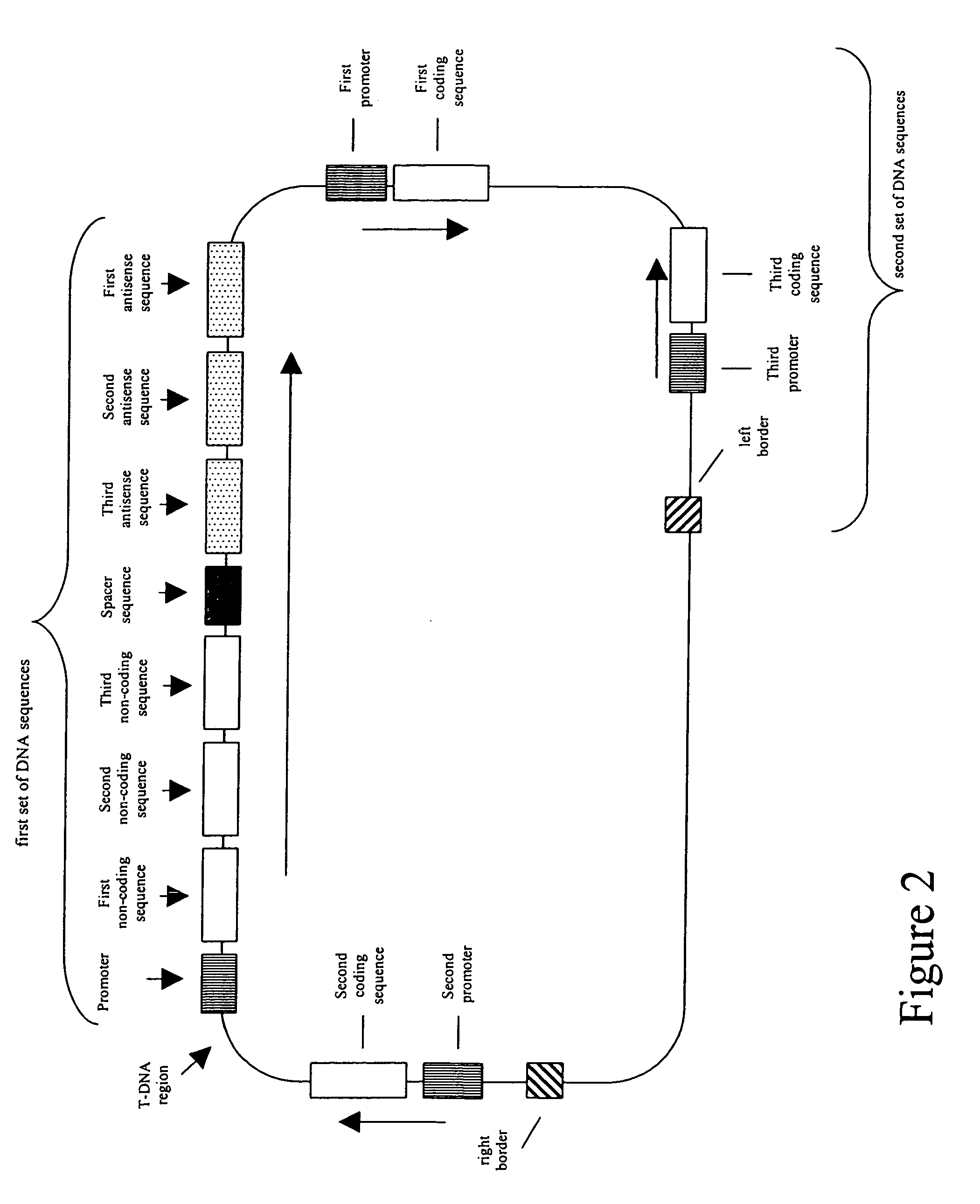
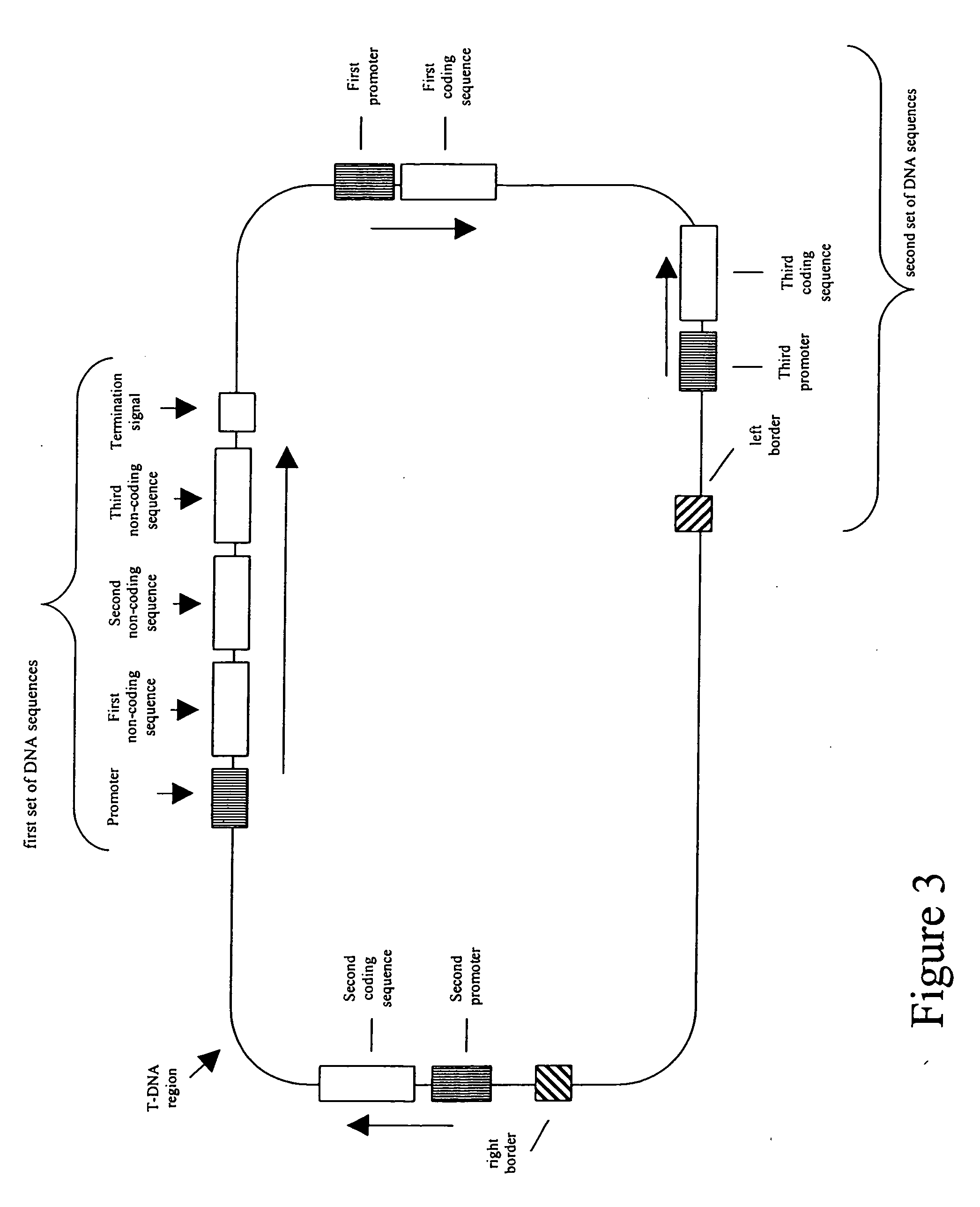
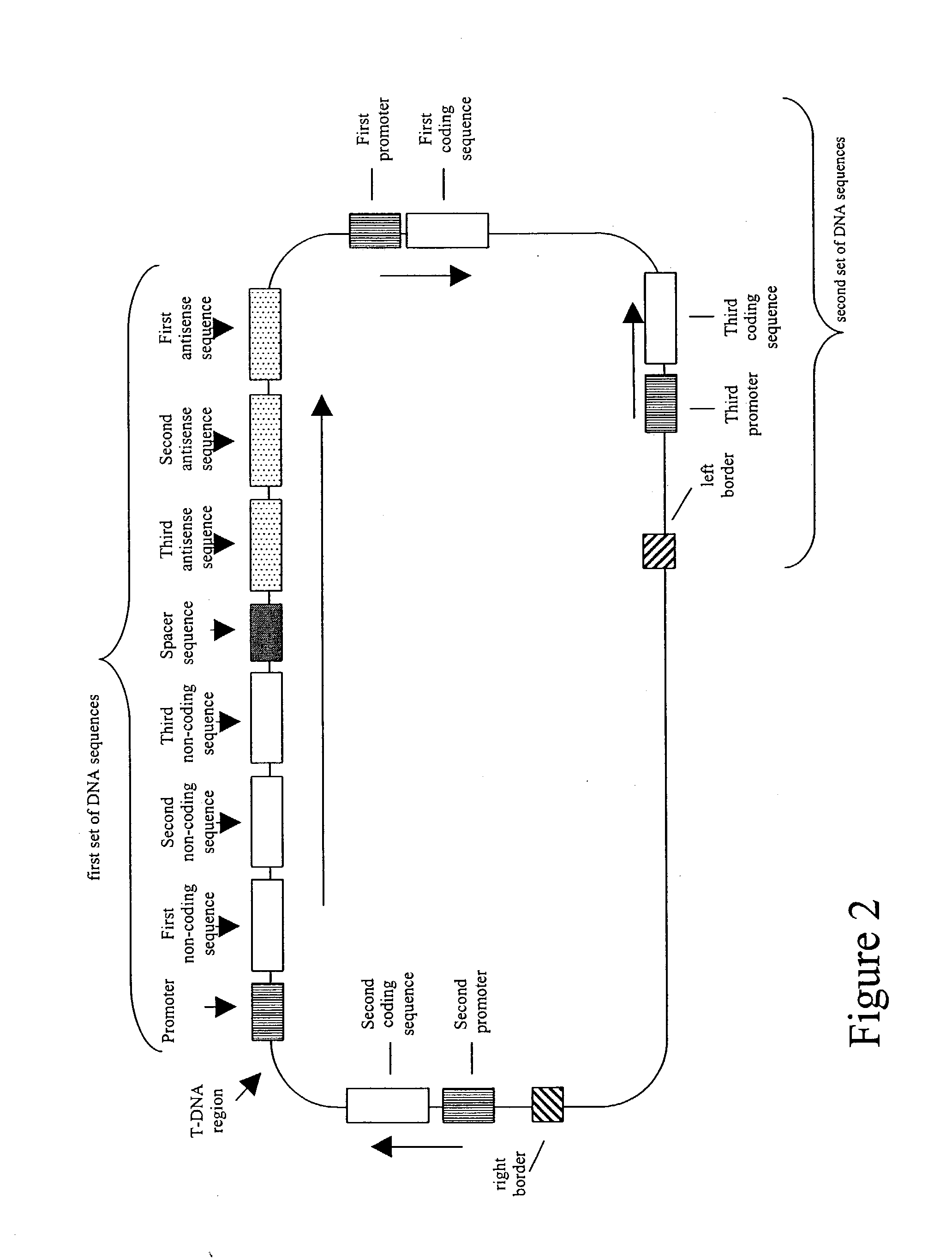
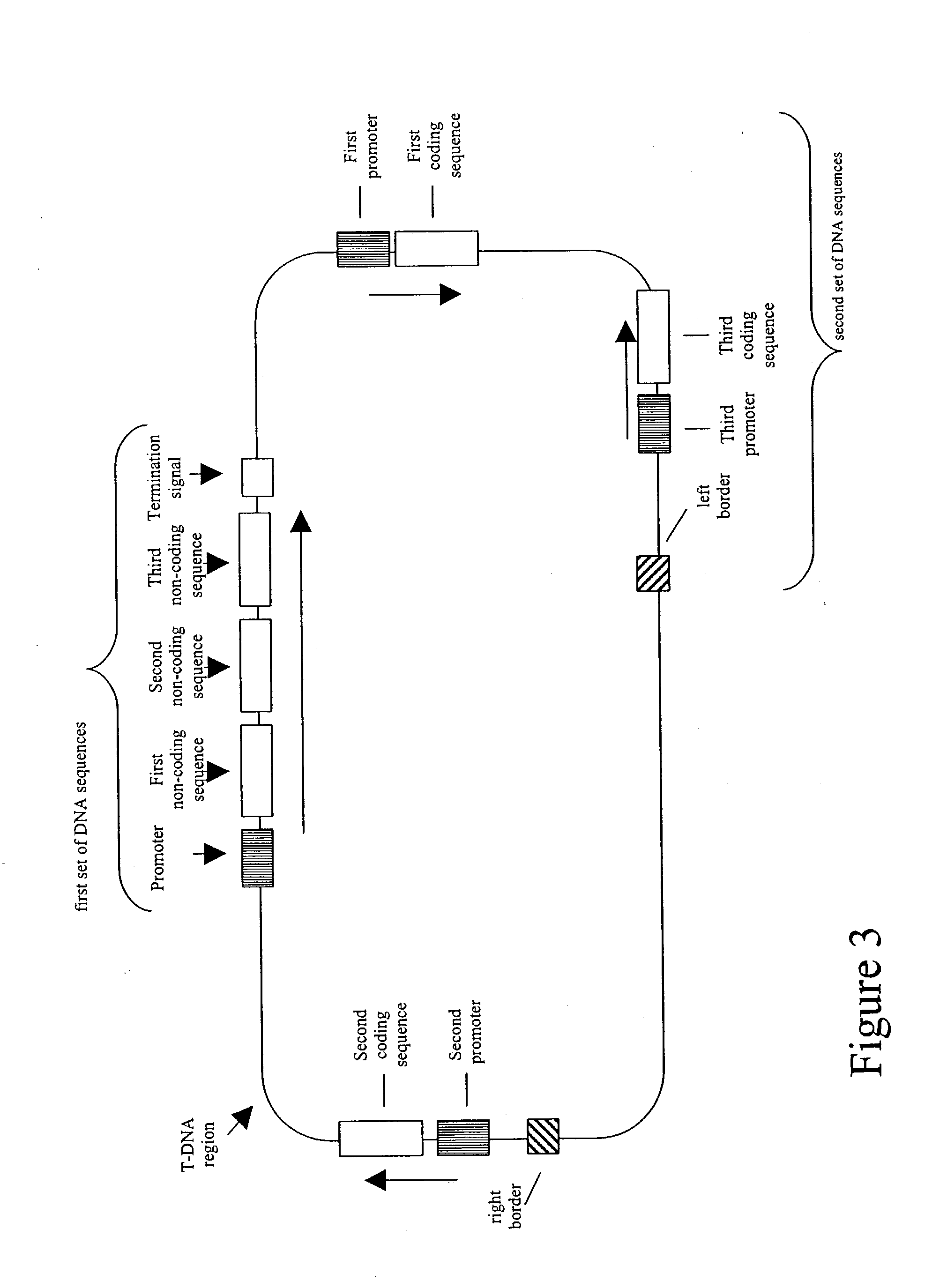
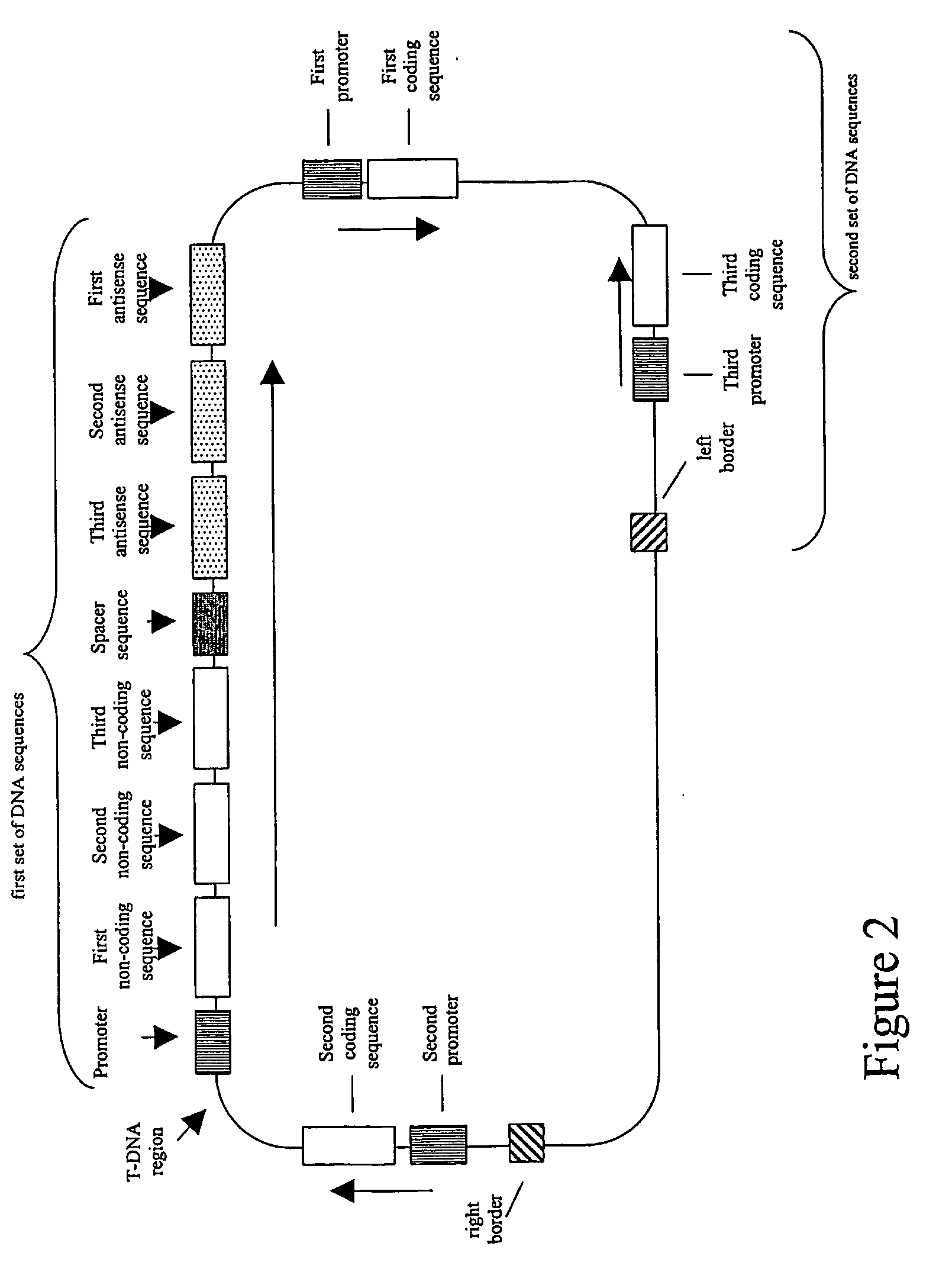
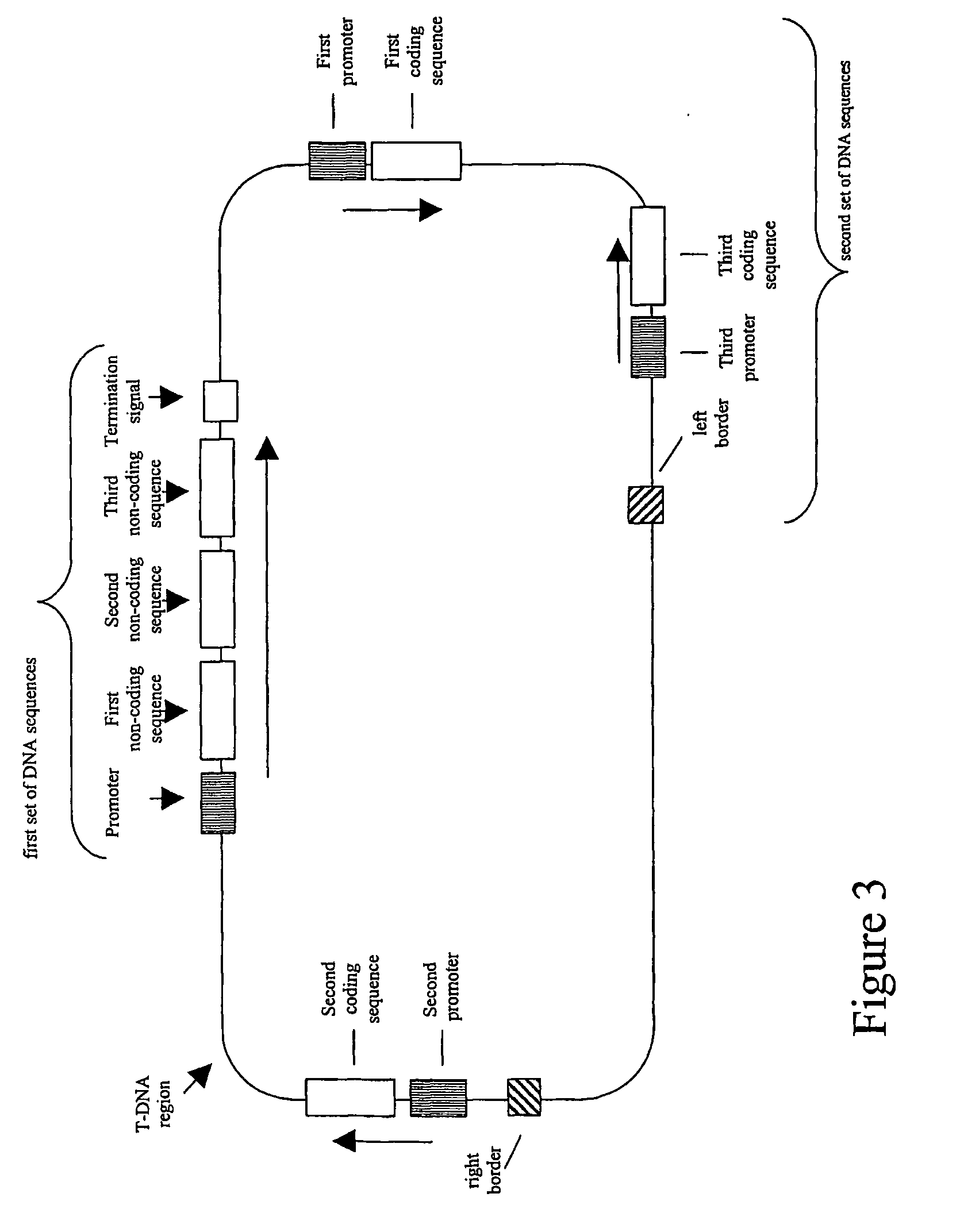
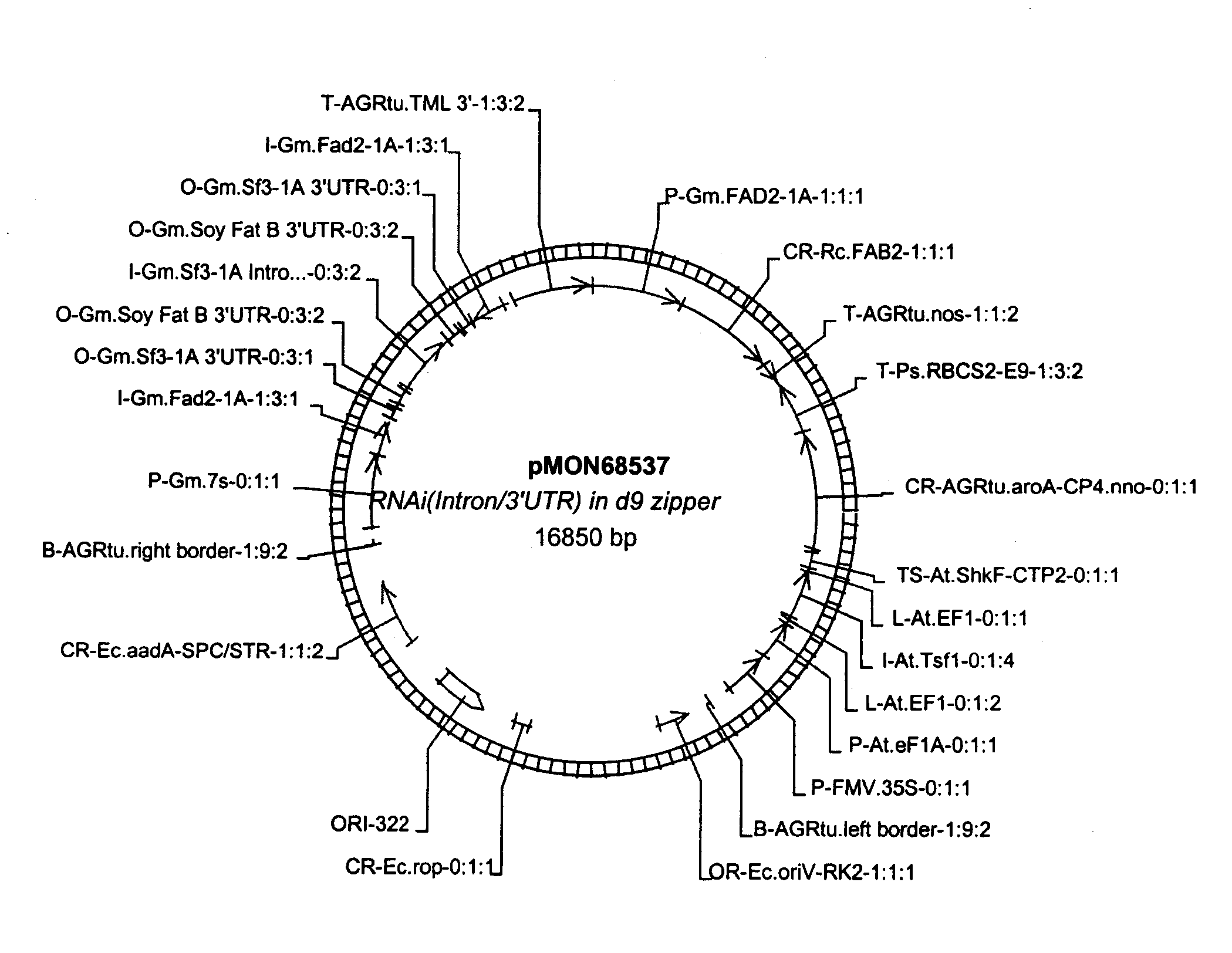
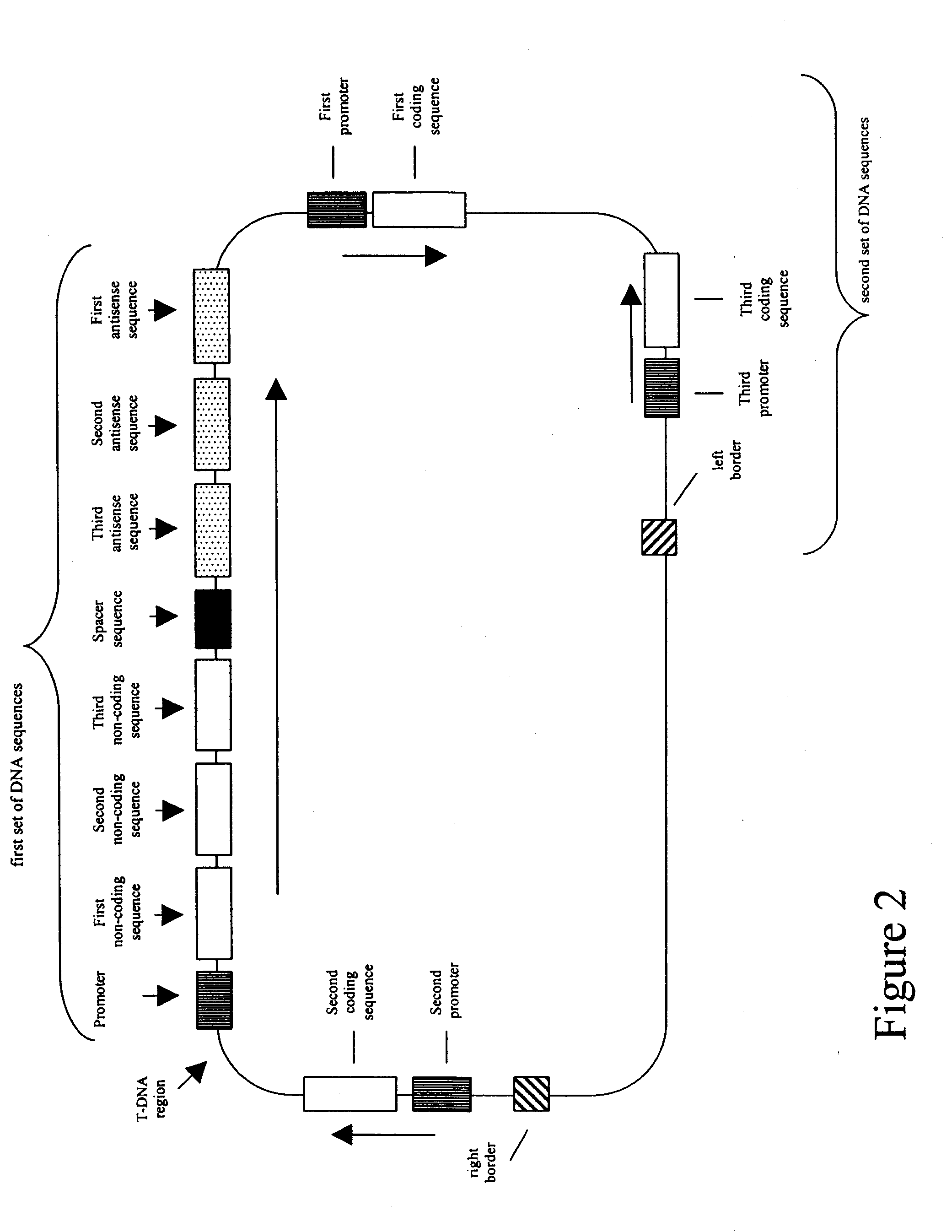
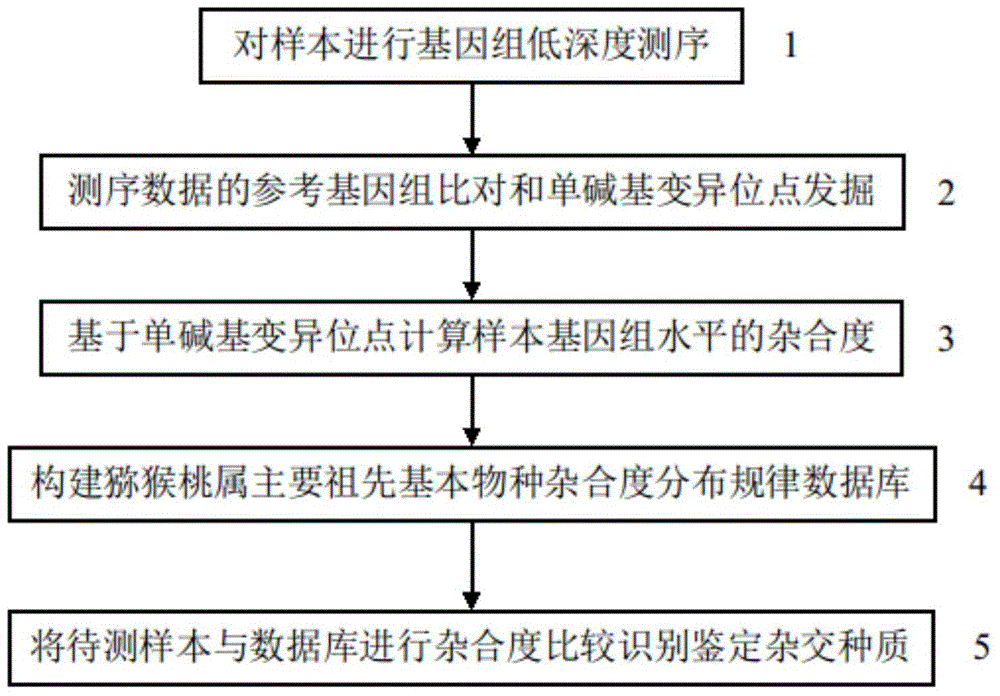
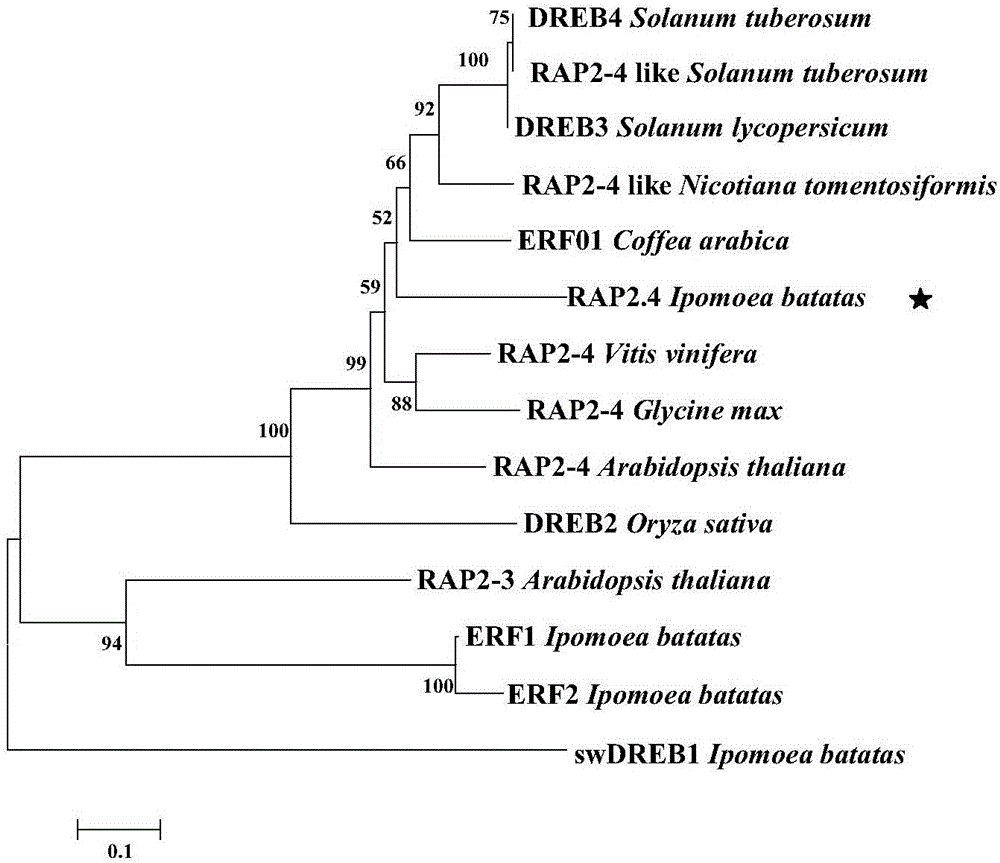
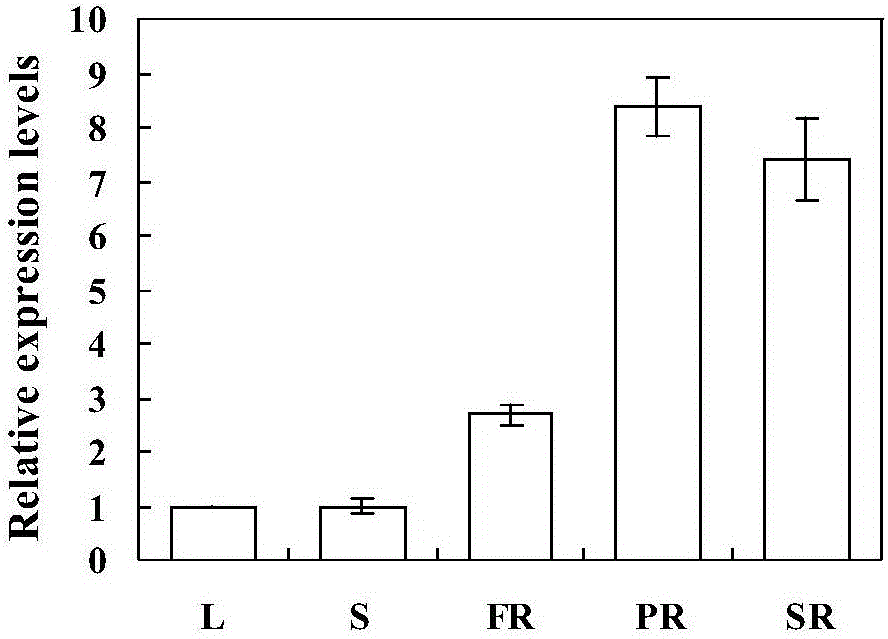
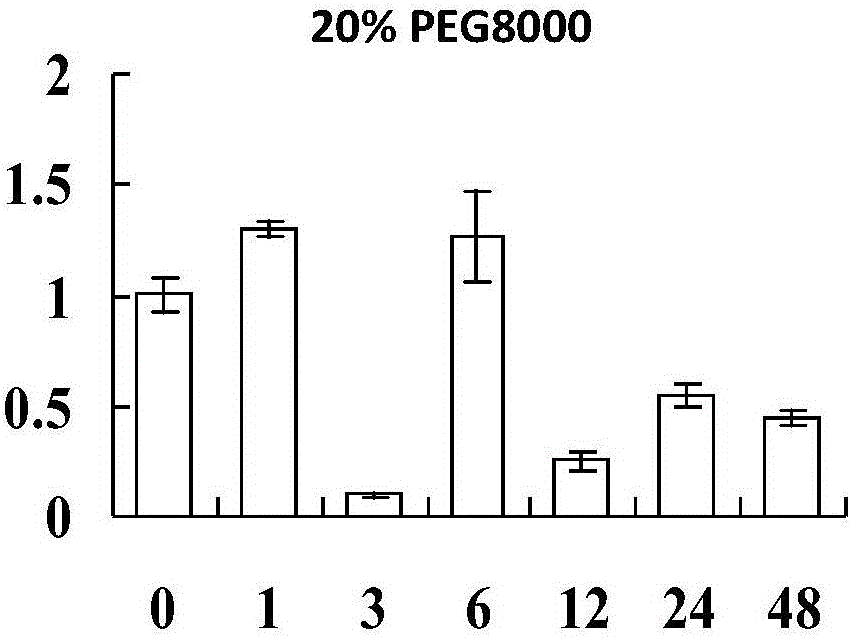
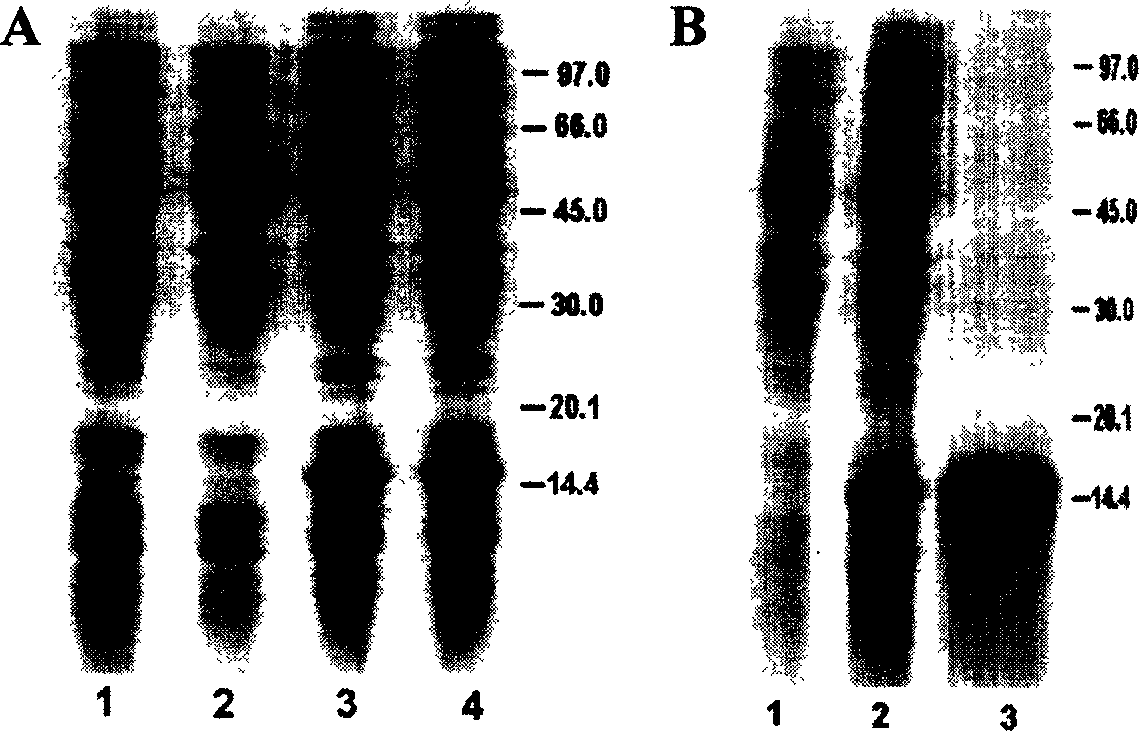
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
210 results about "Plant genetics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Plant genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity specifically in Plants. It is generally considered a field of biology and botany, but intersects frequently with many other life sciences and is strongly linked with the study of information systems. Plant genetics is similar in many ways to animal genetics but differs in a few key areas.
Improved Methods Controlling Gene Expression
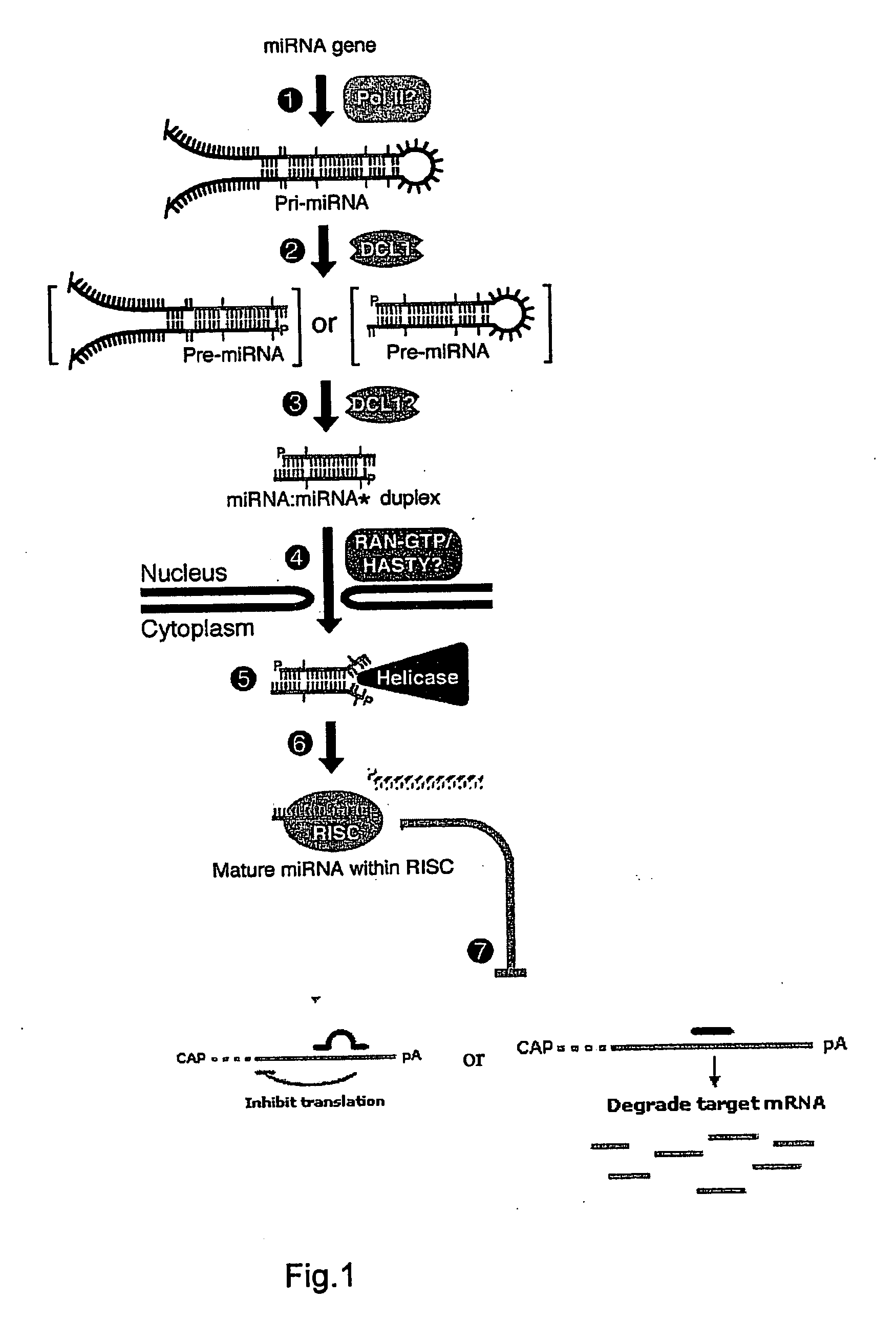
The present invention is in the field of genetics, especially plant genetics, and provides agents capable of controlling gene expression. The present invention specifically provides sequences of naturally occurring, tissue-specifically expressed microRNAs. The invention further provides for transgenic expression constructs comprising sequences encoding said microRNAs. By incorporation of the microRNA encoding sequence the expression from said expression construct is specifically silenced in the tissue where the naturally occurring microRNA is naturally expressed. Thereby the expression profile resulting from the promoter is modulated and leakiness is reduced. The invention further provides for a method for modulating transgenic expression by incorporating sequences encoding said microRNAs into transgenic expression constructs. The compositions and methods of the invention can be used to enhance performance of agricultural relevant crops and for therapy, prophylaxis, research and diagnostics in diseases and disorders, which afflict mammalian species.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Nucleic acid constructs and methods for producing altered seed oil compositions
InactiveUS20060206963A1Increased oleic acid contentReduce saturated fatty acid contentTransferasesBiofuelsFatty acid biosynthesisAdemetionine
The present invention is in the field of plant genetics and provides recombinant nucleic acid molecules, constructs, and other agents associated with the coordinate manipulation of multiple genes in the fatty acid synthesis pathway. In particular, the agents of the present invention are associated with the simultaneous enhanced expression of certain genes in the fatty acid synthesis pathway and suppressed expression of certain other genes in the same pathway. Also provided are plants incorporating such agents, and in particular plants incorporating such constructs where the plants exhibit altered seed oil compositions.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Nucleic acid molecules and other molecules associated with plants
The present invention is in the field of plant genetics. More specifically the invention relates to nucleic acid molecules and nucleic acid molecules that contain markers, in particular, single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and repetitive element markers. In addition, the present invention provides nucleic acid molecules having regulatory elements or encoding proteins or fragments thereof. The invention also relates to proteins and fragments of proteins so encoded and antibodies capable of binding the proteins. The invention also relates to methods of using the nucleic acid molecules, markers, repetitive elements and fragments of repetitive elements, regulatory elements, proteins and fragments of proteins.
Owner:BYRUM JOSEPH +2
Nucleic acid constructs and methods for producing altered seed oil compositions
ActiveUS20050034190A9Suppressing endogenous expressionIncreasing endogenous expressionTransferasesBiofuelsFatty acid biosynthesisAdemetionine
The present invention is in the field of plant genetics and provides recombinant nucleic acid molecules, constructs, and other agents associated with the coordinate manipulation of multiple genes in the fatty acid synthesis pathway. In particular, the agents of the present invention are associated with the simultaneous enhanced expression of certain genes in the fatty acid synthesis pathway and suppressed expression of certain other genes in the same pathway. Also provided are plants incorporating such agents, and in particular plants incorporating such constructs where the plants exhibit altered seed oil compositions.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Nucleic acid constructs and methods for producing altered seed oil compositions
The present invention is in the field of plant genetics and provides recombinant nucleic acid molecules, constructs, and other agents associated with the coordinate manipulation of multiple genes in the fatty acid synthesis pathway. In particular, the agents of the present invention are associated with the simultaneous enhanced expression of certain genes in the fatty acid synthesis pathway and suppressed expression of certain other genes in the same pathway. Also provided are plants incorporating such agents, and in particular plants incorporating such constructs where the plants exhibit altered seed oil compositions.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Nucleic acid constructs and methods for producing altered seed oil compositions
The present invention is in the field of plant genetics and provides recombinant nucleic acid molecules, constructs, and other agents associated with the coordinate manipulation of multiple genes in the fatty acid synthesis pathway. In particular, the agents of the present invention are associated with the simultaneous enhanced expression of certain genes in the fatty acid synthesis pathway and suppressed expression of certain other genes in the same pathway. Also provided are plants incorporating such agents, and in particular plants incorporating such constructs where the plants exhibit altered seed oil compositions.
Owner:FILLATTI JOANNE J +2
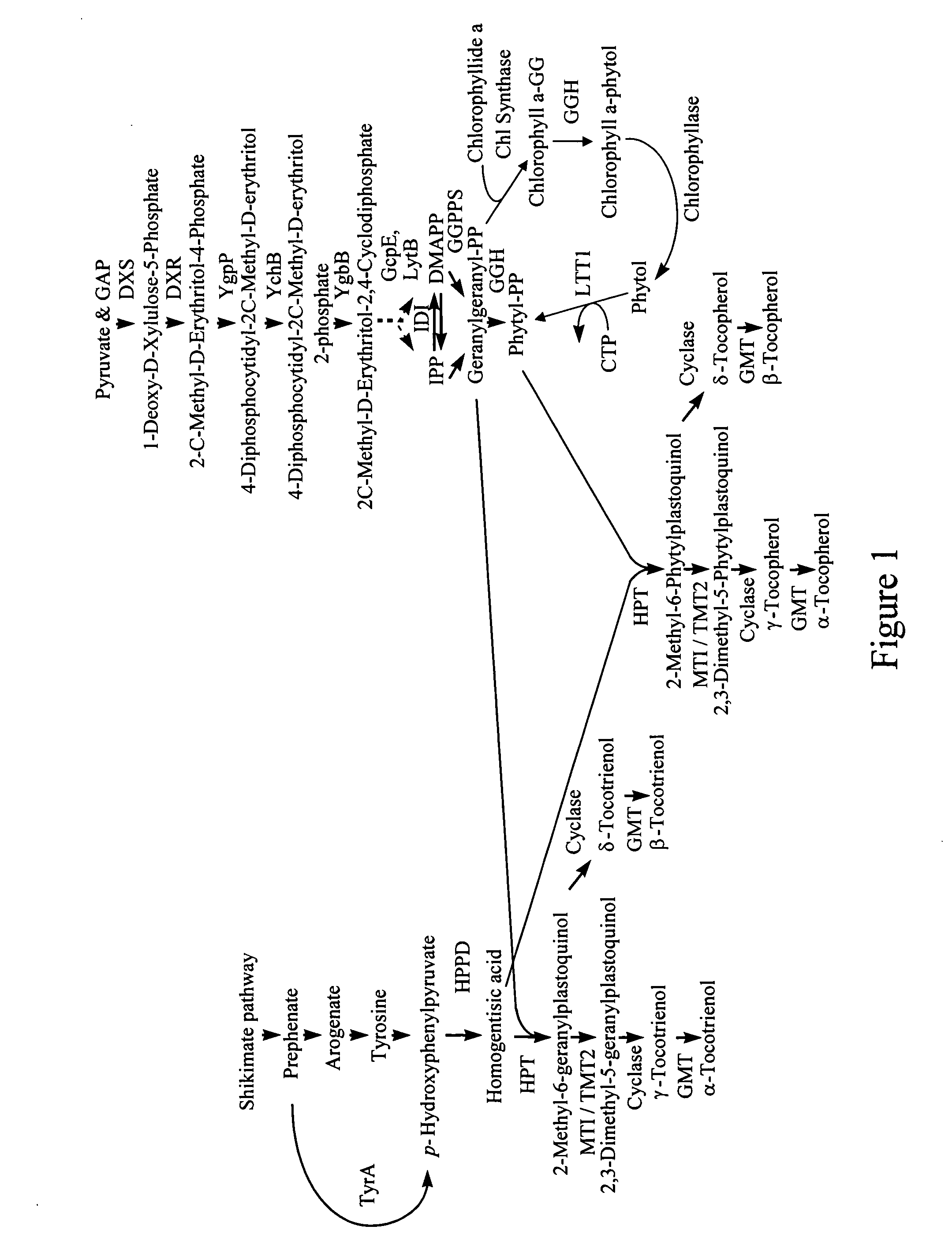
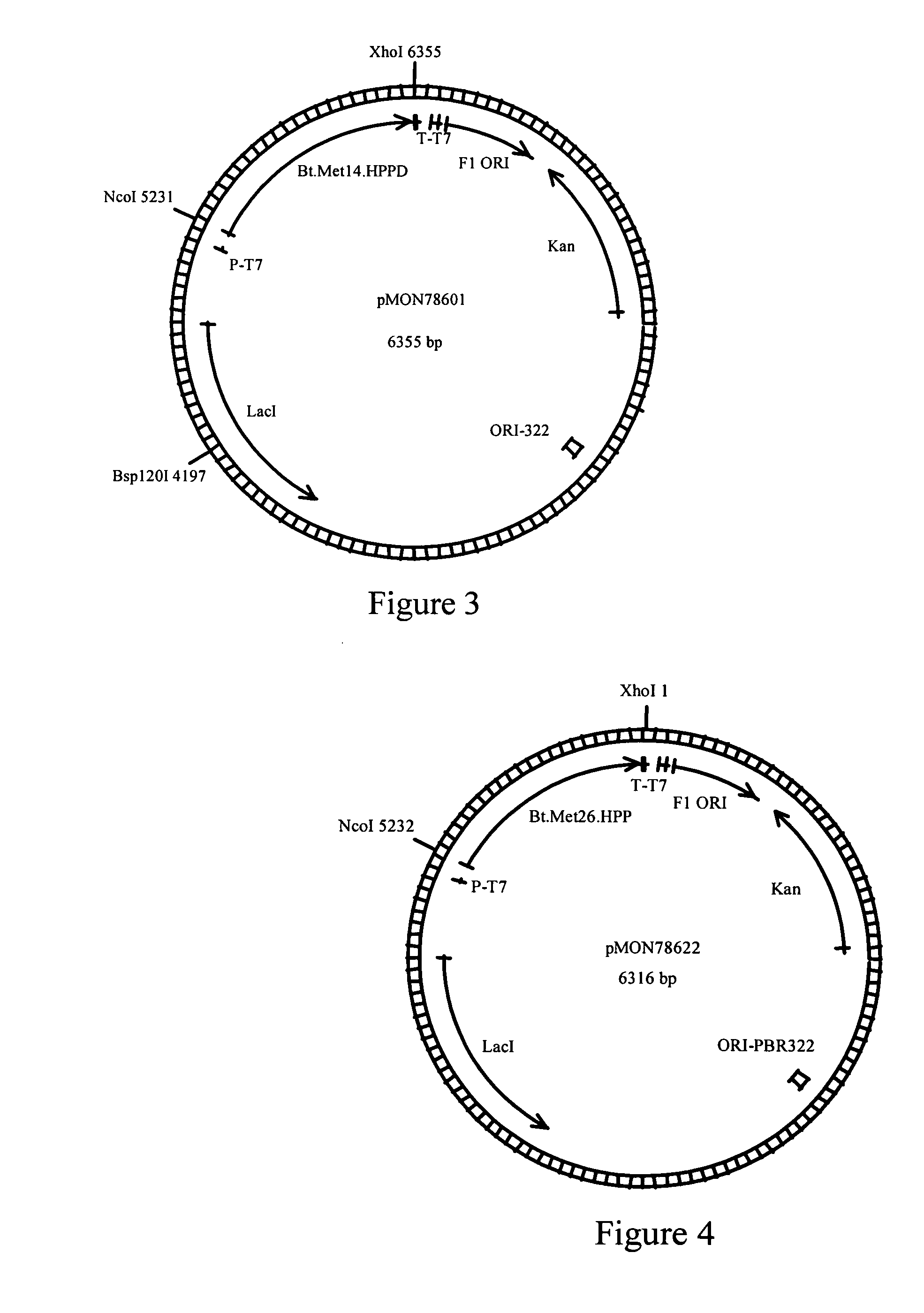
Genes encoding 4-Hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase (HPPD) enzymes for plant metabolic engineering
ActiveUS20050289664A1Improve abilitiesReduce riskSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnology4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase activity
The present invention is in the field of plant genetics and biochemistry. More specifically, the present invention relates to genes and polypeptides associated with the tocopherol biosynthesis pathway, namely those encoding 4-Hydroxyphenylpyruvate Dioxygenase activity, and uses thereof.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Nucleic acid molecules and other molecules associated with plants
InactiveUS20080008996A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementADAMTS ProteinsProtein Fragment
The present invention is in the field of plant genetics. More specifically the invention relates to nucleic acid molecules and nucleic acid molecules that contain markers, in particular, single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and repetitive element markers. In addition, the present invention provides nucleic acid molecules having regulatory elements or encoding proteins or fragments thereof. The invention also relates to proteins and fragments of proteins so encoded and antibodies capable of binding the proteins. The invention also relates to methods of using the nucleic acid molecules, markers, repetitive elements and fragments of repetitive elements, regulatory elements, proteins and fragments of proteins.
Owner:BYRUM JOSEPH
Remediation method for heavy metal cadmium pollution of orchard soil based on galinsoga parviflora
InactiveCN103447290AReduce contentHave patienceContaminated soil reclamationGermplasmSoil heavy metals
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Plant chloroplast development associated protein, and coding gene and use thereof
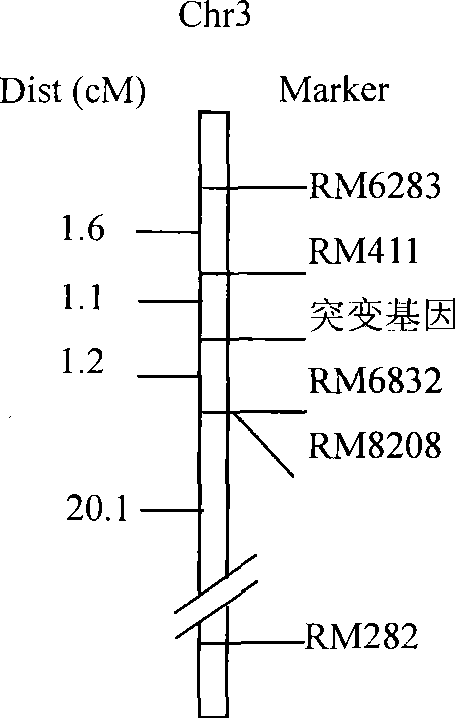
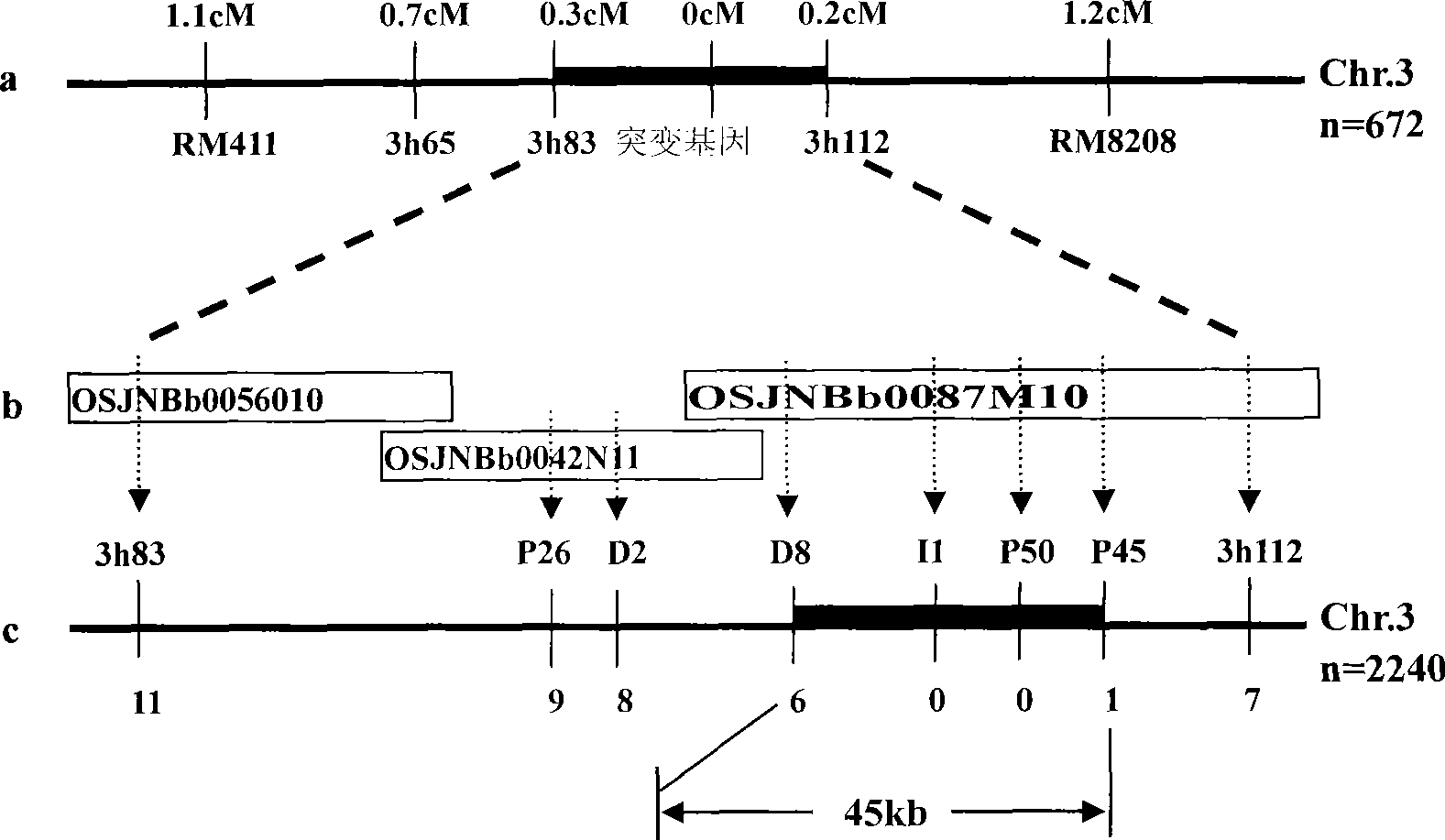
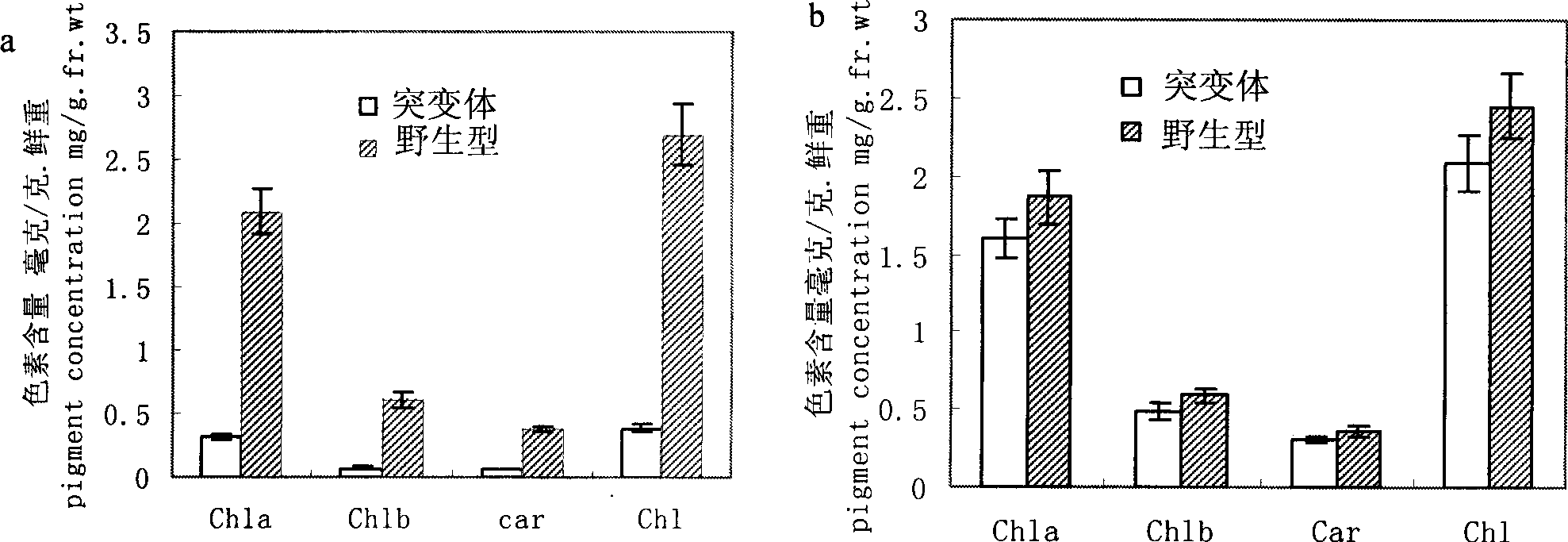
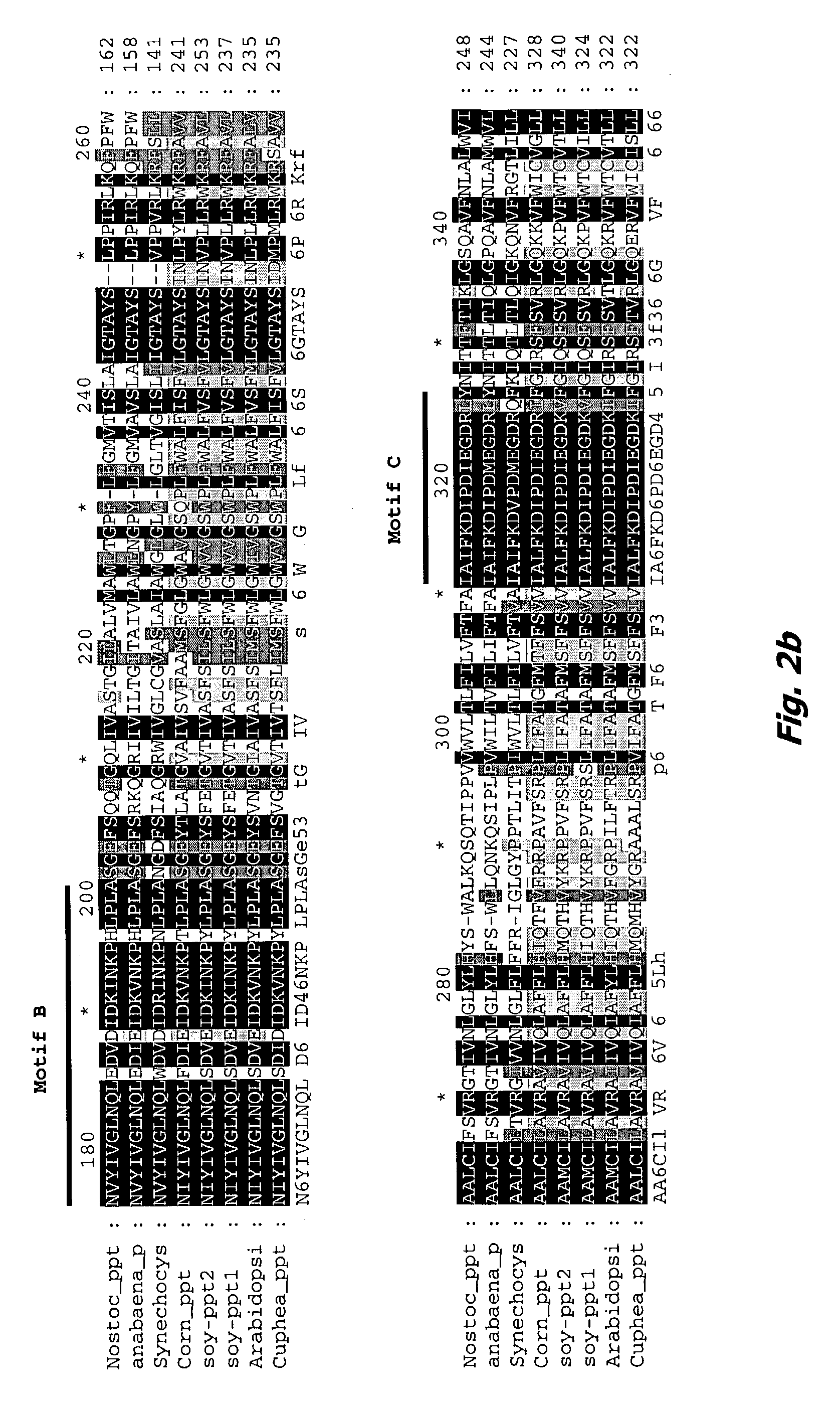
The invention discloses a plant chloroplast-related protein and encoding gene and application thereof. The protein has one of the following amino acid residue sequences: 1) an SEQ ID No.1 amino acid residue sequence in a sequence table; and 2) the SEQ ID No.1 amino acid residue sequence in the sequence table is replaced by one or a plurality of amino acid residues and / or lost and / or added with a protein which is derived from SEQ ID No.1 and has relative development functions of plant chloroplast. When the encoding gene of a rice chloroplast development related protein is destroyed, the plant leaf albino can be caused; and the encoding gene can be applied to the work such as plant genetic improvement and the like, and is an important direction gene, for example, the encoding gene can be uses as a target gene for being applied in rice breeding material sterile lines and changing the color of leaves, and can also be used for two-line hybrid rice seed production or genetic breeding.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Homogentisate prenyl transferase gene (HPT2) from arabidopsis and uses thereof
The present invention is in the field of plant genetics and biochemistry. More specifically, the present invention relates to genes and polypeptides associated with the tocopherol biosynthesis pathway, namely those encoding homogentisate prenyl transferase activity, and uses thereof. In particular, the sequence of the HPT2 gene from Arabidopsis thaliana is disclosed for expression in any plant species to increase the levels of tocopherol.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
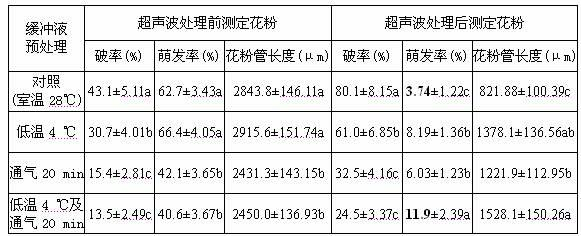
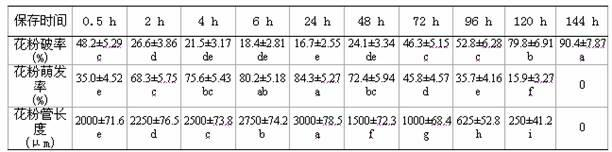
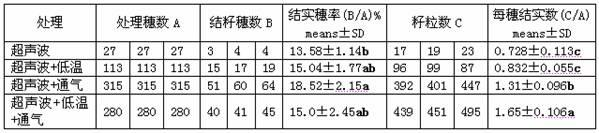
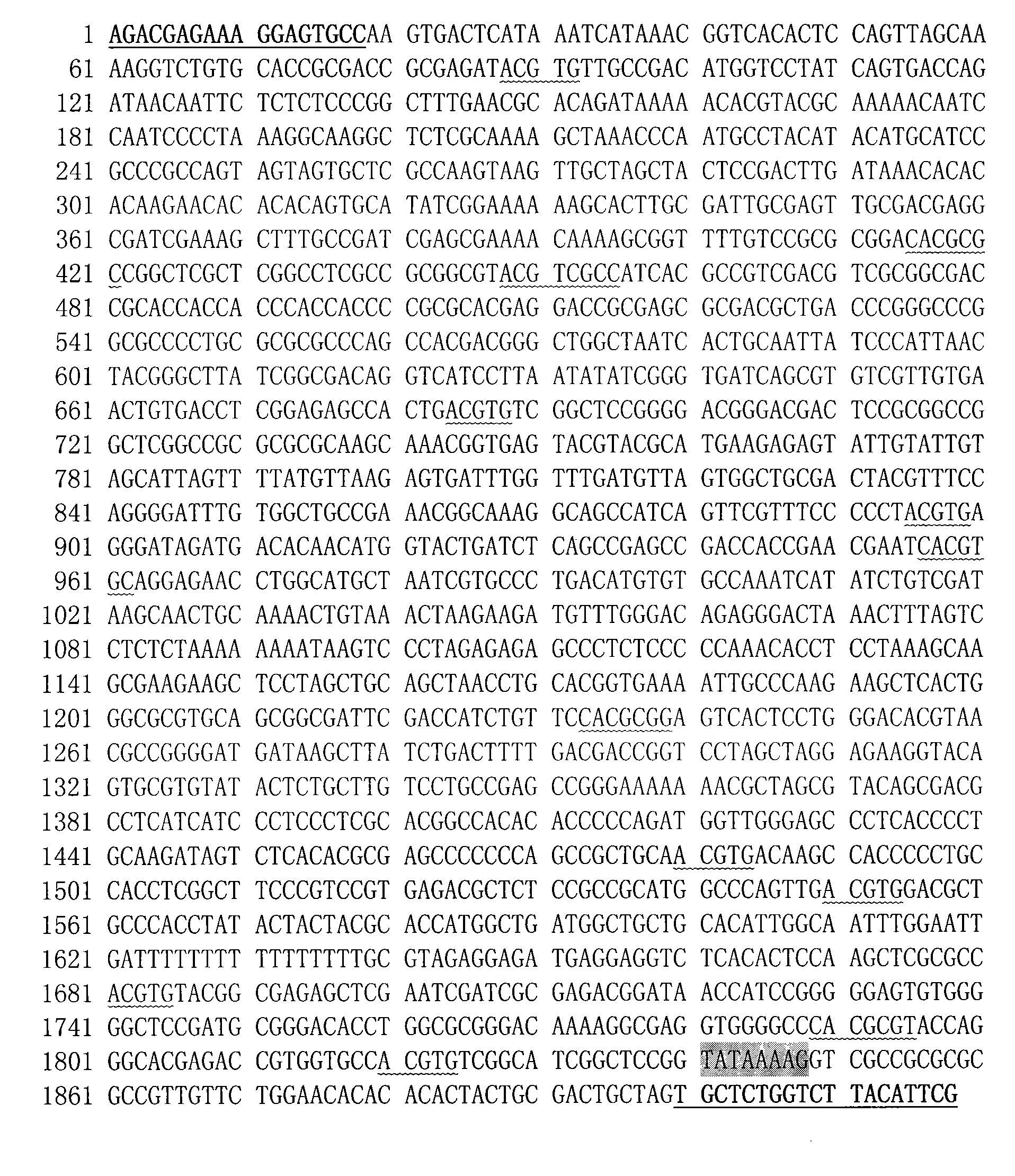
Ultrasonic-assisted pollen mediated plant genetic transformation method
InactiveCN102127567AImprove seed setting rateAvoid the cultivation processVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliSaccharum
The invention relates to an improved ultrasonic-assisted pollen mediated plant genetic transformation method, and aims to obviously increase the setting percentage of the plant fertilized by pollen subjected to ultrasonic treatment, thereby increasing the number of transformants obtained for each treatment. The method comprises the following steps: by using an agrobacterium Ti plasmid carrying an exogenous gene segment, colibacillus plasmid or any other DNA vector as a genetic donor and using plant pollen as a receptor, mixing the pollen and exogenous DNA in a 5-50% sucrose solution subjected to aeration and low-temperature treatment, and transferring the exogenous gene into the receptor pollen under the assisting action of ultrasonic; fertilizing the treated pollen onto the stigma of the plant, and harvesting when the grains become ripe; and in the subsequent growth season, sowing the harvested seeds which are obtained after the fertilization of the transformed pollen, screening the germinated seeds and seedlings, carrying out PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification and Southern hybridization on the DNA of a seedling sample, and further determining the transformant. The method provided by the invention does not need tissue culture, does not have species or genotype dependency, and can shorten the genetic transformation breeding time and save the manpower and material resources.
Owner:AGRI BIOTECH RES CENT OF SHANXI PROVINCE
Nucleic acid molecules and other molecules associated with plants
InactiveUS20070150978A1FermentationVector-based foreign material introductionProtein FragmentAntibody
The present invention is in the field of plant genetics. More specifically the invention relates to nucleic acid molecules and nucleic acid molecules that contain markers, in particular, single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and repetitive element markers. In addition, the present invention provides nucleic acid molecules having regulatory elements or encoding proteins or fragments thereof. The invention also relates to proteins and fragments of proteins so encoded and antibodies capable of binding the proteins. The invention also relates to methods of using the nucleic acid molecules, markers, repetitive elements and fragments of repetitive elements, regulatory elements, proteins and fragments of proteins.
Owner:BYRUM JOSEPH
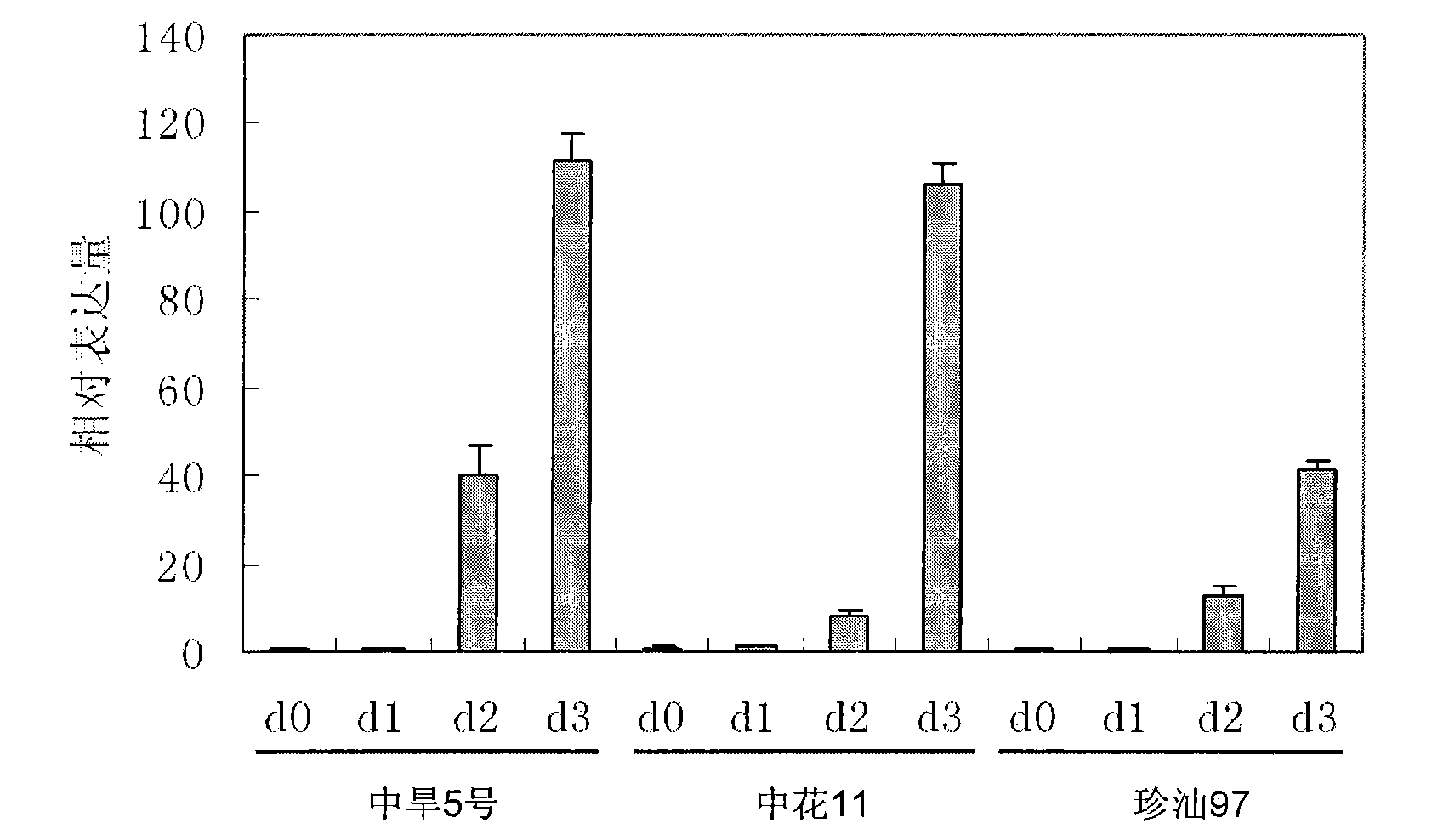
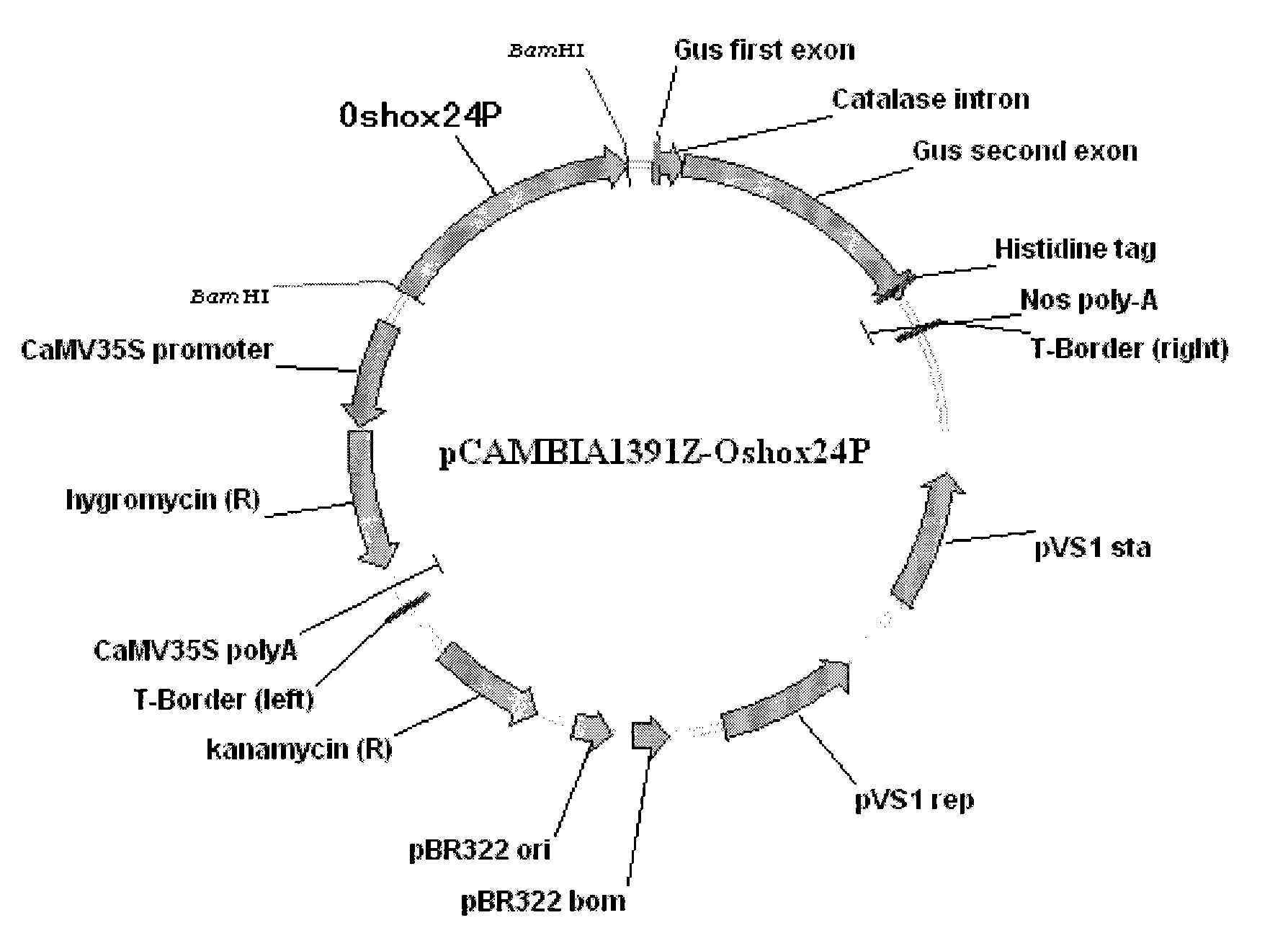
Identification and use of rice drought-inducible promoter Oshox24P
InactiveCN101831430AImprove stress resistanceAngiosperms/flowering plantsDNA/RNA fragmentationPlant genetic engineeringEngineered genetic
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering and relates to the isolation, identification and use of a plant stress specifically inducible promoter Oshox24P. A rice drought-inducible promoter Oshox24P, which has a nucleotide sequence SEQ ID No.1 in a sequence table, is obtained by isolation and identification. The promoter of the invention can be used in plant genetic engineering for plant genetic improvement, in particular for plant drought resistance improvement.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Nucleic acid molecules and other molecules associated with plants
The present invention is in the field of plant genetics. More specifically the invention relates to nucleic acid molecules and nucleic acid molecules that contain markers, in particular, single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and repetitive element markers. In addition, the present invention provides nucleic acid molecules having regulatory elements or encoding proteins or fragments thereof. The invention also relates to proteins and fragments of proteins so encoded and antibodies capable of binding the proteins. The invention also relates to methods of using the nucleic acid molecules, markers, repetitive elements and fragments of repetitive elements, regulatory elements, proteins and fragments of proteins.
Owner:BYRUM JOSEPH
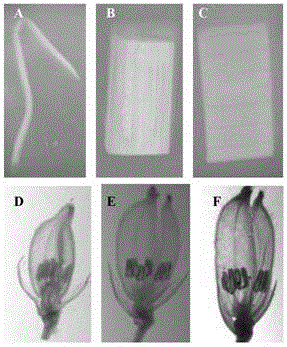
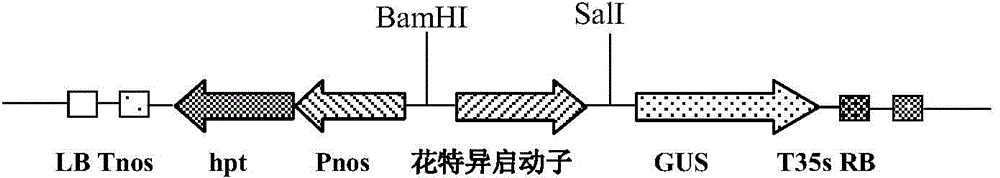
Identification and application of plant anther specific expression promoter
ActiveCN103820445AReduce adverse effectsAvoid Biosafety ConcernsBacteriaFermentationPlant geneticsPlant biology
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant biology and particularly relates to separation, function identification and application of a rice anther specific expression promoter. The disclosed promoter is specifically expressed in a plant anther and has good application prospects in the field of plant genetic modification.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF MOLECULAR CROP DESIGN +1
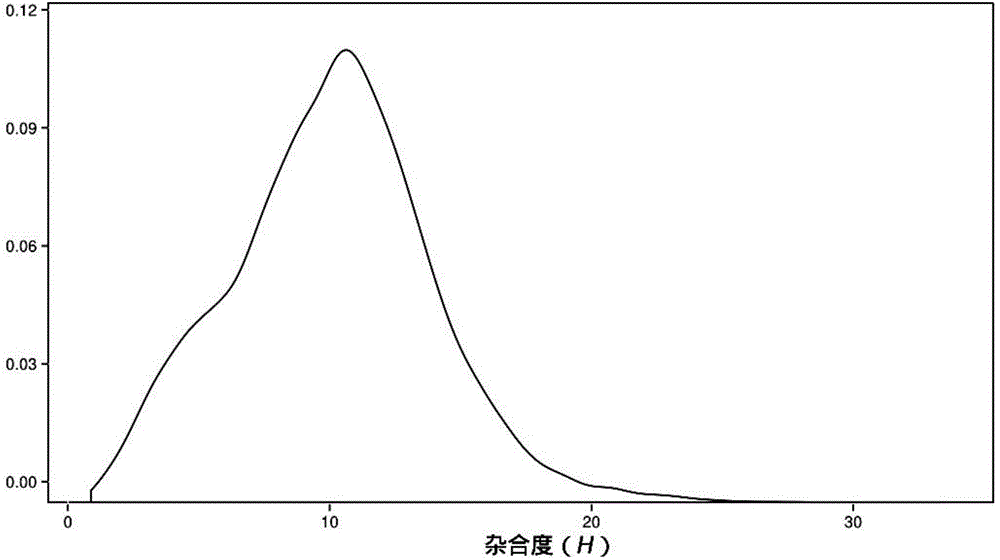
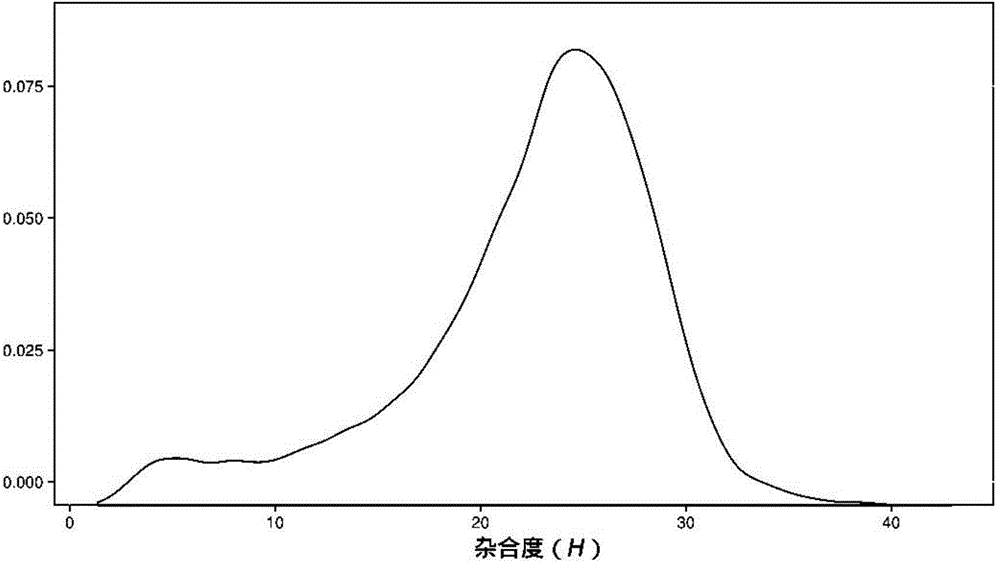
Method for identifying hybrid germplasm of actinidia based on genome heterozygosity
InactiveCN104630382AShorten the timeLower Sequencing CostsMicrobiological testing/measurementActinidiaGermplasm
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Plant induction type promoter and application of plant induction type promoter
ActiveCN105524925APlant peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionAgricultural sciencePromoter activity
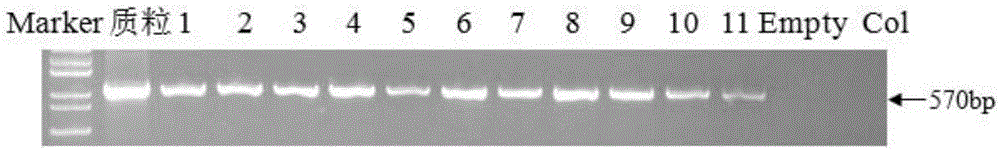
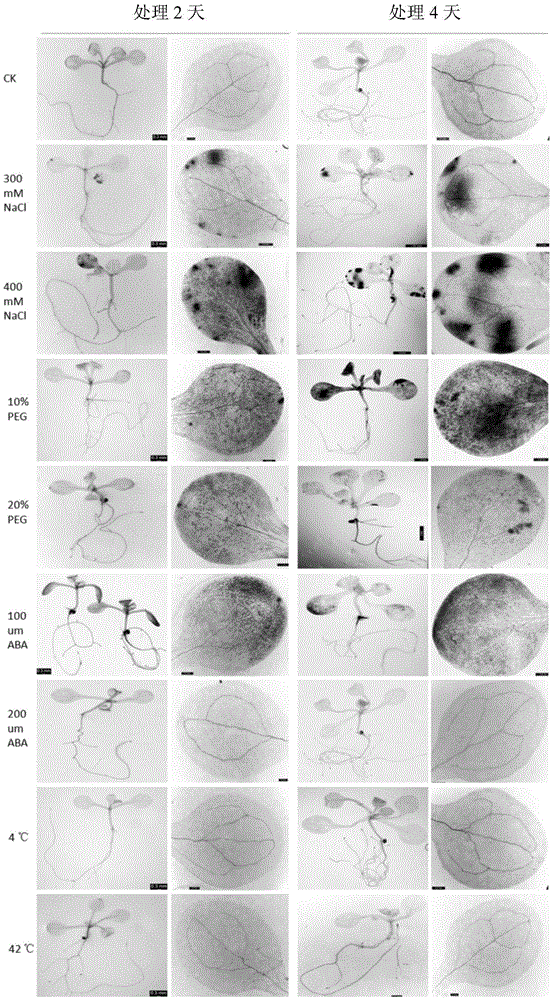
The invention discloses a plant induction type promoter and application of the plant induction type promoter. The nucleotide sequence of the promoter is the nucleotide sequence shown by SEQ ID No.1 in a sequence table. Experiments prove that under the conditions of different concentrations and different processing time of NaCl, PEG and ABA, the promoter HbHAK2 can drive the GUS gene expression; and under the non-processed (comparison), low temperature (4 DEG C) and high temperature (42 DEG C) stress, the HbHAK2 cannot drive the GUS gene expression. The result shows that the HbHAK2-744bp promoter is a novel induction type promoter; and high promoter activity can be realized under the salt or drought stress or the ABA induction; and the target gene expression can be inducted for adapting to the environment. The promoter can be applied to stress-tolerance gene engineering vector construction, plant stress-tolerance molecular mechanism study and crop salt-resistant and drought-resistant transgenic breeding. An economic fast and effective path is provided for plant genetic modification.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Transformation method utilizing red fluorescent protein as selection marker of rice transformation
ActiveCN102199619AImprove reliabilityIncrease positive rateVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyFluorescence microscope
The invention provides a transformation method utilizing a red fluorescent protein as a selection marker. The method comprises the following steps of: synthesizing a fluorescent protein (FP) gene and modifying according to the bias of a rice codon, wherein the modified FP gene is used as a selective marker gene of rice transformation and plant regeneration; driving the FP gene by a callus / seed coat-specific promoter, closely connecting with a target gene, and transferring to rice embryonic calli under the mediation of Agrobacterium tumefaciens; screening for three times by a fluorescence microscope in 30 days after coculture; and further verifying an obtained transgenic seedling by utilizing a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and Southern hybridization. The result shows that the positive rate of the transgenic seedling is up to 80 percent, which proves that FP serving as the selection marker of plant transformation is completely feasible. By the method, the potential hazard of the traditional selection markers such as antibiotic and herbicide resistance genes and the like to environment and food safety is effectively reduced. The invention provides a novel safe plant genetic transformation screening system.
Owner:BEIJING WEIMING KAITUO CROP DESIGN CENT COMPANYLIMITED +1
Method for creating cymbidium resource for high-efficiency generation of 2n male gametes
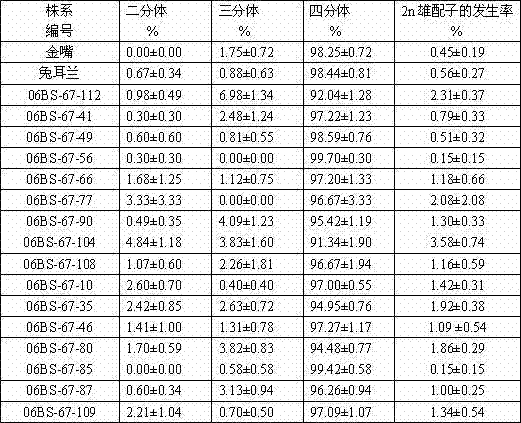
ActiveCN103704126AIncrease vitalityPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsBiotechnologyMale gamete generation
Owner:英德君泓兰花股份有限公司
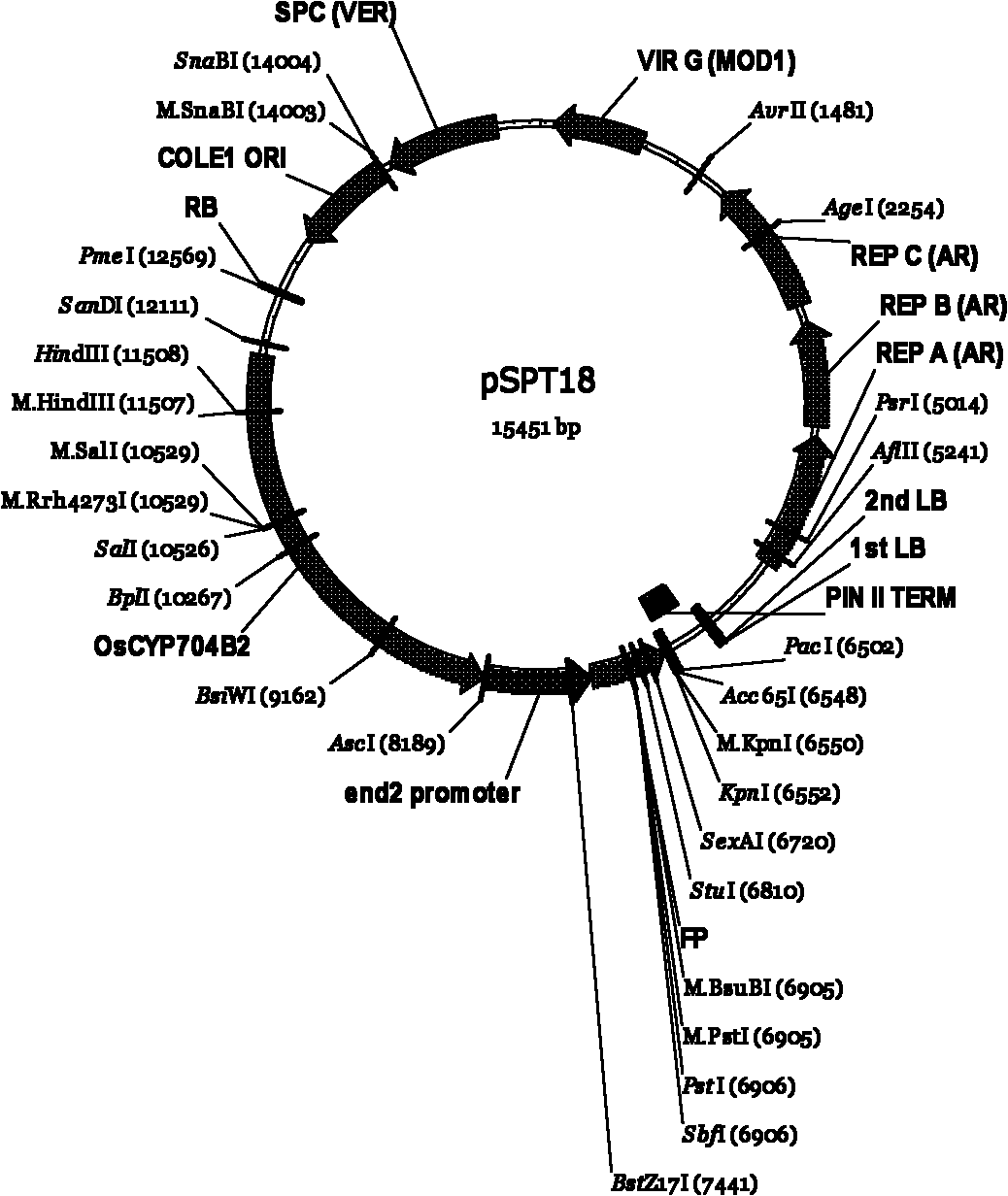
Multi-gene binary expression vector constructed by using homologous recombination and preparation method and application of multi-gene binary expression vector
InactiveCN102329812AHigh co-transformation efficiencyVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsTransformation efficiencyGenetic engineering
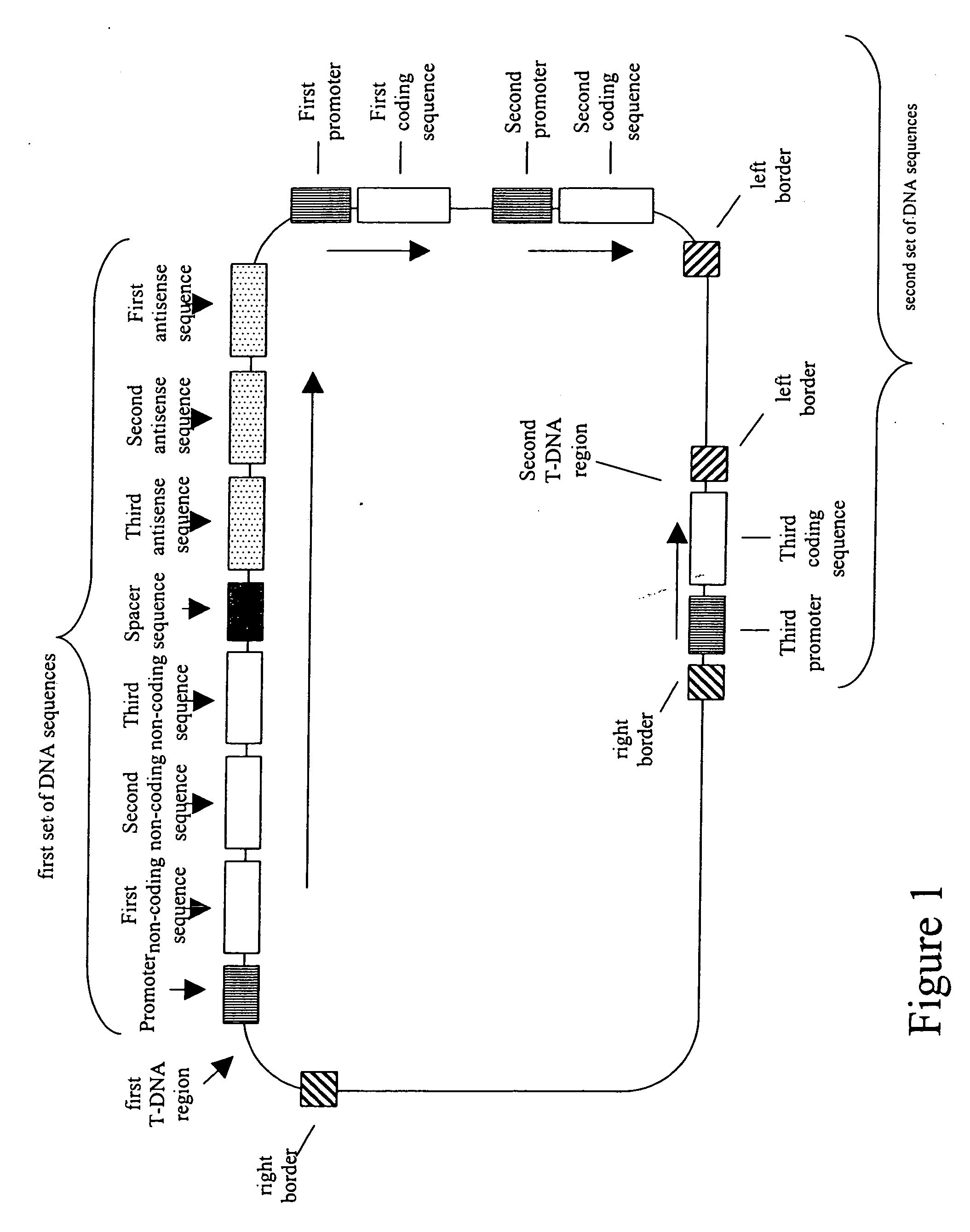
The invention relates to the field of gene engineering, in particular to a multi-gene binary expression vector constructed by using homologous recombination. The multi-gene binary expression vector is formed by connecting single genes or multiple genes into a multi-gene polymer through polyclonal enzyme cutting sites so as to form a homologous recombination intermediate vector and adding the single-gene or multi-gene polymer into a basic binary vector by homologous recombination, wherein the homologous recombination can be performed for multiple times, so that the T-DNA length of the basic binary vector is gradually increased. The invention also discloses a construction method of the multi-gene binary expression vector and application in plant transgenes. The multi-gene binary expression vector applied in plant genetic modification can transfer multiple target genes at the same time, and has the advantage of high co-transformation efficiency.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Composition used for plants direct gene conversion
InactiveCN101016553ASolve the degradabilitySolve the transformation of multiple copiesVector-based foreign material introductionPollenPlant cell
The invention discloses a composition of plant direct gene transformation, transforming method and appliance, which is characterized by the following: making the component include goal gene and free nucleic acid component of adjusted and controlled element, transforming buffer liquid and transforming assistance component; co-culturing; soaking; surface-daubing; injecting; dripping; spraying; transforming with dip flower method or through genetic gun bombardment, supersonic wave and electric shock method. This component can be used to receptor plant cell direct transformation of fertilized ovum, suspended cell, protoplast, single-layer cell and diachyma cell and can be used to seed, receptor plant pollen, pistil, flower pillar, pollen pipe and ovary, which possesses impotent meaning for plant genetic seeding, variety improvement and gene functional analysis.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Plant starch synthesis-associated protein OsFLO10 as well as encoding gene and application thereof
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering, and relates to plant starch synthesis-associated protein OsFLO10 as well as an encoding gene and an application thereof. The protein is shownin following (a) or (b): (a) protein consisting of an amino acid sequence shown in sequence 1 in a sequence table; (b) protein which is derived from the sequence 1, obtained by the amino acid sequence shown in the sequence 1 by substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or more amino acid residues and associated with plant gluten sorting. The plant starch synthesis-associated protein OsFLO10 affects synthesis of starch in plant endosperm. After the encoding gene of the protein is introduced into plants with abnormal starch synthesis, transgenic plants with normal starch synthesis canbe cultivated. The protein and the encoding gene thereof can be applied to plant genetic improvement.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Gene for encoding sweet potato ERF (ethylene responsive factor) transcription factor
InactiveCN105671058AIncrease biomassPositive regulation of drought toleranceBacteriaPlant peptidesNucleotideADAMTS Proteins
The invention discloses a gene for encoding sweet potato ERF (ethylene responsive factor) transcription factor, this gene being a nucleotide sequence shown as in SEQ ID No. 1. A protein encoded by the gene is an amino acid sequence shown as in SEQ ID No. 2. Complete cDNA for encoding ERF transcription factor is isolated from sweet potato and connected to a plant expression vector, a plant is converted by means of Agrobacterium infection to provide a transgenic plant, the transgenic plant has greater root development and higher biomass, drought resistance of the transgenic plant is improved, and this gene is also applicable to plant genetic improvement.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Antibacterial peptide gene of Chinese prawn containing single whey acidic protein structure domain and its coded antibacterial peptide and application
The present invention discloses one kind of antibacterial peptide gene of Chinese prawn containing single whey acidic protein structure domain and its coded antibacterial peptide and application in preparing antibacterial active recombinant protein. The recombinant antibacterial peptide gene of Chinese prawn containing single whey acidic protein structure domain of the present invention may be applied in antibacterial feed additive, food preservation, animal and plant genetic conversion and medicine development.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Thermostatic male-killing device for rice seed production
InactiveCN104855271AImprove accuracyStable temperature controlPlant genotype modificationAutomatic controlEngineering
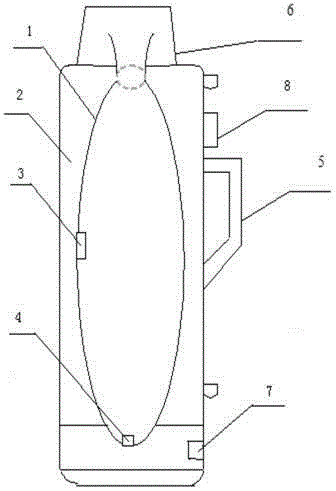
The invention relates to a thermostatic male-killing device for rice seed production, belonging to the technical field of plant genetic breeding technology. The thermostatic male-killing device for rice seed production is characterized in that a container body (1) is located in an outer shell (2), a middle electric heating device (3) is arranged at the middle part inside the container body (1), and a bottom electric heating device (4) is arranged at the bottom; a bottle cap (6) is arranged at the bottleneck which is at the upper part of the container body (1); a handle (5) is arranged at the outer side of the outer shell (2); a thermostatic control device (8) is arranged at the upper part of the outer side of the outer shell (2), and an externally connected power socket (7) is arranged at the lower part of the outer side of the outer shell (2); the middle electric heating device (3), the bottom electric heating device (4) and the thermostatic control device (8) are connected with the externally connected power socket (7) through wires and are connected with an outer power source. The thermostatic male-killing device controls temperature in the male-killing device automatically through a thermostatic controller, and the temperature after being set is kept constant basically, so that the high-temperature male-killing effect is guaranteed, the male-killing accuracy is improved, the labor intensity is reduced, and the work efficiency is increased.
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY
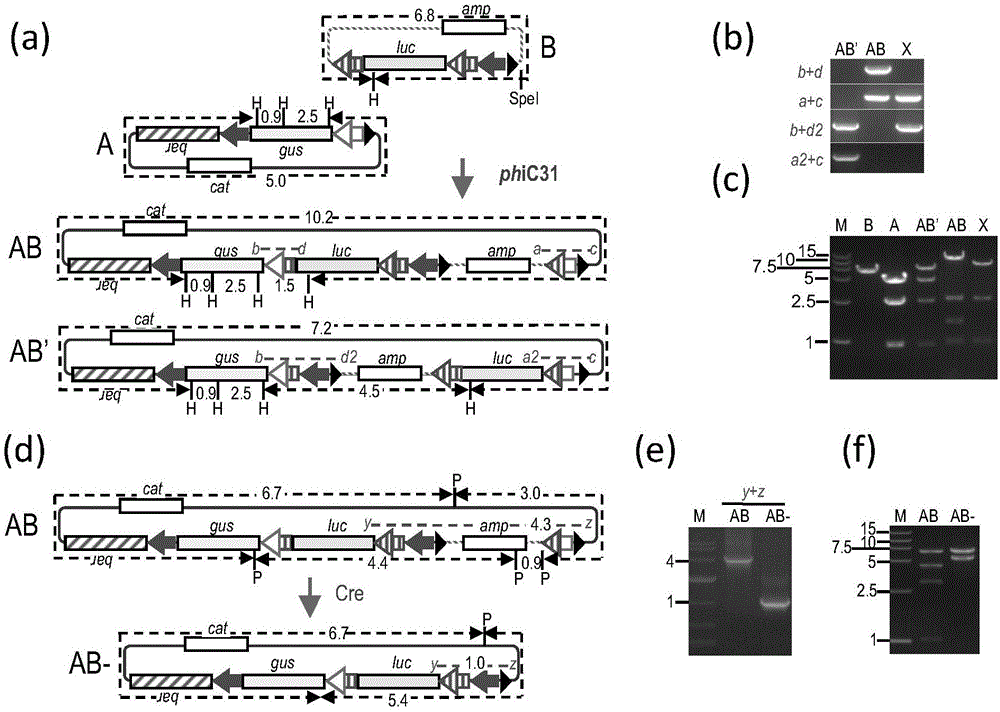
In-vitro gene stacking technology compatible with recombinase-mediated in-vivo gene stacking and application of in-vitro gene stacking technology
ActiveCN105112440AMeet the needs of overlayFast preparation methodVector-based foreign material introductionSite-specific recombinationIn vivo
The invention discloses in-vitro gene stacking technology compatible with recombinase-mediated in-vivo gene stacking and application of in-vitro gene stacking technology. The in-vitro gene stacking technology includes element forming of in-vitro gene stacking series vector and an in-vitro gene stacking method. The in-vitro gene stacking method includes: utilizing an irreversible site-specific recombination system for cointegration between two DNA molecules; utilizing a reversible site-specific recombination system to delete unneeded DNA sequences; utilizing a second irreversible site-specific recombination system to transfer multigene vectors which are stacked well in vitro into a binary vector suitable for agrobacterium transformation for plant genetic transformation, or directly integrating the multigene vectors on a specific seat of a genome in a targeted manner through site-specific recombination in vivo. The in-vitro gene stacking technology meets needs of in-vitro gene stacking and is compatible with an in-vivo recombinase-mediated gene stacking system.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
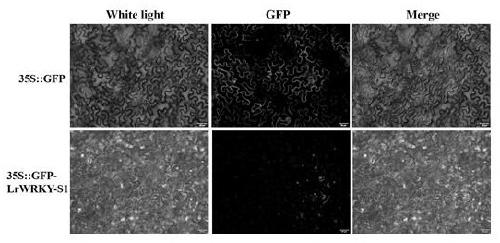
Susceptible fungal gene LrWRKY-S1 of lily and application thereof
InactiveCN111235165ABroaden the thinking of disease prevention and controlSusceptible to infectionPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyFungal gene
The invention discloses a susceptible fungal gene LrWRKY-S1 of lily and application thereof. A nucleotide sequence of the LrWRKY-S1 gene is shown by SEQ ID NO.1 and an amino acid sequence coded thereby is shown by SEQ ID NO.2. Biological functions of the protein are studied by a bacteriostasis experiment. Experimental results show the protein makes plants more susceptible to pathogenic fungi suchas Botrytis cinerea, fusarium oxysporum and Colletotrichum orbiculare. As found as well, the LrWRKY-S1 gene has a low expression level in lilium regale with high resistance, and a homologous gene thereof has high expression levels in lilium davidii, lilium longifolorum and lilium lancifolium with important economic values. The gene and the application thereof provide an efficient susceptible genefor genetic engineering reconstruction, lays a foundation for further cultivation of fungus-resistant / susceptible lily or new materials or new species of other plants, can provide theoretical and technical support for later application of the gene in plant genetic improvement, broadens ideas for prevention and control of plant diseases and has very extensive application values.
Owner:YANGTZE NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Universal SSR (simple sequence repeat) molecular marker CSSR1 for chrysanthemum and related plants and application thereof
ActiveCN103773760ABroad application prospectsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFingerprintPolymerase chain reaction
The invention provides a universal SSR (simple sequence repeat) molecular marker CSSR1 for chrysanthemum and related plants, which is used for PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification of the marker CSSR1 primer sequences disclosed as SEQ ID NO. 1 and 2. The invention also provides application of the SSR marker in identification of intergeneric cross hybrids of chrysanthemum and Ajania. Besides, the invention also provides a method for amplifying the SSR molecular marker, which establishes a universal SSR molecular marker technical system among chrysanthemum, Ajania and Opisthopappus plant materials. The marker can be used for intrageneric and intergeneric hybrid identification of chrysanthemum, Ajania and Opisthopappus, plant genetic diversity analysis, fingerprint construction, molecular marker assisted breeding and the like, and has very wide application prospects.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Method for excavating natural hybridization germplasm and breeding new varieties of kiwi fruits
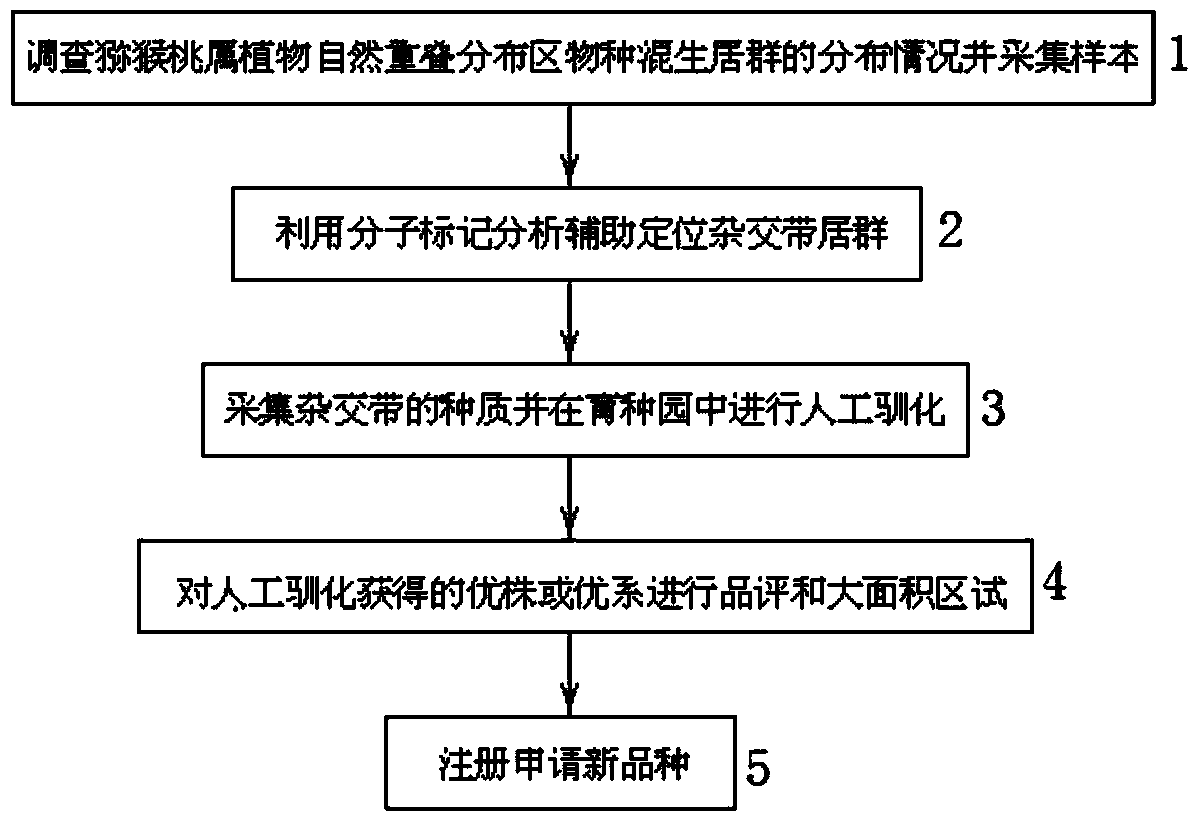
InactiveCN104160908AShorten the breeding periodReduce geographic areaCultivating equipmentsPlant genotype modificationActinidiaGermplasm
The invention discloses a method for excavating natural hybridization germplasm and breeding new varieties of kiwi fruits and relates to the field of plant genetic breeding and biotechnology. The method comprises the steps of (1) surveying distribution conditions of mixed populations of species in a naturally overlapped distribution region of actinidia plants and collecting samples; (2) analyzing populations for assisting in positioning in a hybridization band through molecular markers; (3) collecting germplasm of the hybridization band and performing artificial domestication on the germplasm in a breeding garden; (4) commenting on and performing large-scale regional trial on superior plants or varieties obtained through artificial domestication; (5) registering and applying for new varieties. Compared with traditional artificial hybridization breeding, by means of the method, the breeding cycle is shortened greatly, the excavation geographic area of the target hybridization germplasm is narrowed down, blindness and randomness in utilization of the traditional natural germplasm of the kiwi fruits can be overcome, singular germplasm unexpected by traditional artificial breeding can be screened and domesticated, and problems caused by biosecurity are avoided.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com