Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
949 results about "Anesthetic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
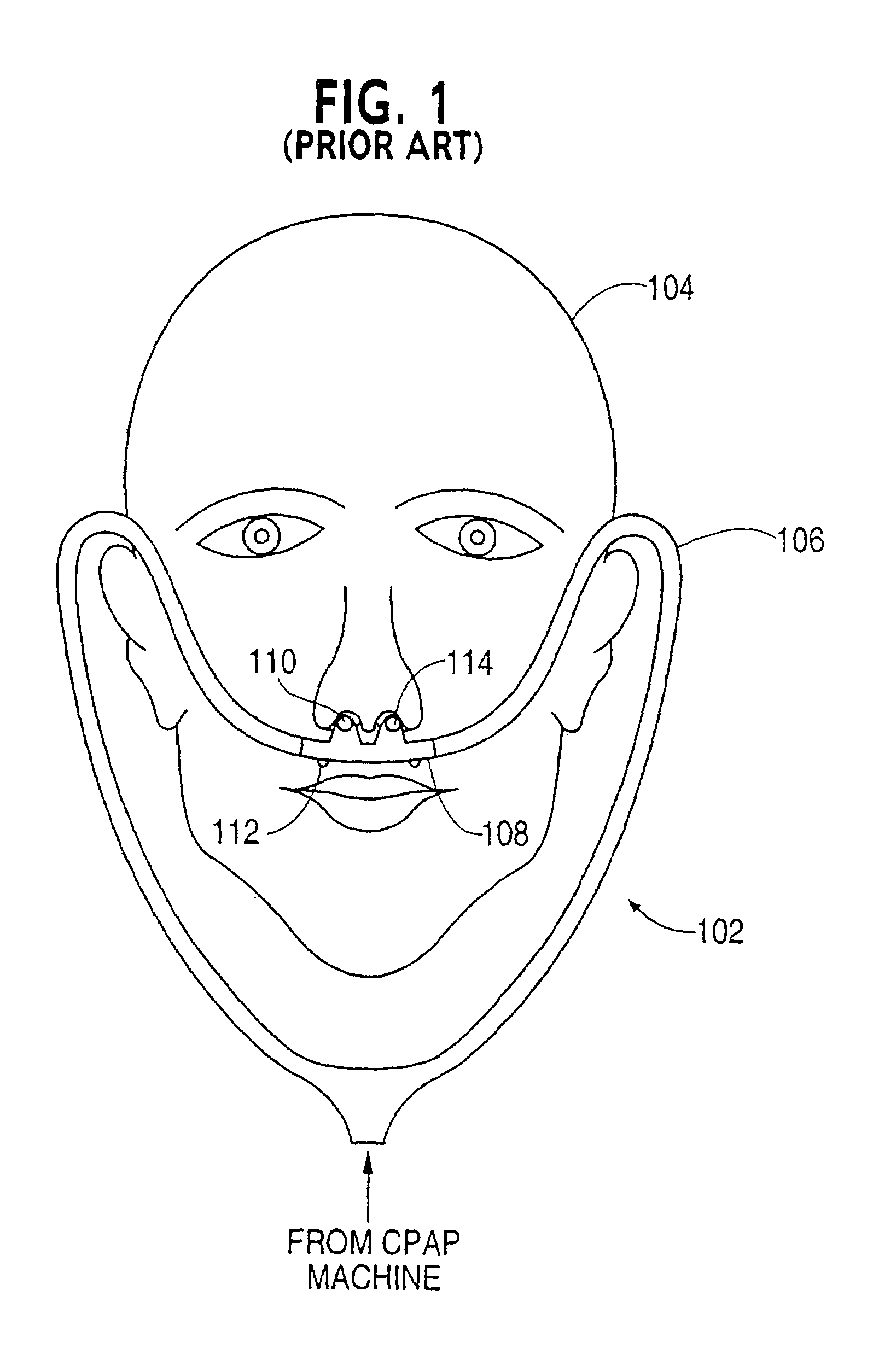
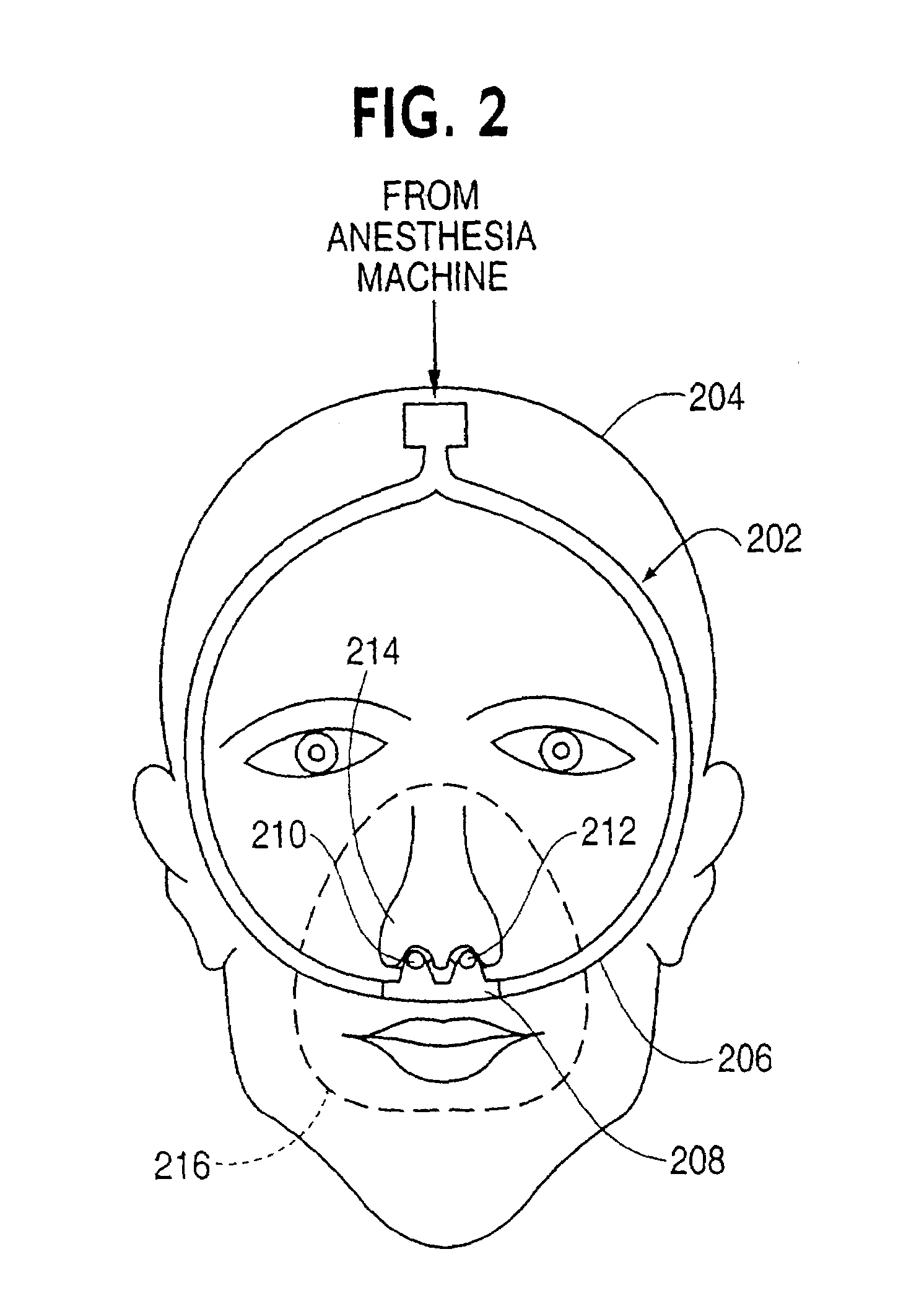
An anesthetic (American English) or anaesthetic (British English; see spelling differences) is a drug used to induce anesthesia — in other words, to result in a temporary loss of sensation or awareness. They may be divided into two broad classes: general anesthetics, which result in a reversible loss of consciousness, and local anesthetics, which cause a reversible loss of sensation for a limited region of the body without necessarily affecting consciousness.
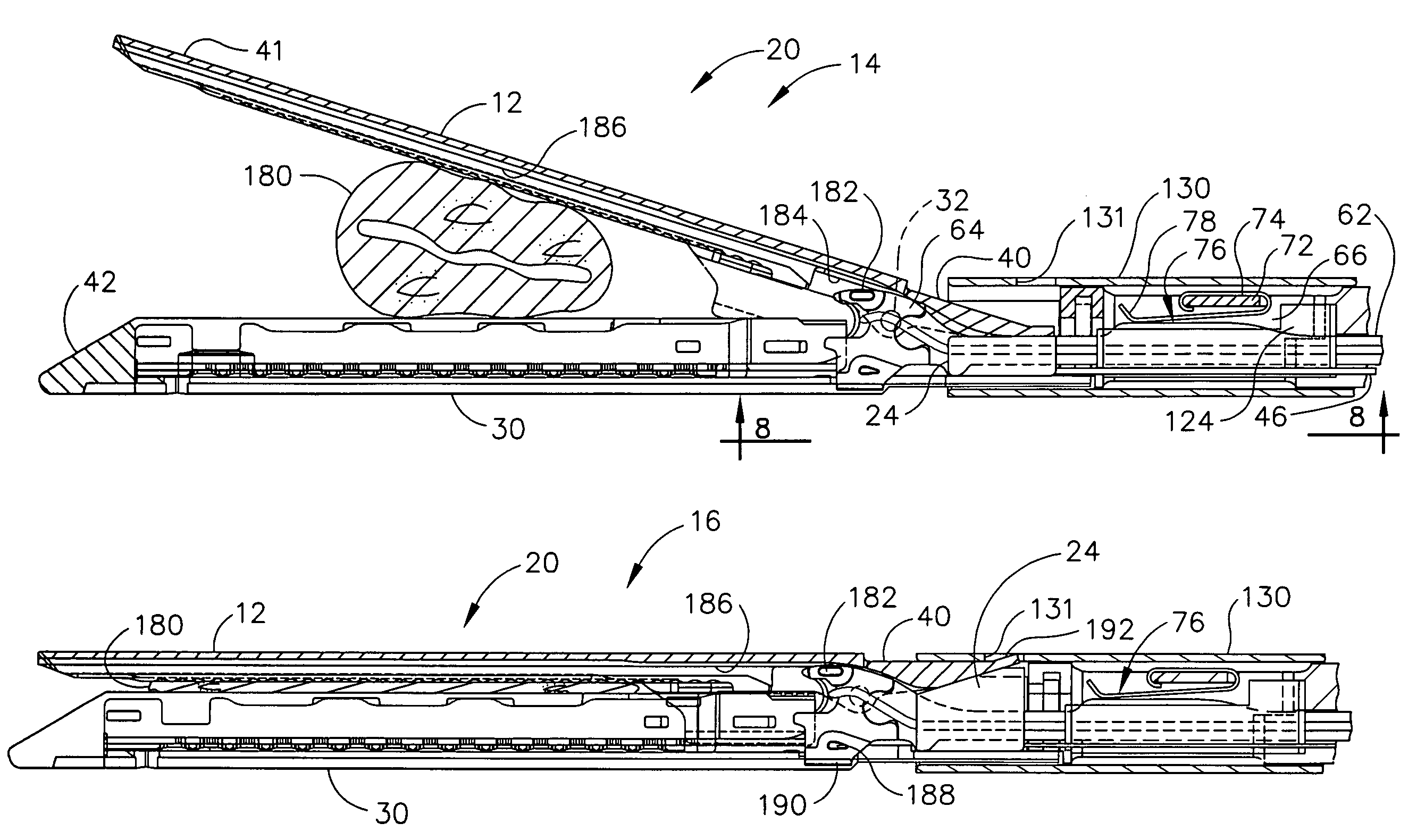
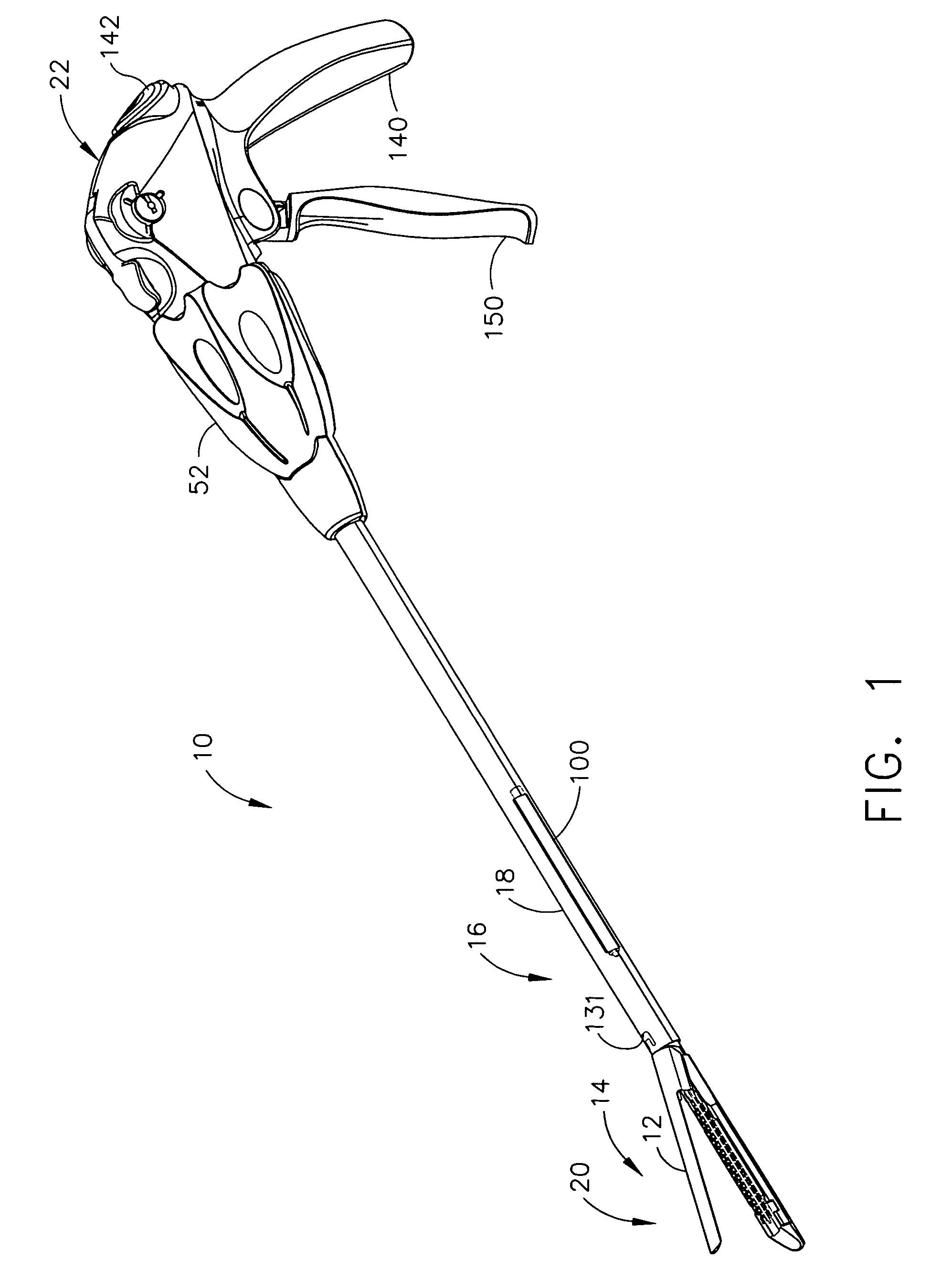
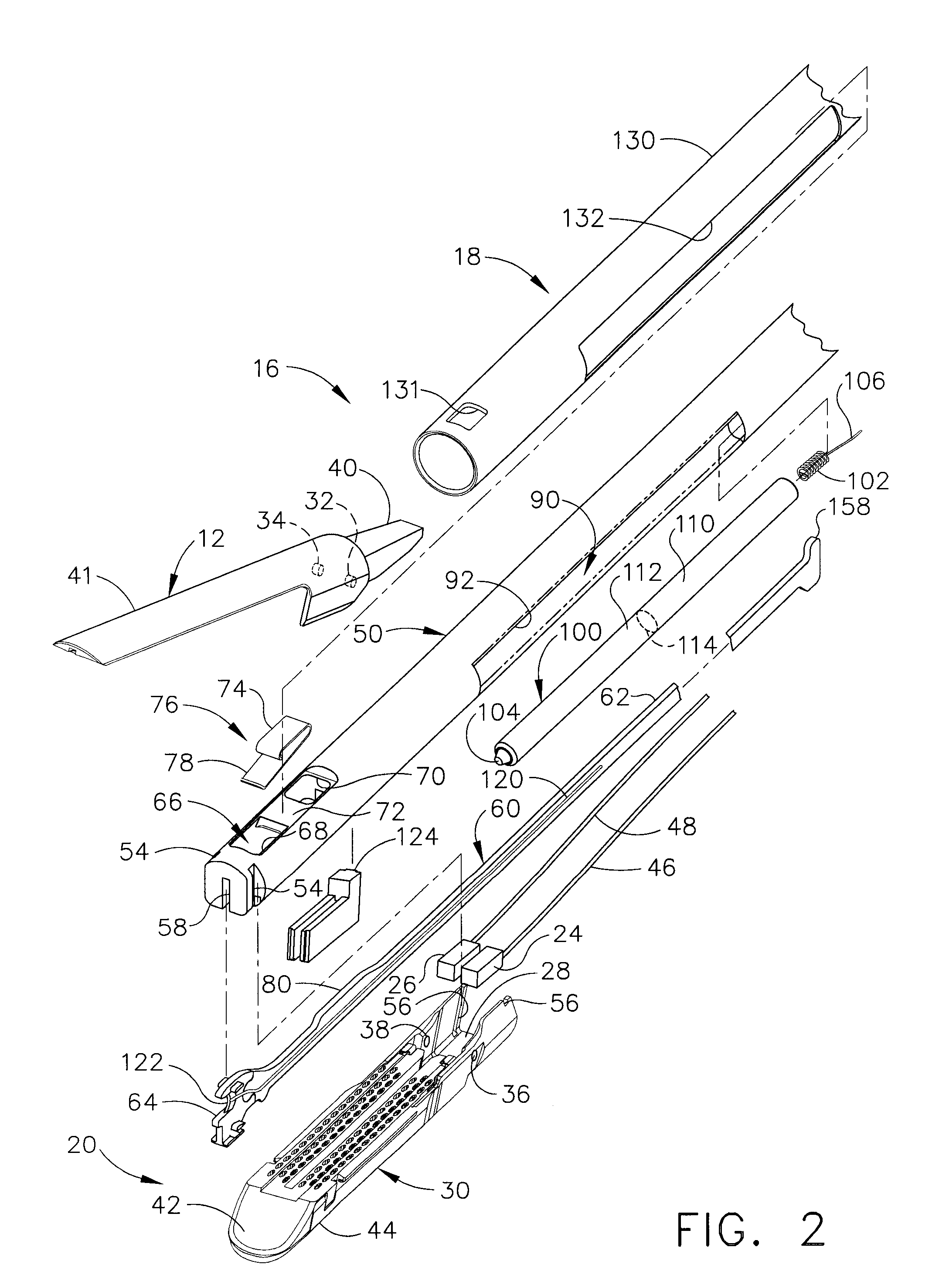
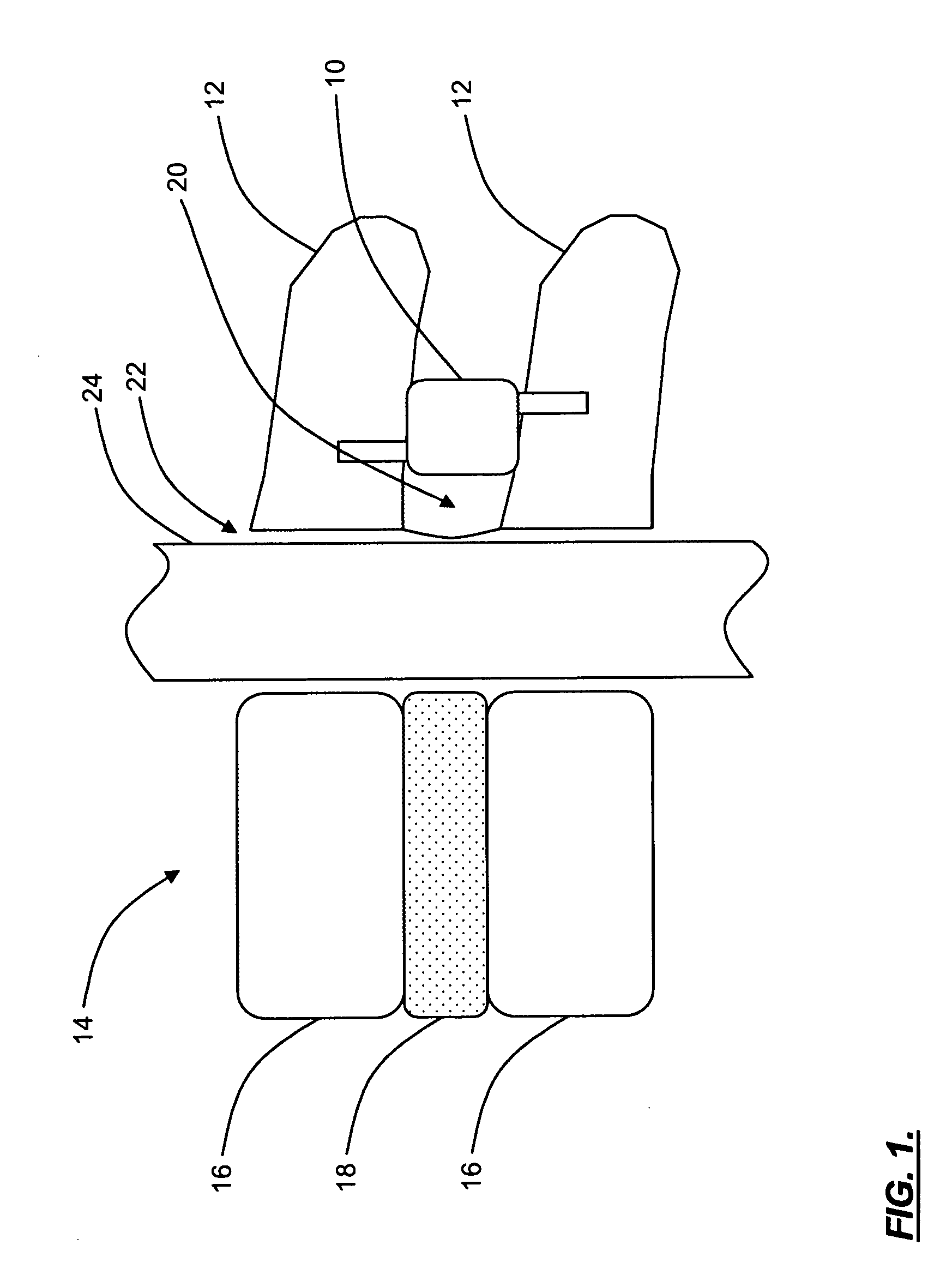
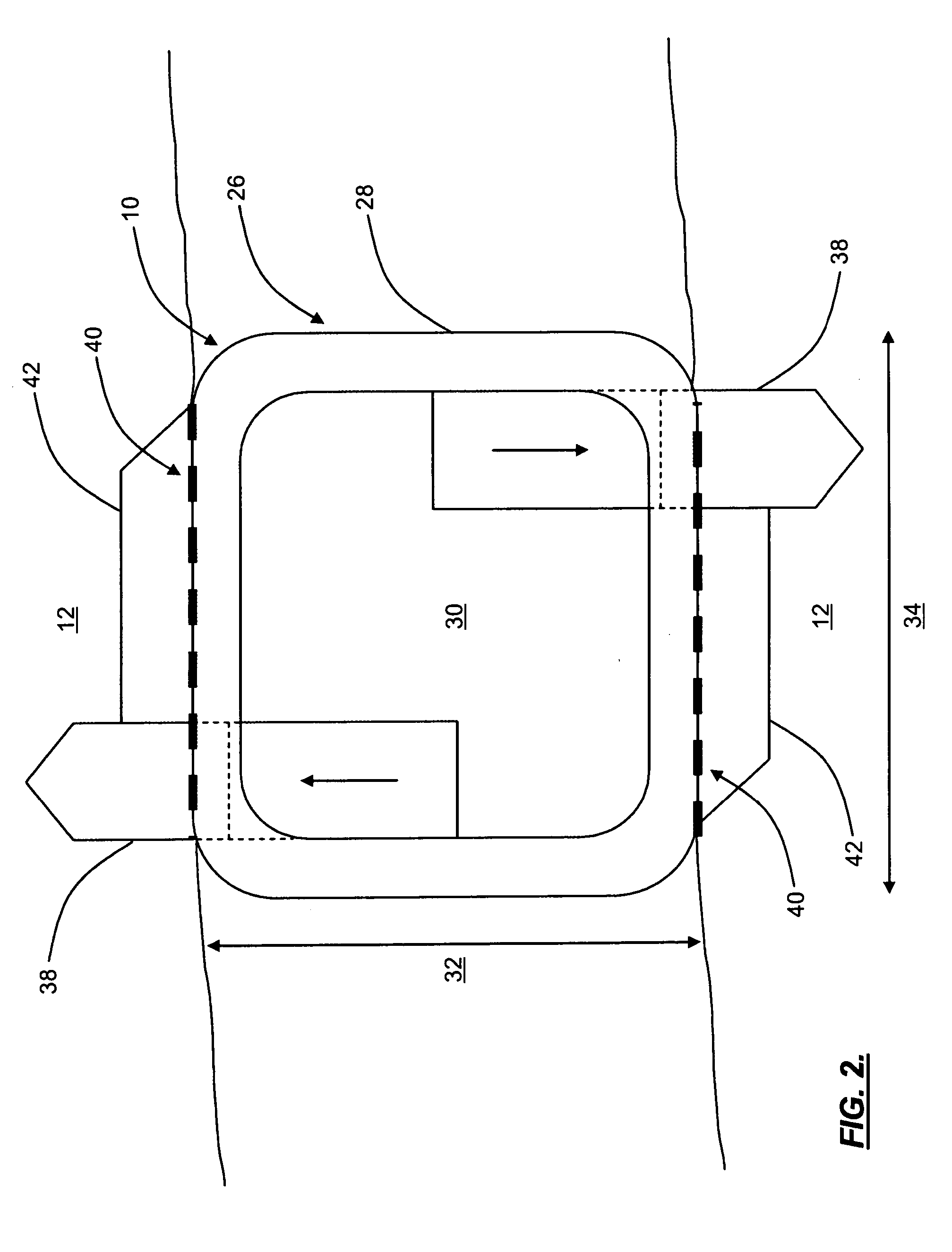
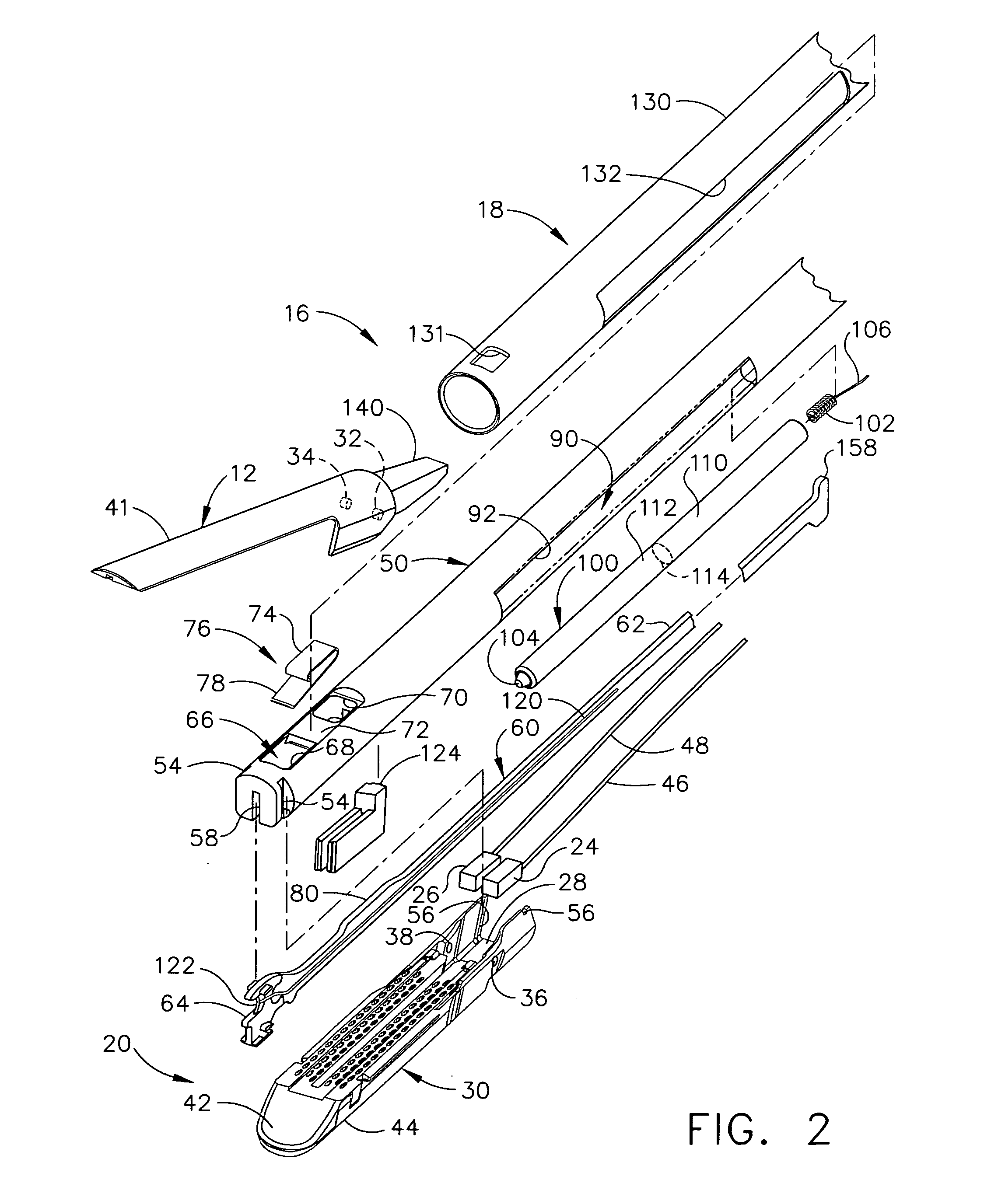
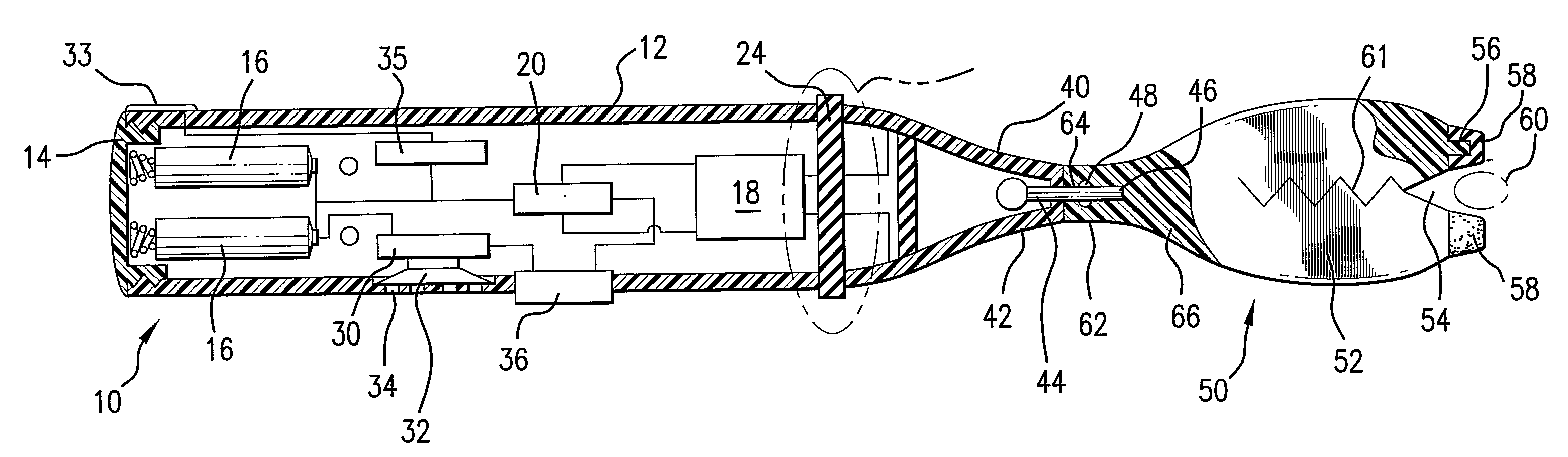
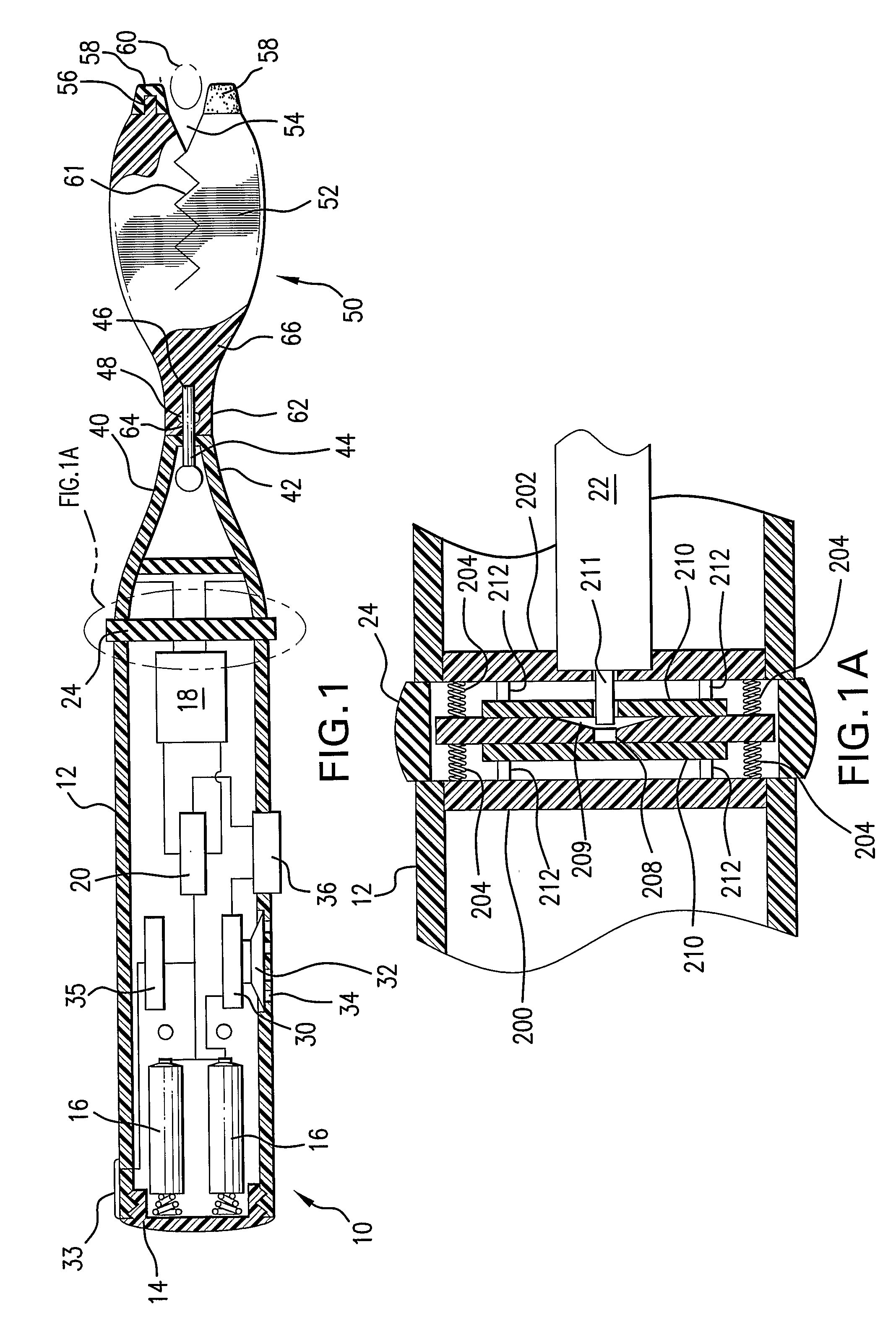
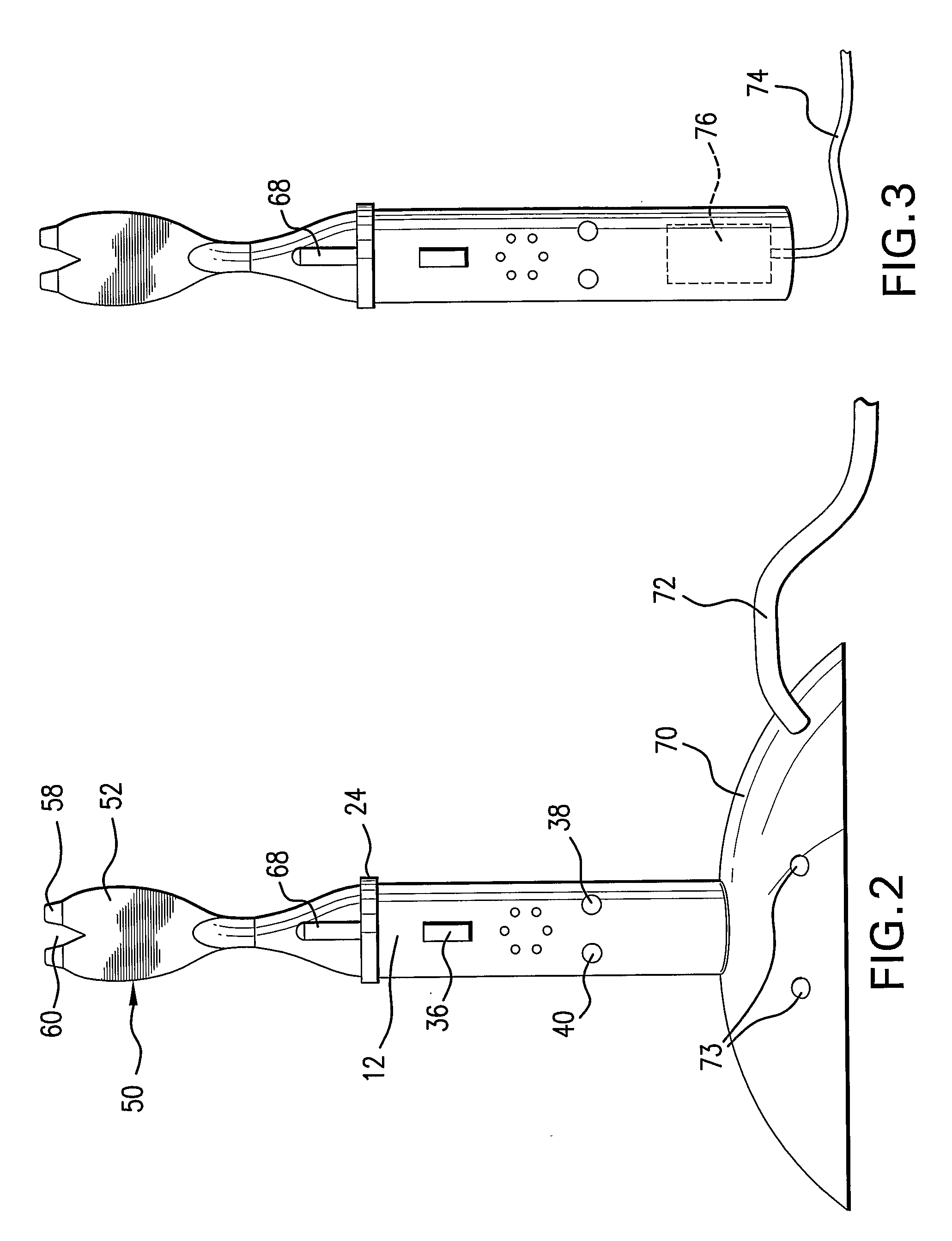
Surgical instrument having fluid actuated opposing jaws
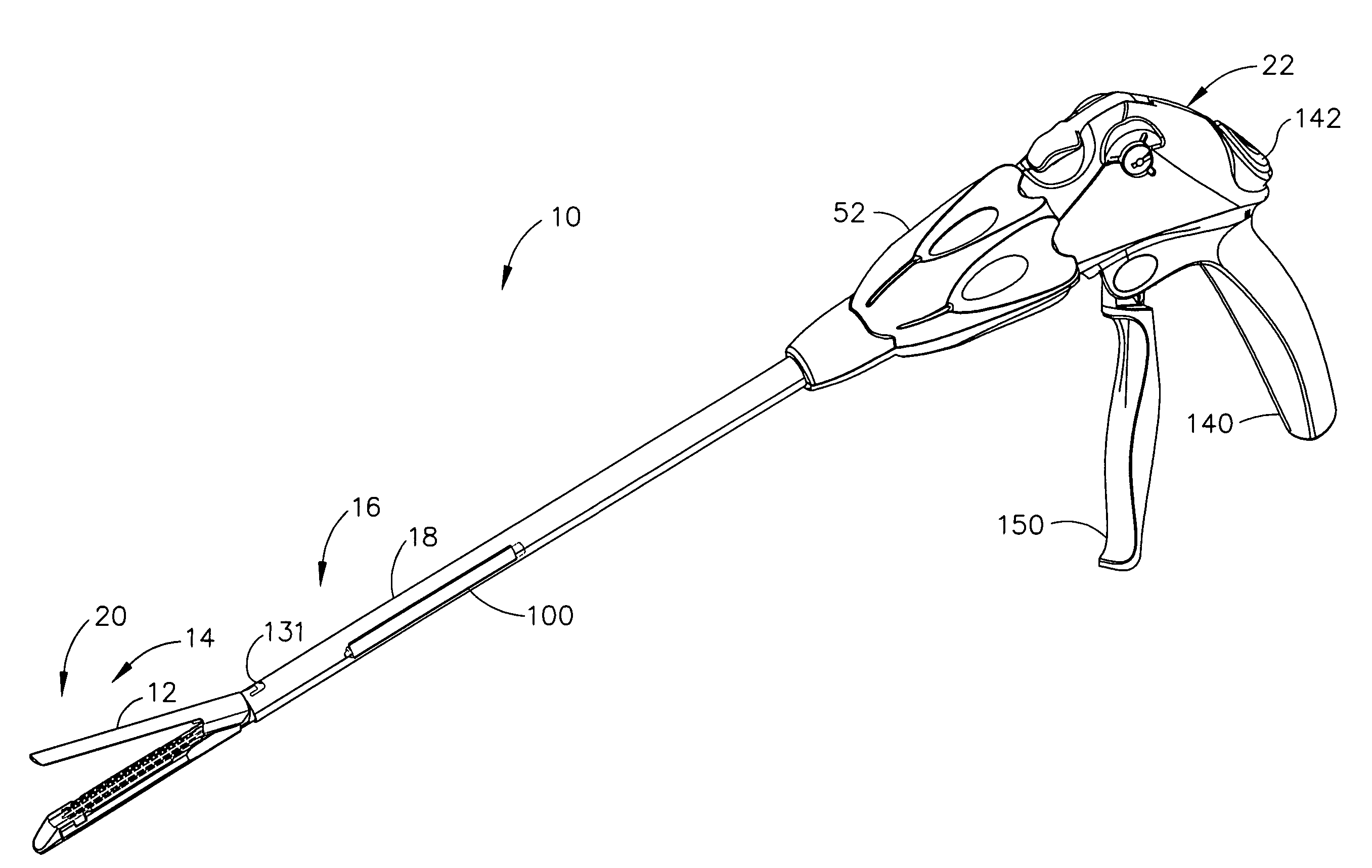
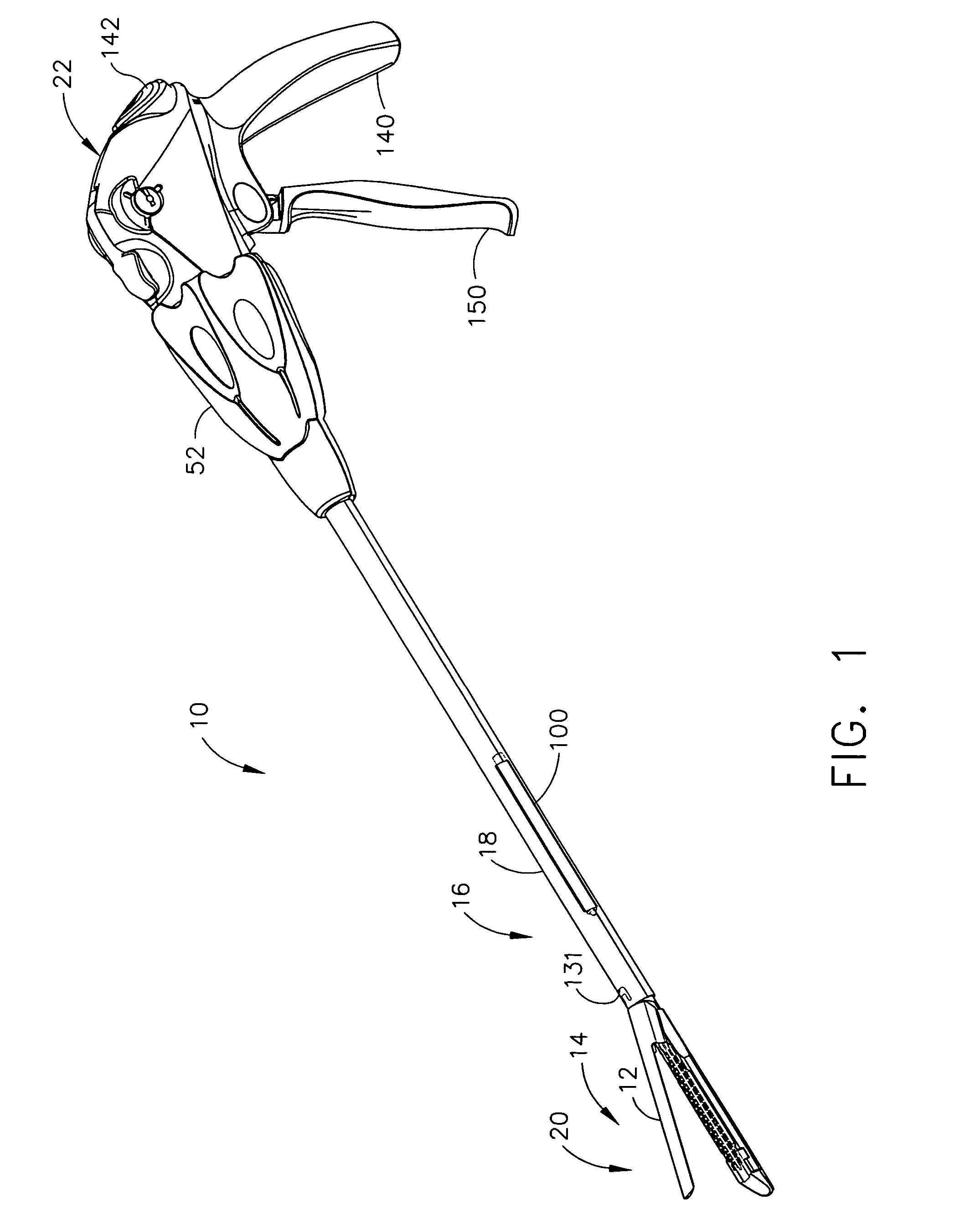
A surgical stapling and severing instrument enables minimally invasive surgical procedures by having upper and lower jaws (i.e., anvil and staple channel) that are positioned with an elongate shaft and handle through surgical openings, and in particular through a cannula of a trocar. A pair of fluid actuator bladders (lift bags) are positioned in the staple channel beneath a proximally projecting lever tray so that transfer of fluid from the handle causes closing and clamping of the anvil. The bi-directional fluid control may be mechanically produced at the handle or by activating an electroactive polymer actuator. Once firing is sensed, an EAP plunger in a medical substance syringe inserted into the elongate shaft is activated to dispense a medical substance (e.g., anesthetics, adhesives, cauterizing substances, antibiotics, etc.) and is guided along a firing bar to a cutting surface of an E-beam placing the substance on tissue as severed.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Interspinous distraction devices and associated methods of insertion
In various exemplary embodiments, the present invention provides a plurality of novel interspinous distraction devices and associated methods of insertion. The interspinous distraction devices of the present invention are designed and configured to effectively treat such conditions as lumbar spinal stenosis and degenerative disc disease. Advantageously, the interspinous distraction devices of the present invention may be inserted through conventional open procedures, typically requiring a relatively large incision and a general anesthetic, or through novel minimally-invasive procedures, typically requiring only a local anesthetic. These novel minimally-invasive procedures and related enabling devices are also disclosed and described herein.
Owner:ZIMMER BIOMET SPINE INC
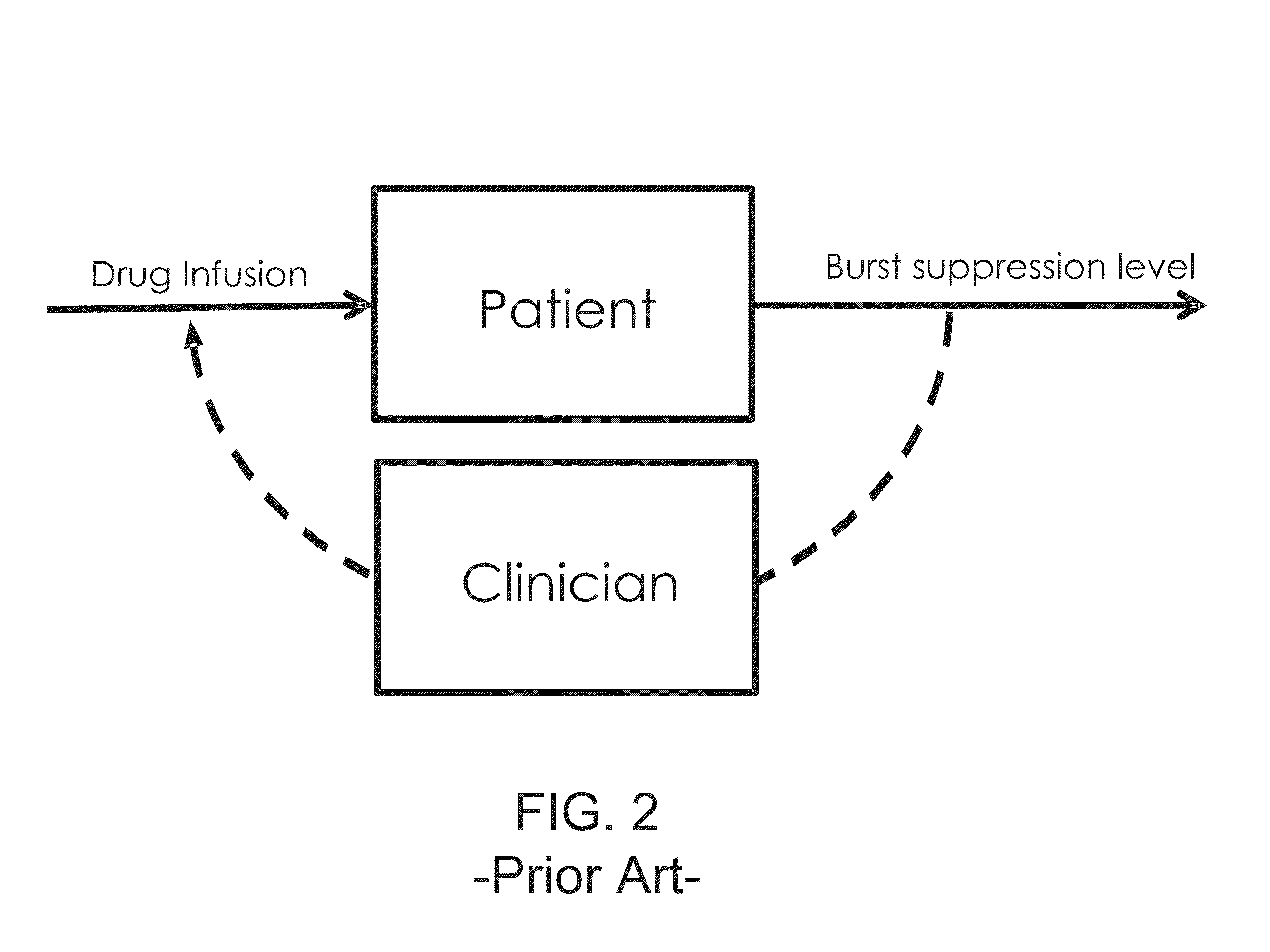
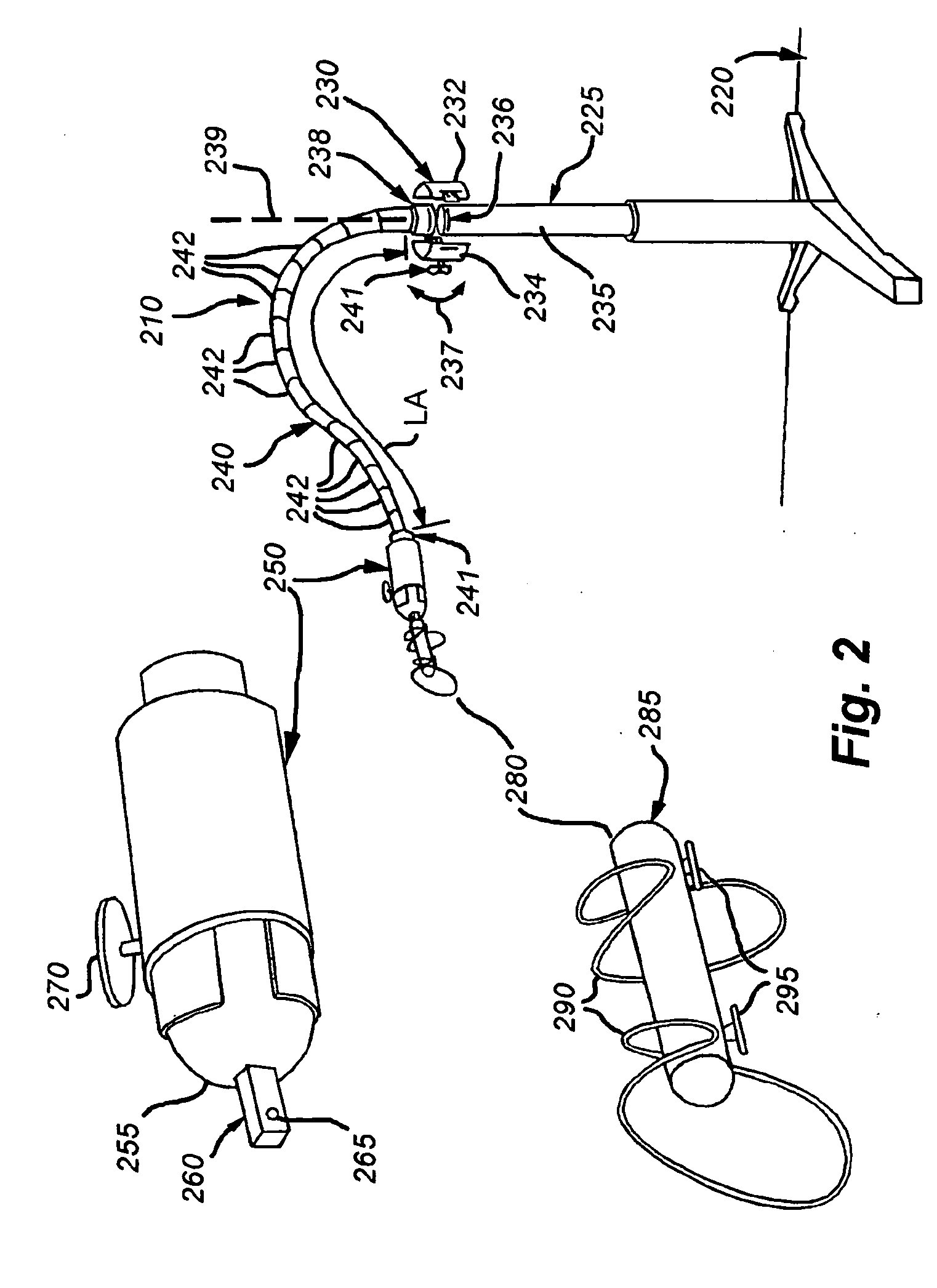
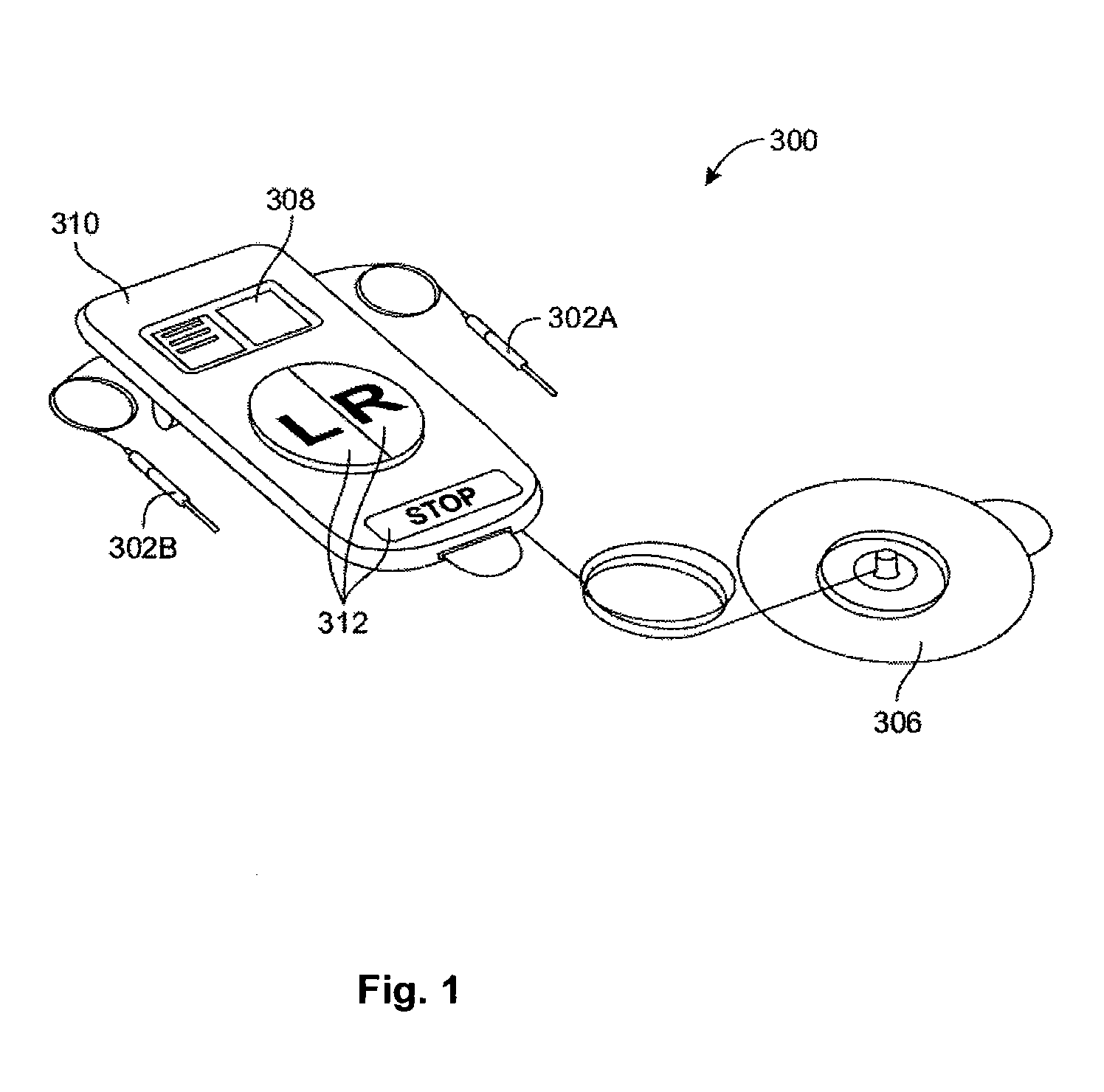
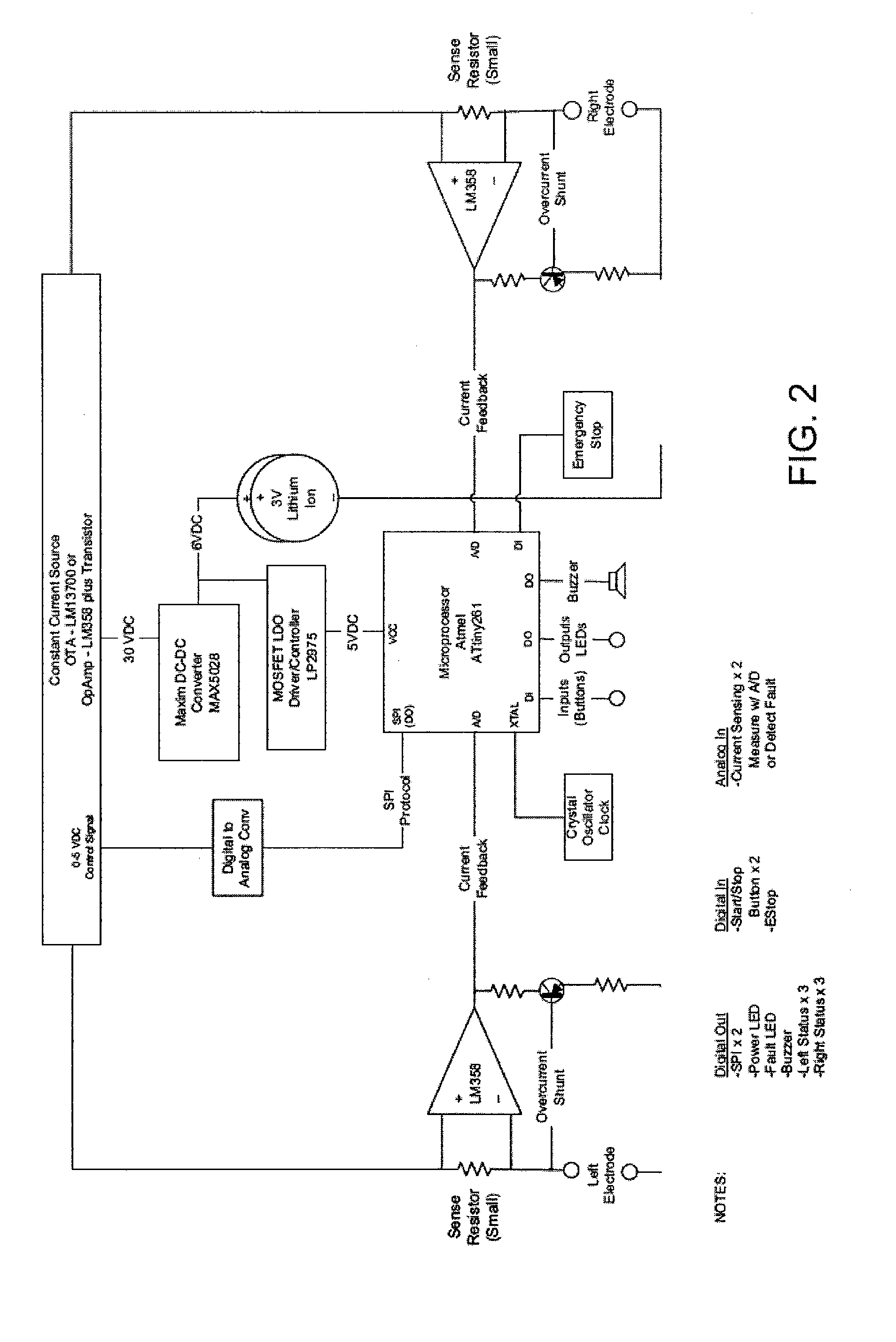
System and method for monitoring and controlling a state of a patient during and after administration of anesthetic compound
A system and method for monitoring and controlling the administration of at least one drug having anesthetic properties are provided. The method includes arranging a plurality of sensors configured to acquire physiological data from a patient and reviewing the physiological data from the plurality of sensors and an indication from a user interface. The method also includes assembling the physiological data into sets of time-series data and analyzing the sets of time-series data to determine signature profiles consistent with the administration of at least one drug. The method further includes identifying, using signature profiles, at least one of a current state and a predicted future state of the patient, controlling the administration of the least one drug to attain the predicted future state, and then generating a report including information regarding at least one of the current state and the predicted future state of the patient induced by the drug.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Medical and dental implant devices for controlled drug delivery
Implantable devices and methods for use in the treatment of osteonecrosisare provided. The device includes at least one implant device body adapted for insertion into one or more channels or voids in bone tissue; a plurality of discrete reservoirs, which may preferably be microreservoirs, located in the surface of the at least one implant device body; and at least one release system disposed in one or more of the plurality of reservoirs, wherein the release system includes at least one drug selected from the group consisting of bone growth promoters, angiogenesis promoters, analgesics, anesthetics, antibiotics, and combinations thereof. The device body may be formed of a bone graft material, a polymer, a metal, a ceramic, or a combination thereof. The device body may be a monolithic structure, such as one having a cylindrical shape, or it may be in the form of multiple units, such as a plurality of beads.
Owner:MICROCHIPS INC
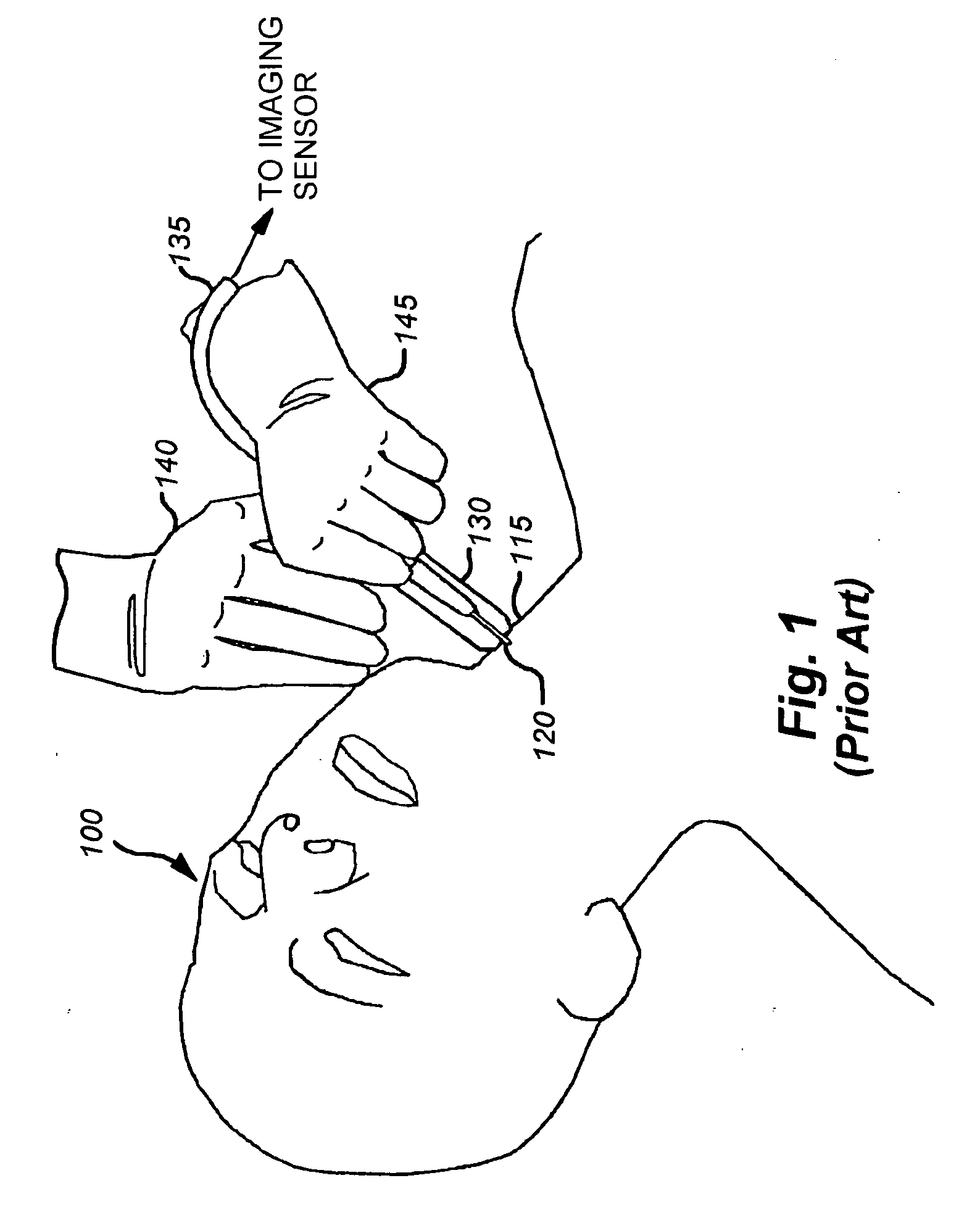
Method and device for painless injection of medication
InactiveUS7637891B2Simple and inexpensive to performSimple and inexpensive to and operateAmpoule syringesAutomatic syringesMedication injectionMedical treatment
A device for painlessly injecting medications, and a method for providing a substantially painless injection of medication into a patient that does not require the use of an anesthetic, that does not require the medical personnel to spend a substantial amount of time performing the injection procedure, that is relatively simple and inexpensive to perform and operate, and that provides a relatively high degree of safety for both the medical personnel and for the patient. The injection needle can have an outside diameter greater than 0.20 mm and less than about 0.38 mm. The medicament can be injected painlessly through the needle and into the patient at a substantially constant volumetric flow rate of about 0.05 μL / s to about 50 μL / s.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT CINCINNATI
Regional anesthetic
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Surgical instrument having fluid actuated opposing jaws
A surgical stapling and severing instrument enables minimally invasive surgical procedures by having upper and lower jaws (i.e., anvil and staple channel) that are positioned with an elongate shaft and handle through surgical openings, and in particular through a cannula of a trocar. A pair of fluid actuator bladders (lift bags) are positioned in the staple channel beneath a proximally projecting lever tray so that transfer of fluid from the handle causes closing and clamping of the anvil. The bi-directional fluid control may be mechanically produced at the handle or by activating an electroactive polymer actuator. Once firing is sensed, an EAP plunger in a medical substance syringe inserted into the elongate shaft is activated to dispense a medical substance (e.g., anesthetics, adhesives, cauterizing substances, antibiotics, etc.) and is guided along a firing bar to a cutting surface of an E-beam placing the substance on tissue as severed.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
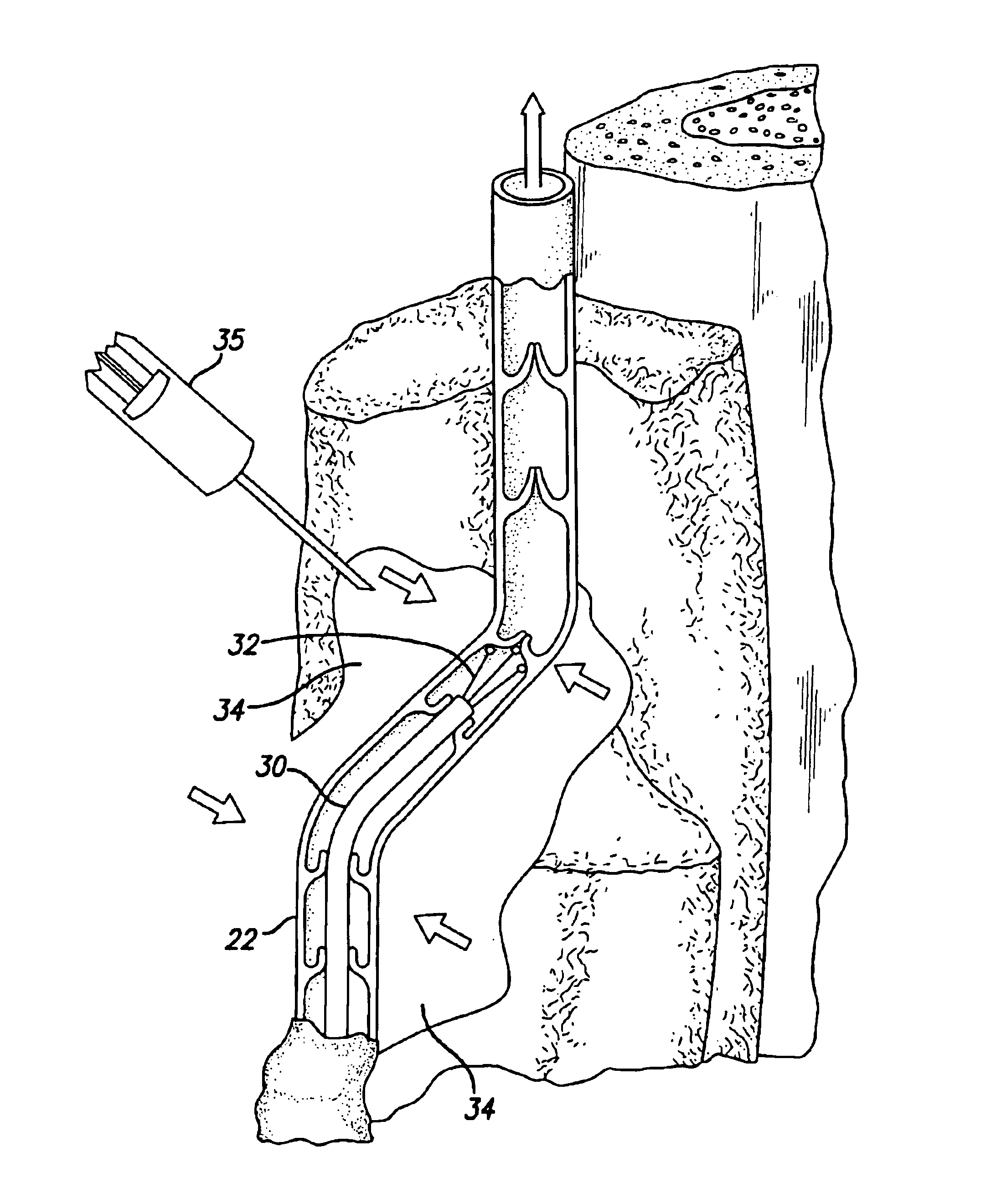
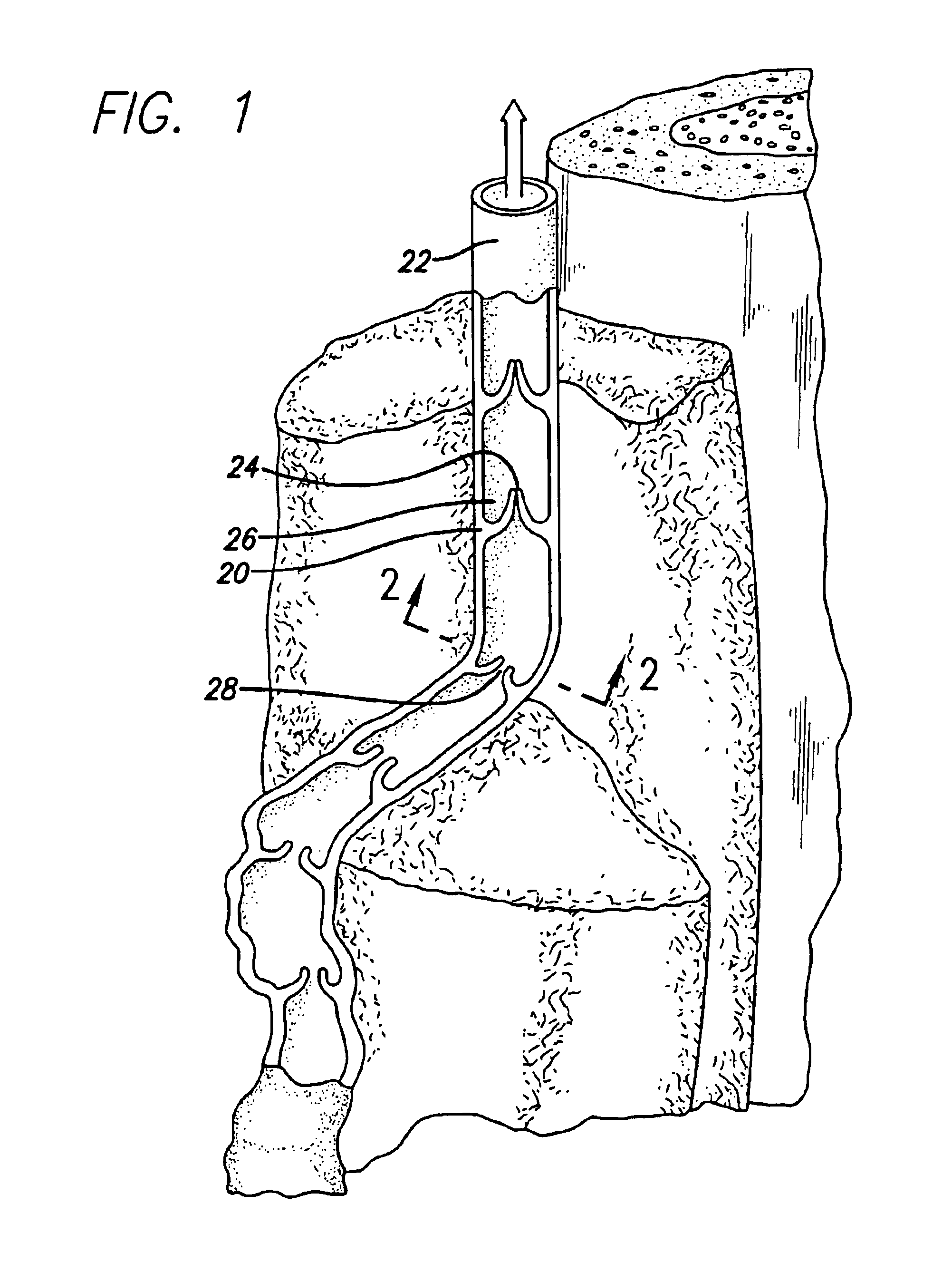
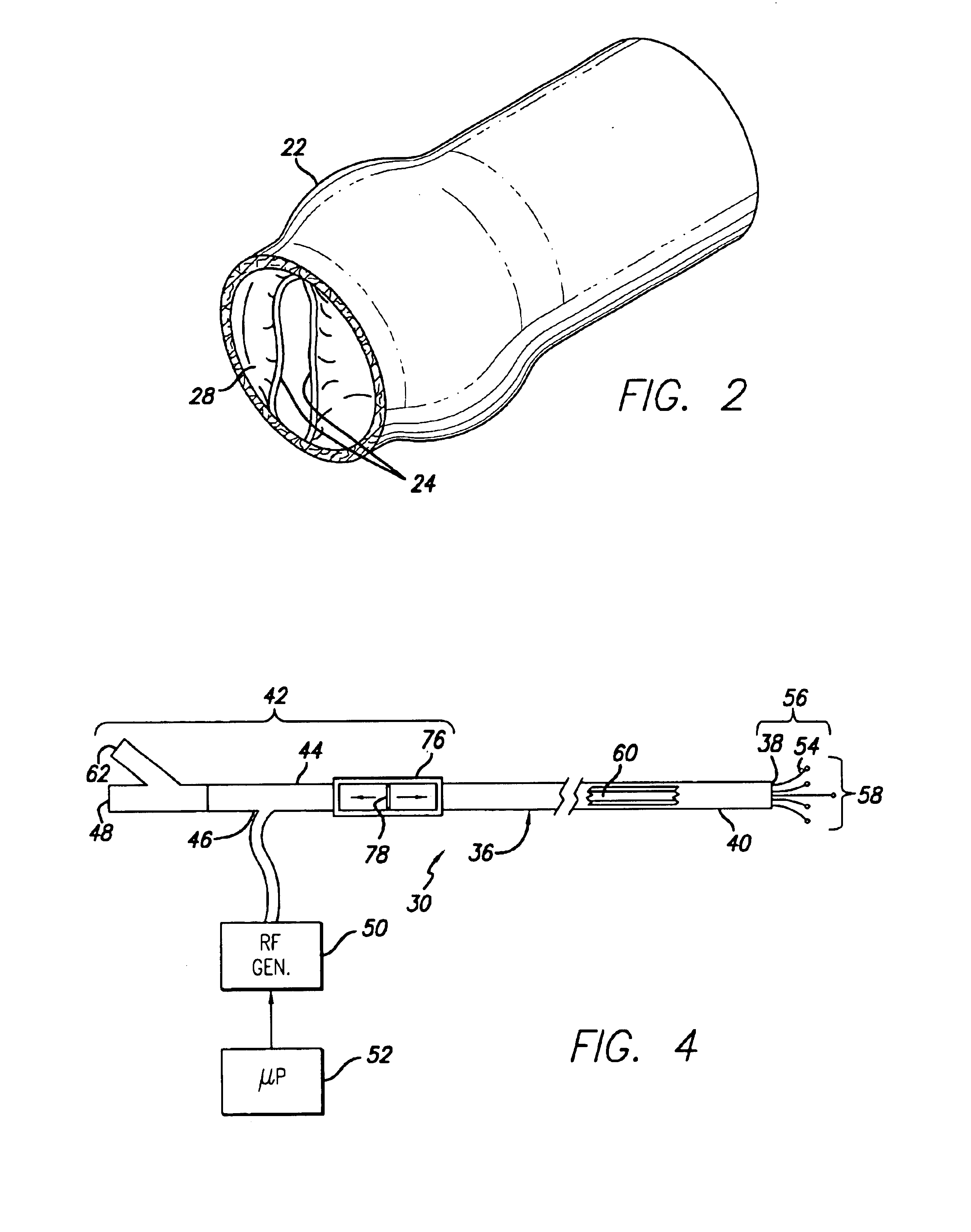
Apparatus for applying energy to biological tissue including the use of tumescent tissue compression
InactiveUS6969388B2Inhibition formationGood effectStatic indicating devicesDiagnosticsAnatomical structuresTumescence
An electrode catheter is introduced into a hollow anatomical structure, such as a vein, and is positioned at a treatment site within the structure. Tumescent fluid is injected into the tissue surrounding the treatment site to produce tumescence of the surrounding tissue which then compresses the vein. The solution may include an anesthetic, and may further include a vasoconstrictive drug that shrinks blood vessels. The tumescent swelling in the surrounding tissue causes the hollow anatomical structure to become compressed, thereby exsanguinating the treatment site. Energy is applied by an electrode catheter in apposition with the vein wall to create a heating effect. The heating effect causes the hollow anatomical structure to become molded and durably assume the compressed dimensions caused by the tumescent technique. The electrode catheter can be moved within the structure so as to apply energy to a large section of the hollow anatomic structure. In a further aspect, the location of the electrodes is determined by impedance monitoring. Also, temperature sensors at the treatment site are averaged to determine the site temperature.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Controlled-release nano-diffusion delivery systems for cosmetic and pharmaceutical compositions
InactiveUS20040208902A1High affinityLimited surface areaBiocideCosmetic preparationsAntioxidantAdditive ingredient
The present invention discloses the utilization of zeolites for controlled-release of cosmetic and pharmaceutical compositions by nano-diffusion technology. The treatment and protection of skin surface requires that certain compositions be delivered to the skin surface and allowed to remain on the skin surface for as long as possible before such ingredients are absorbed into deeper layers of skin and carried into the bloodstream. Zeolites do not absorb into the skin, which is useful for topical delivery of cosmetic and pharmaceutical compositions, for example antiaging, anti-wrinkle, antioxidants, skin whitening, acne treatment, rosacea treatment, sun screens, UV blocks, anesthetics, skin soothers, anti-irritants, anti-inflammatory agents, vitamins, hormones, and such that are electronically attached to the outer surfaces of such zeolites and are released to the outer surface of skin by a diffusion-controlled thermodynamic process.
Owner:GUPTA SHYAM K
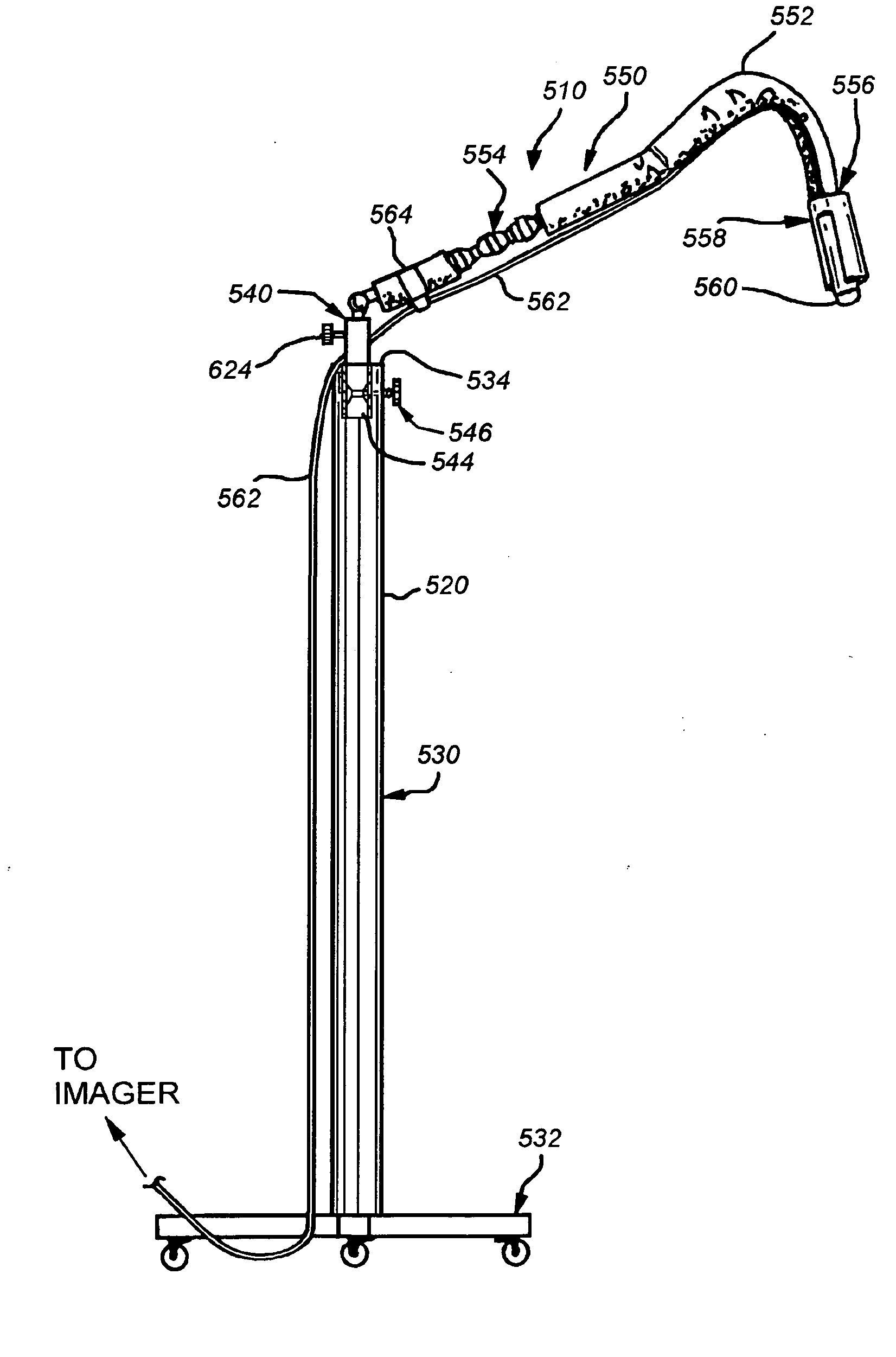
Biomedical positioning and stabilization system
InactiveUS20070129634A1Minimal effortGood flexibilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesAnatomical structuresPrimary operation
This invention provides a support device that allows the adjustable, yet rigid placement of a probe or other medical instrument against a region of interest / treatment on a patient. The system and method of rigid fixation, positioning, and adjustment contemplated herein is useful for a broad array of medical procedures including, but not limited to, ultrasound-guided anesthetic delivery. In an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, a flexible armature is attached to a rigid stand placed upon the floor, or attached to another stable surface such as a bed rail, wall, ceiling or piece of equipment. A joint connects the armature to an instrument holder able to accommodate and rigidly attach an ultrasound sensing probe or other medical device. The medical device then remains rigidly attached to the described invention during the procedure. Furthermore, this set position is resistant to minor patient motion or other disturbances. If required, small alterations can be made by the operator during the procedure with minimal effort. Such adjustment may be desirable, for example, if access to a new anatomical structure is needed. In this manner, the primary operator is able to maintain a ‘hands-free’ approach.
Owner:WELLAN MEDICAL SOLUTIONS +1
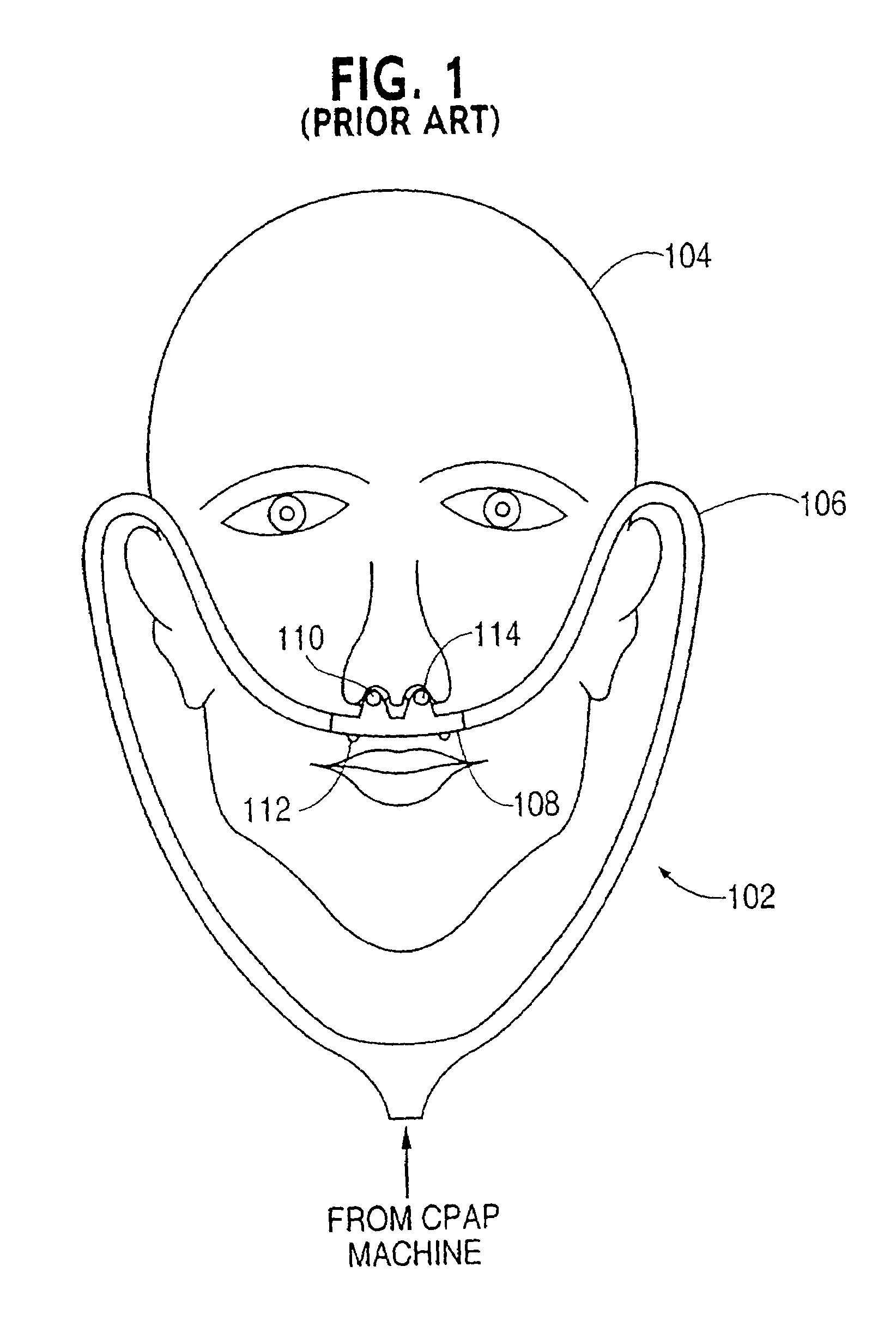
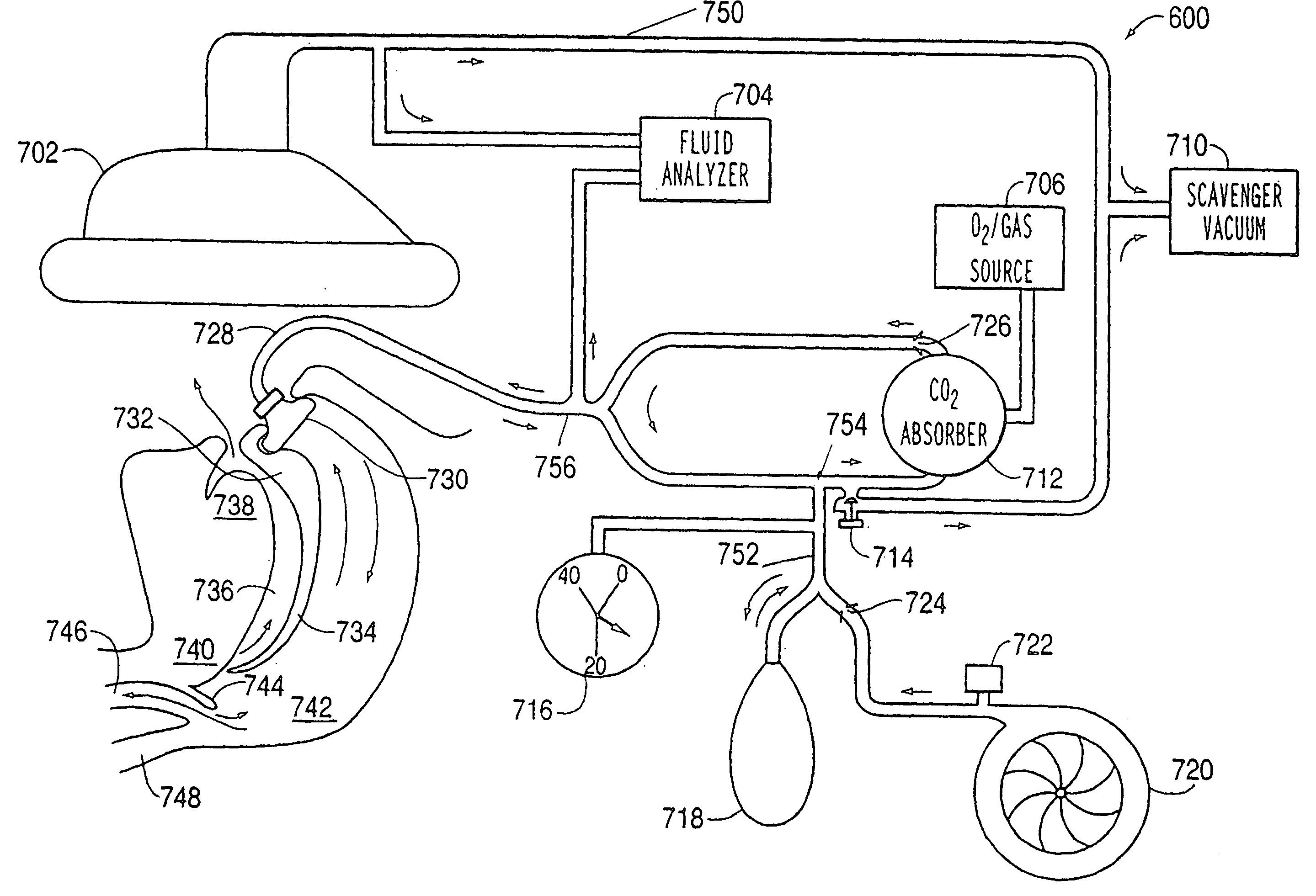
Nasal gas delivery system and method for use thereof
A gas administering method for administering gas to an airway of a patient having a nasal vestibule and for use with a gas administering apparatus comprises a primary gas source that is operable to provide gas and a nasal vestibular portion arranged so as to receive the gas from the primary gas source. Further, the nasal vestibular portion is capable of releasing the primary gas into the nasal vestibule. The method comprises inserting the nasal vestibular portion into the nasal vestibule, forming a seal between the nasal vestibular portion and an inner surface of the nasal vestibule, administering an amount of a gas from the primary gas source at a constant flow rate into the nasal vestibule via the nasal vestibular portion, and administering an anesthetic to the patient. The anesthetic induces depression of a portion of the nervous system of the patient. Furthermore, the seal promotes airway pressure buildup that is sufficient to prevent obstruction of the airway during depression of at least a portion of the nervous system and prevents escape of the gas from between the nasal vestibule and the nasal vestibular portion.
Owner:NOBLE LINDA
Therapeutic microparticles
Biodegradable, compression resistant microparticles adapted for injection through a catheter system, such as is useful for selective embolization procedures. The microparticles can optimally be neutrally buoyant relative to a target bodily fluid. Various active agents may be included in the microparticles, such an anesthetic which can reduce pain during an embolization procedure. The invention further comprises methods and equipment for testing and delivering compression resistant microparticles.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Injection device for administering a vaccine
InactiveUS7670314B2Simple and inexpensive to prepareSimple and inexpensive to and operateAmpoule syringesAutomatic syringesMedication injectionInjection device
A manually-powered injection device that self-administers a painless injection. The injection device provides a method for substantially painless injections of vaccine and other medication into a patient that does not require the use of an anesthetic, that does not require the medical personnel to spend a substantial amount of time performing the injection procedure, that is relatively simple and inexpensive to perform and operate, and that provides a relatively high degree of safety for both the medical personnel and for the patient. The injection needle can have an outside diameter greater than 0.10 mm and less than about 0.38 mm. The vaccine or other medicament can be injected painlessly through the needle and into the patient at a substantially constant volumetric flow rate of about 0.05 μL / s to about 50 μL / s, typically over a 3- to 5-minute period of time. The injection device is configured for easy handling, and is manually powered by the use of the hand or fingers of the medical technician, patient or other person.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT CINCINNATI
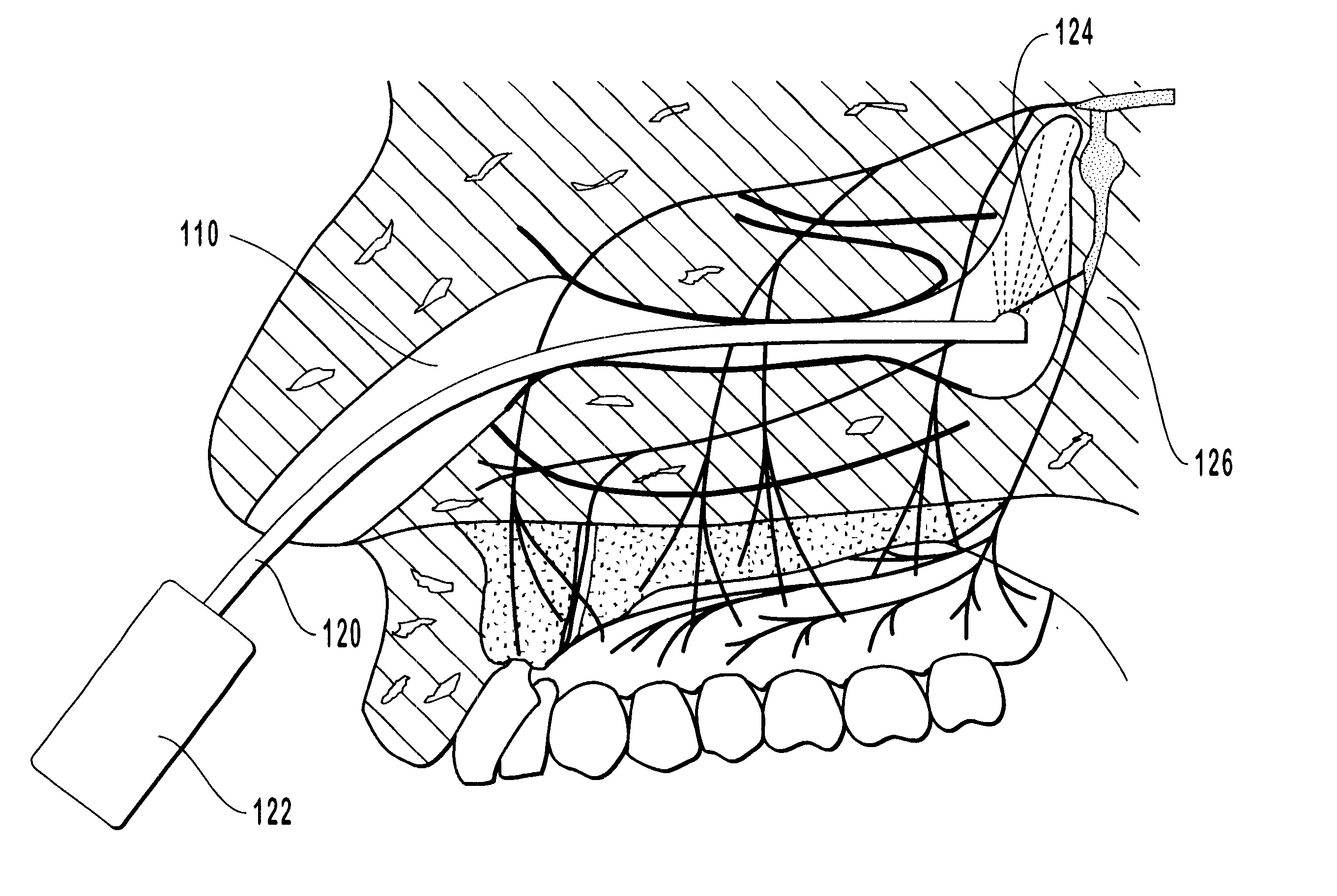
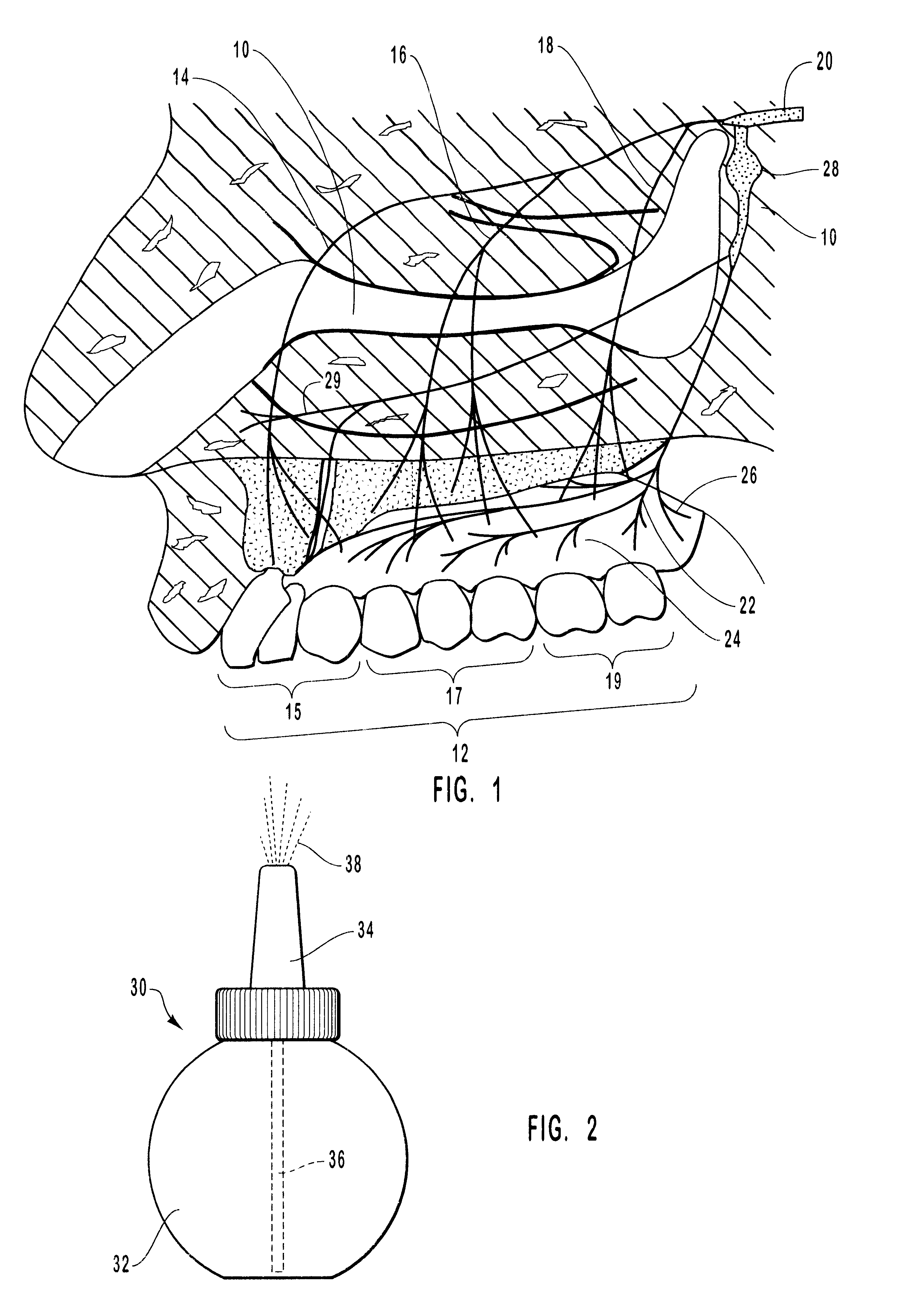
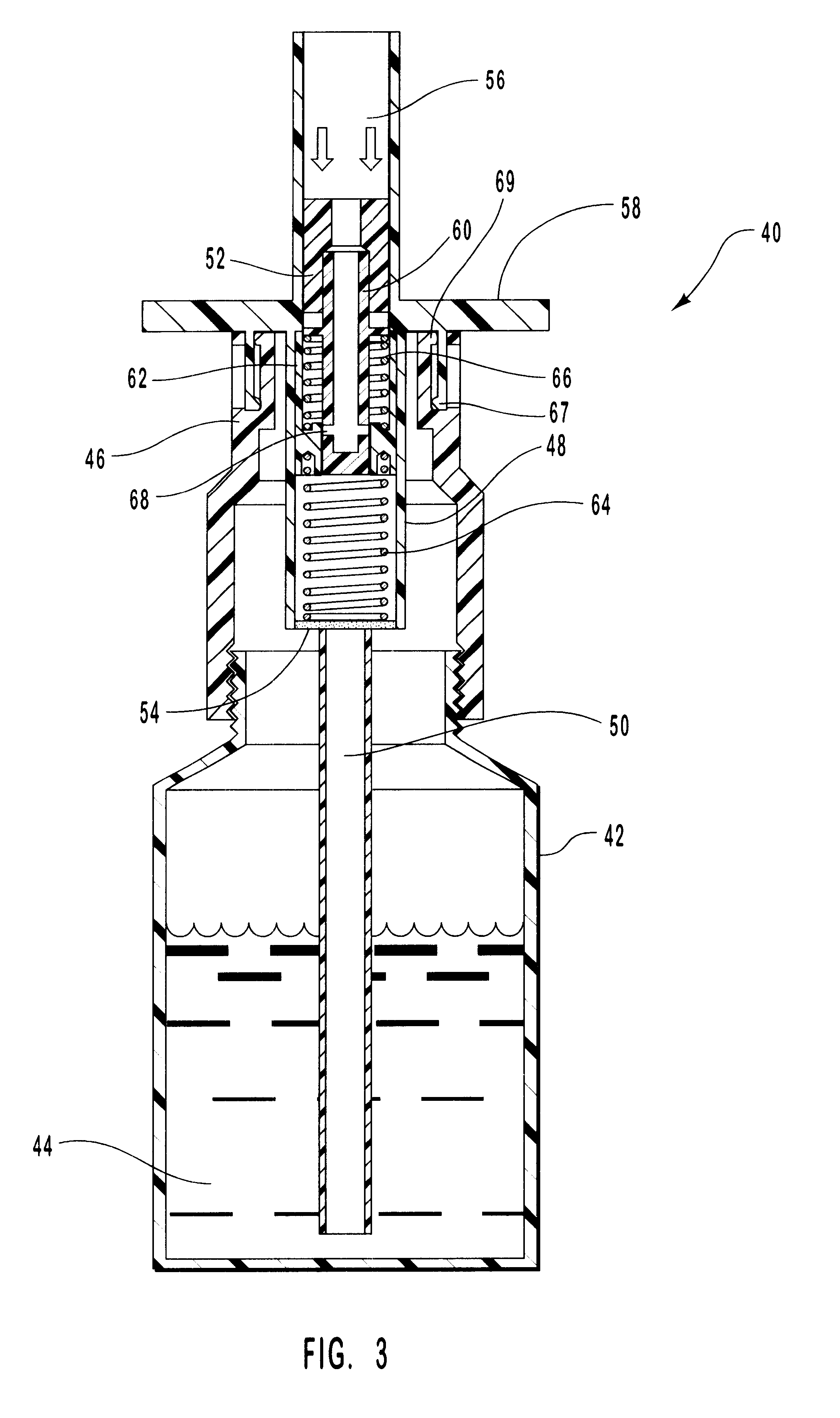
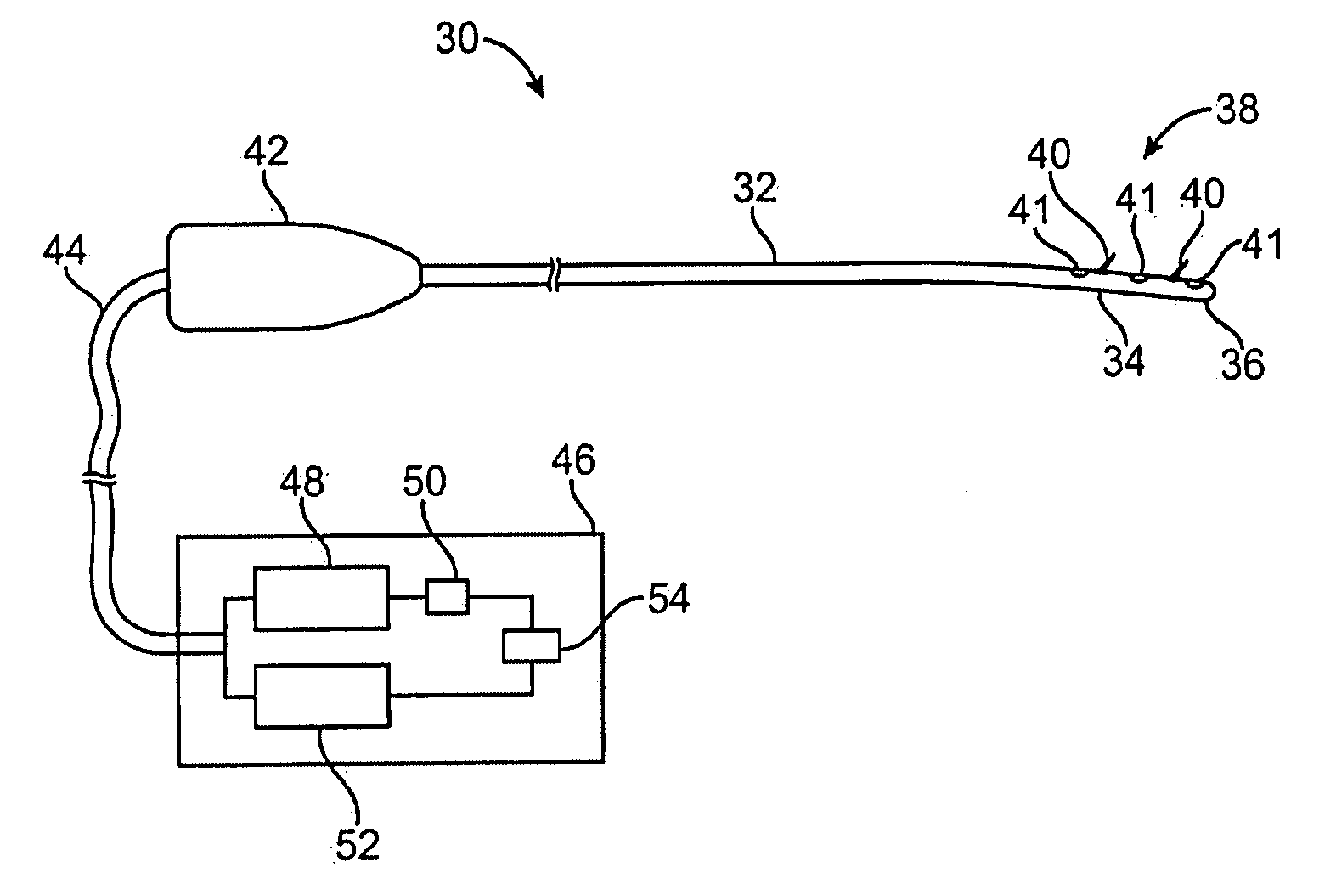
Methods and kits for maxillary dental anesthesia by means of a nasal deliverable anesthetic
Methods and systems for anesthetizing a portion or all of a patient's maxillary dental arch using a nasal delivered anesthetizing composition. The process generates anesthesia sufficient for facilitation of operative dentistry, endodontics, periodontics or oral surgery for teeth of the maxillary arch. The dental nasal spray process consists of inserting one or more dispensing devices through the patient's nostril and delivering metered dosages of anesthetic solution or gel into the nasal cavity. The process may utilize a single solution which is a mixture of anesthetic agents, vasoconstricting agents and other physiological inert agents or two separate solutions, wherein one solution contains the vasoconstricting agents and the other solution contains the anesthetic agents. Anesthetic diffusion through the thin walls of the nasal cavity allows for the blocking of nerve impulses originating from the maxillary dentition and surrounding tissues. Anesthesia of specific oral regions such as right versus left sides of the dental arch, anterior versus posterior teeth, and soft tissue anesthesia may be controlled through modification of the dosage volume and the selection of right or left nostril insertion and agent delivery.
Owner:ST RENATUS +1
Systems for treatment of nasal tissue
InactiveUS20080027423A1Small sizeIncrease airflowUltrasound therapySurgical instrument detailsPain managementAnalgesic agents
Systems for the treatment of nasal tissue, particularly the nasal turbinates, are described. One method for reducing the size of the inferior nasal turbinate is to apply ultrasound energy to the tissue regions beneath the surface of the turbinate tissue. One instrument may be used to deliver ultrasound energy and provide an infusion or injection of a fluid directly into the turbinate being treated, e.g., to bulk up the size of the turbinate to ensure that the ultrasound energy is properly delivered directly into the intended turbinate tissue. Fluids containing anesthetics, fluids infused with analgesics, etc. may be used for pain management while other medications, such as non-steroidal drugs, steroidal drugs, anti-inflammatory drugs, anti-histamines, anti-bacterial drugs, etc., can also be used. Such assemblies can also be utilized with other instruments as a system. For example, such a probe can be used with nasal speculums or imaging instrument in treating tissue.
Owner:CHOI GEORGE Y
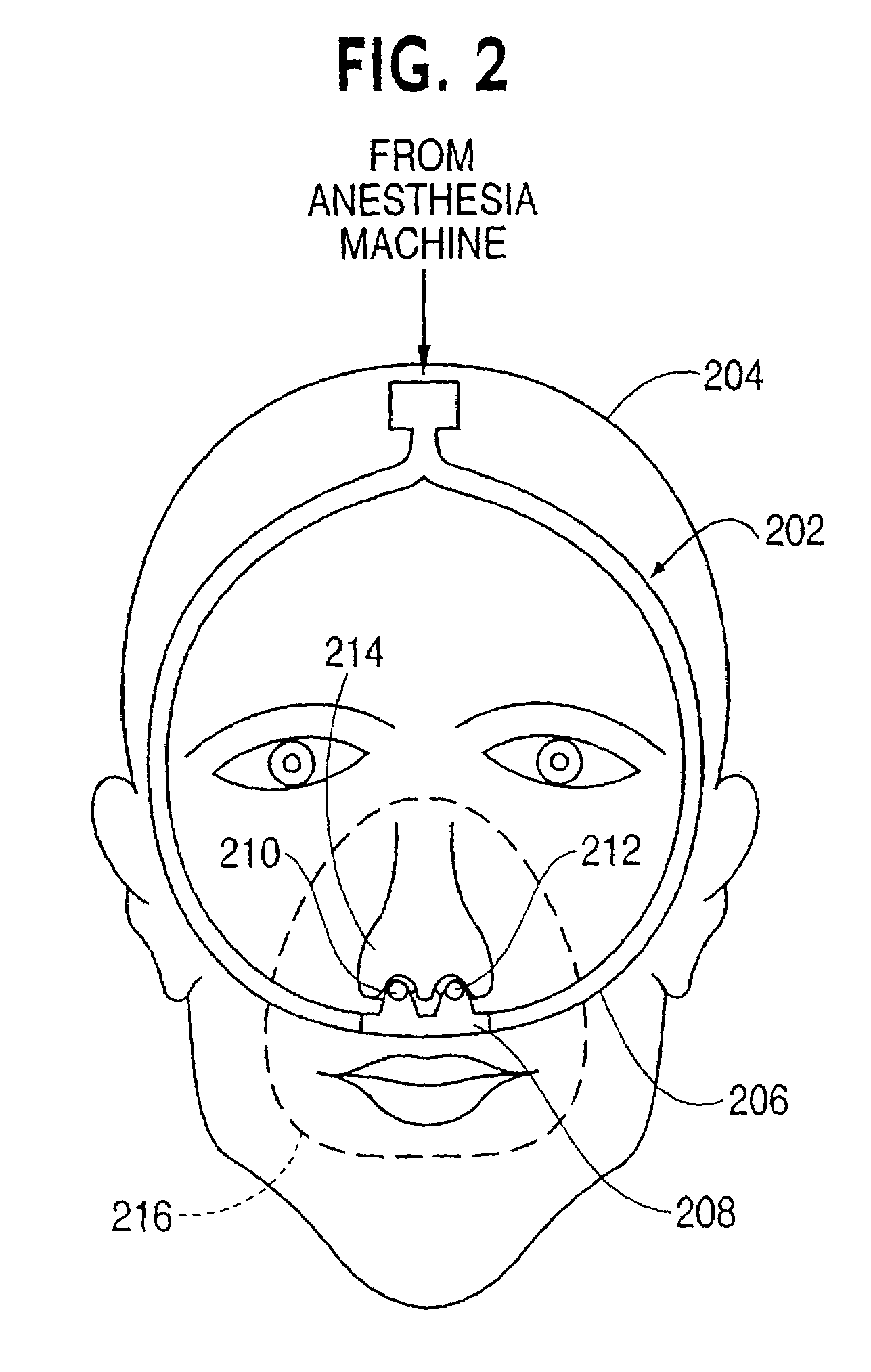
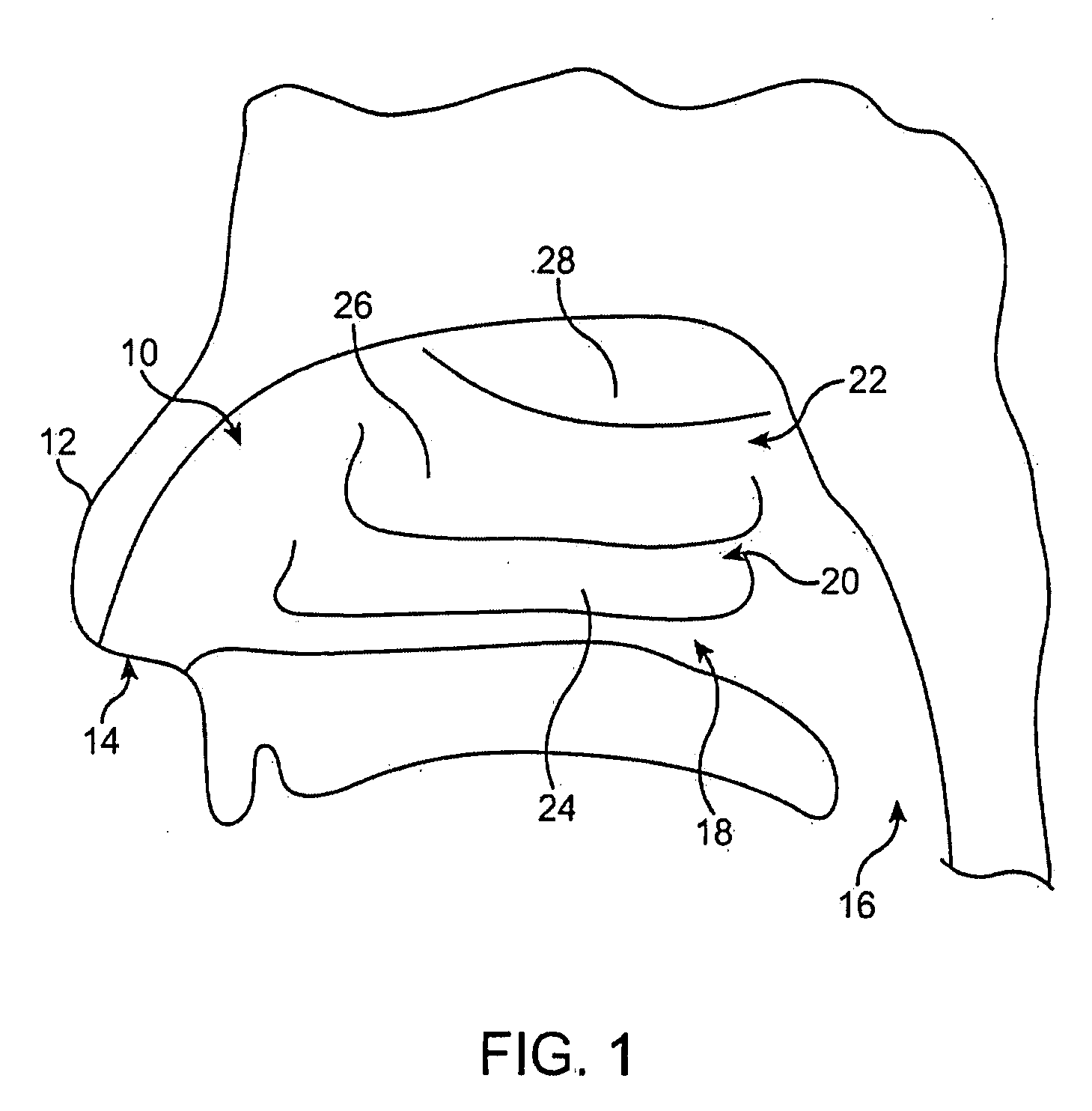
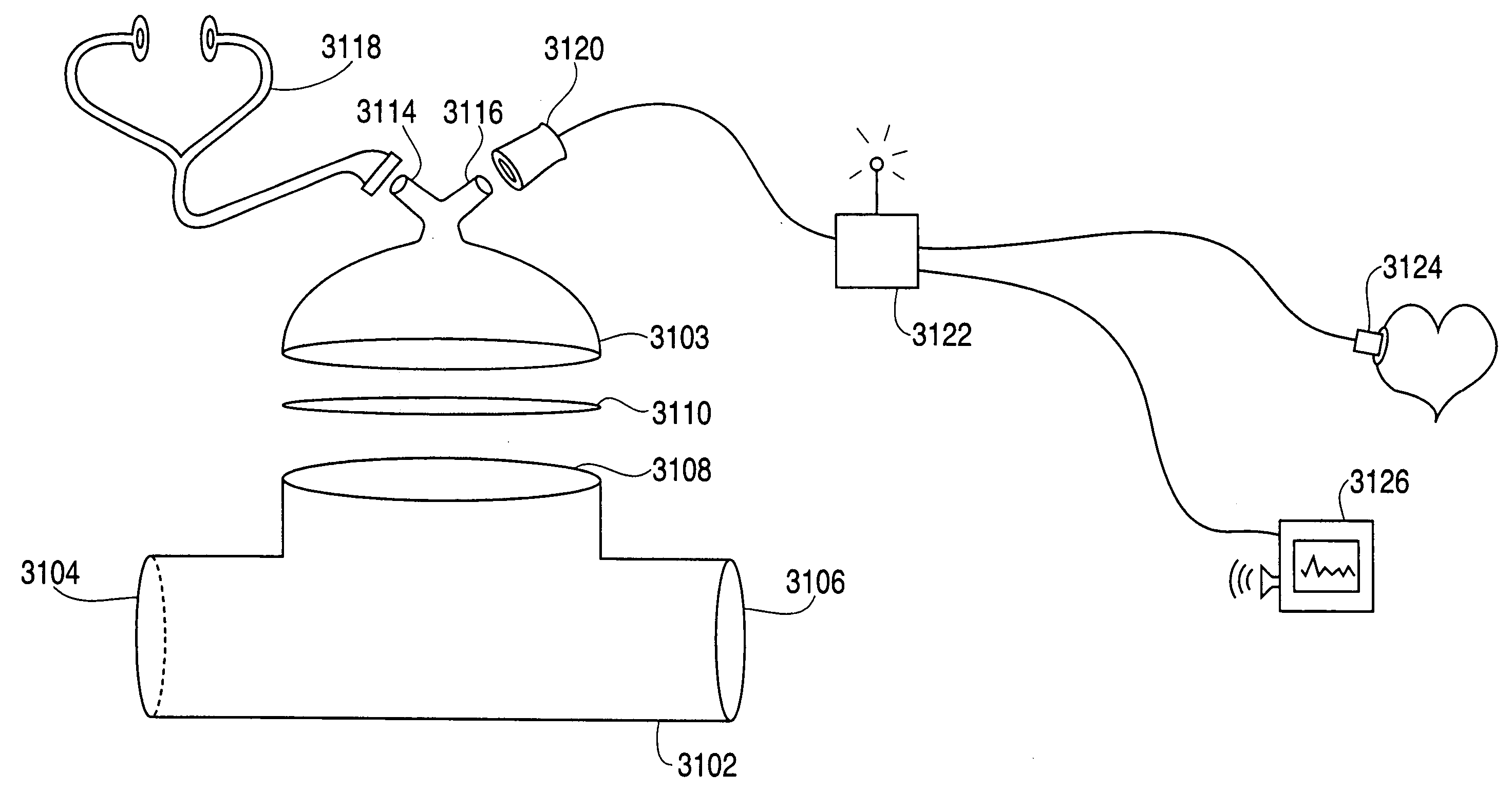
Method and device to administer anesthetic and or vosactive agents according to non-invasively monitored cardiac and or neurological parameters
InactiveUS20090124867A1Efficiently safely teachingPumping capacity is overwhelmedMedical simulationRespiratorsCardiac cycleWhole body
A method of and a device for non-invasively measuring the neurological depressed state and the hemodynamic state of a human patient and involving steps and units of non-invasively measuring EEG, cardiac cycle period, electrical-mechanical interval, mean arterial pressure, and ejection interval and converting the EEG into a neurological index as well as converting the measured electrical-mechanical interval, mean arterial pressure and ejection interval into the cardiac parameters such as Preload, Afterload and Contractility, which are the common cardiac parameters used by an anesthesiologist. A general anesthetic is administered based upon the converted neurological index. A vasoactive agent is independently administered based upon the converted cardiac parameters as necessary in order to restore cardiovascular homeostasis in the patient. The converted neurological and hemodynamic state of a patient are displayed on a screen as an index value and a three-dimensional vector with each of its three coordinates respectively representing Preload, Afterload and Contractility. Therefore, a medical practitioner looks at the screen and quickly obtains the important and necessary information.
Owner:THE COOPER HEALTH SYST
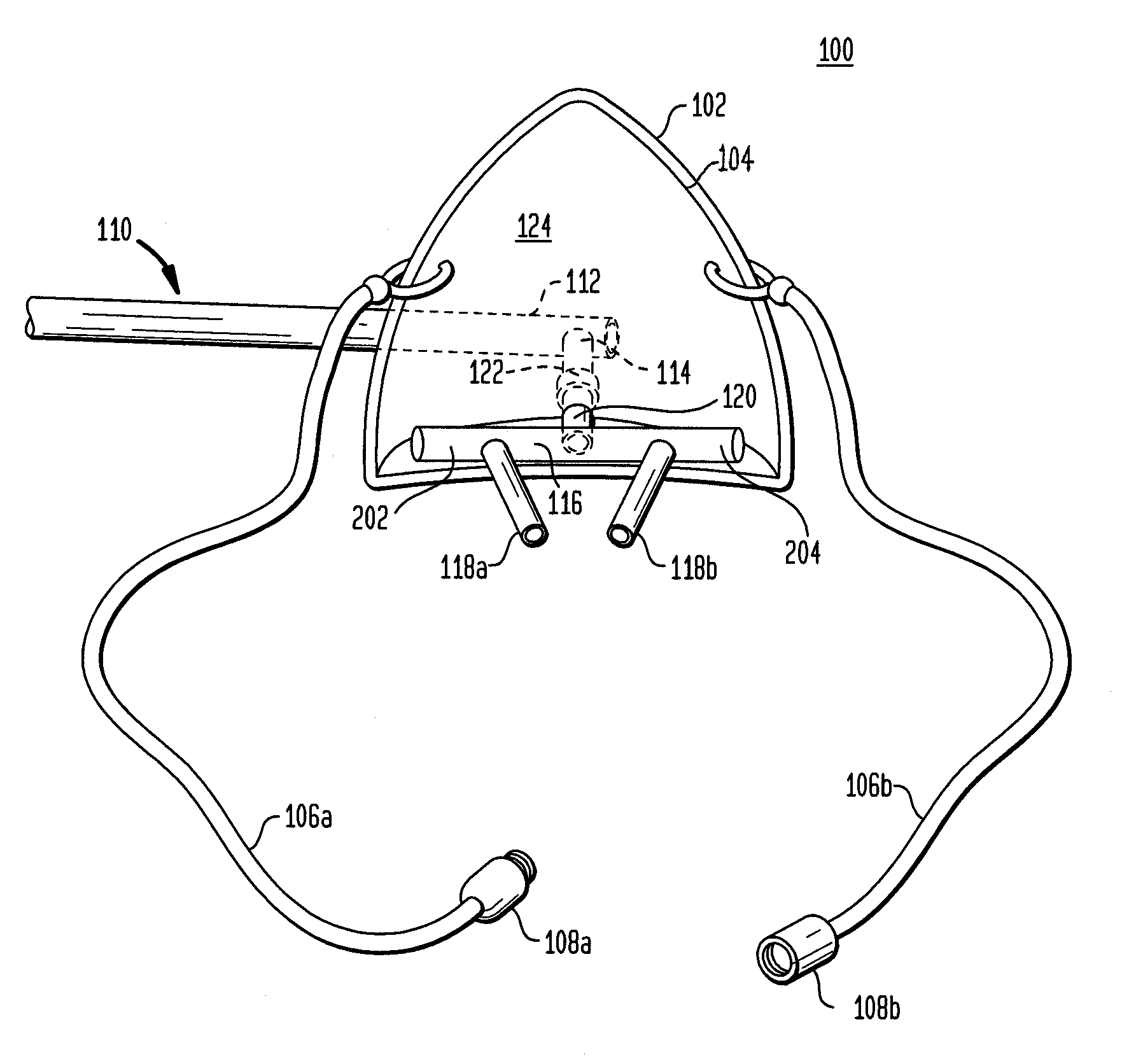
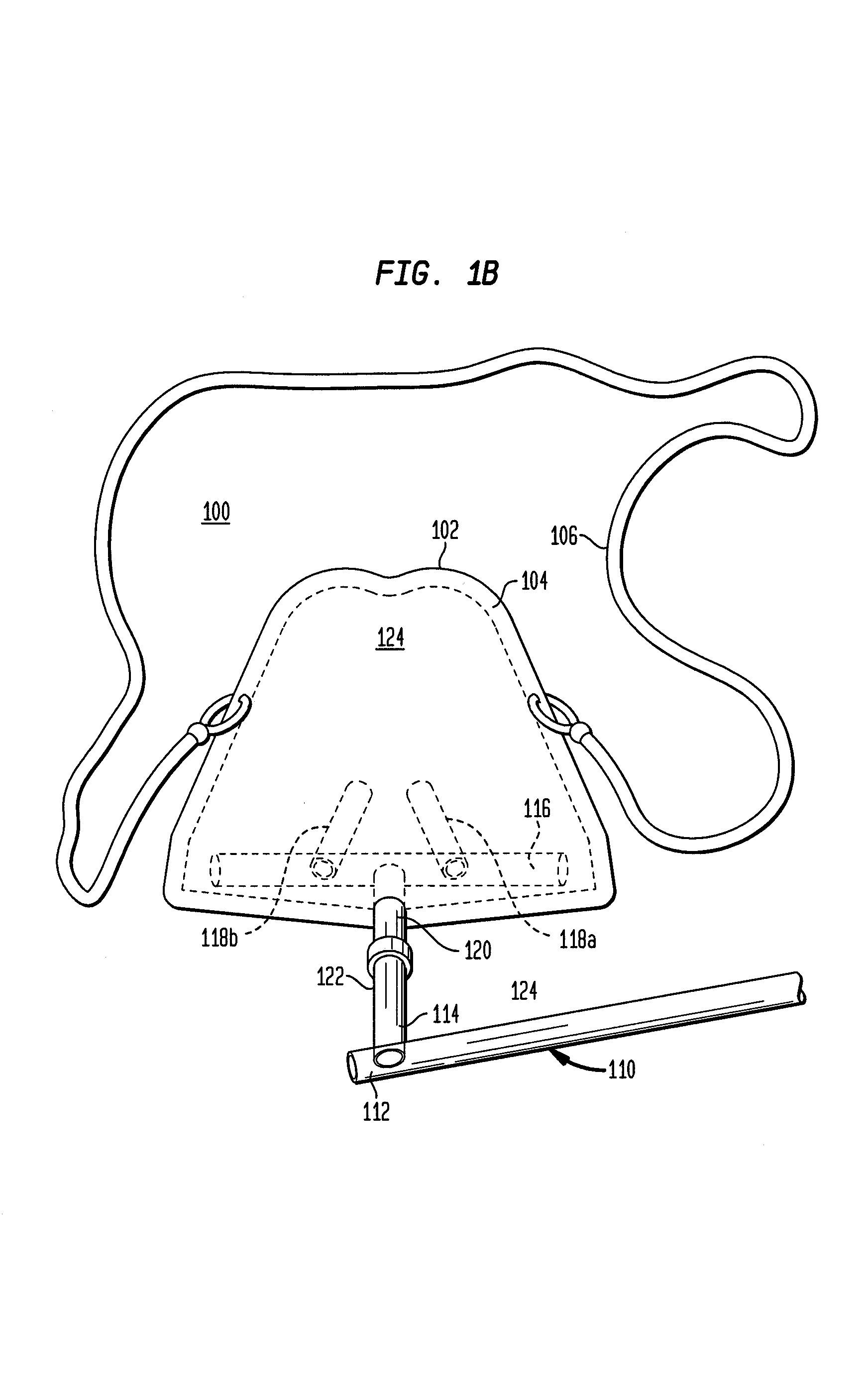
Nasal mask assembly for nasal delivery
InactiveUS7255107B1Maintain comfortConstant delivery of oxygenRespiratorsBreathing filtersNose partsInternal cavity
A nasal mask assembly is configured to provide a direct flow of a fluid, e.g., breathable air, oxygen or anesthesia, directly into the patient's nasal cavity by combining the nasal prongs of a nasal cannula with a nasal cup. The nasal cup is made of clear plastic and has a general shape of a human nose such that it easily and comfortably fits over a patient's nose. An input port extends through the nasal cup into the internal cavity of the nasal cup and a fluid source is connected to the input port via a source tube system. The nasal cup can be molded to approximate the surface of a patient's face surrounding the patient's nose. The nasal prongs are extended in length. The source tube is rotatably connected to the external end of the input port of the nasal cup.
Owner:GOMEZ ROY C
Nasal gas delivery system and method for use thereof
InactiveUS20060174889A1Convenient and continuous operation of C-PAPReduce riskRespiratorsBreathing filtersNasal vestibuleNervous system
A gas administering method for administering gas to an airway of a patient having a nasal vestibule and for use with a gas administering apparatus comprises a primary gas source that is operable to provide gas and a nasal vestibular portion arranged so as to receive the gas from the primary gas source. Further, the nasal vestibular portion is capable of releasing the primary gas into the nasal vestibule. The method comprises inserting the nasal vestibular portion into the nasal vestibule, forming a seal between the nasal vestibular portion and an inner surface of the nasal vestibule, administering an amount of a gas from the primary gas source at a constant flow rate into the nasal vestibule via the nasal vestibular portion, and administering an anesthetic to the patient. The anesthetic induces depression of a portion of the nervous system of the patient. Furthermore, the seal promotes airway pressure buildup that is sufficient to prevent obstruction of the airway during depression of at least a portion of the nervous system and prevents escape of the gas from between the nasal vestibule and the nasal vestibular portion.
Owner:NOBLE LINDA
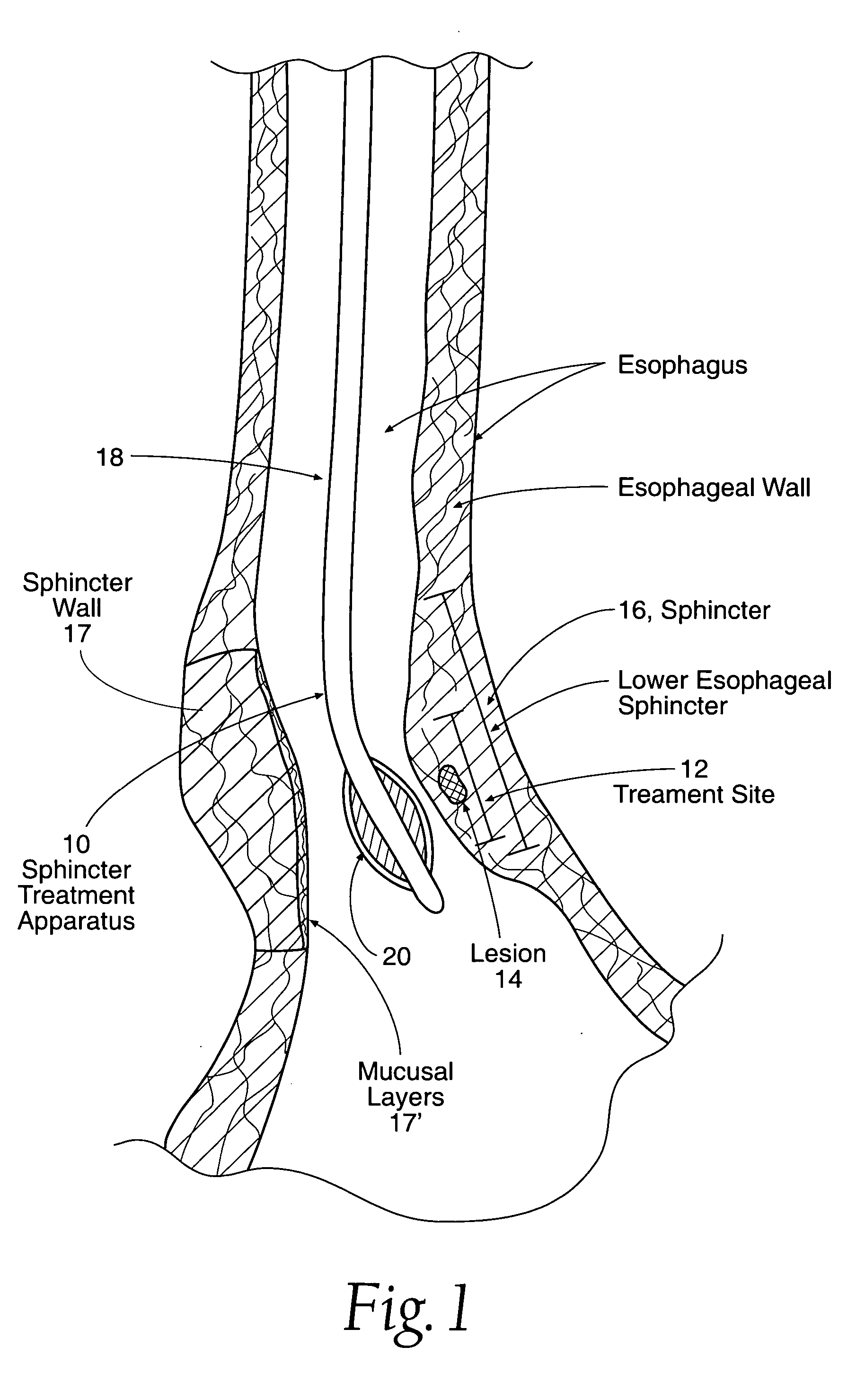
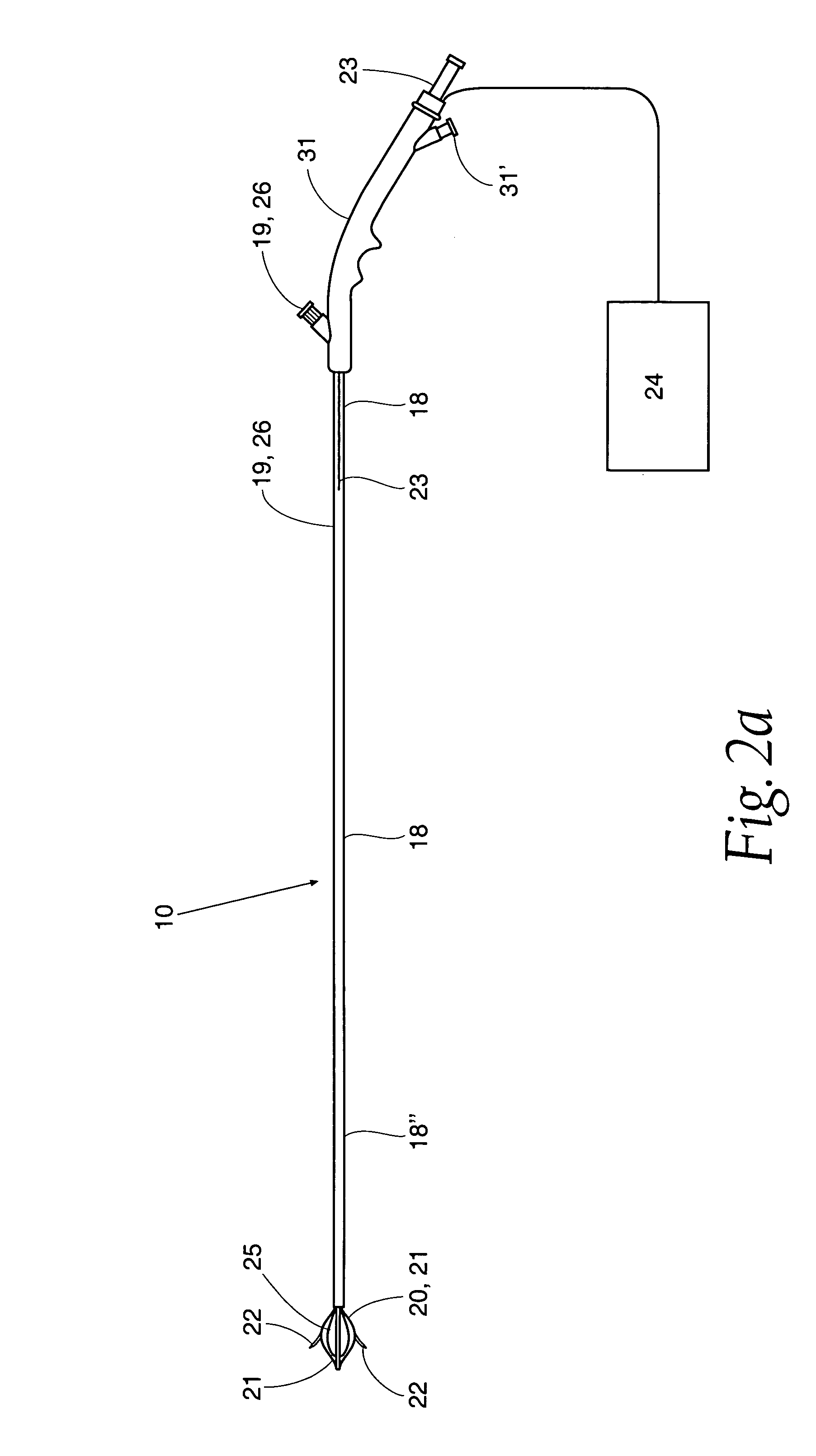
Sphincter treatment apparatus
An apparatus treats tissue at or near a sphincter. The apparatus has an elongated member having at least one lumen including an inflation lumen, and a basket assembly including a first and a second arm. An inflatable member is coupled to the inflation lumen and has a deployed and a non-deployed state. In the deployed state, the inflatable member expands the basket assembly into contact with tissue. At least one of the first and second arms of the basket assembly has a fluid lumen having an aperture for conveying a fluid from the basket assembly. A source of fluid is coupled to the fluid lumen for conveyance of fluid through the aperture. The fluid can be, e.g., an electrolytic solution, and / or an anti-infection agent, and / or an echogenic media, and / or a steroid, and / or an anesthetic, and / or a medicament, and / or a tissue cooling agent. The source can be a drug delivery device.
Owner:MEDERI THERAPEUTICS
Bioactive factors in wound healing topical compositions and methods
InactiveUS20060240116A1Promote repairPeptide/protein ingredientsUnknown materialsCutaneous woundMicrobial agent
A topical composition for treating a cutaneous wound includes whole colostrum or one or more growth factors, as well as a base by which the whole colostrum or one or more growth factors are carried. The topical composition may also include, without limitation, immunomodulators, lactoferrin, enzymes, vitamins, minerals, amino acids, or combinations thereof. Other components may also be included in the topical composition, including, but not limited to, antiseptics, antimicrobial agents, and anesthetics. When applied to a wound, the bioactive topical composition promotes healing of the treated wound.
Owner:JOLLEY DAVID
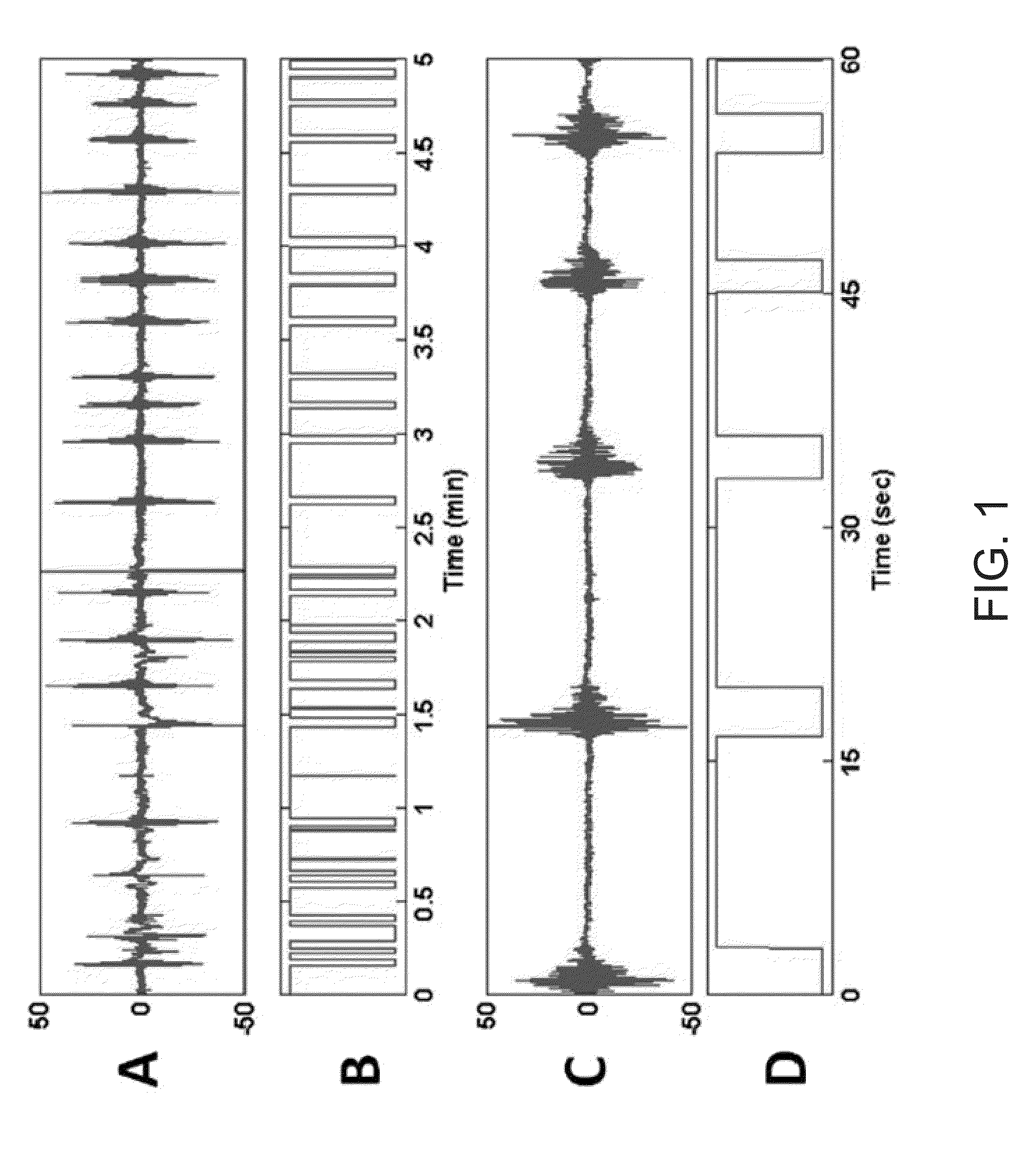
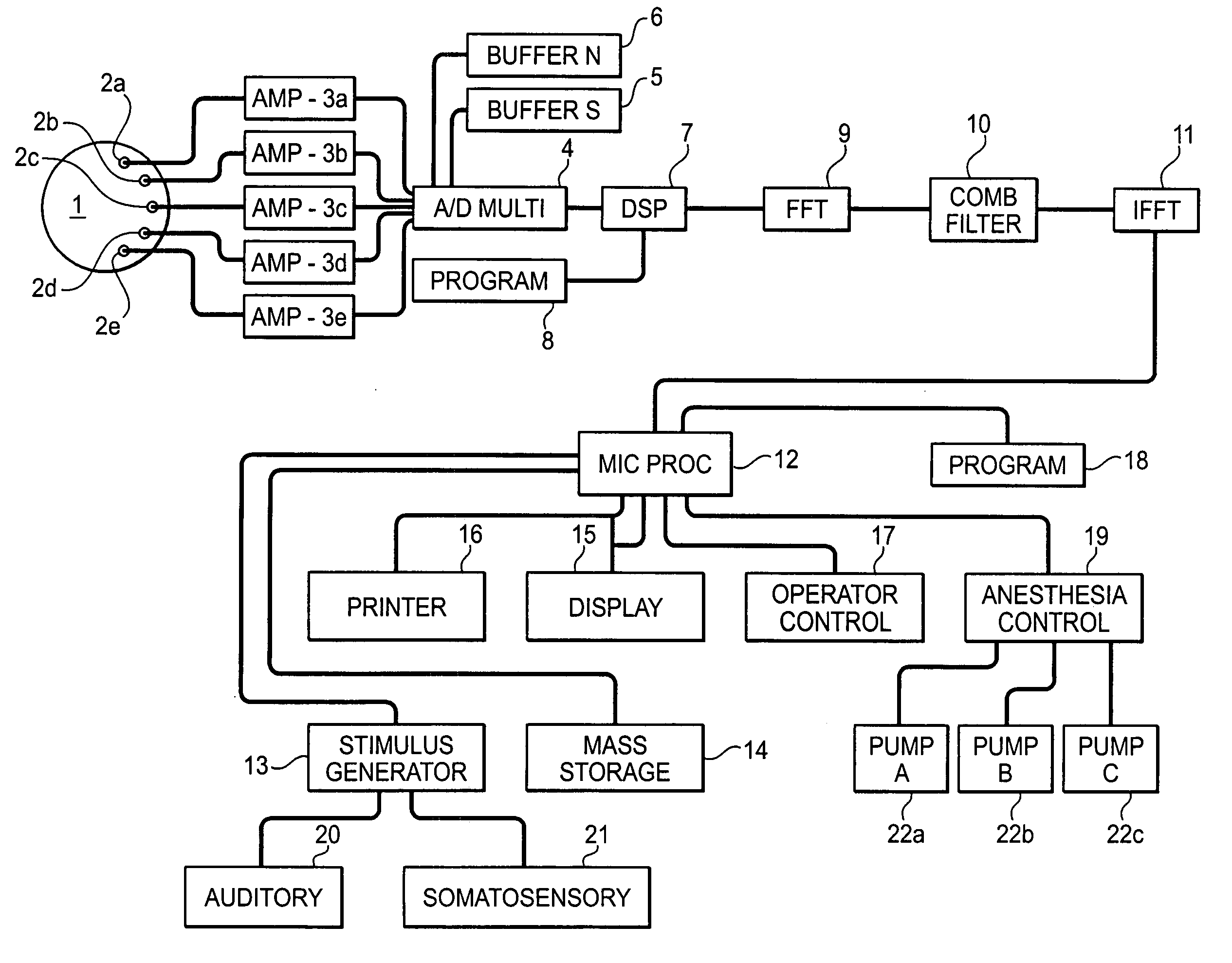
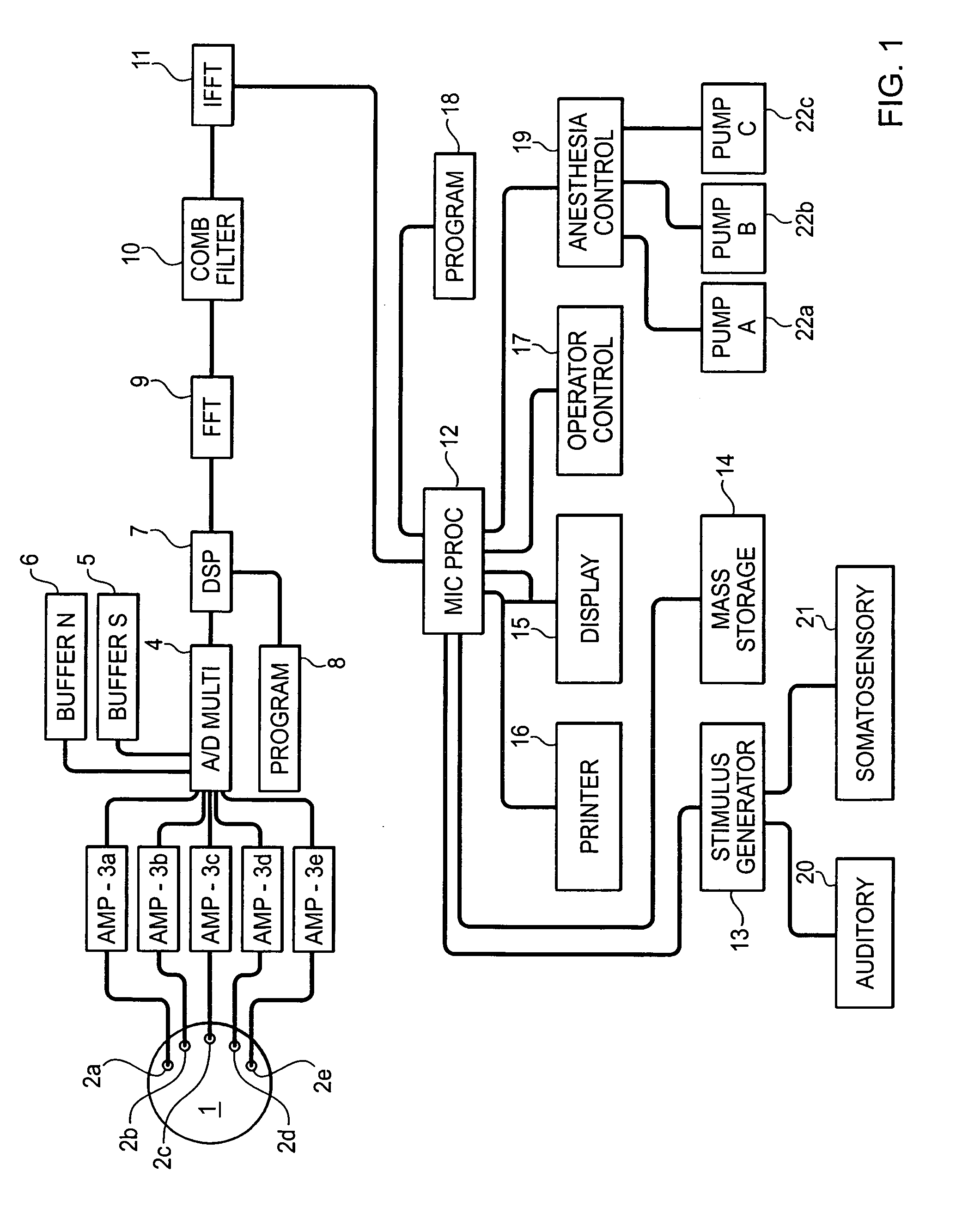
System and method for guidance of anesthesia, analgesia and amnesia
A method for monitoring anesthetization of a patient, includes the steps of removably connecting a plurality of electrodes to the scalp of the patient and administering sufficient anesthesia to the patient so that the patient attains a plane of anesthesia selected by an operator. The brain waves of the patient are then amplified and digitized after the patient has been anesthetized, before beginning the medical procedure, to obtain a first set of digital data. The brain waves of the patient are then amplified and digitized during the medical procedure to provide a second set of digital data and the first and second sets of digital data are analyzed in at least one of a time domain and a frequency domain. Separate trajectories are then computed from the data analysis trajectories for at least two different indices of an anesthetic state of the patient during the medical procedure, the indices being selected from a group including a Depth Index (DI), a Memory Index (MI) and a Pain Index (PI). A system for providing anesthesia to a patient, includes a plurality of electrodes, a first arrangement allowing an operator to administer anesthesia to the patient until the patient has attained a selected plane of anesthesia and a second arrangement coupled to the electrodes for amplifying and digitizing brain waves of the patient after the patient has been anesthetized, before the medical procedure has been begun to obtain a first set of digital data, the second arrangement amplifying and digitizing ongoing brain waves of the patient during the medical procedure to provide a second set of digital data in combination with a third arrangement analyzing the first and second sets of digital data in at least one of a time domain and a frequency domain, a fourth arrangement computing from the data analysis separate trajectories for at least two different indices of a state of the patient during the medical procedure, the indices being selected from a group including a Depth Index (DI), a Memory Index (MI) and a Pain Index (PI), a fifth arrangement providing control signals when any of the trajectories indicates that the patient is deviating from the selected plane of anesthesia and a sixth arrangement automatically adjusting two different anesthetic agents administered to the patient based on the control signal to restore the patient to the selected plane of anesthesia.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Nasal gas delivery system and method for use thereof
InactiveUS7047969B2Reduce riskOperating means/releasing devices for valvesBreathing filtersNasal vestibuleNervous system
Owner:NOBLE LINDA
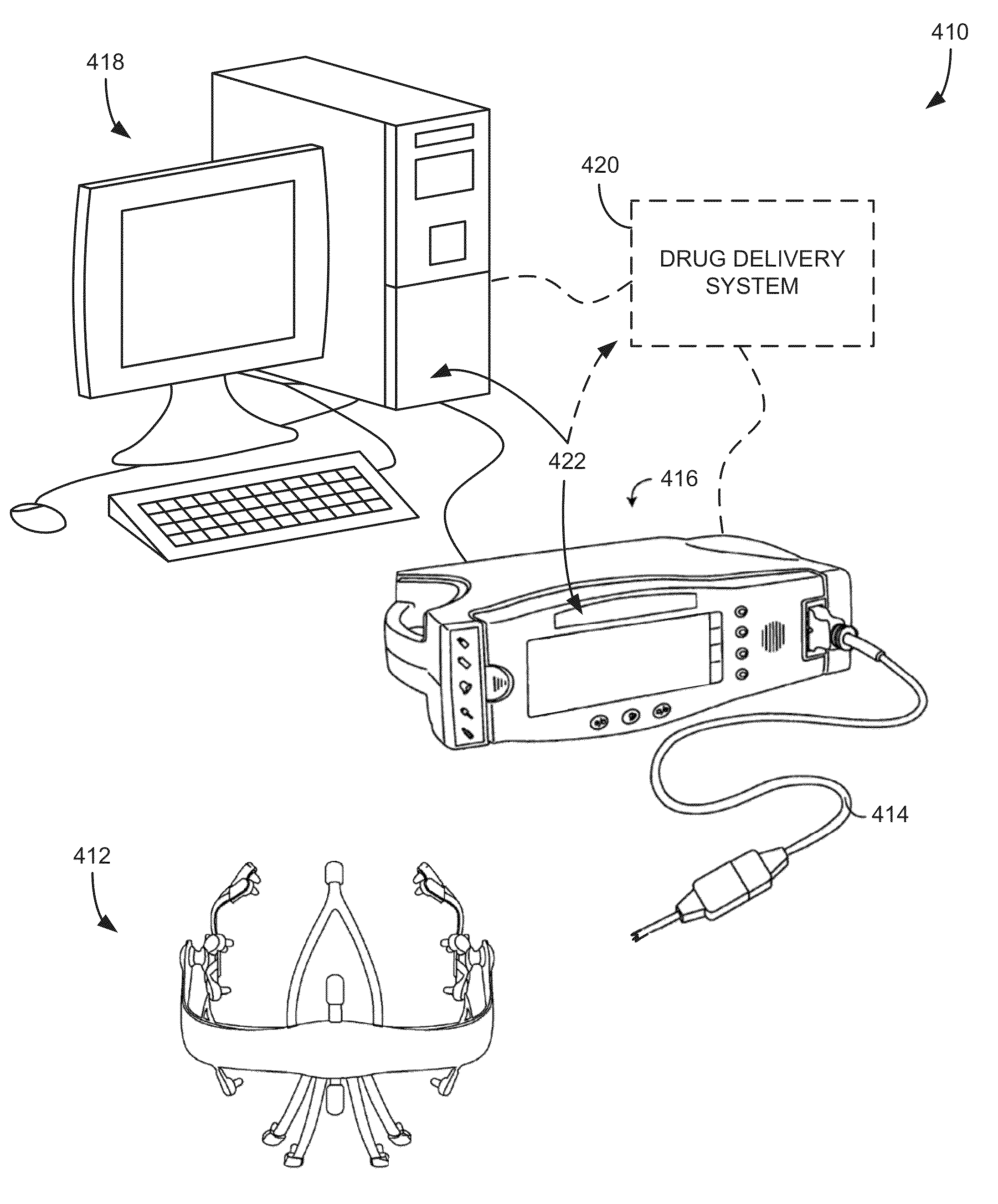
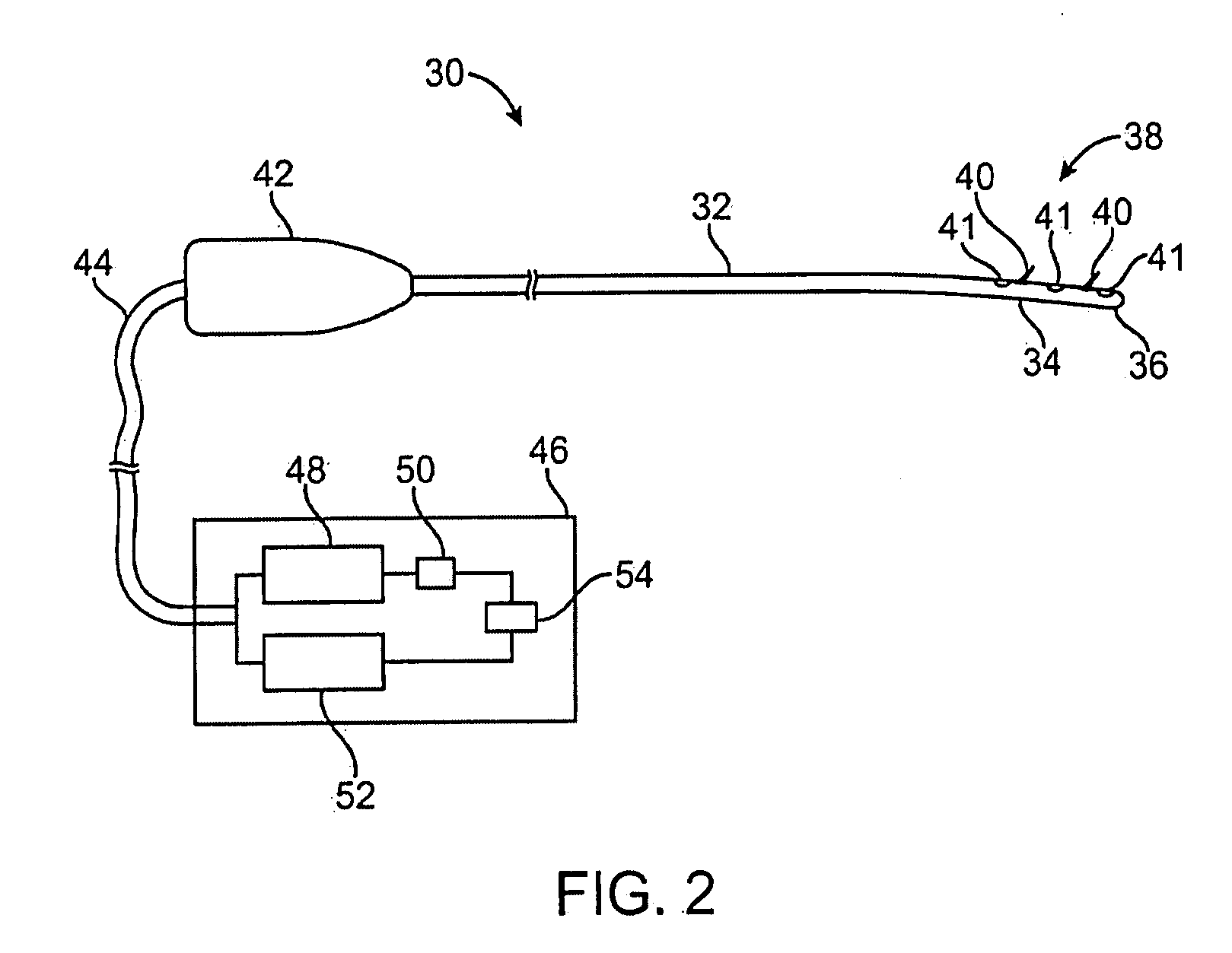
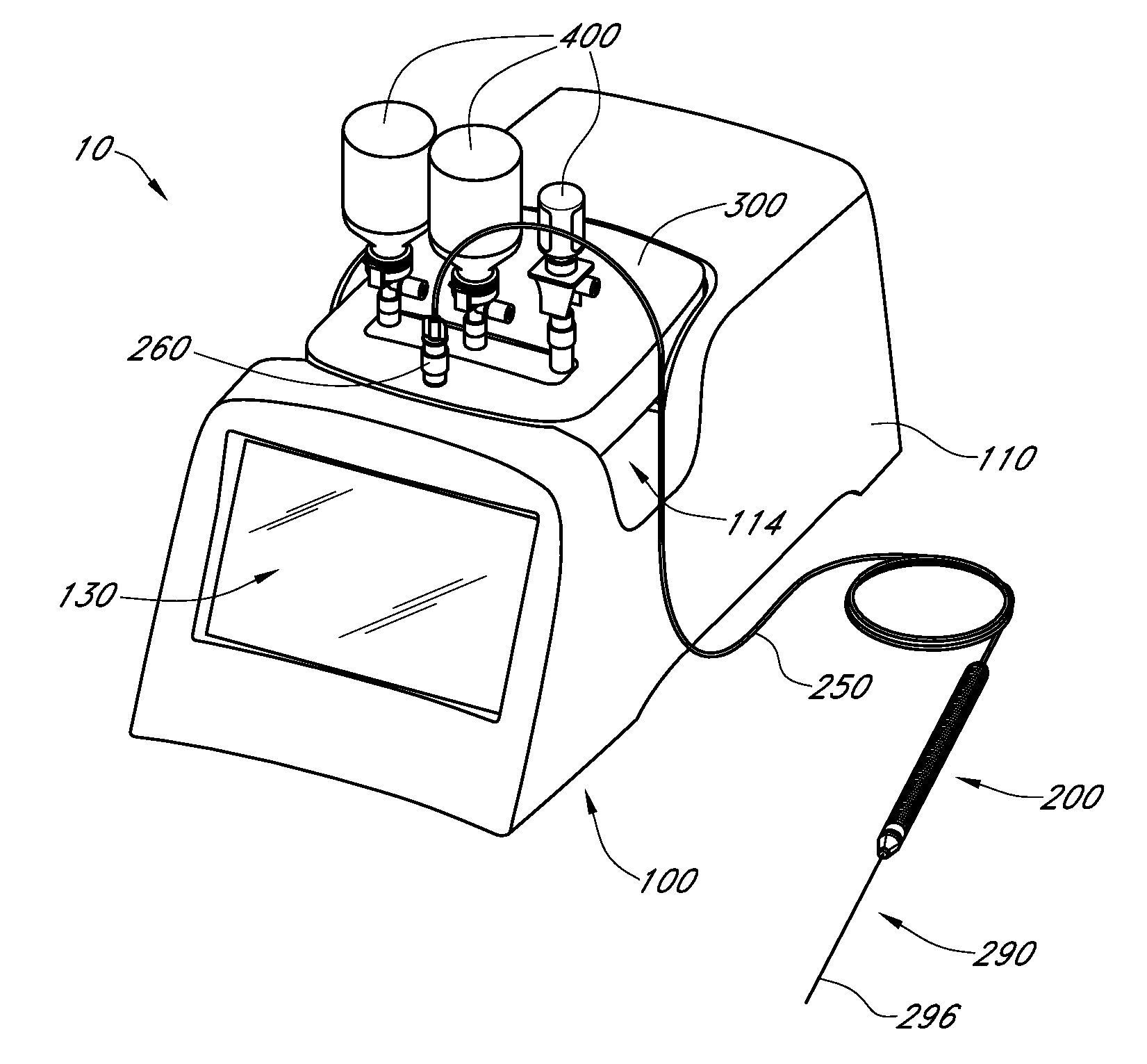
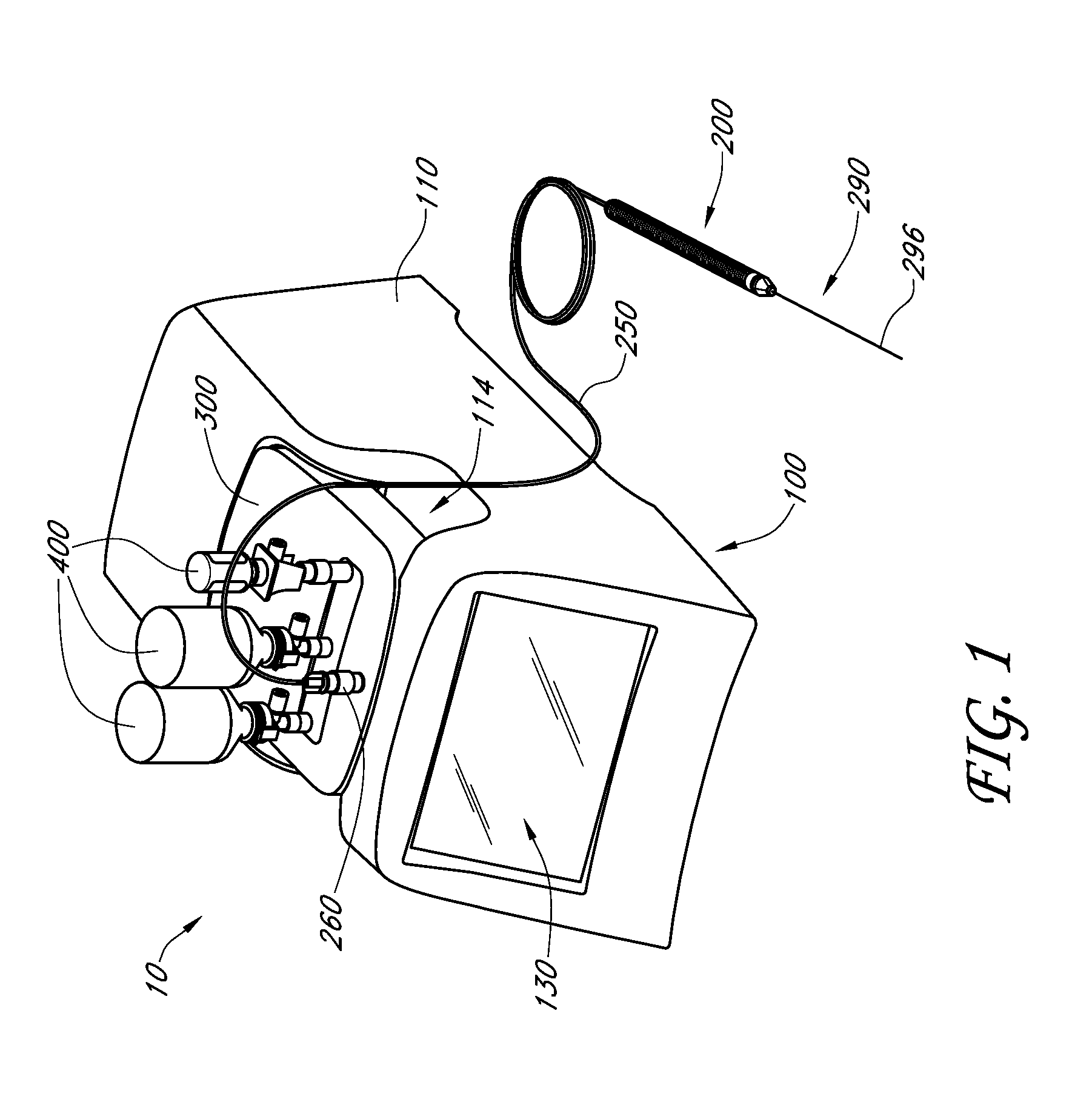
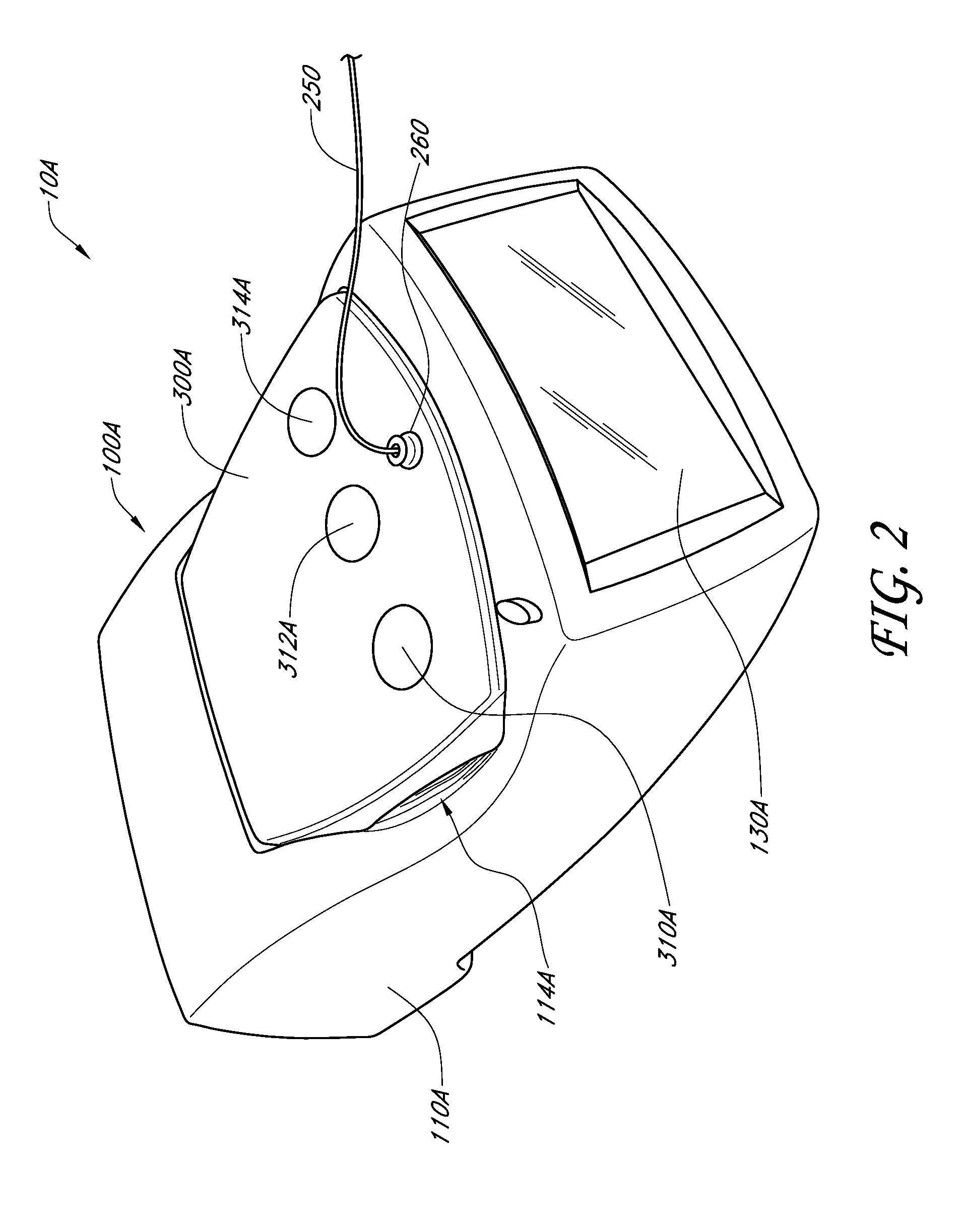
Imaging-guided anesthesia injection systems and methods
InactiveUS20130041258A1Precise deliveryPatient benefitUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAutomatic syringesAnatomical structuresDisplay device
Devices and systems for injecting fluids, such as anesthetics, to or near nerve tissue or other targeted anatomical location are disclosed herein. A conduit is generally configured to place the fluid delivery module in fluid communication with a needle that is configured to be inserted into the patient's anatomy. One or more medicaments (e.g., anesthetics) and / or other materials contained within containers (e.g., vials) that are secured to the injection system can be selectively delivered into an anatomy through the needle. Nerve stimulation and / or imaging technologies (e.g., ultrasound) can be used to locate a targeted anatomical location. Aspiration can be used to confirm needle location. An overlay on the imaging display can include, in addition to real-time imaging data, data and other information relating to back pressure at or near the needle tip, volumes or other amounts of fluids delivered by and remaining within the system, stimulation level and / or the like.
Owner:CARTICEPT MEDICAL
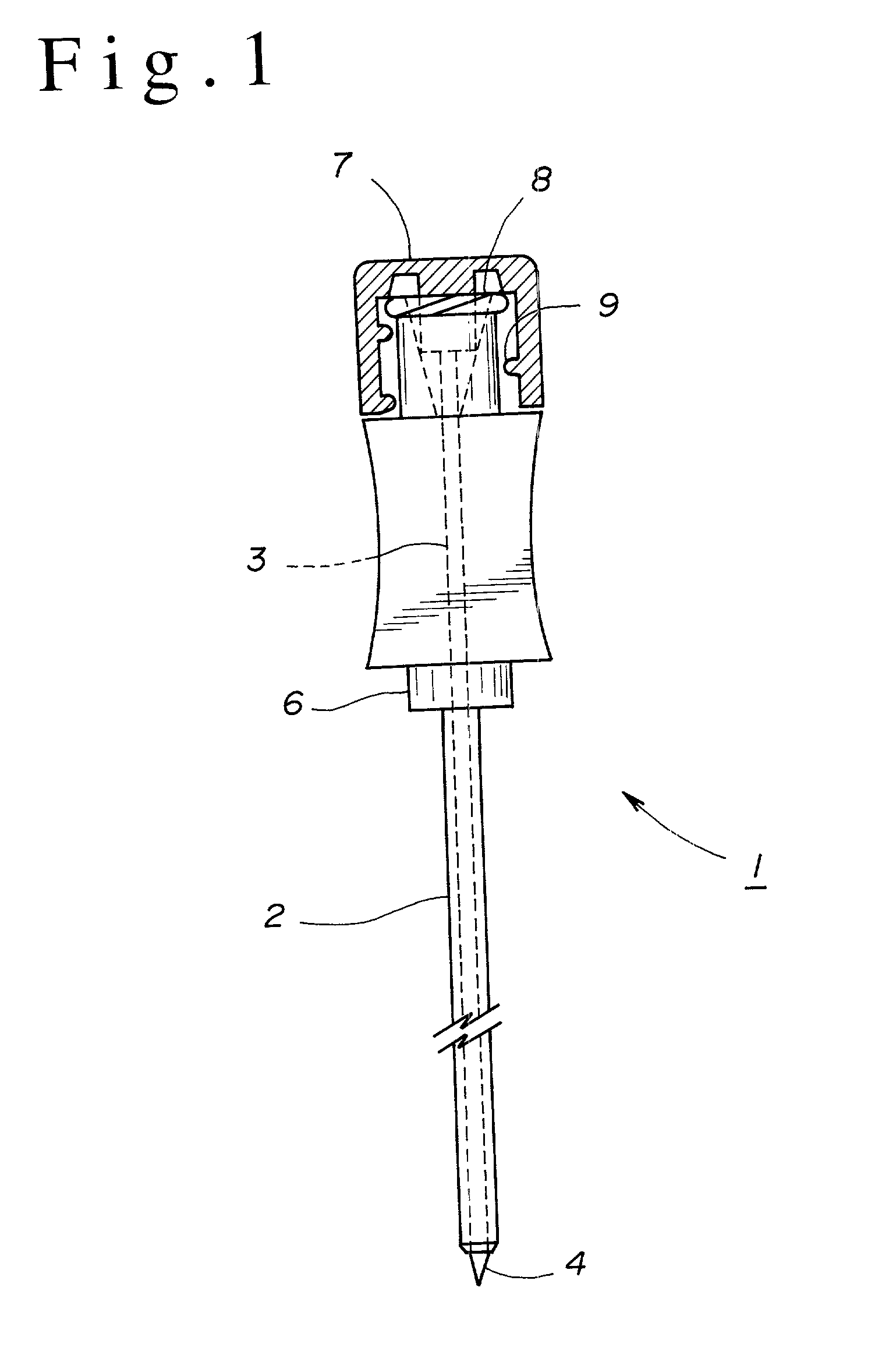
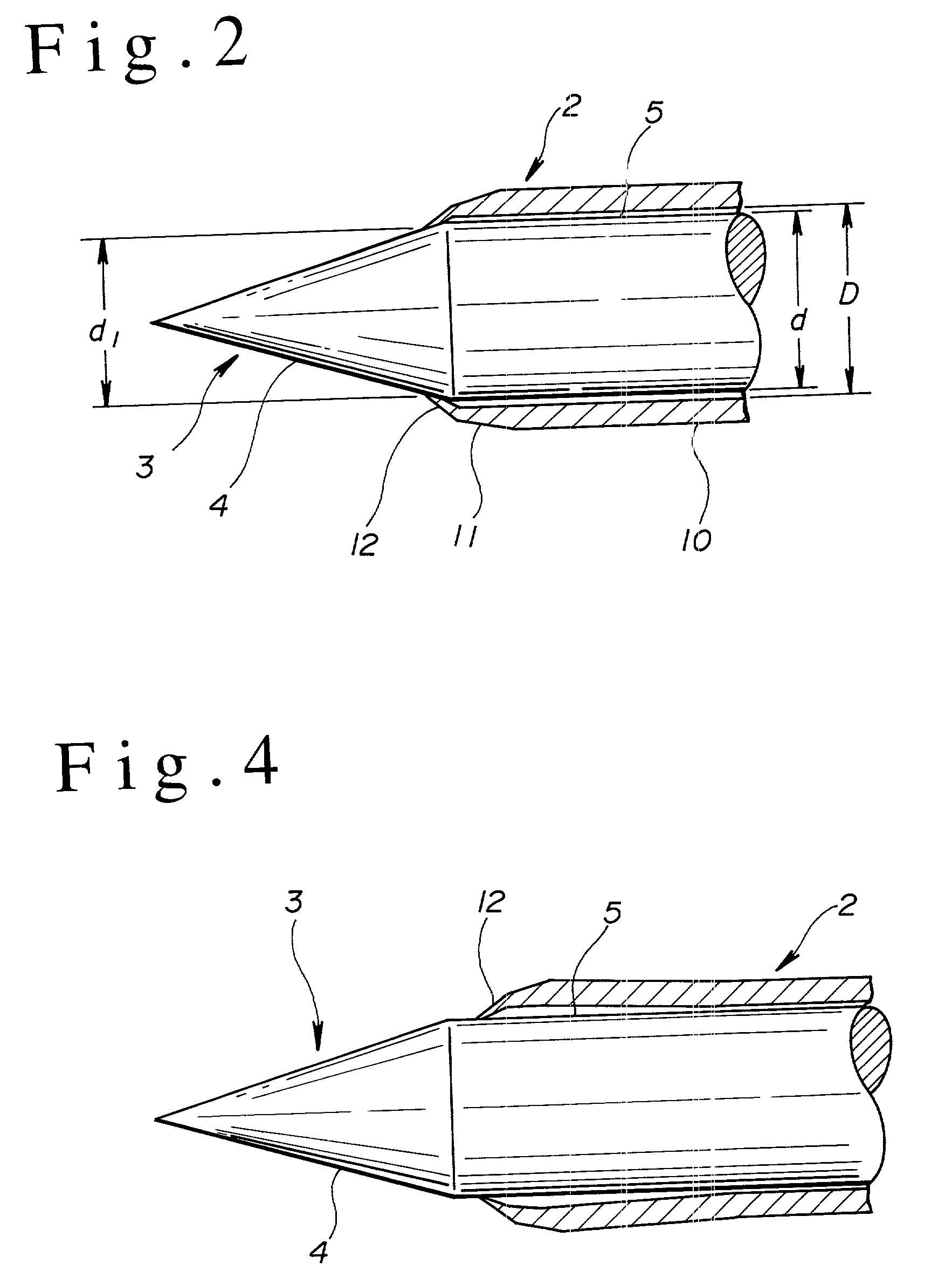
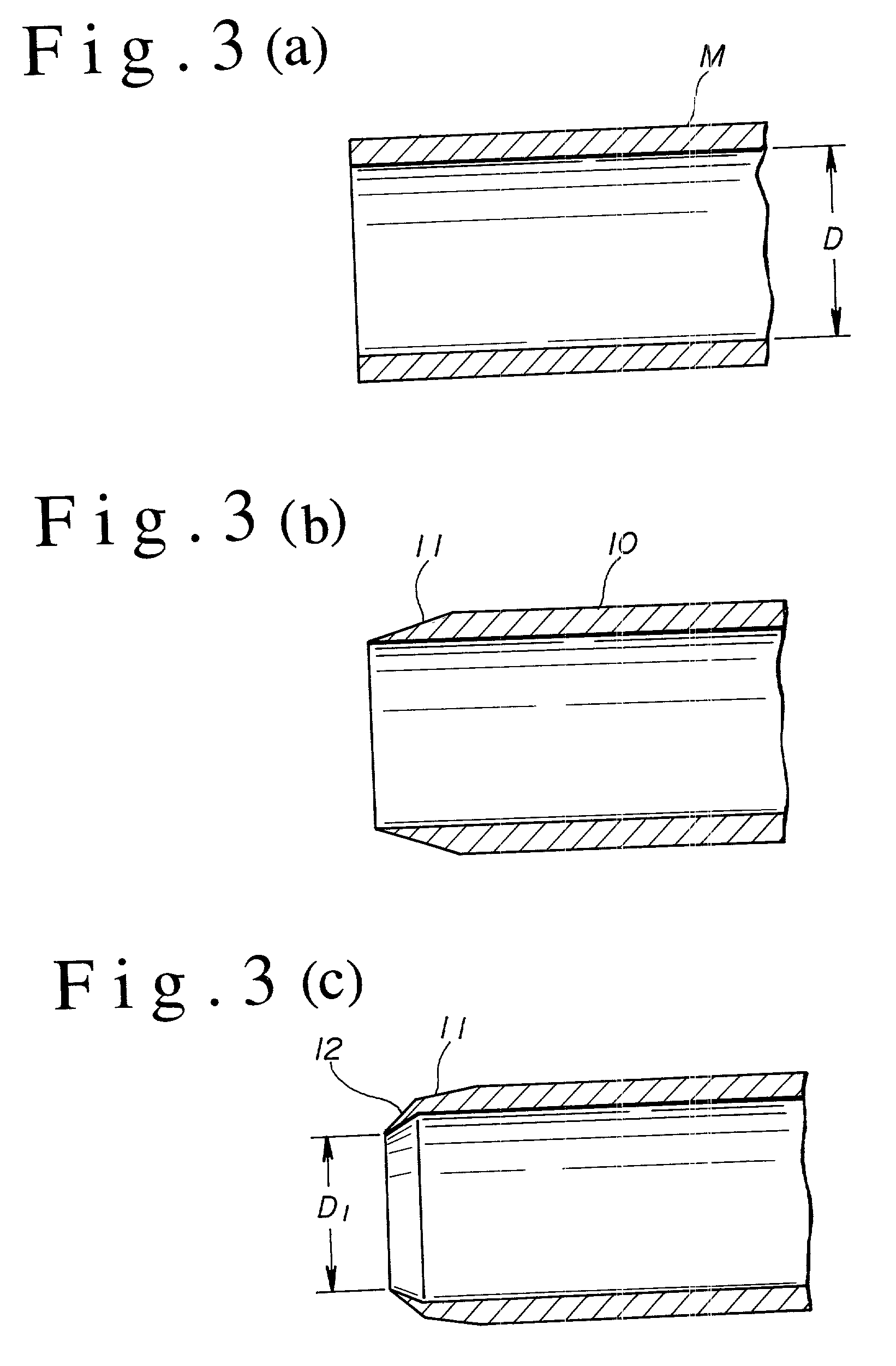
Medical anesthetic needle
A medical anesthetic needle (1) is provided that includes an inner needle (3) of a straight needle shape, having a pencil-pointed tip (4), and an outer needle (2) of a straight tubular shape, having the inner needle inserted thereinto and therethrough from the rear end thereof. A foremost-end part (12) of a hollow, truncated conical shape or the like of the outer needle (2) is formed so that the minimum inner diameter thereof is smaller than the outer diameter of the main body (5) of the inner needle (3). When the inner needle (3) is inserted into and through the outer needle (2), the circumferential fore-end edge of the foremost-end part (12) is in close contact with the circumferential surface of the tip (4) or the main body (5) of the inner needle (3), and no gaps are thus formed therebetween. Therefore, when needled, a patient's nervous tissue is unlikely to be nipped in a gap between the inner and outer needles to cause pain to the patient.
Owner:DR JAPAN
Method and device for painless injection of medication
InactiveUS20100076400A1Simple and inexpensive to performSimple and inexpensive to and operateAmpoule syringesAutomatic syringesMedication injectionAnesthetic
A method for providing a substantially painless injection of medication into a patient, including inserting an injection needle having an outside diameter greater than 0.20 mm and less than about 0.38 mm, and injecting a medicament through the needle and into the patient at a substantially constant volumetric flow rate of about 0.05 μL / s to about 50 μL / s that provides a painless injection. The method does not require the use of an anesthetic or that the medical personnel to spend a substantial amount of time performing the injection procedure, is relatively simple and inexpensive to perform and operate, and provides a relatively high degree of safety for both the medical personnel and for the patient.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT CINCINNATI
Apparatus and Method for Reducing Pain During Skin Puncturing Procedures
ActiveUS20080255483A1Easily and inexpensively utilizedFree from painTooth pluggers/hammersSurgeryInjection siteHand held
A handheld instrument for minimizing pain during administration by injection of a liquid, such as, an anesthetic that has a main body, a vibration unit mounted in the main body when initiated to cause the main body to vibrate, and a detachable tip cantilever mounted on the main body to vibrate with it, the tip having a free end characterized by a bifurcation to form two spaced projections defining a space between them, whereby the spaced projections can be placed in proximity to, adjacent to and bracketing a preselected injection site on a human or animal and the tissue at said preselected injection site and vibrated while an injection is given.
Owner:BING INNOVATIONS
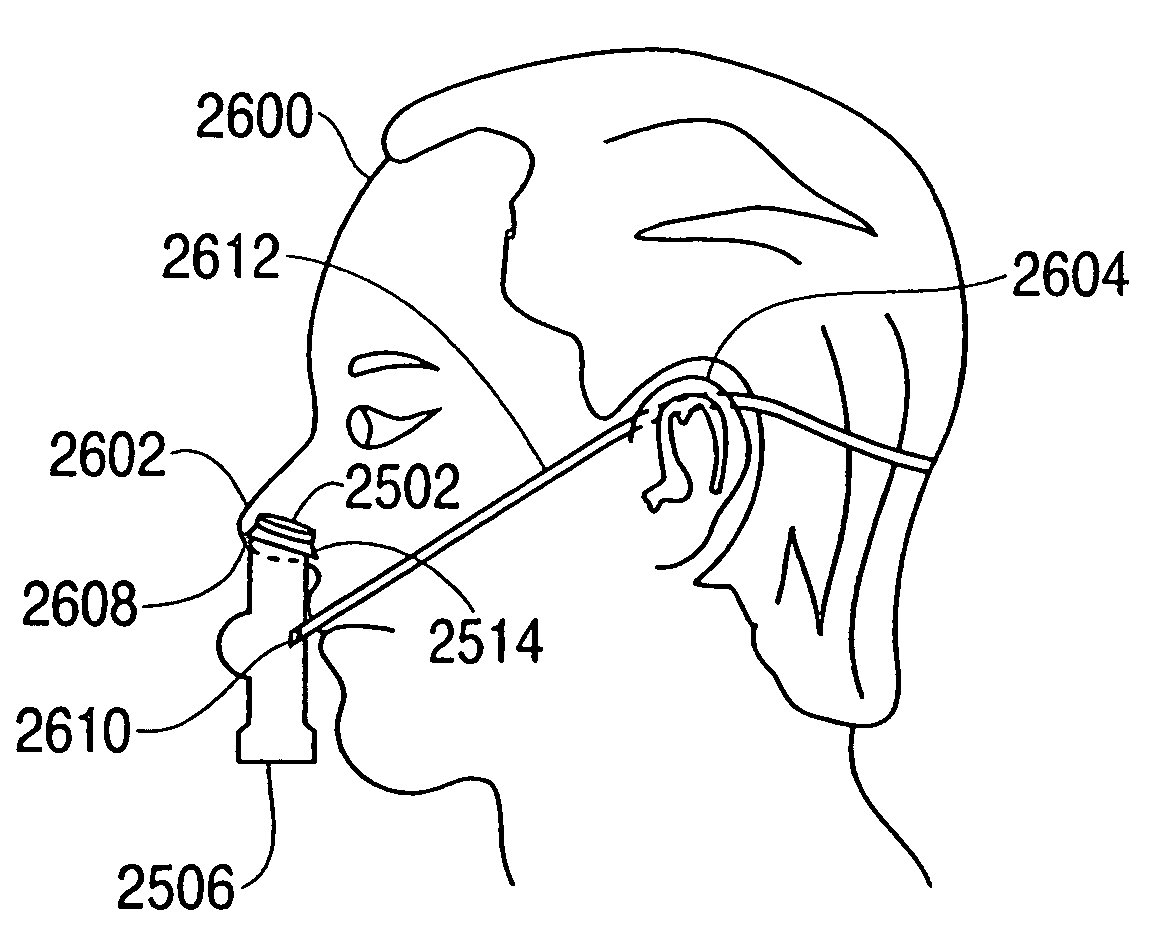
Iontophoresis Methods
ActiveUS20090163848A1Reduction in patient discomfortEnhanced and real-time monitoringOrganic active ingredientsElectrotherapyDrugs solutionTympanic Membranes
A method of anesthetizing a tympanic membrane of an ear of a patient using iontophoresis is disclosed. The method involves delivering an anesthetizing drug solution to an ear canal of the patient's ear, wherein the drug solution includes an anesthetic and a buffer, and wherein the drug solution has a pH in the range of about 6.5 to about 7.5; and applying an amount of current to the drug solution, wherein the amount of applied current is increased at a rate of less than about 0.5 milliamp per second until a maximum current is achieved.
Owner:TUSKER MEDICAL
Apparatus and methods for treatment of nasal tissue
InactiveUS20070244529A1Small sizeIncrease airflowUltrasound therapyElectrotherapyPain managementAnalgesic agents
Apparatus and methods for the treatment of nasal tissue, particularly the nasal turbinates, are described herein. One method for reducing the size of the inferior nasal turbinate is to apply ultrasound energy to the tissue regions beneath the surface of the turbinate tissue. One instrument may be used to deliver ultrasound energy and to provide an infusion or injection of a fluid directly into the turbinate being treated. The injected fluid can be used to bulk up the size of the turbinate to ensure that the ultrasound energy is properly delivered directly into the intended turbinate tissue. Accordingly, fluids containing anesthetics, fluids infused with analgesics, etc. may be used for pain management while other medications, such as non-steroidal drugs, steroidal drugs, anti-inflammatory drugs, anti-histamines, anti-bacterial drugs, etc., can also be used.
Owner:CHOI GEORGE Y
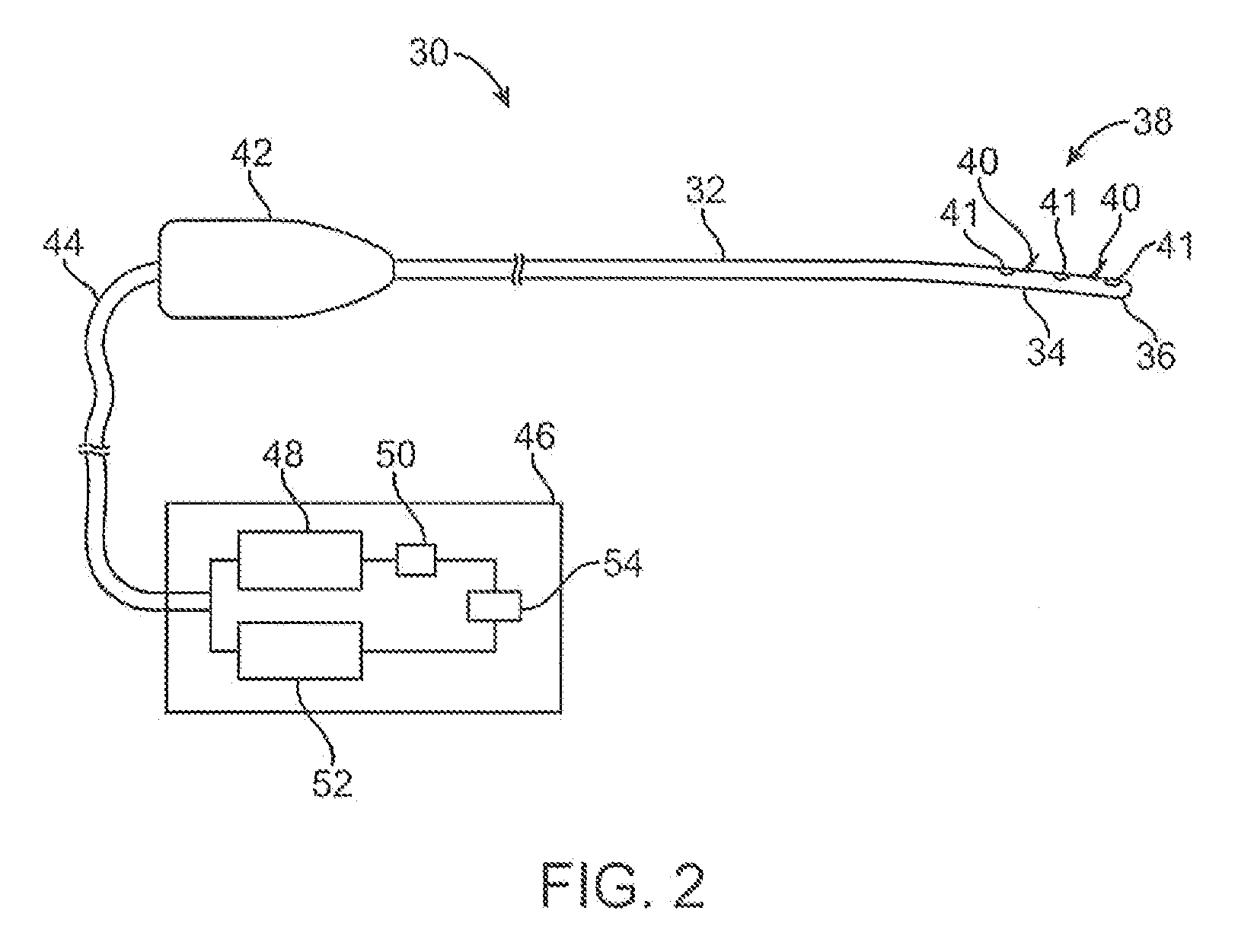
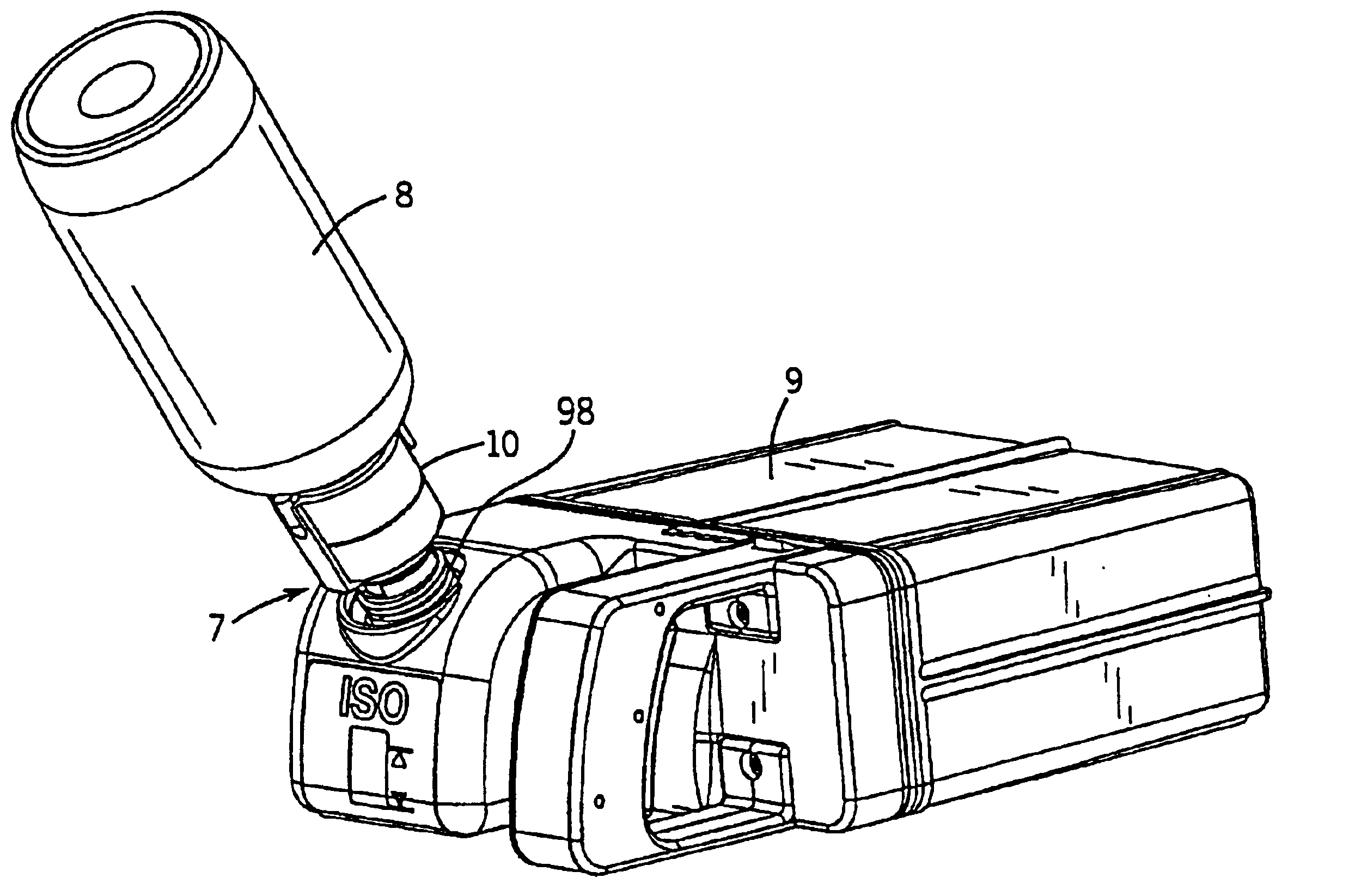
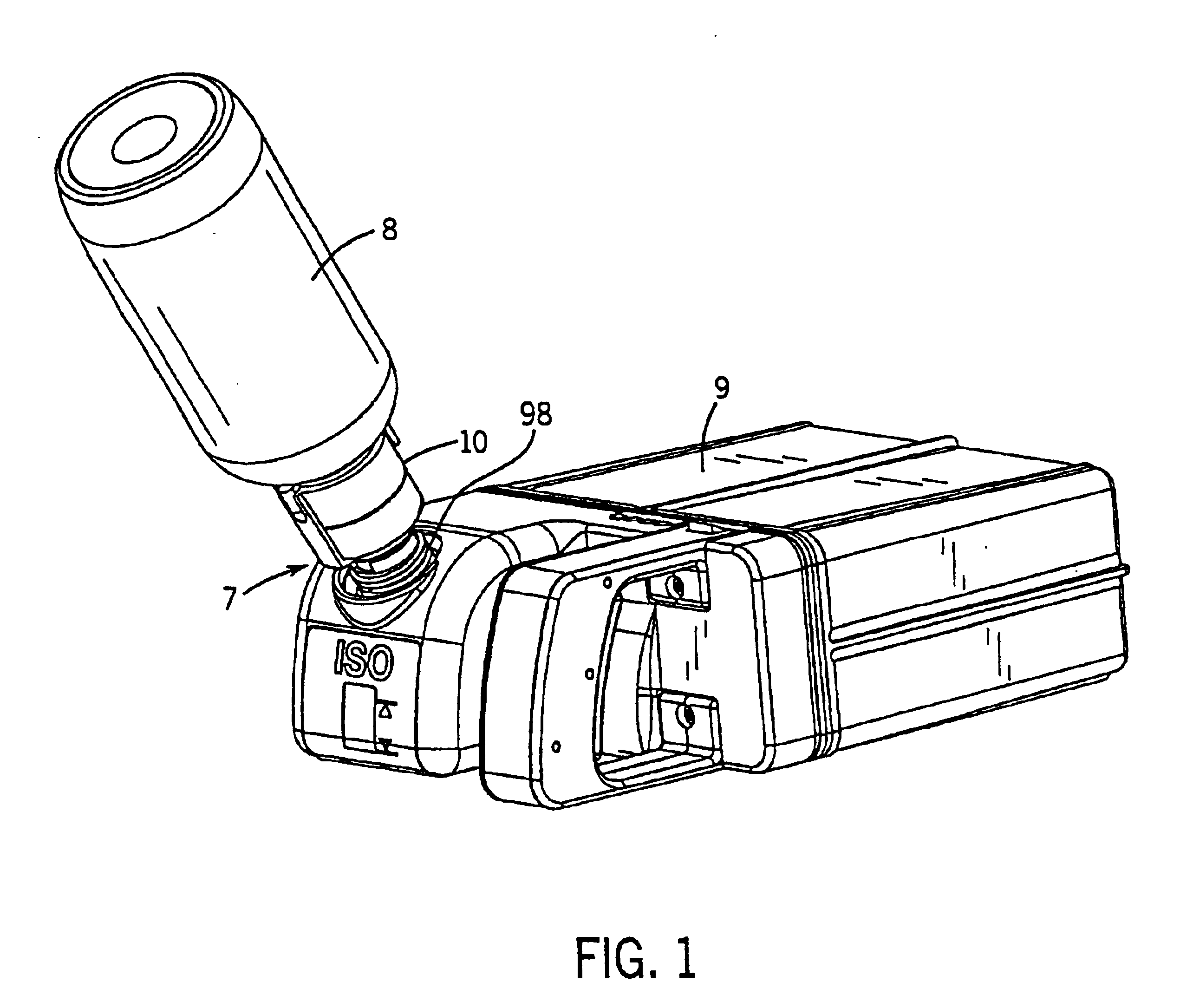
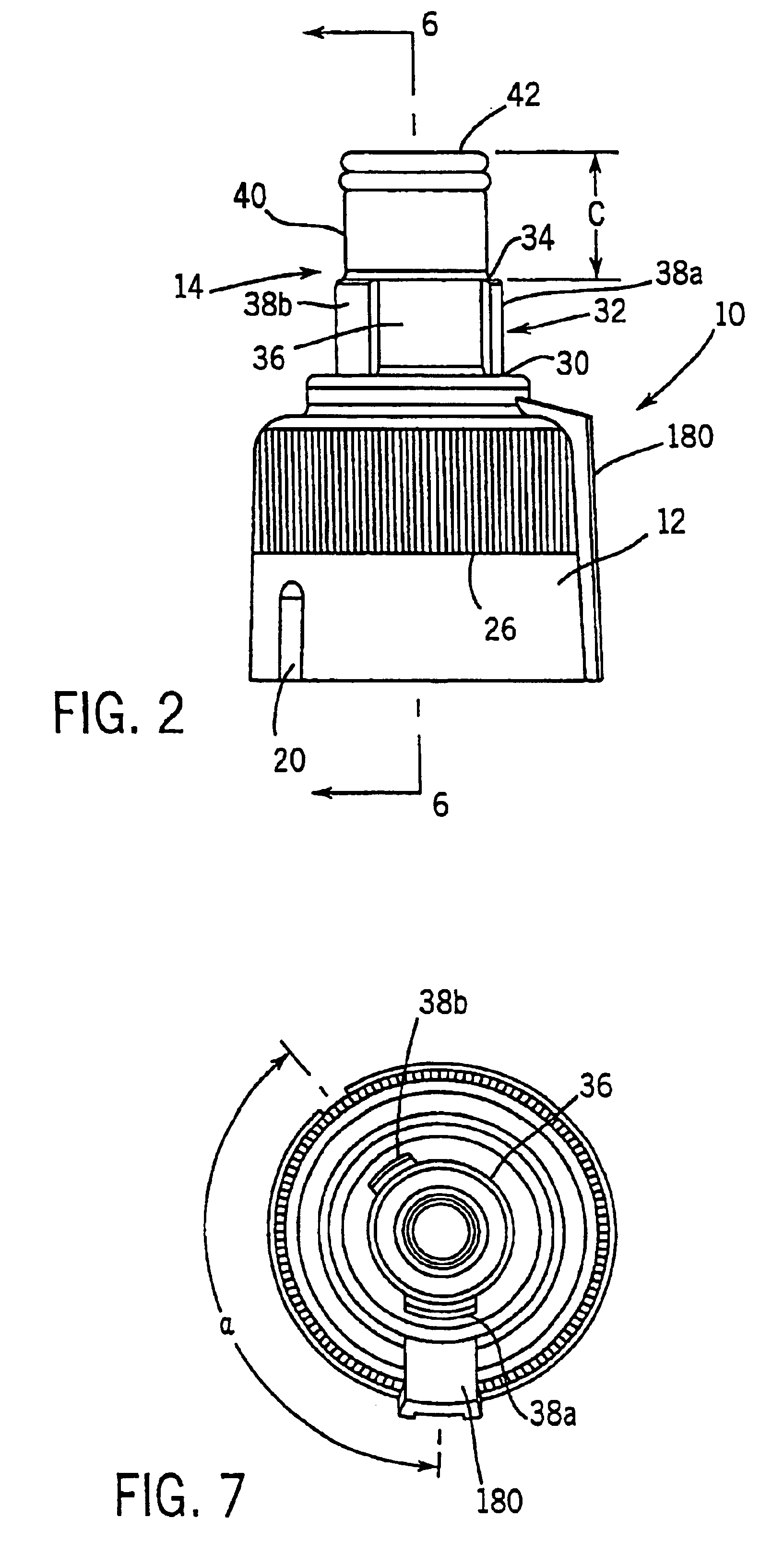
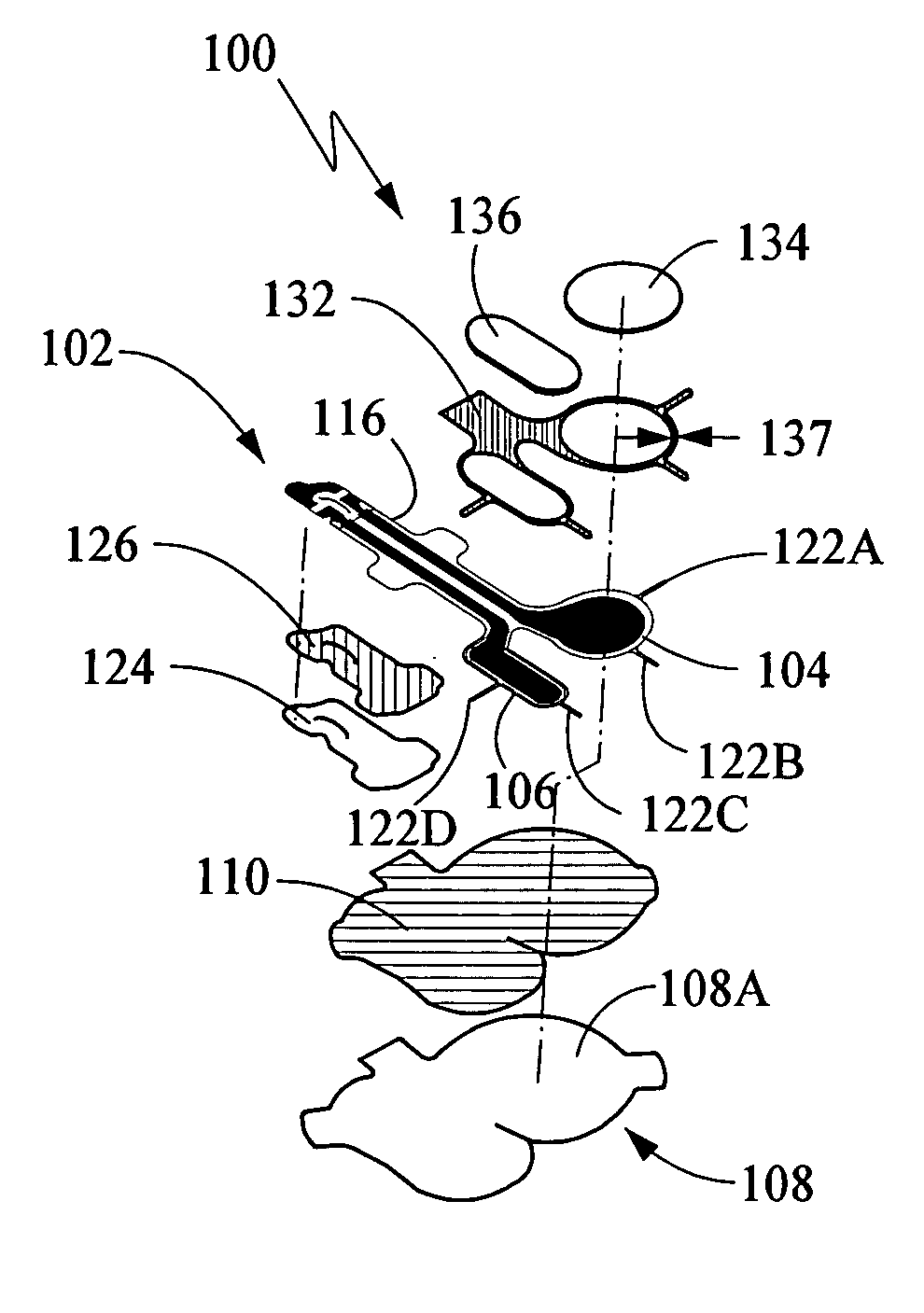
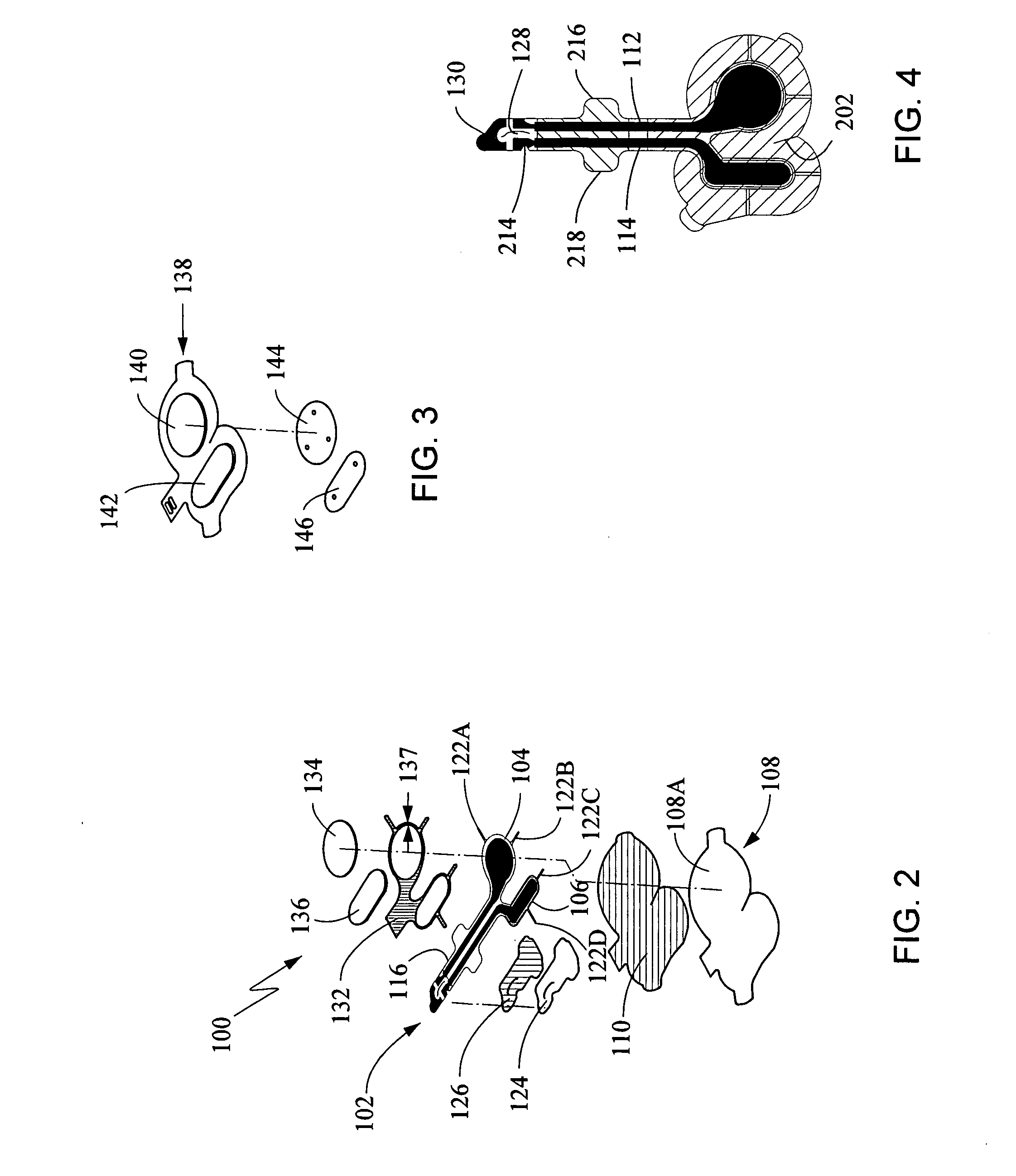
Keyed anesthetic vaporizer filling system
A system for facilitating the delivery of a liquid anesthetic agent from an anesthetic bottle to an anesthetic vaporizer. The system includes a bottle adapter, an anesthetic bottle and a filler arrangement positioned on the anesthetic vaporizer. The bottle adapter and filler arrangement each include a keyed configuration such that only the correct type of anesthetic agent can be emptied into the anesthetic vaporizer. The bottle adapter includes an adapter valve assembly that engages a filler valve assembly contained within the filler. The dimensions and arrangement of the adapter valve assembly and the filler valve assembly insure anesthetic agent is delivered to the anesthetic vaporizer only when the anesthetic agent can safely flow from the anesthetic bottle to the anesthetic vaporizer.
Owner:DATEX OHMEDA
Electrically assisted lidocaine and epinephrine delivery device having extended shelf-stability
InactiveUS20050228336A1Great confidenceFewer returnsOrganic active ingredientsElectrotherapyLidocaineAnesthetic
Highly shelf-stable electrically assisted transdermal drug delivery systems for delivering epinephrine, typically with an anesthetic such as lidocaine, are provided along with methods for making the highly shelf-stable epinephrine-containing transdermal delivery device. Highly shelf-stable packaged electrode assemblies for transdermal delivery of epinephrine also are provided.
Owner:VYTERIS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com