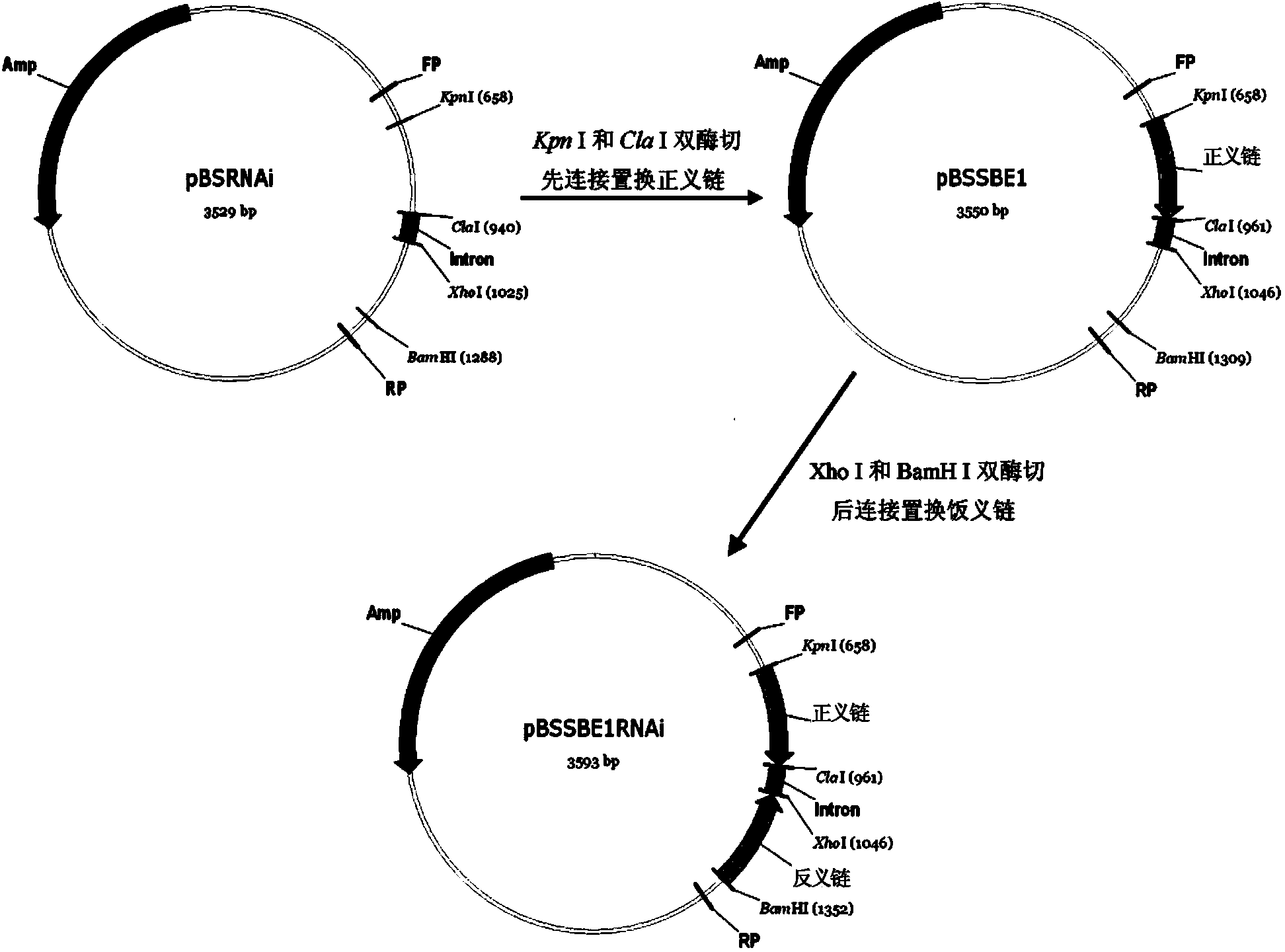
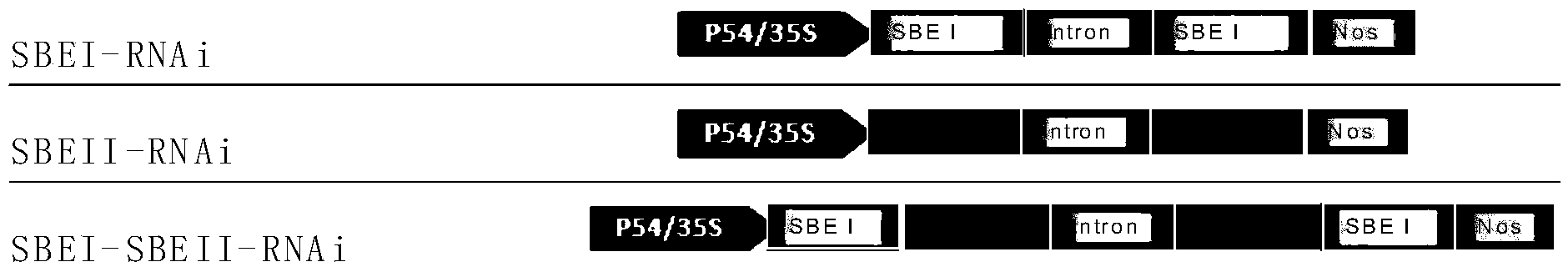
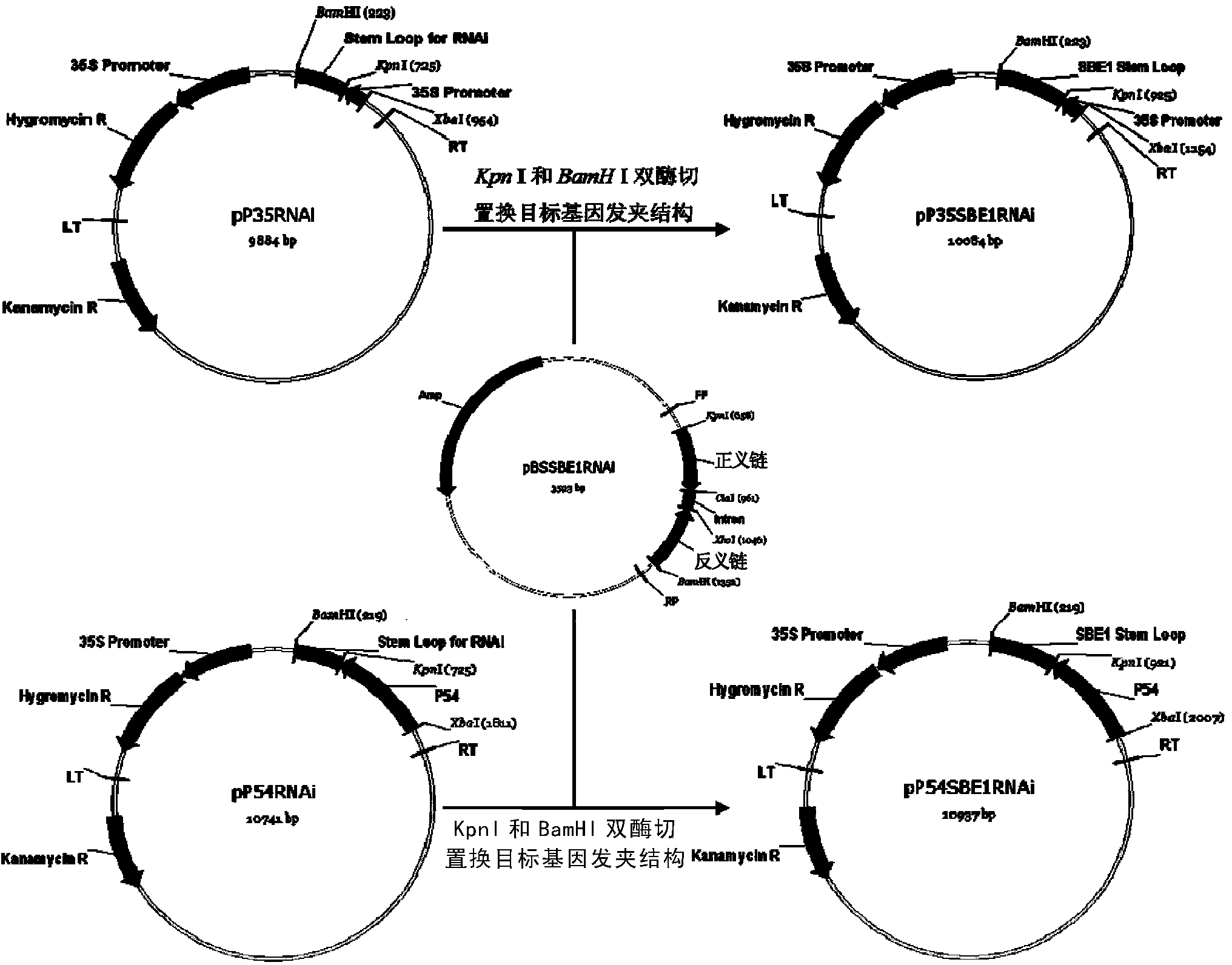
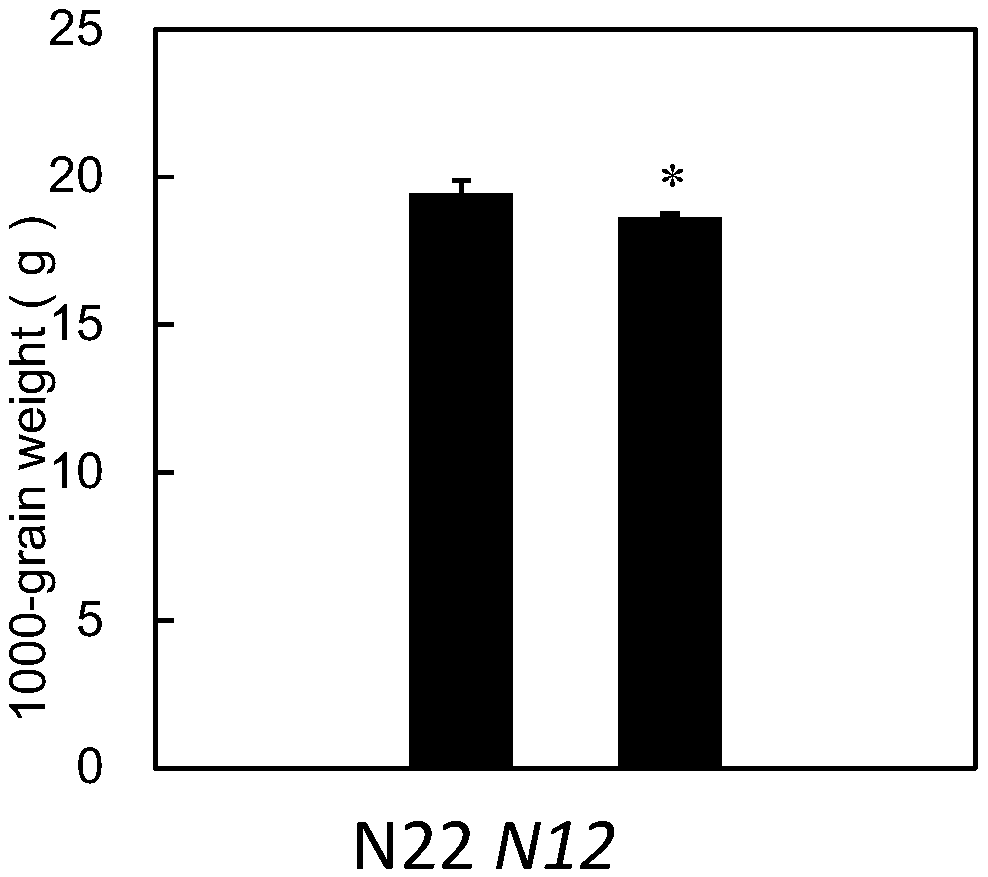
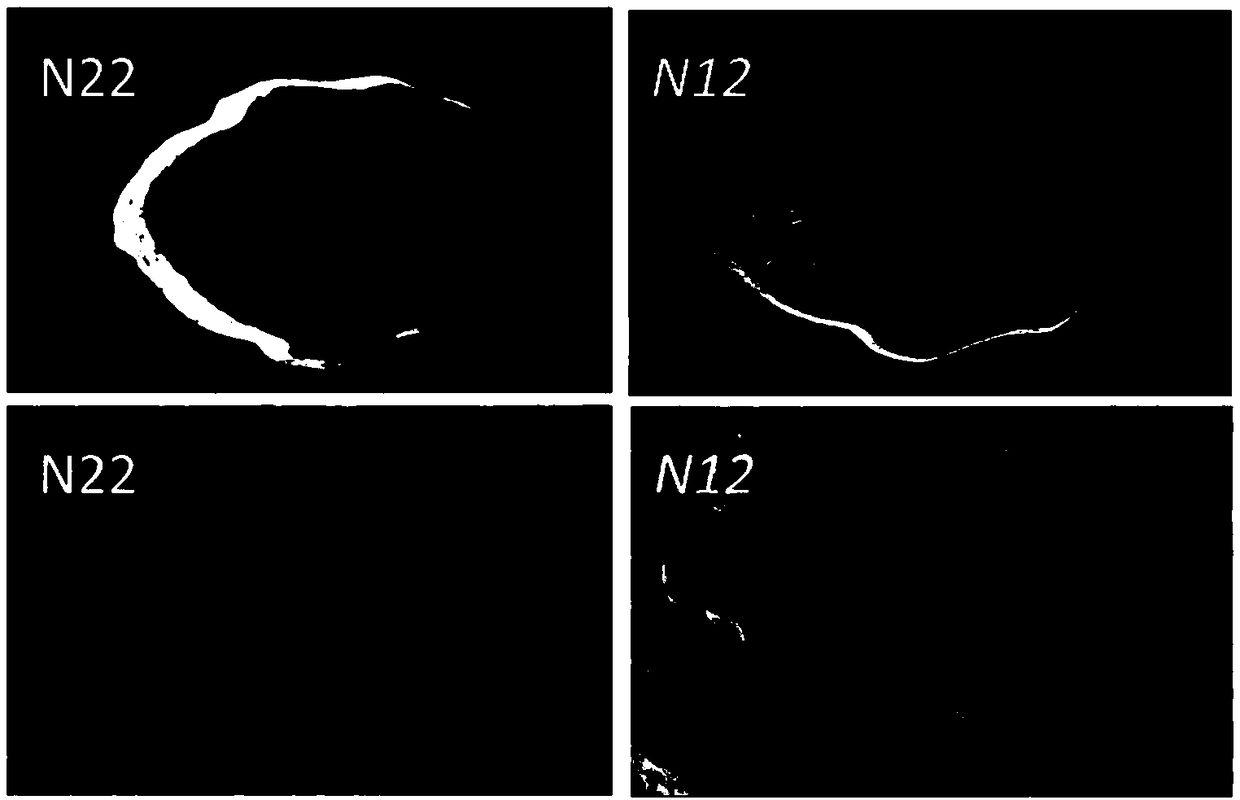
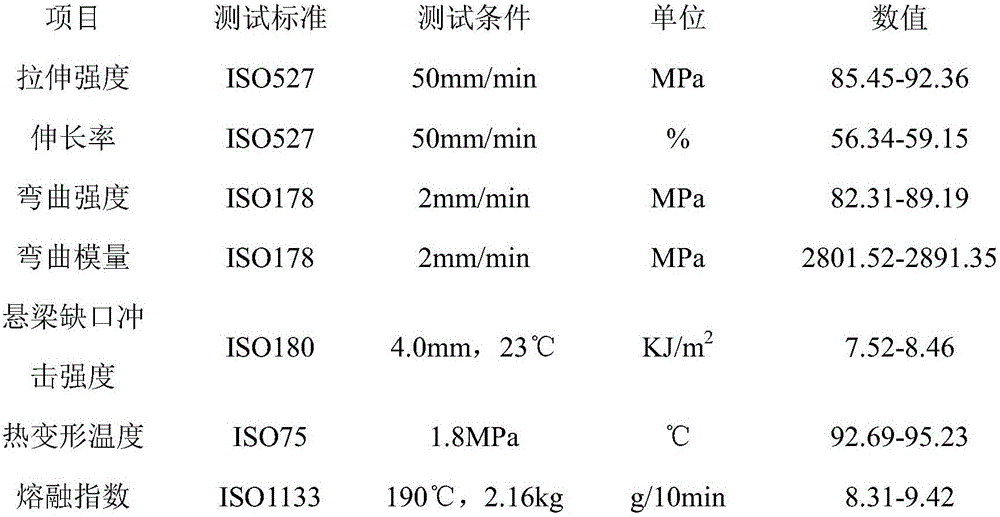
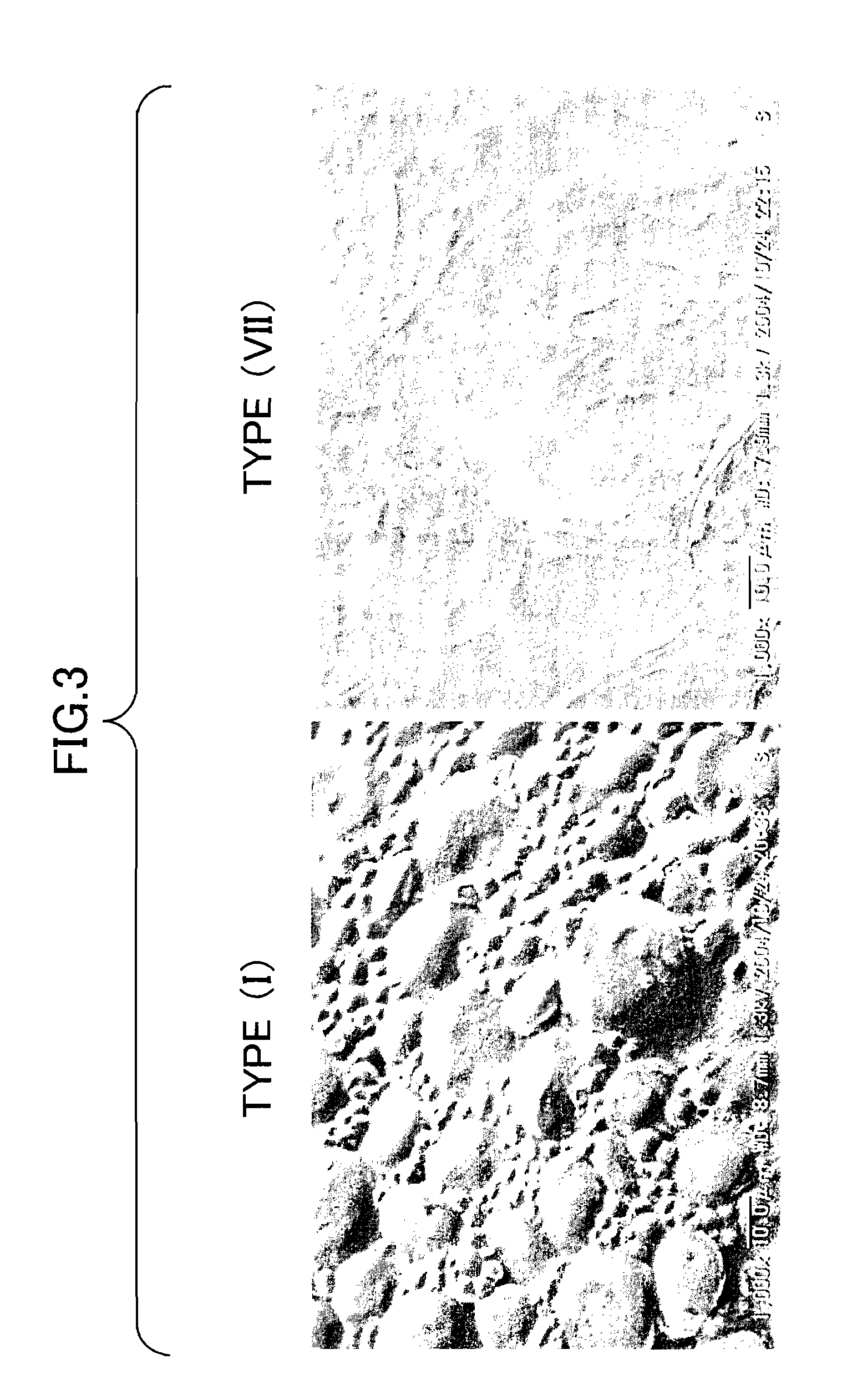
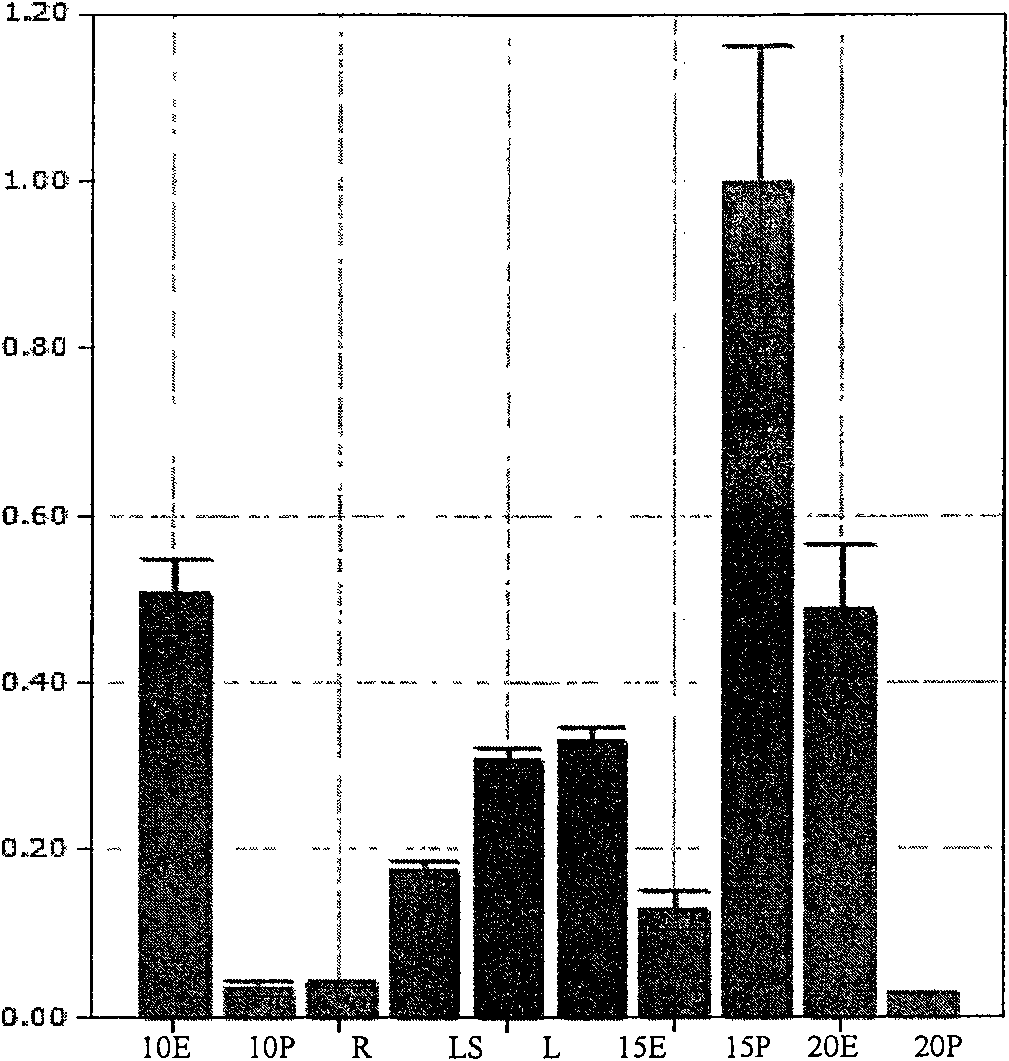
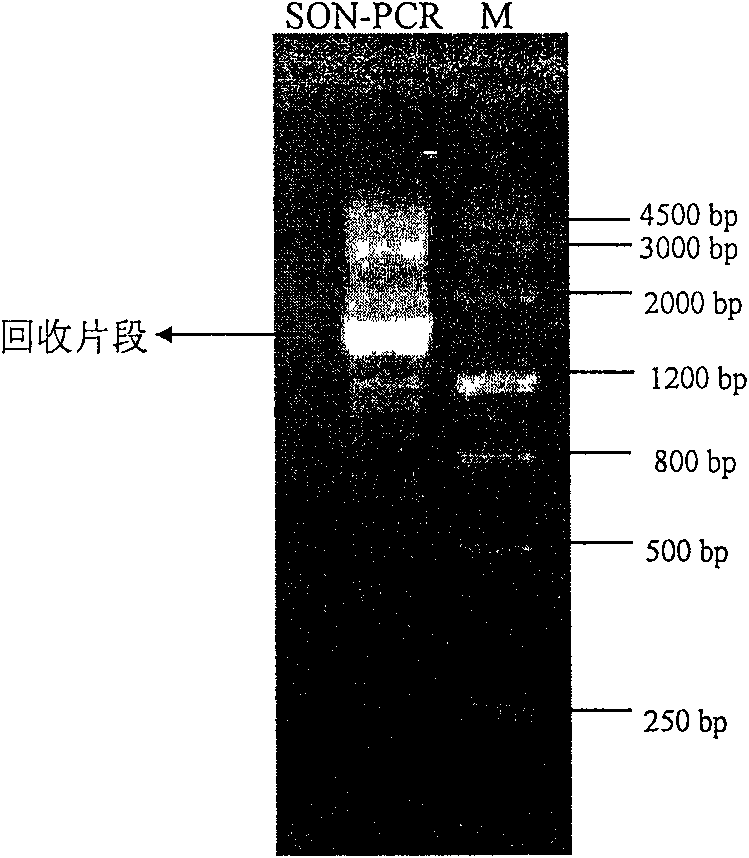
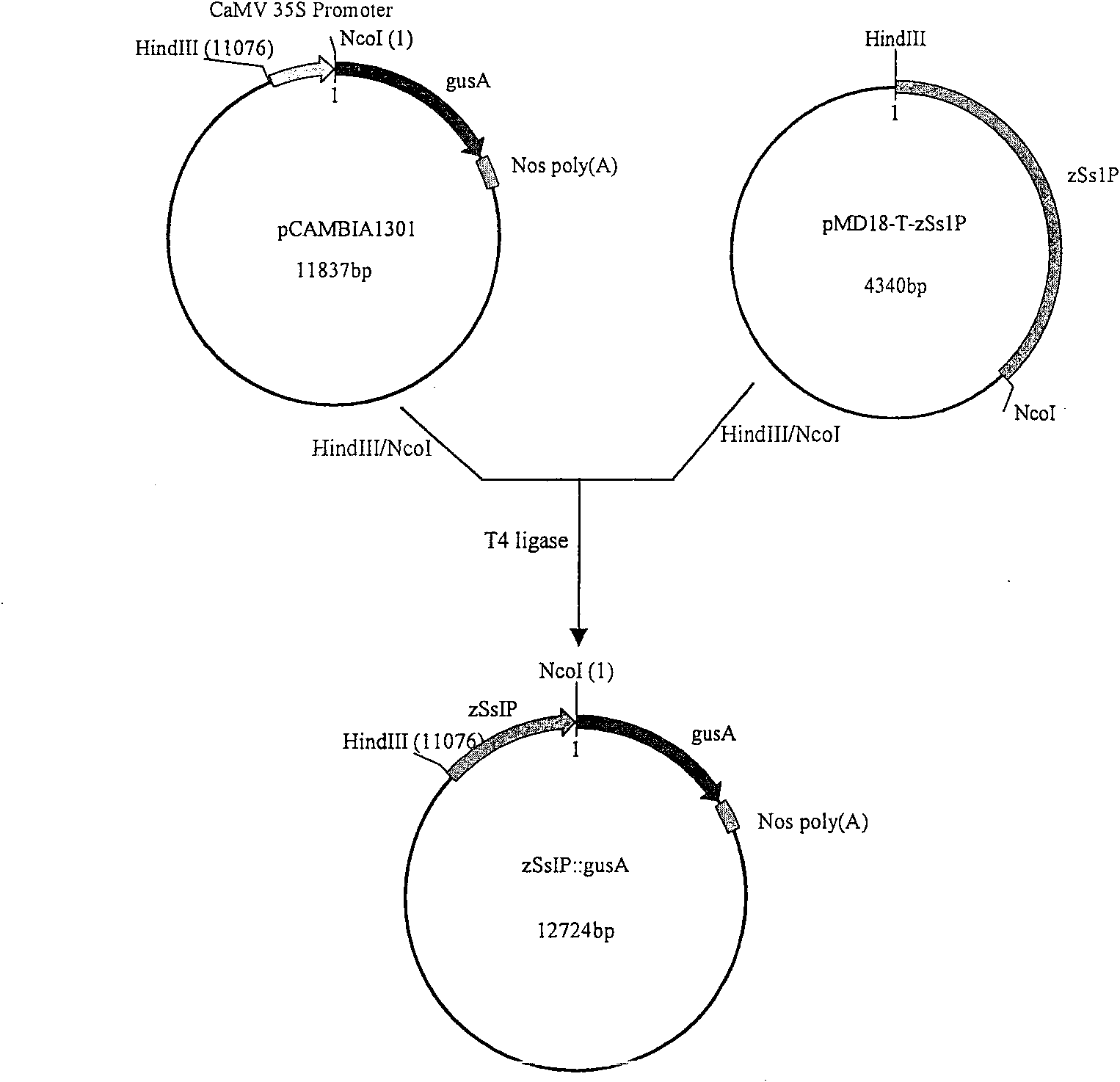
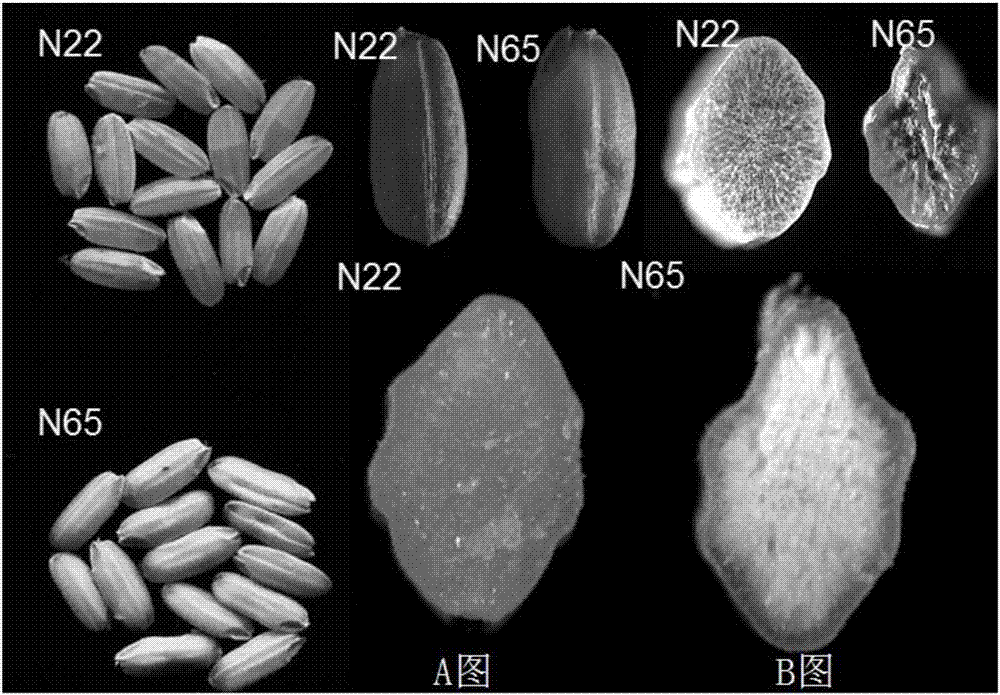
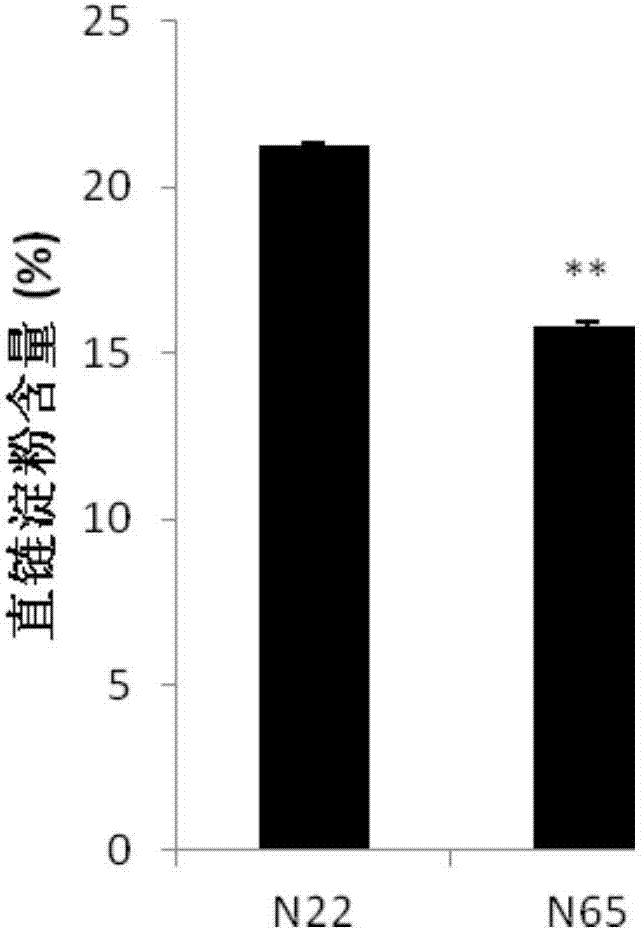
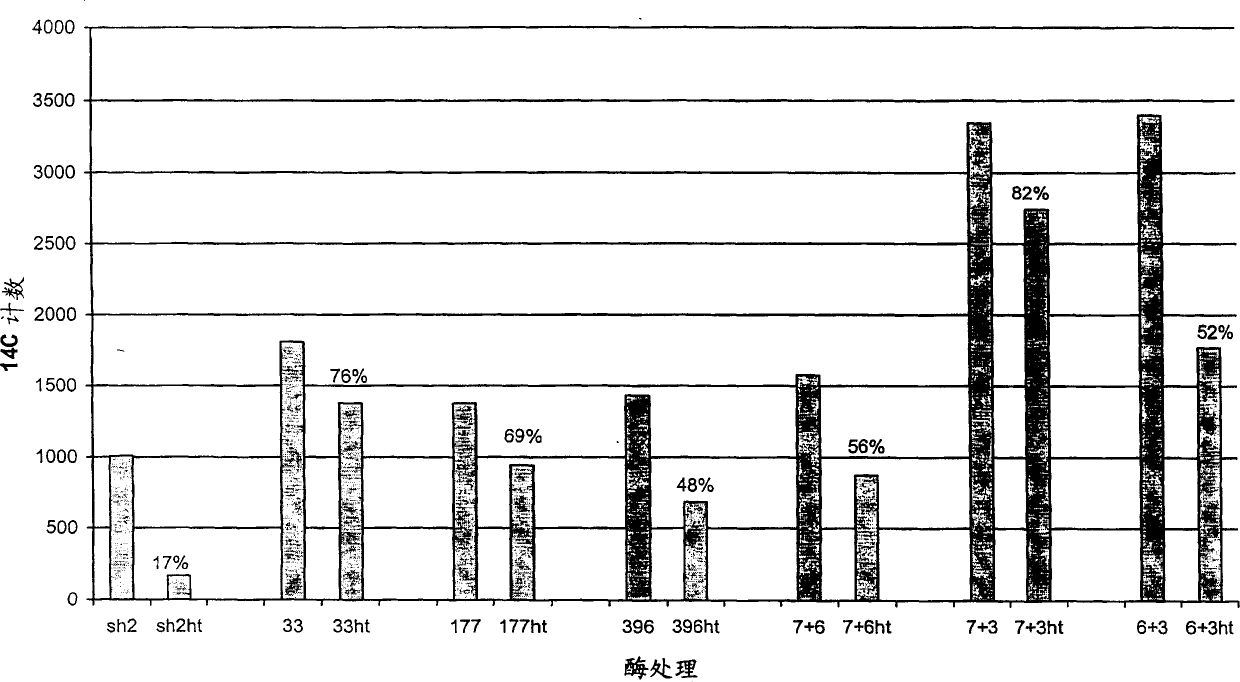
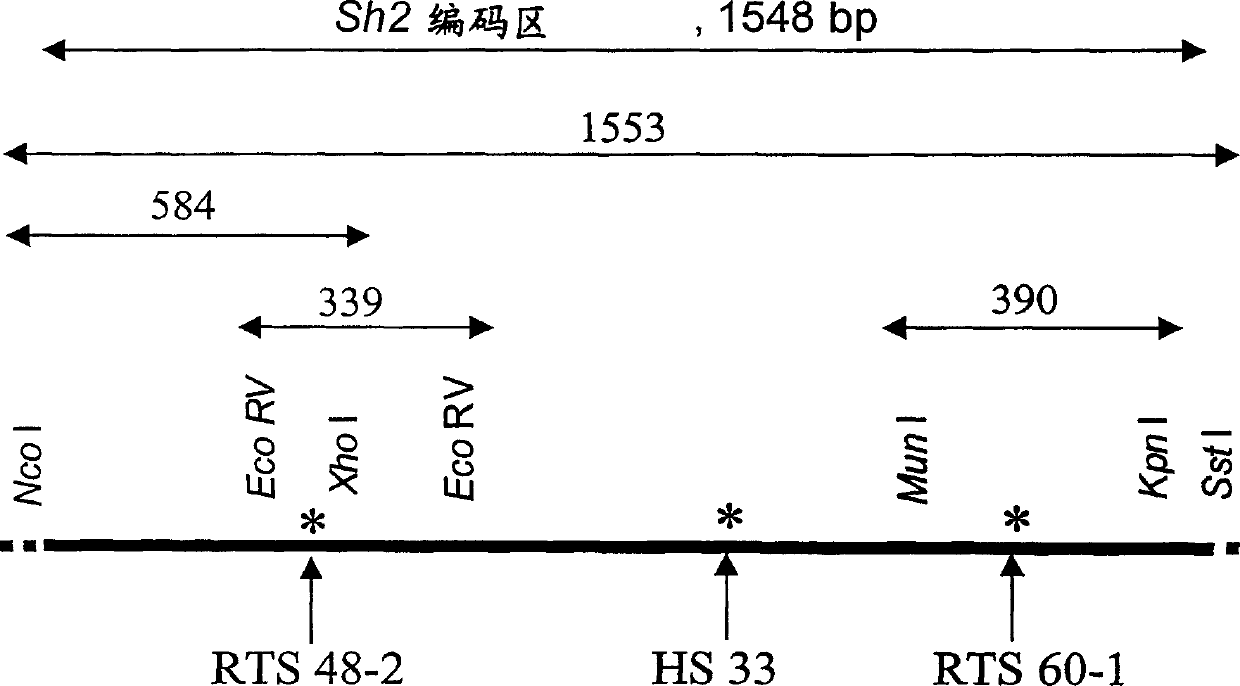
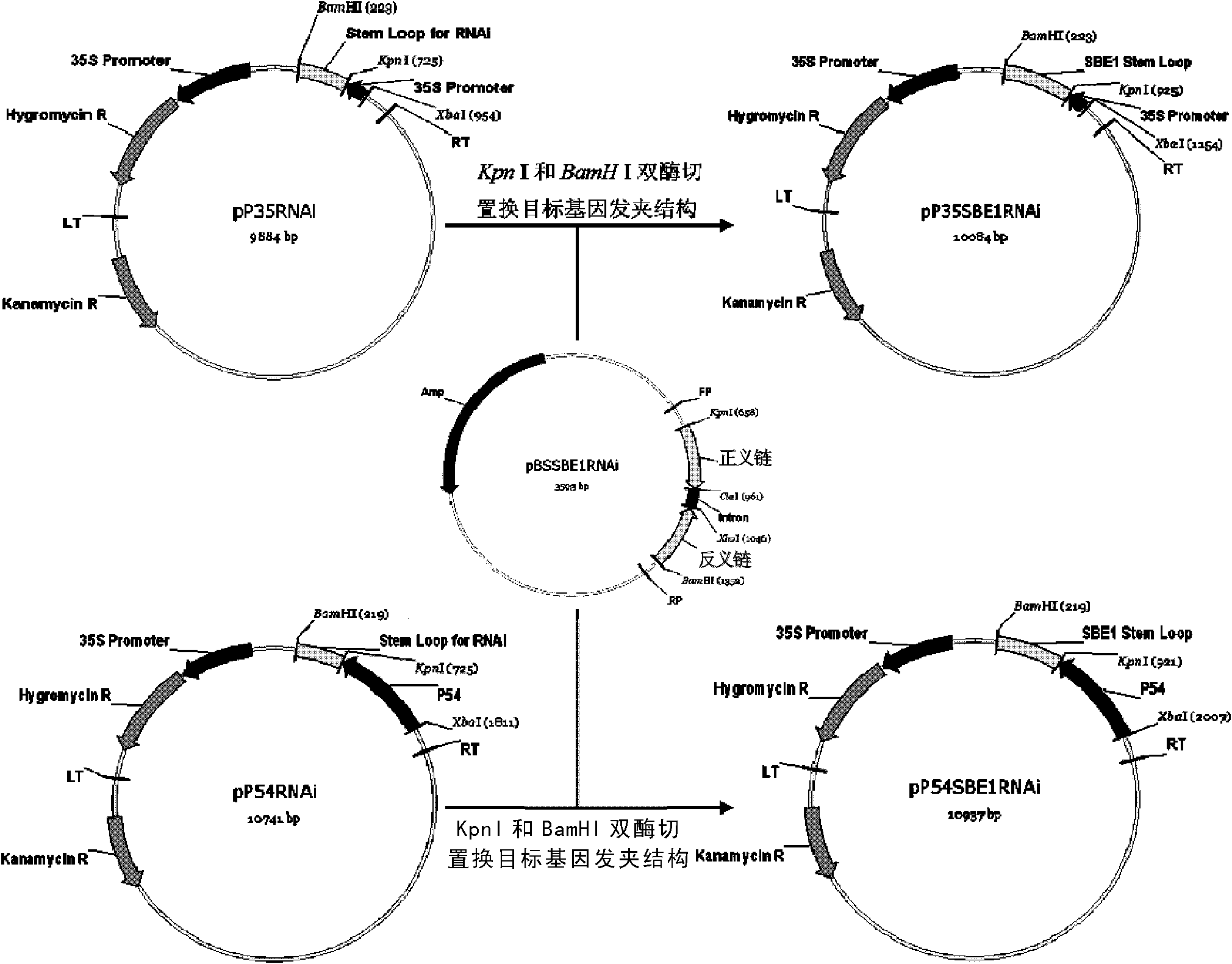
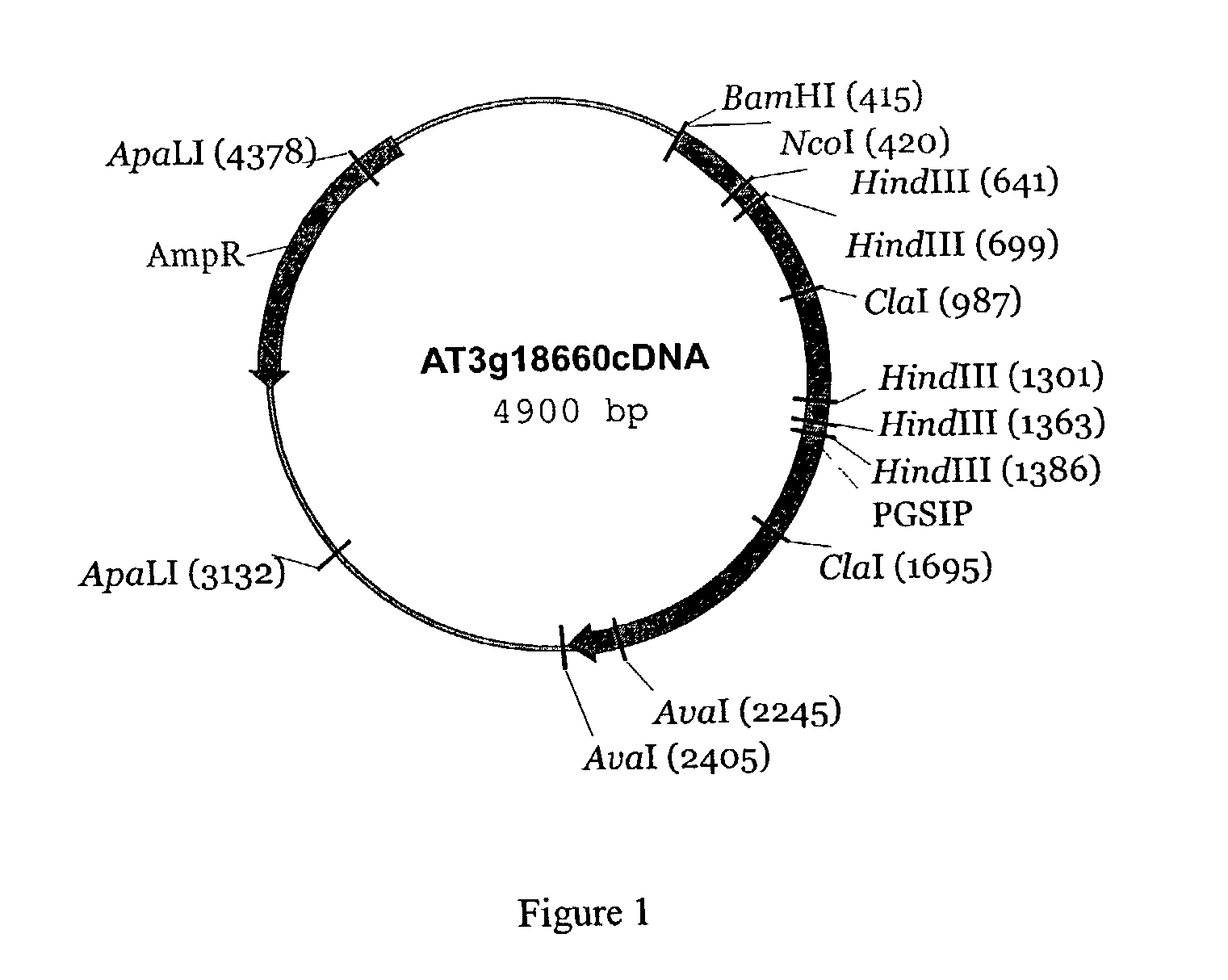
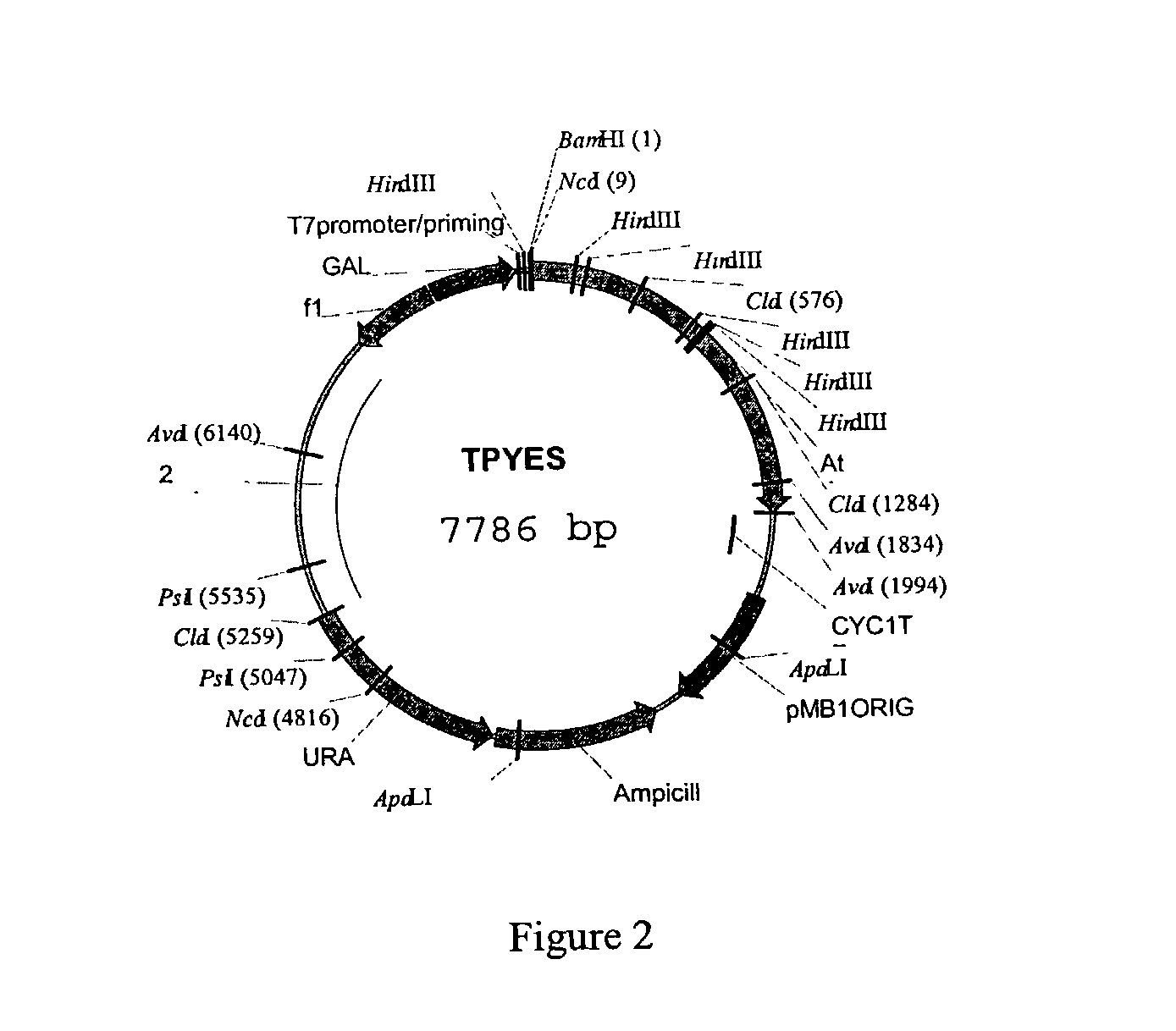
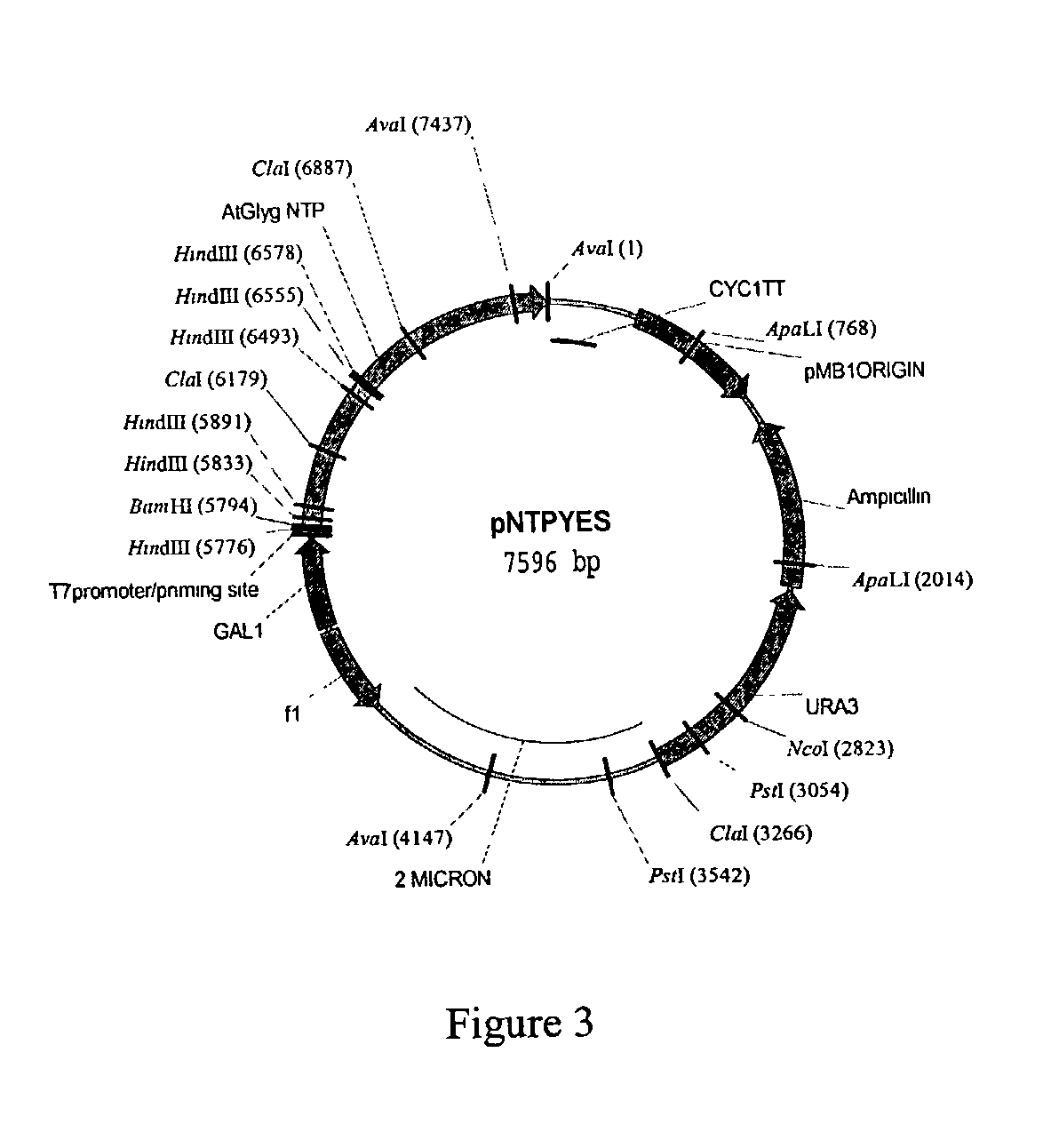
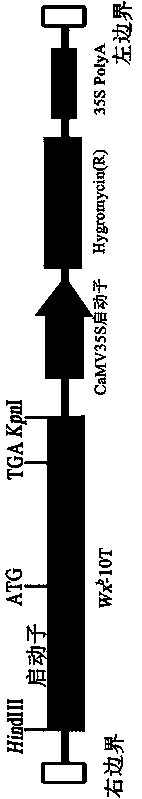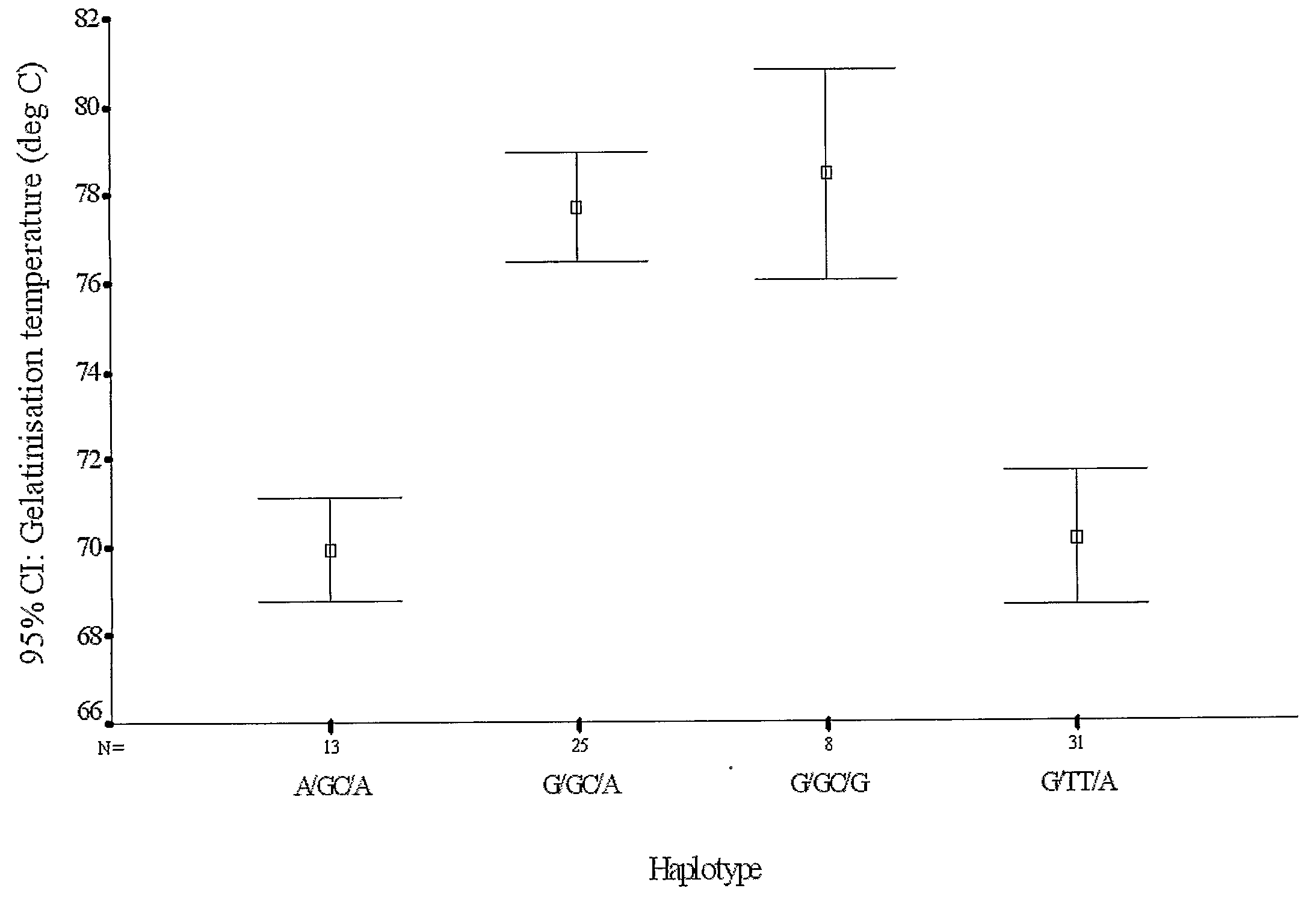Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
104 results about "Starch synthesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
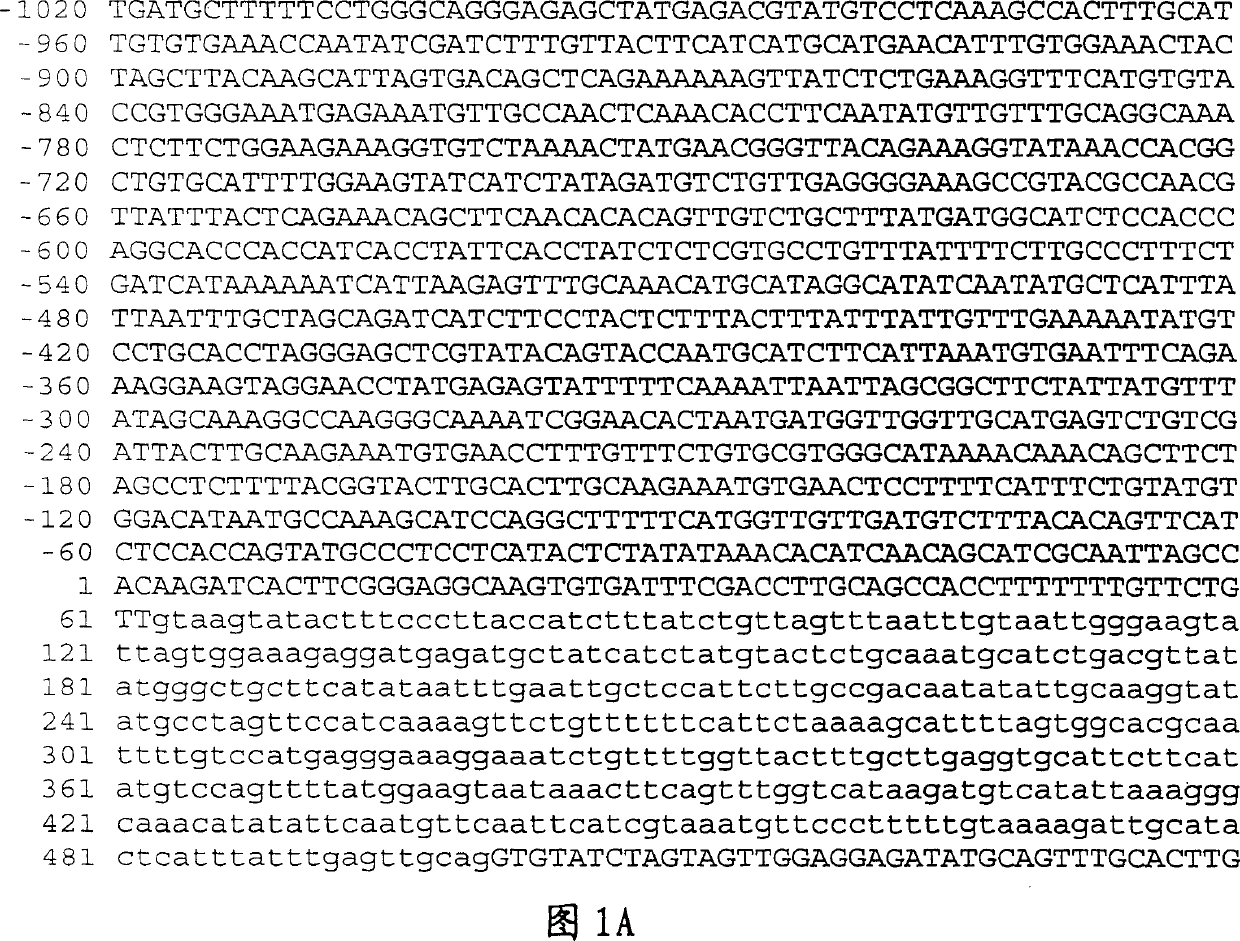
The structure and synthesis of starch. The synthesis of starch in plant cells begins with the enzyme ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase (AGPase), which catalyses the reaction of glucose-1-phosphate with ATP to form ADP-glucose (liberating pyrophosphate).
Plants and processes for obtaining them
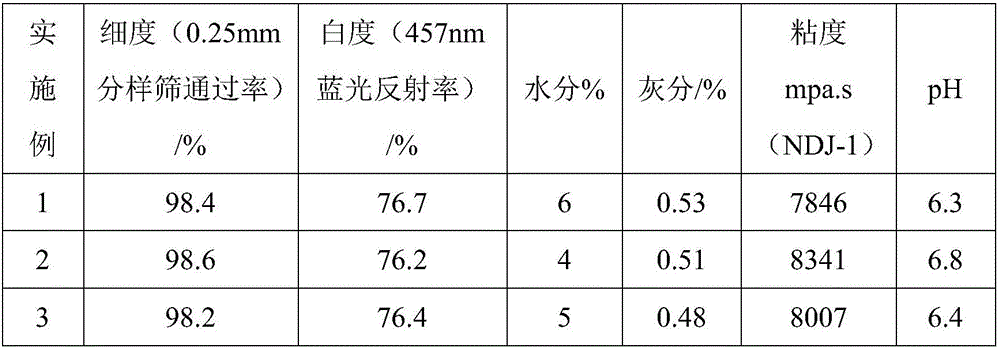
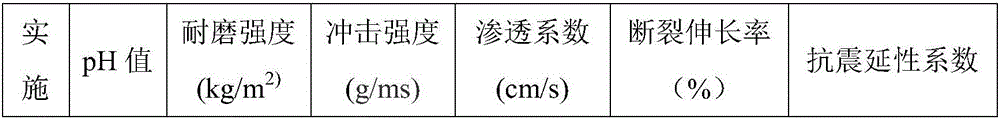
InactiveUS6013861AIncrease depositionAlteration of fine structureOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationStarch synthaseStarch synthesis
Plants, particularly cereal plants, which have improved ability to synthesise starch at elevated or lowered temperatures and / or to synthesise starch with an altered fine structure are produced by inserting into the genome of the plant (i) a gene(s) encoding a form of an enzyme of the starch or glycogen biosynthetic pathway, particularly soluble starch synthase and / or branching enzyme and / or glycogen synthase, which display an activity which continues to increase over a temperature range over which the activity would normally be expected to decrease, and / or (ii) a gene(s) encoding sense and anti-sense constructs of enzymes of the starch biosynthetic pathway, particularly soluble starch synthase and / or branching enzyme and / or glycogen synthase, which alters the natural ratios of expression of the said enzymes or inserts enzymes with special structural characteristics which alter the natural branching pattern in starch.
Owner:ZENECA LTD
Barley with altered branching enzyme activity and starch and starch containing products with an increased amylose content
ActiveUS7521593B2Lower Level RequirementsReduced activitySugar derivativesTransferasesHordeum vulgareStarch synthesis
Barley having a reduced level of SBEIIa activity produces grain having a high relative amylose content. The barley might additionally have reduced levels of SBEIIb activity. The barley grain of this invention can be of a non-shrunken phenotype despite a lesion in the amylopectin synthesis pathway.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
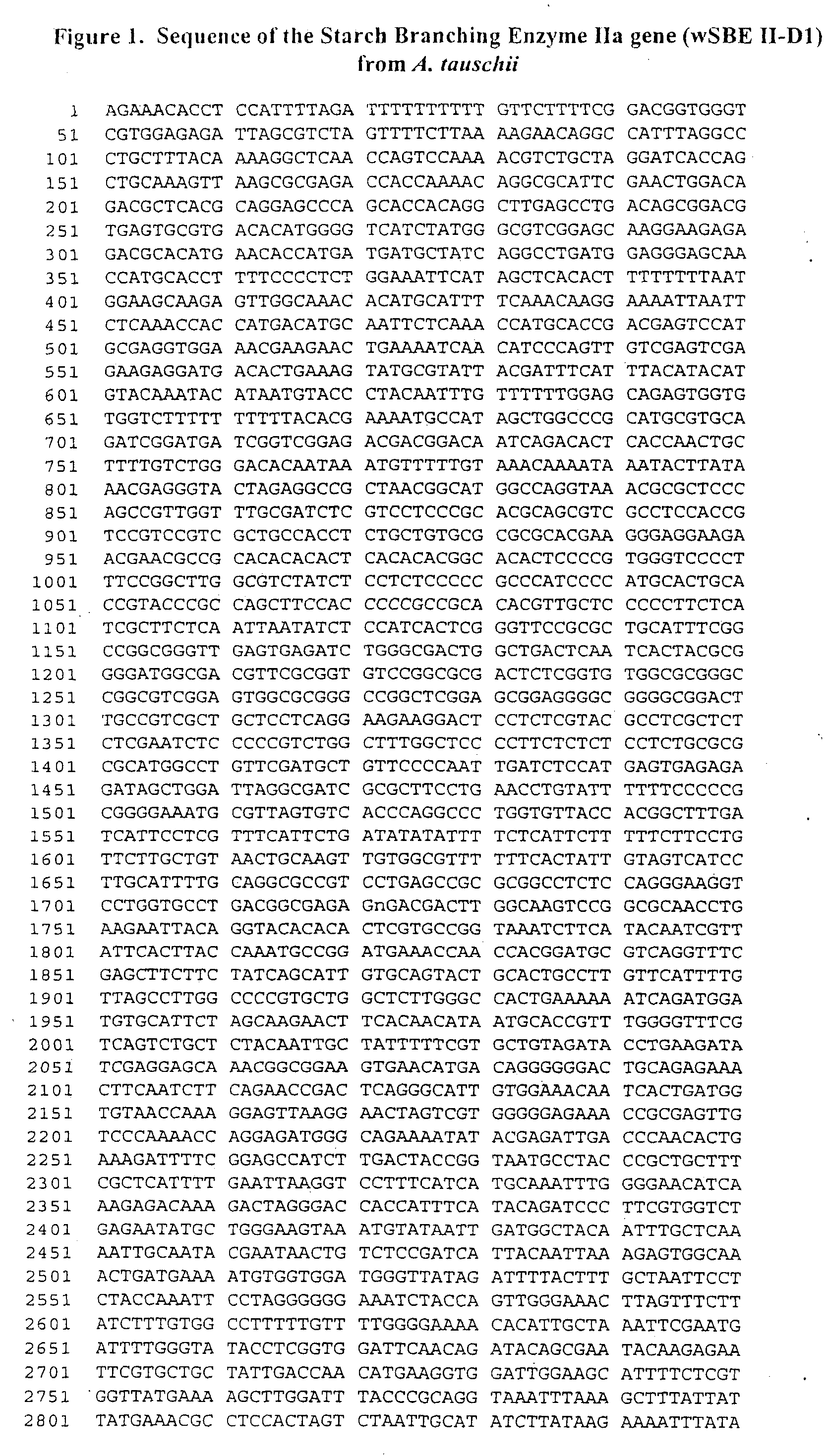
Nucleic acid molecules which code for enzymes derived from wheat and which are involved in the synthesis of starch
Nucleic acid molecules are described which encode enzymes involved in starch synthasis in plants. These enzymes are wheat isoamylases.The invention furthermore relates to vectors and host cells which contain the above-described nucleic acid molecules, in particular to transformed plant cells and plants which can be regenerated from these and which have an increased or reduced activity of the isoamylases according to the invention.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Wheat with altered branching enzyme activity and starch and starch containing products derived therefrom
Wheat having a reduced level of SBEIIa activity, that may have a relative high amylose content. Wheat having a mutant SBEIIa gene in the A genome. The wheat might additionally have reduced levels of SBEIIb activity. The wheat grain of this invention can be of a non-shrunken phenotype despite a lesion in the amylopectin synthesis pathway, and may also have a high relative amylose content.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG +1
Barley with altered branching enzyme activity and starch and starch containing products with an increased amylose content
InactiveUS20090226592A1Reduced activityReduce enzyme activityDough treatmentTransferasesHordeum vulgareStarch synthesis
Barley having a reduced level of SBEIIa activity produces grain having a high relative amylose content. The barley might additionally have reduced levels of SBEIIb activity. The barley grain of this invention can be of a non-shrunken phenotype despite a lesion in the amylopectin synthesis pathway.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Wheat with altered branching enzyme activity and starch and starch containing products derived therefrom
ActiveUS20110070352A1Reduce the ratioDough treatmentFood genetic modificationStarch synthesisBulgur wheat
Wheat having a reduced level of SBEIIa activity, that may have a relative high amylose content. Wheat having a mutant SBEIIa gene in the A genome. The wheat might additionally have reduced levels of SBEIIb activity. The wheat grain of this invention can be of a non-shrunken phenotype despite a lesion in the amylopectin synthesis pathway, and may also have a high relative amylose content.
Owner:ARISTA CEREAL TECH
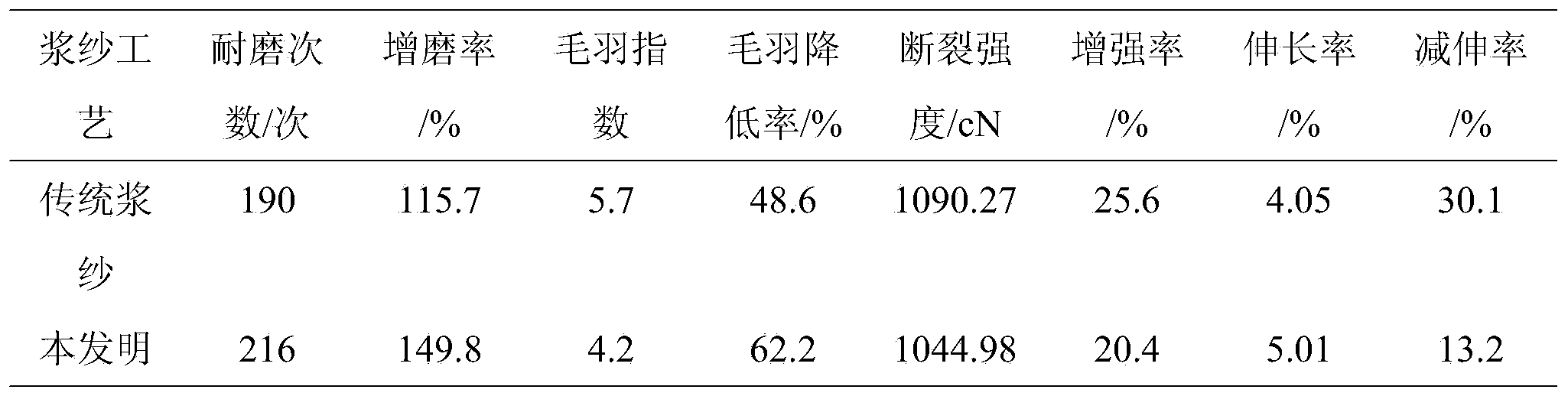
Jean warp sizing slurry and sizing process
ActiveCN103966849AImprove wear resistanceImprove surface propertiesFibre treatmentDenimProcess engineering
The invention provides a jean warp sizing slurry and a sizing process. The slurry is prepared from DSC-14 starch, PVA, LMA-95 synthesis slurry, emulsified oil and a smoothing agent. In comparison with the prior art, the sizing slurry and process ensures that the warp abrasion resistance is greatly improved, the weaving performance is enhanced and the cost is lowered. Besides, the use amount of slurry and pollution are reduced, the existing technological process does not need to be changed significantly, the investment is relatively low and the effect can be taken rapidly.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SANSEN TEXTILE
Method for increasing amylose content of plants
InactiveCN104017829AOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationStarch-branching enzyme IIStarch synthase
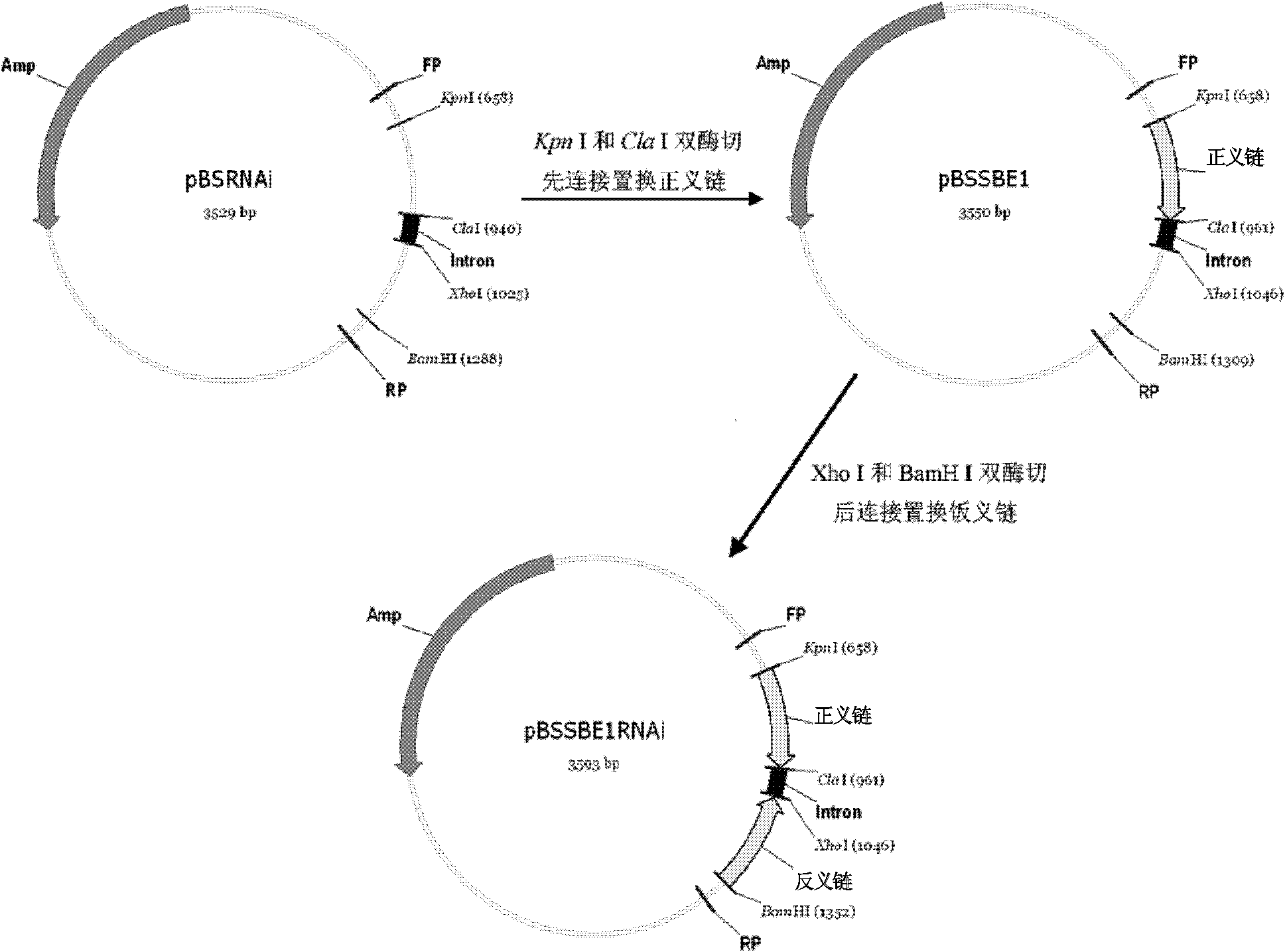
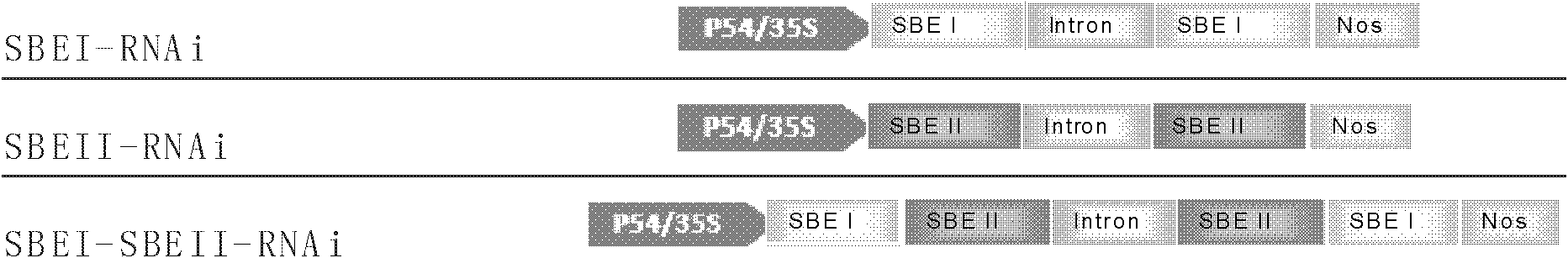
The invention relates to a method for increasing the amylose content of plants. The invention provides enzymes, namely granule-bound starch synthase I (GBSS i), starch branching enzyme I (SBE I) and / or starch branching enzyme II (SBE II) which are applicable to genetic engineering operation in a starch synthesis path and are capable of remarkably changing starch composition of the plants. The invention also provides a novel method capable of favorably adjusting starch in plants, which comprises the following step of reducing the expression of the enzymes to obtain a series of transgenic plants which are different in amylose and amylopectin contents and proportions. The invention also provides a construct or carrier for adjusting the starch composition of plants.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
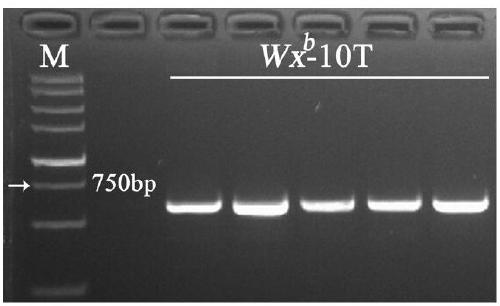
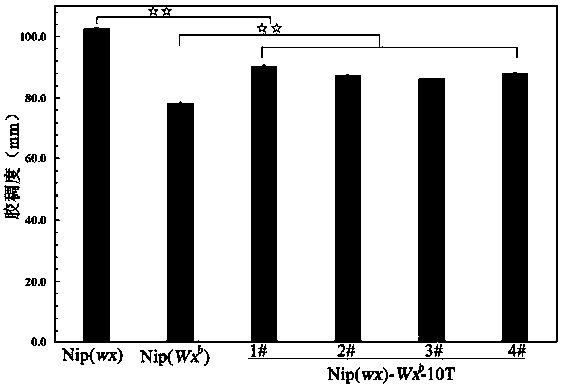
Construction of gene expression vector Wxb-10T, preparation of transgenic rice and primer
ActiveCN108949753AFermentationGlycosyltransferasesGenetically modified riceGranule-Bound Starch Synthase
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology and relates to construction of a gene expression vector Wxb-10T, preparation of transgenic rice and a primer. The primer is shown in a sequencetable of SEQ ID NO. 3-8. The allele Wxb in the conventional japonica rice serves as a template, and the rice expression vector Wxb-10T substituted by single nucleotides at the tenth exon of the alleleis constructed. The vector carries a full-length Wxb allele sequence with single base mutation, and by utilizing an agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated method, the transgenic rice with transgenosis ofWxb-10T in glutinous rice is obtained. The transgenic rice of a homozygous line is bred, the amylose content of the transgenic rice is generally about 12%, and the gel consistency and starch viscosity index of the transgenic rice are close to those of currently popular excellent edible soft rice. The method is realized by introducing a rice expression vector modified by specific nucleotide sitesof granule-bound starch synthase GBSSI coding genes Wx into the glutinous rice.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Gene capable of improving quality of plant fruit amylopectin, encoding product and application of gene
ActiveCN106337056AHigh expressionHigh activityFermentationGlycosyltransferasesBiotechnologyNucleotide
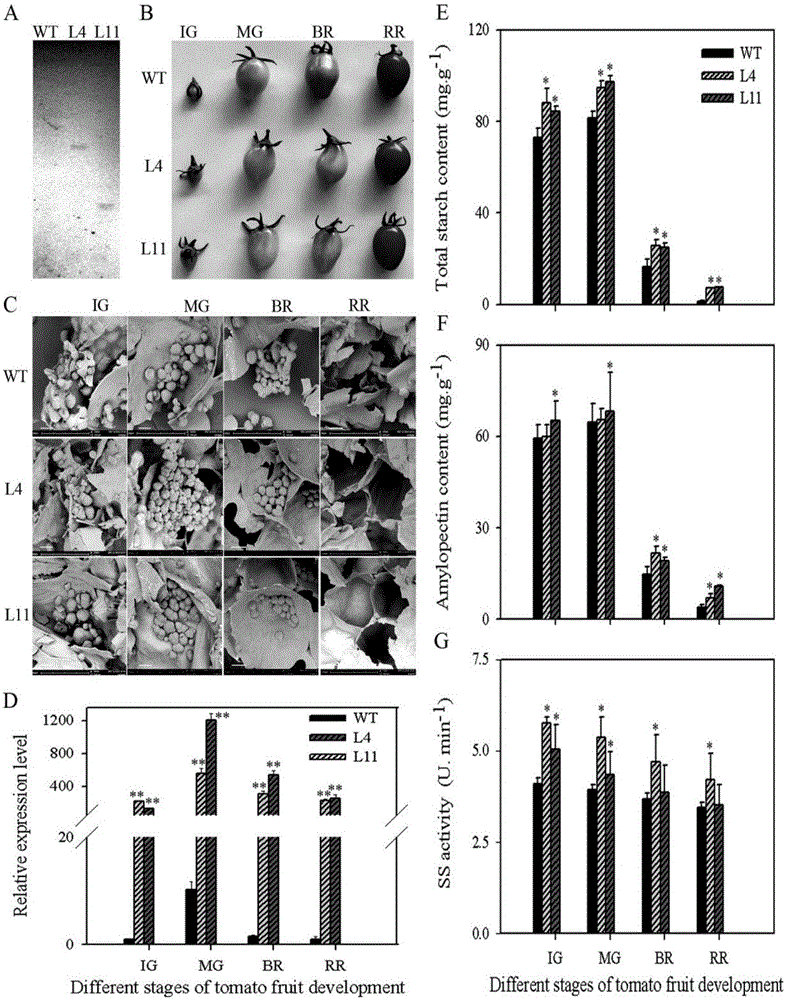
The invention relates to a banana fruit soluble starch synthetase gene MaSSIII-1 which has the nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:1, and protein which is encoded by the banana fruit soluble starch synthetase gene MaSSIII-1 has the nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:2. The invention also relates to application of the banana fruit soluble starch synthetase gene MaSSIII-1. The gene MaSSIII-1 provided by the invention can improve the quality of fruit amylopectin and improve the quality of the fruit. For example, the gene is introduced into a tomato, two independent strains of 35S promoter driven MaSSIII-1 transgenic tomatoes are obtained, the shapes of starch granules (obvious cross cracks occur on the surfaces of the starch granules) are changed through overexpression of the MaSSIII-1A, the expression quantity of the MaSSIII-1 is increased, the enzymatic activity of SS (soluble starch synthetase) is improved and the amylopectin content is increased.
Owner:INST OF TROPICAL BIOSCI & BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
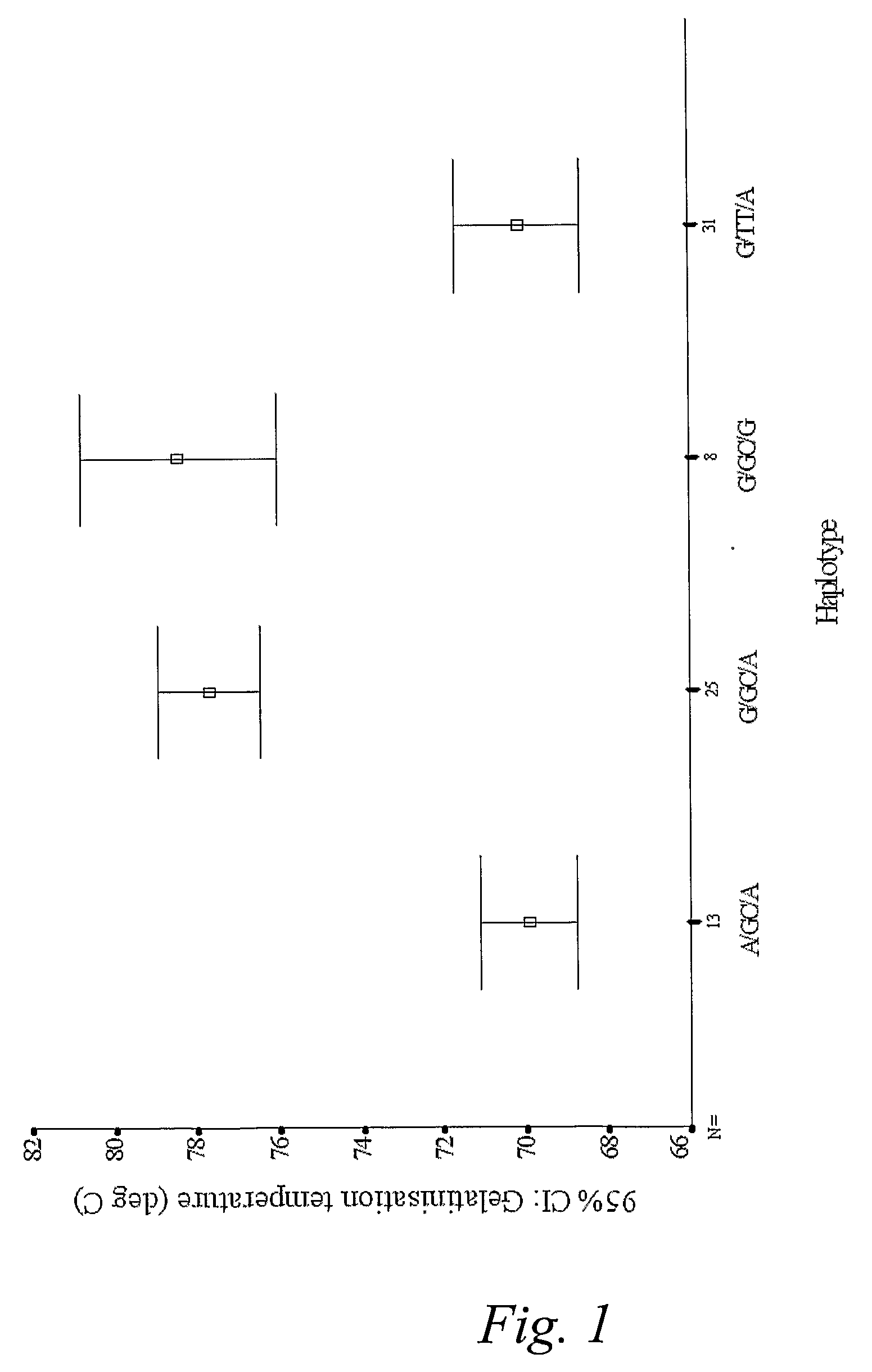
Gelatinization Temperature Manipulation
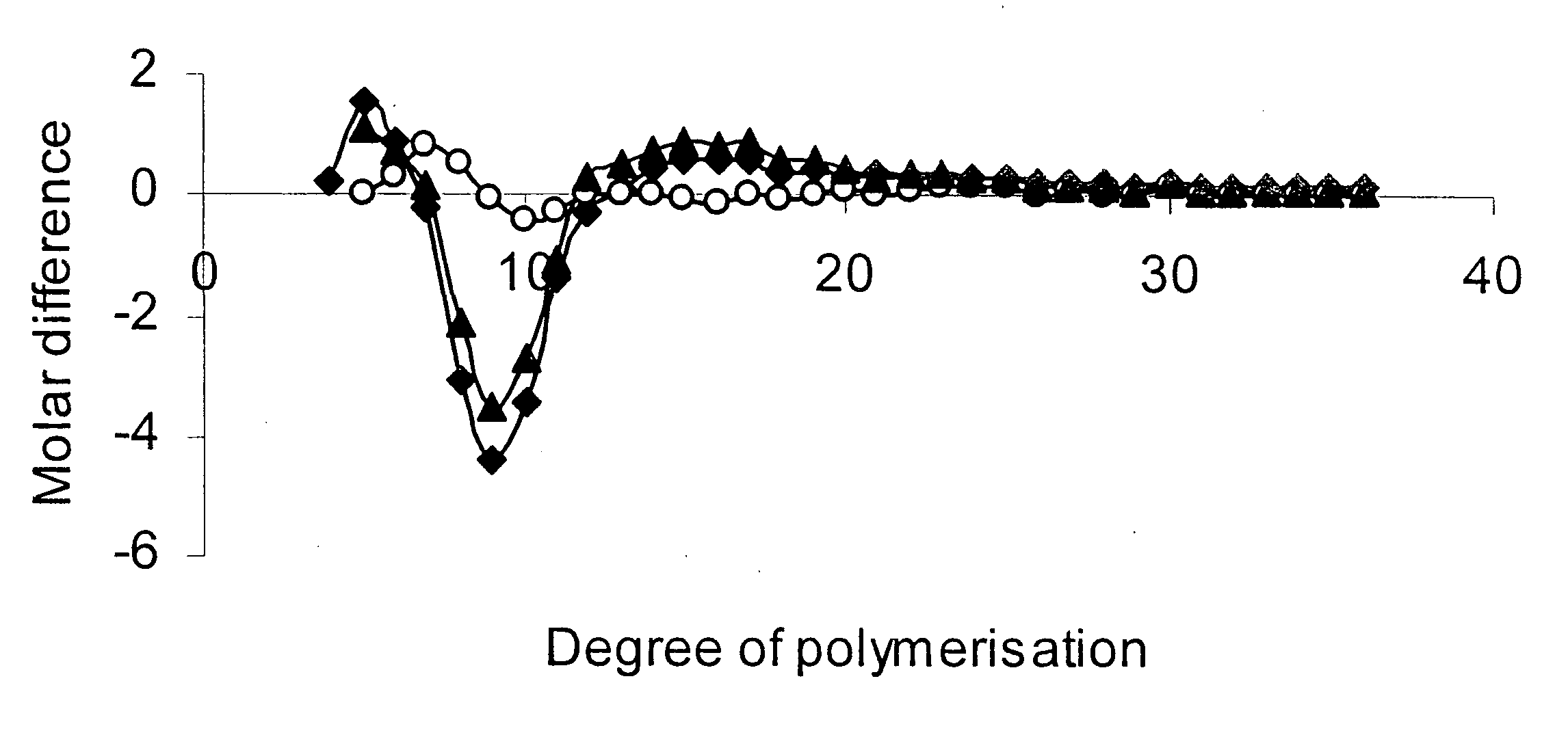
The subject invention relates to plants and the starch produced by plants. In particular, the invention relates to processes for the modification of a plant so that the starch produced by the plant comprises amylopectin of an altered structure and / or the starch has an altered gelatinization temperature. The processes principally comprise engineering gene involved in amylopectin synthesis. In a preferred embodiment the starch synthase IIa gene is modified. Also disclosed are processes for altering genes to provide plant which produce starch having a desired gelatinization temperature, and methods of identifying the changes that can be made in genes to achieve a desired gelatinization temperature in the starch produced by a plant comprising such genes. Further disclosed are modified plants and the starch products of the plants.
Owner:SOUTHERN CROSS UNIVERSITY
Nucleic acid molecules encoding wheat enzymes involved in starch synthesis
InactiveUS6897358B2Increased substance permeabilityImprove breathabilityDough treatmentBacteriaPlant cellStarch synthesis
The invention relates to nucleic acid molecules which code for enzymes and which are involved in the synthesis of starch in plants. These enzymes concern isoamylases derived from wheat. The invention also relates to vectors and host cells which contain the described nucleic acid molecules, especially transformed plant cells and plants which can be regenerated therefrom, which exhibit an increased or reduced activity of the inventive isoamylases.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Gene OsHsp70cp-2 related with rice endosperm flour as well as encoding protein and application thereof
The invention discloses a gene OsHsp70cp-2. The gene OsHsp70cp-2 is a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) molecule shown in (1) or (2) or (3) or (4), namely (1) a DNA molecule shown in SEQ ID NO.1; (2) a DNAmolecule shown in SEQ ID NO.2; (3) a DNA molecule which is hybridized with a DNA sequence limited in (1) or (2) under the strict condition and is used for encoding protein; (4) a DNA molecule which has 90% of homology or more with the DNA sequence limited in (1) or (2) or (3) and is used for encoding the protein related with synthesis of plant starch. The protein related with plant endosperm flouraffects the development process of plant amyloplast. The abnormal development of the amyloplast in the plant seeds is caused by inhibiting the expression of the protein encoding gene, so as to culture a transgenic plant with endosperm variation and a transgenic plant with abnormal plant amyloplast.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Method for cultivating starch-content-increased transgenic plant through multi-gene transformation
InactiveCN103173485AImprove conversion rateHigh total starch contentTransferasesFermentationGranule-Bound Starch SynthaseSucrose synthetase
The invention discloses a method for cultivating a starch-content-increased transgenic plant through multi-gene transformation. According to the transgenic plant cultivation method provided by the invention, a selection marker gene, an adenosine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase small subunit gene, an adenosine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase large subunit gene, a sucrose synthase gene, and a granule-bound starch synthase gene are introduced into a target plant, such that a transgenic plant is obtained. The total starch content of the transgenic plant is higher than that of the target plant. As a result of experiment of the invention, a plurality of genes can be simultaneously transferred in one-time through one time of gene gun bombardment, such that transgenic material cultivation period and work load can be greatly shortened. Specifically, the 4 genes related to starch metabolism are simultaneously transferred in, such that the total starch content of a transgenic regenerated plant is higher than that of wild-type plant.
Owner:NORTHEAST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Graphene three-dimensional printing material
InactiveCN106633720AHigh tensile strengthHigh heat distortion temperatureAdditive manufacturing apparatusPolymer scienceFlexural strength
The invention discloses a graphene three-dimensional printing material, and belongs to the technical field of materials for three-dimensional printing. The graphene three-dimensional printing material is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 5 to 8 parts of graphene, 26 to 32 parts of waste plastics, 32 to 42 parts of polylactic acid, 16 to 25 parts of sodium tripolyphosphate, 20 to 26 parts of n-butyl acetate, 12 to 20 parts of a specific synthesis agent and 5 to 10 parts of a starch synthesis agent. The graphene three-dimensional printing material prepared in the invention has the characteristics of high tensile strength, high bending strength and high notch impact strength, high heat deflection temperature and high melt index and the like, and the product printed through a three-dimensional printing technology is high in quality, high in impact and high in strength and has a broad market prospect.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHUMENG SANTI TECH CO LTD
Binary vector construction method for improving corn amylose content by utilizing genetic engineering
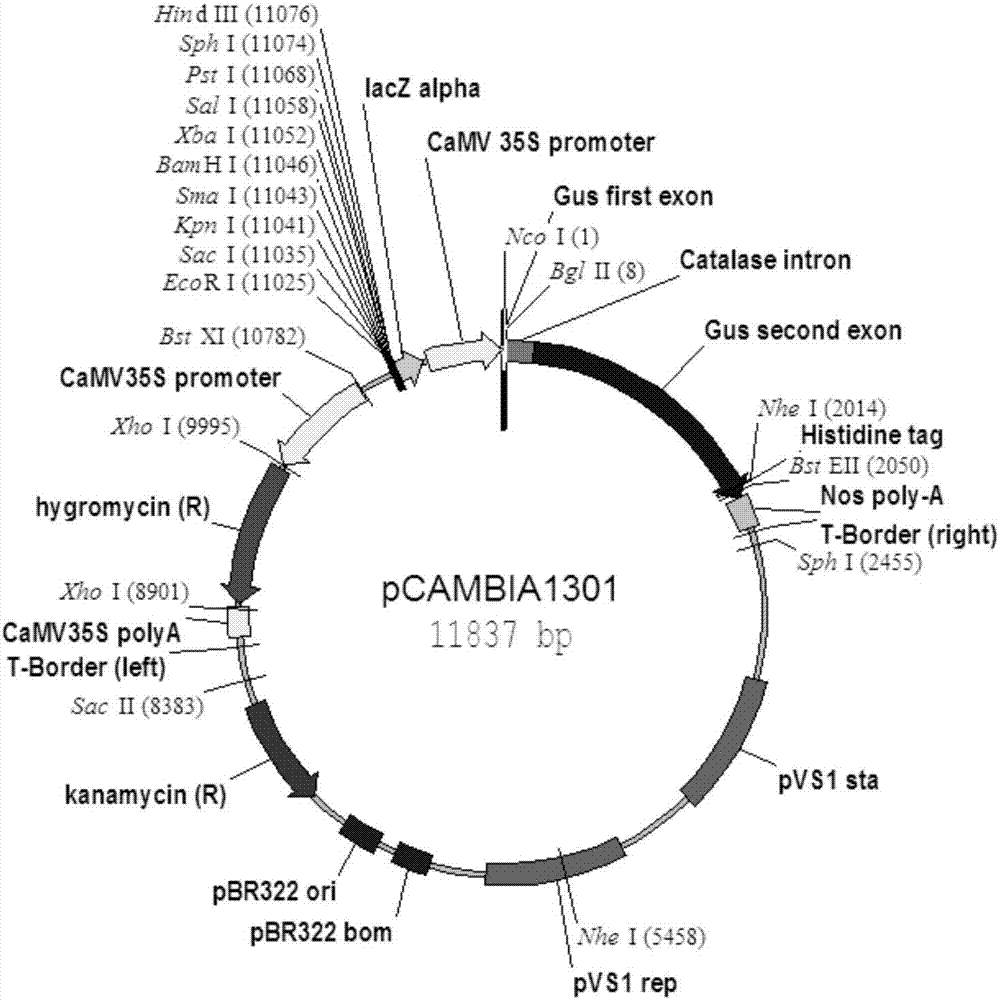
InactiveCN103484494AReduced number of branchesIncrease the relative contentClimate change adaptationVector-based foreign material introductionGenetic engineeringGene expression
The invention discloses a binary vector construction method for improving corn amylose content by utilizing genetic engineering. The binary vector construction method comprises: designing a primer to amplify the ninth extron and intron part sequence (315bp) and the ninth extron antisense sequence (155bp), and also to amplify sbe2b promoter, simultaneously linking an integrated DNA fragment containing sense and antisense extrons and introns and the promoter into multiple cloning sites (MCS) of a pCAMBIA3301 carrier; and then replacing 35S and GUS fragments of the pCAMBIA3301 carrier containing sbe2b RNAi three fragments in MCS by a ss1 promoter fragment and a ss1 gene cDNA fragment, so that the expression carrier contains both antisense sbe2b cDNA fragment controlled by sbe2b promoter and ss1 full-length cDNA fragment controlled by ss1 promoter. The sbe2b RNAi fragment contained in the expression carrier provided by the invention is capable of reducing activity of SBEIIb enzyme and reducing branch number when starch is synthesized, and thus the relative content of amylose is improved; and also the ss1 gene expression fragment contained in the carrier is capable of improving the activity of corn endosperm SSI enzyme, and thus the total starch content is improved.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Transgenic element and application thereof, method for differentiating male sterility line and fertile maintainer line, and expanding propagation method of male sterile line of maize
InactiveCN104611364AHigh purityReduce the cost of seed productionFermentationPlant genotype modificationHybrid seedNucleotide sequencing
The invention relates to the technical field of agriculture and in particular relates to a transgenic element and an application thereof, a method for differentiating a male sterility line and a fertile maintainer line, and an expanding propagation method of the male sterile line of maize. A functional nucleotide sequence controlling the male fertility of the maize and a nucleotide sequence controlling starch synthesis are transferred into the maize together, and then backcross transformation is performed to obtain a hybrid maintainer line. As the nucleotide sequence controlling starch synthesis in the maintainer line inhibits the starch synthesis and increase the sugar content to lead to kernel shrinking, the sterility line and the maintainer line can be doubly differentiated from quality and appearance, and the accuracy is improved. The male sterility line and the fertile maintainer line of the hybrid female parent of the maize can be differentiated accurately and efficiently by use of the method, and then the male sterility line of the hybrid female parent can be applied to expanding propagation and applied to the production of hybrid seeds. Meanwhile, the difference in quality and appearance is more prone to mechanical identification, and therefore, the working efficiency can be greatly improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG XINAN CHEM INDAL GROUP
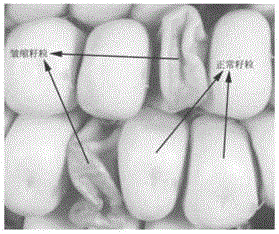
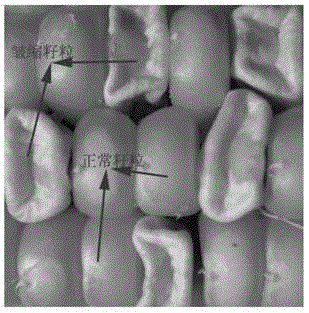
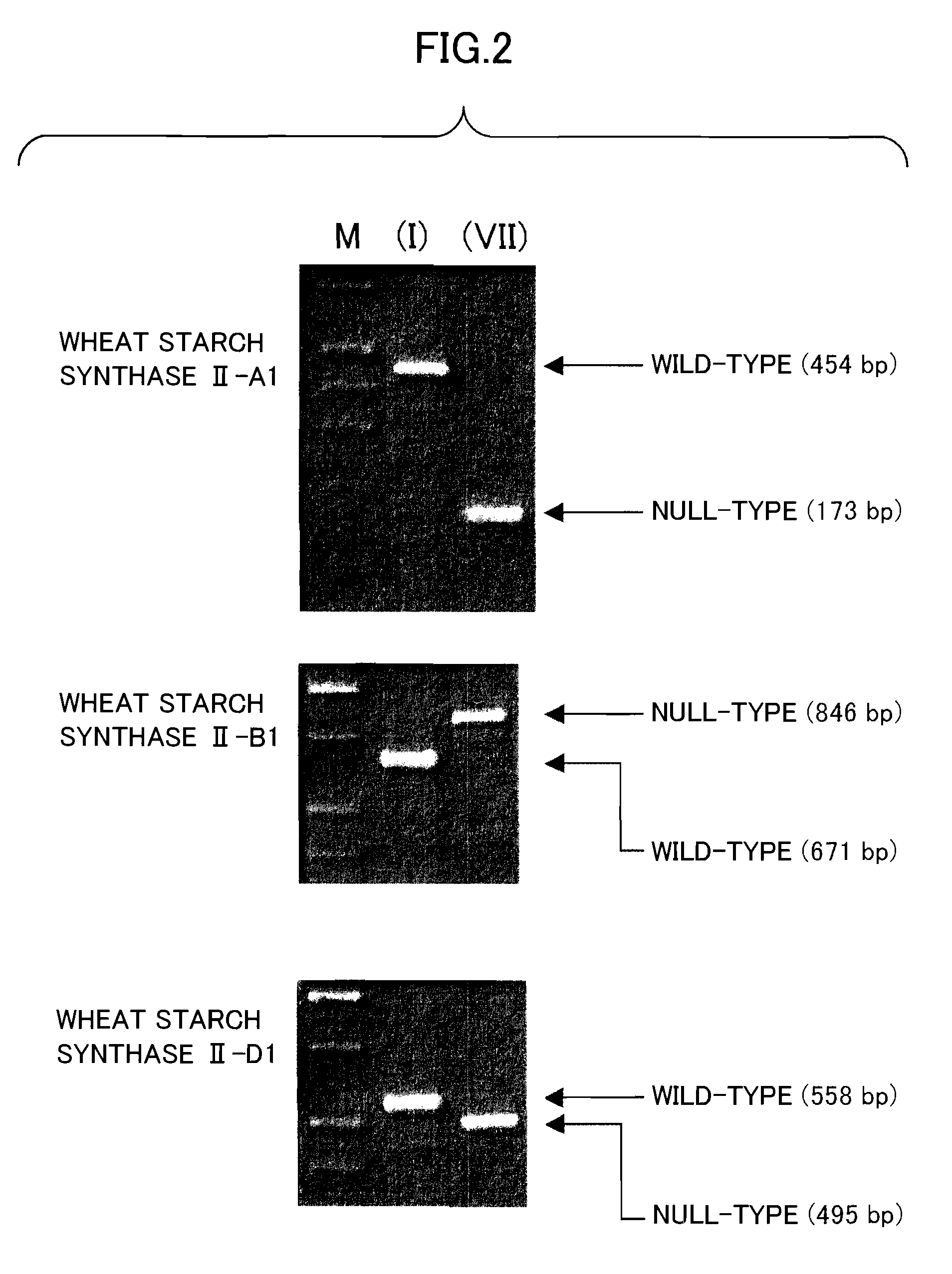
Wheat having new starch and method for producing it
ActiveUS8053628B2Dough treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementGranule-Bound Starch SynthaseBiotechnology
The object of the present invention is to provide a wheat which accumulates a starch with a novel property by controlling the expression of the enzymes described in claims.The present invention provides a wheat, which does not express any of the following proteins (1)-(6): (1) Wheat Starch Synthase II-A1 Protein encoded by Wheat Starch Synthase II-A1 gene of SEQ ID NO:1, (2) Wheat Starch Synthase II-B1 Protein encoded by Wheat Starch Synthase II-B1 gene of SEQ ID NO:3, (3) Wheat Starch Synthase II-D1 Protein encoded by Wheat Starch Synthase II-D1 gene of SEQ ID NO:5, (4) Granule Bound Starch Synthase A1 Protein encoded by Granule Bound Starch Synthase A1 gene of SEQ ID NO:7, (5) Granule Bound Starch Synthase B1 Protein encoded by Granule Bound Starch Synthase B1 gene of SEQ ID NO:9, and (6) Granule Bound Starch Synthase D1 Protein encoded by Granule Bound Starch Synthase D1 gene of SEQ ID NO:11.
Owner:NIPPON FLOUR MILLS +1
Vegetable starch synthetase genetic promoter and use thereof
InactiveCN101555480APlay a regulatory roleHas space-time specific expression characteristicsFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention discloses a vegetable starch synthetase genetic promoter and use thereof. The promoter is separated from corn genome DNA with a nucleotide sequence which is showed as listed nucleotide sequence SEQ ID NO: 1; length of the nucleotide sequence is 1655bp. The vegetable starch synthetase genetic promoter of the invention can promote high expression of gene in leaf and seed without expression in root. The promoter is applicable to driving of gusA gene expression. The promoter plays an important role in vegetable starch quality improvement and vegetable biological reactor.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Oryza sativa floury endosperm related gene OscyMDH, protein encoded by same and application
ActiveCN107475266AGenetic improvementBarriers to starch synthesisOxidoreductasesFermentationHigh homologyStarch synthesis
The invention discloses an oryza sativa floury endosperm related gene OscyMDH, a protein encoded by the same and an application. The gene OscyMDH refers to DNA molecules shown as the following 1), 2), 3) or 4): 1) DNA molecules shown as SEQ ID NO.1; 2) DNA molecules shown as SEQ ID NO.2; 3) DNA molecules hybridized with DNA sequences limited in 1) or 2) under stringent conditions and encoding the protein; 4) DNA molecules having 90% or higher homology with DNA sequences limited in 1), 2) or 3) and encoding plant starch synthesis related protein. The invention further provides the protein encoded by the gene. The protein affects synthesis of starch in plant endosperm, and transgenic plants with normal starch synthesis can be cultured by transferring the protein encoding gene into plants with abnormal starch synthesis. The protein and the protein encoding gene can be applied to genetic improvement of the plants.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Heat stable mutants of starch biosynthesis enzymes
InactiveCN1503842AIncrease productionImprove toleranceHydrolasesMutant preparationPlant tissueNucleotide
The present invention relates to novel mutant polynucleotide molecules encoding enzymes with enhanced thermostability. When expressed in plants, these polynucleotides lead to increased yield in plants grown under conditions of heat stress. In one embodiment, the polynucleotide molecule of the present invention encodes maize endosperm ADP glucose pyrophosphorylase (AGP) and soluble starch synthase (SSS) enzyme activities. Also contemplated by the present invention are plants and plant tissues grown to contain or transformed with such mutant polynucleotides and expressing a polypeptide encoded by such polynucleotides. The invention also relates to methods for isolating polynucleotides and polypeptides within the scope of the invention. The present invention also provides methods of increasing yield in plants grown under conditions of heat stress.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Preparation method of novel 3D printing clay material
InactiveCN106316346AImprove wear resistanceHigh impact strengthAdditive manufacturing apparatusCeramic materials productionMaterials preparationAsh preparation
The invention discloses a preparation method of a novel 3D printing clay material and belongs to the technical field of 3D printing material preparation. The novel 3D printing clay material is prepared from clay, calcium carbonate powder, plant ash, a specific synthesis agent, a starch synthesis agent and water according to a mass ratio of 20-30: 8-16: 6-10: 5-8: 4-6: 10-25. The preparation method comprises clay preparation, calcium carbonate powder preparation, plant ash preparation, normal temperature crushing, modification with a specific synthesis agent and a starch synthesis agent, and extruding granulation. The clay material has the advantages of high wear resistance, impact strength, shock strength, good plasticity, molding easiness and high precision, is suitable for a 3D printing molding technology, promotes 3D printing molding technology promotion and has a wide market prospect.
Owner:NANNING MENGHUAN 3D ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD
Method for regulating content of starch in corn kernel based on ZmMIKC2a gene
ActiveCN107254475AIncrease or decrease amylose contentIncrease or decrease amylosePlant peptidesFermentationAmylaseAgricultural science
The invention discloses a method for regulating the content of starch in a corn kernel based on a ZmMIKC2a gene and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. The method comprises the following steps: I) constructing a ZmMIKC2a gene over-expression vector to obtain a ZmMIKC2a gene over-expression plant; II) knocking out the ZmMIKC2a gene in a target corn to obtain a ZmMIKC2a gene deletion plant. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the positive regulation effect of the ZmMIKC2a gene on corn kernel starch synthesis related genes is utilized; the content of amylose in the target corn and the ratio of the amylase to total starch are improved or reduced through a gene engineering method, so that a new transgenic corn variety with high amylose, low amylopectin or high amylopectin / low amylose is obtained; the method is of great practical significance in developing the new transgenic corn variety with a specific function by utilizing a gene engineering technology.
Owner:INST OF TOBACCO ANHUI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
High-bending-strength rice straw 3D printing material
InactiveCN106589998AHigh strengthHigh impact strengthAdditive manufacturing apparatusFlexural strengthPotassium
The invention belongs to the technical field of 3D printing material preparation and discloses a high-bending-strength rice straw 3D printing material. The high-bending-strength rice straw 3D printing material is prepared from, by weight, 72-116 parts of rice straw powder, 29-45 parts of polylactic acid, 10-14 parts of potassium hexaphoshpate, 11-15 parts of diethylene glycol butylether acetate, 9-12 parts of polypropylene resin, 3-5 parts of butadiene styrene rubber, 15-24 parts of a specific synthesis agent and 6-13 parts of a starch synthesis agent. The high-bending-strength rice straw 3D printing material is high in toughness and impact strength; products printed by means of 3D printing have advantages of high quality, high impact resistance, high strength, nontoxicity, low carbon, environment friendliness, low cost, wood color, recyclability, high economic value and promising market prospect.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHUMENG SANTI TECH CO LTD
Application of histone deacetylase gene to regulation and control on development of rice seed starch
InactiveCN103525843AIncrease productionImprove qualityHydrolasesFermentationHistone deacetylaseWild type
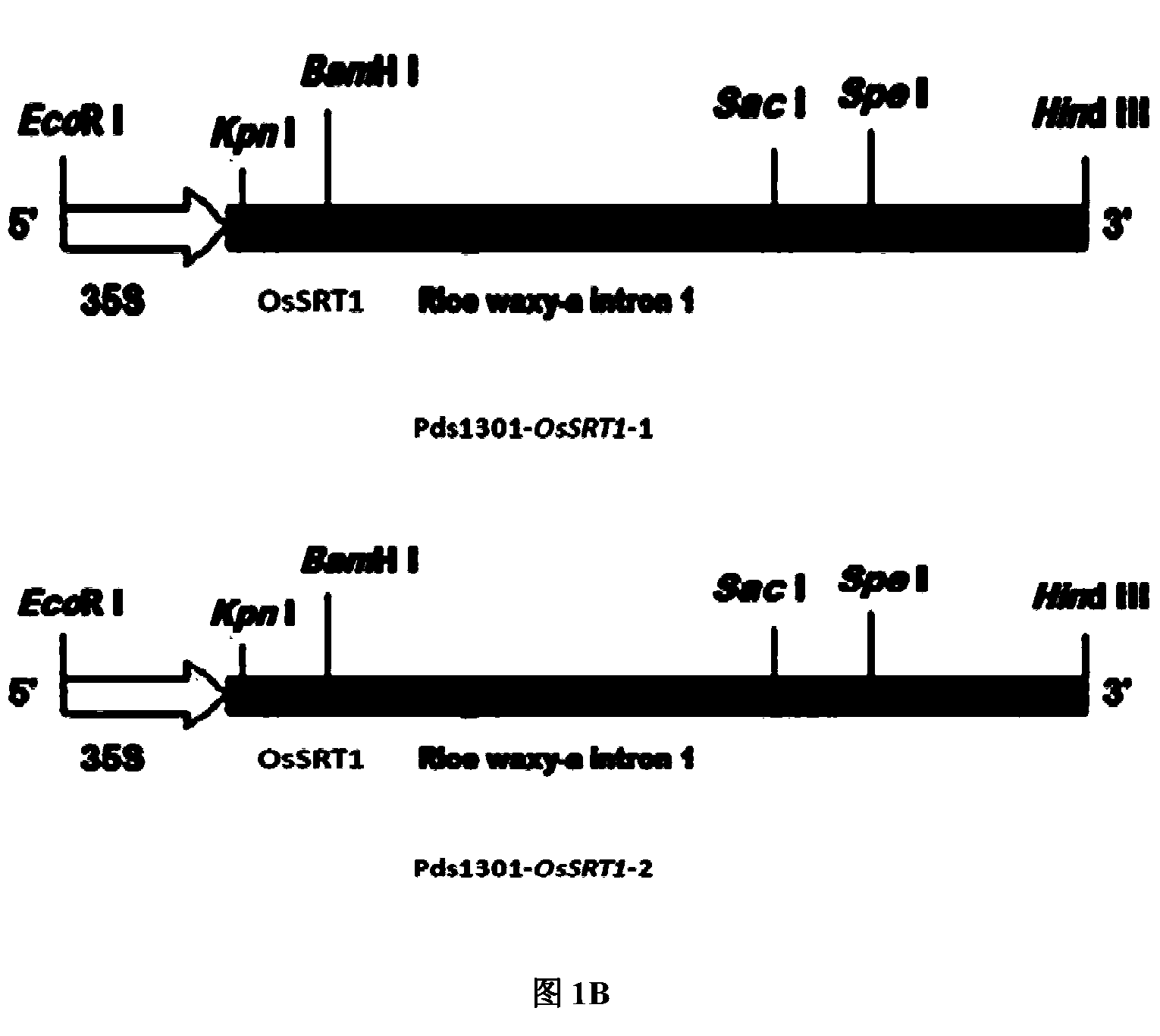
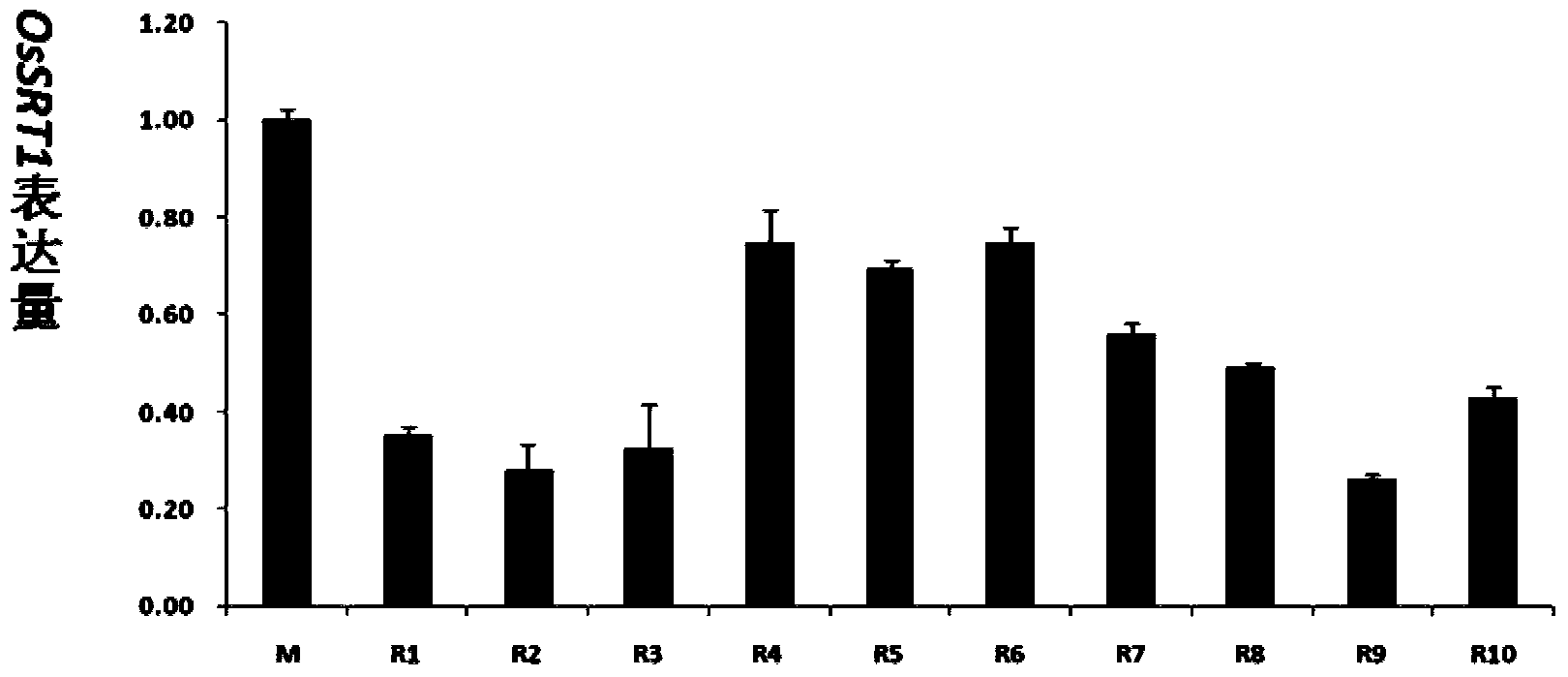
The invention belongs to the field of plant transgenes and relates to application of a histone deacetylase OsSRT1 gene to regulation and control on development of rice seed starch. H3K9 acetylation of an OsSRT1 inhibited plant is found to be obviously enhanced, which indicates that the gene is histone H3K9 deacetylase gene. According to research on the transgenic plant which inhibits the gene, the fertility of the plant is obviously reduced, and most of seeds stop developing three days after fertilization and are withered gradually. According to observation, the endosperm starch content of the seeds is reduced two days after the seeds are fertilized. According to Realtime-PCR detection on the change of starch synthesis genes, in the seeds which are fertilized for one day and two day, the expression quantity of the starch synthesis genes of the OsSRT1 inhibited plant is obviously reduced compared with that of the wild type. The OsSRT1 is confirmed to regulate and control starch synthesis by influencing histone acetylation.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Method of adjusting content of plant amylose and amylopectin
InactiveCN103146756AOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationStarch-branching enzyme IIStarch synthase
The invention relates to a method of adjusting a content of plant amylose and amylopectin. The invention provides an enzyme which is suitable for genetic engineering operation and can substantially change starch composition in the plant, wherein the enzyme is granule-bound starch synthase I (GBSS I), starch branching enzyme I (SBE I) and / or starch branching enzyme II (SBE II). The invention further provides a novel method of well adjusting starch composition in the plant, and the method comprises reducing expression of the enzyme, and thus obtaining a series of transgene plants with different content ratios of amylose and amylopectin The invention further provides a constructor or a carrier for adjusting starch composition in the plant.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Starch modification
InactiveUS20030200564A1Increase nutritionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementStarch synthesisBiology
The present invention relates to a method of altering starch synthesis in a plant by modifying the starch priming activity of the plant. In particular, this is achieved by altering the expression or activity of a starch primer which is preferably encoded by the sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1 or a sequence substantially homologous thereto. Also provided are plants in which the starch priming activity has been altered and plant parts.
Owner:GEMSTAR CAMBRIDGE
Plant expression vector and application thereof in preparing phosphorylation modified rice starch
ActiveCN104232681AIncrease contentAchieve modificationVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsGranule-Bound Starch SynthaseBiotechnology
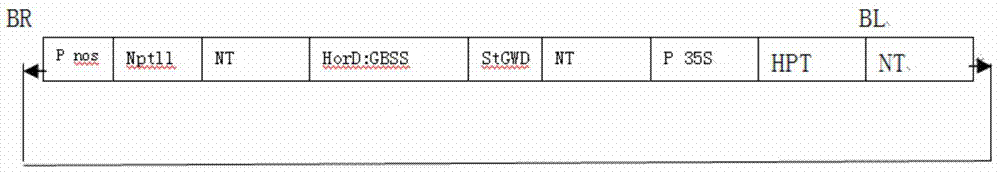
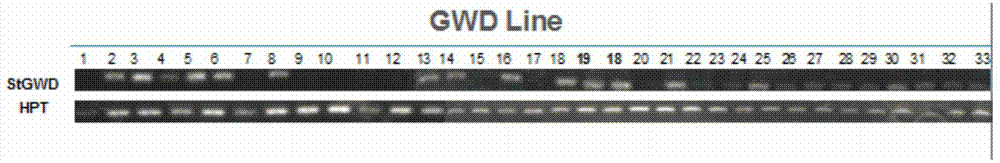
The invention discloses a plant expression vector and the application thereof in preparing phosphorylation modified rice starch. The plant expression vector comprises a target gene inserting into an original vector and a promoter, wherein the target gene comprises a transit peptides gene segment of granule-bound starch synthase and a potato glucan-water dikinase gene which are sequentially connected, and the promoter is a barley endosperm specific promoter HorD. For the plant expression vector and the application thereof in preparing phosphorylation modified rice starch, the potato glucan-water dikinase gene is transferred into rice, and the starch of the rice can be phosphorylated through the expression of the potato glucan-water dikinase gene, so that the modification of the starch is realized. The potato glucan-water dikinase is led to amyloid through the transit peptides of the granule-bound starch synthase, and phosphorylation modification is performed on the starch. According to the invention, the expression of the potato glucan-water dikinase gene in the rice endosperm can be promoted through the barley endosperm specific promoter HorD, and the phosphorus content in the rice starch is greatly increased.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Novel preparation method of octenyl succinic starch ester
The present invention relates to a novel preparation method of starch octenyl succinate, the main technical point of which is to carry out hot alkali pretreatment on starch, and then adopt two methods of direct modification or modification after freeze-drying and then carry out octenyl Synthesis of starch octenyl succinate to improve the emulsification performance of the final product starch octenyl succinate. The invention has simple operation steps and low cost, and the octenyl succinic acid starch ester treated with hot alkali freeze-intervention has a higher degree of substitution and better emulsifying performance than the starch ester without pretreatment.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method for regulating starch contents of rice grains based on ZmMIKC2a gene
The invention discloses a method for regulating starch contents of rice grains based on a ZmMIKC2a gene. The ZmMIKC2a gene is a DNA molecule, of which the nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.1. The method comprises the following steps: building an excessive expression carrier of the ZmMIKC2a gene, and importing the excessive expression carrier into a target paddy rice genome to obtain an excessive expression plant of the ZmMIKC2a gene of which straight-chain starch content and the proportion of the straight-chain starch to total starch in seed grains are both higher than that of the target paddy rice. According to the method, positive regulation effects of the ZmMIKC2a gene on a plant seed grain starch synthesis related gene is used, by adopting a genetic engineering method, the straight-chain starch content and the proportion of the straight-chain starch to the total starch in the paddy rice seed grains are changed, so that a new variety of genetically modified paddy rice with high straight-chain starch is obtained, and important practical meaning on development of the new variety of genetically modified paddy rice with a specific function by utilizing a genetic engineering technology is achieved.
Owner:INST OF TOBACCO ANHUI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com