Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
484 results about "Pyrazolopyrimidine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Pyrazolopyrimidines are a series of isomeric heterocyclic chemical compounds with the molecular formula C₆H₅N₃. They form the central core of a variety of more complex chemical compounds including some pharmaceuticals and pesticides.
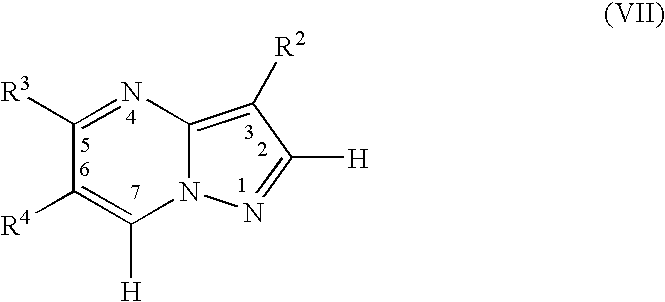
Pyrazolopyrimidines as therapeutic agents
Owner:ABBVIE DEUTSHLAND GMBH & CO KG
Pyrazolopyrimidines as protein kinase inhibitors
In its many embodiments, the present invention provides a novel class of pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine compounds as inhibitors of protein and / or checkpoint kinases, methods of preparing such compounds, pharmaceutical compositions including one or more such compounds, methods of preparing pharmaceutical formulations including one or more such compounds, and methods of treatment, prevention, inhibition, or amelioration of one or more diseases associated with the protein or checkpoint kinases using such compounds or pharmaceutical compositions. The invention also relates to the inhibition of hepatitis C virus (HCV) replication. In particular, embodiments of the invention provide compounds and methods for inhibiting HCV RNA-dependent RNA polymerase enzymatic activity. The invention also provides compositions and methods for the prophylaxis and treatment of HCV infection.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Novel pyrazolopyrimidines as cyclin dependent kinase inhibitors
In its many embodiments, the present invention provides a novel class of pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine compounds as inhibitors of cyclin dependent kinases, methods of preparing such compounds, pharmaceutical compositions containing one or more such compounds, methods of preparing pharmaceutical formulations comprising one or more such compounds, and methods of treatment, prevention, inhibition, or amelioration of one or more diseases associated with the CDKs using such compounds or pharmaceutical compositions.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Substituted pyrazolopyrimidines
InactiveUS20070281949A1Improve actionReduce releaseBiocideNervous disorderChemical compositionCompound (substance)
Owner:CEPHALON INC
Pyrazolopyrimidines as kinase inhibitors
The present invention relates generally to inhibitors of the kinases and more particularly to novel pyrazolopyrimidine compounds.
Owner:SMITHKLINE BECKMAN CORP
Pyrazolopyrimidines as cyclin dependent kinase inhibitors
In its many embodiments, the present invention provides a novel class of pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine compounds as inhibitors of cyclin dependent kinases, methods of preparing such compounds, pharmaceutical compositions containing one or more such compounds, methods of preparing pharmaceutical formulations comprising one or more such compounds, and methods of treatment, prevention, inhibition, or amelioration of one or more diseases associated with the CDKs using such compounds or pharmaceutical compositions.
Owner:PHARMACOPEIA DRUG DISCOVERY +1
Pyrazolopyrimidines as protein kinase inhibitors
In its many embodiments, the present invention provides a novel class of pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine compounds as inhibitors of protein and / or checkpoint kinases, methods of preparing such compounds, pharmaceutical compositions including one or more such compounds, methods of preparing pharmaceutical formulations including one or more such compounds, and methods of treatment, prevention, inhibition, or amelioration of one or more diseases associated with the protein or checkpoint kinases using such compounds or pharmaceutical compositions.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
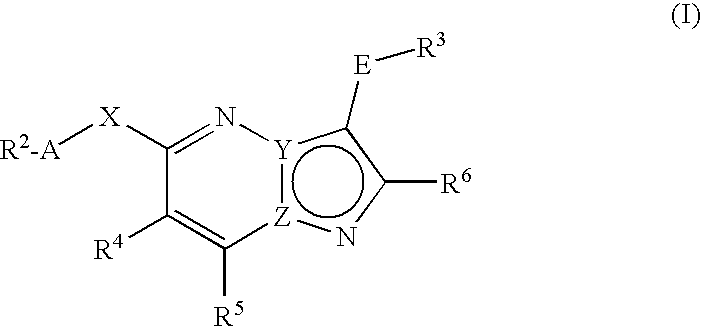
Fused heterocycles as lck inhibitors
There is provided fused heterocycles of imidazopyridazine or pyrazolopyrimidine derivative represented by the formula (I), which have excellent Lck inhibitory activity and are useful for a medicament particularly an immunosuppressive agent.[wherein one of Y and Z is C atom, and the other is N atom; —X— is —N(R1)— or the like, —R1 represents hydrogen or the like, -A- represents bond or the like,—R2 is cycloalkyl, aryl or the like, -E- is bond or the like, —R3 is aryl, aromatic heterocycle or the like, —R4, —R5 and —R6 are the same or different, each being hydrogen or the like.]
Owner:ASTELLAS PHARMA INC
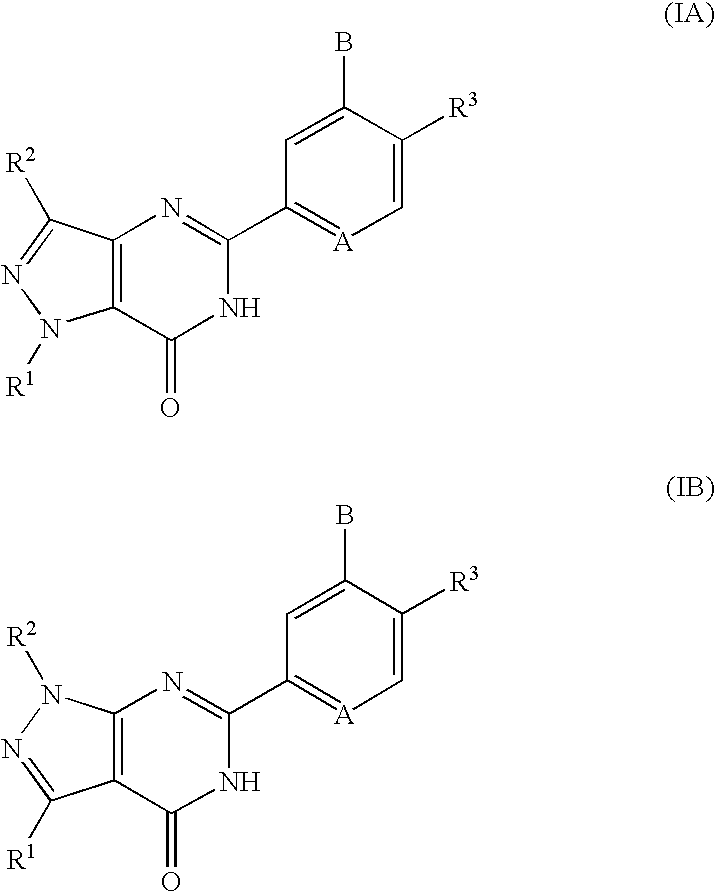
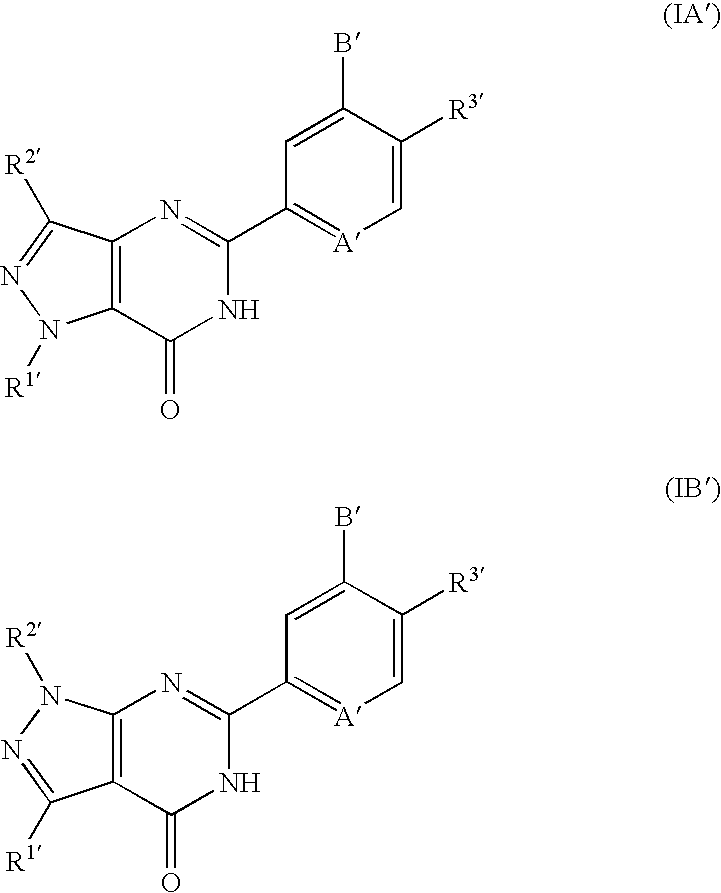
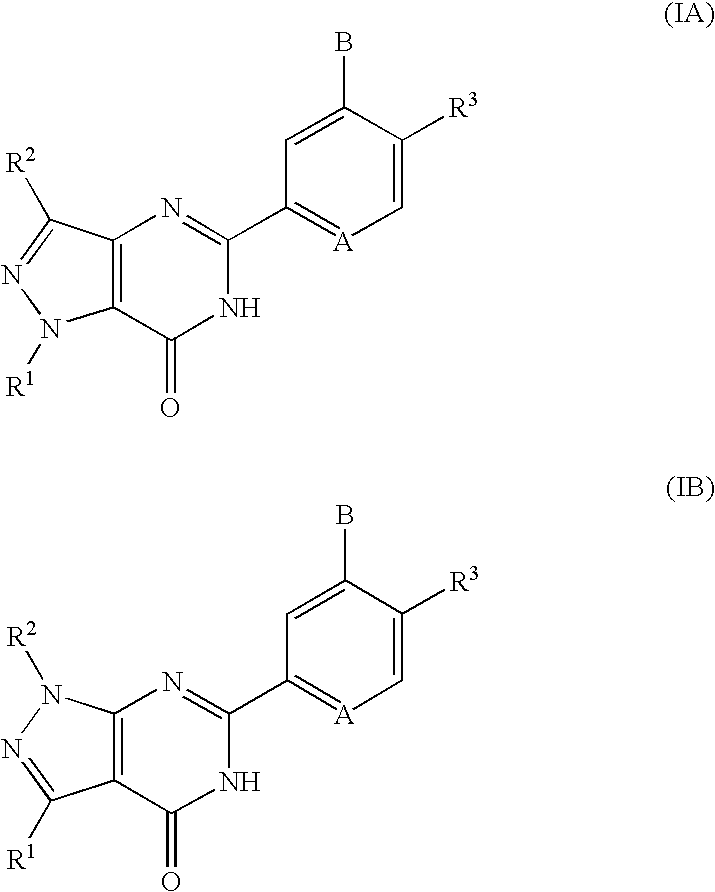
Pyrazolopyrimidinone derivatives having PDE7 inhibiting action
InactiveUS20050148604A1Increase level of intracellular cAMPInhibits T cell activationAntibacterial agentsBiocideBiological activationT cell
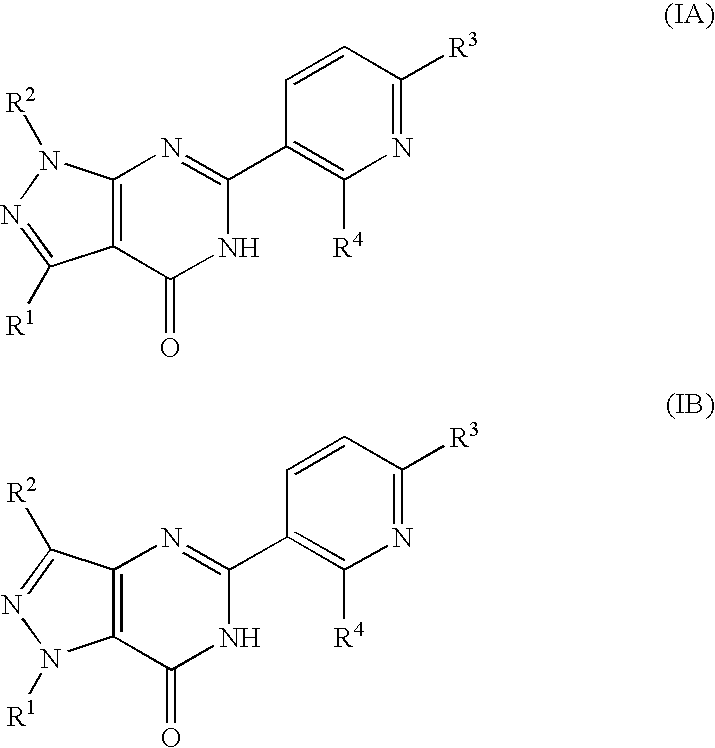
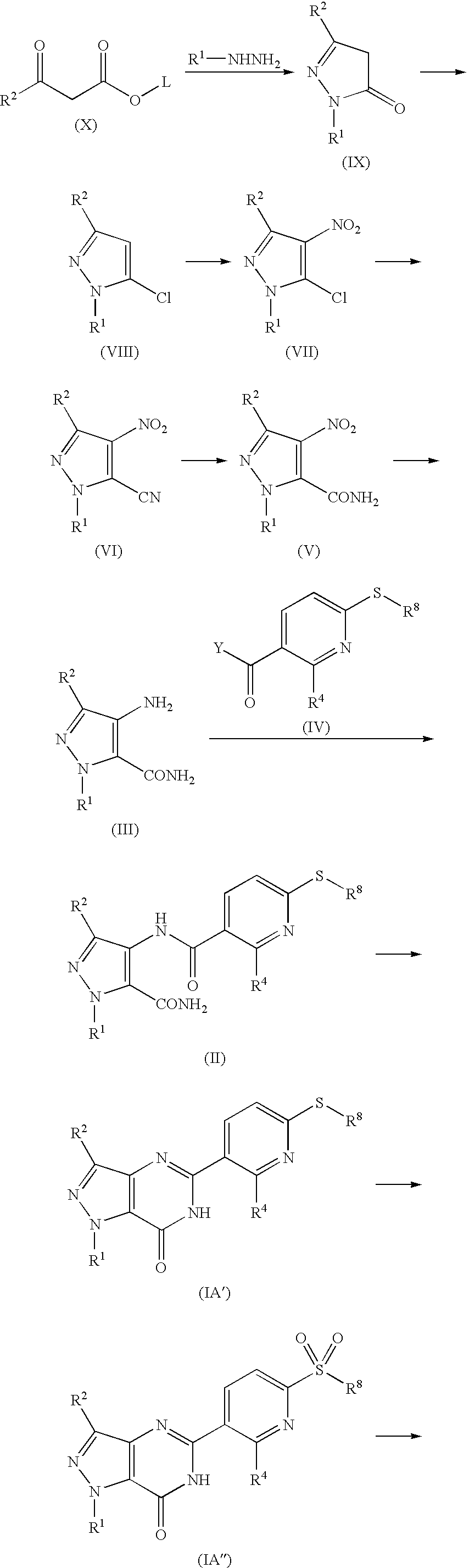
Pyrazolopyrimidinone derivatives expressed by the following general formula (IA) or (IB): and the following general formula (IA′) or (IB′): where the symbols are as disclosed in the specification, are provided as desired compounds. These compounds have the action of selectively inhibiting PDE7, thereby increasing the intracellular cAMP level and inhibiting the activation of T cells. Thus, they are useful for prevention and treatment of various allergic diseases and inflammatory or immunological diseases.
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD
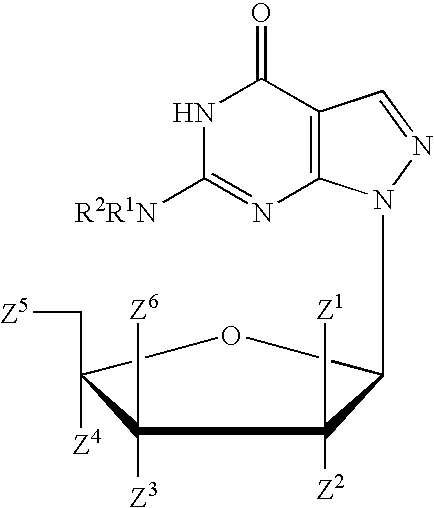
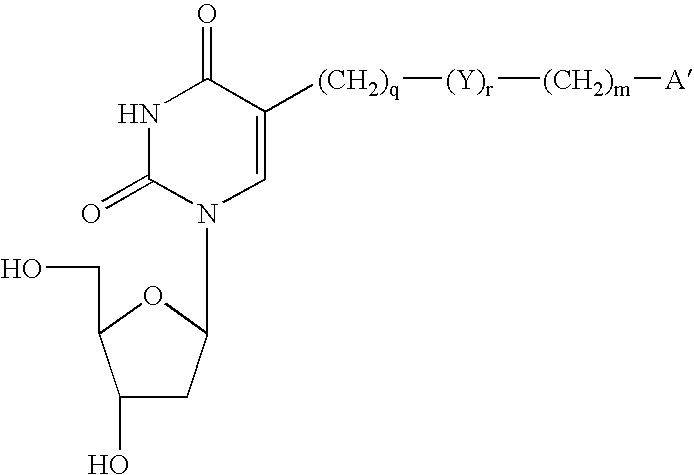
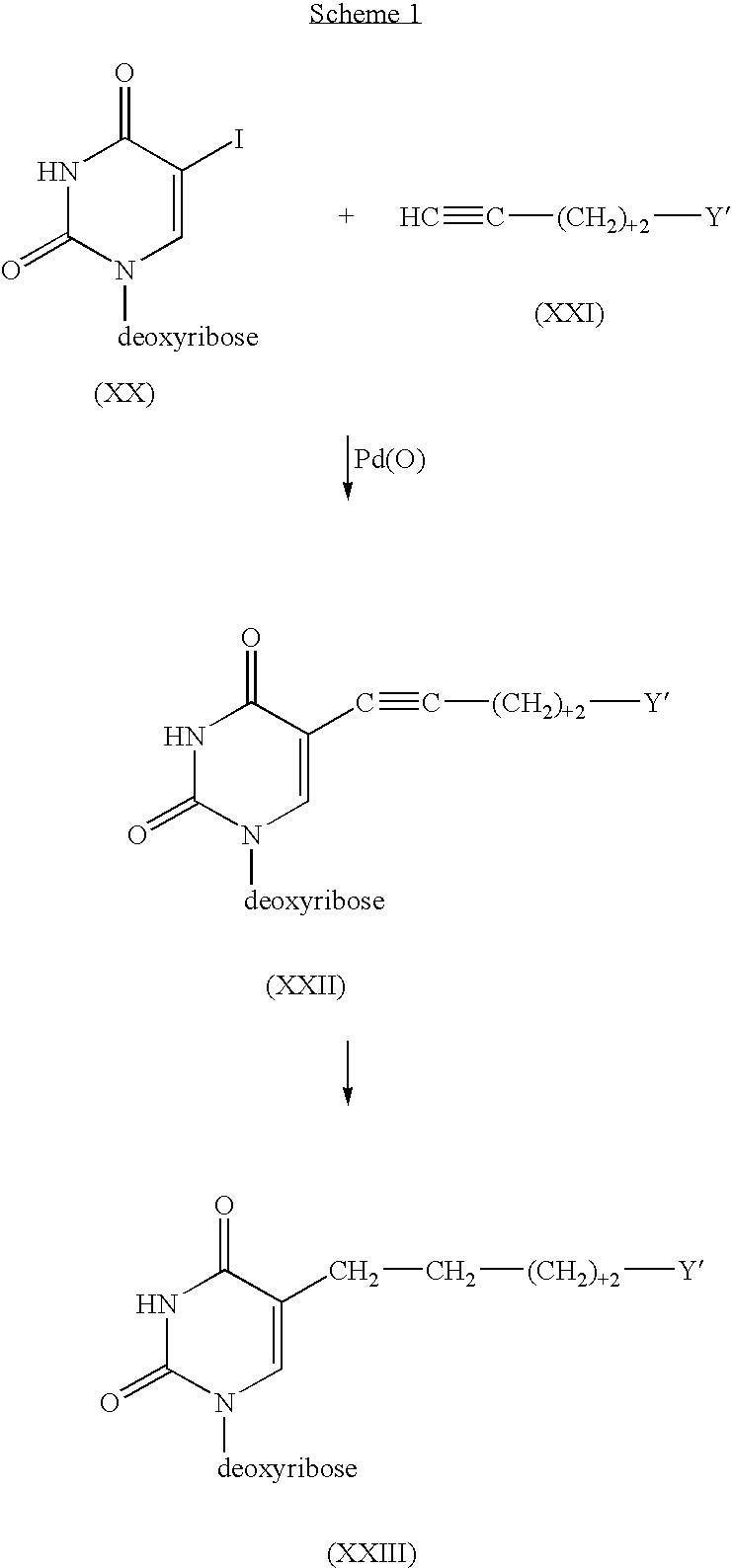
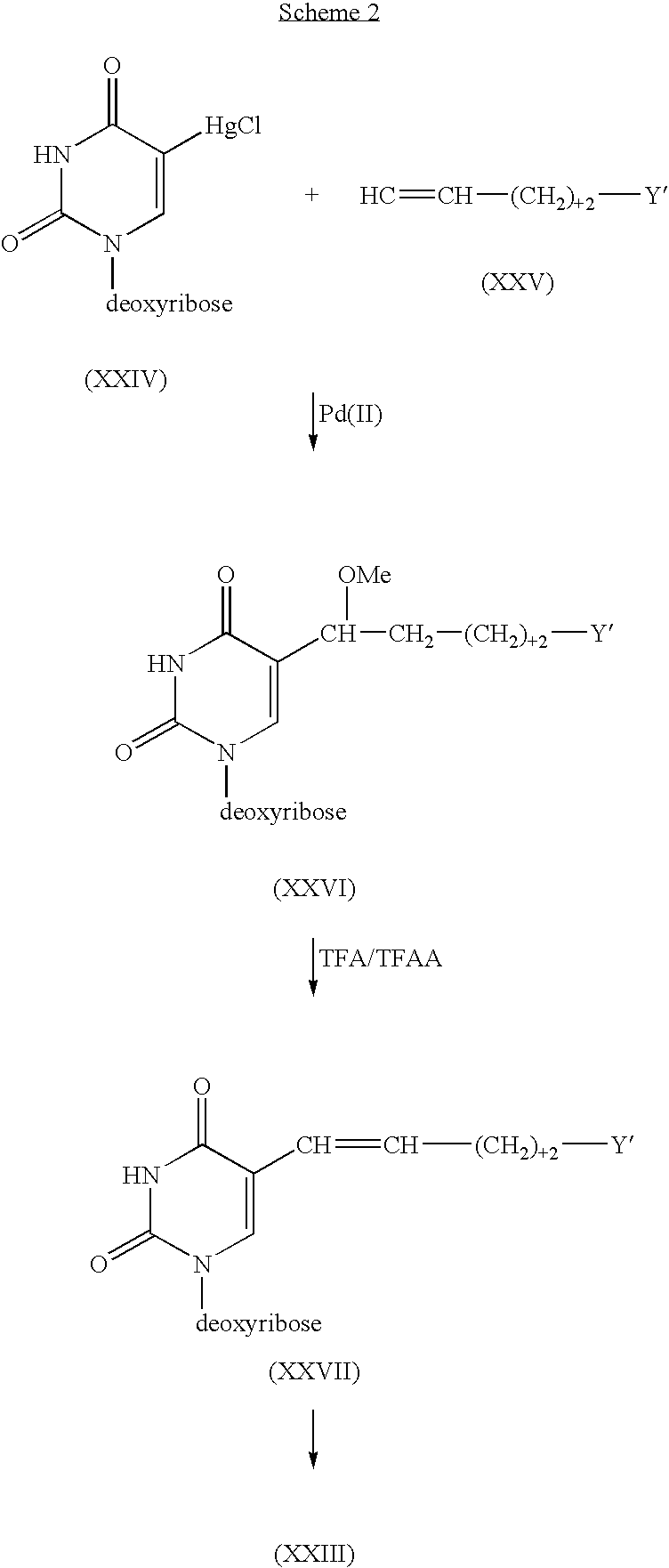
Process for the synthesis of pyrazolopyrimidines
The present invention provides a nucleoside comprising a pyrazolopyrimidine base and a process for producing the same. In particular, the processes of the present invention comprises using a halogenated pyrazolopyrimidine base and removing the halogen after the base is coupled to a sugar moiety. The presence of the halogen on the nucleoside base allows facile and economical production of a large quantity of nucleosides.
Owner:EPOCH BIOSCI
Pyrazolopyrimidines
Owner:BAYER CROPSCIENCE AG
Process for the synthesis of pyrazolopyrimidines
InactiveUS6962991B2Cheap productionSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationHalogenSugar moiety
The present invention provides a nucleoside comprising a pyrazolopyrimidine base and a process for producing the same. In particular, the processes of the present invention comprises using a halogenated pyrazolopyrimidine base and removing the halogen after the base is coupled to a sugar moiety. The presence of the halogen on the nucleoside base allows facile and economical production of a large quantity of nucleosides.
Owner:DRUG ROYALTY TRUST 9 +1
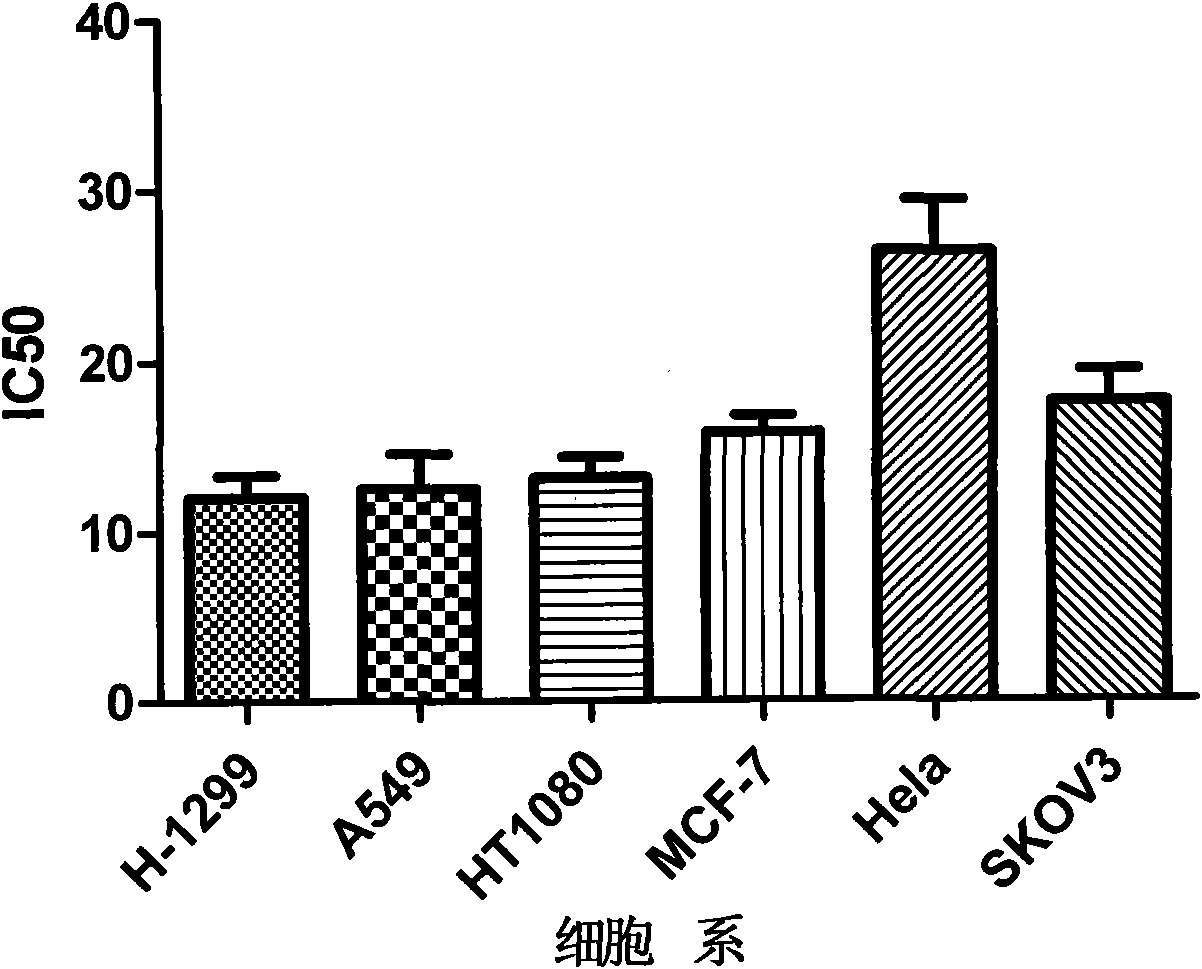
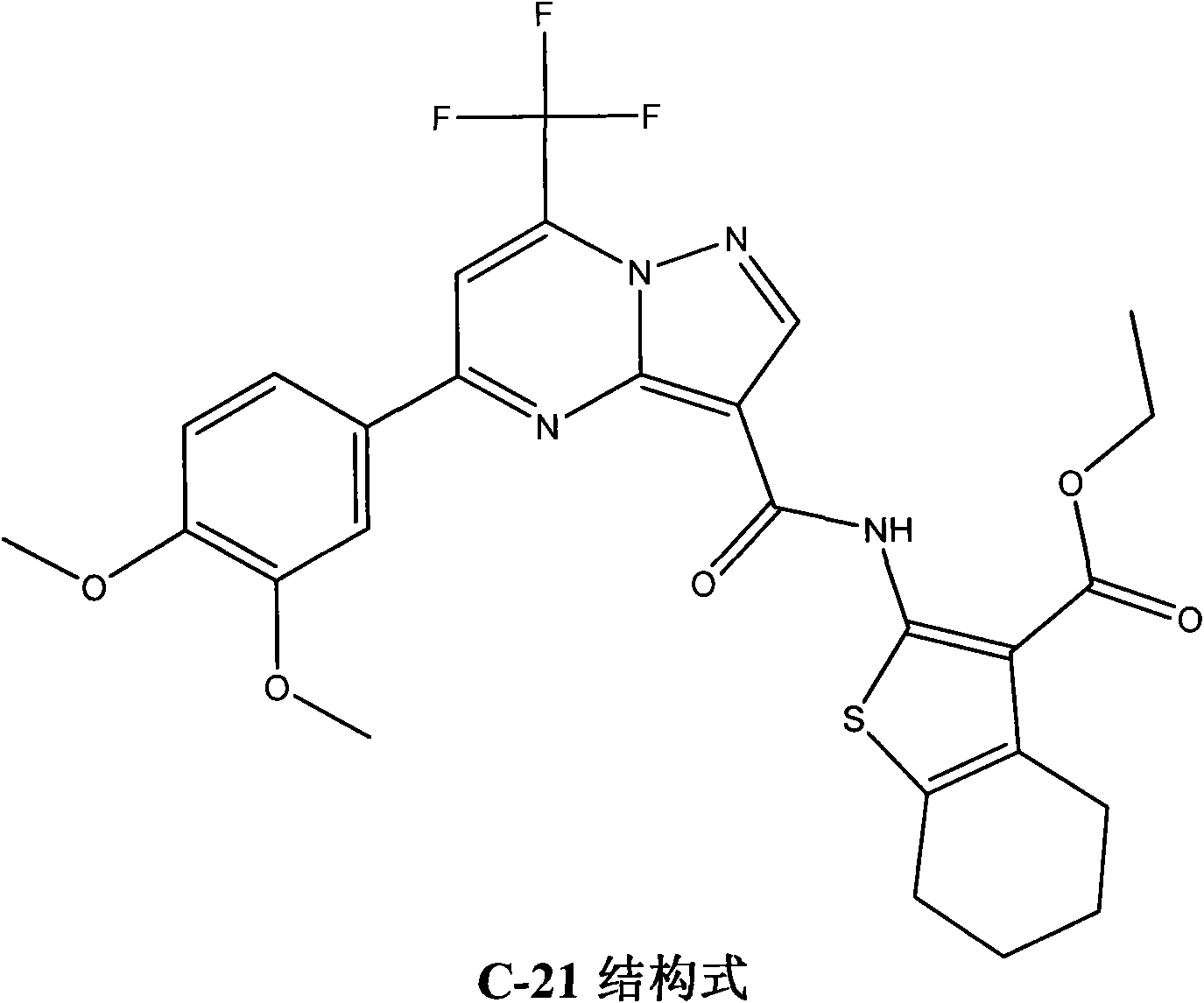
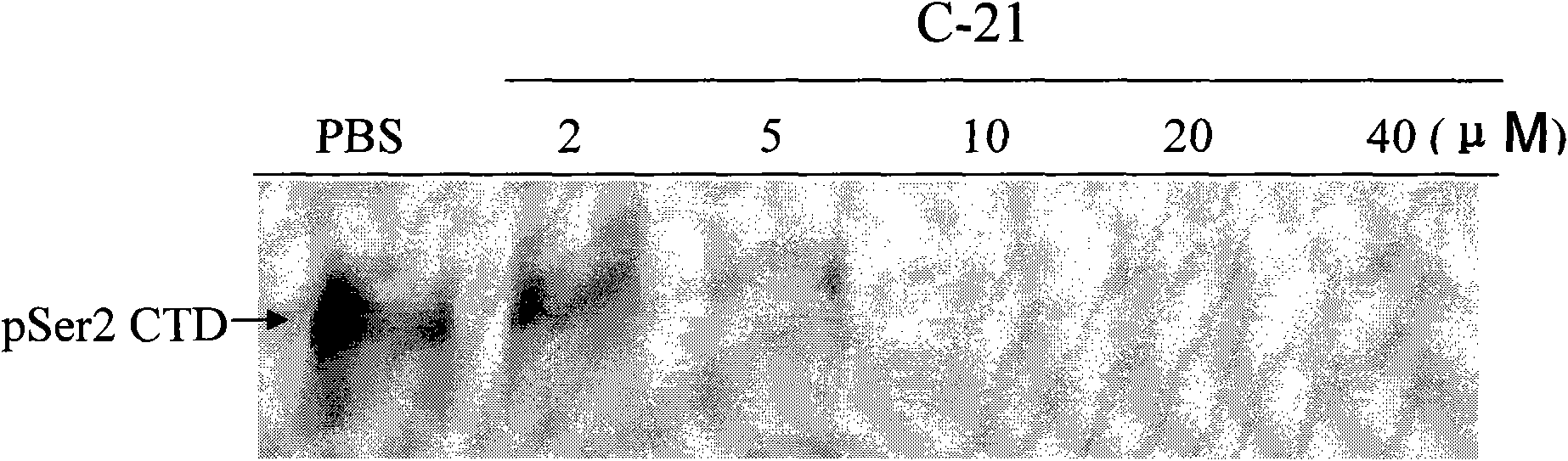
Application of N-(thiofuran-2) pyrazolo (1, 5-a) pyridine-3-formanides compounds for preparing antineoplastic
The invention searches the novel micromolecule inhibitor pyrazolo (1, 5-a) miazines compounds of cyclin-dependent kinase CDK9 (cyclin-dependent kinase) through the virtual screening of a computer, biometrically measures activity thereof, and validates interaction mechanism. The invention specifically comprises the following steps: the three-dimensional crystal conformation of the cyclin-dependent kinase family member CDK9 is obtained in a way of homology modeling; and micromolecule three-dimensional database is screened with DOCK (molecular docking). The invention uses a MTT tumor cell growth inhibition test to biometrically measures the activity of the selected compounds, researches the selected compounds pyrazolo (1, 5-a) miazines with high activety in a way of molecular mechanism, validates the inhibiting effect of the compounds to the activity of CDK9 kinase, and clarifies the interaction mechanism of the compounds for inhibiting the external activity and the molecule of various malignancies such as lung cancer, osteosarcoma, oophoroma, cervical carcinoma, breast cancer, etc.
Owner:INST OF HEMATOLOGY & BLOOD DISEASES HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI & PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE
Pyrazolopyrimidines as protein kinase inhibitors
In its many embodiments, the present invention provides a novel class of amino-substituted pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine compounds as inhibitors of protein and / or checkpoint kinases, methods of preparing such compounds, pharmaceutical compositions including one or more such compounds, methods of preparing pharmaceutical formulations including one or more such compounds, and methods of treatment, prevention, inhibition, or amelioration of one or more diseases associated with the protein or checkpoint kinases using such compounds or pharmaceutical compositions.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Trisubstituted and tetrasubstituted pyrazolopyrimidines as cyclin dependent kinase inhibitors
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Novel pyrazolopyrimidines as cyclin dependent kinase inhibitors
In its many embodiments, the present invention provides a novel class of pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine compounds as inhibitors of cyclin dependent kinases, methods of preparing such compounds, compositions containing one or more such compounds, methods of preparing pharmaceutical formulations comprising one or more such compounds, and methods of treatment, prevention, inhibition, or amelioration of one or more diseases associated with the CDKs using such compounds or compositions.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Pyrazolopyrimidines, a process for their preparation and their use as medicine
The invention relates to pyrazolopyrimidine derivatives as well as their pharmaceutically acceptable salts. The invention further relates to a process for the preparation of such compounds. The compounds of the invention are mGluR5 modulators and are therefore useful for the control and prevention of acute and / or chronic neurological disorders.
Owner:MERZ PHARMA GMBH & CO KGAA
Pyrazolopyrimidines as cyclin dependent kinase inhibitors
In its many embodiments, the present invention provides a novel class of pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine compounds as inhibitors of cyclin dependent kinases, methods of preparing such compounds, pharmaceutical compositions containing one or more such compounds, methods of preparing pharmaceutical formulations comprising one or more such compounds, and methods of treatment, prevention, inhibition, or amelioration of one or more diseases associated with the CDKs using such compounds or pharmaceutical compositions.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC +1
Cross-linking oligonucleotides
Owner:DRUG ROYALTY TRUST 9
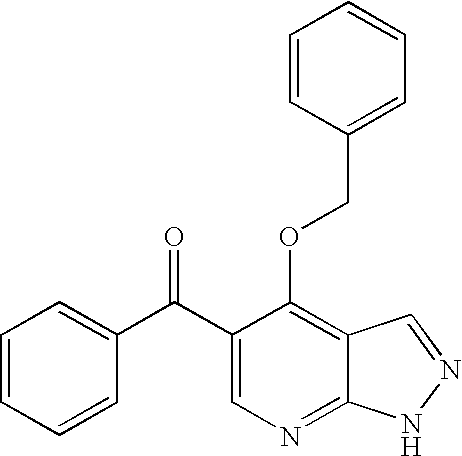
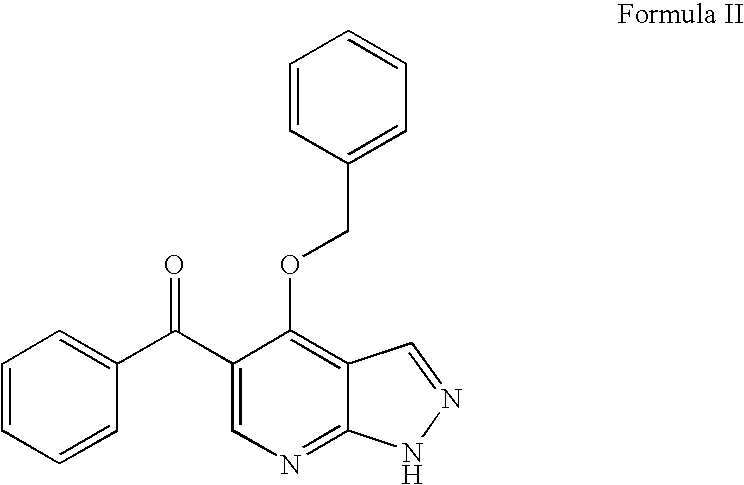
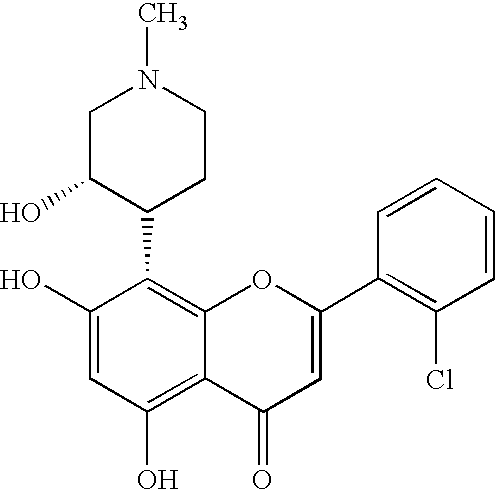
Pyrazolopyrimidine compound and pharmaceutical composition thereof as well as pharmaceutical application of pyrazolopyrimidine compound
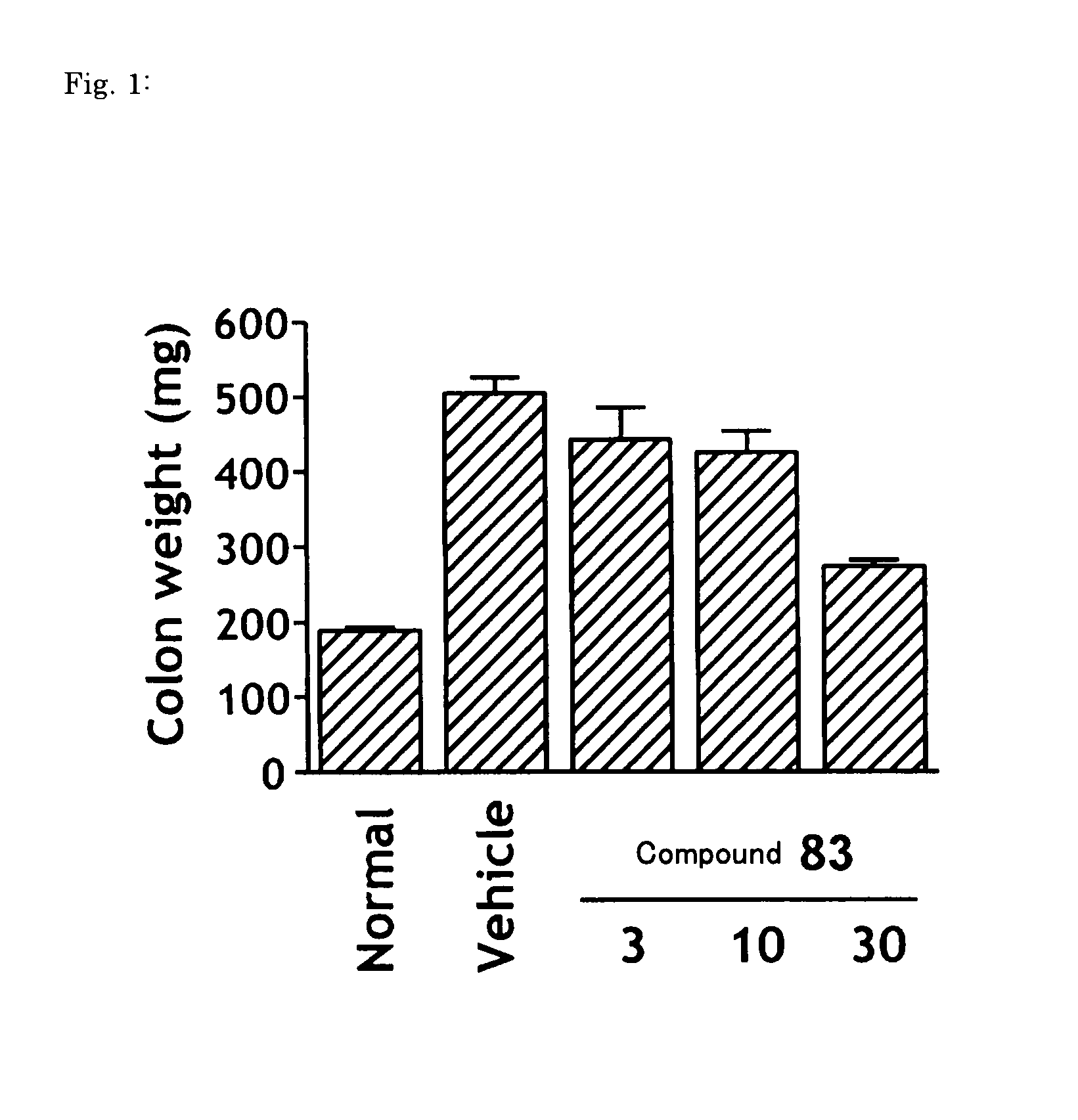
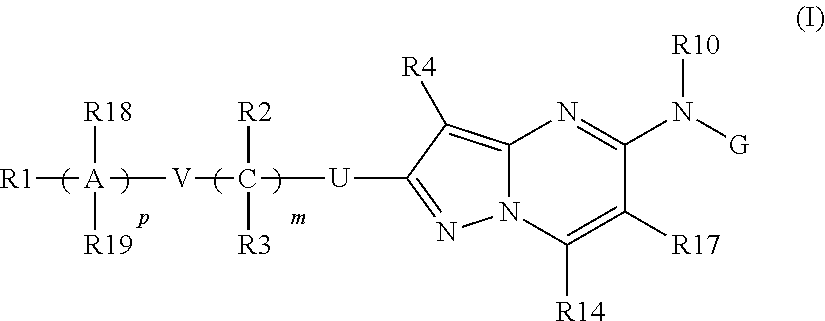
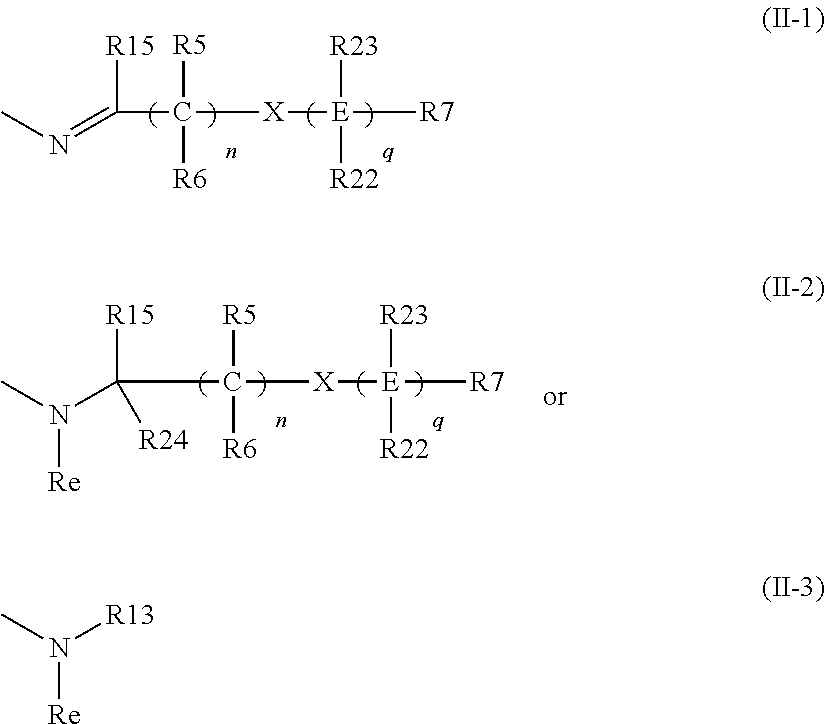
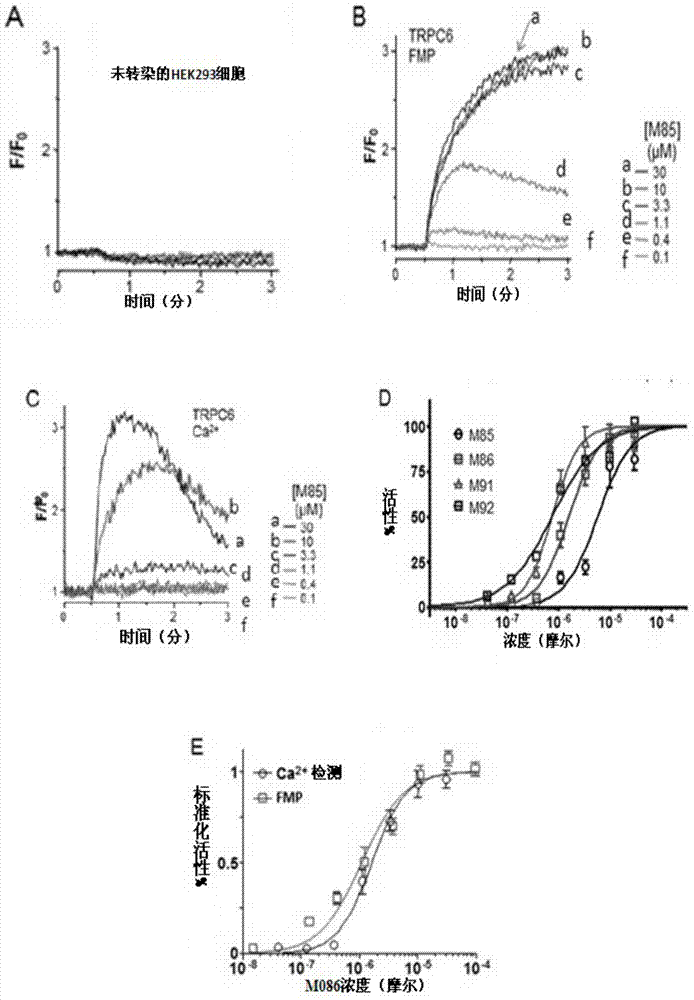
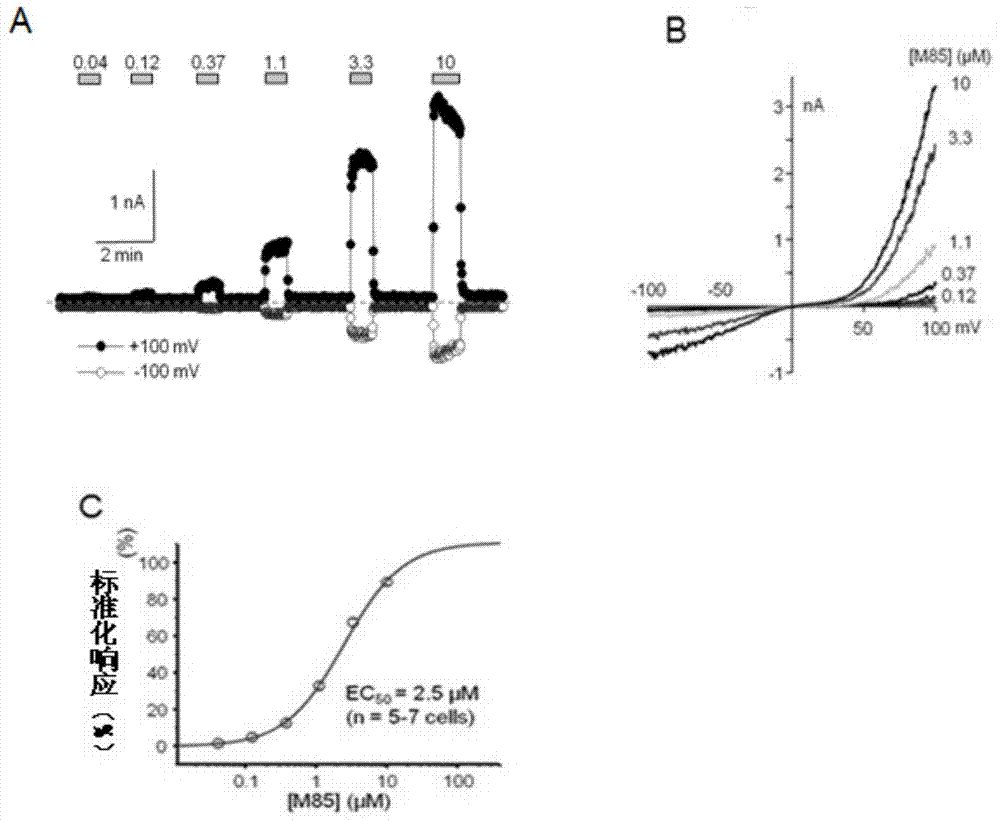
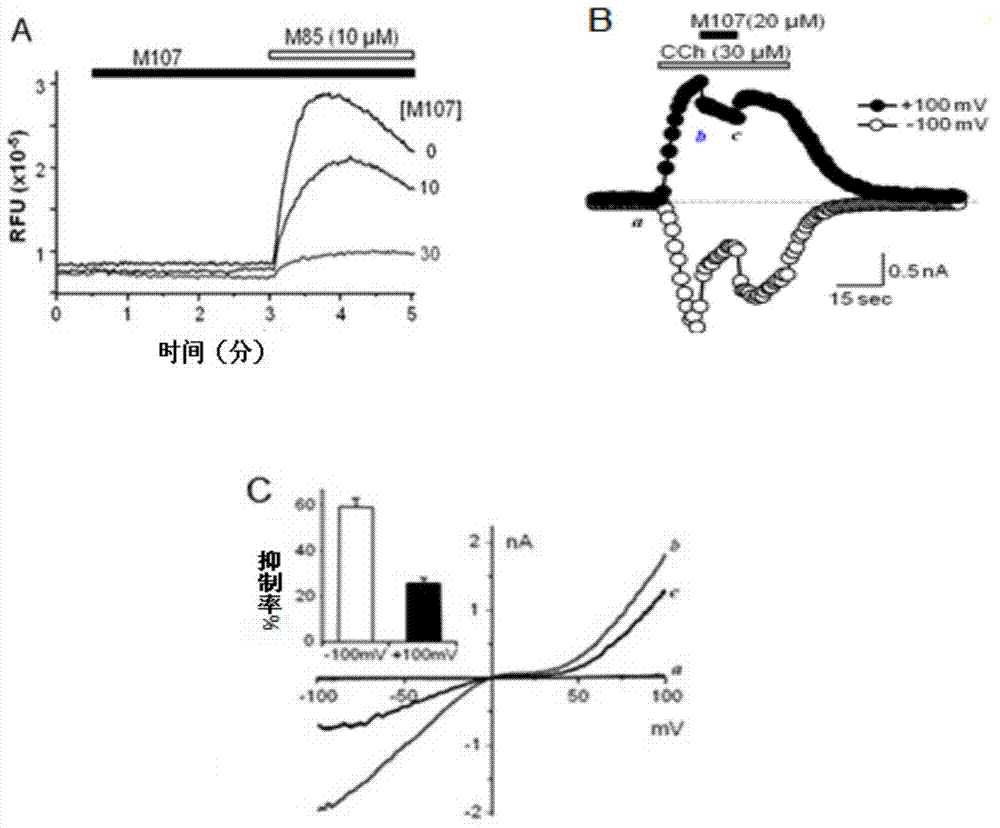
The invention provides a pyrazolopyrimidine compound shown as a structural formula (I), a pharmaceutical composition taking the pyrazolopyrimidine compound as an active component, a preparation method of the pyrazolopyrimidine compound and the pharmaceutical composition as well as an application of the pyrazolopyrimidine compound and the pharmaceutical composition in preparation of a TRPC6 (Transient Receptor Potential Channel 6) adjustor probe medicine and related medicines for preventing and treating glomerulopathy and myocardial hypertrophy. The pyrazolopyrimidine compound and derivatives provided by the invention can be used to prepare medical preparations in various forms which comprise oral liquids, injections, pulmonary inhalation preparations and transdermal preparations, specifically injections, oral liquids, troches, capsules, granules, aerosols, dry powder inhalation, patches and the like.
Owner:泸州天演生物医药科技有限公司
Pyridinylpyrazolopyrimidinone derivatives as PDE 7 inhibitors
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD
Tetrahydropyrazolopyrimidine compounds
ActiveUS20130324547A1High expressionLower Level RequirementsBiocideOrganic chemistrySystemic lupus erythematosusNephritis
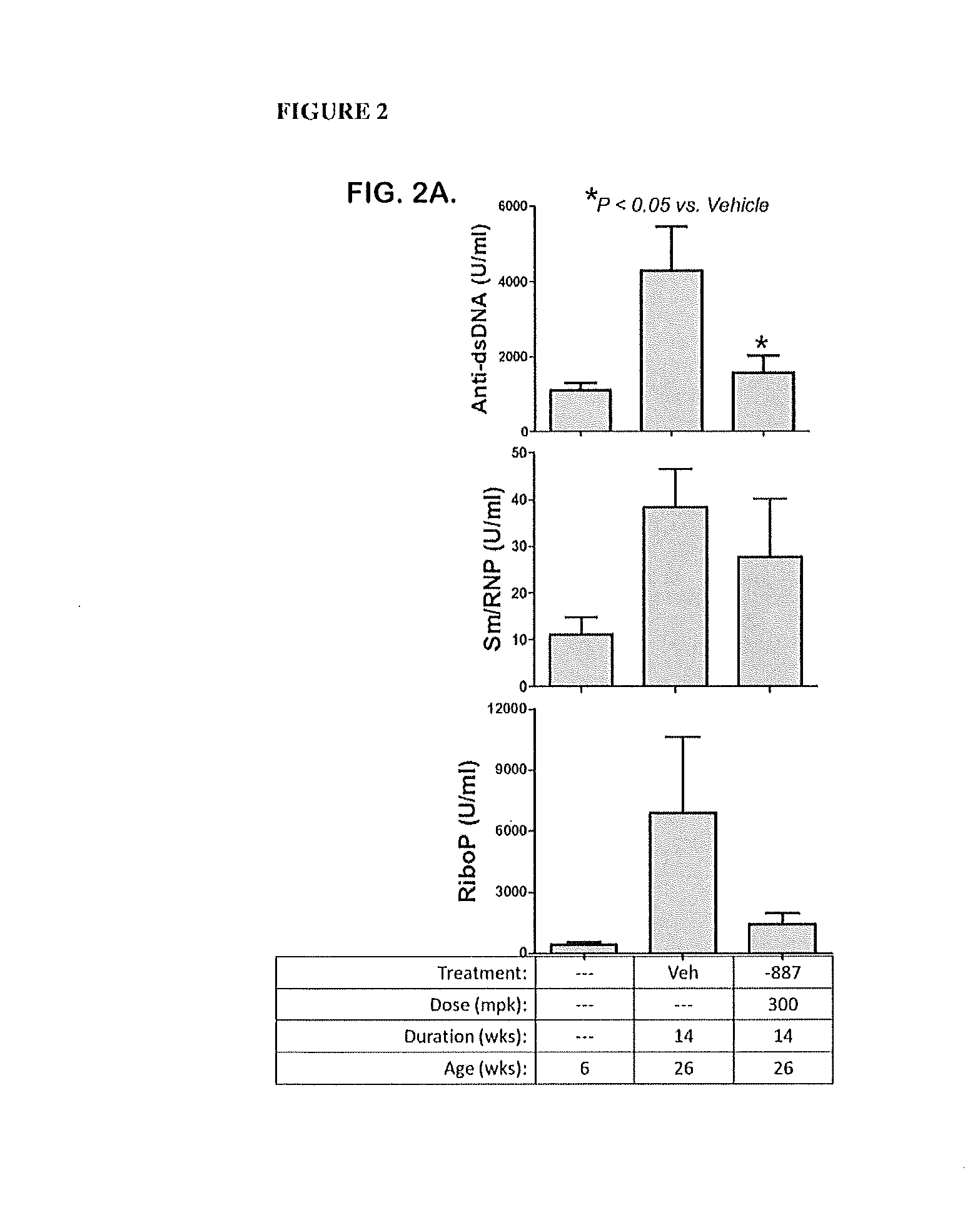
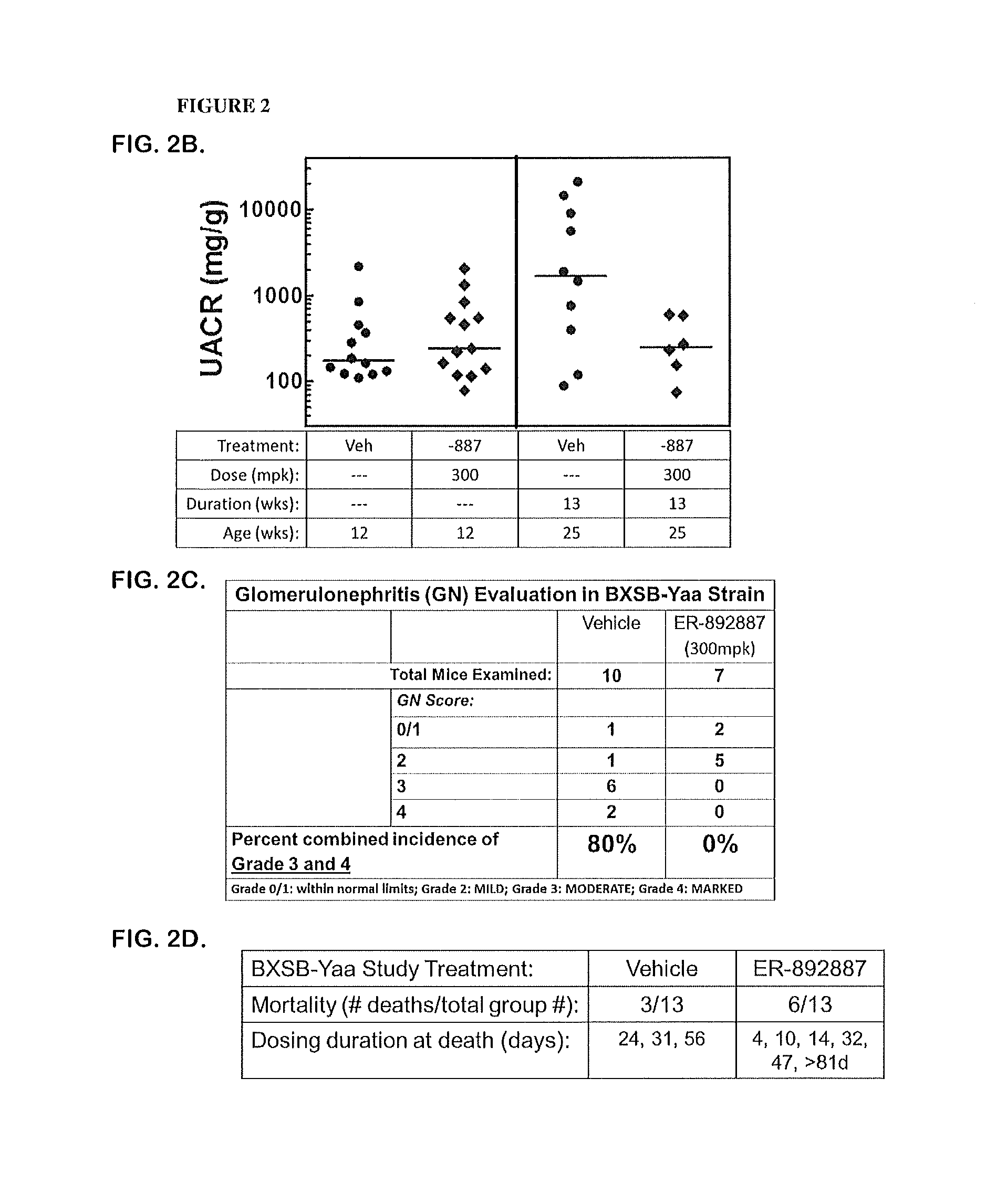
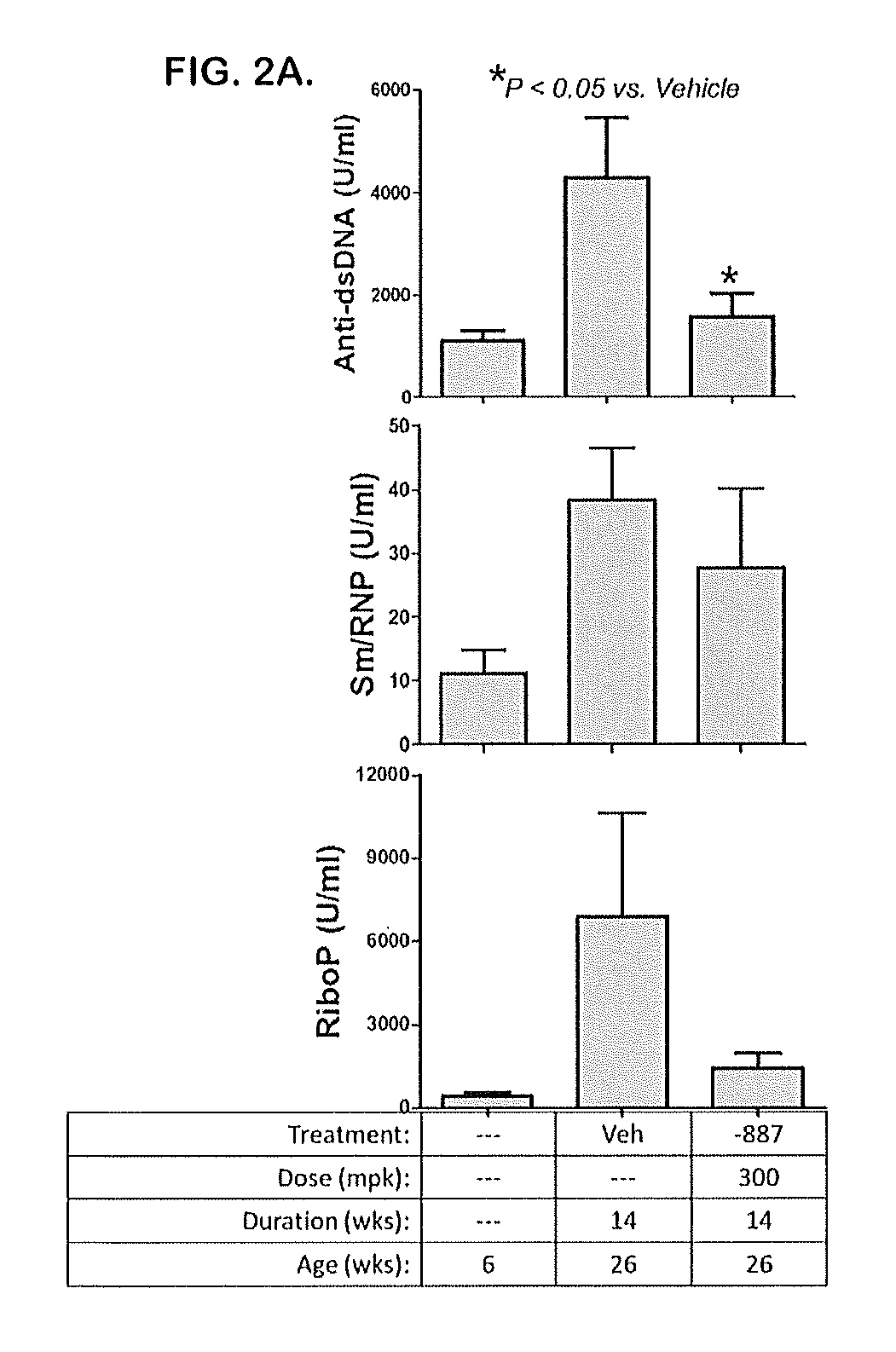
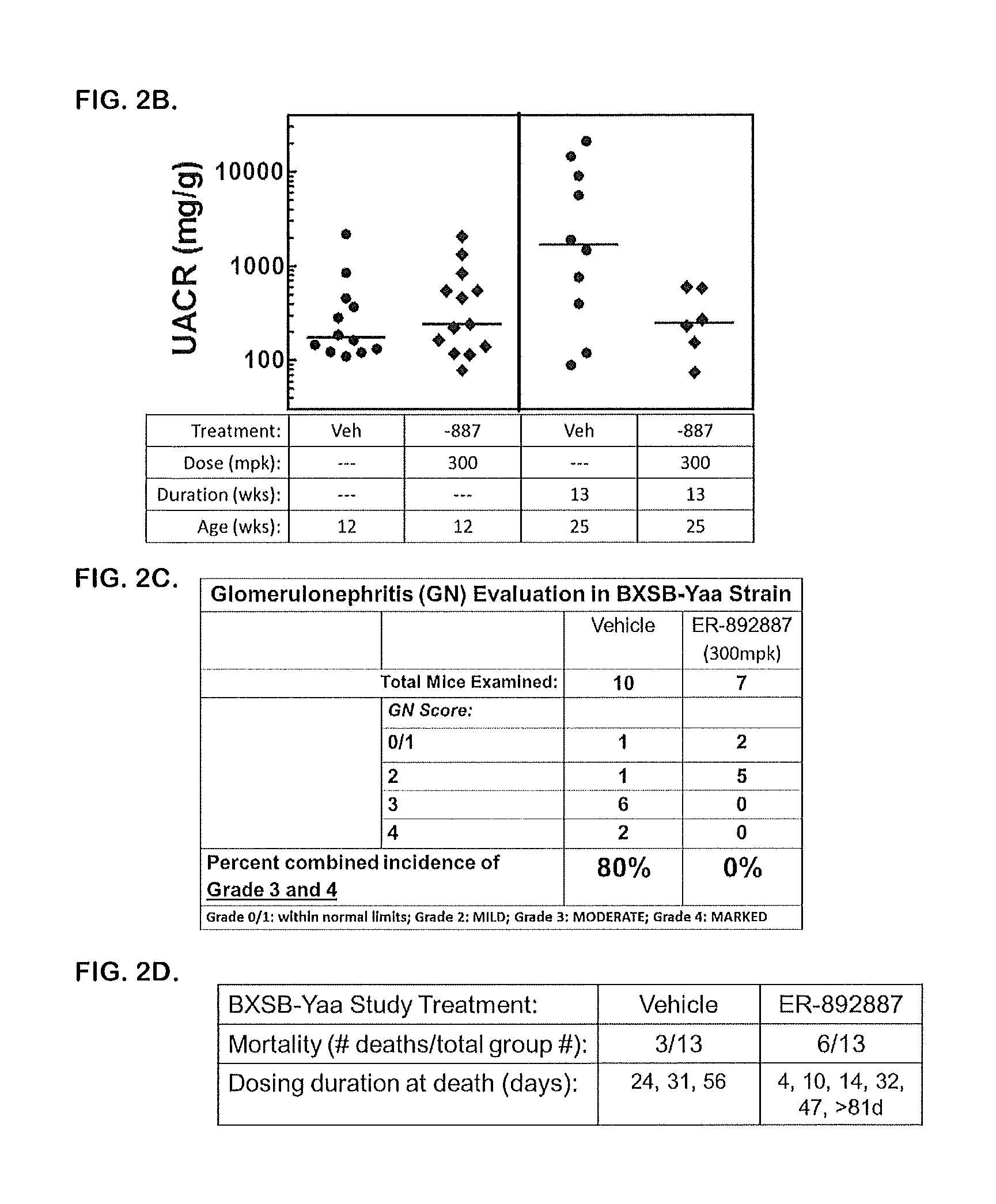
Embodiments of the disclosure relate to tetrahydropyrazolopyrimidine compounds that act as antagonists or inhibitors for Toll-like receptors 7 and / or 8, and their use in pharmaceutical compositions effective for treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and lupus nephritis
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Tetrahydropyrazolopyrimidine compounds
ActiveUS9126999B2High expressionLower Level RequirementsBiocideOrganic chemistryMedicineToll-like receptor
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Pyrazolopyrimidines
Owner:BAYER CROPSCIENCE AG
Pyrazolopyrimidine compound
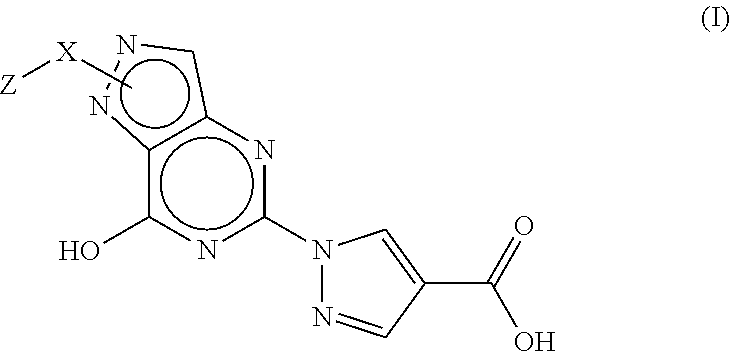
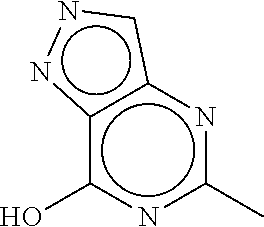
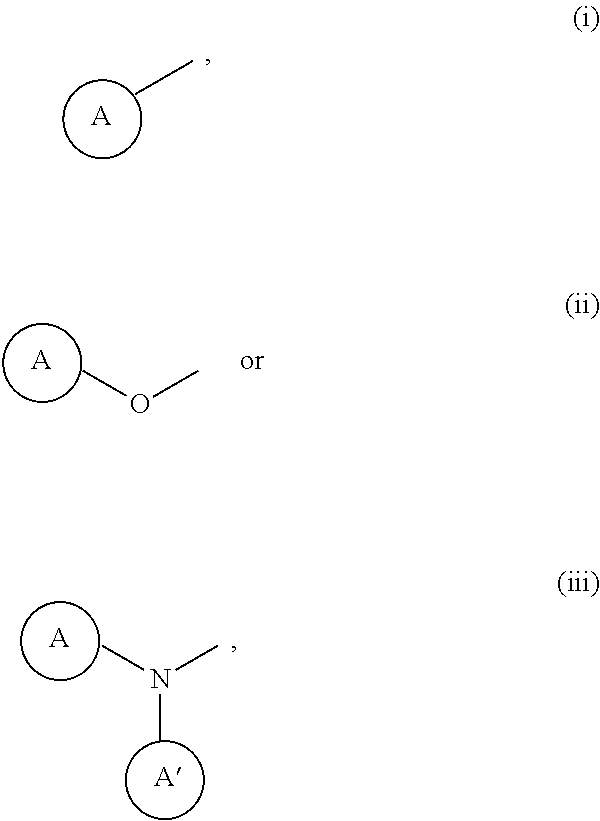
InactiveUS20150239889A1Excellent HIF-PHD inhibitionReduce usageNervous disorderOrganic chemistryArylAlicyclic Hydrocarbons
Provided is a pyrazolopyrimidine compound represented by formula (I) having an HIF-PHD inhibitory effect, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.[In the formula,represents an optionally substituted 7-hydroxypyrazolo[4,3-d]pyrimidine-5-yl,X represents a simple bond or an optionally substituted straight-chain alkylene,Z represents hydrogen atom, or formula (i), formula (ii) or formula (iii)andrings A and A′ are independently an optionally substituted aryl, an optionally substituted heteroaryl, an optionally substituted alicyclic hydrocarbon, or an optionally substituted non-aromatic heterocycle.]
Owner:MITSUBISHI TANABE PHARMA CORP
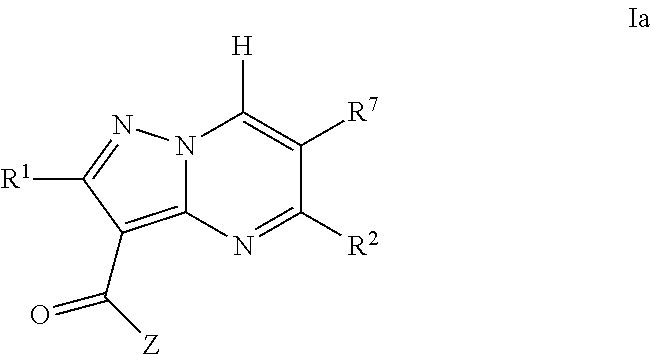
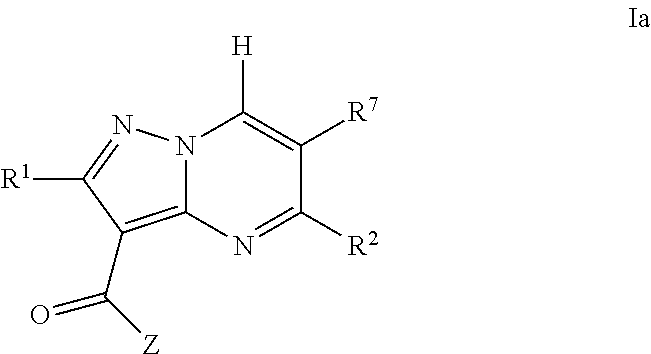
Pyrazolopyrimidine jak inhibitor compounds and methods
The invention provides JAK kinase inhibitors of Formula Ia, enantiomers, diasteriomers or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, wherein R1, R2, R7 and Z are defined herein, a pharmaceutical composition that includes a compound of Formula Ia and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, adjuvant or vehicle, and methods of treating or lessening the severity of a disease or condition responsive to the inhibition of a JAK kinase activity in a patient.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
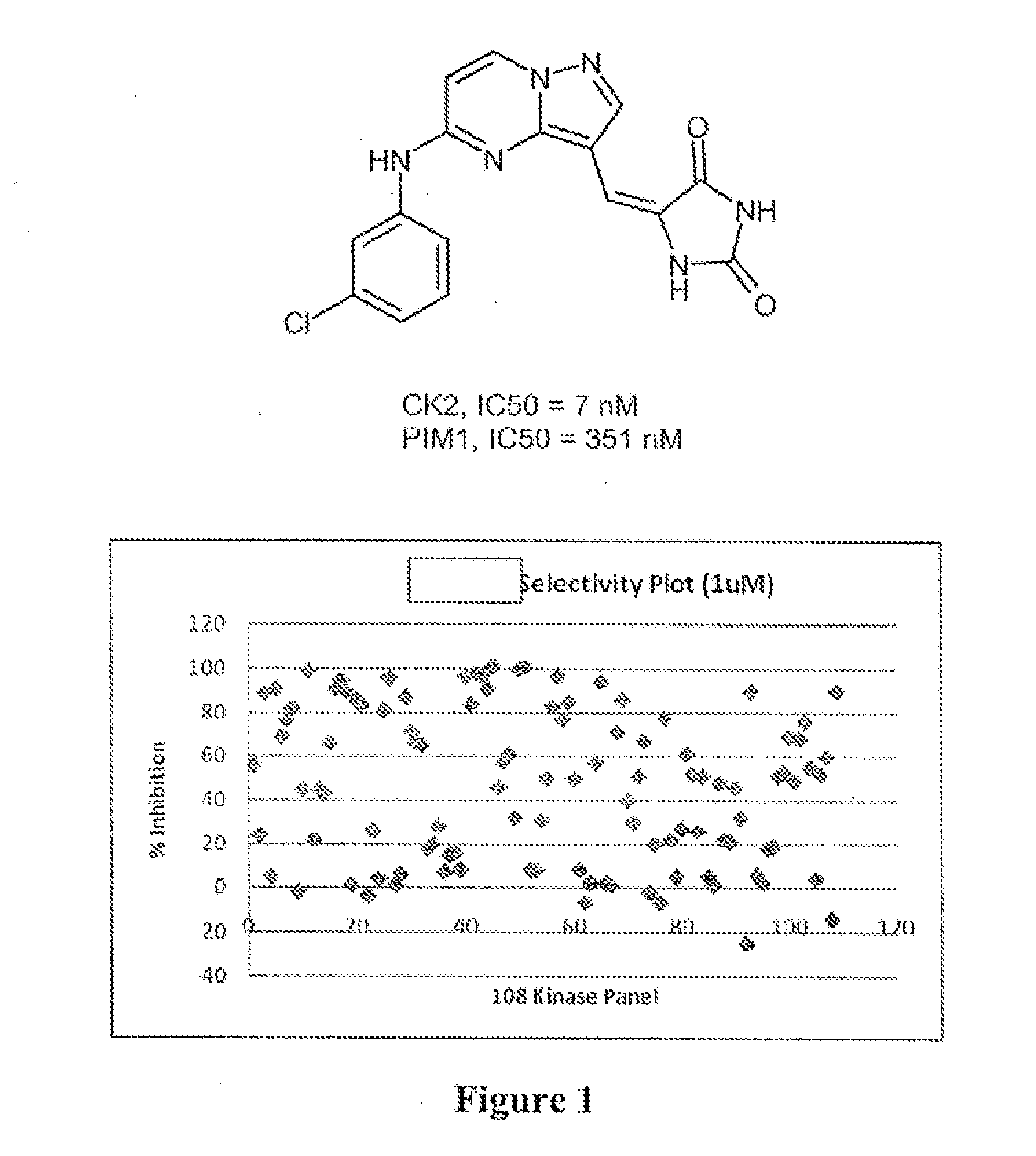
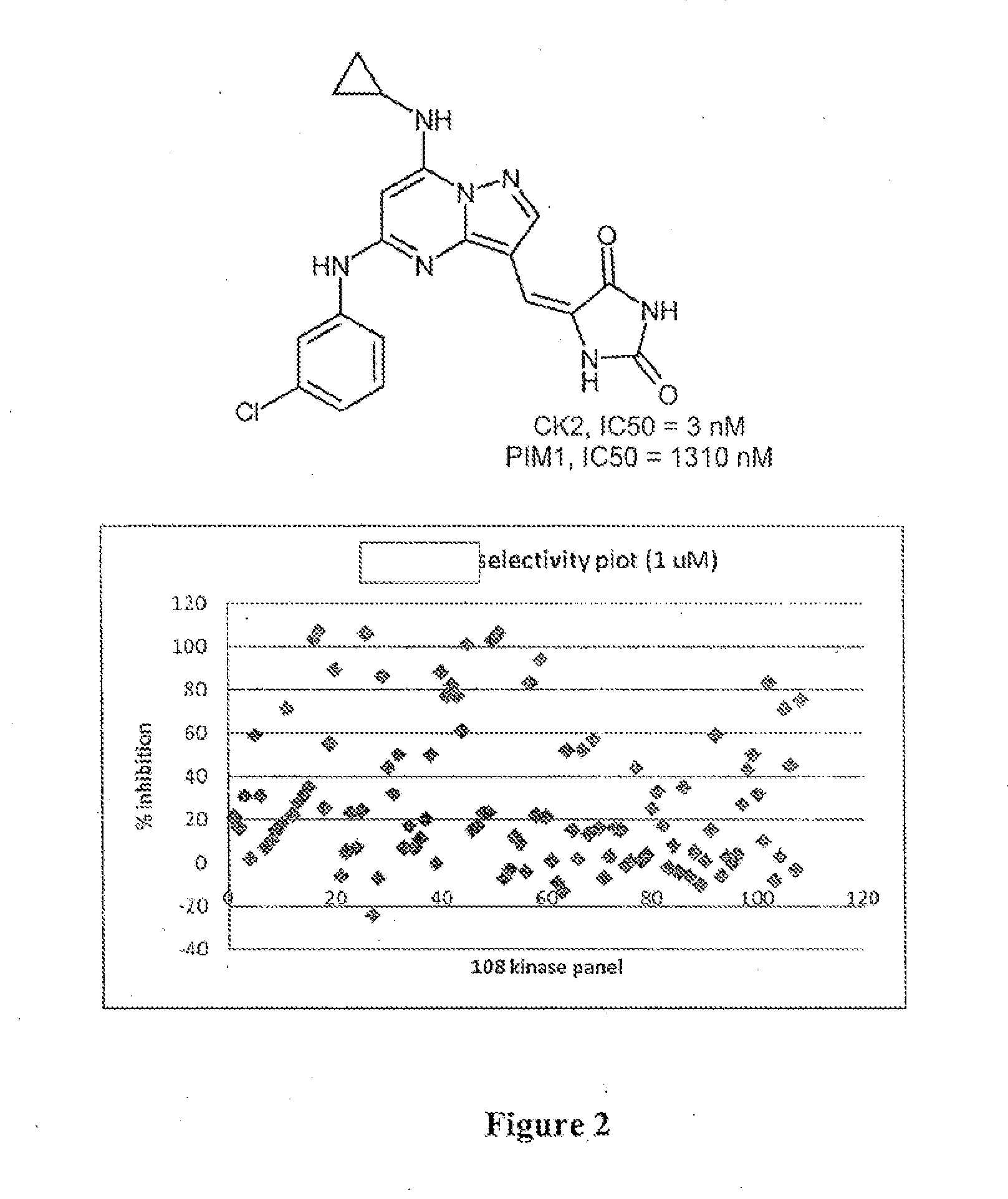
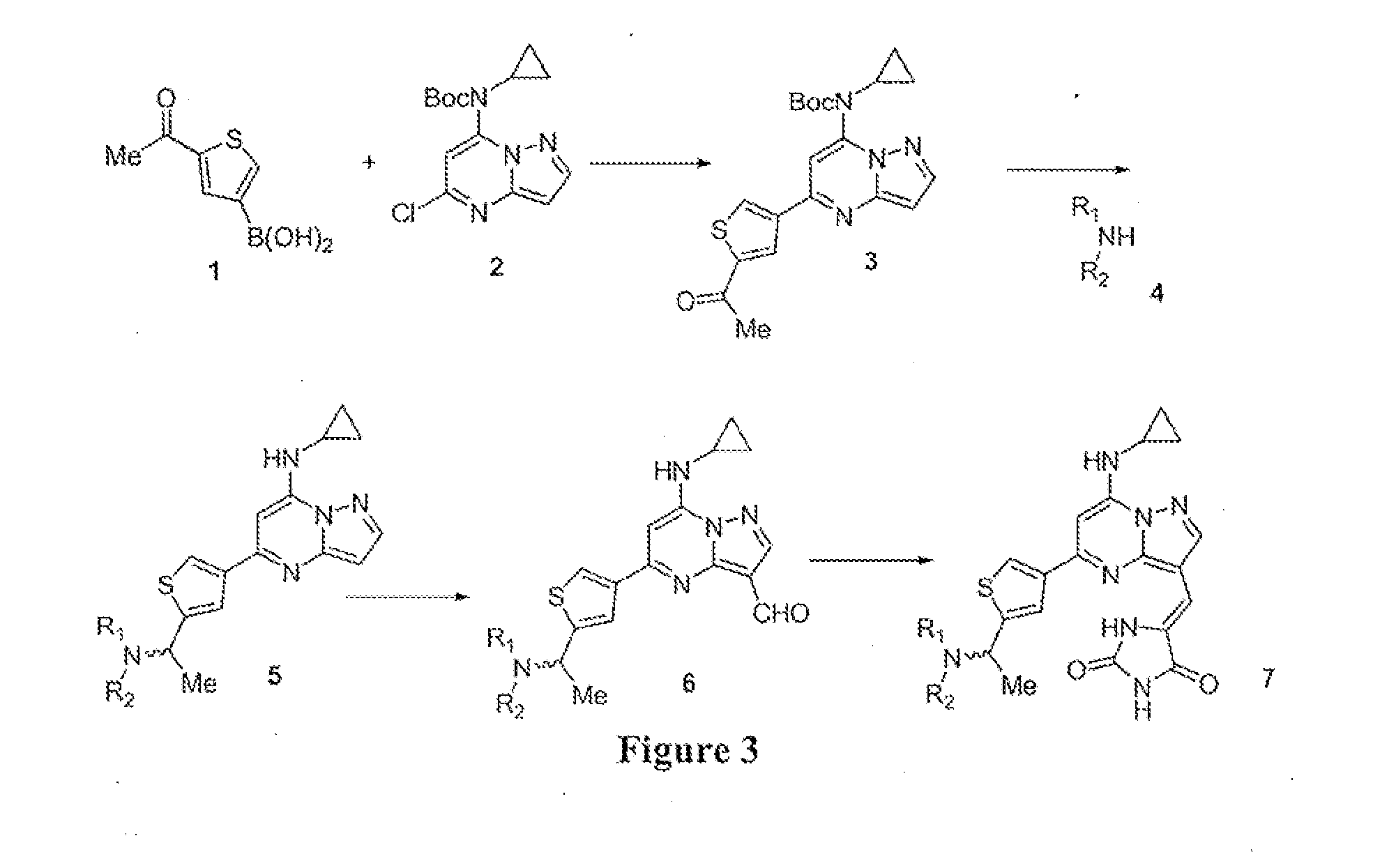
Pyrazolopyrimidines and related heterocycles as ck2 inhibitors
ActiveUS20110152240A1Good treatment effectIncreased apoptosisBiocideNervous disorderDiseaseCancer research
The invention provides compounds that inhibit protein kinase CK2 activity (CK2 activity), and compositions containing such compounds. These compounds and compositions are useful for treating proliferative disorders such as cancer, as well as other kinase-associated conditions including inflammation, pain, and certain immunological disorders, and have the following general formula:
Owner:SENHWA BIOSCIENCES INC
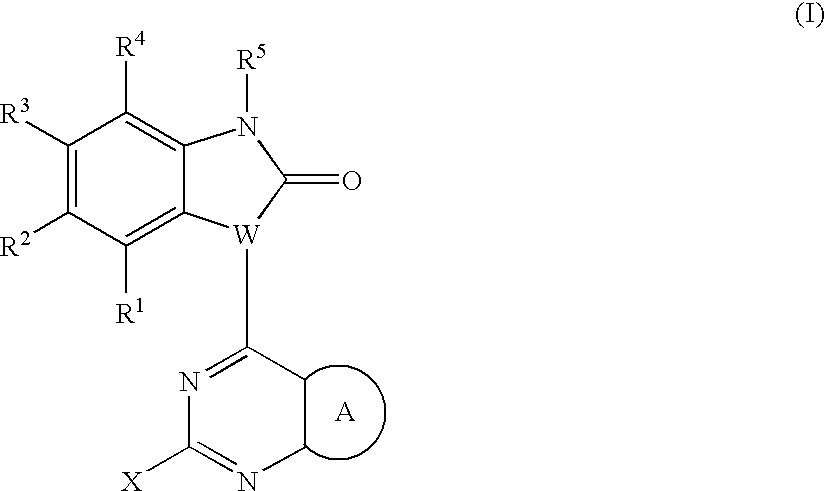
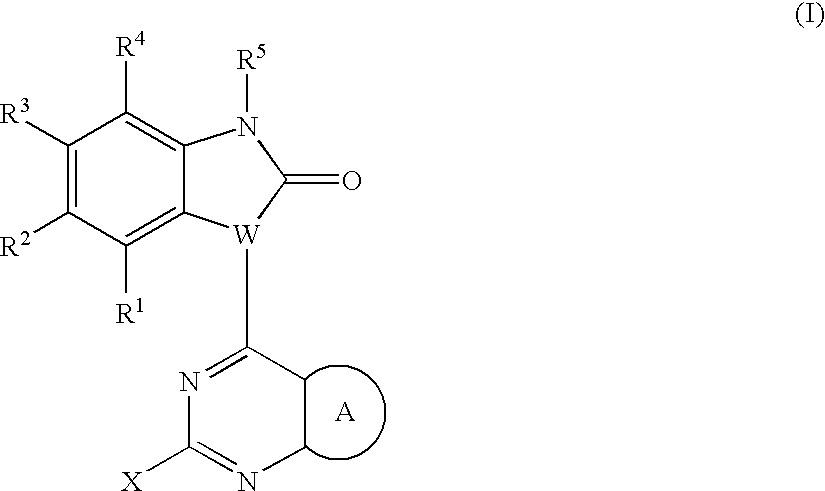
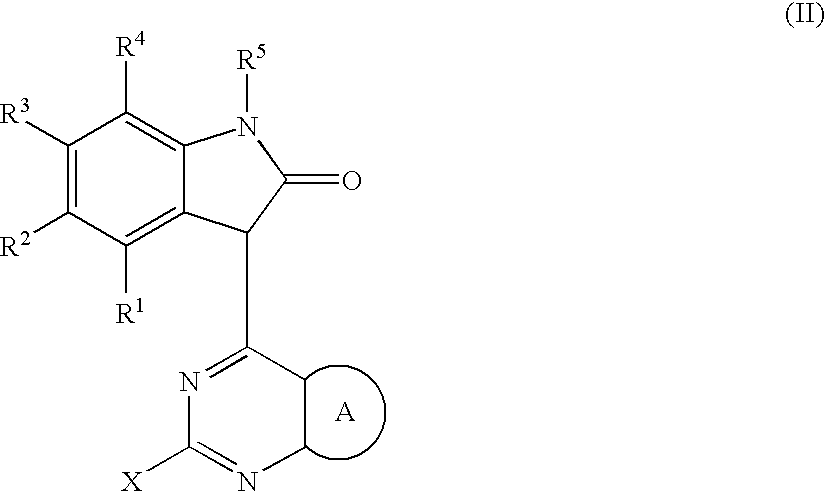
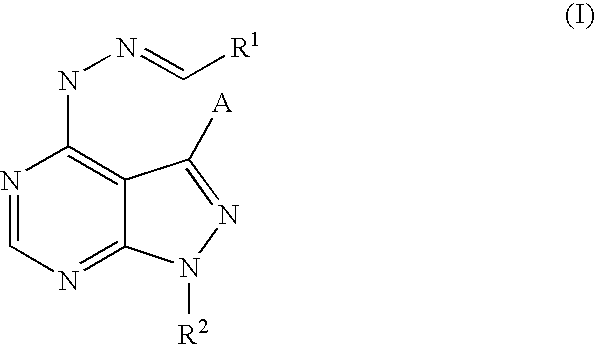
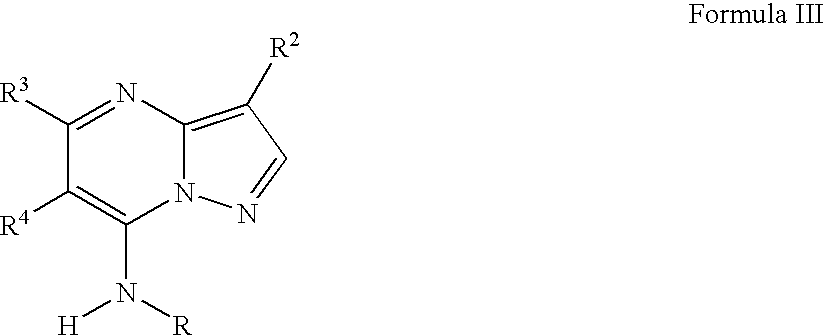
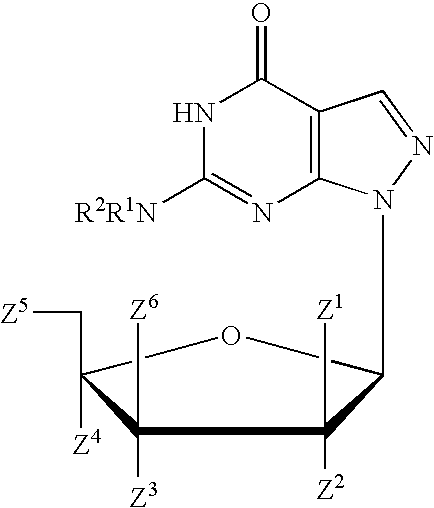
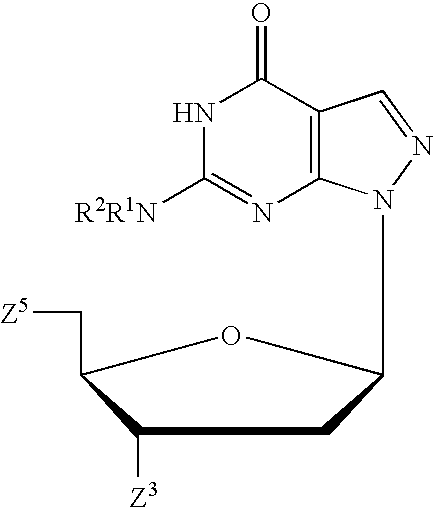
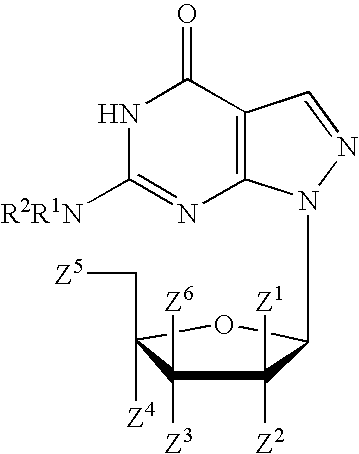
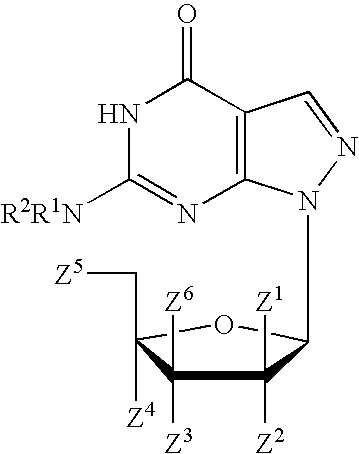
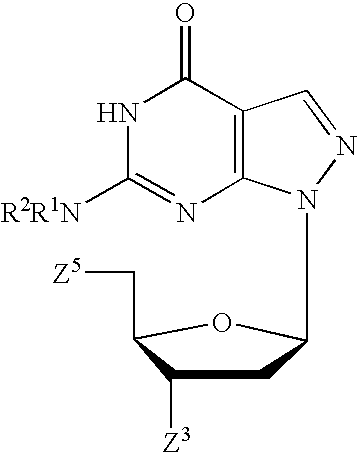
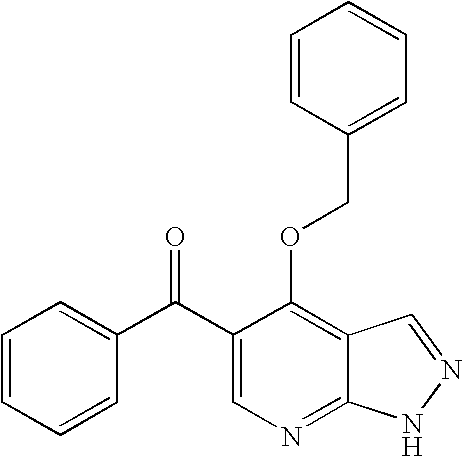
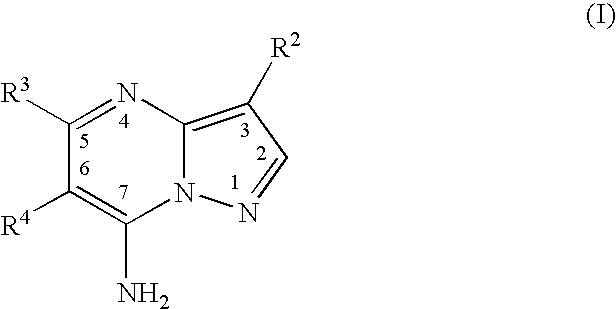
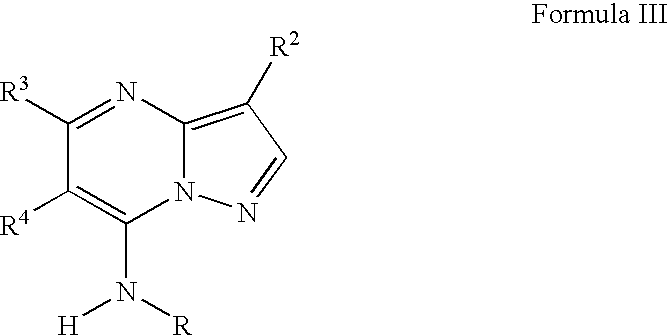
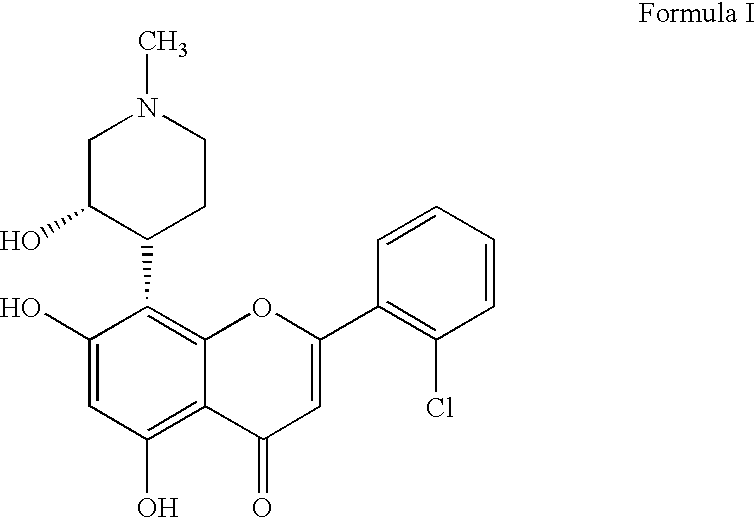
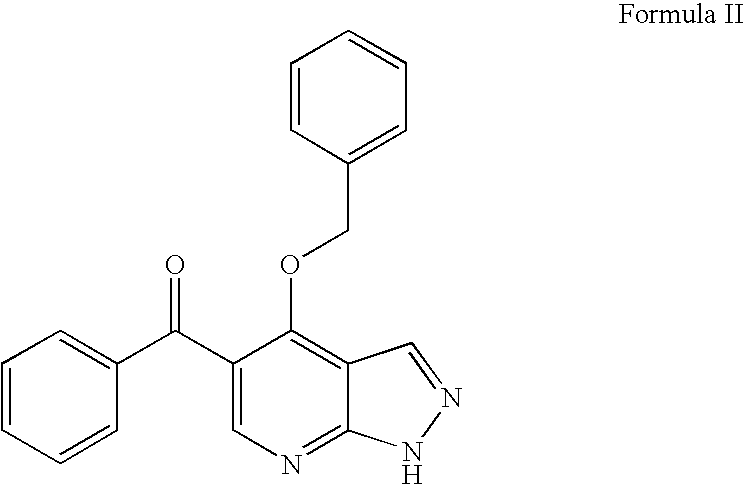
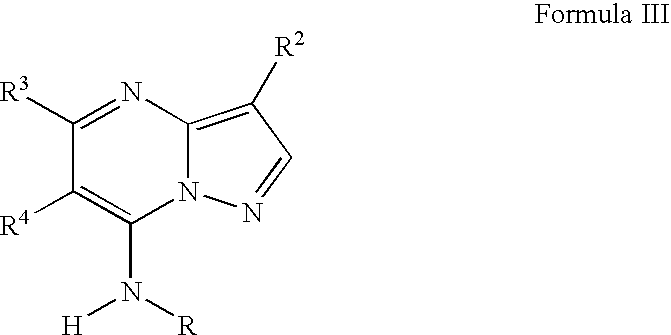
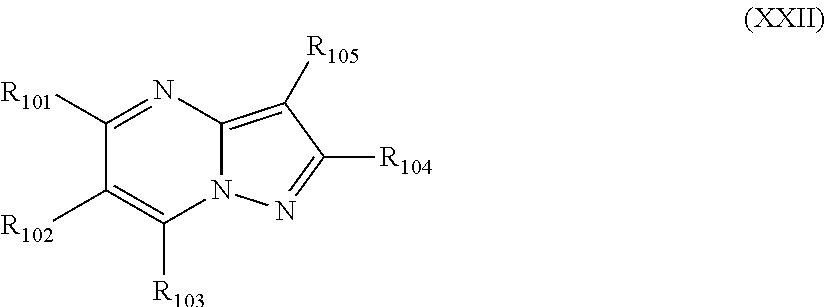
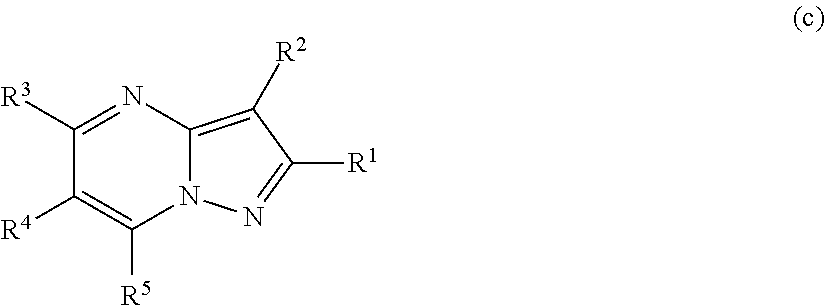
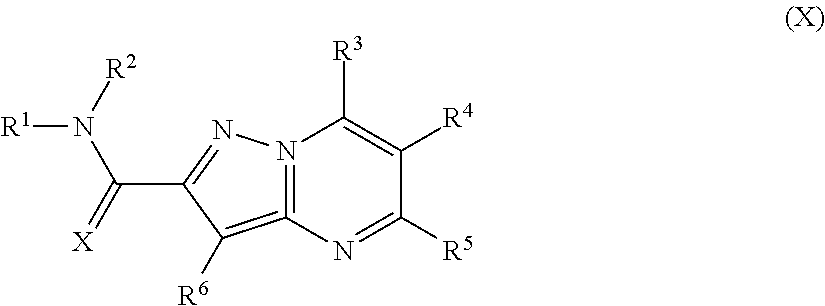
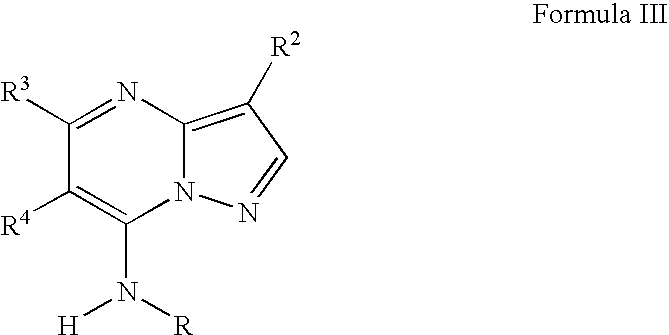
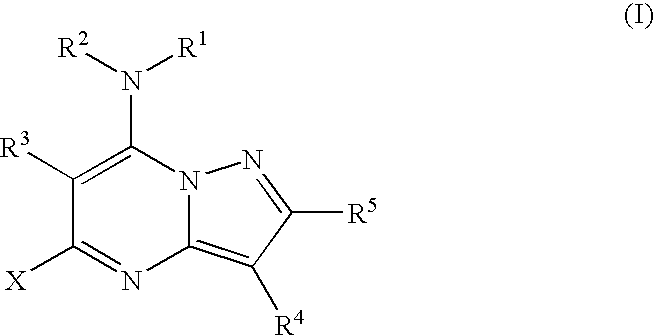
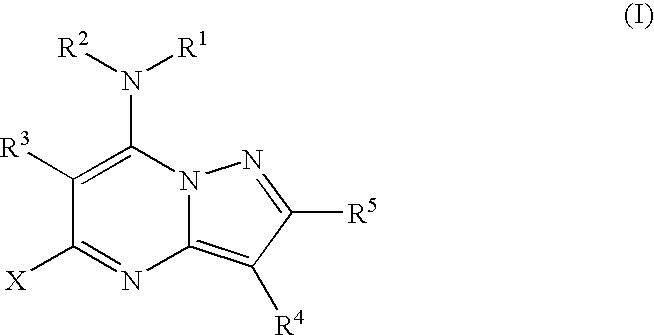
PYRAZOLO[1,5-a]PYRIMIDINES
In its many embodiments, the present invention provides certain pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine compounds which can have utility as inhibitors of cyclin dependent kinases as well as methods of preparing such compounds. The compounds can have potential utility for the treatment, prevention, inhibition, or amelioration of one or more diseases associated with the CDKs.
Owner:SCHERING CORP
Pyrazolo-pyrimidine compounds
Owner:EA PHARMA CO LTD
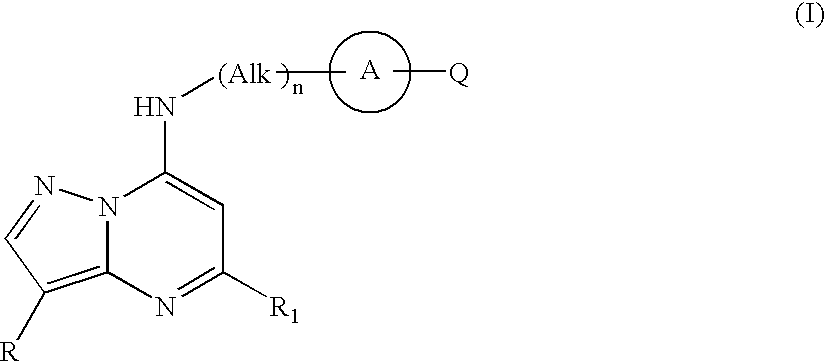
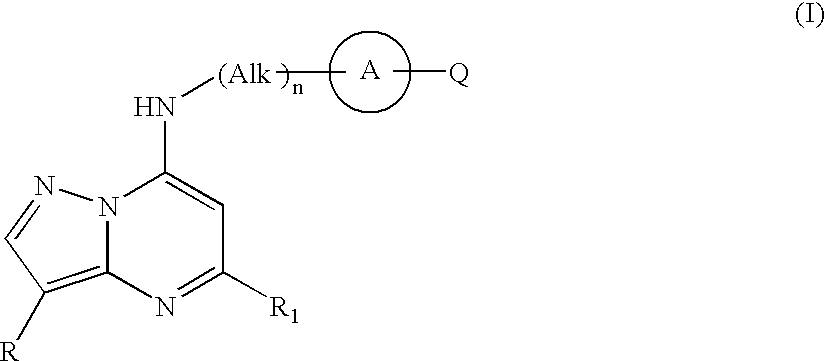
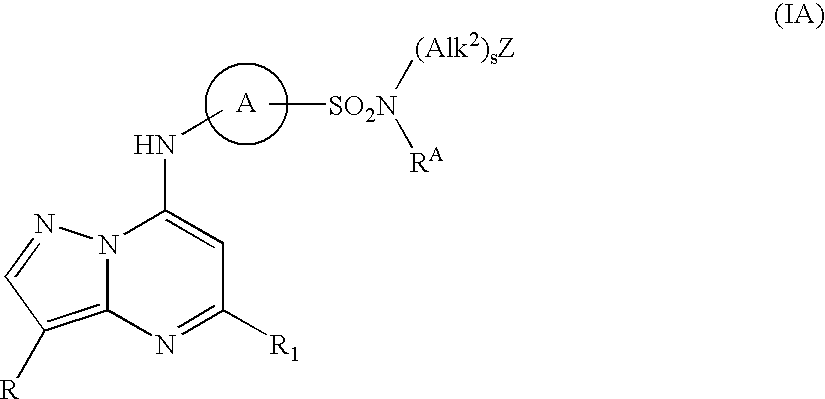
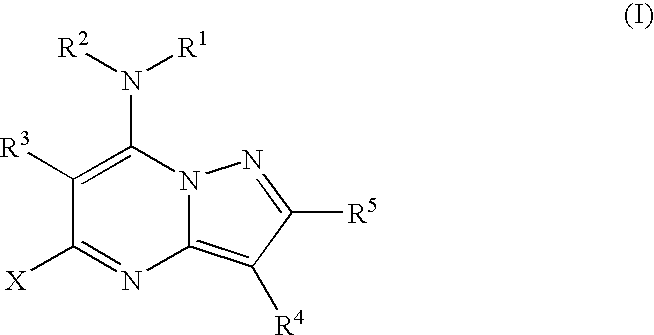
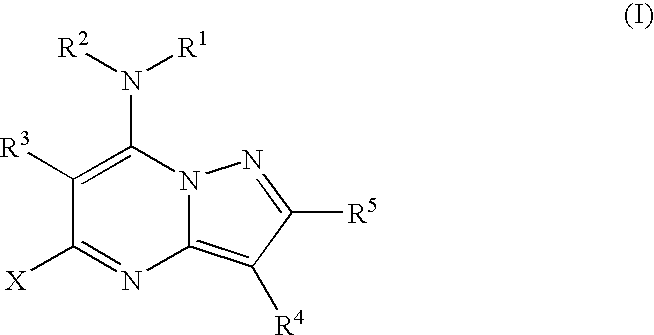
Pyrazolopyrimidine compounds and their use in medicine
Compounds of formula (I) or salts, N-oxides, hydrates or solvates thereof are inhibitors of kinase activity, and useful for the treatment of, for example, cancer, psoriasis or restenosis: wherein ring A is an optionally substituted carbocyclic or heterocyclic radical. Alk represents an optionally substituted divalent C1-C6 alkylene radical. n is 0 or 1. Q represents a radical of formula -(Alk1)p (X)r-(Alk2)s-Z wherein in any compatible combination Z is hydrogen or an optionally substituted carbocyclic or heterocyclic ring; Alk1 and Alk2 are optionally substituted divalent C1-C6 alkylene radicals which may contain a —O—, —S— or —NRA— link, wherein RA is hydrogen or C1-C6 alkyl; X represents —O—, —S—, —(C═O)—, —(C═S)—, —SO2—, —SO—, —C(═O)O—, —OC(═O)—, —C(═O)NRA—, —NR AC(═O)—, —C(═S)NRA, —NRAC(═S)—, —SO2NRA—, —NRASO2—, —OC(═O)NRA—, —NRAC(═O)O—, or —NRA— wherein RA is hydrogen or C1-C6 alkyl. p, r and s are independently 0 or 1. R1 represents a radical -(Alk3)a-(Y)b-(Alk4)d-B wherein a, b and d are independently 0 or 1; Alk3 and Alk4 are optionally substituted divalent C,-C3 alkylene radicals; Y represents a monocyclic divalent carbocyclic or heterocyclic radical having from 5 to 8 ring atoms, —O—, —S—, or —NRA— wherein RA is hydrogen or C1-C6 alkyl; B represents hydrogen or halo, or an optionally substituted monocyclic carbocyclic or heterocyclic ring having from 5 to 8 ring atoms, or in the case where Y is —NRA— and b is 1, then RA and the radical -(Alk4)d-B taken together with the nitrogen to which they are attached may form an optionally substituted heterocyclic ring. R represents hydrogen, halo, C1-C6 alkyl, C1-C6 alkoxy, C1-C6 alkylthio, phenyl, benzyl, cycloalkyl with 3 to 6 ring atoms, or a monocyclic heterocyclic group having 5 or 6 ring atoms.
Owner:VERNALIS (R&D) LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com






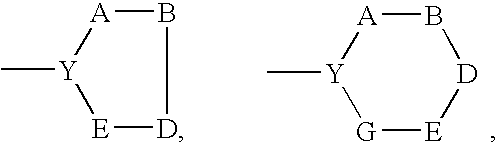





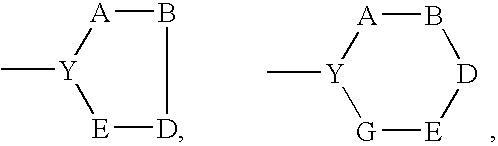
![PYRAZOLO[1,5-a]PYRIMIDINES PYRAZOLO[1,5-a]PYRIMIDINES](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/d51da6d3-05ae-4771-b4a3-5af602f1b303/US20070275963A1-20071129-C00001.png)
![PYRAZOLO[1,5-a]PYRIMIDINES PYRAZOLO[1,5-a]PYRIMIDINES](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/d51da6d3-05ae-4771-b4a3-5af602f1b303/US20070275963A1-20071129-C00002.png)
![PYRAZOLO[1,5-a]PYRIMIDINES PYRAZOLO[1,5-a]PYRIMIDINES](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/d51da6d3-05ae-4771-b4a3-5af602f1b303/US20070275963A1-20071129-C00003.png)