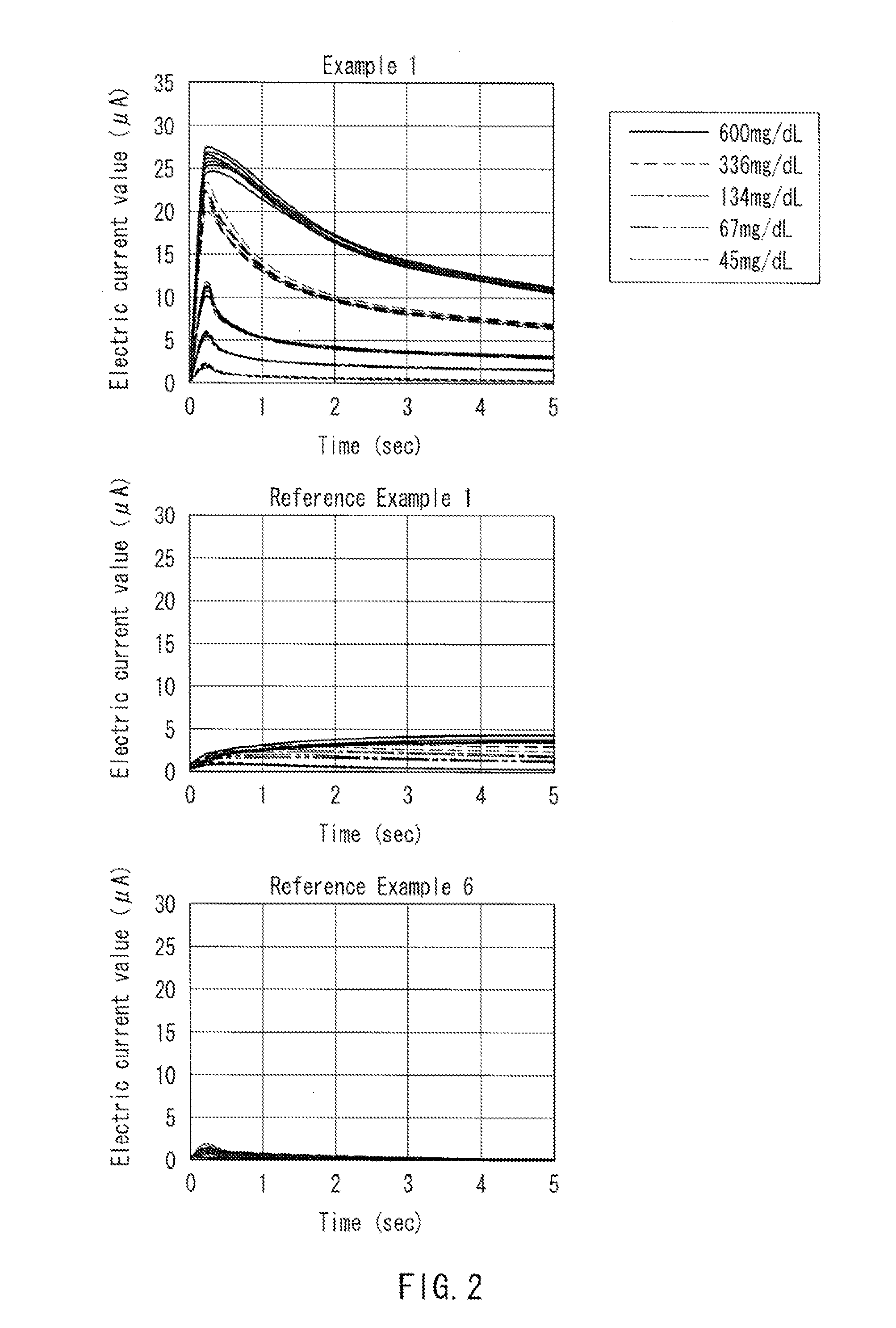
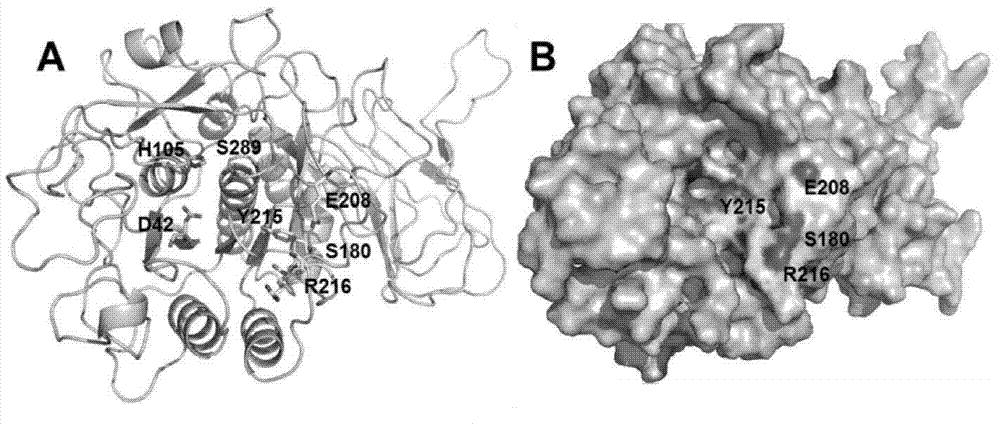
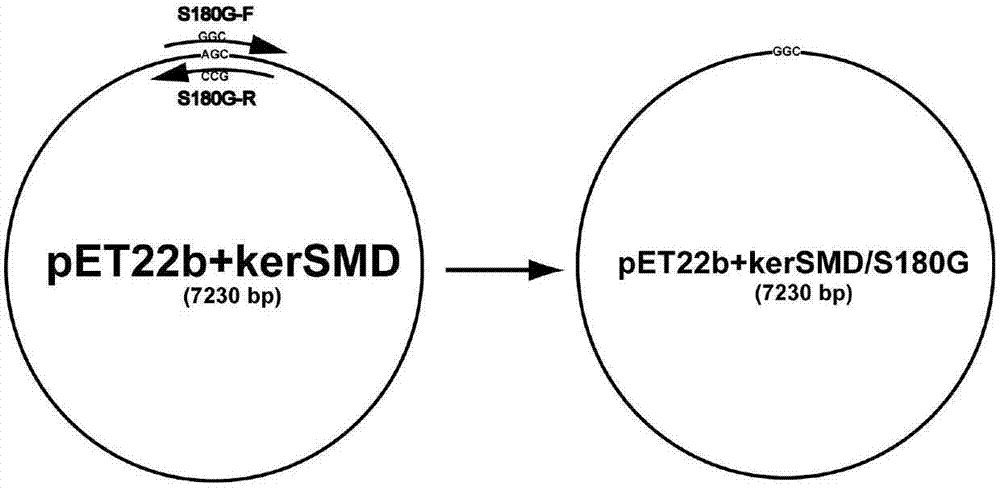
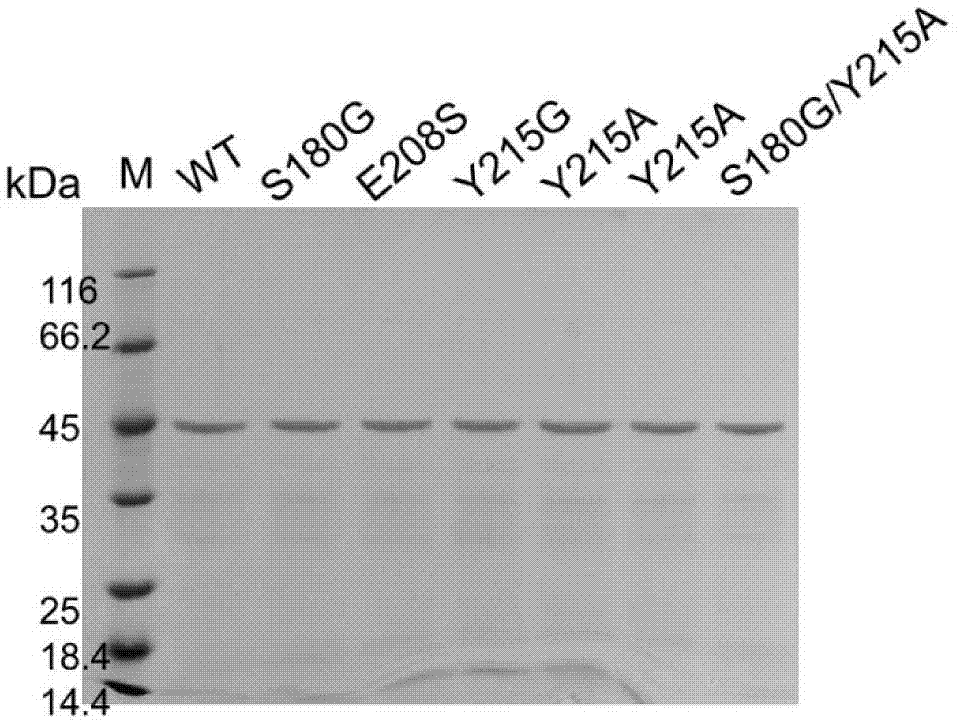
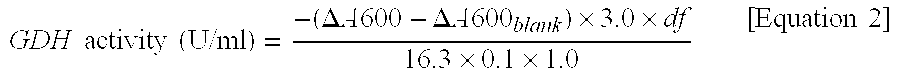Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
88results about How to "Increased substrate specificity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
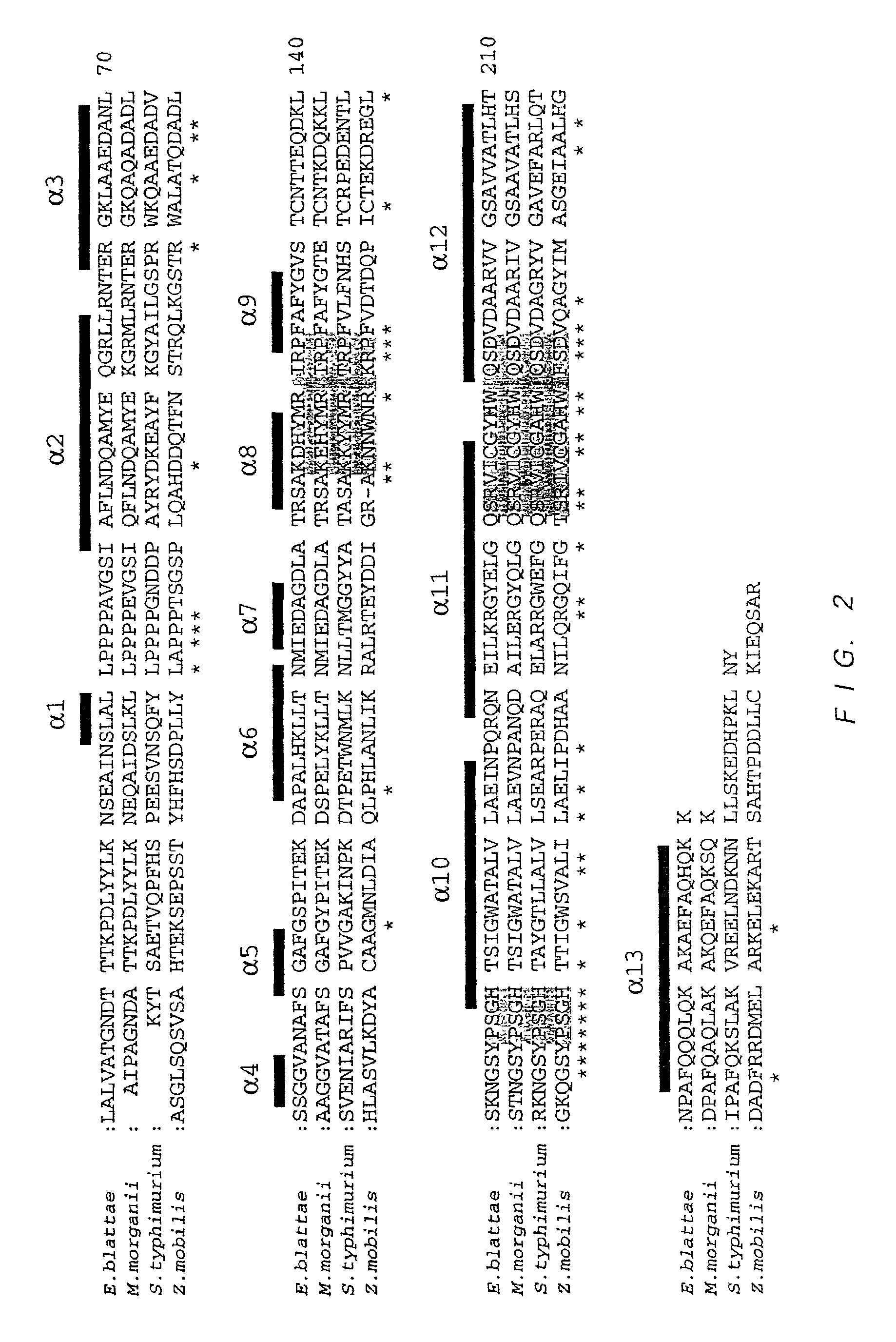
Method of selectively determining glycated hemoglobin
InactiveUS7235378B2Easily and accurately determinedEliminate the effects ofMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingProteinase activityHemoglobin F
Owner:ARKRAY INC
Forms of soluble pyrroloquinoline quinone-dependent glucose dehydrogenase
InactiveUS7132270B2Increased substrate specificityImprove propertiesFungiBacteriaMutated proteinGlucose polymers
The present invention relates to improved variants of soluble pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ)-dependent glucose dehydrogenases (s-GDH), to genes encoding mutated s-GDH, to mutant proteins of s-GDH with improved substrate specificity for glucose, and to different applications of these s-GDH variants, particularly for determining concentrations of sugar, especially of glucose in a sample.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
Method of selectively determining glycated hemoglobin
InactiveUS20030162242A1Easily and accurately determinedEliminate the effects ofMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingProteinase activityHemoglobin F
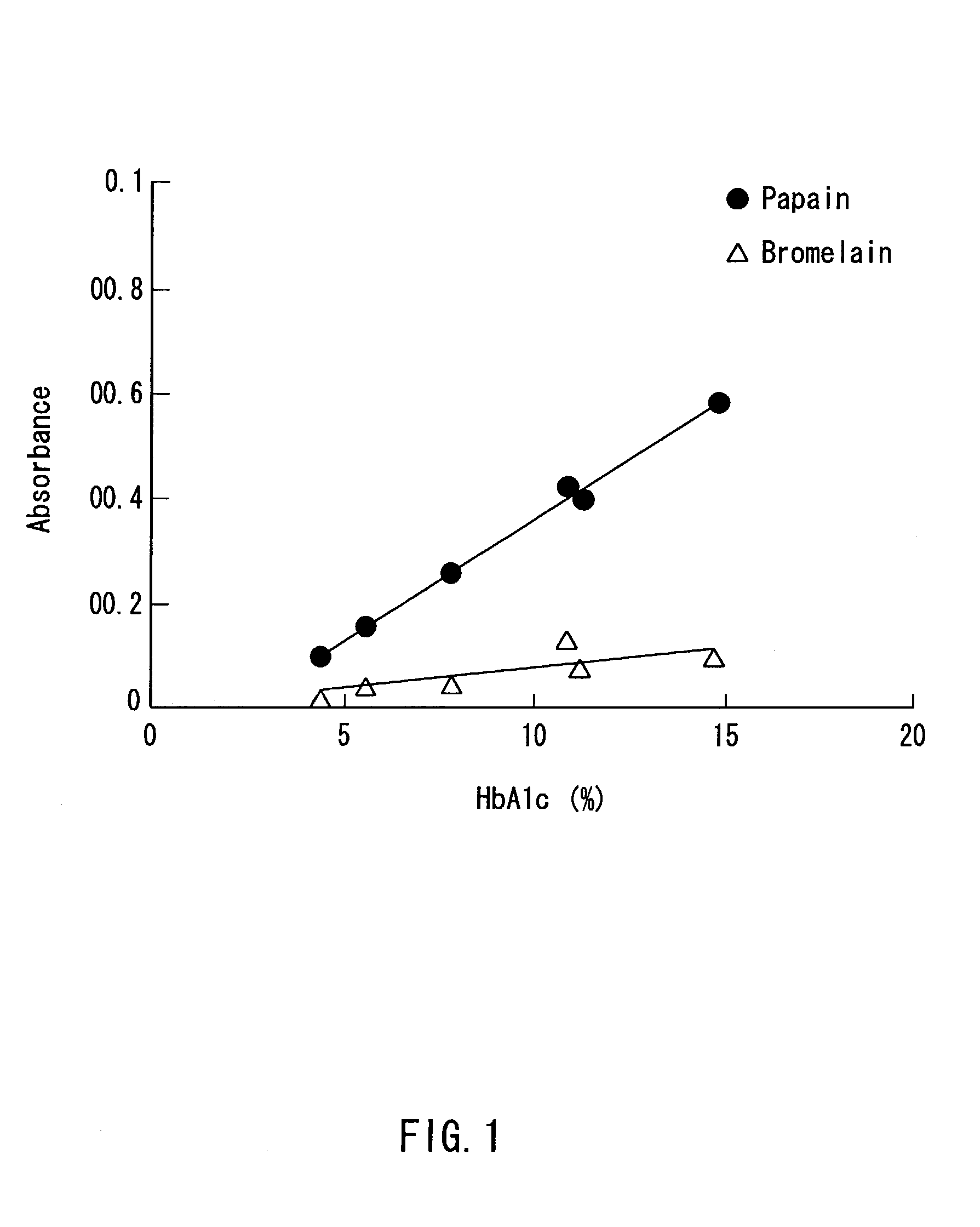
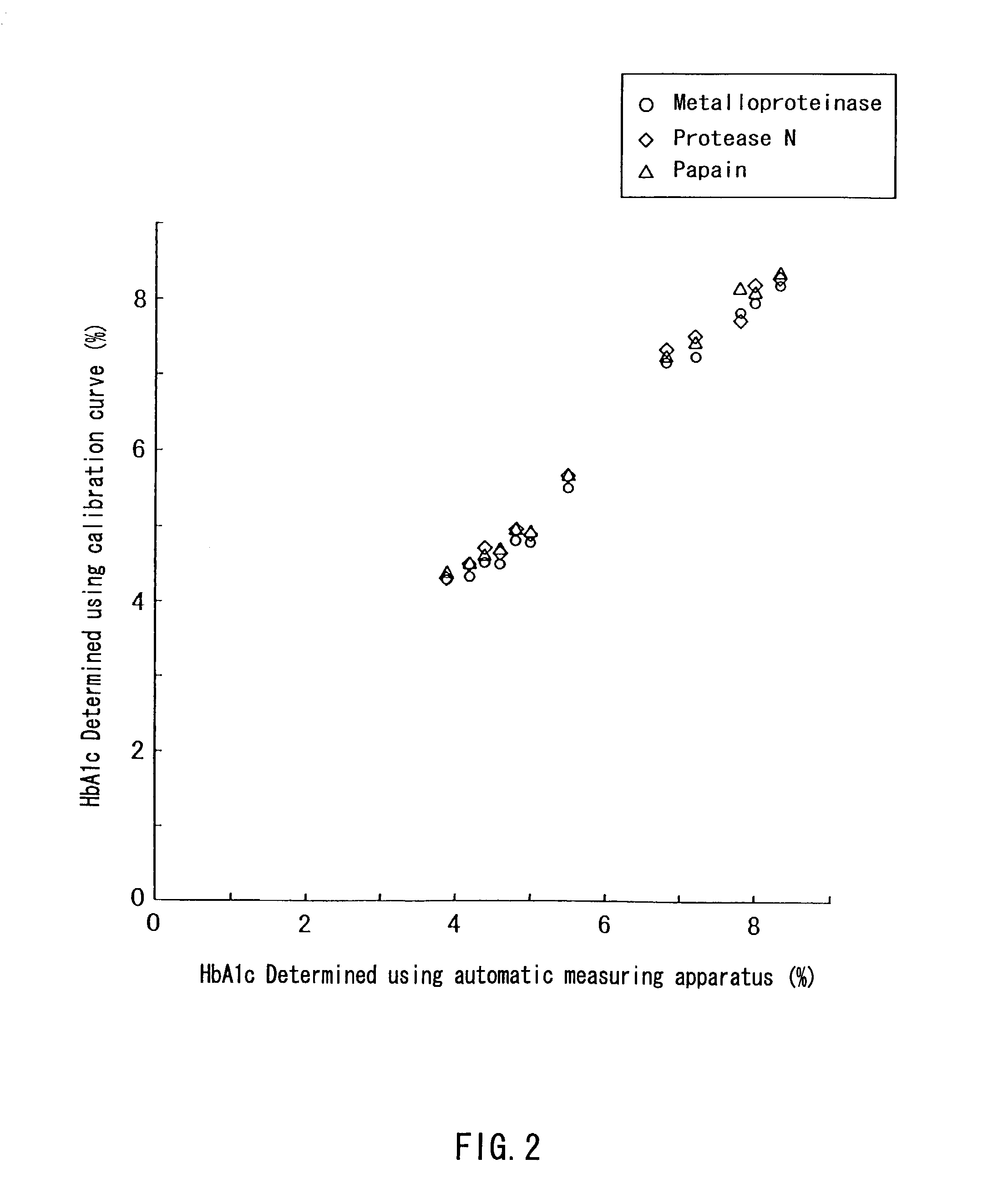
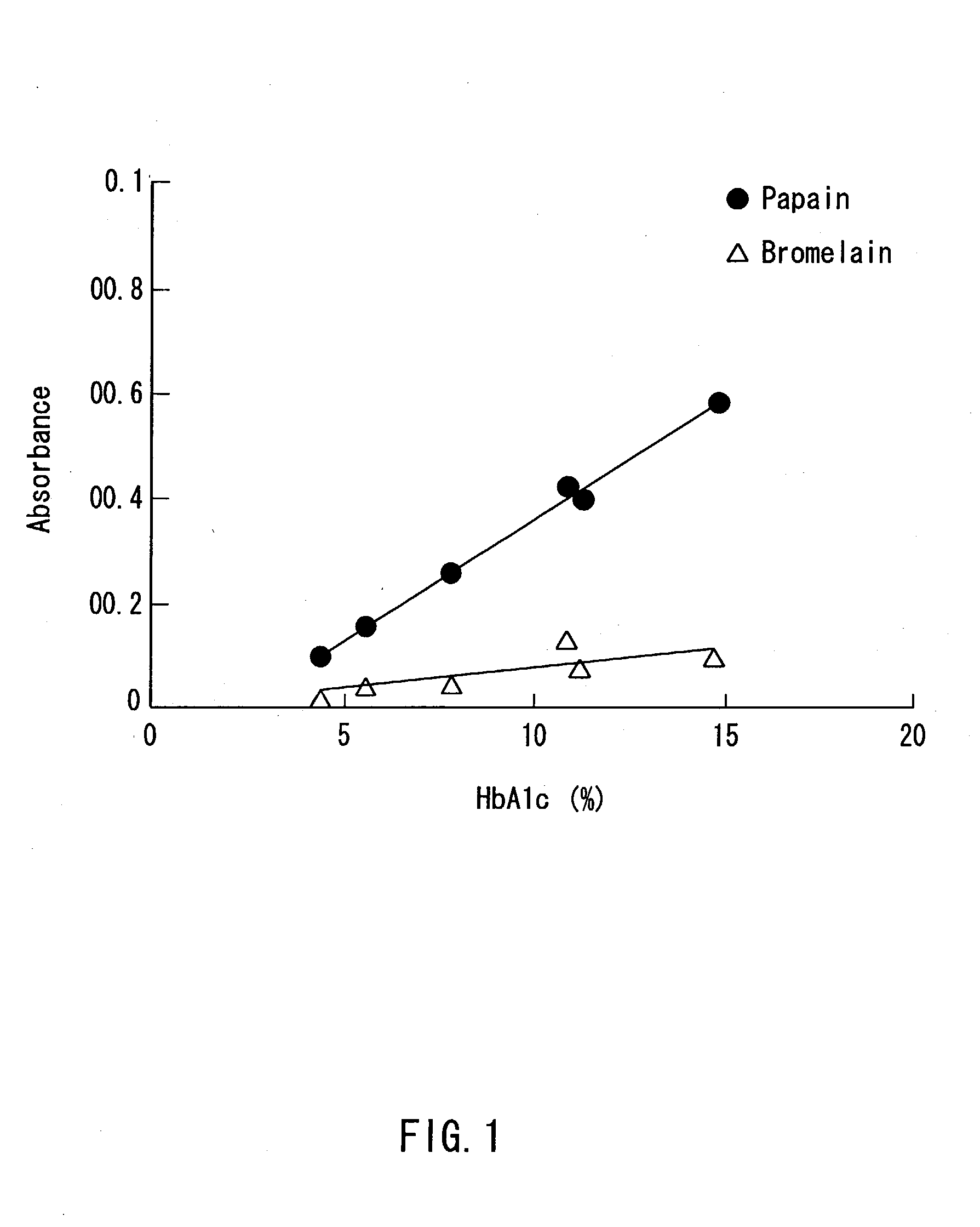
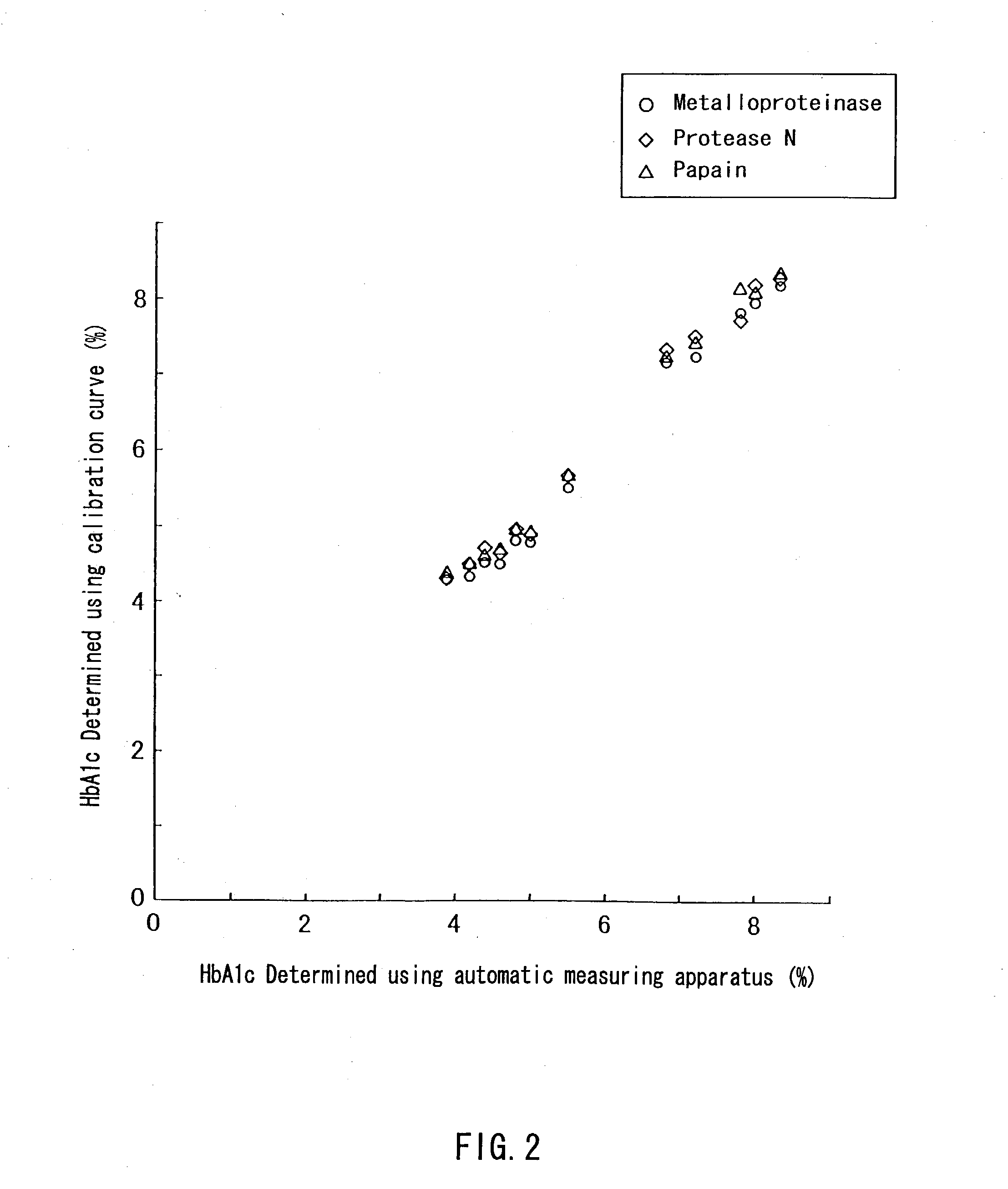
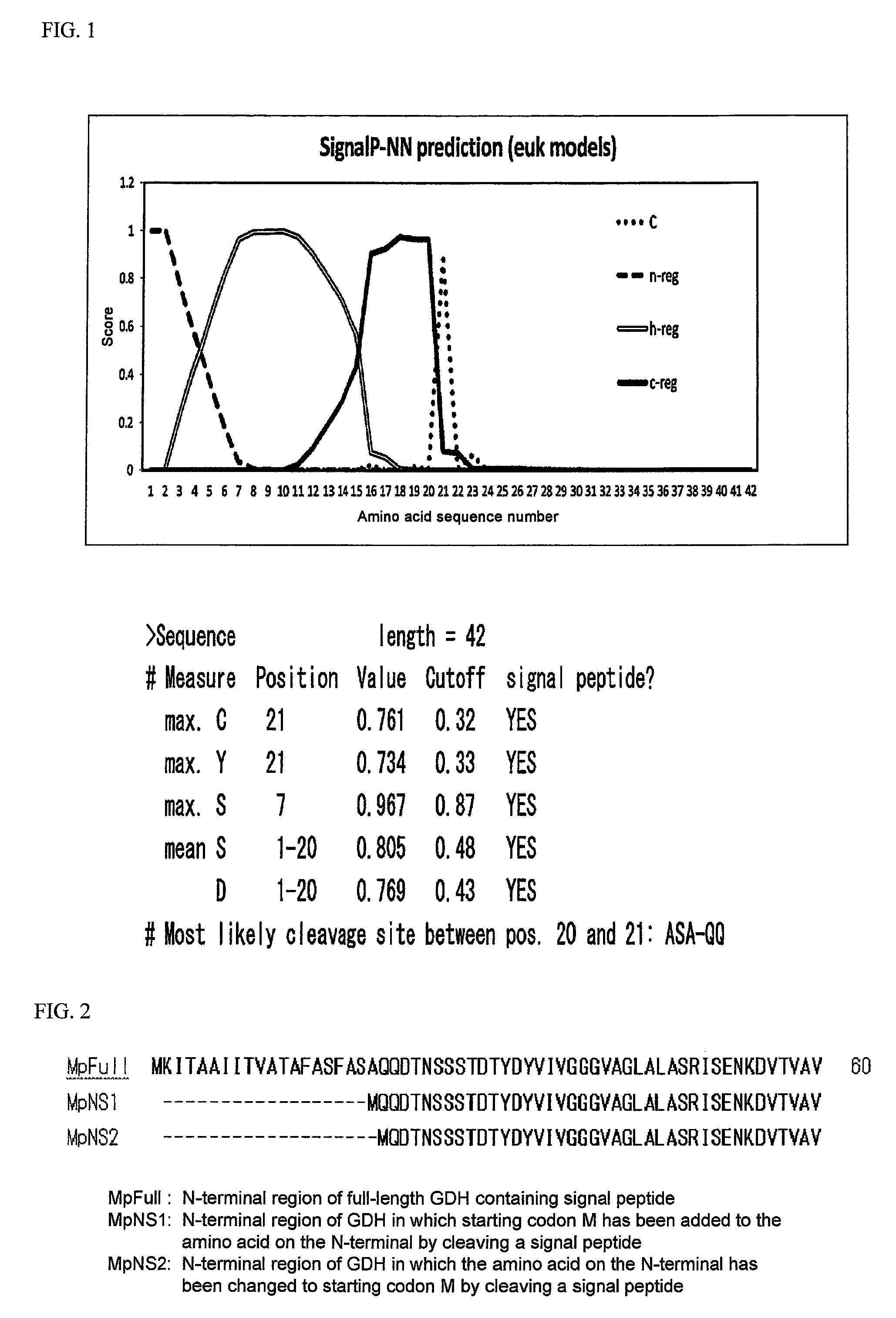
A method of determining glycated hemoglobin is provided, by which a ratio of the glycated hemoglobin in a sample can be determined accurately and easily. The ratio of glycated hemoglobin can be determined by degrading a glycated hemoglobin in a whole blood sample selectively with a protease to give a glycated hemoglobin degradation product`; causing a redox reaction between a glycation site of the glycated hemoglobin degradation product and a fructosyl amino acid oxidoreductase; and determining this redox reaction. Further, as shown in FIG. 1, in a whole blood sample, there is a correlation between the ratio of the glycated hemoglobin determined by this method and an HbA1c concentration. Thus, without determining the glycated alpha-amino group as a characteristic structure of HbA1c, an amount of HbA1c can be determined accurately and easily from the determined ratio of the glycated hemoglobin.
Owner:ARKRAY INC
Glucose dehydrogenase and process for producing the dehydrogenase
InactiveUS7741090B2Increased substrate specificityImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsBiotechnologyMicroorganism
A novel glucose dehydrogenase, which is an enzyme that has high substrate specificity, can be produced at a low cost, is not affected by oxygen dissolved in a measurement sample and, in particular, has superior thermal stability is obtained by culturing a microorganism belonging to the genus Burkhorderia and having glucose dehydrogenase producing ability in a medium and collecting glucose dehydrogenase from the medium and / or cells of the microorganism.
Owner:SODE
Mutant Glucose Dehydrogenase
ActiveUS20080206833A1Improved substrate specificityIncreased substrate specificityFungiSugar derivativesSubstrate SpecificitiesGlucose dehydrogenase activity
A mutant glucose dehydrogenase having an improved substrate specificity to glucose, which is a protein comprising the amino acid sequence depicted in SEQ ID NO:3 or an amino acid sequence having the substitution, deletion, insertion or addition of one or more amino acid residues excluding amino acid 365 in the amino acid sequence depicted in SEQ ID NO:3 and having a glucose dehydrogenase activity, the amino acid residue corresponding to amino acid 365 being substituted by other amino acid residue.
Owner:ARKRAY INC
Flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase, method for producing flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase, and glucose measurement method using thereof
ActiveUS20140287445A1Increased substrate specificityImprove stabilityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsEscherichia coliHeat stability
A flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase (FAD-GDH), which in addition to having high substrate specificity and adequate desirable heat stability, is suitable for efficient production, preferably using E. coli, yeast or molds and the like as host cells. The FAD-GDH has amino acid substitutions at positions equivalent to one or more locations selected from the group consisting of position 213, position 368 and position 526 in the amino acid sequence described in SEQ ID NO: 8. The FAD-GDH is acquired from a culture by inserting a gene encoding the FAD-GDH into host cells such as E. coli. A preferable example of the FAD-GDH is FAD-GDH, in which a signal peptide region present in an N-terminal region has been deleted from the amino acid sequence of Mucor-derived FAD-GDH, and which has the aforementioned amino acid substitutions. The FAD-GDH can be preferably used in clinical diagnosis.
Owner:KIKKOMAN CORP
Glucose Sensor
ActiveUS20130075276A1Reduced responseIncreased substrate specificityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsEnvironmental chemistryWorking electrode
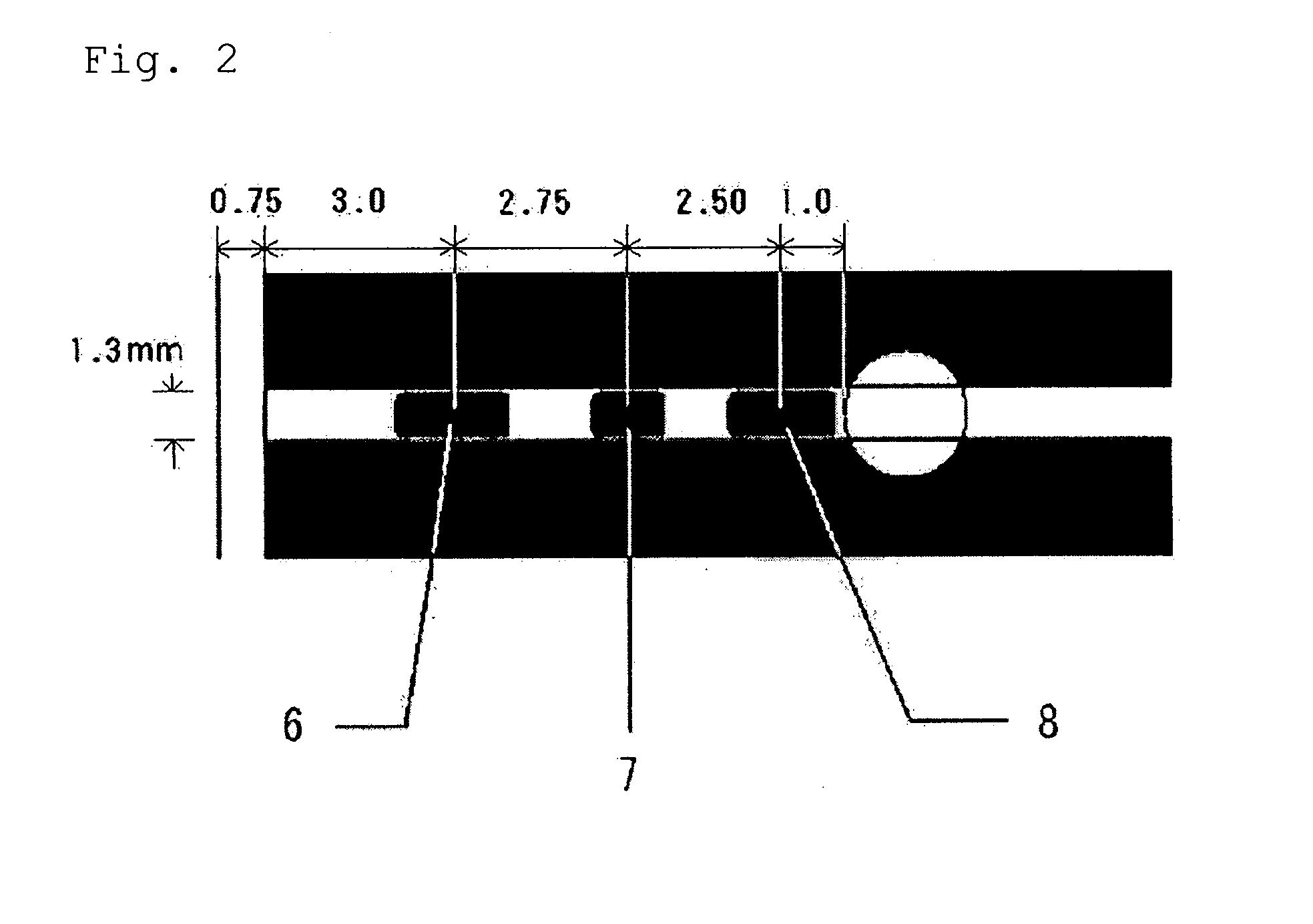
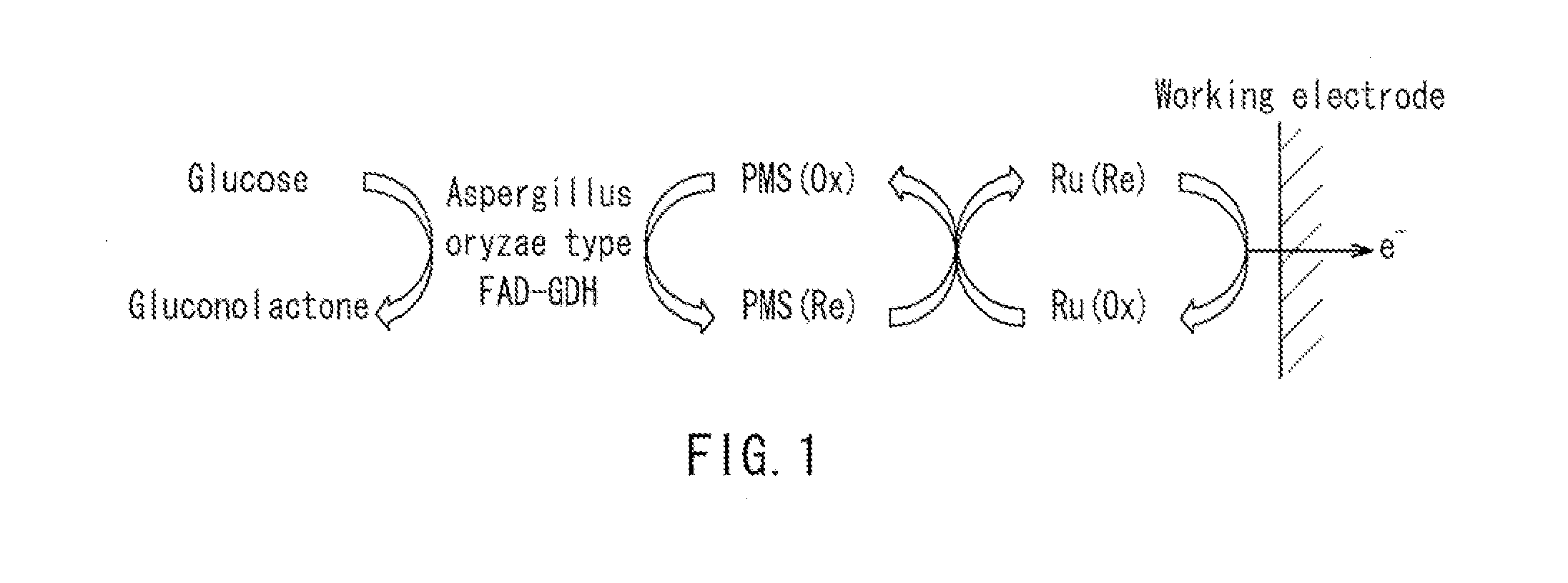
Provided is a glucose sensor that is capable of measuring a glucose concentration even in the case where Aspergillus oryzae type FAD-GDH (flavin adenine dinucleotide-glucose dehyrogenase) and a ruthenium compound are used in combination. The glucose sensor includes an insulative substrate, an electrode system having a working electrode and a counter electrode provided on the substrate, and a reagent layer provided on the electrode system, wherein the reagent layer contains Aspergillus oryzae type FAD-GDH, a ruthenium compound, and PMS (phenazine methosulfate).
Owner:ARKRAY INC
Higher-substrate-specificity keratinase mutant and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104726436AIncrease enzyme activityStrong specificityHydrolasesAnimal feeding stuffWater solubleSite-directed mutagenesis
The invention discloses a higher-substrate-specificity keratinase mutant and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the field of enzyme engineering. Analysis is performed to obtain the optimal mutant site to perform site-directed mutagenesis, thereby obtaining the excellent mutant with higher keratinase enzyme activity and substrate specificity. The keratinase and mutant thereof can effectively hydrolyze feather, wool and other non-water-soluble keratin substrates, and can be used for leather textile industry and feed industry.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Selective exosite inhibition of papp-a activity against igfbp-4
ActiveUS20100310646A1Improve transcription efficiencyInhibit bindingAntibacterial agentsFungiDifferential inhibitionProteinase activity
The present invention relates in one embodiment to PAPP-A exosite(s) interactors such as antibodies which bind to a region comprising LNR3 of PAPP-A and efficiently inhibit proteolysis of IGFBP-4, but not -5. The region comprising LNR3 represents a substrate binding exosite, which can be targeted for selective proteolytic inhibition. Accordingly, the present invention relates in one embodiment to differential inhibition of natural protease substrates by exosite targeting.
Owner:AARHUS UNIV
Cephalosporin C acylase mutant
The invention relates to a cephalosporin C acylase mutant. Cephalosporin C acylase is constructed through a point mutation method, in comparison with wild type cephalosporin C acylase coming from Pseudomonas sp.GK16, the activity of the cephalosporin C acylase is improved by 20.5-150 times, and the cephalosporin C acylase mutant can be used for producing 7-ACA through a one-step enzymatic method.
Owner:上海邦林生物科技有限公司
Structured construct and producing method therefor
InactiveUS20070003975A1Reduce the amount requiredReduce environmental impactBiological material analysisSynthetic resin layered productsEnzymePolyhydroxyalkanoates
Owner:CANON KK
Flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase having improved substrate specificity
ActiveUS20140302542A1Increased substrate specificityReduced responseMicroorganismsMicrobiological testing/measurementAmino acidMaltose
A flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase having high substrate specificity for D-glucose and decreased reactivity to D-xylose and / or maltose. More specifically, a flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase having one or more amino acid substitutions at a position corresponding to position 78, position 79, position 81, position 121, position 122, position 123, position 569 and position 612 of Mucor-derived flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase. The flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase enables D-glucose to be measured accurately without being susceptible to the effects of the presence of D-xylose and / or maltose, even under conditions of mounting a large amount of an enzyme such as in glucose sensors.
Owner:KIKKOMAN CORP
Flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase, method for producing flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase, and glucose measurement method
ActiveUS9074239B2Increased substrate specificityImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisEscherichia coliAmino acid substitution
A flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase (FAD-GDH), which in addition to having high substrate specificity and adequate desirable heat stability, is suitable for efficient production, preferably using E. coli, yeast or molds and the like as host cells. The FAD-GDH has amino acid substitutions at positions equivalent to one or more locations selected from the group consisting of position 213, position 368 and position 526 in the amino acid sequence described in SEQ ID NO: 8. The FAD-GDH is acquired from a culture by inserting a gene encoding the FAD-GDH into host cells such as E. coli. A preferable example of the FAD-GDH is FAD-GDH, in which a signal peptide region present in an N-terminal region has been deleted from the amino acid sequence of Mucor-derived FAD-GDH, and which has the aforementioned amino acid substitutions. The FAD-GDH can be preferably used in clinical diagnosis.
Owner:KIKKOMAN CORP
Pyrroloquinoline quinone-dependent glucose dehydrogenase
InactiveUS7037698B2Reduced responseIncreased substrate specificityFungiSugar derivativesAmino acid compositionAcyl CoA dehydrogenase
A modified pyrroloquinoline quinone-dependent glucose dehydrogenase having a low reactivity with respect to maltose, galactose, etc. is provided. A modified pyrroloquinoline quinone-dependent glucose dehydrogenase including an amino acid sequence in which one or more amino acids in a region corresponding to a first region consisting of amino acids at positions 326 to 354 in pyrroloquinoline quinone-dependent glucose dehydrogenase derived from Acinetobacter calcoaceticus are substituted as compared with an amino acid sequence of the corresponding wild-type enzyme.
Owner:AMANO ENZYME INC
SiRAN and expression carrier for inhibiting human VEGF gene expression and their pharmaceutical use
ActiveCN1580259ASmall doseHigh specificitySugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsDrugGene expression
The invention publish a kind of siRNA and express carrier, which can control men's VEGF gene expression, and their application in preparing drug for affection relation to VEGF gene. The invention get a group VEGF orders by biocomputer technology and work out a group of siRNA to induce RNA disturbance basing on the RNA disturbance technology. After this, compose.
Owner:徐根兴
Glucose dehydrogenase mutant and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110438098AIncreased substrate specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisAmino acid changeGlucose dehydrogenase
The invention belongs to the field of a biological technology, and particularly relates to a glucose dehydrogenase mutant and a preparation method thereof. Glucose dehydrogenase is from aspergillus terreus, and the mutant is obtained by replacing the 406th amino acid of the glucose dehydrogenase with other amino acids. Compared with the prepared FAD-GDH mutant with wild type FAD-GDH, the activityand the substrate selectivity are greatly improved.
Owner:遵义医科大学珠海校区
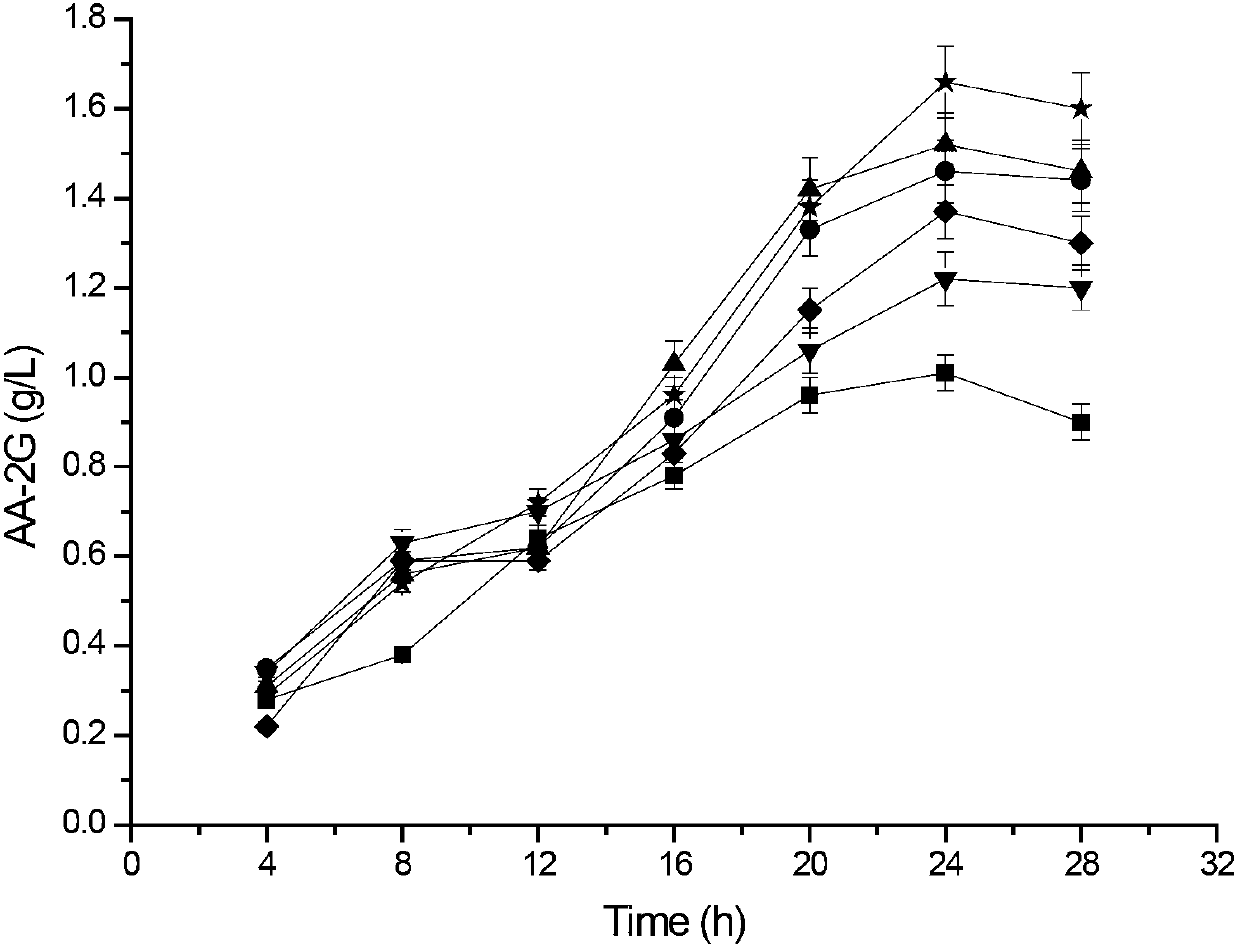
Cyclodextrin glycosyl transferase with improved maltodextrin substrate specificity and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102994468AIncreased substrate specificityIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesArginineWild type
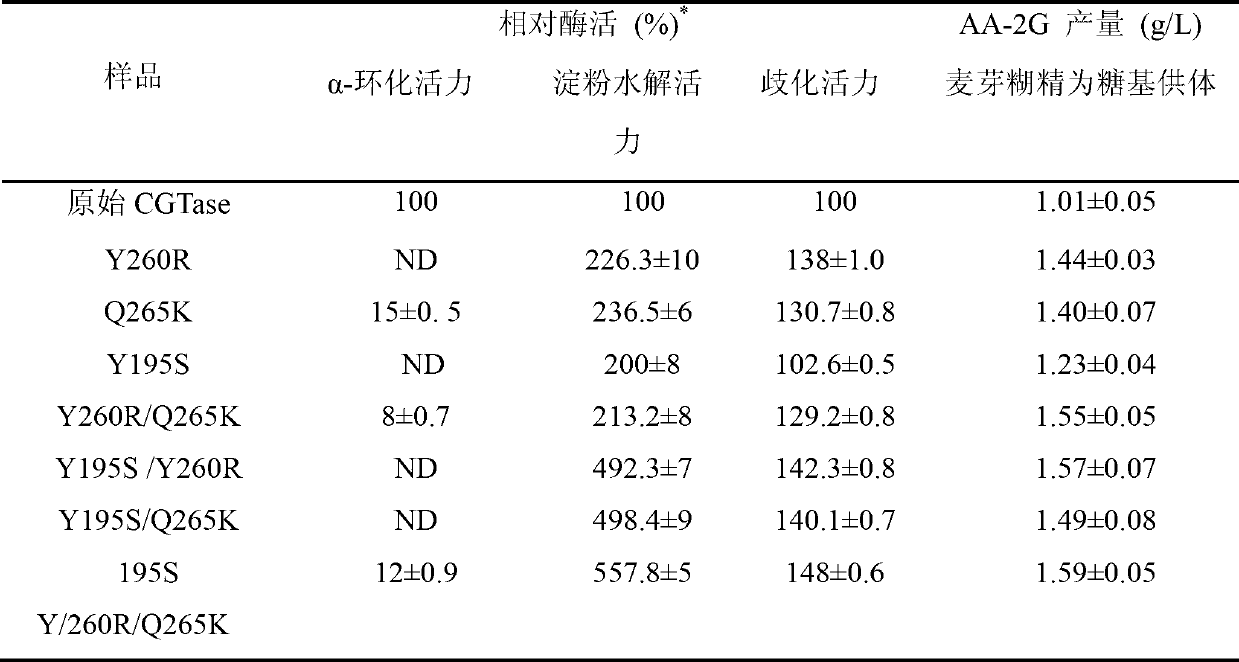
The invention discloses cyclodextrin glycosyl transferase with improved maltodextrin substrate specificity and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering. 195-bit tyrosine (Tyr) of CGTase of P.macerans strain JFB05-01 (CCTCC NO:M208063) is replaced by serine (Ser), 260-bit tyrosine (Tyr) is replaced by arginine (Arg), and 265-bit glutamine (Gln) is replaced by lysine (Lys), so that the AA-2G yield is respectively improved by 23 percent, 44 percent and 40 percent. According to combined mutation of the mutant strains, double mutants Y195S / Y260R, Y195S / Q265K and Y260R / Q265K and A three-point mutant Y195S / Y260R / Q265K are obtained. A Glycosyl donor is produced by the maltodextrin, so that the AA-2G yield is respectively improved by 57 percent, 49 percent, 55 percent and 59 percent; and compared with the mild type CGTase, the mutant strains facilitate the production of the AA-2G for glycosyl donors by using maltodextrin.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Penicillin acylase, as well as high-yield strain and application thereof
InactiveCN103184182AIncrease vitalityIncreased substrate specificityBacteriaHydrolasesAchromobacter xylosoxidansPenicillin
The invention provides penicillin acylase, as well as a high-yield strain and an application thereof, belonging to the field of bio-pharmaceuticals. The strain is Achromobacter xylosoxidans K18 with the collection number of CCTCC NO: M2012541. The penicillin acylase is obtained by fermenting the strain K18. The amino acid sequence of the penicillin acylase is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2, and the gene sequence of the penicillin acylase is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. The invention further provides the application of the penicillin acylase in synthesis of beta-lactam type antibiotics. The strain K18 is the high-yield strain of the penicillin acylase, and when fermentation is performed through a culture medium containing an inducing agent, the yield of the penicillin acylase can be above 200U / L. The penicillin acylase produced by the strain K18 has the advantages of high temperature resistance, capability of keeping higher activity under an acidic environment, higher specificity of a substrate, strong organic solvent tolerance and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Cyclodextrin glycosyl transferase with improved maltodextrin substrate specificity and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103122341AIncreased substrate specificityIncrease productionBacteriaTransferasesCyclodextrinWild type
The invention discloses a cyclodextrin glycosyl transferase with improved maltodextrin substrate specificity and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the fields of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering. According to the invention, for CGTase derived from peanibacillus macerans, lysine at a 47th site, tyrosine at a 89th site, asparaginate at a 94th site and aspartic acid at a 196th site are respectively mutated into leucine K47L, phenylalanine Y89F, praline N94P and tyrosine D196Y, so that AA-2G yields are respectively increased by 30.7%, 10.9%, 10.0% and 31.7%. Complex mutation is carried out on the mutant strains to obtain double mutants namely K47L / Y89F, K47L / N94P, K47L / D196Y, Y89F / N94P, Y89F / D196Y and N94P / D196Y, three-point mutants namely K47L / Y89F / N94P, K47L / Y89F / D196Y, K47L / N94P / D196Y and Y89F / N94P / D196Y and a four-point mutant namely K47L / Y89F / N94P / D196Y. Yields of AA-2G produced by the mutants while maltodextrin is utilized as a glycosyl donor are respectively increased by 42.6%, 11.0%, 37.6%, 43.6%, 43.6%, 41.6%, 44.5%, 50.5%, 20.8%, 35.6% and 64.4%. Compared with the wild type CGTase, the mutants is more beneficial to production of the AA-2G while the maltodextrin is utilized as the glycosyl donor.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Protein having flavin adenine dinucleotide-dependent glucose dehydrogenase activity
InactiveUS20150267178A1Improve thermal stabilityMaintain good propertiesAnimal cellsBacteriaFlavin adenine dinucleotideGlucose dehydrogenase activity
The present invention provides a protein derived from a thermophilic filamentous fungus having flavin adenine dinucleotide-dependent glucose dehydrogenase activity. The present invention provides an enzyme for glucose measurement that has better thermal stability than that of conventional enzymes while being unaffected by dissolved oxygen, not requiring the addition of a coenzyme, and maintaining the excellent properties of FADGDH in terms of having excellent substrate specificity (particularly low reactivity with maltose).
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Amadoriase having altered substrate specificity
ActiveUS9062286B2Increased substrate specificityLow figureBacteriaSugar derivativesCrystallographyHemeprotein
Owner:KIKKOMAN CORP
Maltose substrate specificity improved cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102965353AIncreased substrate specificityIncrease productionBacteriaTransferasesWild typeTyrosine
The invention discloses maltose substrate specificity improved cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering. The 47th lysine (Lys) of CGTase of P.macerans strain HFB05-01 (CTCC NO:M208063) is respectively replaced by phenylalanine (Phe), tyrosine (Tyr) and proline (Pro), so that the output of AA-2G is respectively improved by 17.1%, 22.1% and 32.9%. Compared with the wild CGTase, the mutant strains are more conductive to producing AA-2G for glycosyl donors by utilizing maltose, so that important industrial application prospect is provided.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Mutant glucose dehydrogenase
ActiveUS7604969B2Increased substrate specificityReduced responseFungiBacteriaGlucose dehydrogenase activityGlucose polymers
Owner:ARKRAY INC
Myrmecridium flexuosum nuk-21, novel lactose oxidase isolated from myrmecridium flexuosum nuk-21, and method for conversion of lactose into lactobionic acid by novel lactose oxidase
A Myrmecridium flexuosum NUK-21, a novel lactose oxidase isolated from the Myrmecridium flexuosum NUK-21 and a method for conversion of lactose into lactobionic acid (LBA) by the novel lactose oxidase are disclosed herein. The Myrmecridium flexuosum NUK-21 produces high yields of the novel lactose oxidase and the novel lactose oxidase has higher reactivity and specificity of converting lactose into lactobionic acid.
Owner:NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF KAOHSIUNG
Porous coordinatively unsaturated metal complex
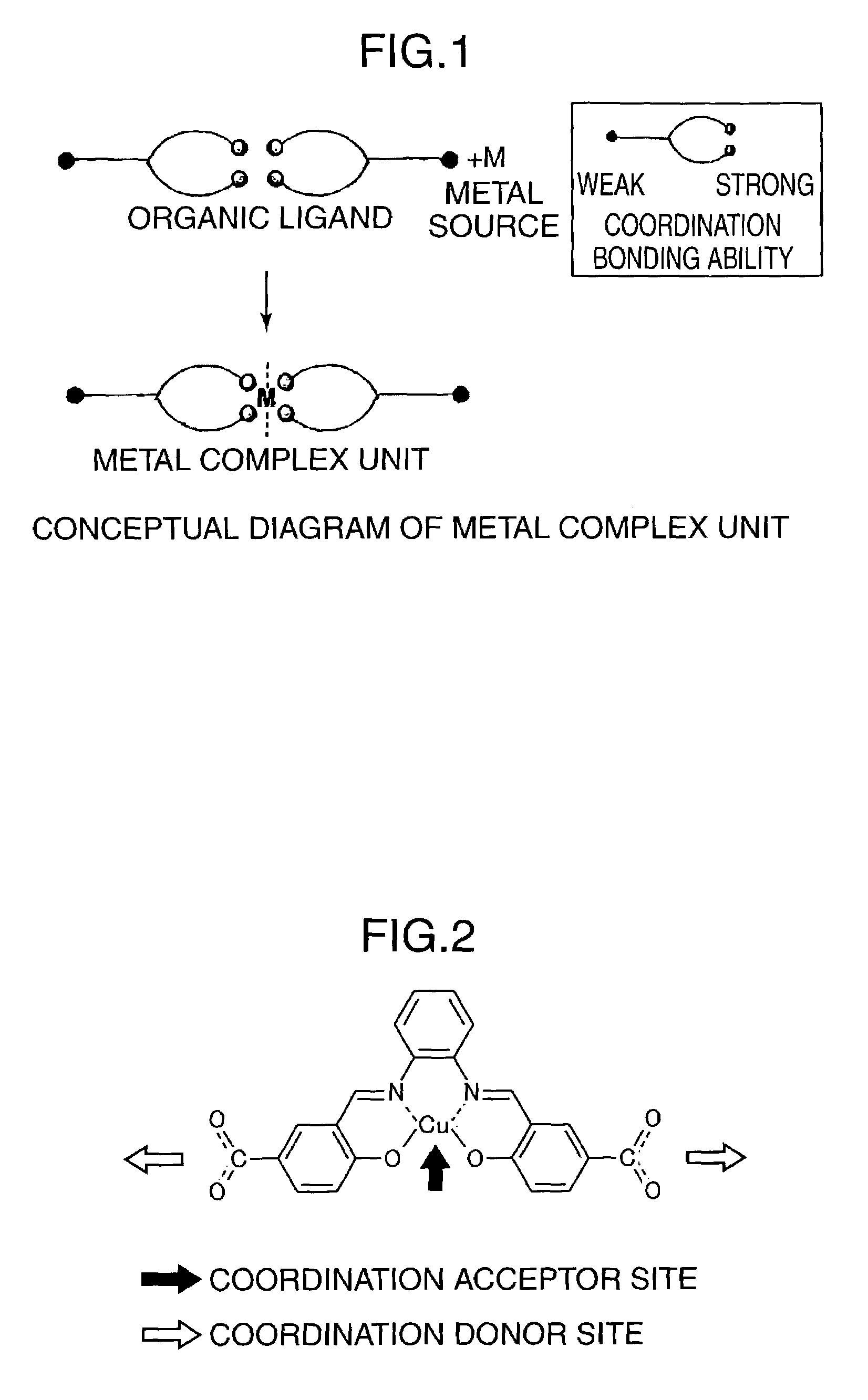
InactiveUS7009066B2Good choiceSecurely holdOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsCoordination complexMaterials science
A porous coordinatively unsaturated metal complex comprises metal complex units. Each metal complex unit includes a first metal and an organic ligand. The metal complex units are connected one another through a second metal (a connecting metal). The porous coordinatively unsaturated metal complex has voids formed by the connection. Voids have a size of 10 Å or more. The first metal is rendered to a coordinatively unsaturated state in the metal complex unit. With this arrangement, not only low-molecular weight compounds but also general compounds can be introduced as substrates. Further, the porous coordinatively unsaturated metal complex has high catalytic activity or high molecule retainability.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
Variant nucleoside-5′-phosphate producing enzyme
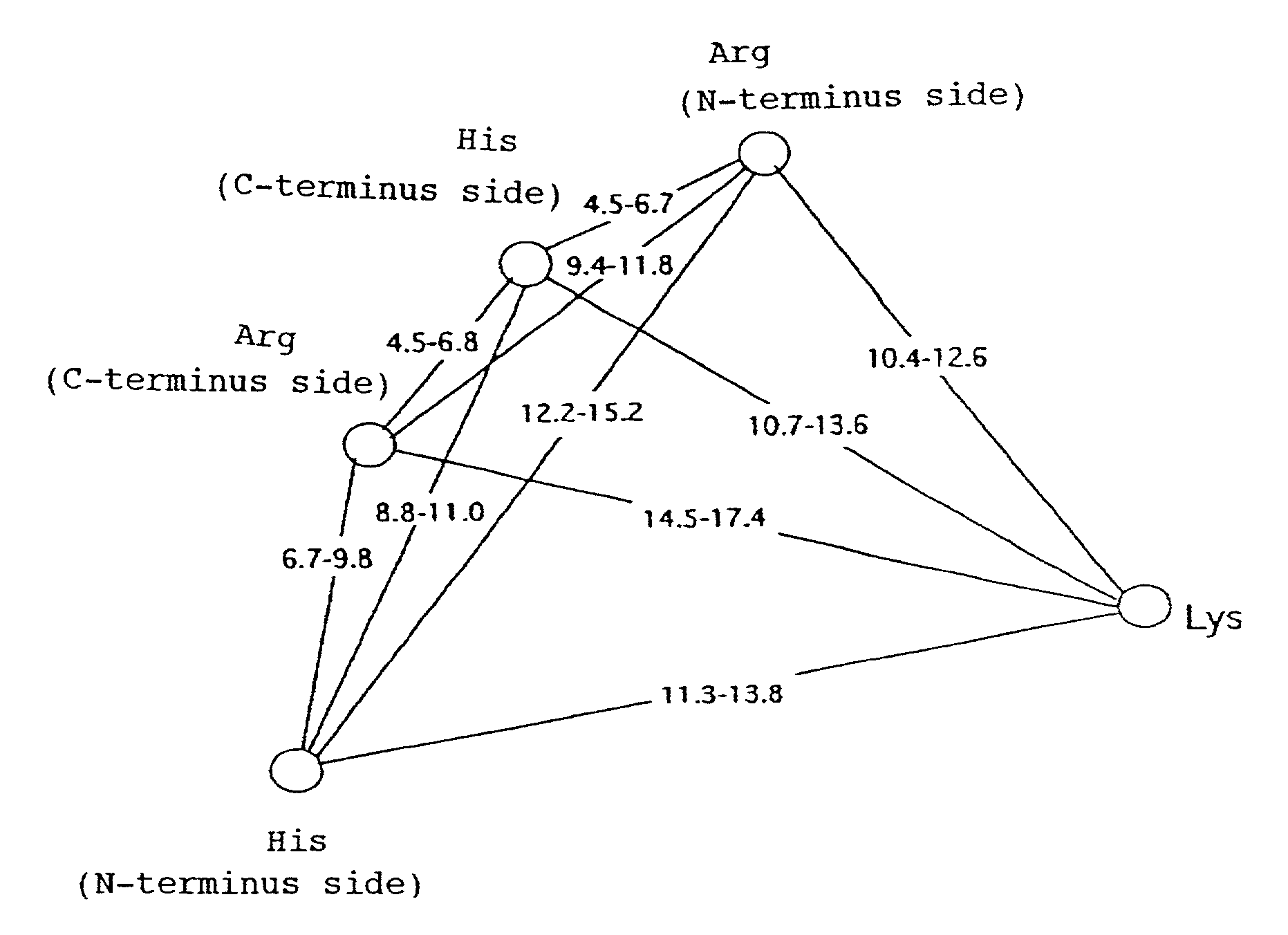
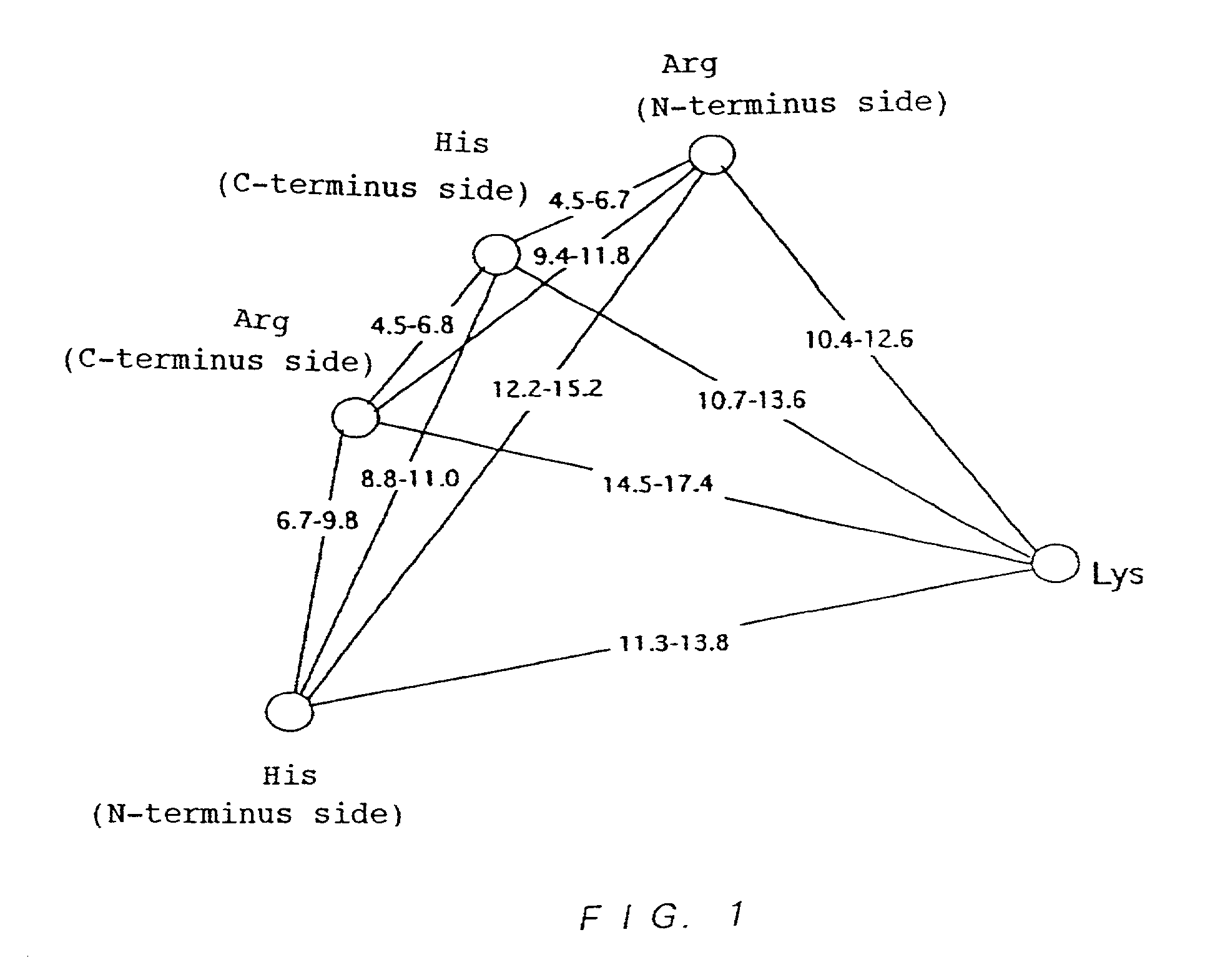
InactiveUS6987008B1Improve productivityIncrease flexibilitySugar derivativesBacteriaPhosphorylationPhosphate
There is provided a mutant nucleoside-5′-phosphate producing enzyme with improved nucleoside-5′-phosphate producing ability of a nucleoside-5′-phosphate producing enzyme that has transphosphorylation activity and / or phosphatase activity and has one Lys residue, two Arg residues and two His residues with distances between their Cα's within a particular ranges and a space around them allowing a binding of a nucleoside, of which mutation is designed by using the crystal structure of EB-AP.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
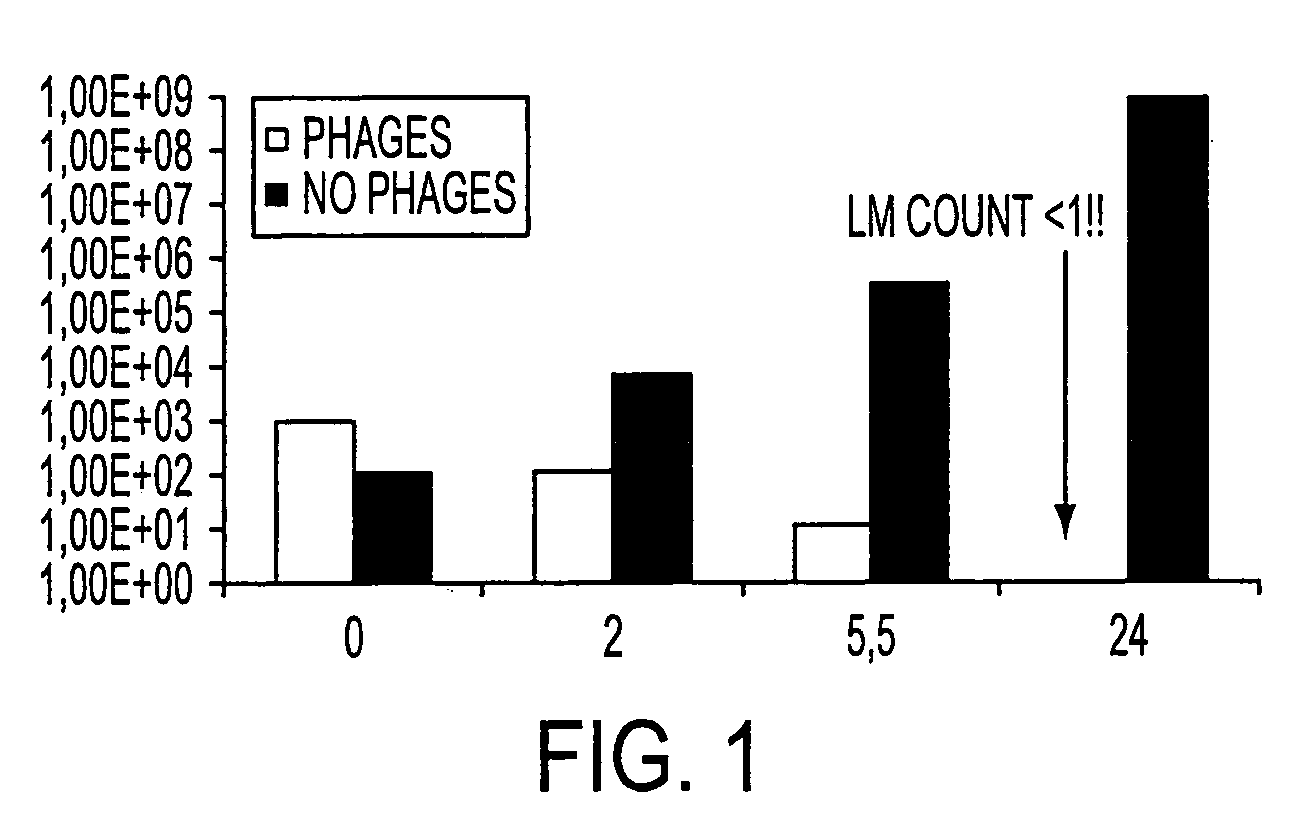
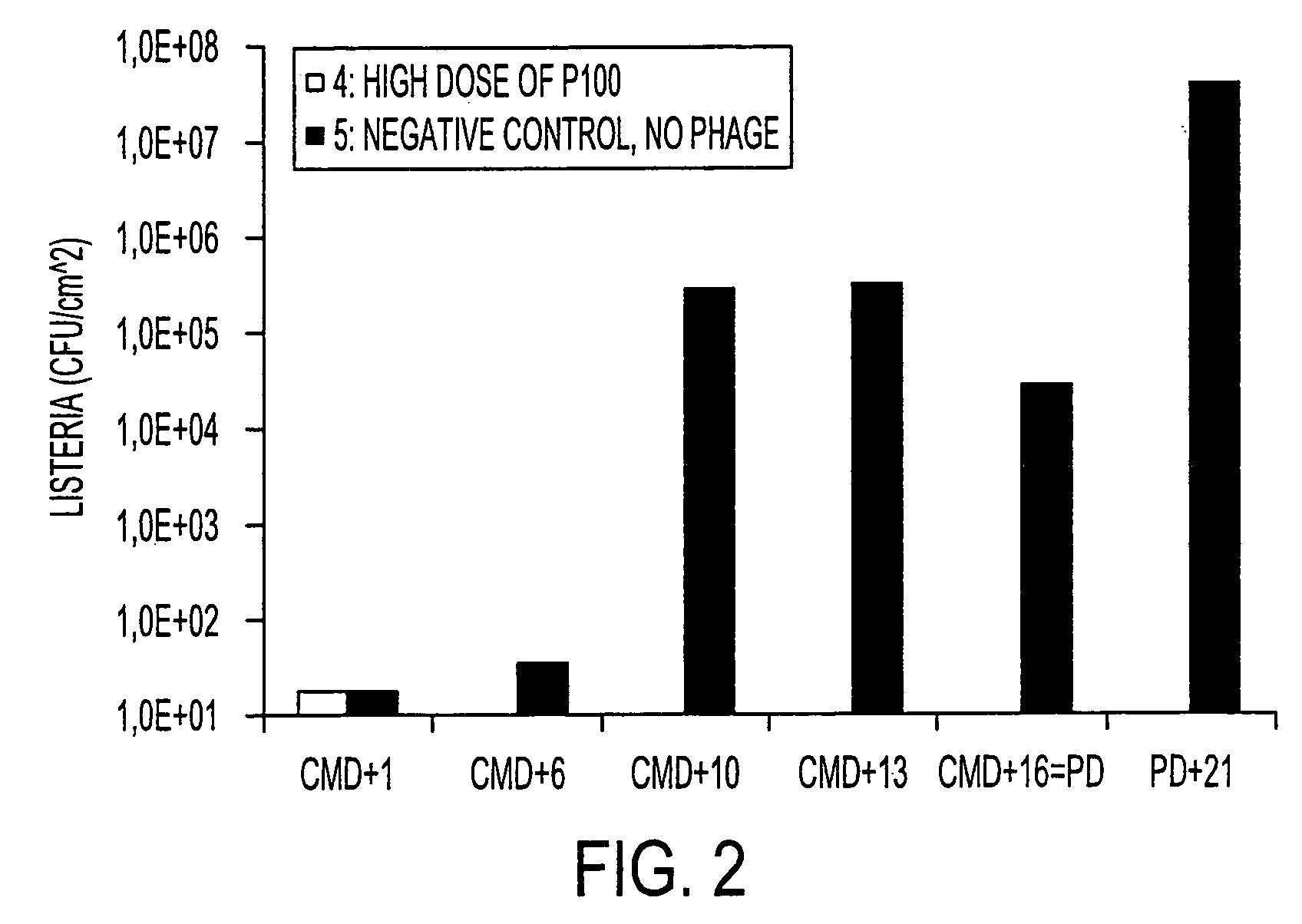
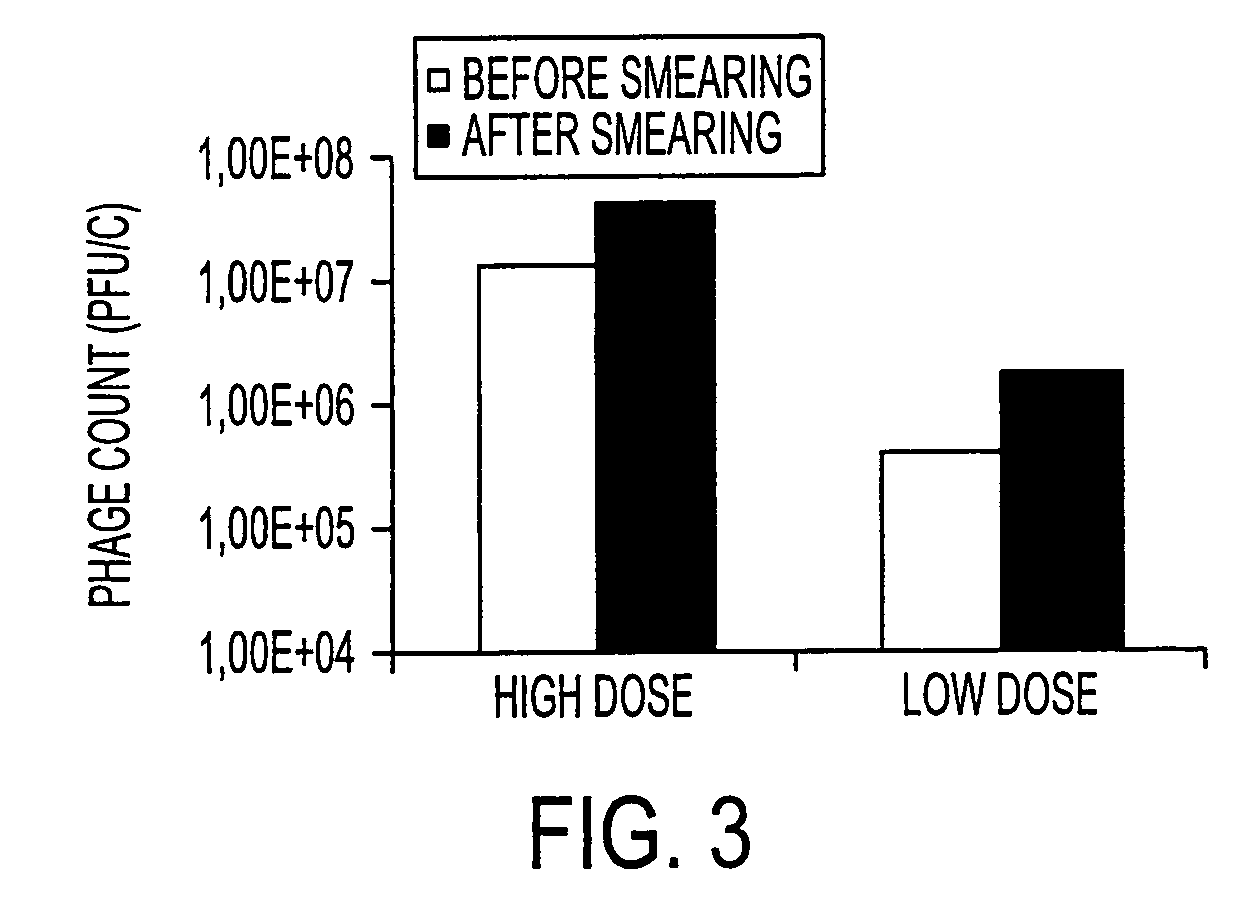
Virulent phages to control Listeria monocytogenes in foodstuffs and in food processing plants
ActiveUS7438901B2Shorten the counting processIncreased substrate specificityAntibacterial agentsBiocideBiotechnologyBacteroides
The present invention relates to virulent (lytic) Listeria monocytogenes phage from the Myoviridae family, preferably P100, alone or in combination with other virulent phages. P100 and the endolysin from P100 can be administered to food products, to the components that will be added to food products, and / or to the infrastructure of the food processing plants within which such food products are processed, or the containers or wraps in which such foods are stored and / or shipped, in order to reduce Listeria monocytogenes contamination. P100 can also be used in the present invention to identify Listeria monocytogenes bacteria present on (or within) foodstuffs, as well as those Listeria monocytogenes bacteria present in the equipment or the general environment of the food processing plants in which the foodstuffs are being processed and in animals infected with Listeria monocytogenes. The phage and the endolysin of the present invention can also be used to treat animals infected with Listeria monocytogenes. P100 will kill the bacteria that are within its host range with great efficiency and will propagate to high titer thereon. P100 can be combined with other lytic phage, and / or with other antimicrobial agents to reduce or eliminate Listeria.
Owner:EBI FOOD SAFETY
Method for synthesizing lactam compound
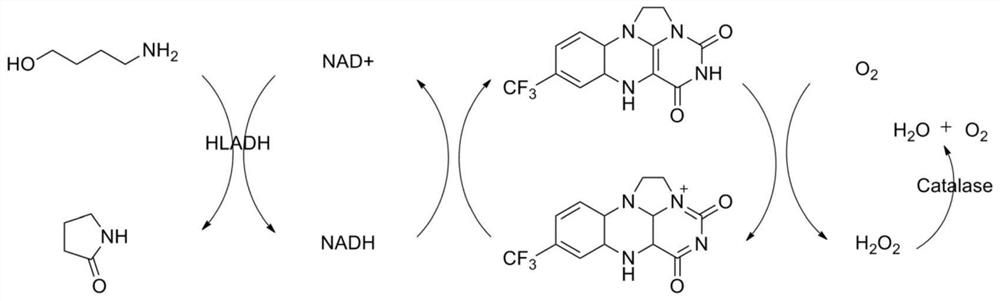
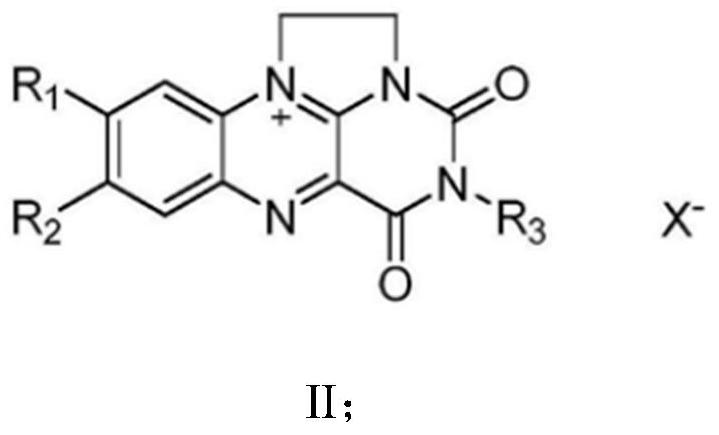
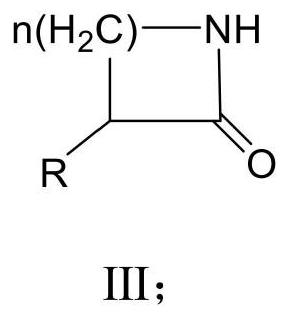
PendingCN112695062ANo generationHigh catalytic efficiencyFermentationEnzymatic synthesisPtru catalyst
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing a lactam compound. Amino alcohol, alcohol dehydrogenase, flavin molecules, cofactors and catalase react in a solvent. The invention constructs a green and environment-friendly method for enzymatic synthesis of the lactam compound. Compared with common toxic chemical catalysts, the alcohol dehydrogenase is selected as a catalyst, the method has the characteristics of high substrate specificity, no pollution, high catalytic efficiency and the like, the solvent is a buffer aqueous solution, no toxic solvent is used, no by-product is generated, and the product is easy to separate.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Porous coordinatively unsaturated metal complex
InactiveUS20040014598A1Good choiceSecurely holdGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCoordination complexMaterials science
A porous coordinatively unsaturated metal complex comprises metal complex units. Each metal complex unit includes a first metal and an organic ligand. The metal complex units are connected one another through a second metal (a connecting metal). The porous coordinatively unsaturated metal complex has voids formed by the connection. Voids have a size of 10 Å or more. The first metal is rendered to a coordinatively unsaturated state in the metal complex unit. With this arrangement, not only low-molecular weight compounds but also general compounds can be introduced as substrates. Further, the porous coordinatively unsaturated metal complex has high catalytic activity or high molecule retainability.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
Mutant glyphosate degrading enzyme and cloning, expression and application thereof
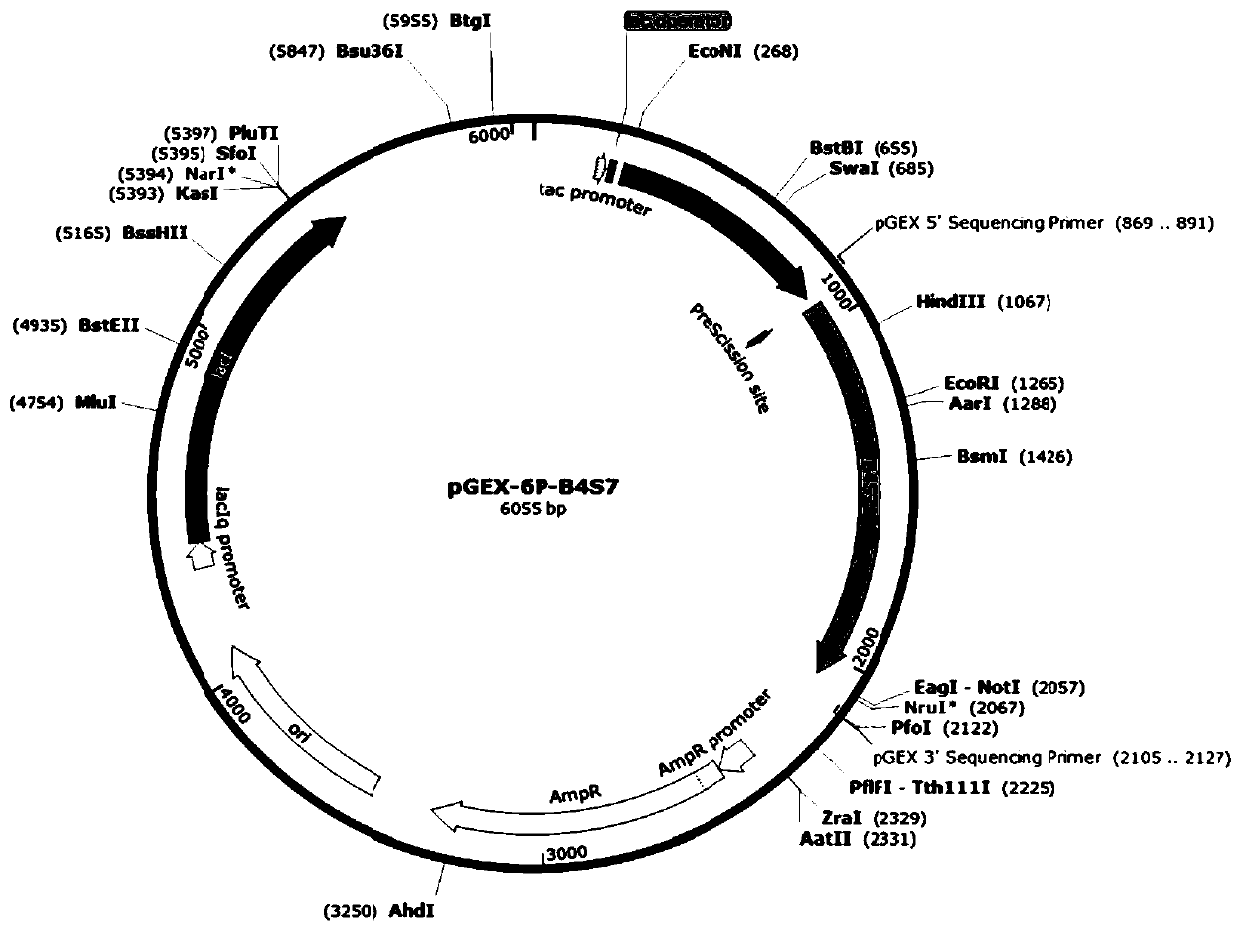
InactiveCN110272880AImprove degradation efficiencyIncreased substrate specificityOxidoreductasesFermentationDecompositionPhenylalanine
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biology, and particularly relates to a glyphosate degrading enzyme mutant which is obtained by a site-directed mutation technology and has improved catalytic activity and substrate specificity on glyphosate. According to the glyphosate degrading enzyme mutant B4S7-F63X disclosed by the invention, on the basis of an existing glyphosate degrading enzyme B4S7, the modified glyphosate degrading enzyme is mutated into alanine or histidine at the 63rd-position phenylalanine. Compared with the existing literature reports and patent data, the B4S7-F63A has the highest catalytic efficiency on glyphosate, the B4S7-F63H has the highest substrate specificity on glyphosate. After being introduced into a plant, the glyphosate degrading enzyme coding gene is expected to endow the plant with glyphosate resistance, to realize high-efficiency decomposition of the glyphosate, and to solve the problem of residue of the glyphosate in the plant. The product has great application potential in the fields of cultivating novel glyphosate-resistant crops and cultivating novel herbicide-resistant plants capable of degrading glyphosate.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com