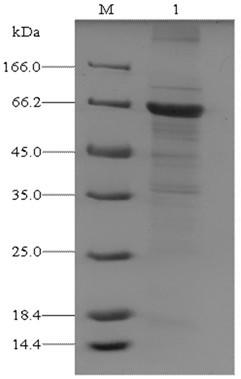
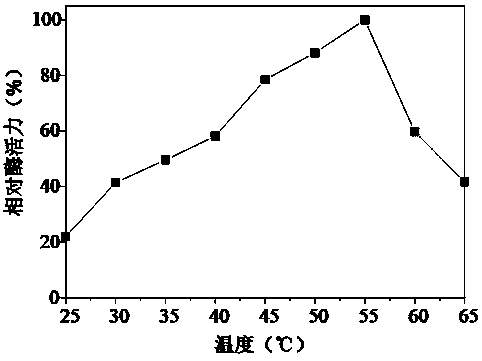
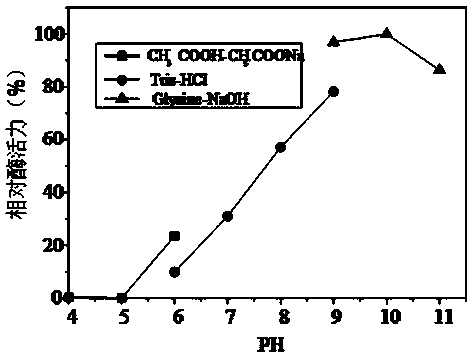
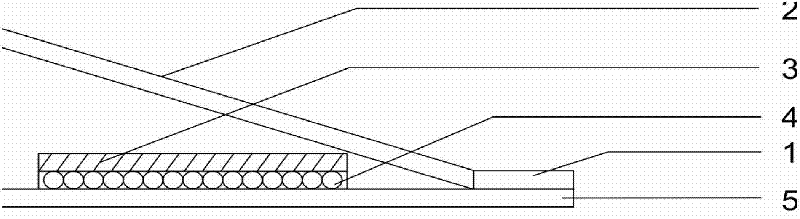
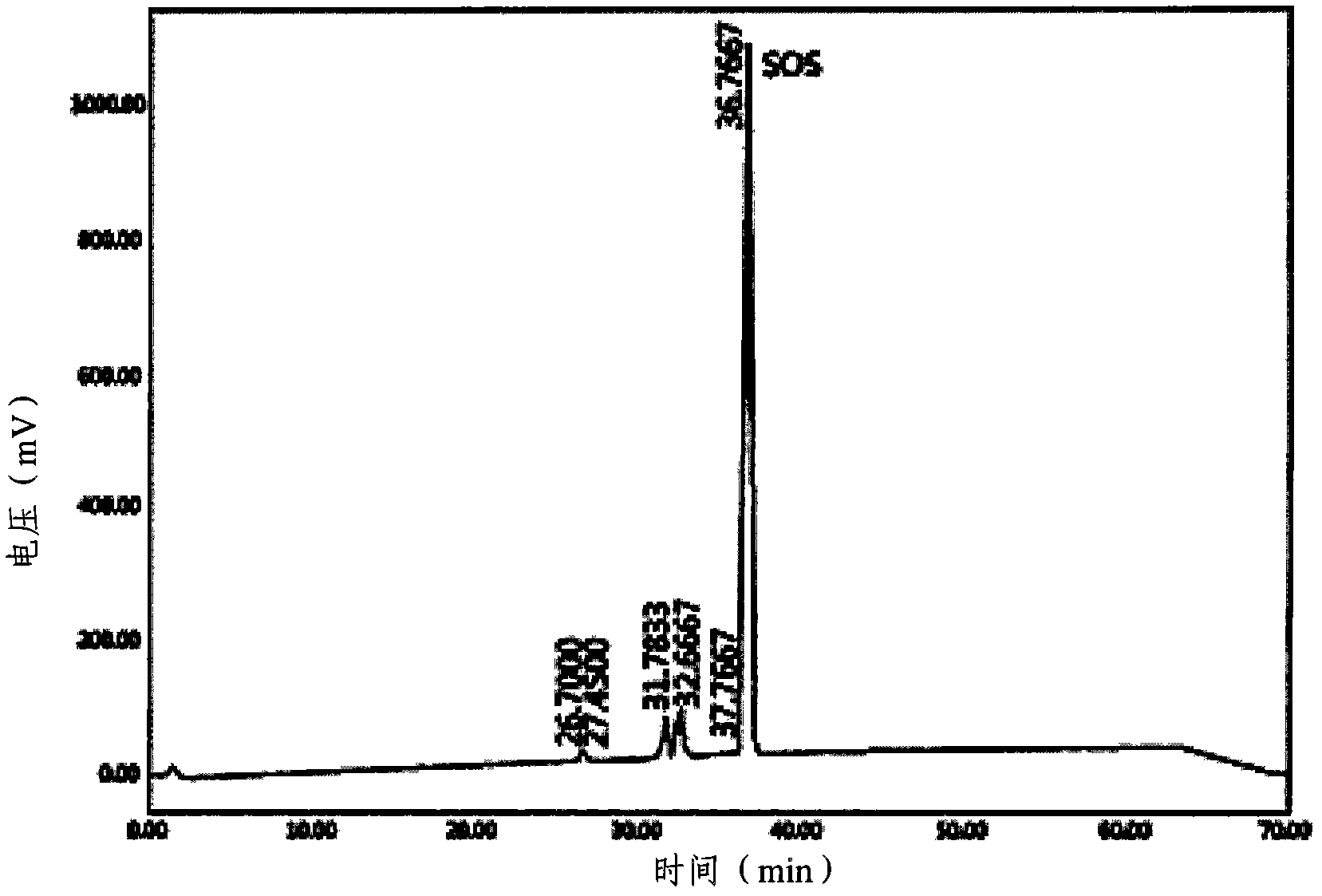
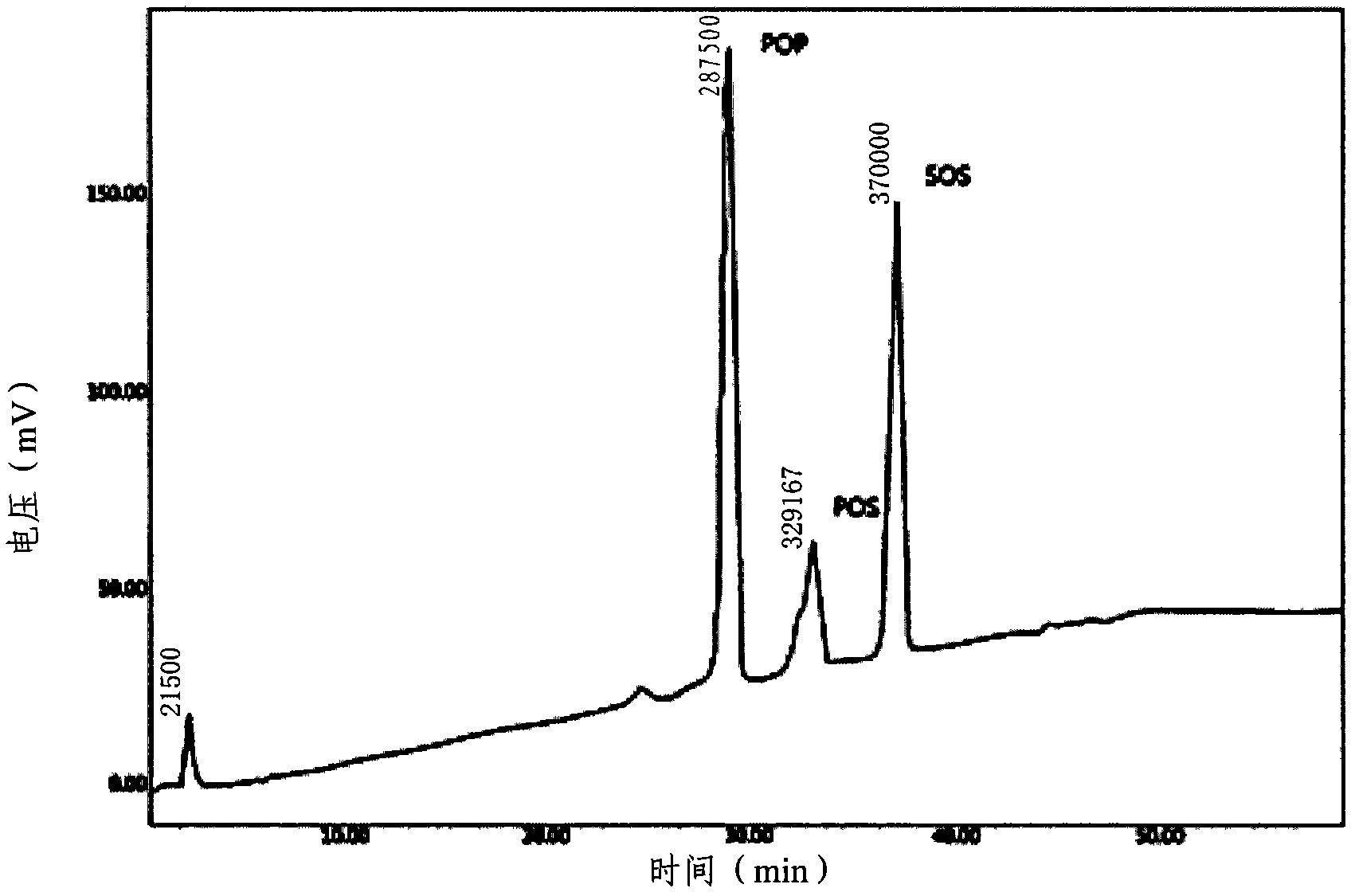
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
611 results about "Specific enzyme" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Enzymes are specific in their action which means that an enzymes will act on only one substrate or group of closely related substrate. For example, hexokinase catalyses the conversion of hexoses like glucose, fructose and mannose to their 6-phosphate derivatives but glucokinase is specific for the glucose only.
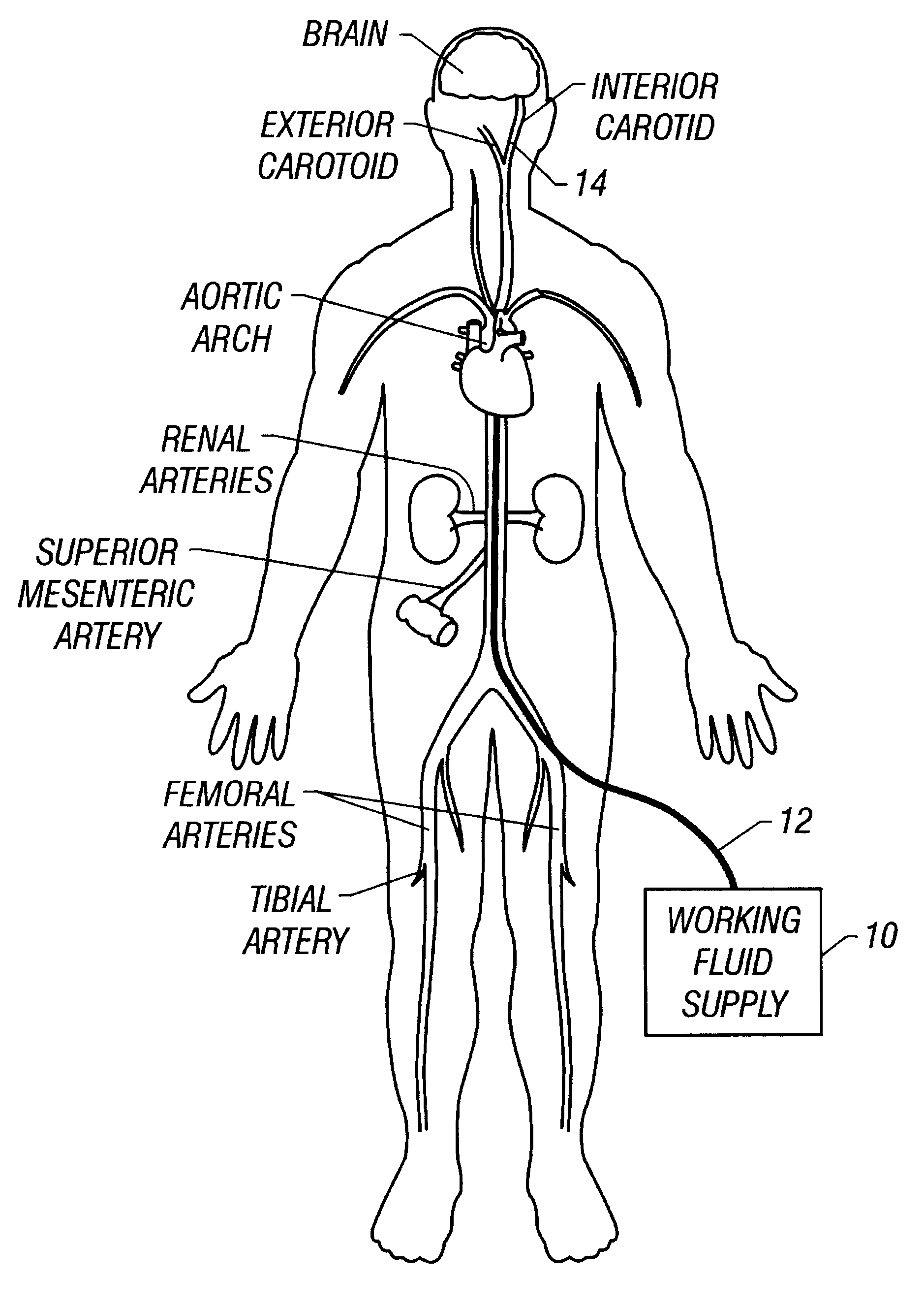
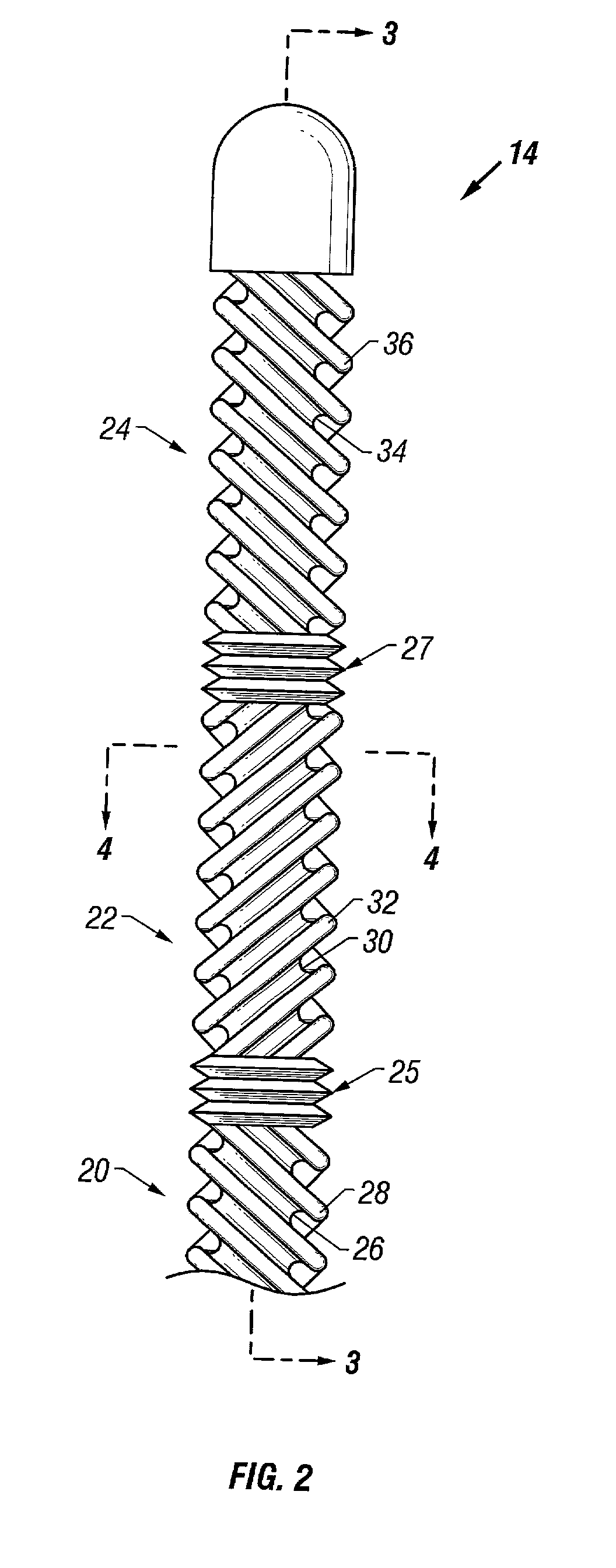
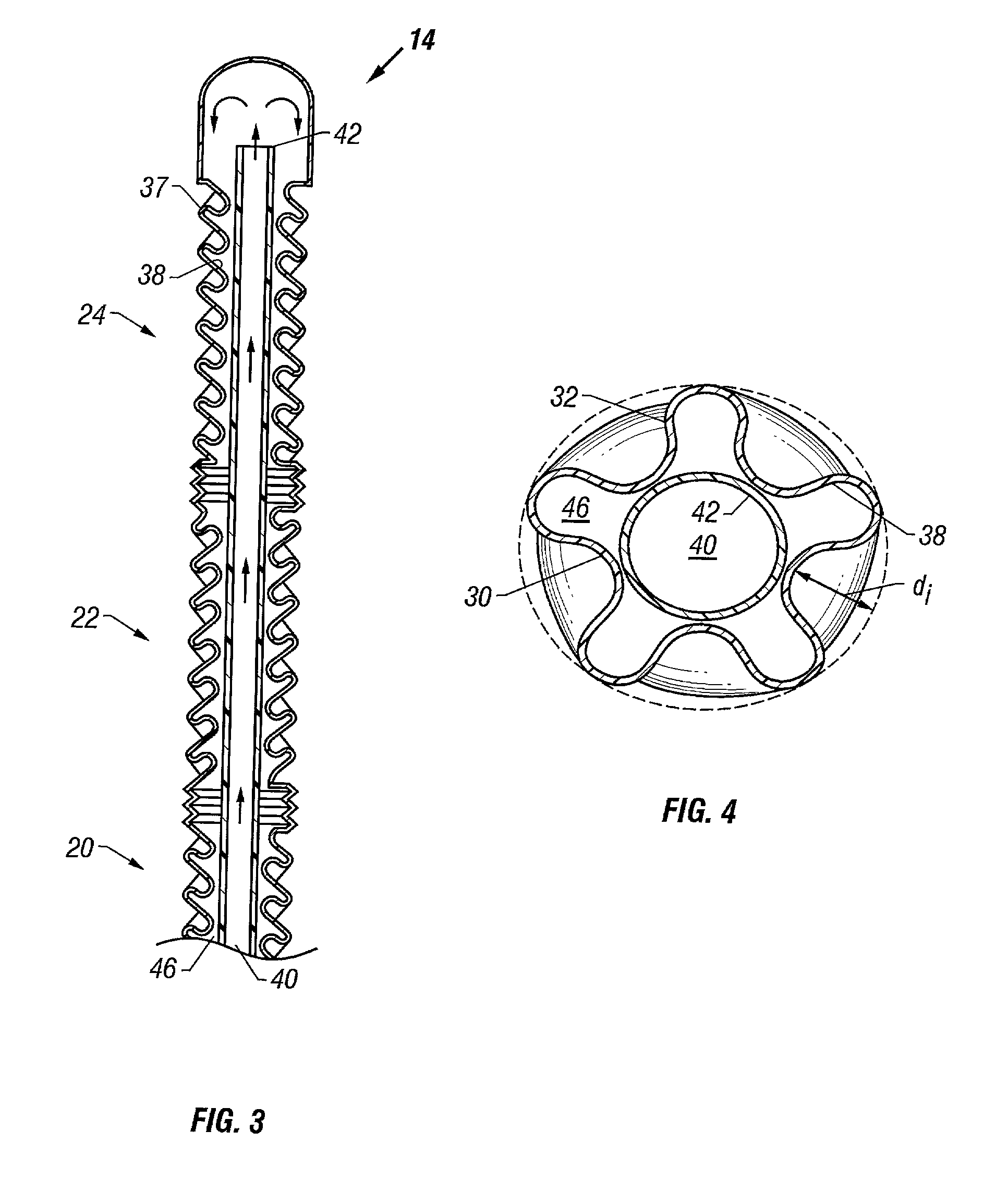
Method and apparatus for location and temperature specific drug action such as thrombolysis
A method is provided of localizing a drug action where the drug is present throughout a vascular system. The localization occurs to within a volume of blood in a blood vessel, the vascular system having an initial temperature substantially within a first temperature range. A temperature-specific enzyme is delivered throughout a vascular system including a volume of blood in a blood vessel, the temperature-specific enzyme having a working temperature within a prespecified temperature range that does not substantially overlap the first temperature range. A heat transfer element is delivered to a blood vessel in fluid communication with the volume of blood. The temperature of the heat transfer element is adjusted such that the volume of blood in the blood vessel is heated or cooled to the prespecified temperature range. In this way, the action of the temperature-specific enzyme is substantially limited to the volume of blood heated or cooled. In an alternative embodiment, the temperature-specific enzyme is localized to the volume of blood in the blood vessel, and the heat transfer element is disposed in fluid communication with the volume of blood in the blood vessel. The enzyme localization may occur by way of direct injection or by way of injection through a lumen of a catheter. The injection lumen of the catheter may be disposed at least partially adjacent or in combination with the heat transfer element and its associated inlet and outlet lumens.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Enzyme-activated anti-tumor prodrug compounds
Disclosed are enzyme-activated anti-tumor and anti-metastatic prodrug compounds. The specific enzymes are collagenase(IV) and elastase. Also disclosed are methods of making and using such compounds.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM PHARMA INC
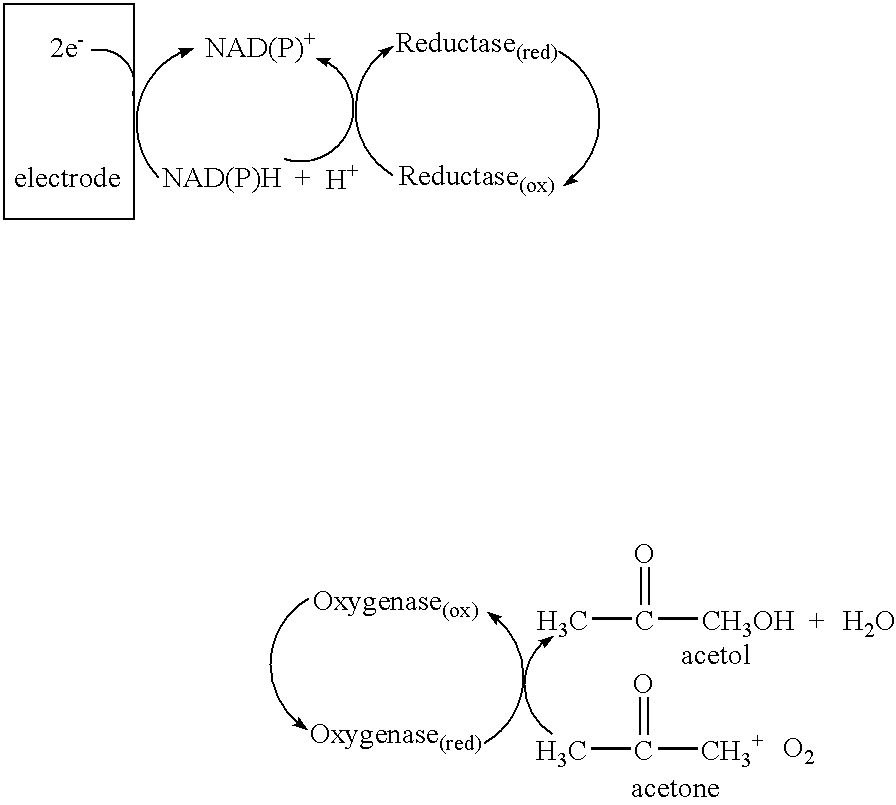
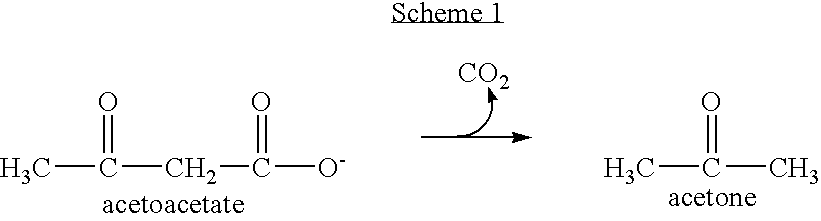
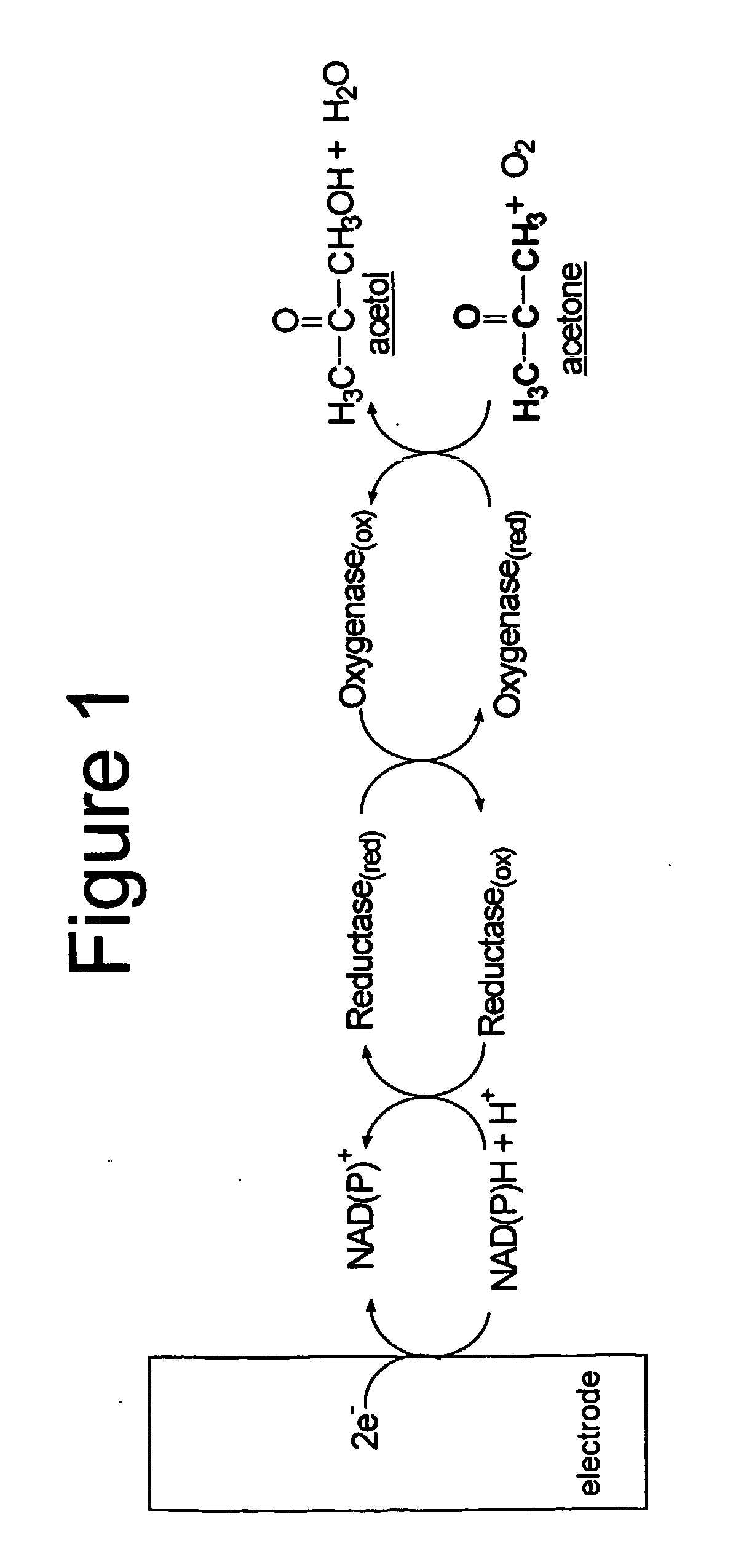
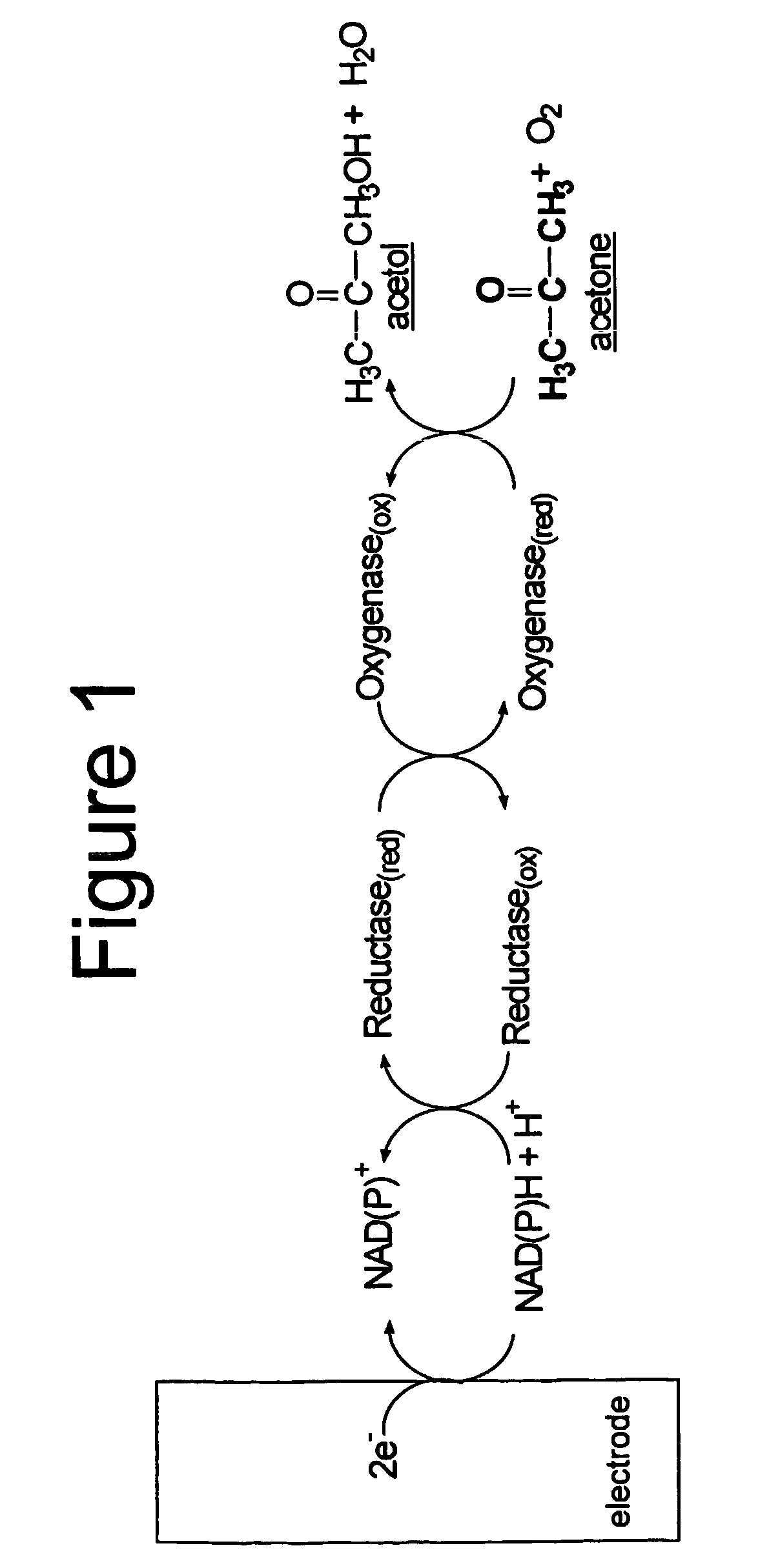
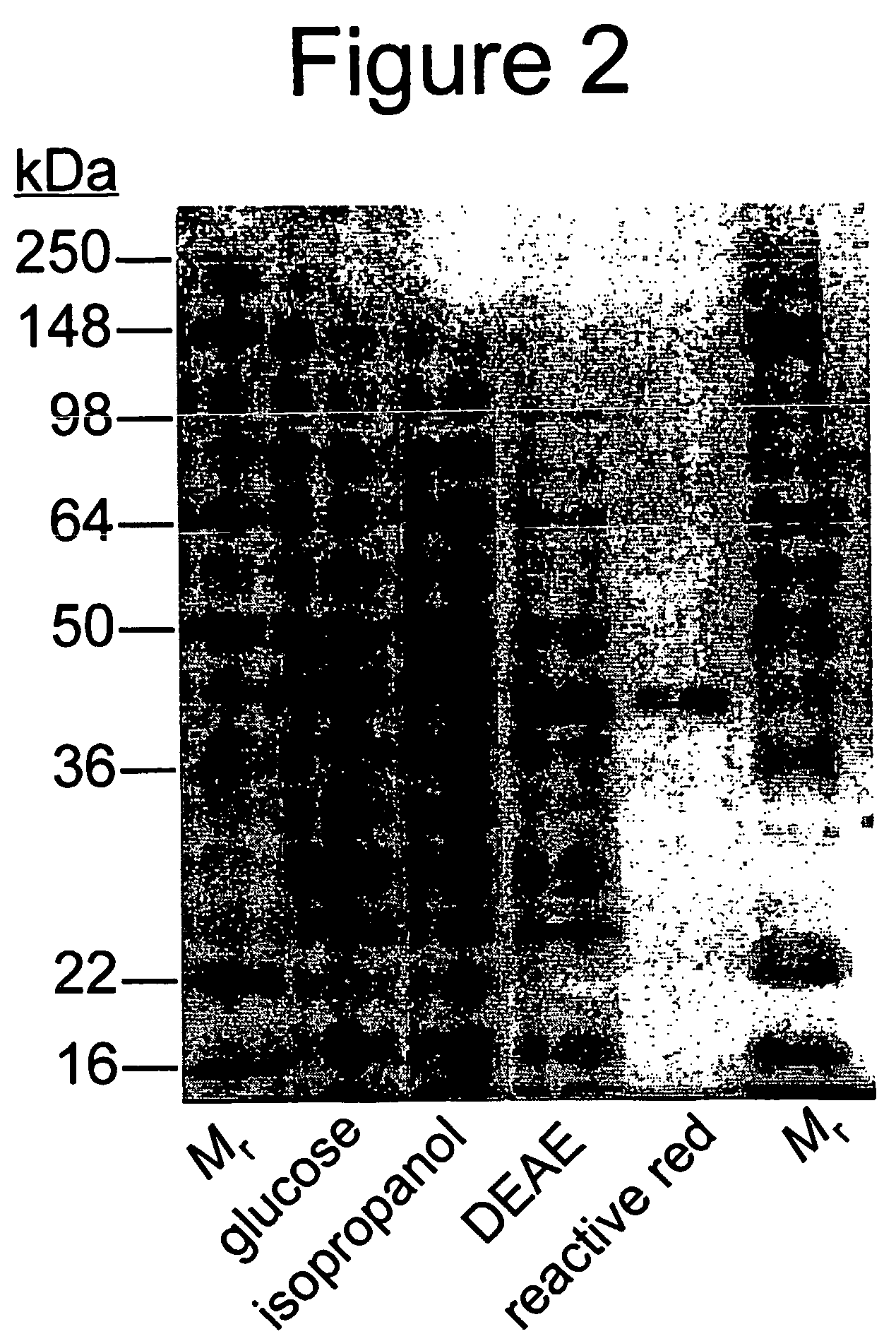
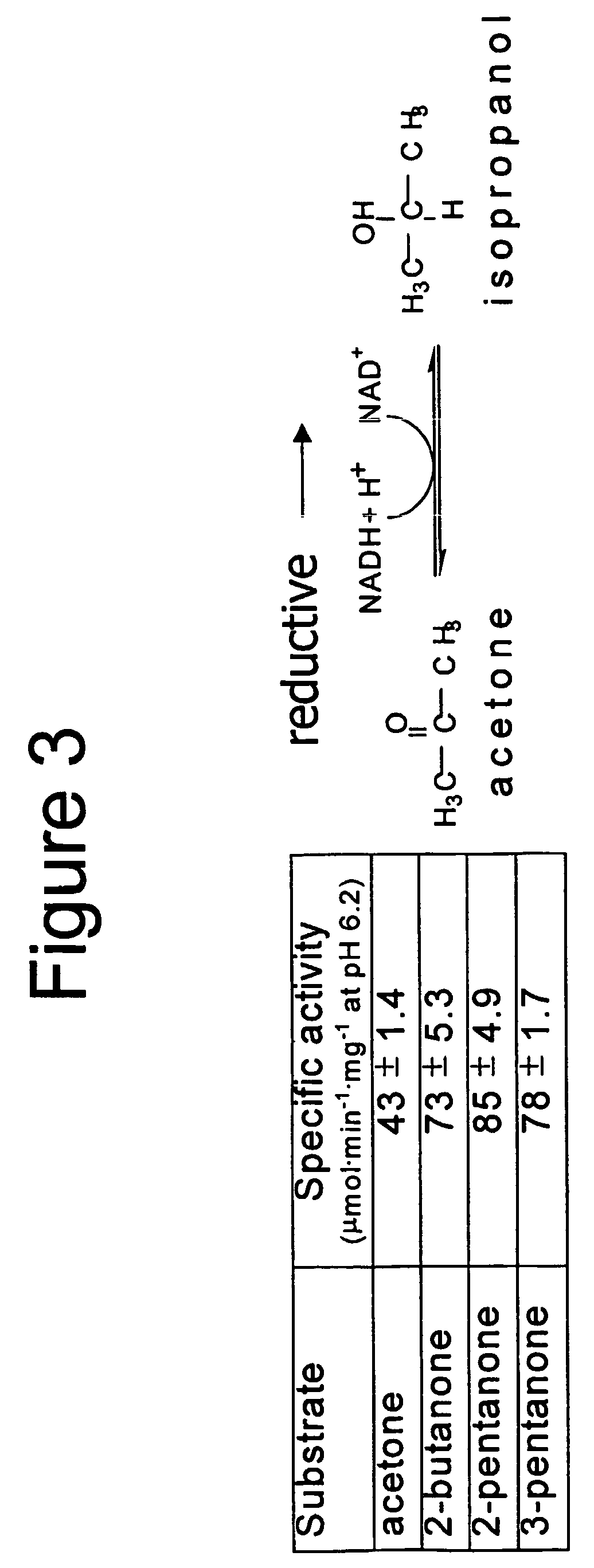
Enzyme-based system and sensor for measuring acetone
InactiveUS20050084921A1Easy to transportLow costElectrolysis componentsSugar derivativesSpecific enzymeEnzyme system
Described are enzyme systems specific for acetone and methods of using these enzyme systems to detect acetone in biological or environmental samples. Biosensors containing these enzyme systems are disclosed, in which detection of acetone may be achieved by linking electrochemical, photometric, or other detection means to one or more acetone-specific enzyme reactions or pathways. Methods of using such acetone-specific biosensors include subject management of weight loss, disease detection, and bioavailability monitoring of therapeutics.
Owner:INVOY HLDG INC
Method and apparatus for location and temperature specific drug action such as thrombolysis
Owner:INNERCOOL THERAPIES INC
Composition for odor control
ActiveUS20050115895A1Promote growthInhibition productionSpecific water treatment objectivesWater contaminantsSpecific enzymeWaste stream
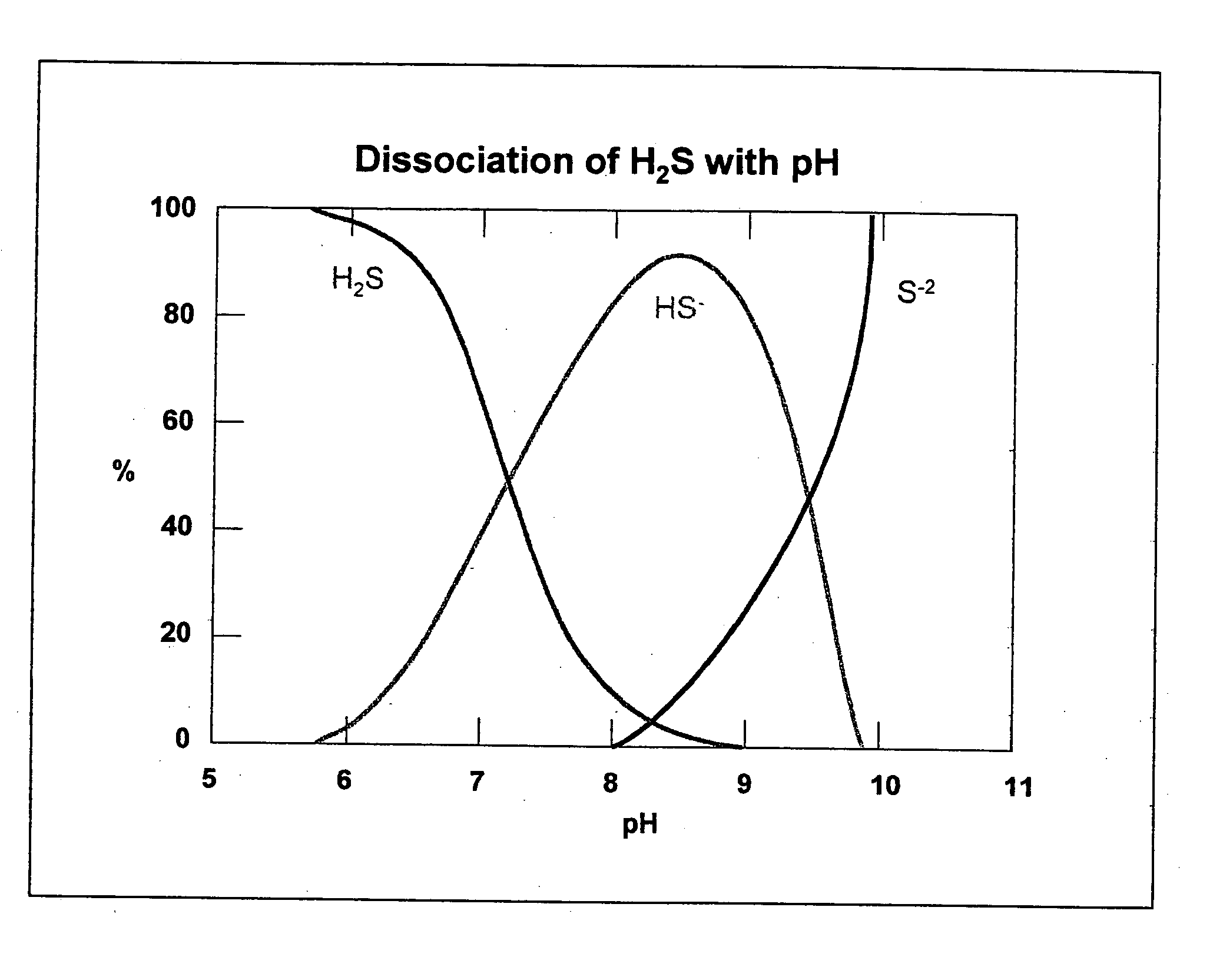
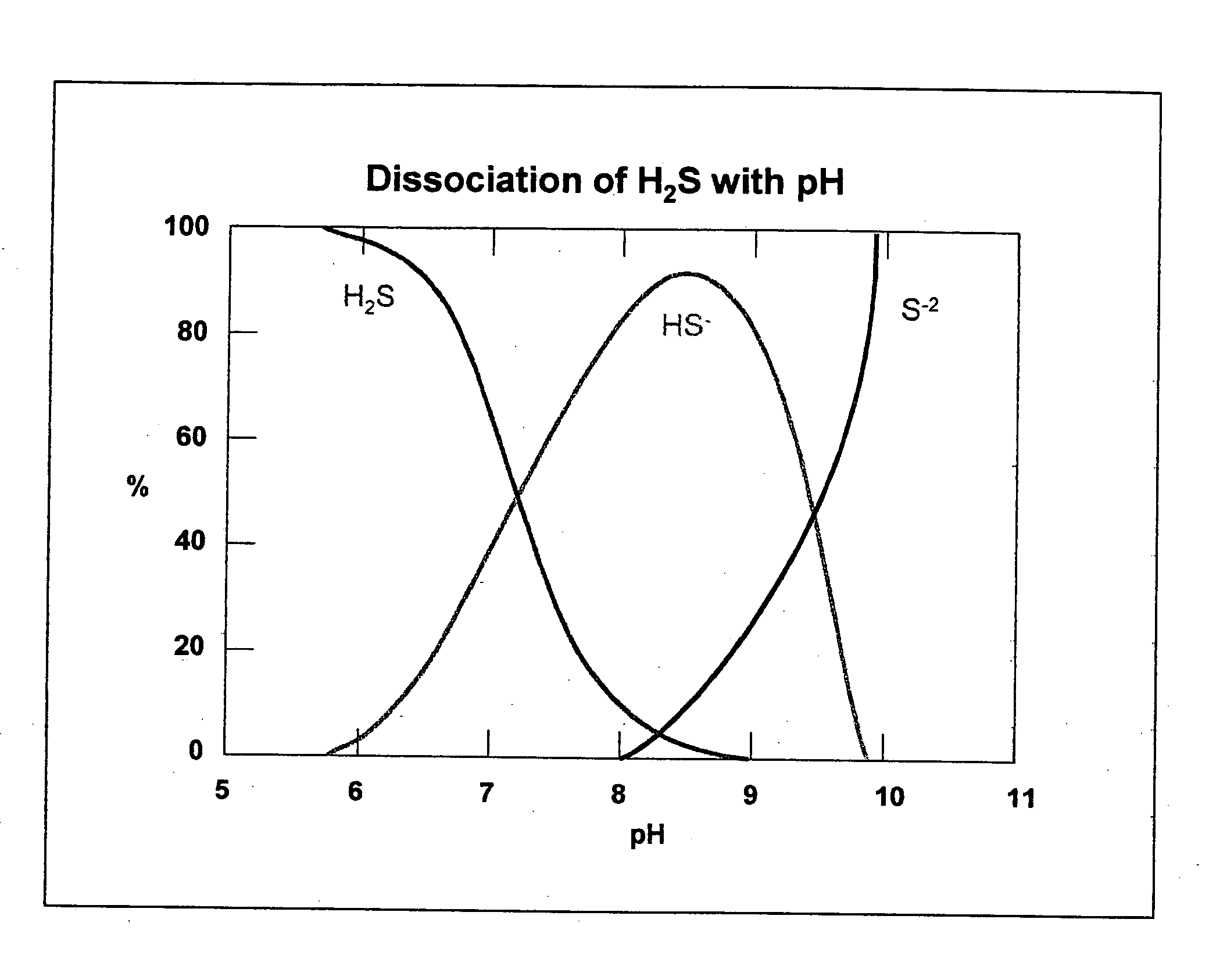
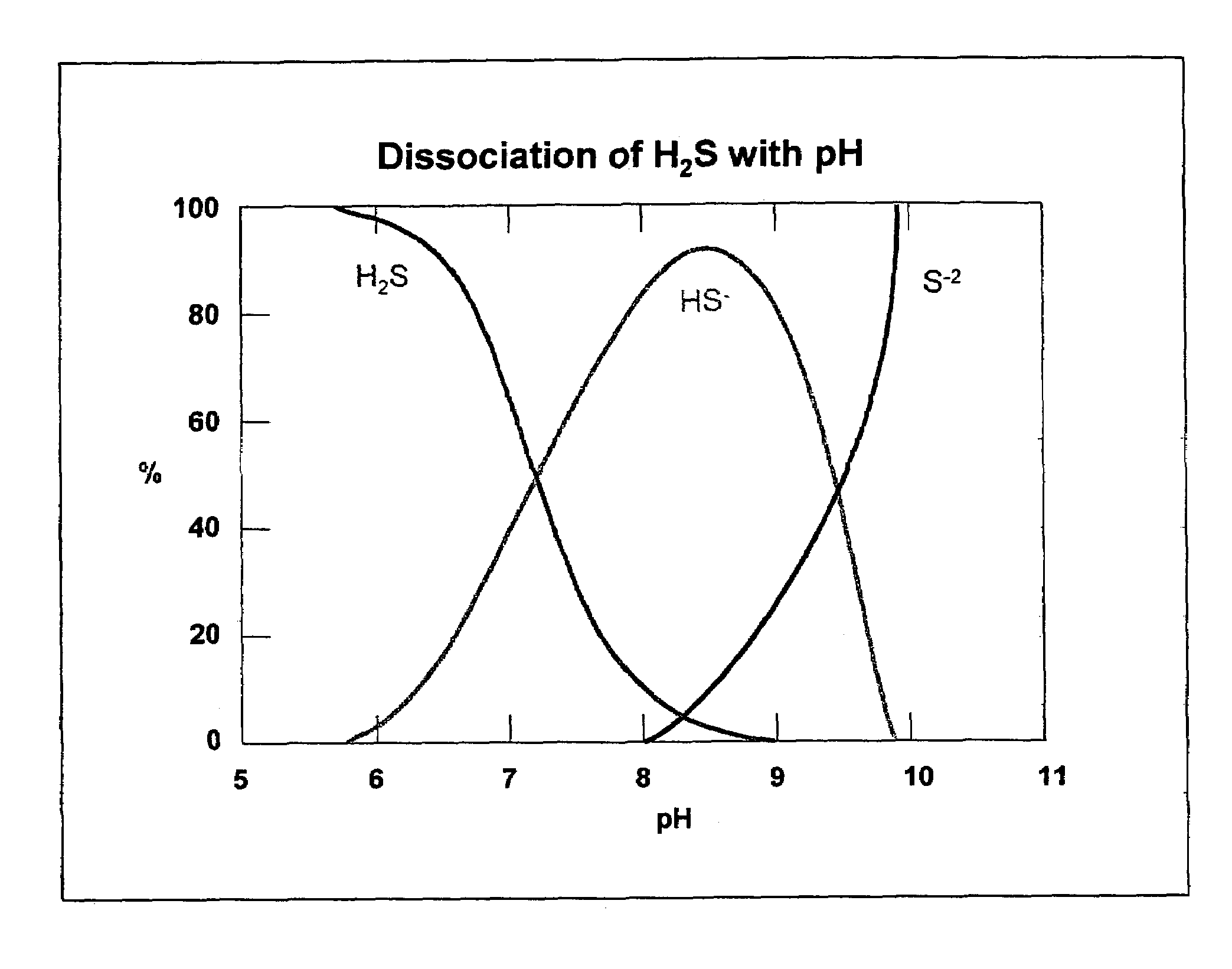
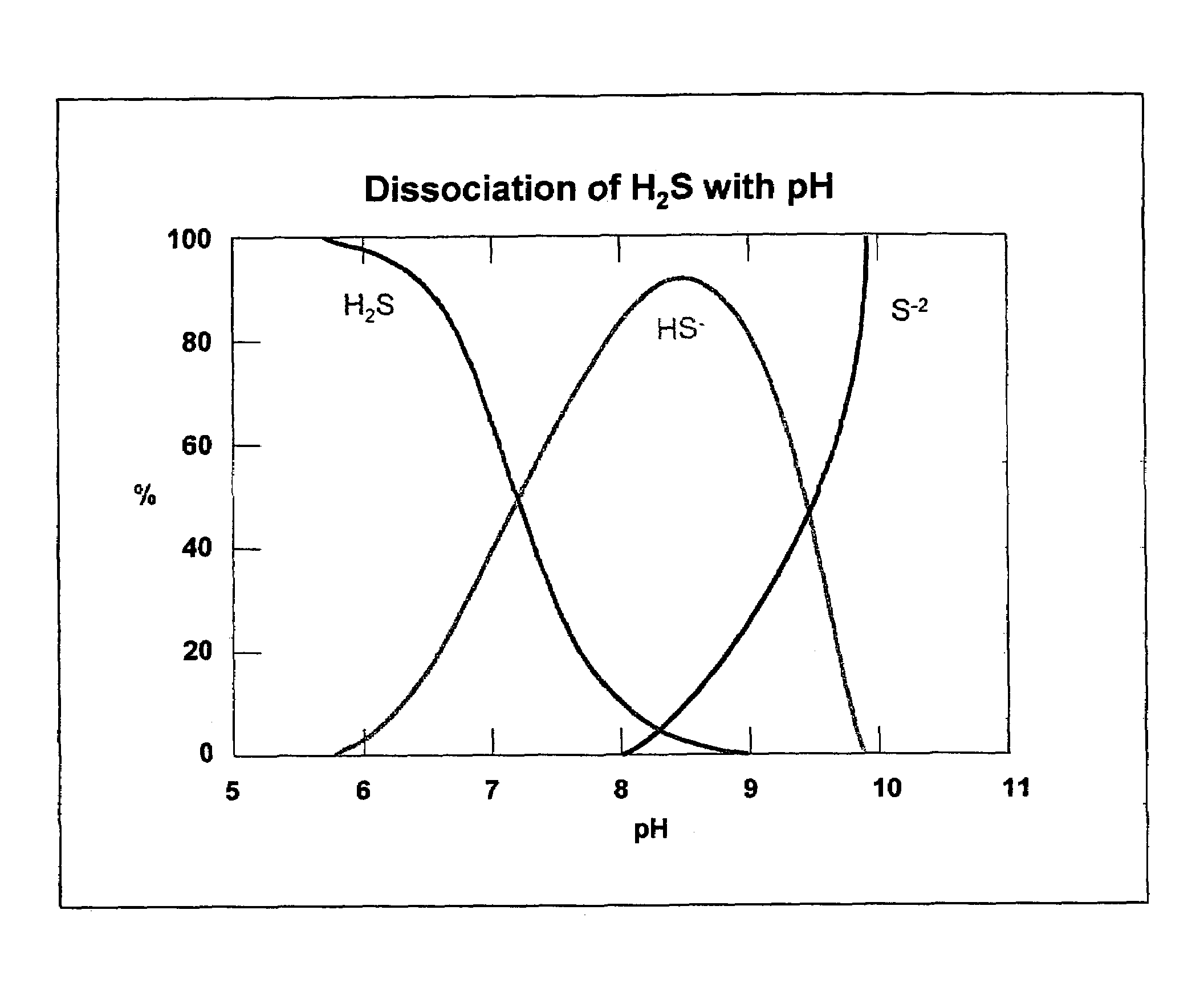
A synergistic composition is provided for controlling odor from waste products. The composition comprises a combination of nitrate salt, sulfide-consuming compound, pH-elevating compound, sulfide-oxidizing, nitrate-reducing bacteria, and sulfide-oxidizing enzyme. The method includes adding a sufficient amount of the composition to a waste stream to provide sufficient sulfide-consuming compound to effect immediate removal of sulfide. The composition incorporates a pH elevating compound, which both decreases the amount of gaseous H2S and puts the aqueous phase into a pH range where naturally occurring bacteria can more easily metabolize the sulfide. The composition also includes one or more nitrate salts which will accomplish longer term prevention of odors. Specific bacteria are incorporated into the formulation to insure that the nitrate has the right type and amount of bacteria present to prevent formation of and / or consume sulfide. Specific enzymes are incorporated into the formulation to promote oxidation of sulfide.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
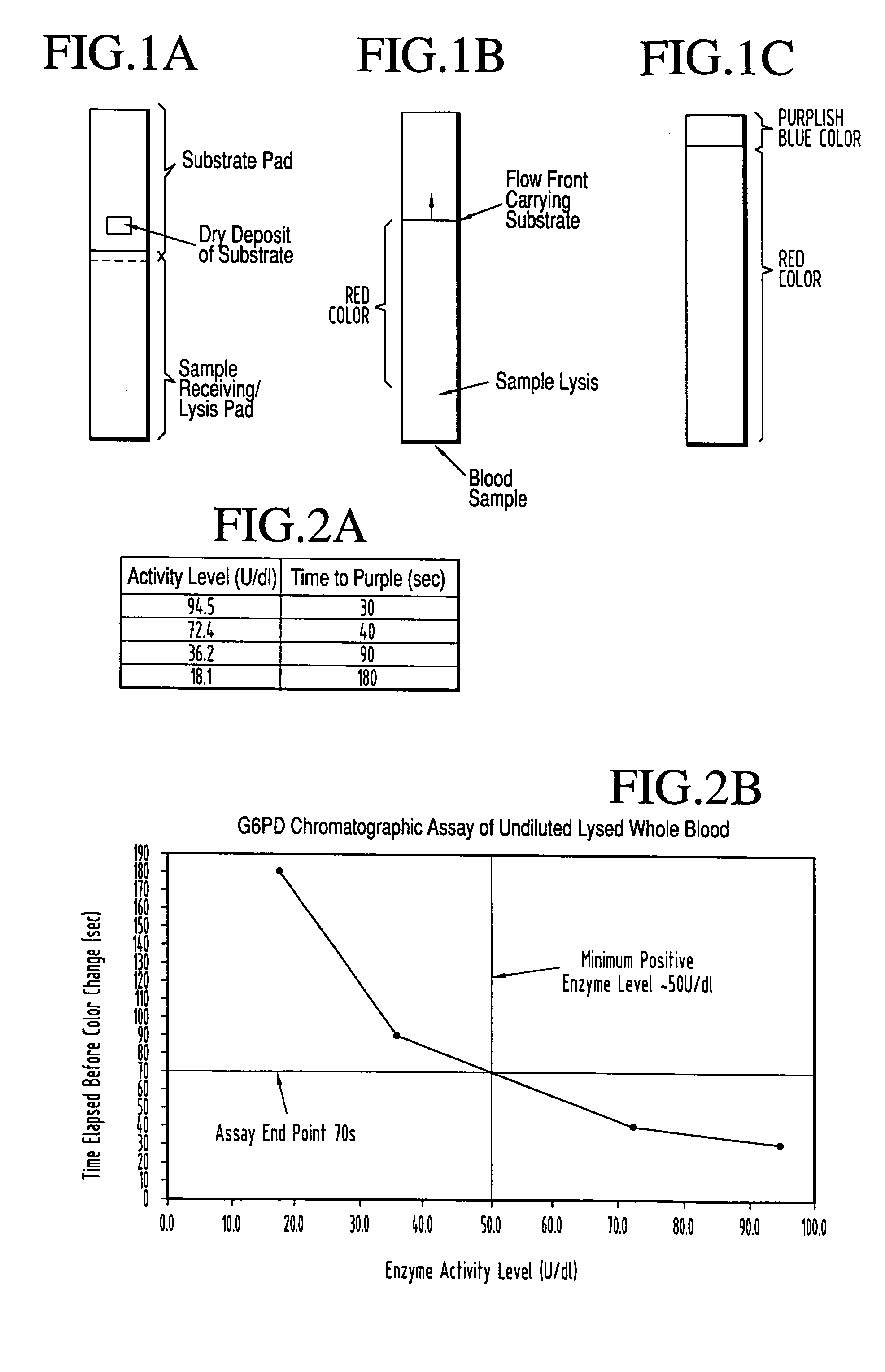
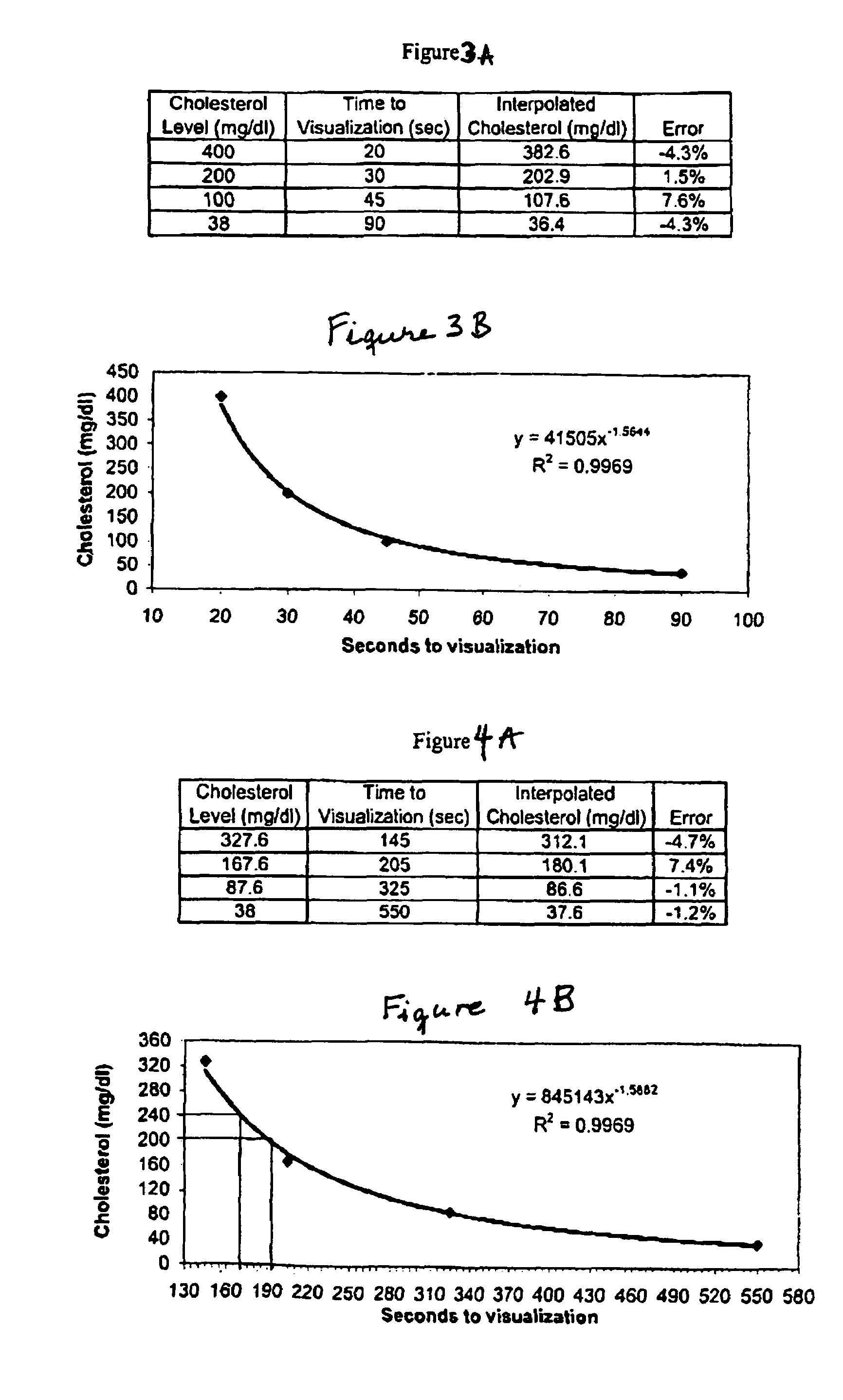
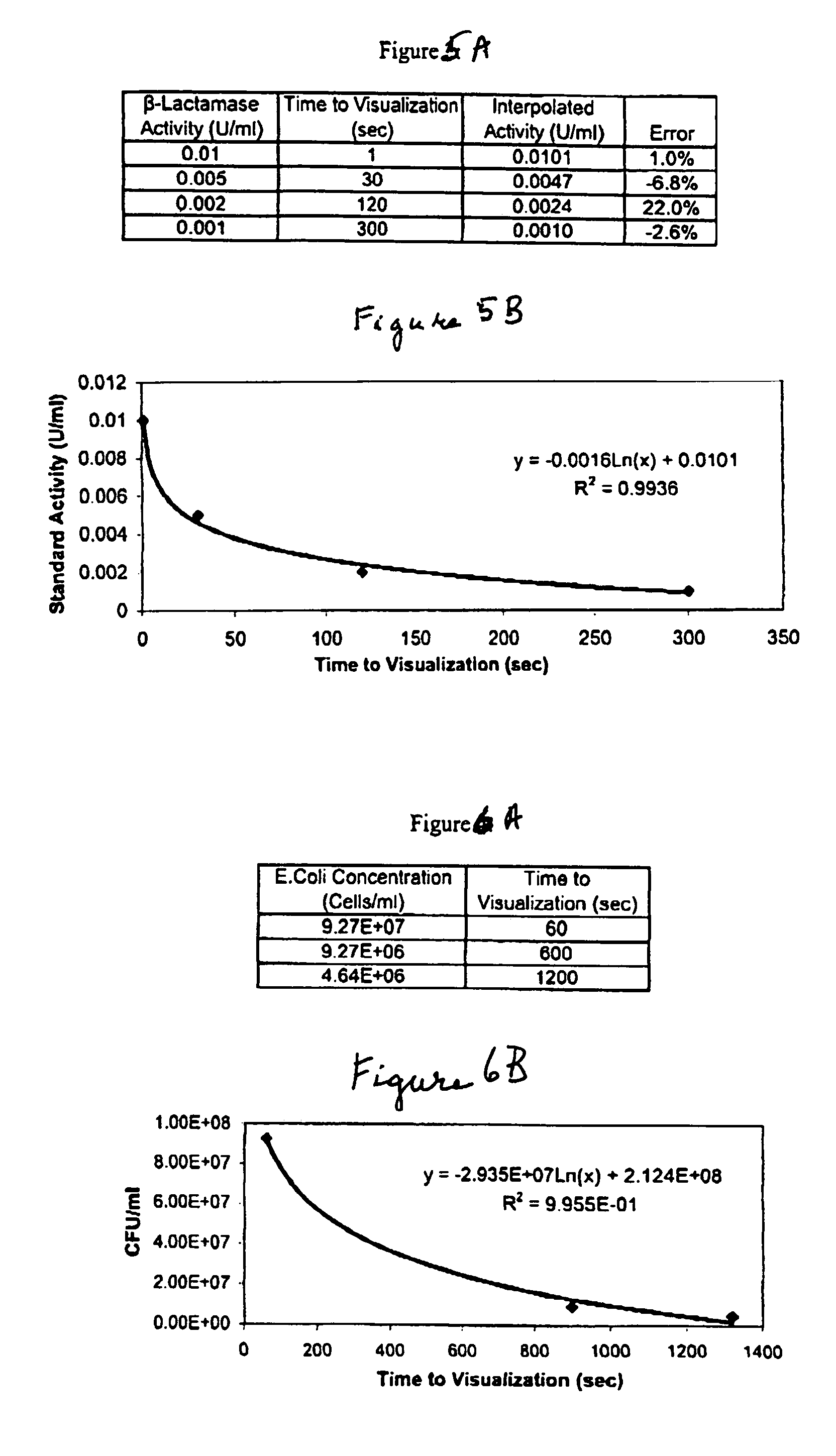
Dry chemistry, lateral flow-reconstituted chromatographic enzyme-driven assays
InactiveUS20040241779A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSpecific enzymeAssay
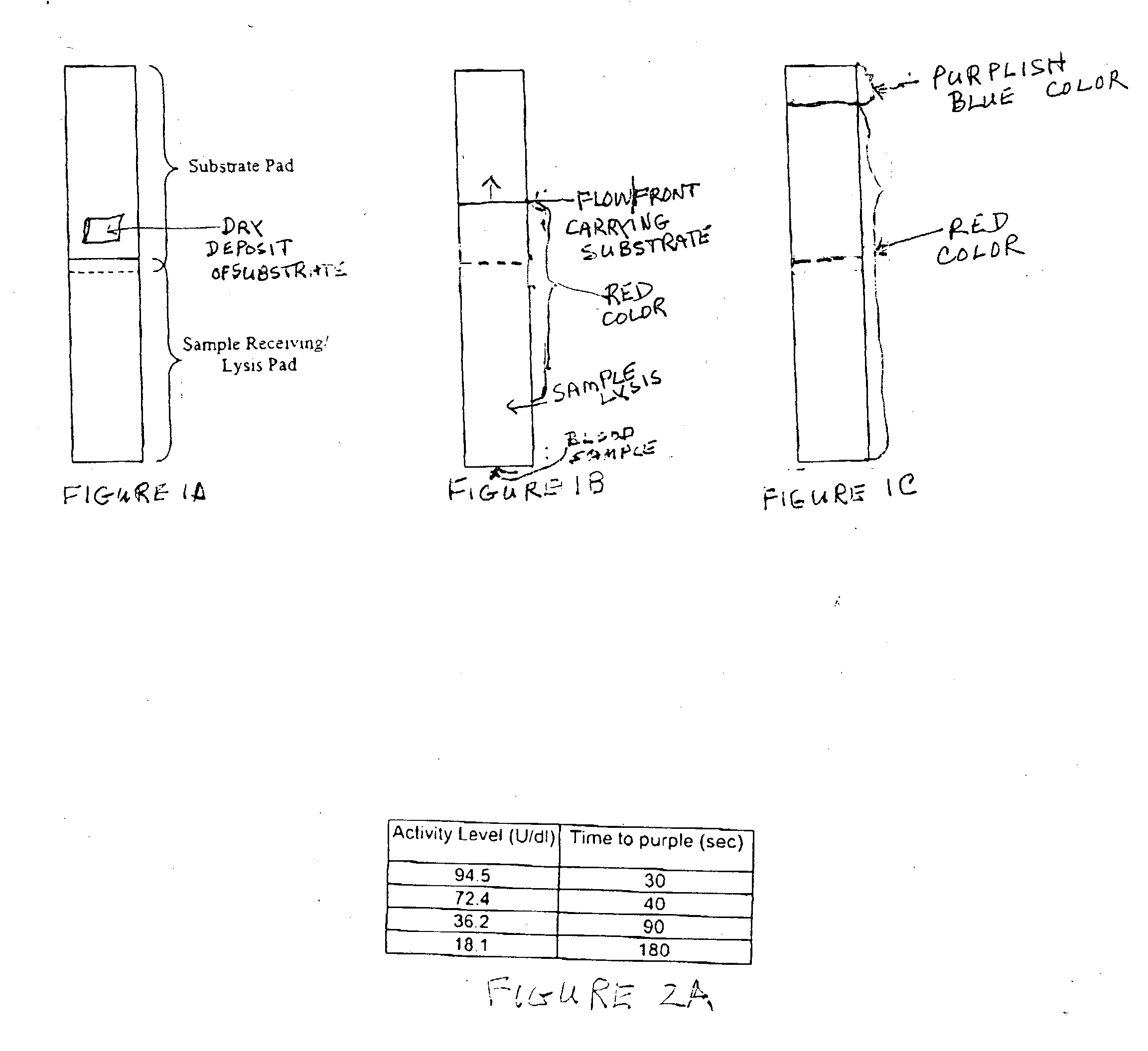
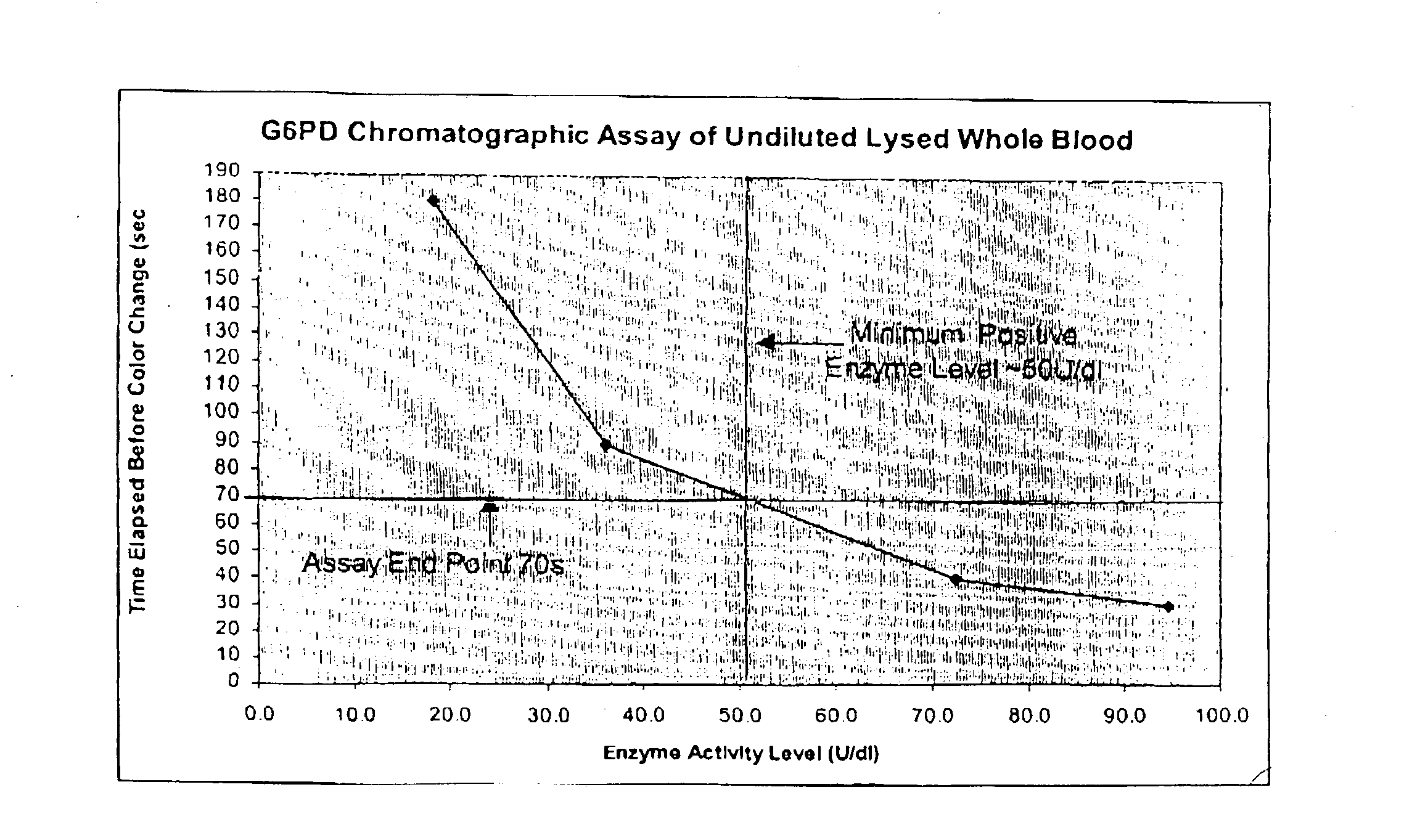
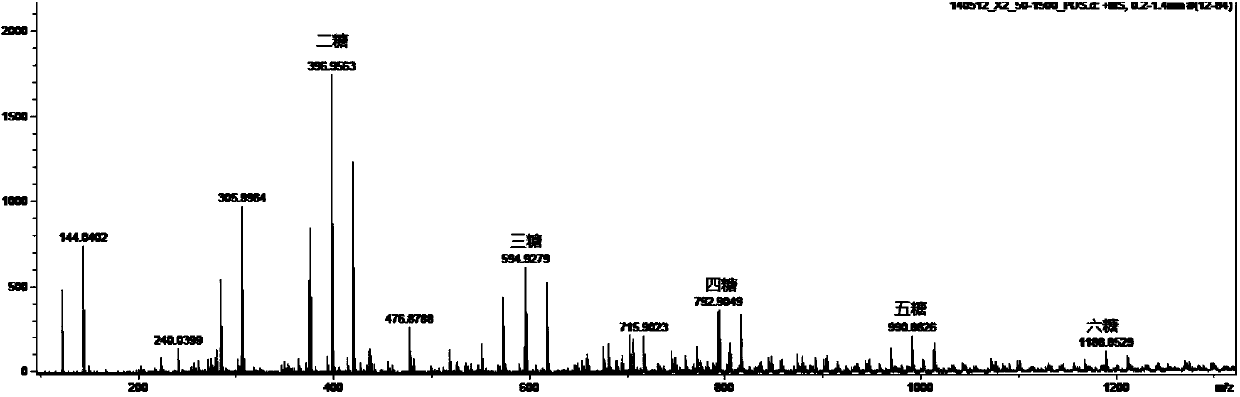
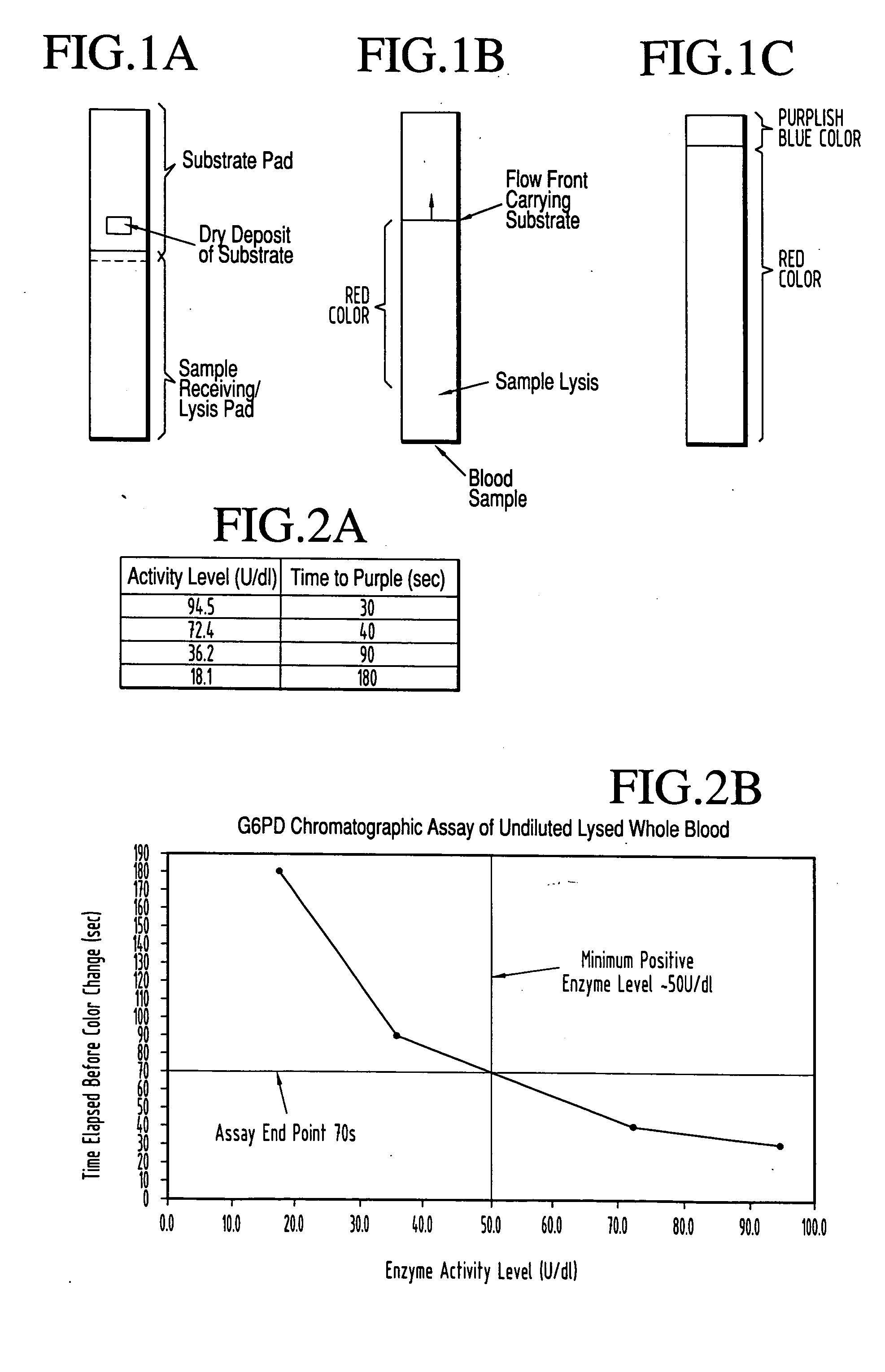
A lateral flow chromatographic assay format for the performance of rapid enzyme-driven assays is described. A combination of components necessary to elicit a specific enzyme reaction, which are either absent from the intended sample or insufficiently present therein to permit completion of the desired reaction, are predeposited as substrate in dry form together with ingredients necessary to produce a desired color upon occurrence of the desired reaction. The strip is equipped with a sample pad placed ahead of the substrate deposit in the flowstream, to which liquid sample is applied. The sample flows from the sample pad into the substrate zone where it immediately reconstitutes the dried ingredients while also intimately mixing with them and reacting with them at the fluid front. The fluid front moves rapidly into the final "read zone" wherein the color developed is read against predetermined color standards for the desired reaction. Pretreatment pads for the sample, as needed, (e.g. a lysing pad for lysing red blood cells in whole blood) are placed in front of the sample pad in the flow path as appropriate. The assay in the format of the invention is faster and easier to perform than analogous wet chemistry assays. A specific assay for glucose-phosphate dehydrogenase ("G-6PD") in this format is disclosed.
Owner:BINAX INC
MicroRNA quantitative detection analytic method by utilizing isothermal amplification to synthesize fluorescent nano silver cluster probe
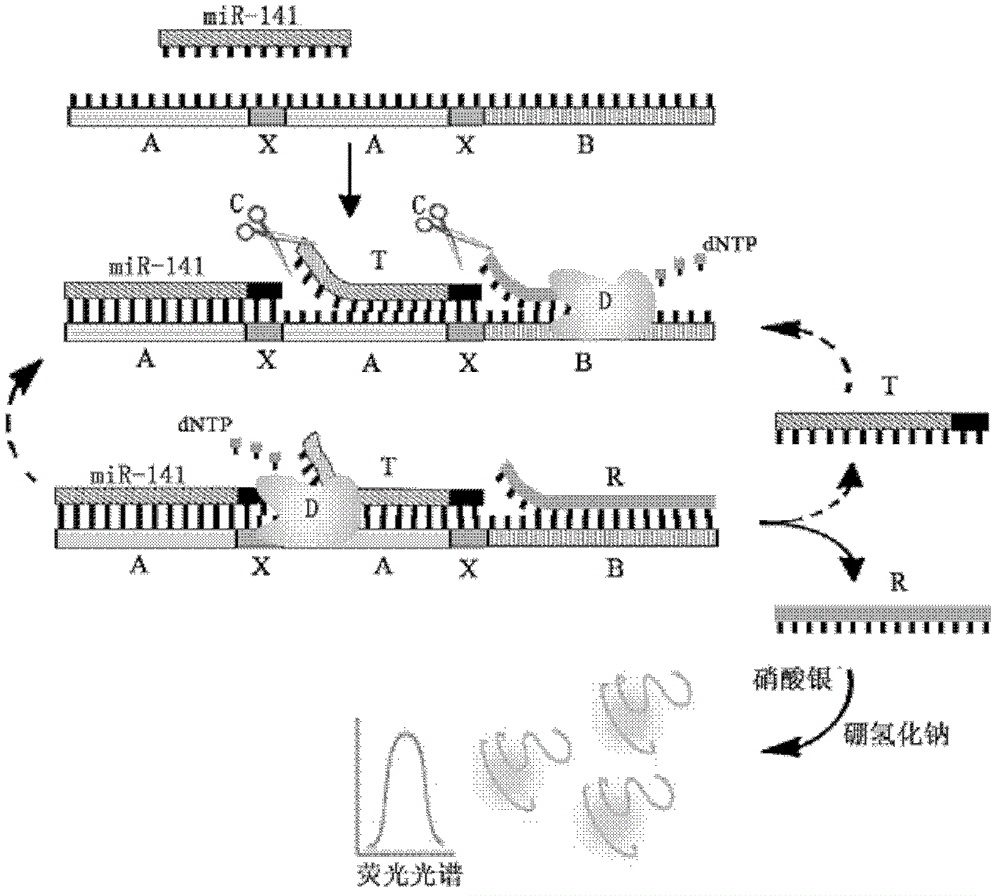
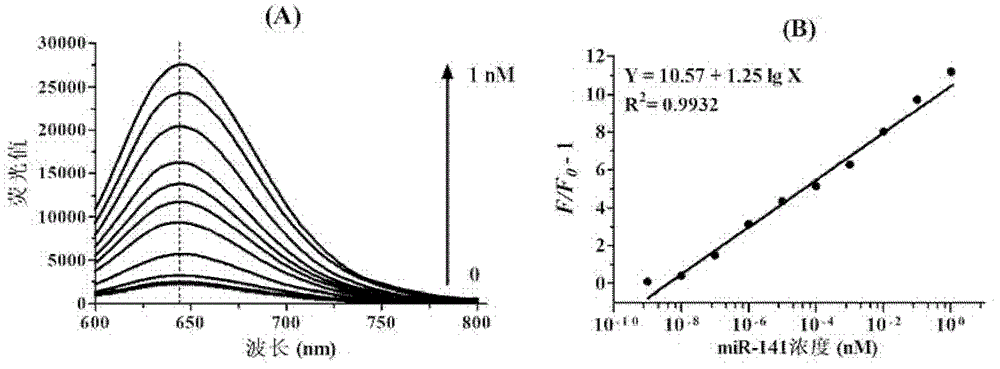
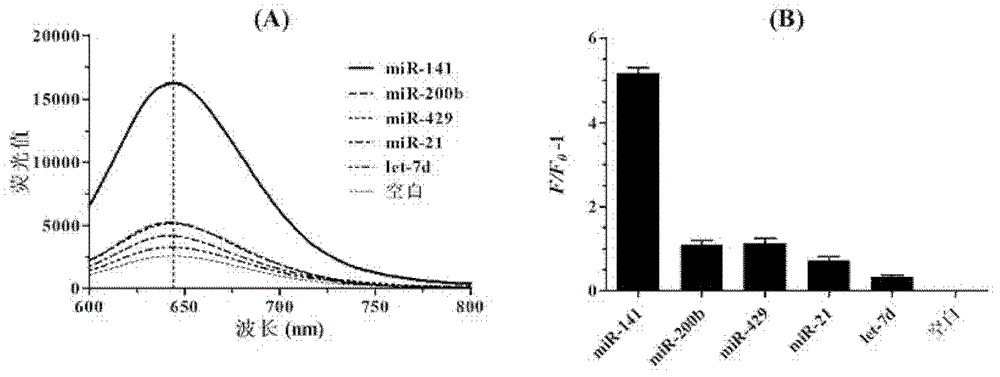
The invention provides a microRNA quantitative detection analytic method by utilizing isothermal amplification to synthesize a fluorescent nano silver cluster probe. The method is as below: a DNA amplification template containing three kinds of functional sequences is designed: a sequence binding with a target microRNA, a nicking endonuclease enzyme sequence and a DNA complementary sequence for synthesis of fluorescent nano cluster; when the target microRNA and the DNA amplification template are combined, isothermal amplification reaction and specific enzyme reaction of nicking endonuclease are induced to obtain a large number of single-stranded DNA products; the DNA sequence for synthesis of fluorescent nano silver cluster and a silver nitrate solution are employed to prepare the fluorescent nano silver cluster probe under the reduction of sodium borohydride; fluorescence signal of the reaction system are determined, and a fluorescence change value is calculated; the value is compared with a standard working curve to calculate the concentration of the target microRNA. The method has the advantages of high sensitivity, strong specificity, wide linear detection range, low background signal and simple operation, and can be widely applied to microRNA detection of biological samples such as tissue, blood or cells.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Dry chemistry, lateral flow-reconstituted chromatographic enzyme-driven assays
InactiveUS7425302B2Easy to observeHigh detection sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAdditive ingredientPeroxidase
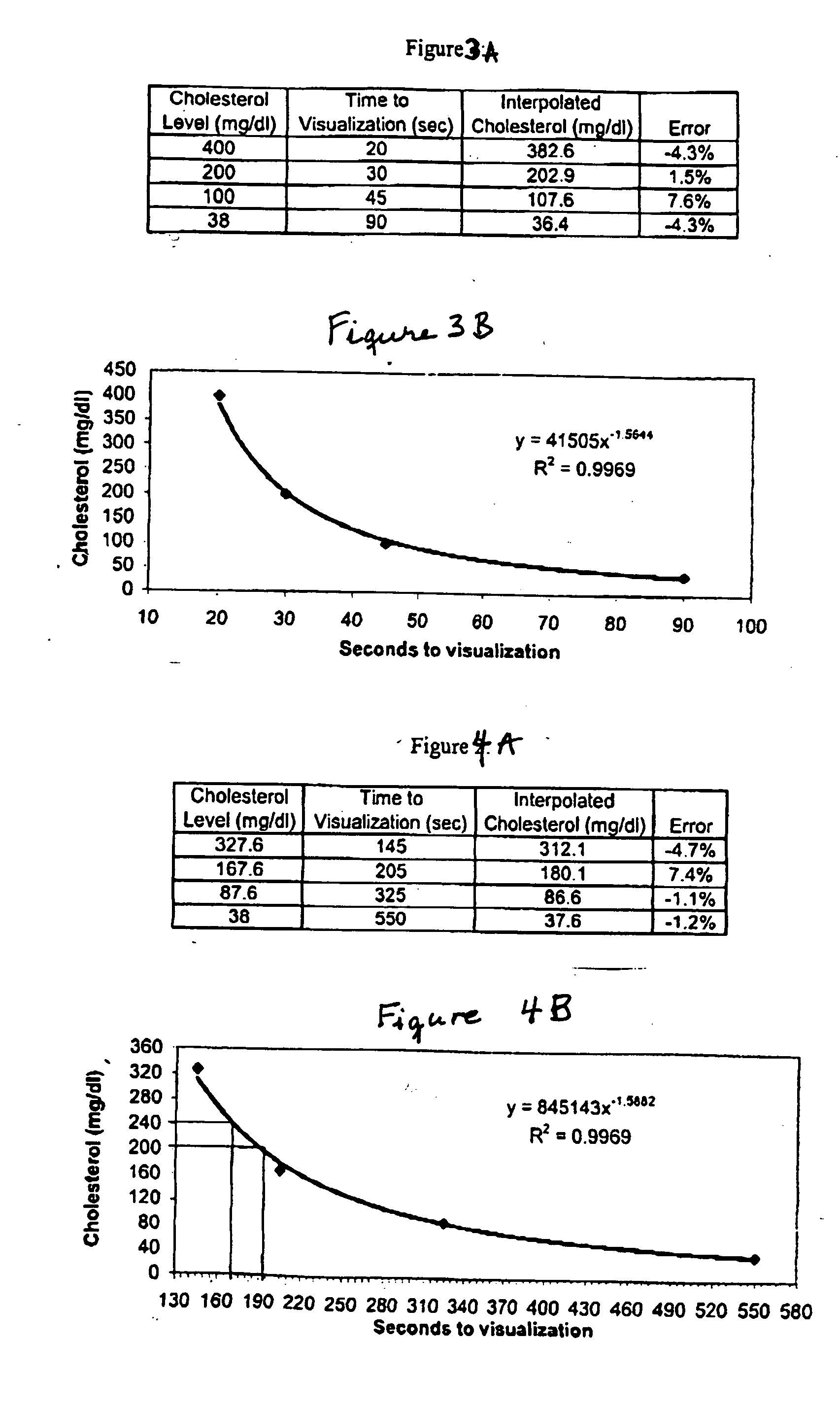
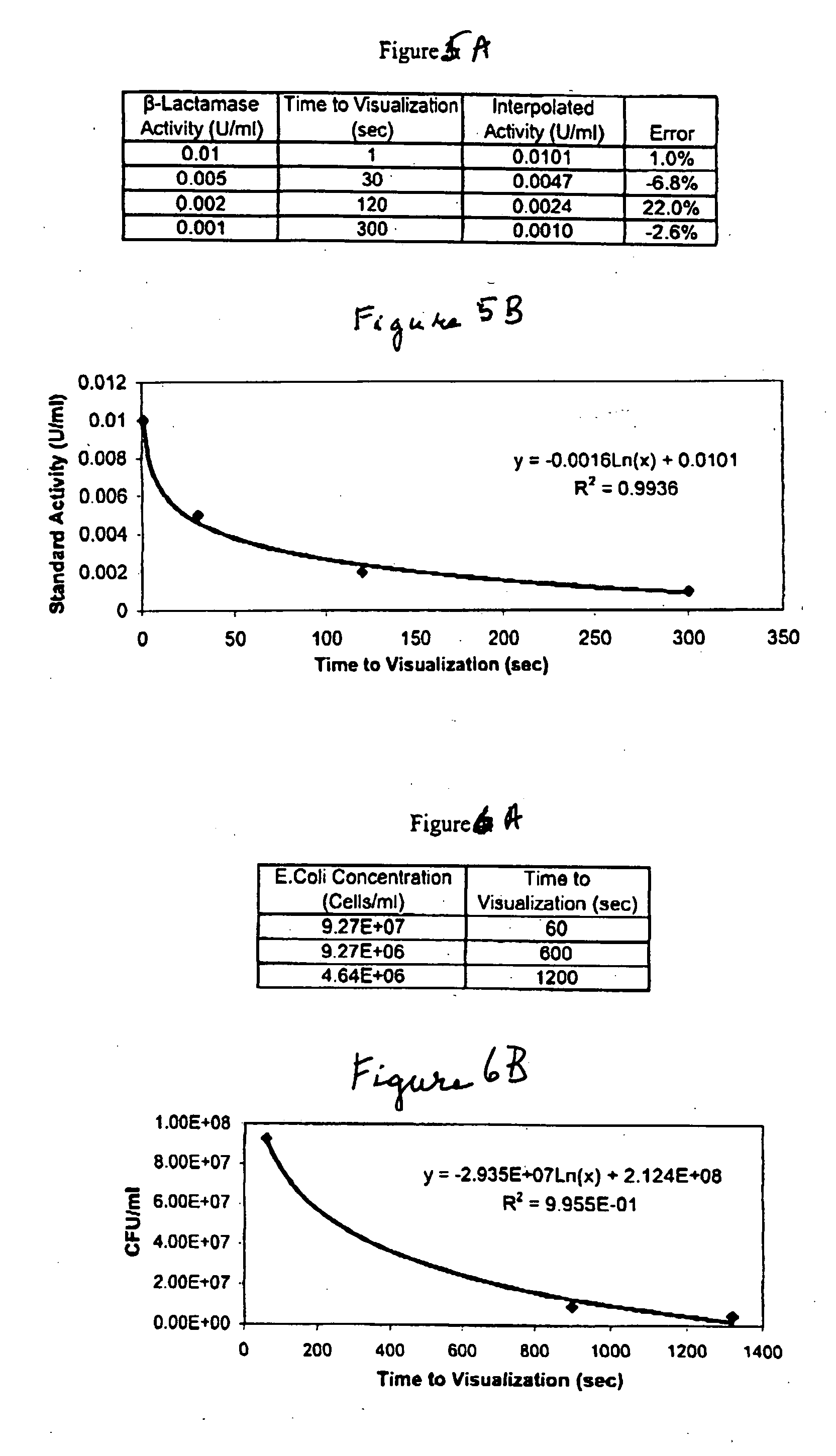
A lateral flow chromatographic assay format for the performance of rapid enzyme-driven assays is described. A combination of components necessary to elicit a specific enzyme reaction, which are either absent from the intended sample or insufficiently present therein to permit completion of the desired reaction, are predeposited as substrate in dry form together with ingredients necessary to produce a desired color upon occurrence of the desired reaction. The strip is equipped with a sample pad placed ahead of the substrate deposit in the flowstream, to which liquid sample is applied. The sample flows from the sample pad into the substrate zone where it immediately reconstitutes the dried ingredients while also intimately mixing with them and reacting with them at the fluid front. The fluid front moves rapidly into the final “read zone” wherein the color developed is read against predetermined color standards for the desired reaction. Pretreatment pads for the sample, as needed, (e.g. a lysing pad for lysing red blood cells in whole blood) are placed in front of the sample pad in the flow path as appropriate. The assay in the format of the invention is faster and easier to perform than analogous wet chemistry assays.Specific assays for glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (“G-6PD”), total serum cholesterol, β-lactamase activity and peroxidase activity are disclosed.
Owner:ABBOTT DIAGNOSTICS SCARBOROUGH INC
Enzyme-based system and sensor for measuring acetone
InactiveUS7794994B2Easy to transportLow costBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSpecific enzymeEnzyme system
Described are enzyme systems specific for acetone and methods of using these enzyme systems to detect acetone in biological or environmental samples. Biosensors containing these enzyme systems are disclosed, in which detection of acetone may be achieved by linking electrochemical, photometric, or other detection means to one or more acetone-specific enzyme reactions or pathways. Methods of using such acetone-specific biosensors include subject management of weight loss, disease detection, and bioavailability monitoring of therapeutics.
Owner:INVOY HLDG INC
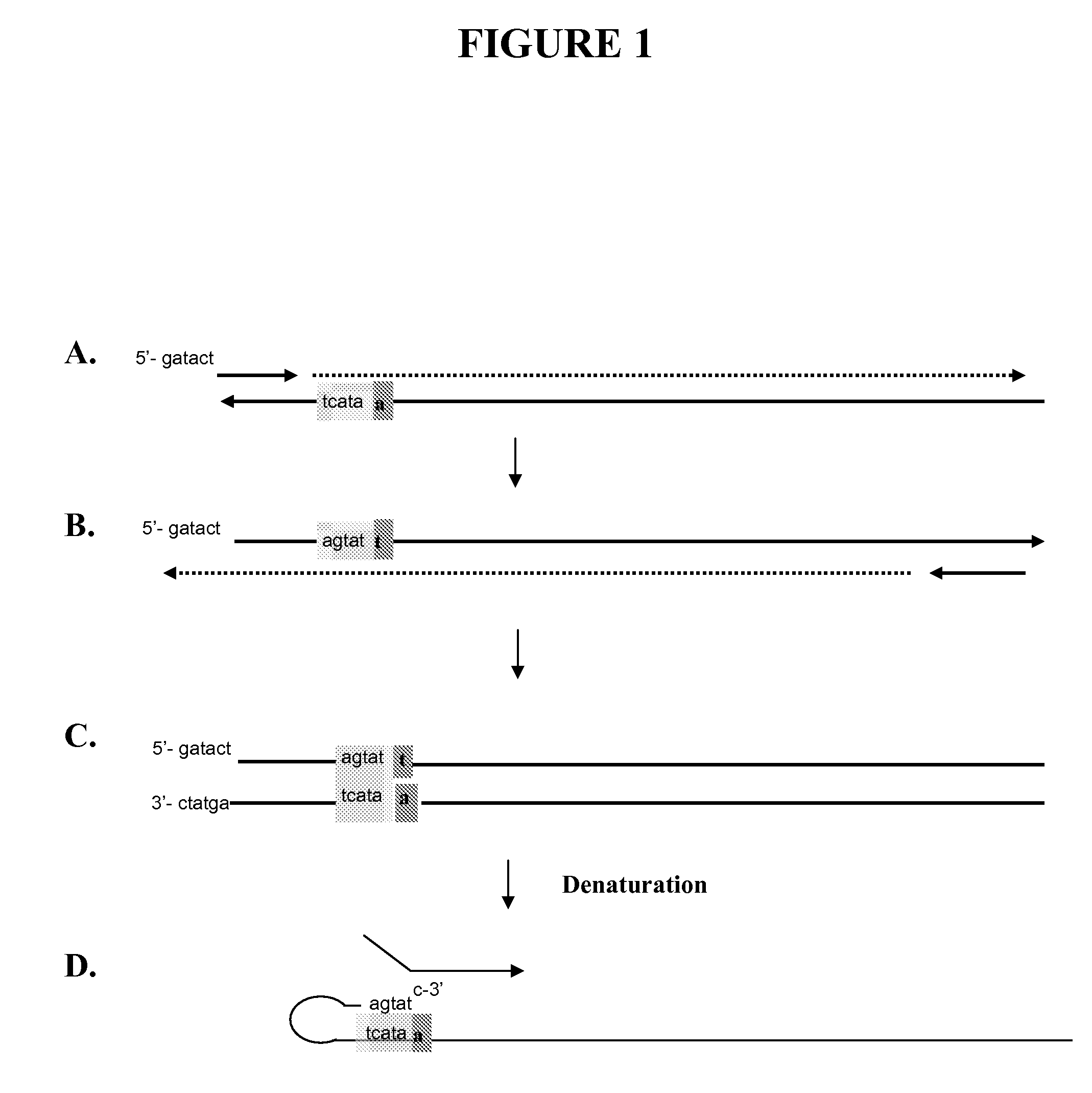
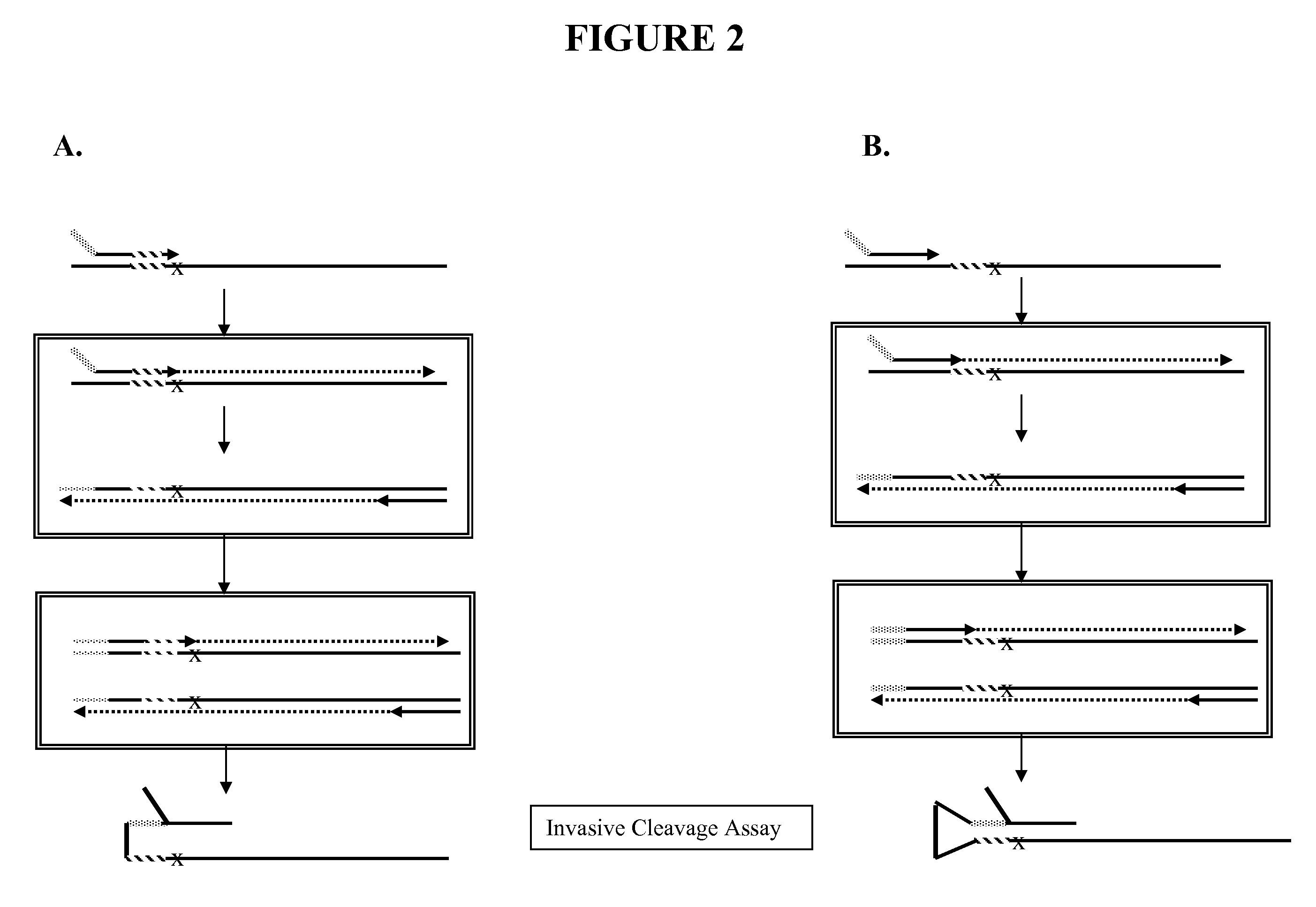
Snap-Back Primers And Detectable Hairpin Structures
The present invention provides methods, compositions, and kits comprising snap-back primers used for forming 3′ hairpin structures, 5′ hairpin structures, and double hairpin structures. The hairpin structures may be used for detecting target sequences (e.g., such as small RNA target sequence), for detecting polymorphisms in target sequences (e.g., such as polymorphisms located near the 5′ or 3′ ends of the target sequence), or other nucleic acid characterization methods. In certain embodiments, the hairpin structures form invasive cleavage structures (e.g., in combination with a probe or upstream oligonucleotide) which may be cleaved by structure-specific enzymes in order to detect the presence or absence of a particular nucleotide or nucleotide sequence.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Removing odoriferous sulfides from wastewater
ActiveUS7285217B2Promote growthInhibition productionSpecific water treatment objectivesWater contaminantsSpecific enzymeWaste stream
A synergistic composition is provided for controlling odor from waste products. The composition comprises a combination of nitrate salt, sulfide-consuming compound, pH-elevating compound, sulfide-oxidizing, nitrate-reducing bacteria, and sulfide-oxidizing enzyme. The method includes adding a sufficient amount of the composition to a waste stream to provide sufficient sulfide-consuming compound to effect immediate removal of sulfide. The composition incorporates a pH elevating compound, which both decreases the amount of gaseous H2S and puts the aqueous phase into a pH range where naturally occurring bacteria can more easily metabolize the sulfide. The composition also includes one or more nitrate salts which will accomplish longer term prevention of odors. Specific bacteria are incorporated into the formulation to insure that the nitrate has the right type and amount of bacteria present to prevent formation of and / or consume sulfide. Specific enzymes are incorporated into the formulation to promote oxidation of sulfide.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
Recombinant bacillus subtilis capable of increasing yield of N-acetylneuraminic acid
The invention discloses recombinant bacillus subtilis capable of increasing the yield of N-acetylneuraminic acid, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. Supply of phosphoenolpyruvic acid in the synthesis pathway of N-acetylneuraminic acid is increased by taking bacillus subtilis (bacillus subtilis 168 delta nagP delta nagP delta gamP delta gamA delta nagA delta nagB delta 1dh delta pta::lox72; delta ctc::p43-Gna1, pP43NMK-AGE-NeuB) as an expression host and knocking out ptsG of a glucose specific enzyme EIICBA component of a phosphotransferase system, and therefore the synthesis passway is enhanced; compared with an original strain, the recombinant bacillus subtilis has the advantages that the yield of N-acetylneuraminic acid is increased to 660 mg / L from 190 mg / L, and a foundation is laid for improving N-acetylneuraminic acid production from bacillus subtilis in metabolic engineering.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Test media and quantiative or qualitative method for identification and differentiation of biological materials in a test sample
InactiveUS20050196825A1Reduces effective shelf lifeDifficult to controlMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisPink colorEscherichia coli
A test medium and method for detecting, quantifying, identifying and differentiating up to four (4) separate biological materials in a test sample. A test medium is disclosed which allows quantifying and differentiating under ambient light aggregates of biological entities producing specific enzymes, which might include general coliforms, E. coli, Aeromonas, and Salmonella in a single test medium. A new class of nonchromogenic substrates is disclosed which produce a substantially black, non-diffusible precipitate. This precipitate is not subject to interference from other chromogenic substrates present in the test medium. In one embodiment, the substrates are selected such that E. coli colonies present in the test medium show as substantially black, general coliforms colonies show in the test medium as a blue-violet color, Aeromonas colonies present in the test medium show as a generally red-pink color, and Salmonella colonies show as a generally teal-green color. Other microorganisms and color possibilities for detection and quantification thereof are also disclosed. An inhibitor and method for making a test medium incorporating the inhibitor are disclosed.
Owner:MICROLOGY INC
Diagnostic method of mucopolysaccharidoses
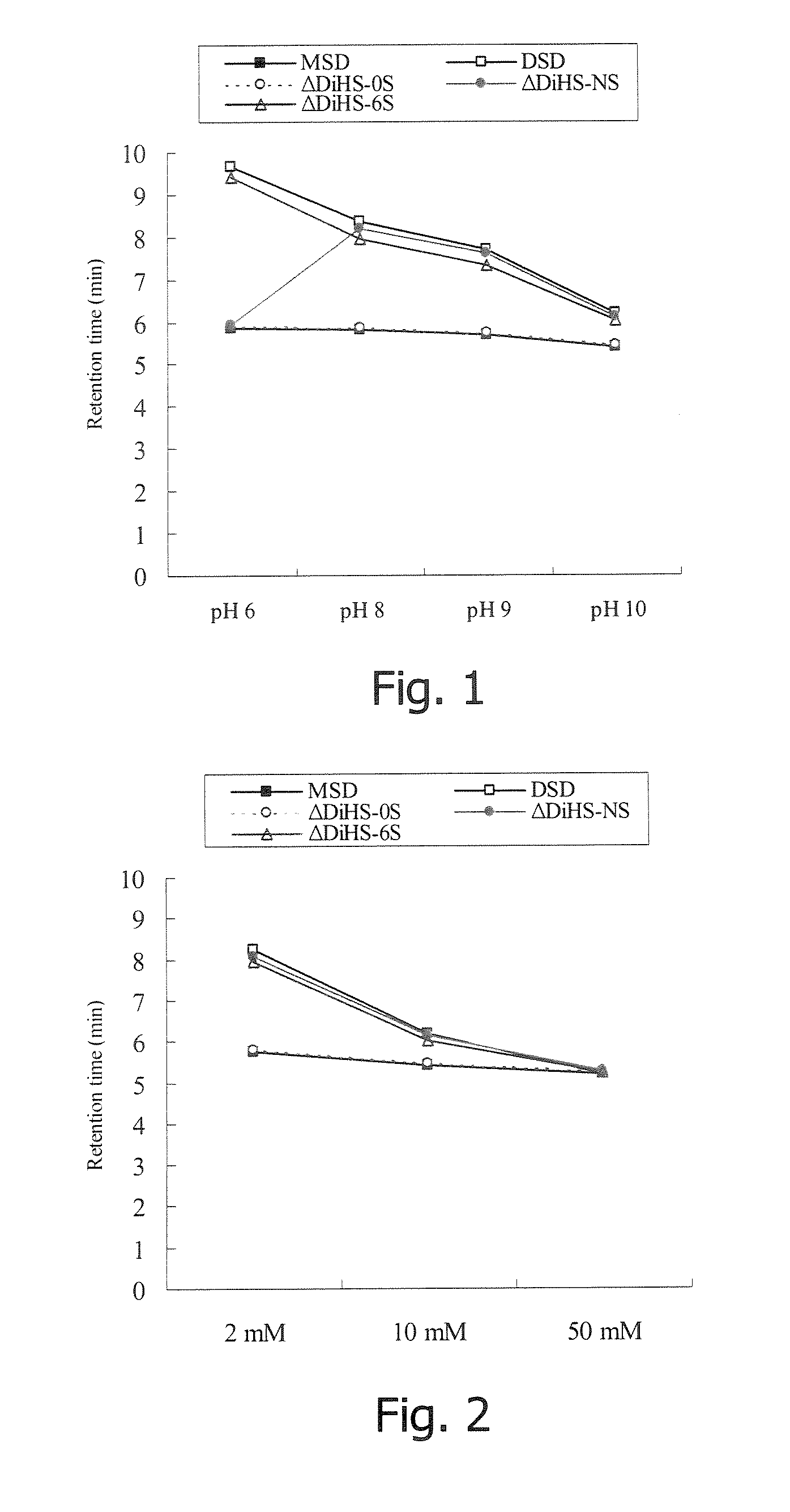
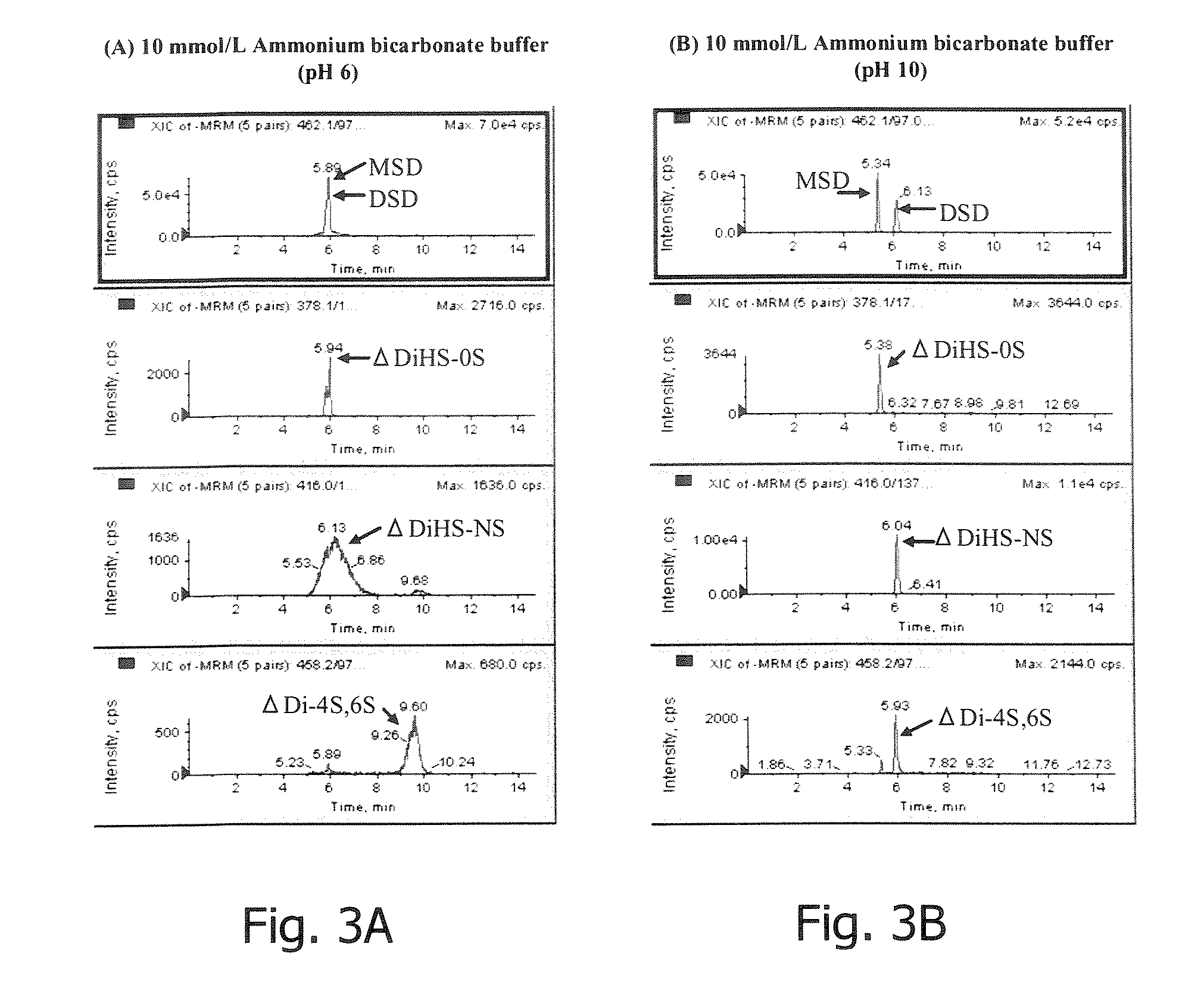
InactiveUS20070161074A1Accurate and highly sensitive and convenient diagnosisAvoid developmentMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisSpecific enzymeUltrafiltration
Provision of a method for accurate diagnosis of mucopolysaccharidoses, including determining the level of glycosaminoglycan in a biological sample with high sensitivity and with ease. A diagnostic method of mucopolysaccharidoses including the following steps (1) and (2): (1) a step including (a) filtering a biological sample with an ultrafiltration filter, digesting the sample on the filter with a glycosaminoglycan-specific enzyme, centrifuging the digested sample to obtain a filtrate, or (b) digesting a biological sample with a glycosaminoglycan-specific enzym, filtering the sample with an ultrafiltration filter to obtain a filtrate, applying the filtrate obtained by (a) or (b) to a liquid chromatograph / mass spectrometer, and analyzing glycosaminoglycan-derived disaccharides, and (2) a step of diagnosing a subject as having mucopolysaccharidosis, chemically diagnosing effect of treatment of mucopolysaccharidoses, or determining types of mucopolysaccharidoses, on the basis of quantitative concentration data and disaccharide composition obtained in step (1).
Owner:SAINT LOUIS UNIVERSITY
Fermentation material for composite microorganism and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101186896AImprove palatabilityIncrease profitFungiBacteriaCell culture mediaEnzyme inducer
The invention relates to a composite microorganism ferment material which is characterized in that production strains select production strains of which the growth rate is quick and the enzyme production quantity is large by combining with through ray inducement and production performance detection. The processing technique employs innovative symbiosis compatibility design of probiotics and multi-compound fermentation technology, the number of the live probiotics in the products achieves five billion per gram, and the products simultaneously contain polyoses, polypeptide, organized enzyme, organic acid, phytosterin, triterpennoids saponin and the like active metabolite. Specific enzyme producing inducer is added to growth medium, the latest single creature venting valve is employed on the package, which not only can be added to complete feed of livestock or poultry but also can be directly added into feedstuff, thereby effectively promoting breakdown and absorption of giant molecule nutrient substance in the intestinal canal of livestock or poultry, thereby eliminating the action of anti-nutritional factors in the feedstuff, remarkably increasing utilization ratio of the feedstuff, and reducing the feeding cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHUANGBO ECOLOGICAL ENG
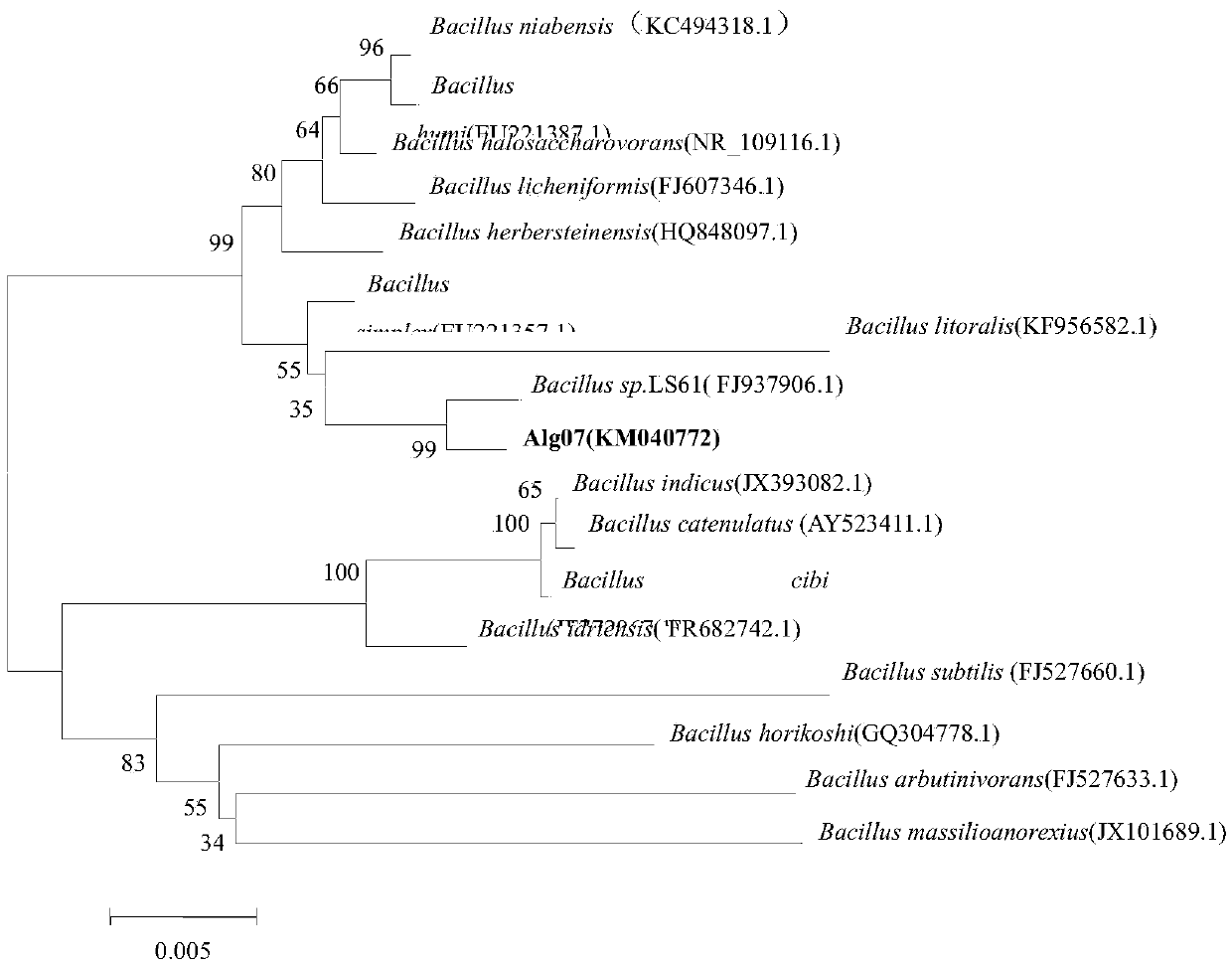
Bacillus sp capable of producing alginate lyase and application thereof
ActiveCN104195080AIncrease enzyme activitySimple nutritional requirementsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSpecific enzymeAlginate lyase
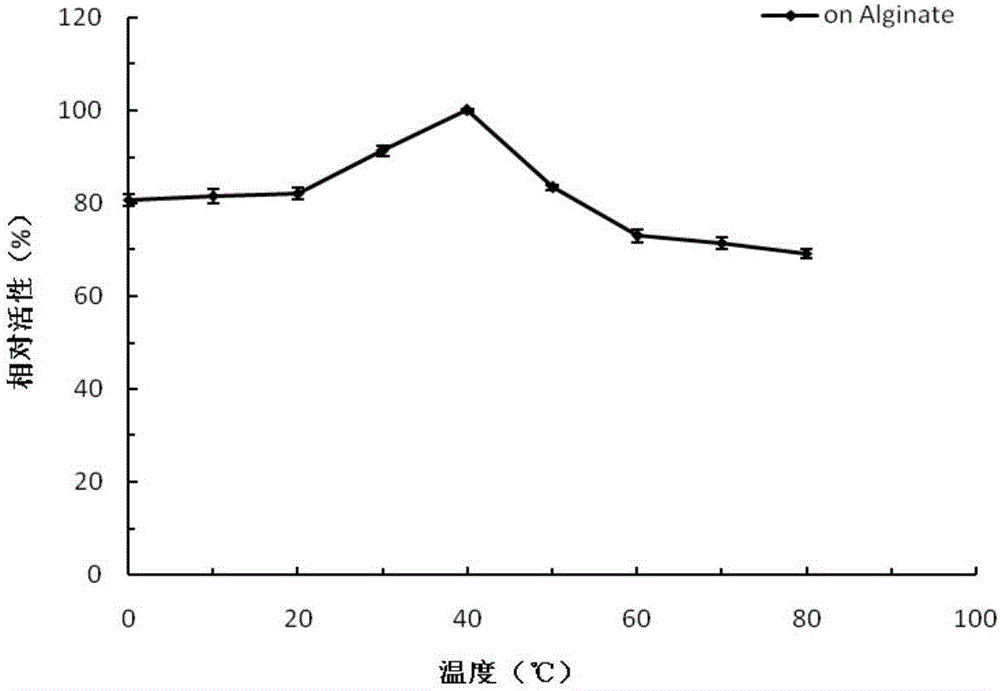
The invention provides Bacillus sp Alg07 capable of producing an alginate lyase. The preservation number of the Bacillus sp Alg07 is CGMCC No.9391. The Bacillus sp Alg07 provided by the invention has the advantages that requirement on nutrition is low and fermentation time is short; a crude enzyme is easily prepared, and the crude enzyme can be obtained through centrifugation; the alginate lyase produced by the Bacillus sp Alg07 has high enzyme activity, the specific enzyme activity of an unpurified crude enzyme can reach 20000-40000 U / mg (563U / mL); the alginate lyase produced by the Bacillus sp Alg07 has good stability, is not obviously changed in enzyme activity after being preserved at 40 DEG C for 24 hours and is high and stable in enzyme activity at pH of 5.5-8.5; and the produced alginate lyase is capable of degrading sodium alginate to generate alginate-derived oligosaccharide with biological activity.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Methods of formulating enzyme cocktails, enzyme cocktails for the removal of egg-based and grass-based stains and/or soils, compositions and products comprising same
InactiveUS20050059567A1Non-surface-active detergent compositionsDetergent compounding agentsSpecific enzymeChromatography
Methods of formulating enzyme cocktails based on the presence of enzyme-hydrolysable components in a target stain and / or soil. More specifically, the formulation of an enzyme cocktail comprising a specific enzyme for each component in a target stain and / or soil, optionally wherein each enzyme is incorporated at a level corresponding to the level of an enzyme-hydrolysable component in said target stain and / or soil. Further, enzyme cocktails for removing egg-based and grass-based stains, optionally formulated in accordance with the methods disclosed herein. Moreover, compositions and products comprising the enzyme cocktails disclosed herein and methods of using same.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Dry chemistry, lateral flow-reconstituted chromatographic enzyme-driven assays
ActiveUS20040203086A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPeroxidaseAdditive ingredient
A lateral flow chromatographic assay format for the performance of rapid enzyme-driven assays is described. A combination of components necessary to elicit a specific enzyme reaction, which are either absent from the intended sample or insufficiently present therein to permit completion of the desired reaction, are predeposited as substrate in dry form together with ingredients necessary to produce a desired color upon occurrence of the desired reaction. The strip is equipped with a sample pad placed ahead of the substrate deposit in the flowstream, to which liquid sample is applied. The sample flows from the sample pad into the substrate zone where it immediately reconstitutes the dried ingredients while also intimately mixing with them and reacting with them at the fluid front. The fluid front moves rapidly into the final "read zone" wherein the color developed is read against predetermined color standards for the desired reaction. Pretreatment pads for the sample, as needed, (e.g. a lysing pad for lysing red blood cells in whole blood) are placed in front of the sample pad in the flow path as appropriate. The assay in the format of the invention is faster and easier to perform than analogous wet chemistry assays. Specific assays for glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase ("G-6PD"), total serum cholesterol, beta-lactamase activity and peroxidase activity are disclosed.
Owner:ABBOTT DIAGNOSTICS SCARBOROUGH INC
Method for detecting pig plague virus specific antibody and its ELISA reagent kit
InactiveCN101144818AGuaranteed specificityGuaranteed Differential DiagnosisMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorElisa kitSwine Fever Virus
The invention discloses a method for detecting the specific antibody of classical swine fever virus and a special ELISA kit thereof. The kit includes a classical swine fever virus antigen and an enzyme-labeled classical swine fever virus single-epitope specific antibody; the said swine fever virus antigen is a polypeptide containing one or more than one amino acid residue sequence described in sequence 1. The detection reagent of the classical swine fever virus specific antibody of the present invention can carry out effective detection to the classical swine fever virus specific antibody by solid-phase antigen competition ELISA (blocking method); The B cell epitope ensures the differential diagnosis, and the high degree of conservation of the epitope among various strains ensures the specificity of detection.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +2
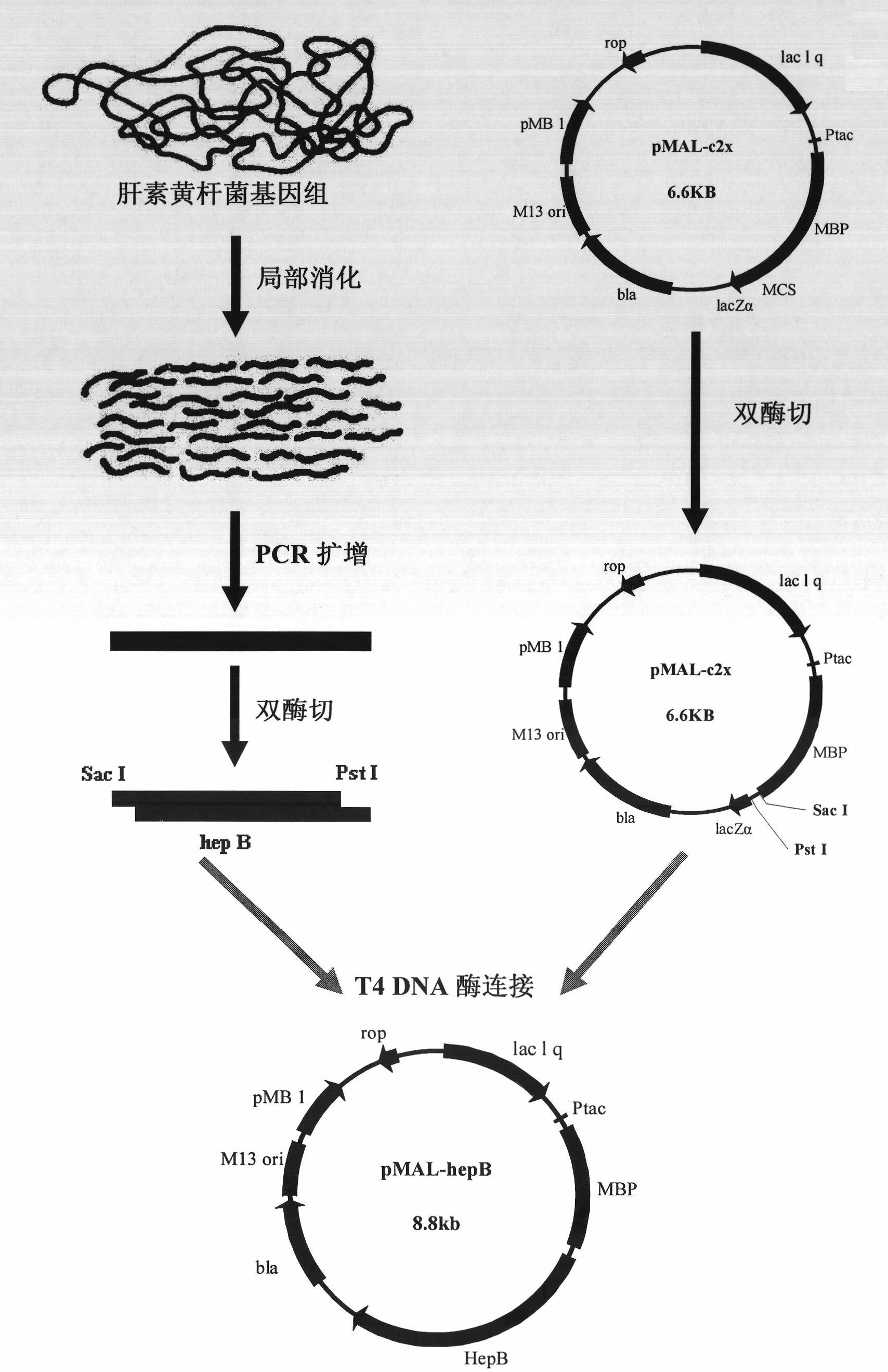
Heparanase II fusion protein and coding gene and expression method thereof
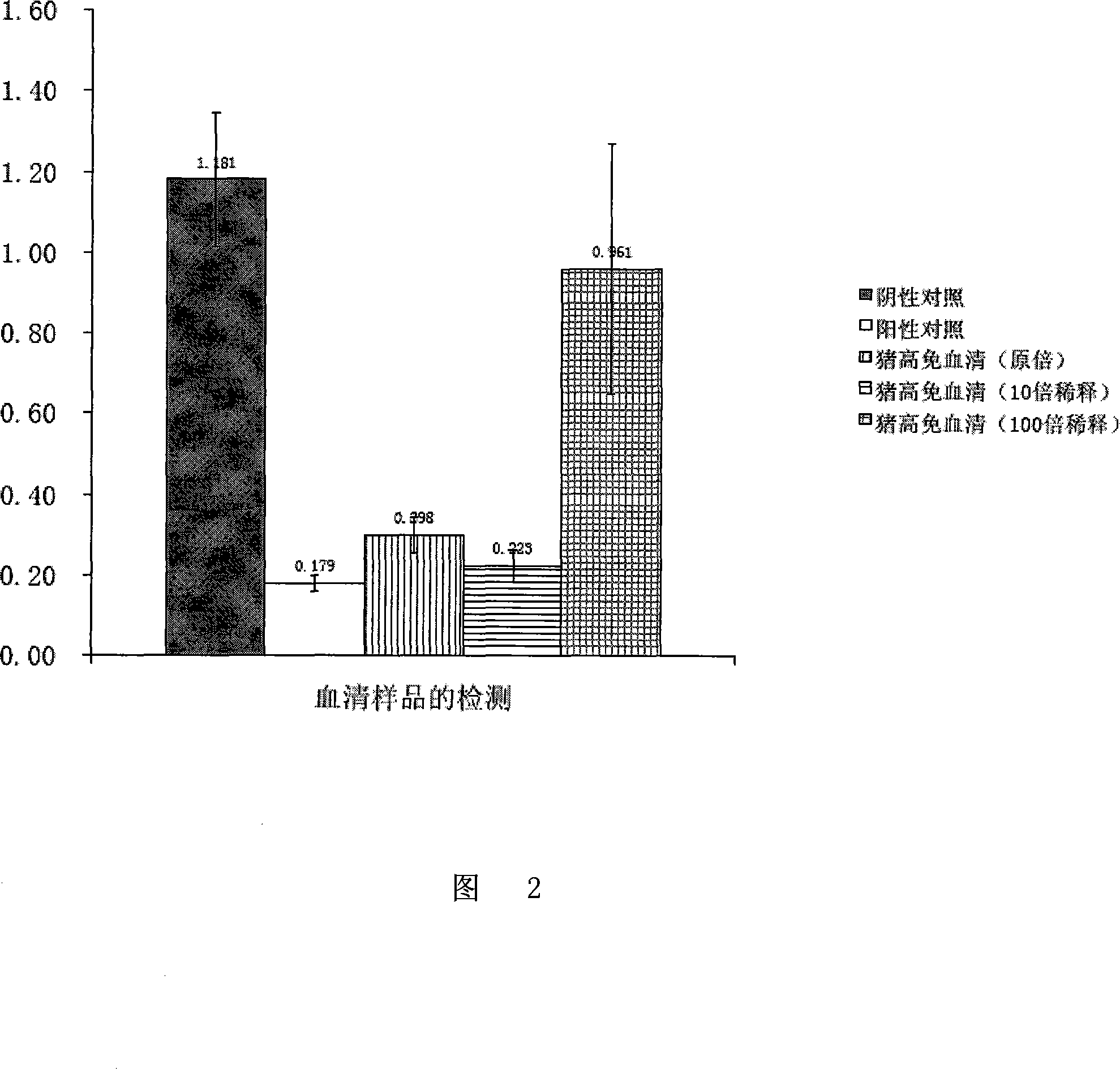
The invention discloses a heparanase II fusion protein, and a coding gene and an expression method thereof. The fusion protein (named MBP-HepB) is a protein of a) or b), wherein a) is a protein consisting of an amino acid sequences shown from the 1st position to 1,118th position of a sequence 2 in a sequence table; and b) is a protein in which one or more amino acid is substituted, and / or deleted and / or added in the amino acid sequence of a sequence 2 in a sequence table and which has heparanase activity and derives from the a). The coding gene of the protein is also in the protection scope of the invention. The gene is introduced into the protein heparanase expressed in the recombinant escherichia coli, the enzyme activity reaches 118.4IU / L fermentation liquor, the expression quantity reaches 179mg / L fermentation liquor, and the specific enzyme activity reaches 0.66IU / mg. The one-step purification of the fusion protein can also be realized by affinity separation.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Novel alginate lyase, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109295043AHigh activityStrong toleranceFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionPolymannuronic acidEscherichia coli
The invention discloses an alginate lyase (Alg509) derived from marine bacteria and a gene thereof, and also disclosed a method for recombinant expression and preparation of the alginate lyase. According to the method, the alg509 gene is cloned into an E. coli expression vector, and the vector is transformed into an E. coli host strain to obtain a recombinant engineering strain which can heterologously express the enzyme. The alginate lyase Alg509 disclosed in the invention has high enzyme activity, the specific enzyme activity can reach up to 48000 U / mg and above, the optimum reaction pH is 10, the optimum reaction temperature is 55 DEG C, and the enzyme activity has no dependence on various metal ions. The enzyme is active to sodium alginate, poly-guluronic acid (polyG) and ploymannuronic acid (polyM), and can completely degrade sodium alginate to produce alginate oligomers such as alginate disaccharide, alginate trisaccharide, alginate tetrasccharide, etc. The enzyme exhibits strongbasophilia, has certain tolerance to high pH, has certain potential of industrial applications, and can be widely applied in the fields of agriculture, food, feed additive, medicine and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Chromogenic medium of coliform group and quick detection card thereof
ActiveCN102311990AShorten detection timeImprove detection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyZoology
The invention discloses a chromogenic medium of a coliform group and a quick detection card thereof. The medium contains peptone, yeast extract, lactose, common salt, sodium pyruvate, SDS, sodium dihydrogen phosphate, a specific enzyme chromogenic substrate and IPTG. The quick detection card consists of, in a bottom-up order: a negative film, a water absorption and moisture retention layer, a medium layer and a covering membrane, with the above medium adsorbed on the medium layer. The chromogenic medium of a coliform group and the detection card that are provided in the invention can detect coliform groups in drinking water, surface water or foodstuff, with short detection time and high efficiency. The chromogenic medium and the detection card of the invention can conduct qualitative detection to coliform groups, and simultaneously can carry out quantitative analysis. And a positive result has obvious color development and is convenient for observation, odds for emergence of false positive and false negative can be reduced, and the detection result is accurate.
Owner:GUANGDONG DAYUAN OASIS FOOD SAFETY TECH CO LTD +1
Ketone reductase mutant and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104342410ASignificantly high specific enzyme activityMild reaction conditionsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSpecific enzymeWild type
The invention relates to a ketone reductase mutant and a preparation method thereof. The ketone reductase mutant comes from a saccharomyces cerevisiae wild type ketone reductase, is capable of converting 5-hydroxyl-3-oxohexanoate into corresponding cis 3,5-dihydroxylhexanoate, and has one or more mutants of I46V, S127N and Q144K. The ketone reductase mutant has obvious high specific enzyme activity which is improved by 2-100 times compared with that of the wild type ketone reductase, can be utilized to biologically catalyze 5-hydroxyl-3-oxohexanoate to product corresponding cis 3,5-dihydroxylhexanoate. The reaction conditions are mild, requirements on equipment are low, the production process does not need high temperature or cooling, and energy consumption is low. Because enzyme catalysis has efficient specific selectivity, the process of producing the statin medicine key intermediate cis 3,5-dihydroxylhexanoate, does not generate by-products, and purification is convenient. Additionally, the solvent employed in the reaction is mainly water, "three wastes (waste gas, waste water and industrial residue)" discharge is low, and the reaction is green and environment-friendly.
Owner:NANJING LANGEN BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
Microorganism compositions for degrading straw, preparation thereof and method for degradation of straw
InactiveCN1544610ADegradation reachesLower pHMicroorganismsSolid waste disposalBacterial strainChrysosporium species
The invention discloses a microbe combination of degraded stalks and its preparing method as well as a method of degrading the stalks, where the microbe combination includes: liquid bacterial strain, and solid bacterial strain, the liquid bacterial strain is made by culturing plant lactobacillus, Streptococcus faecali, and Candida utilis in the culture medium and the solid bacterial strain is made by culturing Phanerochaete chrysosporium and Pleurotus ostreatus; the method of degrading the stalks by the combination: mixing the liquid bacterial strain with the stalks raw material in weight ratio of 1 to 15000-25000, adding in 0.9% NaCl water solution to make the water ratio reach 65-70%, sealing and fermenting in a sealed container as 25-30deg.C for 7-10 days and take out; adding in the solid bacterial strain and mix uniformly, fermenting at 25-30 deg.C, and when the mycelium grows completely and drying into the finished products. It simulates the ecological mode of biodegrading stalks in the nature, fully uses specific enzyme system of each bacterial strain, and achieves the purpose of biodegrading stalks.
Owner:TIANJIN CITY AGRI BIO TECH RES CENT
Cocoa butter equivalents produced by the enzymatic interesterification process and method for preparing the same
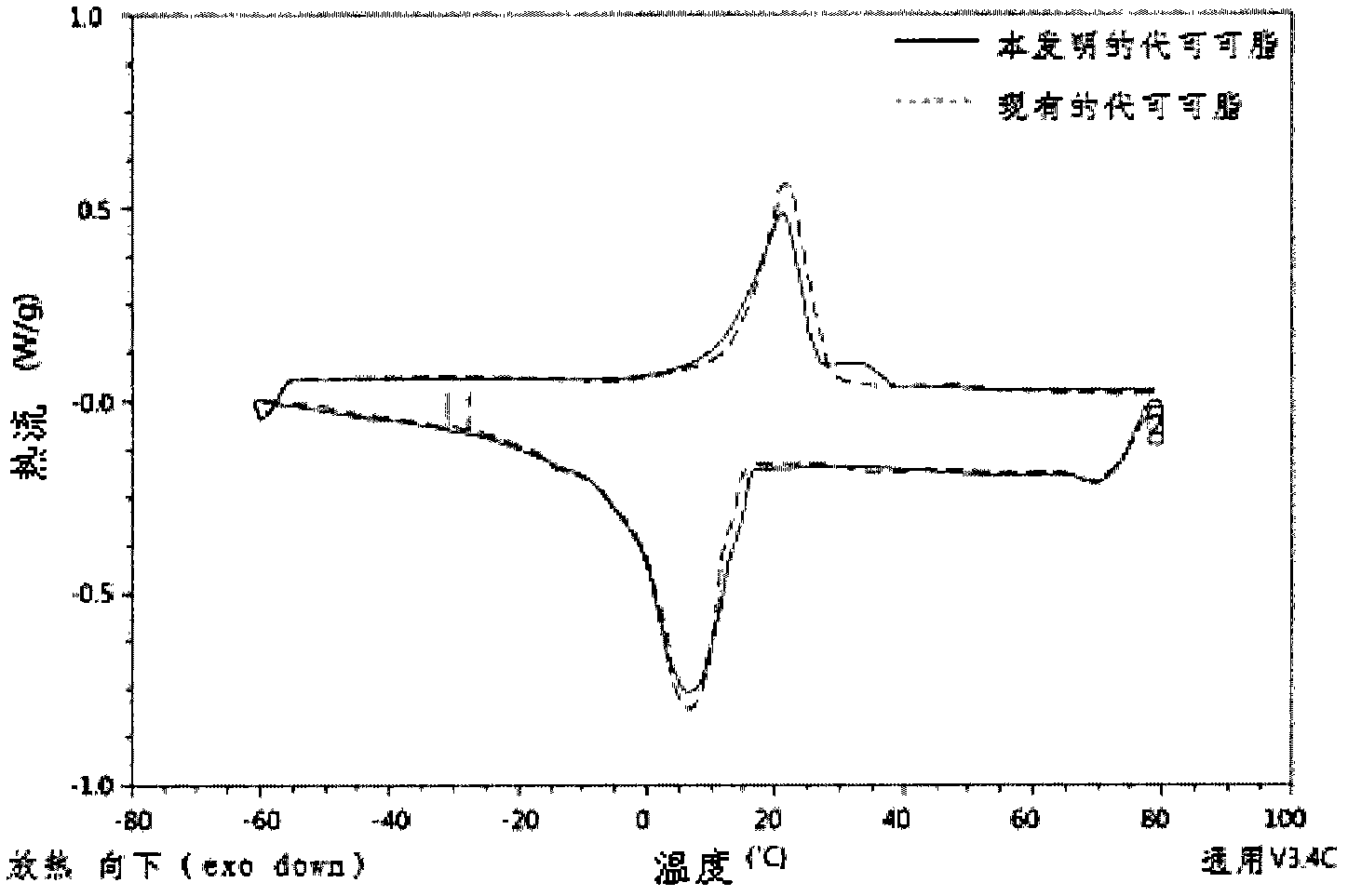
InactiveCN102215696ALow in trans fatty acidsFatty acid esterificationFatty-oils/fats refiningButter cocoaMonoglyceride
The present invention relates to a process for preparing hard butter having high SOS content by mixing oil for preparing butter with fatty acid or fatty acid ester, adding 1,3 regio-specific enzymes to the obtained mixture to carry out interesterification, distilling the obtained reactants to remove fatty aicd, ethyl ester, and monoglyceride and diglyceride formed after the reaction and fractionally extracting the obtained reactants to separate a solid phase, and to cocoa butter equivalents prepared by the hard butter and a process for preparing the same in which the cocoa butter equivalents can replace existing import cocoa butter equivalents with 1 : 1 because of its equivalent chemical properties, and have no difference in taste and properties with natural cocoa butter and also have lower trans fatty acid. Hard butter according to the present invention can make desired triglyceride structure in oil based on the reaction conditions and have a improved purity and yield in the whole process by recycling all of byproduct other than major product in the distillation and fractional distillation process and is eco-friendly matter by using the enzymatic interesterification reaction, and also cocoa butter equivalents made by the hard butter is characterized in replacing existing import cocoa butter equivalents with 1 : 1 because of its equivalent chemical composition and properties in the production of chocolate with no difference in taste.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
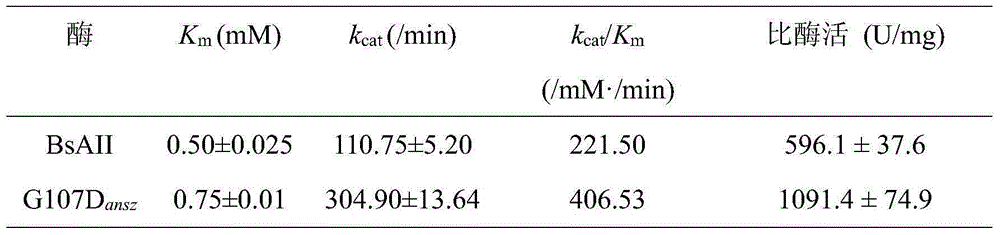
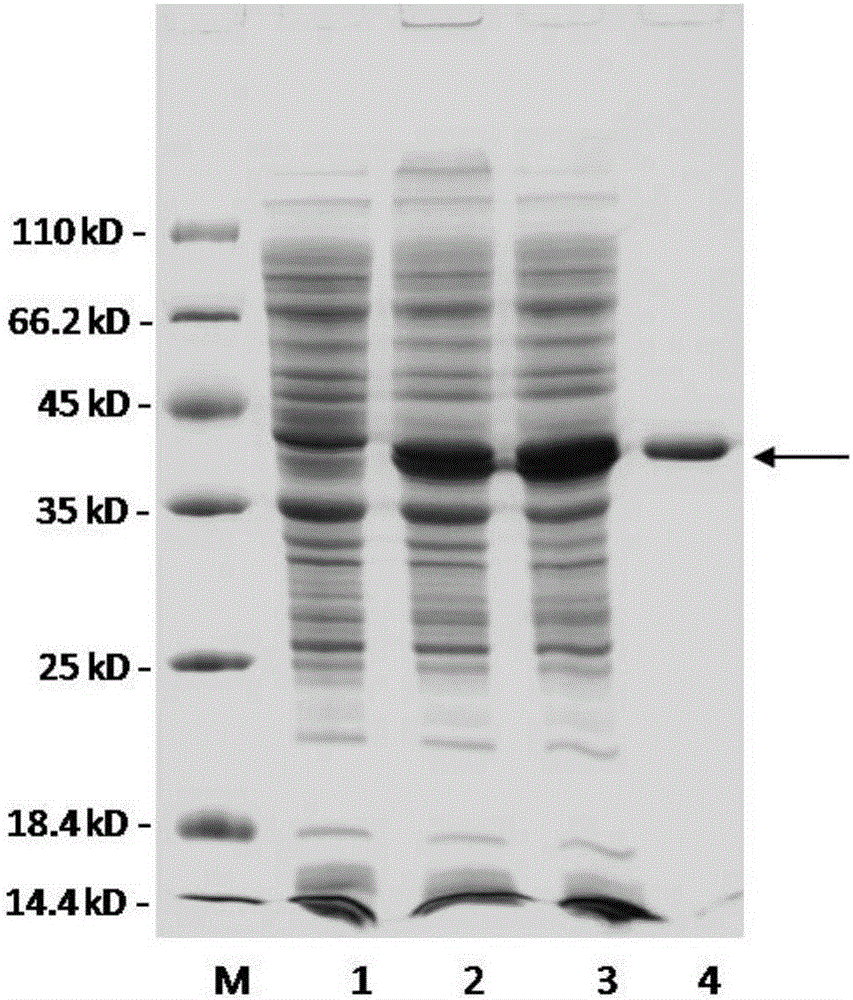
L-asparaginase mutant with improved enzyme activity and construction method thereof
InactiveCN105062997AIncreased potential for industrial applicationsReduce generationBacteriaHydrolasesGlycineSpecific enzyme
The invention discloses an L-asparaginase mutant with the improved enzyme activity and a construction method thereof, and belongs to the field of gene engineering. According to the L-asparaginase mutant, on the basis of amino acid shown in the SEQ ID NO.2, the 107th glycine is mutated into aspartic acid. The obtained mutant is expressed in bacillus subtilis, fermentation is performed in a shake flask for 24 h and then the enzyme activity is 961 U / mL; the enzyme activity of the mutant is improved by 80%, the appetency of a substrate is decreased by 50% compared with protoenzyme, the catalytic efficiency is improved by 84%, and meanwhile the specific enzyme activity is improved by 83%. According to the L-asparaginase mutant, it is shown that the 107th amino acid residue has a great influence on the enzyme catalytic action, a certain foundation is provided for research on the enzyme catalytic mechanism, and the enzyme industrial application potential is improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Full-wheat type growing-finishing pigs diets and processing technique thereof
ActiveCN101455268ALow feed intakeSmall meatAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsBiotechnologyAnimal science
The invention pertains to the field of feed formula design and feed processing technique, specifically relating to an all-wheat type growing and fattening pig diet and its processing technique. The inventive all-wheat type growing and fattening pig diet is composed of the following components in weight percent: 50-70 parts of all-wheat, 4-10 parts of rice bran, 10-25 parts of bean pulp, 1-5 parts of peanut meal, 0.2-1.0 parts of composite vitamins, 0.2-1.0 parts of composite trace elements, and 0.1-0.4 parts of wheat-type-specific enzyme. The processing technique adds a maturing step between the modulation step and the granulation step. By adoption of the growing and fattening pig diet, the invention has low feed cost, faster fatten pigs growth rate, shortened breeding cycle, improved fatten pigs growing production efficiency, greatly improved pig shape and carcass quality, good palatability of the all-wheat type pig diet, good pork quality (stearin meat); and the invention solves the feed resource tensioning problem to some extent.
Owner:SHANDONG NEW HOPE LIUHE GROUP
Truncated recombinant alginate lyase rAly1-T185N, and encoding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN106811454AAchieve production increaseIncrease contentGenetic engineeringFermentationSpecific enzymeEconomic benefits
The invention relates to truncated recombinant alginate lyase rAly1-T185N, and an encoding gene and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the truncated recombinant alginate lyase rT185N is as shown in SEQ ID NO.2; the nucleotide sequence of the encoding gene of the truncated recombinant alginate lyase rT185N is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1. 185 amino acid residues are cut off from the N end of the full-length alginate lyase rAly-1 to obtain T185N truncated enzyme; the expression quantity of the rT185N can reach 1259+ / -2.2 mg / L fermentation liquid, the specific enzyme activity can reach 2895+ / -10.3 U / mg, the expression quantity is increased by about 2.6 times compared with that of full-length protein rAly-1, the aims of increasing yield, saving energy and improving economic benefit are fulfilled, and rT185N can realize one-step purification of fusion protein through nickel column separation.
Owner:WUTONG AROMA CHEM CO LTD
Polypeptide-DNA hydrogel and preparation method
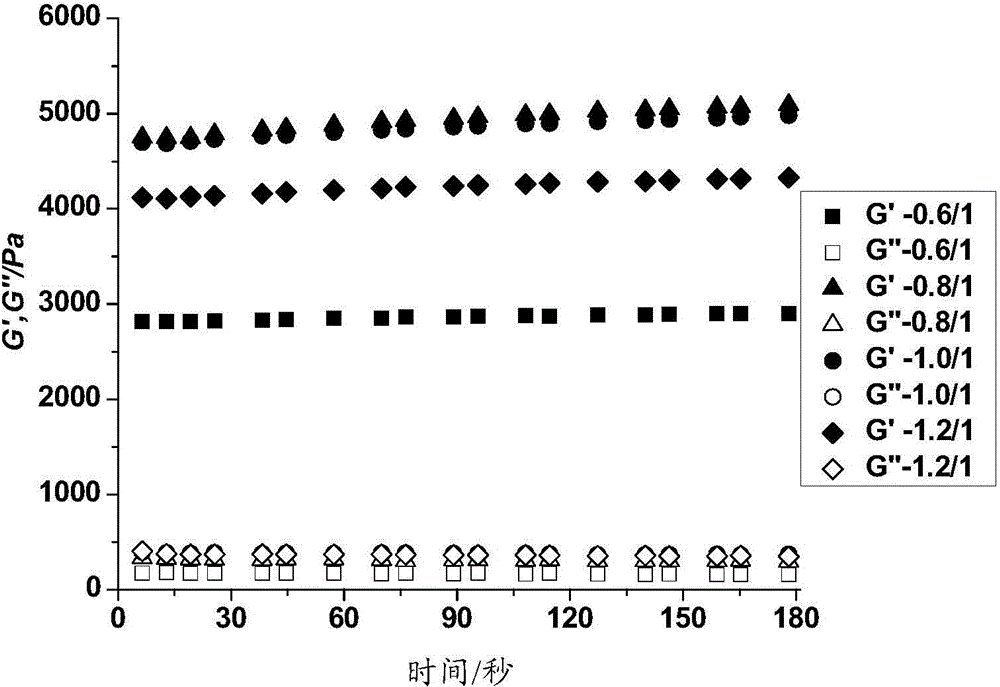
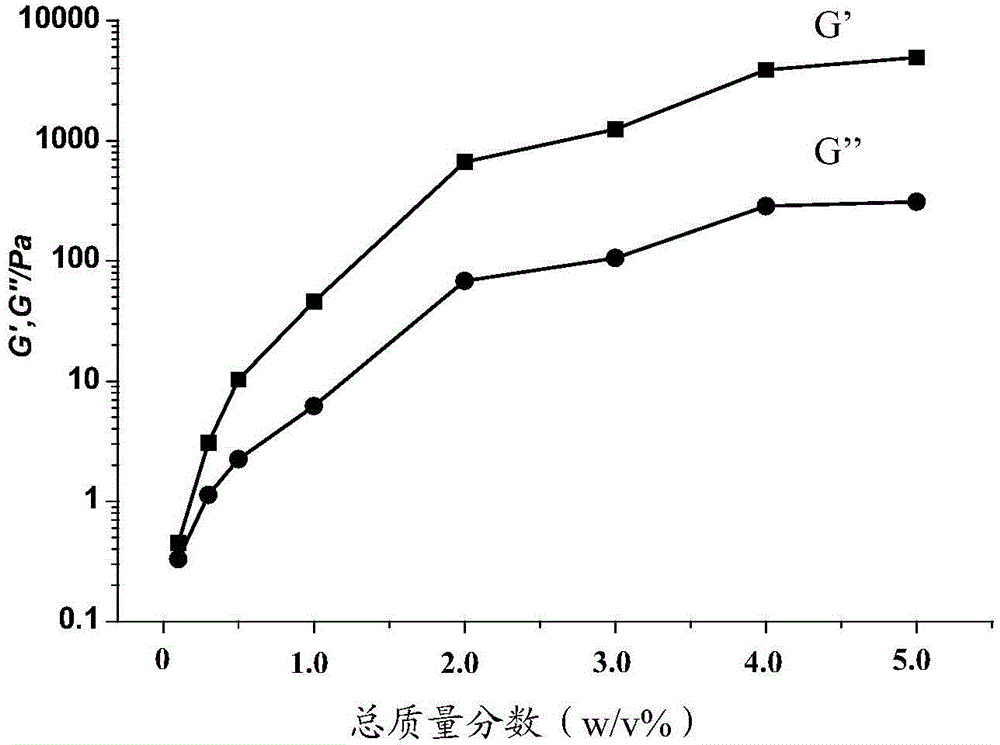
ActiveCN103910893APromote formationHigh mechanical strengthArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsSpecific enzymeBiocompatibility Testing
The invention provides a polypeptide-DNA hydrogel and a preparation method, wherein, the polypeptide-DNA hydrogel comprises the following components: polypeptide, wherein a single chain DNA molecule enables covalent binding on the polypeptide; a double chain DNA molecule, wherein the double chain DNA molecule has two cohesive ends; wherein the cohesive ends and the single chain DNA molecule are complementary, and polypeptide forms a crosslinking structure through the complementation of the cohesive ends of the double chain DNA molecule and the single chain DNA molecule. The mechanical strength of the polypeptide-DNA hydrogel can be adjusted, the biocompatibility is good, and the polypeptide-DNA hydrogel has reversible thermal responsiveness and specific enzyme responsiveness.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Biochemical sensing device
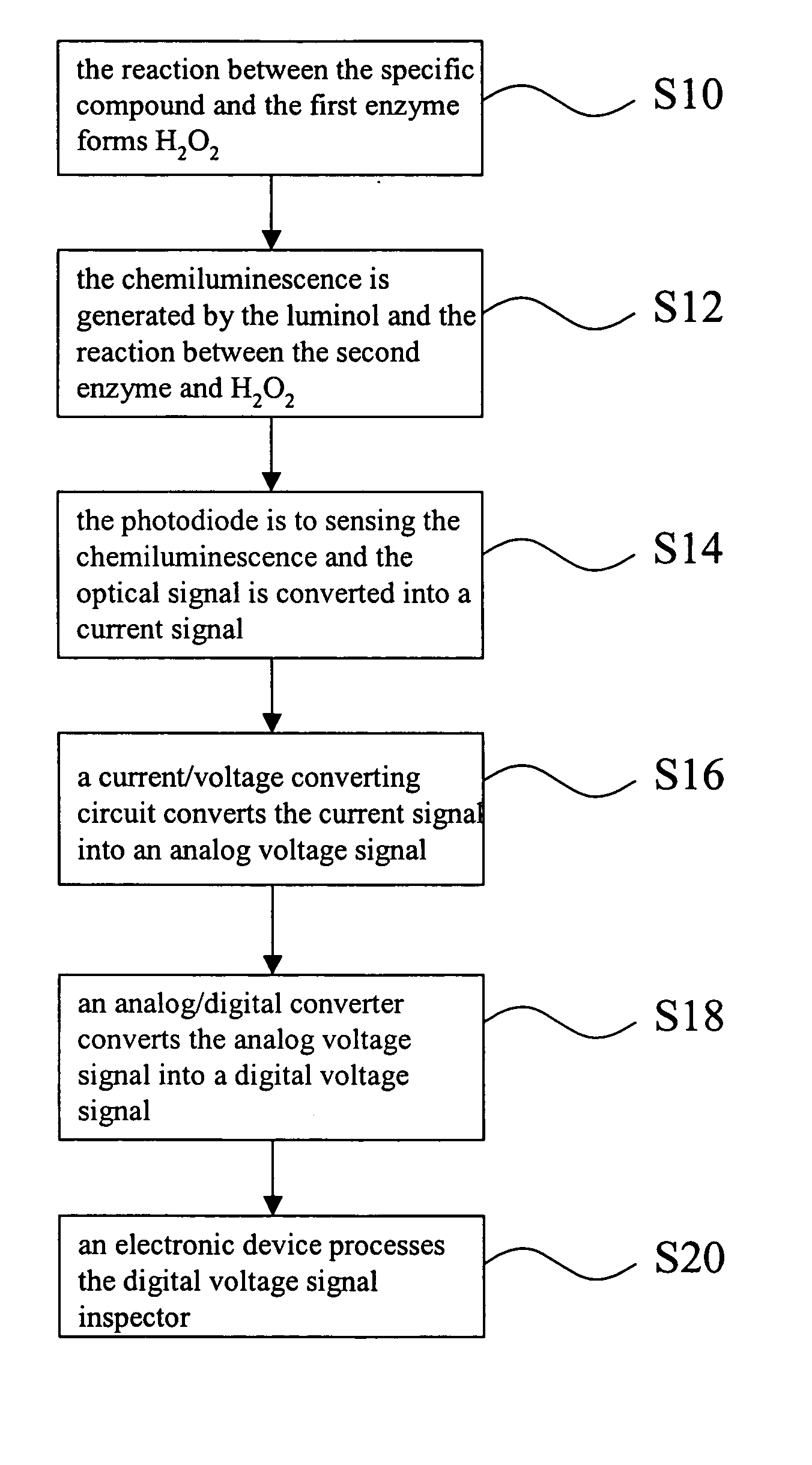
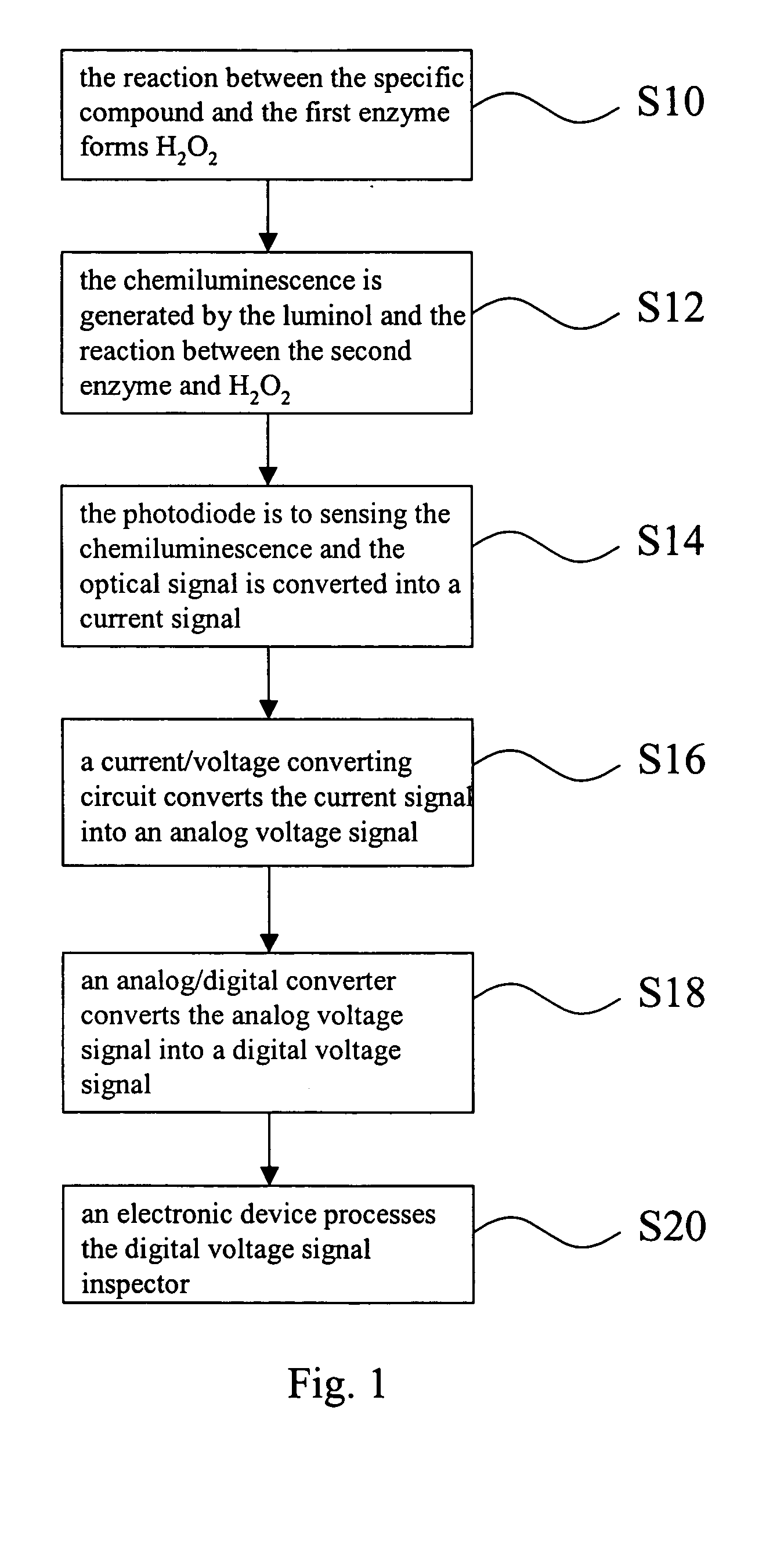
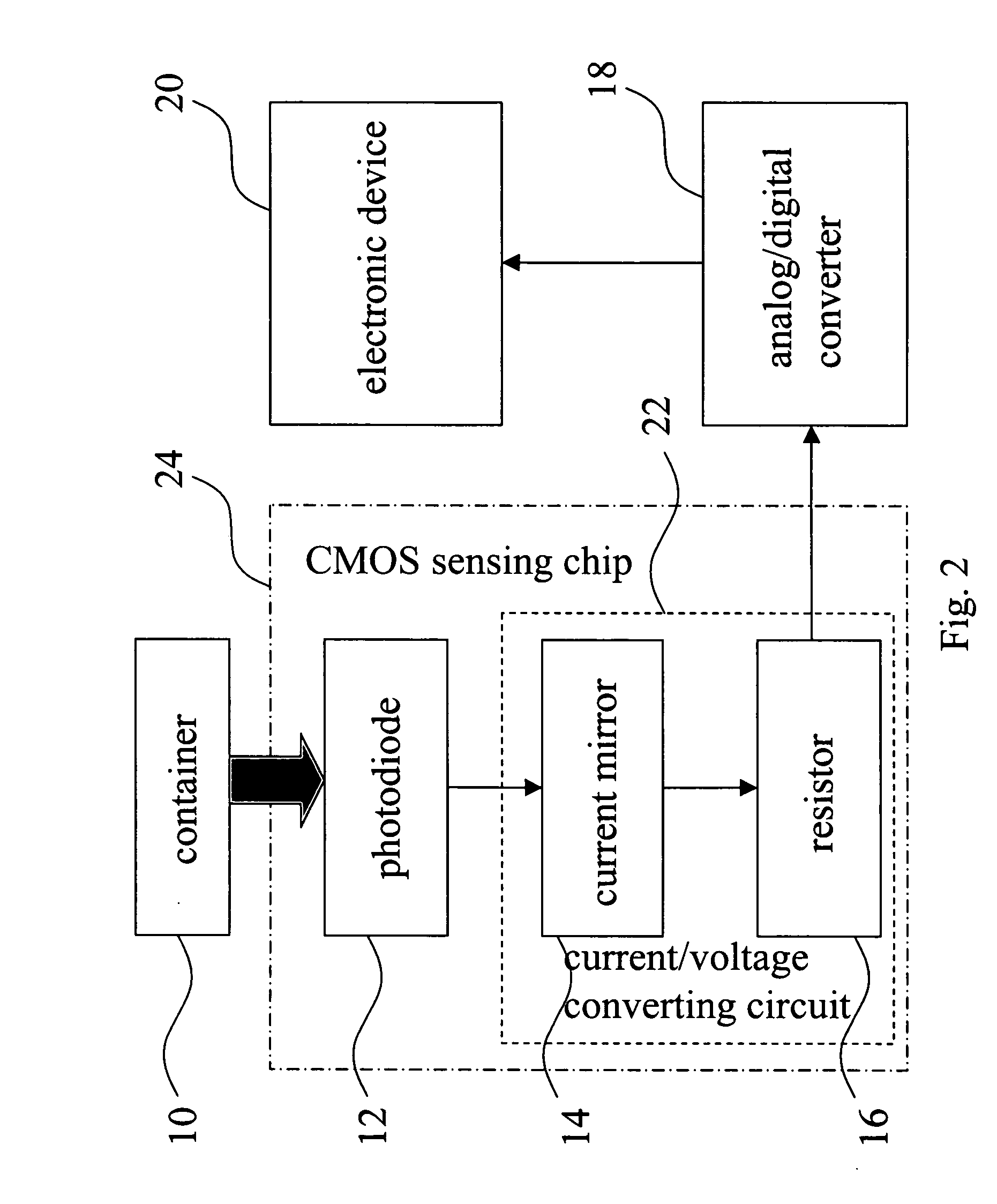
InactiveUS20050100977A1Reduce volume and costSimplifying a biomedical assayBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFrequency spectrumSpecific enzyme
The invention is a biochemical sensing device, including a photodiode capable of sensing the light generated by the reaction made by a specific compound, a specific enzyme, and a luminol as well as converting the optical signal into a current signal. Also, there is a current / voltage converting circuit capable of converting the current signal into an analog voltage signal. In turn, the analog voltage signal can be converted into a digital voltage signal through an analog / digital converter. Finally, by using an electronic device, the digital voltage signal can be received and analyzed, and through the analysis, the amount of the specific compound can be measured. The device of the invention can provide a simple real-time medical assay that can be performed in massive amount. For this reason, the drawbacks of a conventional spectrum analysis instrument of being bulky and expensive can be improved.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com