Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
703 results about "Drought tolerance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Drought tolerance is the ability to which a plant maintains its biomass production during arid or drought conditions. Some plants are naturally adapted to dry conditions, surviving with protection mechanisms such as desiccation tolerance, detoxification, or repair of xylem embolism. Other plants, specifically crops like corn, wheat, and rice, have become increasingly tolerant to drought with new varieties created via genetic engineering.
Drought tolerant plants and related constructs and methods involving genes encoding dtp21 polypeptides
Isolated polynucleotides and polypeptides and recombinant DNA constructs useful for conferring drought tolerance, compositions (such as plants or seeds) comprising these recombinant DNA constructs, and methods utilizing these recombinant DNA constructs. The recombinant DNA construct comprises a polynucleotide operably linked to a promoter that is functional in a plant, wherein said polynucleotide encodes a DTP21 polypeptide.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC +2
Fungal isolates and their use to confer salinity and drought tolerance in plants
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions of endophytic fungi that confer stress tolerance to inoculated plants, including both monocots and dicots. In particular, Fusarium species, isolated from the dunegrass, Leymus mollis, growing in plant communities on Puget Sound beaches of Washington State. Upon inoculating a target plant or plant part with the endophytic fungi, the resulting plant shows stress tolerance, particularly drought and salinity tolerance.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
Generation of Plants with Improved Drought Tolerance
The present invention is directed to plants that display a drought tolerance phenotype due to altered expression of a DR03 nucleic acid. The invention is further directed to methods of generating plants with a drought tolerance phenotype.
Owner:AGRI GENETICS
Methods for enhancing drought tolerance in plants and compositions thereof
ActiveUS7786353B2Increase probabilityImprove traitsBryophytesOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyIncreased tolerance
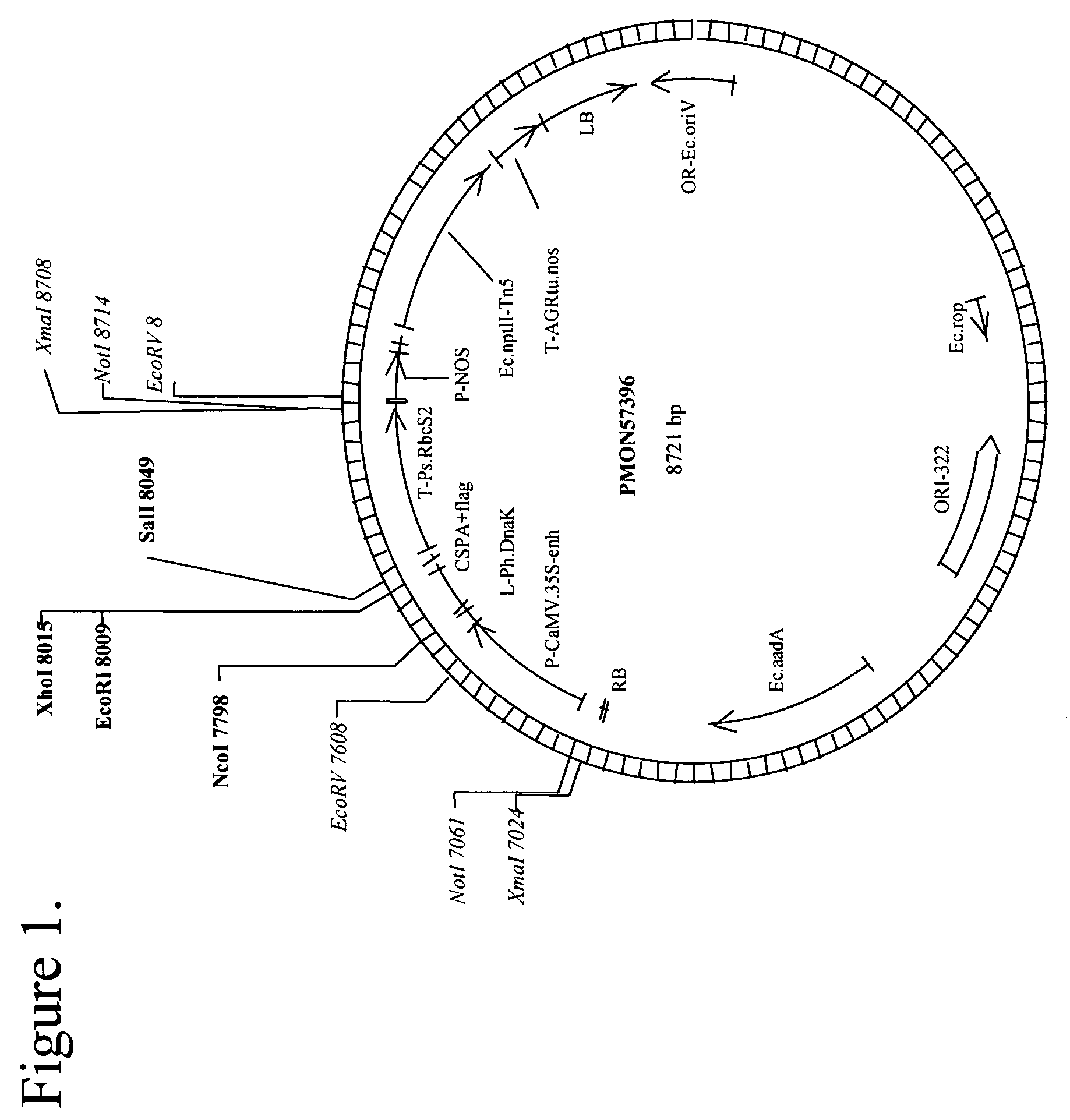
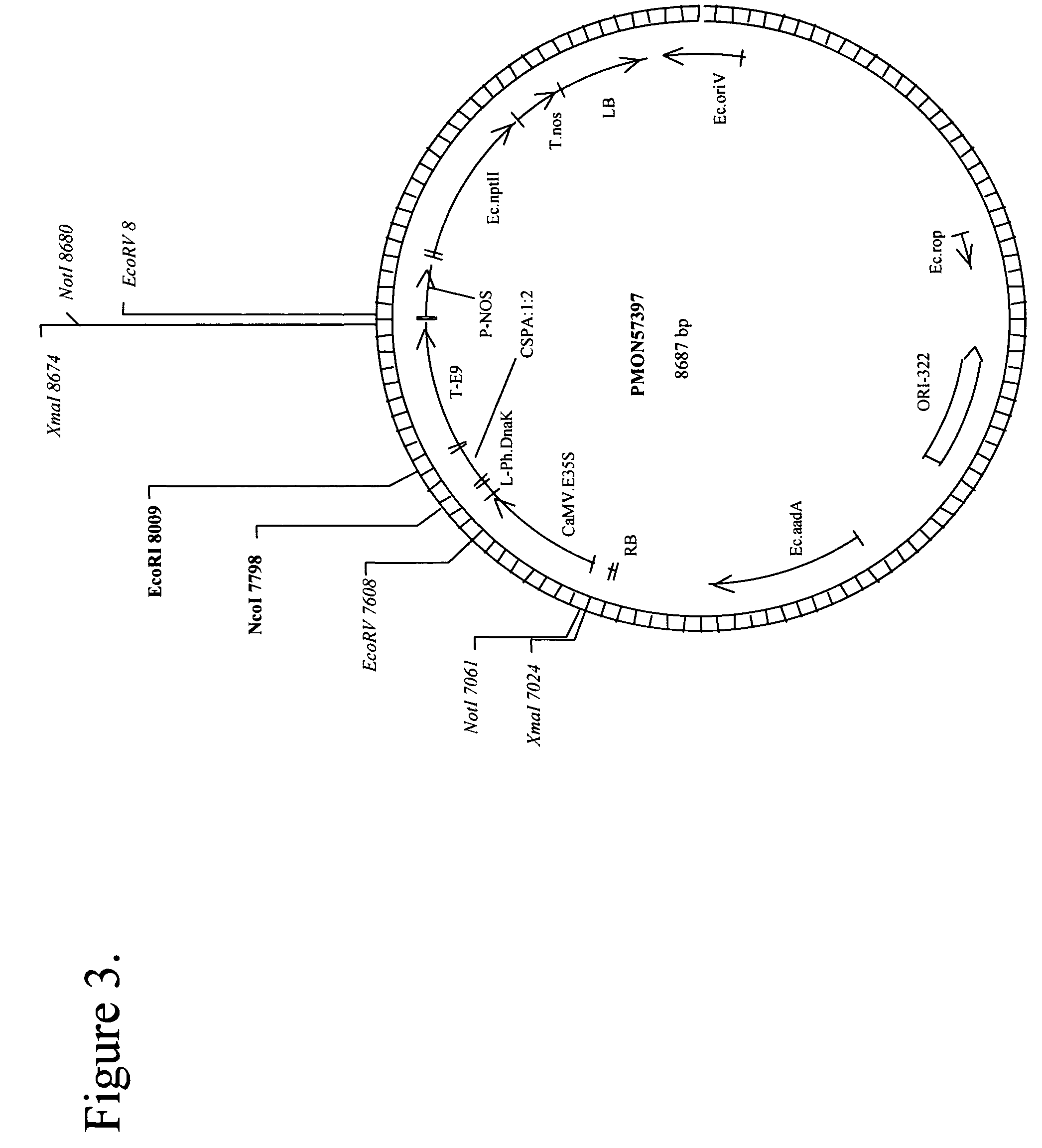
Increased tolerance to drought in a plant is provided by introducing DNA expressing a bacterial cold shock protein.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Plant stress tolerance correlative protein kinase, encoding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN101775381AImprove salt toleranceImprove drought resistanceFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyWild type
The invention discloses plant stress tolerance correlative protein kinase, an encoding gene and application thereof. The protein refers to the protein of 1) or 2): 1) the protein formed by an amino acid sequence shown by a second sequence in a sequence table; or 2) the plant stress tolerance correlative protein which is formed through the substitution and / or lack and / or addition of one or a plurality of amino acid residue radicals on the amino acid residue radical sequence of the second sequence in the sequence table and is derived from the protein of 1). The encoding gene of the protein is introduced into arabidopsis mutant sos2-1 or wild type arabidopsis for improving the salt tolerance and the drought tolerance of transgenic plants.
Owner:BEIJING AGRO BIOTECH RES CENT
Shine clade of transcription factors and their use
InactiveUS20090300790A1Increase in cuticular water lossPromote recoverySugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesNucleic acid sequencingGMO Plants
The present invention relates to the field of transgenic plants with given phenotypes, especially plants with enhanced drought tolerance. Provided are SHINE proteins and nucleic acid sequences encoding these, which are useful in conferring these phenotypes to plants.
Owner:STICHTING WAGENINGEN RES
Methods and materials for improving plant drought tolerance
InactiveUS7241937B2Increasing growth potential and drought toleranceRaise the potentialImmunoglobulinsOxidoreductasesGMO PlantsNucleic acid
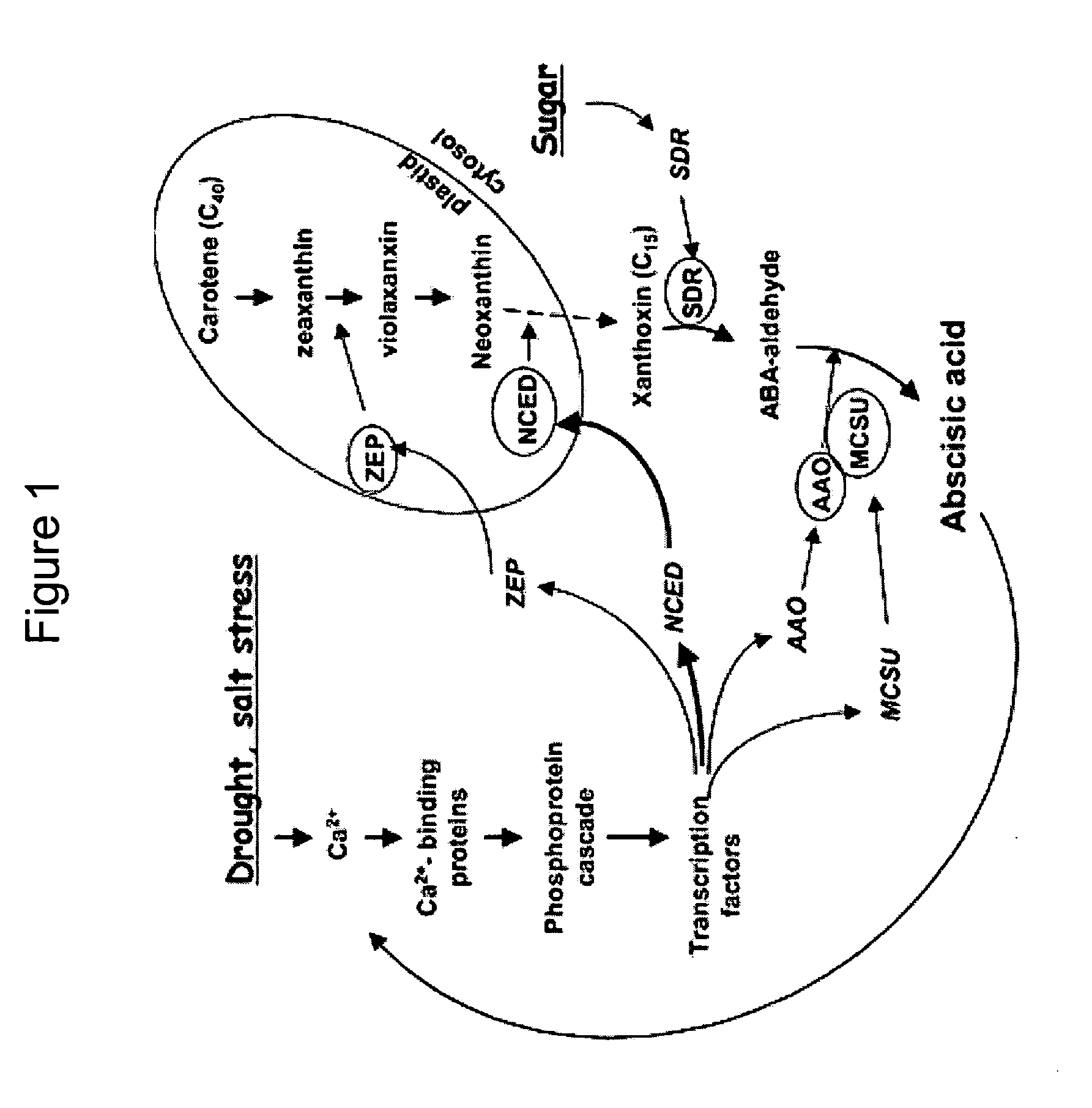
Isolated NCED3 nucleic acids and polypeptides are described herein, together with methods for using such nucleic acids and polypeptides for making transgenic plants with improved drought tolerance.
Owner:CERES INC
Nucleotide sequences and polypeptides encoded thereby for enhancing plant drought tolerance
InactiveUS20060150285A1Improve drought toleranceBryophytesSugar derivativesIncreased toleranceNucleotide sequencing
Isolated polynucleotides and polypeptides encoded thereby are described, together with the use of those products for making transgenic plants with increased tolerance to abiotic stress (e.g., high or low temperature, drought, flood).
Owner:CERES INC
High-efficiency multifunctional foliage fertilizer and production method thereof
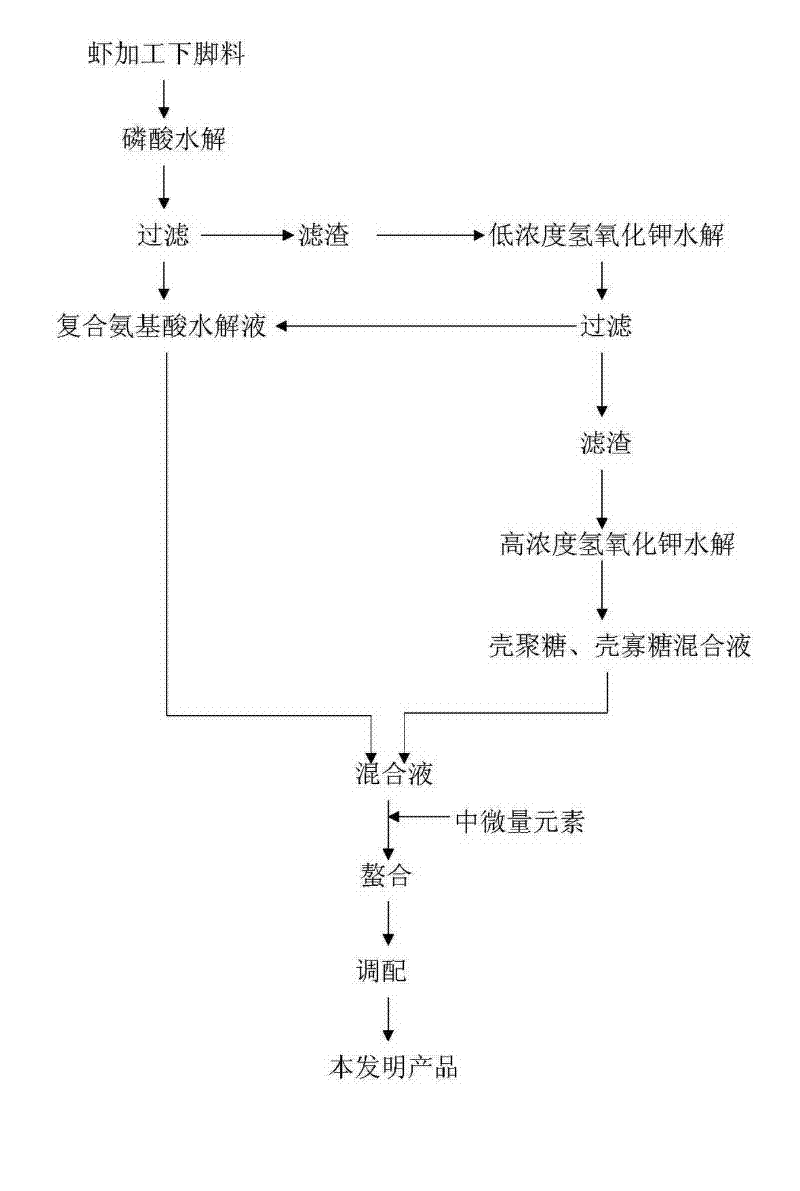
The invention discloses a high-efficiency multifunctional foliage fertilizer and a production method thereof. The foliage fertilizer is prepared by chelating shrimp processing leftovers, which serve as the main raw material, with medium and minor elements. The foliage fertilizer is prepared from 10-30% of amino acids, 2-8% of medium and minor elements, 10-30% of organic nitrogen, 3-20% of phosphorus, 3-20% of potassium, and 10-30% of shrimp peptide protein, chitosan, chitosan oligosaccharide, chitin, glucosamine hydrochloride, astacin and shrimp cephalin. The foliage fertilizer disclosed by the invention enhances the low-temperature tolerance, drought tolerance, salt damage tolerance, chemical damage tolerance and other stress tolerances of crops on the premise of comprehensively and efficiently supplementing necessary nutrients for crops, and has the functions of restoring the wound in the root system, enhancing the disease resistance of the crops, inhibiting disease and pest and the like. The production technique can reduce the acidolysis consumption, avoids introducing abundant inorganic salts and chloride ions to destroy soil ecological equilibrium and influence plant growth, lowers the energy consumption and requirements for equipment strength, and can implement the clean production of complete utilization and zero pollution discharge.
Owner:ZHANJIANG BOTAI BIOCHEM IND
Clone and application of a gene improving rice drought tolerance and relative with ABA synthesis
ActiveCN101173287AAffect normal growthAffect economyPlant peptidesFermentationAgricultural scienceGene conversion
The invention discloses an OsNCEDs gene relative to drought resistance originating from rice. Coded protein has one of the following amino acid sequences: 1). SEQ ID NO: 1, 3 or 5 in sequence list; 2). The amino acid residue sequence for the SEQ ID NO: 1, 3 or 5 in the sequence list pass through replacing, lacking or adding of one to ten amino acid residue and derived protein has the function of controlling drought resistance of plants. The experiment proves that: the gene conversion rice can obviously improve drought resistance of rice. The invention has the advantages of having an important theory and actual meaning upon research of drought resistance mechanism for plants and improving drought resistance and relative characteristics, playing an important role in drought resistance gene engineering improvement for plants (especially for rice crops) and having wide application prospect.
Owner:未名三农生物农业技术有限公司
Facility vegetable mycorrhiza production method
InactiveCN1843073AImprove utilizationImprove efficiencyCultivating equipmentsChemicalsDiseasePlant disease
The invention relates to a method for producing protective vegetable fungus root sprout, comprising the following steps: 1) planting susceptive crop after inoculating the bush AMF for sterilized organic soil or soil, taking the strand roots of plant or fungus root spore as inoculating bacteria; 2) sterilizing seedling soil or medium; 3) loading the sterilized soil into dish, spraying the inoculating bacteria onto soil, 4) sowing on the dish, then covering with sterilized soil for seedling in greenhouse. The invention is characterized by the low cost, good popularity and simple operation. The bacteria can on one side increase the usage of nutrient and water and fertilizer under organic cultivating condition, which results in productivity and quality improvement of vegetable; on the other side can strengthen the disease and drought resistance, reduce disease spread through soil and improve vegetable root condition.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Rapid screening method for drought-enduring variety of rice at seedling stage
InactiveCN102860199ADrought accurateDrought reliableHorticulture methodsGene mappingScreening method
The invention discloses a rapid screening method for drought-enduring variety of rice at seedling stage, comprising the following steps that: after soil drought processing and drought processing simulated by polyethylene glycol (PEG), variety with strong drought tolerance in two processing methods is screened out. By simultaneously performing soil drought and drought simulated by PEG and conjointly analyzing the result, the defects of two drought processing methods can be simultaneously avoided and the advantages of two methods can be exploited to the full. Thus, the experimental result is accurate and the results of the studies of breeding, group construction, gene mapping and the like of the drought-enduring variety and drought-sensitive variety which are screened out are more credible, and the time and the expenditure of researchers are saved.
Owner:RICE RES ISTITUTE ANHUI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Soybean cultivating method with high yield
InactiveCN1509590AGood disease and lodging resistanceGood waterlogging and drought toleranceSeed and root treatmentHorticulture methodsDrought toleranceGermination
A high-yield cultivation method of soybean includes such steps as preparing the plots on the land able to be irrigated by deep ploughing, applying organic fertilizer and mixed fertilizer, choosing seeds, disinfecting, sowing in the nutritive bags on seedbed, breeding in time while holding the temp at a certain value until the germination rate reaches a certain value, removing the ground film, controlling the temp in shed, transplanting by rational close planting, and field managing. Its advantages are high yield and high quality of soybean.
Owner:高雪欢
Transcriptional activators involved in abiotic stress tolerance
InactiveUS7253000B2Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesNucleic acid sequencingNucleotide sequencing
The present invention provides compositions and methods for regulating expression of nucleotide sequences in a plant. Compositions comprise novel nucleic acid sequences encoding a transcription factor involved in modulating gene expression in response to abiotic stress such as cold or drought. Methods for expressing the nucleic acid sequence in a plant and improving cold and / or drought tolerance of plants are also provided.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
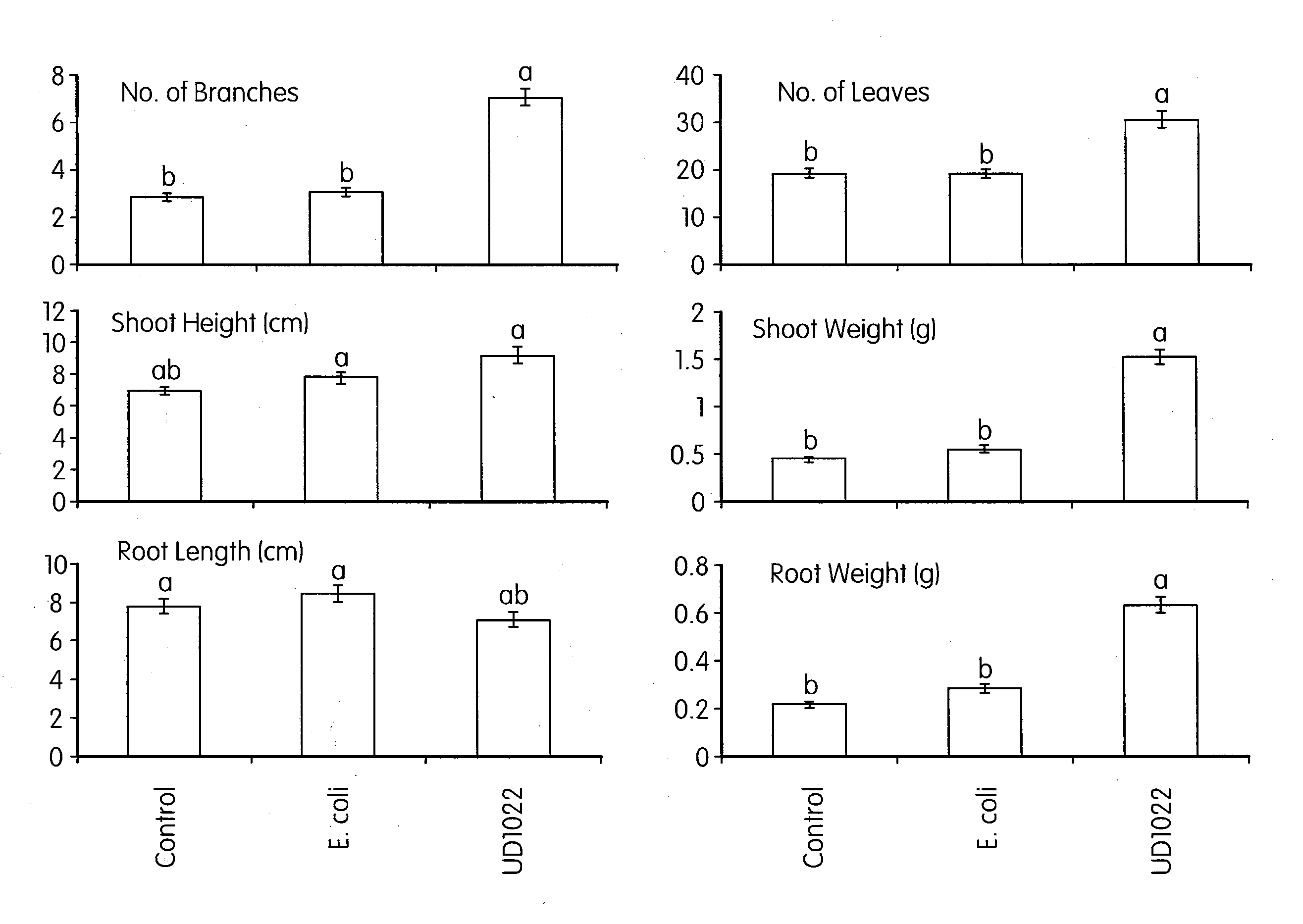
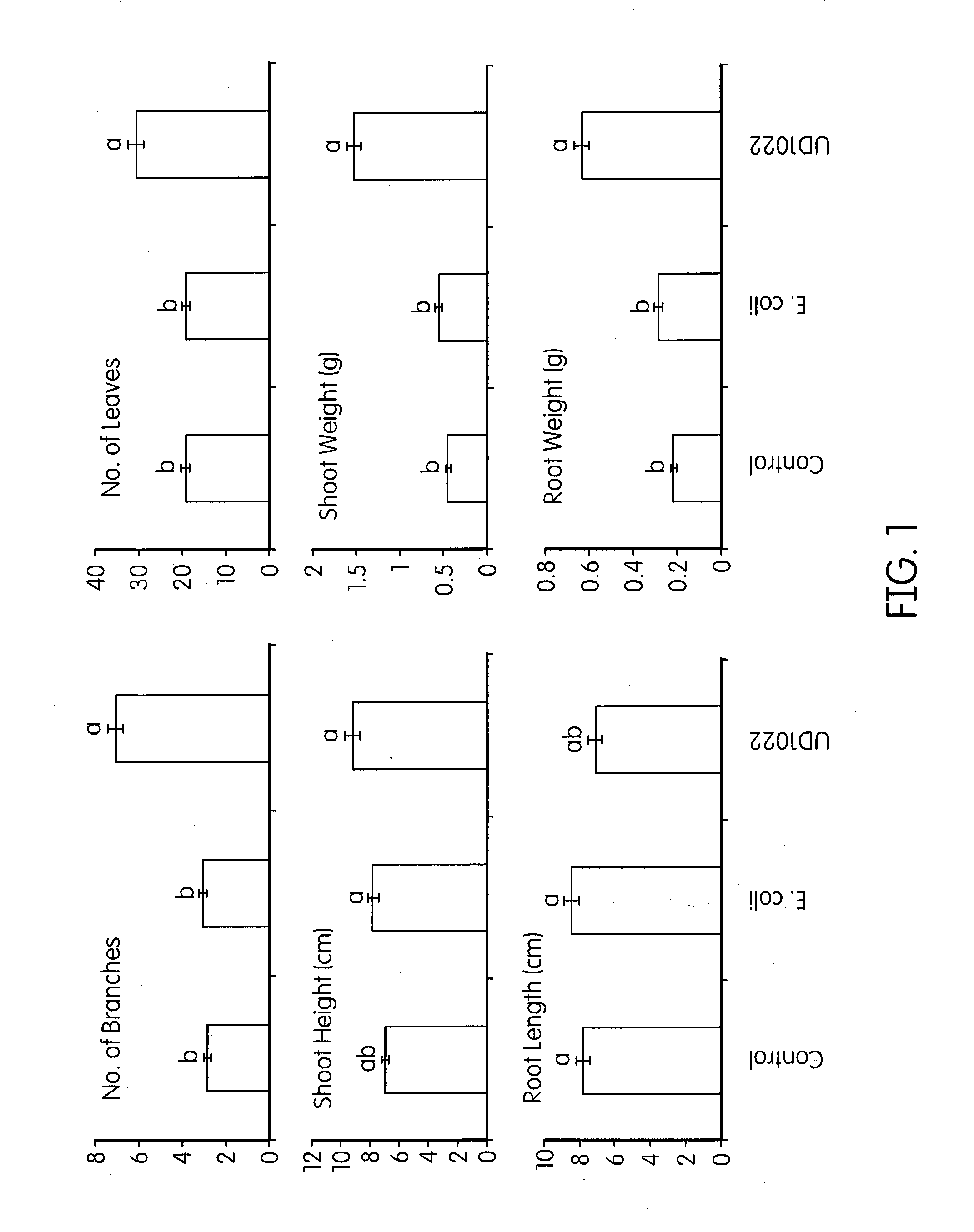
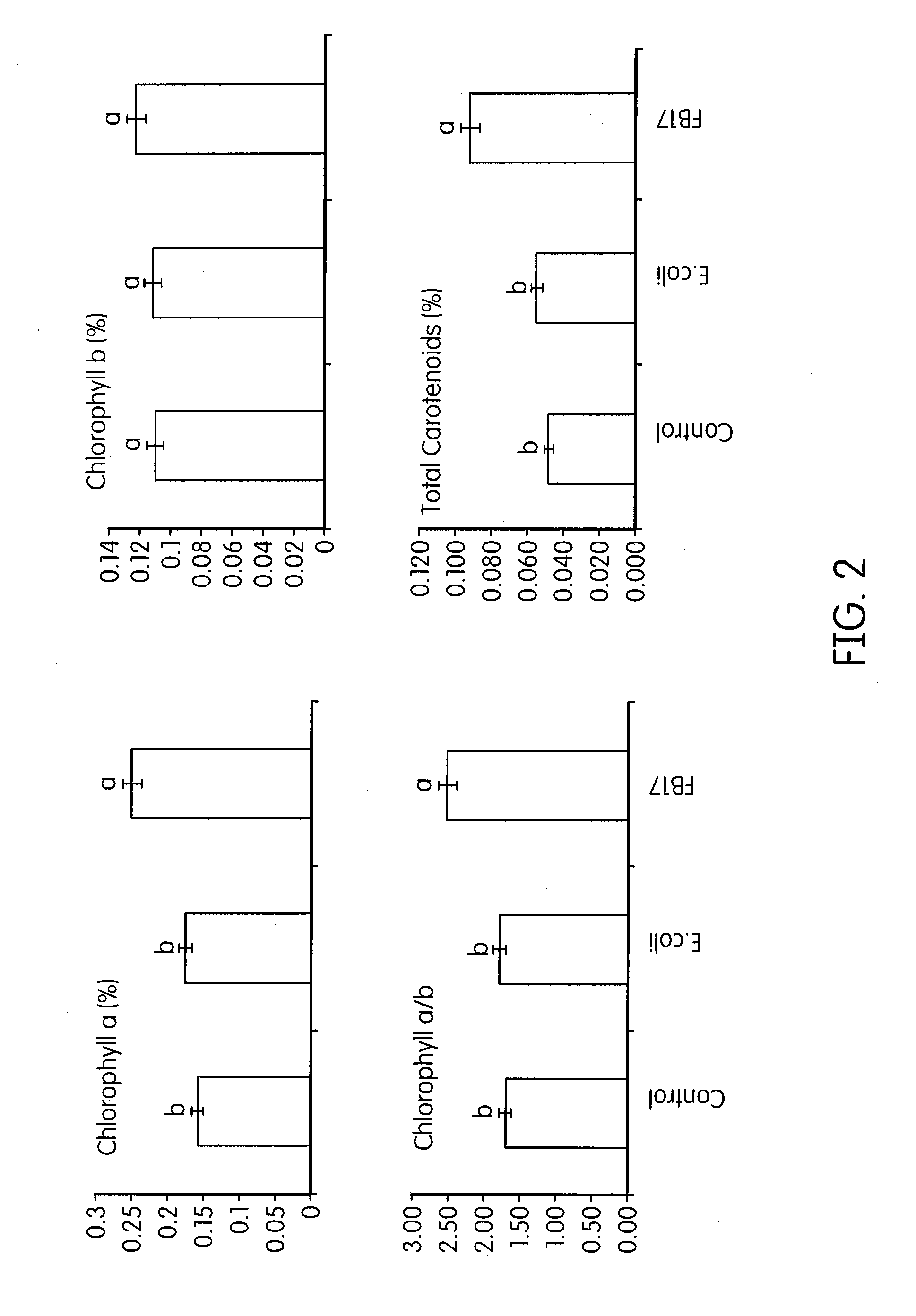
Compositions and methods for increasing biomass, iron concentration, and tolerance to pathogens in plants
Methods for producing greater biomass in a plant, increasing the drought tolerance of a plant, producing a decreased lignin concentration in a plant, producing a greater iron concentration in a plant, or inhibiting fungal infection in a plant comprise administering Bacillus subtilis FB17 to the plant, the seed of the plant, or soil surrounding the plant or the seed in an amount effective to produce greater biomass, increase the drought tolerance, produce a decreased lignin concentration, produce a greater iron concentration, or inhibit fungal infection in the plant compared to an untreated plant, respectively. Agricultural carriers and seed coatings comprising Bacillus subtilis FB17 are provided. The biomass of a plant which has been administered Bacillus subtilis FB17 can be converted to a biofuel or can be used as a food crop or in other uses.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE
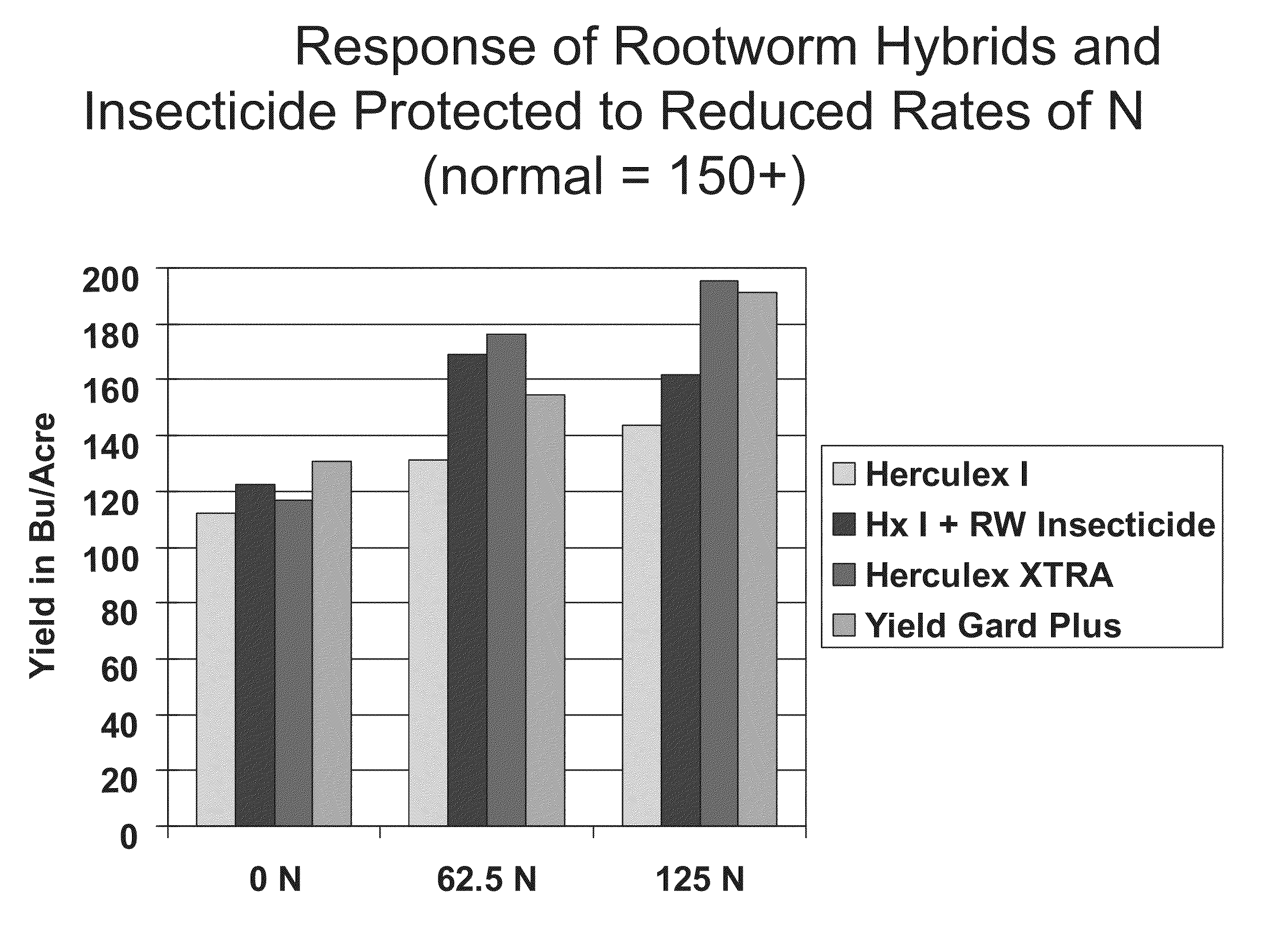
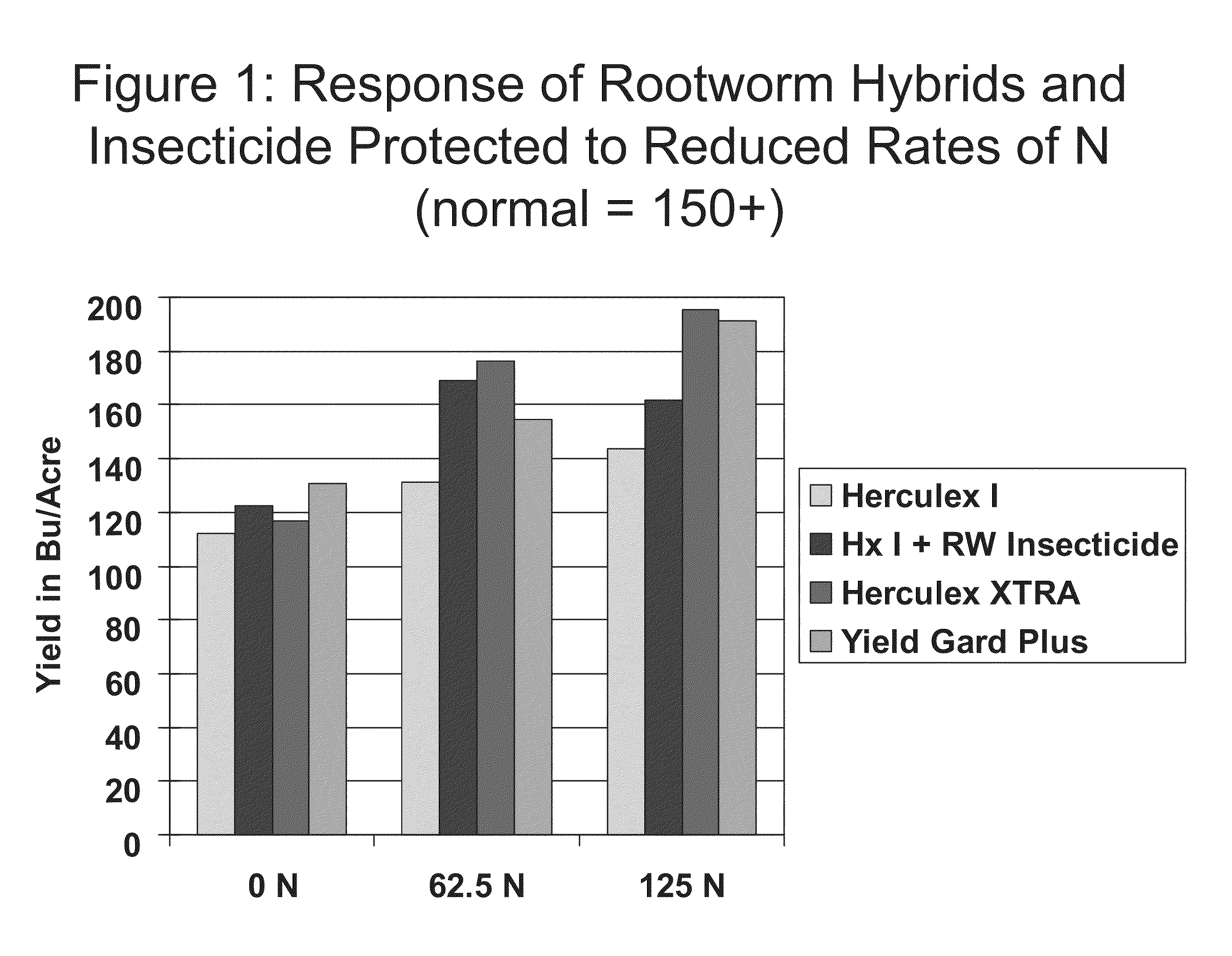
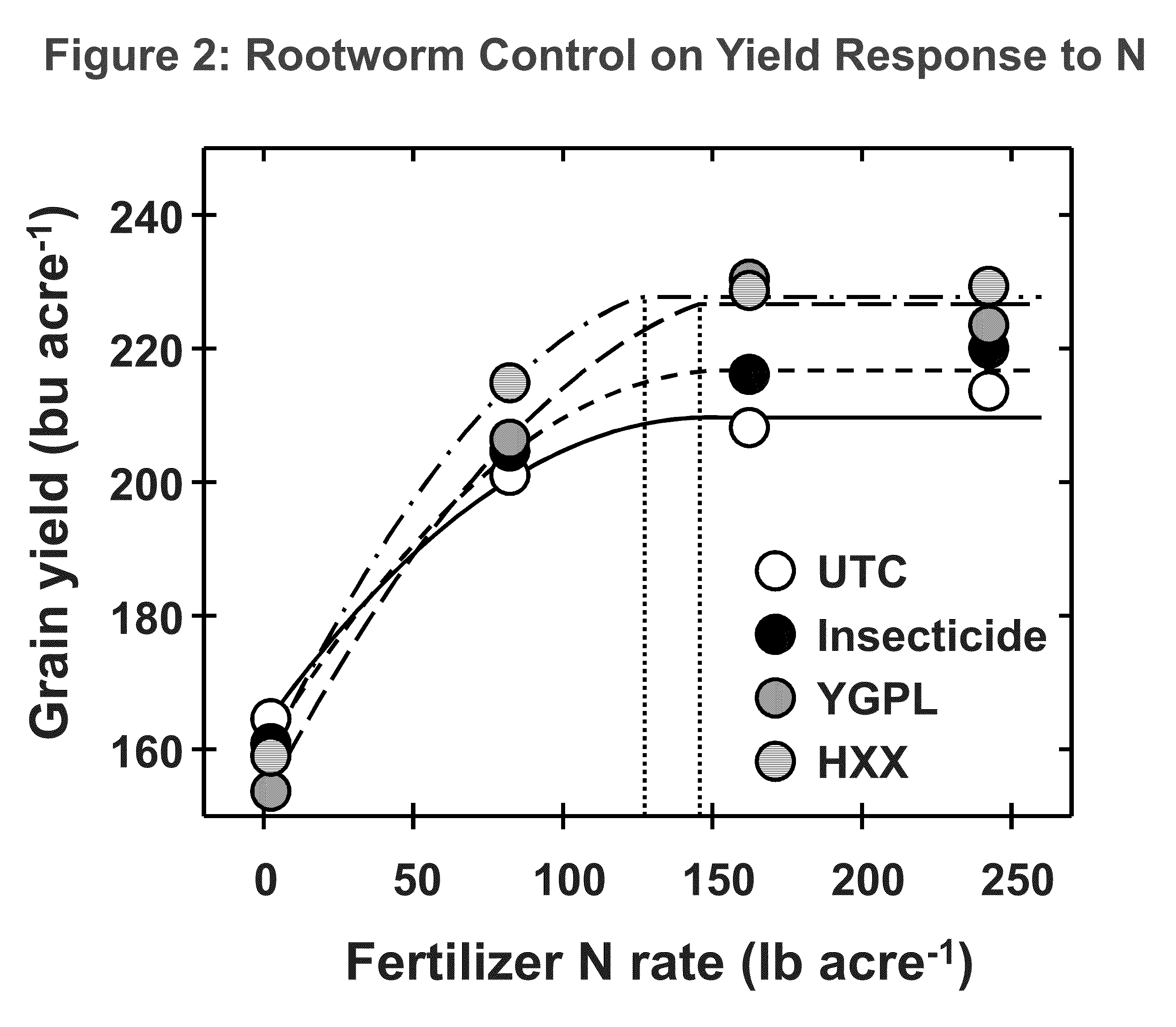
Corn with transgenic insect protection traits utilized in combination with drought tolerance and/or reduced inputs particularly fertilizer
InactiveUS20090300980A1Effective absorptionClimate change adaptationCultivating equipmentsGenetically modified insectPotassium
The subject invention relates in part to the use of insect-protected corn to modify fertility recommendations for given yield targets on any transgenic corn type. The insect-protected plants are unexpectedly more effective at assimilating not only nitrogen but also less valuable nutrients such as phosphorous, potassium and micronutrients such as zinc. The subject invention also relates to the discovery that transgenic corn plants with insect protection traits exhibit drought tolerance. For example, the protected plants are also much more effective at extracting moisture and are therefore more drought resistant and require less supplemental irrigation to produce the same yields as unprotected plants.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
Method for improving drought resistance of drought substrate tall fescue by adopting fine garbage compost
InactiveCN101869031ALarge biomassMeet growthClimate change adaptationFertiliser formsMoisture capacityCompost
The invention relates to a method for improving the drought resistance of drought substrate tall fescue by adopting urban household fine garbage compost, which comprises the following steps of: respectively scattering fine garbage compost of which the particle diameter is respectively 1200nm, 600nm and 300nm uniformly on the surface of soil, wherein the ratio of the particle diameter to parts by weight of the soil is 1:60-80, the temperature is controlled at 20-26 DEG C, the relative humidity is controlled at 40-60%, and natural light permeating a room is used for illuminating; fully watering at the initial stage of seeding; weighing and watering every one or two days according to 55-65% of field moisture capacity after two weeks to maintain the field moisture capacity in the stress range; and measuring each index from the 44th day. The result shows that under the drought stress, the fine compost increases the biomass of the tall fescue to a certain extent, and the research result of growth of root systems of lawn plants can be basically met by matching the compost with the substrate for cultivating turf.
Owner:TIANJIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Pyrophosphatase of ammopiptanthus mongolicus, and coding gene and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering and in particular relates to pyrophosphatase of ammopiptanthus mongolicus, and a coding gene and application thereof. The pyrophosphatase provided by the invention comes from the ammopiptanthus mongolicus, named AmVP1, wherein the amino acid sequence of the pyrophosphatase is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. The coding gene of the pyrophosphatase of the ammopiptanthus mongolicus is one of the following nucleotide sequences: SEQ ID NO.1 and polynucleotide with the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.2. The gene of the invention can be applied to the research of the salt-resisting and drought-enduring molecular mechanism of the ammopiptanthus mongolicus, and is used for improving the salt-resisting and drought-enduring property of plants.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Screening method of drought-resistant eurytopic stable yield wheat variety
ActiveCN105104180AImprove reliabilityEliminate YieldPlant genotype modificationHorticultureScreening methodDrought resistance
The invention discloses a screening method of a drought-resistant eurytopic stable yield wheat variety, and belongs to the technical field of wheat planting. The invention aims to provide a method, which comprises the steps of analyzing interannual variations of variety yields and yield components through successive planting in a field under the condition of natural rainfall; screening dryland wheat varieties of which the drought resistance is high, the yield interannual variation is small, and yield stability is good. The screening method provided by the invention is completely dependent on 3 types of rainfall year types of natural rainfall, the drought resistance, the eurytopicity, and the yield stability of varieties are evaluated through a variable coefficient (C.V.) of the wheat yield and yield components, the dispersion degree of data can be reflected through the C.V., so that the difference of yield and yield components for only one year is eliminated, and the identification reliability is high.
Owner:WHEAT RES INST OF AGRI SCI
Cloning and function expression method of adversity stress AhMYBL6 gene in peanut
ActiveCN103060340AIncreased transcript levelsImprove stress resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationOpen reading frameComplementary deoxyribonucleic acid
The invention relates to a cloning and function expression method of an adversity stress AhMYBL6 gene in peanut. The adversity stress AhMYBL6 gene is synthesized by RT-PCR (reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction) cloning by the steps of preparation and treatment of materials, extraction of RNA (ribonucleic acid) and synthesis of cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid). The open reading frame of the gene is 861bp, and 287 amino acids are coded totally. The homology of the amino acid sequence of the gene with the MYb family proteins GmMYB4, GmMYB29 and GmMYB29A2 of the soybean is higher than 60%. The fluorescent quantitative PCR verifies the expression patterns of the AhMYBL6 under low temperature, salt stress and drought stress; the result indicates that the expression levels of the AhMYBL6 are obviously enhanced after various stress treatment for 1 hour, and kept at high levels all the time thereafter; and the expression level of the AhMYBL6 in the leaf subjected to low-temperature treatment is maximally enhanced by 20 times. After the gene is transferred into peanut by transgenic means, compared with the control, the transgenic plant has obvious characteristics of cold tolerance, salt tolerance and drought tolerance. The AhMYBL6 gene can obviously enhance the stress tolerance of the peanut.
Owner:SHANDONG PEANUT RES INST
Soybean holy bean 9# NAC transcription factor gene GmST1 and application thereof
ActiveCN102660554AImprove salt/drought toleranceImproves salt/drought toleranceFermentationGenetic engineeringTransgeneGenetic engineering
The invention discloses a soybean holy bean 9# NAC transcription factor gene GmST1 and a plant expression vector of the gene GmST1 and further discloses application of the gene GmST1 in improving salt / drought resistance of arabidopsis thaliana and soybean plants. An experiment proves that compared with a non-transgenic plant, the salt / drought resistance of a transgenic plant is greatly improved. Therefore, the theory basis and the practice foundation are provided for improving the salt / drought resistance of plants through genetic engineering means. The soybean holy bean 9# NAC transcription factor gene GmST1 can be widely used for cultivating salt / drought resistant plant varieties.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Plant stress tolerance related protein TaSnRK2.10 as well as coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN102399760AImprove stress resistanceImprove drought toleranceBacteriaTransferasesWater savingSalt resistance
The invention discloses a plant stress tolerance related protein TaSnRK2.10 as well as a coding gene and an application thereof. According to the invention, the protein is the protein shown by the following (a) or (b): (a) a protein formed by amino acid sequences shown in a sequence 2 in a sequence table; and (b) a protein obtained by substituting and / or deleting and / or adding one or more amino acid residues of the amino acid sequences in the sequence 2 in the sequence table, related to plant stress tolerance and derived from the (a). According to the invention, it is proved by experiments that the plant stress tolerance, like drought tolerance, water conservation, salt resistance or cold resistance, can be improved by introducing the genes into the plant. Therefore, according to the invention, the genes and the application thereof has important realistic meaning to develop new drought tolerant, water saving, salt resistant or cold resistant plant.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for promoting salt and drought tolerance of maize and wheat by combining betAíóNHX1íóPPase gene and transgene technology
InactiveCN1769463AImprove salt and drought toleranceFermentationHorticulture methodsBiotechnologyTriticeae
This invention discloses a method for improving the salt resistance and drought resistance of the corn and wheat by aggregating the beta, NHX1, PPase genes with the transfer genes, the steps as follows: regrouping the solution film natrium hydrogen counter-operating protein gene NHX1, the solution film tar phosphatase gene PPase and the Cholinesterase dehydrogenase gene from the escherichia colim to the plant expression carrier, then adding the corn or wheet cells and make them express efficiently, then producing the transfer gene plant; screening out the transfer gene pure cell that has apparently higher salt resistance and drought resistance from the transfer gene plant and its offspring; getting the transfer gene plant with the three object genes through twice tranfering the transfer gene pure cell or making the plant with the different transfer genes mate mutully, then sceening out the ones that have better salt resistance and drought resistance in their offsprings, and making them mute and purify by themselves to creat the new corn and wheat seeds with the salt resistance and drought resistance; or making use of the transfer polymeric material to produce the mixing seeds directly.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Non-irrigation non-maintain solid growth box
InactiveCN101194575AGeneral water supply conservationSelf-acting watering devicesElectricityGreening
The invention relates to a plant stereoscopic planting box which does not need water and electricity and manual irrigating and maintaining and protects environment and saves energy. The invention comprises two large portions like a planting area and a rain water-collecting area. The invention is particularly applied to special facade afforestation such as roof gardens, wall (post) faces and overhead sound-absorbing barriers which are difficult to maintain. The stereoscopic planting box depends on the structural superiority to automatically accumulate water and preserve moisture, and moisture-preserving layers can stop unnecessary vaporization to the largest extent for improving the drought resistance of plants. The invention does not need to irrigate and maintain under normal climatic conditions, and can automatically supply water under bad and draught conditions. The stereoscopic planting box depends on the superiority of exterior design, which is applicable to various shapes. After being installed, the entire planting box is shaded by plants, only plants are exposed on decorative facades to form an integral flower wall (post), the appearance is elegant, and the invention has the performances of quick and convenient dismounting. The stereoscopic planting box depends on the formulation superiority of lightweight nutritious soil, which has lightweight and extensive applying scope, and is particularly applicable to greening of old houses with little bearing.
Owner:上海银鼎工程技术有限公司 +1
Plant cytokinin oxidase
InactiveUS7332316B2Enhanced formation and growthHigh activityFungiBacteriaRoot growthPlant biochemistry
The present invention relates to methods for stimulating root growth and / or enhancing the formation of lateral or adventitious roots and / or altering root geotropism comprising expression of a plant cytokinin oxidase or comprising expression of another protein that reduces the level of active cytokinins in plants or plant parts. The invention also relates to novel plant cytokinin oxidase proteins, nucleic acid sequences encoding cytokinin oxidase proteins as well as to vectors, host cells, transgenic cells and plants comprising said sequences. The invention also relates to the use of said sequences for improving root-related characteristics including increasing yield and / or enhancing early vigor and / or modifying root / shoot ratio and / or improving resistance to lodging and / or increasing drought tolerance and / or promoting in vitro propagation of explants and / or modifying cell fate and / or plant development and / or plant morphology and / or plant biochemistry and / or plant physiology. The invention also relates to the use of said sequences in the above-mentioned methods. The invention also relates to methods for identifying and obtaining proteins and compounds interacting with cytokinin oxidase proteins. The invention also relates to the use of said compounds as a plant growth regulator or herbicide.
Owner:SCHMULLING THOMAS +1
Generation of plants with improved drought tolerance
The present invention is directed to plants that display a drought tolerance phenotype due to altered expression of a DRO2 nucleic acid. The invention is further directed to methods of generating plants with a drought tolerance phenotype.
Owner:AGRI GENETICS
Method for heightening salt tolerance and drought tolerance of cotton by polymeric stress-resistant gene
InactiveCN101624604AImprove salt and drought toleranceVector-based foreign material introductionPlant genotype modificationEscherichia coliAgricultural science
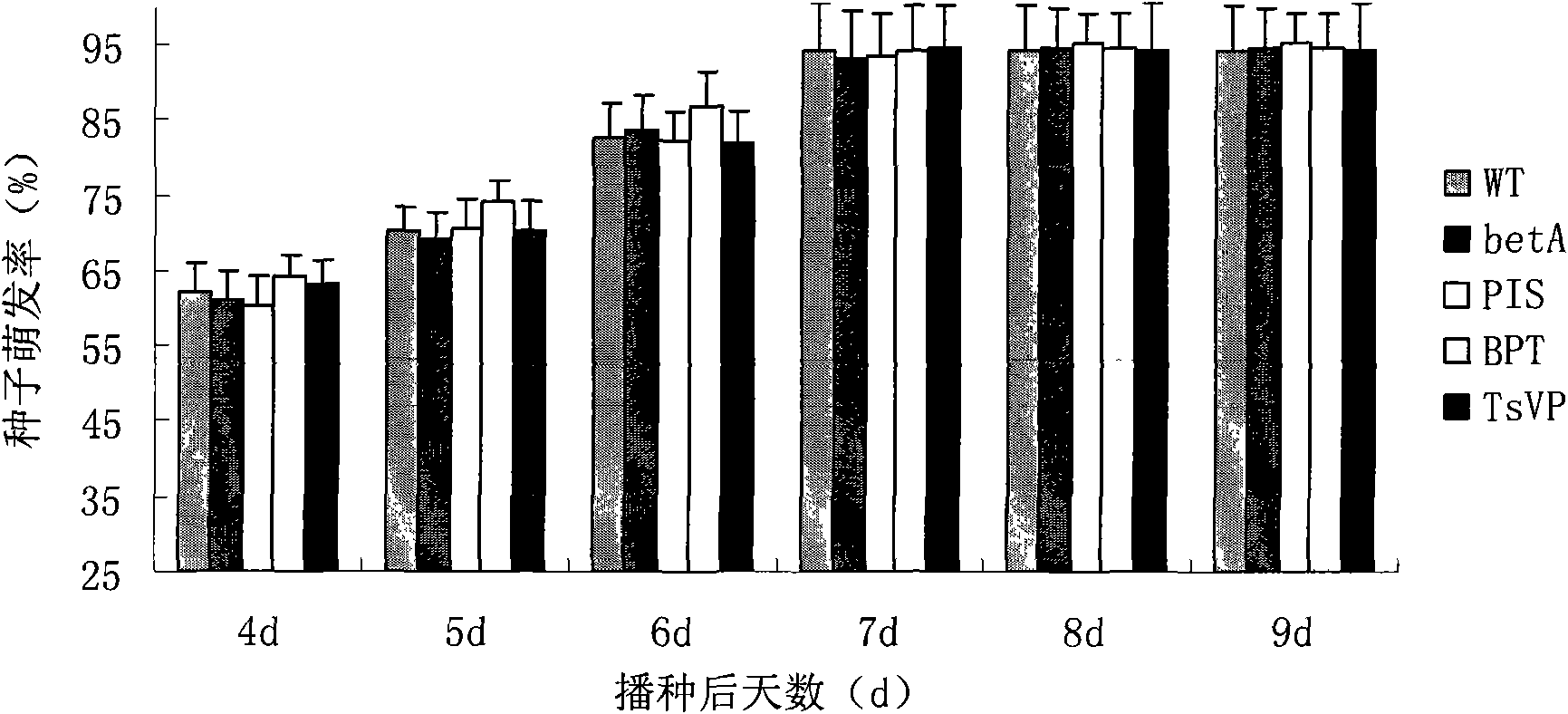
The invention discloses a method for heightening the salt tolerance and the drought tolerance of cotton by polymeric stress-resistant gene, comprising the following steps of: recombining phosphatidyl inositol synthetase gene PIS from a signal transduction pathway of a plant, tonoplast pyrophosphatase gene Ppase isolated from an ion region, and choline dehydrogenase gene betA which is from colon bacillus and gives glycine betaine synthesis capability into a plant expression carrier; transplanting the recombinant into cotton cells to be effectively expressed; regenerating transgene plantlet; selecting transgene homozygote with the obviously heightened salt tolerance and drought tolerance from the transgene plantlet and filial generation thereof; and breeding out new cotton germplasm with good salt tolerance and salt tolerance, so as to create new material for breeding the cotton with good salt tolerance and salt tolerance for breeding the conventional variety or hybrid variety of the cotton.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Transgenic Plant Having Enhanced Drought Tolerance
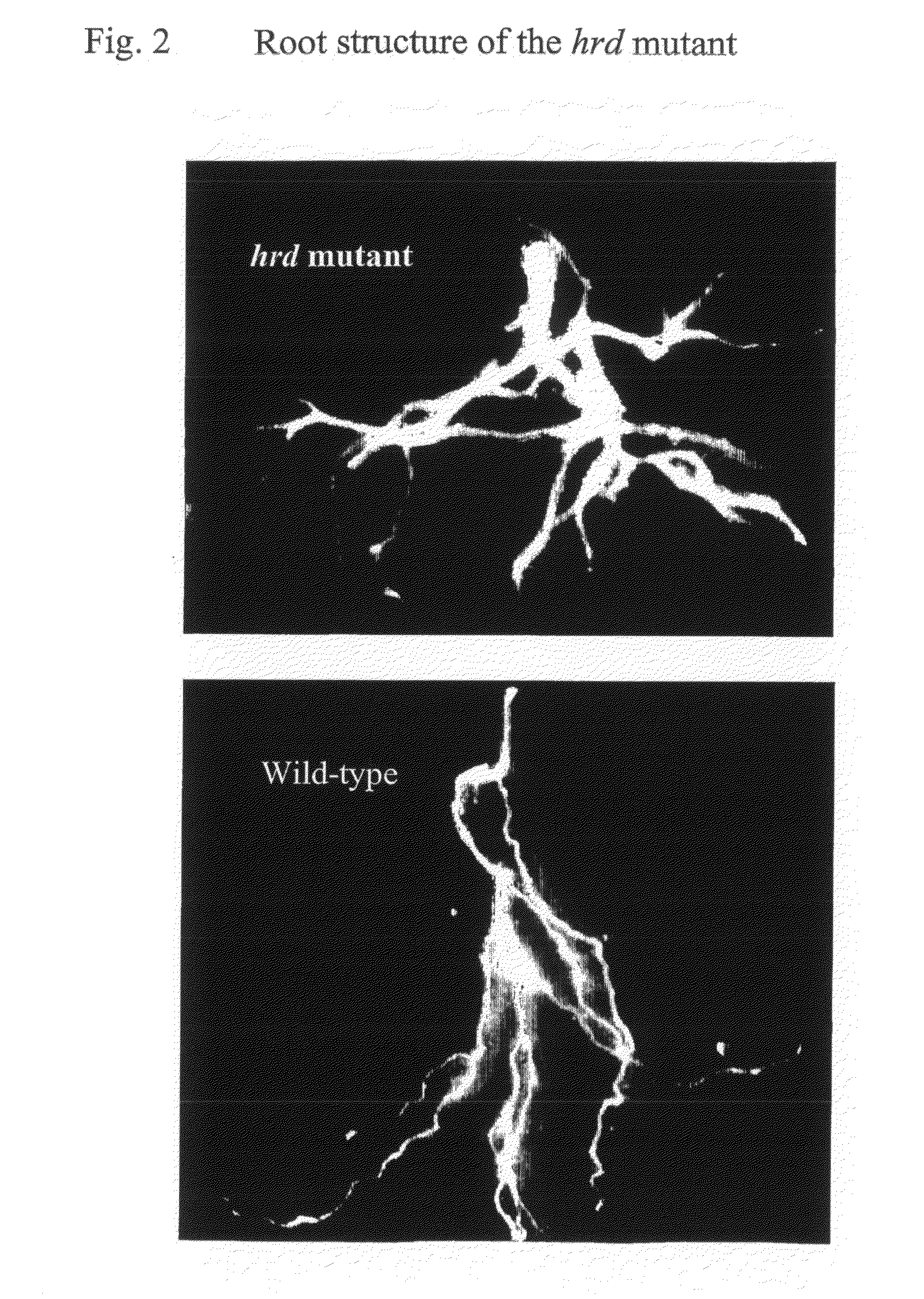
InactiveUS20110209247A1Improve drought toleranceImprove disease resistanceClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesPlant cellGMO Plants
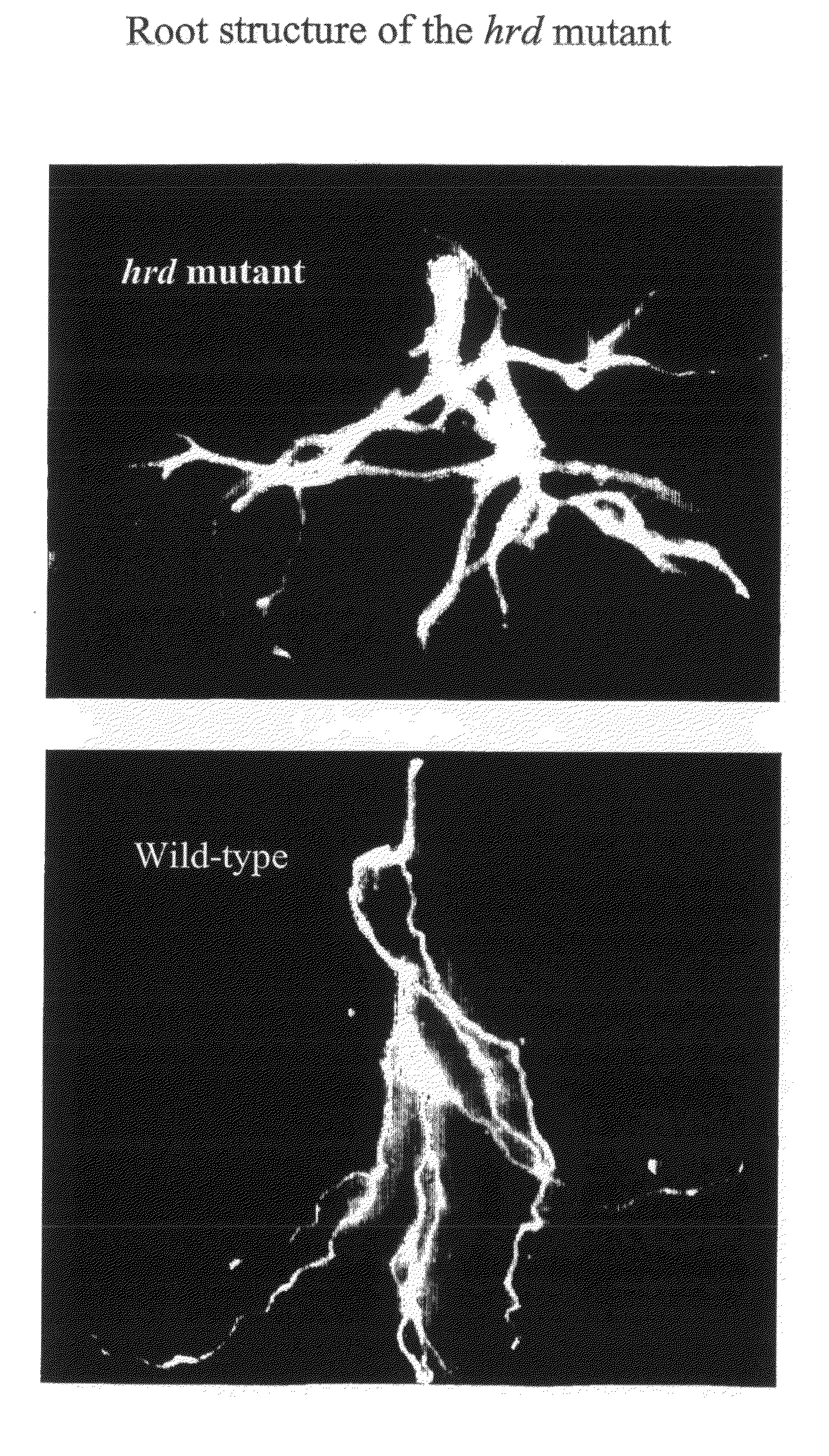
The present invention relates to the field of transgenic plants with novel phenotypes, especially plants with enhanced drought and pathogen resistance. Provided are transgenic crop plants comprising integrated in their genome a chimeric gene, characterized by said chimeric gene comprising a transcription regulatory sequence active in plant cells operably linked to a nucleic acid sequence encoding a protein having the sequence of SEQ ID NO: 3 or a protein at least 70% identical to SEQ ID NO: 3, or an ortholog protein or a functional fragment thereof. In addition to enhanced drought tolerance the transgenic plants may show enhanced disease resistance and enhanced root structure.
Owner:STICHTING WAGENINGEN RES
Seeds production method for pumpkin rootstock
InactiveCN1918970AStrong disease resistanceIncrease productionPlant genotype modificationHorticultureDiseaseRelationship - Father
The invention discloses a sowing method of pumpkin stock, which comprises the following steps: adopting Chinese round pumpkin in the Shandong province to cross for three generations, separating to purify, identifying to sieve self-crossing YN-3 to grow stably under low-temperature and weak light condition as mother, selecting self-crossing CN-3 of Indian long pumpkin to resist low-temperature, drought and disease as father, crossing to obtain the first-filial generation.
Owner:夏瑞金
Method for molecular-marker-assisted selection of cowpea drought tolerant variety
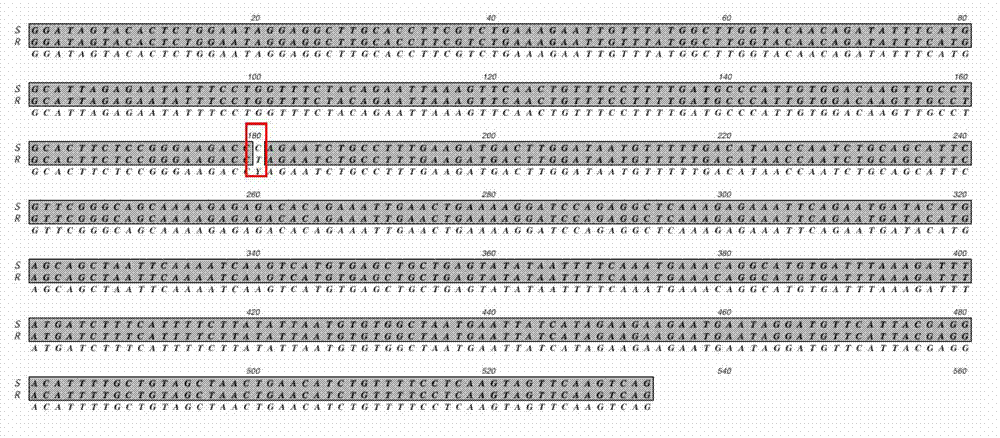
ActiveCN102864242AReduce workloadReduce workload stressMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzyme digestionAgricultural science
The invention discloses a method for molecular-marker-assisted selection of a cowpea drought tolerant variety and belongs to the technical field of vegetable biotechnological breeding. The method includes screening of a cowpea drought tolerant association single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) molecular marker site 1_1286, conversion, amplification and enzyme digestion of SNP to cleaved amplified polymorphic sequence (CAPS) markers, preparation of cowpea materials to be detected, molecular marker detection of seedling drought tolerance of cowpea materials to be detected, phenotype redetection of stay-green Stg of stubbing stems to be detected and agronomic characters and the like. The method has the advantages of being simple and practical, rapid and flexible, accurate in result, low in cost and the like. A molecular marker detection process only needs 4 to 5 hours, and the cost is only about twentieth of that of traditional phenotypic identification. The method can be promoted and applied in vegetable breeding and seed identification sectors.
Owner:上海凌恩生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com