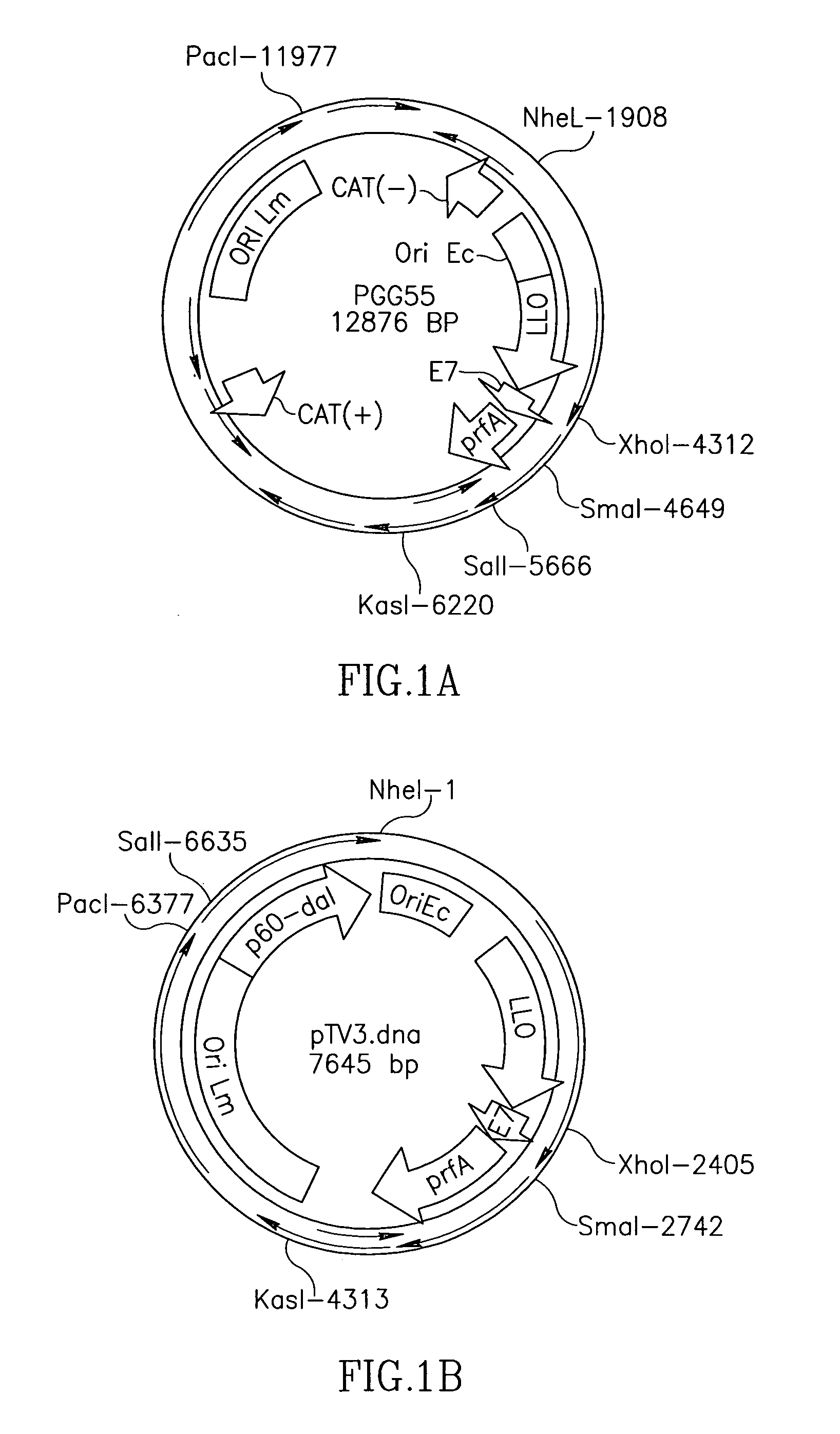
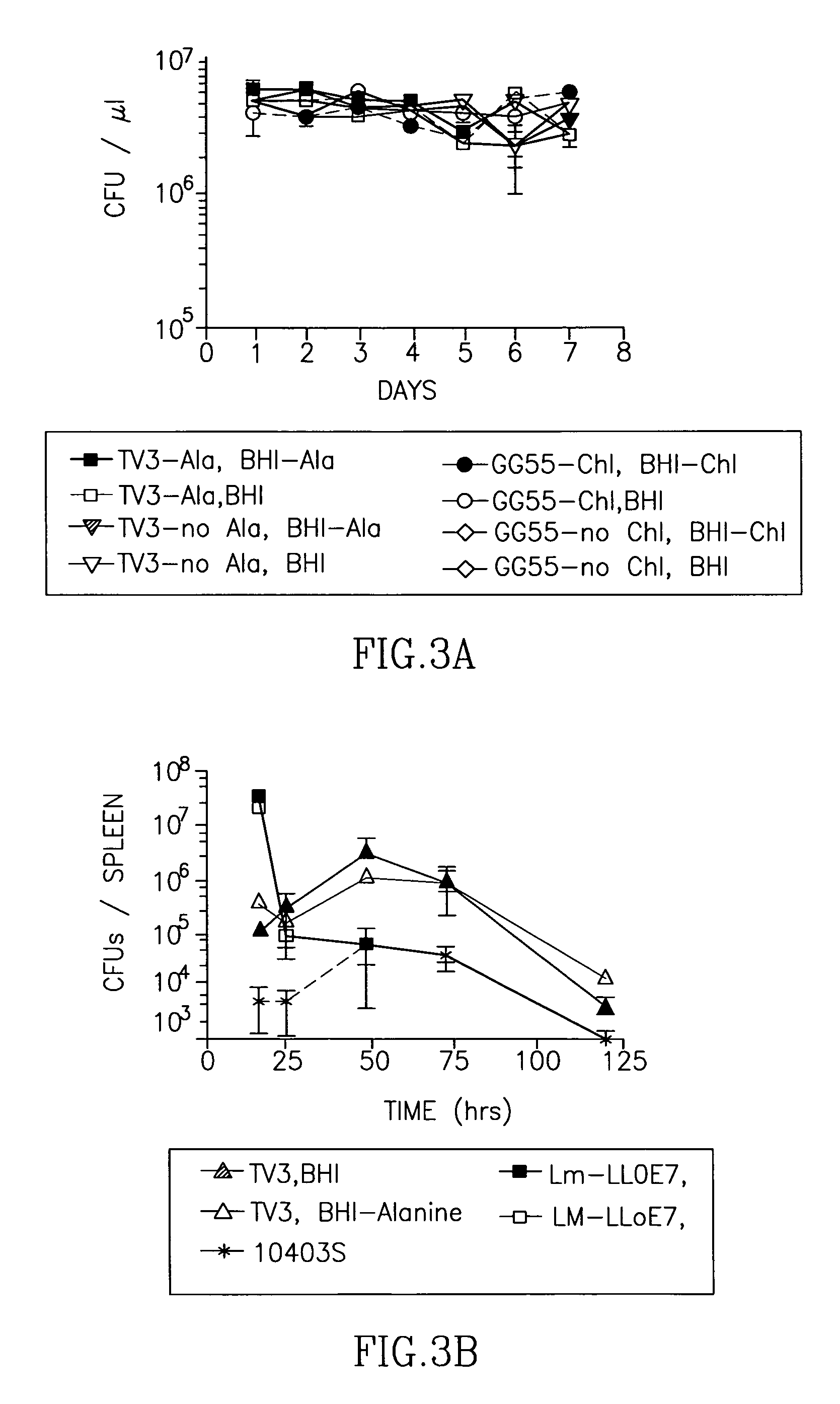
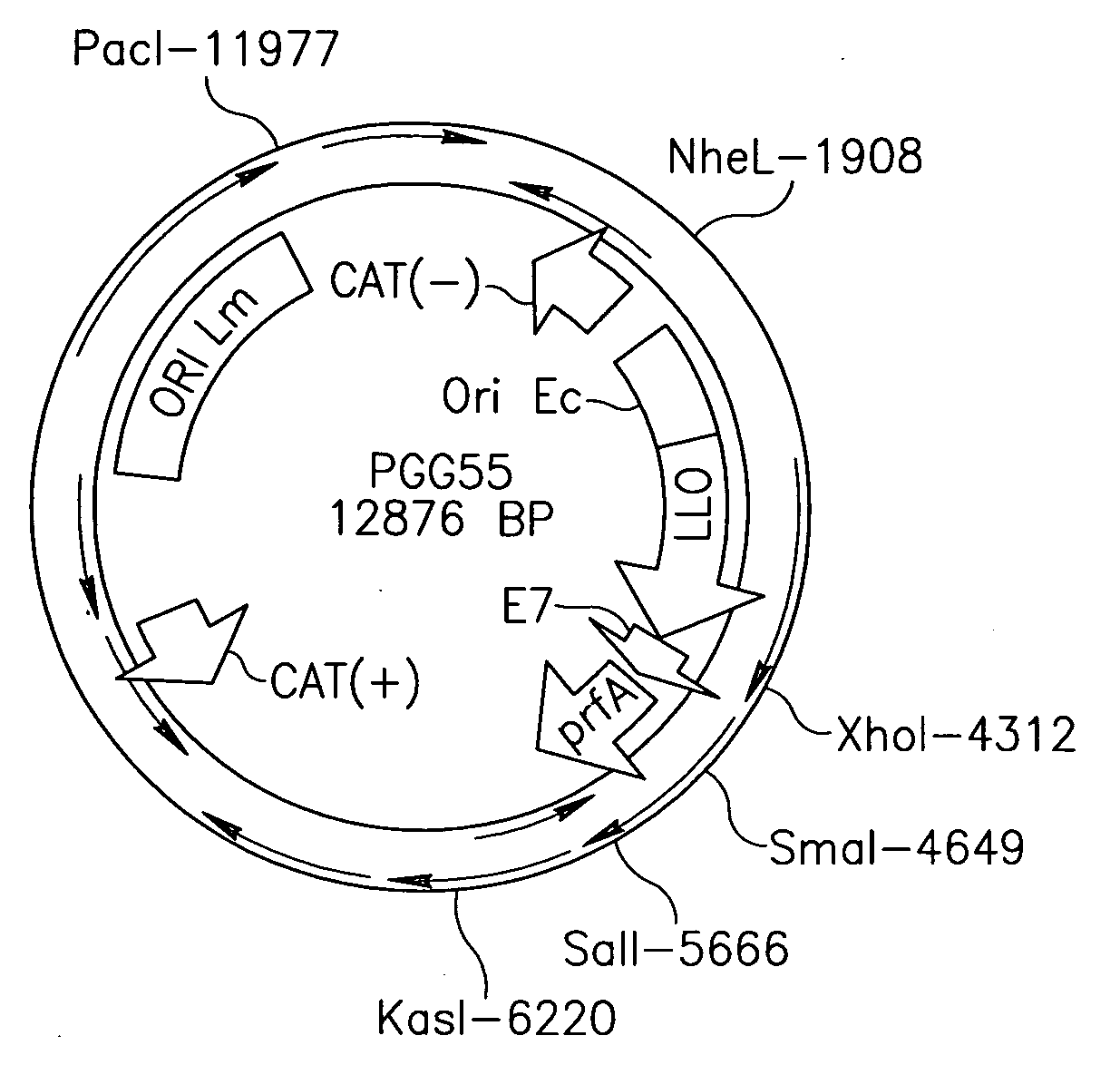
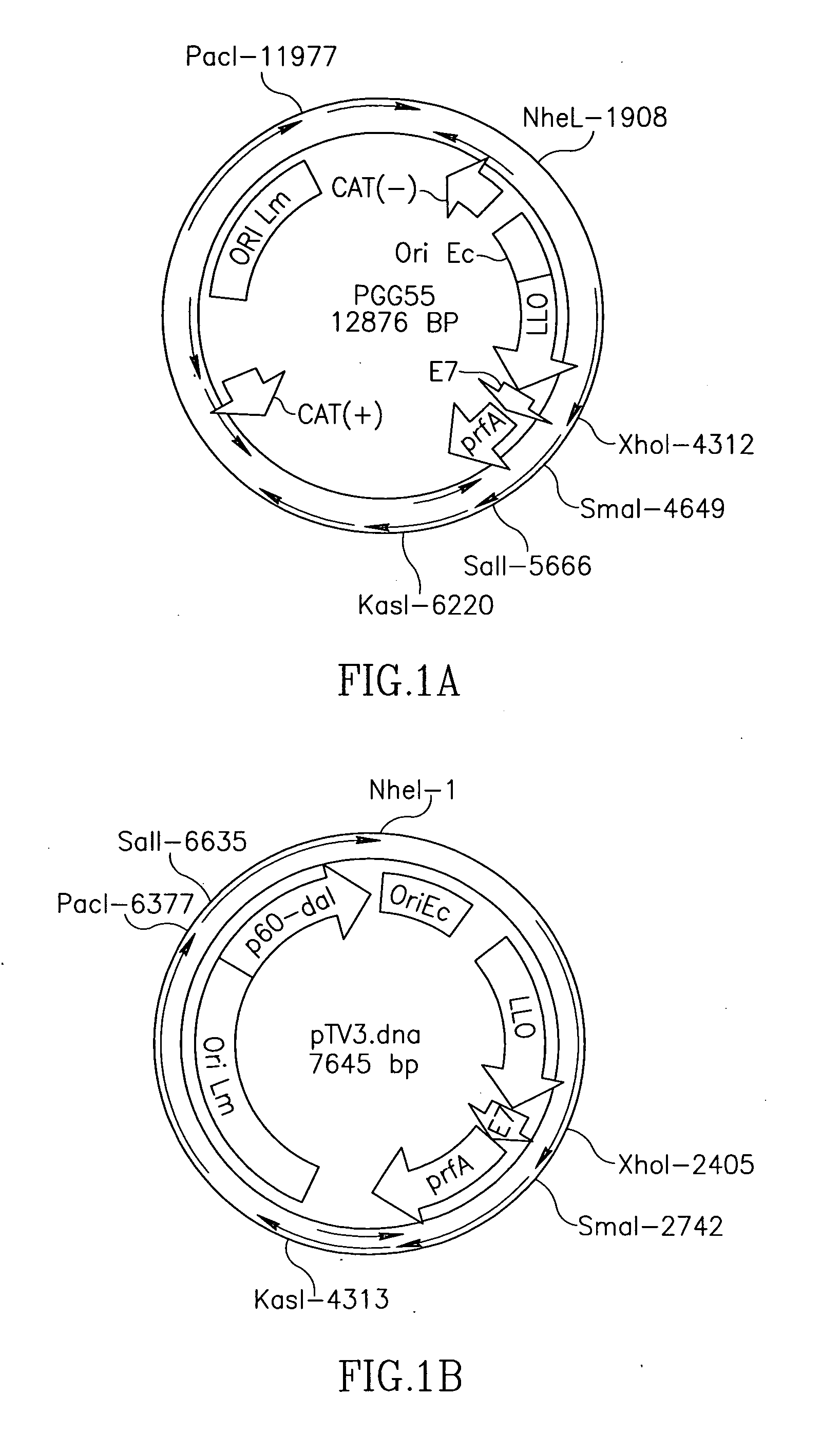
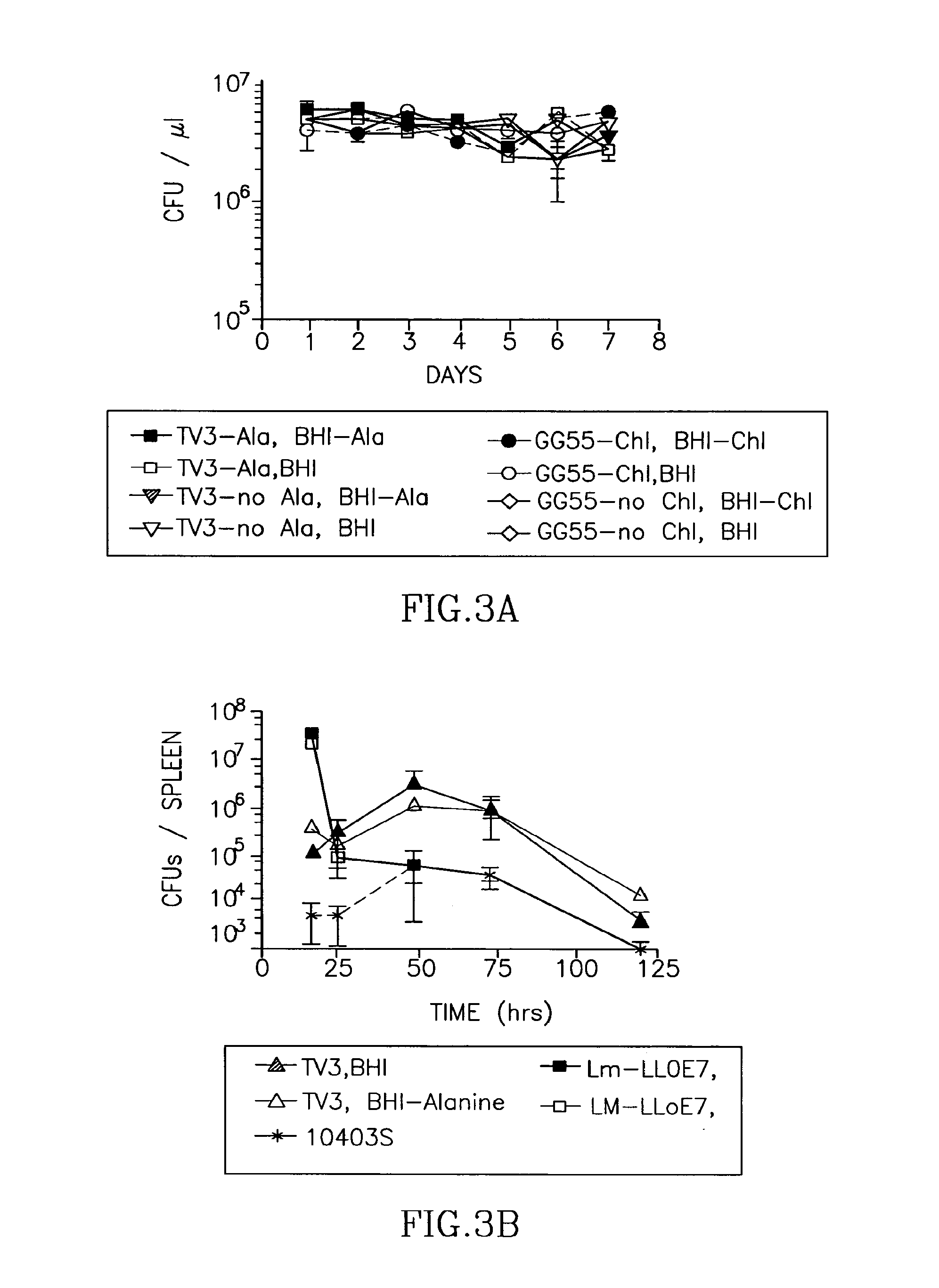
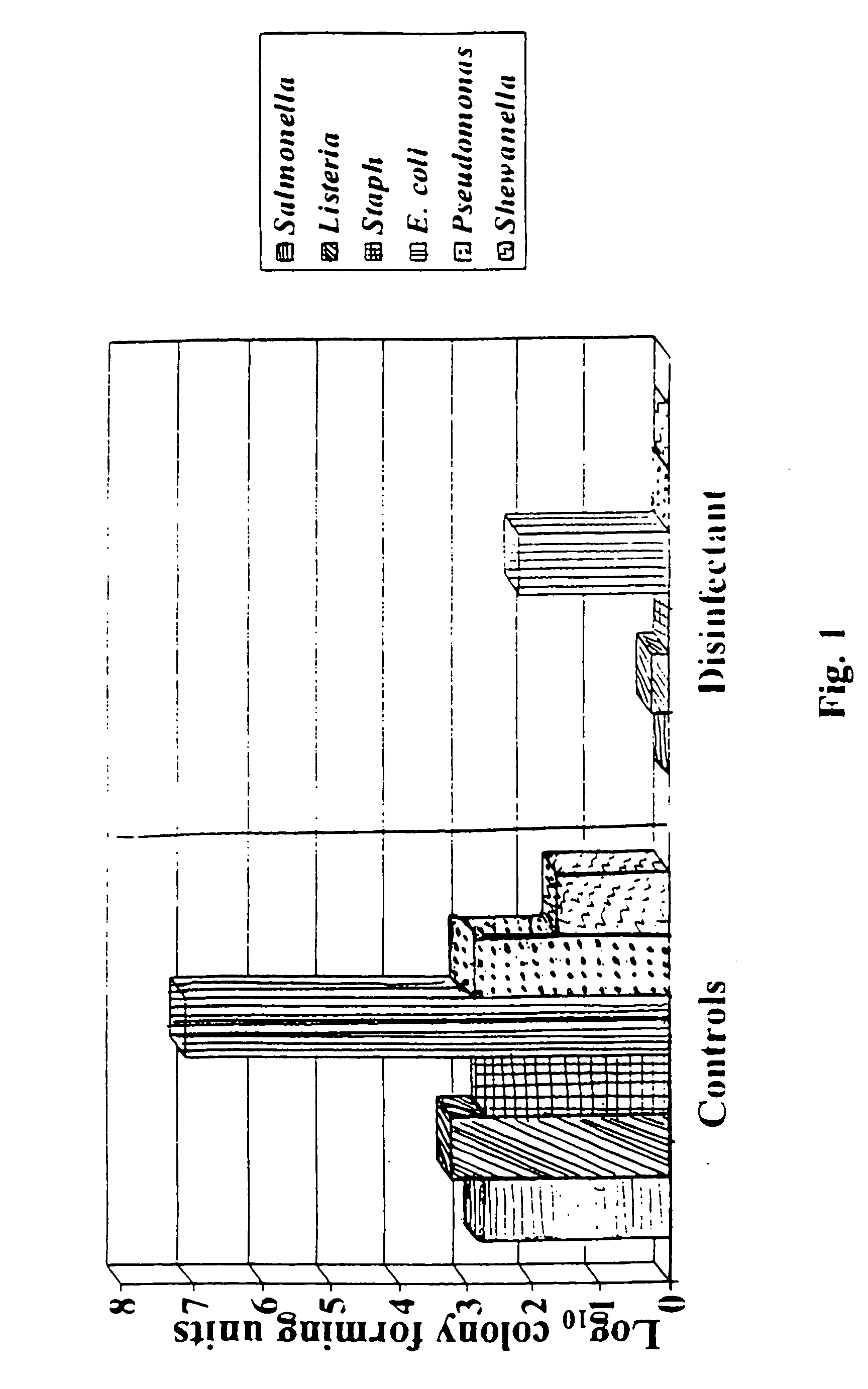
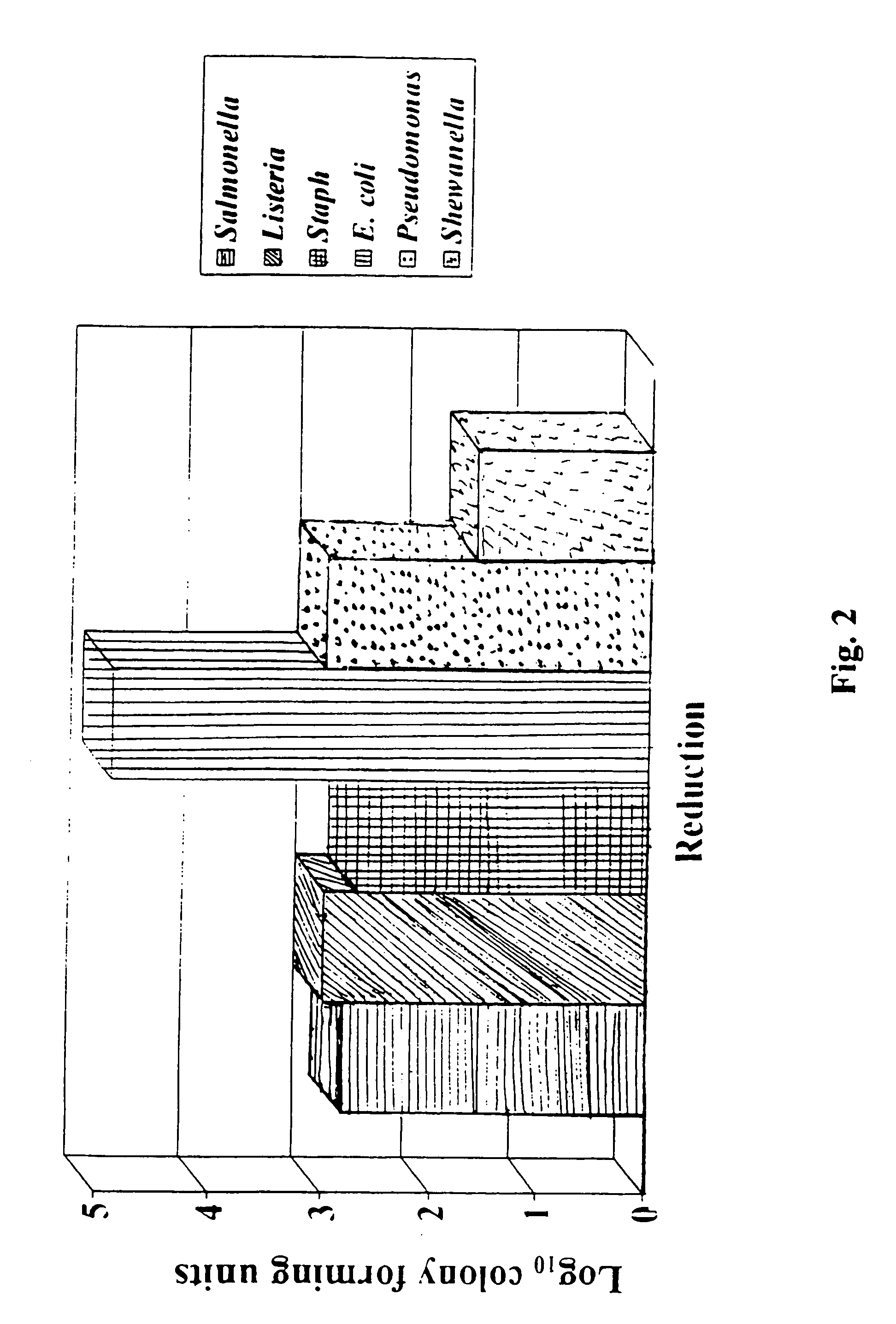
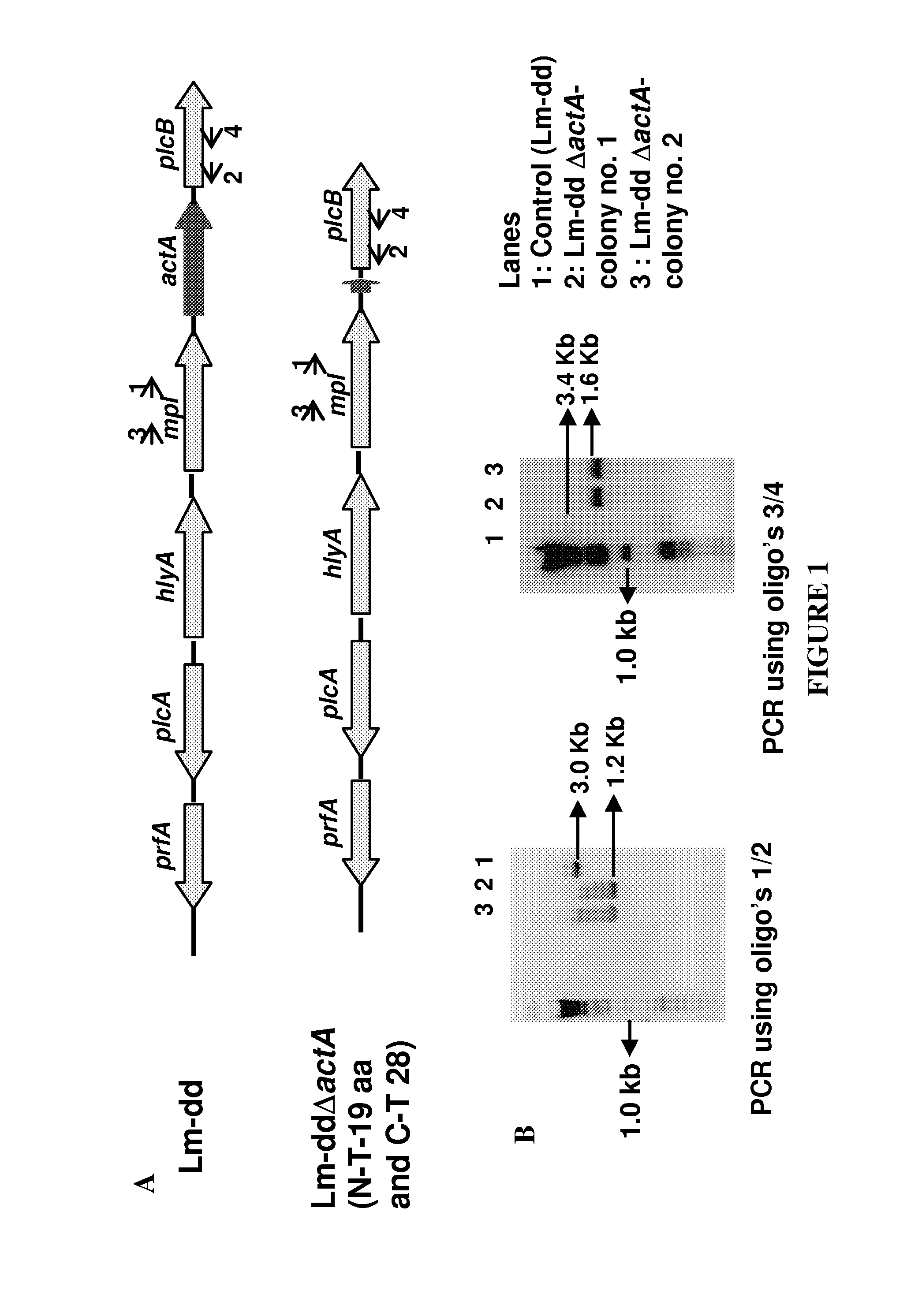
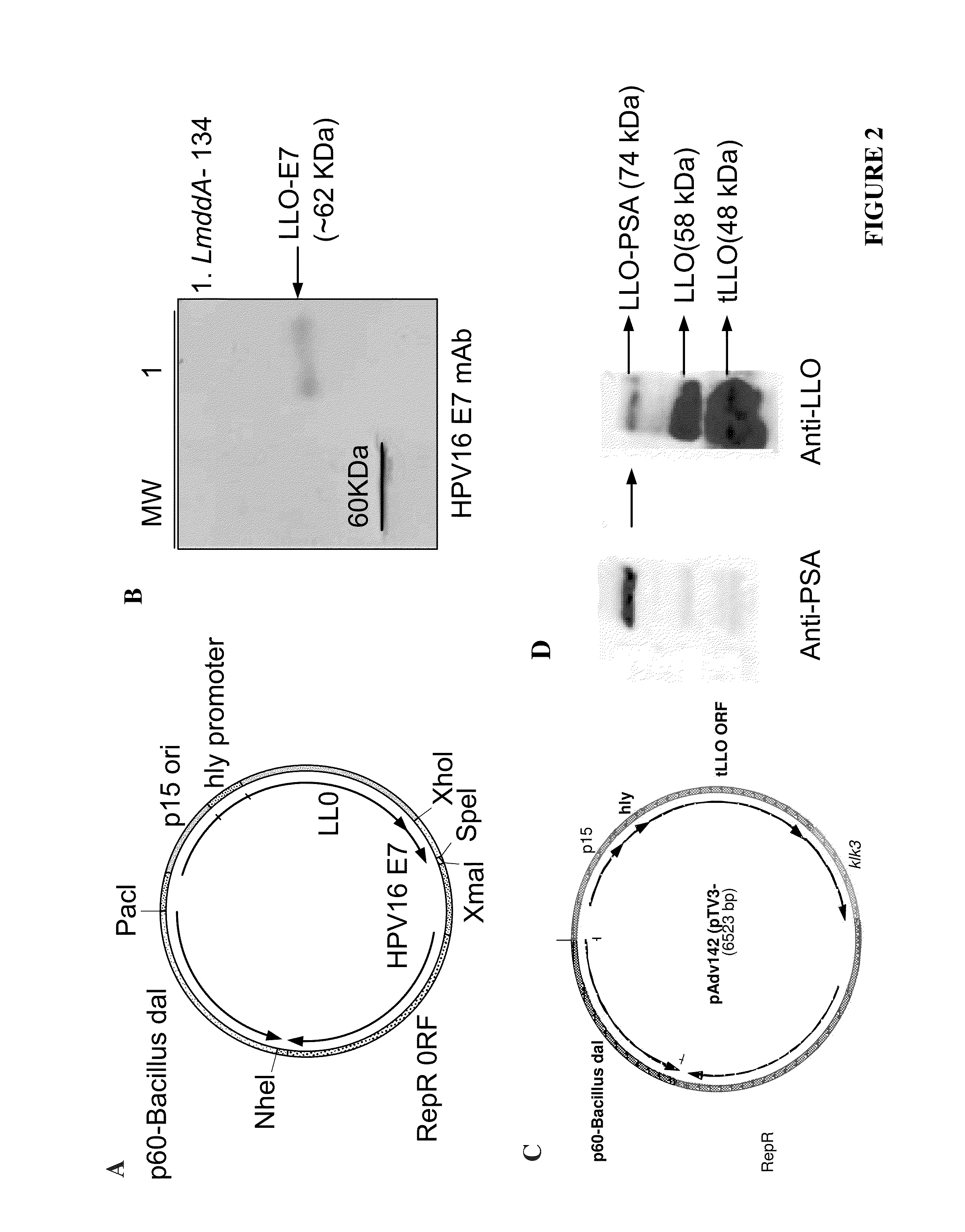
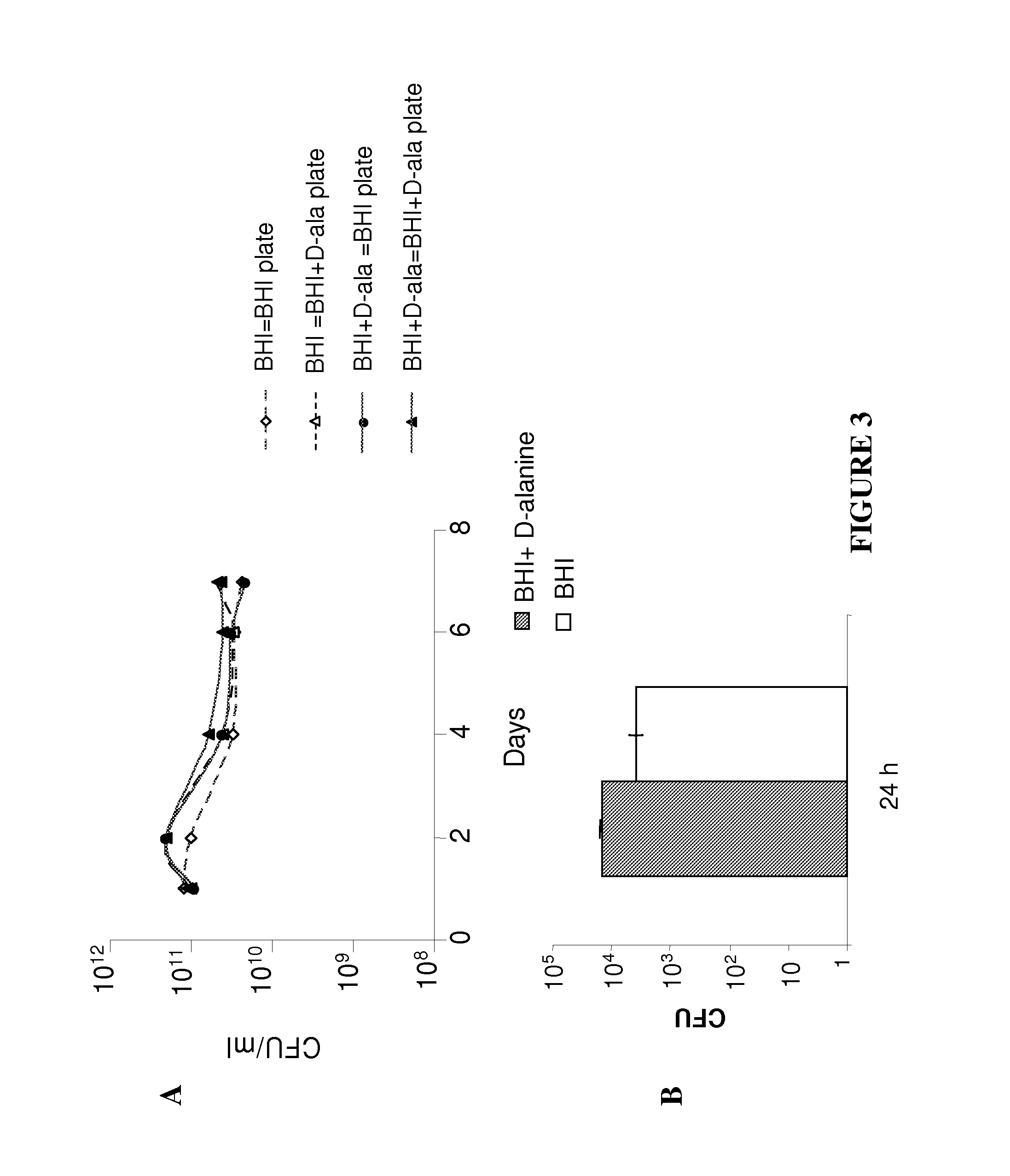
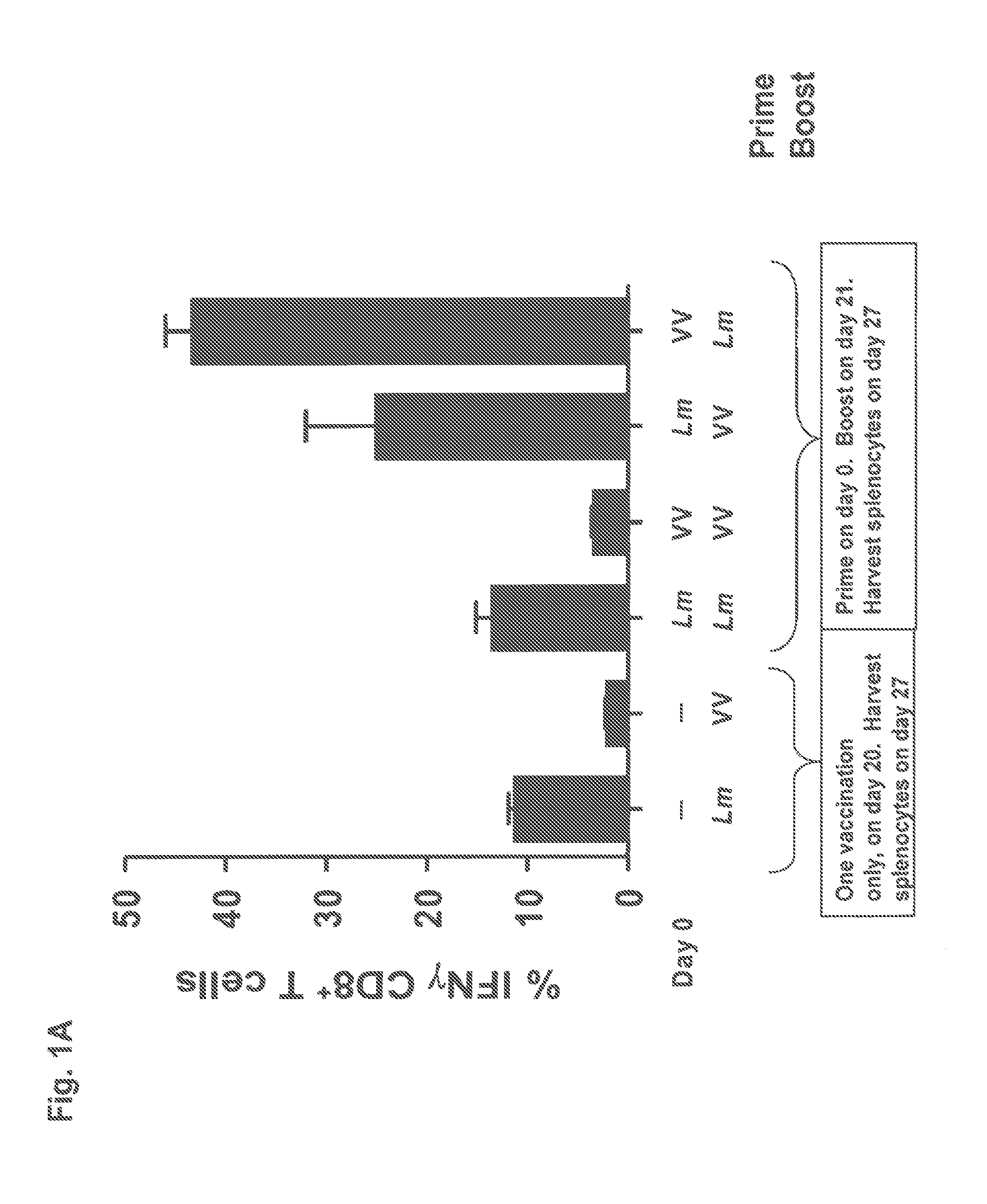
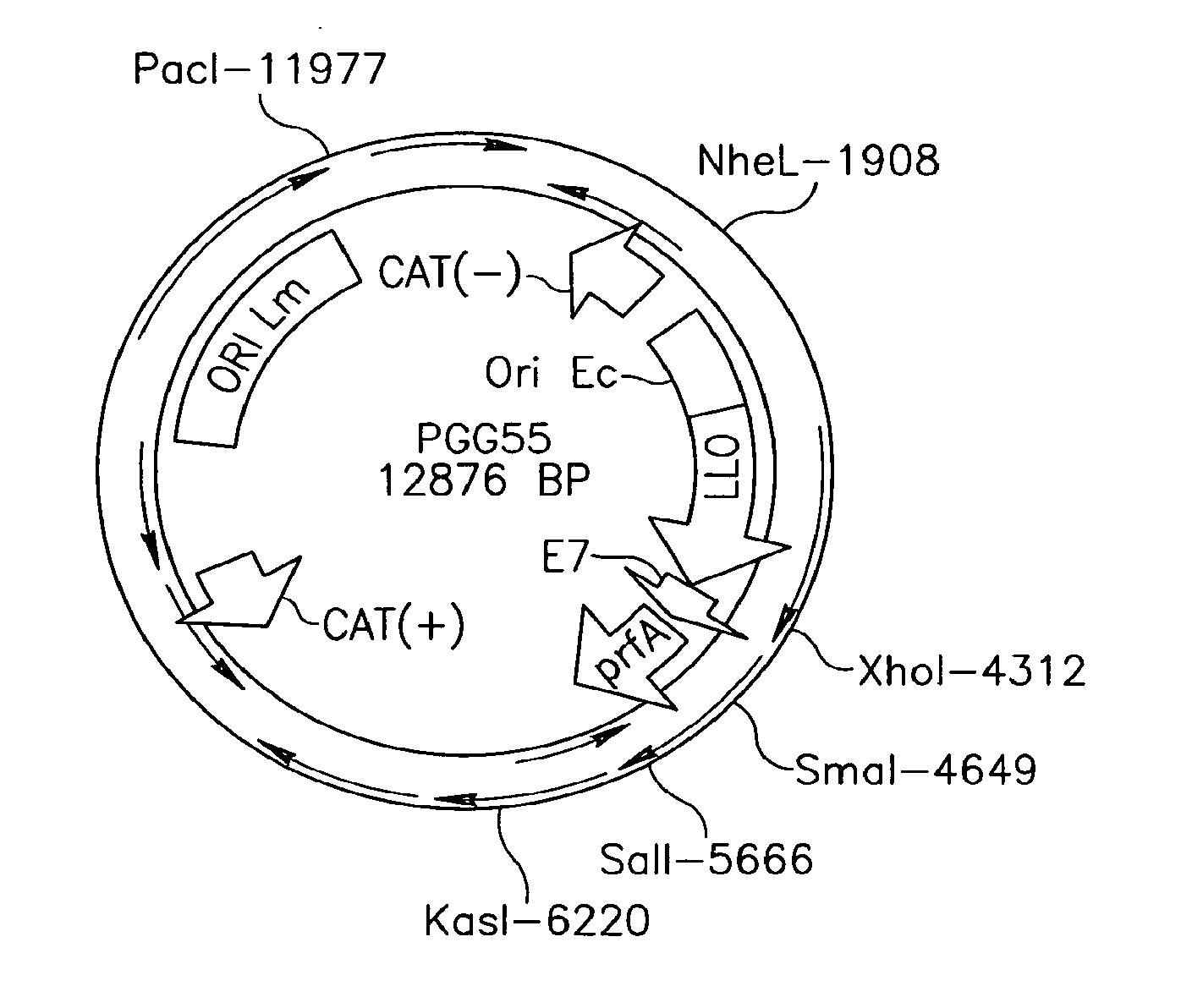
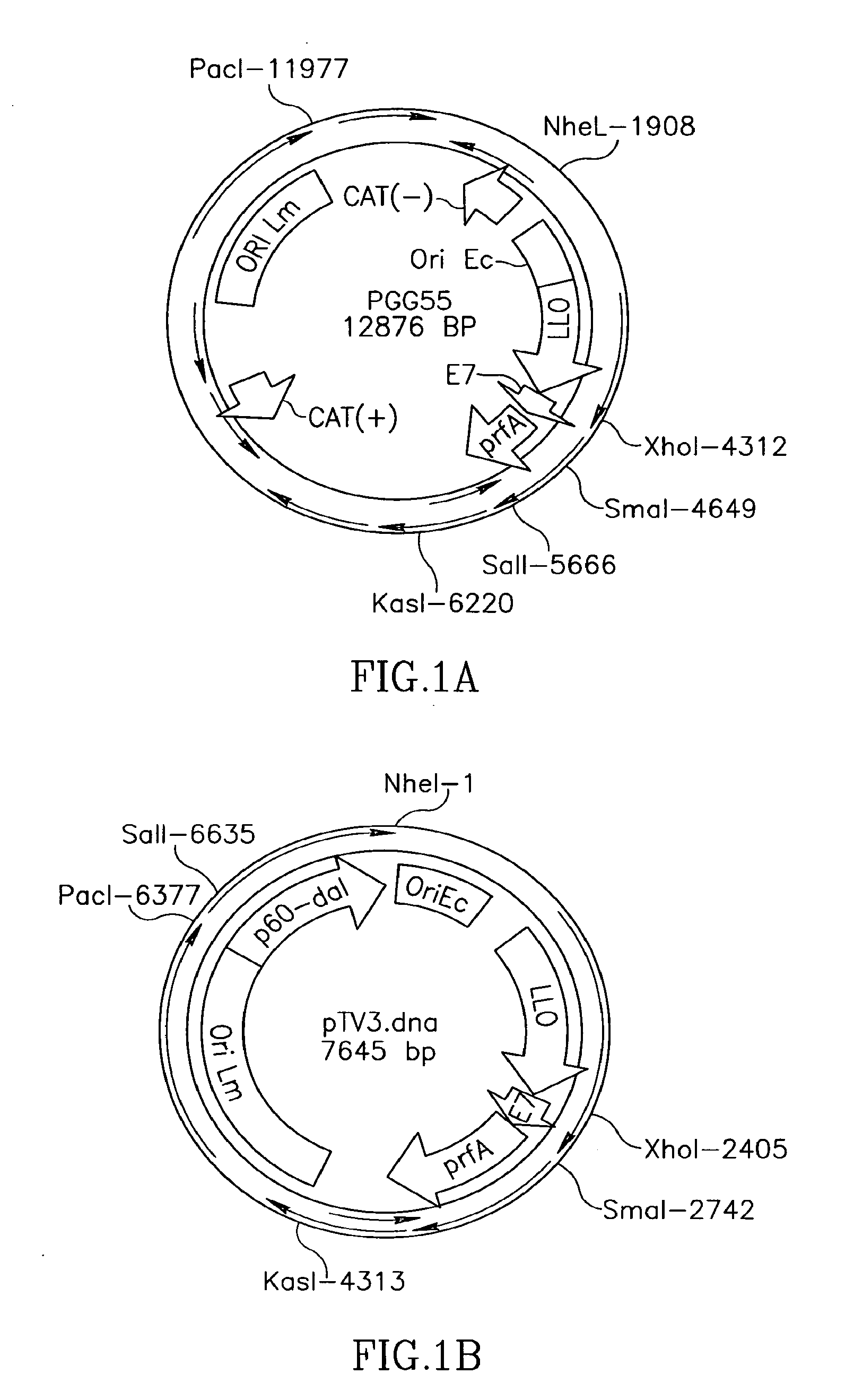
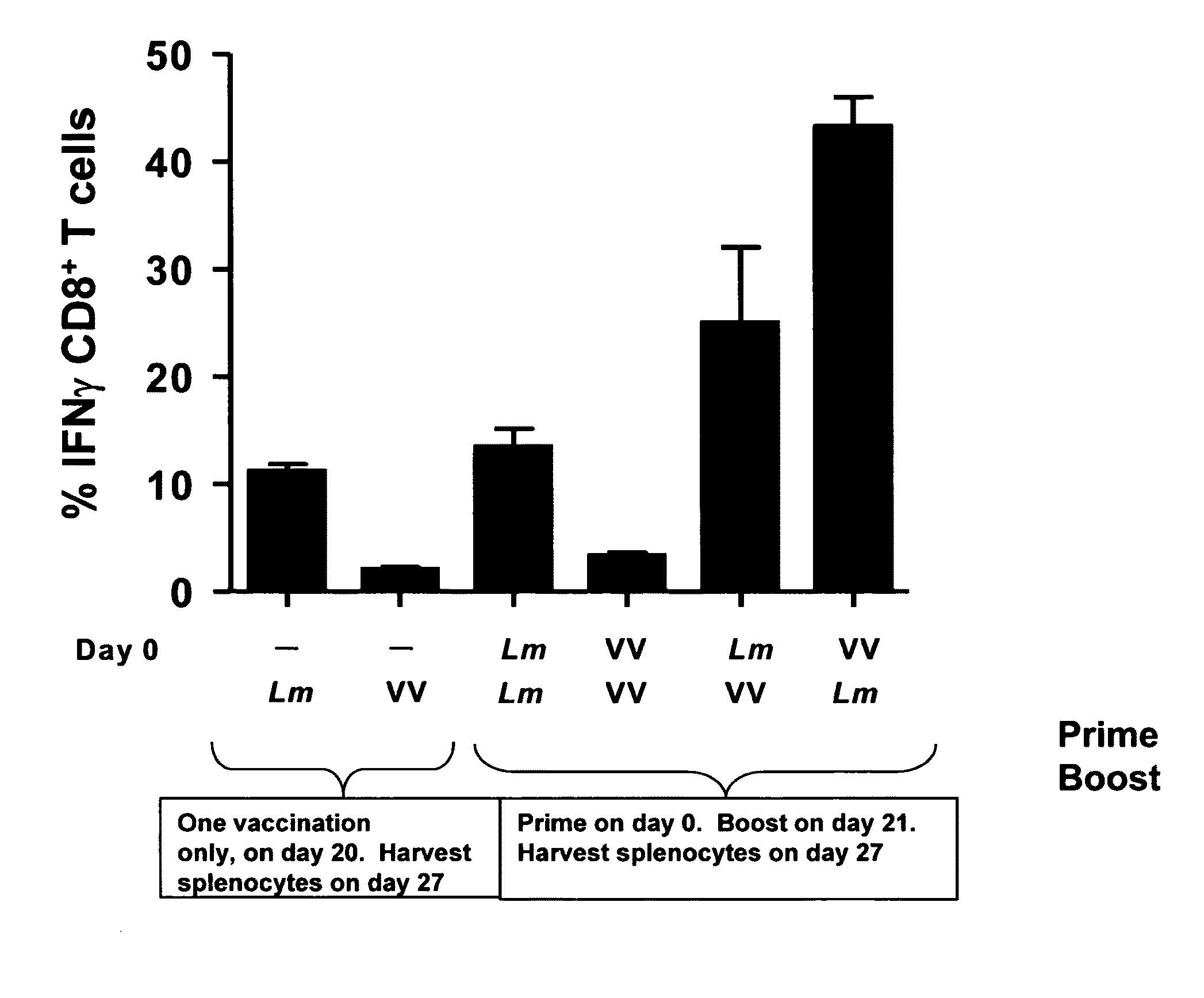
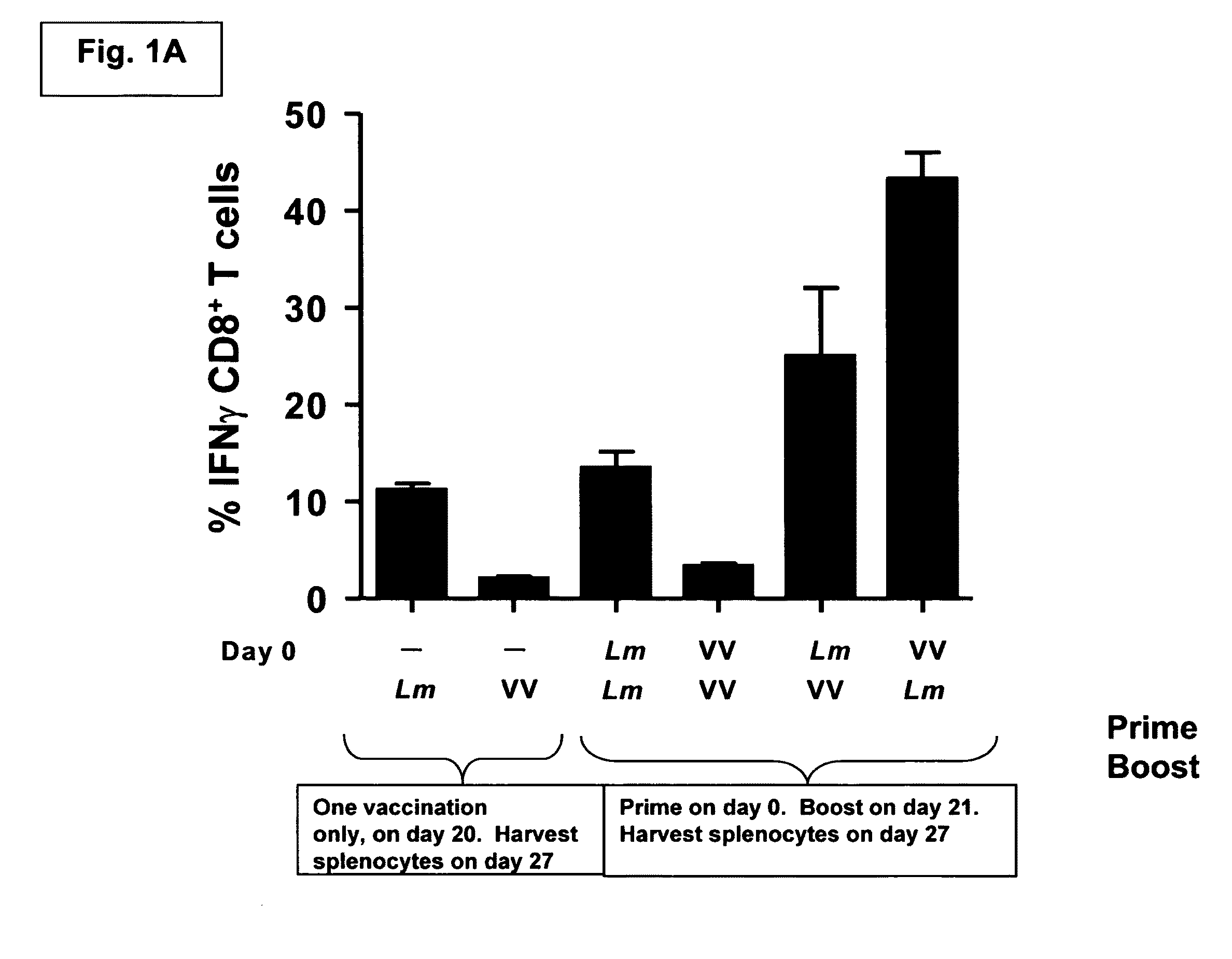
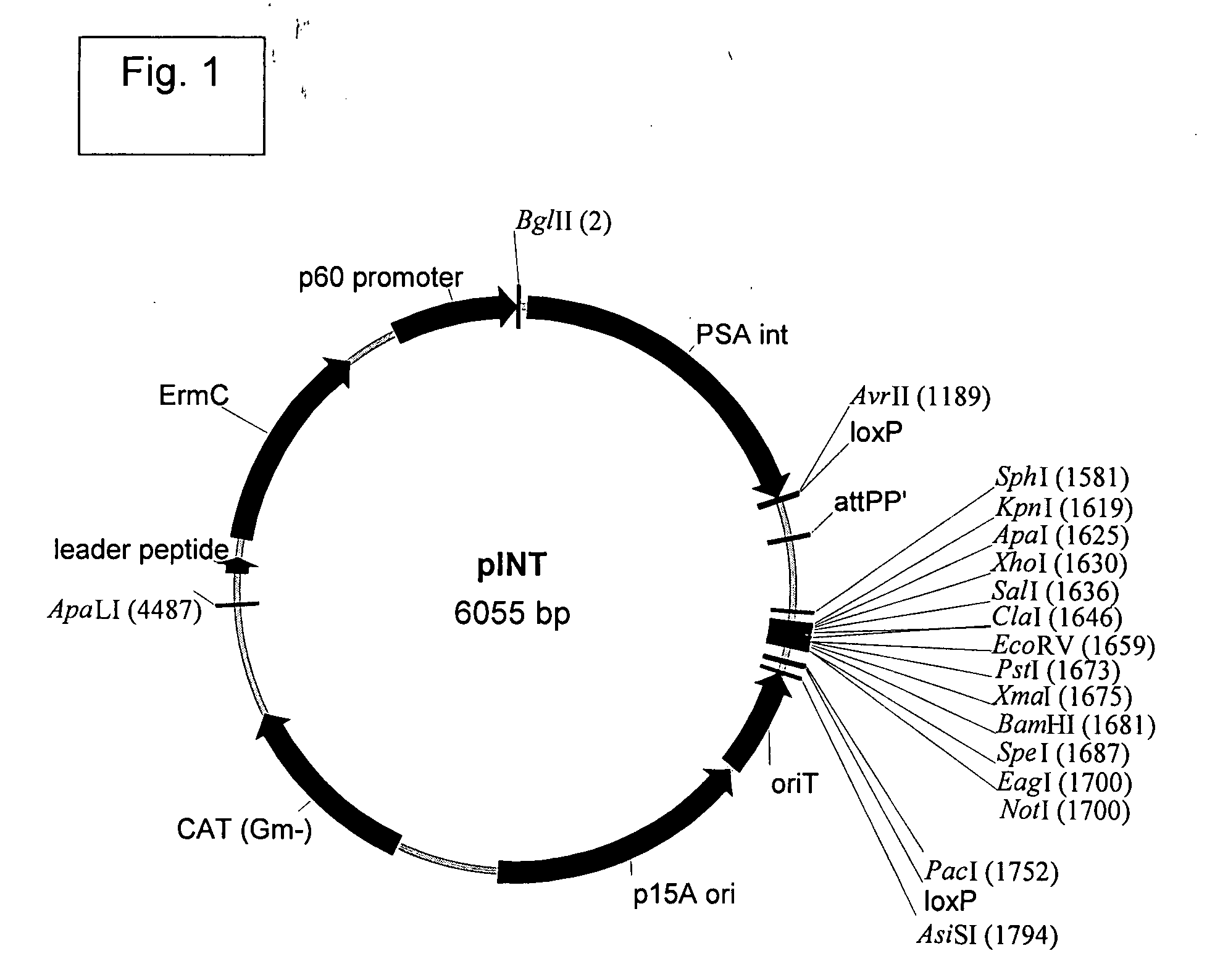
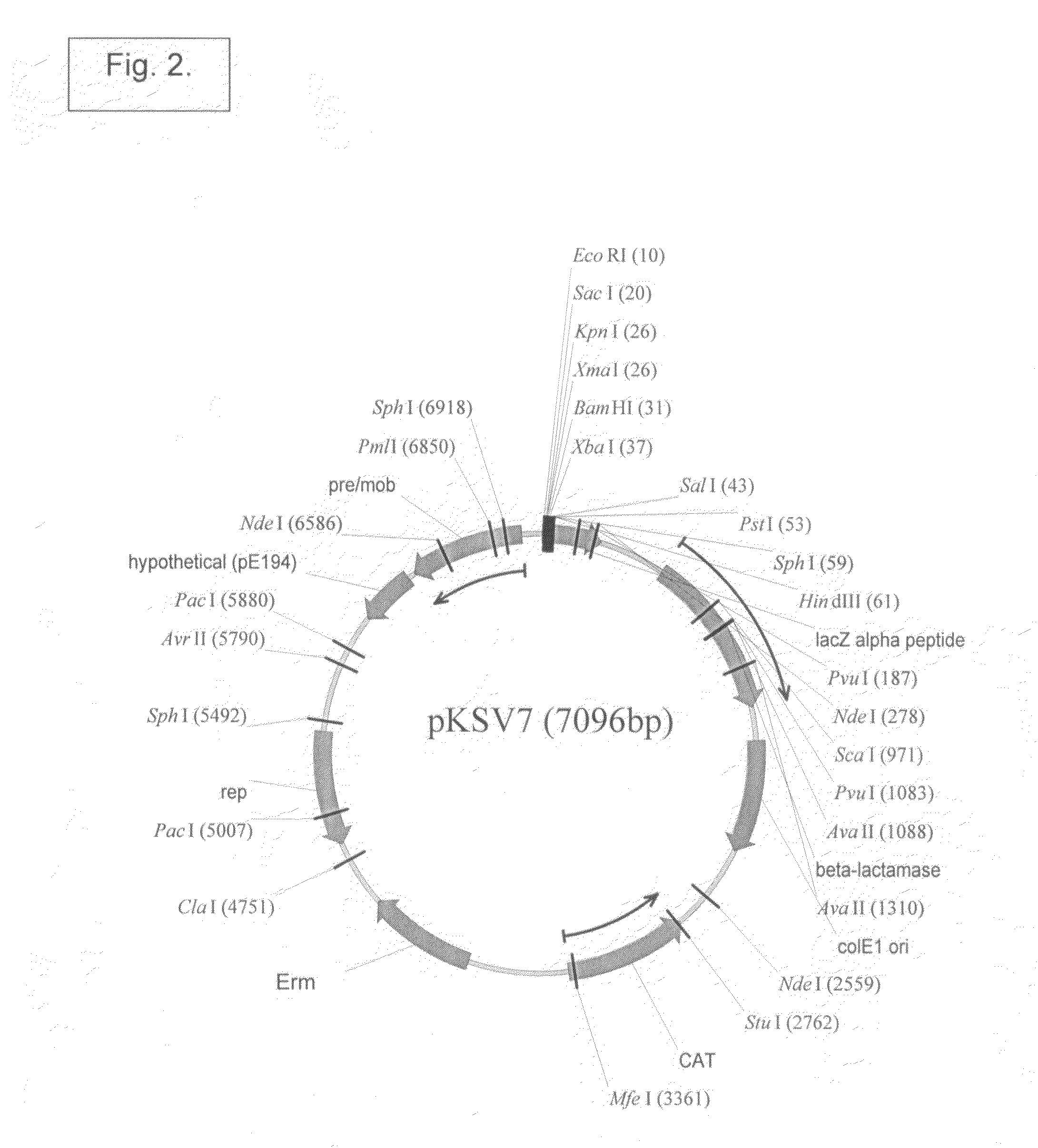
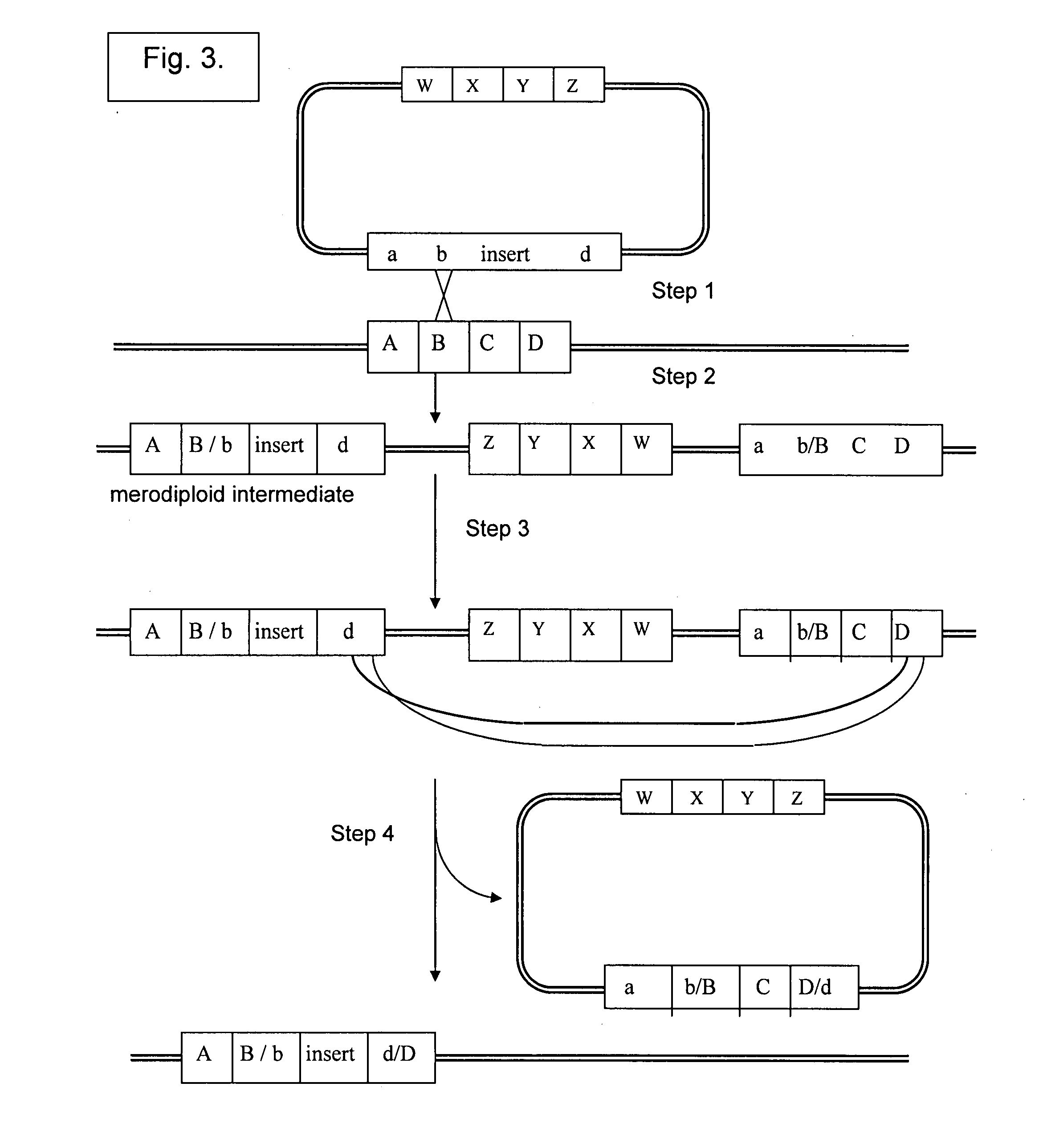
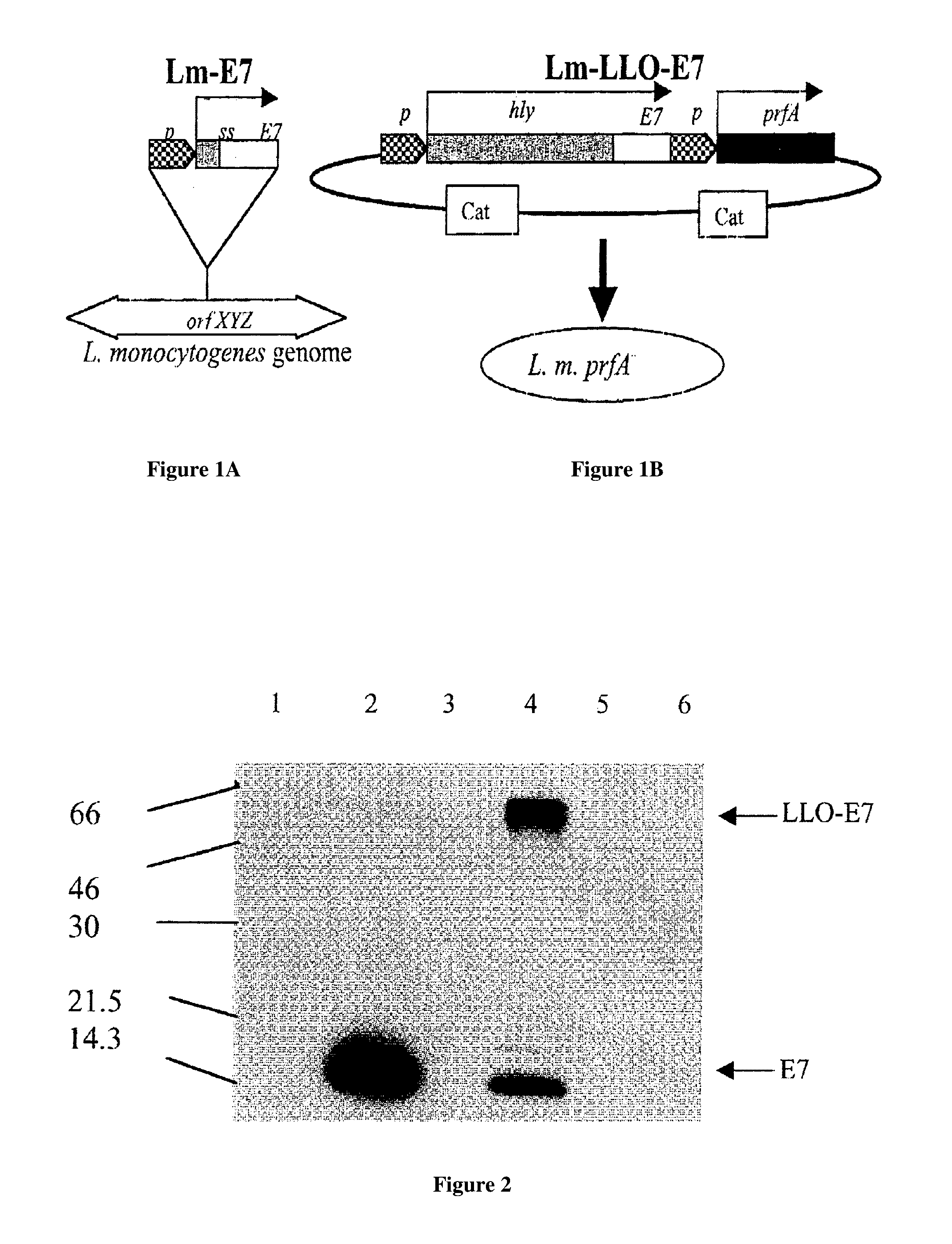
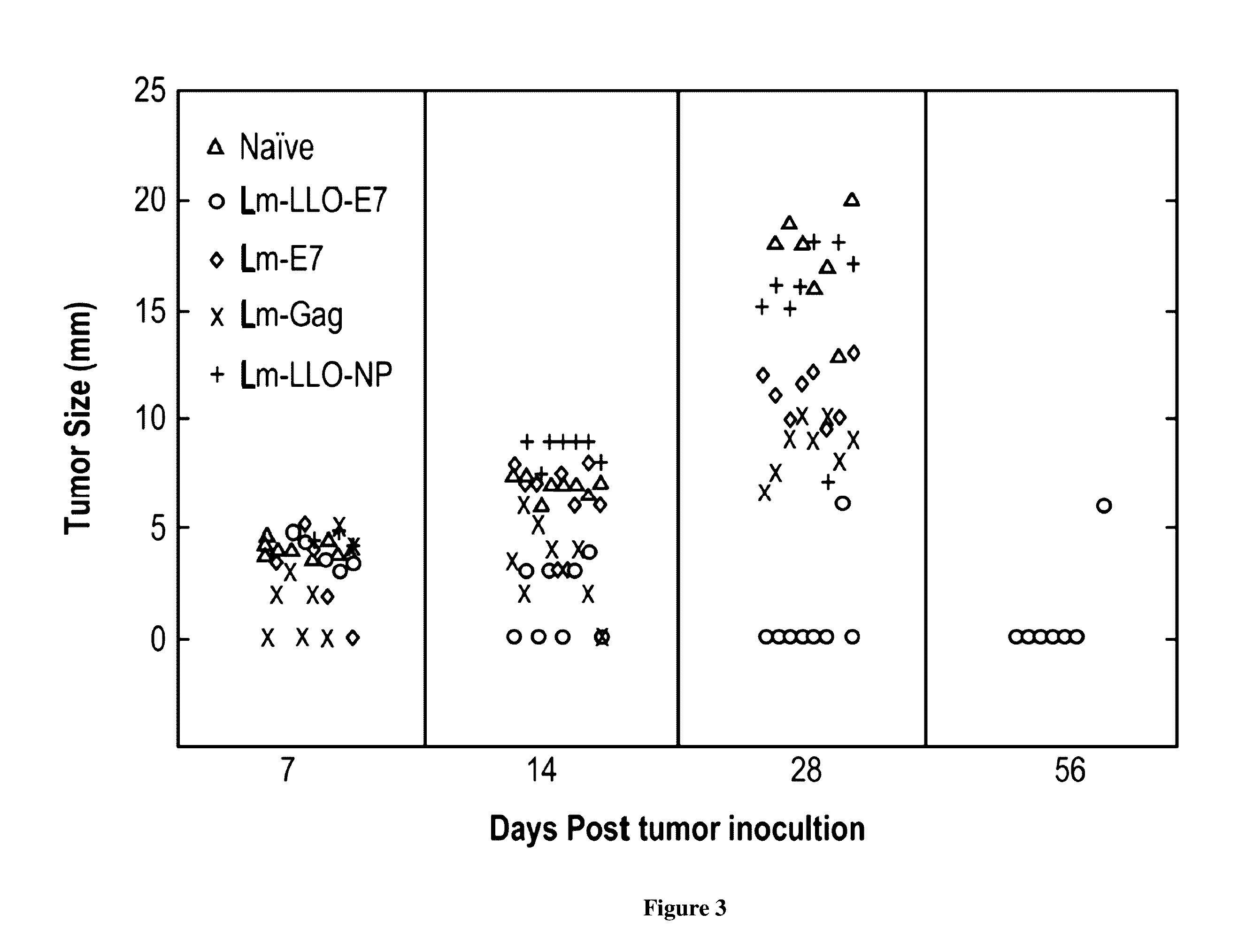
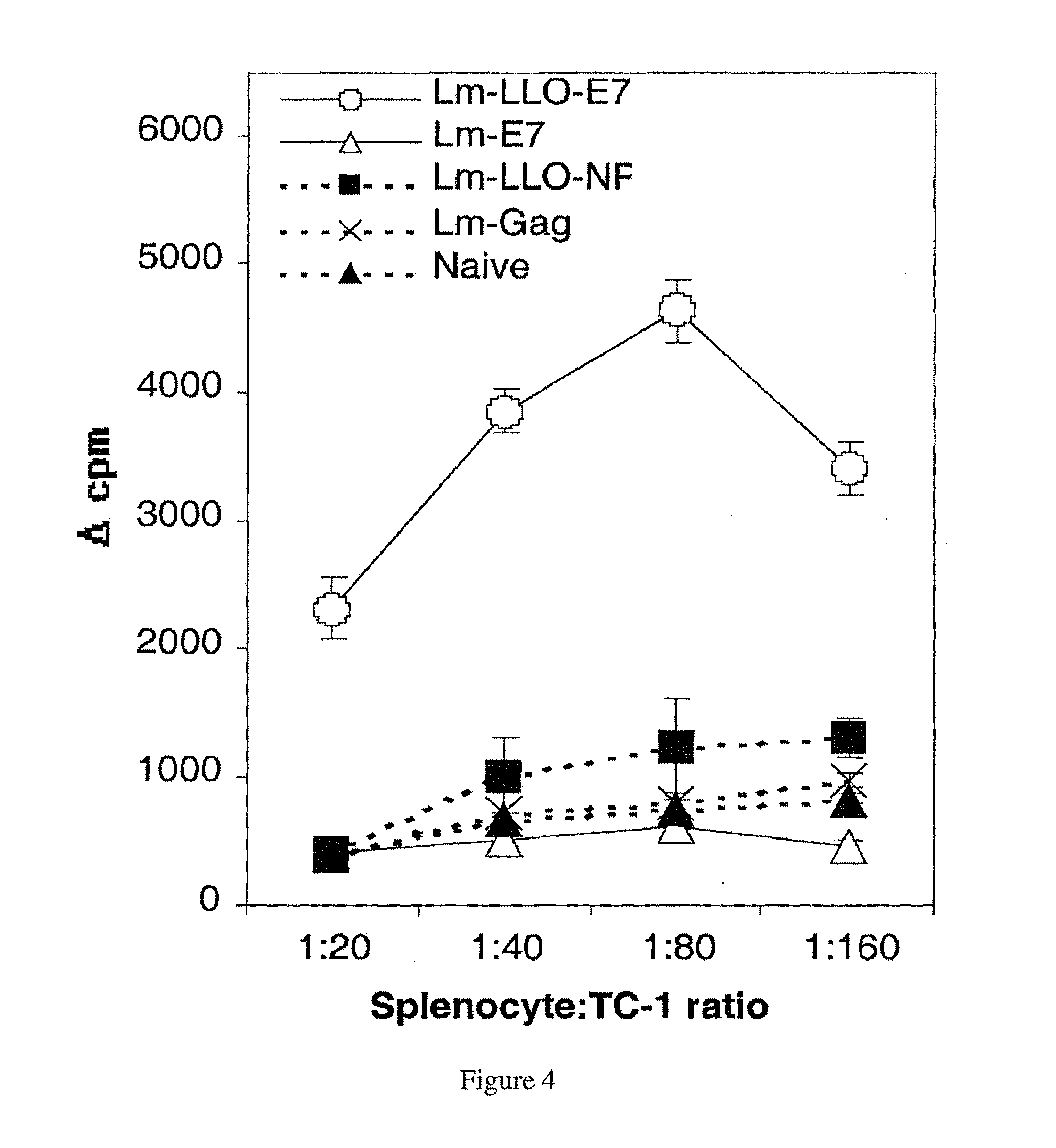
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
187 results about "Listeria" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A foodborne disease caused by the bacterium listeria monocytogenes.
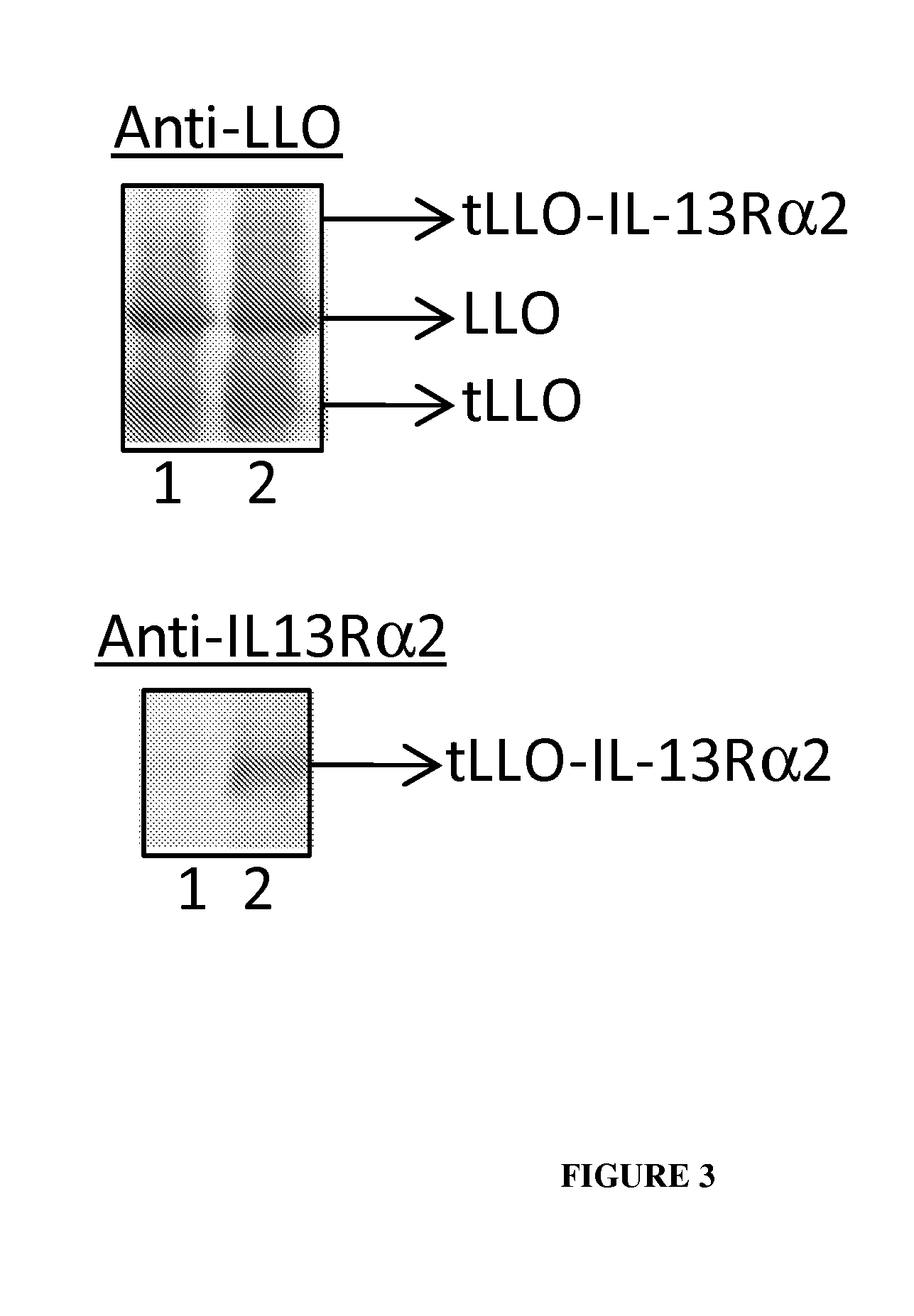
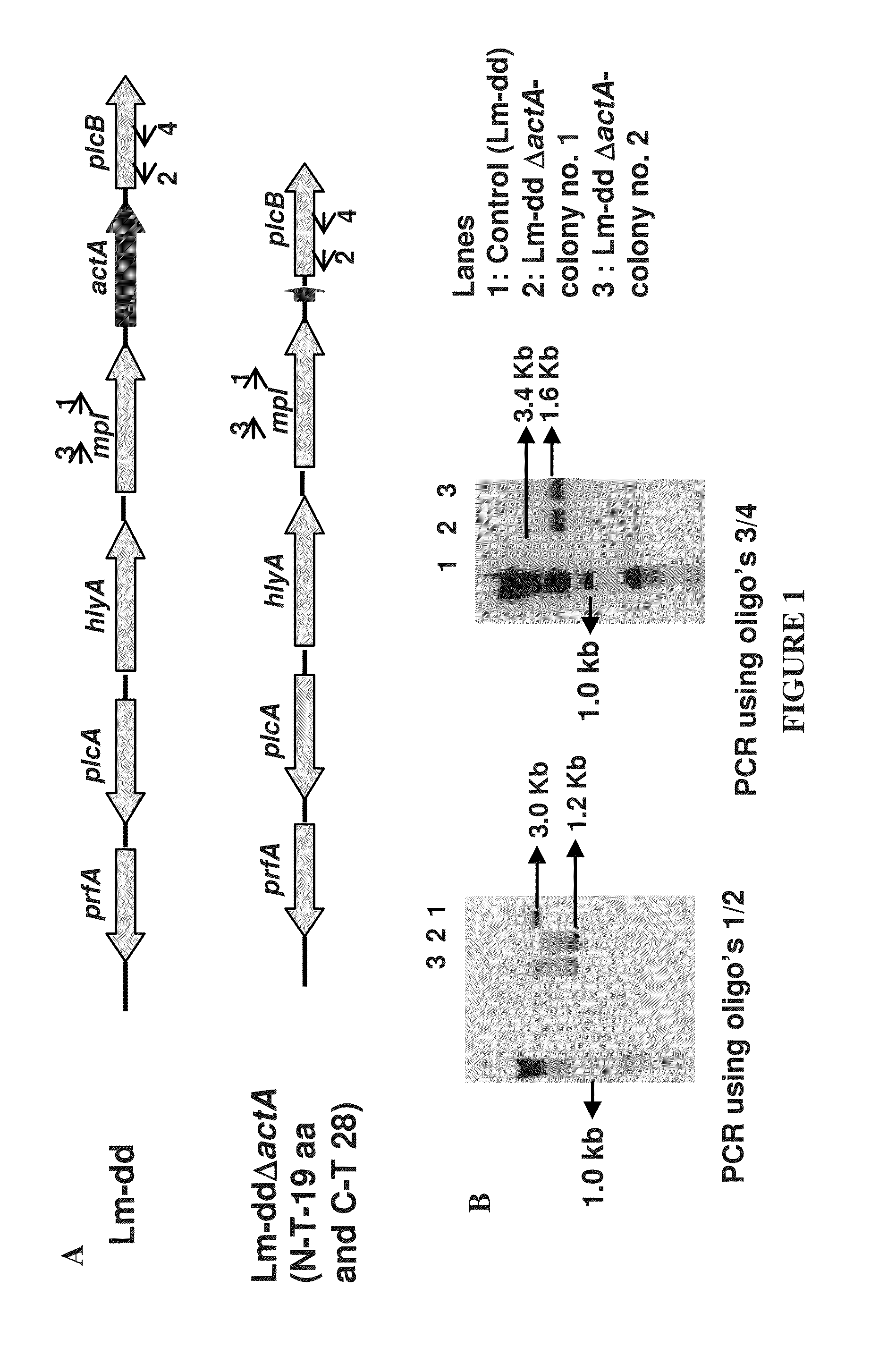
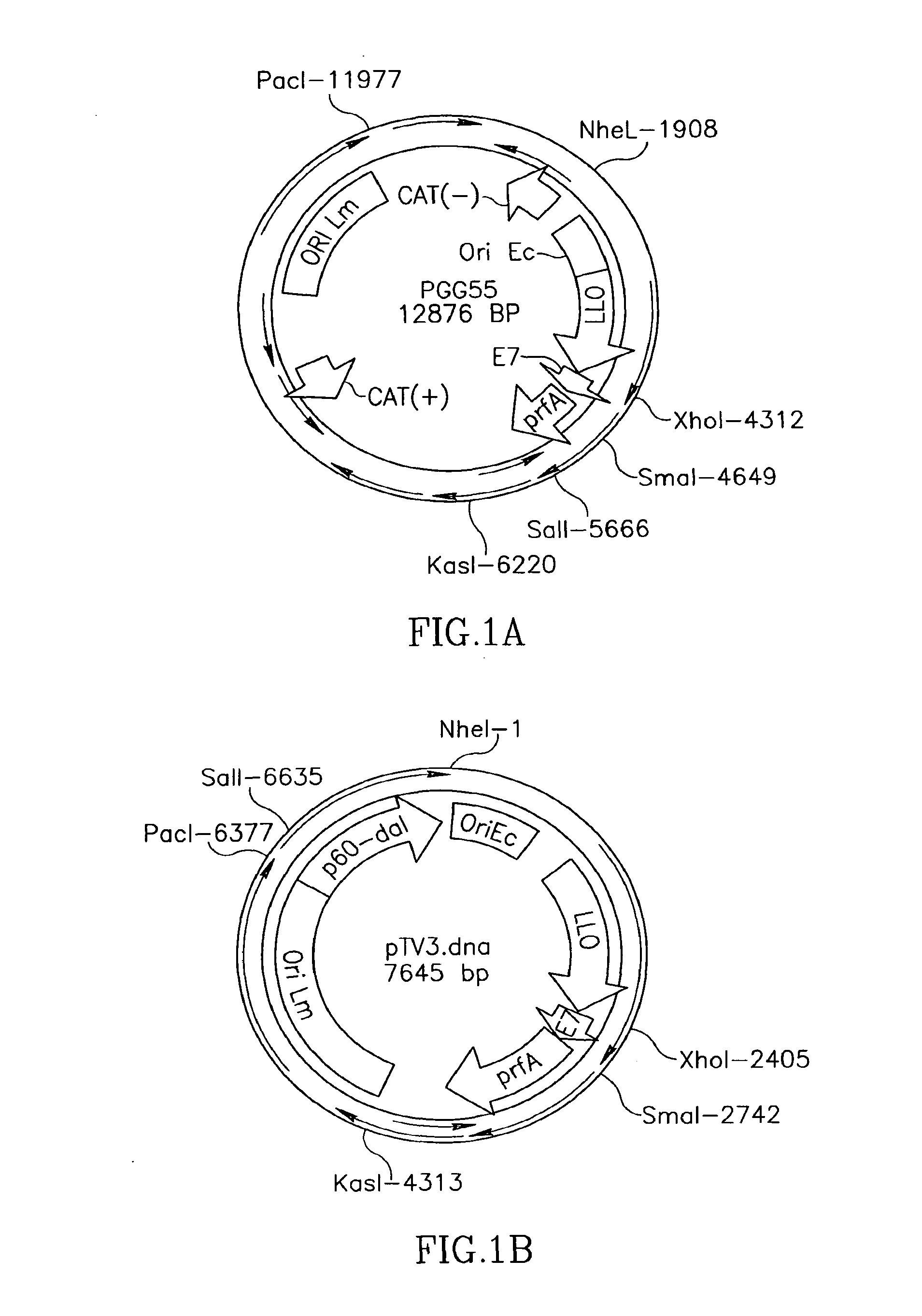
Attenuated Listeria spp. and methods for using the same
Attenuated Listeria bacteria are provided. The subject bacteria are characterized by having a mutation in a gene chosen from the lplA gene and the hly gene. The subject bacteria find use in a variety of applications, where representative applications of interest include, but are not limited to: (a) use of the subject bacteria as adjuvants; (b) use of the subject bacteria as delivery vectors for introducing macromolecules into a cell; (c) use of the subject bacteria as vaccines for eliciting or boosting a cellular immune response; etc.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Cyclic di-amp induction of type i interferon
InactiveUS20120164107A1Increase secretionDecrease c-di-AMP phosphodiesterase activityBiocideBacteriaCyclaseProtein composition
Methods of modulating type-I interferon production in a cell are provided. Aspects of the methods include modulating cytosolic cyclic di-adenosine monophosphate (c-di-AMP) activity in the cell in a manner sufficient to modulate type-I interferon production in the cell. Additional aspects of the invention include c-di-AMP activity modulatory compositions, e.g., c-di-AMP, mutant Listeria bacteria, cyclase and / or phosphodiesterase nucleic acid or protein compositions, etc. The subject methods and compositions find use in a variety of applications, including therapeutic applications.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
High cell density process for growth of Listeria
InactiveUS20060121053A1Increase productionIncrease costAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsAntigenHigh cell
The present invention relates to fed batch culture methods for high cell density growth of Listeria which produce cultures having an OD600 greater than about 2.2 or higher. In particular, the invention provides methods for high cell density growth of Listeria comprising growth in a pH controlled bioreactor and, optionally, the gradual addition of a carbon source, e.g., glucose, with or without one or more additional nutrients, e.g., vitamins, when growth in the initial culture is nearly complete or complete. In one embodiment, the methods of the invention are used to produce Listeria-based compositions, e.g., vaccines comprising Listeria that express a tumor-associated antigen, e.g., an EphA2 antigenic peptide, for eliciting an immune response against hyperproliferative cells.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Live listeria-based vaccines for central nervous system therapy
InactiveUS20110223187A1Bacterial antigen ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsCns tumorRecombinant vaccines
This invention is directed to methods for treating a central nervous system (CNS) tumor or cancer using live Listeria-based recombinant vaccines.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA +1
Antimicrobial food additive and treatment for cooked food, water and wastewater
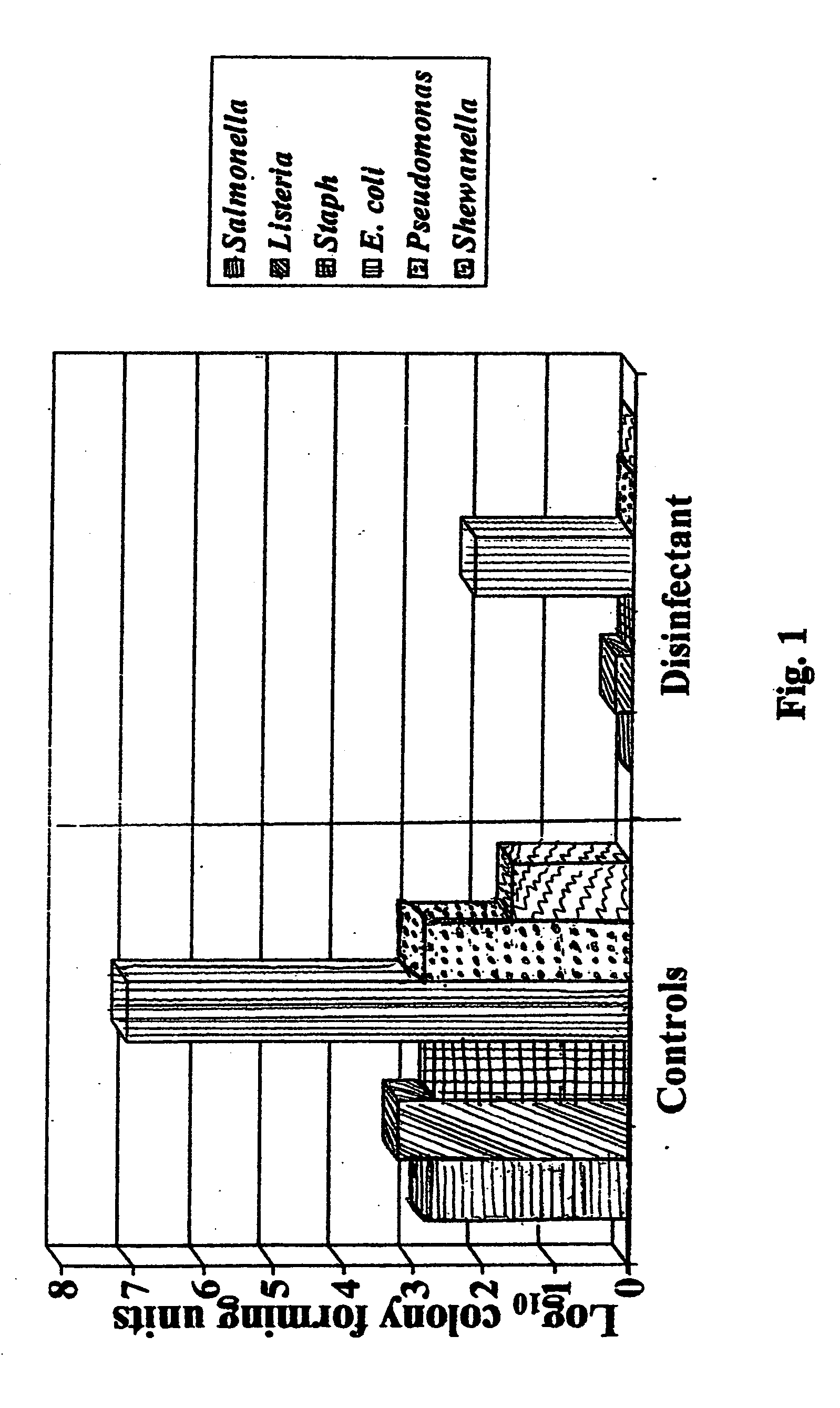
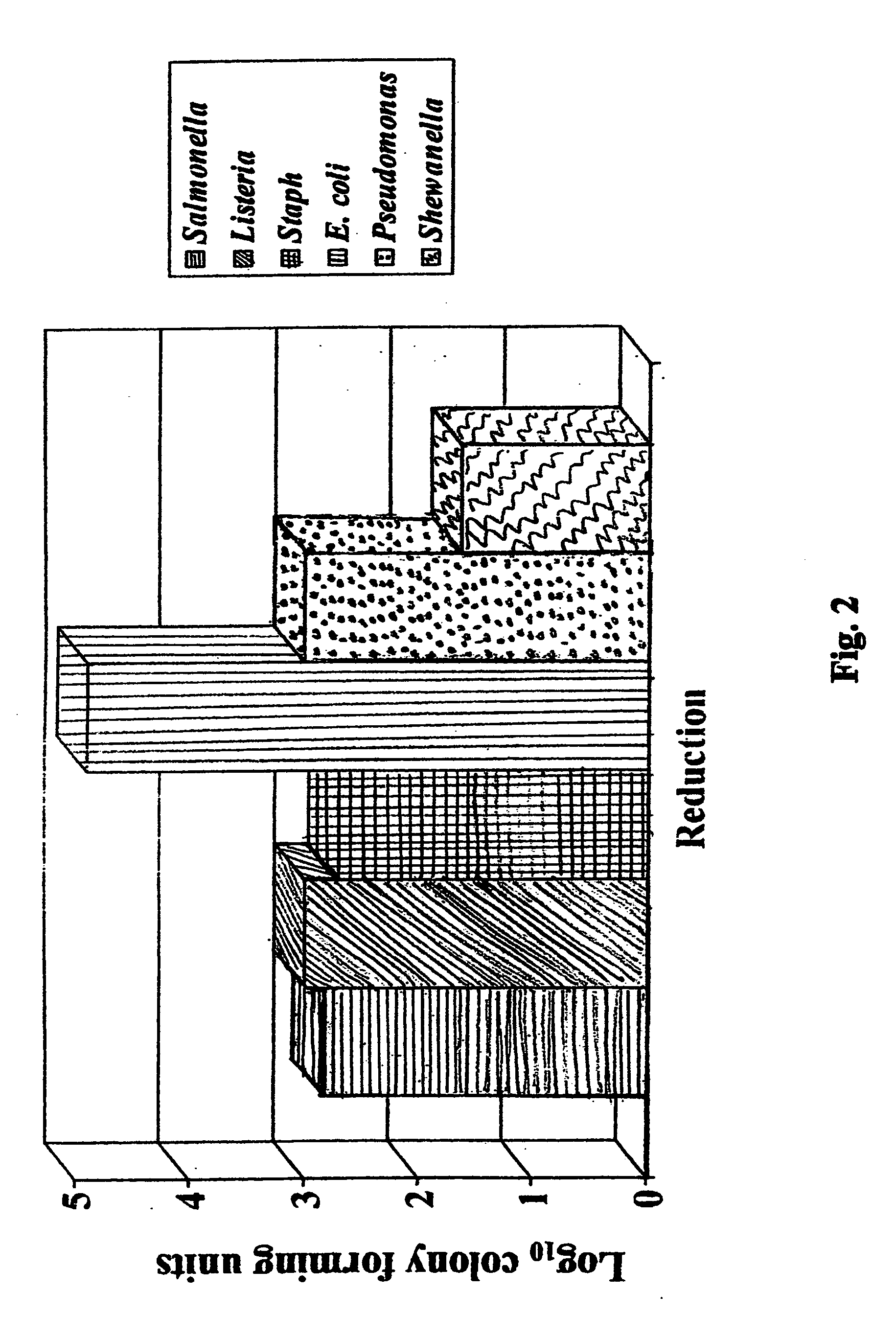
A composition of matter with antimicrobial and antibacterial properties for treatment of water, wastewater, processed food and for use as a food additive is provided. The antimicrobial composition inhibits cellular growth of known pathogenic, indicator and spoilage organisms, such as salmonella, stahphylococcus, listeria, E-coli, aerobic and anerobic organisms in wastewater and the like. The antimicrobial composition of the present invention is useful in many situations and conditions in need of disinfectants and sanitizers. One of the primary benefits of the antimicrobial agent is that it inhibits the growth of bacteria that have become antibiotic resistant. In addition, the antimicrobial composition herein does not have any known toxicity to man or the environment.
Owner:TASKER PRODS IP HLDG CORP
Dual delivery system for heterologous antigens
Provided herein are recombinant Listeria strains expressing a tumor-specific antigenic polypeptide and, optionally, an angiogenic polypeptide wherein a nucleic acid molecule encoding at least one of the polypeptides is operably integrated into the Listeria genome in an open reading frame with a nucleic acid sequence encoding a PEST-containing polypeptide, methods of preparing same, and methods of inducing an immune response, and treating, inhibiting, or suppressing cancer or tumors comprising administering same.
Owner:ADVAXIS
Antimicrobial composition for pre-harvest and post-harvest treatment of plants and animals
ActiveUS7192618B2Minimize growth and spreadReduce Microbial ContaminationHeavy metal active ingredientsFatty acid chemical modificationFood additiveDisinfectant
Owner:CMS TECH INC +1
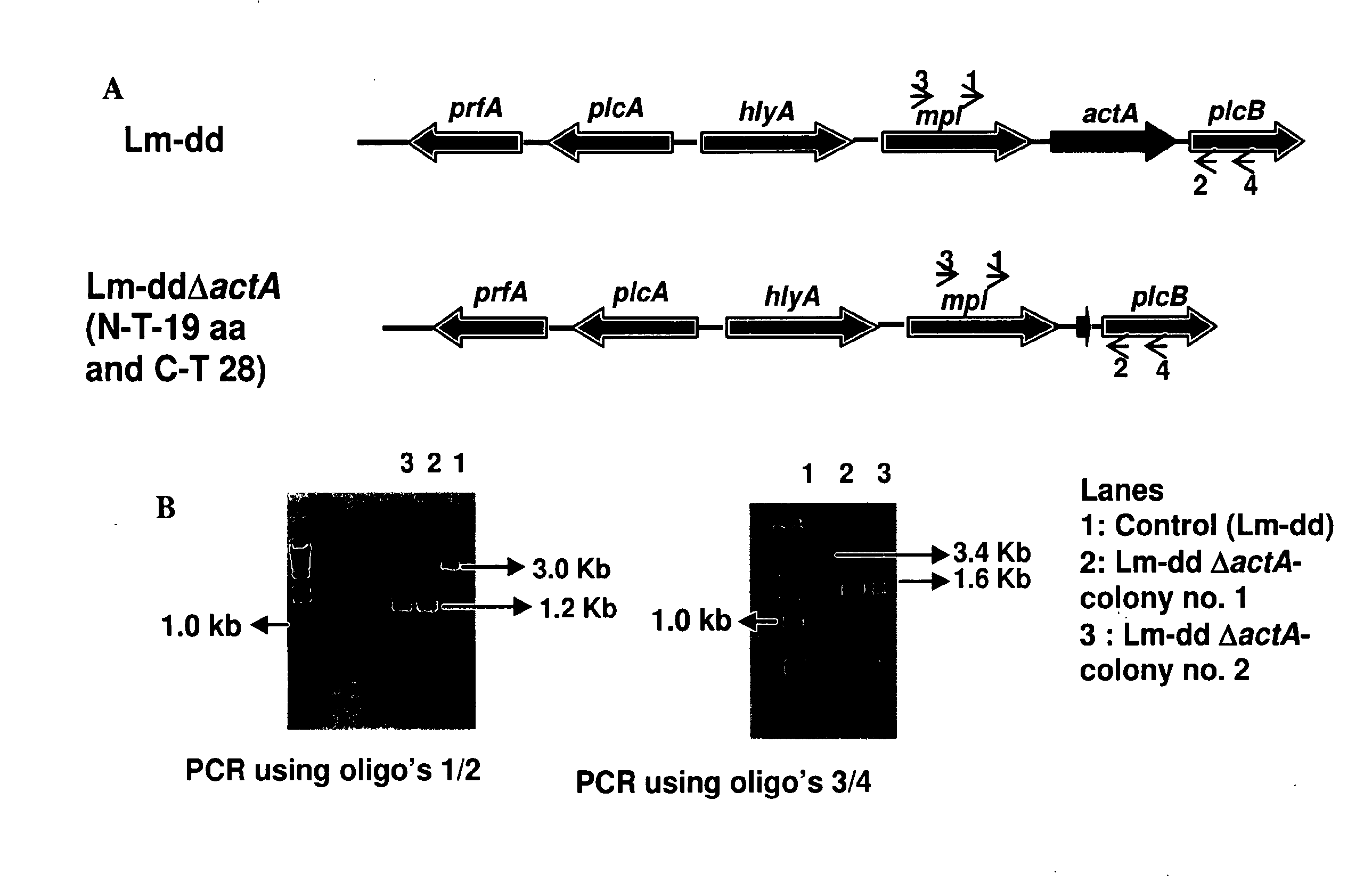
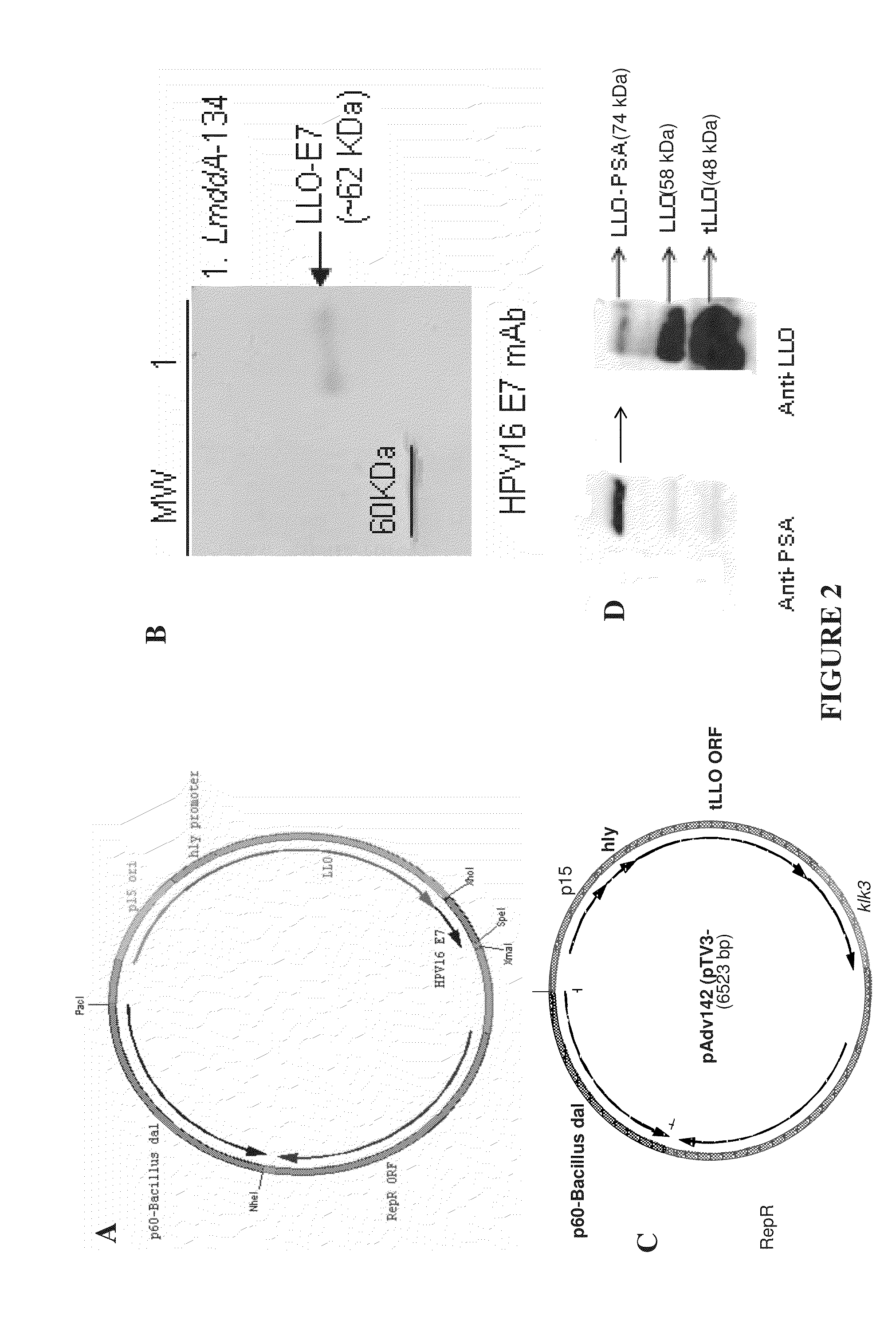
Engineered Listeria and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS7935804B2Improve survivalIncreasing expression and secretionBiocideBacteriaHeterologousHeterologous Antigens
The invention provides a bacterium containing a polynucleotide comprising a nucleic acid encoding a heterologous antigen, as well as fusion protein partners. Also provided are vectors for mediating site-specific recombination and vectors comprising removable antibiotic resistance genes.
Owner:ANZA THERAPEUTICS INC +1
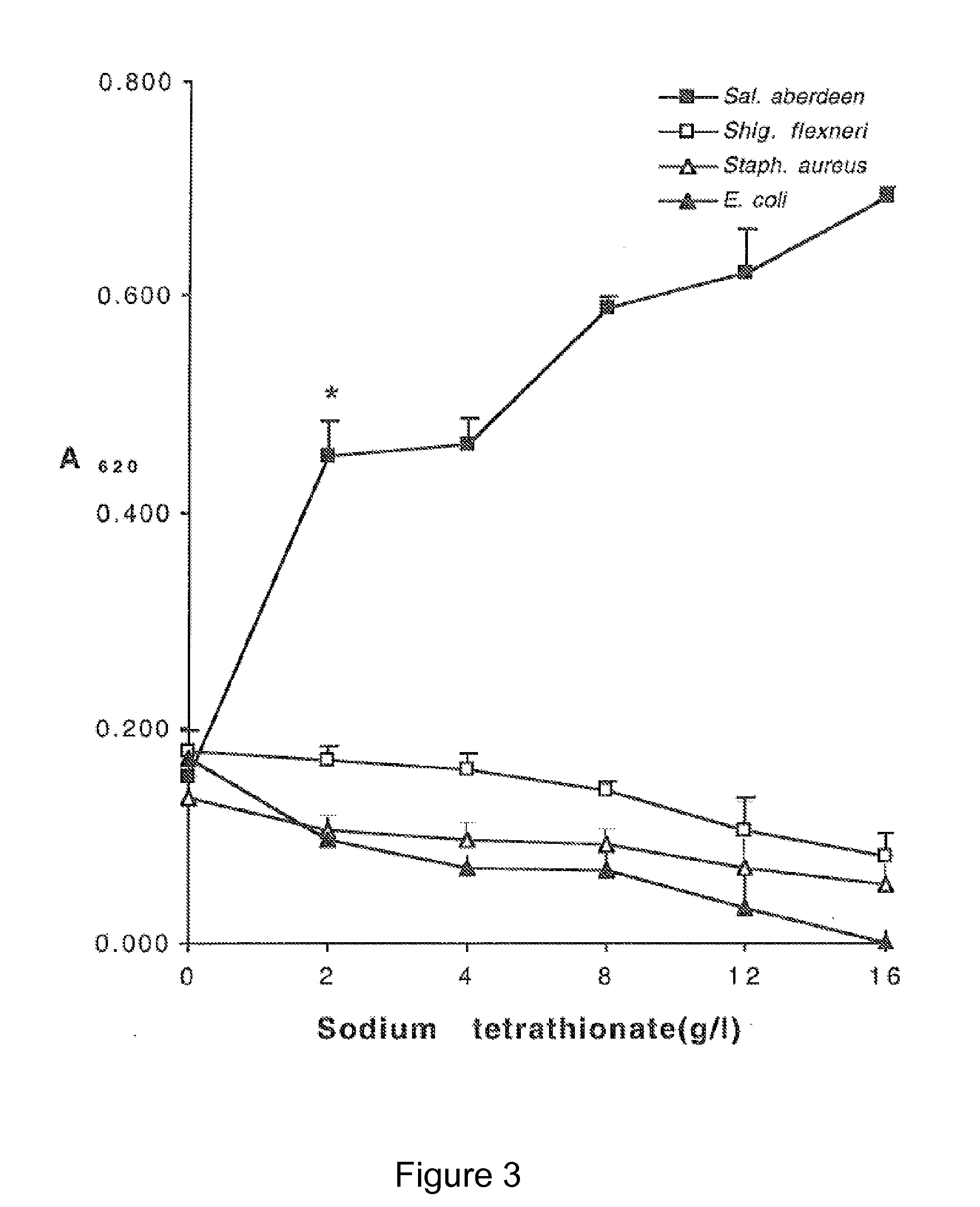
Method for simultaneously detecting salmonella typhimurium, escherichia coli O157:H7 and listeria monocytogenesis
ActiveCN102816850AImprove efficiencySimple and efficient operationMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesPathogenTyping methods
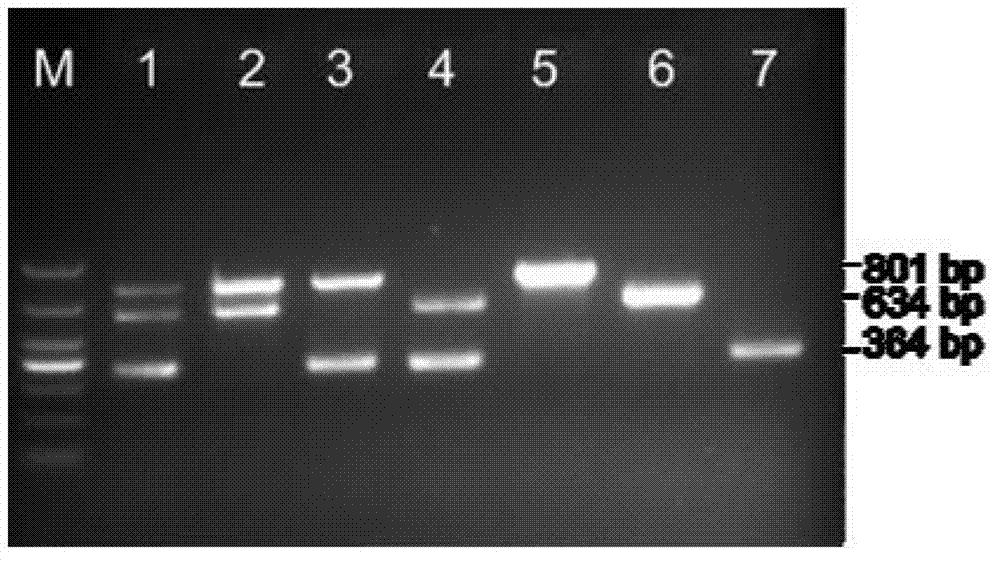
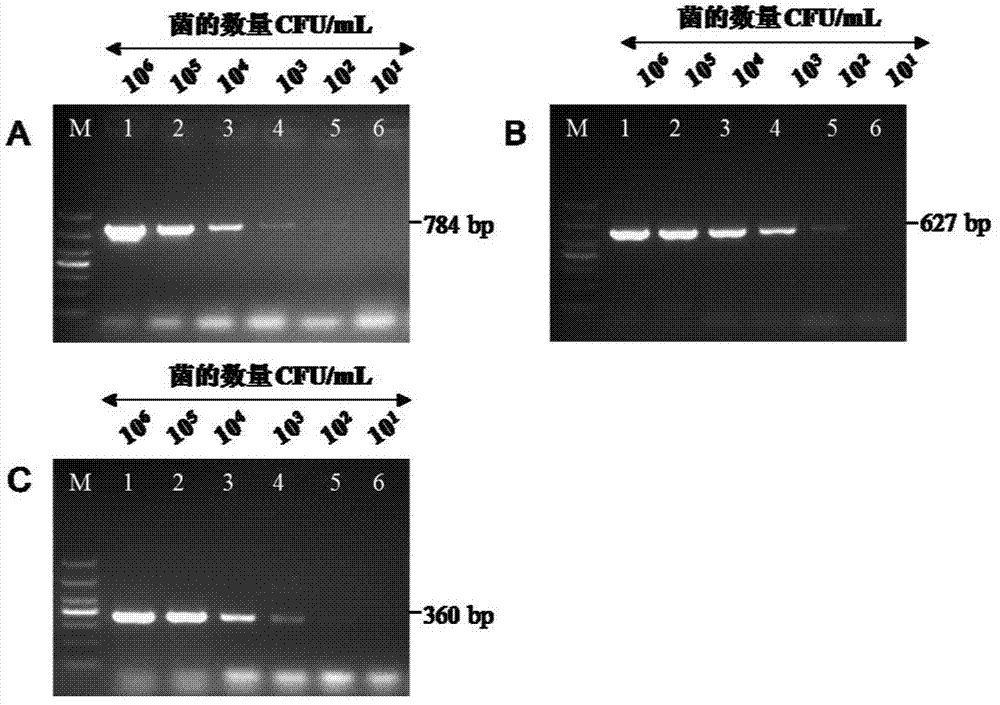
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously and quickly detecting salmonella typhimurium, escherichia coli O157:H7 and listeria monocytogenesis in food. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing nano immunomagnetic particles of the targeted typhimurium, escherichia coli O157:H7 and listeria monocytogenesis so as to capture target bacteria from a detection sample; obtaining the target bacteria by magnetic field separation; treating by adopting propylmercuric bromide azide (PMA) to eliminate the interference of killed bacteria; and finally, extracting DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) to carry out multiple PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection. Compared with a classical bacteria separation and identifying and serological typing method, the method disclosed by the invention is quick and accurate, can be used for only detecting viable bacteria and can be used for simultaneously detecting and identifying the three pathogens.
Owner:WUXI ZODOLABS BIOTECH
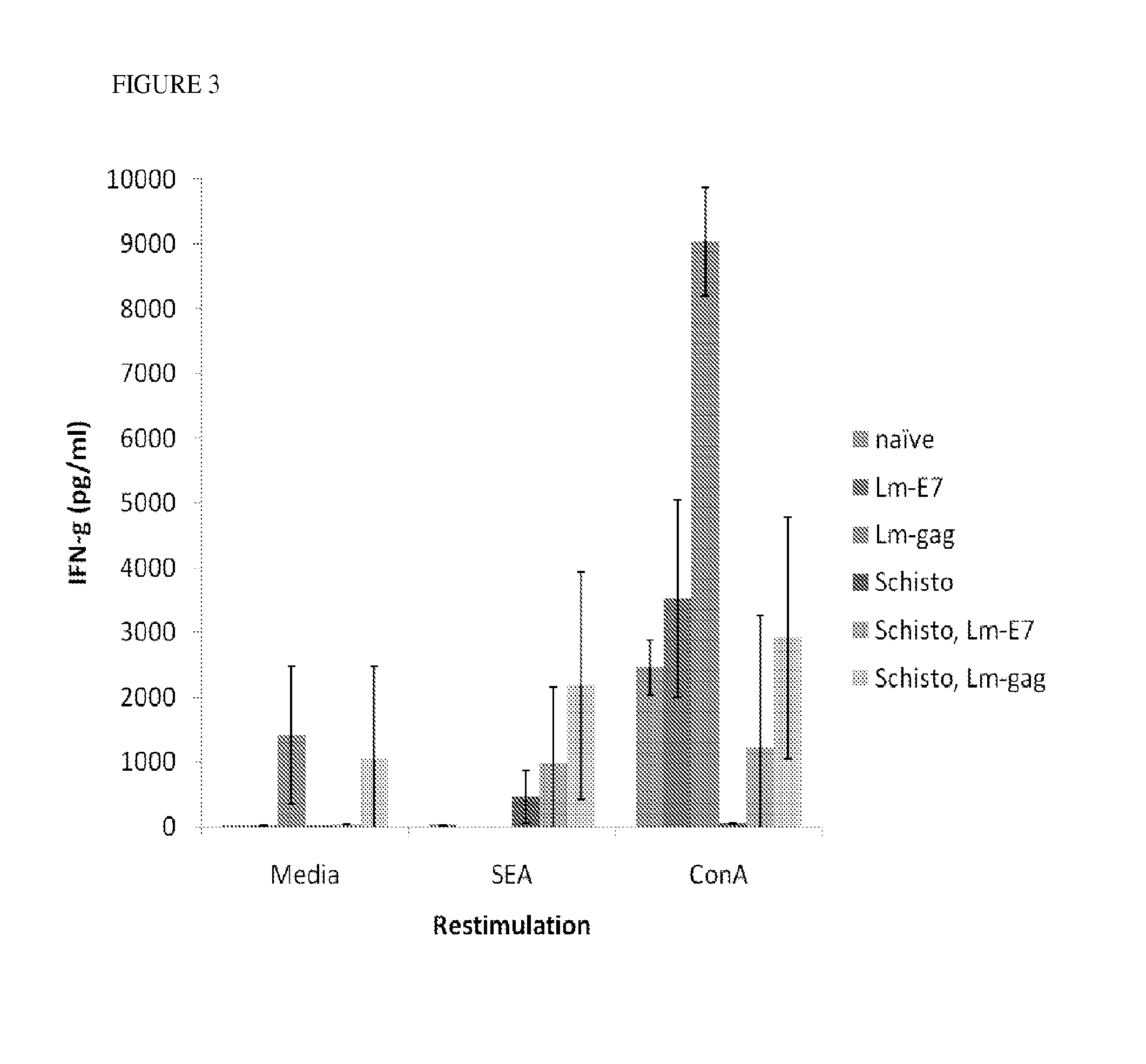
Use of listeria vaccine vectors to reverse vaccine unresponsiveness in parasitically infected individuals
This invention relates to methods of using a Listeria vaccine vector to induce a Th1 immune response in subjects having persistent Th2 immune response profiles.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA +1
Antibiotic resistance free vaccines and methods for constructing and using same
ActiveUS7855064B2Reduce morbidityBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteriaHeterologousHeterologous Antigens
The present invention provides Listeria strains that express a heterologous antigen and a metabolic enzyme, and methods of generating same.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Antibiotic resistance free vaccines and methods for constructing and using same
ActiveUS20080131456A1Reduce morbidityBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteriaHeterologousHeterologous Antigens
The present invention provides Listeria strains that express a heterologous antigen and a metabolic enzyme, and methods of generating same.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
A kind of Lactococcus lactis and the antibacterial peptide produced by the Lactococcus lactis and the application of the antibacterial peptide
InactiveCN102286393ANo inhibitionAntibacterialBacteriaMicroorganism based processesLactobacillusMicroorganism
The invention relates to lactococcus lactis subsp.lactis, antibacterial peptide produced by lactococcus lactis subsp.lactis and the application of antibacterial peptide. In the invention, the collection number of the lactococcus lactis subsp.lactis LLC518 in the General Microorganism Center of China Microorganism Culture Collection Management Committee is CGMCC No. 4584. In the invention, the antibacterial peptide produced by the lactococcus lactis subsp.lactis can restrain micrococcus tetragenus, Bacillus thuringiensis, lactococcus lactis and listeria innocua, particularly, has strong restraint function to L. monocytogenes which can cause serious food poisoning. Thus, the lactococcus lactis subsp.lactis and the antibacterial peptide thereof have active function in food fresh keeping.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Methods and compositions for immunotherapy of cancer
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
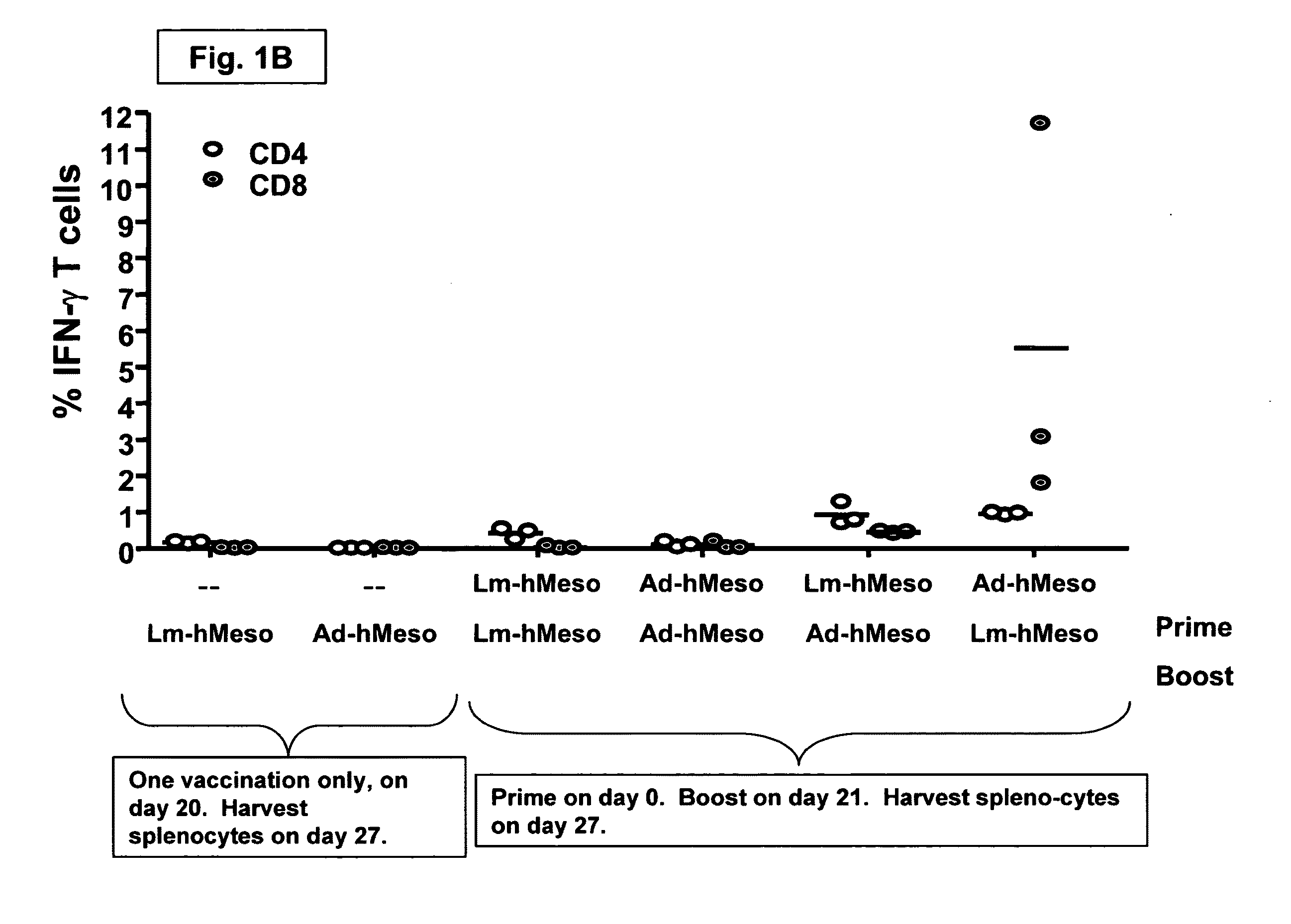
Methods and compositions using Listeria for enhancing immunogenicity by prime boost
Provided herein are prime-boost regimens and materials used therein. The prime-boost regimens enhance the immune response to a target antigen. The vaccines used for boost are comprised of recombinant attenuated metabolically active Listeria that encodes an expressible antigen that is cross-reactive with the target antigen. In some examples, the immune response is a cellular immune response.
Owner:ANZA THERAPEUTICS INC +1
Dual delivery system for heterologous antigens
ActiveUS20140335120A1Tumor rejection antigen precursorsBacteriaHeterologous AntigensOpen reading frame
Provided herein are recombinant Listeria strains expressing a tumor-specific antigenic polypeptide and, optionally, an angiogenic polypeptide wherein a nucleic acid molecule encoding at least one of the polypeptides is operably integrated into the Listeria genome in an open reading frame with a nucleic acid sequence encoding a PEST-containing polypeptide, methods of preparing same, and methods of inducing an immune response, and treating, inhibiting, or suppressing cancer or tumors comprising administering same.
Owner:ADVAXIS
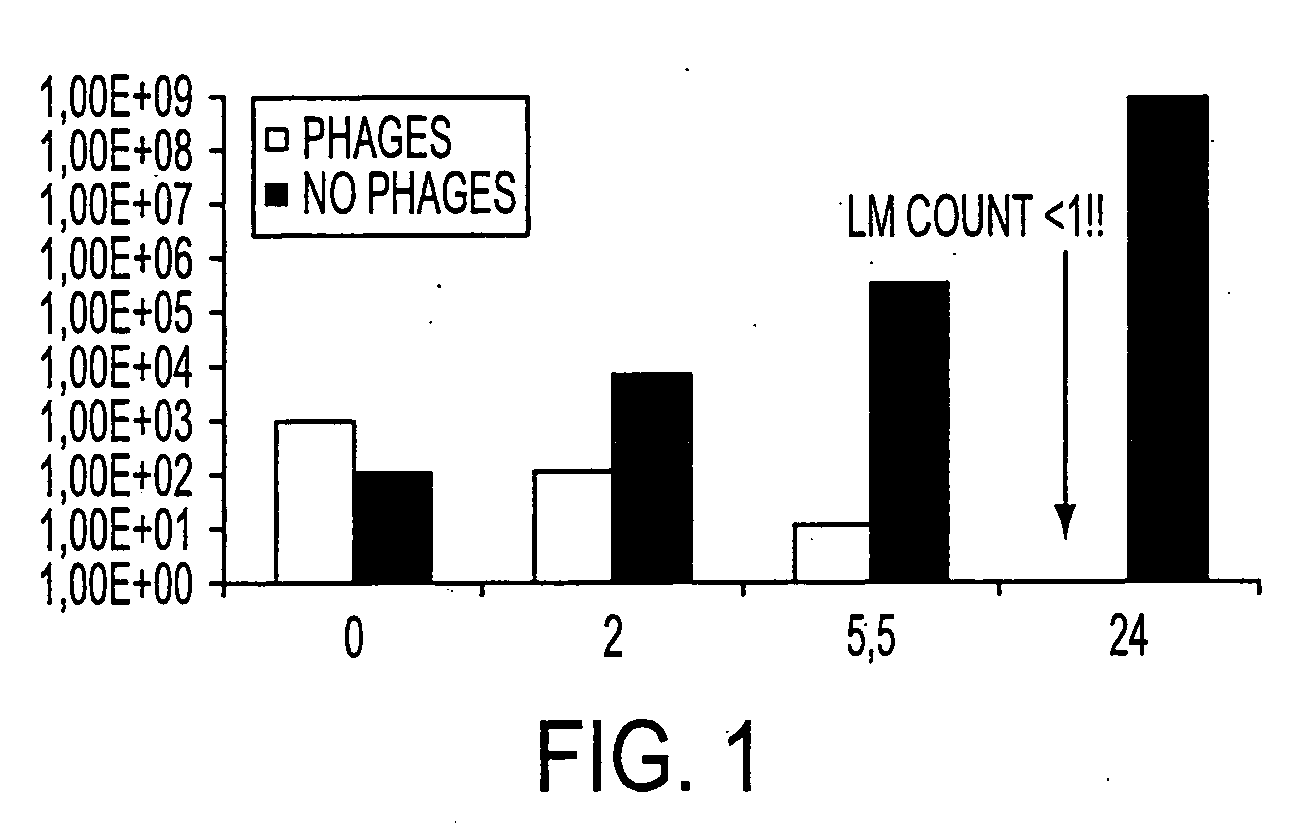
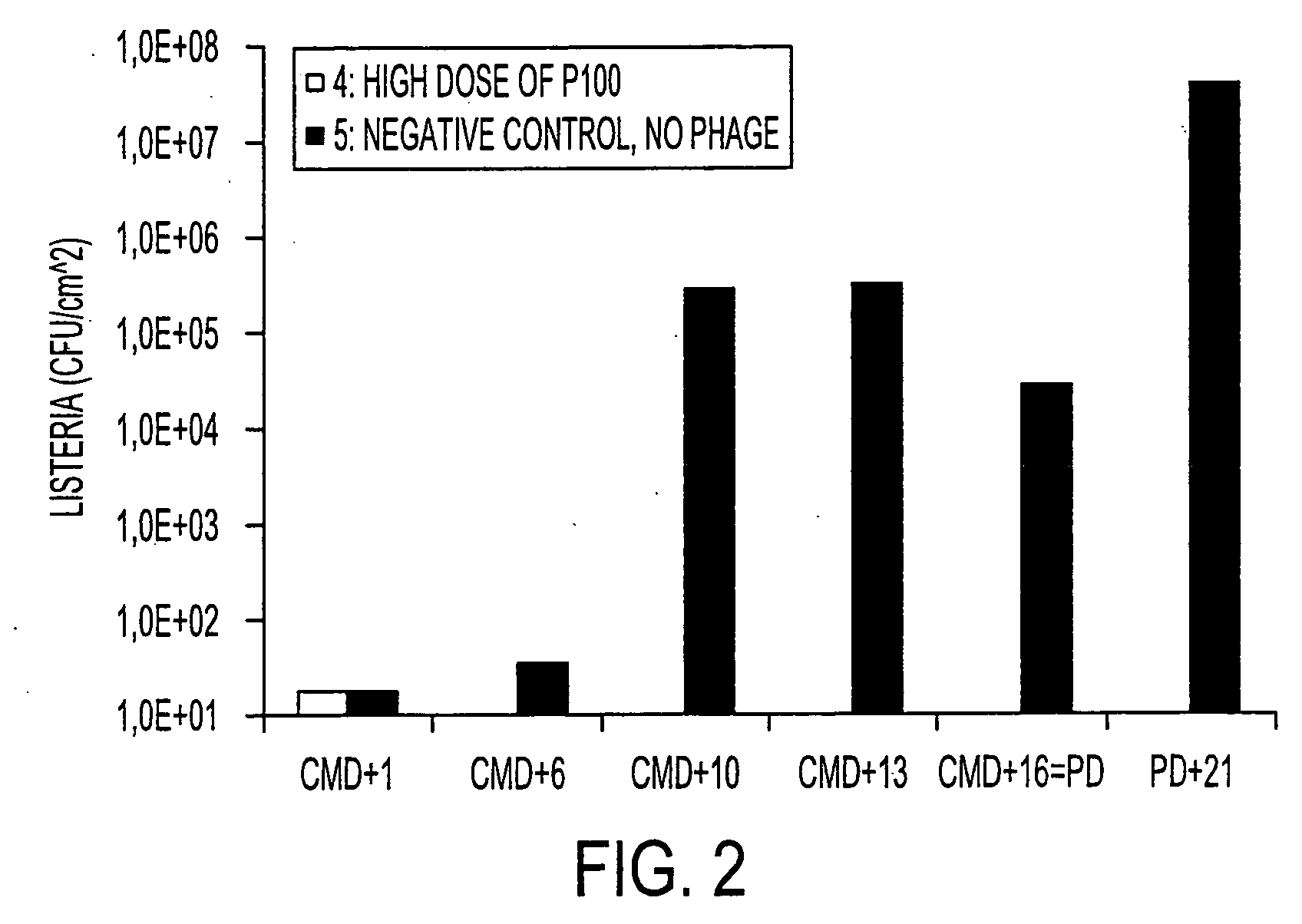
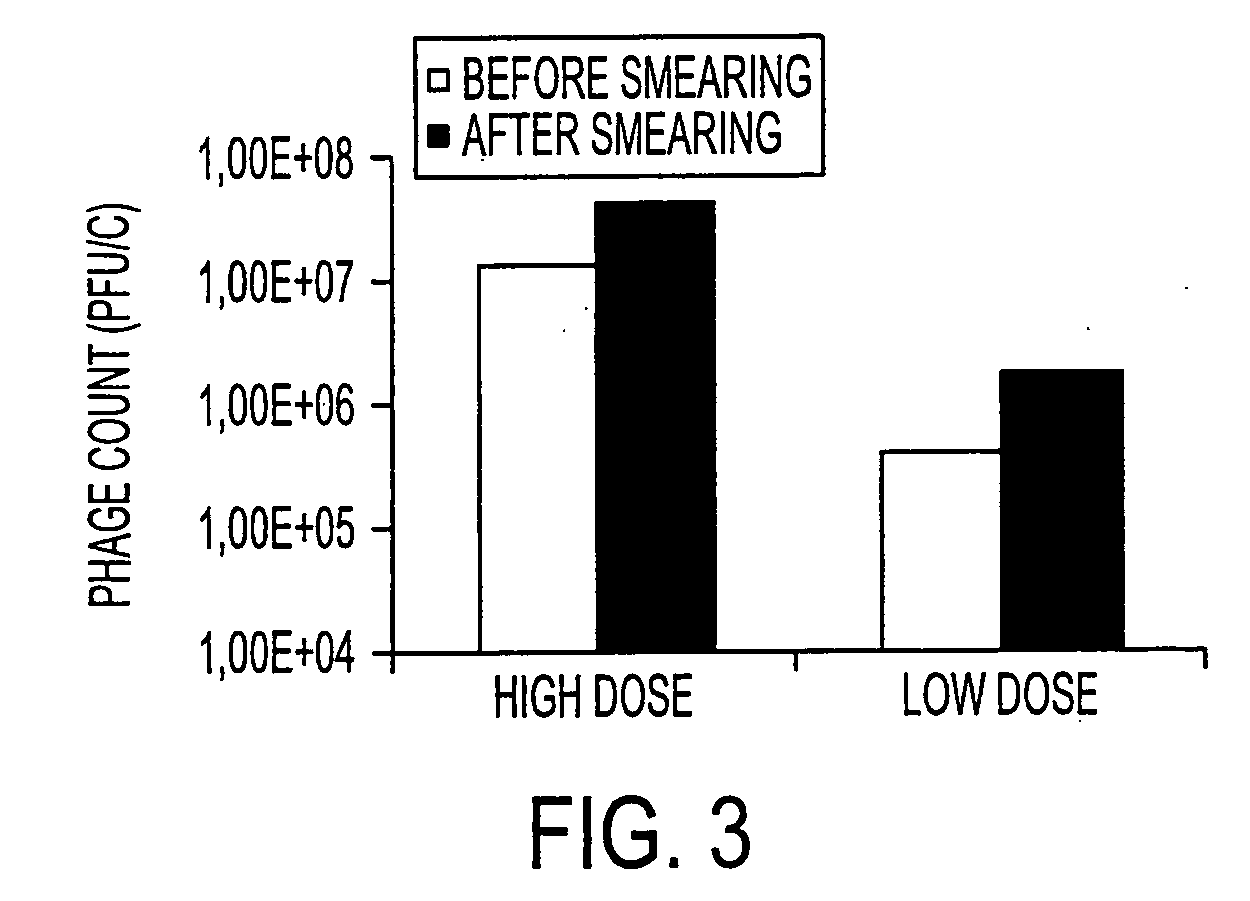
Virulent phages to control listeria monocytogenes in foodstuffs and in food processing plants
ActiveUS20050175594A1Shorten the counting processGrowth inhibitionAntibacterial agentsBiocideBiotechnologyBacteroides
The present invention relates to virulent (lytic) Listeria monocytogenes phage from the Myoviridae family, preferably P100, alone or in combination with other virulent phages. P100 and the endolysin from P100 can be administered to food products, to the components that will be added to food products, and / or to the infrastructure of the food processing plants within which such food products are processed, or the containers or wraps in which such foods are stored and / or shipped, in order to reduce Listeria monocytogenes contamination. P100 can also be used in the present invention to identify Listeria monocytogenes bacteria present on (or within) foodstuffs, as well as those Listeria monocytogenes bacteria present in the equipment or the general environment of the food processing plants in which the foodstuffs are being processed and in animals infected with Listeria monocytogenes. The phage and the endolysin of the present invention can also be used to treat animals infected with Listeria monocytogenes. P100 will kill the bacteria that are within its host range with great efficiency and will propagate to high titer thereon. P100 can be combined with other lytic phage, and / or with other antimicrobial agents to reduce or eliminate Listeria.
Owner:EBI FOOD SAFETY
Antibiotic resistance free Listeria strains and methods for constructing and using same
ActiveUS7858097B2Reduce morbidityBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteriaHeterologousHeterologous Antigens
The present invention provides Listeria strains that express a heterologous antigen and a metabolic enzyme, and methods of generating same.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Antimicrobial composition for pre-harvest and post-harvest treatment of plants and animals
ActiveUS20050191394A1Reduce Microbial ContaminationMinimize growth and spreadHeavy metal active ingredientsFood preservationEscherichia coliFood additive
An antimicrobial, anti-bacterial processing aid, food additive and food ingredient is provided to inhibit cellular growth of known pathogenic, indicator and spoilage organisms, such as salmonella, stahphylococcus, listeria, e coli, and the like. The antimicrobial agent of the present invention is useful as a treatment for animal feed, a treatment for pre-harvest and post-harvest processing of foodstuffs, a treatment for cooked food subject to airborne contaminants and many other conditions in need of disinfectants and sanitizers. One of the primary benefits of the antimicrobial agent is that it inhibits the growth of bacteria that have become antibiotic resistant.
Owner:CMS TECH +1
Dual delivery system for heterologous antigens
Provided herein are recombinant Listeria strains expressing a tumor-specific antigenic polypeptide and, optionally, an angiogenic polypeptide wherein a nucleic acid molecule encoding at least one of the polypeptides is operably integrated into the Listeria genome in an open reading frame with a nucleic acid sequence encoding a PEST-containing polypeptide, methods of preparing same, and methods of inducing an immune response, and treating, inhibiting, or suppressing cancer or tumors comprising administering same.
Owner:ADVAXIS
Methods and compositions using listeria for adjuvant treatment of cancer
InactiveUS9161974B2Easy to adaptBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteria material medical ingredientsRegimenPrime boost
Provided herein are prime-boost regimens and materials used therein. The prime-boost regimens enhance the immune response to a target antigen. The vaccines used for boost are comprised of recombinant attenuated metabolically active Listeria that encodes an expressible antigen that is cross-reactive with the target antigen. In some examples, the immune response is a cellular immune response.
Owner:ADURO BIOTECH
Antibiotic resistance free listeria strains and methods for constructing and using same
ActiveUS20100291140A1Reduce morbidityBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteriaHeterologousHeterologous Antigens
The present invention provides Listeria strains that express a heterologous antigen and a metabolic enzyme, and methods of generating same.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Methods and compositions using listeria for enhancing immunogenicity by prime boost
Provided herein are prime-boost regimens and materials used therein. The prime-boost regimens enhance the immune response to a target antigen. The vaccines used for boost are comprised of recombinant attenuated metabolically active Listeria that encodes an expressible antigen that is cross-reactive with the target antigen. In some examples, the immune response is a cellular immune response.
Owner:ANZA THERAPEUTICS INC +1
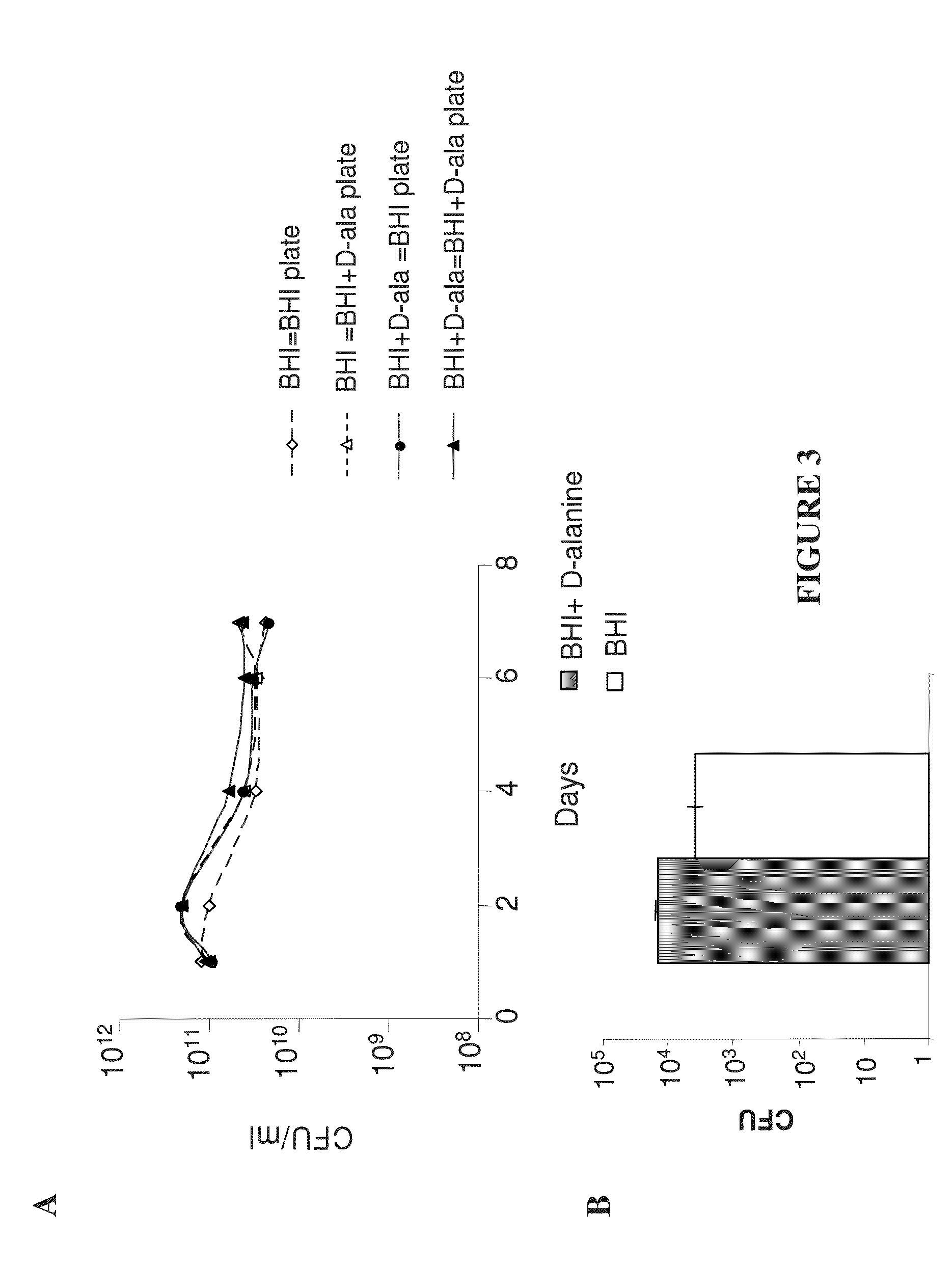
Methods of inducing immune responses through the administration of auxtrophic attenuated dal/dat double mutant Listeria strains
The present invention includes a method of eliciting a T-cell immune response to an antigen in mammal. The method of eliciting a T-cell immune response includes administering mammal an auxotrophic attenuated strain of listeria which expresses the antigen. The auxotrophic attenuated strain of listeria includes a mutation in at least one gene whose protein product is essential for growth of bacteria.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Compositions and methods for the rapid growth and detection of microorganisms
InactiveUS20110159515A1Efficient and rapid growthAvoid recoveryBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementPathogenic microorganismTest sample
The invention relates to assay methods for use in detecting specific materials such as core oligosaccharides derived from microorganisms, particularly pathogenic microorganisms, in a test sample. The invention further relates to compositions and methods for the rapid growth of such microorganisms enabling detection of same significantly earlier than is currently possible. In particular embodiments the invention is directed towards the rapid growth and / or detection of Salmonella, Shigella or Listeria.
Owner:SOLUS SCIENTIFIC SOLUTIONS LIMITED
Methods to prevent vertical transmission of infectious diseases
InactiveUS20080269205A1Prevent vertical transmissionPrevent the spread of diseaseAntiviralsRadiation therapyEscherichia coliMonilinia laxa
The present invention presents a method of preventing vertical transmission of an infectious disease comprising: (a) applying a photosensitizing composition to host tissues of birth canal of a mother during the intrapartum period; and (b) applying light to the host tissues after the step (a) at a wavelength absorbed by the photosensitizing composition so as to inhibit or eliminate infectious disease microorganisms that come into contact with the host tissues. The infectious disease may be caused by human immunodeficiency virus type 1, hepatitis B virus, hepatitis C virus, Group B Streptococcus, cytomegalovirus, Listeria monocytogenes, Chiamydia trachomatis, Escherichia coli, herpes simplex virus, Epstein-Barr virus, Toxoplasma gondii, human papilloma virus, and Candida.
Owner:ONDINE INT
Engineered listeria and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20120121643A1Improve survivalIncreasing expression and secretionBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHeterologous AntigensNucleotide
The invention provides a bacterium containing a polynucleotide comprising a nucleic acid encoding a heterologous antigen, as well as fusion protein partners. Also provided are vectors for mediating site-specific recombination and vectors comprising removable antibiotic resistance genes.
Owner:ANZA THERAPEUTICS INC
Methods for specific rapid detection of pathogenic food-relevant bacteria
InactiveUS20050123946A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesStaphylococcus aureus
The invention relates to a method for the detection of pathogenic food-relevant bacteria, particularly to a method for the simultaneous specific detection of bacteria of the genus Listeria and the species Listeria monocytogenes by in situ-hybridization as well as to a method for the specific detection of bacteria of the species Staphylococcus aureus by in situ-hybridization as well as to a method for the specific detection of bacteria of the genus Campylobacter and the species C. coli and C. jejuni by in situ-hybridization as well as the corresponding oligonucleotide probes and kits, with which the inventive methods may be carried out.
Owner:VERMICON
Recombinant listeria vaccine strains and methods of using the same in cancer immunotherapy
ActiveUS20160367650A1Reduce severityReduce needOrganic active ingredientsViral antigen ingredientsListeria booriaeVaccine strain
The present invention provides methods of treating, protecting against, and inducing an immune response against a human papillomavirus-associated oropharyngeal tumor or cancer, comprising the step of administering to a subject a recombinant Listeria strain expressing a human papillomavirus antigen.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Analytical method of components of fatty acid contained in listeria cells
InactiveCN101936960ABreaking the limits of taxonomyBreak the limitsComponent separationCytochemistryFatty acid
The invention relates to an analytical method of components of fatty acids contained in listeria cells, in particular to a method for carrying out bacteria classification by adopting a cell chemical analysis method, belonging to the technical field of biological engineering. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: rejuvenating listeria; respectively separating and purifying the listeria by using an OXA agar plate and a trypticase soy yeast extract agar plate; culturing the listeria of a single typical colony, and preparing into a bacterial suspension; carrying out inactivation processing by using formaldehyde; averagely filling the bacterial suspension processed by the formaldehyde into centrifuge tubes for washing; carrying out methyl esterification by using a mixed solution of hydrochloric acid and the formaldehyde; and carrying out GC-MS (Gas Chromatograph-Mass Spectrometer) analysis on the prepared fatty acids. The method can not only break through the limit of the traditional bacterial taxonomy and reduce the errors brought about by anthropic factors on the traditional morphological taxonomy, but also provide a strong and powerful tool for the classification and the identification of new strains and virus types; and in addition, the method can be used for identifying the listeria from other bacteria and foods.
Owner:HUBEI INSPECTION & QUARANTINE TECH CENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com