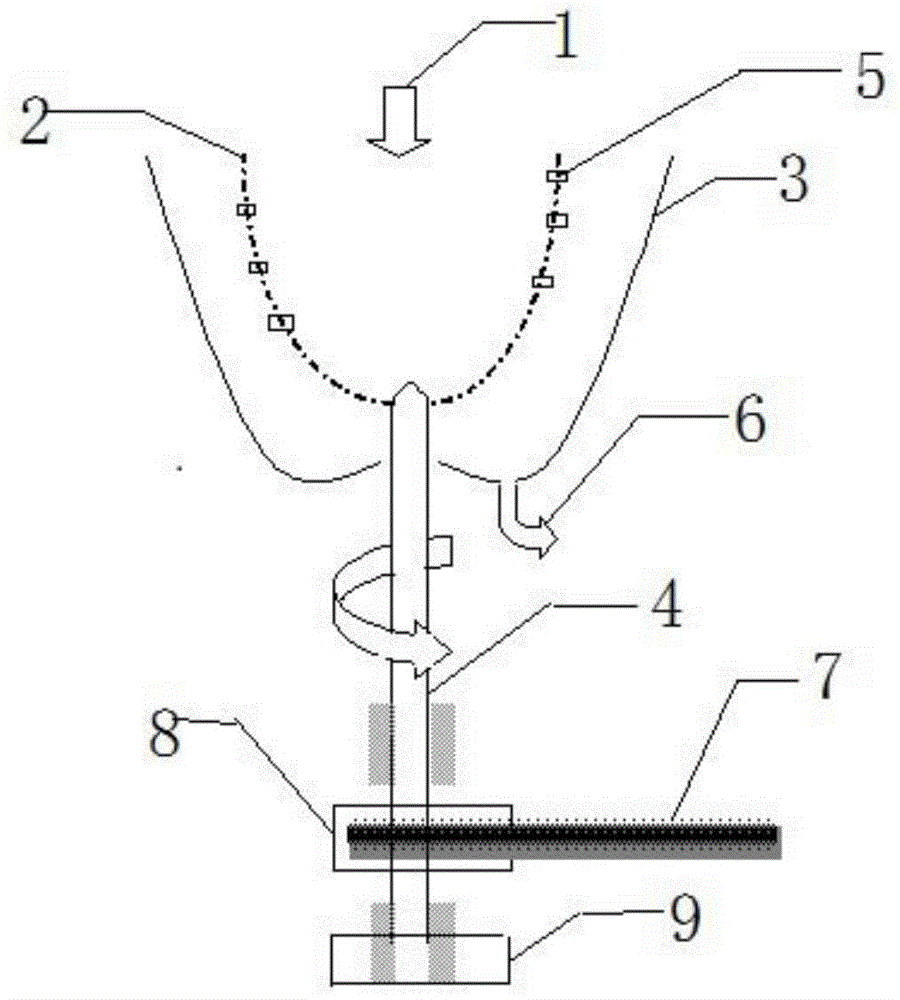
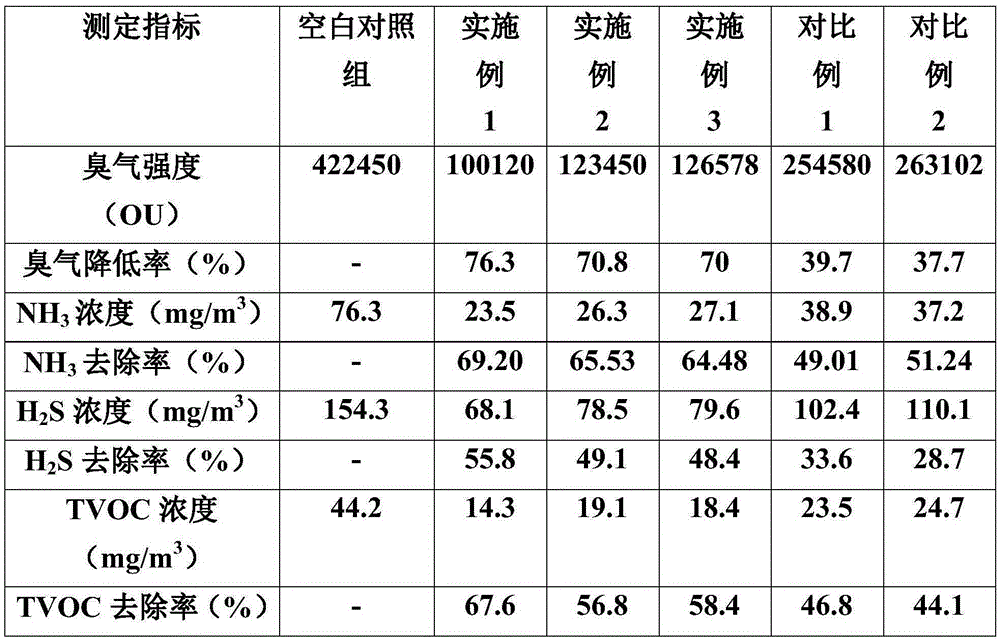
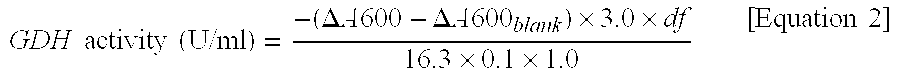Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
358 results about "Mucor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Mucor is a microbial genus of approximately 40 species of moulds commonly found in soil, digestive systems, plant surfaces, some cheeses like tomme de savoie, rotten vegetable matter and iron oxide residue in the biosorption process.
Solanum tuberdsm noodles and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN103689388AFull of nutritionPromote peristalsisFood shearingFood dryingPutrefactionAbdomen diseases
The invention discloses solanum tuberdsm noodles which comprise the following components in parts by weight: 57-94 parts of high gluten wheat flour, 5-30 parts of solanum tuberdsm powder and 1-3 parts of iodized salt. The invention further discloses a manufacturing method of the solanum tuberdsm noodle. The solanum tuberdsm noodle is rich in nutrition and rich in microelements such as selenium; due to the high solanum tuberdsm fiber content, intestines and stomach peristalsis can be prompted, mucus, pneumatosis and putrefaction retained in the enteric cavity can be cleaned, the digestive tract environment is improved, intestines and stomach diseases are prevented, human body metabolism is prompted, and vivotoxin and cancerogenic substances can be rapidly discharged.
Owner:ZHUCHENG LIANGXIN AGRI ECOLOGICAL ENG
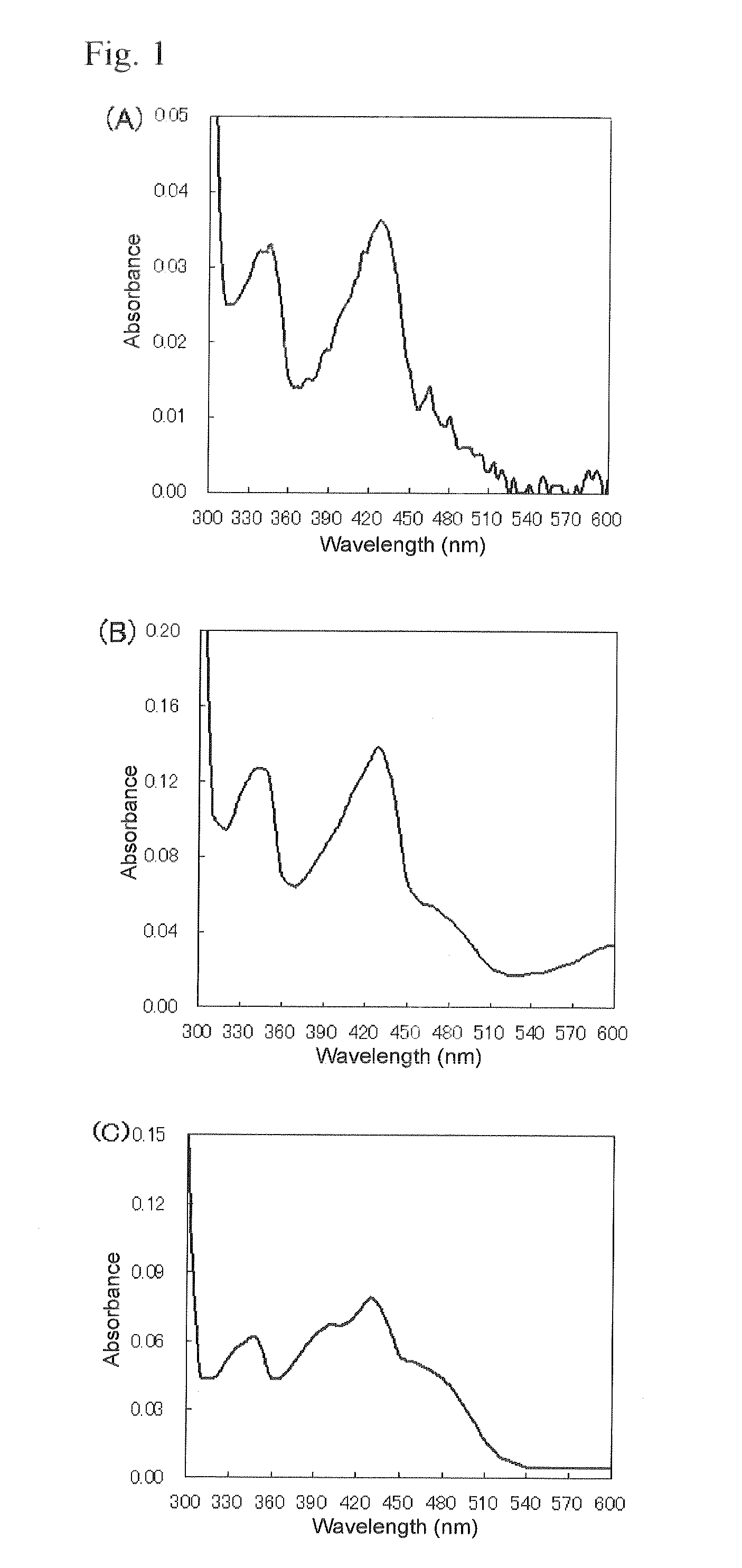
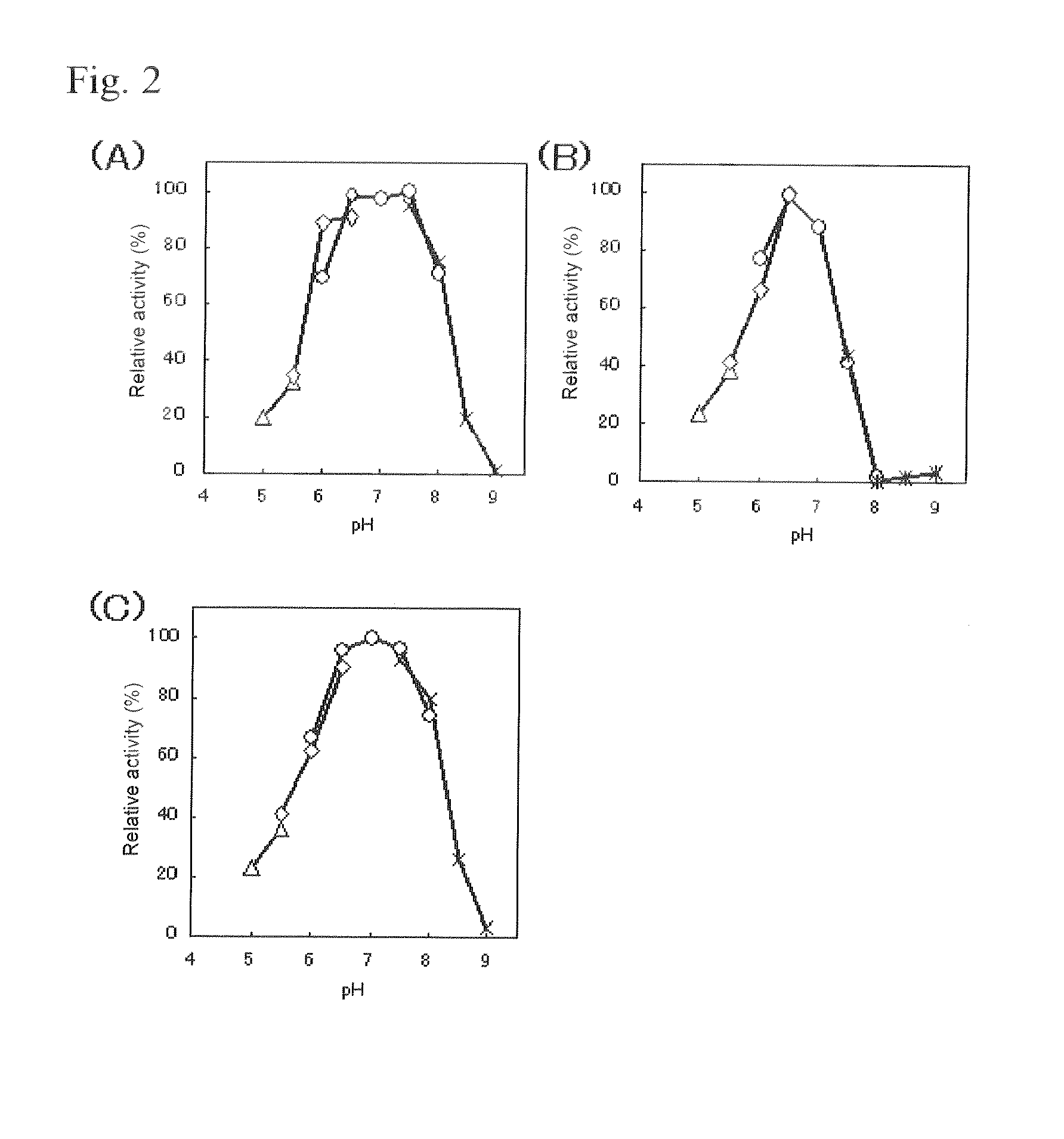
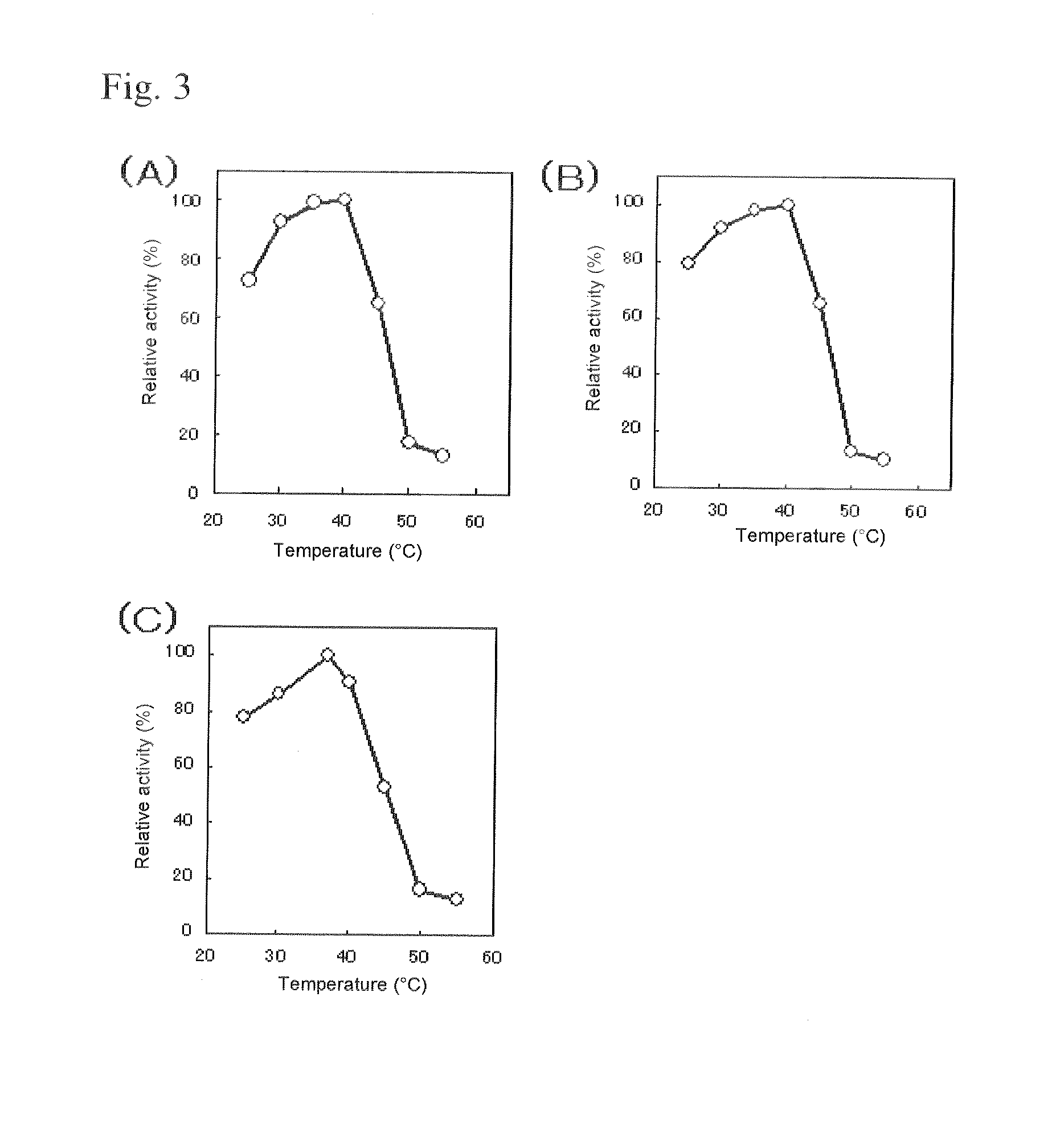
Flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase, method for producing flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase, and glucose measurement method using thereof
ActiveUS20140287445A1Increased substrate specificityImprove stabilityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsEscherichia coliHeat stability
A flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase (FAD-GDH), which in addition to having high substrate specificity and adequate desirable heat stability, is suitable for efficient production, preferably using E. coli, yeast or molds and the like as host cells. The FAD-GDH has amino acid substitutions at positions equivalent to one or more locations selected from the group consisting of position 213, position 368 and position 526 in the amino acid sequence described in SEQ ID NO: 8. The FAD-GDH is acquired from a culture by inserting a gene encoding the FAD-GDH into host cells such as E. coli. A preferable example of the FAD-GDH is FAD-GDH, in which a signal peptide region present in an N-terminal region has been deleted from the amino acid sequence of Mucor-derived FAD-GDH, and which has the aforementioned amino acid substitutions. The FAD-GDH can be preferably used in clinical diagnosis.
Owner:KIKKOMAN CORP
Method for making seasoned fried fish skin food
The invention relates to a method for making a seasoned fried fish skin food, which comprises the following steps: removing fish scales, mucus, blood stains and other impurities on the surface of fish skin, cleaning, draining, soaking in tea water for removing fishy smell, shaping, starching, seasoning, frying, packaging and obtaining a finished product; and starchy seasoning liquid adopted for starching and seasoning comprises the following components by weight percent: 8-12% of sugar, 2-3% of aromatic vinegar, 2-4% of salt, 0.5-1% of ginger juice, 1.8-4% of sesame oil, 2-3% of monosodium glutamate, 1-3% of pepper powder, 3-5% of chili oil, 1.5-3% of yellow rice wine, 20-30% of mixed flour (flour: starch powder is equal to 2:1), 3-5% of yeast powder and the balance of water. The made seasoned fried fish skin food has the advantages of abundant nutrition, beautiful color and luster, crisp, delicious and special taste, and convenient eating, and the preparation method has the advantages of reasonable process, simple operation and stable product quality, thereby having good commercial value.
Owner:TAIXIANG GRP TECH DEV
Flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenases
ActiveUS20110318810A1Accurate measurementAccurate blood glucose levelSugar derivativesBacteriaMicroorganismLactose
A flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase with a high substrate specificity for D-glucose. The flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase which is derived from a microorganism belonging to the genus Mucor. The flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase has a low reactivity for maltose, D-galactose and D-xylose compared to its reactivity for D-glucose, and therefore is relatively unaffected by these saccharide compounds. The flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase is also relatively unaffected by dissolved oxygen, and allows accurate measurement of glucose amounts even in the presence of saccharide compounds other than glucose in samples.
Owner:KIKKOMAN CORP
Method for inhibiting bacterial colonisation
InactiveUS20070110758A1Reduce bacterial infectionReduce inflammationAntibacterial agentsBiocideBacteroidesEpithelium
The present invention relates to a method for inhibiting bacterial colonisation of mucous epithelium in a biological system. The method includes the step of administering to the biological system an effective amount of a mucolytic agent and one or more of colostrum, hyperimmune milk, or a component of colostrum and / or hyperimmune milk that is capable of inhibiting bacterial colonisation in combination with the mucolytic agent.
Owner:CHILDREN YOUTH & WOMENS HEALTH SERVICE +1
Method of using microbial flora for fermenting cigar tobacco leaves
InactiveCN110122920AIncrease aromaIncrease the amount of aromaTobacco treatmentNicotiana tabacumIrritation
The invention belongs to the technical field of cigar tobacco processing, and particularly relates to a method of using microbial flora for fermenting cigar tobacco leaves. According to the method, the natural microbial flora which is harmless to the human body is adopted to ferment the cigar tobacco leaves; particularly, strains of the microbial flora include yeast and also include a mixture composed of one or more of penicillium, aspergillus niger, mucor and rhizopus according to an arbitrary proportion. Preliminary application effects show that after the cigar tobacco leaves are fermented by the microbial strains coming from tea, the sugar-nitrogen ratio of the cigar tobacco leaves is balanced; the defects of pungency, bitterness, astringency and the like which are caused by acid-base imbalance during combustion and smoking are effectively overcome, the defects of green and versicolor tobacco leaves, irritation and the like are also overcome, transformation of substances related tothe smoking taste of the tobacco and formation of a sweet flower fragrance are promoted, the quality of the fragrance of the tobacco leaves is effectively improved, the amount of the fragrance of thetobacco leaves is effectively increased, and the combustion and smoking quality of the tobacco leaves and the industrial applicability of the cigar tobacco leaves are improved.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO HENAN IND
Method for preparing composite Sichuan fermented bean curd
InactiveCN102018181AIncrease the degree of emulsificationImprove nutritional indicatorsFood preparationRhizopusBroad beans
The invention discloses a method for preparing composite Sichuan fermented bean curd, which has the outstanding characteristic that: broad bean paste koji is added in the mixed fermentation process. The method comprises the following steps of: adding mucor and rhizopus chinentis for primary fermentation, adding aspergillus oryzae to prepare the broad bean paste koji, and adding auxiliary materials, yeast powder and lactobacillus powder for secondary fermentation. Compared with the conventional fermented bean curd product, the composite Sichuan fermented bean curd prepared by the method has the advantages that: the emulsifying degree of the fermented bean curd is greatly improved, and the product is red or red brown, has bright color and fine mouthfeel, and is delicious, faint scent and nopeculiar smell; meanwhile, sanitation indexes such as coliforms, aflatoxin B1 and the like are effectively controlled, nutrition indexes such as water-soluble protein, amino acid nitrogen and the like are obviously improved, the fermentation period of the product is obviously shortened, the fermented bean curd can be produced in high-temperature summer, and seasonal production is changed into annual production.
Owner:XIHUA UNIV
Compsns-and methods for trapping and inactivating pathogenic microbes and spermatozoa
Antimicrobial and contraceptive compositions and methods which prevent and / or reduce the risk of transmission of sexually transmitted diseases through sexual activity as well as prevent and / or reduce the risk of pregnancy are provided. The compositions contain (1) a matrix-forming agent, (2) a bio-adhesive agent, (3) a buffering agent, (4) optionally a humectant, (5) optionally a preservative, and (6) water; wherein the composition is suitable for application within the vagina; wherein the compositions form a semisolid matrix on contact with ejaculate (thereby trapping ejaculated microbes and spermatozoa); wherein the composition causes hardening of cervical mucus (thereby decreasing the probability of sperm entry); wherein the composition forms a bio-adhesive layer over vaginal surfaces (thereby preventing or reducing the risk of contact of STD-causing microbes with the vaginal surfaces); wherein the composition maintains an acidic vaginal pH of less than about 5 in the presence of semen ejaculated from the male; and wherein the composition does not significantly impair the natural microbiological balance within the vagina. The antimicrobial and contraceptive compositions may also contain additional antimicrobial and / or contraceptive agents (e.g., nonoxynol-9, octoxynol-9, benzalkonium chloride, phosphorylated hesperidins, sulfonated hesperidins, polystyrene sulfonates, substituted benzenesulfonic acid formaldehyde co-polymers, H2SO4-modified mandelic acids, povidone iodine, itraconazole, ketoconazole, metronidazole, clotrimazole, fluconazole, teraconazole, miconazole, tinidazole, iconazole, chloramphenicol, nystatin, cyclopiroxolamine, and the like).
Owner:RUSH UNIV MEDICAL CENT
Animal feed additives
InactiveUS7217433B2Improve feed utilizationReduce chyme viscosityMicroorganismsMicroorganism based processesDNA constructMucor species
The present invention relates to animal feed additives, which additives comprise a monocomponent xylanase derived from a strain of Byssochlamus, Chaetomium, Humicola, Malbranchea, Mucor, Myceliophthora, Paecilomyces, Talaromyces, Thermoascus, or Thielavia. In other aspects, the invention relates to monocomponent xylanase preparations, DNA constructs, recombinant expression vectors, host cells, and methods of producing monocomponent xylanase preparations.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Food detergent with ocean active matters
ActiveCN1667109AEnsure safetyNon-surface-active detergent compositionsFood preparationFood additiveActive matter
This invention relates to a food detergent that contains ocean active matter. it is constituted by following components as quality portions sea water bittern extract 10~70%, baking sldap 1.5~85% and food additive 0~20%. The sea water bittern extract by wet basis quality portion main contains NaCl 16~86%, MgSO4 2~21%, MgCl 1~25%. Preparation method is that sea water bittern is purified first, then concentration by evaporation at 120 ~ 1560C and crystallisation by cooling and the crystal is crushed. This invention can react with pesticides, insecticide, organic and inorganic pollution, even harmful microorganism, bacteria, and virus, so it can be used to purify fruit, vegetable, poultry and poultry internal organs, or other food of foreign flavor face and mucilage, it is propitious to ensure food safety.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Pharmaceutical composition comprising an extract of pseudolysimachion longifolium and the catalpol derivatives isolated therefrom having antiinflammatory, antiallergic and antiasthmatic activity
ActiveCN101208084ATreat and prevent inflammationOrganic active ingredientsDrug compositionsDiseaseBlood plasma
The present invention relates to a composition comprising an extract of Pseudolysimachion genus plant, and the catalpol derivatives isolated therefrom having anti-inflammatory, antiallergic and anti-asthmatic activity. The extractof Pseudolysimachion genus plantand the catalpol derivatives isolated therefrom shows potent suppressing effect on elevated IgE, IL-4 and IL- 13 levels and eosinophilia in the plasma and BALF, and mucus overproduction in the lung tissues in an OVA-induced asthmatic mouse model. Therefore, it can be used as the therapeutics or functional health food for treating and preventing inflammatory, allergic and asthmatic disease.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF BIOSCI & BIOTECH
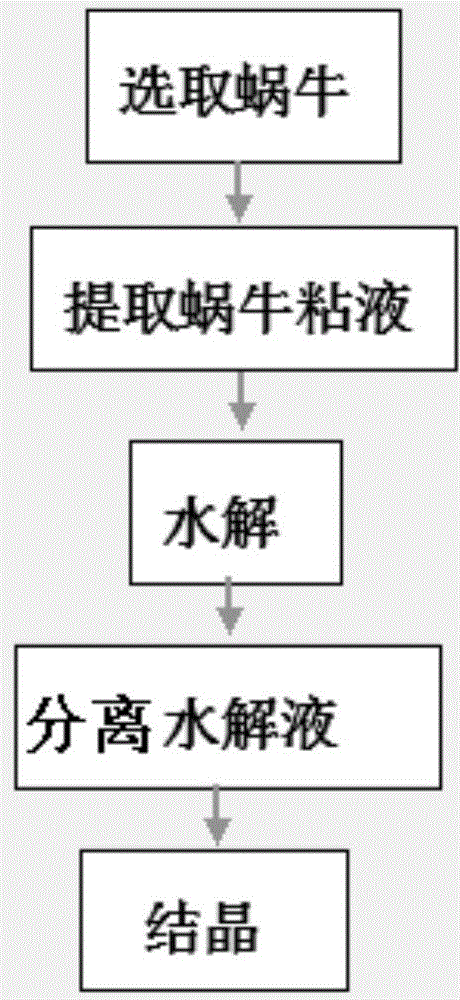
Method for extracting snail slime extract containing active enzymes
The invention belongs to the field of extraction of snail slime and particularly relates to a method for extracting snail slime extract containing active enzymes. Snail slime comprises proteins, the active enzymes, mucin, chondroitin sulfate, protein polysaccharides and hydroxyacetic acid; the active enzymes include cellulase, pectinase, amylase and protease. The method comprises the following steps: collecting the snail slime with the active enzymes by utilizing an extraction device; hydrolyzing the collected snail slime with the active enzymes; separating the hydrolyzed snail slime containing the active enzymes to obtain extract liquor of the snail slime; crystallizing the separated extract liquor of the snail slime. The extract is high in quality.
Owner:南通禹丰迪生物科技有限公司
Production method of purple sweet potato residue dietary fibers
InactiveCN103976370AImprove qualityPromote peristalsisFood ingredient functionsFood preparationDiseaseMotility
The invention provides a production method of purple sweet potato residue dietary fibers, relates to the field of dietary fiber processing. The dietary fibers are processed from purple sweet potato residues, and the dietary fiber product quality is improved by the process of thinning purple sweet potato residue particles, homogenizing, performing high-pressure spray-drying and the like. According to the method, the purple sweet potato residues are used as a raw material for processing the purple sweet potato residue dietary fibers; the purpose of turning wastes into wealth is achieved; a product is rich in dietary fibers and good in quality, and can promote gastrointestinal motility, remove mucus, intestinal gas and septic matter retained in an enteric cavity, discharge toxic substances and cancerogenic substances in excrement, improve a digestive tract environment and prevent gastrointestinal diseases after being eaten often. A new path is opened for comprehensive development and utilization of potato residues and bean dregs, an environment protection effect is achieved, and the production method has high economic and beneficial benefits.
Owner:彭常安
Bee breeding artificial insemination culturing method
InactiveCN101664018AGathering power increasedImprove disease resistanceDead animal preservationAnesthetic roomDisease
The invention discloses a bee breeding artificial insemination culturing method, comprising the following steps: (1) male bee culturing: culturing fine-quality bee breeding by using excellent bee breeding, and culturing a virgin queen before sexual maturity of male bees; (2) semen collection: preparing a semen diluent, placing in a bottle, sterilizing in high temperature, placing the semen diluentin a collection pipe of a semen collector, scraping the semen and mucus of the male bees to the diluent by a sterilized glass rod, and placing the collector into a centrifuge tube of a centrifuge forcentrifugation so as to separate semen when enough semen is rinsed in the diluent; and (3) insemination: selecting the virgin queen of sexual maturity, placing in an anesthetic room, carrying out artificial insemination when the virgin queen is in a comatose state, and removing narcosis after insemination. The swarm cultured by the method in the invention is improved in the aspects of collectionability, disease resistance, stress resistance, oviposition rate, bee milk yield and the like, and the collected royal jelly and pollen yield are enhanced.
Owner:沈卫平
Prepn process of freeze dried sea cucumber powder
InactiveCN1771842AKeep active ingredientsIncrease nutritionFood preservationPropolisAdditive ingredient
The preparation process of freeze dried sea cucumber powder includes the following steps: eliminating surface mucus and fishy smell of sea cucumber and sterilizing with the alcohol solution of propolis tincture; washing with bacteria-free ozone solution to eliminate alcohol and quick freezing at ¿C18 deg.c; crushing the frozen sea cucumber into coarse slurry, freezing and sublimation to dry; ultrafine crushing into 300-400 mesh freeze dried sea cucumber powder; and sealing and cold storing. The freeze dried sea cucumber powder may be served directly or used to compound other sea cucumber product. The low temperature production process has the active components in sea cucumber well maintained.
Owner:齐培谟
Disinfectant for treating bacterial fruit rot of seedless watermelons and shell-breaking-free accelerating bud-forcing method for seedless watermelons
InactiveCN103392727ASolve the problem of inability to produce seedlingsReduce the cost of germinationBiocideDisinfectantsDisinfectantCucumis colocynthis
The invention discloses a disinfectant for treating bacterial fruit rot of seedless watermelons and a shell-breaking-free accelerating bud-forcing method for seedless watermelons, wherein the disinfectant contains 2% Kasumin liquid 300-400 fold and 72% agricultural streptomycin sulphate 1000-1500 fold; and the bud-forcing method comprises: soaking seeds in water of 55 DEG C for 30min, then in the disinfectant for 3h, and in formaldehyde 100 fold for 30min after washed; flushing the seeds with saturated limewash until no mucus on seed surfaces, then flushing the seeds with clear water until no peculiar smell, and removing pericarp and wizened seeds; drying until the surfaces of the seeds turn white; wrapping the seeds with cotton cloth, placing the seeds into a thermotank, accelerating germination at 35 DEG C for 2h, and accelerating germination at 32 DEG C for 12-15h; washing the seeds with water of 35 DEG C, drying and dehydrating the seeds, airing the seeds until the surfaces have no obvious water, and waiting for germination in the thermotank of 32 DEG C. The disinfectant and the method can reduce probability for the seedless watermelons to infect bacterial fruit rot below 2 parts per thousand, have no need of artificial shell breaking, can reduce bud-forcing cost of the seedless watermelons, and raises a seedling rate of the seedless watermelon seeds.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF AGRI SCI +2
Microbial agent suitable for treating urban wastewater and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109082393AStructural balance and stabilityIncrease surface areaFungiBacteriaBacillus megateriumFeces
The invention belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment and particularly relates to a microbial agent suitable for treating urban wastewater and a preparation method thereof. The microbial agent comprises Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus licheniformis, Bacillus megaterium, saccharomycetes, lactic acid bacteria, acetic acid bacteria, photosynthetic bacteria, Actinobacteria, indigenous bacteria, nitrifying bacteria, denitrifying bacteria, phosphorus-accumulating bacteria, Rhodospirillum, Thiobacillus denitrificans, Sphingobacteria, Alcaligenes faecalis, Bifidobacterium, brown rot fungi,Geotrichum candidum, Mucor, Aspergillus oryzae, and Penicillium diversum. The preparation method includes: mixing well Actinobacteria, indigenous bacteria, nitrifying bacteria, denitrifying bacteria,phosphorus-accumulating bacteria and Bifidobacterium, adding the mixture into clean soil, farming earthworms with the soil for 12-14 days, and isolating the earthworms and the soil to obtain earthwormcast containing the mixed bacteria; mixing the earthworm cast containing the mixed bacteria and other bacteria, and immobilizing to obtain the microbial agent.
Owner:南宁市黄陈生猪养殖场
Method for extracting sialic acid from bird's nests
InactiveCN108003202AThe method is simpleEasy to operate and controlEsterified saccharide compoundsSugar derivativesFiltration membraneMucor
The invention belongs to the technical field of deep processing of bird's nest products and particularly relates to a method for extracting sialic acid from bird's nests. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the steps of firstly, crushing the bird's nests until the particle size is 80 meshes, soaking the bird's nest particles in hot deionized water with the temperature of 50 DEG C to 60DEG C for 3 to 4 hours to subject the bird's nest particles to thorough imbibition, carrying out circular grinding with a colloidal mill to obtain bird's nest pulp with the particle size of 120 meshes, subjecting bird's nest cells to wall breaking by a microwave function so as to release the sialic acid from glycoprotein and mucus protein, removing macromolecular substances by using microfiltration and 2-level ultrafiltration of a membrane technology according to the characteristic that the molecular weight of the sialic acid is small, trapping substances of 150Da to 500Da by using a nano-filtration membrane, and subjecting trapped fluid of 150Da to 500Da to concentrating, freezing and microwave vacuum depressurization drying, thereby obtaining the sialic acid. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the content of the obtained sialic acid is 80% or more, and the recovery rate of the sialic acid reaches 90%.
Owner:广西佛斯肽生物科技有限公司
Dried salted marine eel treatment process
The invention relates to the technical field of aquatic product processing, and in particular relates to a dried salted marine eel treatment process which comprises the following steps of: (1) carrying out pretreatment; (2) pickling; (3) drying in cold air at a low temperature; (4) improving the fragrance in hot air at a high temperature; and (5) packaging, wherein the step of carrying out pretreatment specifically comprises the following steps of: removing the head, the tail, the gill and the viscus of fresh marine eel, subsequently splitting along chine, scrubbing the whole body of the marine eel by using a mucus remover which is prepared by mixing salt, starch and ground pepper, so as to remove the mucus on the skin of the marine eel, and the mucus remover is shown in the specification; and the step of pickling specifically comprises the following steps of: soaking the marine eel after the pretreatment into a pickling liquid which is prepared by mixing 3-5% of trehalose, 5-10% of salt, 0.2-0.5% of sodium succinate, 0.2-0.5% of carapace and the balance of purple perilla water, pickling for 30-60 minutes under a vacuum condition, and subsequently taking out and draining off so as to obtain the dried salted marine eel. By utilizing the process, the time for soaking and pickling is greatly shortened, the original nutrition facts of the marine eel are relatively completely maintained, and the finally prepared dried salted marine eel is moderate in salt degree, and is all good in taste, favor and sensory quality.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MARINE DEV RES INST
Non-invasive extraction method of Haliotis discus hannai ino genome DNA
InactiveCN102747069AQuality improvementProtect organizational integrityDNA preparationCuticleNon invasive
The invention discloses a non-invasive extraction method of Haliotis discus hannai ino genome DNA, comprising the steps of using 75% of alcohol to sterilize and irritate pallium of Haliotis discus hannai ino; scraping to obtain a mixture of mucus and epidermal tissue fragments; treating the mixture, centrifugally separating the mixture to obtain precipitate; adding a cell lysate and protease K to the precipitate; after digesting and oscillating, cooling the mixture for a certain time; adding NH4Ac to the sample; centrifugally separating to collect supernate; adding isopropanol to the supernate; after oscillating and mixing uniformly, and then centrifugally separating to obtain precipitate; using ethanol to wash the precipitate; drying the precipitate at room temperature for 5 minutes to obtain the Haliotis discus hannai ino genome DNA. The non-invasive extraction method of the Haliotis discus hannai ino genome DNA is simple, efficient and convenient, does not damage the Haliotis discus hannai ino and does not influence survival ability and production performance.
Owner:DALIAN HAIBAO FISHERY
Pig feed used for reducing pig dung stink, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106912699APromote digestion and absorptionWeight increaseAnimal feeding stuffSnow moldAnimal science
The invention provides a pig feed used for reducing pig dung stink, and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of pig feed. The pig feed is mainly prepared from following raw materials, by weight, 60 to 80 parts of bean dregs, 20 to 25 parts of cassava dregs, 40 to 60 parts of puffed corn flour, 8 to 15 parts of shrimp meal, 2 to 3 parts of citric acid, 5 to 8 parts of vitamin, 30 to 40 parts of mixed mushroom bran, 0.3 to 0.5 part of nitrobacteria, 0.5 to 0.8 part of brevibacterium glutamicus, 0.2 to 0.3 part of mucor, 2 to 4 parts of an enzyme preparation, 5 to 10 parts of carbonized biomass, 20 to 30 parts of folium ginkgo powder, and 6 to 10 parts of herba centipedae. The pig feed is capable of providing pigs with comprehensive and sufficient nutrients, is convenient to be absorbed and digested, is capable of degrading intestinal tract waste residue by microorganisms, absorbing ammonia substances in intestinal tract and pig dung with functional raw materials, promoting growth of pigs via the cooperation effect of the raw materials, reducing pig dung stink, and improving the environment in hog houses.
Owner:广西神龙王农牧食品集团有限公司
Deodorant complex microbial inoculant and preparation method and application thereof
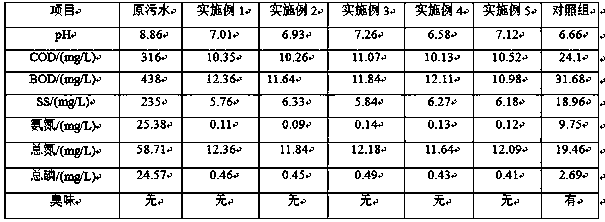
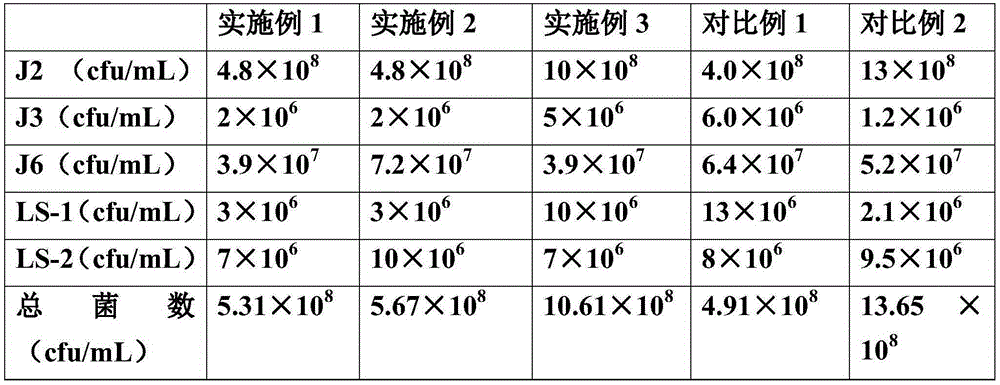
The invention discloses a deodorant complex microbial inoculant and a preparation method and application thereof. The deodorant complex microbial inoculant is prepared from 4.8-10*10<8> cfu / mL of lactic acid bacteria, 2-5*10<6> cfu / mL of mucor, 3.9-7.2*10<7> cfu / mL of saccharomycetes, 3-10*10<6> cfu / mL of bacillus megatherium and 7-10*10<6> cfu / mL of bacillus subtilis, and the total count is 5.31-10.97*10<8> cfu / mL. The deodorant complex microbial inoculant is prepared from various microbial strains through fermentation, the deodorant complex microbial inoculant can grow well in feces due to the characteristics of flora composition, metabolic types, respiration types and functional diversity of effects, the deodorant complex microbial inoculant can grow well in feces and fast occupy favorable ecological niches, and therefore growth and propagation of putrefying bacteria producing repugnant substances can be effectively inhibited or the repugnant substances are directly degraded, repugnant odor in-situ source control is achieved, and the deodorization effect is achieved.
Owner:北京市畜牧业环境监测站 +1
Preparation method and application of Anaphalis lactea volatile oil
InactiveCN102604741ABroad-spectrum bactericidalBroad-spectrum antibacterialBiocideEssential-oils/perfumesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
Disclosed are a preparation method and application of Anaphalis lactea essential oil. Volatile oil in Anaphalis lacteal is extracted by steam distillation and CO2 supercritical extraction, ingredients of the volatile oil are analyzed initially by gas chromatography / mass spectrography, 57 ingredients in the volatile oil are identified and account for more than 94% of the total volatile oil. Antibacterial and bactericidal activities of the volatile oil are researched by the Oxford cup method, and according to the research, the volatile oil has an evident killing or inhibiting function for bacteria, such as staphylococcus, streptococcus, enterobacter, salmonella, shigella, pseudomonas, bacillus, escherichia coli and the like, and fungi, such as candida, cryptococcus, penicillin, aspergillus, mucor, microsporum, trichophyton, epidermophyton and the like. Testing by DPPH (diphenylpicrylhydrazyl) method shows that the volatile oil has fine antioxidant activity. Owing to the fine activity, the volatile oil is widely applicable to the industries of foods, medicines, cosmetics, health-care products and the like.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
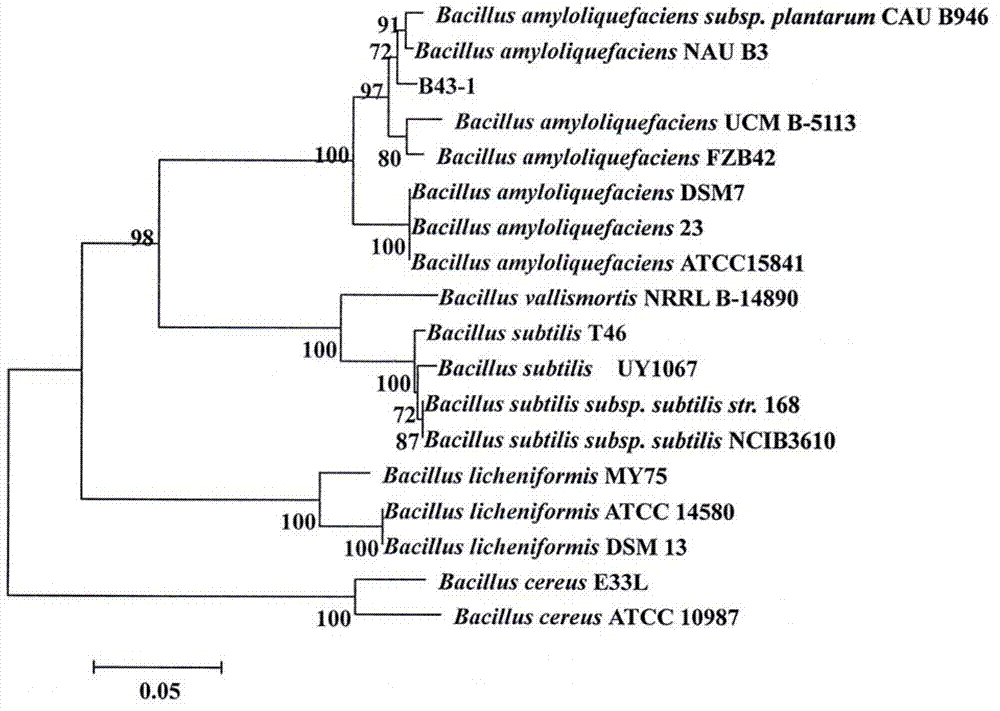
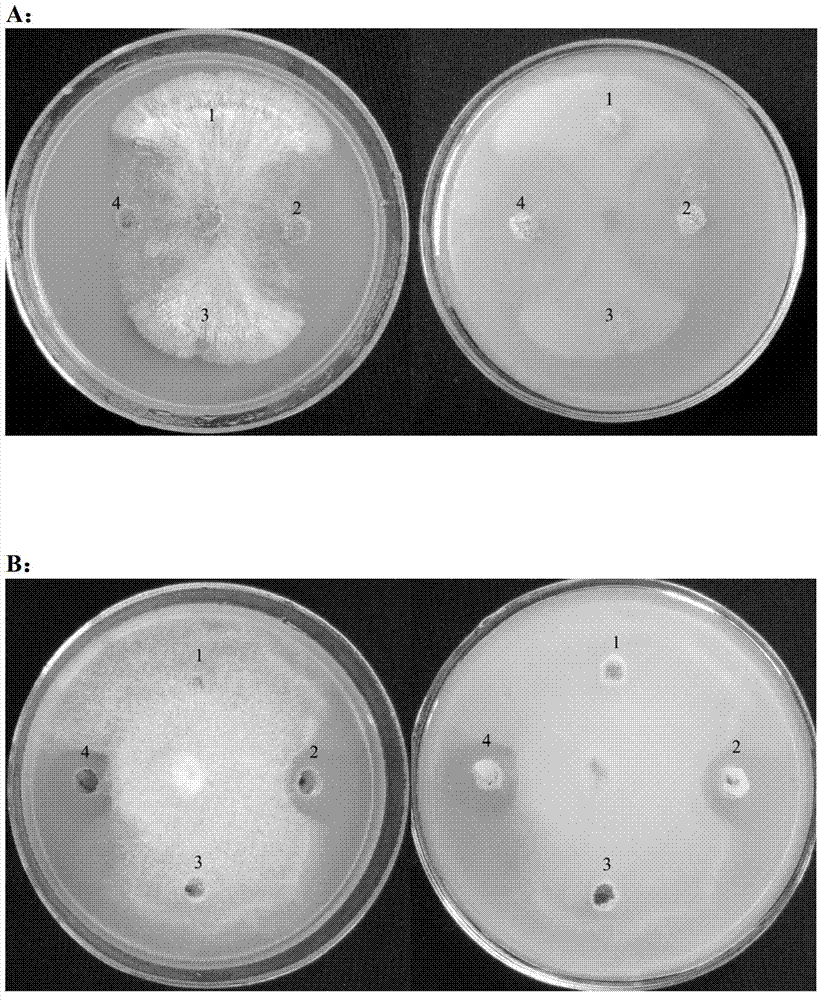
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and application thereof
InactiveCN102776146ASignificant effect of pollution diseaseGood prospects for the development of biopesticidesBiocideBacteriaPlant diseaseFermentation
The invention discloses a bacillus amyloliquefaciens B43-1. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens B43-1 is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CCMCC) on June 8th, 2012; and the preservation number is CCMCC No.6212. A fermentation supernate of the bacillus amyloliquefaciens B43-1 can inhibit edible mushroom diseases caused by multiple pathogenic funguses such as Cladobotryum varium Nees, mucor, trichoderma, neurospora crassa and the like. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens B43-1 is nontoxic and environment-friendly to people and livestock, has a remarkable preventioneffect on edible mushroom pollution diseases, and has better biopesticide development prospects.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Loach fry cultivation method
ActiveCN103828750AMeet nutritional needsPromote growthClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffYolkPrawn
The invention discloses a loach fry cultivation method. In April in spring, when a natural water body is higher than 18 DEG C in temperature, mature loaches which are regular in body form, strong in physique, much in mucus, healthy and scot-free are used as parents; LRH-A2 and DOM are used for hastening parturition; incubating is carried out at the water temperature which is 25 DEG C after oviposition, and loach fry cultivation is carried out after yolk sacs of most fries are basically disappeared after loach fry incubation; the loach fries are transferred to a pond to conduct cultivation according to a conventional summer fingerling cultivation technology after cultivation is carried out for seven days. According to the loach fry cultivation method, mixed feeding is carried out with yolk liquid and juvenile prawn mixed feed, the nutritional requirement of the mouth-opening periods of the loach fries is met, the loach fries rapidly grow, the complex process of rotifer cultivation is eliminated, the whole cultivation process is easy to operate, the labor amount is greatly reduced, meanwhile, the loach fry pond entering cultivation specification is increased, and the fry cultivation survival rate is improved.
Owner:HUAIYIN TEACHERS COLLEGE
Seedling culture method for fresh water pearl culturing clam
InactiveCN101120665AImprove survival rateLow priceClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaFresh water organismGlochidium
The present invention relates to a spat-cultivating method of the freshwater pearl mussel, which belongs to the technical field of the aquatic spat cultivation. The present invention is characterized in selecting the tilapia; the tilapia is temporarily cultivated after immersed in the sodium chloride solution; taking off the outer gill lamella on both sides of the mature mother mussel to put into a container having the water, moving aside the branchial filament with a pin and filtering the gills and the mucus in the water with a bolting silk to separate the lumpish glochidium; putting the temporarily-cultivated tilapia into a parasitic water body and then put into a temporarily-cultivated cylinder to cultivate, the glochidia completes the transformation and the larva mussel completes the shedding. The present invention selects the tilapia having a strong adversity resistance as the parasitic fish for the freshwater cultivated pearly mussel to realize the parasitic transformation and development process of the gloachidia; the parasitic quantity is large; the survival rate of the tilapia is very high in the parasitic period; in addition, the price of the tilapia is low, which can reduce the spat cultivation cost; the present invention has a favorable economic benefit in the freshwater mussel large-scale spat breeding process.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Method for extracting mucus protein of purple common yam rhizomes
InactiveCN104004079APreserve integrityNo chemical residuePeptide preparation methodsPlant peptidesAlpha-amylaseRhizome
The invention discloses a method for extracting mucus protein of purple common yam rhizomes. The method comprises the following steps that first, the purple common yam rhizomes are processed to be fine powder which is soaked, and then water is dried to be removed; second, the powder of the purple common yam rhizomes is placed in a supercritical carbon dioxide extraction kettle to be extracted, residues are obtained, extraction comprises two stages which are conducted before and after every time, the extraction at the first stage is conducted for one hour under the pressure being 41-43 MPa and the temperature being 45-50 DEG C, wherein the flow rate of carbon dioxide is 10-20 kg / h, and the extraction at the second stage is conducted for 2.5-3.5 hours under the pressure being 43-45 MPa and the temperature being 42 DEG C, wherein the flow rate of the carbon dioxide is 10-20 kg / h; third, the obtained residues are soaked again, high-temperature resistance alpha-amylase is added, injection and liquefaction are conducted, then cooling is conducted, and filtering is conducted to obtain clear liquid; fourth, the obtained clear liquid is purified by a lectin resin column, and the mucus protein of the purple common yam rhizomes can be obtained after elution.
Owner:黄香利
Method for improving fruit-bearing rate of almond apricot and armeniaca
InactiveCN101292616AImprove fruit setting rateIncrease productionFertilising methodsCultivating equipmentsFruit setPollen
The invention provides a method for improving the fruit setting rate of almond apricot and prunus dulcis; the method is characterized in that: step I: an orchard is watered 3 days to 10 days before the florescence when the almond apricot and prunus dulcis enter the stage of blooming and fruit setting, irrigating 40t to 80t for each 667 m<2> (1mu is approximately equal to 667m<2>), to increase the secretory mucus of a flowering chapiter and improve the developmental rate of pollen on the flowering chapiter so as to raise the fruit setting rate; step II, 2 kg to 5 kg of mixed aqueous solution of urea, borax and gibberellin is sprayed to each almond apricot and prunus dulcis 3 days to 10 days before the florescence when the almond apricot and prunus dulcis enter the stage of blooming and fruit setting; step III, artificial pollination is conducted, 1 to 2 varieties of pollen appropriate to pollination are collected for artificial pollination. The method of the invention adopts plant growth regulators and artificial pollination technology in the orchards of the almond apricot and prunus dulcis that enter the stage of fruit setting, greatly improves the fruit setting rate of the almond apricot and prunus dulcis and ensures the high and stable yield of the almond apricot and prunus dulcis, thereby promoting the economic benefits of orchards.
Owner:CHINA PAULOWNIA RES CENT
Preparation method of banana extract for fermented cigarette
ActiveCN103146478ASpeed up filteringImprove qualityTobacco treatmentEssential-oils/perfumesMicroorganismFlavor
The invention provides a preparation method of a banana extract for fermented cigarette, belongs to the technical field of tobacco and relates to a preparation method of a tobacco flavor. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) preparation of a culture medium, 2) inoculation, 3) fermentation and 4) separation to obtain the banana extract for fermented cigarette. According to the invention, the banana extract for fermented cigarette is produced by use of a compound bacteria preparation of mucor and rhizopus; the prepared banana extract for fermented cigarette has the characteristic aroma of banana as well as a pleasant sour aroma; and by adding the banana extract into cigarette, the fresh and sweet aroma is increased, the smoke is moderated and the irritation of cigarette is reduced. According to the invention, the tobacco flavor is produced by a microorganism fermentation technology, a way of economically and efficiently producing the natural tobacco flavor in an oriented manner is opened, a novel tobacco flavor that cannot be produced by a traditional flavor production method is developed, and the varieties of the tobacco flavor are increased.
Owner:HUBEI CHINA TOBACCO IND +1
Probiotic strains, a process for the selection of them, compositions thereof, and their use
The present invention relates to a novel process for the selection of new probiotic strains which comprises the following steps: a) selecting for non-pathogenic strains which are capable of surviving in breast milk and / or amniotic fluid, and b) selecting for non-pathogenic strains which are able to be transferred to breast milk and / or amniotic fluid after oral intake in healthy individuals without colonizing other internal organs except mucousas. The invention also provides new Lactobacillus strains, which are: CECT5711 (Lactobacillus coryniformis), CECT5713 (Lactobacillus salivarius subsp. salivarius), CECT5714: (Lactobacillus gasseri, formerly L. acidophilus), CETC5715: (Lactobacillus gasseri), and CECT5716: (Lactobacillus fermentum); and refers to their use for the prophylaxis or treatment against digestive, infective, neuro-degenerative and immune related diseases such as allergies or inflammatory diseases.
Owner:BIOSEARCH SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com