A method for increasing resistant starch and dietary fibre in rice
A rice and starch technology, applied in the fields of botanical equipment and methods, biochemical equipment and methods, and applications, which can solve problems such as rising risks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
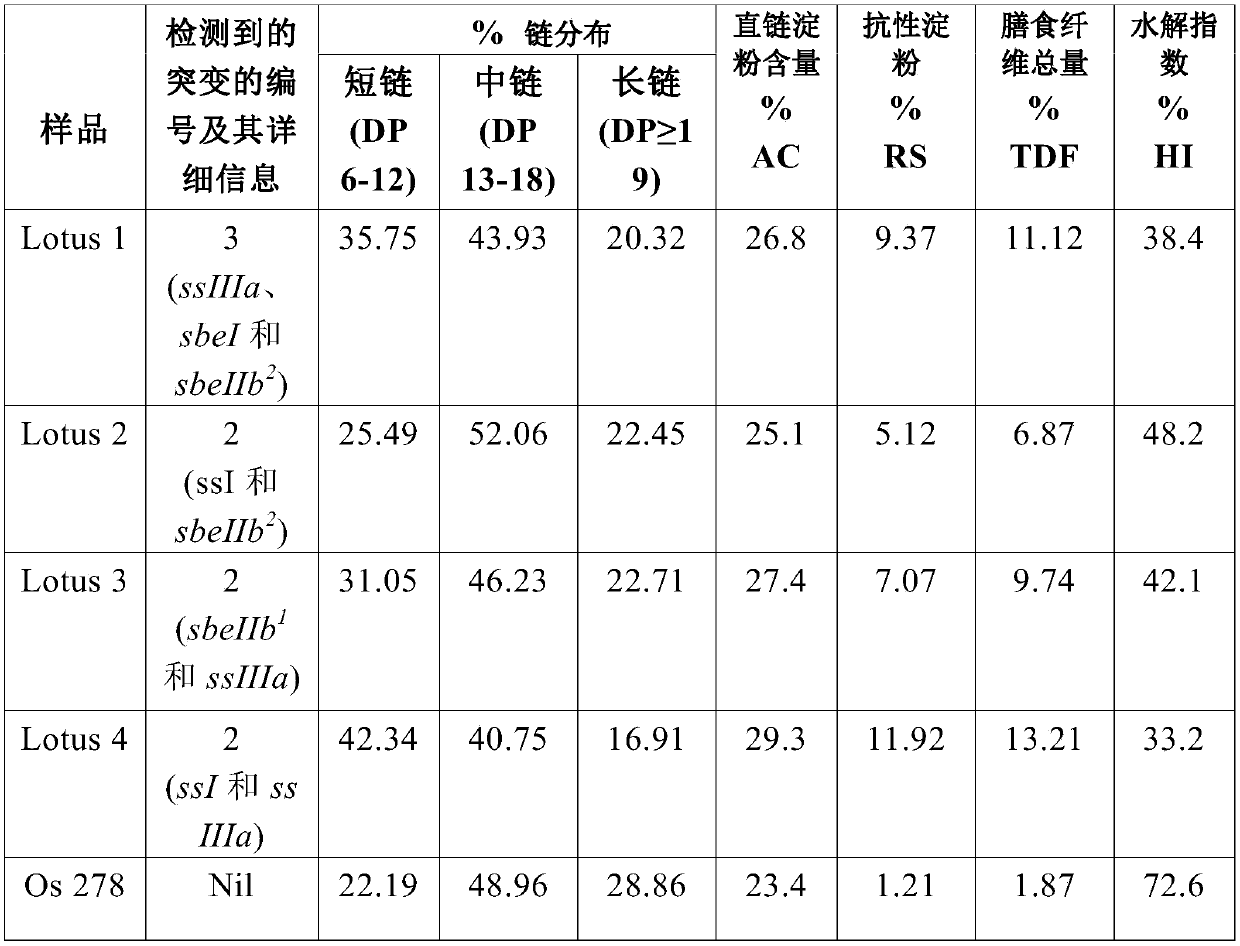
[0059] Example 1: RS Assessment Procedure
[0060] RS content was assessed using the Megazyme kit. The kit was obtained from M / s Megazyme International Ireland Ltd, Bray Business District, Wicklow, Ireland. Duplicate 100 ± 1 mg flour samples were taken in screw cap tubes and gently tapped to ensure that no sample stuck to the tube walls. Add 4 ml of amyloglucosidase (AMG) (3U ml -1) of pancreatic alpha-amylase (3 Ceralpha units / mg, 10 mg / ml). Cap the tube tightly so that it is completely dispersed on a vortex mixer and attached horizontally in a shaking water bath aligned with the direction of motion. Tubes were incubated for 16 hours at 37°C with continuous shaking (200 strokes / min). After incubation, tubes were treated with 4.0 mL of ethanol (99%) under vigorous mixing using a vortex mixer. Thereafter, the tubes were centrifuged at 1,500 xg (approximately 3,000 rpm) for 10 minutes (uncapped). The supernatant was decanted carefully and the pellet was resuspended in 8 ml...
Embodiment 2
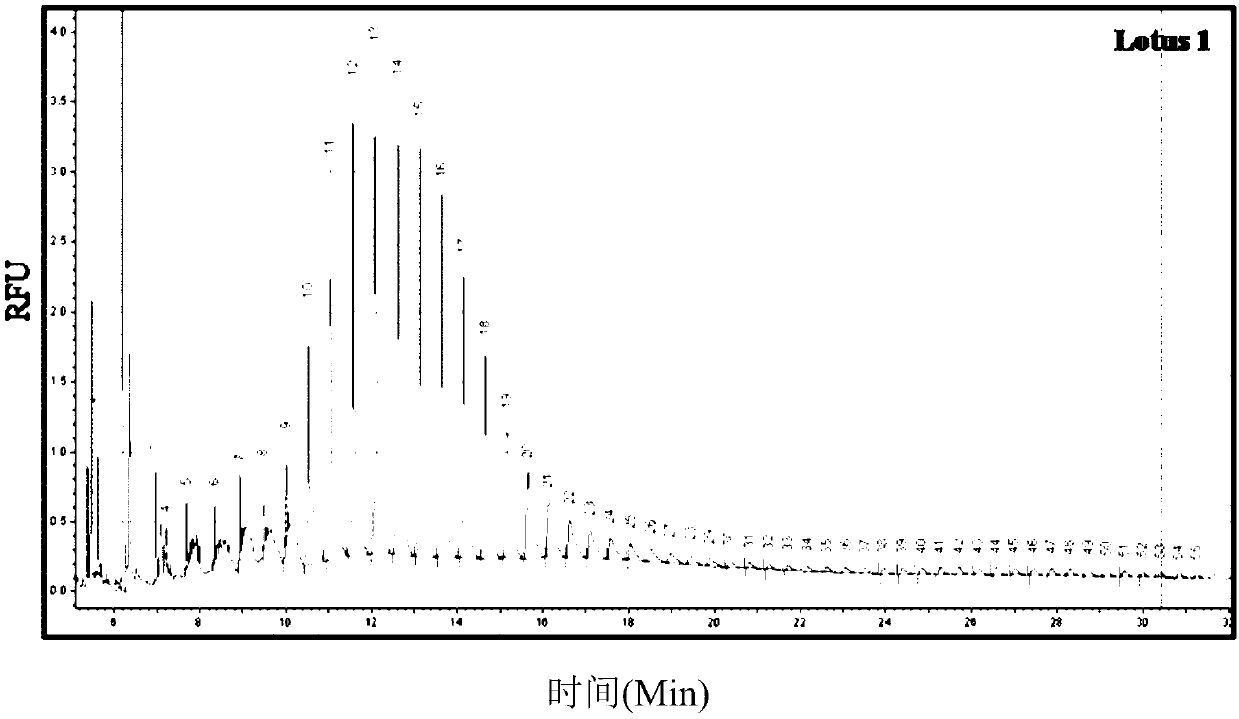
[0061] Example 2: Degree of Polymerization of Amylopectin Chains
[0062] Pure starch was isolated from all mutants and wild type according to the method described by Lumdubwong and Seib (2000). The amylopectin chain length distribution of isolated starches was analyzed by fluorophore-assisted capillary electrophoresis (FACE) as described by Morell, Samuel and O'Shea (1998). Isolated starch was debranched (2 h at 37°C) using isoamylase (10 U) and labeled with 1-aminopyrene-3,6,8-trisulfonic acid (APTS). FACE was performed using a P / ACE system 5010 (Beckman Coulter, CA, USA) equipped with a 488 nm laser module. Debranched samples were separated using N-CHO (PVA) capillaries (Beckman Coulter, CA, USA) (50 m ID and 47 cm total length) with precombustion windows. Maltose was used as internal standard. Separation was performed at 10°C for 30 minutes. Based on the migration time of maltose, the degree of polymerization (DP) was assigned to the peak.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com