Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
189 results about "Chaperonin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Chaperonins are proteins that provide favourable conditions for the correct folding of other proteins, thus preventing aggregation. They prevent the misfolding of proteins, which prevents diseases such as Mad Cow Disease. Newly made proteins usually must fold from a linear chain of amino acids into a three-dimensional form. Chaperonins belong to a large class of molecules that assist protein folding, called molecular chaperones. The energy to fold proteins is supplied by adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Chaperonin proteins may also tag misfolded proteins to be degraded.
Methods for diagnosis and prognosis of epithelial cancers
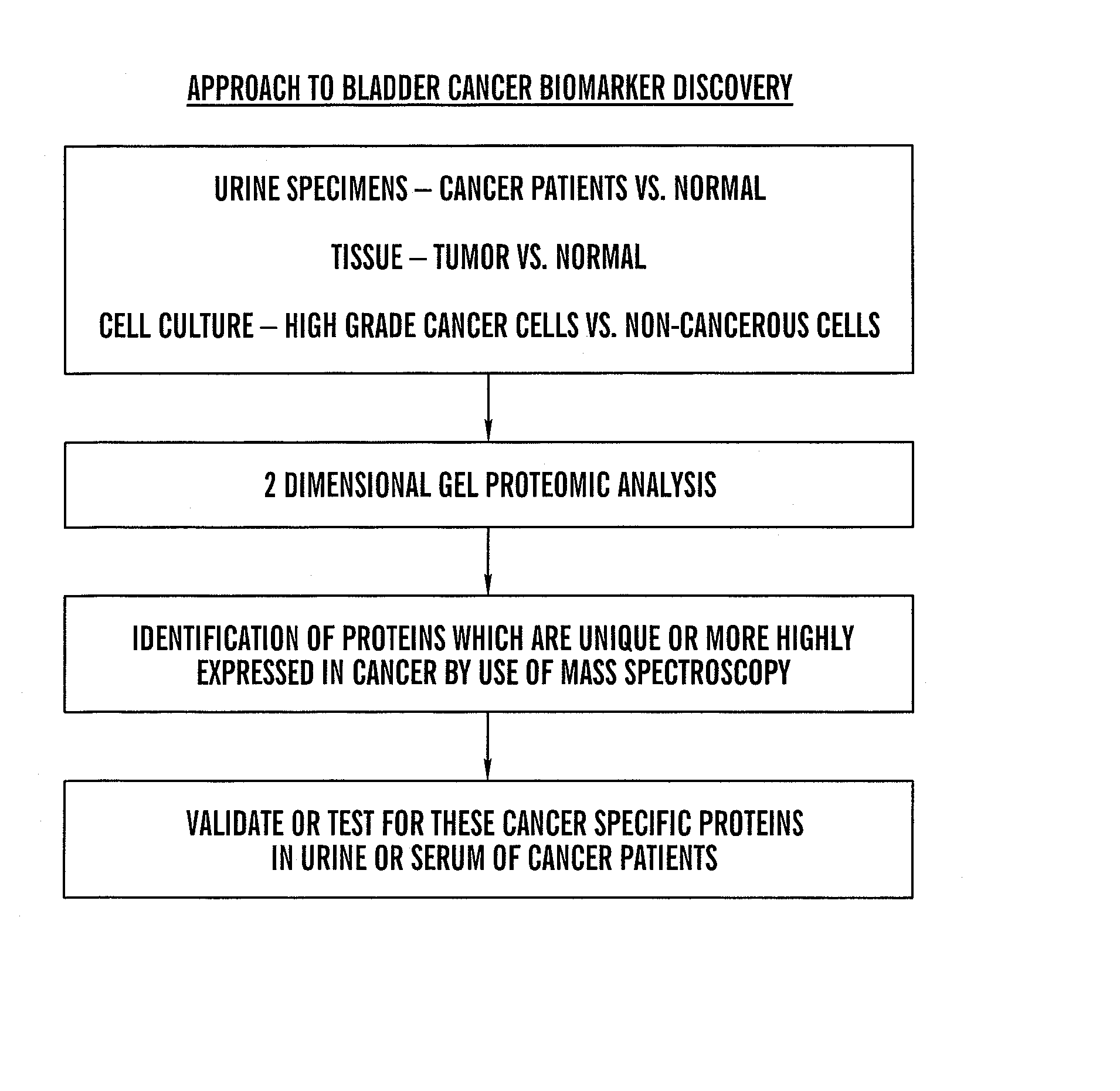
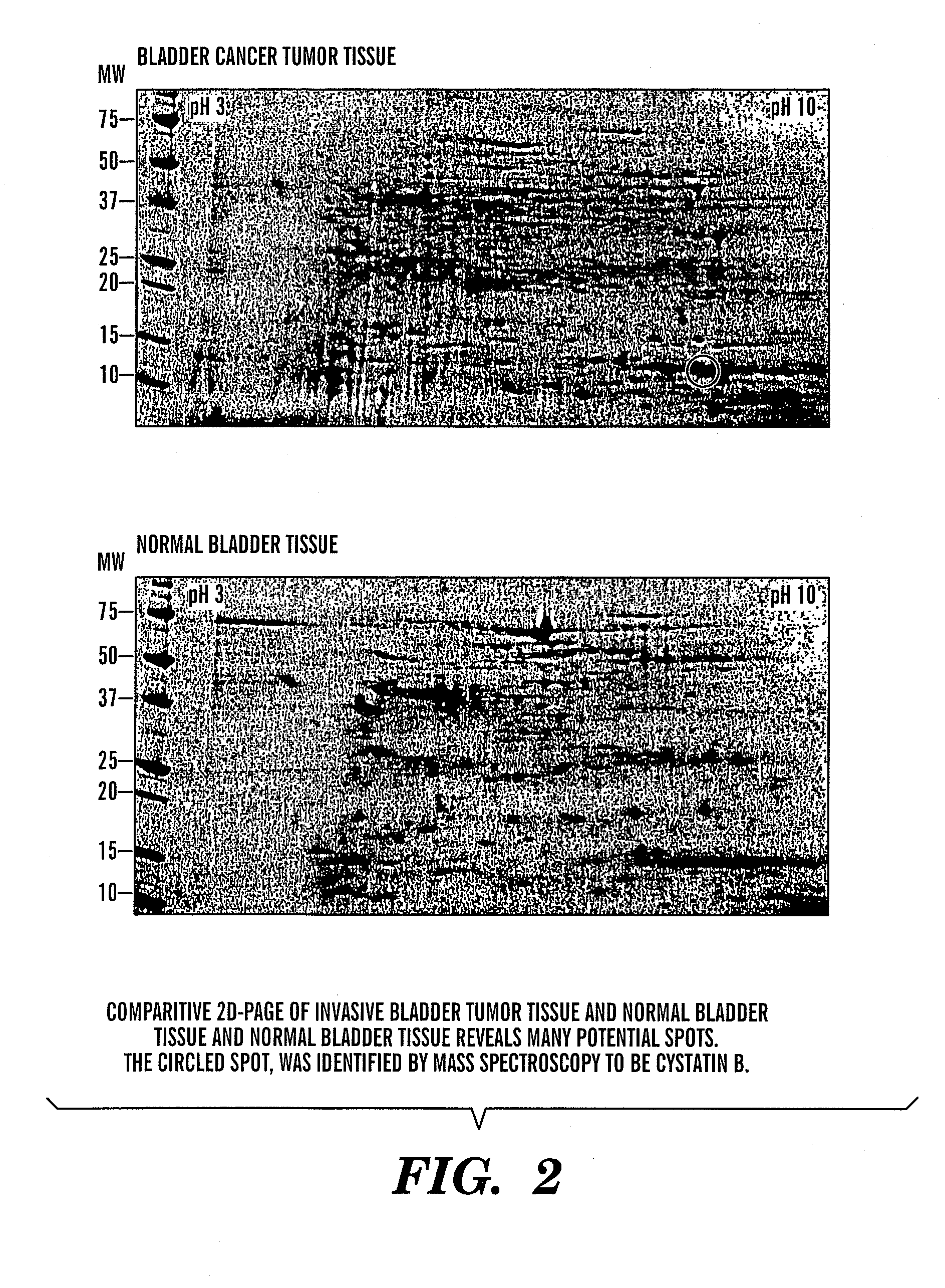
InactiveUS20080064047A1Easy diagnosisQuick and easy and safeBiological material analysisBiological testingBladder cancer patientCystatin B
The present invention is based on the discovery that three proteins, Cystatin B, Chaperonin 10, and Profilin are present in the urine of patients with bladder cancer, a cancer of epithelial origin. Accordingly, the present invention is directed to methods for prognostic evaluation of cancers of epithelial origin and to methods for facilitating diagnosis of cancers of epithelial origin by monitoring the presence of these markers in biological samples. The invention is also directed to markers for therapeutic efficacy.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
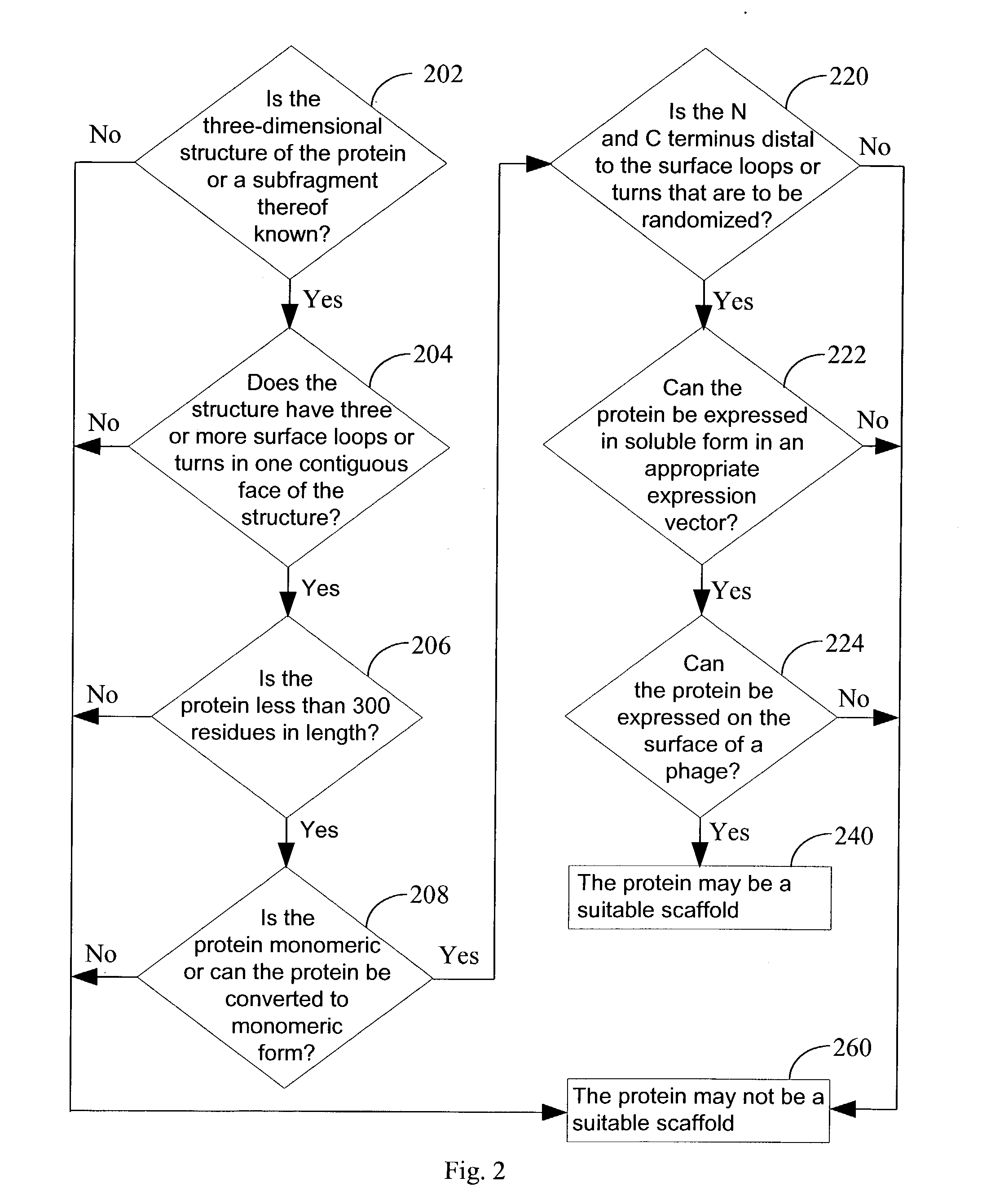
Engineered binding proteins
InactiveUS20040009530A1Unusual thermal stabilityMaterial nanotechnologyPeptide librariesADAMTS ProteinsRubredoxin
Engineered binding proteins are provided. In some cases, the parent protein corresponding to the engineered protein has a three-layer swiveling beta / beta / alpha domain. In other cases, the parent protein corresponding to the engineered protein has a rubredoxin-like fold. At least one portion of the primary sequence of the engineered protein is determined by an engineering scheme. In some case, the engineered protein is characterized by an ability to bind to a compound that the parent protein does not bind. In some cases, the parent protein is derived from a domain of a chaperonin or a rubredoxin. One form of engineering scheme used is a randomization scheme. A method for making libraries of engineered proteins, all based on a single parent protein is provided. Methods to identify proteins that bind to compounds of interest in libraries of engineered libraries is provided. An array of engineered proteins immobilized on a support is provided. Each engineered protein in the array is a chaperonin domain or a rubredoxin that has been subjected to an engineering scheme.
Owner:WILSON DAVID S +1
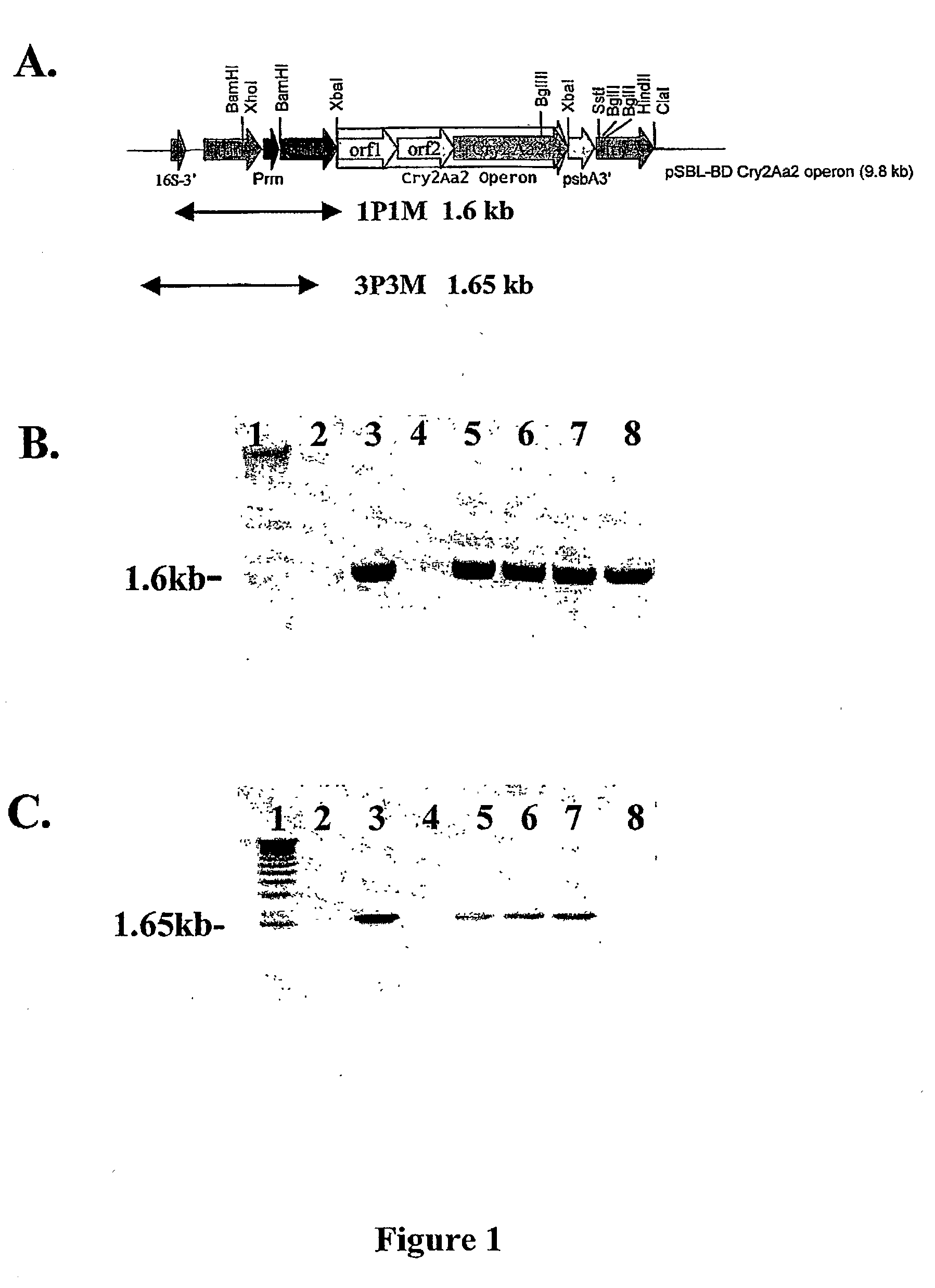
Mutiple gene expression for engineering novel pathways and hyperexpression of foreign proteins in plants
InactiveUS20030041353A1High expressionHigh copy numberClimate change adaptationDepsipeptidesPosition effectOperon
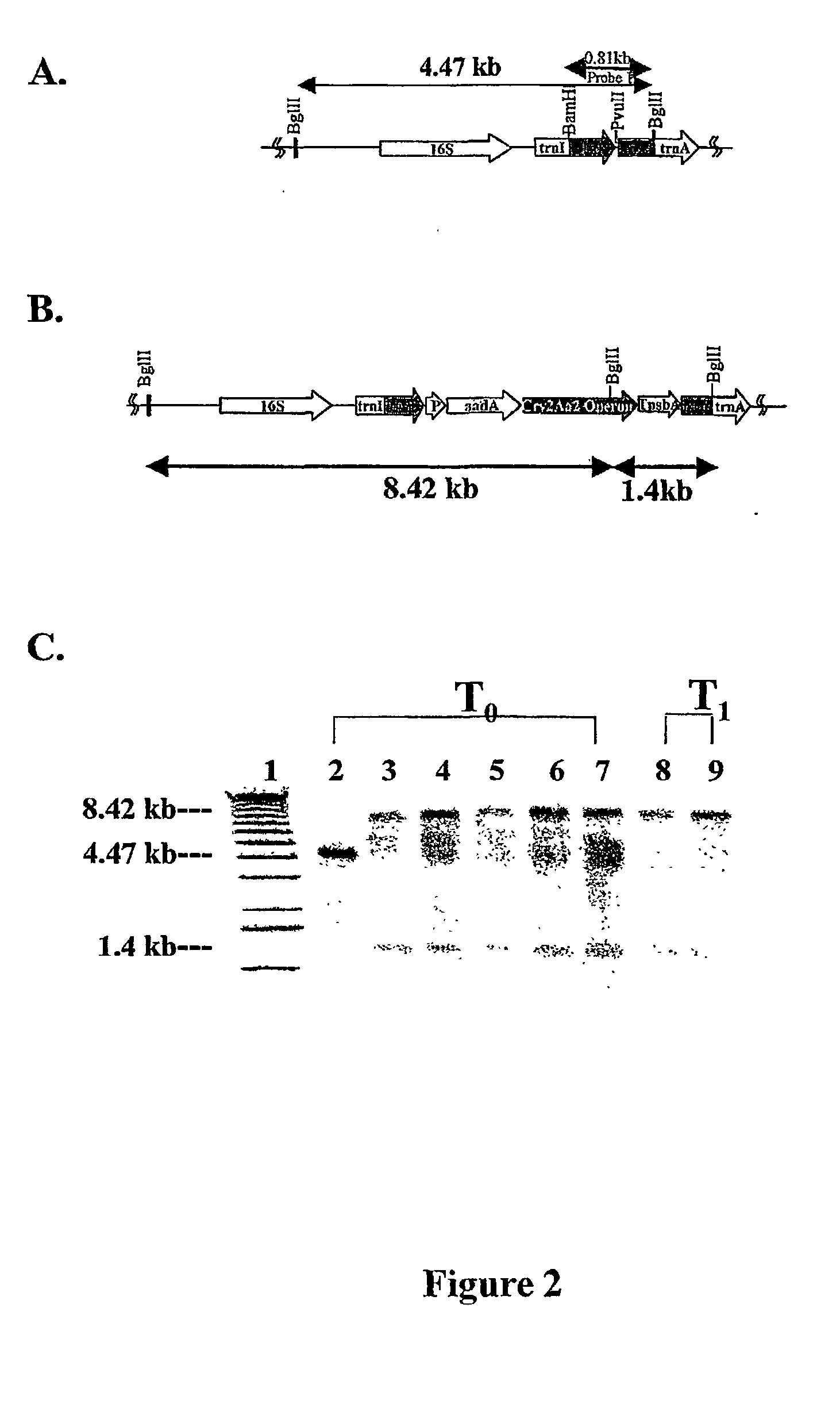
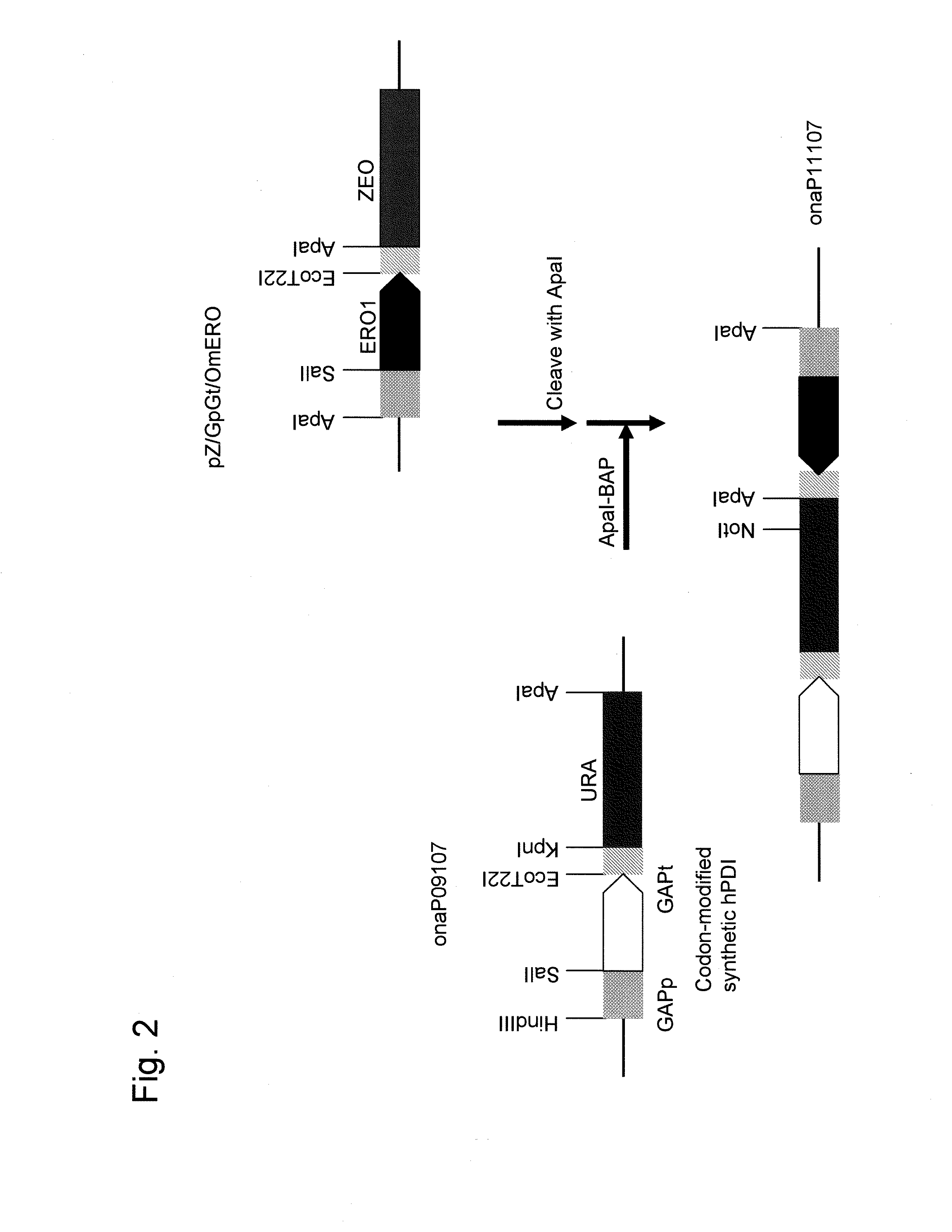
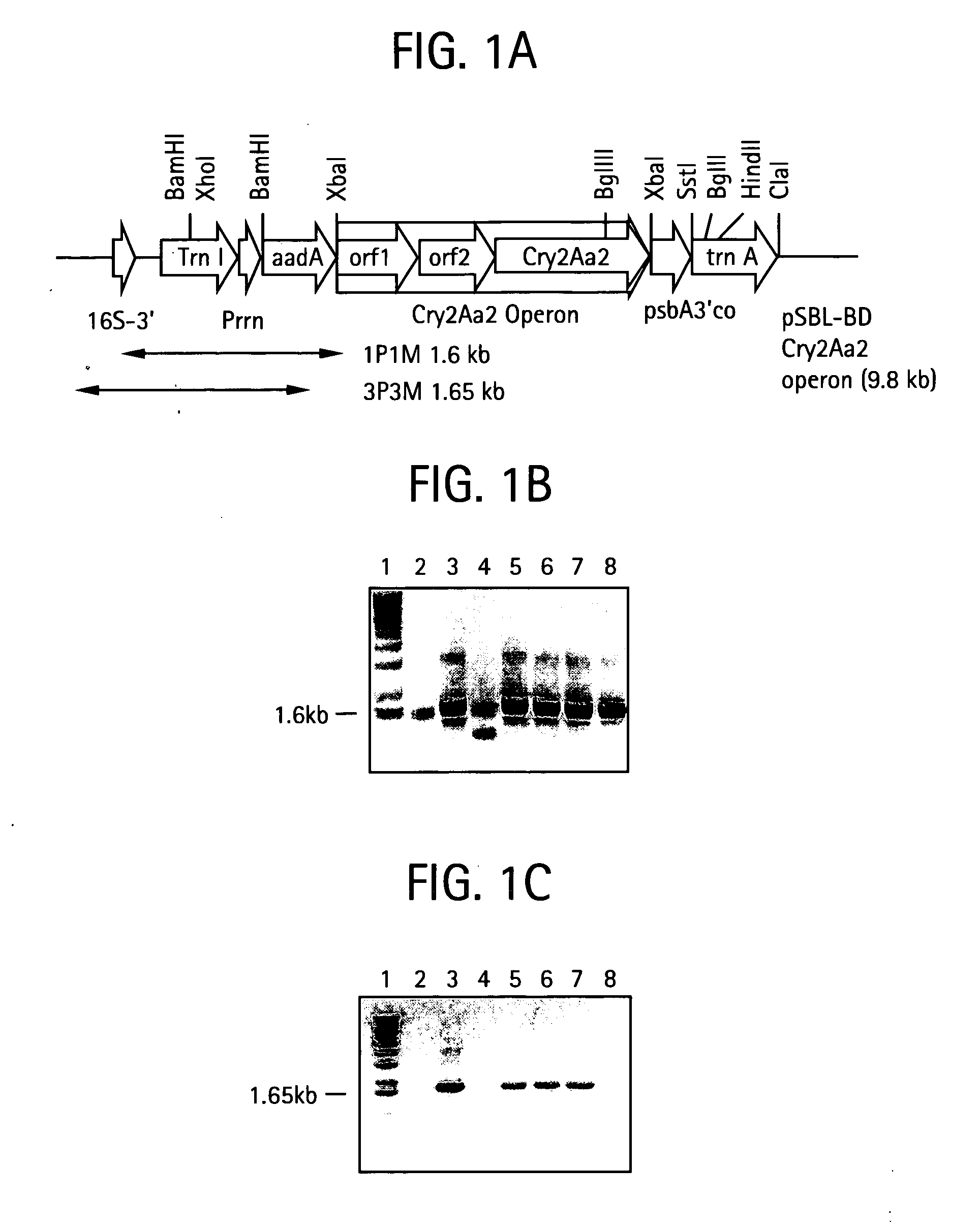
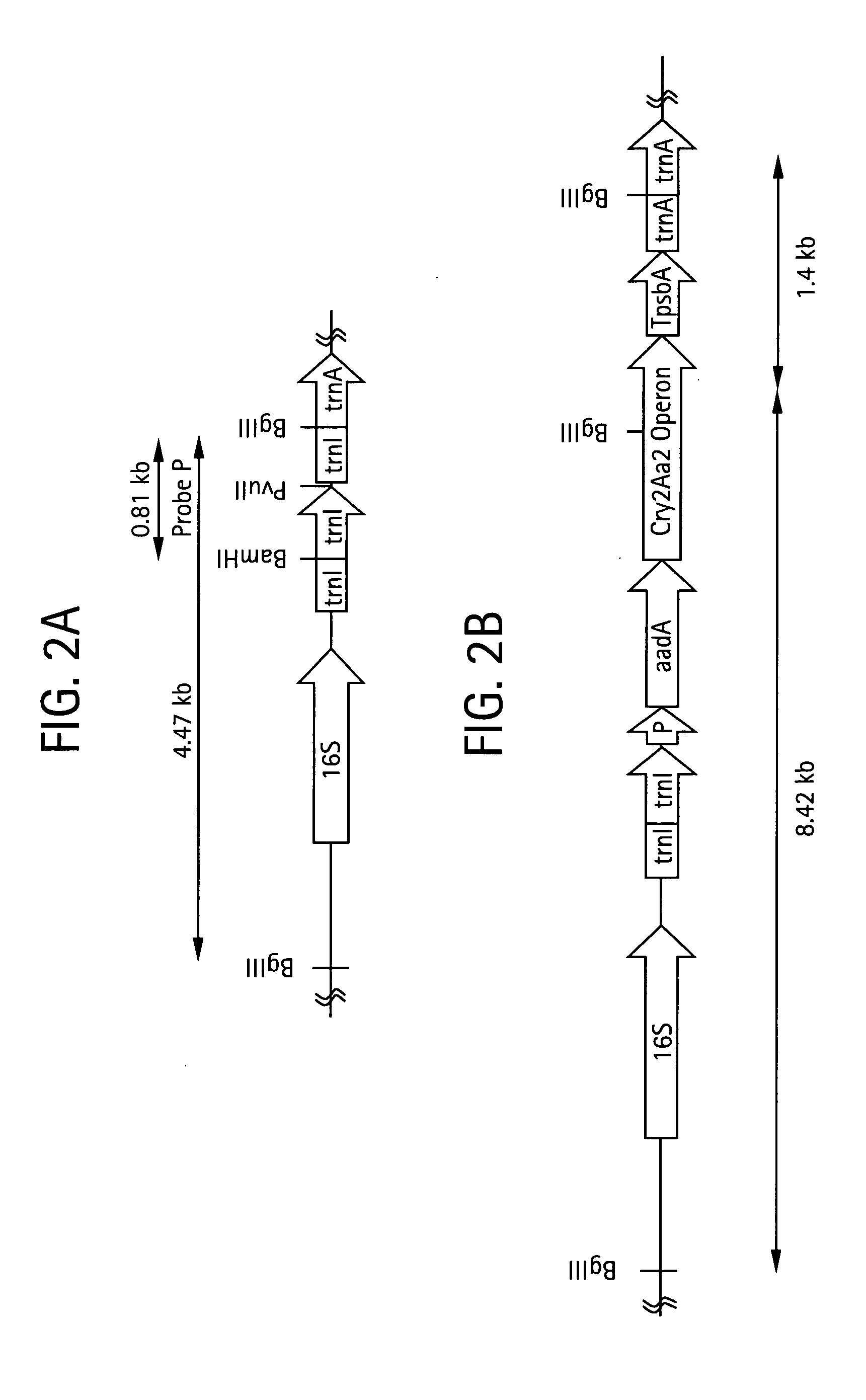
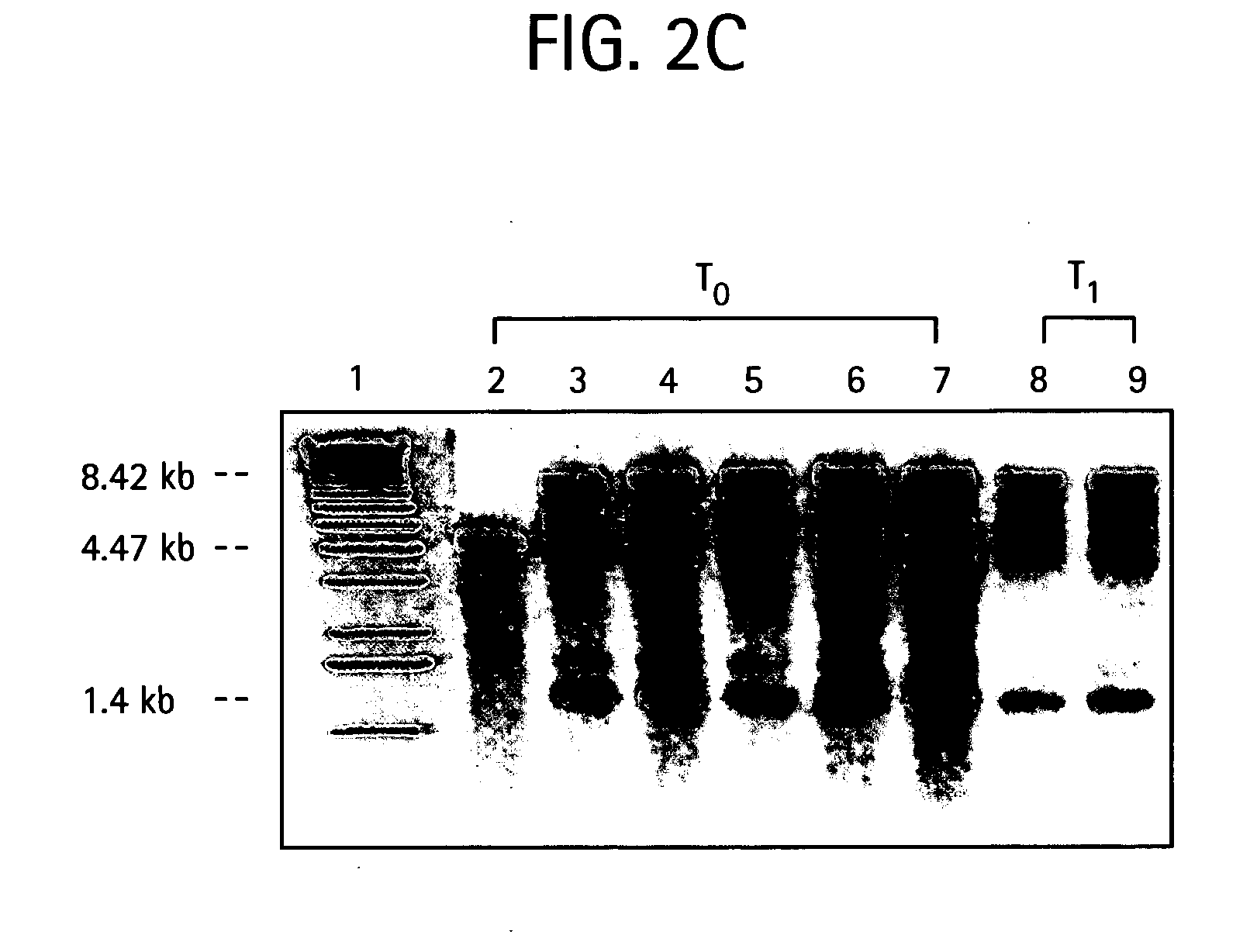
Introducing blocks of foreign genes in a single operon would avoid complications such as position effect and gene silencing inherent in putting one gene at a time into random locations in the nuclear genome. Cloning several genes into a single T-DNA does not avoid the compounded variable expression problem encountered in nuclear transgenic plants. This disclosure shows that a bacterial operon can be expressed in a single integration event as opposed to multiple events requiring several years to accomplish. Expression of multiple genes via a single transformation event opens the possibility of expressing foreign pathways or pharmaceutical proteins involving multiple genes. Expressing the Cry2aA2 operon, including a putative chaperonin to aid in protein folding, in the chloroplast via a single transformation event leads to production of crystalized insecticidal proteins. Expressing the Mer operon via a single transformation event leads to a phytoremediation system.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC +1
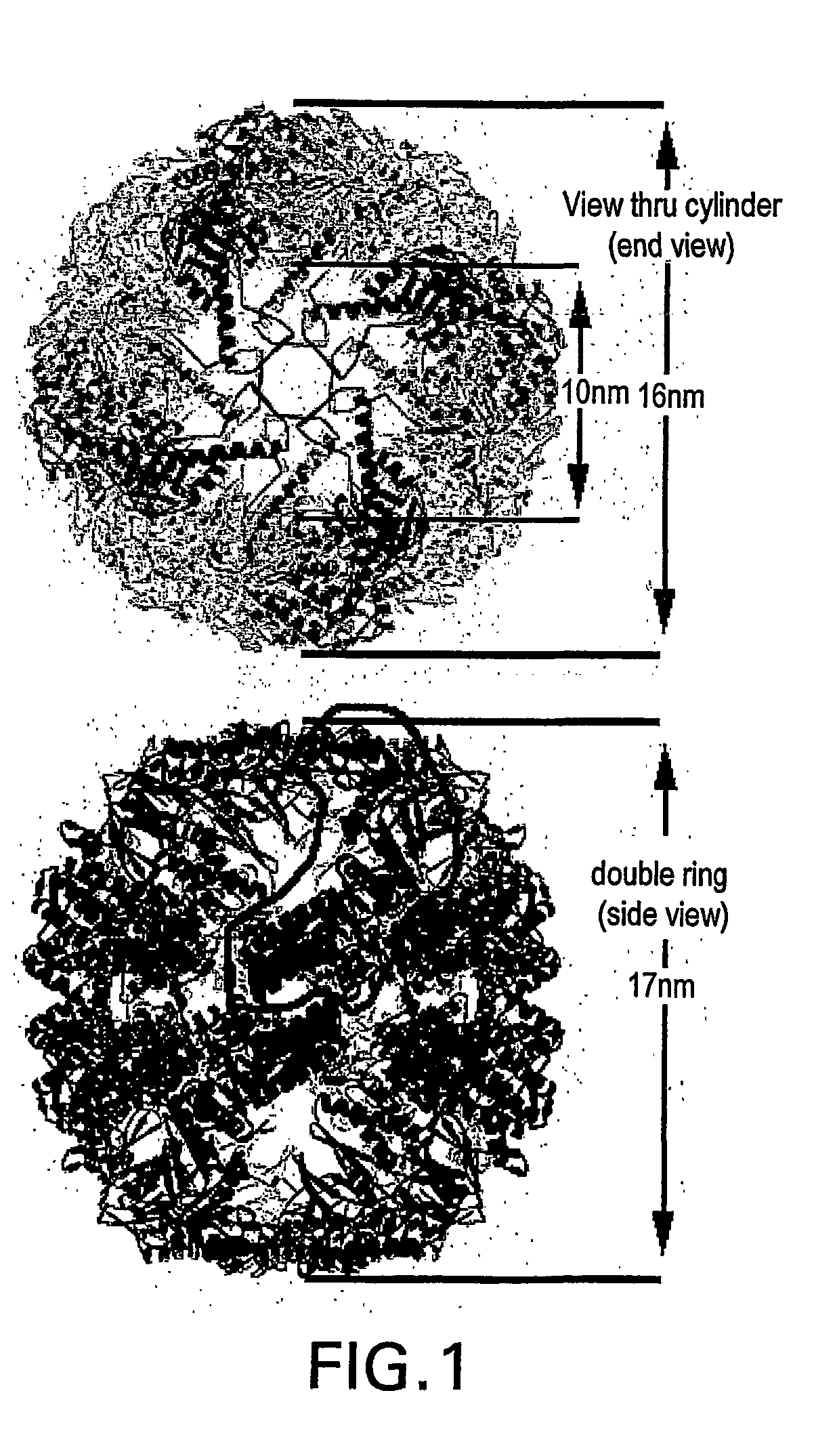
Ordered biological nanostructures formed from chaperonin polypeptides
The following application relates to nanotemplates, nanostructures, nanoarrays and nanodevices formed from wild-type and mutated chaperonin polypeptides, methods of producing such compositions, methods of using such compositions and particular chaperonin polypeptides that can be utilized in producing such compositions.
Owner:NASA
Conotoxin peptides
ActiveUS20120220539A1Inhibit migrationReduce inflammationNervous disorderAntipyreticConotoxinMedicine
The present invention relates conotoxin peptides that are analogs of the α-contoxin peptide RgIA. These conotoxin peptides block the α9α10 subtype of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) and can be used for treating pain, such as neuropathic pain and inflammatory pain, inflammatory disorders, such as rheumatic diseases, and in the treatment of breast cancer.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Chaperone-based therapy for Niemann-Pick disease
The present invention provides a method for treating individuals affected with the acid sphingomyelinase-deficient forms of Niemann-Pick disease (i.e., Type A or Type B Niemann-Pick) by administering small molecules as specific molecular “chaperones” for the deficient acid sphingomyelinase (ASM) enzyme associated with the disease. The molecules are ceramide, sphingomyelin, or phosphonucleotide analogues.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Method for biosynthesis preparation of human GLP-1 polypeptide or analogue thereof
InactiveCN106434717AEasy to separateHigh expressionNucleic acid vectorFusion with protease siteEscherichia coliEnzyme digestion
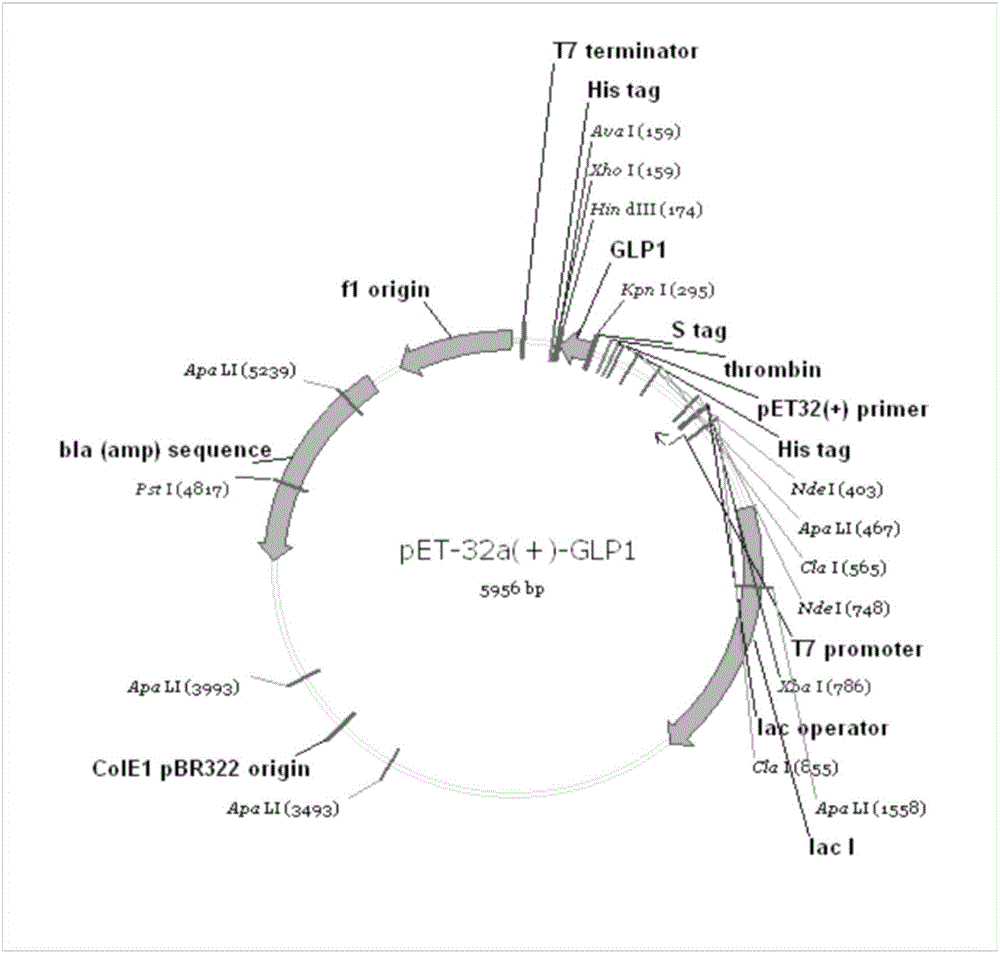
The invention relates to a method for biosynthesis preparation of human glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and an analogue thereof. With adopting of a gene engineering technology, a recombinant escherichia coli expressed GLP-1 fusion protein is constructed, and a protein enzyme digestion site is designed in the fusion protein; a fusion gene has a gene sequence with a form of A-B-C structure, wherein A is a chaperonin gene, B is a nucleotide sequence encoding a connection peptide containing the enzyme digestion site, and C is a gene encoding the GLP-1 or the analogue thereof. After recombinant engineering bacteria is subjected to induced expression, the fusion protein is purified and subjected to enzyme digestion, and then the GLP-1 and the analogue thereof are obtained and are detected to have biological activity. The preparation method of the GLP-1 and the analogue thereof provided by the invention is simple and quick, the production conditions are mild, the product is convenient to separate and extract, the process is simple, and the industrialization prospect is good.
Owner:HANGZHOU JIUYUAN GENE ENG +1
Methods of recovering chaperone proteins and complexes thereof
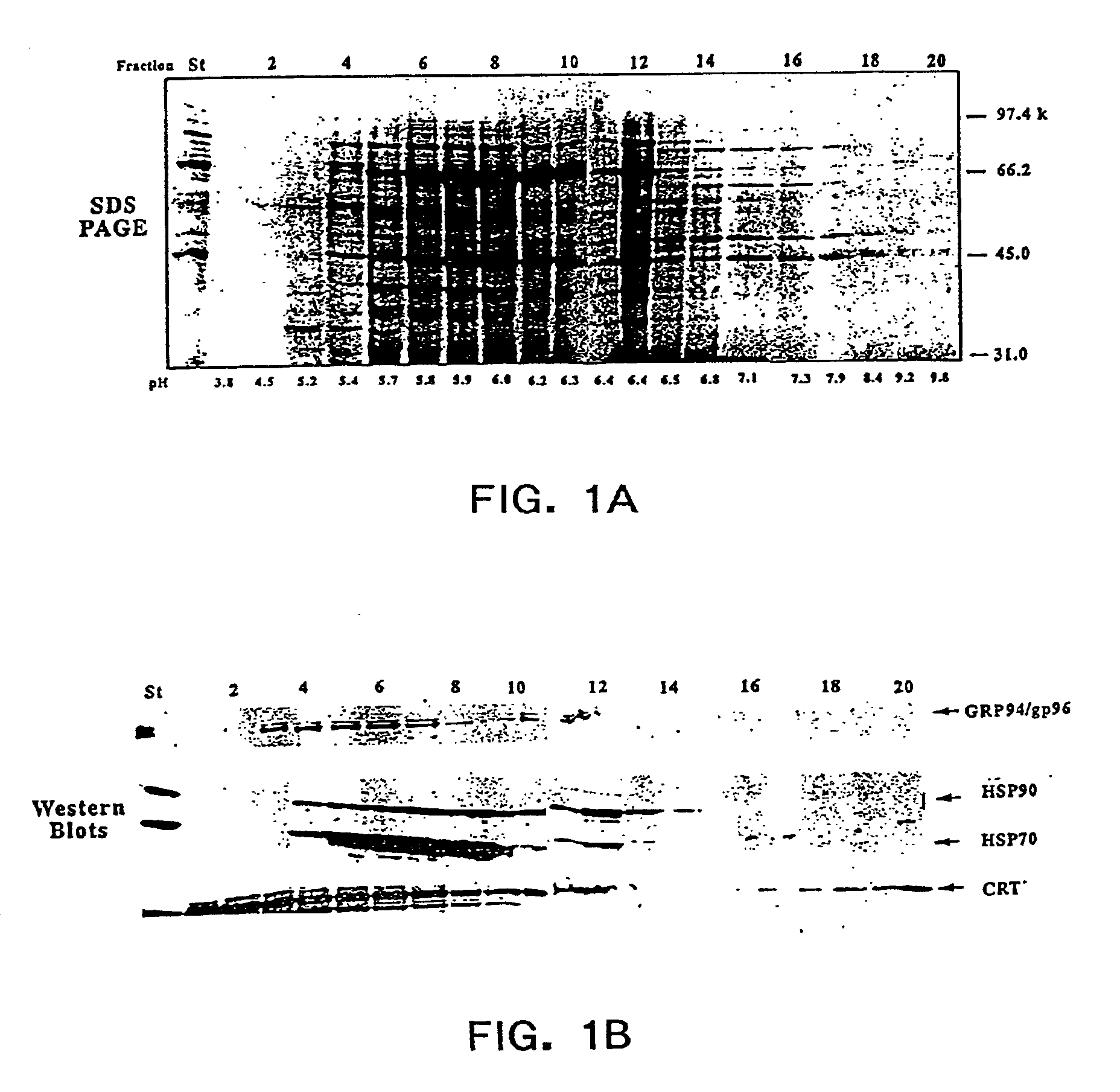
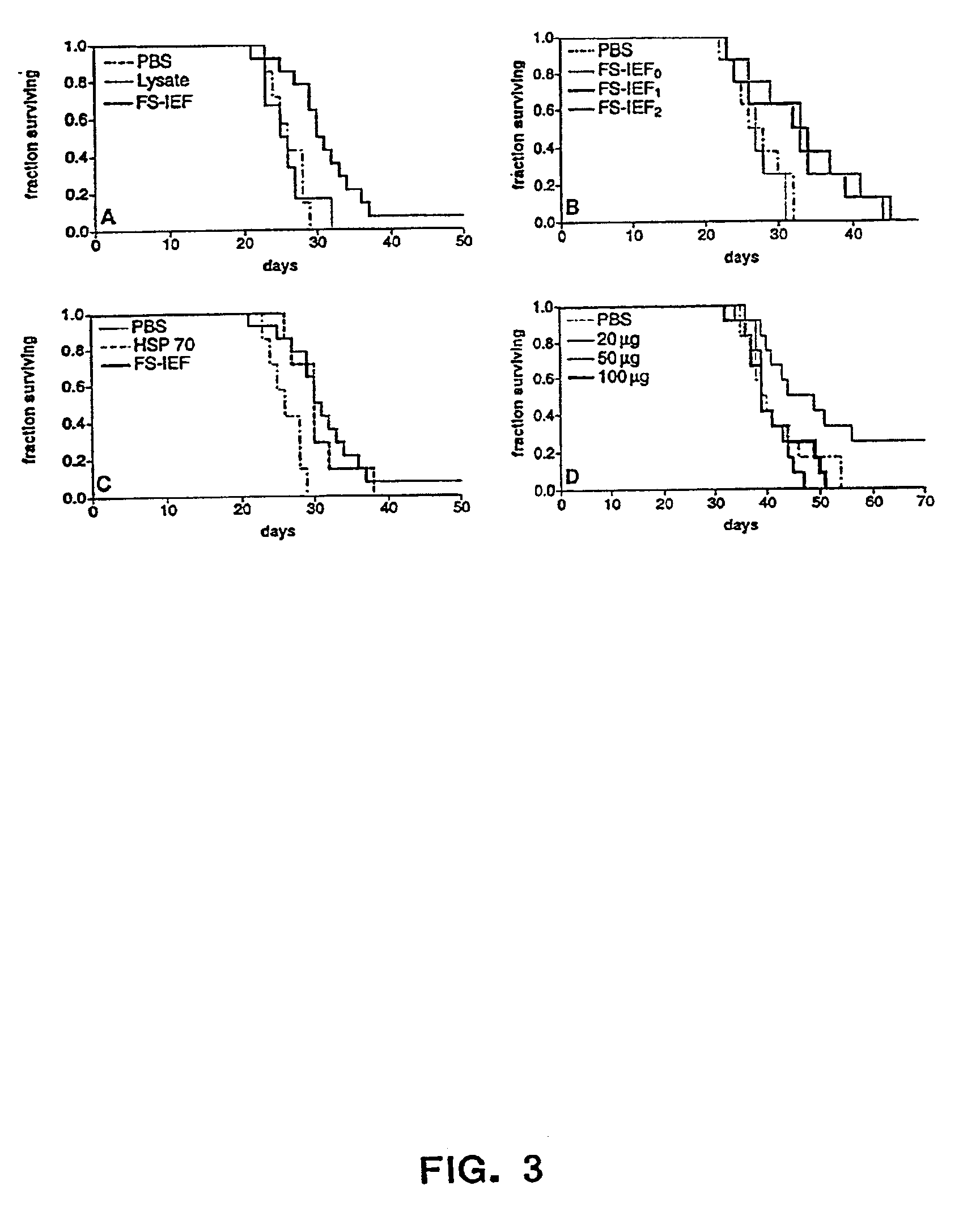
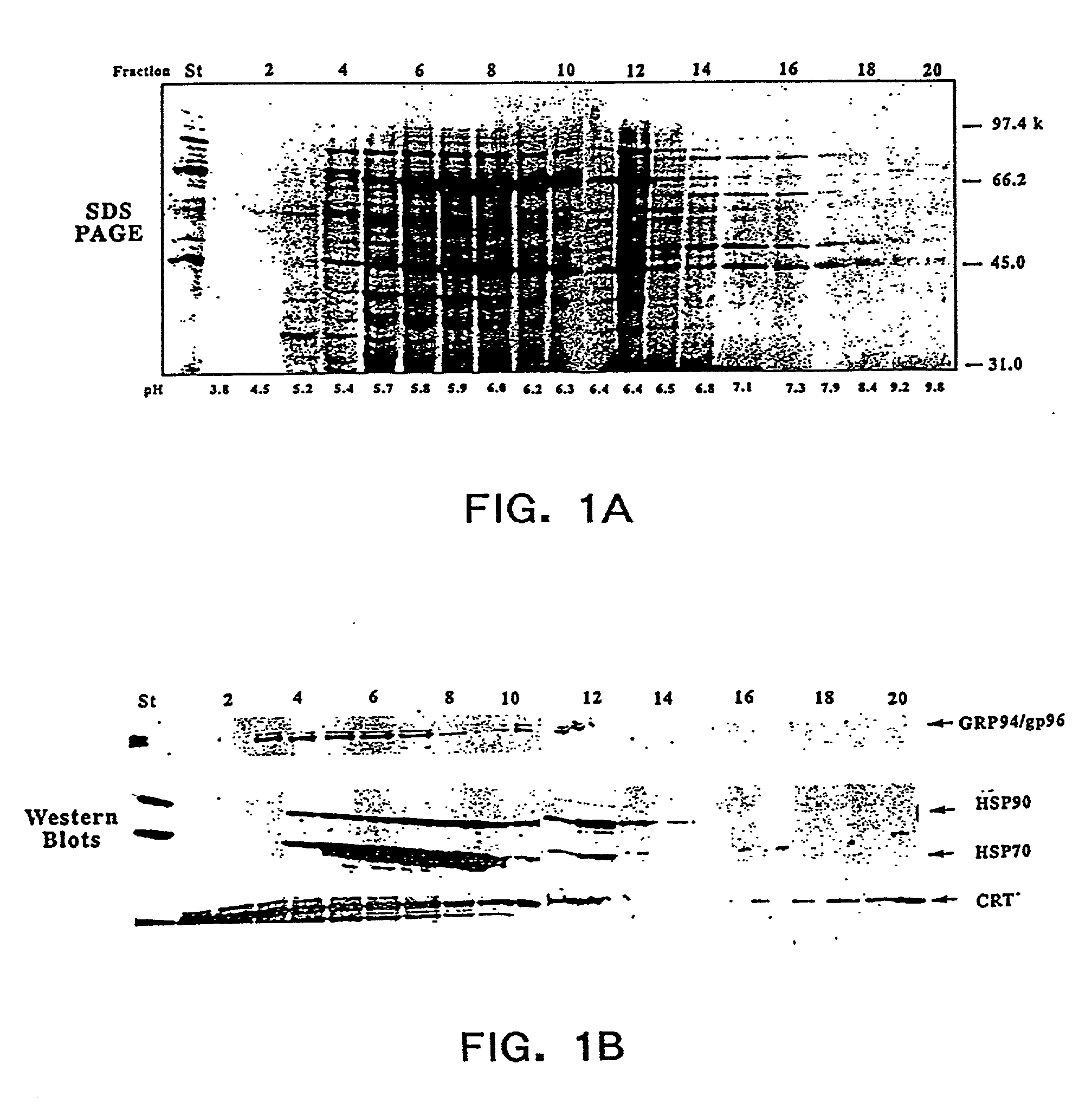
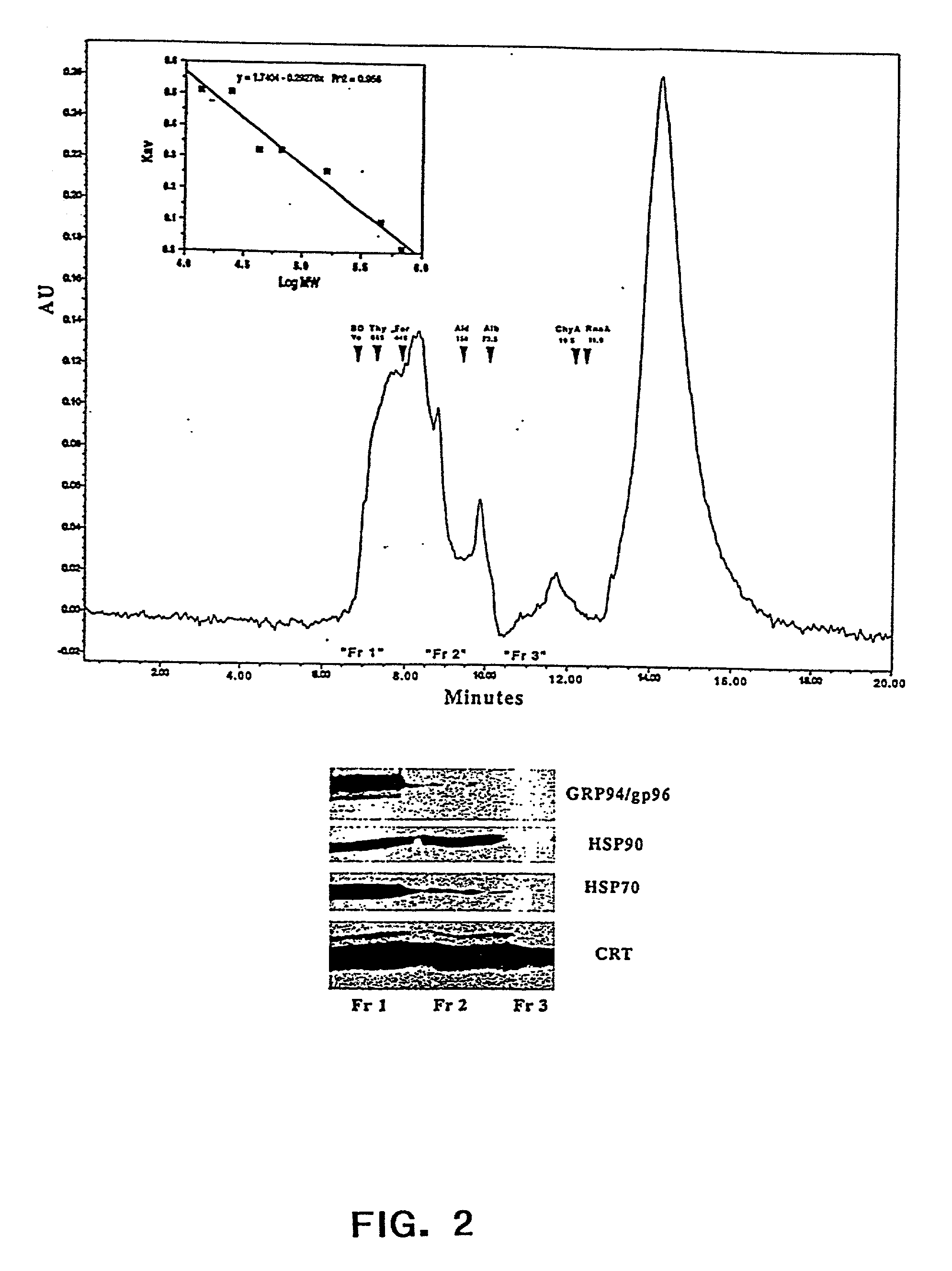
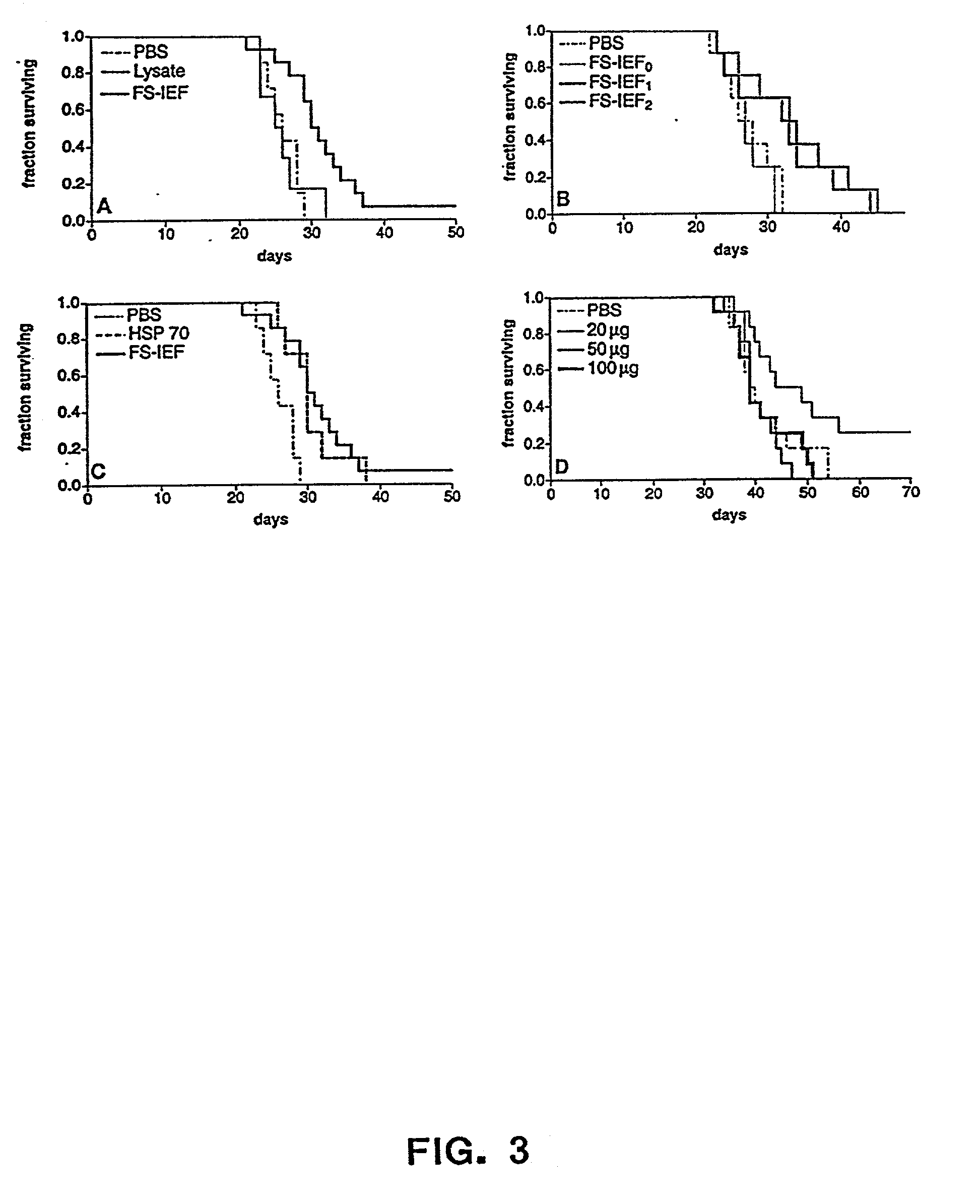
The present invention provides methods for efficient and concomitant recovery of multiple chaperone proteins and / or chaperone protein complexes from a limited sample source. Disclosed are methods involving the use of Free Solution Iso-Electric Focusing (FS-IEF) which can enrich samples containing chaperone proteins and / or chaperone protein complexes from a given sample. The chaperone proteins can be, but are not restricted to calreticulin, gp96, hsp86, hsp84, hsp70, hsp60 and hsp40. The invention also provides methods of recovering chaperone protein complexes for the preparation of vaccines containing chaperone complexes.
Owner:ARIZONA BOARD OF REGRENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA THE
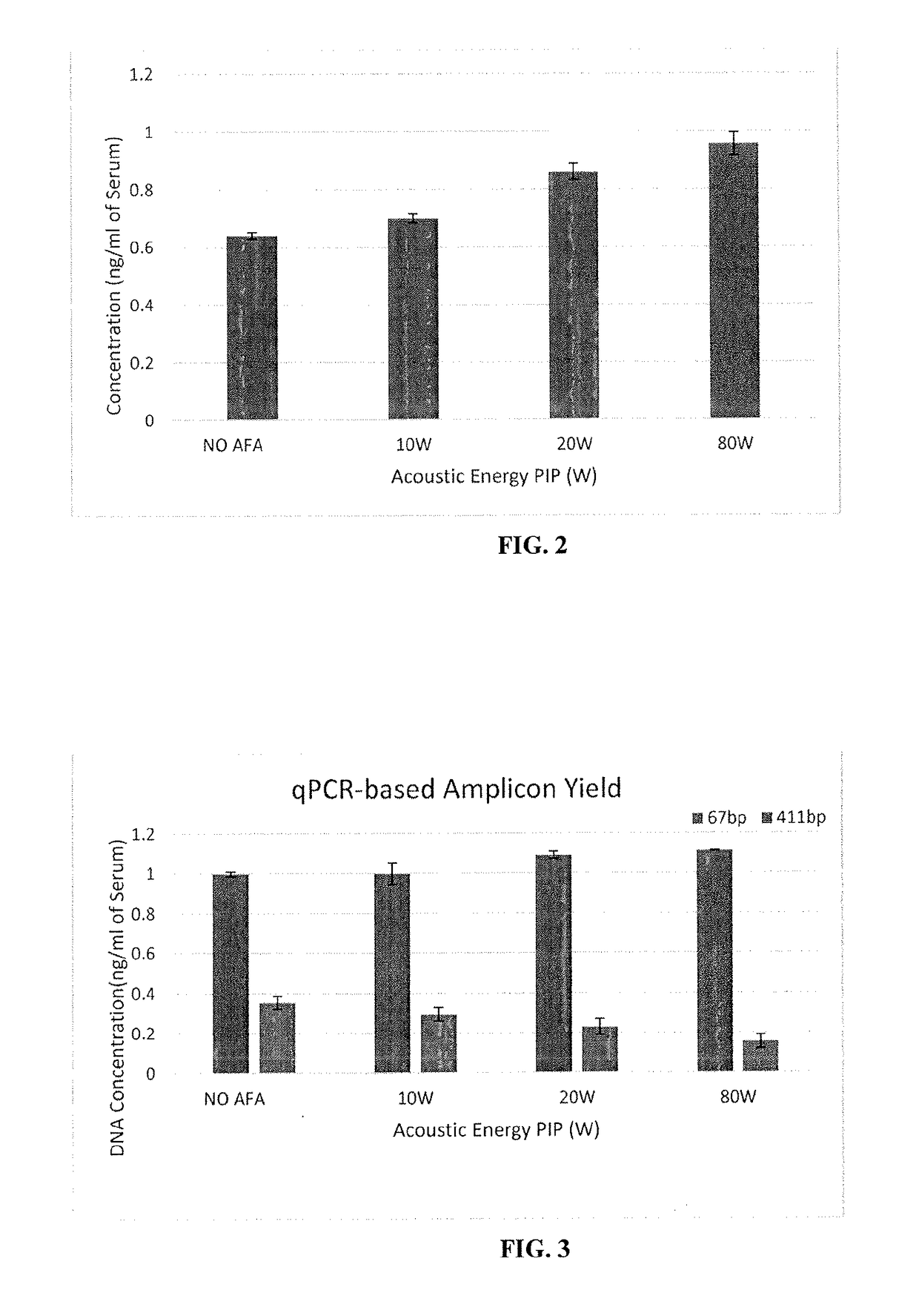
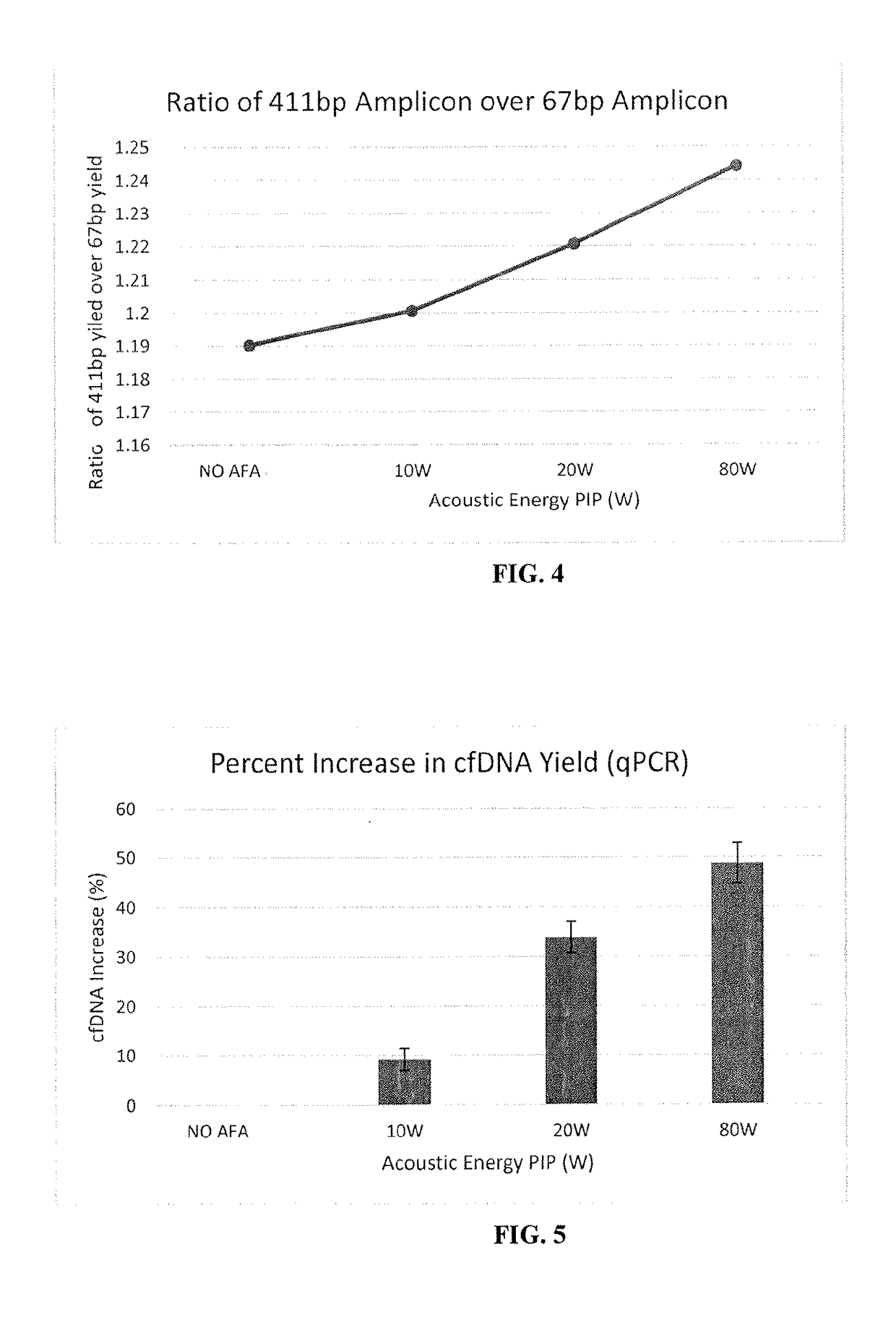
EXTRACTION OF cfDNA FROM BIOLOGICAL SAMPLES
ActiveUS20170283788A1Increased riskDiagnose diseaseMicrobiological testing/measurementElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentHydrogenAcoustic energy
Focused acoustic treatment of samples including a target biomolecule, such as cfDNA, may aid in the recovery of the biomolecule from a sample. cfDNA in a sample, whether chemically stabilized or not, may be linked or otherwise bound to histones or other proteins, e.g., by hydrogen bonds of histones or chaperone proteins to DNA and / or covalent crosslinks of such proteins to the DNA. Focused acoustic energy may remove or disrupt such links, aiding in isolation of the cfDNA from the sample.
Owner:COVARIS INC
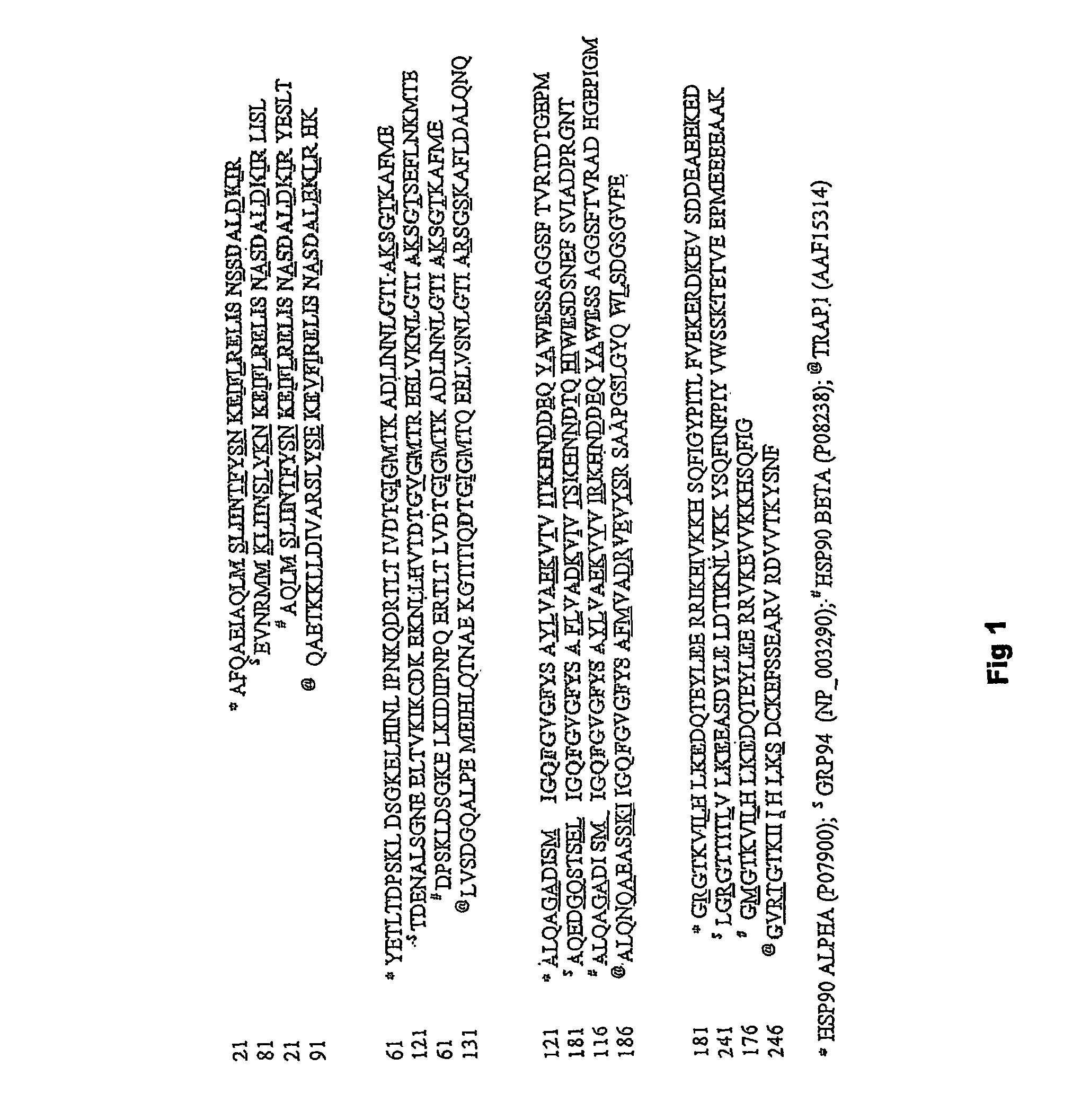
Small molecule compositions for binding to hsp90
Structural differences in binding pockets of members of the HSP90 family can be exploited to achieve differential degradation of kinases and other signaling proteins through the use of designed small molecules which interact with the N-terminal binding pocket with an affinity which is greater than ADP and different from the ansamycin antibiotics for at least one species of the HSP90 family. Moreover, these small molecules can be designed to be soluble in aqueous media, thus providing a further advantage over the use of ansamycin antibiotics. Pharmaceutical compositions can be formulated containing a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier and a molecule that includes a binding moiety which binds to the N-terminal pocket of at least one member of the HSP90 family of proteins. Such binding moieties were found to have antiproliferative activity against tumor cells which are dependent on proteins requiring chaperones of the HSP90 family for their function. Different chemical species have different activity, however, allowing the selection of, for example Her2 degradation without degradation of Raf kinase. Thus, the binding moieties possess an inherent targeting capacity. In addition, the small molecules can be linked to targeting moieties to provide targeting of the activity to specific classes of cells. Thus, the invention further provides a method for treatment of diseases, including cancers, by administration of these compositions. Dimeric forms of the binding moieties may also be employed.
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING INST FOR CANCER RES
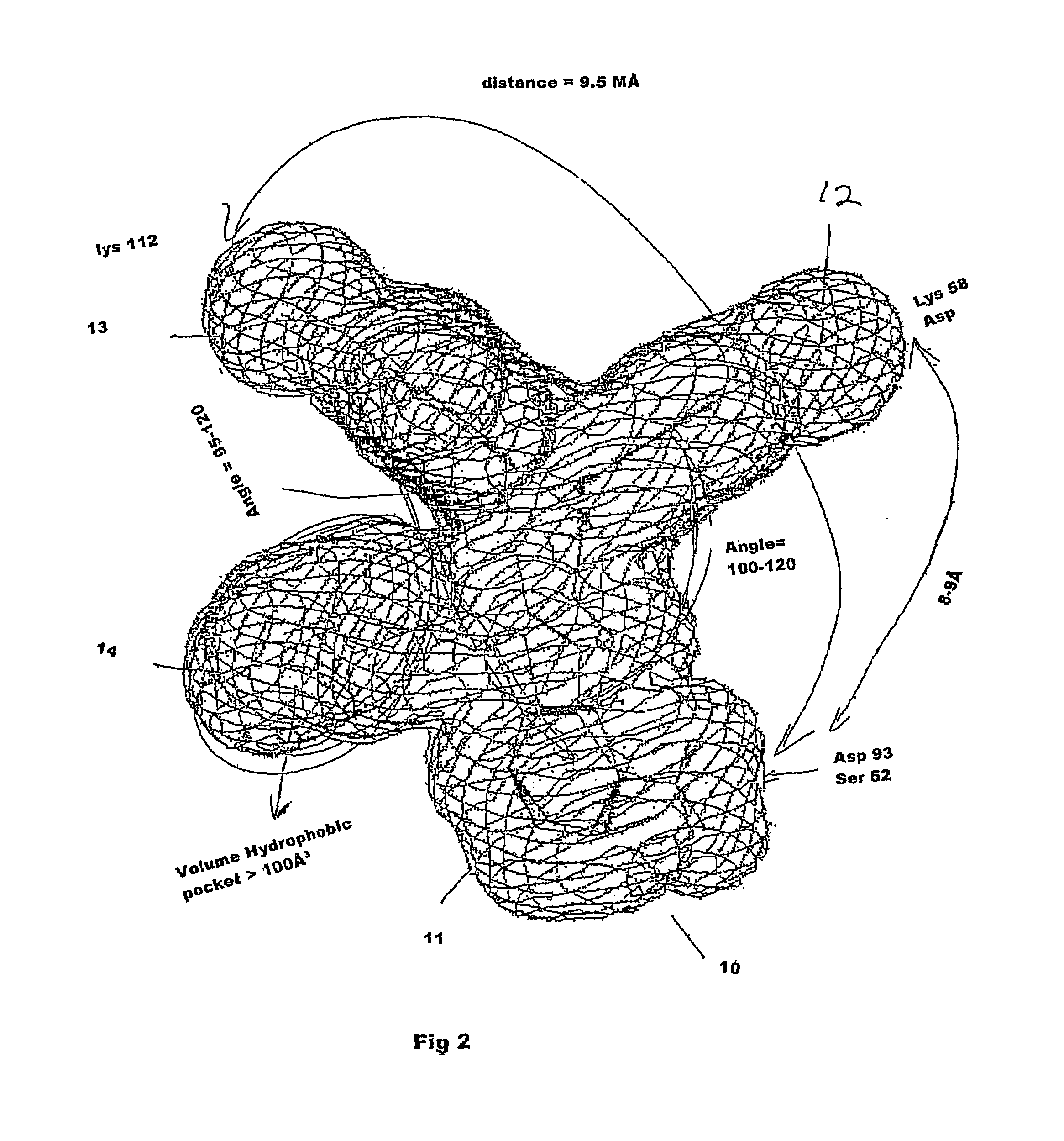
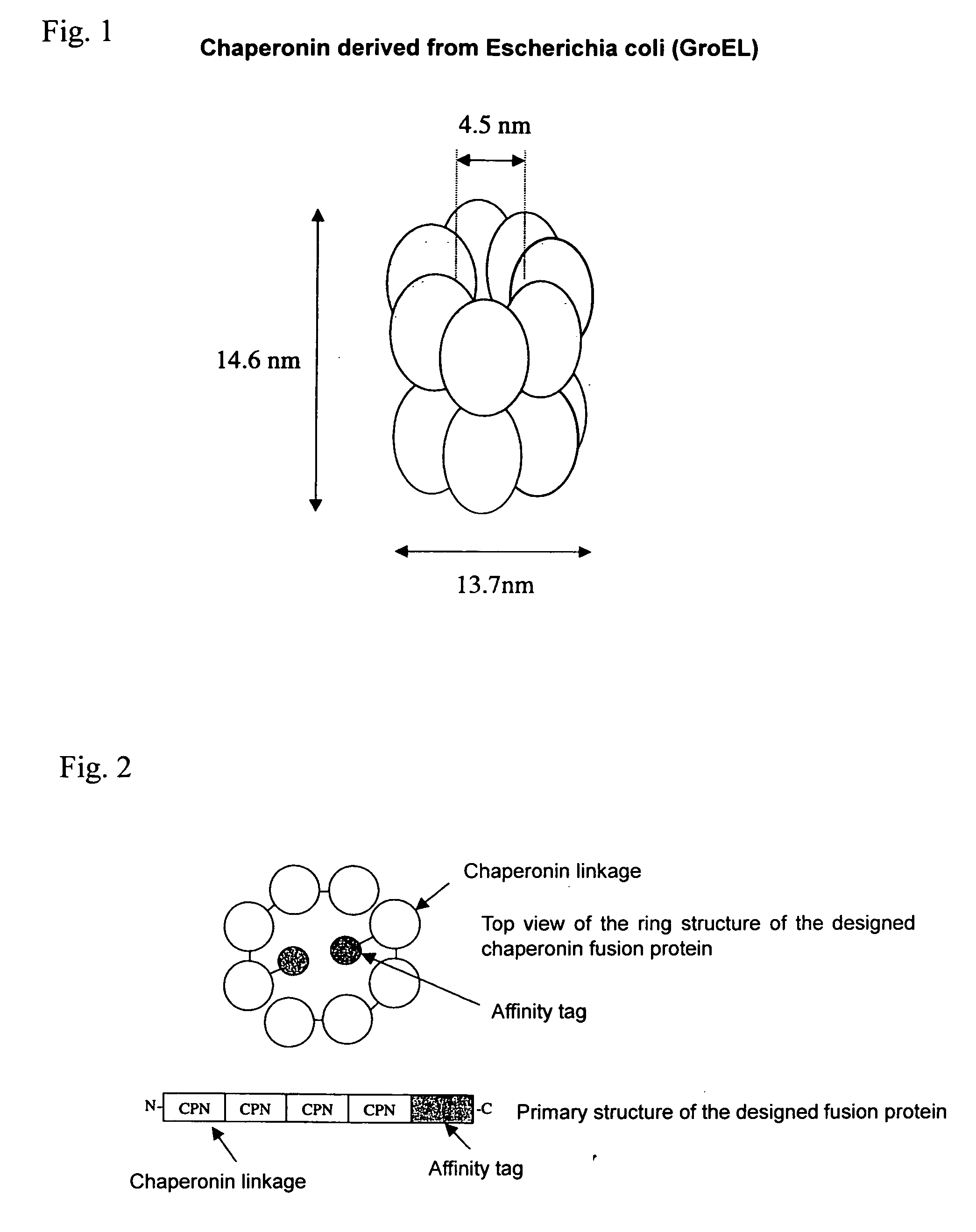
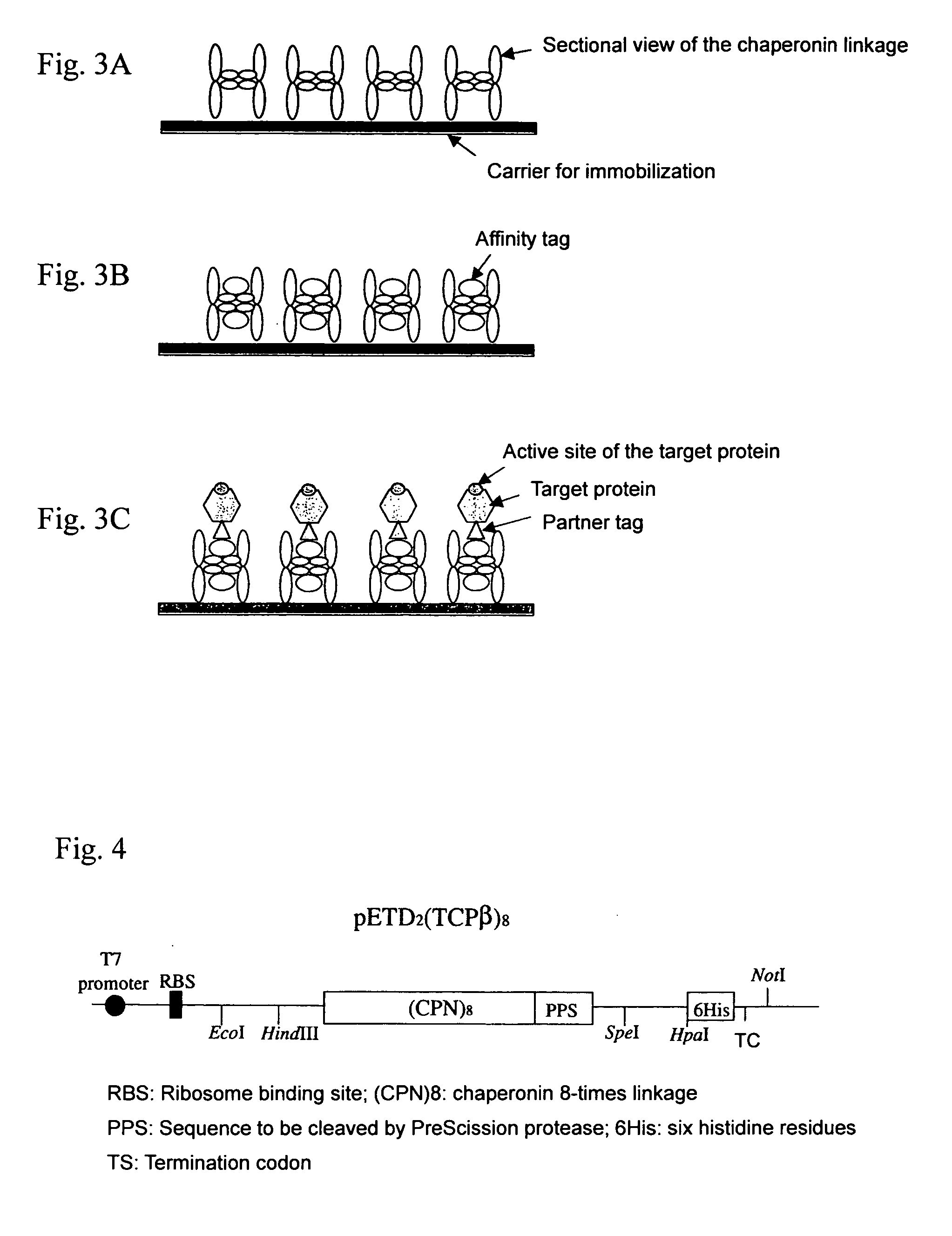
Chaperonin-target protein complex, method of producing the same, method of stabilizing target protein, method of immobilizing target protein, method of analyzing the structure of target protein, sustained-release formulation, and method of producing antibody against target protein
InactiveUS20070059794A1Excessive immune responseEfficient executionSugar derivativesHydrolasesProtein targetChaperonin
The present invention provides a chaperonin-target protein complex and a method of producing the same, and a method of stabilizing the target protein, a method of immobilizing the target protein, a method of analyzing the structure of the target protein, a sustained-release formulation, and a method of producing an antibody against the target protein. The chaperonin-target protein complex in the present invention includes a fusion protein having a chaperonin subunit and an affinity tag linked to the chaperonin subunit via a peptide bond and a target protein for which the affinity tag shows a specific affinity, wherein the target protein is bound to the affinity tag by means of the specific affinity, thereby forming a chaperonin ring structure consisting of a plurality of chaperonin subunits. The chaperonin-target protein in the present invention stabilizes the target protein and surely immobilize on a carrier without causing any change in its stereostructure.
Owner:SEKISUI CHEM CO LTD
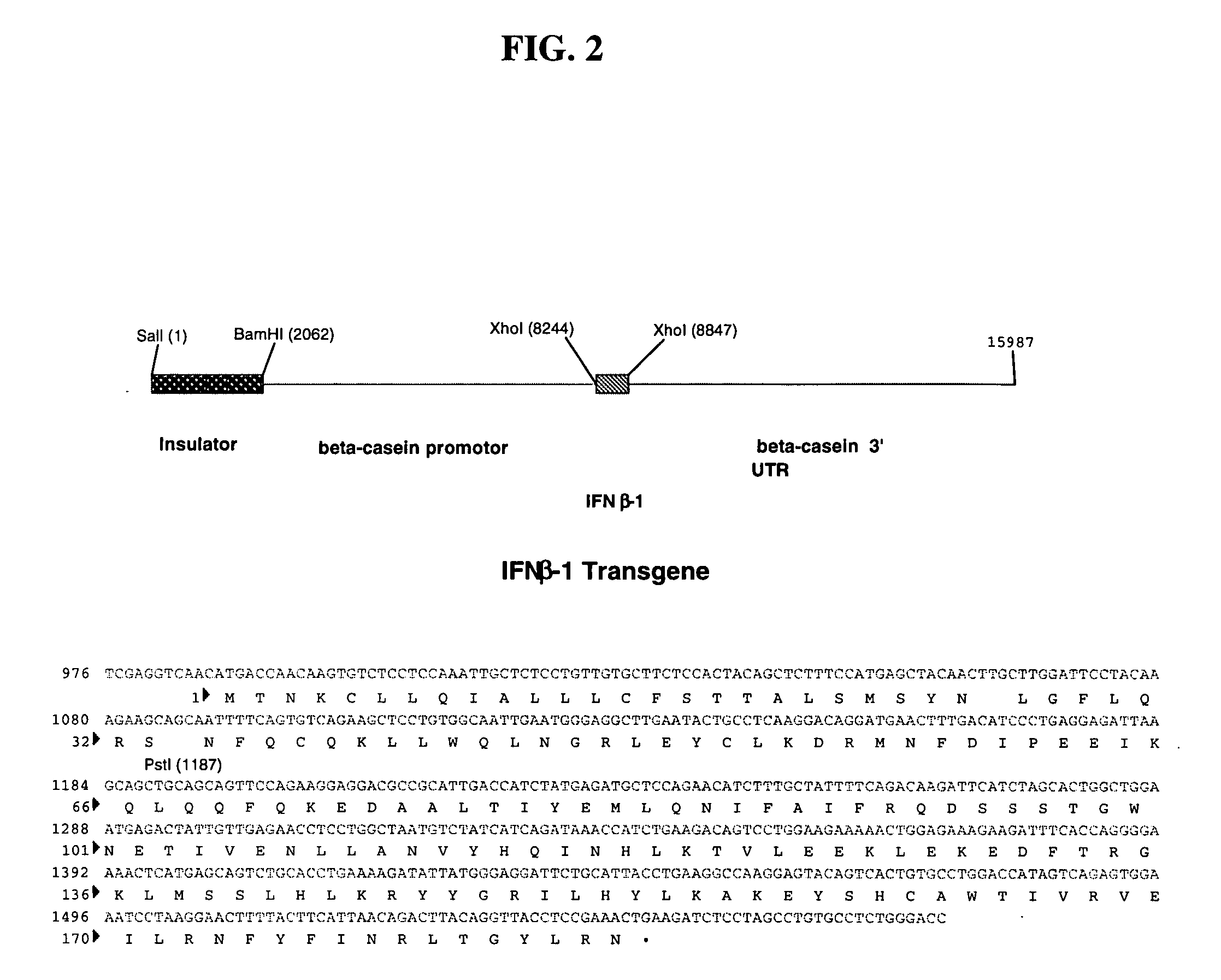
Method for the production of fusion proteins in transgenic mammal milk
InactiveUS20060105347A1Short timeEfficient productionFungiPeptide/protein ingredientsHalf-lifeBiocompatibility Testing
Desirable fusion proteins can be produced in and purified from the milk of transgenic animals. The peptides are made as fusion proteins with a suitable fusion partner such as human alpha-fetoprotein. The fusion partner protein acts to promote and increase the half-life of the overall molecule as well as having therapeutic effects on its own. The fusion protein is typically produced through the use of transgenic animals and can be purified away from the now the milk or other bodily fluid of such an animal by an affinity purification method. A particular advantage of producing peptides via this route, in addition to the obvious advantages of high yield and biocompatibility, is that specific post-translational modifications, such as carboxy terminal amidation, can be performed in the mammary gland. Biologically active polypeptides comprising a therapeutically active polypeptide fused to human alpha-fetoprotein fragment or a variant thereof, methods for the preparation thereof, nucleotide sequences encoding such fusion polypeptides, expression cassettes comprising such nucleotide sequences, self-replicating plasmids containing such expression cassettes, and pharmaceutical compositions containing said fusion polypeptides.
Owner:GTC BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
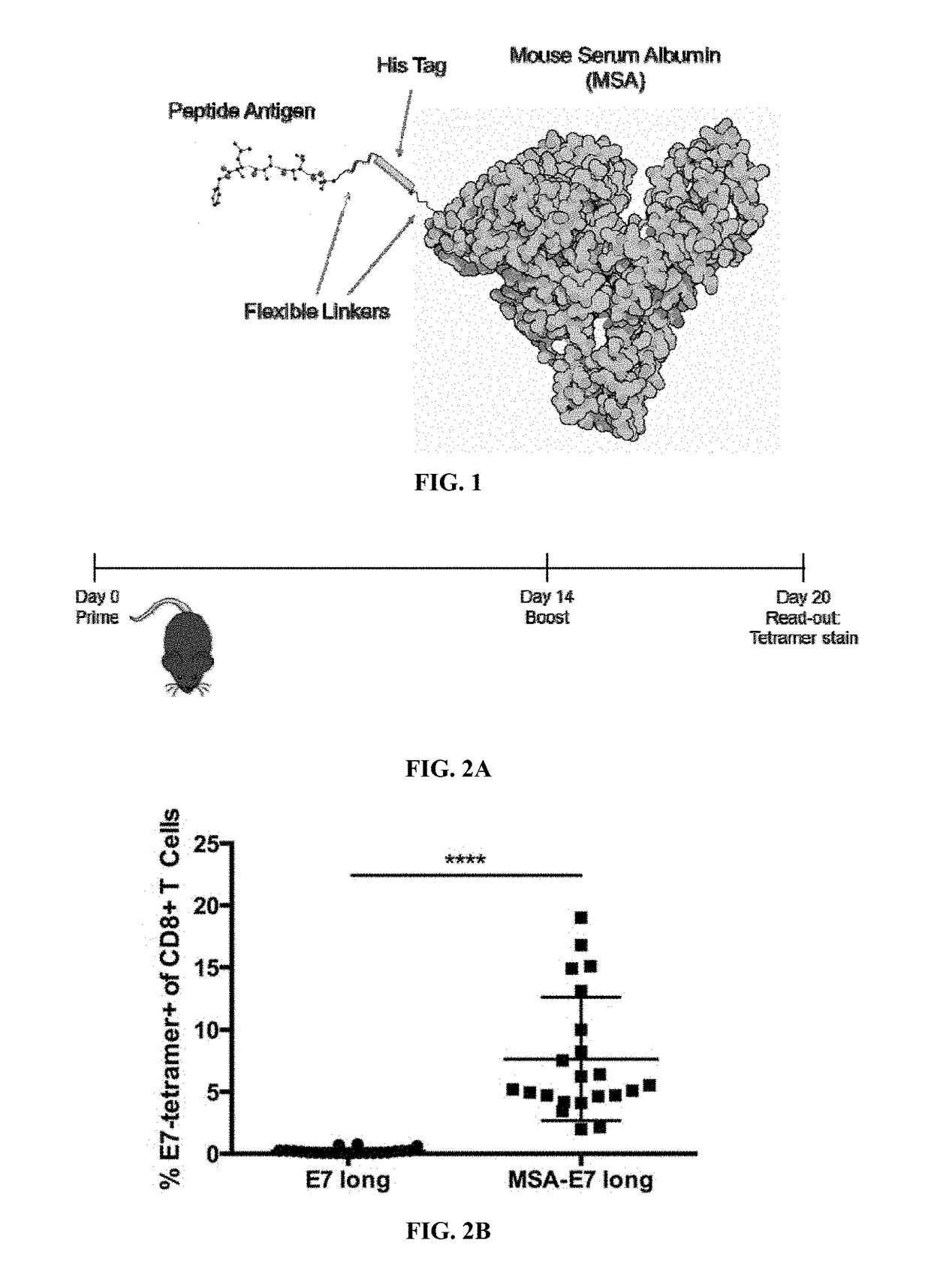
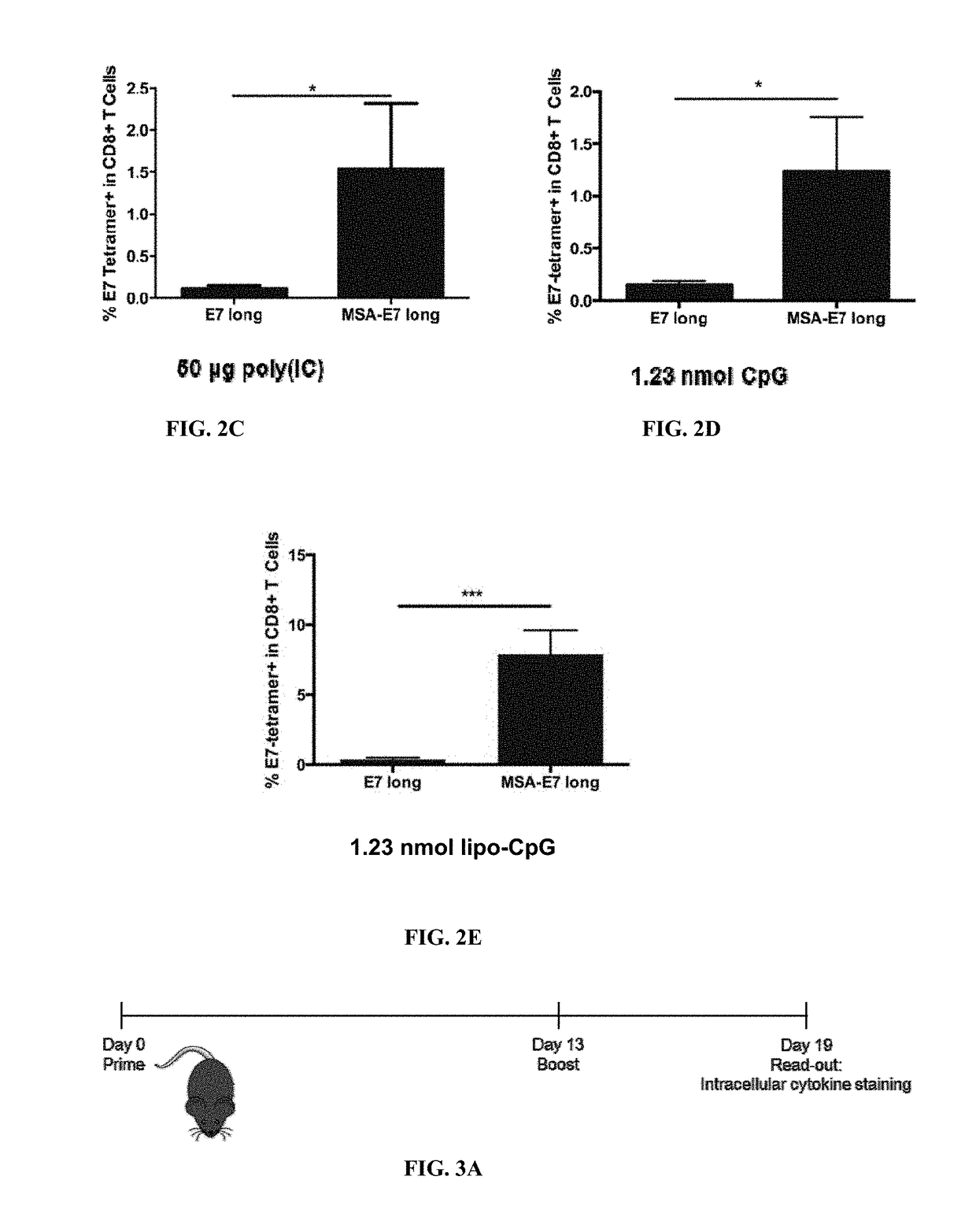
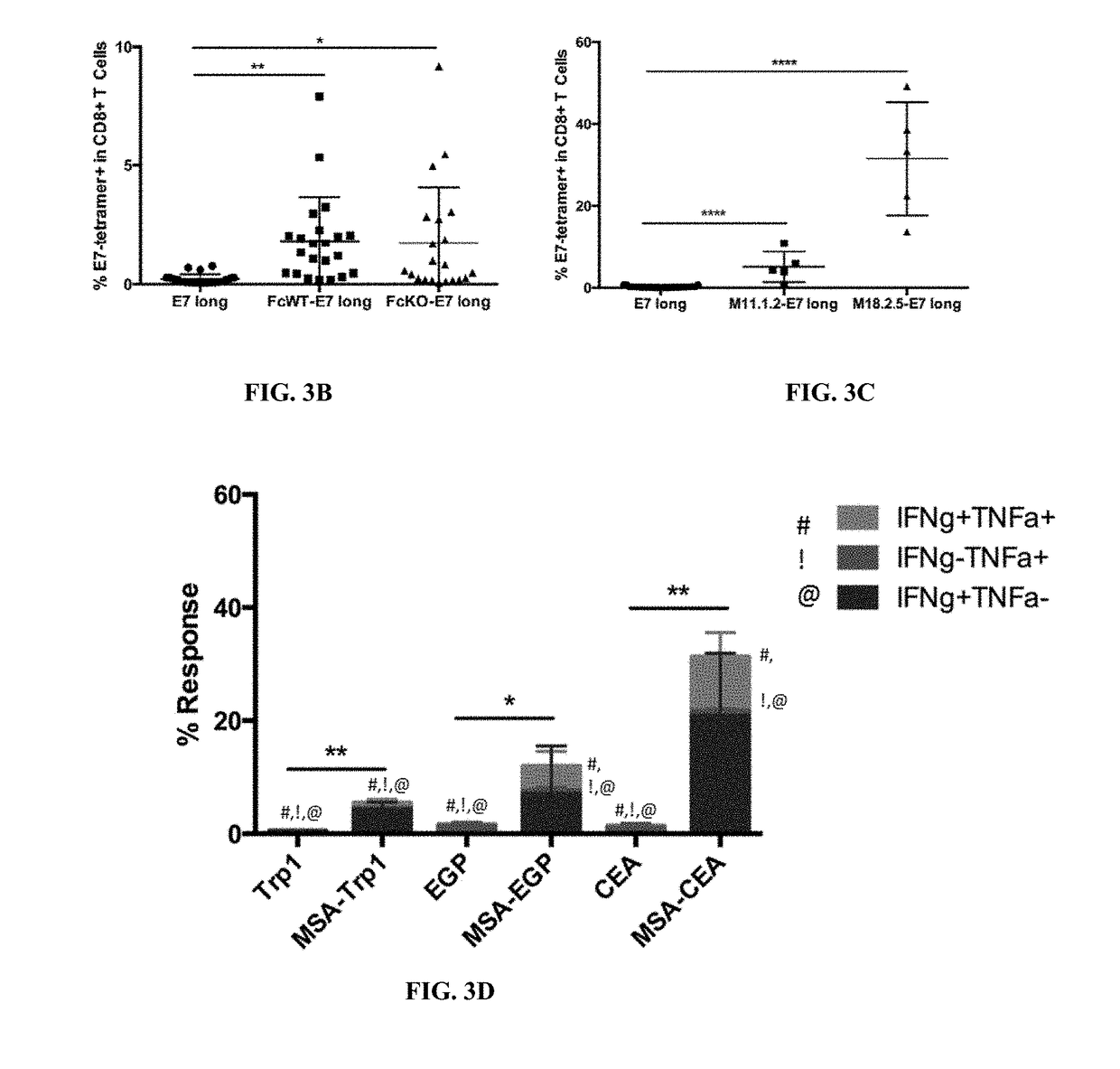
Protein-chaperoned t-cell vaccines
InactiveUS20170252417A1Increase lymph node uptakeEnhance immune responseViral antigen ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPeptide antigenTolerability
Protein antigens are provided. The protein antigens typically include a peptide antigen conjugated or fused to a chaperone protein to form a “chaperone-antigen” that increases lymph node uptake; improves an immune response; or a combination thereof relative to the peptide antigen alone. The immune response can be, for example, increased antigen-specific proliferation, enhanced cytokine production, stimulation of differentiation and / or effector functions, promotion of survival, rescue from exhaustion and / or anergy of T cells, or a combination thereof. Chaperon-antigens can also be used to induce tolerance and increase immune suppressive responses. In the most preferred embodiments, the peptide antigen is fused to the chaperone protein to form a fusion protein. The “chaperone-antigen” can be combined with an adjuvant to form a vaccine and administered to a subject to modulate an immune response to the antigen. Methods of increasing immune responses, treating cancer and infectious and inducing tolerance are also provided.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Methods of recovering chaperone proteins and complexes thereof
The present invention provides methods for efficient and concomitant recovery of multiple chaperone proteins and / or chaperone protein complexes from a limited sample source. Disclosed are methods involving the use of Free Solution Iso-Electric Focusing (FS-IEF) which can enrich samples containing chaperone proteins and / or chaperone protein complexes from a given sample. The chaperone proteins can be, but are not restricted to calreticulin, gp96, hsp86, hsp84, hsp70, hsp60 and hsp40. The invention also provides methods of recovering chaperone protein complexes for the preparation of vaccines containing chaperone complexes.
Owner:ARIZONA BOARD OF REGRENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA THE
Trosine phenol lyase engineering bacteria as well as construction method thereof and application thereof
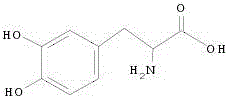
The invention relates to trosine phenol lyase engineering bacteria as well as a construction method thereof and application thereof. A tyrosine phenol lyase gene is constructed to express plasmids; chaperonin is introduced to express the plasmids to obtain the trosine phenol lyase engineering bacteria which are identified as escherichia coli FPLF8 (Escherichia coli HPLF8) preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection on February 19, 2016, with a preservation number being CCTCCNO:M 2016065. The engineering bacteria can be synthesized into levodopa by fermentation and conversion, and are efficiently expressed; the expressed product is stable and high in activity, and can be synthesized into levodopa by conversion in the presence of related substrates; and the process is simple, the cost is low, the yield is high, emission of three wastes is a little, and the application value for industrial production is achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +2
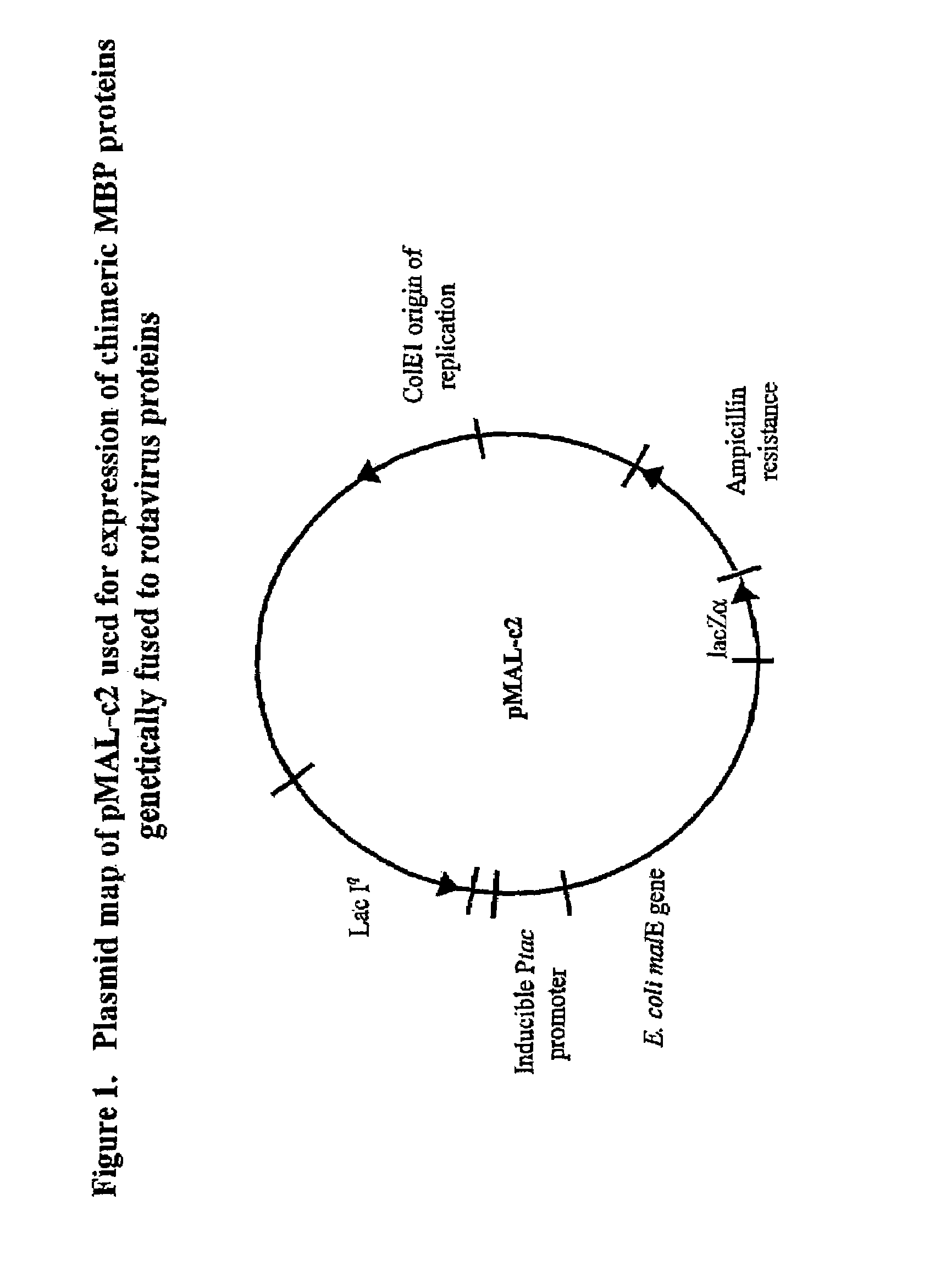
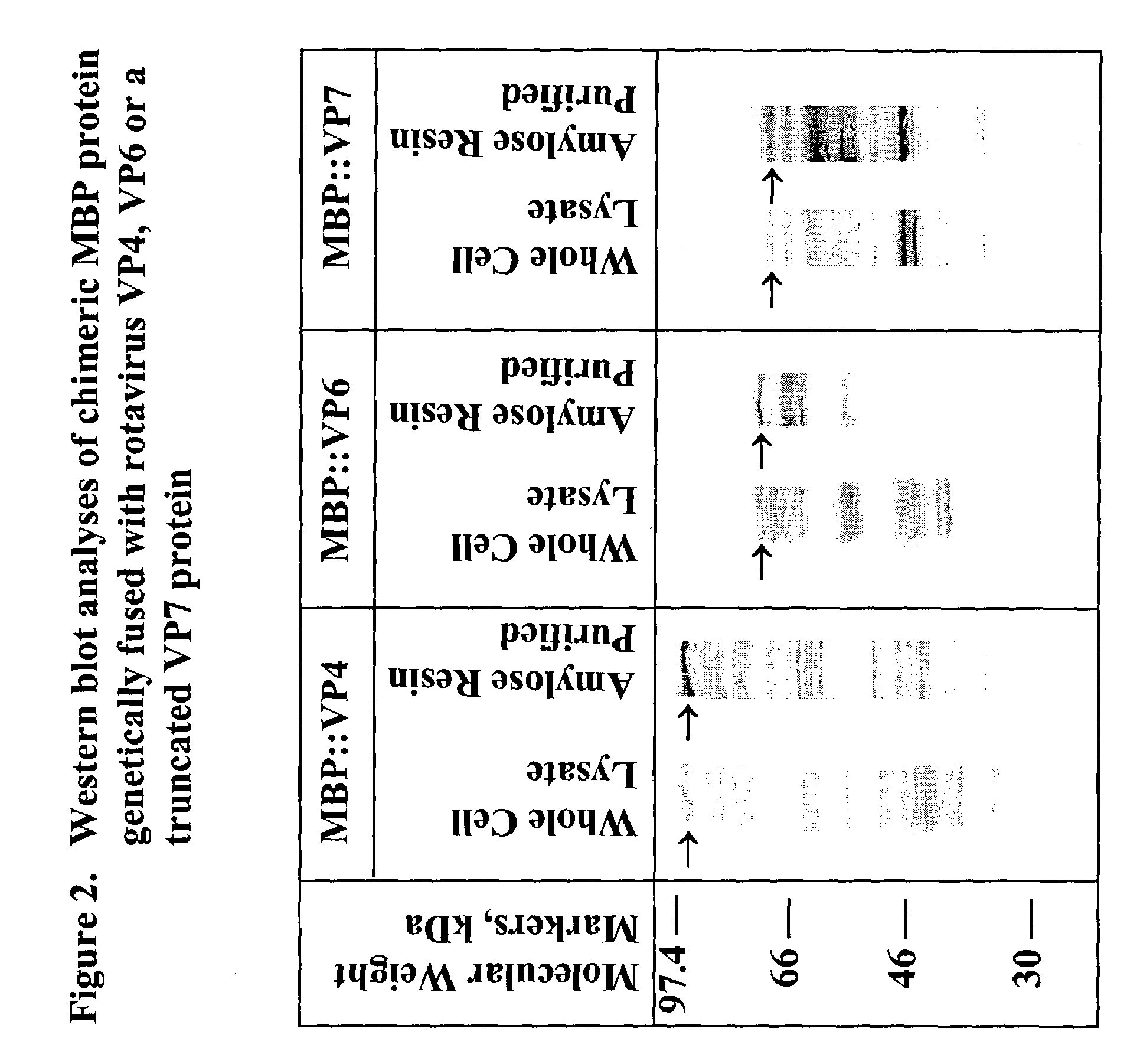
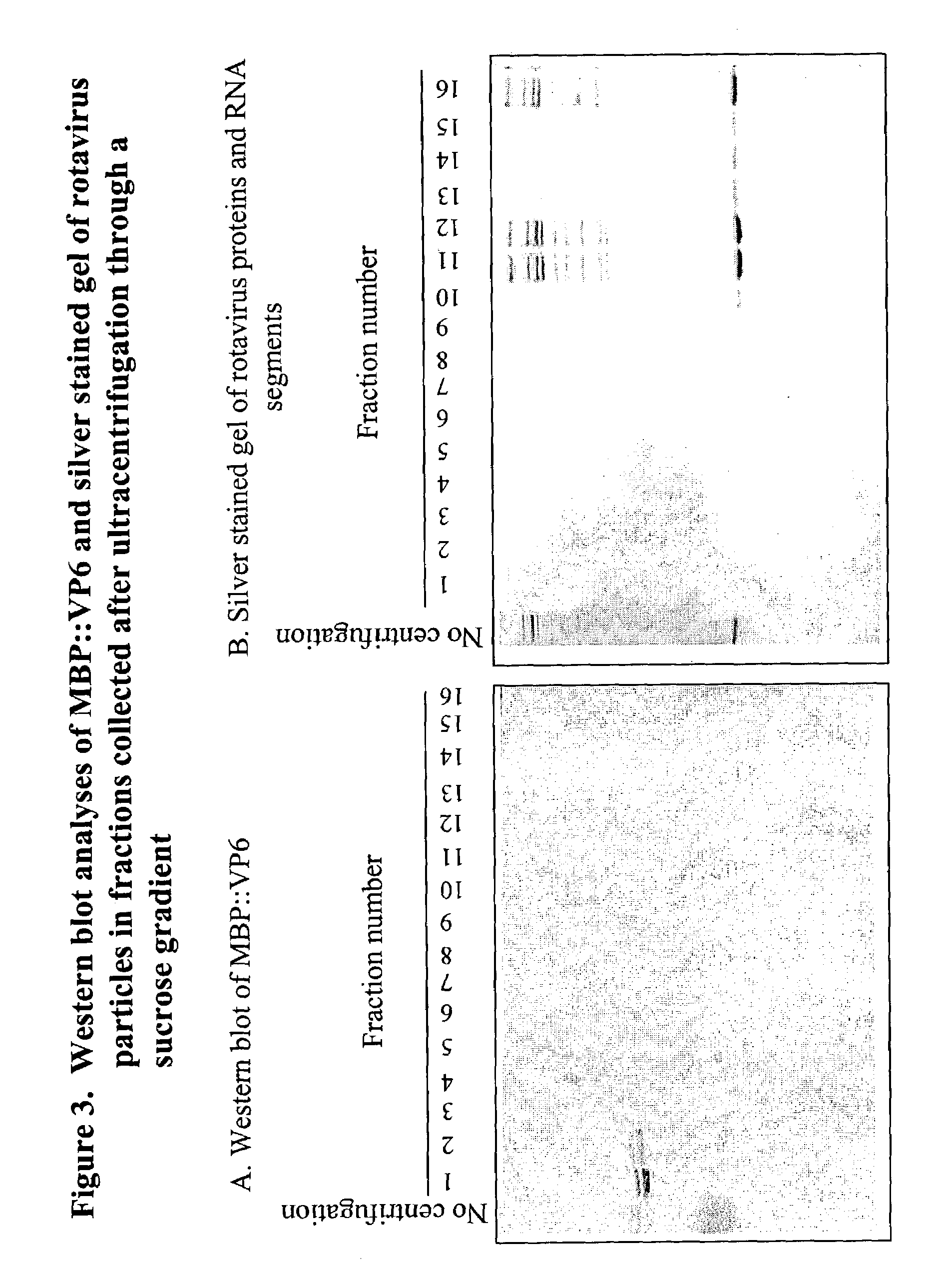
Rotavirus subunit vaccine
The present invention is directed to the generation and use of recombinant rotavirus fusion proteins as immunogens to produce a protective immune response from immunized individuals. In one embodiment, the present invention contemplates a recombinant rotavirus fusion protein vaccine composition comprising a rotavirus subunit protein or immunogenic fragment thereof, and an adjuvant in combination with the recombinant rotavirus subunit fusion protein. In one aspect of this embodiment, the recombinant rotavirus fusion protein comprises a rotavirus subunit protein and a fusion partner protein in genetic association with the rotavirus subunit protein, wherein the fusion partner protein does not interfere with expression and immunogenicity of the rotavirus subunit protein, the fusion partner protein prevents complex formation by the rotavirus subunit protein, and the fusion partner protein facilitates purification of the recombinant rotavirus fusion protein. In another aspect of this embodiment, the rotavirus subunit protein is selected from the group consisting of VP1, VP2, VP3, VP4, VP6, VP7, NSP1, NSP2, NSP3, NSP4 or NSP5. In yet another aspect of this embodiment, the rotavirus subunit protein is VP6.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT CINCINNATI
Chaperonin and osmolyte protein folding and related screening methods
InactiveUS20050196824A1Microbiological testing/measurementPeptide preparation methodsIonic strengthOsmolyte
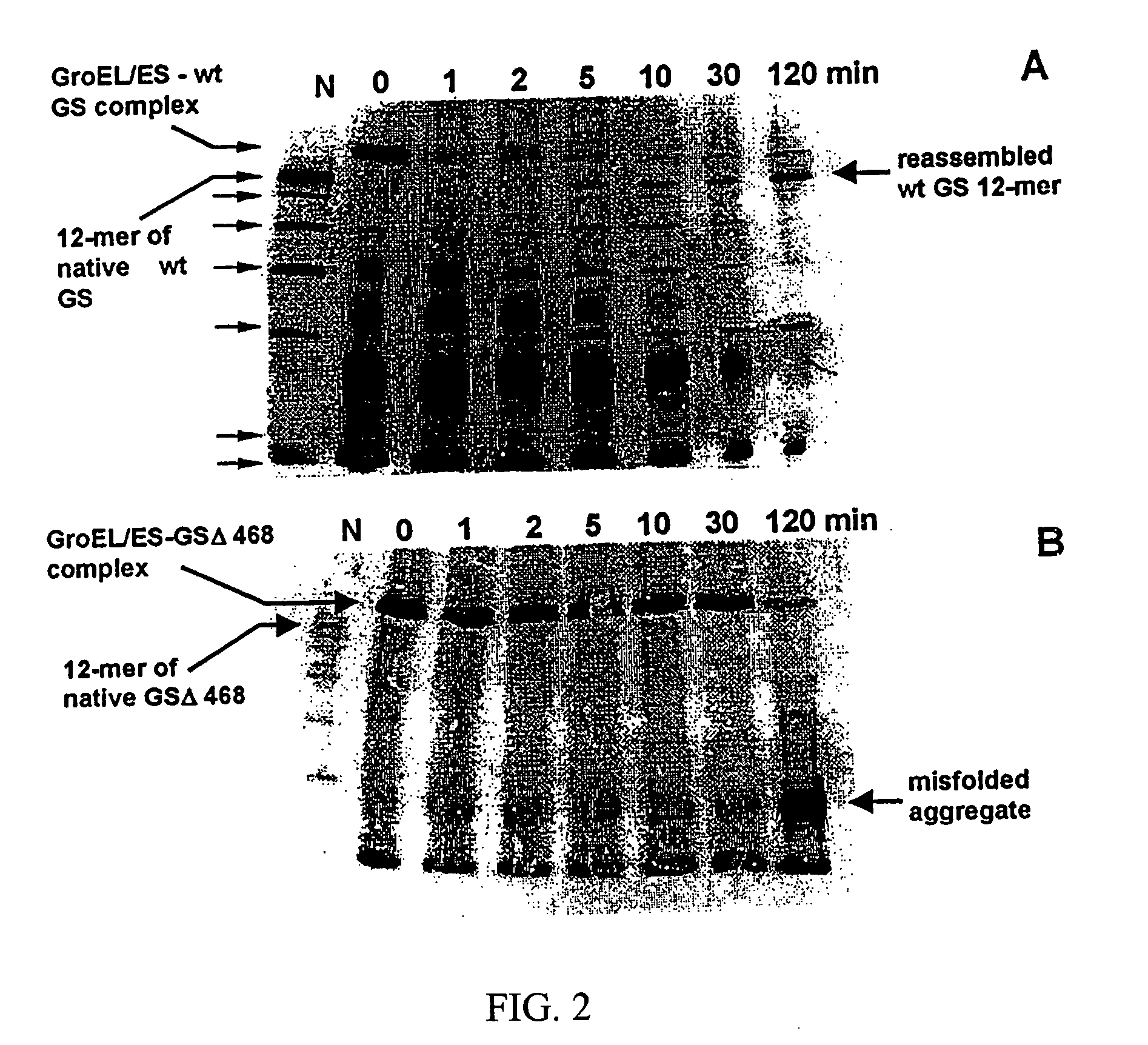
The invention describes an inexpensive in vitro protein folding process for preventing large scale protein misfolding and aggregation, for concentrating aggregation prone chaperonin-protein folding intermediates in a stable non-aggregating form, and for rapidly screening these stable concentrates for the best folding solution conditions. The process comprises: (1) the formation of a chaperone-substrate complex and (2) the release of the substrate using a broad array of folding solutions containing different osmolyte ions, detergents, gradients of ionic strength and pH or other commonly used folding additives. Specifically, when the chaperonin / osmolyte protein process was applied to identify and optimize GSΔ468 bacterial glutamine synthetase mutant refolding conditions that otherwise cannot be folded in vitro by commonly used techniques, 67% of the enzymatic activity was recovered.
Owner:UNIV KANSAS MEDICAL CENT
Method for soluble expression of recombinant protein of human brain natriuretic peptide and application
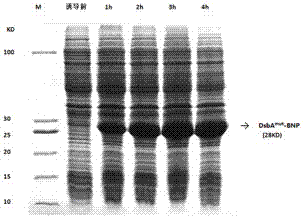
ActiveCN103923937AHigh activitySimple and easy to repeatHormone peptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsProtein targetChaperonin
The invention provides a method for soluble expression of recombinant protein of a human brain natriuretic peptide (Human Brain Natriuretic Peptide, hBNP). The method comprises the following steps: 1) obtaining a recombinant gene, namely obtaining the recombinant gene His-DsbAmut-BNP of expressing the recombinant protein of the human brain natriuretic peptide, wherein the sequence of the recombinant gene comprises a purified tag gene sequence, a molecular chaperone protein gene sequence, a protease recognition site sequence and a human brain natriuretic peptide sequence, which are sequentially arranged along the direction from 5' to 3'; 2) obtaining recombinant plasmids, namely inserting the recombinant gene obtained in the previous step into a carrier vector, so as to obtain the recombinant plasmids containing the recombinant gene; 3) obtaining genetically engineered bacterium, transferring the recombinant plasmids obtained in the previous step into host cells to obtain the genetically engineered bacterium; 4) expressing exogenous genes, fermenting the genetically engineered bacterium, and expressing fusion protein containing the human brain natriuretic peptide; 5) purifying target protein, splitting thallus, collecting fusion protein, removing molecular chaperone and carrying out chromatographic purification by protease digestion, so as to obtain the recombinant protein of the human brain natriuretic peptide.
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG WOTAI BIOTECH
Chaperone expression genomes
InactiveUS7226781B1InterestingEnhance interestPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsForeign proteinChaperonin
A recombinant genome comprising polynucleotides encoding at least two additional molecular chaperones and a protein of interest, recombinant baculovirus vectors providing molecular chaperones and a method for producing a foreign protein using said genomes and vectors.
Owner:BELYAEV ALEXANDER S
Use of biomarkers for the diagnosis and prognosis of lung cancer
InactiveUS20100240546A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningMinichromosome maintenanceSelenium-Binding Proteins
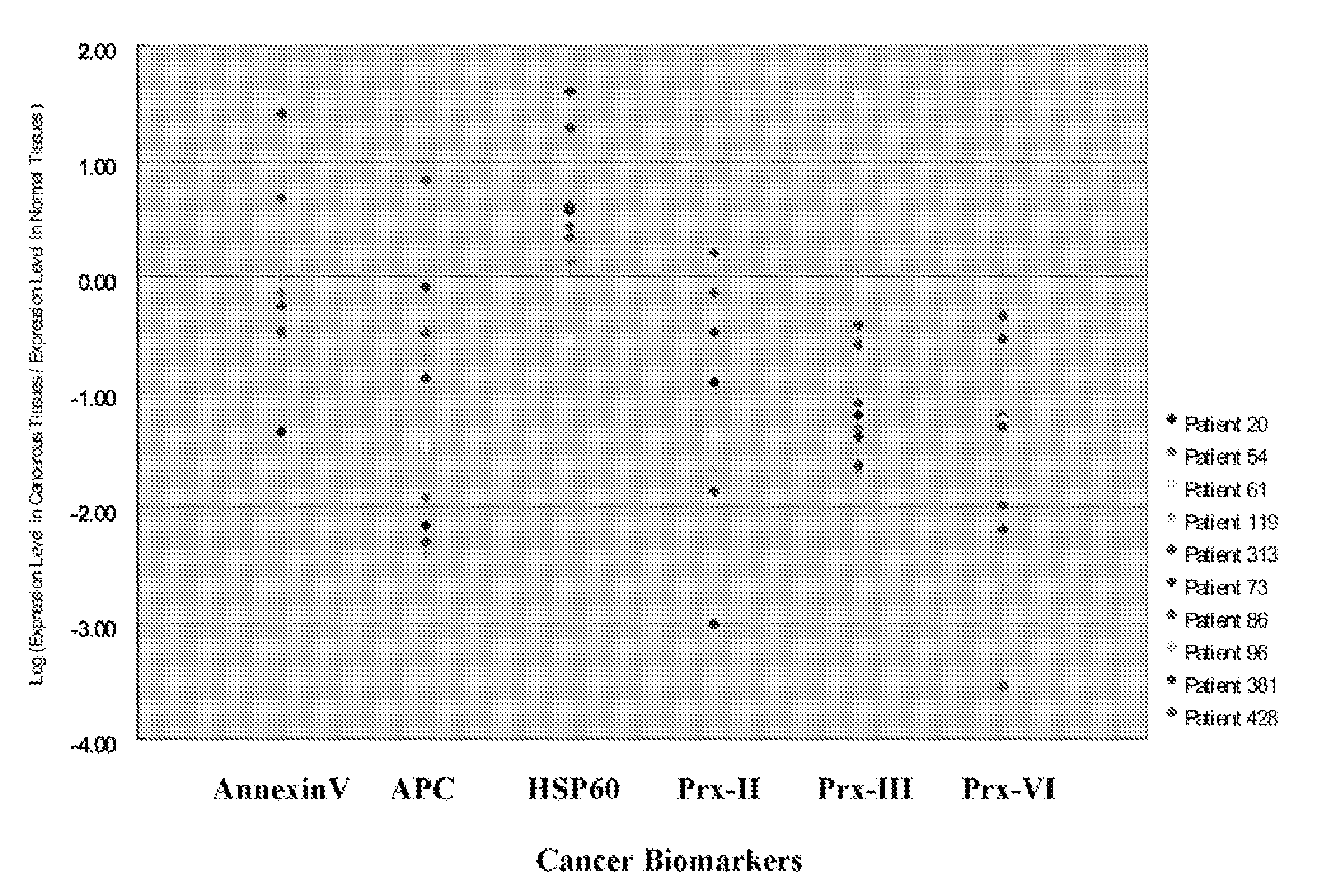
A method for identifying, diagnosing, and monitoring cancerous lung tissues in a subject may include measuring the expression of at least one biomarker in a biological sample in the subject, and comparing the expression against a normal value. When a differential expression of the at least one biomarker between the biological sample and the normal value is more than 1.5-fold, the lung tissue sample is cancerous. The at least one biomarker is selected from the group consisting of peroxiredoxin I, peroxiredoxin II, peroxiredoxin III, peroxiredoxin IV, peroxiredoxin VI, chaperonin, amyloid-P-component, annexin V, dihydropyrimidinase-like 2 protein, glutamate carboxypeptidase, 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate mutase, thymidine phosphorylase, prolyl-4 hydroxylase, selenium binding protein 1, β-mitochondrial ATP synthase H+ transporting F1 complex, laminin-binding protein, minichromosome maintenance deficient protein 5 variant, keratin 9, keratin 10, napsin A aspartic peptidase, M2-type pyruvate kinase, and apolipoprotein A-I.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Use of molecular chaperones for the enhanced production of secreted, recombinant proteins in mammalian cells
ActiveUS7244616B2Enhanced chaperone protein expressionEnhancing yield of recombinantFactor VIIProtease inhibitorsBiotechnologyADAMTS Proteins
The present invention relates to a method for increased production of a secreted, recombinant protein product through the introduction of molecular chaperones in a mammalian host cell. The present invention also relates to a mammalian host cell with enhanced expression of a secreted recombinant protein product by coexpressing at least one chaperone protein.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
SlpA as a tool for recombinant protein and enzyme technology
ActiveUS20090291892A1Reduce distractionsReduce unspecific adsorptionAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsFK506 bindingEnzyme
Disclosed are a recombinant DNA molecule encoding a fusion protein comprising a SlpA chaperone and a target polypeptide wherein human FK506 binding proteins (FKBPs) are excluded as target polypeptides, a corresponding expression vector encoding said fusion protein as well as host cells transformed with said expression vector. Also disclosed are a method for producing the fusion protein, a recombinantly produced fusion protein comprising a SlpA chaperone and a target polypeptide. A further aspect of the invention is the use of the recombinantly produced fusion protein, and a reagent kit containing a recombinantly produced fusion protein comprising a SlpA chaperone and a target polypeptide.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS
Method for high-level secretory production of protein
This invention provides a means for high-level secretory production of a protein, and, in particular, a protein having a complicated structure such as an antibody, in a host cell such as a yeast cell. This invention provides a method for high-level secretory production of a foreign protein with the use of a transformed host cell having one or more types of chaperone protein genes and via suppression of O sugar chain inherent to a host cell such as a yeast cell.
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD +1
Method for identifying target protein of drug and method for screening therapeutic agent for diabetes using the target protein
InactiveUS20090041754A1High principal effectReduced adverse side effectCompound screeningApoptosis detectionDrugBiguanide
A method for identifying a target protein of a compound having a pharmacological action by detecting a tertiary structural change of a target protein by binding a compound having a pharmacological action to a target protein with the use of a molecular chaperone protein having a characteristic of binding to a protein by recognizing a tertiary structural change of the protein is disclosed. Further, a method for screening a therapeutic agent for diabetes using a target protein of biguanide which is a therapeutic agent for diabetes and was found by the identification method, a screening tool which can be used in the screening method and a pharmaceutical composition for treating diabetes containing a substance obtained by the screening method are disclosed.
Owner:ASTELLAS PHARMA INC
Allosteric chaperones and uses thereof
InactiveUS20150147309A1High activityGood curative effectBiocideCompound screeningAcid alpha-glucosidaseLysosome
The present invention relates to an allosteric non-inhibitory chaperone of the lysosomal acid alpha-glucosidase (GAA) for use in the treatment of a pathological condition characterized by a deficiency of the lysosomal acid alpha-glucosidase (GAA), to pharmaceutical composition thereof, to a method for increasing the activity of GAA in a subject and to a method for identifying an allosteric non-inhibitory chaperone for GAA.
Owner:FOND AZIONE TELETHON +1
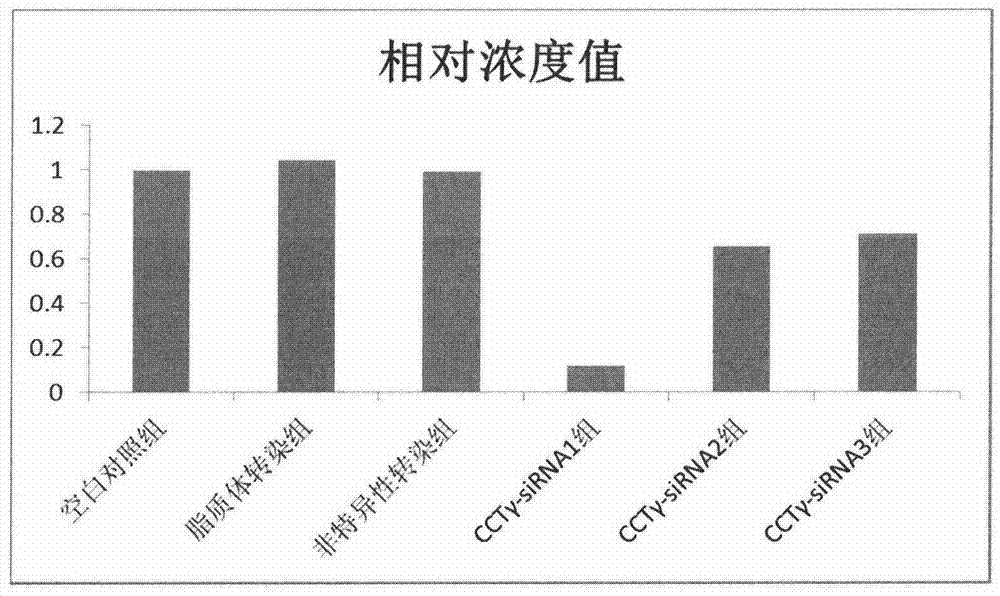
Application of chaperonin CCTgamma in preparation of tumour diagnosis reagent
ActiveCN104721836AHigh selectivitySimplify the process of quantitative detectionOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementCandidate Gene Association StudyChaperonin
The invention relates to an application of chaperonin CCTgamma in preparation of a tumour diagnosis reagent and in particular relates to a new application of the chaperonin CCTgamma in preparation of an osteosarcoma diagnosis reagent. The inventor adopts bioinformatics method analysis for carrying out gene screening based on high-throughput sequencing results, a candidate gene CCTgamma is picked out, and further molecular cell biology experiments prove that CCTgamma has a good correlation with osteosarcoma, can be used for preparing an auxiliary osteosarcoma diagnosis and treatment preparation and has important clinical application value.
Owner:QINGDAO MEDINTELL BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
Method for high-level secretory production of protein
ActiveUS20110014651A1Accelerating foreign protein secretionFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyForeign protein
This invention provides a means for high-level secretory production of a protein, and, in particular, a protein having a complicated structure such as an antibody, in a host cell such as a yeast cell. This invention provides a method for high-level secretory production of a foreign protein with the use of a transformed host cell having one or more types of chaperone protein genes and via suppression of O sugar chain inherent to a host cell such as a yeast cell.
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD +1
Multiple gene expression for engineering novel pathways and hyperexpression of foreign proteins in plants
InactiveUS20040210966A1High expressionHigh copy numberClimate change adaptationDepsipeptidesPosition effectChloroplast
Owner:AUBURN UNIV +1
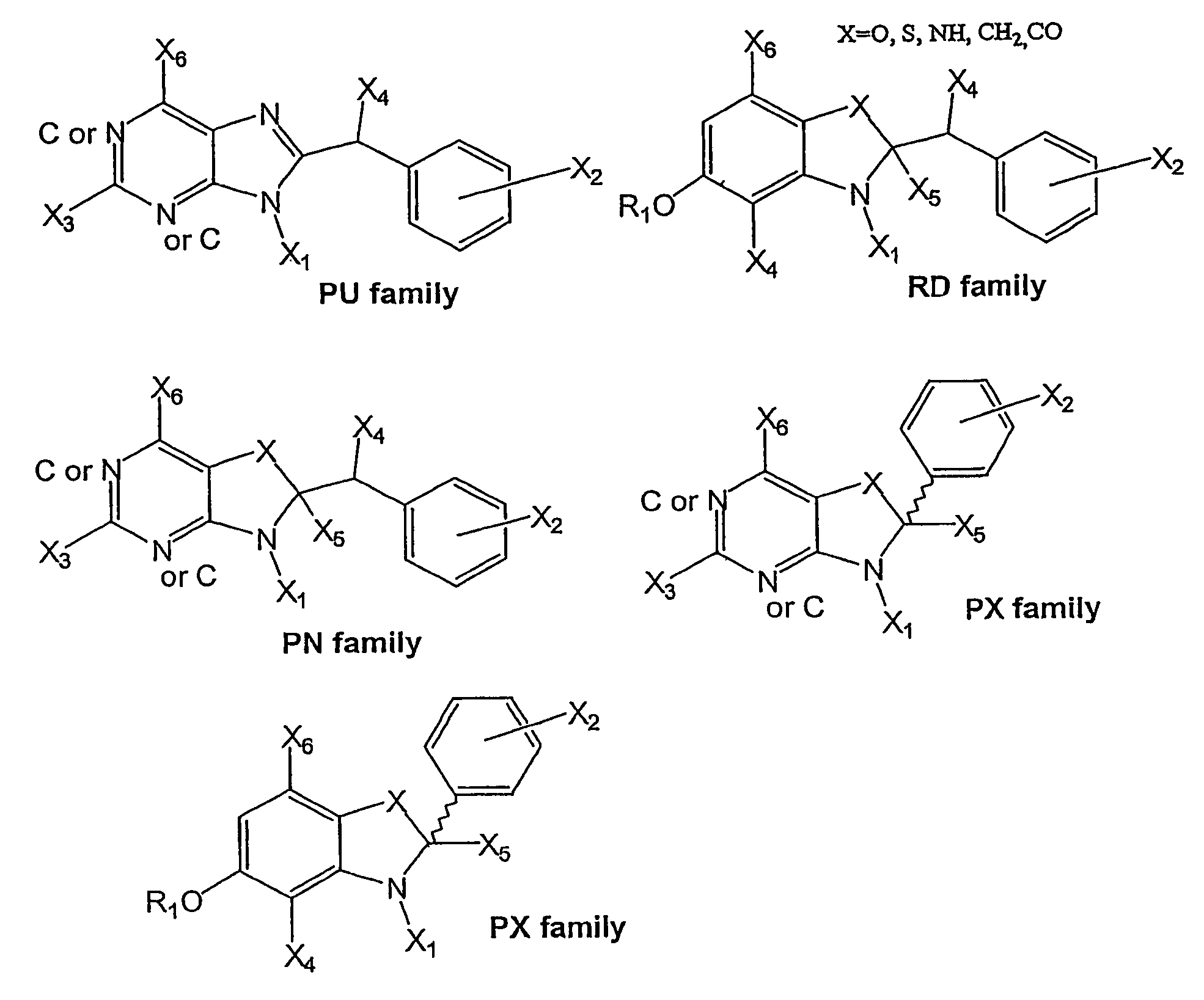
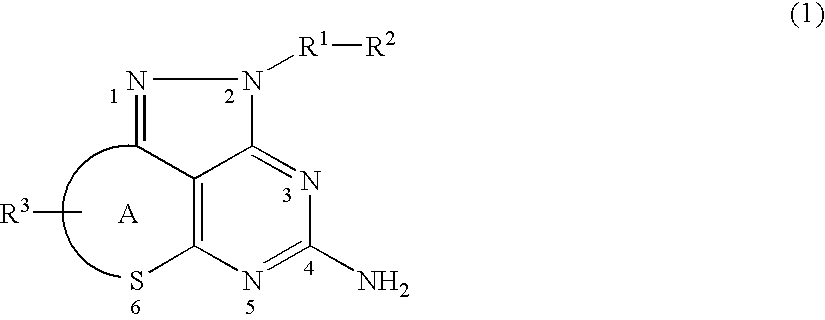
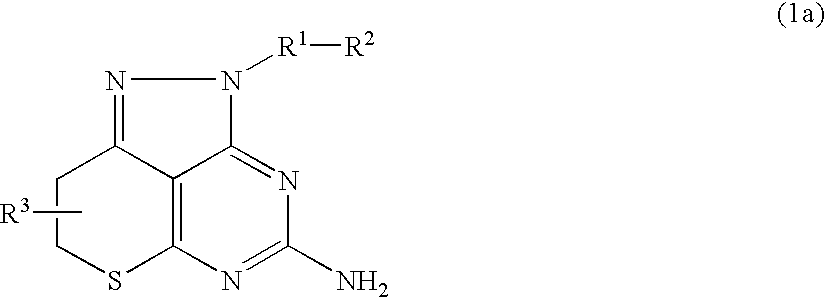
Pyrazolopyrimidine derivative
Problem to be SolvedTo provide a novel compound inhibiting the effect of HSP90, in particular a novel compound inhibiting the function of HSP90 as a chaperone protein and having antitumor activity.SolutionThe present invention provides a pyrazolopyrimidine compound represented by the formula (1) having various substituents which inhibits the ATPase activity of HSP90 and which has antitumor activity, an HSP90 inhibitor comprising the compound represented by the formula (1), a medicament comprising the compound represented by the formula (1), an anticancer agent comprising the compound represented by the formula (1), a pharmaceutical composition comprising the compound represented by the formula (1) and a method for treating cancer using the compound represented by the formula (1).
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD
Sperm protective polypeptides and uses thereof
The present invention relates to polypeptides capable of binding chaperone receptors, composition and methods for protecting, restoring, or improving the physiological properties of sperm cells. More particularly, the invention relates to protection of the motility, survival, fertility capability, resistance to cooling, freezing, and thawing of sperm cells put in contact with chaperone polypeptides.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com