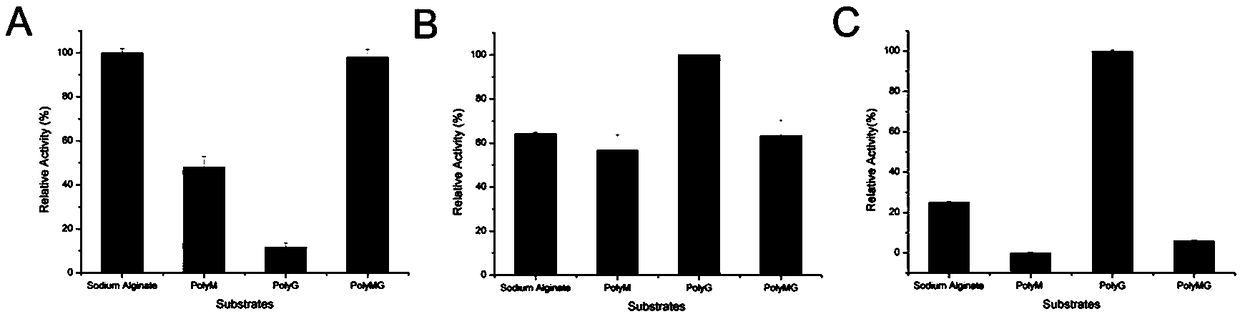
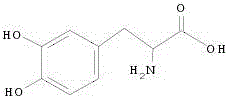
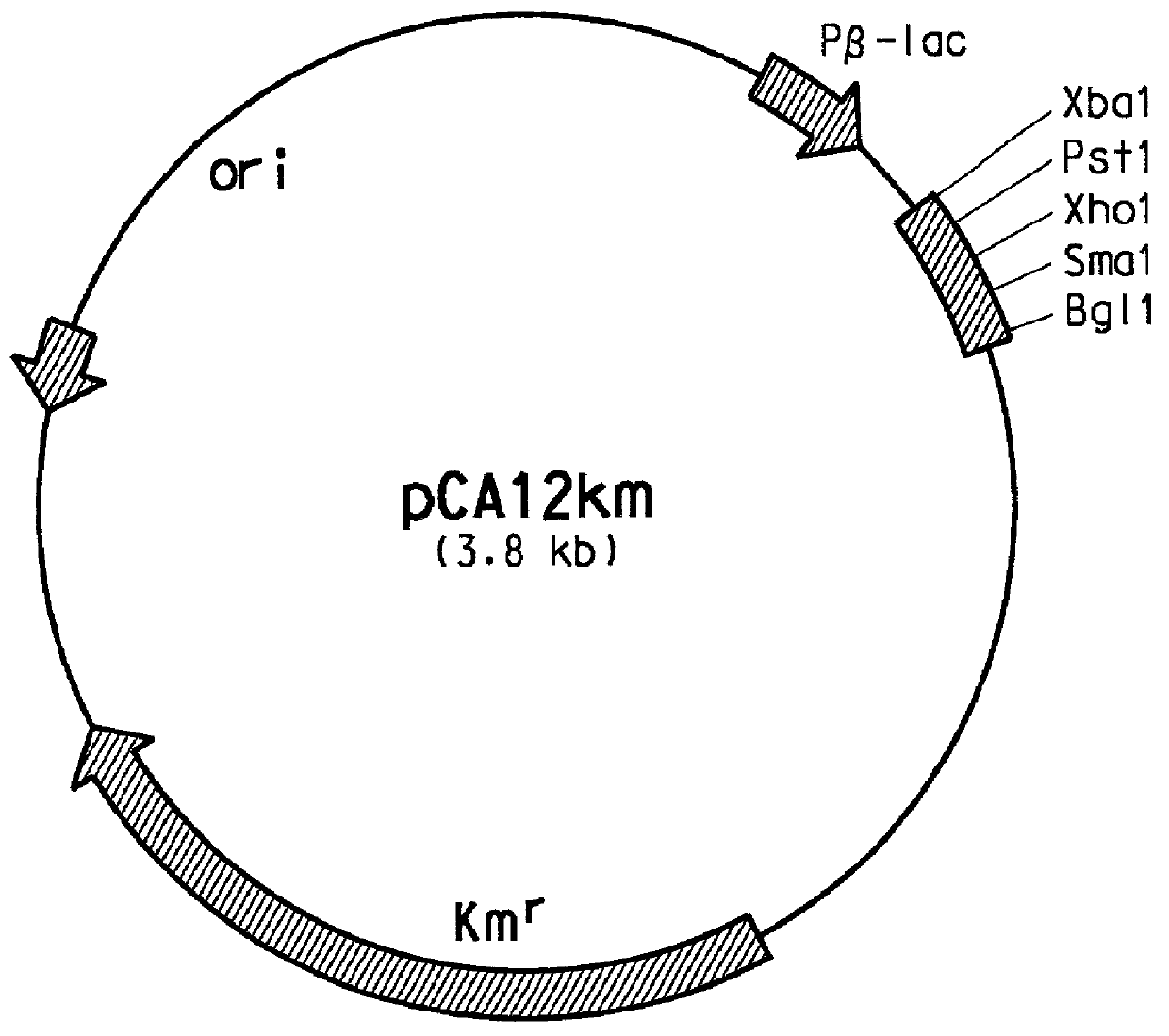
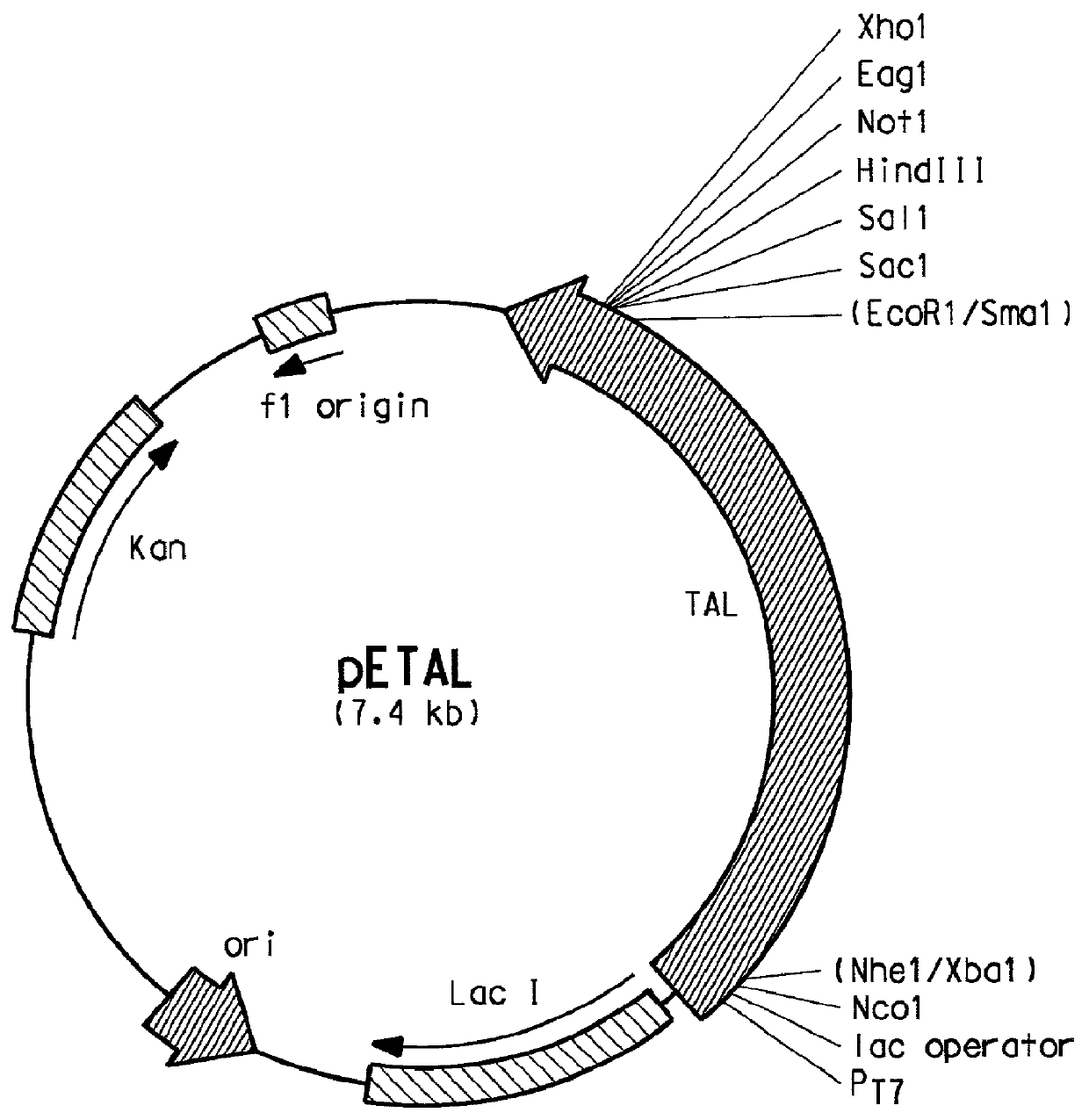
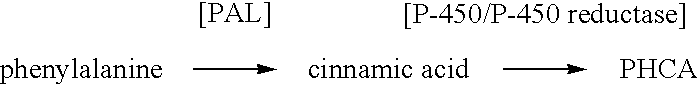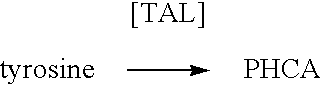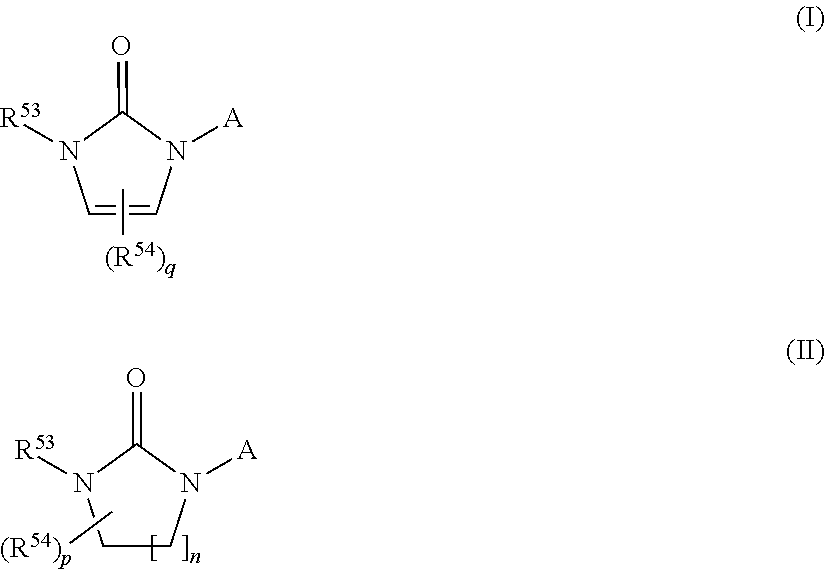Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
685 results about "Lyase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In biochemistry, a lyase is an enzyme that catalyzes the breaking (an "elimination" reaction) of various chemical bonds by means other than hydrolysis (a "substitution" reaction) and oxidation, often forming a new double bond or a new ring structure.
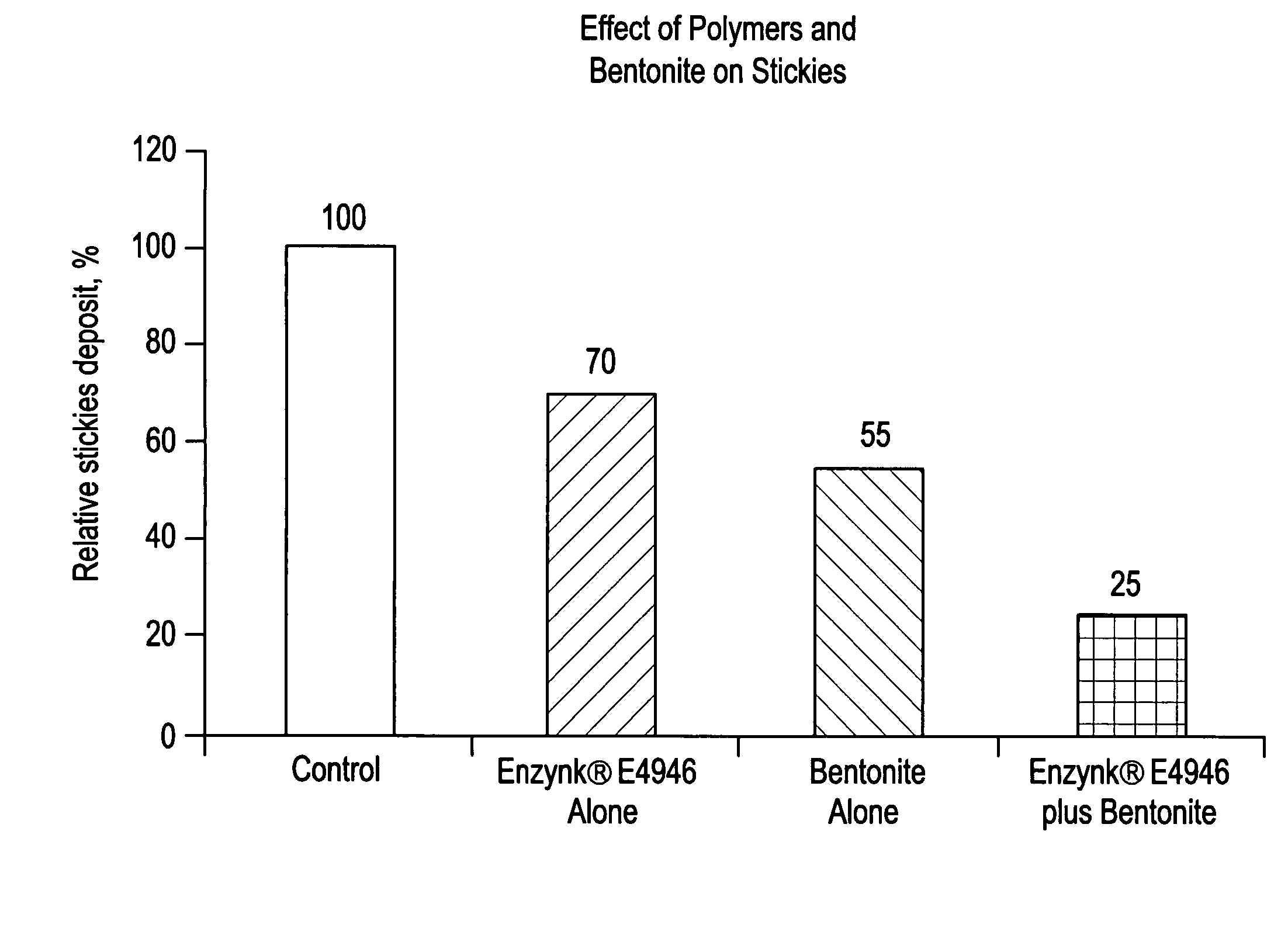
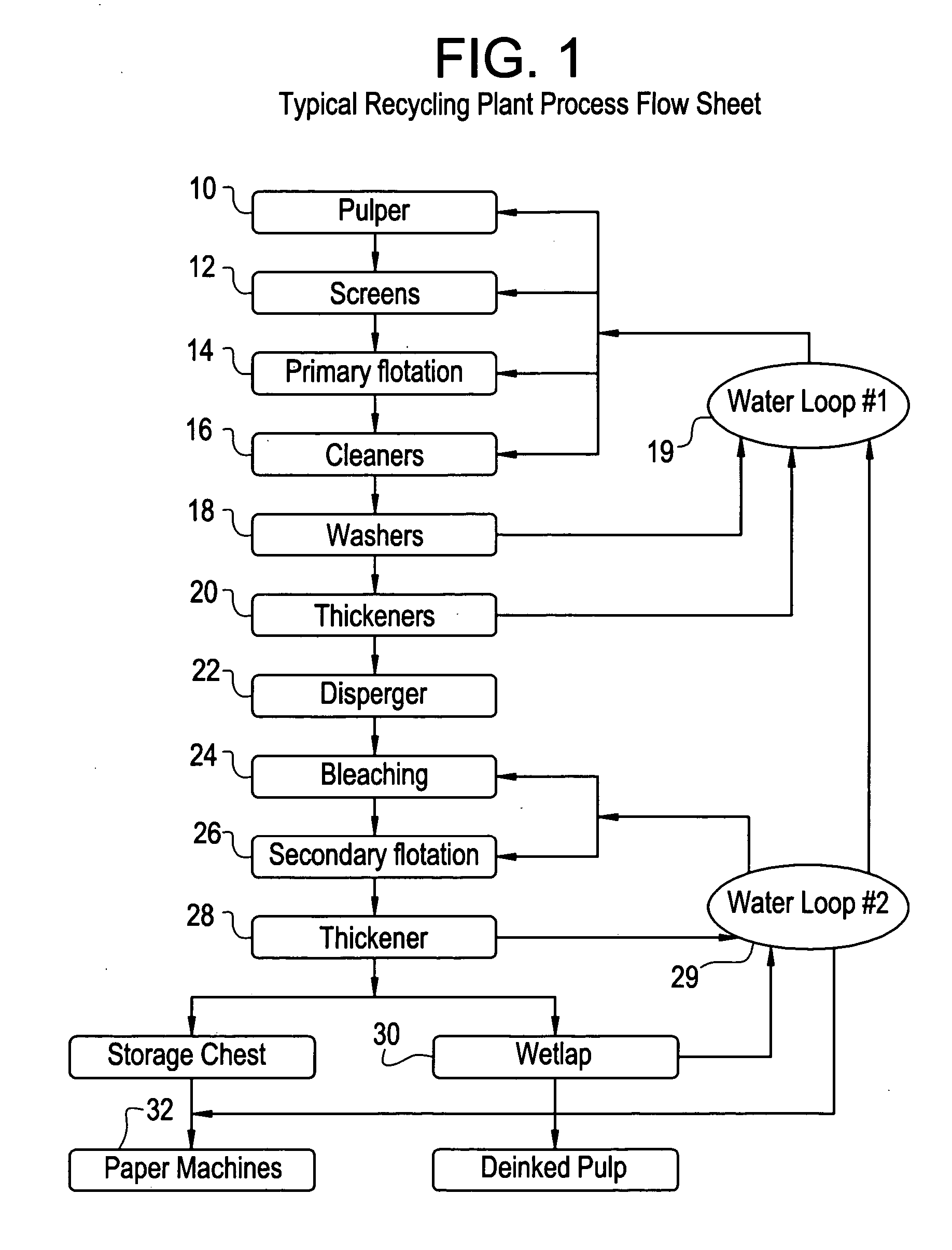
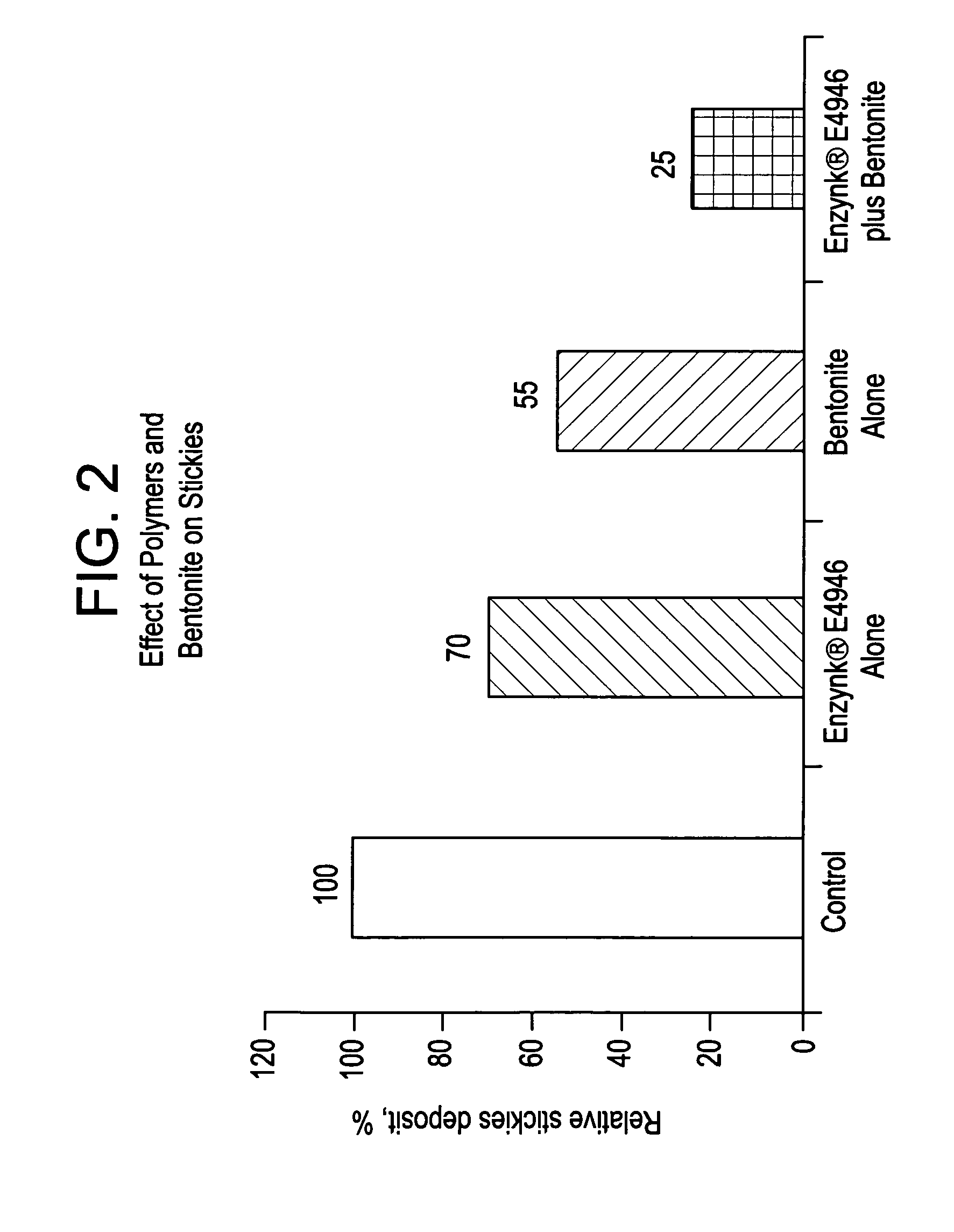
System for control of stickies in recovered and virgin paper processing
InactiveUS20060048908A1Good removal effectEasy to controlFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpMachine wet endPectinaseAmylase
Enhanced removal and / or control of adhesives or sticky materials, “stickies”, from recovered paper stock or virgin pulp fibers is achieved using a combination of enzyme treatment with adsorbents and / or absorbents. Pulp stock to be treated is typically obtained from old magazines, newspapers, household waste, but may include corrugated boxes and office waste. Virgin pulps may include mechanical, chemical, or semi-chemical pulps. Enzymes typically include hydrolases such as cellulases, hemicellulases, pectinases, amylases, and lipases such as esterases, lyases such as pectate lyases, and oxidoreductases. Adsorbents include activated bentonite, microparticles, talc, clay and modified silica. Absorbents typically include water soluble polymers, dispersants, coagulatants and agglomerants.
Owner:ENZYMATIC DEINKING TECH LLC
Compositions of prokaryotic phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and methods of treating cancer using compositions thereof
ActiveUS7537923B2High catalytic activityImprove stabilityNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsWild typeCancer therapy
The present invention is directed to phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) variants produced by prokaryotes, wherein such prokaryotic PAL variant has a greater phenylalanine-converting activity and / or a reduced immunogenicity as compared to a wild-type PAL. The invention provides compositions of prokaryotic PAL and biologically active fragments, mutants, variants or analogs thereof, as well as methods for the production, purification, and use of such compositions for therapeutic purposes, including the treatment of cancer.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
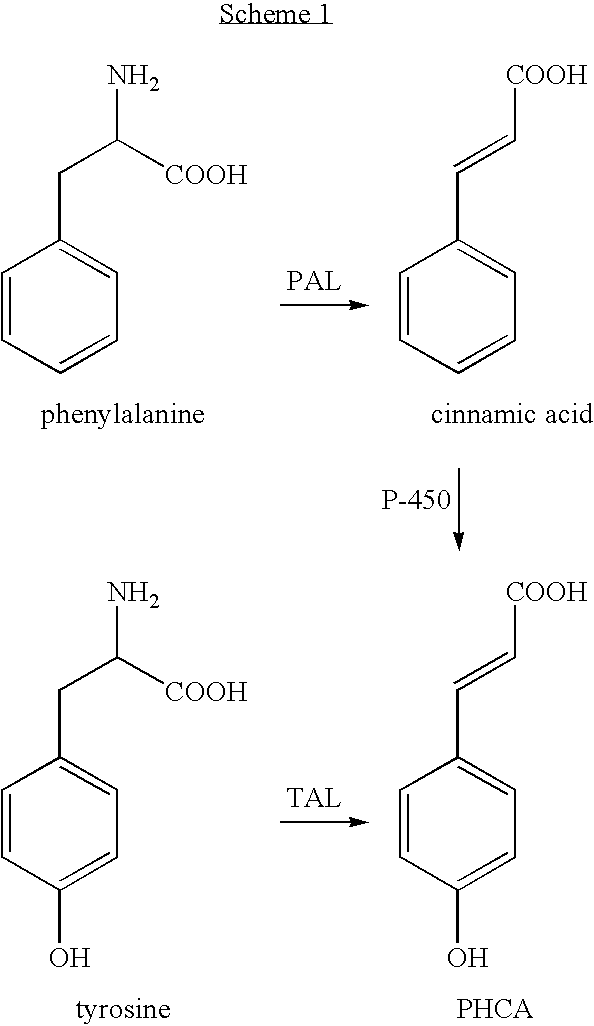
Bioproduction of para-hydroxycinnamic acid
The present invention provides several methods for biological production of para-hydroxycinnamic acid (PHCA). The invention is also directed to the discovery of new fungi and bacteria that possess the ability to convert cinnamate to PHCA. The invention relates to developing of a new biocatalyst for conversion of glucose to PHCA by incorporation of the wild type PAL from the yeast Rhodotorula glutinis into E. coli underlining the ability of the wildtype PAL to convert tyrosine to PHCA. The invention is also directed to developing a new biocatalyst for conversion of glucose to PHCA by incorporation of the wildtype PAL from the yeast Rhodotorula glutinis plus the plant cytochrome P-450 and the cytochrome P-450 reductase into E. coli. In yet another embodiment, the present invention provides for the developing of a new biocatalyst through mutagenesis of the wild type yeast PAL which possesses enhanced tyrosine ammonia-lyase (TAL) activity.
Owner:GATENBY ANTHONY A +4
Use of bacterial phage-associated lysing proteins for preventing and treating bacterial infections in humans, animals and fowl
InactiveUS20060292135A1Change propertiesImprove purification effectCarbon-nitrogen lyasesPeptide/protein ingredientsFowlLyase
A composition and method for treating bacterial infections by the use of an effective amount of at least one lytic specific for the bacteria causing specific. The lytic enzyme is genetically coded for by a bacteriophage which may be specific for said bacteria. The enzyme may be at least one lytic protein or peptides in a natural or modified form.
Owner:NEW HORIZONS DIAGNOSTICS
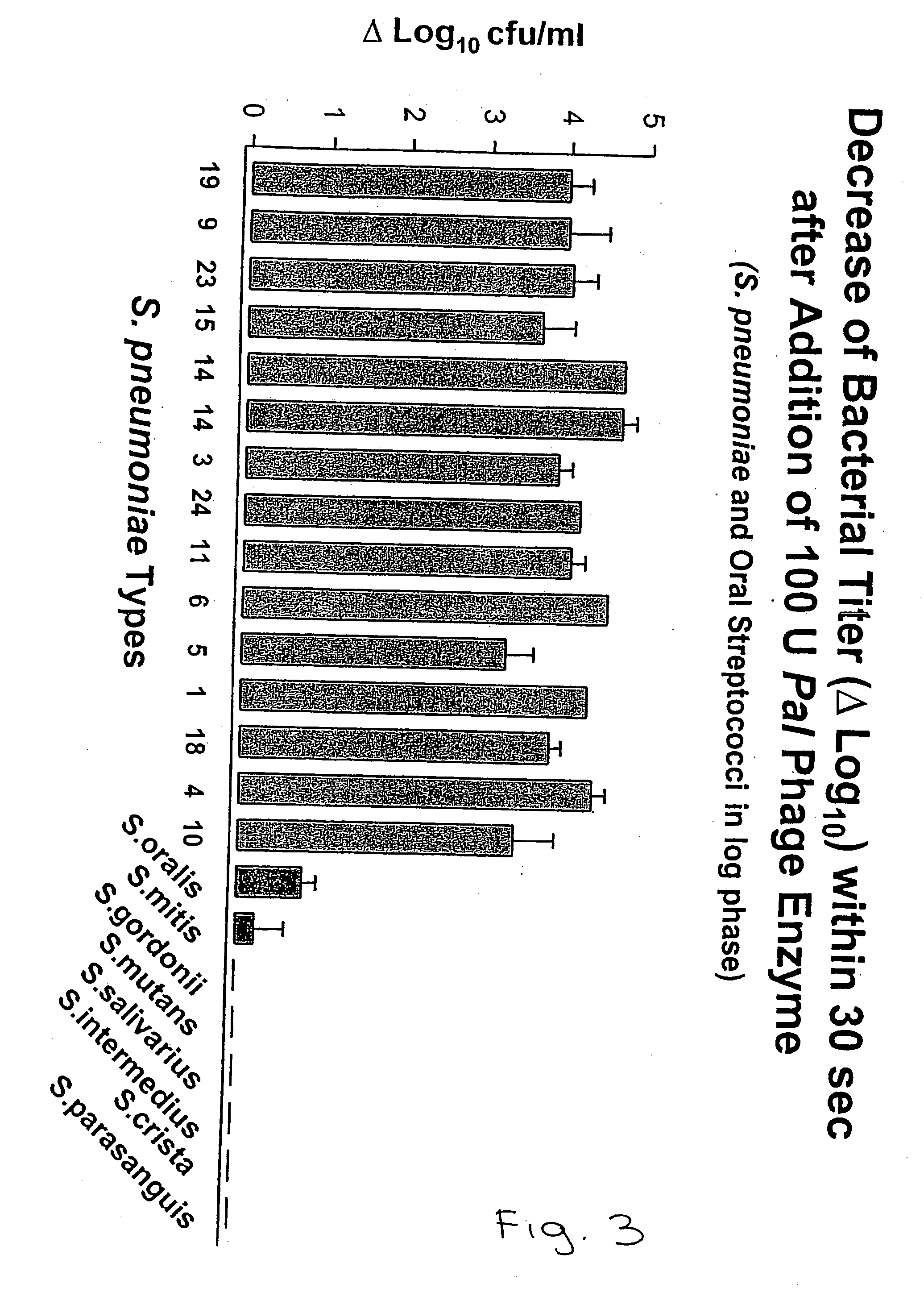
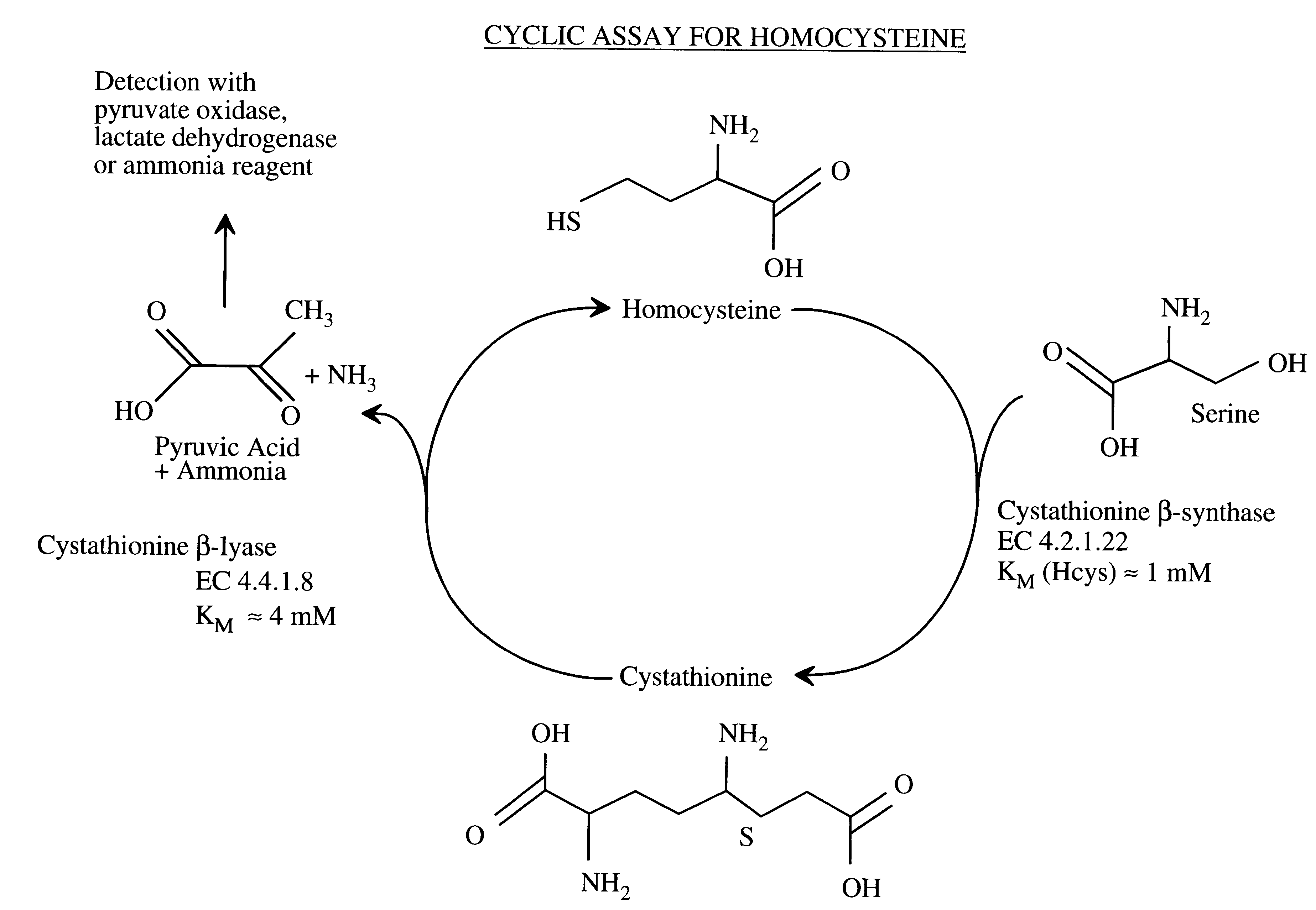
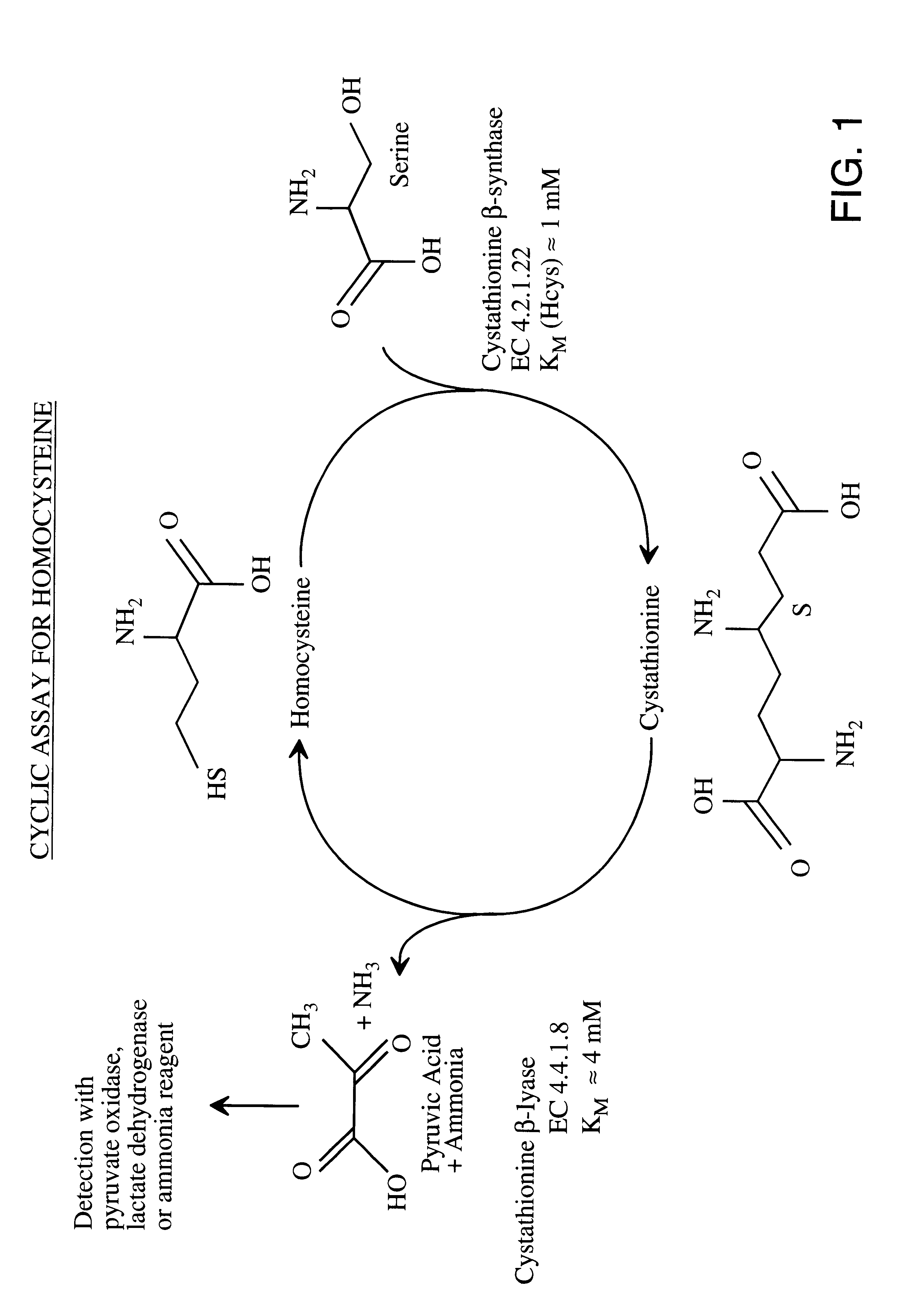
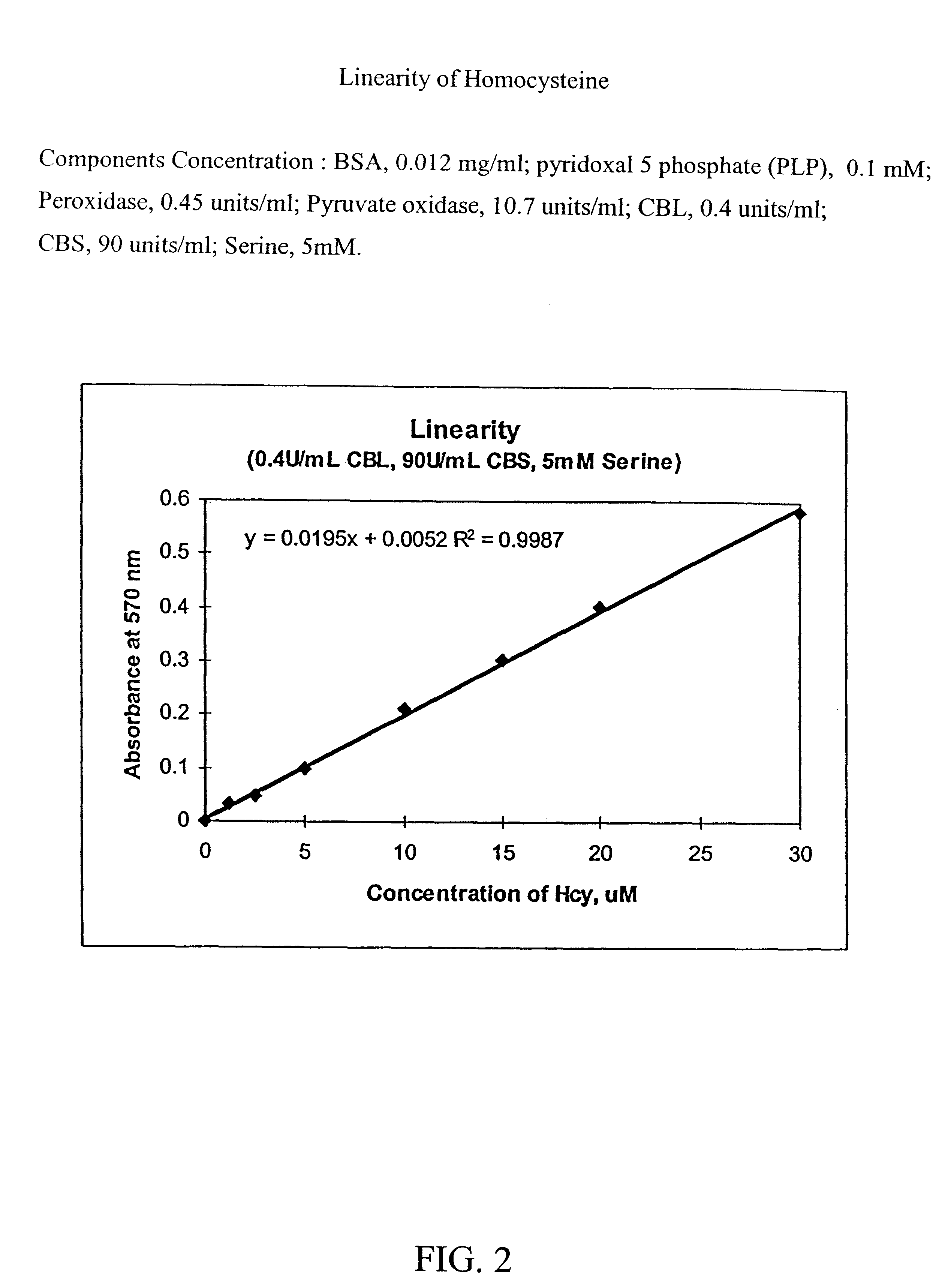
Method for the determination of homocysteine
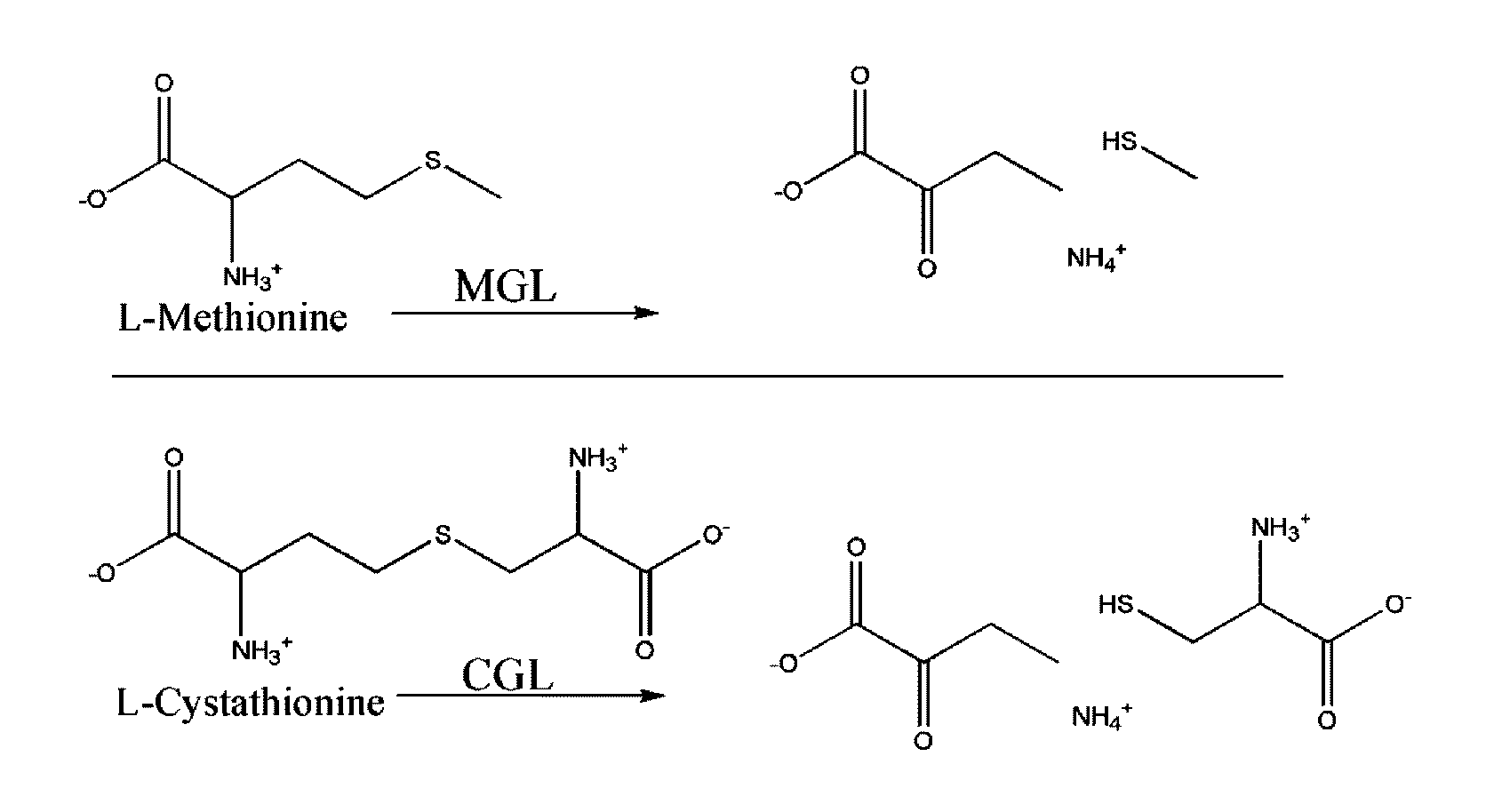
The invention relates to a method for determining homocysteine concentration in samples in which homocysteine is condensed using an enzyme cystathionine .beta. sythase to form cystathionine. Pyruvate and / or ammonia are released from cystathionine by action of an enzyme, cystathionine .beta. lyase, and homocysteine is regenerated. The release of pyruvate and / or ammonia can be correlated to the concentration of homocysteine present in the sample.
Owner:GENZYME CORP +1
Enzymatic reactions in the presence of keto acids
ActiveUS7445911B2Efficient and high yieldImprove bioavailabilityCarbon-nitrogen lyasesOxidoreductasesLyaseKeto acid
Conversion in vitro of X-Gly to X-alpha-hydroxy-Gly or X—NH2 (X being a peptide or any other compound having a carbonyl group capable of forming a covalent bond with glycine) is accomplished enzymatically in the presence of keto acids, or salts or esters thereof, to provide a good yield without the necessity of catalase or similar enzymatic reaction enhancers. Peptidylglycine α-amidating monooxygenase (PAM) is a preferred enzyme for catalyzing the conversion. Alternatively, peptidylglycine α-hydroxylating monooxygenase (PHM) is utilized to convert X-Gly to X-alpha-hydroxy-Gly which may be recovered, or optionally may be simultaneously or sequentially converted to an amide by either a Lewis base or action of the enzyme peptidyl α-hydroxyglycine α-amidating lyase (PAL). Both PHM and PAL are functional domains of PAM.
Owner:ENTERIS BIOPHARMA
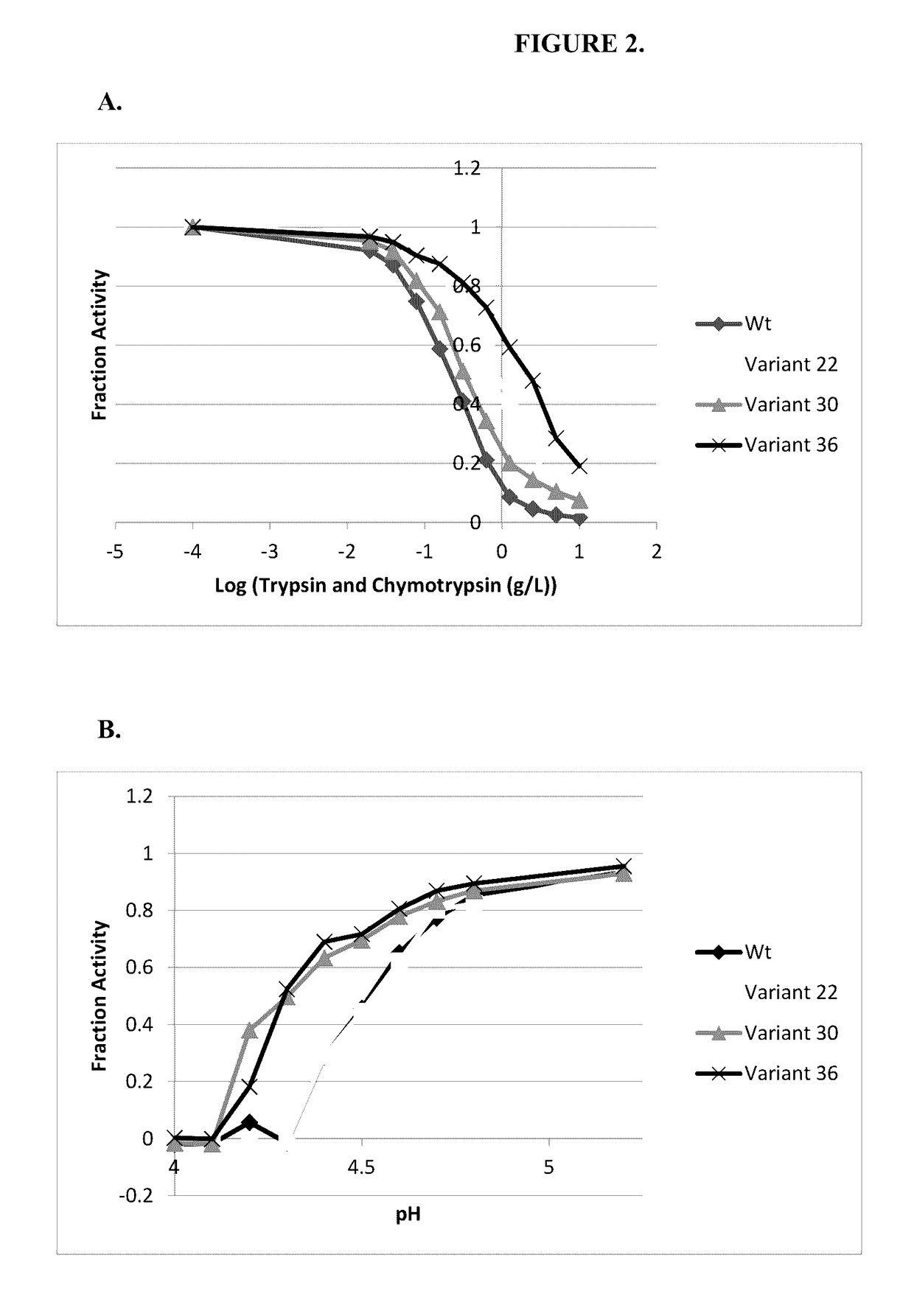
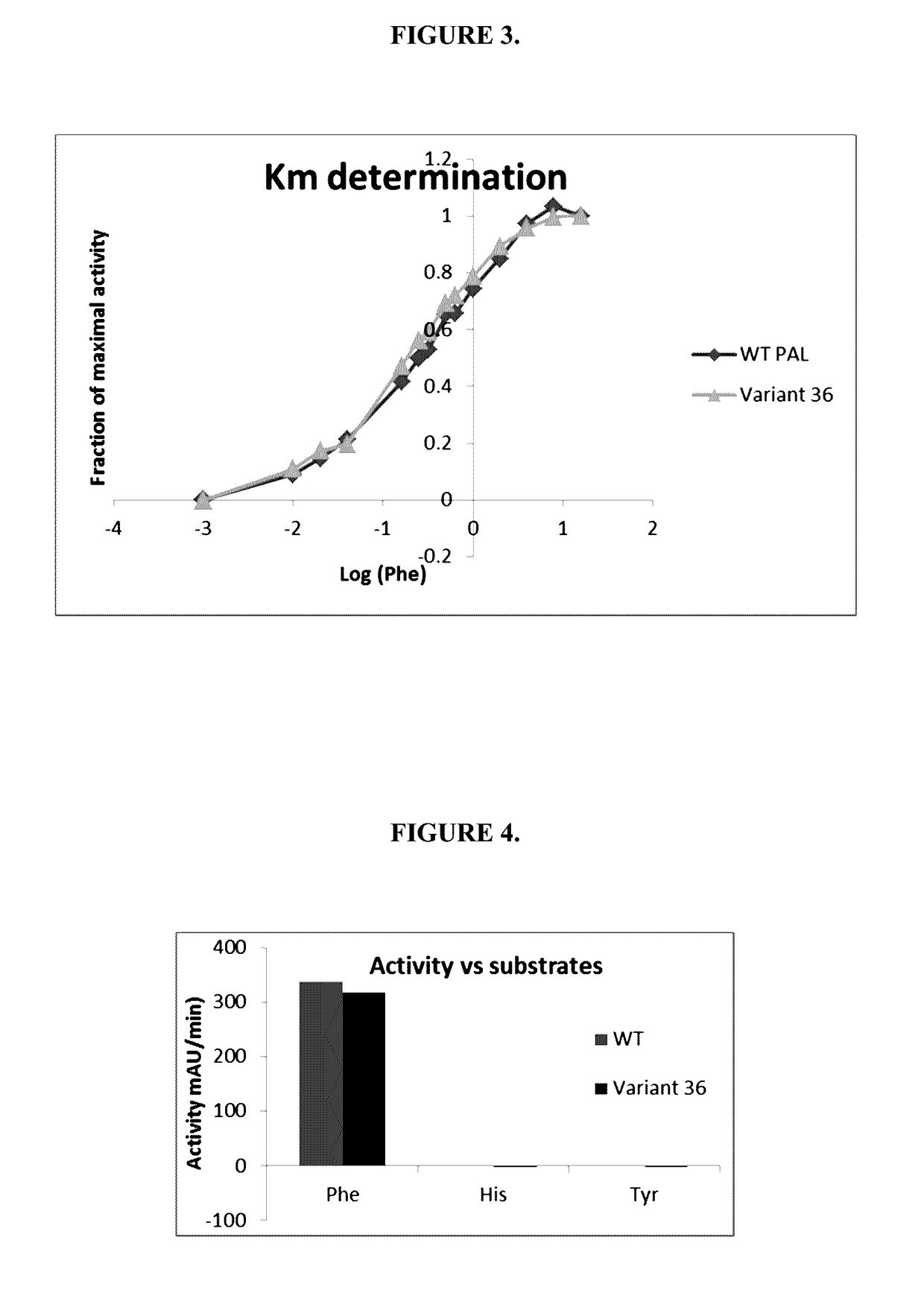
Variants and chemically-modified variants of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase
The present invention pertains to the use of the protein phenylalanine ammonia-lyase, as well as the biologically-active derivatives of the said protein for preventing or treating diseases associated with a phenylalanine imbalance in a human or animal body. More particularly, the present invention relates to the therapeutic use of the above-cited molecules for preventing or treating a phenylalanine imbalance in vivo. This invention also deals with therapeutic compositions comprising a pharmaceutically active amount of the above-described therapeutic molecules as well as with therapeutic methods using the said therapeutic compositions. Finally, the present invention relates to processes for selecting more therapeutically-effective variants of said protein as well as to the selected variants themselves.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST +1
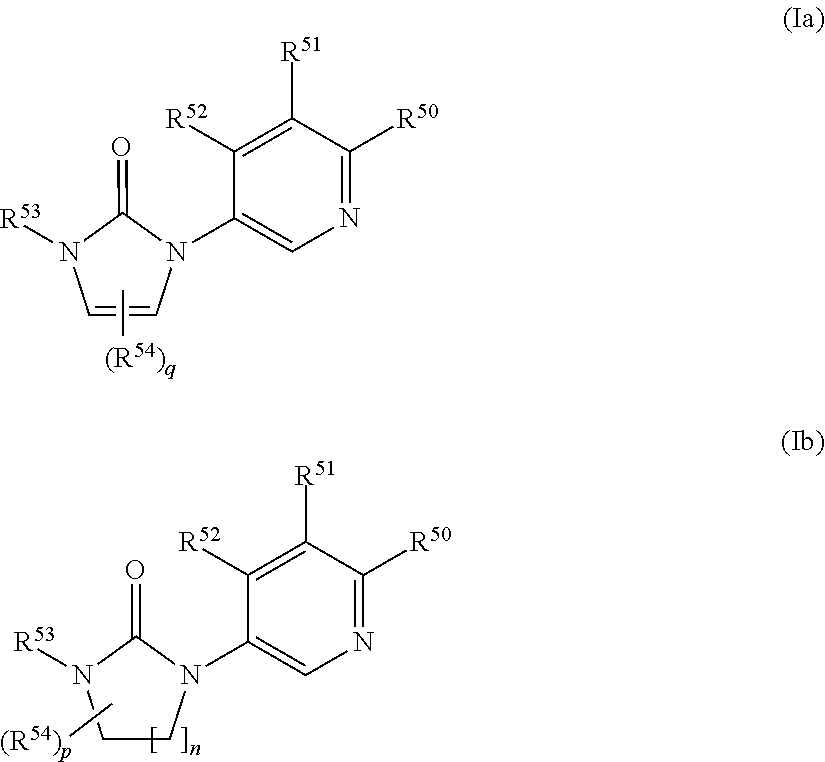
Inhibitors of CYP 17
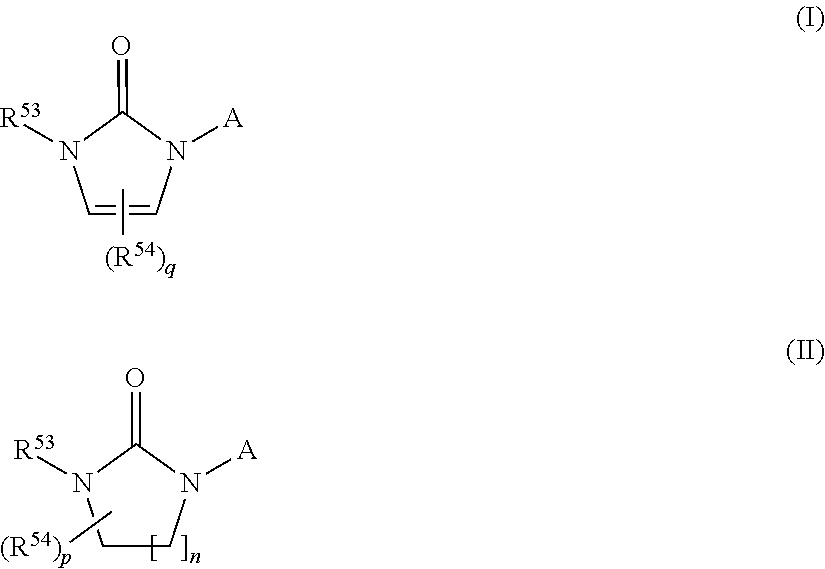
The present invention provides compounds of Formula (I) and (II), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof,where R53, R54, p, q, and n are as defined herein. The compounds of the present invention have been found to be useful as 17α-hydroxylase / C17,20-lyase inhibitors.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
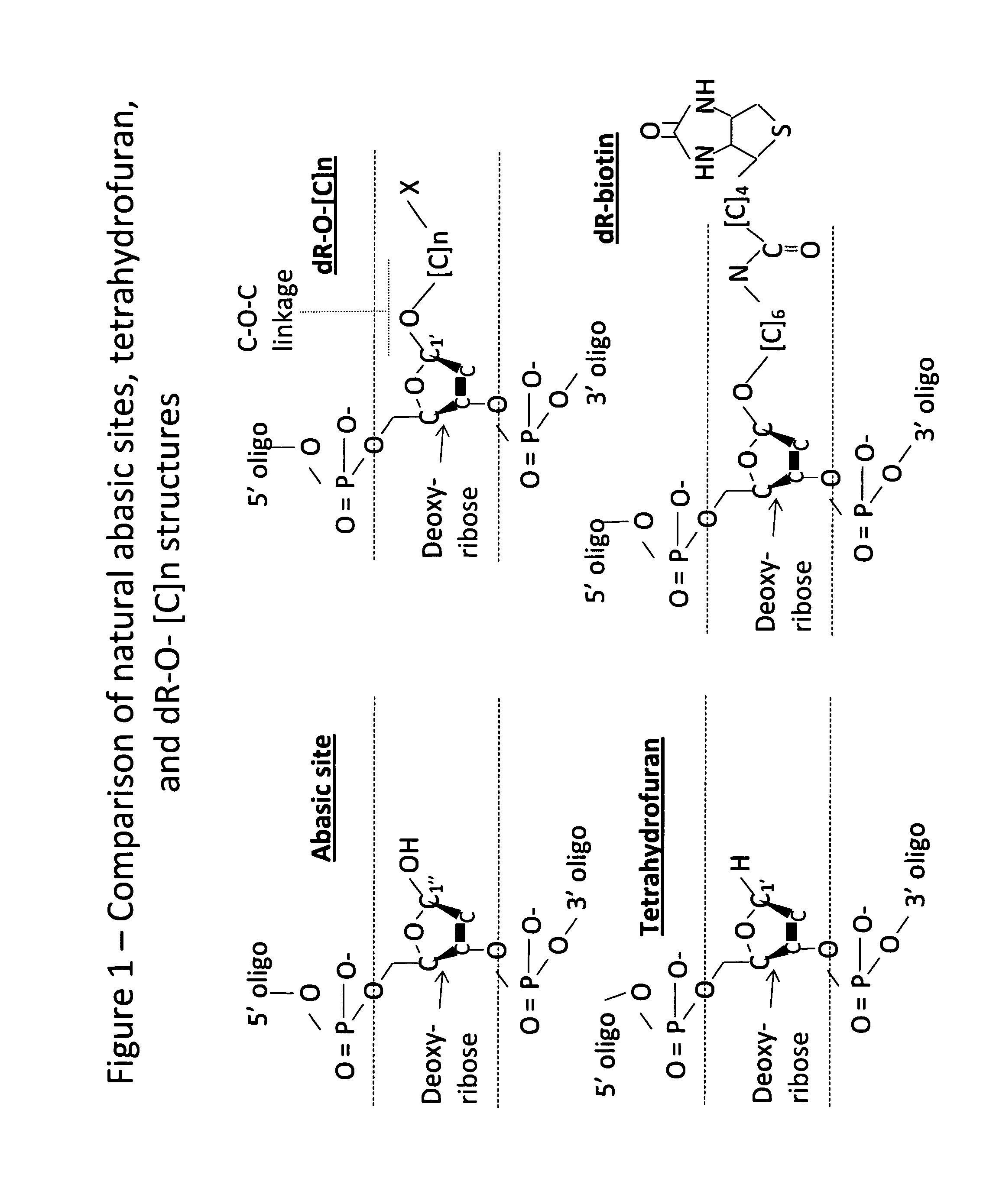
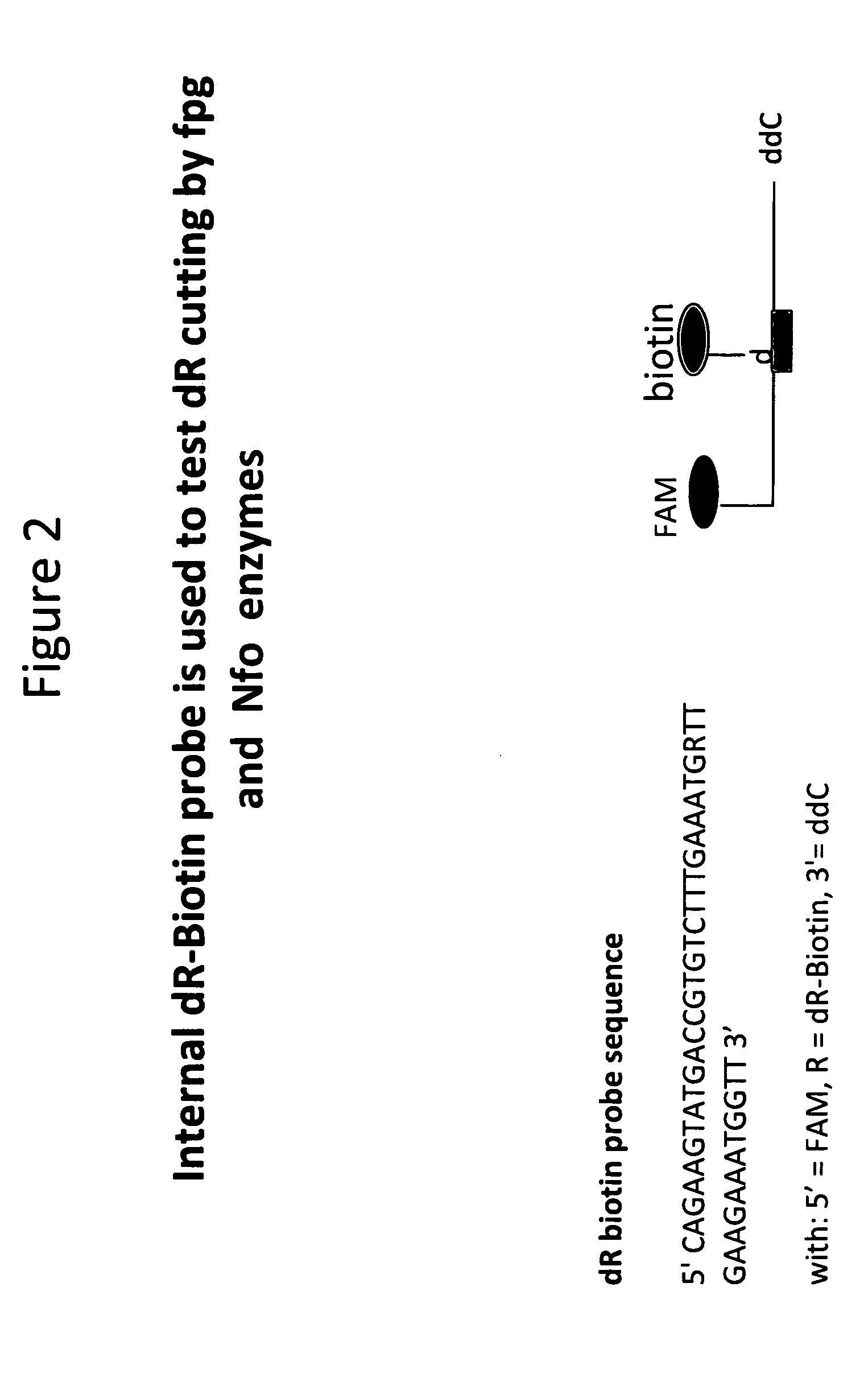
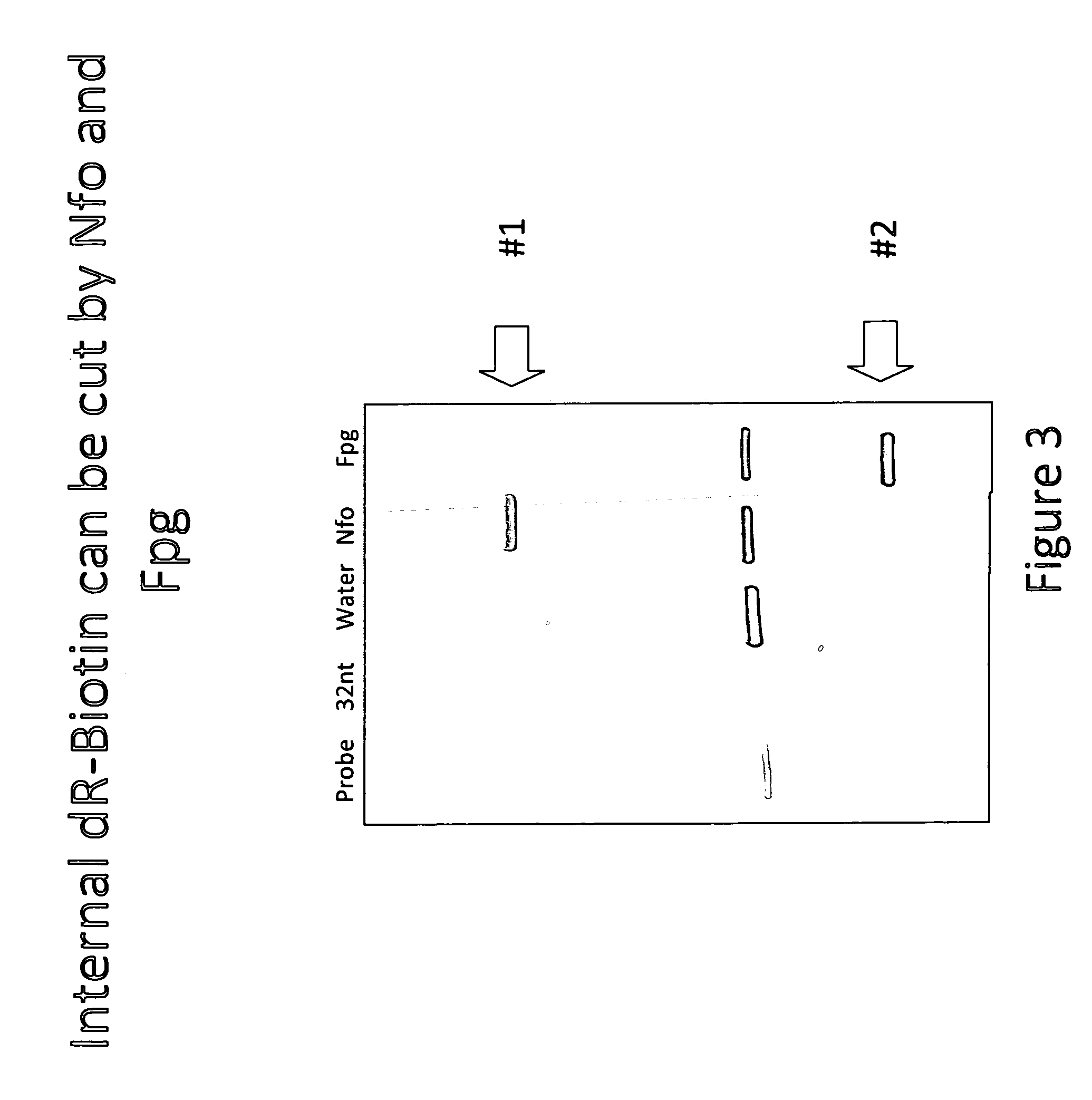
DNA Glycosylase/Lyase and AP Endonuclease substrates
ActiveUS20110053153A1Prevent polymerase extensionMaterial nanotechnologySugar derivativesLyaseOligonucleotide
A new class of nucleic acid substrates for AP endonucleases and members of the glycosylase / lyase family of enzymes is described. Representatives of each family, the enzymes Nfo and fpg, respectively, cleave nucleic acid backbones at positions in which a base has been replaced by a linker to which a variety of label moieties may be attached. The use of these synthetic substrates embedded within oligonucleotides is of utility in a number of applications.
Owner:ABBOTT DIAGNOSTICS SCARBOROUGH INC
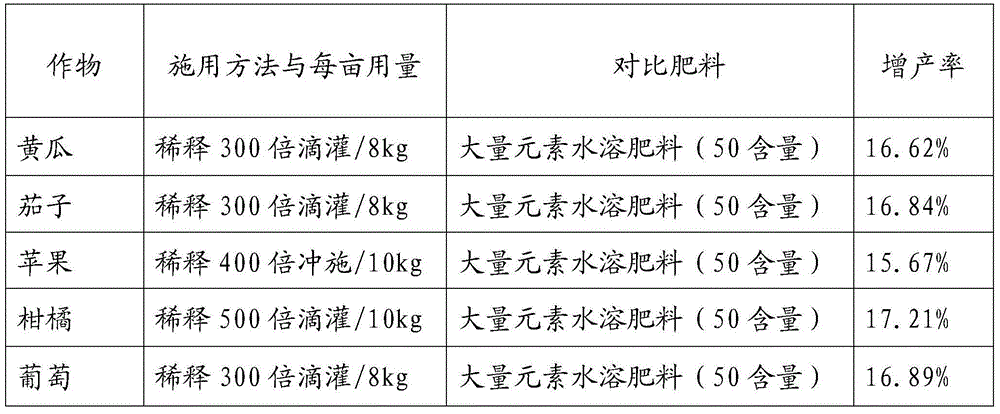
Seaweed oligosaccharide micro-ecology drip irrigation fertilizer and preparation method thereof
The present invention belongs to the technical field of seaweed fertilizers, and particularly relates to a seaweed oligosaccharide micro-ecology drip irrigation fertilizer, which comprises, by weight, 10-60% of a seaweed oligosaccharide solution, 10-50% of a molasses solution, 20-40% of a composite microorganism bacterial solution, and 10-40% of large, medium and trace elements, wherein crushed seaweed and water are mixed, a biological lyase is added to carry out enzymolysis so as to obtain a seaweed enzymolysis liquid, and extraction and pressure filtration are performed under an alkaline condition so as to obtain the seaweed oligosaccharide solution. The invention further provides a preparation method of the seaweed oligosaccharide micro-ecology drip irrigation fertilizer. According to the present invention, the effective component in the seaweed is substantially retained, the utilization rate of crops on the nutrients can be substantially improved, the preparation period is substantially shortened, the necessary organic matter and the trace elements can be supplemented, the composite microorganism bacterial solution is added, functions of disease resistance, stress tolerance, phosphorus dissolving, potassium dissolving, and soil physical structure increasing are provided, and various types of soil-borne diseases can be effectively prevented and controlled.
Owner:寿光圣德源生物科技有限公司
METHODS FOR TREATING CANCER USING 17alpha-HYDROXYLASE/C17,20-LYASE INHIBITORS
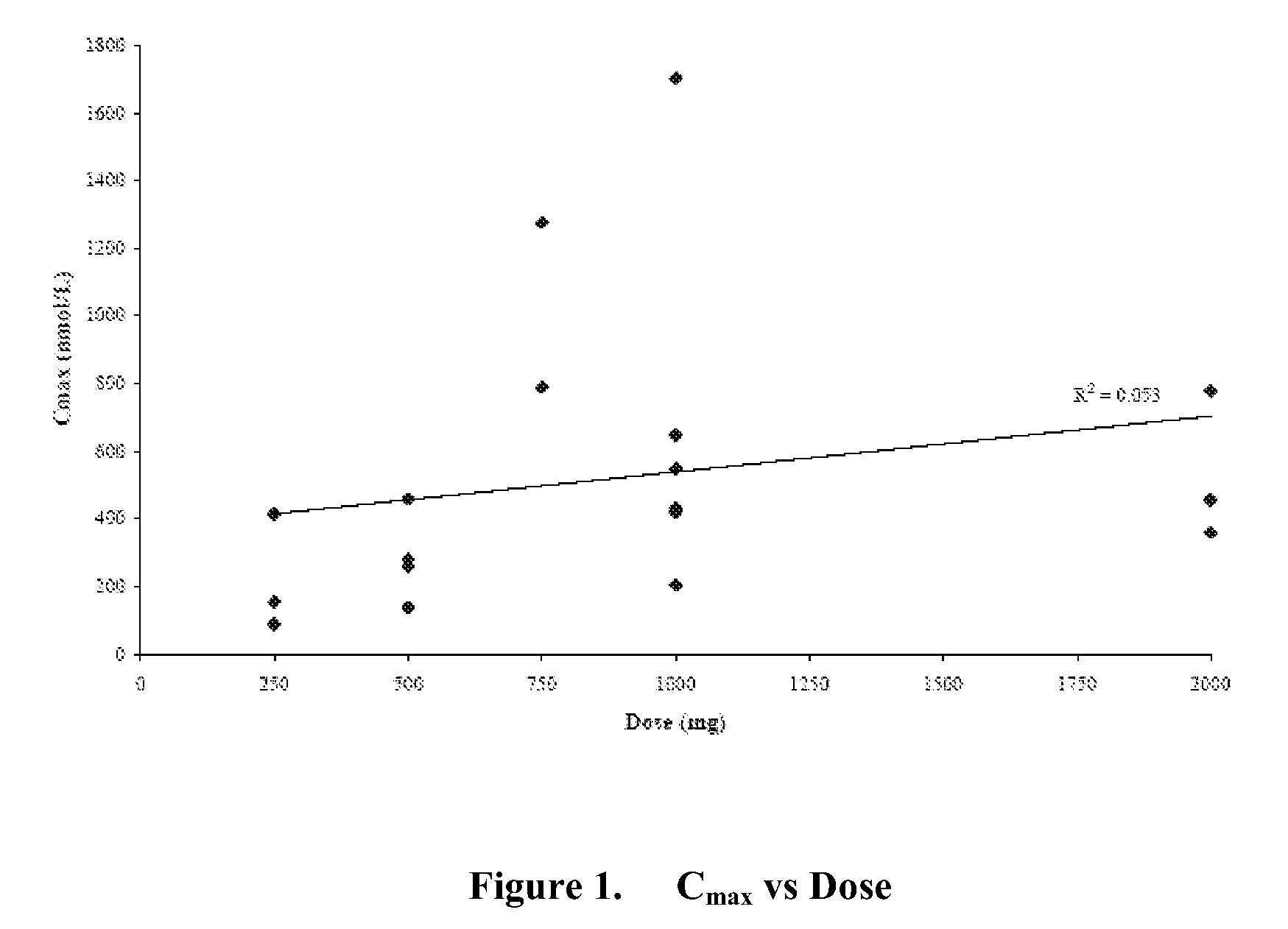
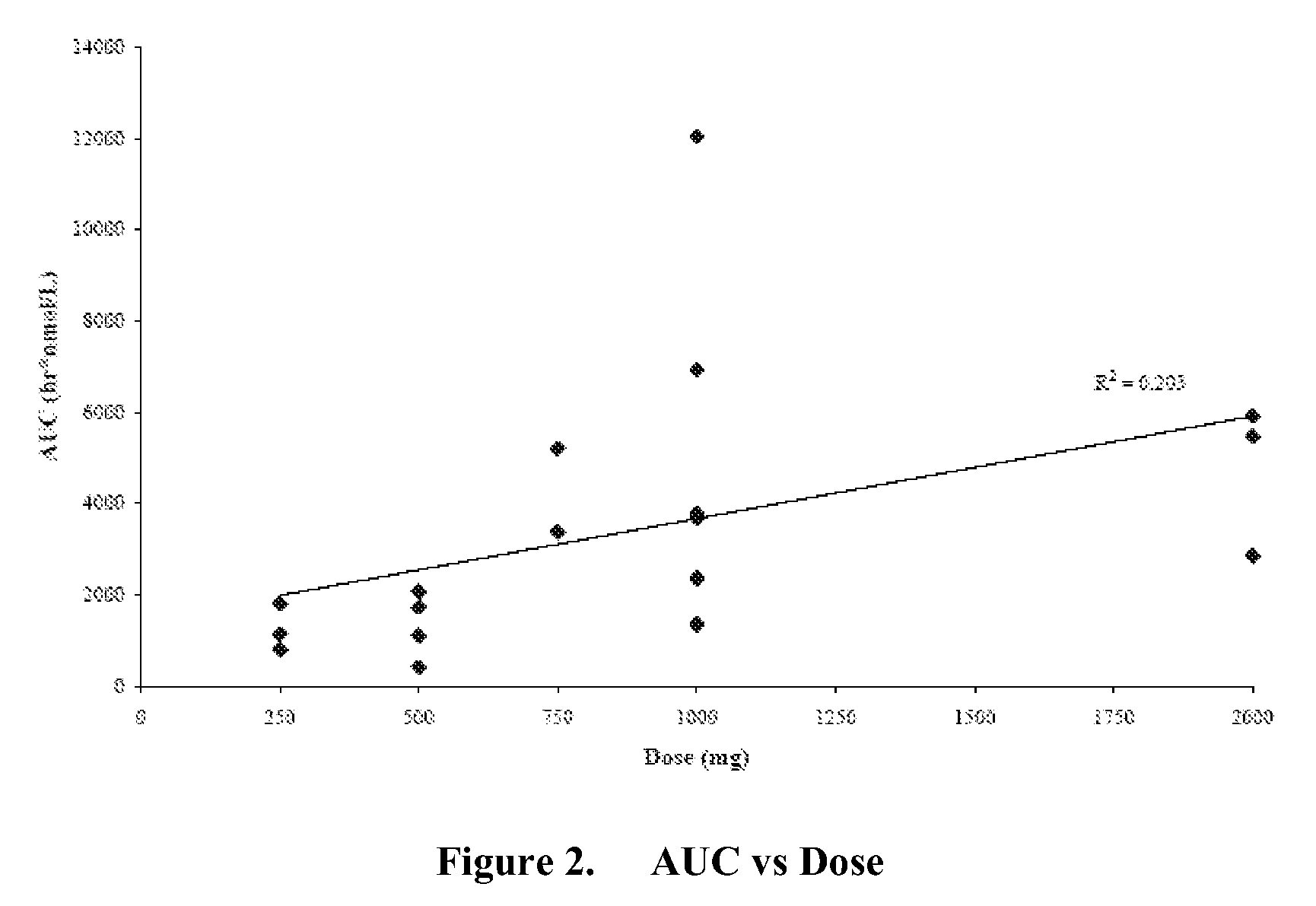
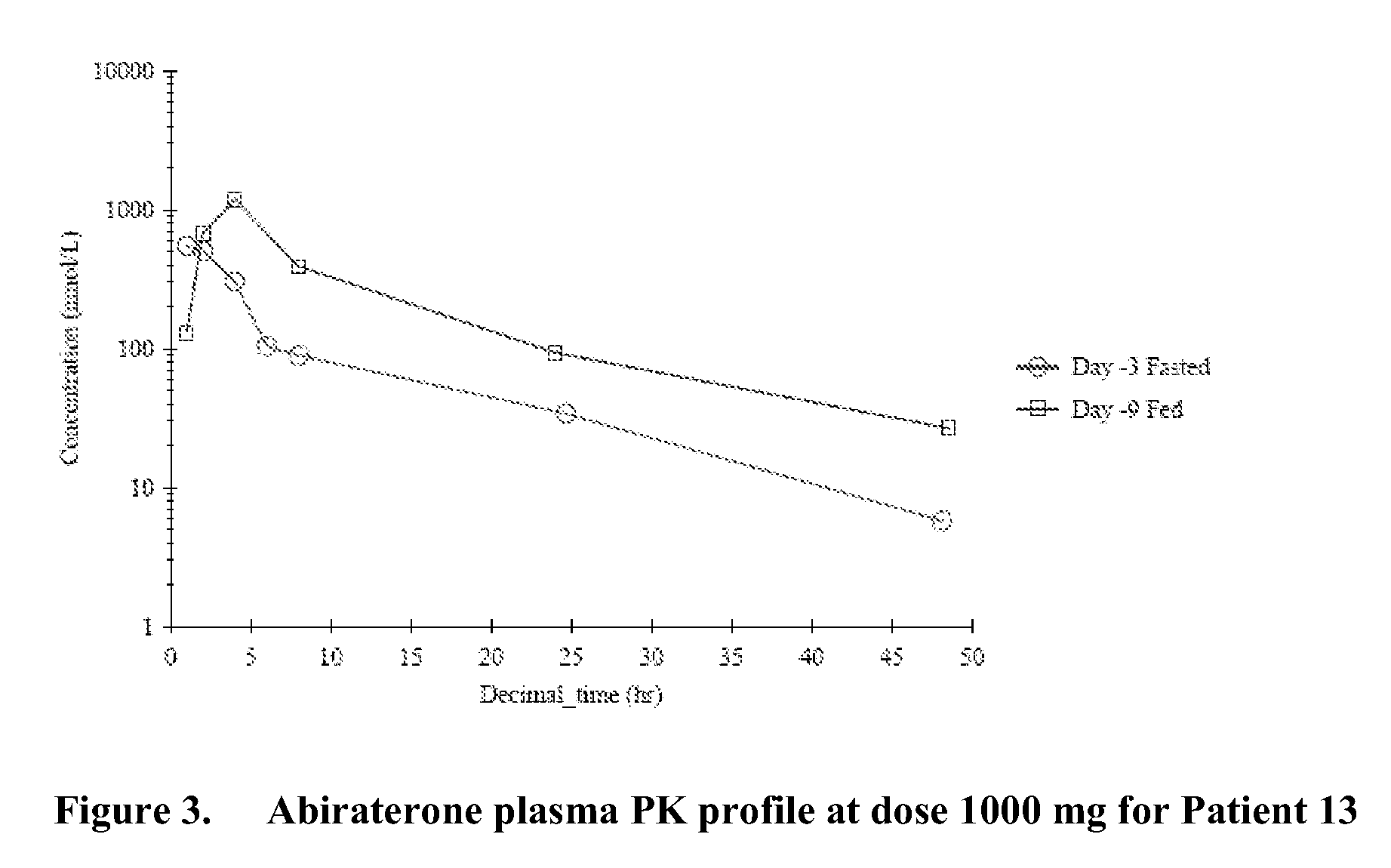
InactiveUS20090124587A1Reducing and avoiding progressReduced plasma concentrationOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsMetaboliteRegimen
Owner:AUERBACH ALAN H +1
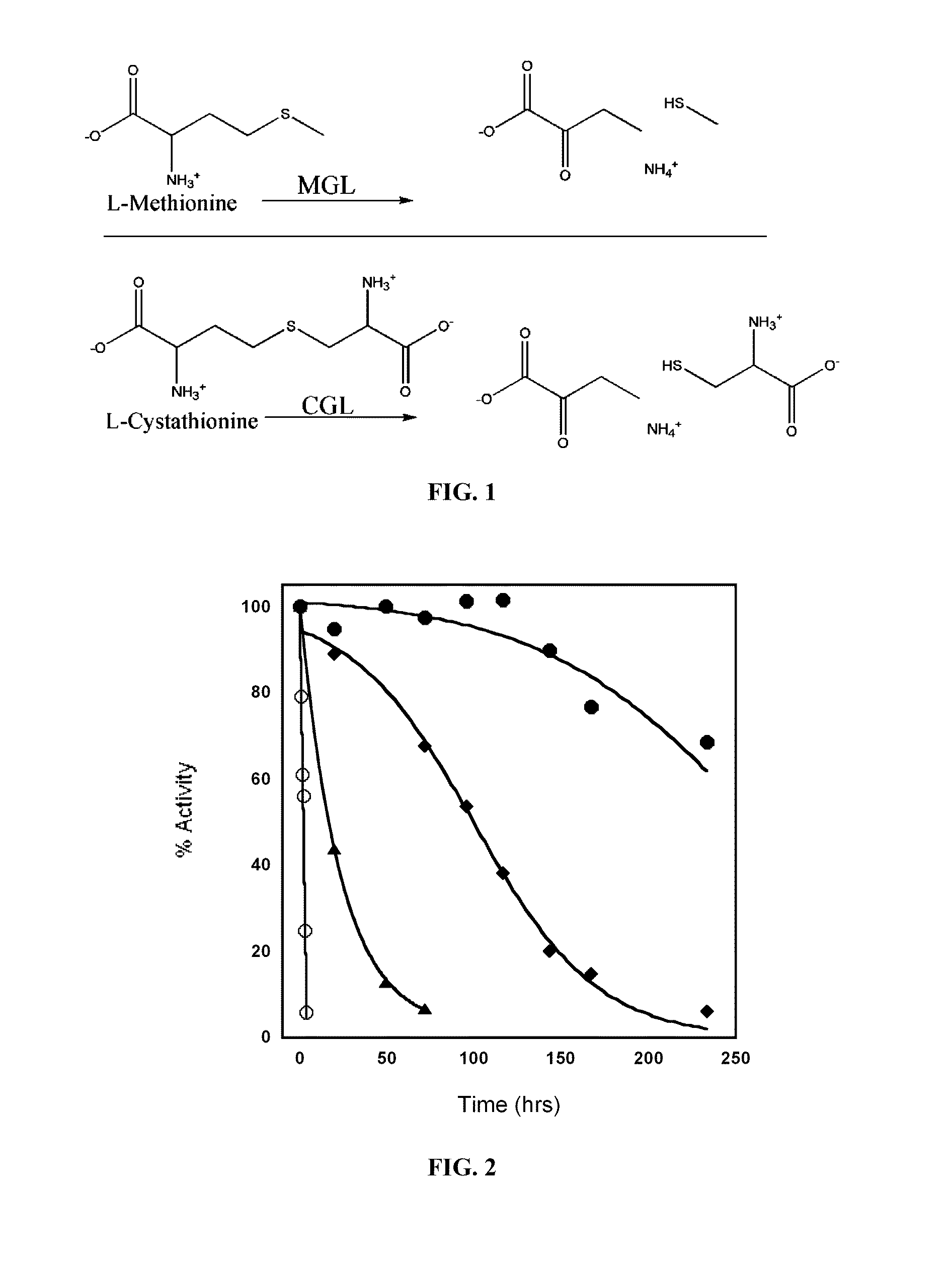
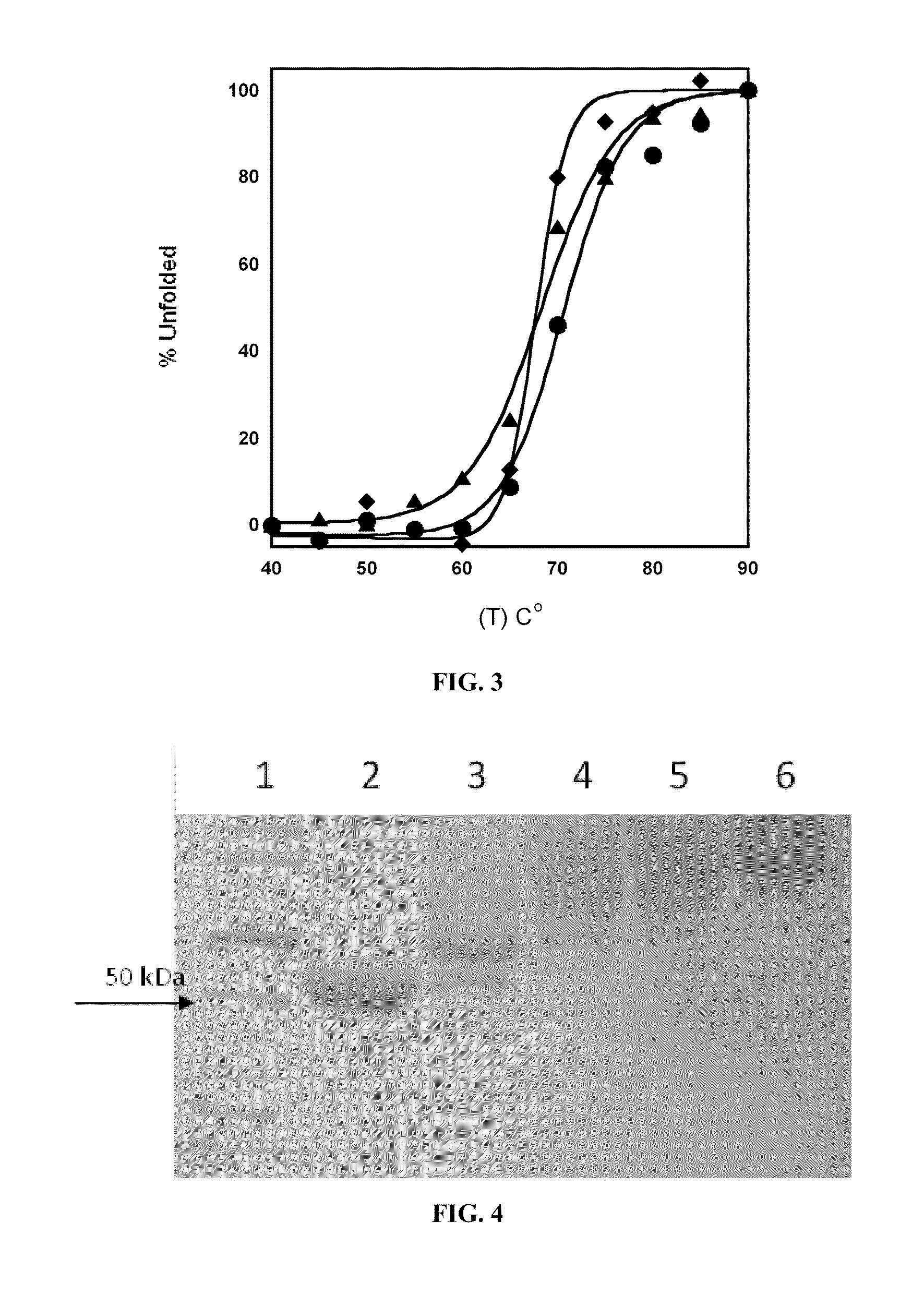
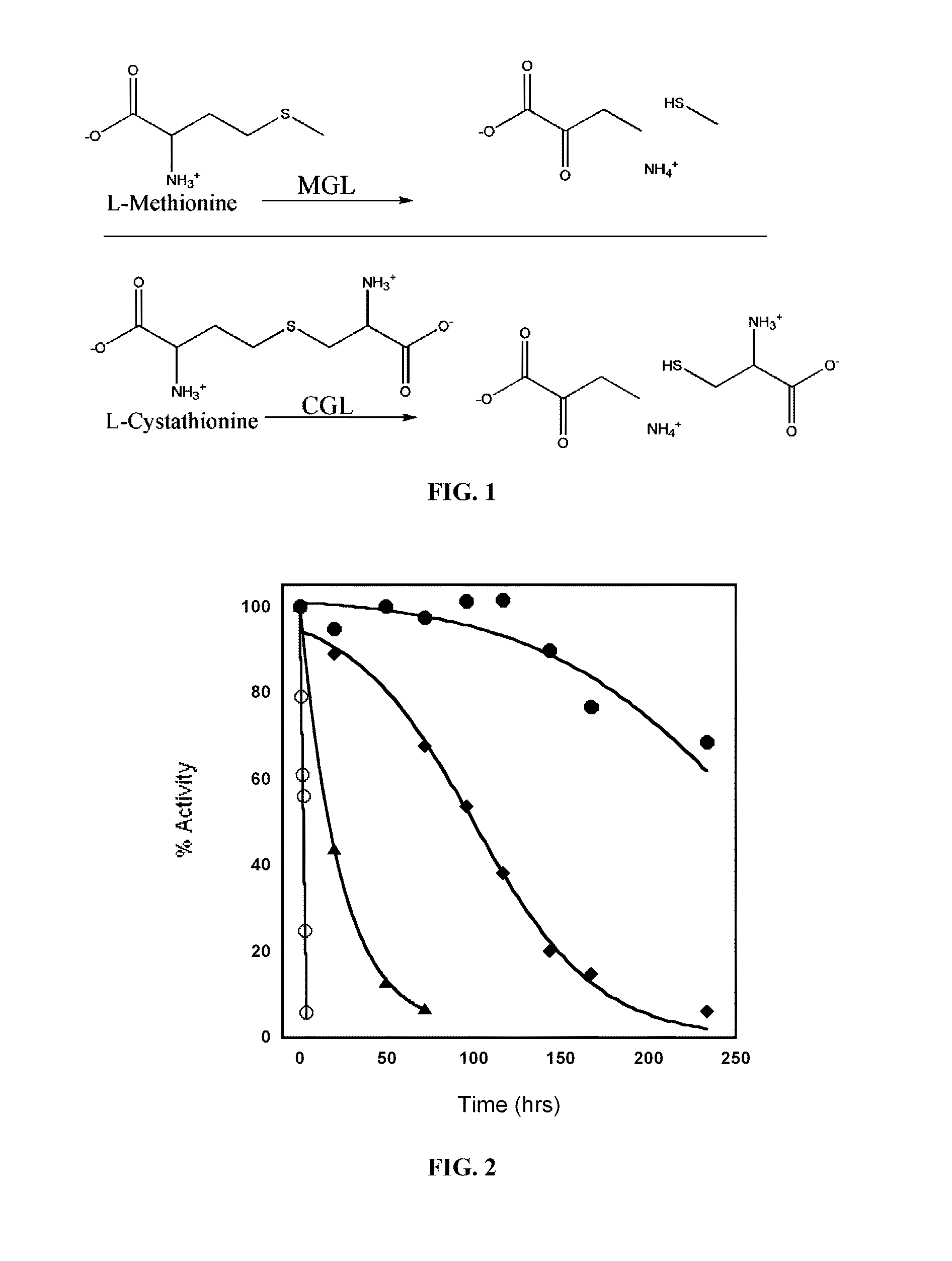
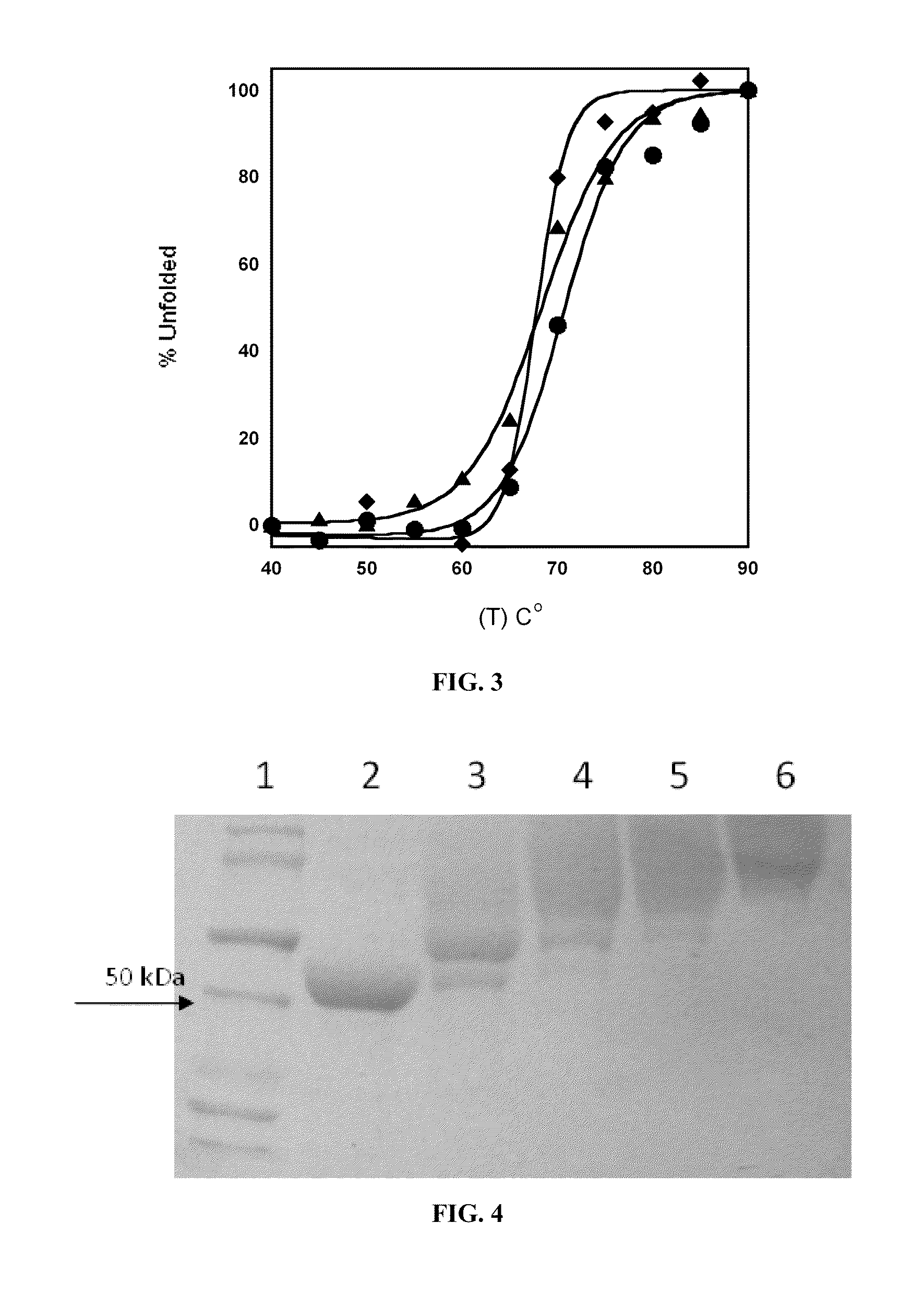
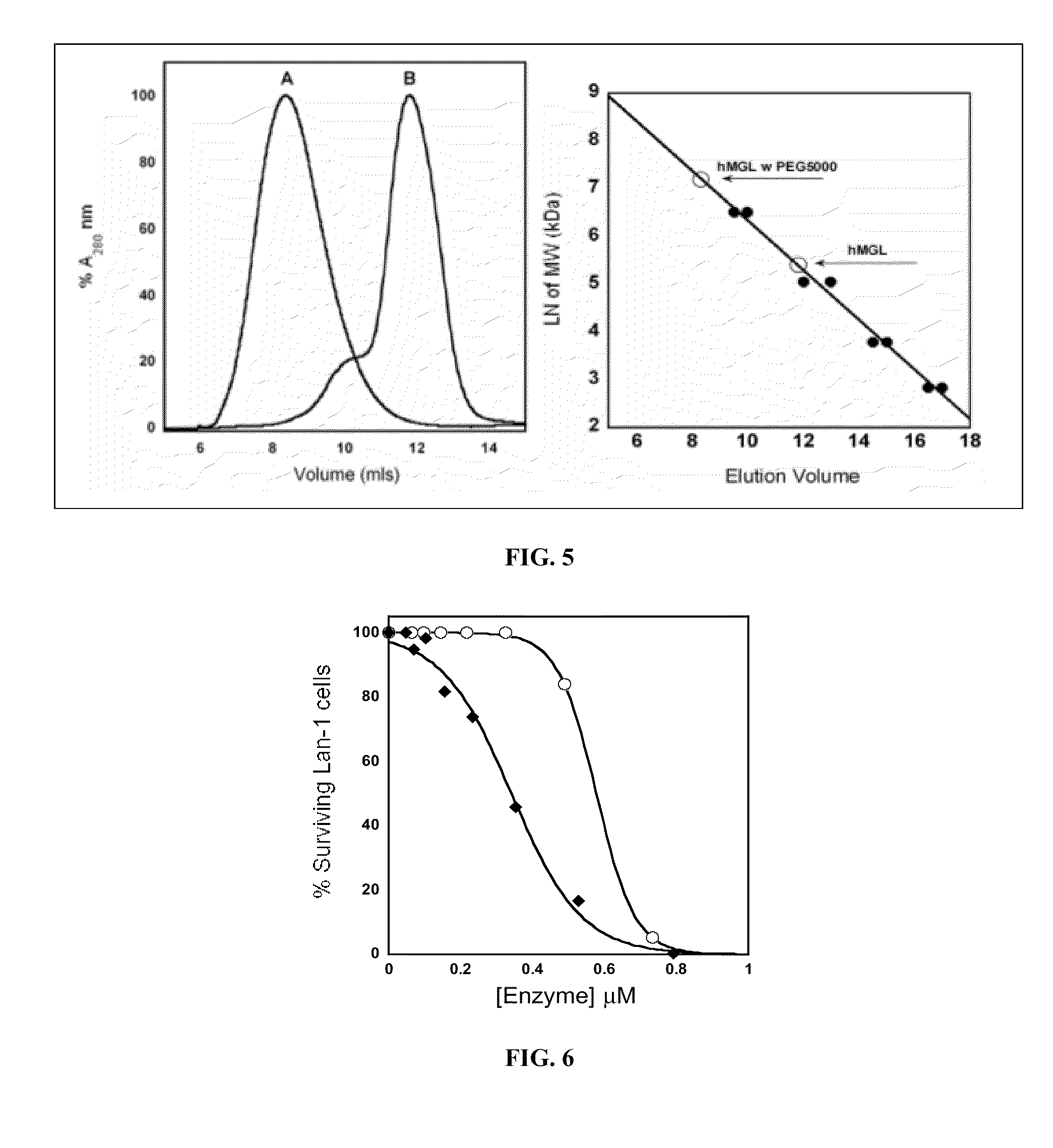
Engineered enzymes with methionine-gamma-lyase enzymes and pharmacological preparations thereof
ActiveUS20110200576A1Low immunogenicityIncrease serum stabilityBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsAmino acid substitutionLyase
Methods and composition related to the engineering of a novel protein with methionine-γ-lyase enzyme activity are described. For example, in certain aspects there may be disclosed a modified cystathionine-γ-lyase (CGL) comprising one or more amino acid substitutions and capable of degrading methionine. Furthermore, certain aspects of the invention provide compositions and methods for the treatment of cancer with methionine depletion using the disclosed proteins or nucleic acids.
Owner:AEMASE
Composition and method of treating mastitis
InactiveUS20070077235A1Improve purification effectPromote sportsBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsLyaseMastitis
A composition and method for treating bacterial infections by the use of an effective amount of at least one lytic specific for the bacteria causing specific. The lytic enzyme is genetically coded for by a bacteriophage which may be specific for said bacteria. The enzyme may be at least one lytic protein or peptides in a natural or modified form.
Owner:LOOMIS LAWRENCE +1
Composition containing bifida ferment lysate and preparation method and application of composition to cosmetics
InactiveCN110464693AReduce churnHigh glossCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsWrinkle skinFreeze-drying
The invention belongs to the field of cosmetics, and particularly relates to a composition containing bifida ferment lysate and a preparation method and application of the composition to the cosmetics. The composition includes a bifida ferment lysate composition, a peptide composition and a rice extract, and the composition is prepared from the following components in parts by mass: 1-40 parts ofthe bifida ferment lysate, 1-20 parts of the peptide composition, and 1-20 parts of the rice extract, and the composition further includes 1-20 parts of a moisturizing composition, and the bifida ferment lysate composition includes bifida freeze-dried powder, and a bifida freeze-dried powder lyase solution. The composition containing the bifida ferment lysate has the beneficial effects that a formula is reasonably set, functions are various, wrinkles can be significantly reduced, the pigment content is reduced, skin glossiness is increased, the skin color is brightened, skin elasticity is increased, the skin barrier is repaired, the water loss is reduced, the composition has no stimulation to the skin, and at the same time, the composition has the functions of preventing skin aging and keeping moisture for a long time, and makes the skin obtain a healthy and natural bright white state.
Owner:天津宝恒未来科技有限公司
Coding genes and applications of alginate lyases
ActiveCN108929878AHigh catalytic efficiencyStrong thermal stabilityFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionGenetic engineeringExtracellular proteins
The invention relates to alginate lyases, and in particular, relates to coding genes and applications of three algin-degrading alginate lyases. The alginate lyases comprise alginate lyases AlgAT0, AlgAT1 and AlgAT5 respectively. The coding genes of the alginate lyases have the base sequences of SEQ ID NO.1, SEQ ID NO.2 and SEQ ID NO.3 respectively. The alginate lyase genes are cloned into escherichia coli and pichia pastoris by a genetic engineering method. The AlgAT0, AlgAT1 and AlgAT5 are cloned into an expression vector of pichia pastoris; after fermentation condition optimization, fermentation is performed for 120 h, the concentrations of extracellular proteins are 0.312 g / L, 1 g / L and 9.39 g / L respectively, and the enzyme activities are 64666.67 U / mL, 126666.67 U / mL and 136025.6 U / mLrespectively. An escherichia coli recombinant strain and a pichia pastoris strain capable of producing alginase are obtained. The recombinant enzymes have stable properties and can be used for algin conversion with high added value, the enzyme activities of the three enzymes are much higher than values those reported so far, and the three enzymes have quite good potential for industrial application.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Trosine phenol lyase engineering bacteria as well as construction method thereof and application thereof
The invention relates to trosine phenol lyase engineering bacteria as well as a construction method thereof and application thereof. A tyrosine phenol lyase gene is constructed to express plasmids; chaperonin is introduced to express the plasmids to obtain the trosine phenol lyase engineering bacteria which are identified as escherichia coli FPLF8 (Escherichia coli HPLF8) preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection on February 19, 2016, with a preservation number being CCTCCNO:M 2016065. The engineering bacteria can be synthesized into levodopa by fermentation and conversion, and are efficiently expressed; the expressed product is stable and high in activity, and can be synthesized into levodopa by conversion in the presence of related substrates; and the process is simple, the cost is low, the yield is high, emission of three wastes is a little, and the application value for industrial production is achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +2
Bioproduction of para-hydroxycinnamic acid
InactiveUS20010053847A1Increased substrate specificityEnhanced TAL activitySugar derivativesBacteriaTyrosine ammonia-lyase activityTyrosine
The present invention provides several methods for biological production of para-hydroxycinnamic acid (PHCA). The invention is also directed to the discovery of new fungi and bacteria that possess the ability to convert cinnamate to PHCA. The invention relates to developing of a new biocatalyst for conversion of glucose to PHCA by incorporation of the wild type PAL from the yeast Rhodotorula glutinis into E. coli underlining the ability of the wildtype PAL to convert tyrosine to PHCA. The invention is also directed to developing a new biocatalyst for conversion of glucose to PHCA by incorporation of the wildtype PAL from the yeast Rhodotorula glutinis plus the plant cytochrome P-450 and the cytochrome P-450 reductase into E. coli. In yet another embodiment, the present invention provides for the developing of a new biocatalyst through mutagenesis of the wild type yeast PAL which possesses enhanced tyrosine ammonia-lyase (TAL) activity.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Engineered enzymes with methionine-gamma-lyase enzymes and pharmacological preparations thereof
ActiveUS8709407B2Low immunogenicityIncrease serum stabilityCarbon-sulfur lyasesSugar derivativesAmino acid substitutionLyase
Owner:AEMASE
Enzymatic reactions in the presence of keto acids
Owner:ENTERIS BIOPHARMA
Alpha-ketoglutarate producing yeast engineering strain and construction method thereof
The invention discloses an alpha-ketoglutarate producing yeast engineering strain and a construction method thereof, which belong to the field of genetic engineering. In the method, a molecular approach is adopted, and the yeast engineering strain Y.lipolytica ACL with improved ATP-citrate lyase activity is obtained by over-expressing an ATP-ATP-citrate lyase ACL coding gene from a mouse into a strain Yarrowia lipolytica WSH-Z06 for producing alpha-ketoglutarate by a fermentation method. Compared with a parent strain, the genetic engineering strain provided by the invention can intracellularly accumulate acetyl coenzyme A with the dry cell weight (DCW) of 0.89 mM / g by adopting glycerol as the unique carbon source so as to achieve the ACL activity of 3.56 U / mg protein improved by 7.5 times, achieve the alpha-ketoglutarat yield of 45.3 g / L which is 1.29 times that of parent protein and reduce the pyruvic acid yield to 17.2 g / L which is 68.8 percent of that of the parent strain, and has vast application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for remodelling cell wall polysaccharide structures in plants
InactiveUS20030159178A1Reduce the ratioImprove gel propertiesSurgical adhesivesDead animal preservationReticulum cellNucleotide
Methods for providing transgenic plants and parts hereof that, relative to the wild type state, is modified in a complex cell wall polysaccharide structure including pectins and hemicelluloses, the modification being in the overall glycosidic linkage pattern or the monosaccharide profile, comprising transforming a plant cell with a nucleotide sequence that causes an altered production of a complex cell wall polysaccharide-modifying enzyme such as endo-rhamnogalacturonan hydrolase, an endo-rhamnogalacturonan lyase, an endo-galactanase, an endo-arabinanase, an arabinofuranosidase, a galactosidase such as a beta-galactosidase, a xylosidase and an exo-galacturosidase. The modification can occur in vivo or post harvest, in which latter case the modifying enzyme is separated in the growing plant from its substrate, e.g. by targeting the enzyme to the Golgi, the endoplasmic reticulum or a vacuole, or is in a form that is inactive in the plant. After harvest the enzyme is brought into contact with its substrate or it is activated to provide the desired post harvest modification of the cell wall polysaccharide. The transgenic plant materials have improved functionalities and are useful in food and feed manufacturing and as pharmaceutically or medically active substances.
Owner:POALIS
Engineered phenylalanine ammonia lyase polypeptides
ActiveUS9611468B2Improve toleranceReduce sensitivityCarbon-nitrogen lyasesNervous disorderLyasePolynucleotide
The present invention provides engineered phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) polypeptides and compositions thereof, as well as polynucleotides encoding the engineered phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) polypeptides.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
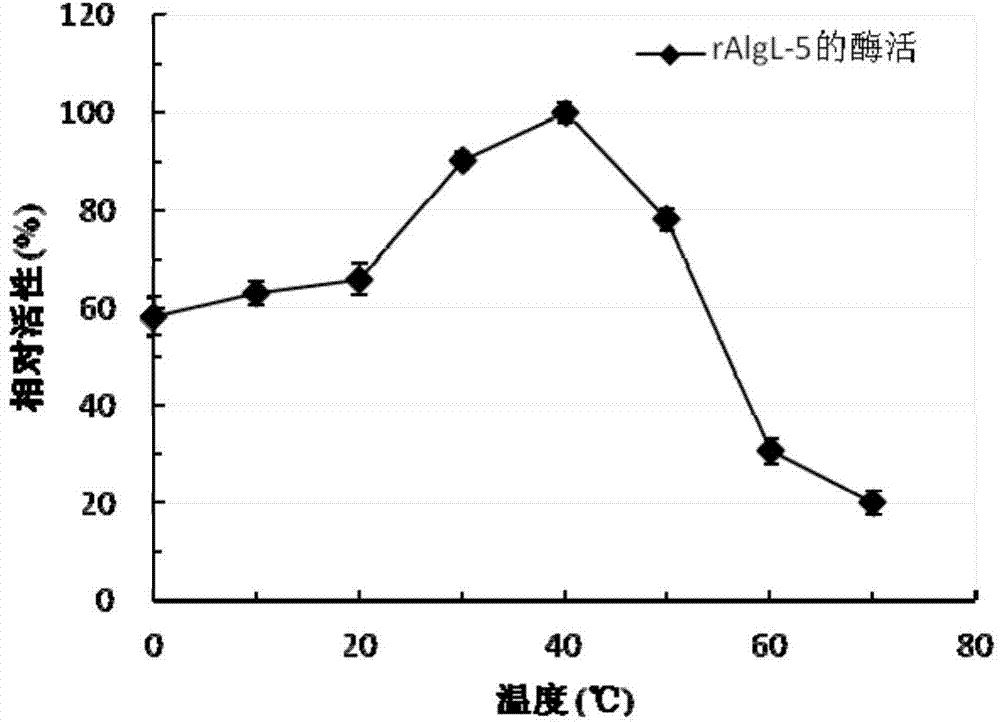
Incision-type sodium alginate lyase as well as encoding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN104293754AStable in naturePotential for industrial applicationsBacteriaFermentationTrisaccharideLyase
The invention relates to incision-type sodium alginate lyase as well as an encoding gene and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the incision-type sodium alginate lyase AlgL-5 is as shown in SEQ ID NO.2. A gene for encoding the incision-type sodium alginate lyase AlgL-5 is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1. Main oligosaccharide products generated in a process of degrading sodium alginate by using the incision-type sodium alginate lyase AlgL-5 include unsaturated disaccharide, unsaturated trisaccharide, unsaturated tetrasccharide and unsaturated pentasaccharide. Pentasaccharide is the smallest unsaturated oligosaccharide substrate of lyase, and disaccharide is the smallest unsaturated oligosaccharide product of lyase. The recombinant enzyme is stable in property and has certain industrial application potential.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Reverse-resisting yield-increasing preparation for plant
The invention relates to a plant resistance agent, in particular to a leaf surface preparation for rice disease-resistant and yield increase, which belongs to the field of plant nutrition physiology. The preparation consists of a proline, a methionine, phenylalanine and other basic components as well as a trace element, an additive and water. The preparation is directly added through the leaf surface, with the resistance effect on disease, such as rice blast, etc.; the key point is that the methionine is transmitted into ethylene, which activates an oxidase and lyase system in vivo, promotes the phenylalanine and the proline to synthesize a lignin and strengthens host cell wall; cell allergic necrosis reaction is formed; a plant protection is generated, such as a flavonoid and a phenolic acid, etc. The invention can be sprayed in breach period and full heading period of the rice, and with test, control effect of rice blast is more than 75 percent, which is similar to that of a tricyclazole, moreover, disease index of the invention is lower than that of the tricyclazole. Compared with the rice field sprayed with the tricyclazole, the rice field sprayed with the invention has yield increase of 12 kg.
Owner:祖小力
Composition for treatment of an ocular bacterial infection
A composition for treatment of bacterial infections of the eye is disclosed which comprises a lytic enzyme composition specific for the infecting bacteria, and a carrier for delivering said lytic enzyme. The carrier for delivering at least one lytic enzyme to the eye may be but is not limited to the use of an isotonic solution.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
Lyase for killing staphylococcus and application of lyase
ActiveCN103122347ARapid lysisIncrease enzyme activityAntibacterial agentsBiocideMethicillin resistanceAdenosine
The invention discloses a lyase for killing staphylococcus and an application of the lyase and also discloses an amino acid sequence and an encoding gene sequence of the lyase. A recombined lyase constructed by using the disclosed encoding gene can realize soluble expression in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3); the lyase can be used for efficiently killing various types of staphylococcus including clinically-separated methicillin-sensitive staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) and methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in vitro and can also be used as an antibiotic for treating staphylococcus infection in vivo; and the disclosed lyase can also be used for rapidly cracking the cell wall of the staphylococcus and releasing substances in cells, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP), DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) and the like, and various detections on the staphylococcus can be realized through detecting released substances.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Vibrio FC509 strain and culturing method and application thereof
The invention relates to a Vibrio FC509 strain and a culturing method and application thereof. The Vibrio FC509 strain is collected in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on 12, March, 2014, with a collection number of CGMCC NO.8913 and an address of Institute of Microbiology Chinese Academy of Sciences NO.1 West Beichen Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing. The Vibrio sp. FC509 strain obtained by first-time separation is capable of preparing glycosaminoglycan lyase which has a specific activity of 110,000U / mg to hyaluronic acid and specific activity of 45,000U / mg to chondroitin sulfate; enzyme activity is tens to hundreds times that of the known commercialized glycosaminoglycan lyase, can be applied to fields such as medicines, cosmetics and the like, and is wide in application prospect.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Enzymolysis treatment method of algae
The invention provides an enzymolysis treatment method of algae. The method comprises the steps of material preparation, pretreatment, enzyme treatment and centrifugating. In the enzyme treatment step, the adopted enzyme is a composite enzyme which comprises proteinase, cellulase and pectinase in a mass ratio of 3:1:2. The proteinase is any one of papain, bromelin, carboxypeptidase and chymopapain. The cellulase is any one of cellobiohydrolase, endoglucanase, beta-glucosaccharase and cellobiase. The pectinase is any one of protopectinase, lyase and polygalacturonase. According to the enzymolysis treatment method of algae, the extraction rate of sodium alginate is 38.0-50.9%, and the extraction rate of alga glycine is 7.5-11.8%.
Owner:SHANDONG HETIANWANG BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Novel vibrionaceae vibrio bacterial strain and application thereof
The invention relates the vibrionaceae vibrio strain and its application. The invention relates the vibrionaceae vibrio strain from gulfweed, and the output of algin lyase made by the vibrionaceae vibrio strain is 2-37 times than that of algin lyase made with now technology. The algin lyase can be used to make algin oligosaccharide.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Glycosaminoglycan lyase and encoding gene and application thereof
The invention relates to glycosaminoglycan lyase and an encoding gene and an application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the glycosaminoglycan lyase is as shown in SEQ ID NO.2; the nucleotide sequence of the encoding gene of the glycosaminoglycan lyase is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1; the specific activity of the glycosaminoglycan lyase prepared in the invention to hyaluronic acid is 110,000 U / Mg, and the specific activity to chondroitin sulfate is 45, 000 U / Mg; the enzyme activity is tens to hundreds of times as large as that of the existing commercial glycosaminoglycan lyase (such as CSaseABC, CSaseAC, I and II and the like), and the glycosaminoglycan lyase can be used in such fields as medicine and cosmetics and the like, thereby having a broad application prospect.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com