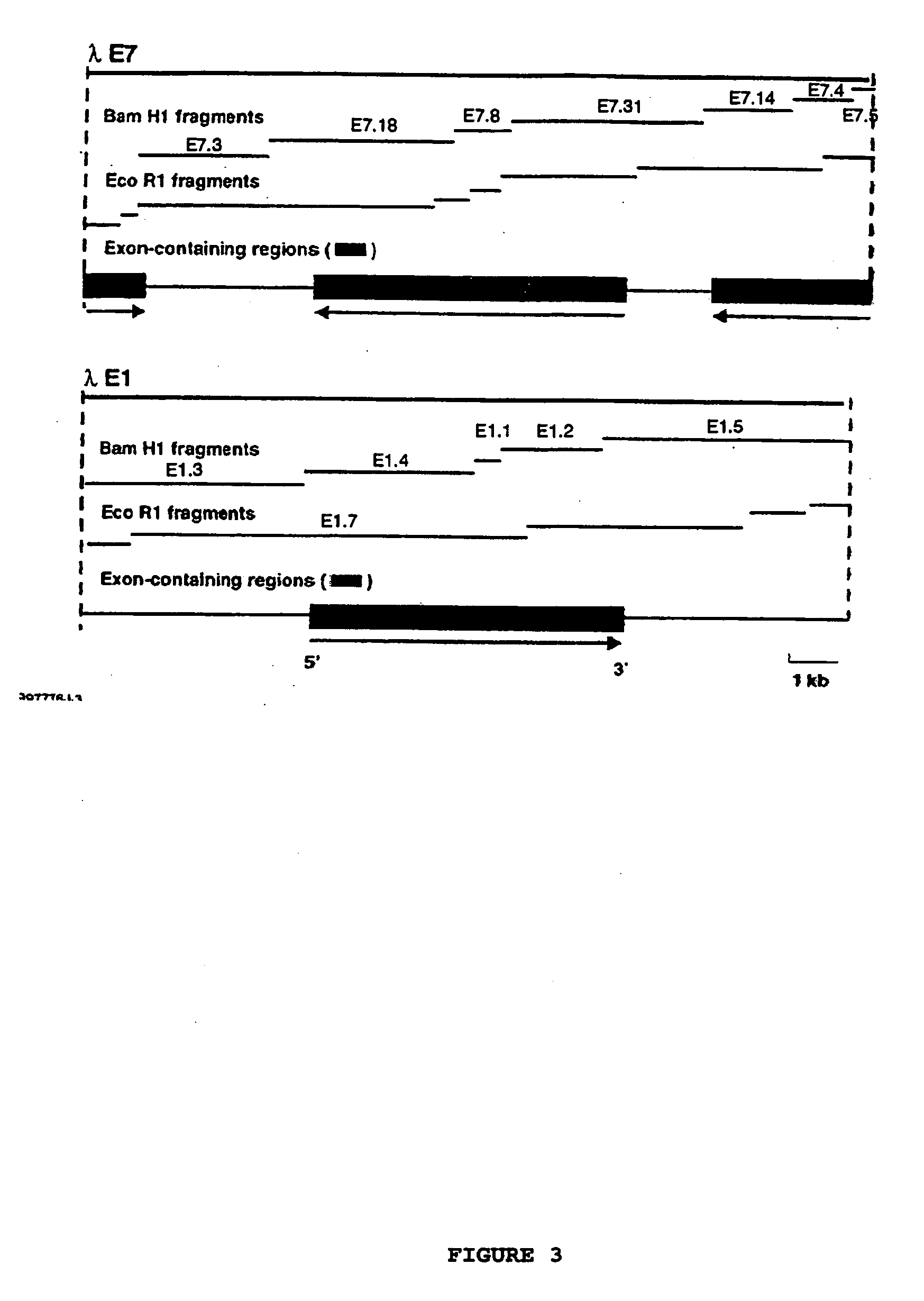
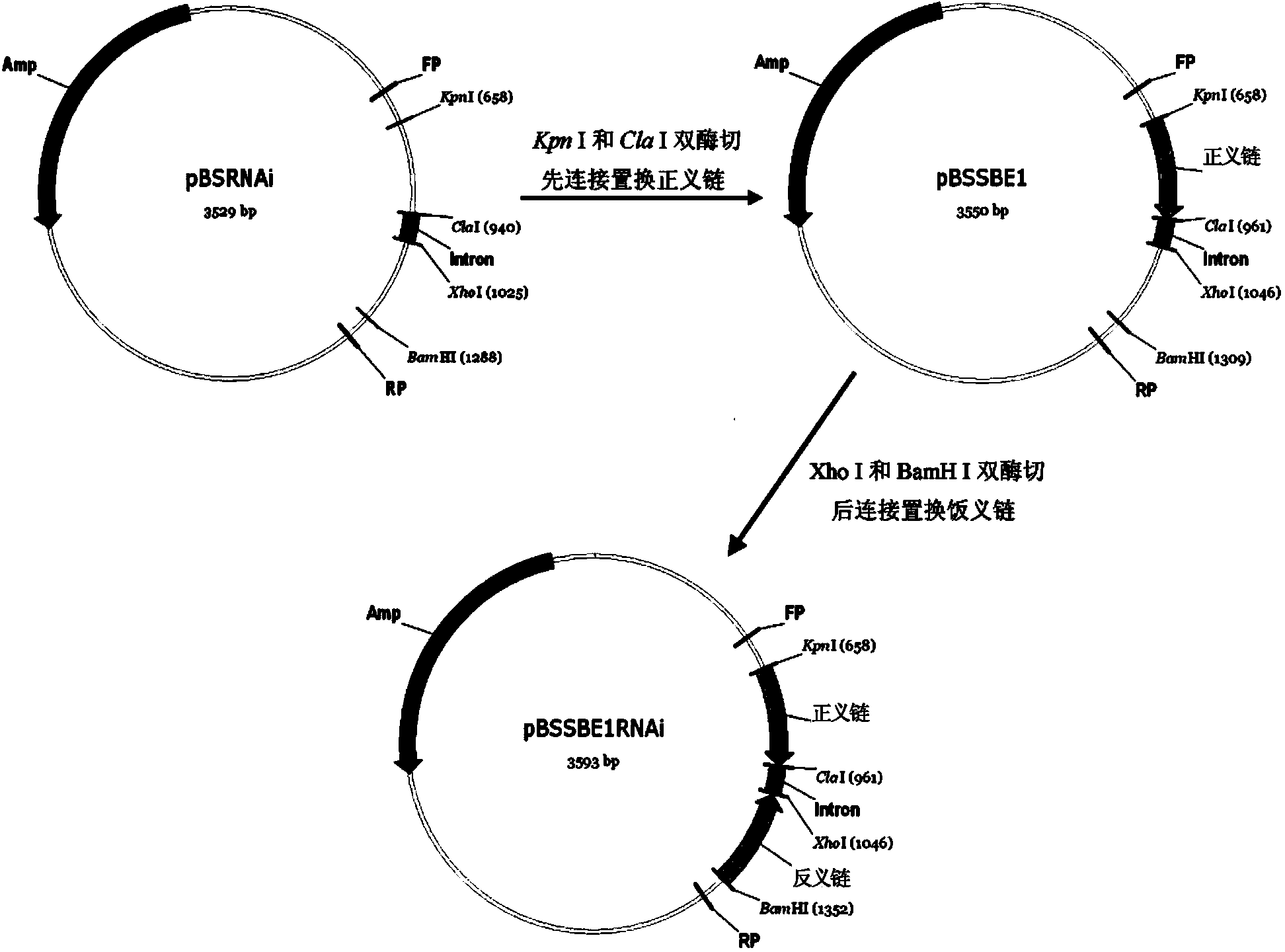
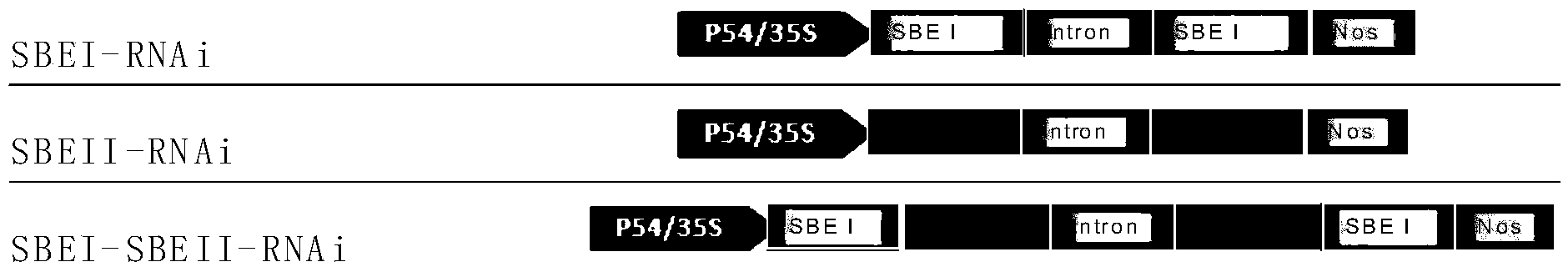
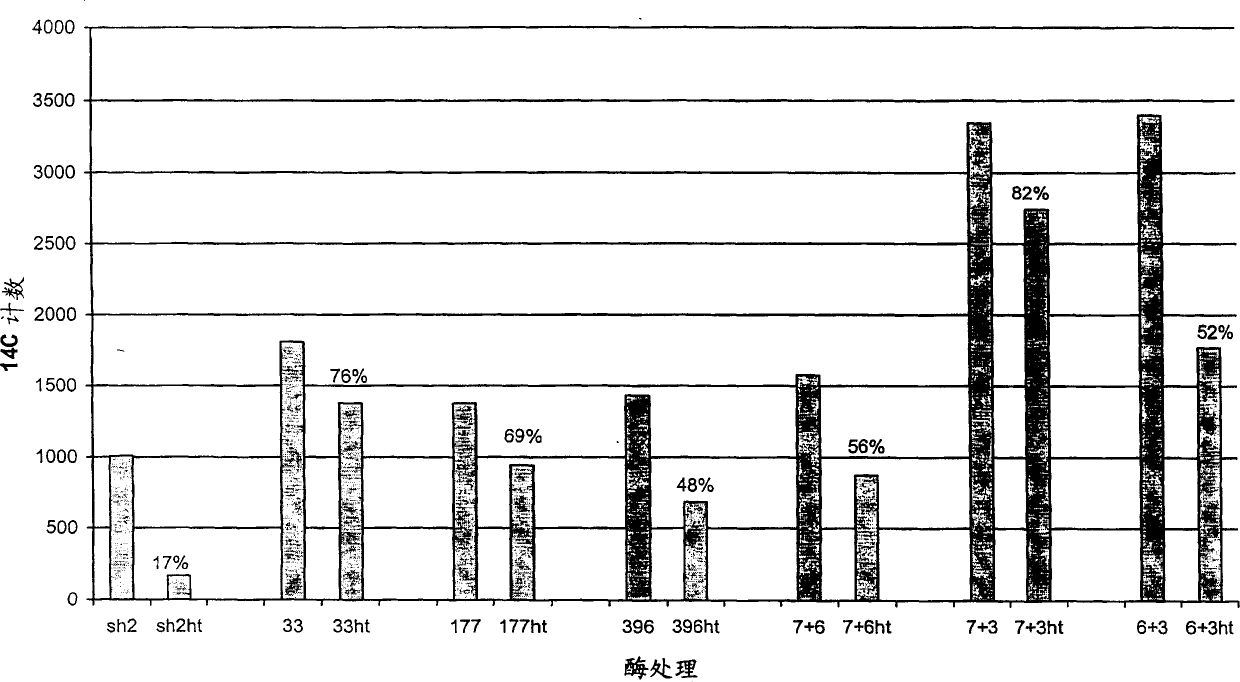
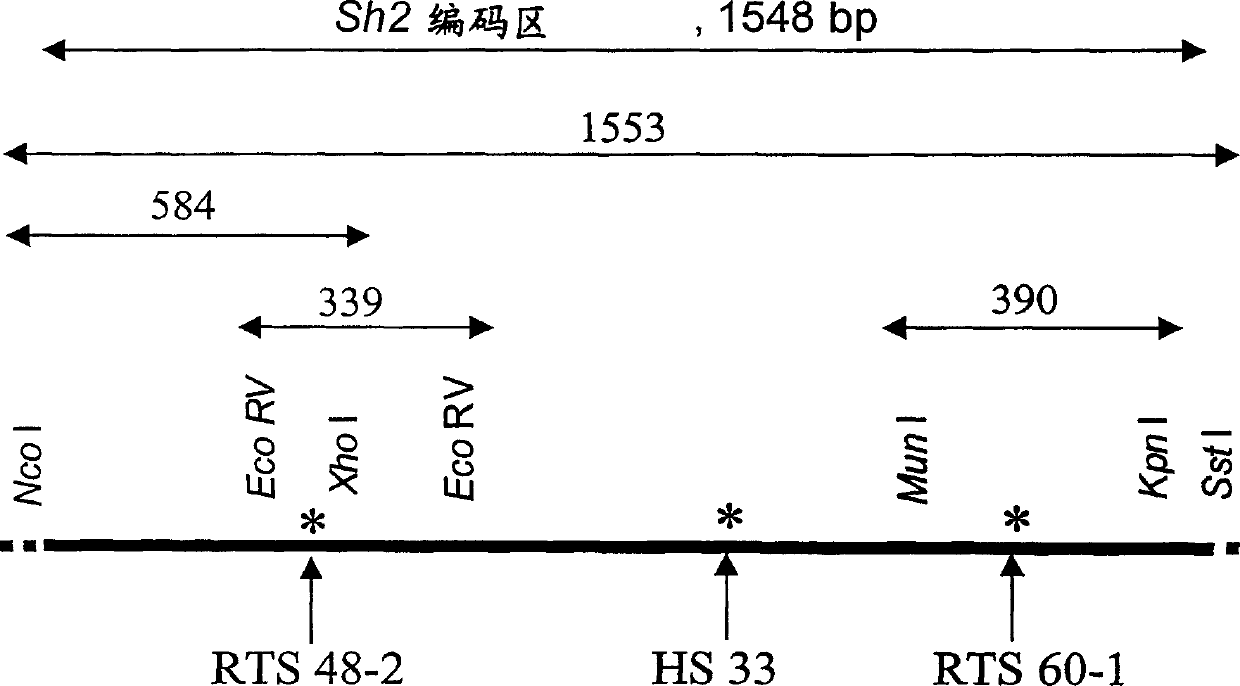
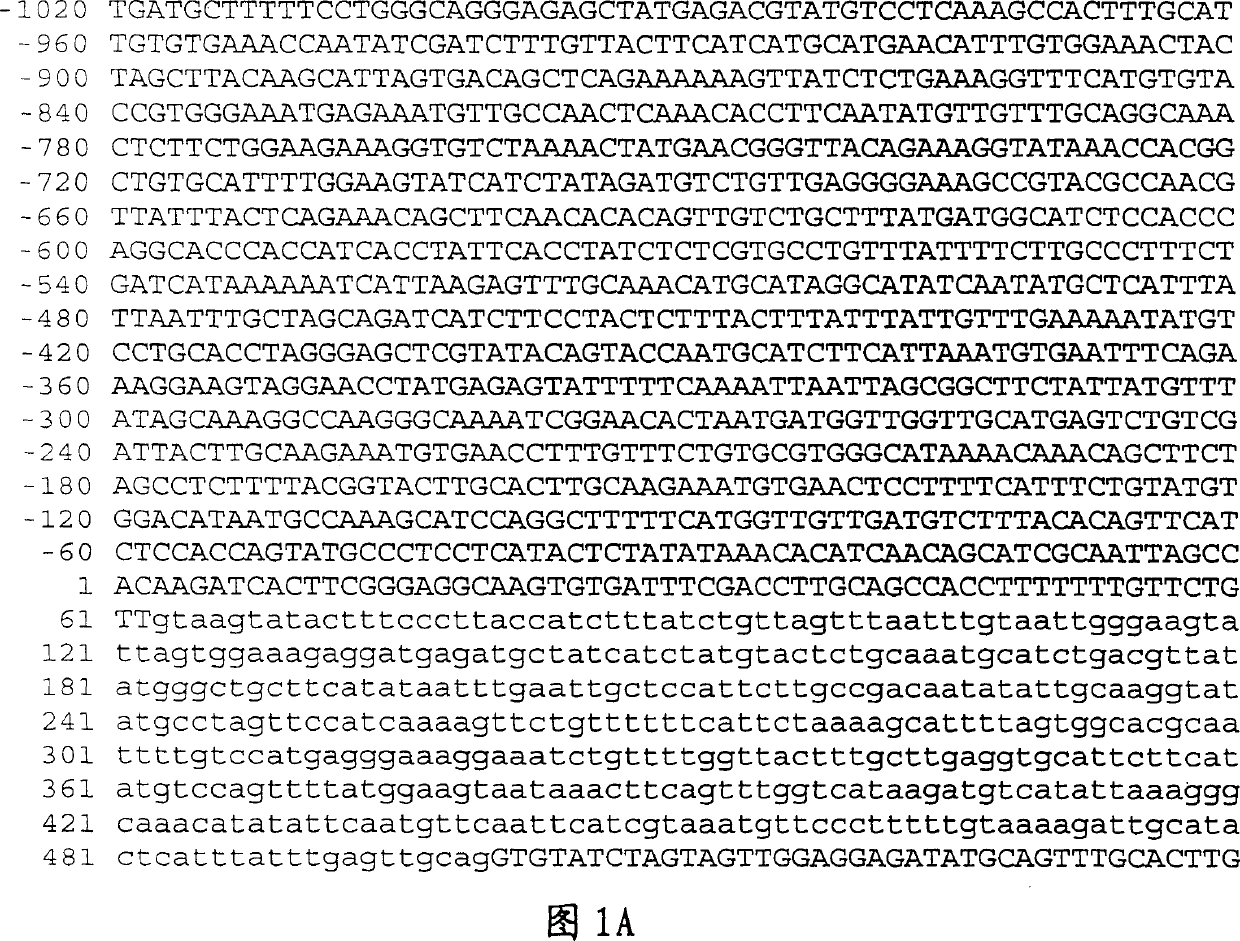
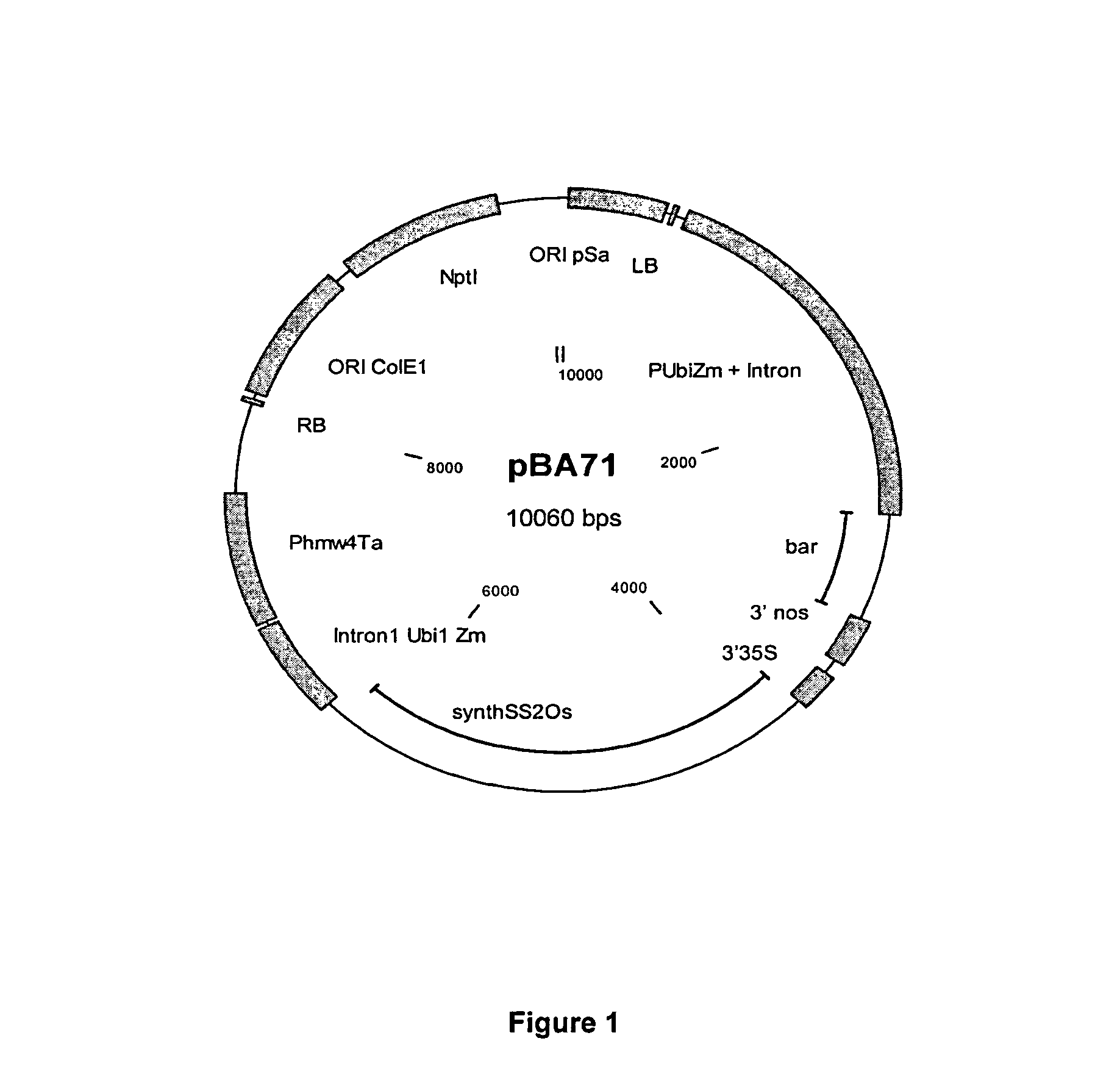
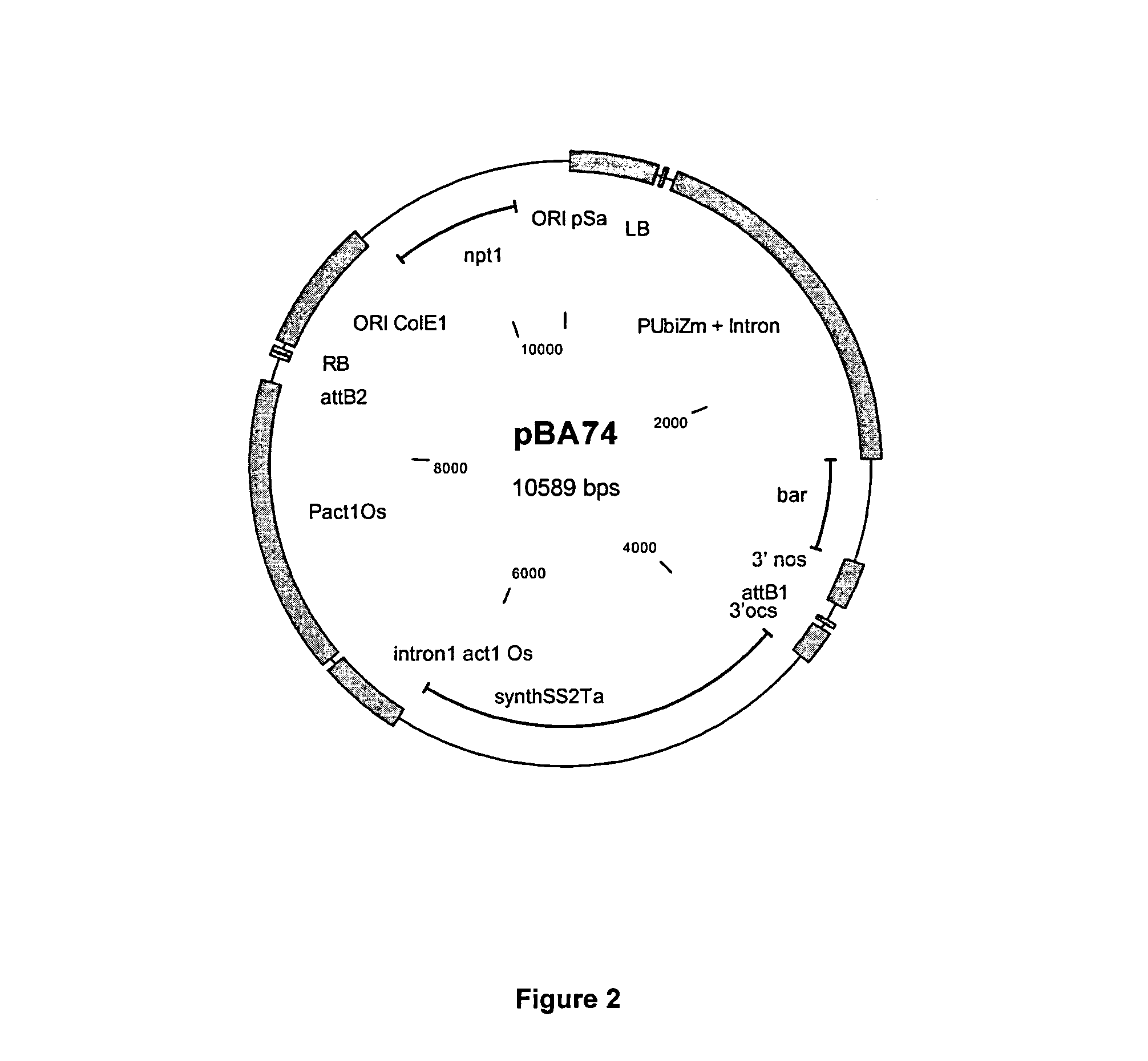
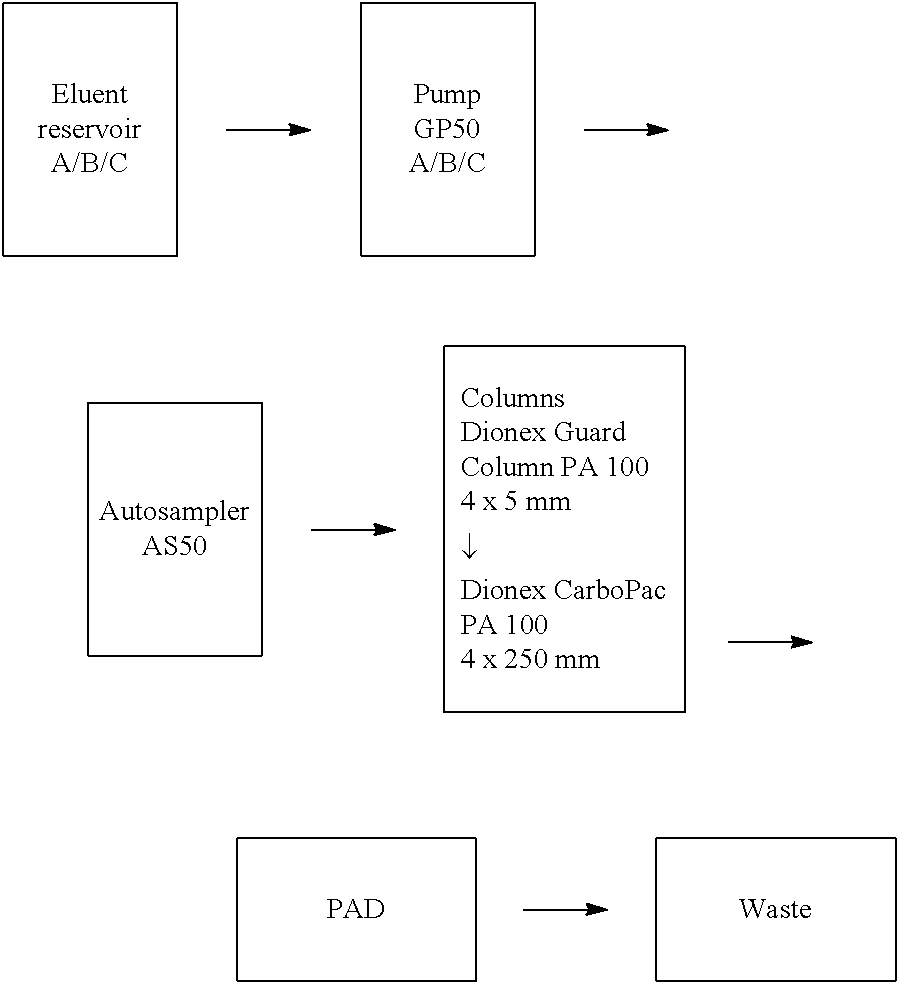
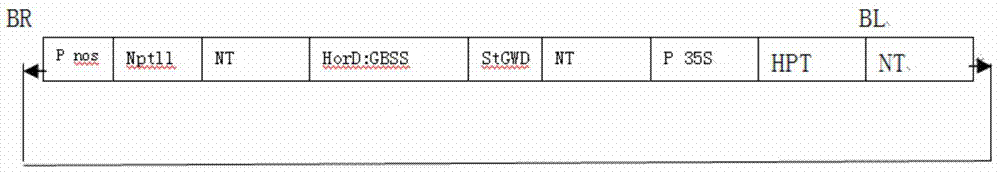
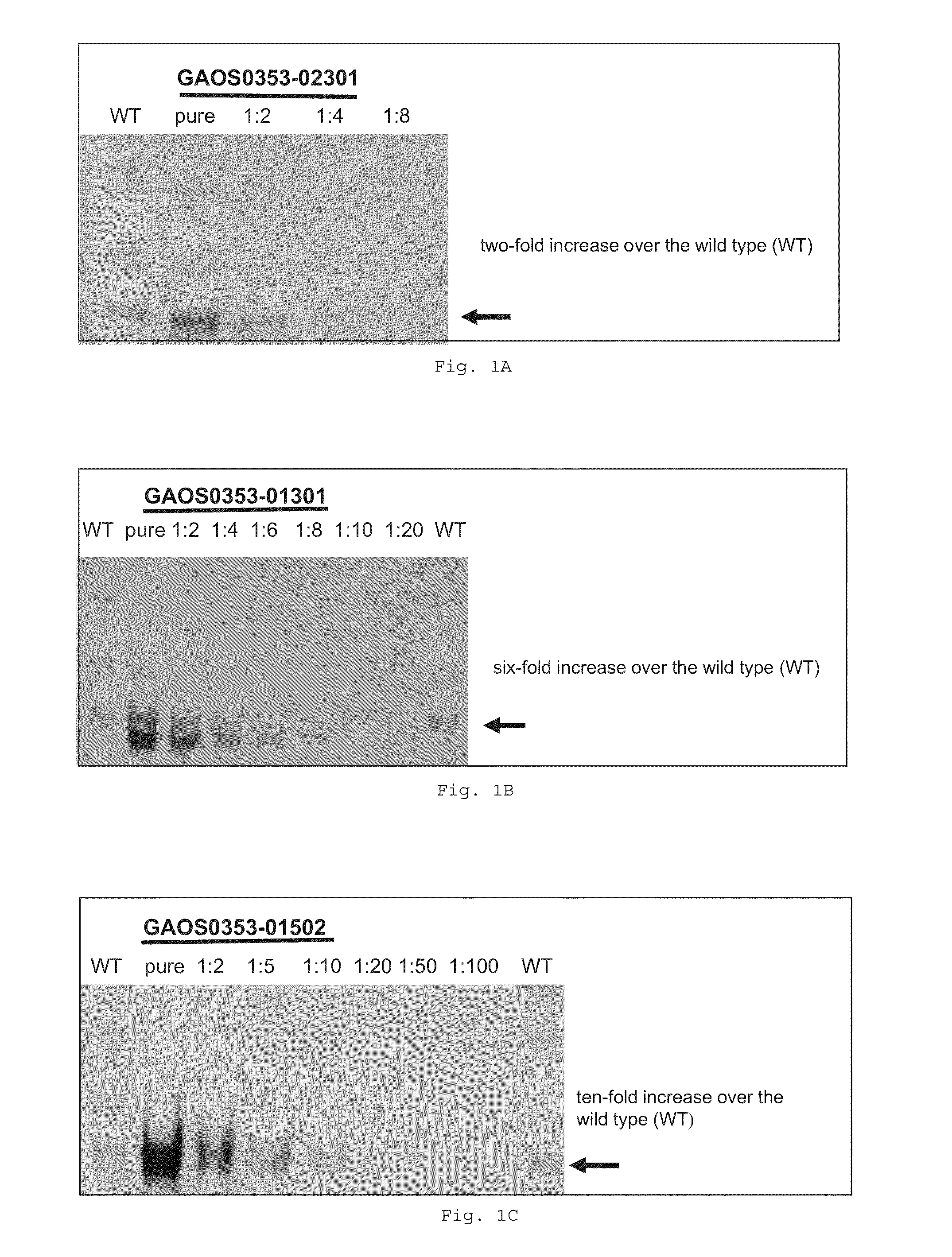
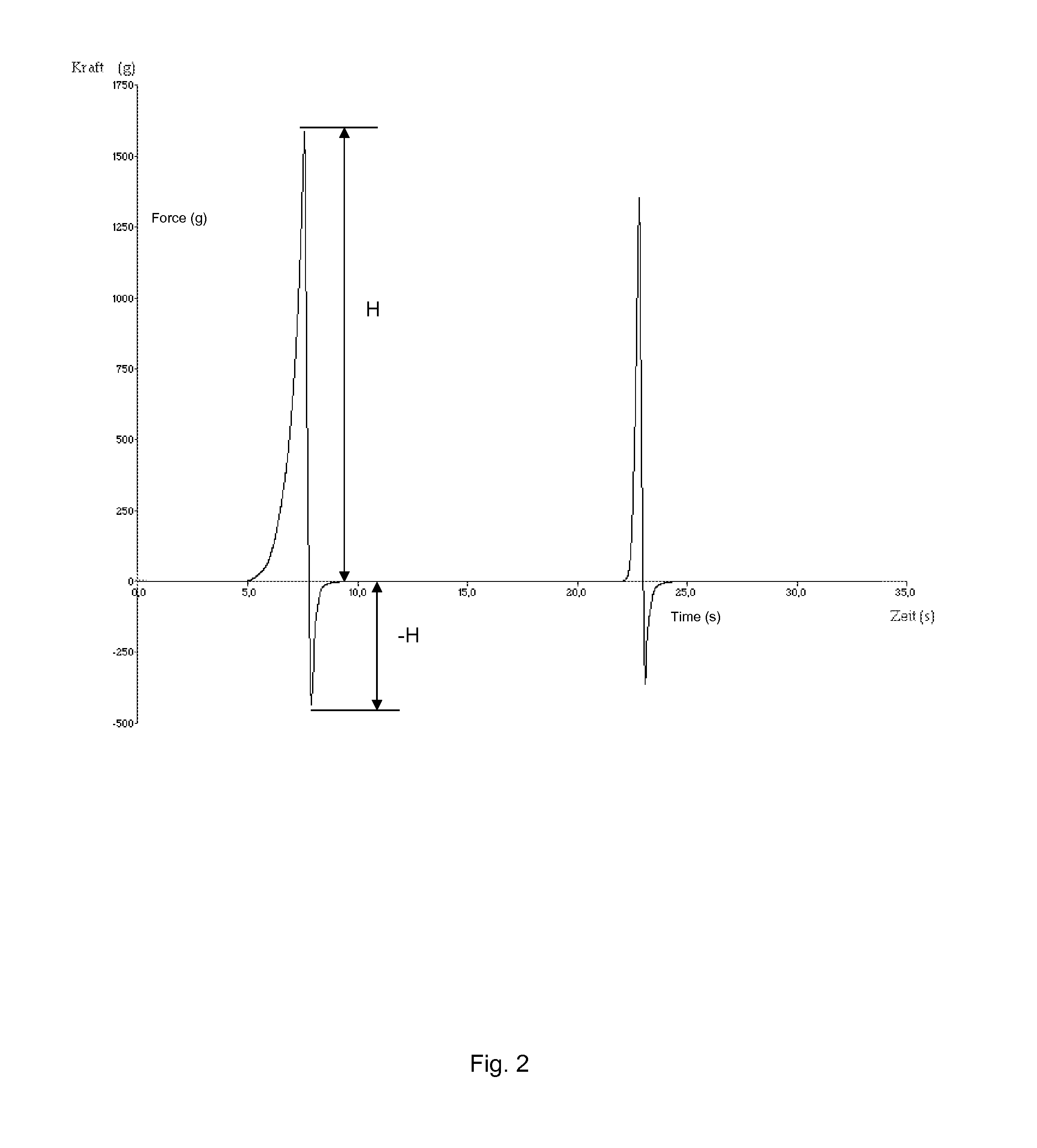
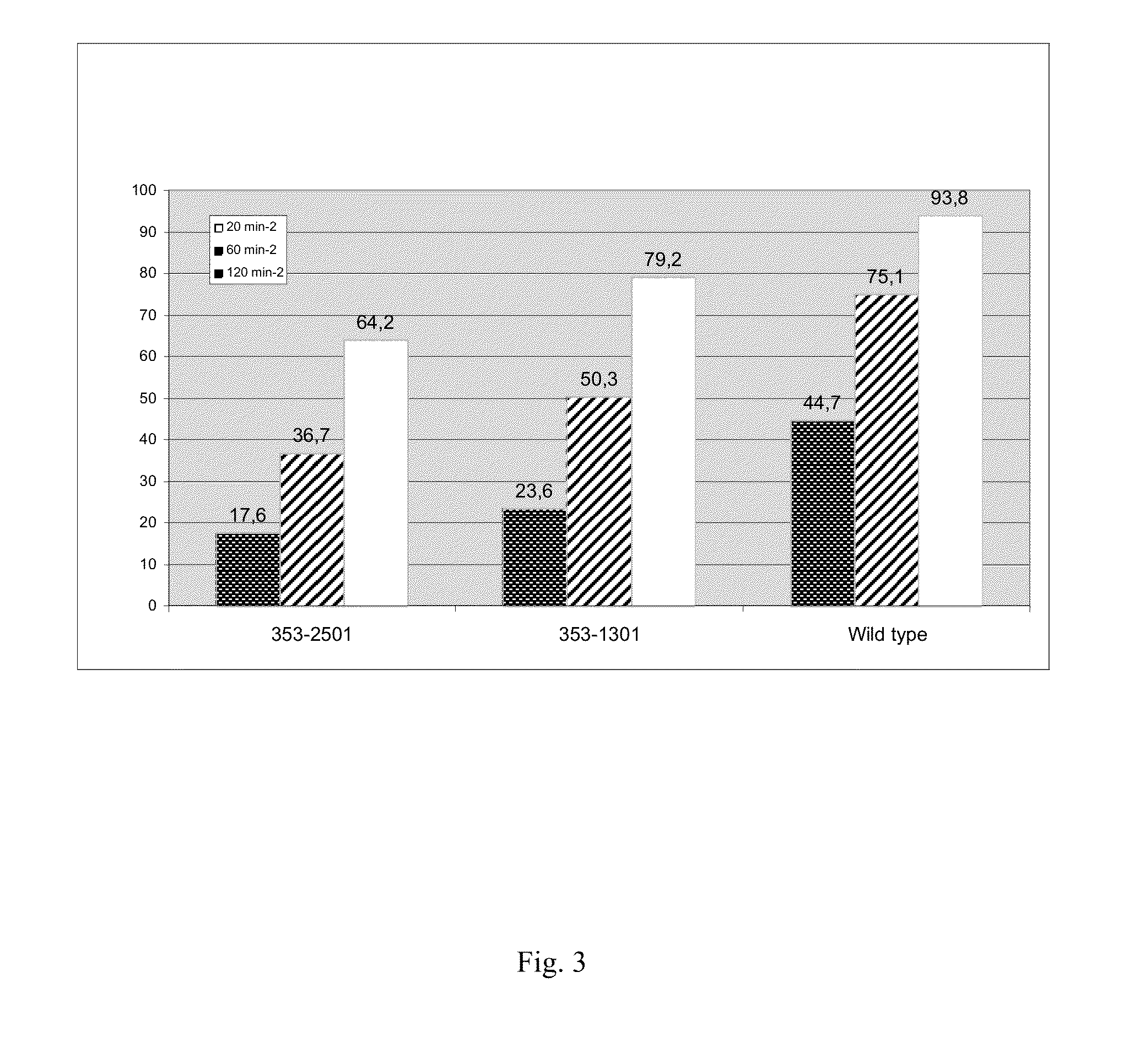
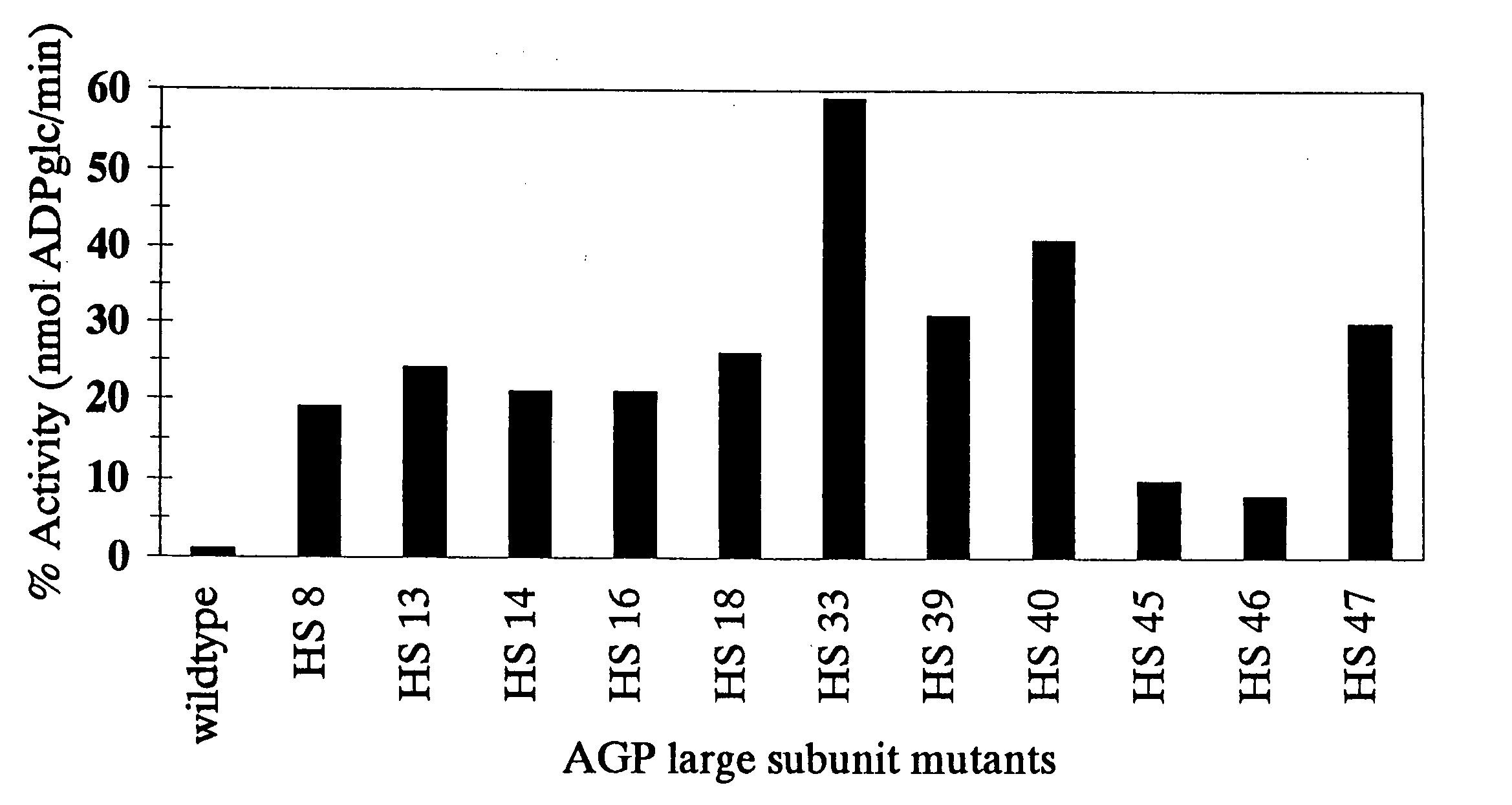
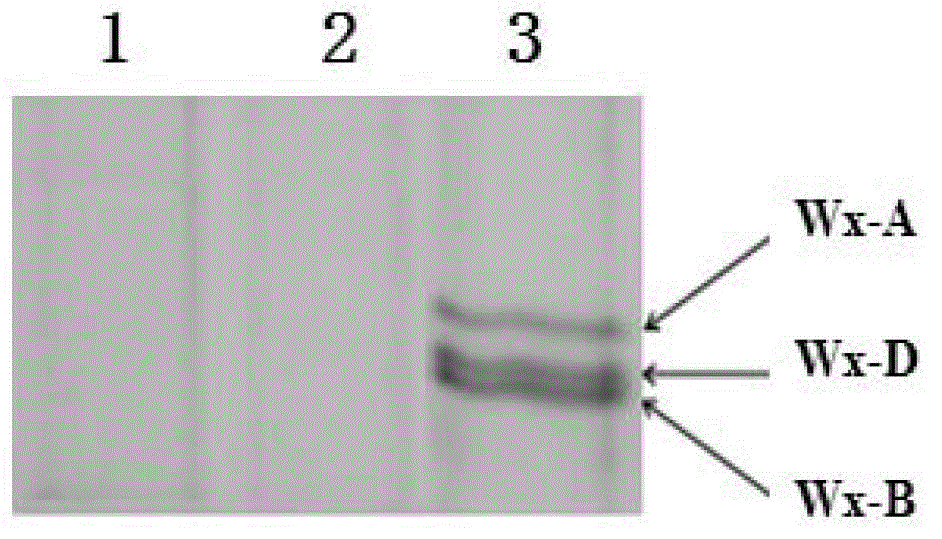
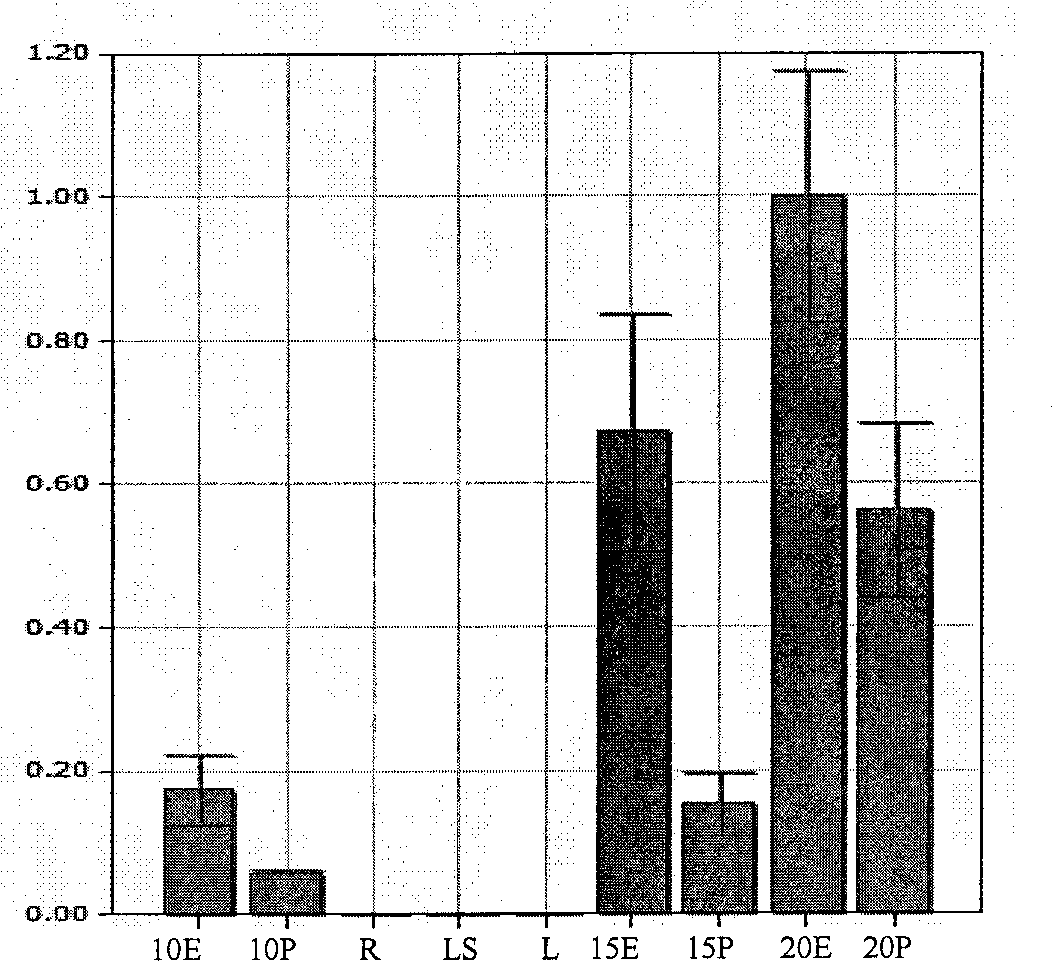
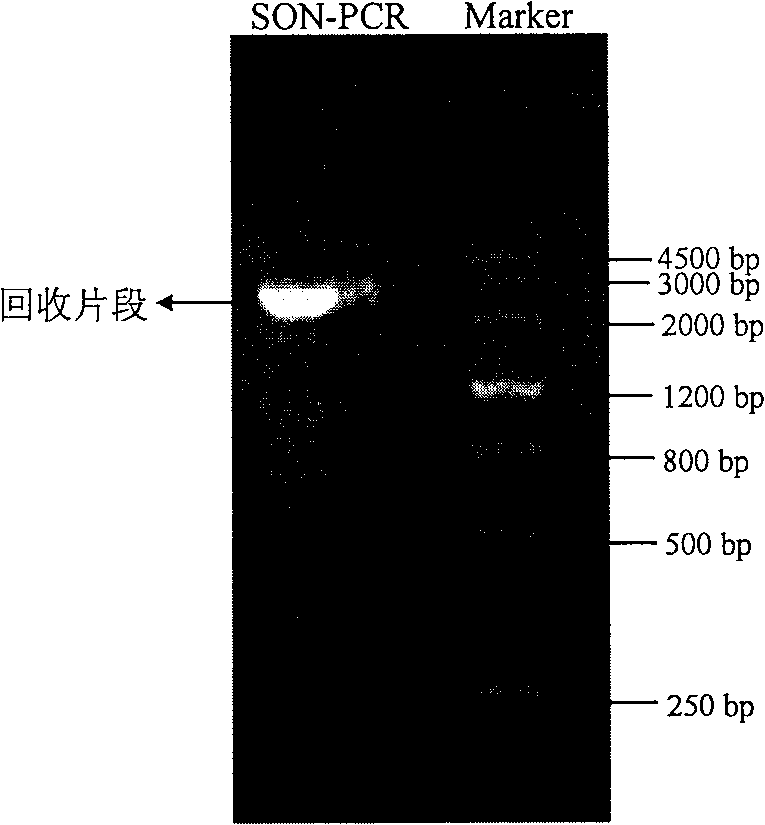
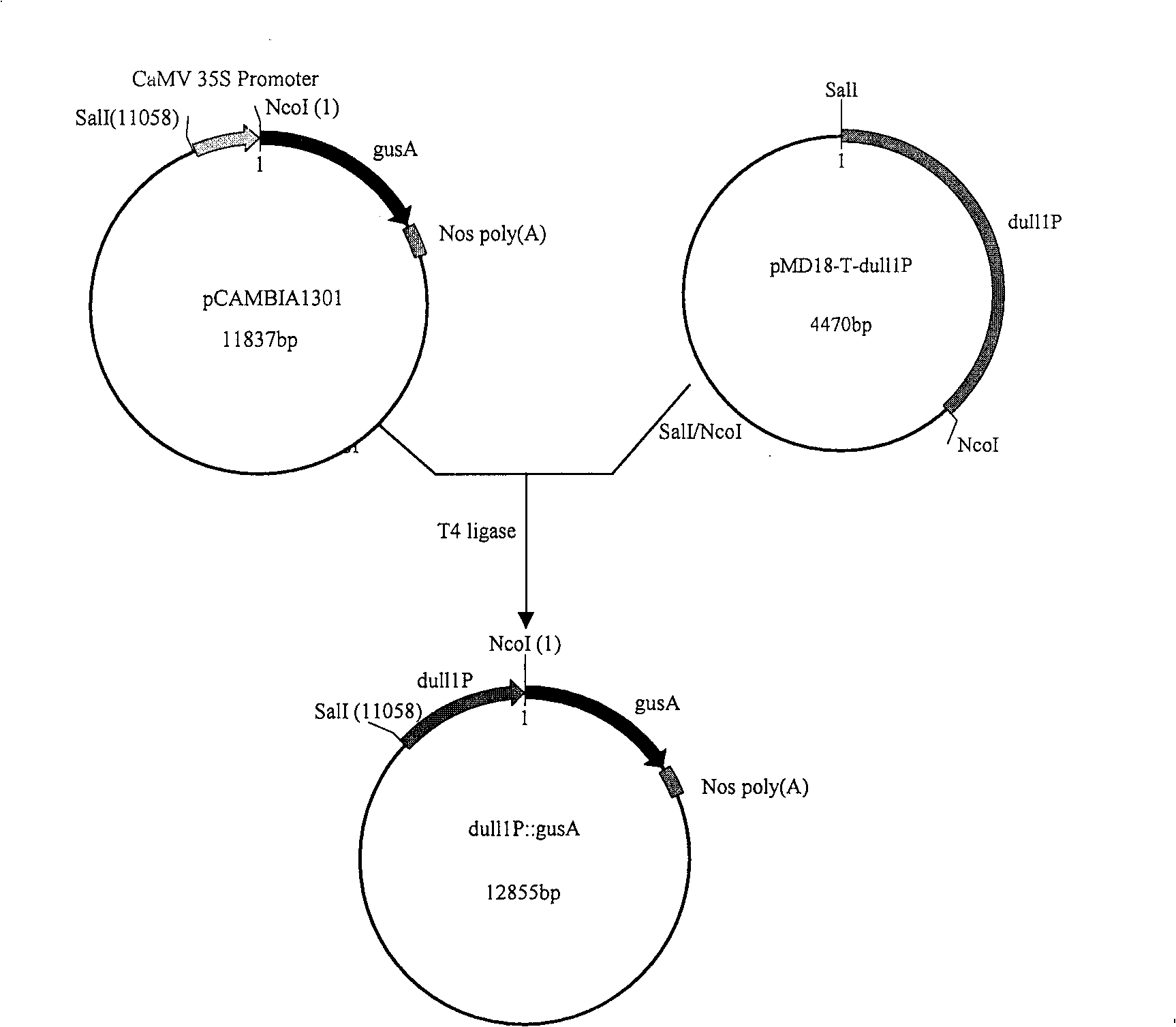
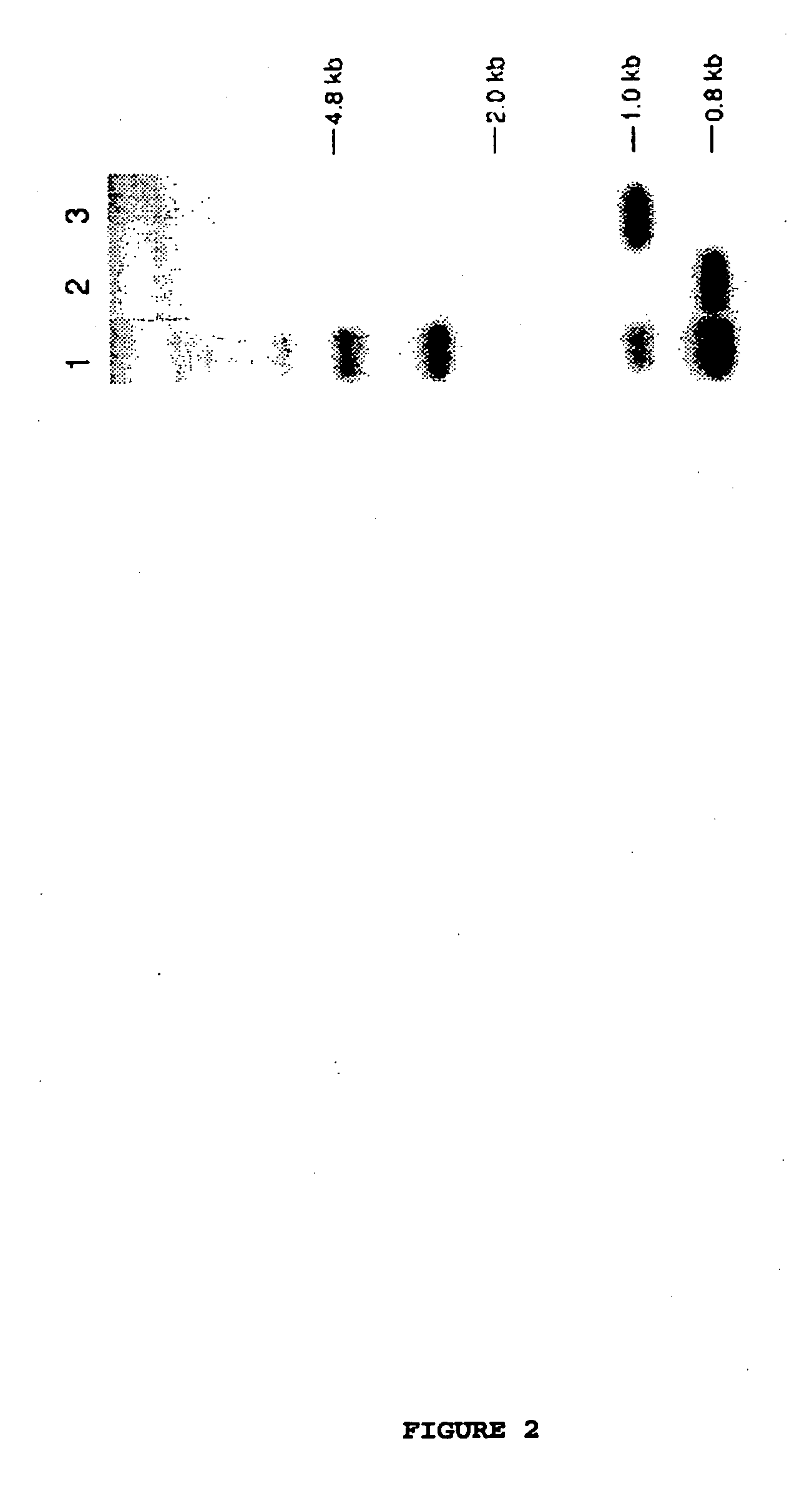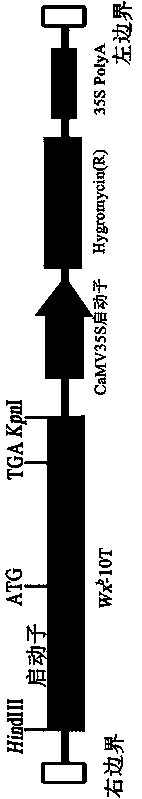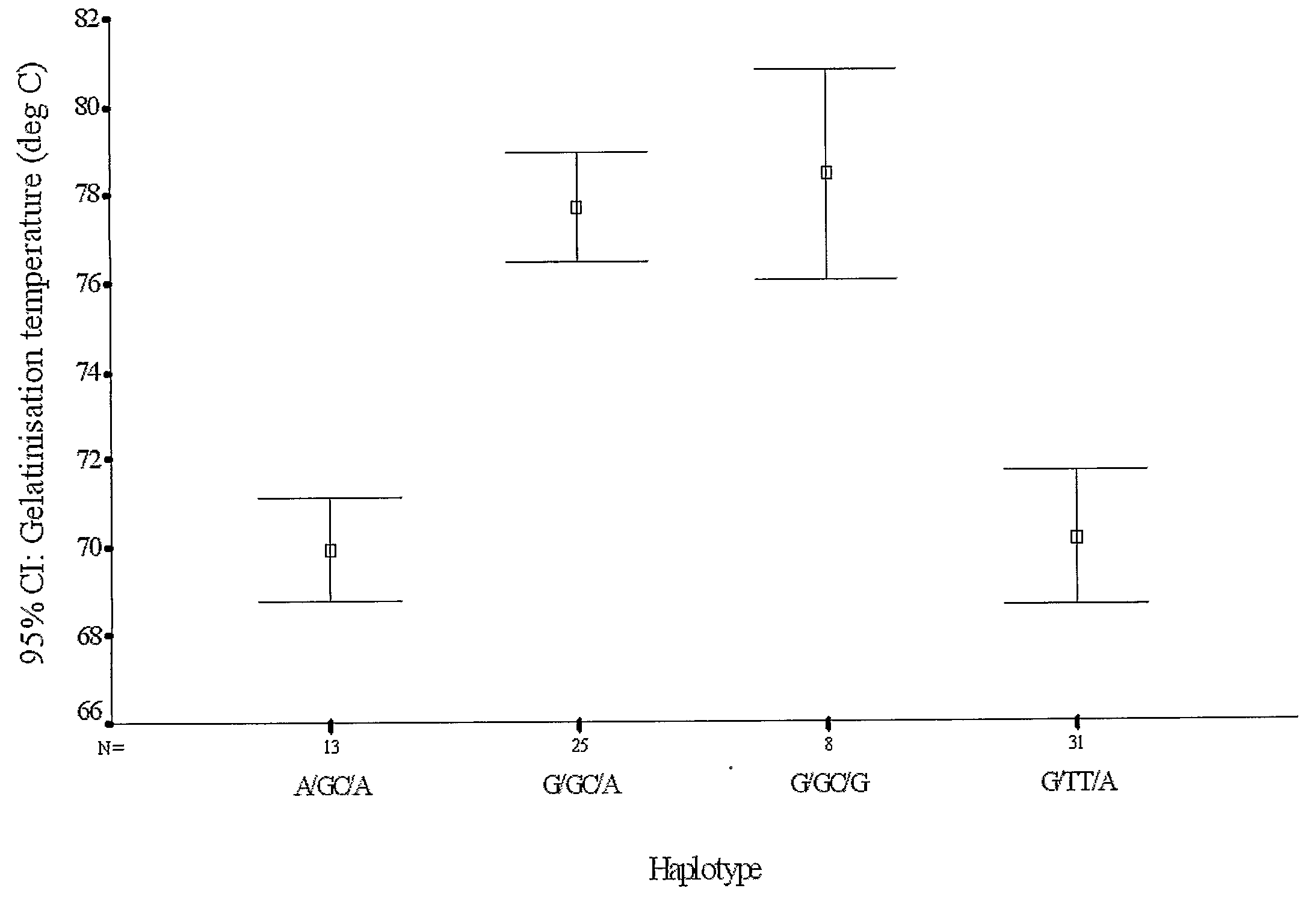Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
53 results about "Starch synthase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In enzymology, a starch synthase (EC 2.4.1.21) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction ADP-glucose + (1,4-alpha-D-glucosyl)ₙ ⇌ ADP + (1,4-alpha-D-glucosyl)ₙ₊₁ Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are ADP-glucose and a chain of D-glucose residues joined by 1,4-alpha-glycosidic bonds, whereas its two products are ADP and an elongated chain of glucose residues. Plants use these enzymes in the biosynthesis of starch.
Plants and processes for obtaining them
InactiveUS6013861AIncrease depositionAlteration of fine structureOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationStarch synthaseStarch synthesis
Plants, particularly cereal plants, which have improved ability to synthesise starch at elevated or lowered temperatures and / or to synthesise starch with an altered fine structure are produced by inserting into the genome of the plant (i) a gene(s) encoding a form of an enzyme of the starch or glycogen biosynthetic pathway, particularly soluble starch synthase and / or branching enzyme and / or glycogen synthase, which display an activity which continues to increase over a temperature range over which the activity would normally be expected to decrease, and / or (ii) a gene(s) encoding sense and anti-sense constructs of enzymes of the starch biosynthetic pathway, particularly soluble starch synthase and / or branching enzyme and / or glycogen synthase, which alters the natural ratios of expression of the said enzymes or inserts enzymes with special structural characteristics which alter the natural branching pattern in starch.
Owner:ZENECA LTD
Regulation of gene expression in plants
InactiveUS20060010517A1TransferasesOther foreign material introduction processesStarch-branching enzyme IIStarch synthase
The present invention relates to a nucleic acid sequence encoding an enzyme of the starch biosynthetic pathway in a cereal plant, wherein the enzyme is selected from the group consisting of starch branching enzyme I, starch branching enzyme II, starch soluble synthase I, and debranching enzyme, with the proviso that the enzyme is not soluble starch synthase I of rice, or starch branching enzyme I of rice or maize.
Owner:BIOGEMMA SAS +1
Method for increasing amylose content of plants
InactiveCN104017829AOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationStarch-branching enzyme IIStarch synthase
The invention relates to a method for increasing the amylose content of plants. The invention provides enzymes, namely granule-bound starch synthase I (GBSS i), starch branching enzyme I (SBE I) and / or starch branching enzyme II (SBE II) which are applicable to genetic engineering operation in a starch synthesis path and are capable of remarkably changing starch composition of the plants. The invention also provides a novel method capable of favorably adjusting starch in plants, which comprises the following step of reducing the expression of the enzymes to obtain a series of transgenic plants which are different in amylose and amylopectin contents and proportions. The invention also provides a construct or carrier for adjusting the starch composition of plants.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Application of corn ZmWx gene in increase of corn yield and improvement of grain characteristics
InactiveCN105349559AIncreased amylose content in endospermIncrease productionFermentationGlycosyltransferasesStarch cornComplementary deoxyribonucleic acid
The invention discloses an application of a corn ZmWx gene in increase of the corn yield and improvement of grain characteristics. A ZmWx gene sequence is cloned in corn endosperm cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid), the ZmWx gene encodes GBSSI (granule-bound starch synthase I), the GBSSI and an endosperm specific promoter form a fusion gene, the fusion gene is recombined in a plant expression carrier with a transgenic technology to transform corn, and corn transgenetic plants with yield increased and grain characteristics improved are obtained; alternatively, GBSSI overexpressed corn and mutant AGPase overexpressed high-starch corn are hybridized, a transgenetic polymer is obtained through screening, and the corn transgenetic plants whose grain yield, starch content and hundred-grain weight are remarkably higher than those of recipient materials are produced. The application provides a basis and a means for development and preparation of high-starch and high-amylose starch corn and also develops a new approach for increase of the corn yield and improvement of the starch quality.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
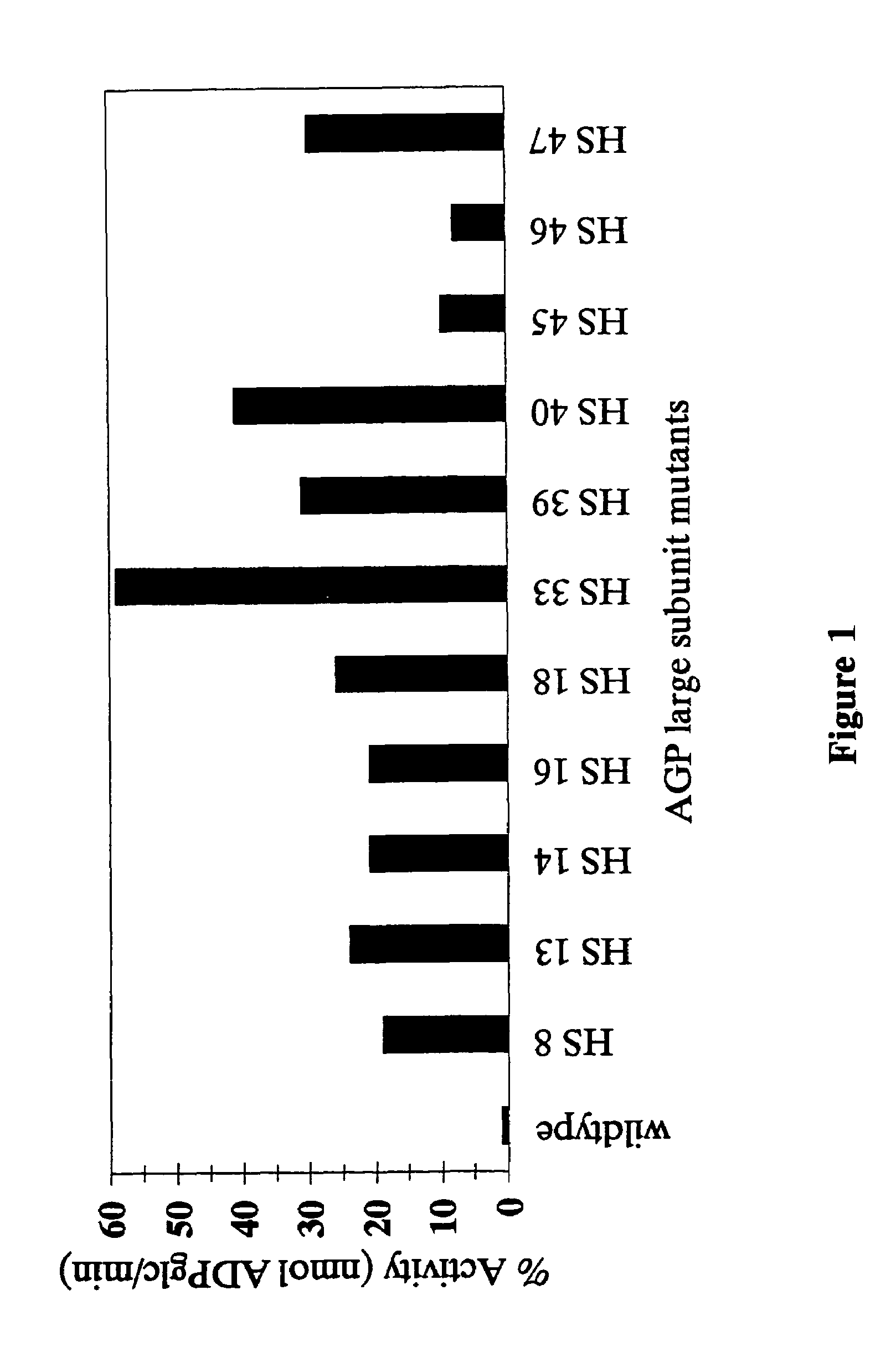
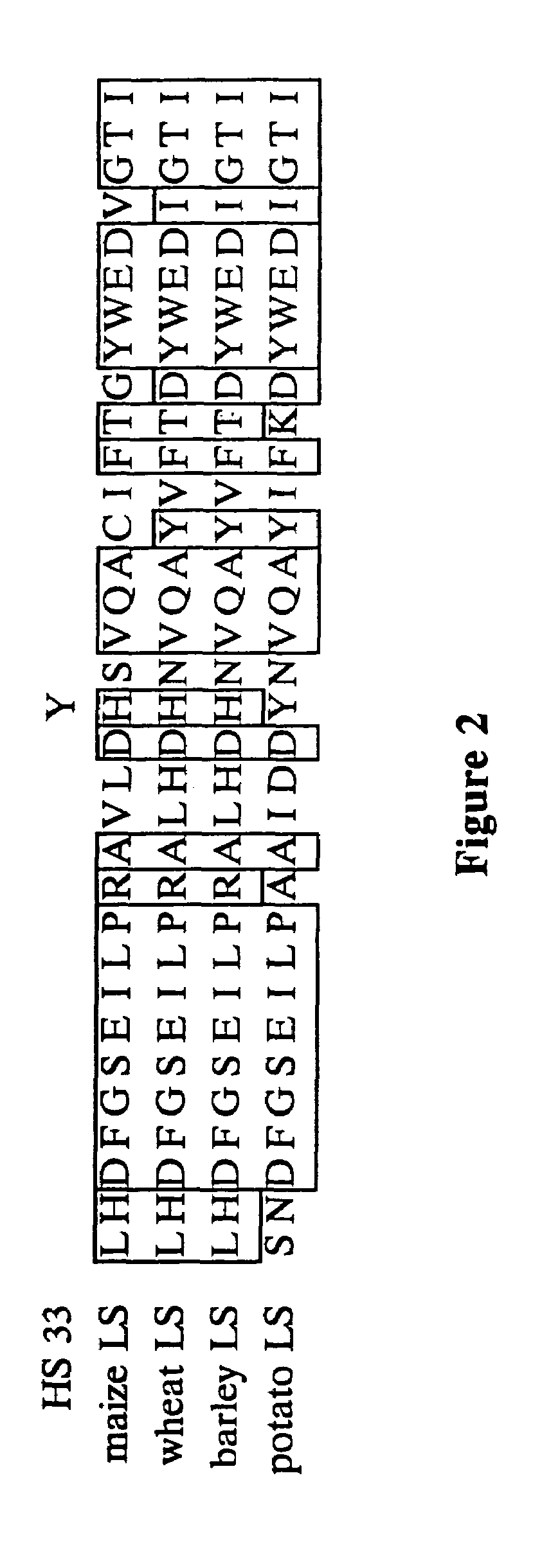
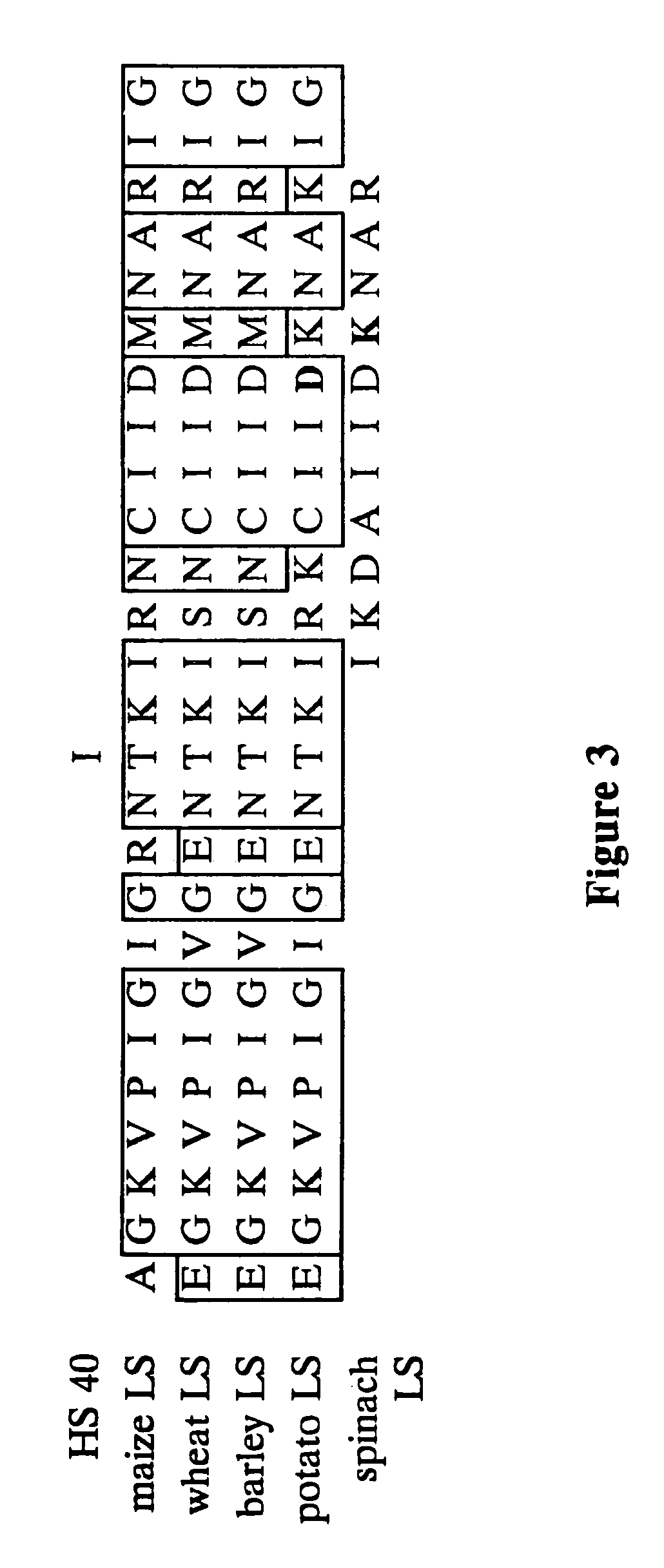
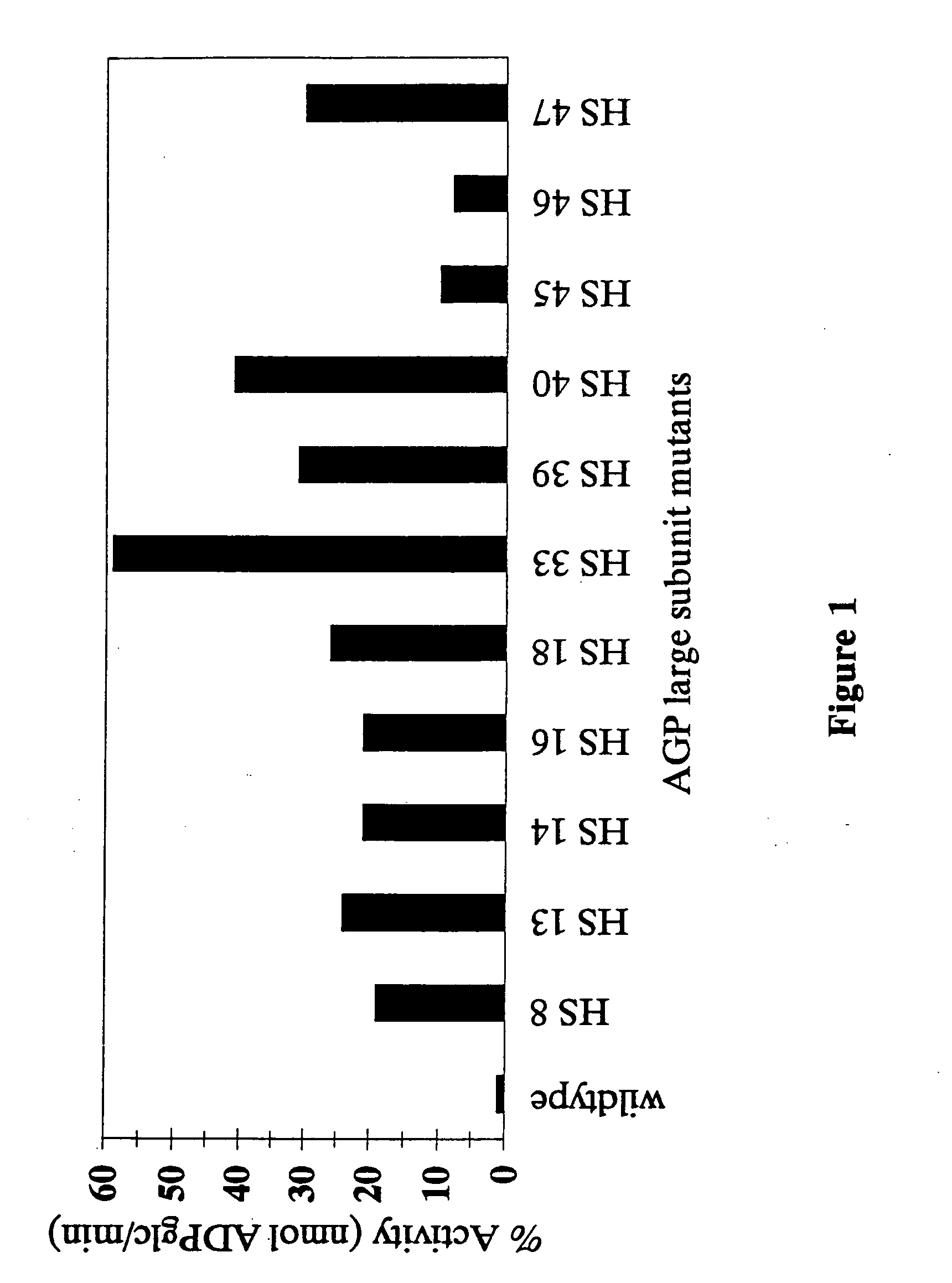
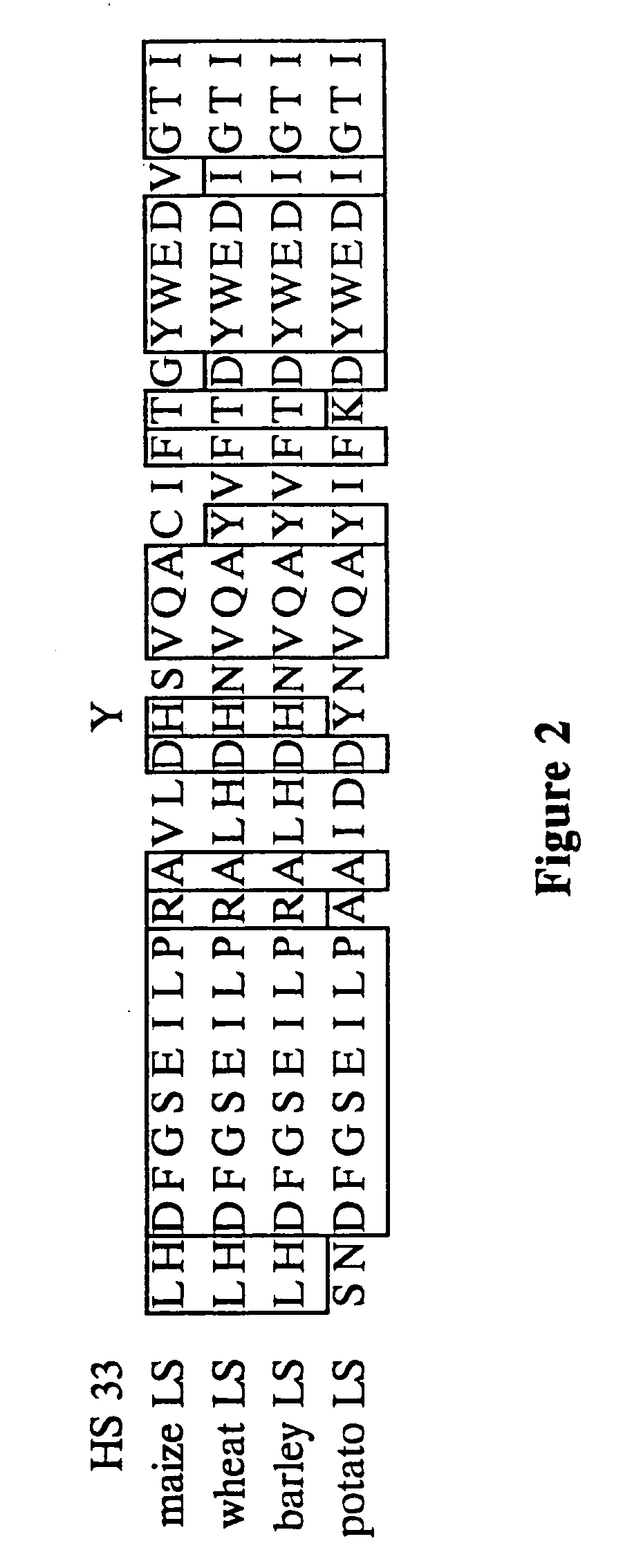
Nucleic acids encoding heat stable mutants of plant ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase
InactiveUS7312378B2Increase crop yieldImprove toleranceSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideHeat stability
The subject invention pertains to novel mutant polynucleotide molecules that encode enzymes that have increased heat stability. These polynucleotides, when expressed in plants, result in increased yield in plants grown under conditions of heat stress. The polynucleotide molecules of the subject invention encode maize endosperm ADP glucose pyrophosphorylase (AGP) and soluble starch synthase (SSS) enzyme activities. Plants and plant tissue bred to contain, or transformed with, the mutant polynucleotides, and expressing the polypeptides encoded by the polynucleotides, are also contemplated by the present invention. The subject invention also concerns methods for isolating polynucleotides and polypeptides contemplated within the scope of the invention. Methods for increasing yield in plants grown under conditions of heat stress are also provided.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Method for adjusting starch composition of root crops
ActiveCN101665786AStable genetic traitsVector-based foreign material introductionPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyNucleotide
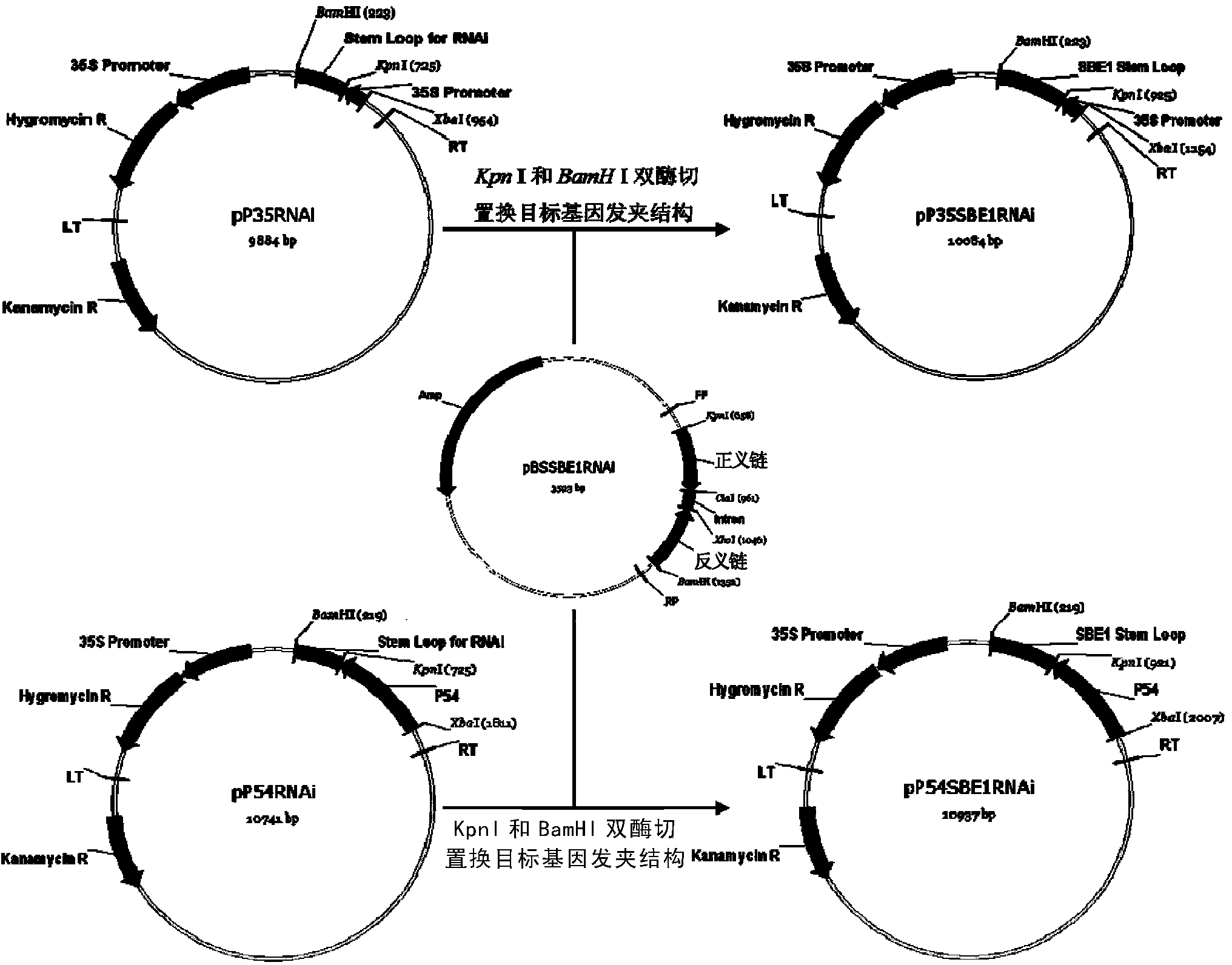
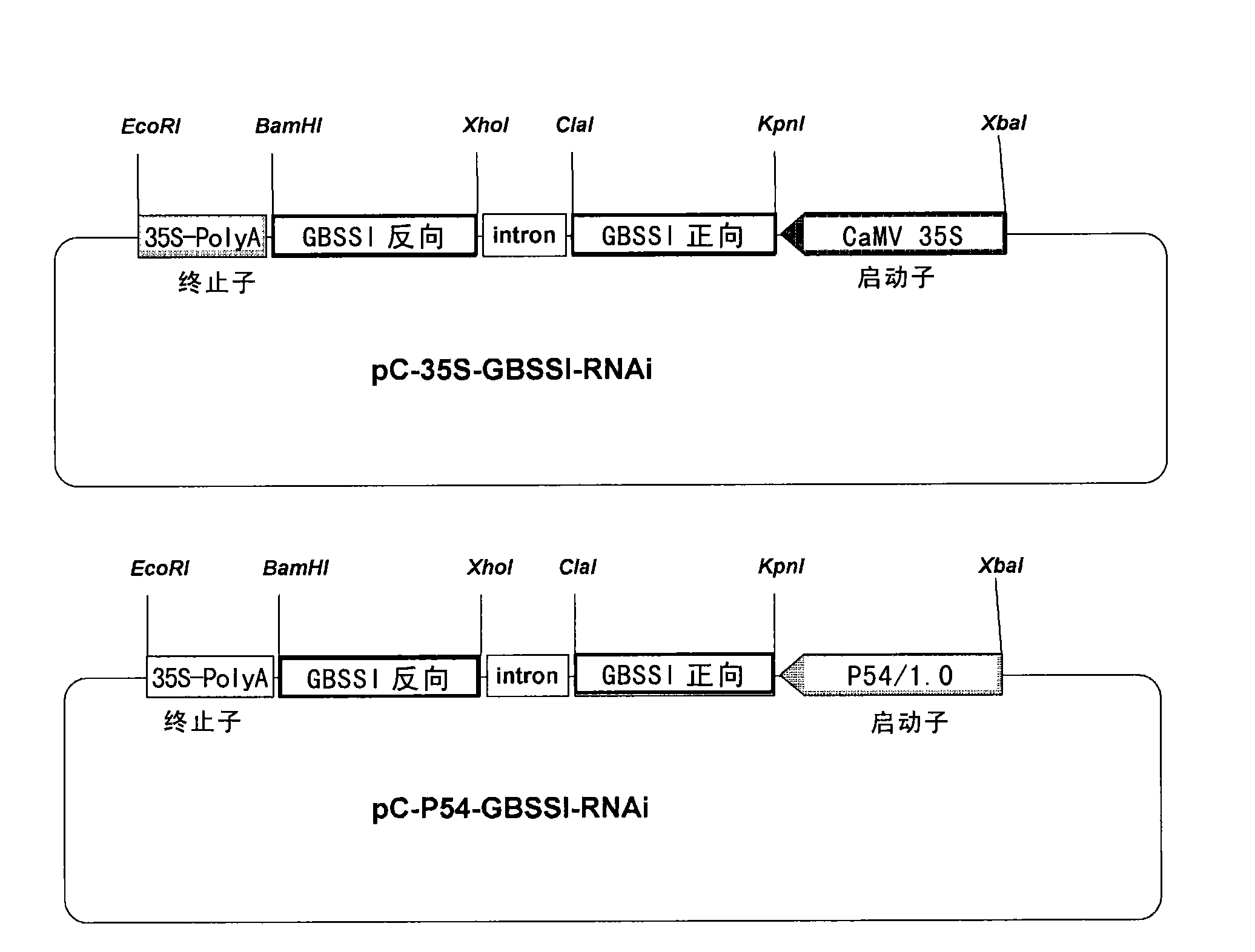
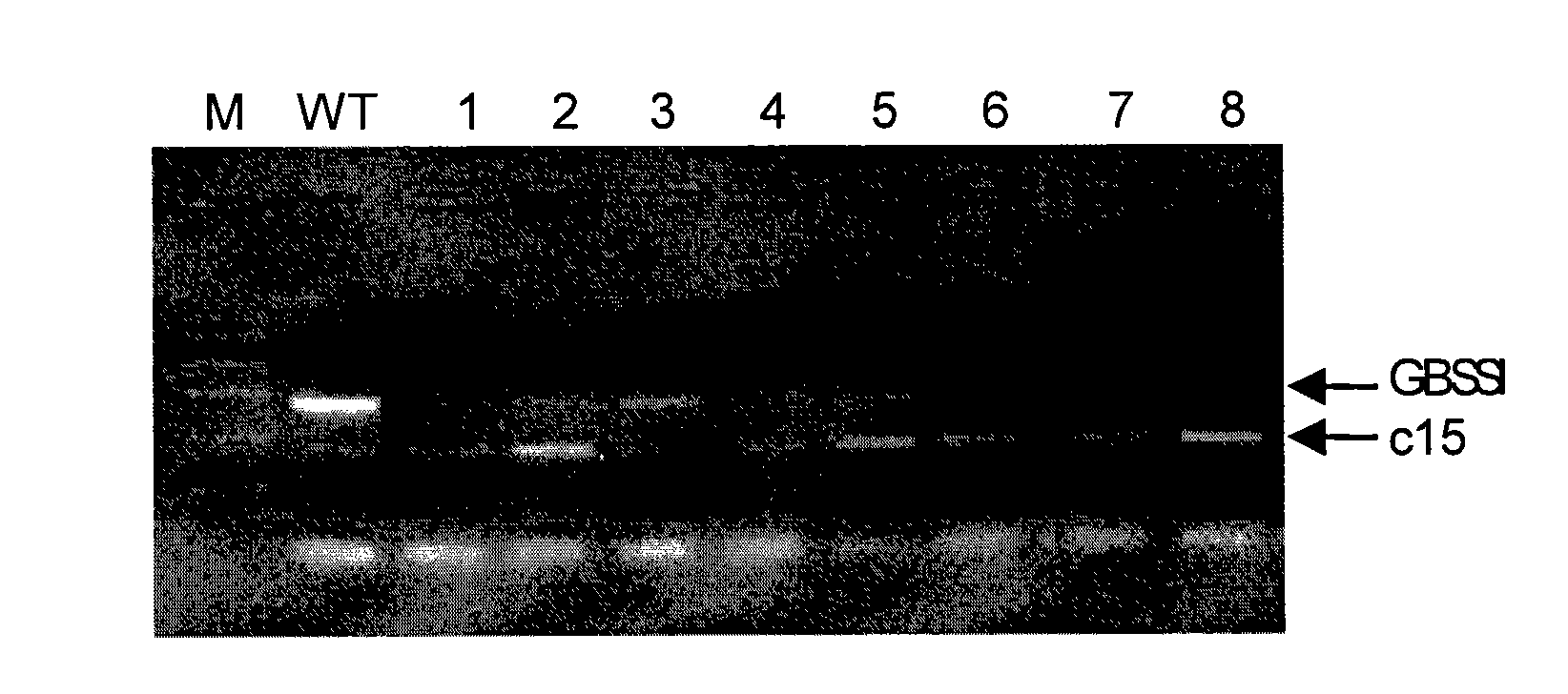
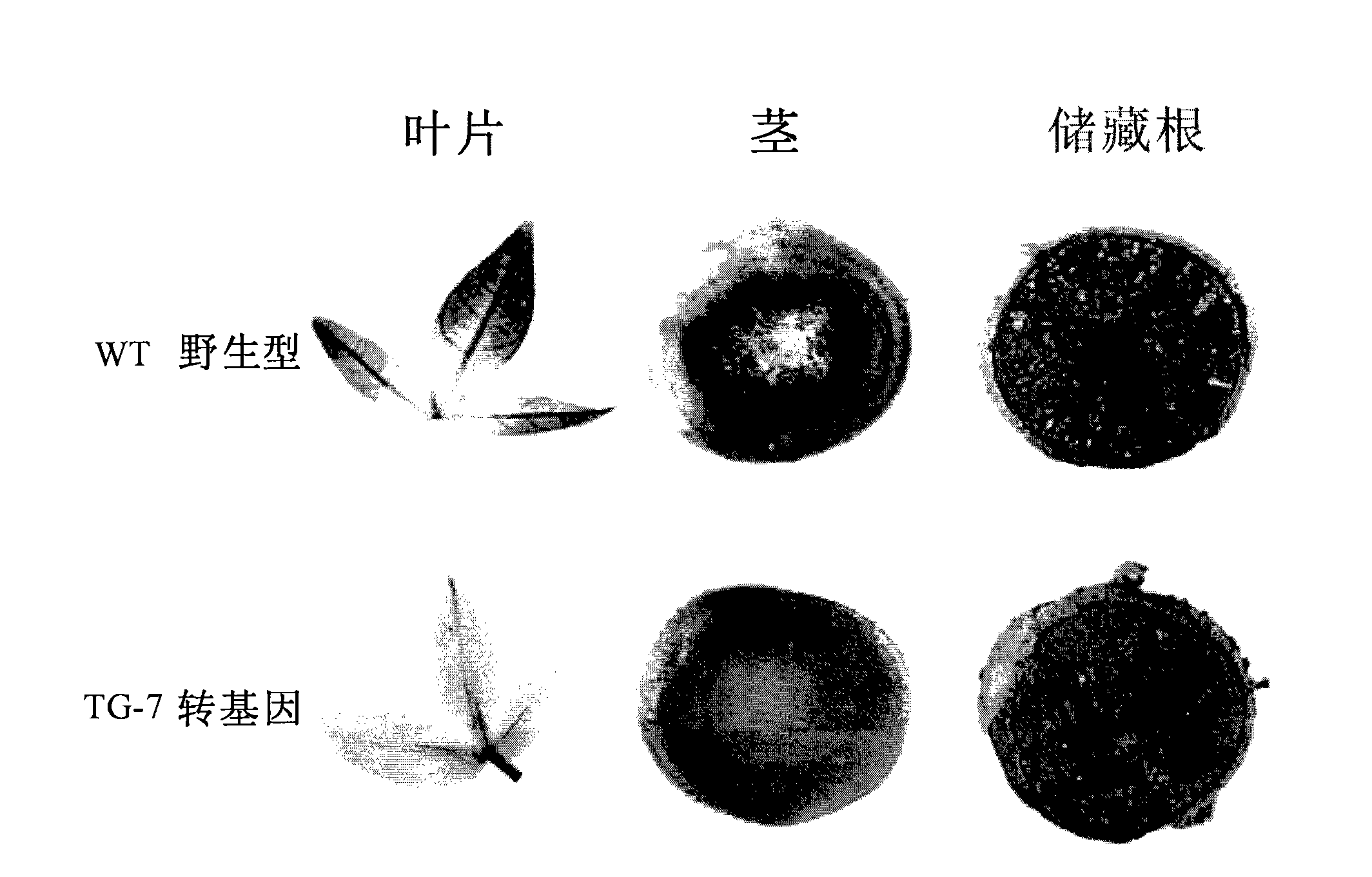
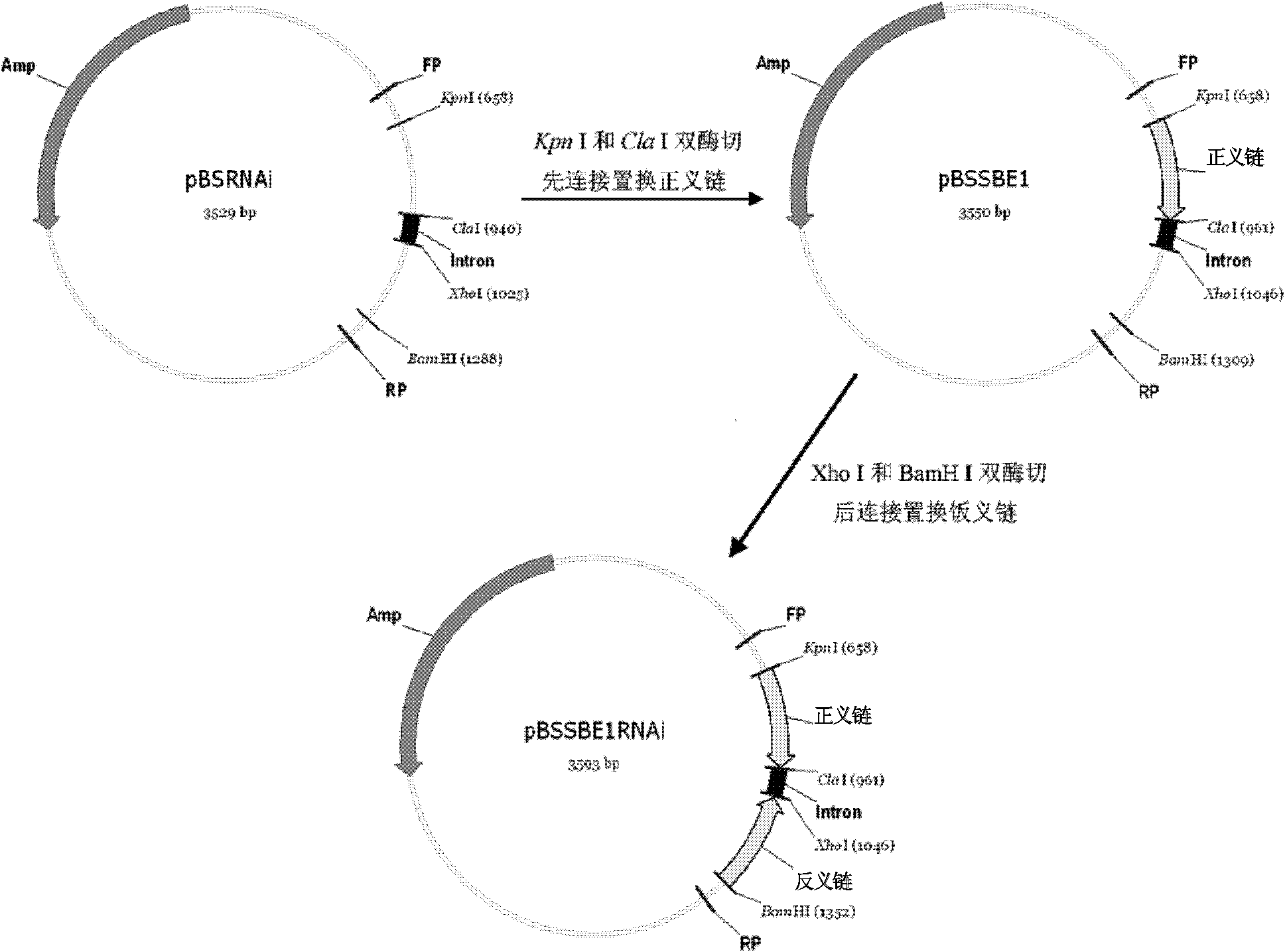
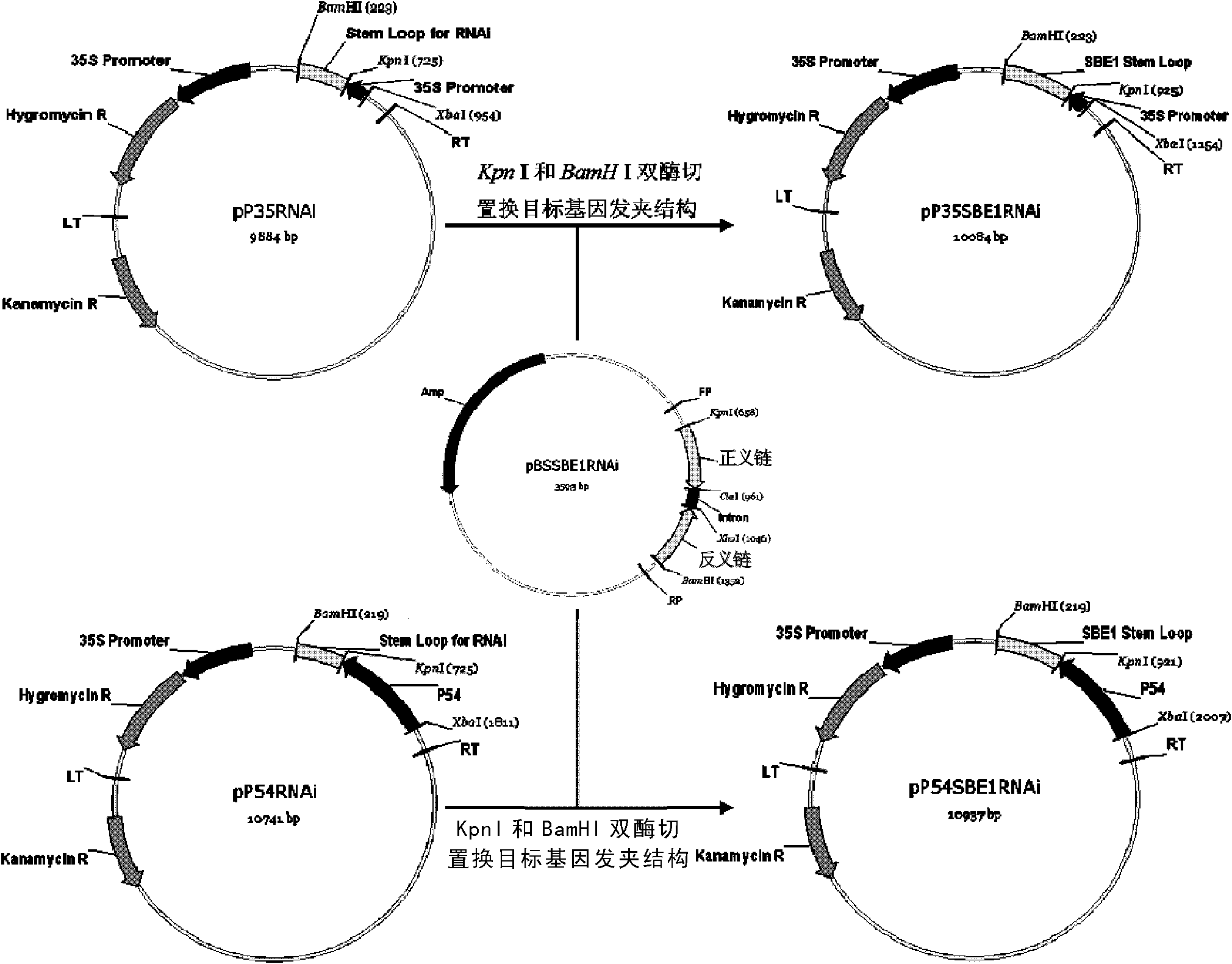
The invention relates to a method and a substance for adjusting starch composition of root crops. The invention discloses polynucleotide constructs which is expressed by specific interference granulebound starch synthase I (GBSSI) and can be processed after being introduced into plant., and a brand-new way for changing the starch quality of the plant by interrupting the expression of GBSSI genesbased on micro-molecular RNA interface technology to achieve the aim of adjusting the starch composition in the plant.
Owner:江苏三黍生物科技有限公司
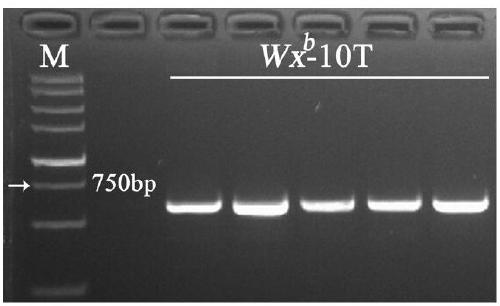
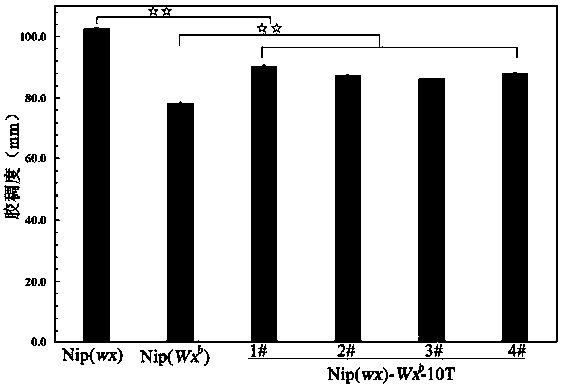
Construction of gene expression vector Wxb-10T, preparation of transgenic rice and primer
ActiveCN108949753AFermentationGlycosyltransferasesGenetically modified riceGranule-Bound Starch Synthase
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology and relates to construction of a gene expression vector Wxb-10T, preparation of transgenic rice and a primer. The primer is shown in a sequencetable of SEQ ID NO. 3-8. The allele Wxb in the conventional japonica rice serves as a template, and the rice expression vector Wxb-10T substituted by single nucleotides at the tenth exon of the alleleis constructed. The vector carries a full-length Wxb allele sequence with single base mutation, and by utilizing an agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated method, the transgenic rice with transgenosis ofWxb-10T in glutinous rice is obtained. The transgenic rice of a homozygous line is bred, the amylose content of the transgenic rice is generally about 12%, and the gel consistency and starch viscosity index of the transgenic rice are close to those of currently popular excellent edible soft rice. The method is realized by introducing a rice expression vector modified by specific nucleotide sitesof granule-bound starch synthase GBSSI coding genes Wx into the glutinous rice.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
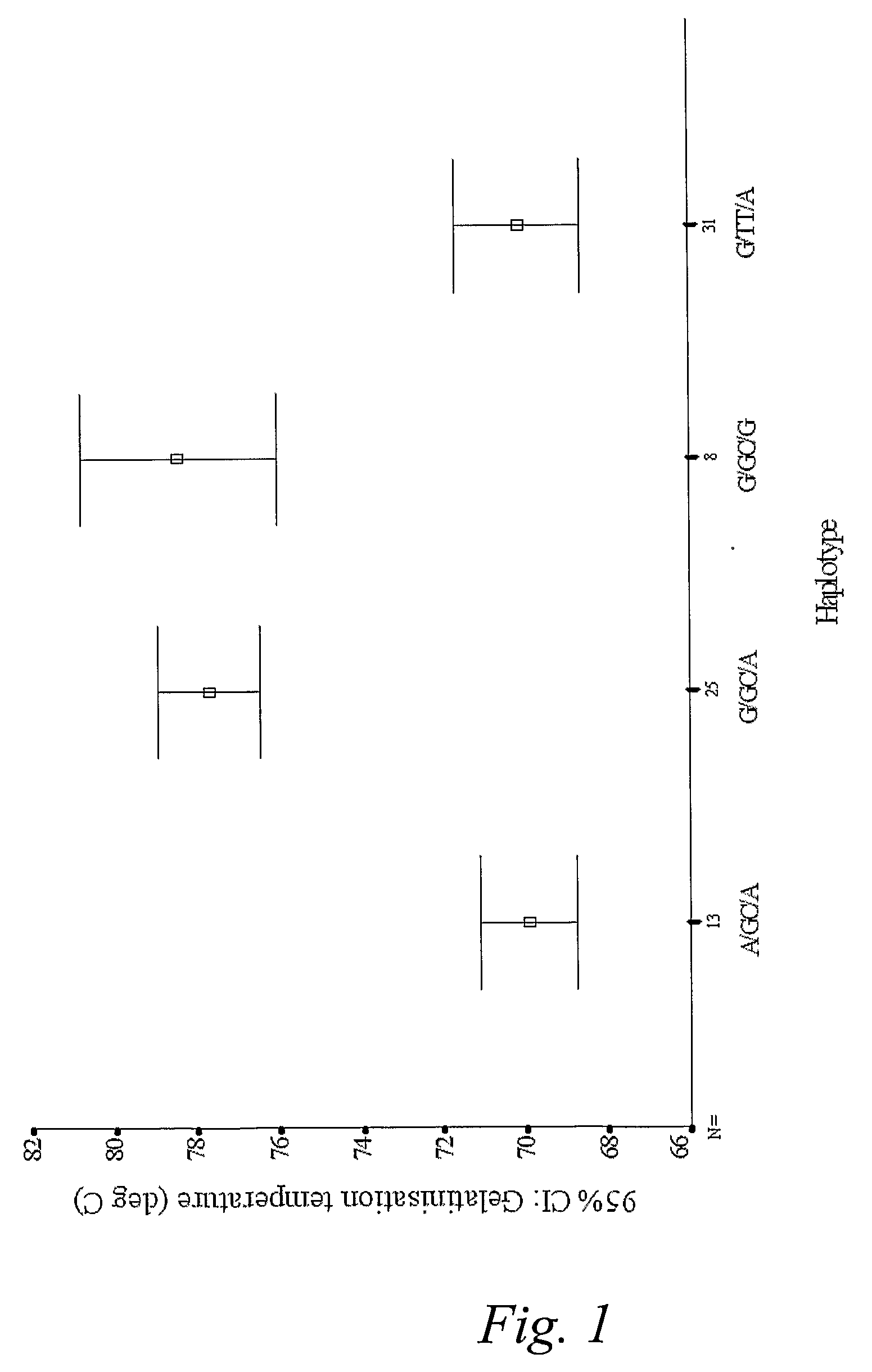
Gelatinization Temperature Manipulation
The subject invention relates to plants and the starch produced by plants. In particular, the invention relates to processes for the modification of a plant so that the starch produced by the plant comprises amylopectin of an altered structure and / or the starch has an altered gelatinization temperature. The processes principally comprise engineering gene involved in amylopectin synthesis. In a preferred embodiment the starch synthase IIa gene is modified. Also disclosed are processes for altering genes to provide plant which produce starch having a desired gelatinization temperature, and methods of identifying the changes that can be made in genes to achieve a desired gelatinization temperature in the starch produced by a plant comprising such genes. Further disclosed are modified plants and the starch products of the plants.
Owner:SOUTHERN CROSS UNIVERSITY
Method for cultivating starch-content-increased transgenic plant through multi-gene transformation
InactiveCN103173485AImprove conversion rateHigh total starch contentTransferasesFermentationGranule-Bound Starch SynthaseSucrose synthetase
The invention discloses a method for cultivating a starch-content-increased transgenic plant through multi-gene transformation. According to the transgenic plant cultivation method provided by the invention, a selection marker gene, an adenosine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase small subunit gene, an adenosine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase large subunit gene, a sucrose synthase gene, and a granule-bound starch synthase gene are introduced into a target plant, such that a transgenic plant is obtained. The total starch content of the transgenic plant is higher than that of the target plant. As a result of experiment of the invention, a plurality of genes can be simultaneously transferred in one-time through one time of gene gun bombardment, such that transgenic material cultivation period and work load can be greatly shortened. Specifically, the 4 genes related to starch metabolism are simultaneously transferred in, such that the total starch content of a transgenic regenerated plant is higher than that of wild-type plant.
Owner:NORTHEAST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Cereal seed starch synthase ii alleles and their uses
InactiveUS20170006815A1Increase amylose contentHigh in proteinMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringBiotechnologyStarch synthase
Owner:MONTANA STATE UNIVERSITY
Transgenic rice with excellent eating quality and cultivation method
ActiveCN103146746AReduced apparent amylose contentImprove taste qualityVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsGenetically modified riceOrganism
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
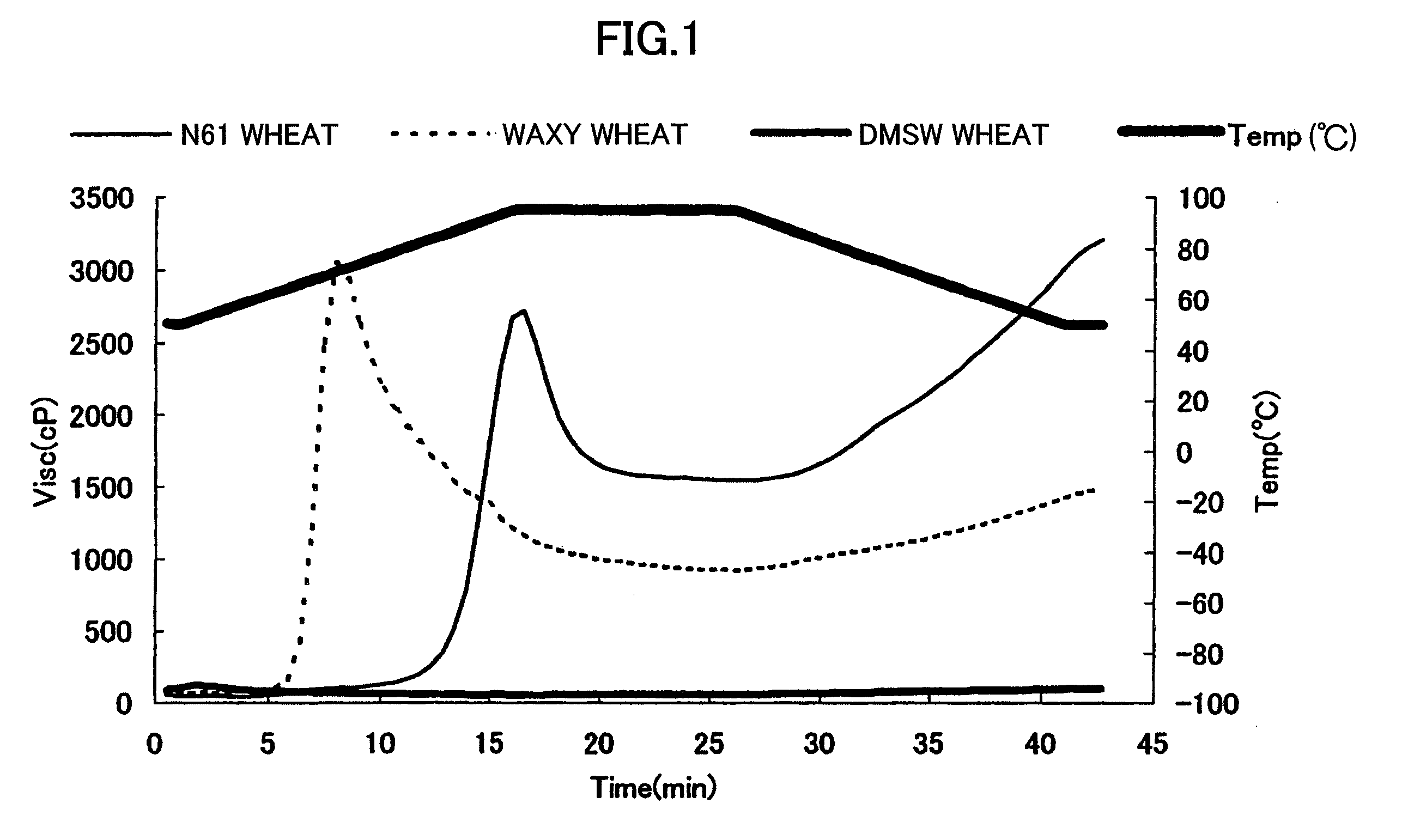
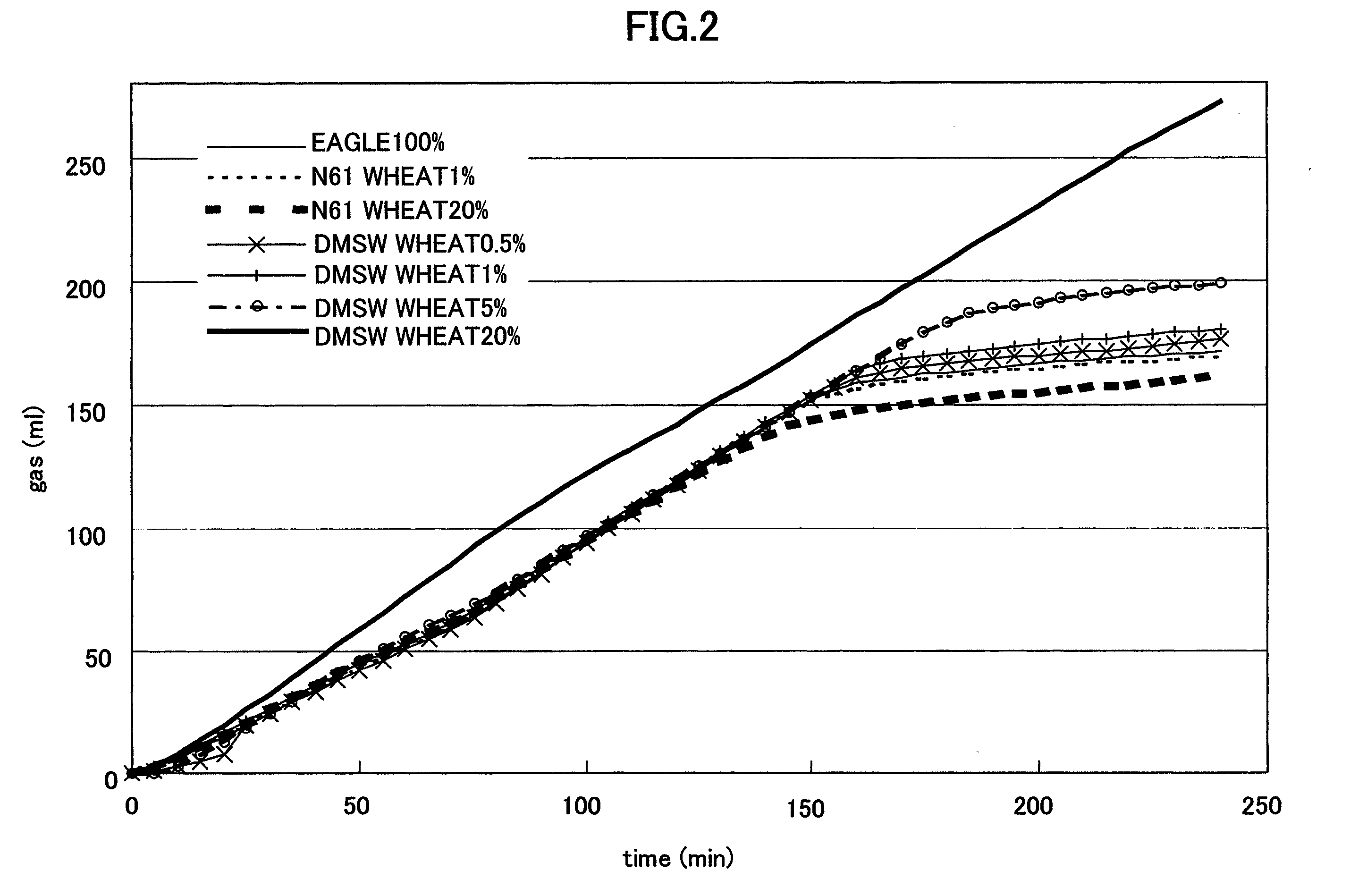
Wheat having new starch and method for producing it
ActiveUS8053628B2Dough treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementGranule-Bound Starch SynthaseBiotechnology
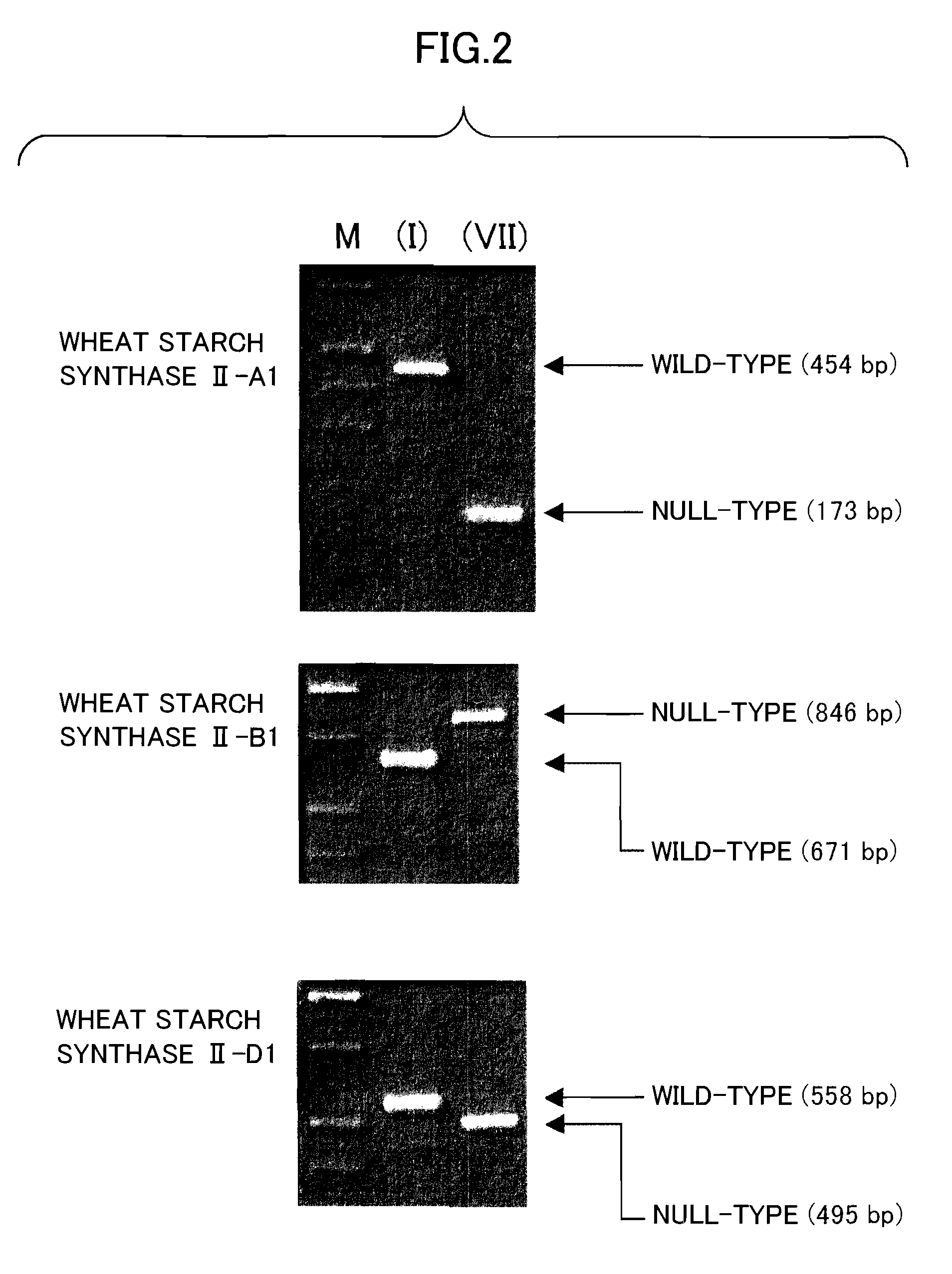
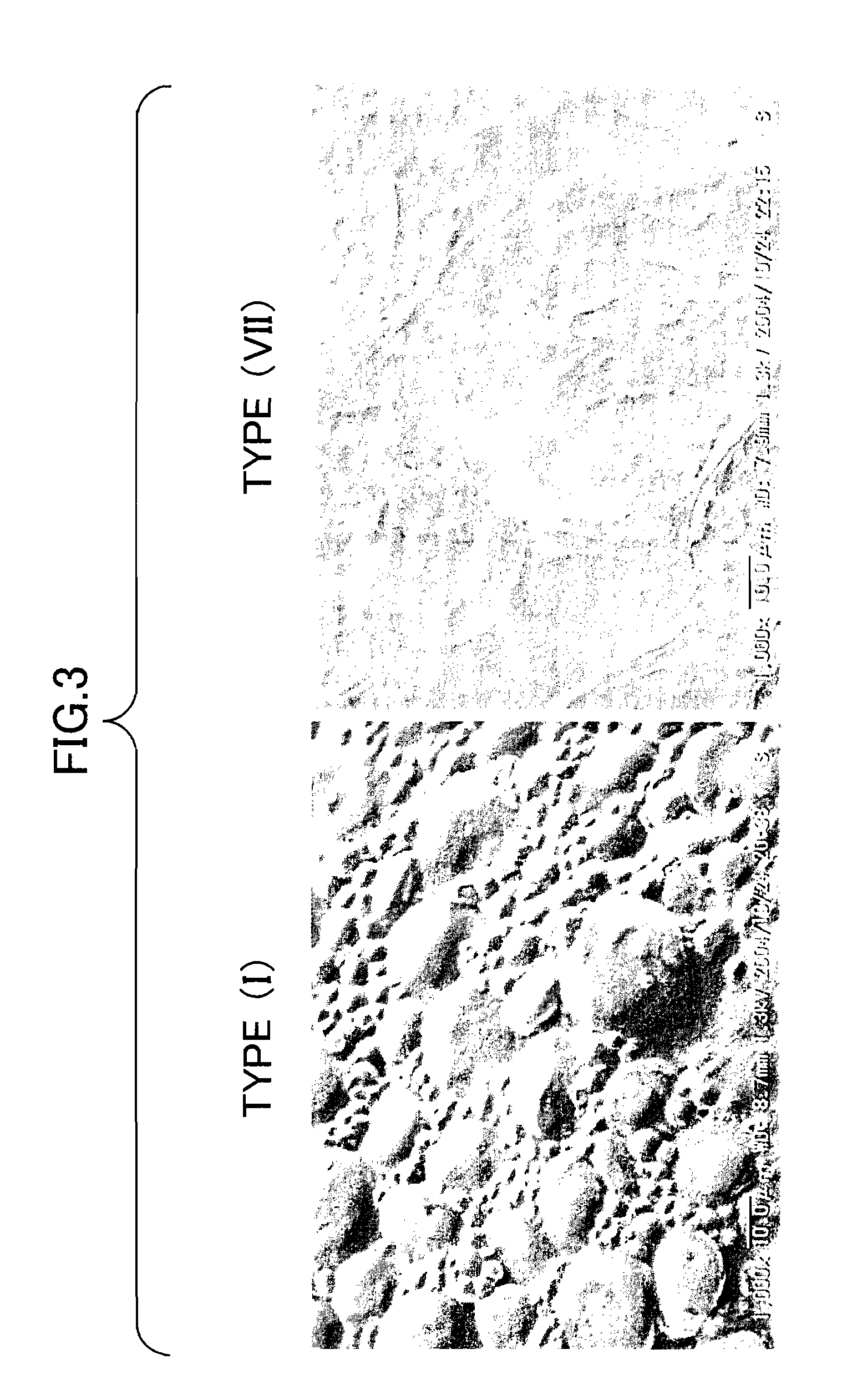
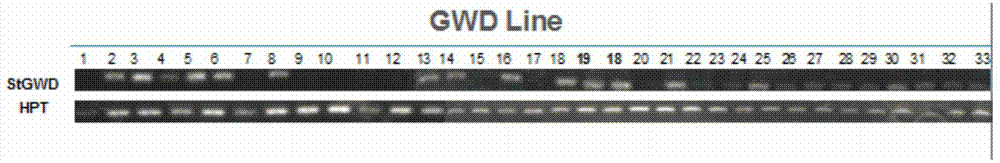
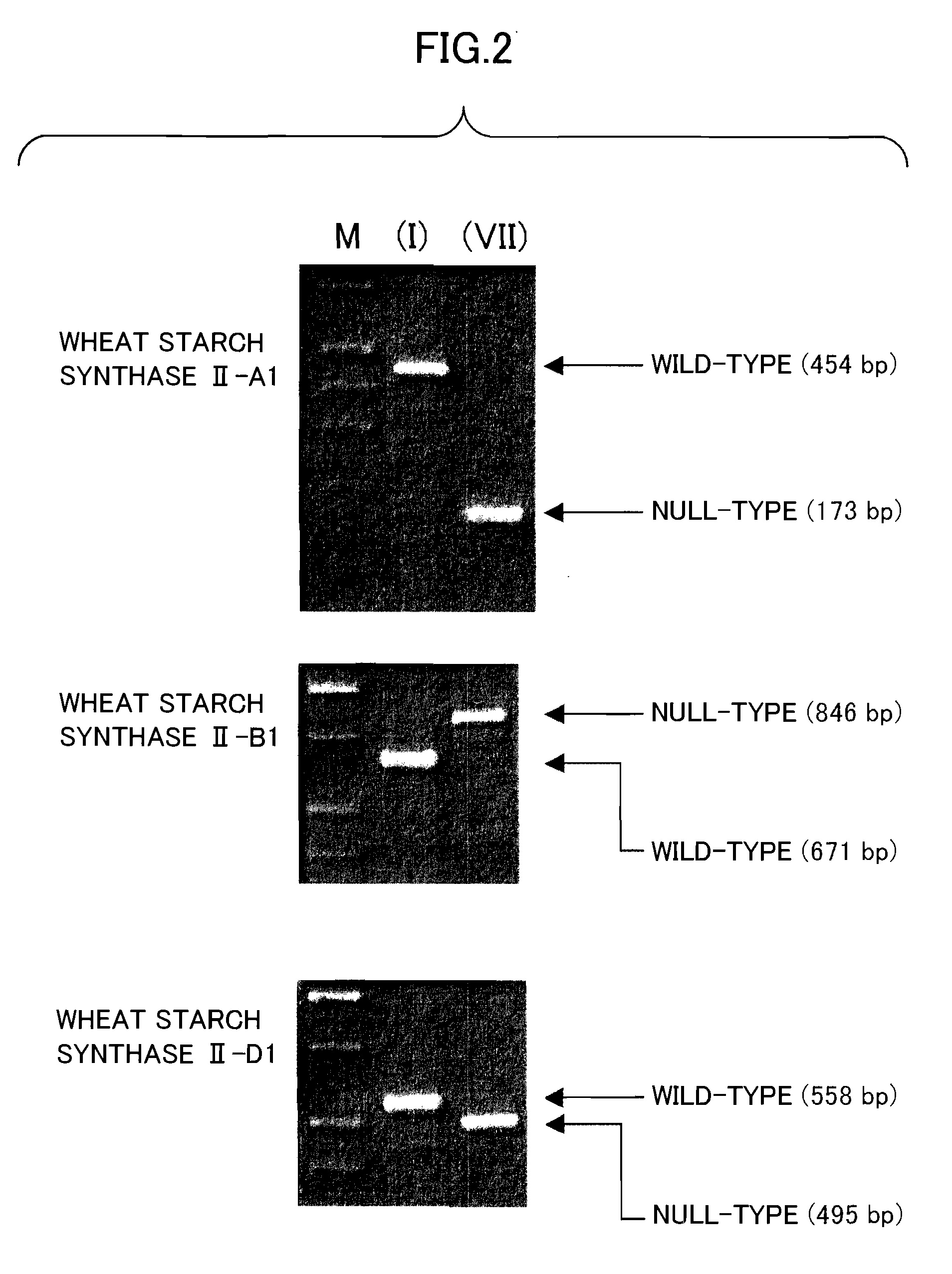
The object of the present invention is to provide a wheat which accumulates a starch with a novel property by controlling the expression of the enzymes described in claims.The present invention provides a wheat, which does not express any of the following proteins (1)-(6): (1) Wheat Starch Synthase II-A1 Protein encoded by Wheat Starch Synthase II-A1 gene of SEQ ID NO:1, (2) Wheat Starch Synthase II-B1 Protein encoded by Wheat Starch Synthase II-B1 gene of SEQ ID NO:3, (3) Wheat Starch Synthase II-D1 Protein encoded by Wheat Starch Synthase II-D1 gene of SEQ ID NO:5, (4) Granule Bound Starch Synthase A1 Protein encoded by Granule Bound Starch Synthase A1 gene of SEQ ID NO:7, (5) Granule Bound Starch Synthase B1 Protein encoded by Granule Bound Starch Synthase B1 gene of SEQ ID NO:9, and (6) Granule Bound Starch Synthase D1 Protein encoded by Granule Bound Starch Synthase D1 gene of SEQ ID NO:11.
Owner:NIPPON FLOUR MILLS +1
Heat stable mutants of starch biosynthesis enzymes
InactiveCN1503842AIncrease productionImprove toleranceHydrolasesMutant preparationPlant tissueNucleotide
The present invention relates to novel mutant polynucleotide molecules encoding enzymes with enhanced thermostability. When expressed in plants, these polynucleotides lead to increased yield in plants grown under conditions of heat stress. In one embodiment, the polynucleotide molecule of the present invention encodes maize endosperm ADP glucose pyrophosphorylase (AGP) and soluble starch synthase (SSS) enzyme activities. Also contemplated by the present invention are plants and plant tissues grown to contain or transformed with such mutant polynucleotides and expressing a polypeptide encoded by such polynucleotides. The invention also relates to methods for isolating polynucleotides and polypeptides within the scope of the invention. The present invention also provides methods of increasing yield in plants grown under conditions of heat stress.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
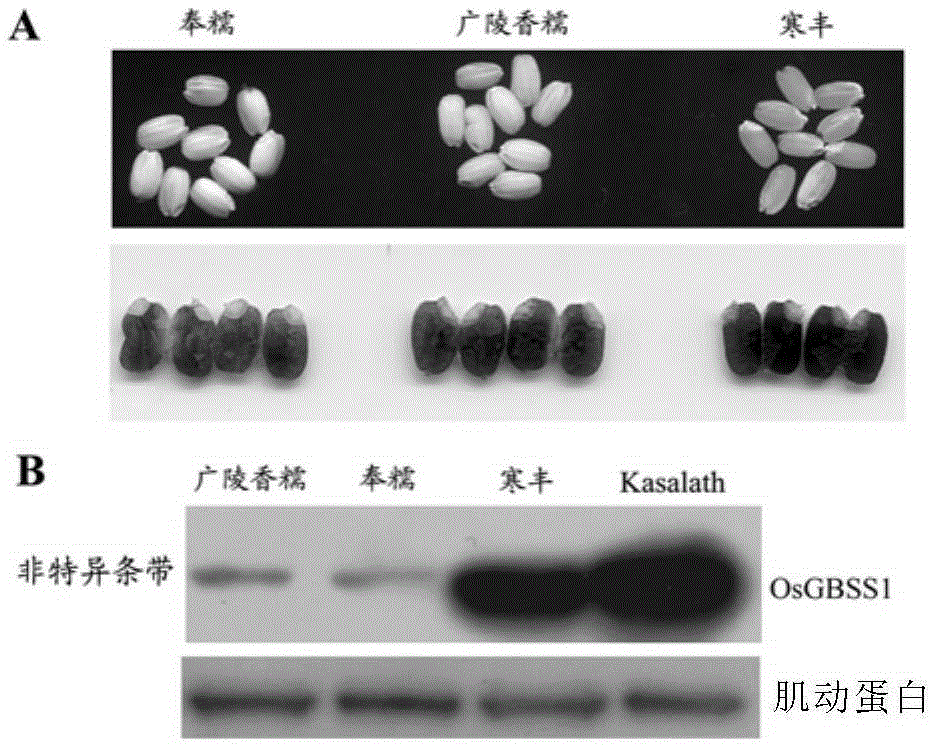
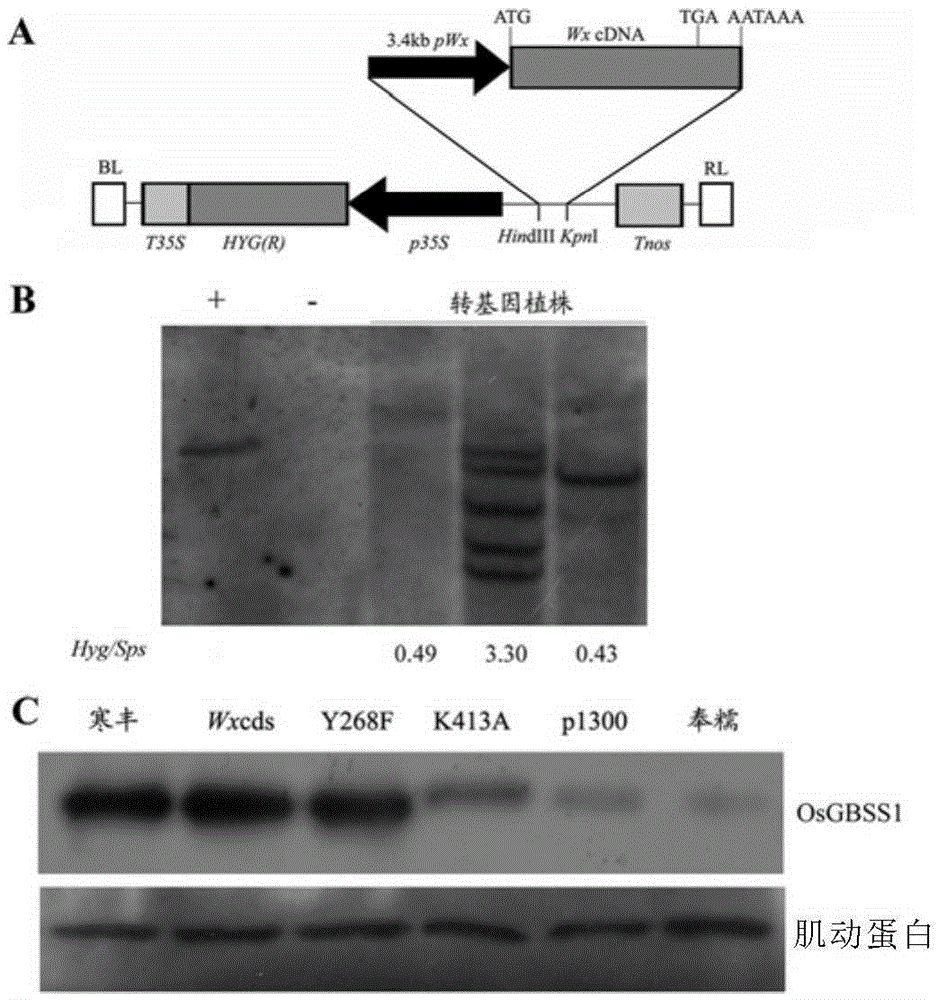
Mutant OsGBSS1 enzyme and preparation method and application thereof
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
Compositions and methods for producing starch with novel functionality
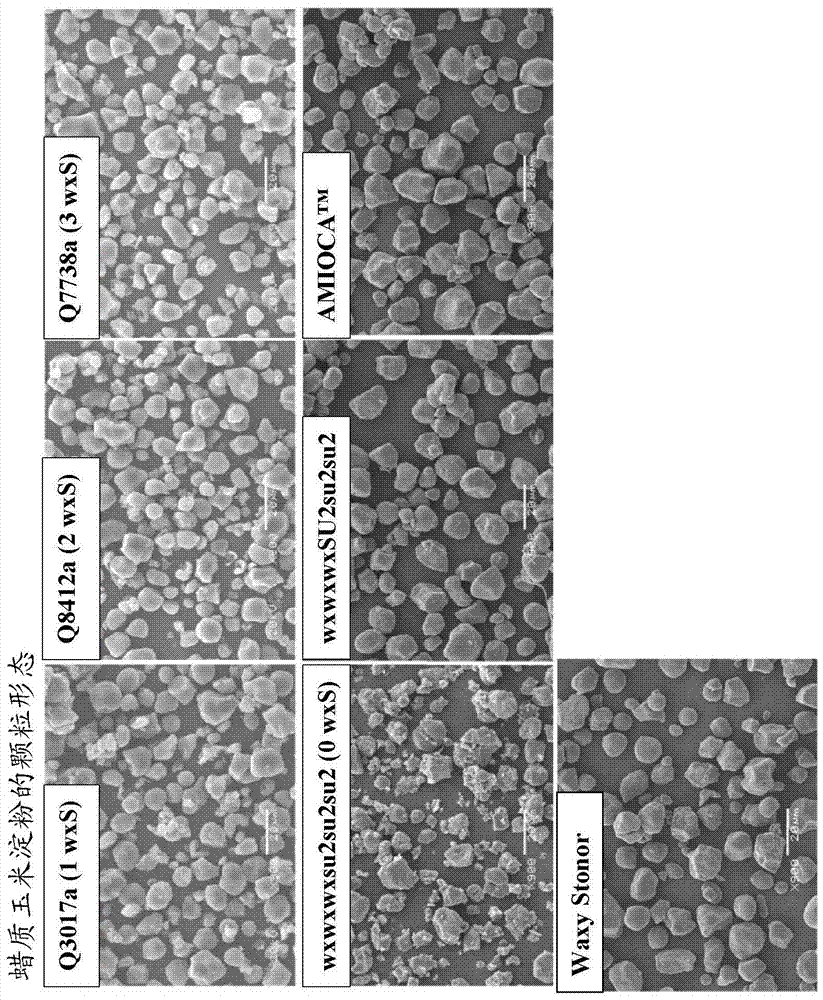
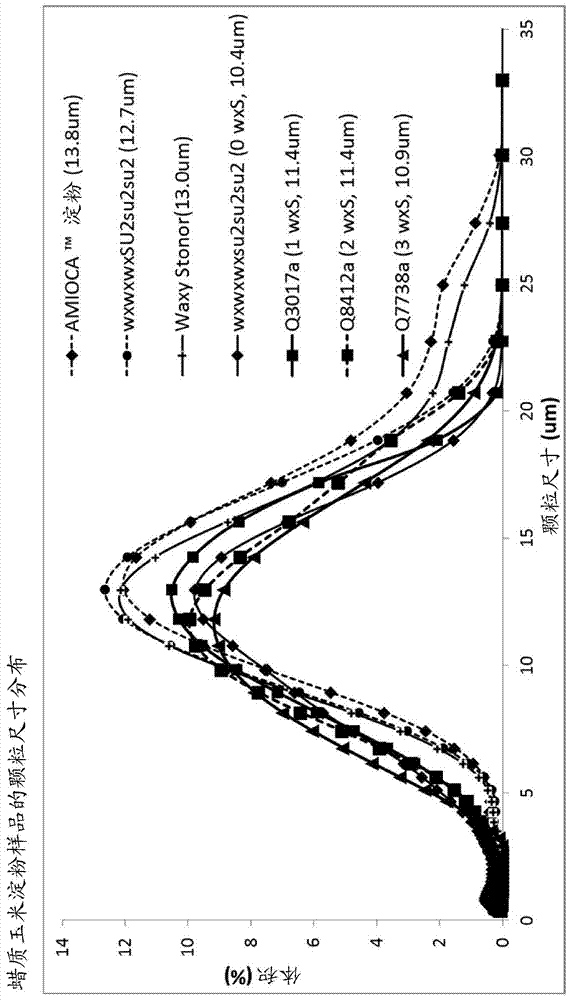
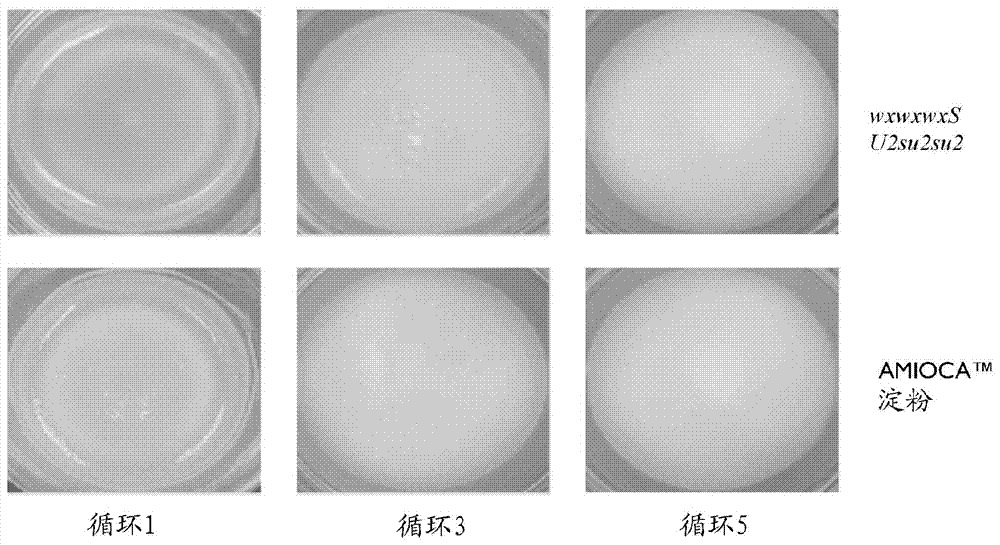
This invention disclosure relates to novel maize starch. The starch can be made from the newly developed waxy sugary-2 double-mutant maize that has low activity of Granule Bound Starch Synthase I (GBSSI), which results in low amylose level. The starch from newly developed waxy sugary-2 double-mutant is freeze-thaw stable and has high viscosity. In comparison with the starch of the existing waxy sugary-2 double-mutant maize, the new waxy sugary-2 double-mutant maize starch showed, inter alia, improved pasting profile, starch granule integrity, larger starch granule size, and higher viscosity.
Owner:CORN PROD DEV INC
Method of adjusting content of plant amylose and amylopectin
InactiveCN103146756AOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationStarch-branching enzyme IIStarch synthase
The invention relates to a method of adjusting a content of plant amylose and amylopectin. The invention provides an enzyme which is suitable for genetic engineering operation and can substantially change starch composition in the plant, wherein the enzyme is granule-bound starch synthase I (GBSS I), starch branching enzyme I (SBE I) and / or starch branching enzyme II (SBE II). The invention further provides a novel method of well adjusting starch composition in the plant, and the method comprises reducing expression of the enzyme, and thus obtaining a series of transgene plants with different content ratios of amylose and amylopectin The invention further provides a constructor or a carrier for adjusting starch composition in the plant.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Wheat starch and wheat flours and foodstuffs containing these wheat starch/wheat flours
The present invention relates to wheat flours, the starch component whereof has an amylose content between 15.0 wt. % and 30.0 wt. % and which have a content of resistant starch of more than 5.0 wt. % and foodstuffs containing these wheat flours. Further, the present invention relates to methods for the production of said wheat flours and the use thereof as resistant starch, as a prebiotic or for the production of foodstuffs with decreased glycemic index. The present invention also relates to nucleic acid molecules which code for a soluble starch synthase II, and vectors containing such nucleic acid molecules. Further, the present invention also relates to host cells and plants which contain such nucleic acid molecules or vectors.
Owner:BASF AG
Plant expression vector and application thereof in preparing phosphorylation modified rice starch
ActiveCN104232681AIncrease contentAchieve modificationVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsGranule-Bound Starch SynthaseBiotechnology
The invention discloses a plant expression vector and the application thereof in preparing phosphorylation modified rice starch. The plant expression vector comprises a target gene inserting into an original vector and a promoter, wherein the target gene comprises a transit peptides gene segment of granule-bound starch synthase and a potato glucan-water dikinase gene which are sequentially connected, and the promoter is a barley endosperm specific promoter HorD. For the plant expression vector and the application thereof in preparing phosphorylation modified rice starch, the potato glucan-water dikinase gene is transferred into rice, and the starch of the rice can be phosphorylated through the expression of the potato glucan-water dikinase gene, so that the modification of the starch is realized. The potato glucan-water dikinase is led to amyloid through the transit peptides of the granule-bound starch synthase, and phosphorylation modification is performed on the starch. According to the invention, the expression of the potato glucan-water dikinase gene in the rice endosperm can be promoted through the barley endosperm specific promoter HorD, and the phosphorus content in the rice starch is greatly increased.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Wheat having new starch and method for producing it
ActiveUS20090285960A1Retrogradation tolerance of gelatinized starch is improvedRaise the peak temperatureDough treatmentBaking mixturesBiotechnologyGranule-Bound Starch Synthase
The object of the present invention is to provide a wheat which accumulates a starch with a novel property by controlling the expression of the enzymes described in claims.The present invention provides a wheat, which does not express any of the following proteins (1)-(6): (1) Wheat Starch Synthase II-A1 Protein encoded by Wheat Starch Synthase II-A1 gene of SEQ ID NO:1, (2) Wheat Starch Synthase II-B1 Protein encoded by Wheat Starch Synthase II-B1 gene of SEQ ID NO:3, (3) Wheat Starch Synthase II-D1 Protein encoded by Wheat Starch Synthase II-D1 gene of SEQ ID NO:5, (4) Granule Bound Starch Synthase A1 Protein encoded by Granule Bound Starch Synthase A1 gene of SEQ ID NO:7, (5) Granule Bound Starch Synthase B1 Protein encoded by Granule Bound Starch Synthase B1 gene of SEQ ID NO:9, and (6) Granule Bound Starch Synthase D1 Protein encoded by Granule Bound Starch Synthase D1 gene of SEQ ID NO:11.
Owner:NIPPON FLOUR MILLS +1
Overexpression of starch synthase in plants
InactiveUS20130117894A1High activityImprove enzymatic activityEnzymesFermentationRice plantsStarch synthase
The present invention relates to a process for increasing the phosphate content of starches of genetically modified plant cells in comparison with starches from corresponding wild-type plant cells by introducing a foreign nucleic acid molecule which codes for a soluble starch synthase II. The present invention furthermore relates to the overexpression of this soluble starch synthase II in the genetically modified plant cells. Furthermore, the present invention relates to rice starch and rice flour with improved quality characteristics, to rice grains comprising this rice starch, and to rice plants on which these rice grains grow.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Heat stable mutants of starch biosynthesis enzymes
InactiveUS20080109921A1Increase crop yieldImprove toleranceSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideENCODE
The subject invention pertains to novel mutant polynucleotide molecules that encode enzymes that have increased heat stability. These polynucleotides, when expressed in plants, result in increased yield in plants grown under conditions of heat stress. The polynucleotide molecules of the subject invention encode maize endosperm ADP glucose pyrophosphorylase (AGP) and soluble starch synthase (SSS) enzyme activities. Plants and plant tissue bred to contain, or transformed with, the mutant polynucleotides, and expressing the polypeptides encoded by the polynucleotides, are also contemplated by the present invention. The subject invention also concerns methods for isolating polynucleotides and polypeptides contemplated within the scope of the invention. Methods for increasing yield in plants grown under conditions of heat stress are also provided.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Cross-linked starch biosynthesis recombinant gene YXI and application thereof
The invention discloses a cross-linked starch biosynthesis recombinant gene YXI and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO:1, glgC55 of the ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase coding gene is separated out from a mutant strain of escherichia coli JM109-3, and an ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase (AGPase) small subunit coding gene (SSU cDNA) and a starch grain-combined starch synthase coding gene GBSSI promoter are respectively separated out from potatoes. An AGPase subunit composed of 431 amino acids is coded by glgC55, wherein four specific mutations, which are K39E, V71A, I248V and K304E, exist, the first two appear in the Rossmann fold regions of the oligomeric subunit N-terminal metabolic groups, and the latter two appear in oligomeric subunit C-terminal heterogeneously regulated and oligomerized LbH groups.
Owner:宁夏晨曦农业科技服务有限公司
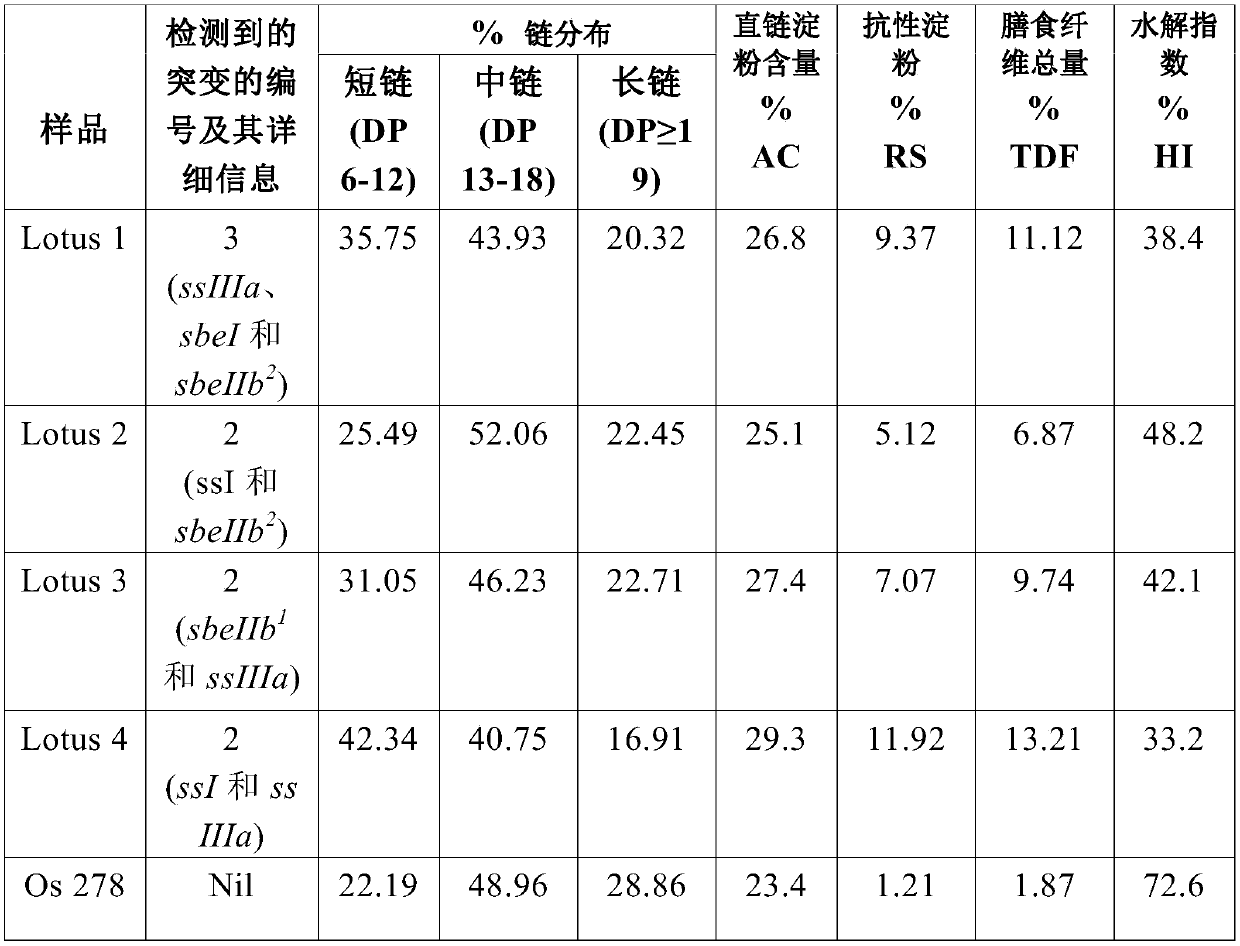
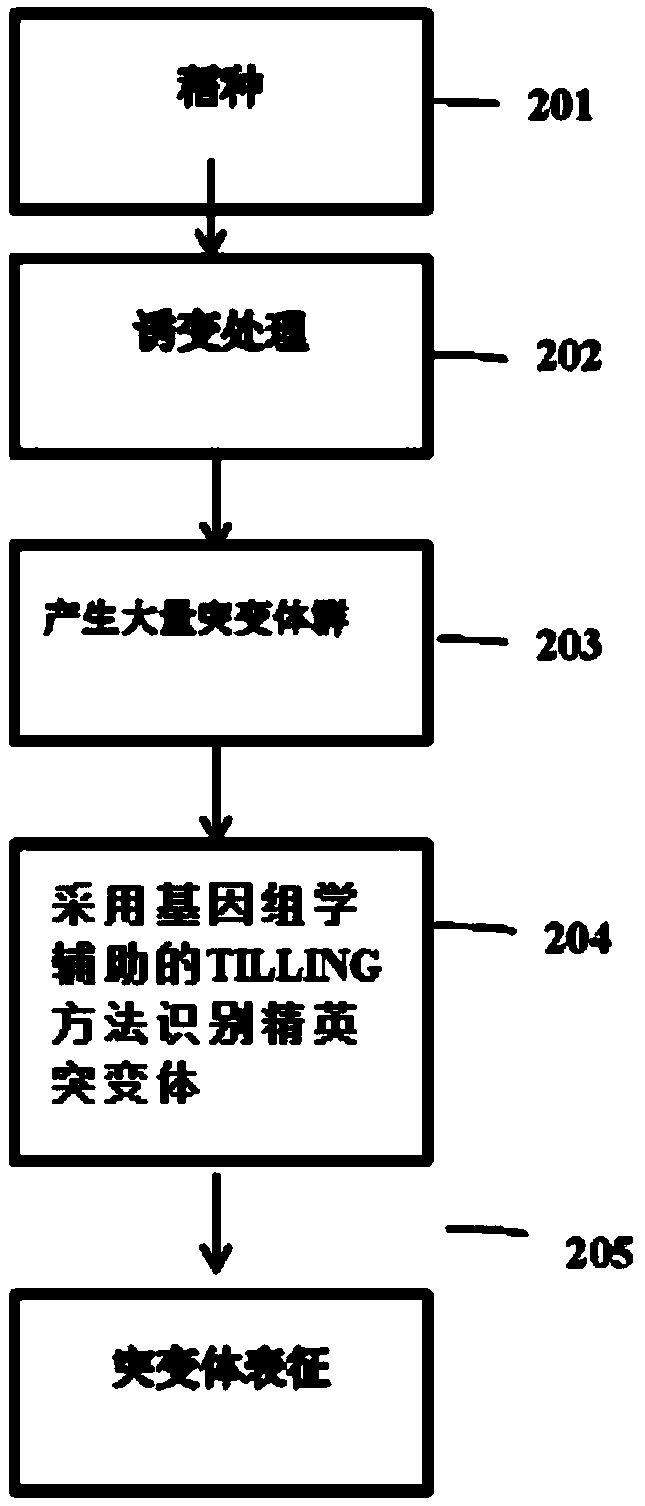
A method for increasing resistant starch and dietary fibre in rice
InactiveCN109689874AIncrease expansionHypoglycemic responseGlycosyltransferasesVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyGain weight
The present invention discloses mutations in the starch synthase genes associated with enhanced dietary fibre and resistant starch levels in the endosperm of a suitable variety of rice. The dietary fiber and resistant starch are enhanced to an extent to significantly reduce the hydrolysis index values of the rice grains to 35-40%. These rice varieties are in great demand for diabetic population and provide a number of other health benefits such as reduced body weight gain, cardiac health and colon health. As this strategy does not involve the use of genetic manipulation technologies, it can bedirectly employed in the rice breeding programmes without any restrictions.
Owner:ウダヤアグロファーム +1
Method for cultivating soft rice by using transcriptional activation factor sample effector nuclease technology
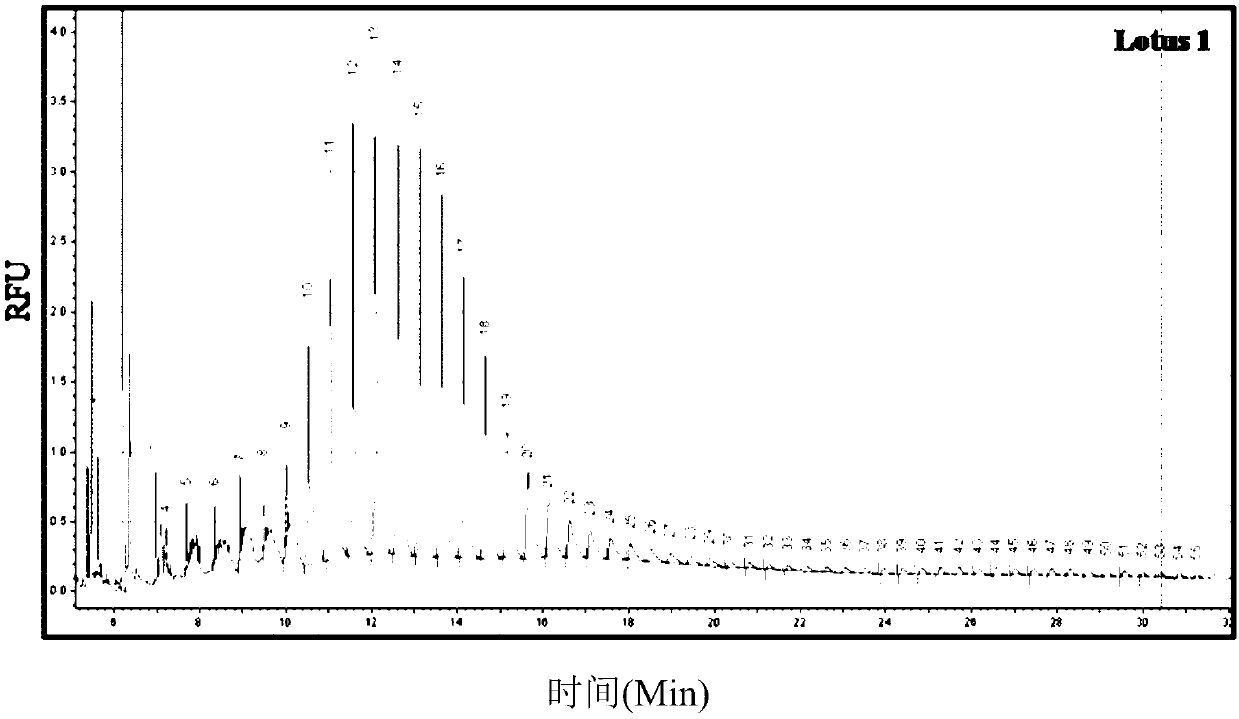
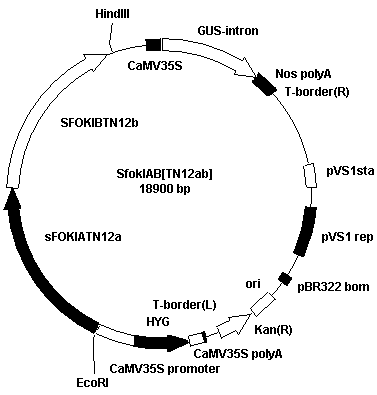
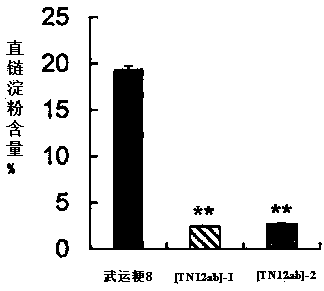
The invention discloses a method for cultivating soft rice by using a transcriptional activation factor sample effector nuclease technology. The method for cultivating the soft rice by using the transcriptional activation factor sample effector nuclease technology comprises the specific steps that according to gene sequence analysis, two segments of specific nucleotide sequences are screened out from a rice starch synthase GBSSI genomic DNA, transcriptional activation factor effector recognition modules of two segments of target site sequences are separately established, and the transcriptional activation factor effector recognition modules are connected with an FokI II nuclease expression unit in series. A plant expression vertor SFokIAB[TN12ab] of the target GBSSI gene TALEN is obtained,and then the expression vector is converted to rice through agrobacterium-mediated transformation. By using the method for cultivating the soft rice by using the transcriptional activation factor sample effector nuclease technology, content of amylose in the rice can be significantly reduced, and thus the superior soft rice is obtained.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
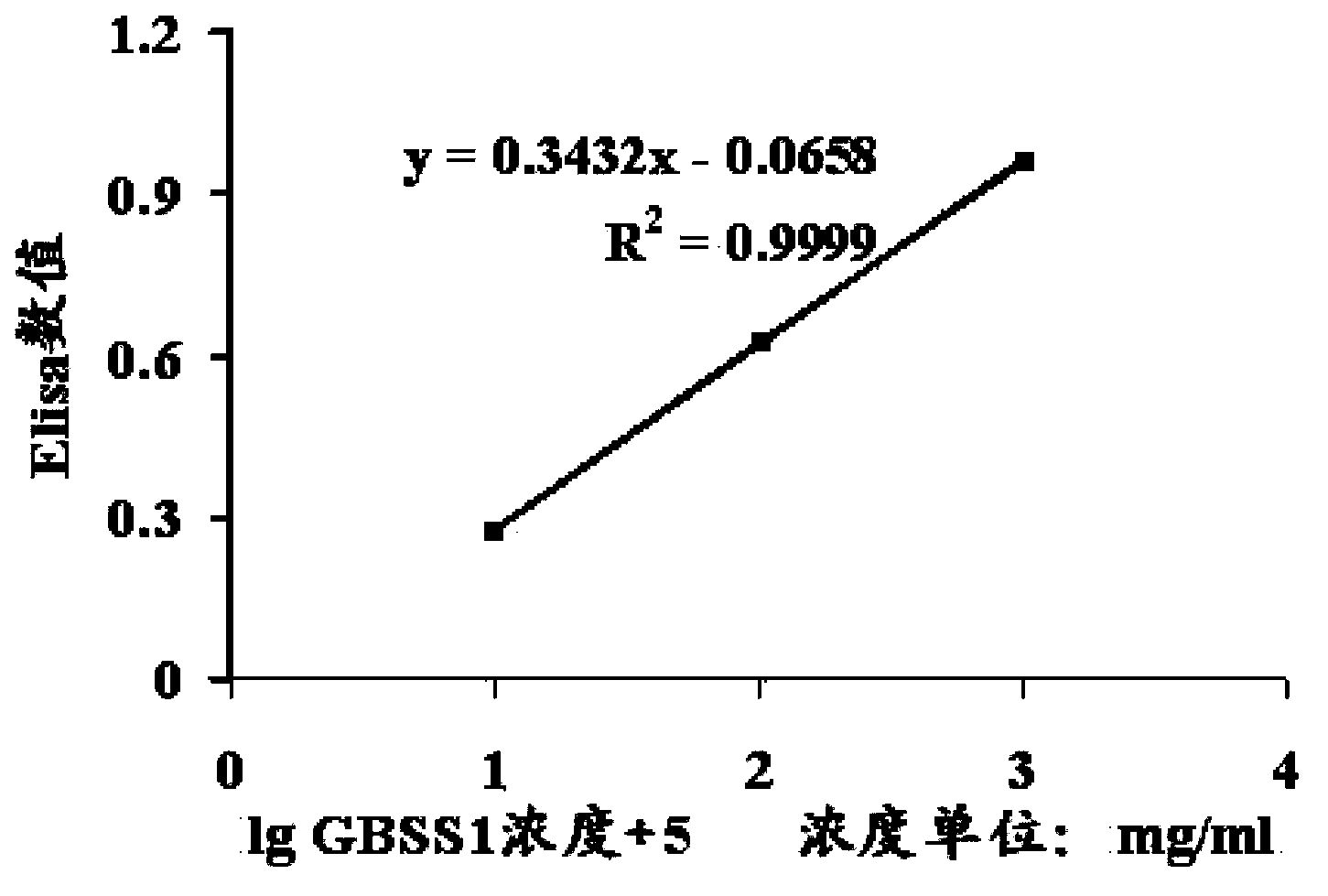
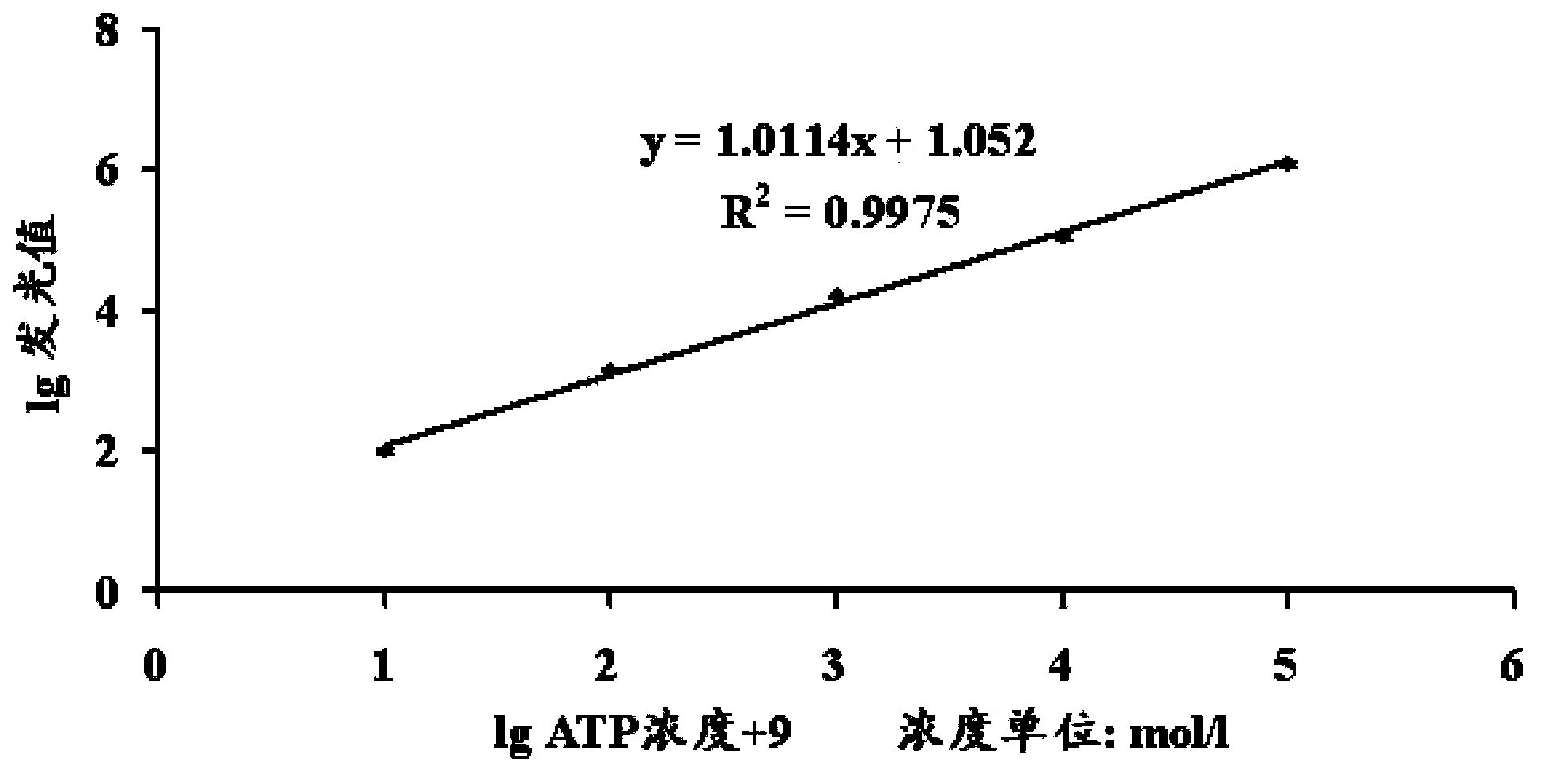
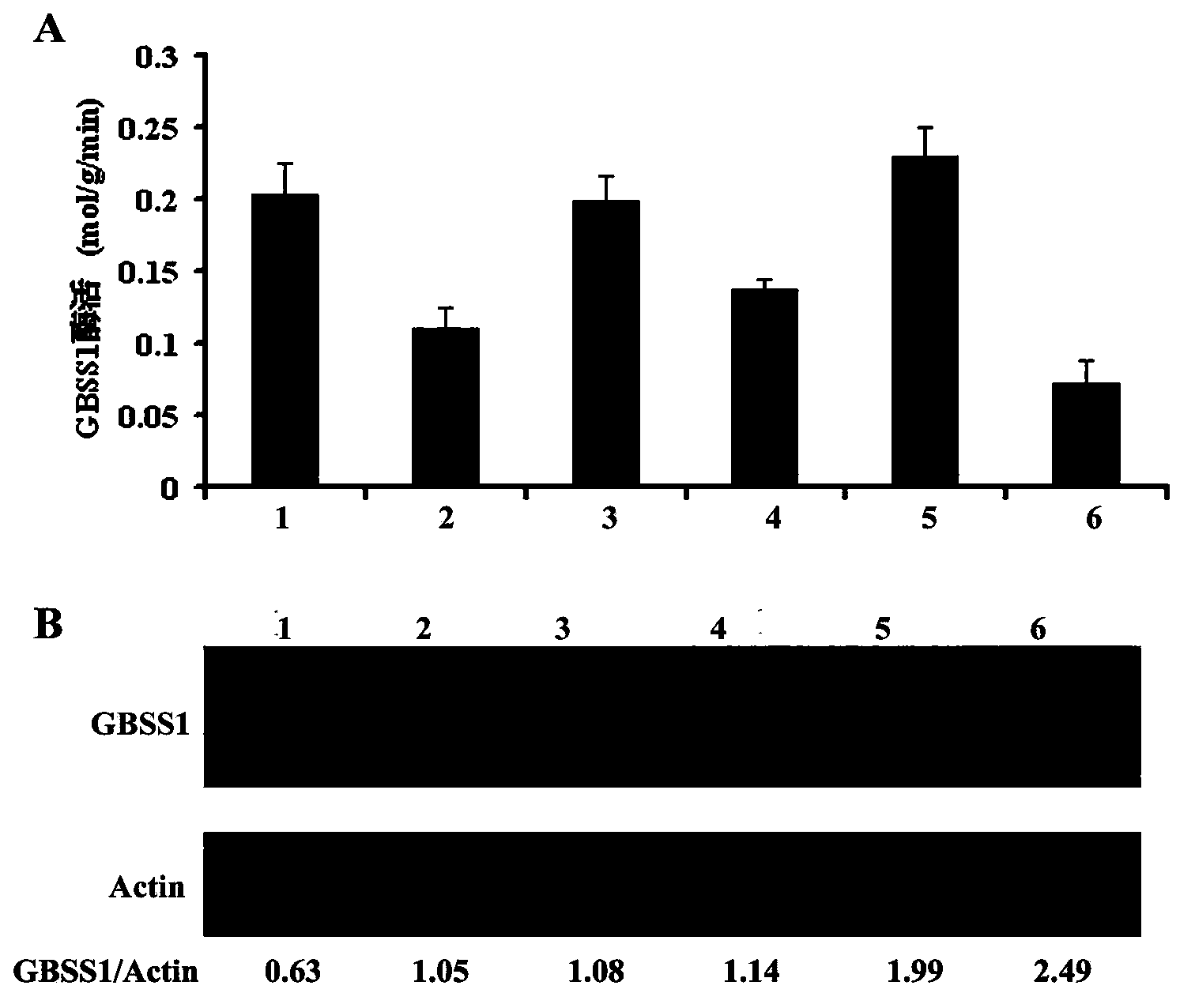
GBSS1 specific enzyme activity determination method
InactiveCN103808929AMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisGranule-Bound Starch SynthaseSpecific enzyme
The present invention relates to a GBSS1 specific enzyme activity determination method, and provides a granule-bound starch synthase (GBSS1 enzyme) specific enzyme activity determination method, wherein an ELISA technology is adopted to carry out quantitation on the enzyme extract in the GBSS1 protein level and the previous GBSS1 enzyme activity determination steps are simplified.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
New method for formulation of full waxy starch wheat germplasm
InactiveCN102747100AComprehensive agronomic traits are goodBacteriaVector-based foreign material introductionGranule-Bound Starch SynthaseAgricultural science
The invention discloses a method for cultivation of full waxy wheat. The method for cultivation of full waxy wheat provided in the invention includes the following step of: inhibiting the expression of GBSS (granule-bound starch synthase) I gene in target wheat to obtain the full waxy wheat. The inhibition of expression of the GBSS I gene in the target wheat is realized by transferring a DNA fragment as shown in formula "SEQforward-X-SEQbackward" into the target wheat. Specifically, the SEQforward is the top 288 nucleotides in sequence 1 of a sequence table; the SEQbackward is in reverse complement with the SEQforward; the X is a spacer sequence between the SEQforward and the SEQbackward, and in sequences, the X is not complementary with and the SEQforward and the SEQbackward. Experiments prove that the wheat GBSS I gene can be silenced through a transgene silencing technology (RNAi) to obtain a GBSS I gene expression-inhibiting full waxy wheat new germplasm, and the transgenic material has excellent comprehensive agronomic characters, thus being able to be directly used for selective breeding of wheat low-amylose new strains (varieties) or be used as a patent material of breeding.
Owner:INST OF CEREAL & OIL CROPS HEBEI ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
Starch synthase gene promoter with seed-specific expression and application thereof
InactiveCN101525622AUncover regulatory pathwaysPlay a regulatory roleFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyPlanting seed
In the invention, a Genomic walking method is employed to design a specific nested primer according to a cDNA sequence (GenBank Accession No.: AF036891) of a maize dull 1 gene, maize genome is taken as a template to separate a maize starch synthase gene dull 1 promoter from maize. The promoter has a spatiotemporal specific expression property, can drive target genes to efficiently express in plant seeds at grain filling stage, but is not expressed at leaves, leaf veins and roots, and has wide use in research of plant bioreactor. The promoter lays a foundation for researching an expression regulating and control mechanism of plant starch anabolism, creates a condition for starch biosynthesis regulation and control in gene engineering technology, and plays an important role in the research of plant starch improvement and the plant bioreactor.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Cereal flour composition containing wheat flour from sweet wheat and food product using the same
ActiveUS20100055283A1Superb textureStrong sweetnessDough treatmentBaking mixturesGranule-Bound Starch SynthaseStarch synthase
An object of the present invention is to provide a cereal flour raw material that can provide products having superb texture. A further object of the present invention is to provide a food product manufactured using such a cereal flour raw material.The present invention provides a cereal flour composition that contains wheat flour prepared from a type of wheat that does not express the three wheat starch synthase II proteins, and also does not express the three wheat granule bound starch synthase proteins, and another type of cereal flour; and a food product manufactured using such a cereal flour composition.
Owner:NAT AGRI & FOOD RES ORG +1
Mutant OsGBSS1 enzyme and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103695381AMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationGranule-Bound Starch SynthaseStarch synthase
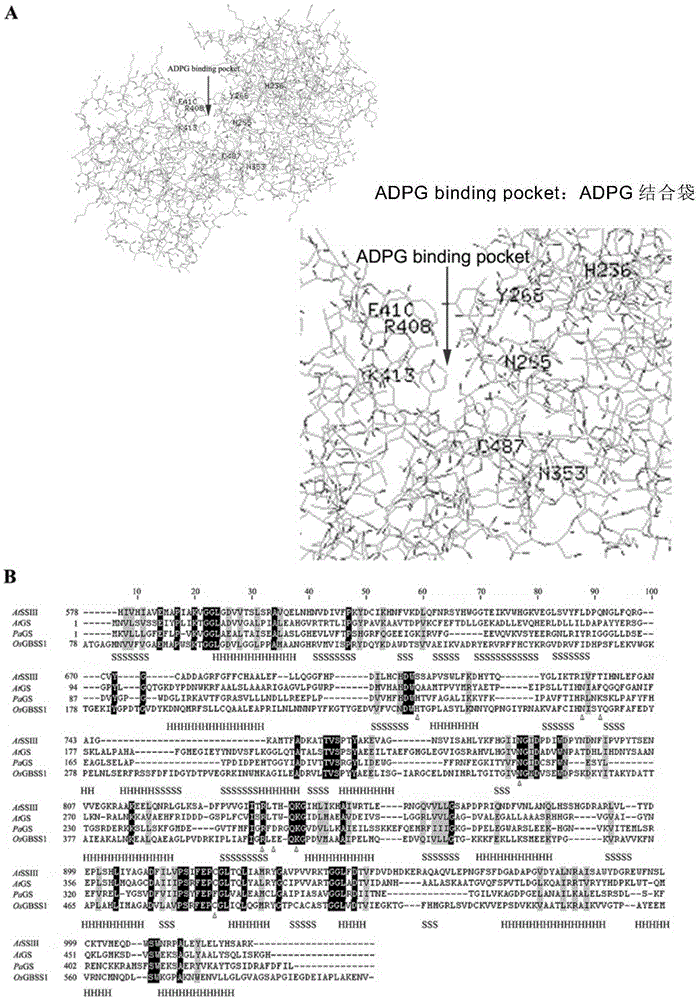
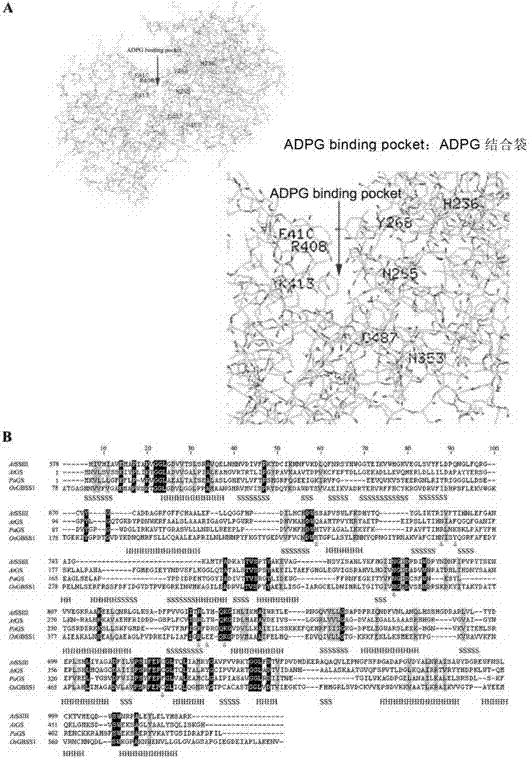
The invention discloses a granule-bound starch synthase which has mutation at one or more amino acid loci selected from the following groups and corresponding to an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1: H236, N265, Y268, N353, R408, E410, K413, C487, A114, EA314-315, and T543, and has significantly reduced enzymatic activity. Therefore, the invention reveals the relation between specific amino acid residues and amylose content, and the enzyme can regulate the amylose content in paddy rice, thereby improving edible quality of paddy rice.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A kind of transgenic rice with good eating quality and breeding method
ActiveCN103146746BLow viscosityReduce amylose contentVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsGenetically modified riceAgricultural science
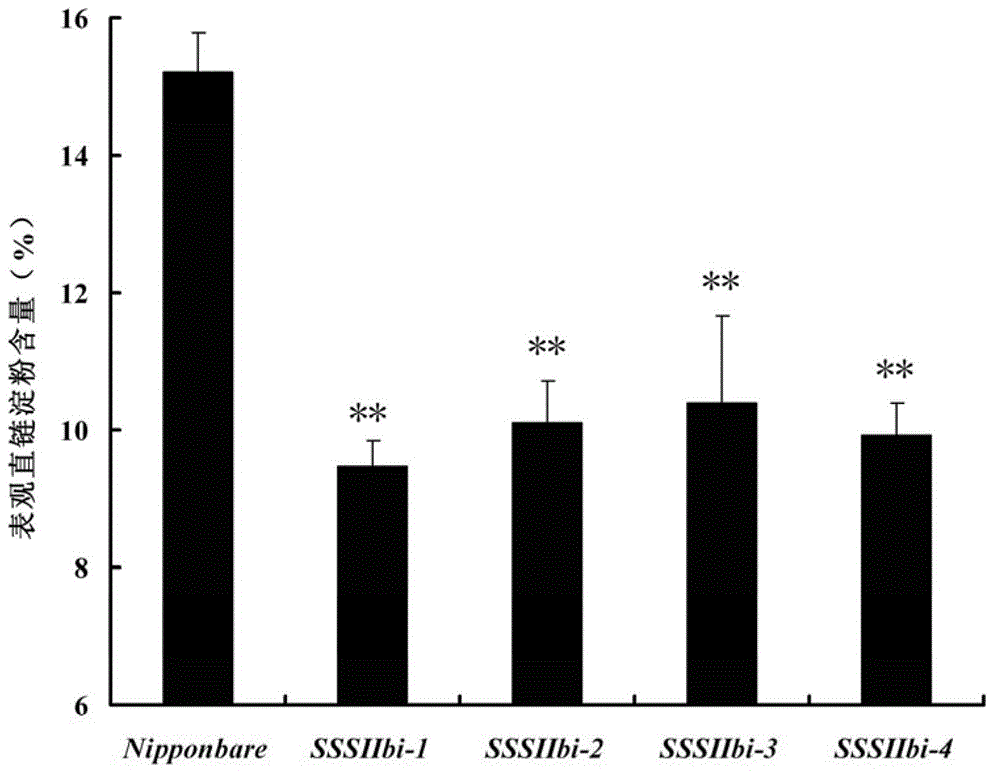
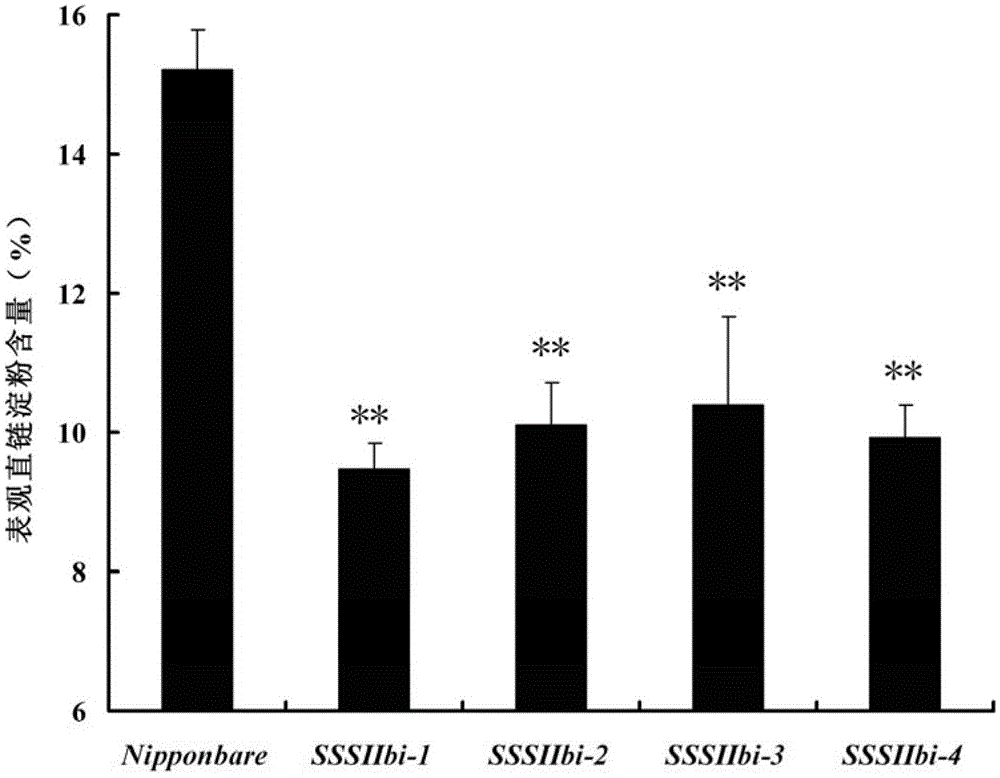
The invention discloses a method for reducing apparent amylose content of rice and improving the starch viscosity so as to improve the eating quality of the rice, and belongs to the technical field of organisms. The method is achieved by disturbing soluble starch synthase SSSIIb gene expression in paddy; a ribonucleic acid (RNA) interference carrier of the SSSIIb gene is built; and the transgenic rice of disturbing the SSSIIb gene is obtained by an agrobacterium mediated method. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) experiment shows that a target gene is integrated into rice genome; and homozygous transgenic rice is obtained in a breeding manner. The amylose content in rice endosperm of the transgenic rice is obviously reduced in comparison with the unconverted parent Nipponbare. A rapid viscosity tester analysis shows that the starch viscosity of the transgenic rice is reduced; the gelatinization temperature is reduced; and the eating characteristics of the rice are obviously improved.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com