Maltose substrate specificity improved cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase and preparation method thereof
A substrate specificity, glycosyltransferase technology, applied in the fields of botanical equipment and methods, microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of maltose substrate specificity (low conversion rate, etc.) The effect of improved substrate specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Example 1: Cyclodextrin Glucosyltransferase with Improved Substrate Specificity
[0020] The cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase of the present invention is based on the gene sequence published by GenBank AF047363.1, and the lysine at position 47 is mutated into phenylalanine, tyrosine or proline, respectively K47F , K47Y and K47P.
[0021] Amino acid substitution can be carried out at position 47 of the mature region by chemical total synthesis or site-directed mutagenesis.
Embodiment 2
[0022] Example 2: Preparation method of cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase with improved substrate specificity
[0023] This example uses the PCR method as an example for illustration, but the protection of the invention is not limited to the method of obtaining mutations only through the PCR method. The preparation method of mutant enzymes K47F, K47Y and K47P is as follows:
[0024] 1) Site-directed mutation
[0025] Site-directed mutagenesis of single mutant enzymes K47F, K47Y and K47P, using the rapid mutation kit MutanBEST kit to express vector cgt / pET-20b(+) 1 for the template,
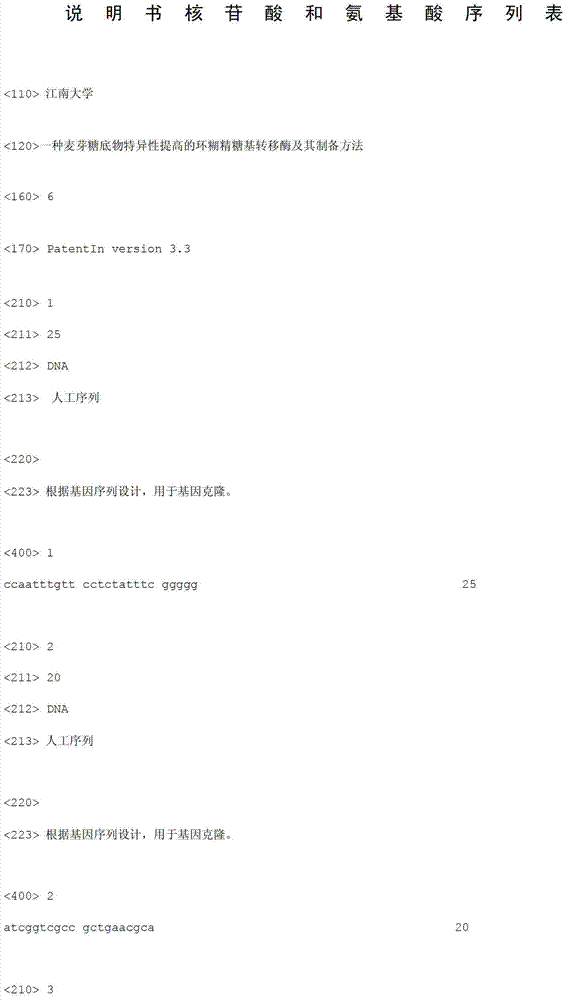
[0026] The apex mutation primers introducing the K47F codon are:
[0027] Forward primer: 5'-CCAATTTG TTC CTCTATTTCGGGGG-3', the underline is the mutant base;
[0028] Reverse primer: 5'-ATCGGTCGCCGCTGAACGCA-3';
[0029] The apex mutation primers introducing the K47Y codon are:
[0030] Forward primer: 5'-CCAATTTG TAC CTCTATTTCGGGGG-3', the underline is the mutant base;
[0031] Reverse ...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Example 3: This example illustrates the analysis of enzyme activity and the synthesis and detection of AA-2G.
[0042] 1) Enzyme activity assay method:
[0043] Method for measuring α-cyclization activity by methyl orange method: Take 0.1mL of appropriately diluted enzyme solution, add it to 0.9mL of 3% soluble starch solution prepared in advance with 50mM phosphate buffer (pH6.5), at 40°C After reacting for 10 min, add 1.0 mL of 1.0 M hydrochloric acid to stop the reaction, then add 1.0 mL of 0.1 mM methyl orange prepared with 50 mM phosphate buffer, incubate at 16°C for 20 min, and measure the absorbance at 505 nm. One enzyme activity unit defines the amount of enzyme required to produce 1 μmol α-cyclodextrin per minute under the conditions.
[0044] Determination of starch hydrolysis activity: Add appropriate amount of enzyme solution to 50mM phosphate buffer (pH6.5) containing 1% soluble starch, react at 50°C for 10min, and then use DNS method to measure the concentr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com