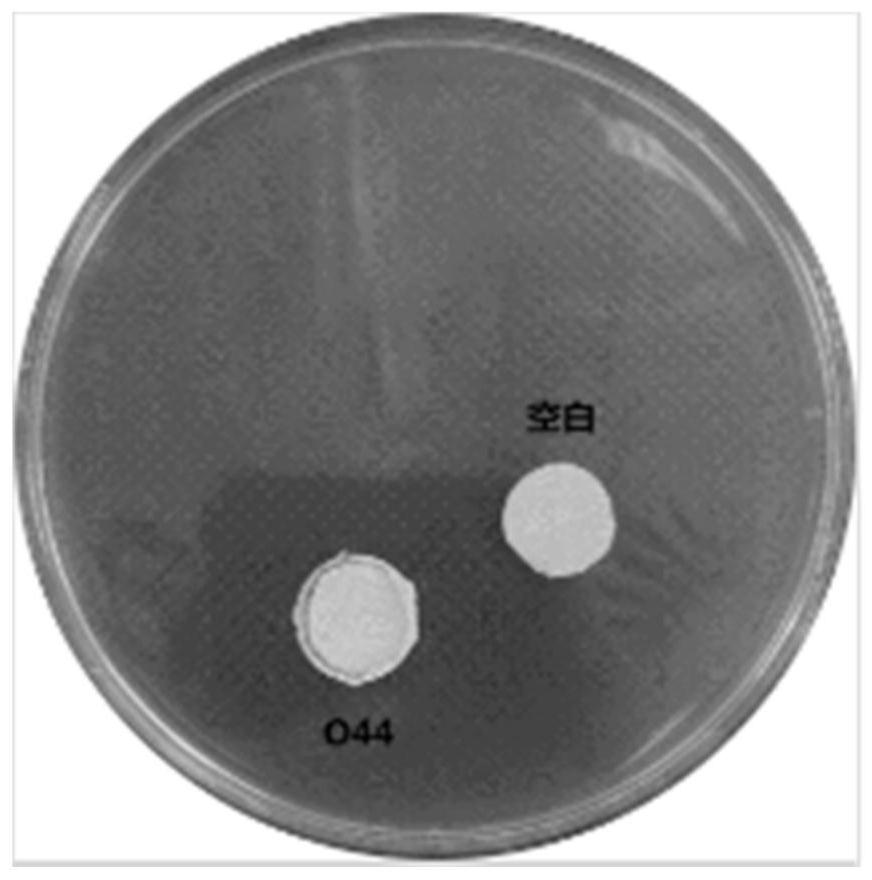
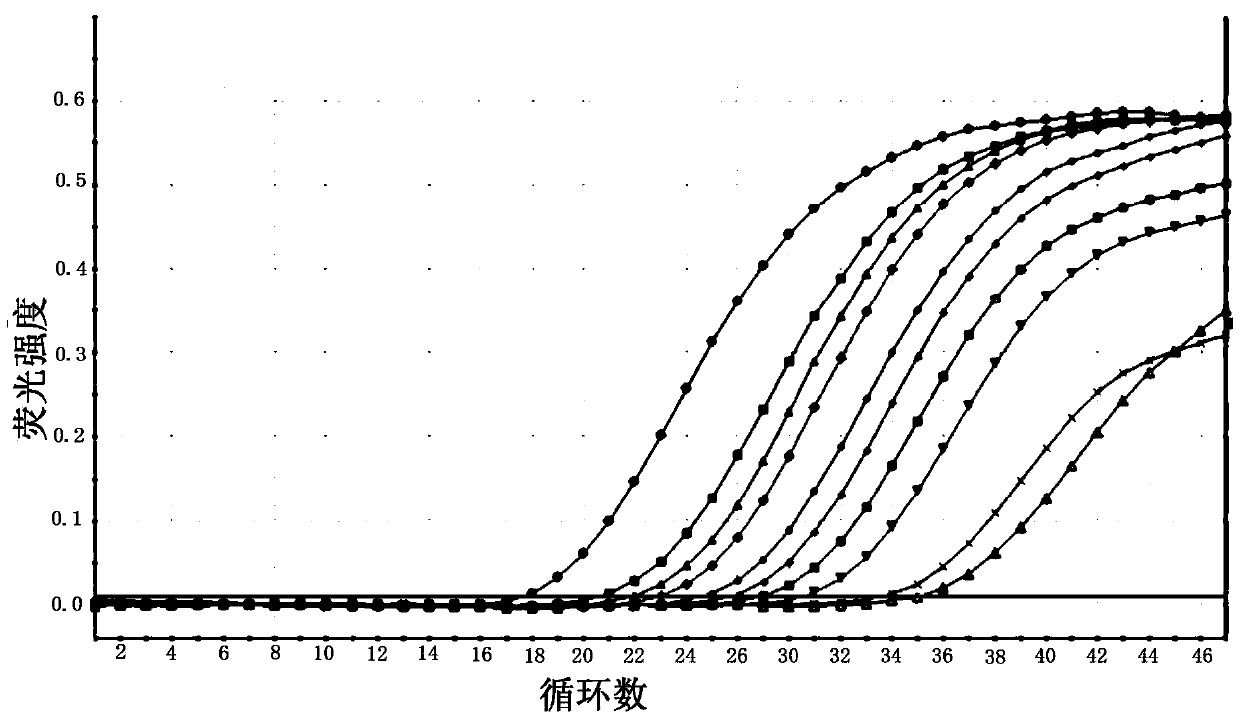
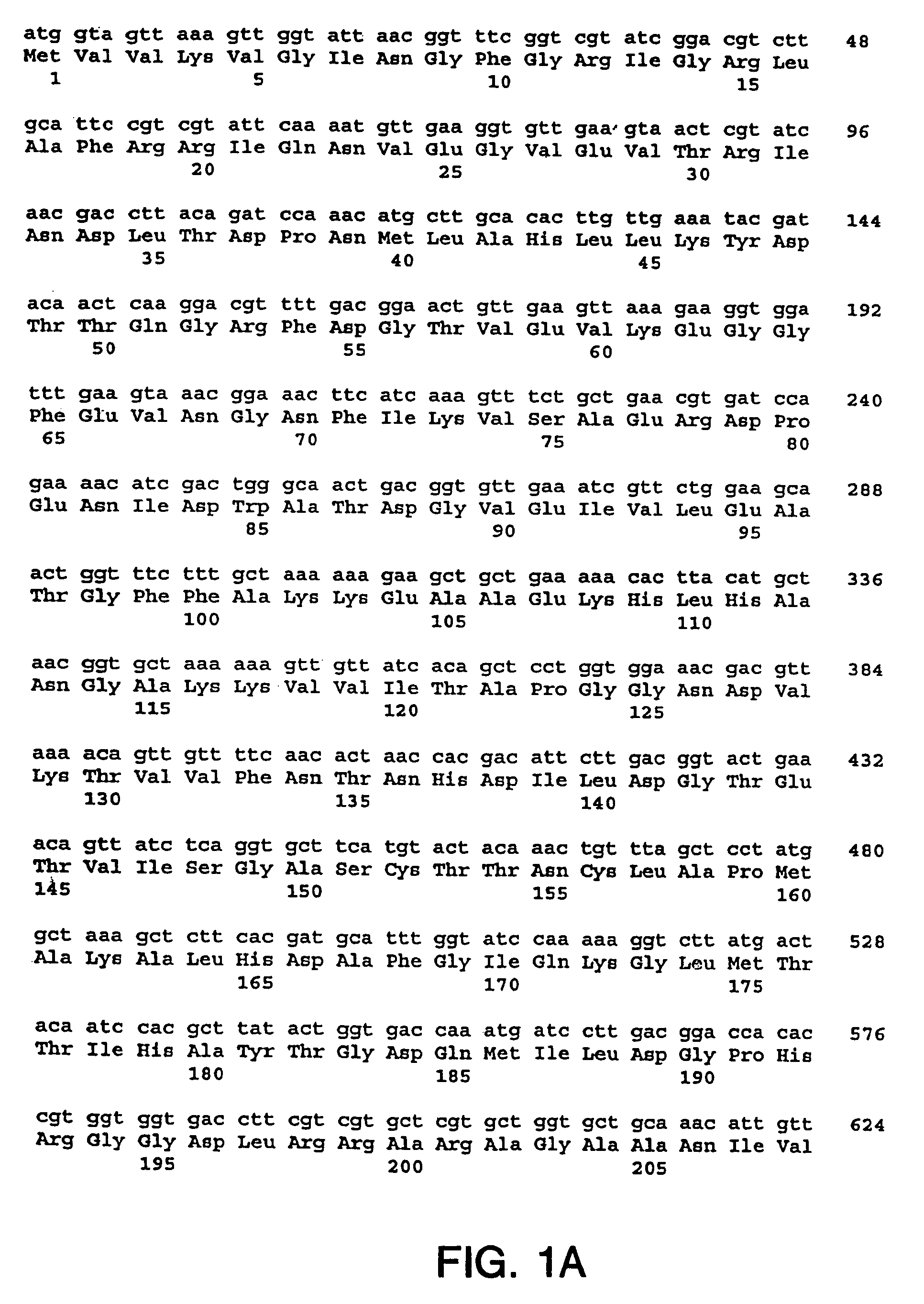
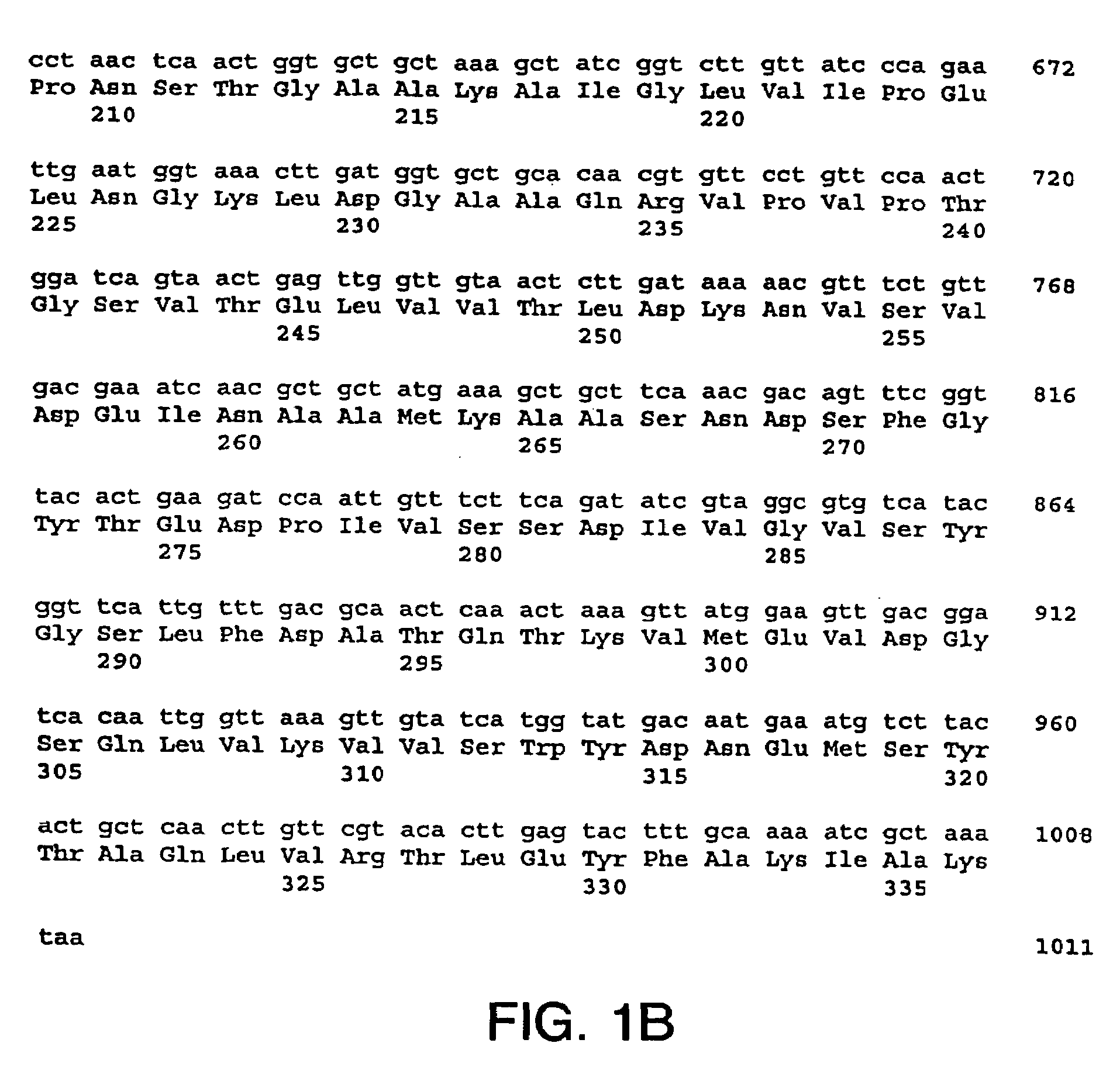
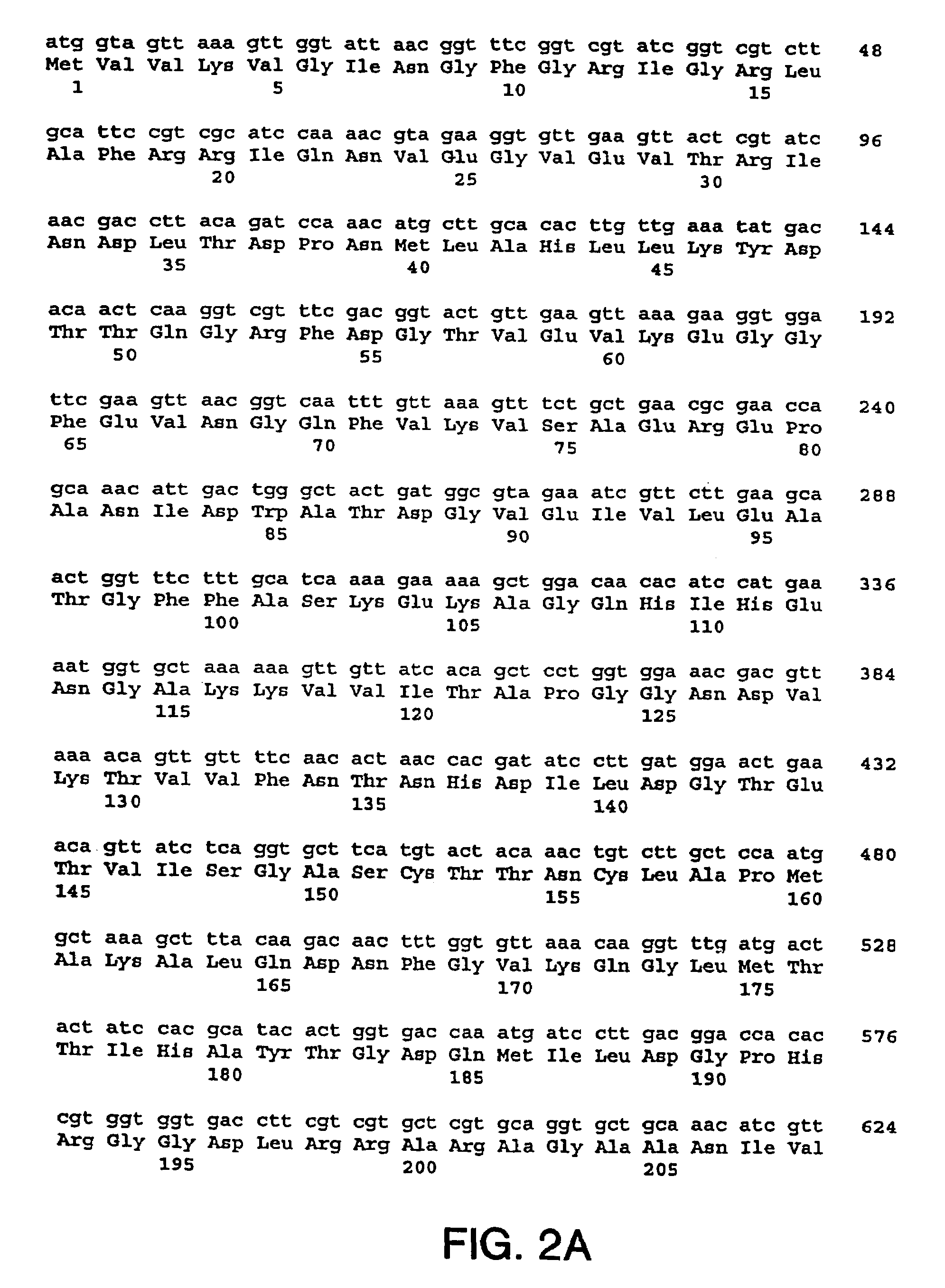
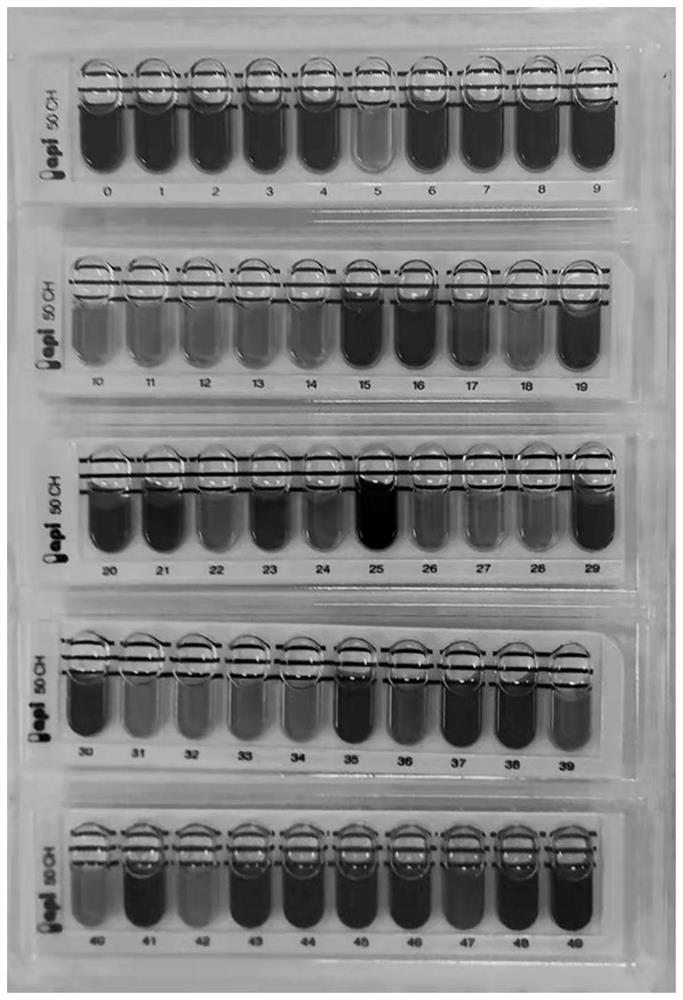
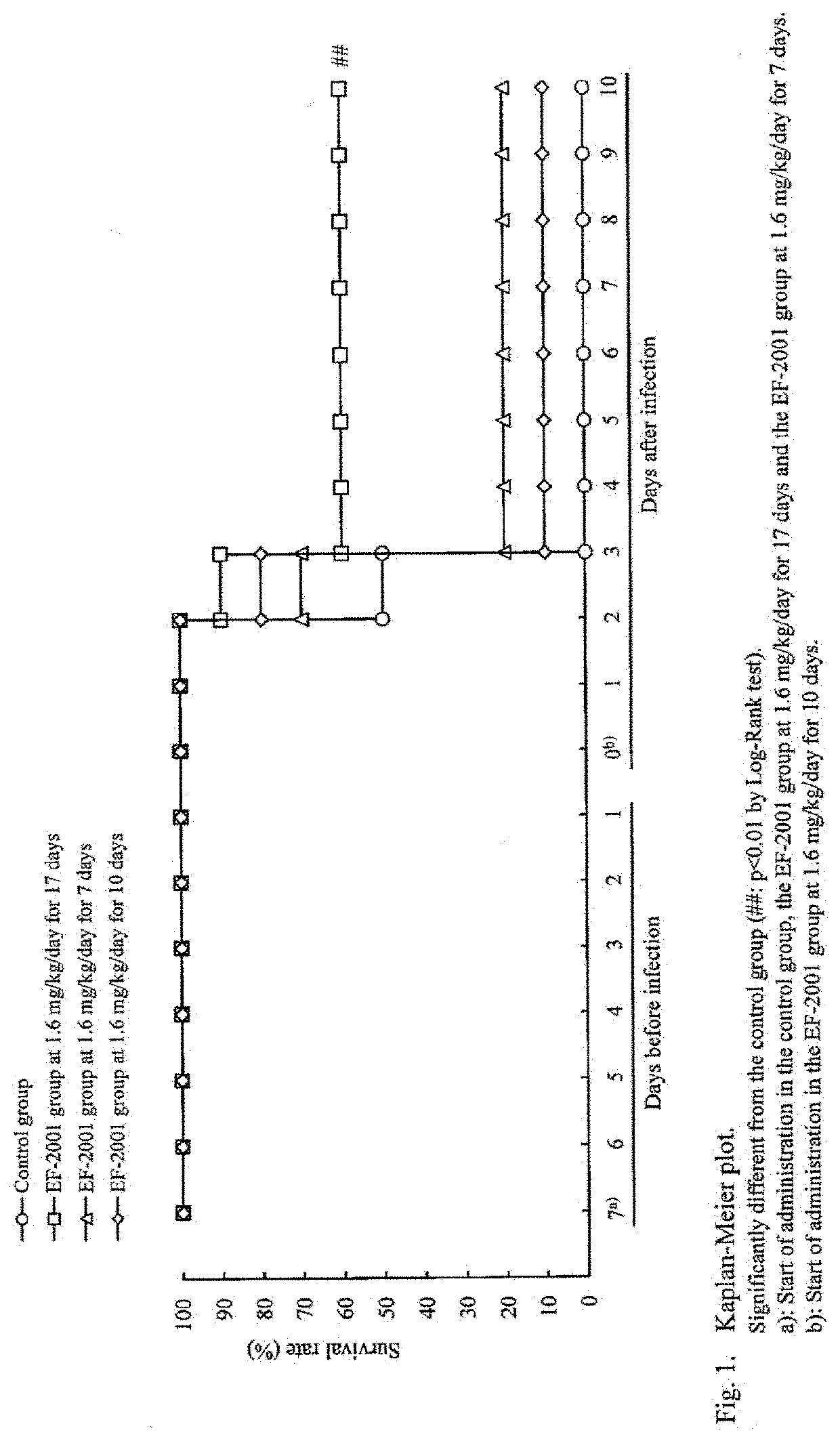
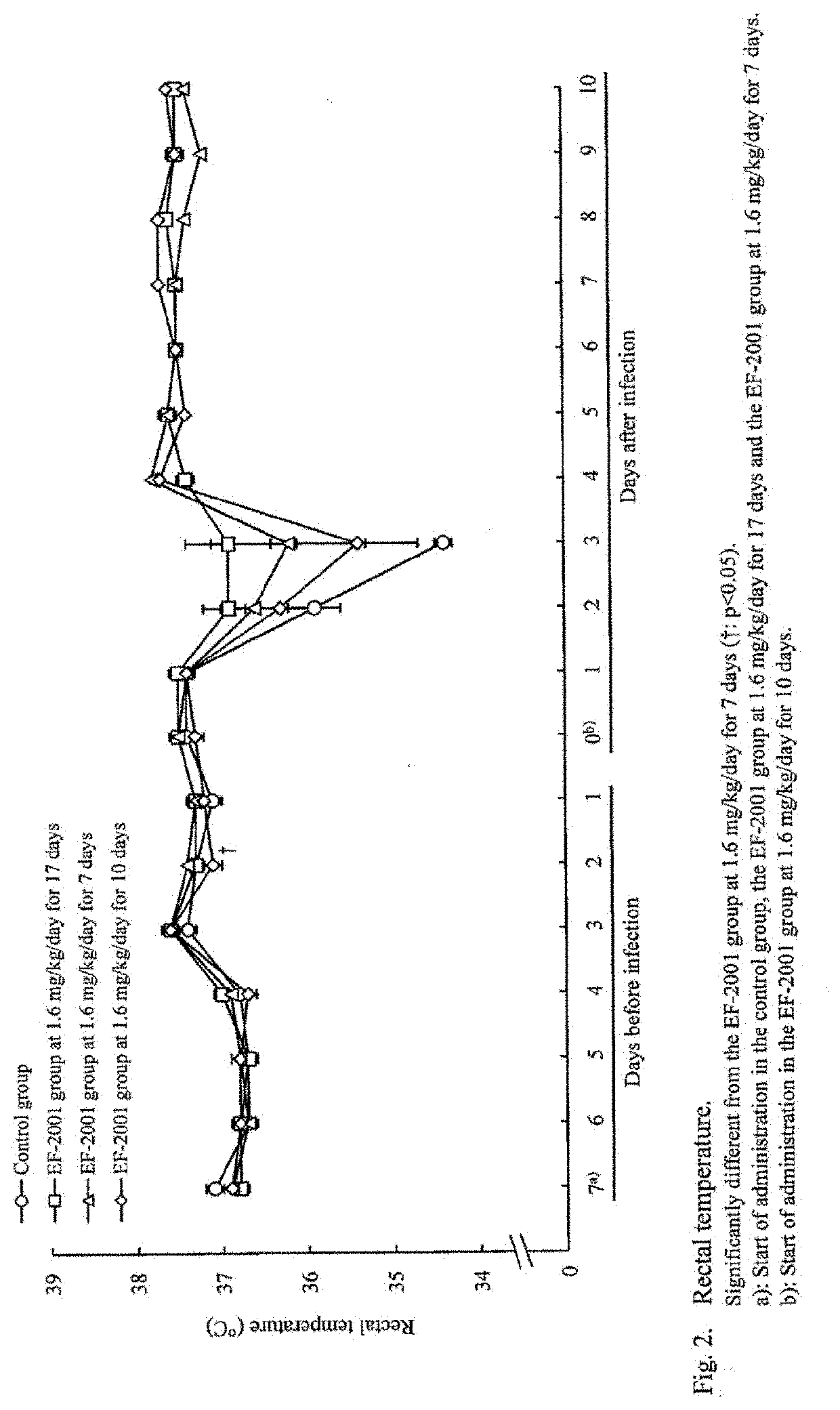
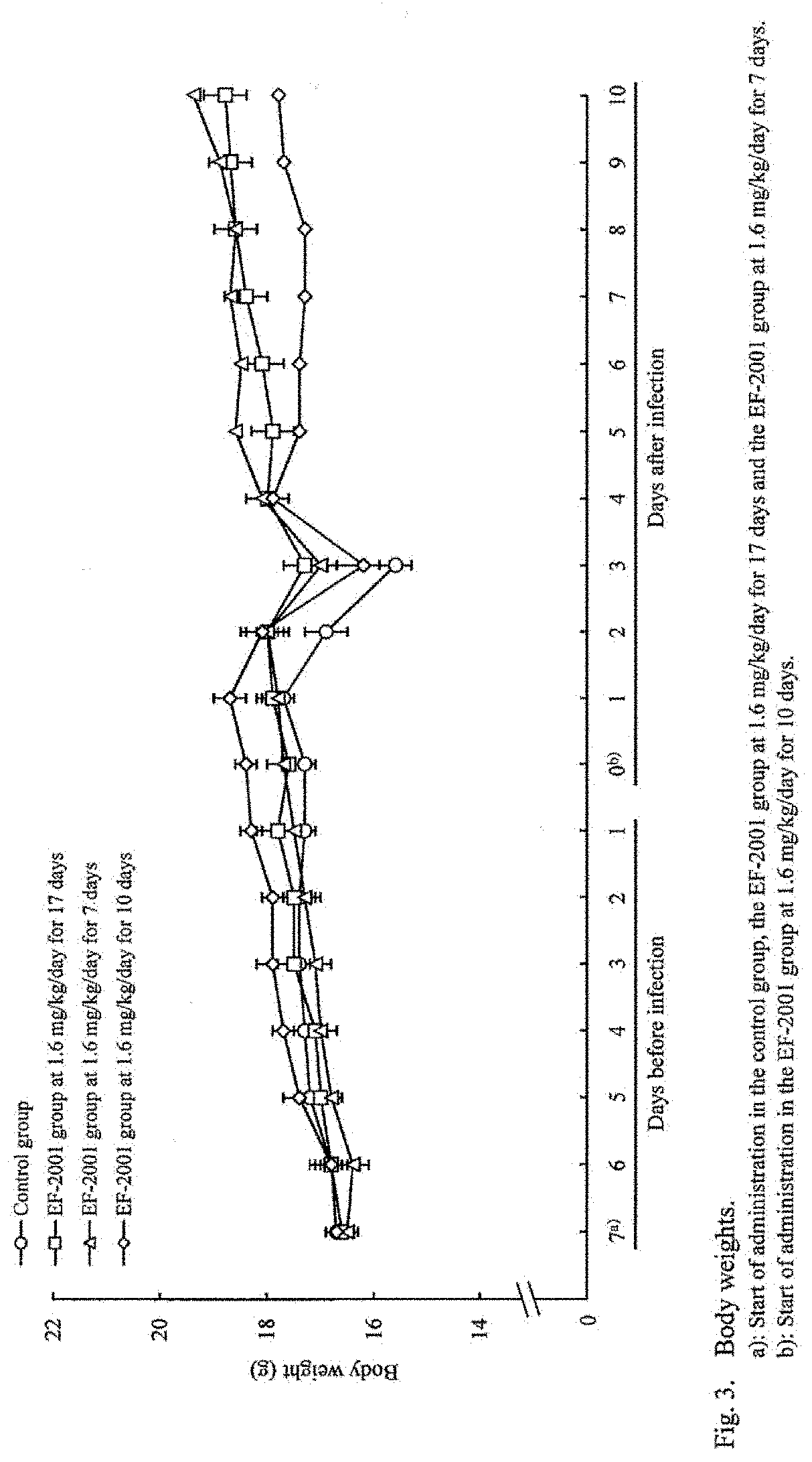
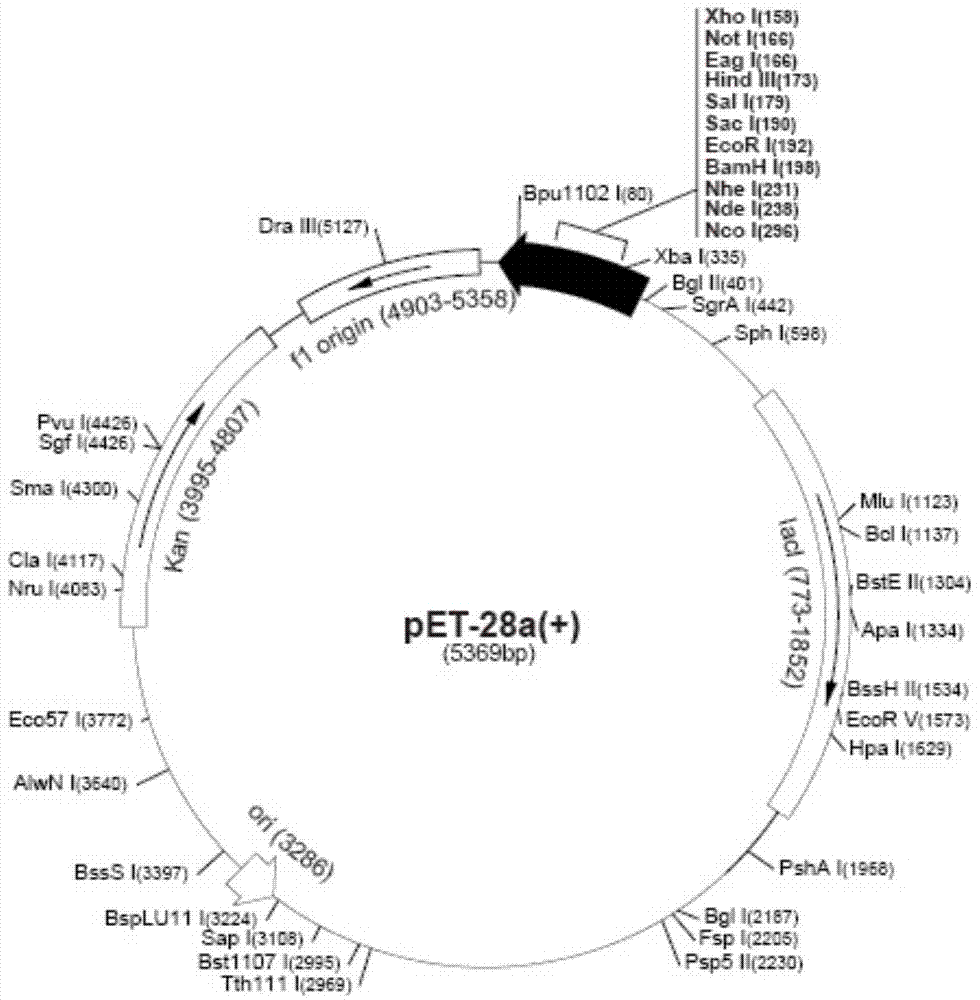
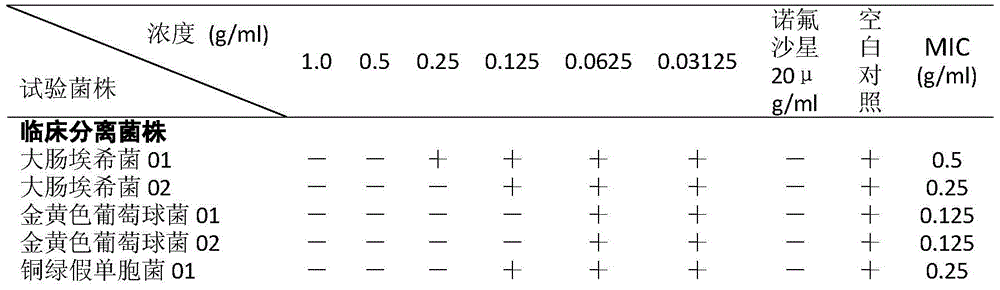
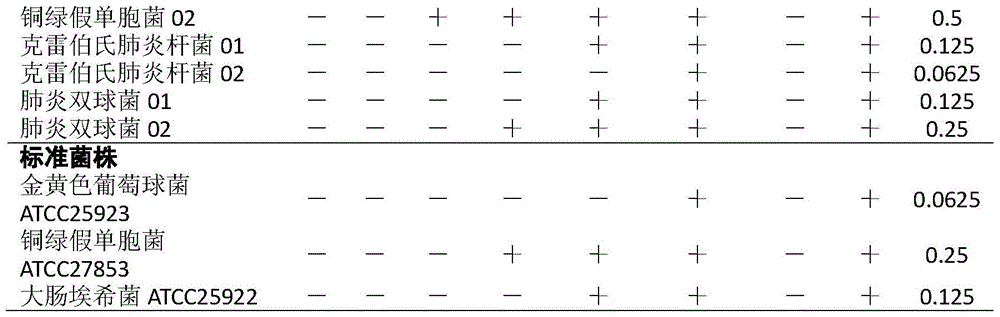
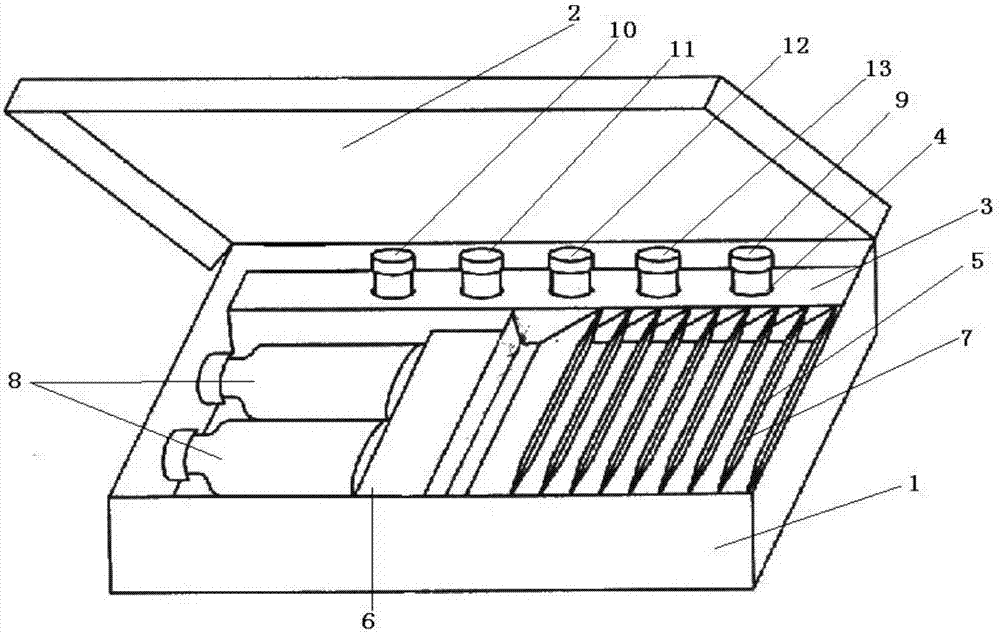
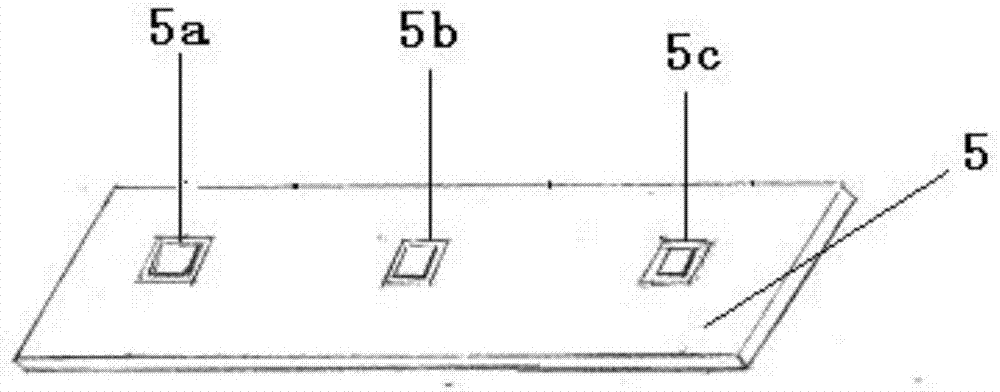
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
41 results about "Streptococcus infection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Infections with bacteria of the genus Streptococcus.
Tilapia immune potentiator and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a tilapia immune potentiator and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of an aquatic compound feed additive. The preparation method is characterized by comprising the following steps: fully mixing curcumin, glutamine, betaine and a carrier; and crushing the components into dry powder. The tilapia immune potentiator has the advantages of stable raw material source, simple preparation process, wide material selection range and low cost; starting from an immune mechanism of fish, Chinese herbal medicines and a western medicine-glutamine dipeptide are supplemented in the immune potentiator; and by means of combination of the traditional Chinese medicines and the western medicine, immunity of the fish is improved. By utilizing the tilapia immune potentiator, the immunity and oxidation resistance of the fish are improved, the capability of tilapia on resisting pathogenic streptococcus infection is strengthened, and growth of the tilapia is promoted.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI +2
Kit and process for PCR amplification detecting type 2 pig streptococcus virulence gene
InactiveCN101020929AEasy diagnosisConvenient researchMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationVirulent characteristicsStreptococcus infection
The (Streptococcus suis Serotype 2 (SS2) virulence gene PCR amplification kit includes a SS2DNA contrast template, a PCR amplification detecting reagent, an agarose gel electrophoresis reagent and a DNA gradient standard. The PCR amplification detecting process includes the measurement of 7 important SS2 genes, diagnosing Streptococcus infection and SS2 infection based on whether to amplify specific Streptococcus gene, specific SS2 gene and 5 relevant important SS2 virulence genes, and predicting the virulence, invasiveness trend and disease prognosis fast and early. The present invention is favorable to the clinical diagnosis of borderline case and early warning, and is hopeful to be applied in emergency detection of human SS2 infection, etc.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CENT FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION
Care solution for cleaning nasal cavity and preparation method of care solution
ActiveCN103735581AReduce inhibitionWeak tastePharmaceutical non-active ingredientsRespiratory disorderNasal cavityStreptococcus infection
The invention discloses a care solution for cleaning a nasal cavity and a preparation method of the care solution. The care solution is prepared from 5,000 parts of traditional Chinese medicine distillate, 0.1-2 parts of preservatives, 1-100 parts of glyceryl polymethacrylate, 20-100 parts of tween 80, 30-80 parts of sodium chloride, 20-60 parts of a pH conditioning agent and 4658-4928.9 parts of purified water. The osmotic pressure of the care solution is 280-310mosm / Kg, and the pH value is 5.5-7.0. The preparation method of the care solution mainly comprises the following steps: by taking one or combination of houttuynia cordata, mint, honeysuckle and radix angelicae as raw materials, carrying out steam distillation to obtain the traditional Chinese medicine distillate; matching with auxiliary materials, and then filtering and carrying out split charging, so as to obtain the care solution. The solution disclosed by the invention has a strong inhibiting effect on nasal common microbe streptococcus infection, staphylococcus, bacillus influenza, influenza viruses and rhinoviruses, and can achieve the target of preventing rhinitis infection and recurrence.
Owner:刘少华
Group B streptococcus antigens
ActiveUS7914794B2Antibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsStreptococcus infectionMicrobiology
Group B streptococcus (GBS) proteins and polynucleotides encoding them are disclosed. Said proteins are antigenic and therefore useful vaccine components for the prophylaxis or therapy of streptococcus infection in animals. Also disclosed are recombinant methods of producing the protein antigens as well as diagnostic assays for detecting streptococcus bacterial infection.
Owner:ID BIOMEDICAL CORP LAVAL
Application of streptococcus pneumoniae protein to resisting infection of S. pneumoniae
ActiveCN109456393AIncrease infectionReduced Colonization Protection ExperimentAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsPneumonia mrsaStreptococcus mitis
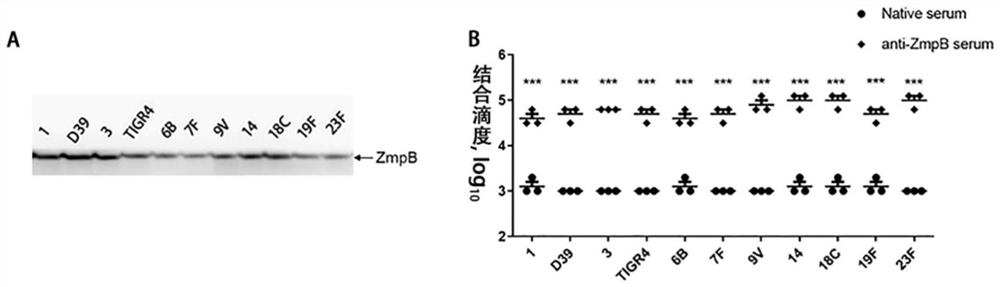
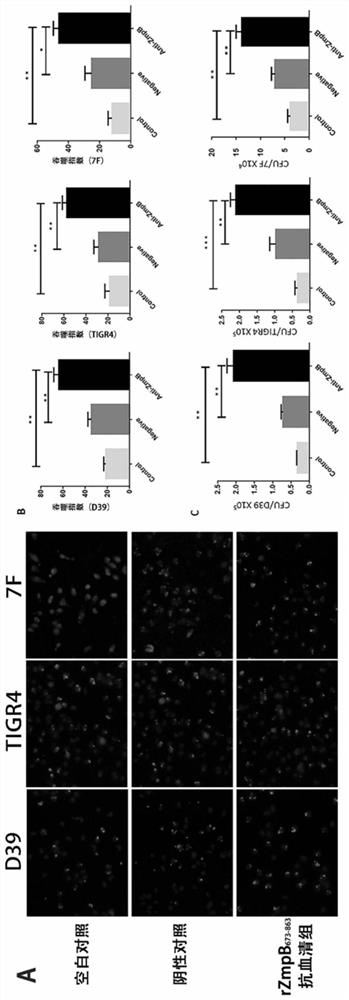
The invention provides application of S. pneumoniae protein to resisting infection of S. pneumoniae. The endopeptidase O (PepO) of S. pneumoniae is a subcutaneous immunologic adjuvant, and the prepared S. pneumoniae protein vaccines have the good protection effects on resisting infection of S. pneumoniae through mixing and fusing expression of the subcutaneous immunologic adjuvant and 673rd to 863rd amino acid peptide fragment of zinc metal protease B (ZmpB).
Owner:CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Group B streptococcus nucleic acid assay kit based on PCR (polymerase chain reaction) fluorescent probe method
InactiveCN105368946AEasy to operateSimple methodMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesForward primerFluorescence
The invention provides a group B streptococcus nucleic acid assay kit based on a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) fluorescent probe method. The group B streptococcus nucleic acid assay kit comprises nucleic acid releasing agents and PCR reaction fluid, wherein the nucleic acid releasing agents include 0.05-0.5mM / L surfactin, 100-300mM / L potassium chloride, 0.05-3% sodium dodecyl sulfate and 0.01-1% ethyl alcohol, the PCR reaction fluid comprises a forward primer, a reverse primer and a probe, the forward primer and the reverse primer are used for target polynucleotide amplification, and the probe is used for target polynucleotide assay. The group B streptococcus nucleic acid assay kit has the advantages that a nucleic acid release method is adopted, a pathogen coat protein structure is rapidly destroyed by strong protein denaturants, group B streptococcus-DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) in unknown samples such as genital secretions and rectum secretions of perinatal pregnant women can be assayed rapidly, and assay sensitivity can be up to 500 copies / ml, so that reliable experimental bases are provided for group B streptococcus infection diagnosis, and the problems of poor assay specificity and low sensitivity of the prior art can be solved.
Owner:SANSURE BIOTECH INC
Streptococcus suis vaccines and diagnostic tests
InactiveUS20070111236A1Accurate responseAccurate measurementAntibacterial agentsBacteriaAntigenDiagnostic test
The invention relates to Streptococcus suis infection in pigs, vaccines directed against those infections and tests for diagnosing Streptococcus suis infections. The invention provides an isolated or recombinant nucleic acid encoding a capsular gene cluster of Streptococcus suis or a gene or gene fragment derived thereof. The invention further provides a nucleic acid probe or primer allowing species or serotype-specific detection of Streptococcus suis. The invention also provides a Streptococcus suis antigen and vaccine derived thereof.
Owner:STICHTING WAGENINGEN RES
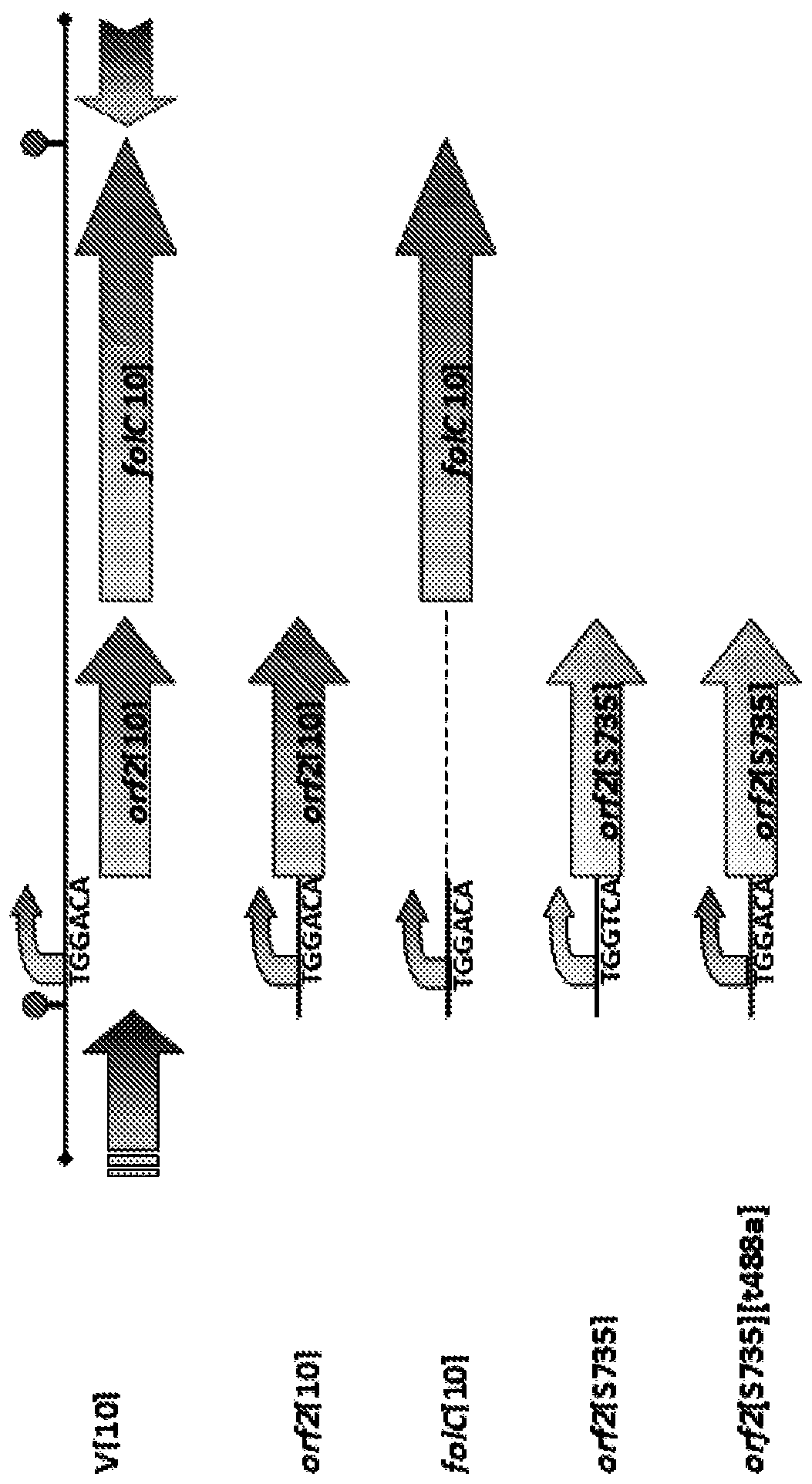
Attenuating bacterial virulence by attenuating bacterial folate transport
PendingCN110582296ALow toxicityEnhance immune responseAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsStreptococcus infectionMicrobiology
The invention relates to bacterial infections, vaccines directed against those infections and bacterial vaccines. More particularly, the invention relates to vaccines directed against Streptococcus infections in pigs. Provided is a [Delta]FolT mutant of a bacterium having reduced capacity to transport folate, wherein the capacity has been reduced by functionally deleting folate transporter (FolT)function. The present invention provides a method to reduce virulence of a bacterium comprising reducing the capacity of the bacterium to transport folate.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM VETMEDICA GMBH
Method and kit for detecting group B streptococcus infection
InactiveCN105063173ASimple structureEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementBenzoic acidGlycine
The invention discloses a method for detecting group B streptococcus infection, which is characterized in that a detection reagent prepared from hippuric acid or hippurate analogue as a chromogenic substrate and a buffer solution is adopted, and hippuricase in group B streptococcus can be used for specifically recognizing glycine and benzoic acid in the chromogenic substrate and hydrolyzing amido bonds for linking glycine and benzoic acid to change the color of the chromogenic substrate, so that whether group B streptococcus is infected or not in a detected sample is judged. The invention also discloses a kit for detecting group B streptococcus infection. The detection method disclosed by the invention is simple, professional training required for the bacterial streaking technology is not needed, identification results can be obtained only by simple sample adding and short-time incubation, the detection time is far shorter than the time required for culture by a culture medium, and visual identification results are intuitive and accurate. The kit disclosed by the invention is simple in structure, convenient in operation and good in performance. Statistics show that by adopting the kit for detection, the positive predictive value is more than 85%, and the negative predictive value is more than 97%.
Owner:AUTOBIO DIAGNOSTICS CO LTD
Fusion protein vaccine capable of inhibiting Streptococcus and/or preventing Streptococcus infection
ActiveCN106554421AEasy to removeReduce dosageAntibacterial agentsFungiSide effectStreptococcus infection
The invention discloses a fusion protein vaccine capable of inhibiting Streptococcus and / or preventing Streptococcus infection. With fusion protein obtained through linkage of sortase A and a cholera toxin B subunit through connecting peptide, the Th17 cell activation level is remarkably increased, the effects of preventing pathogenic bacteria from settling and quickly removing the pathogenic bacteria can be realized, and the fusion protein has protecting effects on Group A Streptococcus of different serotypes and has the superiority of high efficiency, broad spectrum and low cost. With the fusion protein, the use amount of immunogen is reduced, the production technology is simplified, and the production cost is reduced. Meanwhile, the vaccine adopts the way of mucosal immunity, has the characteristics of being free of tissue damage, free of local side effects and convenient to use, and is easy to popularize and use.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
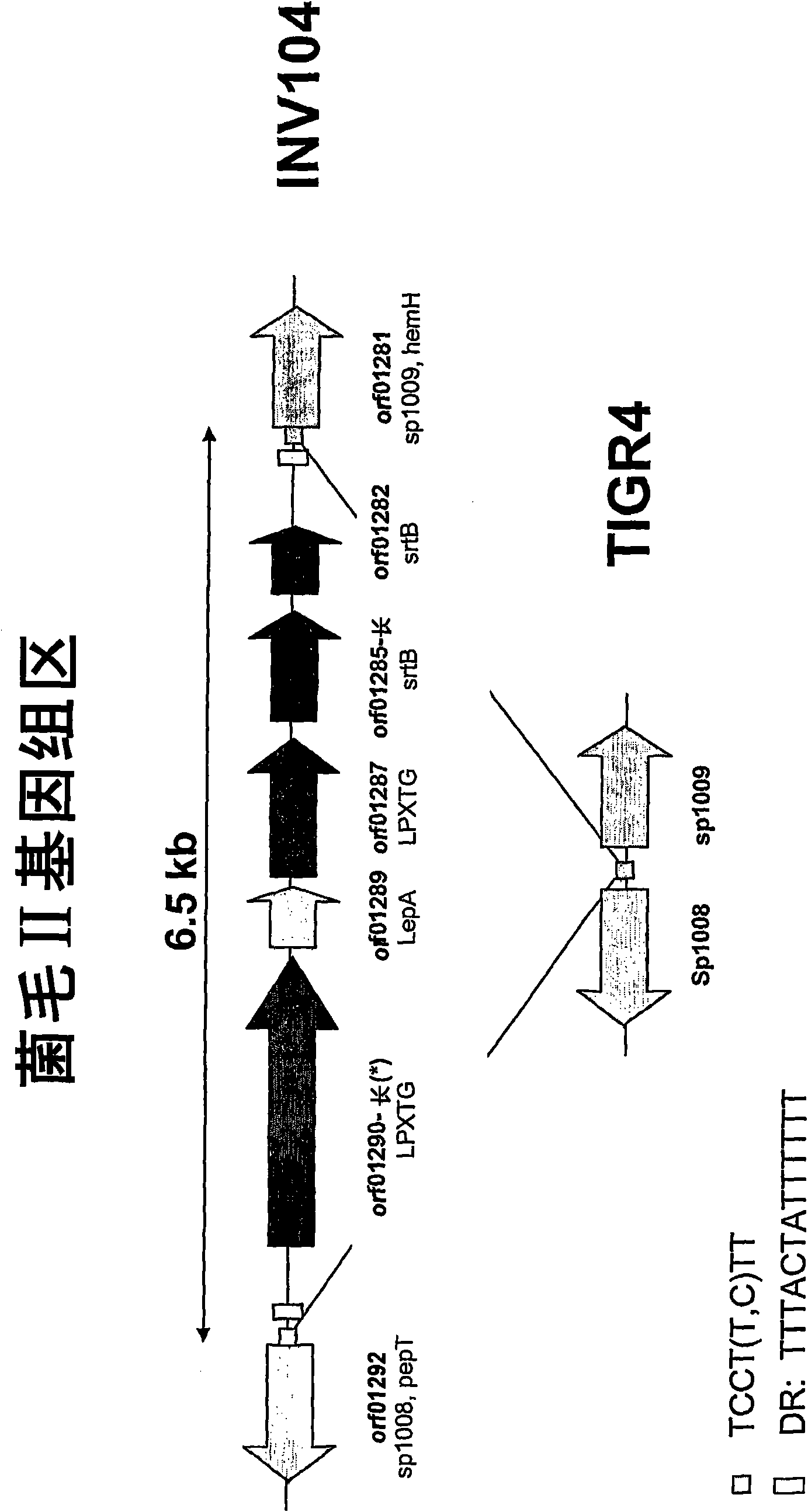
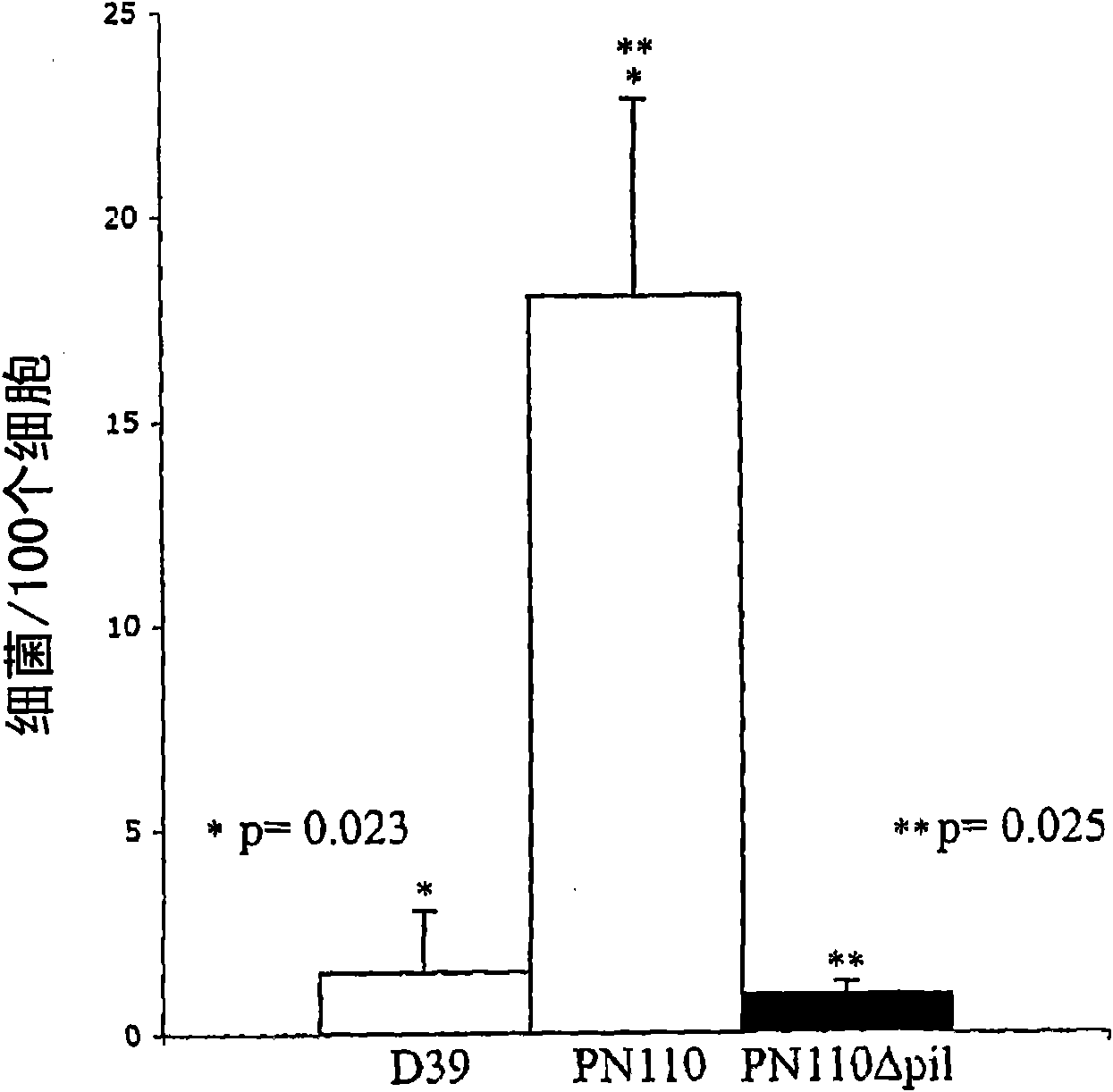
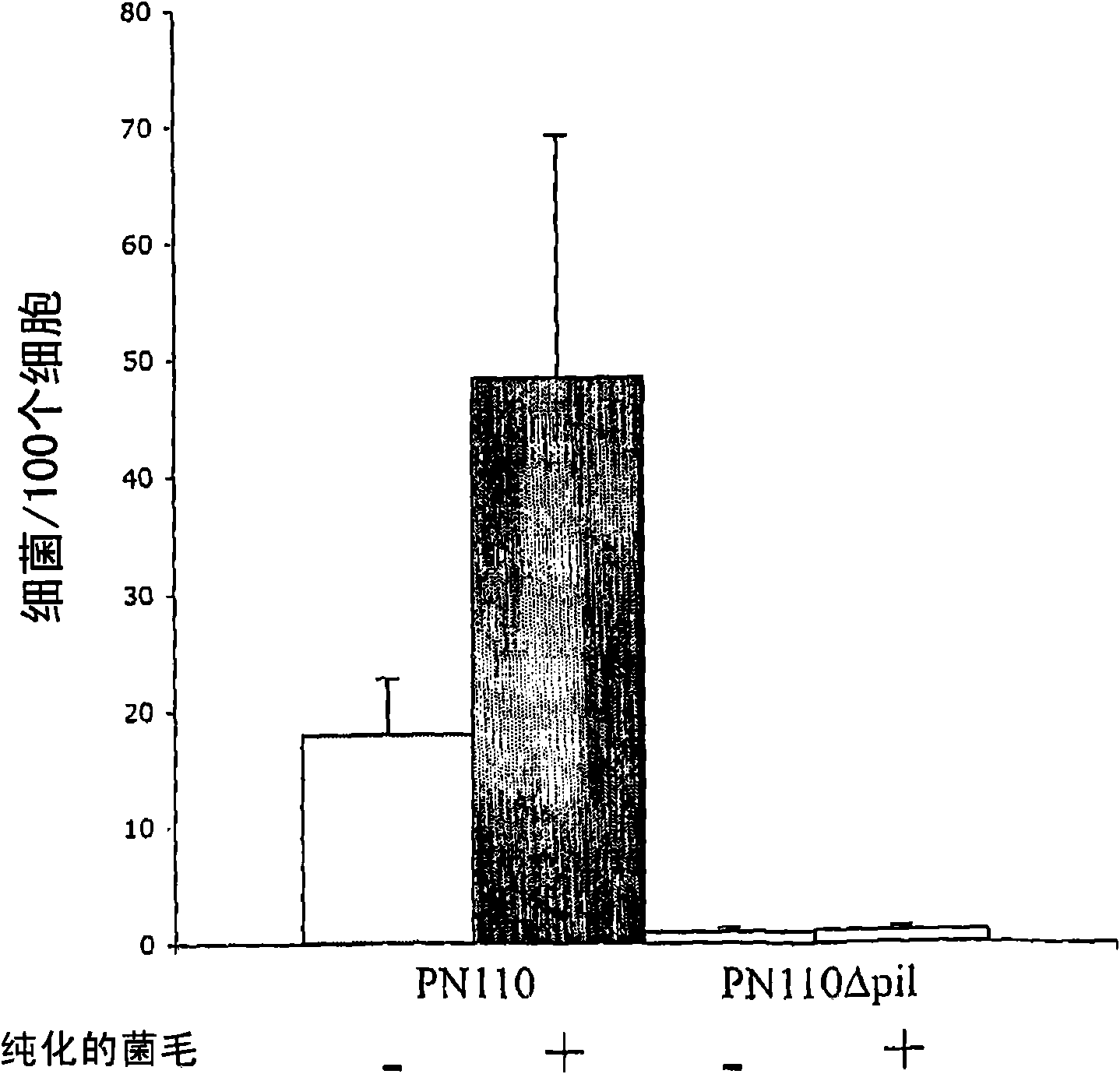
Streptococcus pneumoniae pilus antigens
Polypeptides from Streptococcus pneumoniae are described. In some aspects the polypeptides include pili polypeptides from a second pili island (pilus II island (INVl 04B)) identified in Streptococcus pneumoniae isolate INVl 04. In other aspects the polypeptides include pili polypeptides and non-pilus polypeptides from Streptococcus pneumoniae strains 23F, INV200, and OXC141 that are absent from Streptococcus pneumoniae isolate INV104. The polypeptides, including fragments and variants thereof, may be used in immunogenic compositions for prophylactic or therapeutic immunization against Streptococcus pneumoniae. The polypeptides are also disclosed to be used in compositions useful for the production of antibodies and immunostimulants. Also presented are methods of inhibiting Streptococcus pneumoniae, methods of treating Streptococcus pneumoniae infection, methods of identifying inhibitors of Streptococcus pneumoniae and methods for diagnosing / detecting Streptococcus pneumoniae infection.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Immunization of dairy cattle with chimeric GapC protein against Streptococcus infection
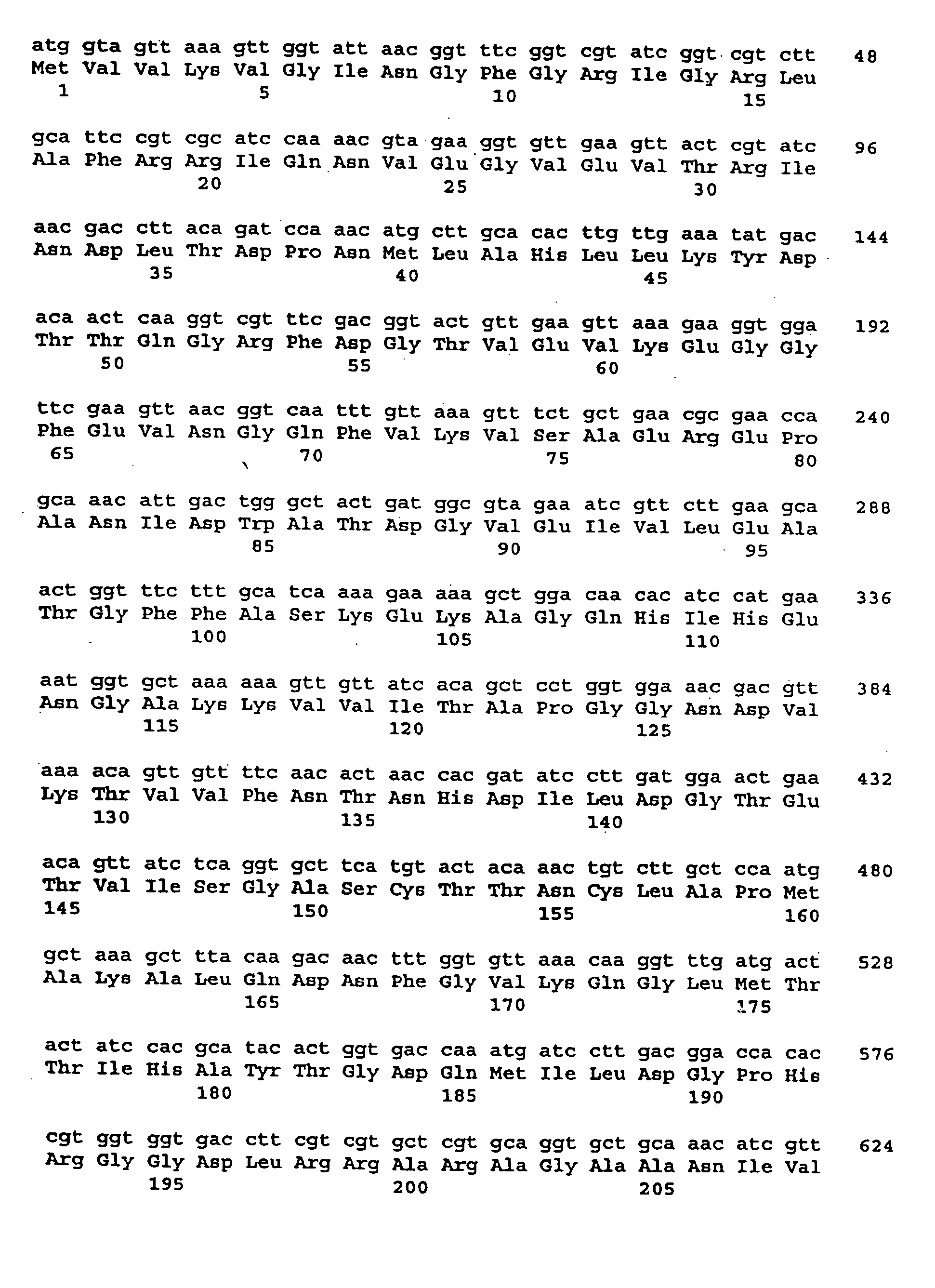
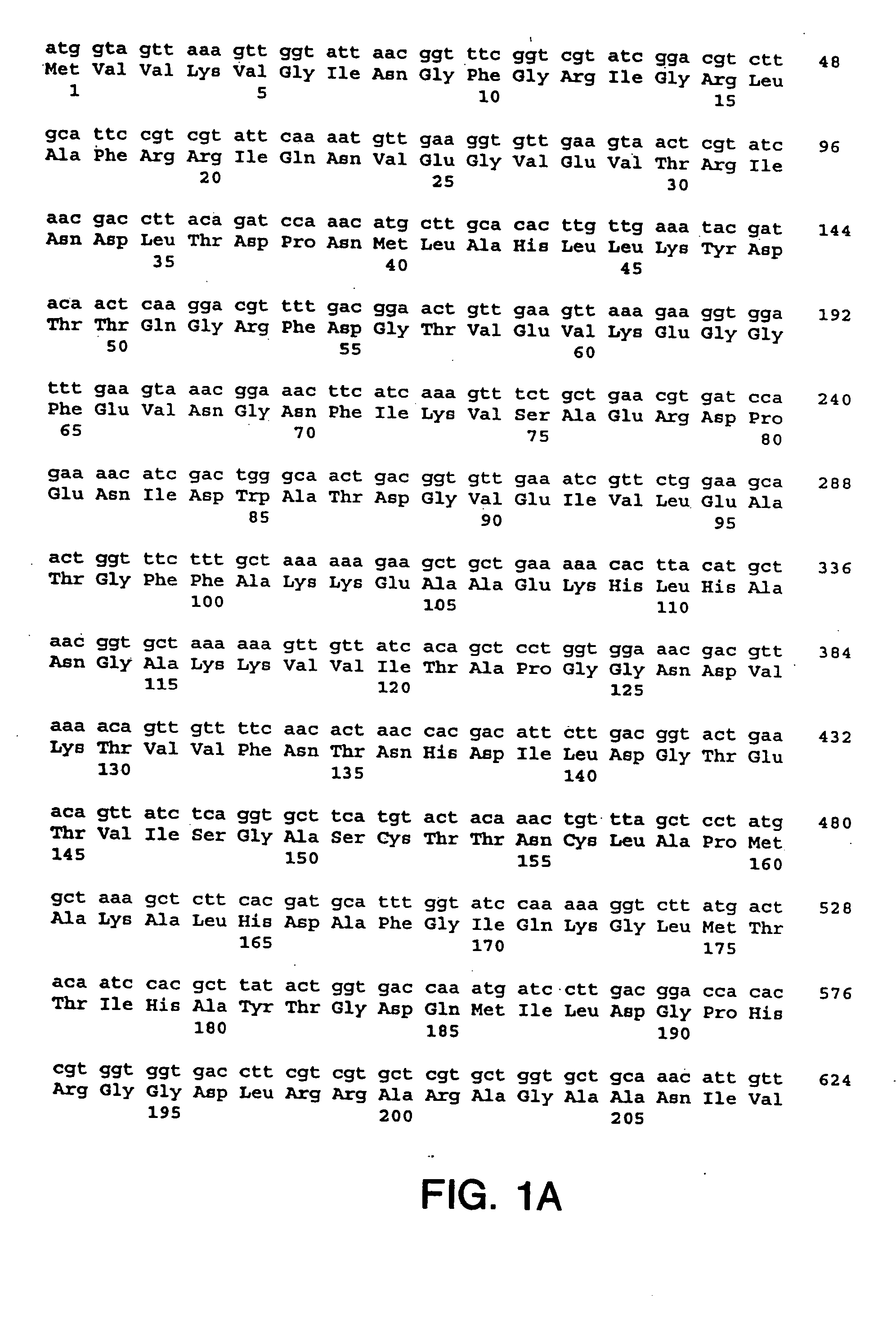
The recombinant production of Gap4, a chimeric GapC plasmin binding protein comprising the entire amino acid sequence of the Streptococcus dysgalactiae GapC protein in addition to unique amino acid sequences from the Streptococcus parauberis and Streptococcus agalactiae GapC proteins, is described. Also described is the use of Gap4 chimeric GapC protein in vaccine compositions to prevent or treat streptococcal infections in general and mastitis in particular.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN
Lactobacillus paracasei for preventing infant streptococcus infection and application of lactobacillus paracasei
The invention belongs to the technical field of screening and application of probiotics, and particularly relates to a Lactobacillus paracasei strain for preventing streptococcus infection of infants and an application of the Lactobacillus paracasei strain. The lactobacillus paracasei has a very strong antibacterial effect on beta-hemolytic streptococcus and is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection on May 24, 2021, and the preservation number of the lactobacillus paracasei is CCTCC (China Center for Type Culture Collection) NO: M2021591. The strain can effectively prevent streptococcus infection, especially streptococcus infection of infants, can significantly reduce the level of inflammatory factors in the body, alleviate the degree of shedding of intestinal mucosa layers, keep the mesenteric structure complete, and alleviate inflammatory cell infiltration and splenomegaly, and has outstanding effects. The lactobacillus paracasei can be used for preparing food, health care products, medicines or skin care products with the function of preventing streptococcus infection, and the application prospect is wide.
Owner:山东百沃生物科技有限公司
Prophylactic and/or Therapeutic Agents for Streptococcus Pneumoniae Infection
PendingUS20210379124A1Prevention and/or treatmentAntibacterial agentsUnknown materialsStreptococcus pneumoniaeStreptococcus infection
Provide is a novel prophylactic and / or therapeutic agent for Streptococcus pneumoniae infection. It was found that a bacterium belonging to the genus Enterococcus can prevent and / or treat Streptococcus pneumoniae infection. The prophylactic and / or therapeutic agent for Streptococcus pneumoniae infection, comprises a bacterium belonging to the genus Enterococcus. Also provided are: a medicine for prevention and / or treatment of Streptococcus pneumoniae infection, comprising a bacterium belonging to the genus Enterococcus; and a food for prevention and / or treatment of Streptococcus pneumoniae infection, comprising a bacterium belonging to the genus Enterococcus.
Owner:NUTRI CO LTD
Establishment and application of Streptococcus suis type 2 cell wall protein antibody detection method
InactiveCN104762246AIncreased sensitivityImprove featuresBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliStreptococcus infection
Belonging to the technical field of veterinary microbiology and animal immunology, the invention discloses cloning of Streptococcus suis type 2 cell wall protein gene main functional domain fragment and application of the recombinant protein expressed by the fragment in Streptococcus suis type 2 antibody detection. The invention prepares an expression strain Escherichia coli BL21 / pET28a-sspA able to secrete Streptococcus suis type 2 cell wall protein SspA, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M2014344. The invention also discloses establishment of an SspA recombinant protein based ELISA detection method and application in detection of Streptococcus suis type 2 antibodies. A large number of SSPA antibodies exist in swine infected serum, and the antibody of the protein cannot be detected in immune serum. The method provided by the invention can be employed to detect swine serum antibody and can distinguish Streptococcus suis type 2 infection and immune animals.
Owner:广西壮族自治区动物疫病预防控制中心 +1
Application of porcine beta-defensin 2 peptide fragment to preparation of medicine composition for preventing and treating streptococcus suis infection
InactiveCN111150835AReduce mortalityReduce tissue loadAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsInfectious DisorderStreptococcus infection
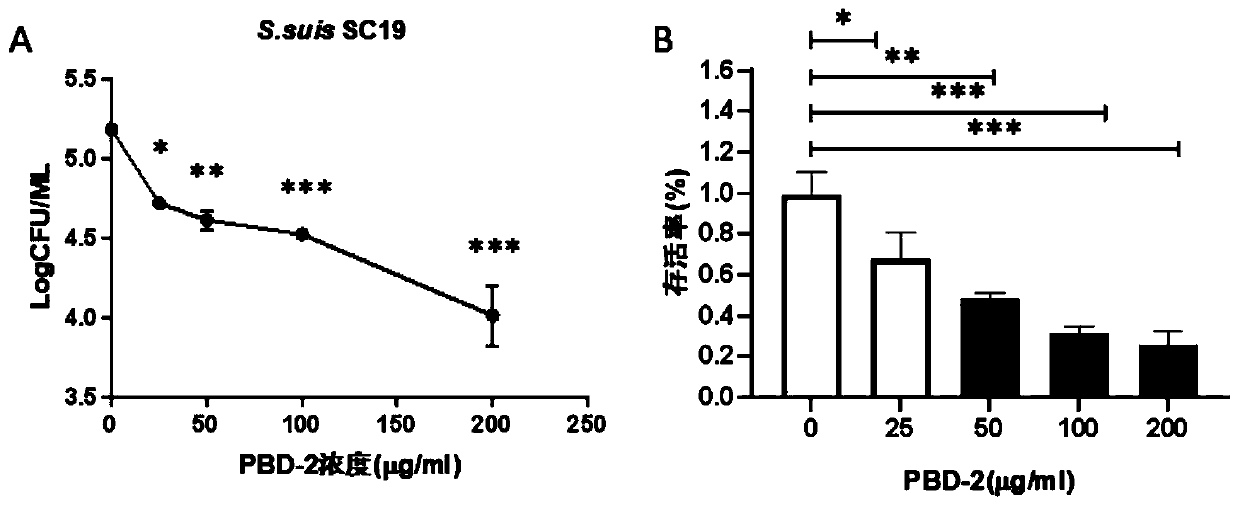
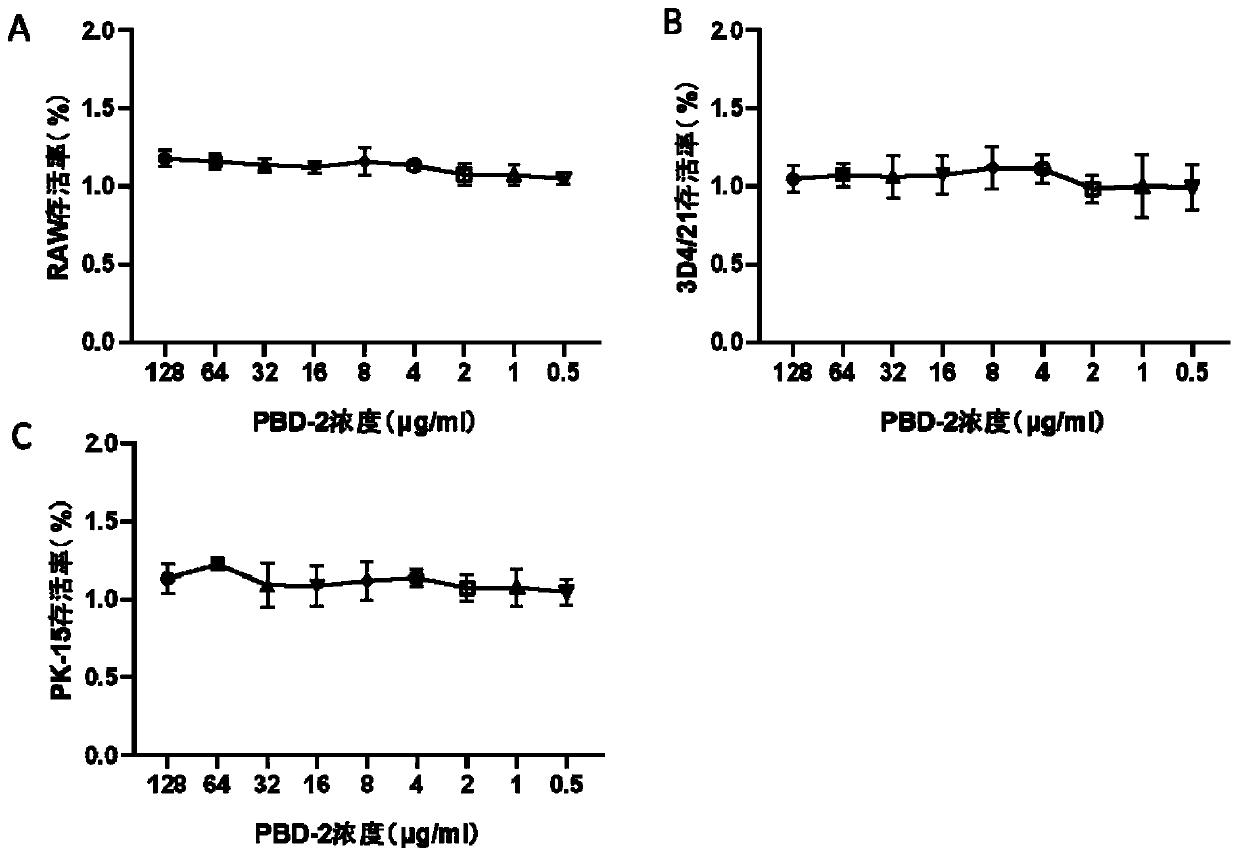
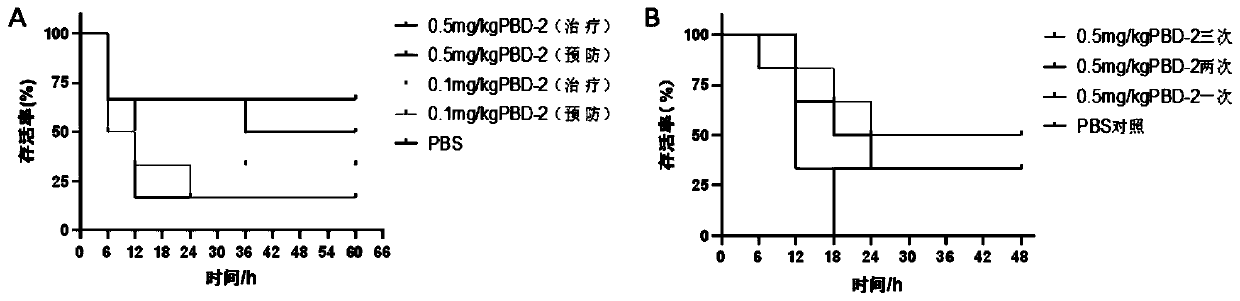
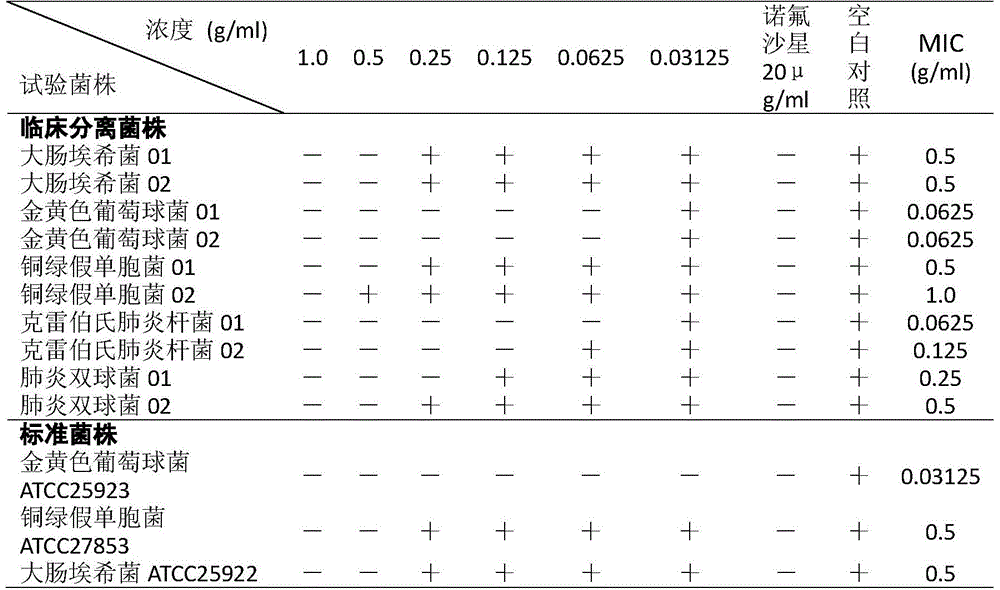
The invention belongs to the technical field of prevention and treatment of animal infectious diseases, and particularly relates to application of a PBD-2 (Porcine Beta-Defensin 2) peptide fragment topreparation of a medicine composition for preventing and treating streptococcus suis infection. The PBD-2 peptide fragment has no cytotoxicity in vitro and has an obvious inhibition effect on streptococcus suis growth. Through PBD-2 treatment, the mortality rate, the inflammatory cytokine level, the tissue bacterial load quantity and the pathology damage degree of mice infected with streptococcussuis can be obviously reduced. The invention provides basic candidate medicine for pharmaceutical application of the PBD-2 peptide fragment to preparation of medicine for preventing and treatment thestreptococcus suis infection.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Immunogenic complex for eliciting protective immunity against group b streptococcus
ActiveUS10888610B2Improving immunogenicityExpand the scope of protectionAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsStreptococcus infectionTGE VACCINE
The present invention relates to an immunogenic complex comprising an amino acid sequence having at least 80% sequence identity with the amino acid sequence of the N-terminal region of a group B Streptococcus surface protein, and a capsular polysaccharide. The immunogenic complex is capable of eliciting protective immunity against group B Streptococcus. The invention further pertains to an immunogenic product comprising the immunogenic complex and an immunogenic fusion protein, the vaccine, the immunogenic complex, or the immunogenic product for use in a method of preventing or treating a group B Streptococcus infection, as well as a method of preventing or treating a group B Streptococcus infection.
Owner:MINERVAX
A kind of nasal cavity cleaning care solution and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103735581BGood anti-inflammatory effectGood antibacterial effectPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsRespiratory disorderNasal cavityStreptococcus infection
The invention discloses a care solution for cleaning a nasal cavity and a preparation method of the care solution. The care solution is prepared from 5,000 parts of traditional Chinese medicine distillate, 0.1-2 parts of preservatives, 1-100 parts of glyceryl polymethacrylate, 20-100 parts of tween 80, 30-80 parts of sodium chloride, 20-60 parts of a pH conditioning agent and 4658-4928.9 parts of purified water. The osmotic pressure of the care solution is 280-310mosm / Kg, and the pH value is 5.5-7.0. The preparation method of the care solution mainly comprises the following steps: by taking one or combination of houttuynia cordata, mint, honeysuckle and radix angelicae as raw materials, carrying out steam distillation to obtain the traditional Chinese medicine distillate; matching with auxiliary materials, and then filtering and carrying out split charging, so as to obtain the care solution. The solution disclosed by the invention has a strong inhibiting effect on nasal common microbe streptococcus infection, staphylococcus, bacillus influenza, influenza viruses and rhinoviruses, and can achieve the target of preventing rhinitis infection and recurrence.
Owner:刘少华
Method for detecting group B streptococcus infections
The invention discloses a method for detecting group B streptococcus infections and belongs to methods for determining characteristics of in-vivo blood. According to the method, a kit contains reagents for detection, such as a negative control serum, a positive control serum, a concentrated phosphate buffer, an adsorbent, isosulfocyanic acid fluorescein-labeled sheep anti-human-IgM globulin and a mounting medium and a biological thin sheet, and reaction areas of the biological thin sheet are coated with group B streptococci. A determination method comprises the steps of adding an IgG antibody removed diluted serum into the reaction areas, carrying out incubation, rinsing and spin-drying, then, adding the isosulfocyanic acid fluorescein-labeled sheep anti-human-IgM globulin, forming isosulfocyanic acid fluorescein-labeled sheep anti-human-IgM globulin fluorescent complexes around thalli, and generating green-yellow fluorescence. According to the method disclosed by the invention, indexes such as sensitivity and specificity are all higher than that of the existing methods.
Owner:TIANJIN BAODI HOSPITAL
Group A Streptococcus Pharmaceutical Compositions and Methods Thereof
InactiveUS20110250221A1Safe and effectiveAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsMedicineTherapeutic treatment
Isolated proteins and immunogenic fragments thereof, for use in the treatment and prevention of a Group A Streptococcus infection are provided. In particular, the invention provides pharmaceutical compositions and methods of prophylactic and / or therapeutic treatment of a Group A Streptococcus infection.
Owner:UNIV OF WOLLONGONG
Immunization of dairy cattle with GapC protein against Streptococcus infection
The GapC plasmin binding protein genes of Streptococcus dysgalactiae (S. dysgalactiae), Streptococcus agalactiae (S. agalactiae), Streptococcus uberis (S. uberis), Streptococcus parauberis (S. parauberis), and Streptococcus iniae (S. iniae) are described, as well as the recombinant production of the GapC proteins therefrom. Also described is the use of the GapC proteins from those species in vaccine compositions to prevent or treat bacterial infections in general, and mastitis in particular.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN
Immunization of dairy cattle with GapC protein against streptococcus infection
The GapC plasmin binding protein genes of Streptococcus dysgalactiae (S. dysgalactiae), Streptococcus agalactiae (S. agalactiae), Streptococcus uberis (S. uberis), Streptococcus parauberis (S. parauberis), and Streptococcus iniae (S. iniae) are described, as well as the recombinant production of the GapC proteins therefrom. Also described is the use of the GapC proteins from those species in vaccine compositions to prevent or treat bacterial infections in general, and mastitis in particular.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN
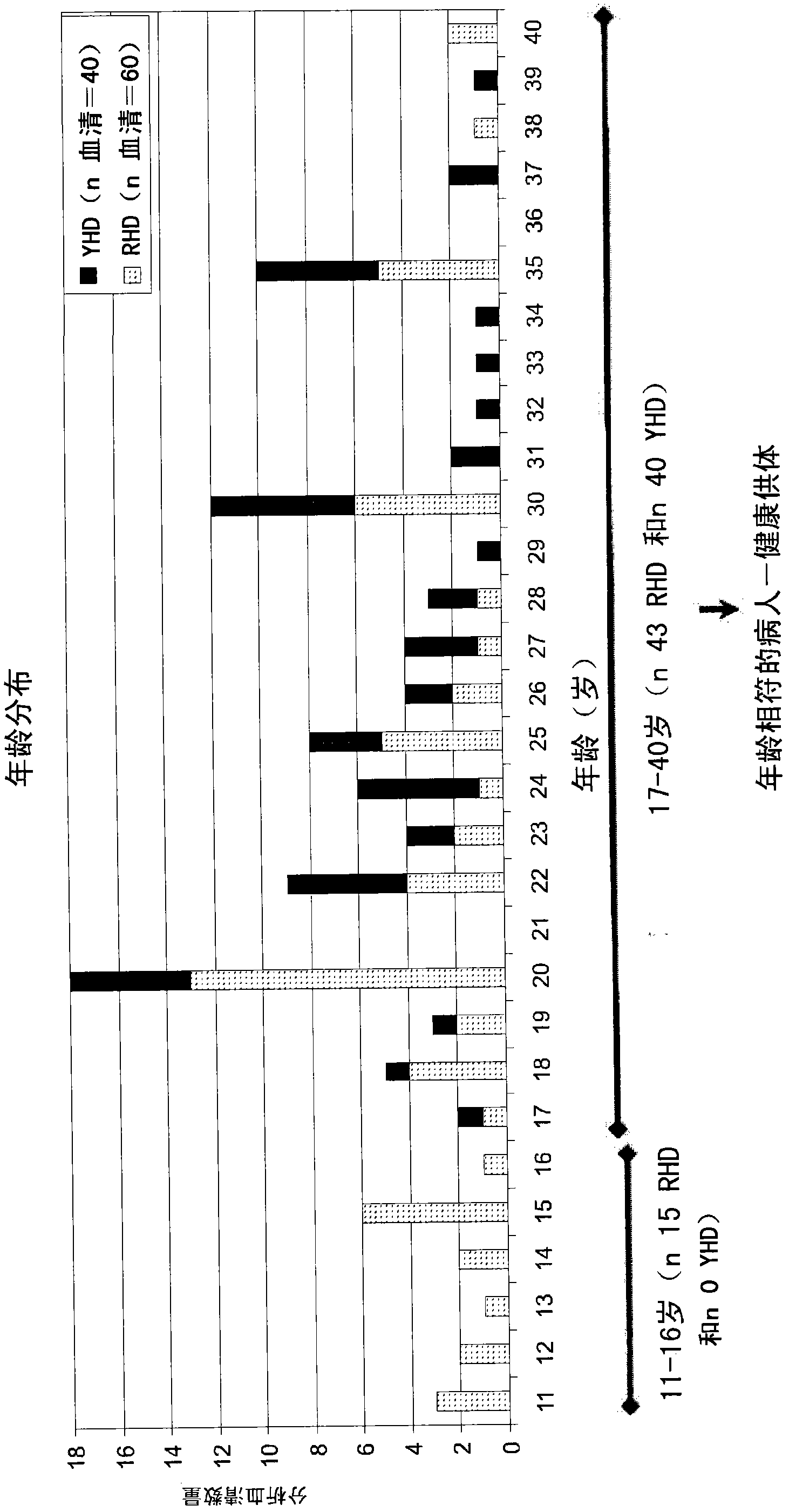
Diagnostic and therapeutic methods for rheumatic heart disease based upon group a streptococcus markers
This invention is in the field of identifying patients having rheumatic heart disease (RHD) associated with Streptococcus pyogenes (Group A Streptococcus; GAS) infection and identifying patients at risk of developing RHD associated with GAS infection. The invention also provides methods and compositions for preventing and treating RHD associated with GAS infection.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Application of Streptococcus pneumoniae protein in resisting Streptococcus pneumoniae infection
ActiveCN109456393BIncrease infectionReduced Colonization Protection ExperimentAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsStreptococcus infectionAmino acid peptide
The invention provides the application of Streptococcus pneumoniae protein in resisting Streptococcus pneumoniae infection. The Streptococcus pneumoniae endopeptidase O (PepO) of the present invention is a subcutaneous immune adjuvant, mixed and fused with the 673rd to 863rd amino acid peptide of zinc metalloprotease B (ZmpB), and the prepared Streptococcus pneumoniae Protein vaccines have a good protective effect against Streptococcus pneumoniae infection.
Owner:CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Immunogenic complex for eliciting protective immunity against group b streptococcus
ActiveUS20190282681A1Improving immunogenicityExpand the scope of protectionAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsImmunogenicityAmino acid
The present invention relates to an immunogenic complex comprising an amino acid sequence having at least 80% sequence identity with the amino acid sequence of the N-terminal region of a group B Streptococcus surface protein, and a capsular polysaccharide. The immunogenic complex is capable of eliciting protective immunity against group B Streptococcus. The invention further pertains to an immunogenic product comprising the immunogenic complex and an immunogenic fusion protein, the vaccine, the immunogenic complex, or the immunogenic product for use in a method of preventing or treating a group B Streptococcus infection, as well as a method of preventing or treating a group B Streptococcus infection.
Owner:MINERVAX
Immunization of dairy cattle with chimeric GapC protein against Streptococcus infection
InactiveUS20050142615A1Antibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsStreptococcus infectionMastitis
The recombinant production of Gap4, a chimeric GapC plasmin binding protein comprising the entire amino acid sequence of the Streptococcus dysgalactiae GapC protein in addition to unique amino acid sequences from the Streptococcus parauberis and Streptococcus agalactiae GapC proteins, is described. Also described is the use of Gap4 chimeric GapC protein in vaccine compositions to prevent or treat streptococcal infections in general and mastitis in particular.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN
Streptococcus and its inactivated cow mastitis vaccine
ActiveCN103800901BVarious dosage formsComprehensive and effective preventionBacterial antigen ingredientsImmunological disordersActive componentMastitis
The invention discloses streptococcus and a dairy cow mastitis vaccine obtained by inactivating the streptococcus. The active components of the dairy cow mastitis vaccine are an inactivated strain SAWR-6 (streptococcus agalactiae-6), an inactivated strain SDTR-9 (streptococcus dysgalactiae-9) and an inactivated strain SURF-5 (streptococcus uberis-5). The invention also provides a dairy cow mastitis vaccine, of which the active components are inactivated strains and capsular polysaccharides, wherein the inactivated strains are an inactivated strain SAWR-6, an inactivated strain SDTR-9 and an inactivated strain SURF-5; the capsular polysaccharides are strain SAWR-6 capsular polysaccharide, strain SDTR-9 capsular polysaccharide and strain SURF-5 capsular polysaccharide. The vaccine disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high efficiency, universality, safety, stability, various preparations and the like, a powerful guarantee is provided to safe, effective and comprehensive and effective prevention of streptococcus infected dairy cow mastitis, and the vaccine is a new milestone for the development of dairy cow mastitis vaccine.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA HUAXI BIOTECH
Lactobacillus paracasei and application thereof in prevention of streptococcus infection of infants
The invention belongs to the technical field of screening and application of probiotics, and particularly relates to a novel lactobacillus paracasei strain and an application of the lactobacillus paracasei strain. The provided lactobacillus paracasei is separated from fresh excrement of healthy infants, and is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection on May 24, 2021, and the preservation number of the lactobacillus paracasei is CCTCC (China Center for Type Culture Collection) NO: M2021590. The strain has a very strong antibacterial effect on beta-hemolytic streptococcus, can improve the immunity of a host, relieve inflammatory response and effectively prevent and treat infection caused by streptococcus, and is particularly suitable for preventing streptococcus infection of infants.
Owner:QINGDAO VLAND BIOTECH GRP
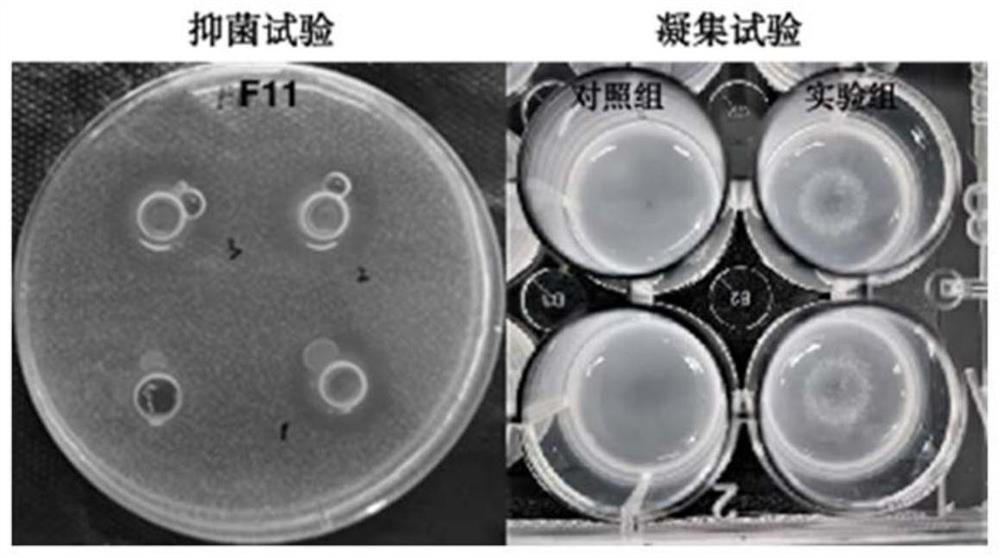
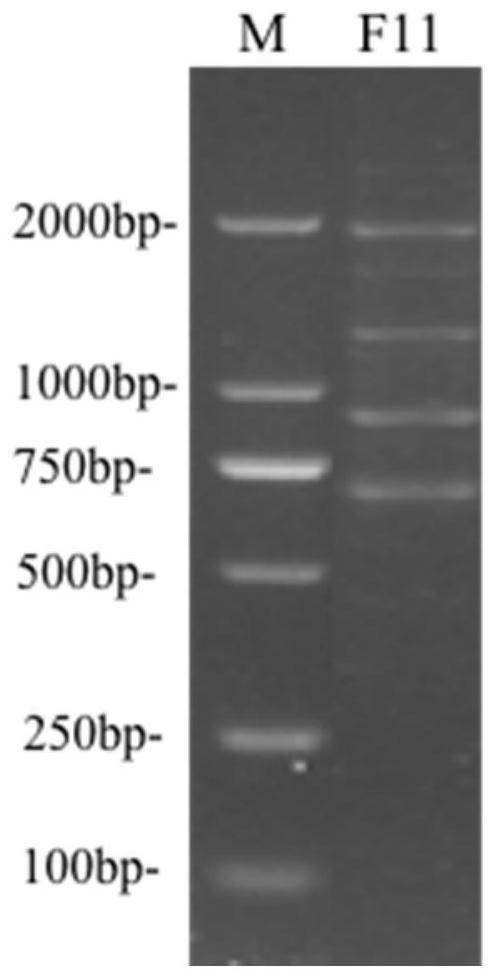
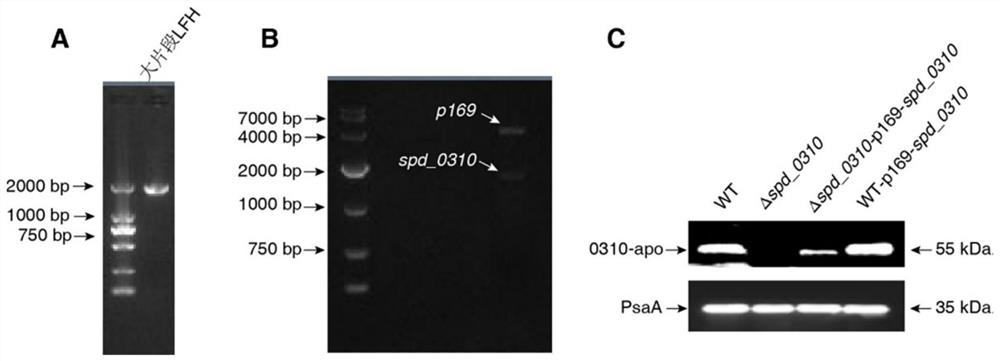
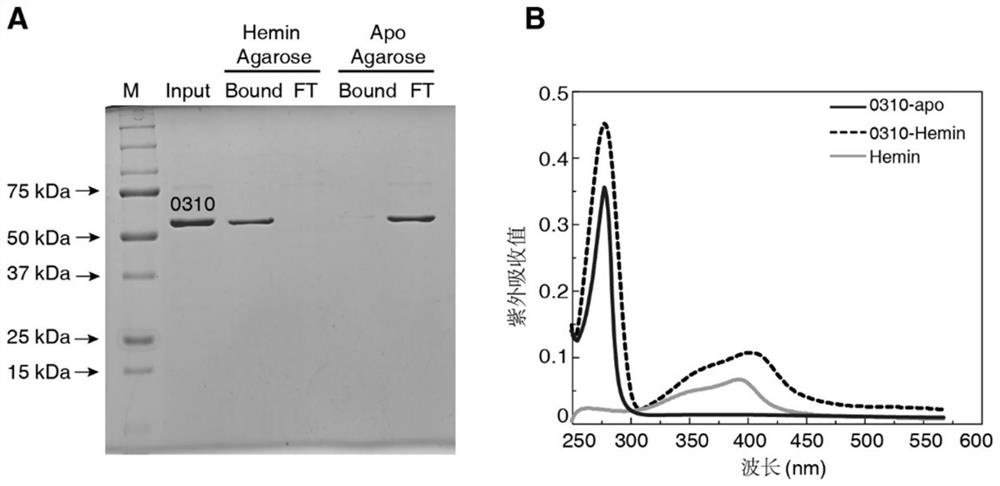
Application of spd_0310 protein as a target in the preparation of drugs for preventing and treating Streptococcus pneumoniae infection
ActiveCN110812484BReduce conservatismHighly conservativeAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAntimicrobial drugStreptococcus infection
The invention discloses the application of SPD_0310 protein as a target in the preparation of medicines for preventing and treating Streptococcus pneumoniae infection. In the present invention, it was found that the expression level of SPD_0310 in the triple mutant strain in which the three main iron transport genes of Streptococcus pneumoniae were knocked out at the same time was increased and could grow normally, indicating that the SPD_0310 protein may be involved in the interaction of various iron transport proteins. The present invention also found that the spd_0310 gene knockout strain has reduced infectivity to mice. Based on this, SPD_0310 can be used to prepare antibodies to the protein, so as to facilitate the development of antibody drugs. In addition, the present invention also found that the active center of the protein can bind heme, and proved that porphyrins can be used as substrates to compete with heme, indicating that porphyrins can be used as inhibitors of SPD_0310 to inhibit Streptococcus pneumoniae toxicity, which has broad application prospects in the field of antibacterial drugs.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
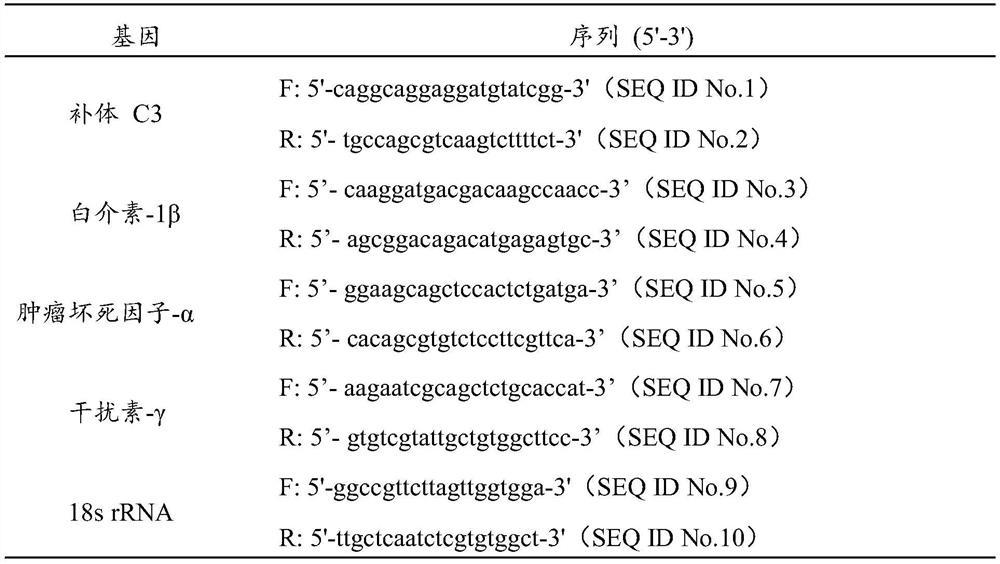
Tilapia feed additive for reducing pro-inflammatory response and enhancing immune response, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110432404BReduce expressionPromote healthy farmingAntibacterial agentsAntipyreticBiotechnologyAnimal science
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com