Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
39 results about "Maxillary arch" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Maxillary arch. Etymology: L, maxilla, upper jaw, arcus, bow. the curved bony ridge of the upper jawbone, in the shape of a horseshoe, including the dentition and supporting structures.
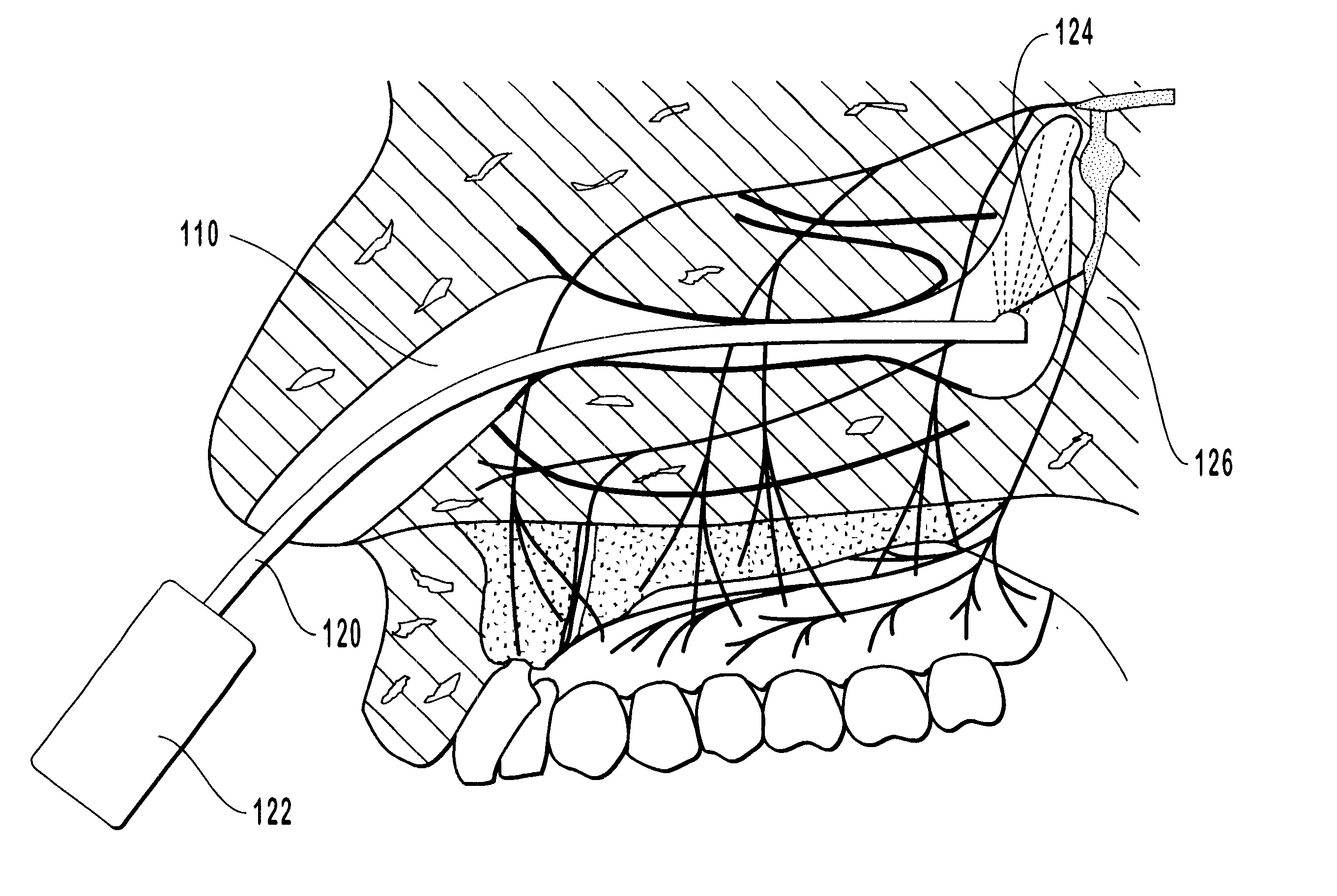
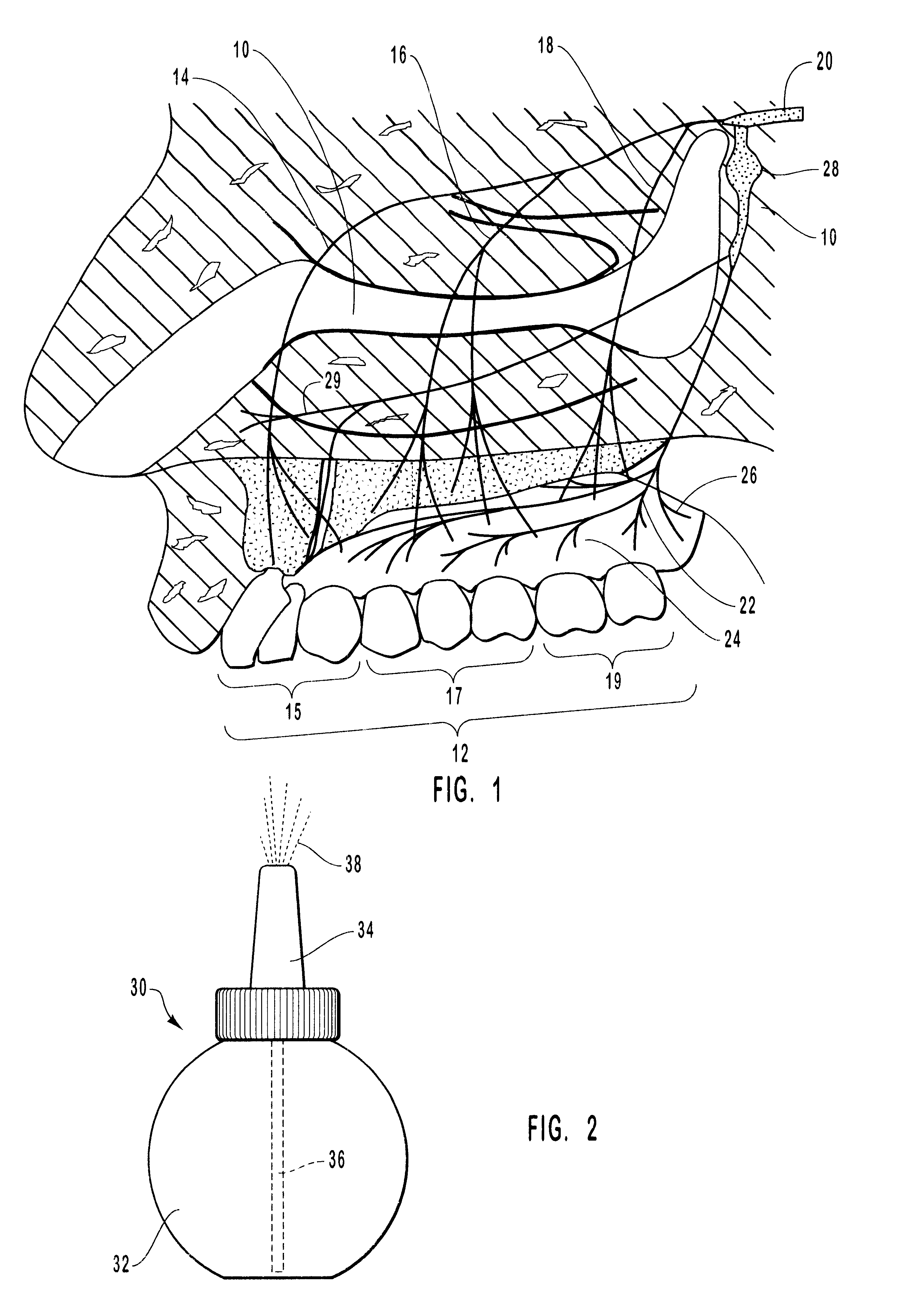
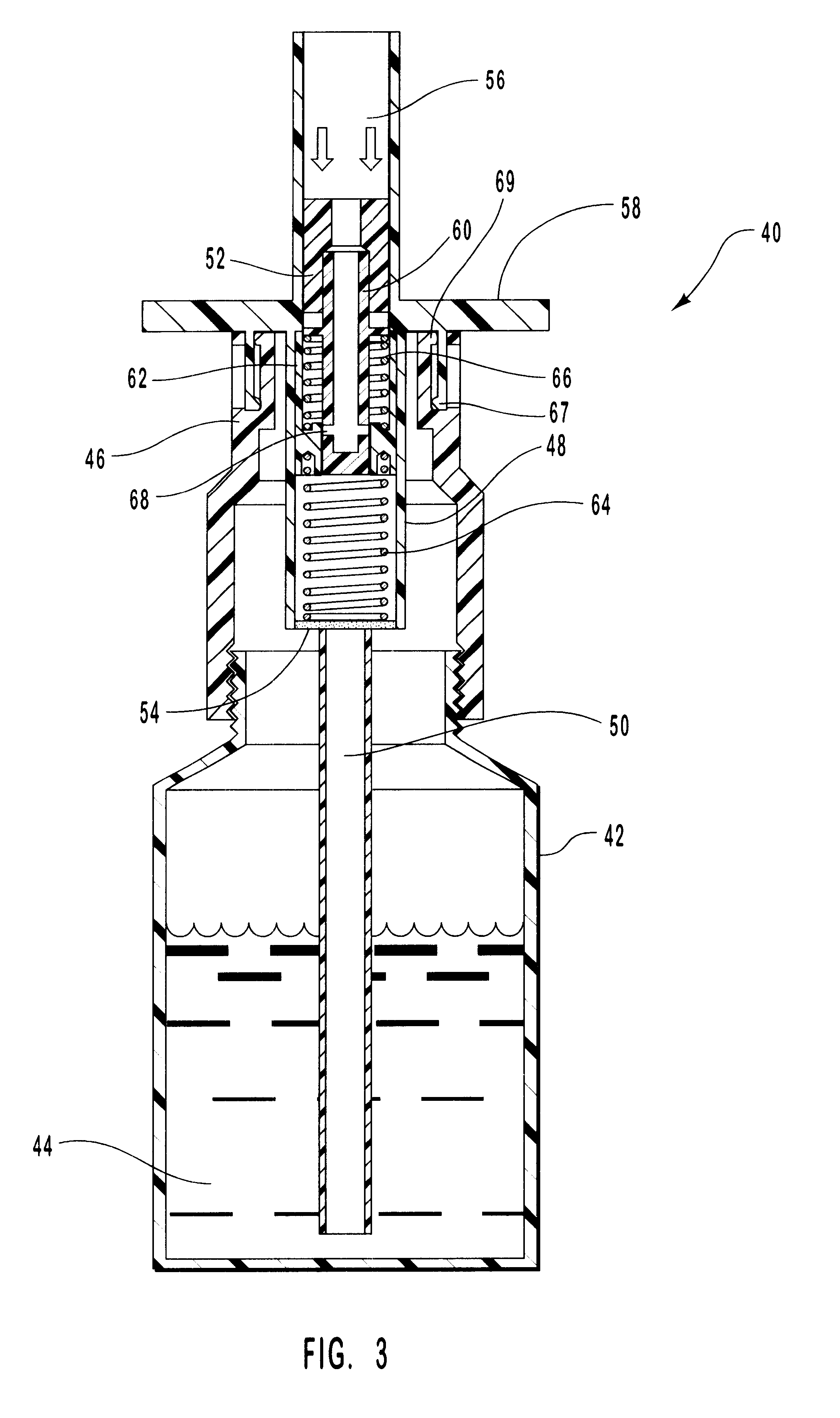
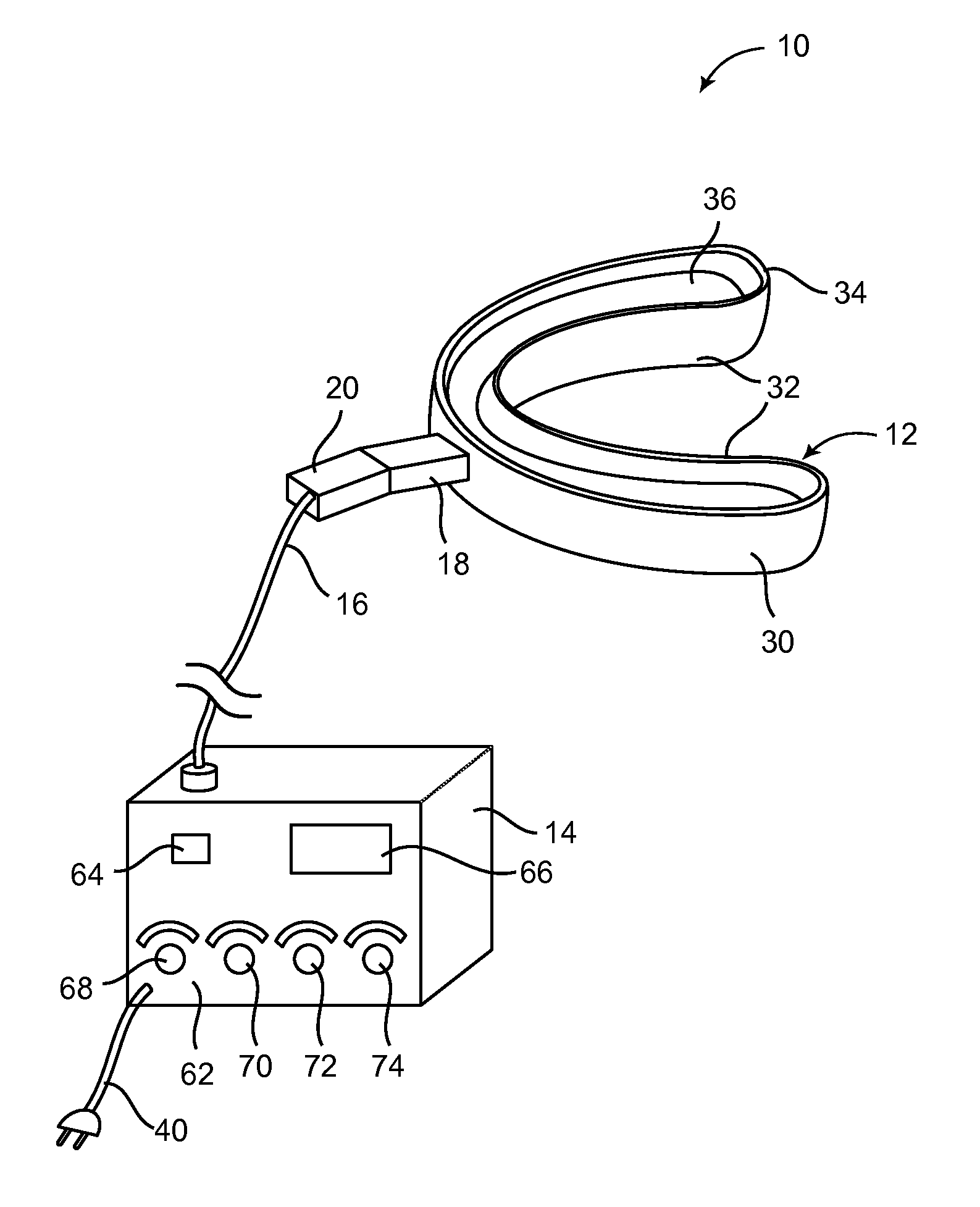
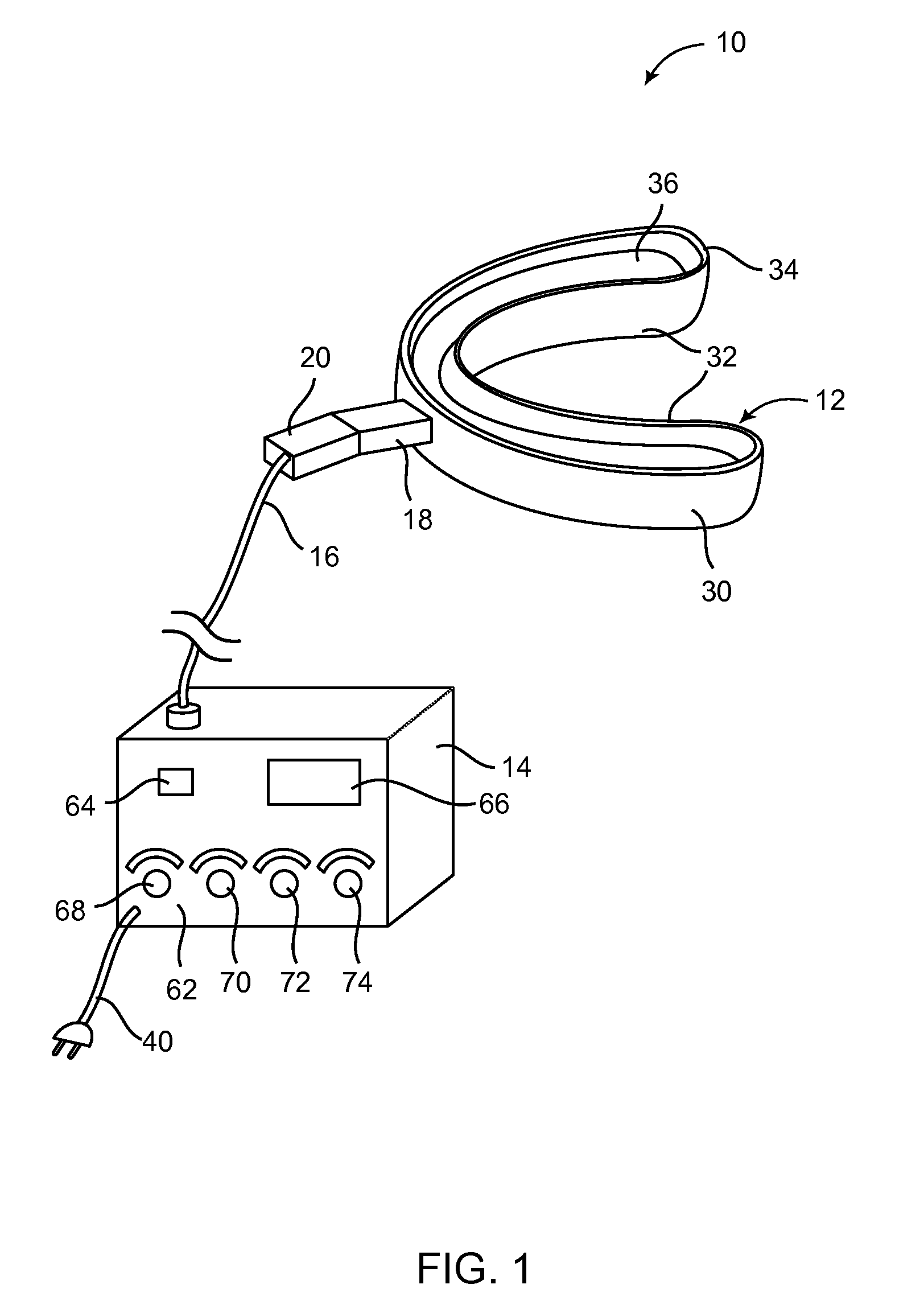
Methods and kits for maxillary dental anesthesia by means of a nasal deliverable anesthetic
Methods and systems for anesthetizing a portion or all of a patient's maxillary dental arch using a nasal delivered anesthetizing composition. The process generates anesthesia sufficient for facilitation of operative dentistry, endodontics, periodontics or oral surgery for teeth of the maxillary arch. The dental nasal spray process consists of inserting one or more dispensing devices through the patient's nostril and delivering metered dosages of anesthetic solution or gel into the nasal cavity. The process may utilize a single solution which is a mixture of anesthetic agents, vasoconstricting agents and other physiological inert agents or two separate solutions, wherein one solution contains the vasoconstricting agents and the other solution contains the anesthetic agents. Anesthetic diffusion through the thin walls of the nasal cavity allows for the blocking of nerve impulses originating from the maxillary dentition and surrounding tissues. Anesthesia of specific oral regions such as right versus left sides of the dental arch, anterior versus posterior teeth, and soft tissue anesthesia may be controlled through modification of the dosage volume and the selection of right or left nostril insertion and agent delivery.
Owner:ST RENATUS +1
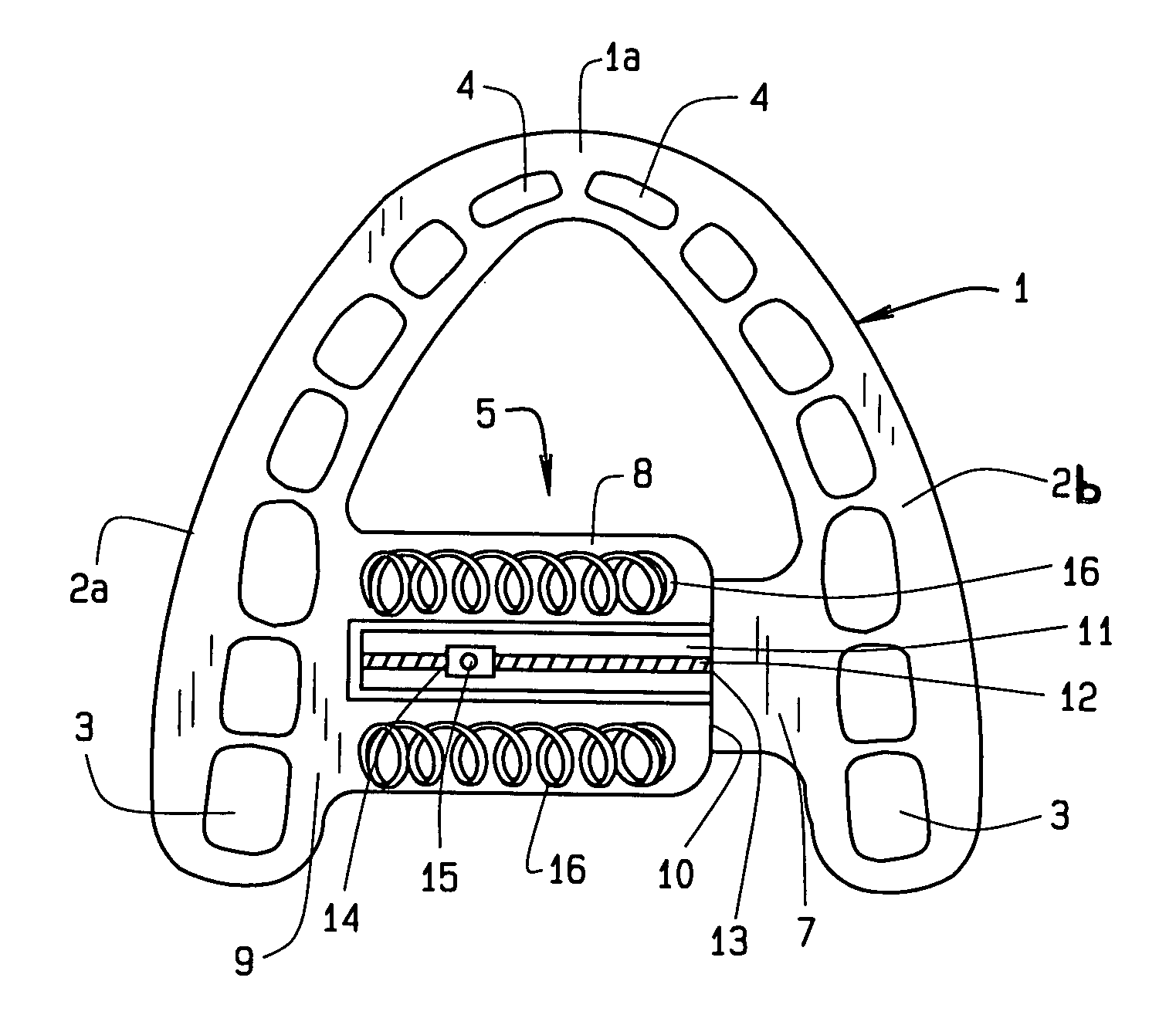
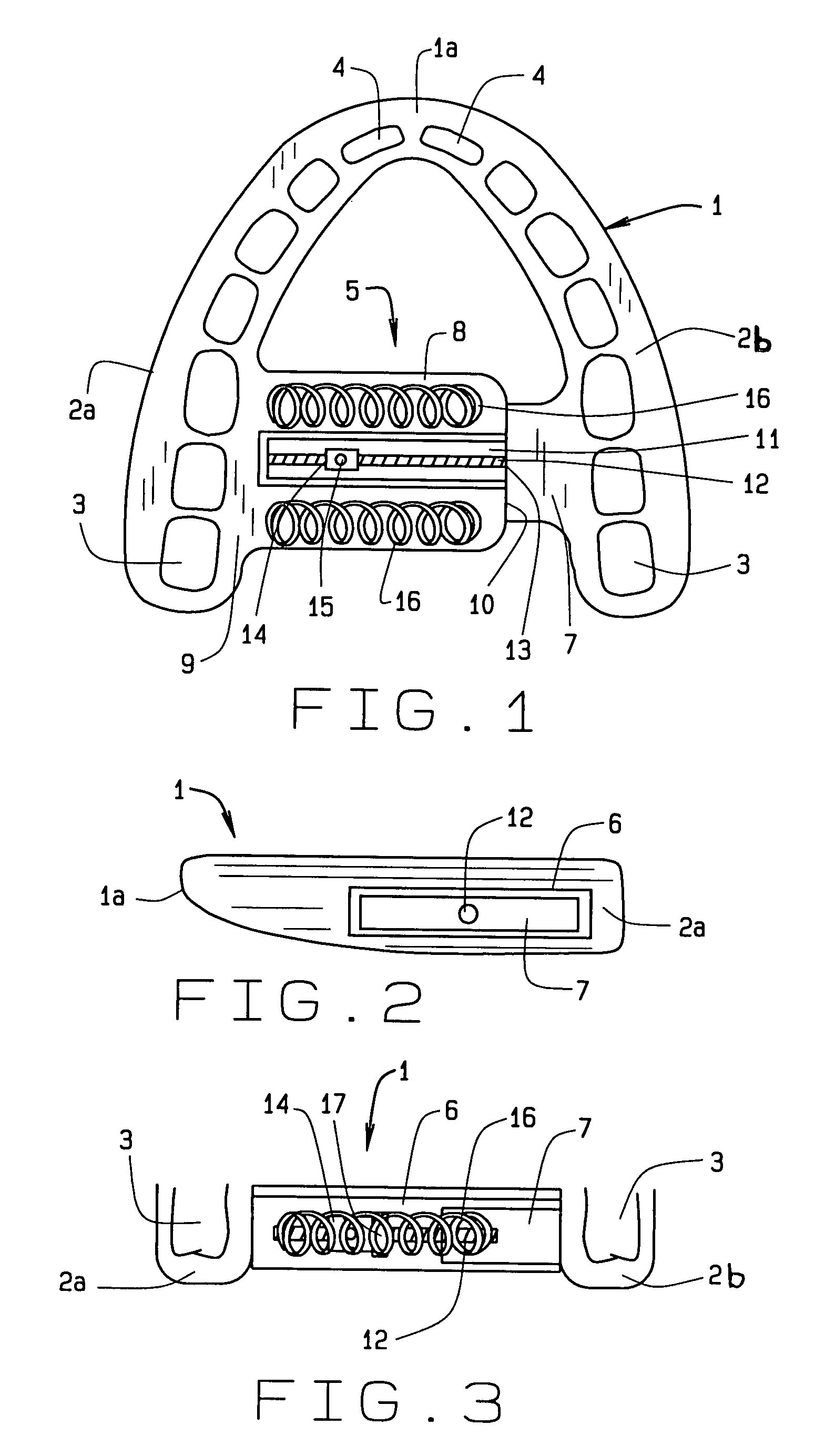
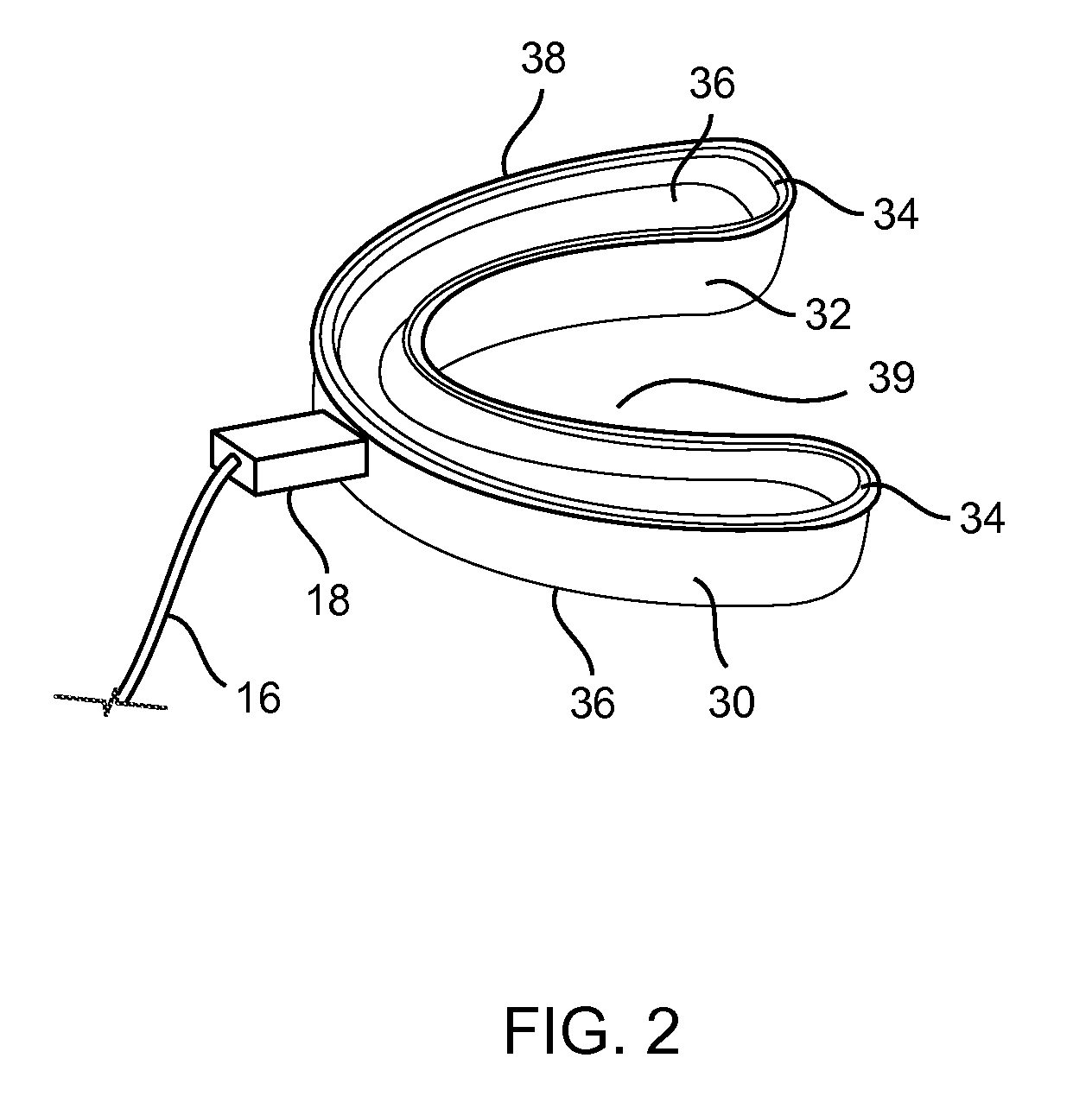
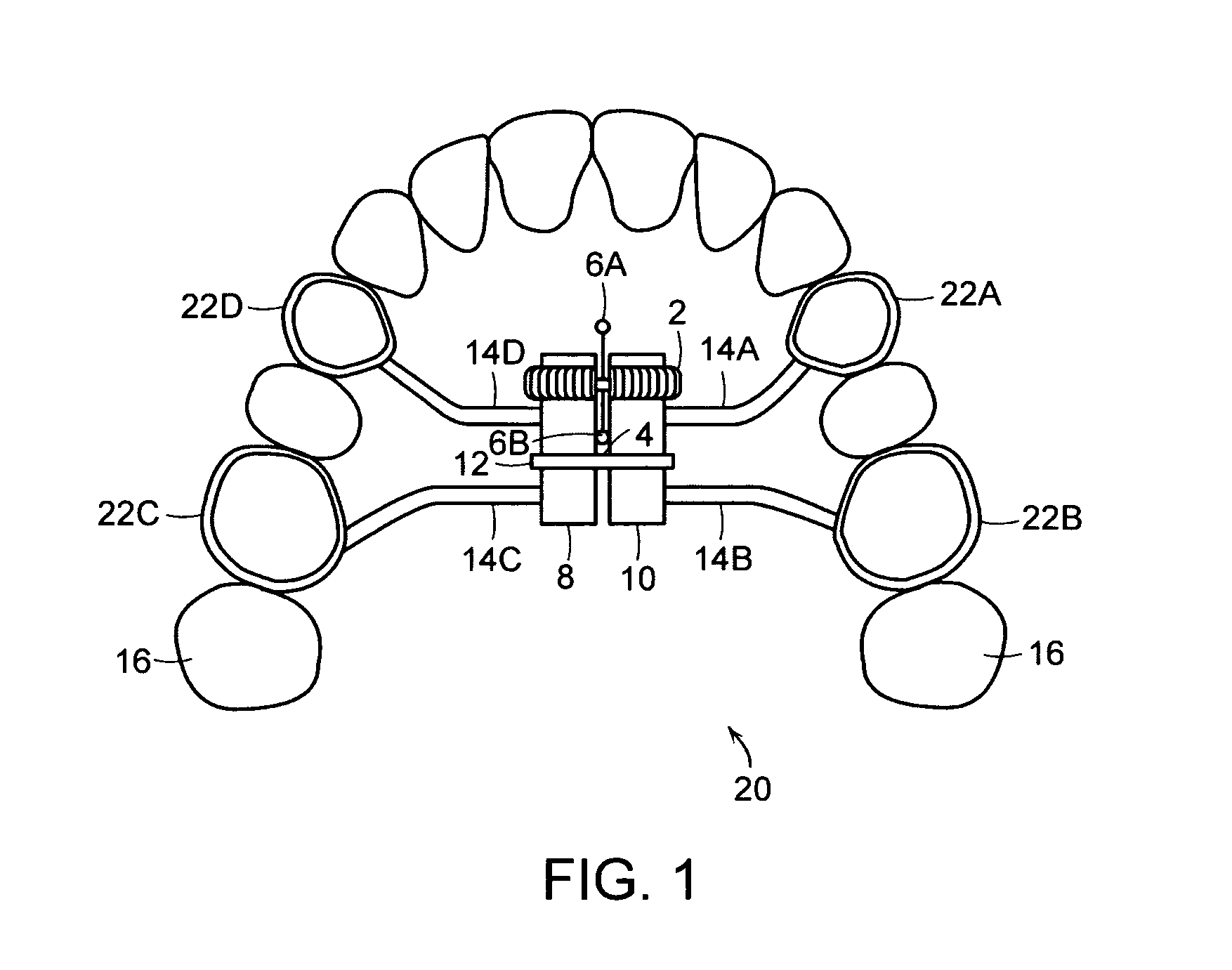
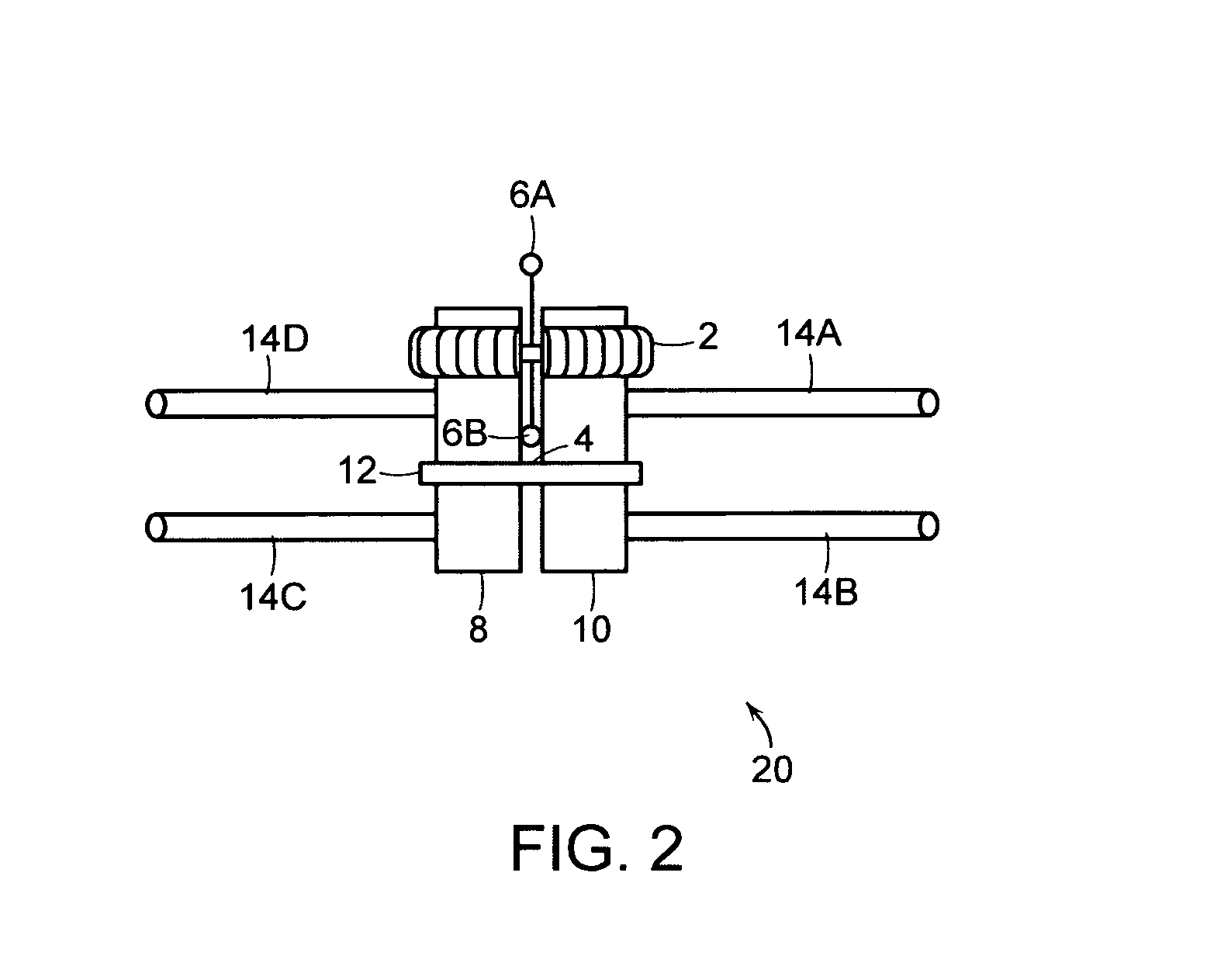
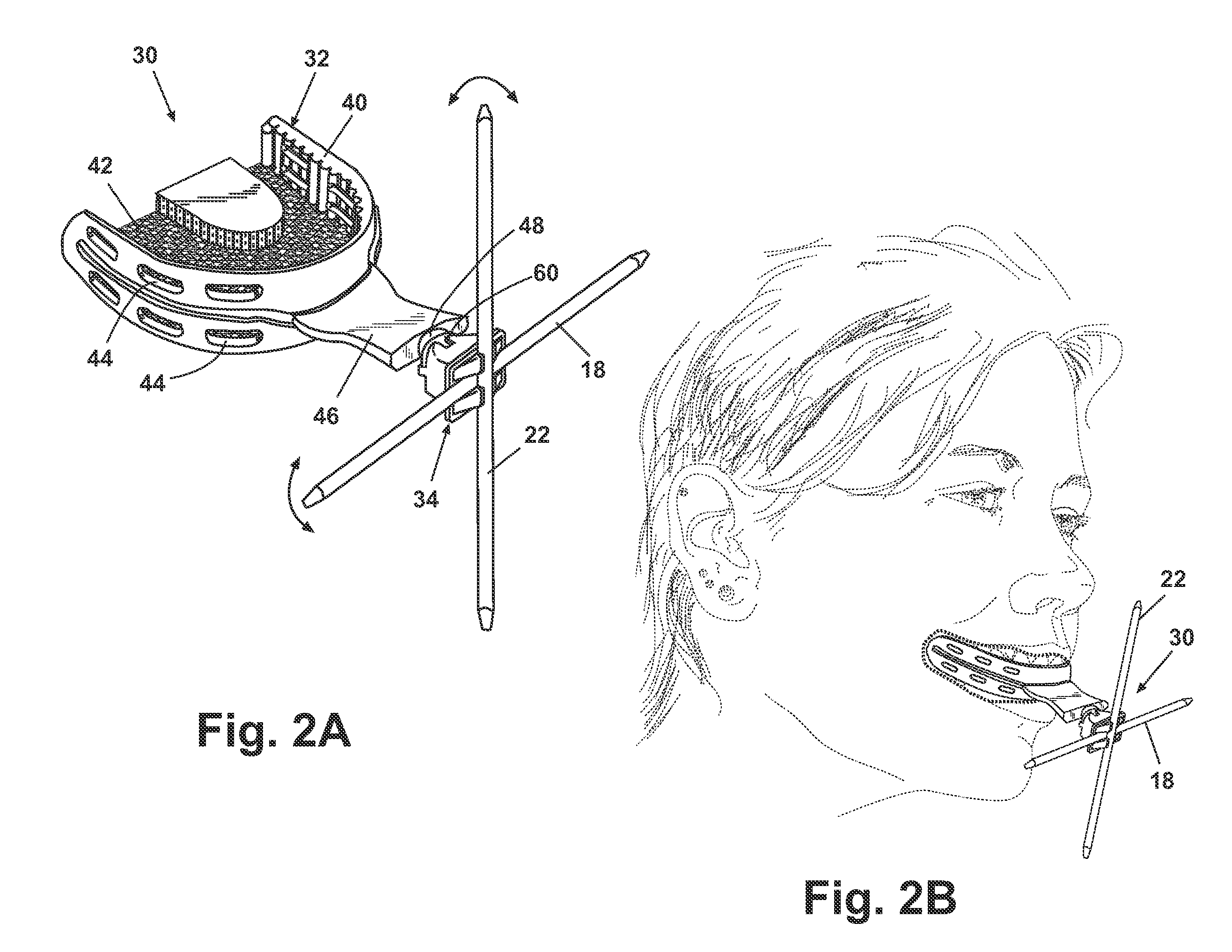
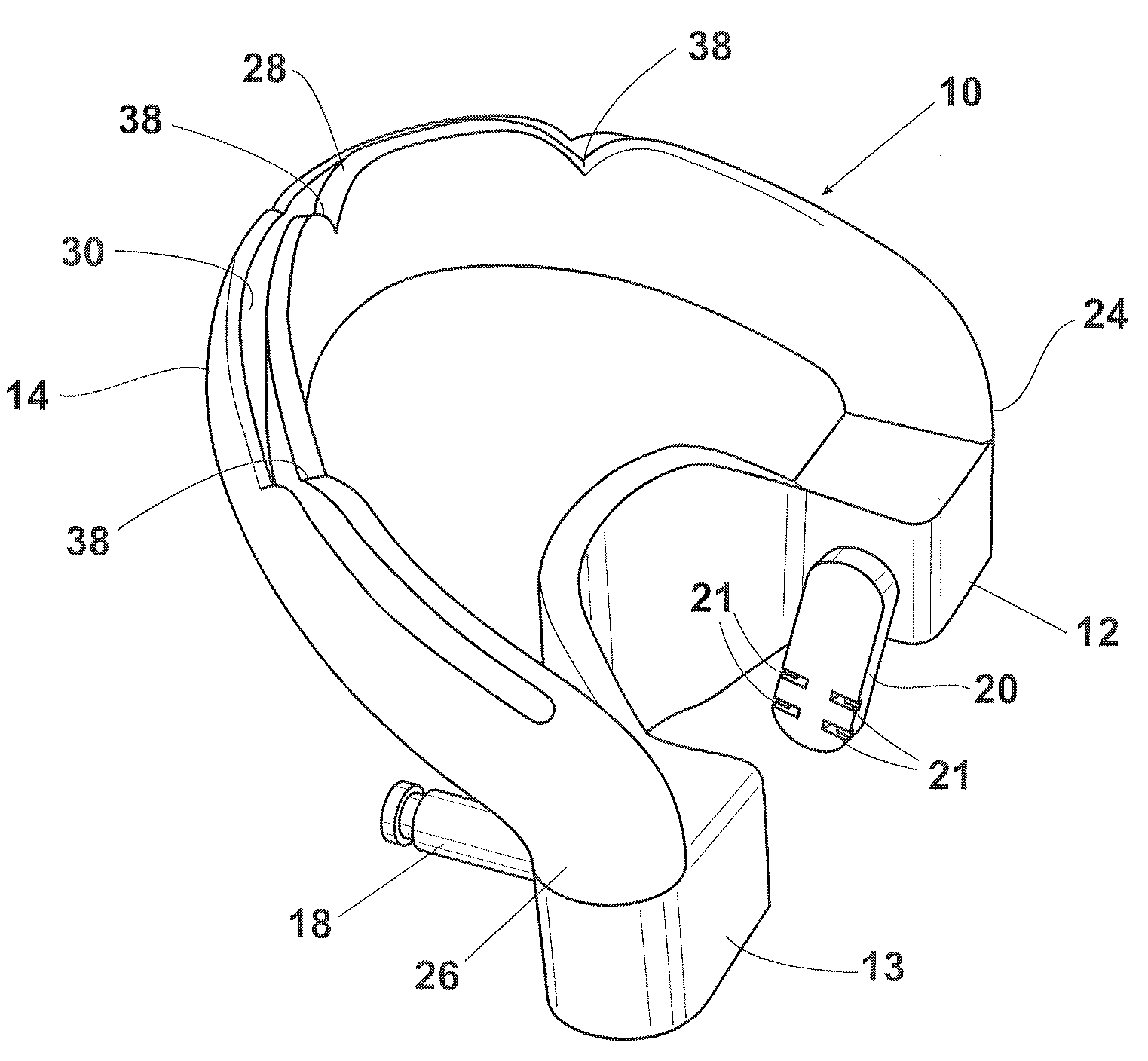
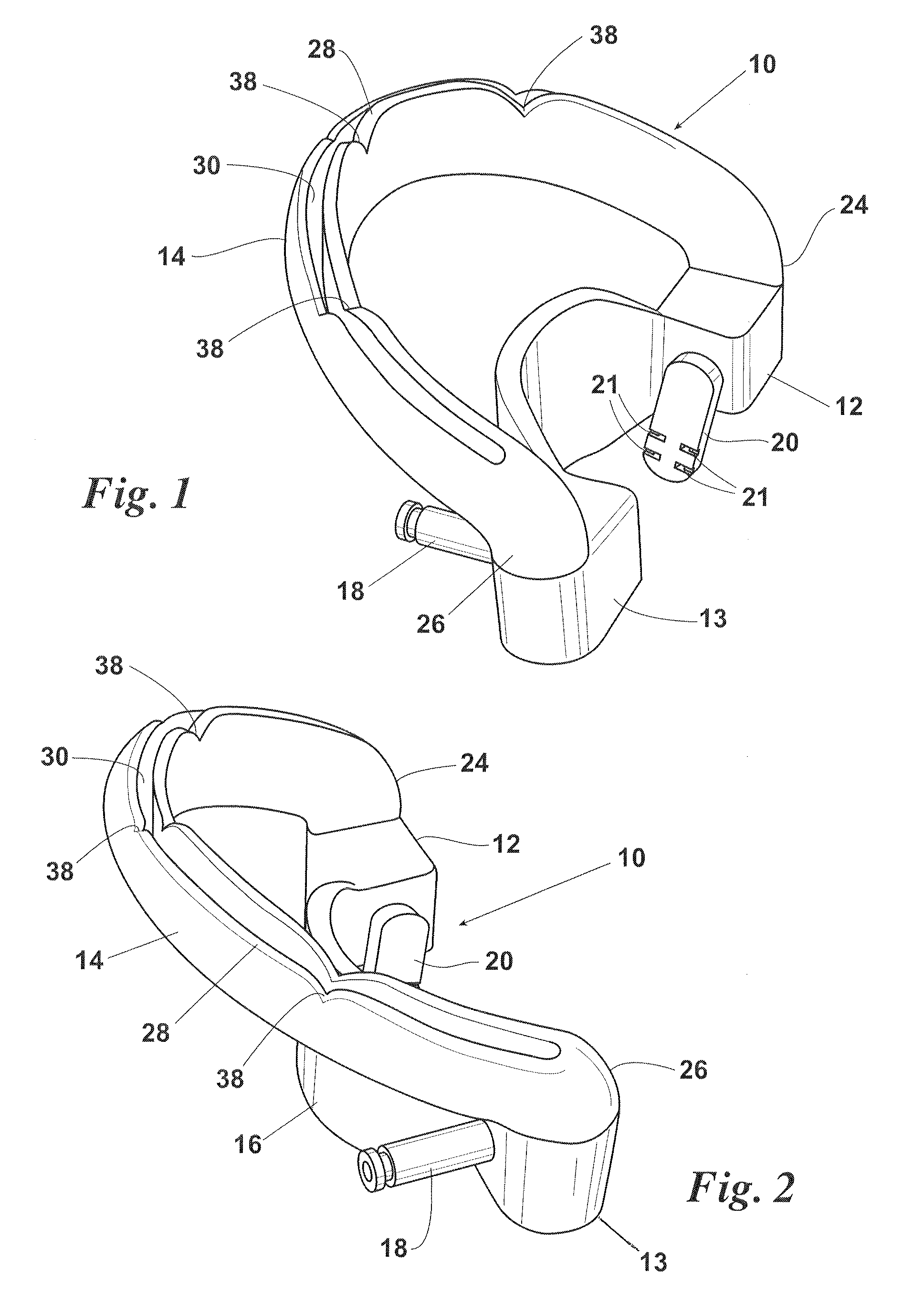
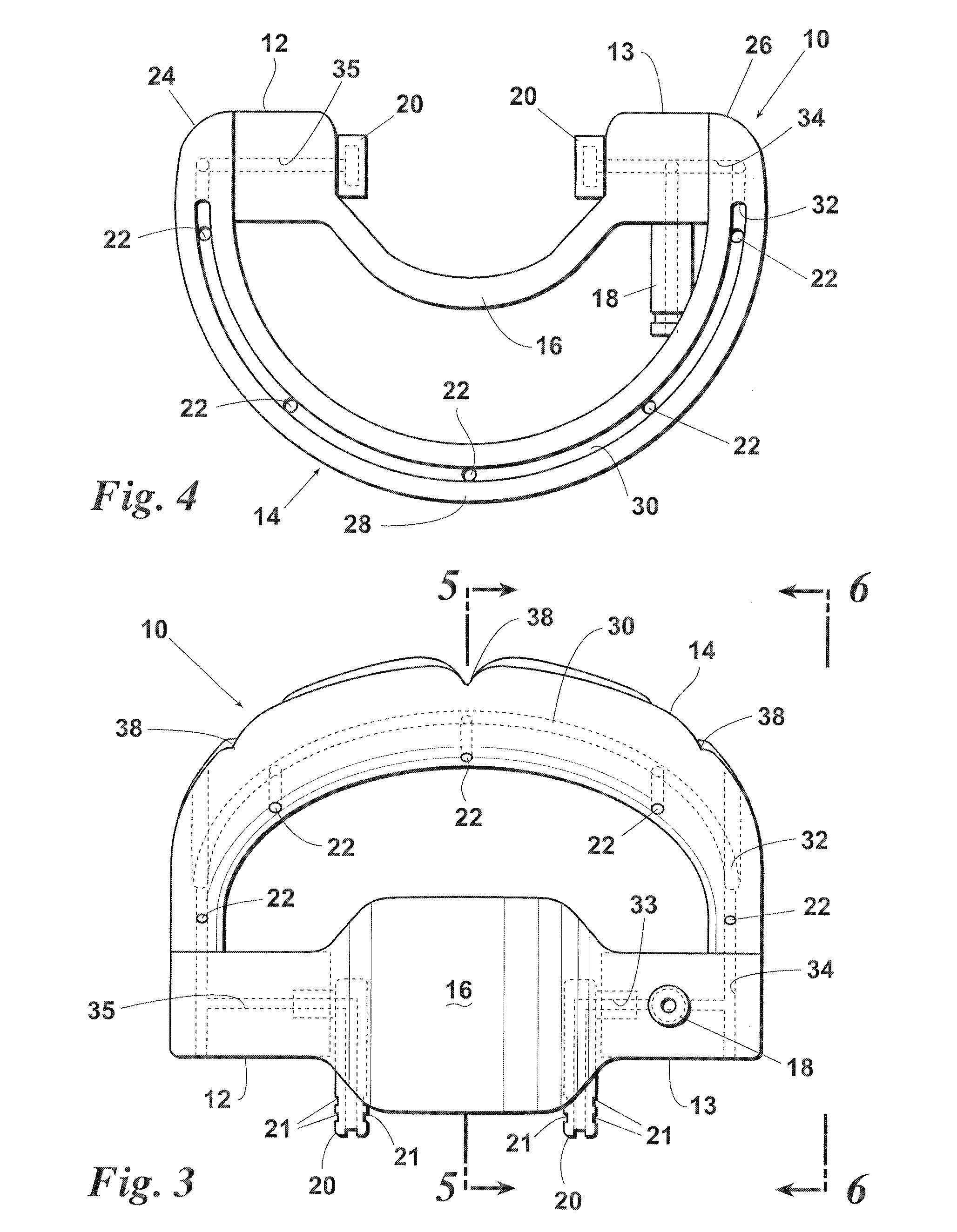
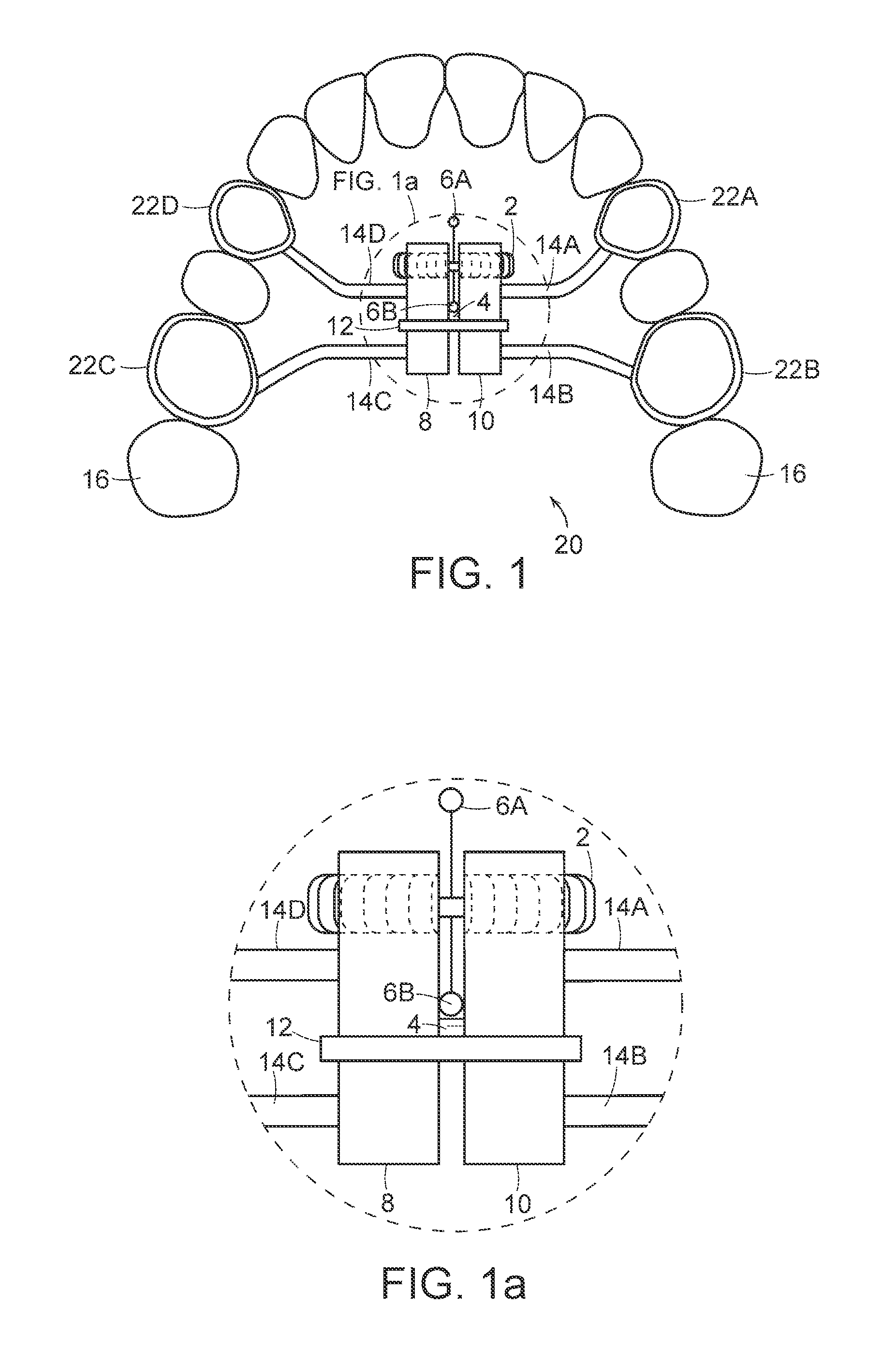
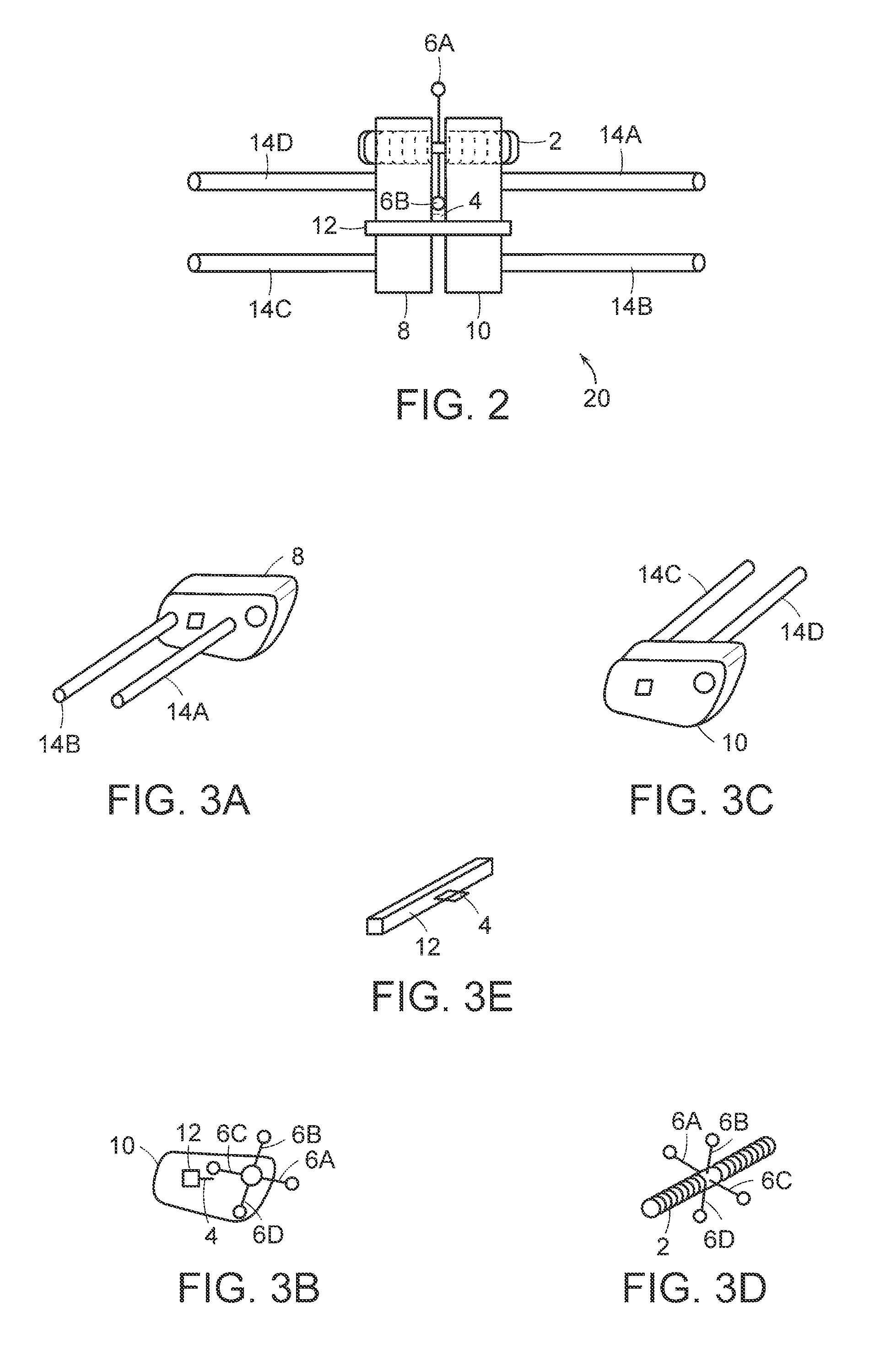
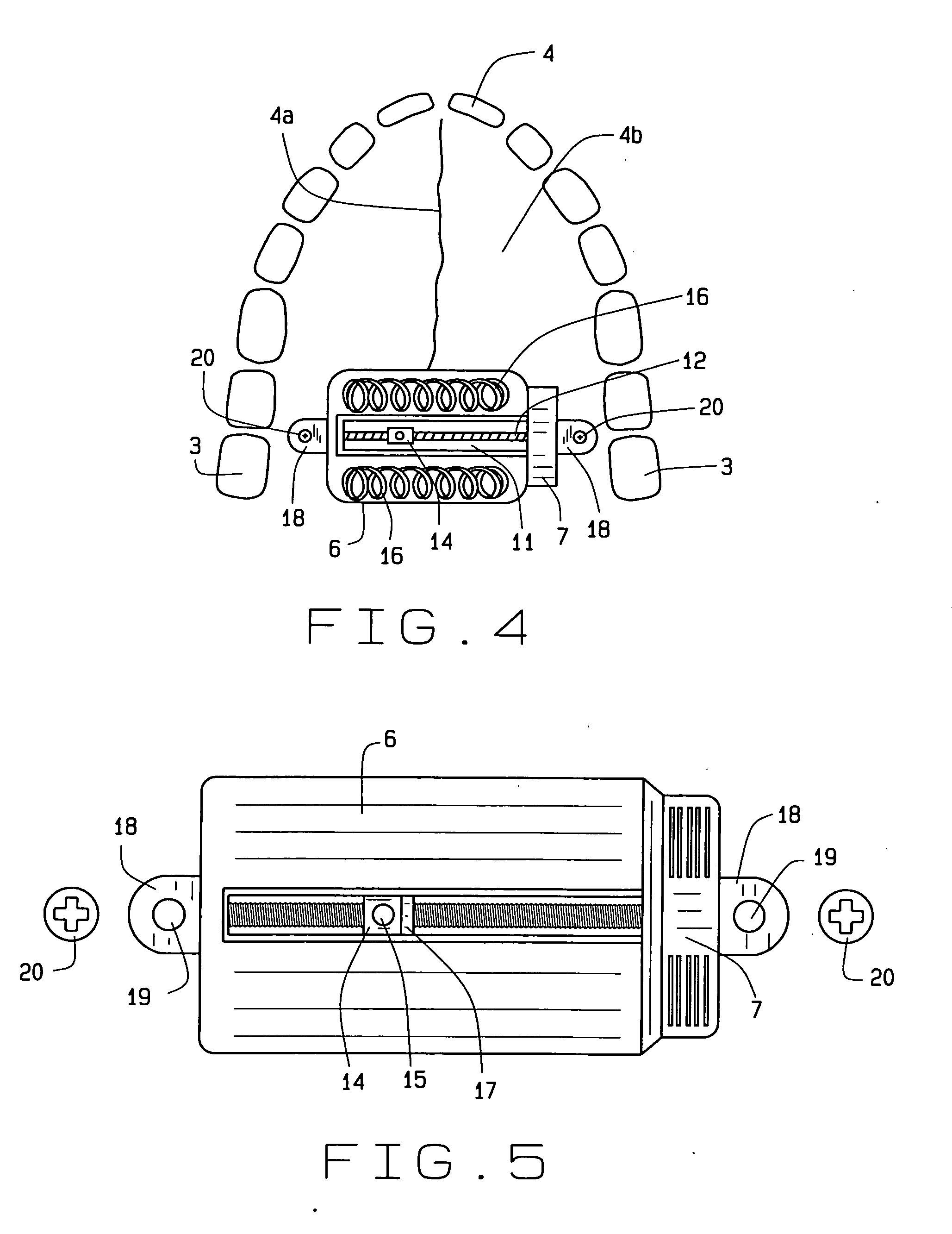
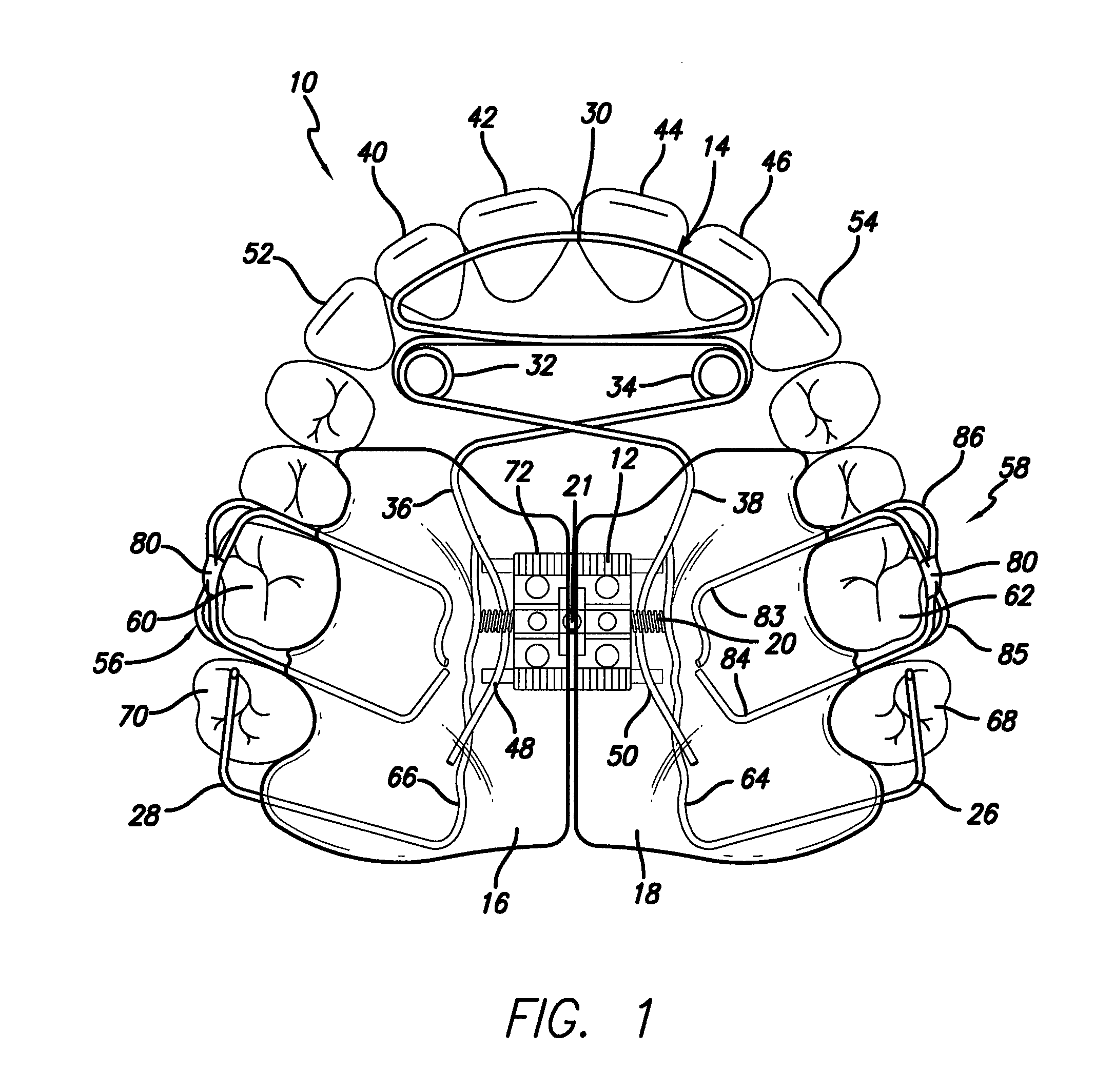
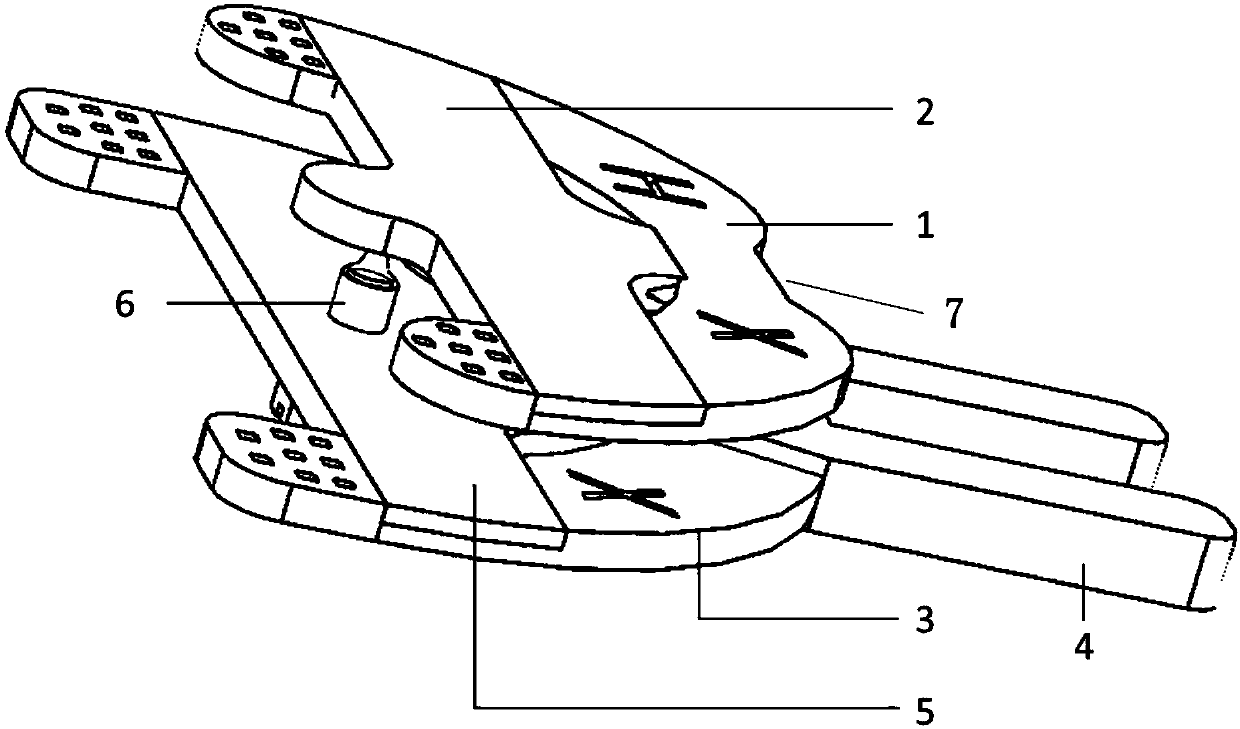
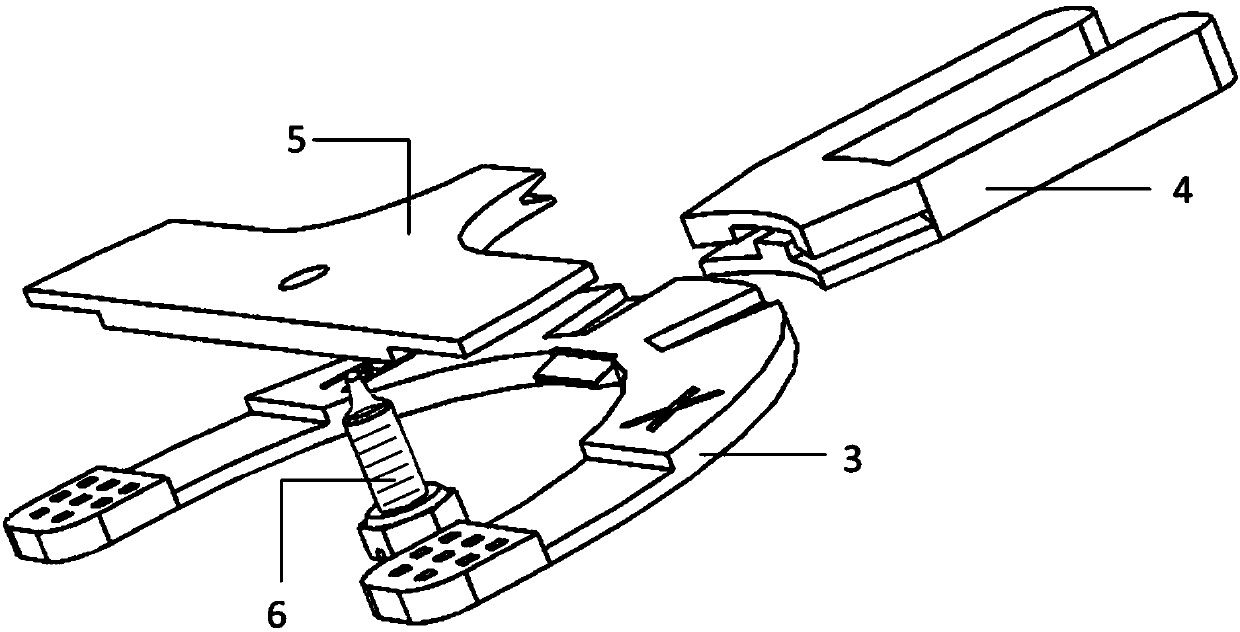
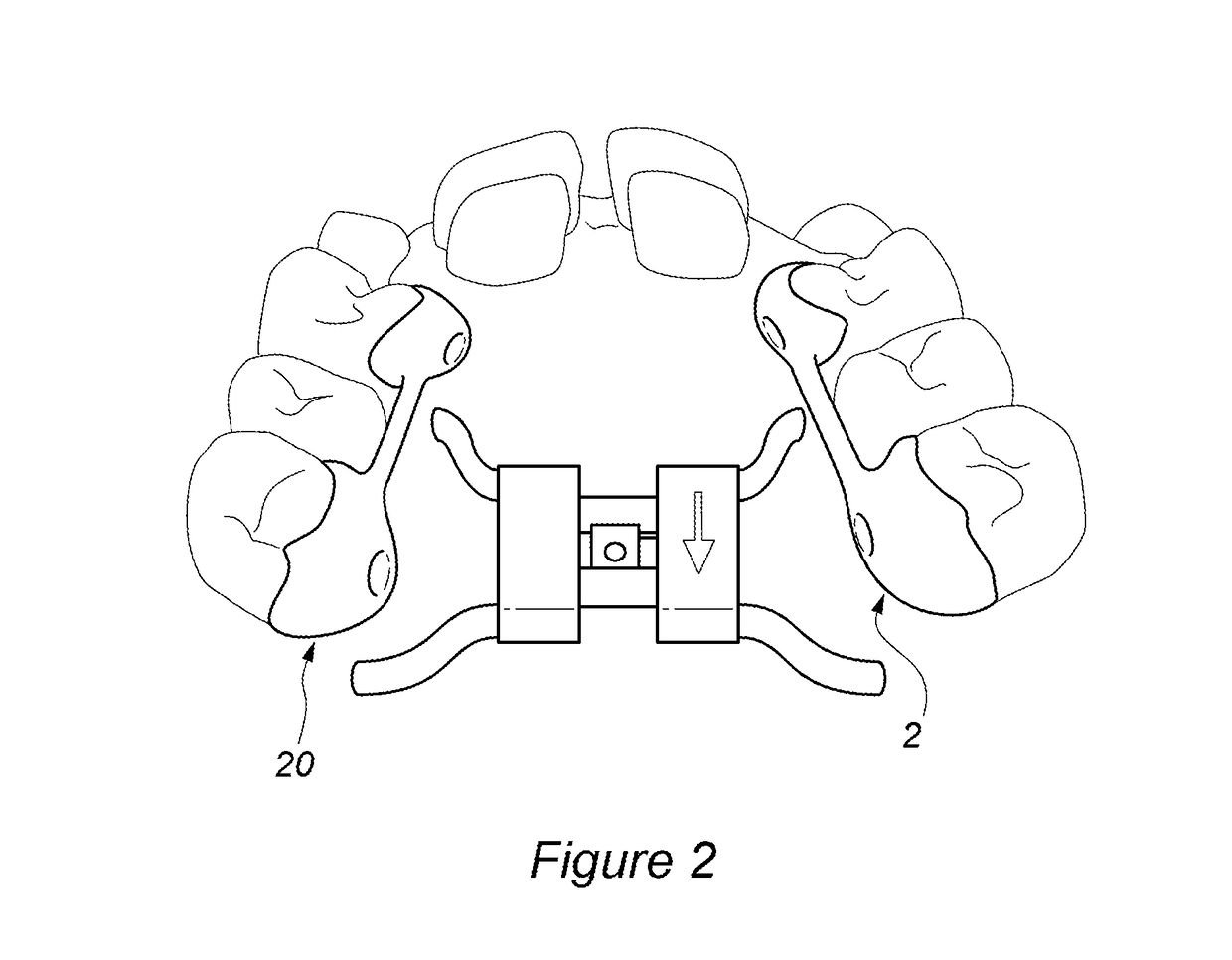
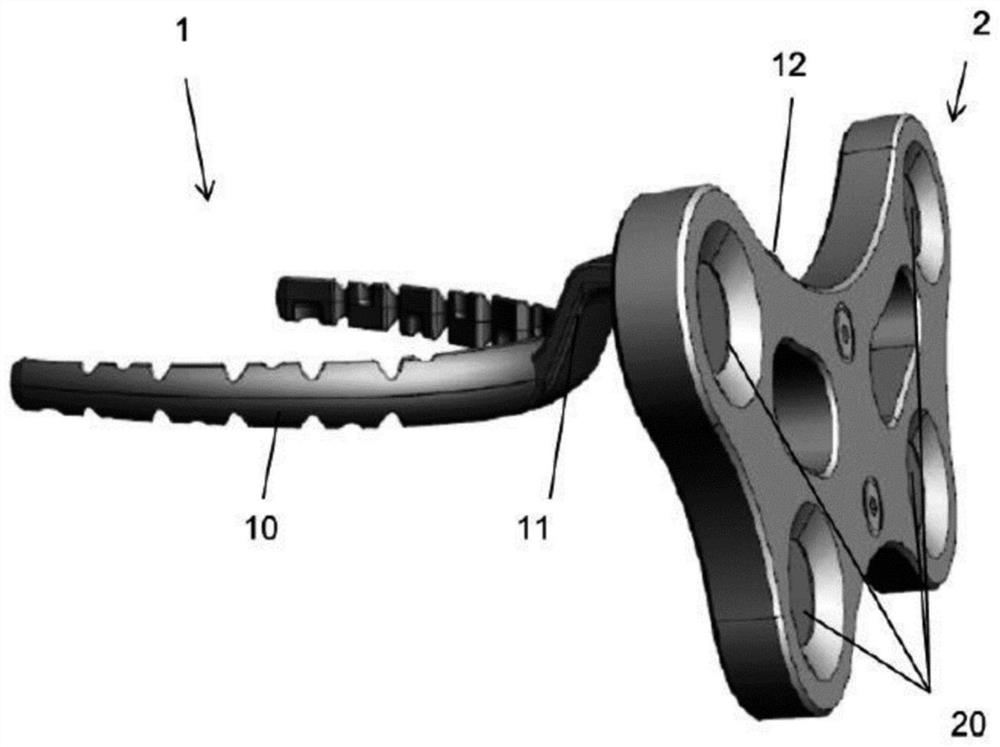
Maxillary arch expander unbanded to teeth
An orthodontic arch expander joins to a mouthpiece proximate to the rear of the mouthpiece. The transparent mouthpiece has a desired arc that fits over the teeth of the upper jaw. The mouthpiece has two wings that join near the incisors and then become parallel and spaced apart around the molars. Near the molars, an arch expander joins to the mouth piece. The arch expander has two telescoping shells with a threaded jack and cooperating springs. Each shell joins to a corresponding wing of the mouthpiece. Turning the jack lengthens a rod that pushes the shells outwards against the mouthpiece thus widening the maxillary arch without brackets or bands upon the teeth. An alternate embodiment has the arch expander attaching directly to the palatal bone through screws placed through a grommet at the end of each shell by an orthodontist or oral surgeon.
Owner:WILLIAMS MICHAEL O
Palatal expansion device and methods
InactiveUS20070218416A1Promote activationMore patient friendlyOthrodonticsDental toolsEngineeringBiological activation
The present invention relates to a palatal expansion device that has a screw having an activator (e.g., one or more activation arms) wherein the screw connects two blocks, each block having an opening for receiving the screw; a stabilizer attached to the blocks; and an anti-wind-back mechanism (e.g., a spring extension) positioned opposite the activation mechanism. In another embodiment, the present invention includes a palatal expansion device that has at least one screw, wherein the screw connects with one or more blocks and the blocks have an opening for receiving the screw. The device further includes one or more stabilizers attached to the blocks; a ratchet that engages the screw; and a built-in activator that communicates with the ratchet. This design allows essentially unidirectional rotation of the screw. The ratchet system includes, in one aspect, a pin / pocket arrangement, or a ratchet wheel / spring arrangement. The present invention involves kits and methods for expanding the maxillary arch or mandible using the palatal expansion devices of the present invention.
Owner:KELES AHMET OZLEM
Full arch ultrasonic cleaner apparatus and method of use
A cleaner apparatus for use in a dental prophylaxis process includes an applicator defining a curved occlusal wall, a buccal wall, a lingual wall, and a distal wall, each of the buccal wall, the lingual wall and distal walls extending outwardly from the occlusal wall and forming a curved applicator configured to receive a patient's teeth in one of the maxillary arch and mandibular arch of the patient. The applicator being configured to receive and contain a cleaning agent in the cavity during a teeth cleaning process. An ultrasonic transducer is embedded within each of the buccal wall and the lingual wall of the applicator. A controller is electrically coupled to the transducers for powering the transducers and controlling the operation thereof, and the cleaner apparatus for cleaning a full arch of a patients teeth via cavitation of the cleaning agent resulting from ultrasonic radiation transmitted from the transducers.
Owner:ZHAO KUN
Palatal expansion device and methods
InactiveUS7074036B1Promote activationMore patient friendlyOthrodonticsDental toolsBiological activationMechanical engineering
The present invention relates to a palatal expansion device that has a screw having one or more activation arms wherein the screw connects two blocks, each block having an opening for receiving the screw; a stabilizer attached to the blocks; and a spring extension positioned opposite the activation arms, wherein the spring extension is attached to the stabilizer. The present invention involves methods for expanding the maxillary arch, and kits including the device.
Owner:KELES AHMET OZLEM
Facial plane indicator
A device for determining the position of at least one of a dental patient's dental midline and incisal plane relative to the patient's facial midline. The device includes an impression / bite tray for obtaining a dental impression of at least one of the patient's maxillary arch and mandibular arch, and a plane indicator including at least one of a vertical alignment bar and a horizontal alignment bar, pivotally mounted to the impression / bite tray for rotatable movement relative to the impression / bite tray. The at least one of the vertical alignment bar and the horizontal alignment bar can be aligned with the dental patient's facial midline and an imaginary plane perpendicular to the facial midline, respectively, by rotating the plane indicator relative to the impression / bite tray while the impression / bite tray is retained in the patient's mouth during positioning and securing of the at least one of a vertical alignment bar and a horizontal alignment bar.
Owner:INCISAL EDGE PRODS
Orthodontic appliance
InactiveUS20110236847A1Effectively and efficiently combineUseful and effective to accomplish craniofacial modificationOthrodonticsDental toolsOrthodonticsMaxillary arch
A palatal expansion orthodontic appliance comprising, an advancer for advancing the upper front teeth, an expansion screw for controlling the expansion of two acrylic halves that each contain a Hang Clasp and optionally a molar intrusion wire. The two acrylic halves share and anchor the wire ends of the advancer, the Hang clasps and any molar intrusion wires. The orthodontic appliance simultaneously expands the maxillary arch and advances the upper front teeth. Methods of manufacture, including kits for the manufacture of the orthodontic appliance are also included.
Owner:HANG WILLIAM M
Dental isolation block
A dental isolation block adapted for maintaining the mouth of the dental patient open, while keeping the work field dry and exposed with the lip retracted and the tongue suppressed to facilitate performance of a dental procedure by a dental practitioner. The dental isolation block includes a first and second bite platform capable of being disposed between the maxillary arch and mandibular arch, a lip retractor with a first end adjacent the first bite platform and a second end adjacent the second bite platform, and a tongue shield extending between the first and second bite platform. The lip retractor may include a channel for receiving and directing saliva to a suction drain and suction holes all in fluid communication with a dental office suction system. A suction extension may be affixed to the first and / or second bite platform to further evacuate saliva from entering the work field. The dental isolation block can be positioned such that the lip retractor retracts the upper lip if the work field is on the upper arch or to retract the lower lip if the work field in on the lower arch.
Owner:ISOLATION BLOCK
Palatal expansion device and methods
InactiveUS7780445B2Promote activationMore patient friendlyOthrodonticsDental toolsEngineeringMaxillary arch
The present invention embodies to a palatal expansion device that includes one or more stabilizers attached to the blocks; a ratchet that engages the screw; and a built-in activator that communicates with the ratchet. This design allows essentially unidirectional rotation of the screw. The ratchet system embodies a pin / pocket arrangement, or a ratchet wheel / spring arrangement. The present invention involves kits and methods for expanding the maxillary arch or mandible using the palatal expansion devices of the present invention.
Owner:KELES AHMET OZLEM
Maxillary arch expander unbanded to teeth
An orthodontic arch expander joins to a mouthpiece proximate to the rear of the mouthpiece. The transparent mouthpiece has a desired arc that fits over the teeth of the upper jaw. The mouthpiece has two wings that join near the incisors and then become parallel and spaced apart around the molars. Near the molars, an arch expander joins to the mouth piece. The arch expander has two telescoping shells with a threaded jack and cooperating springs. Each shell joins to a corresponding wing of the mouthpiece. Turning the jack lengthens a rod that pushes the shells outwards against the mouthpiece thus widening the maxillary arch without brackets or bands upon the teeth. An alternate embodiment has the arch expander attaching directly to the palatal bone through screws placed through a grommet at the end of each shell by an orthodontist or oral surgeon.
Owner:WILLIAMS MICHAEL O
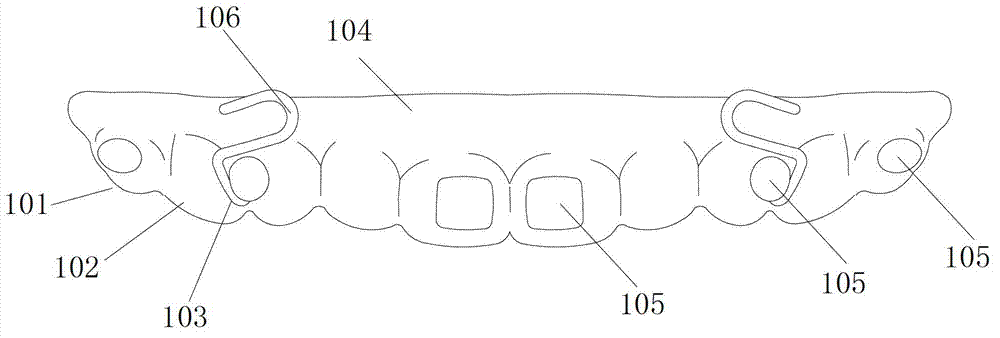
Diaphragm pressing type maxillary traction device and manufacture method thereof
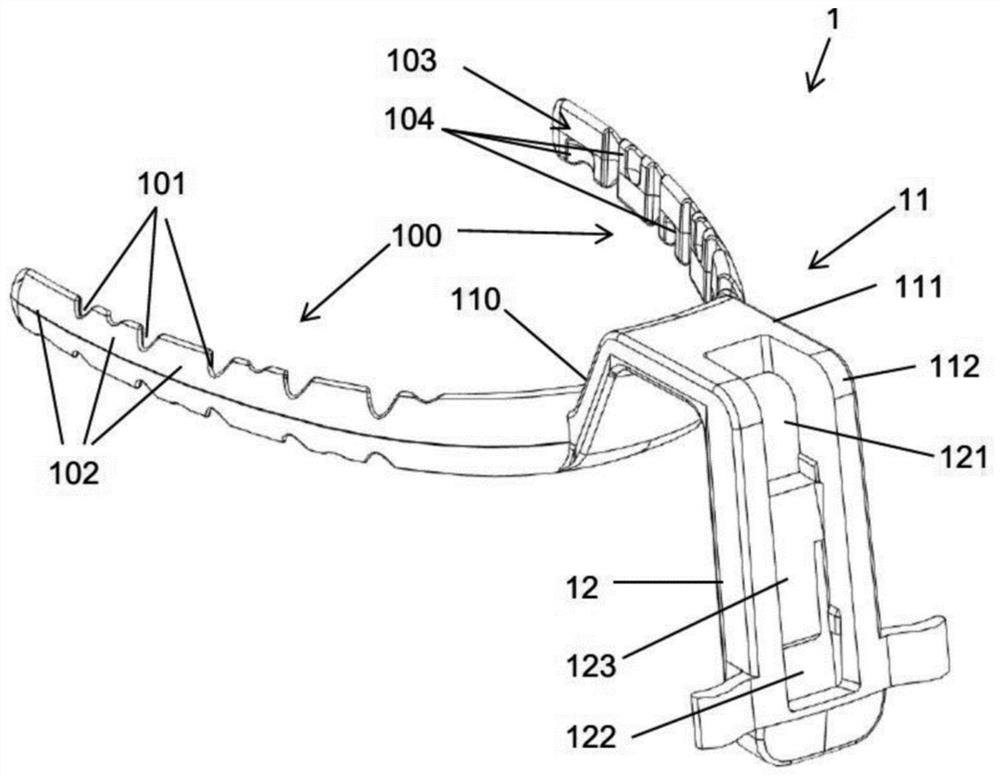
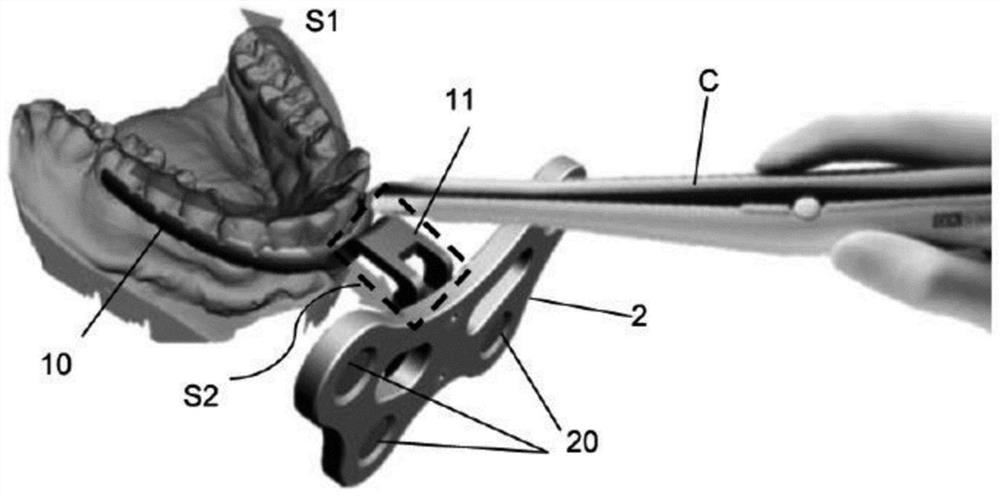
The invention relates to a diaphragm pressing type maxillary traction device and a manufacture method of the diaphragm pressing type maxillary traction device, in particular to a diaphragm pressing type maxillary traction device for orthodontics and a manufacture method of the diaphragm pressing type maxillary traction device, and belongs to the technical field of medical apparatus and instruments for orthodontics. The diaphragm pressing type maxillary traction device comprises an upper jaw pad (101) and a traction hook (103); diaphragms (104) for covering maxillary arch, partial mucosa at buccolabial side and most of the mucosa at a palatal side are arranged on a base plate (102) of the upper jaw pad (101); the base plate (102) is provided with bumps (105) for fixing the position in buccal surface areas relative to the primary central incisor, the deciduous cuspid and the second deciduous molar; the tail end of the traction hook (103) is wrapped into the base plate (102); and a head (106) of the traction hook (103) is extended from a position between the deciduous cuspid and the second deciduous molar to the labial and positioned in the labial surface of the deciduous cuspid.
Owner:王震东 +1
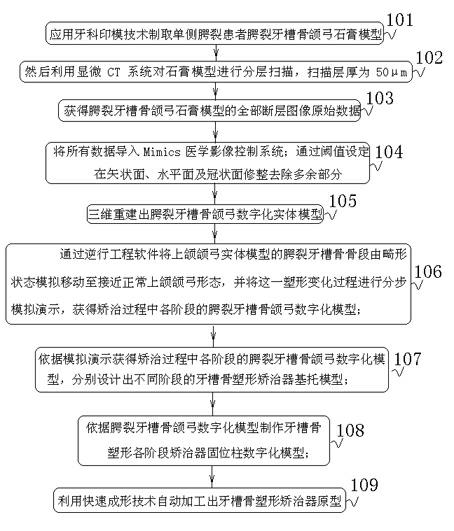
Shape appliance digitalizing method of cleft palate alveolar bone
InactiveCN102169519AHigh precisionRealize individual precise designSpecial data processing applicationsShape changeNon invasive
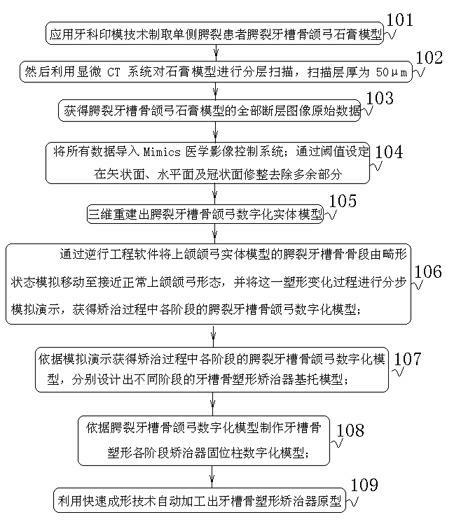
The invention belongs to a non-invasive treating method of congenital cleft palate in the medical field, especially relating to a shape appliance digitalizing method of a cleft palate alveolar bone, which comprises the following steps of: 1) obtaining the jaw arch fault information of a cleft palate alveolar bone by using the microscopic CT (computed tomography) technology, wherein the thickness of a scanning layer is 50 mu m; 2) moving the cleft palate alveolar bone segment of a maxillary arch solid model to approach to a normal maxillary arch form from an abnormal form in a simulation manner in reverse engineering software, and simulating and demonstrating the shape change process step by step; 3) obtaining a digitalized model of the cleft palate alveolar bone jaw arch in each stage in the process of remedying according to the simulation and demonstration; 4) manufacturing an appliance retention column digitalized model used in each stage of shaping the alveolar bone according to the digitalized model of the cleft palate alveolar bone jaw arch; and 5) automatically processing a prototype of an alveolar bone shape appliance by using the rapid forming technology. A digitalized designing and manufacturing method of the shape appliance of a cleft palate alveolar bone independent of the experience and handwork of a doctor is provided.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
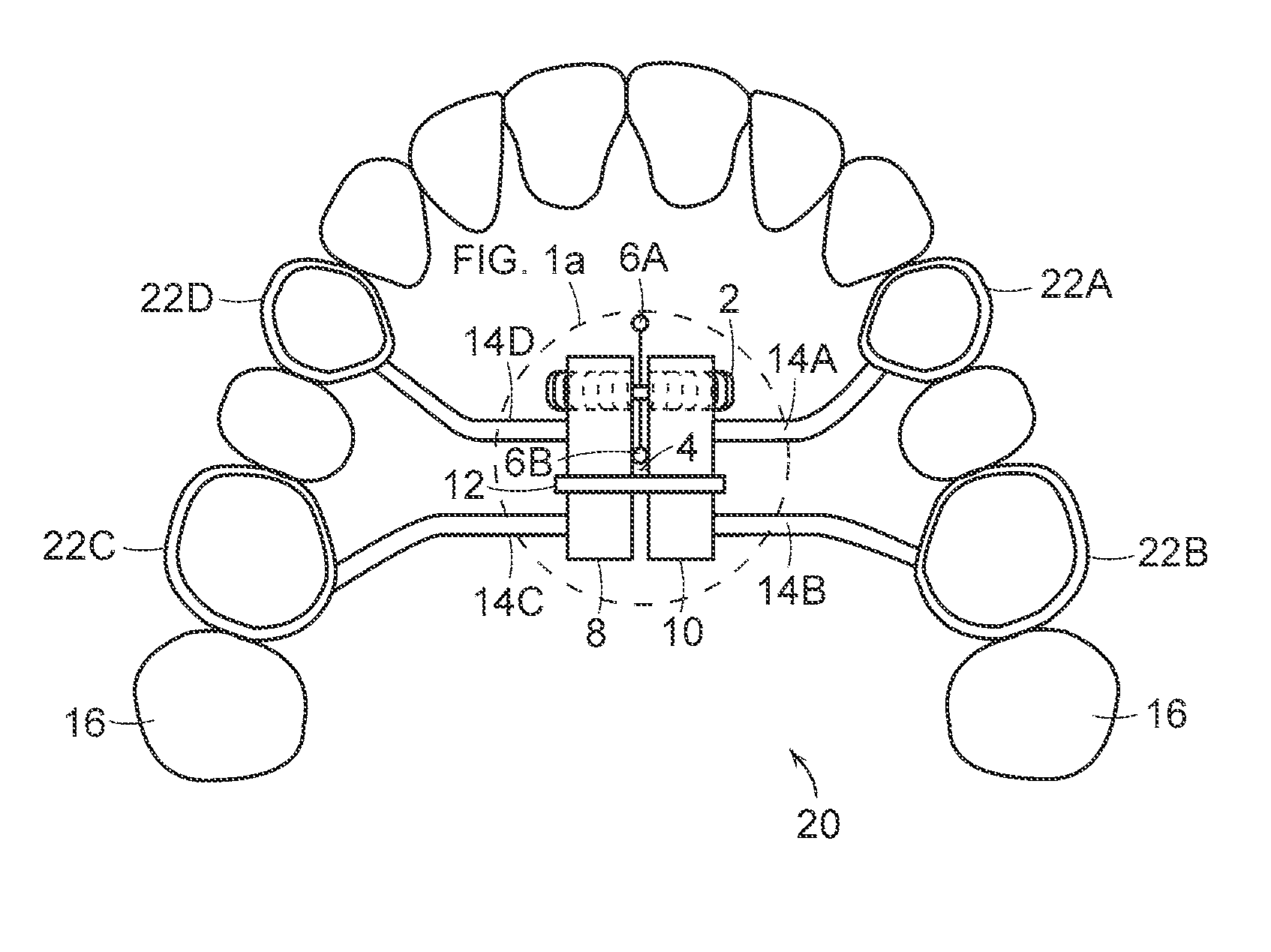
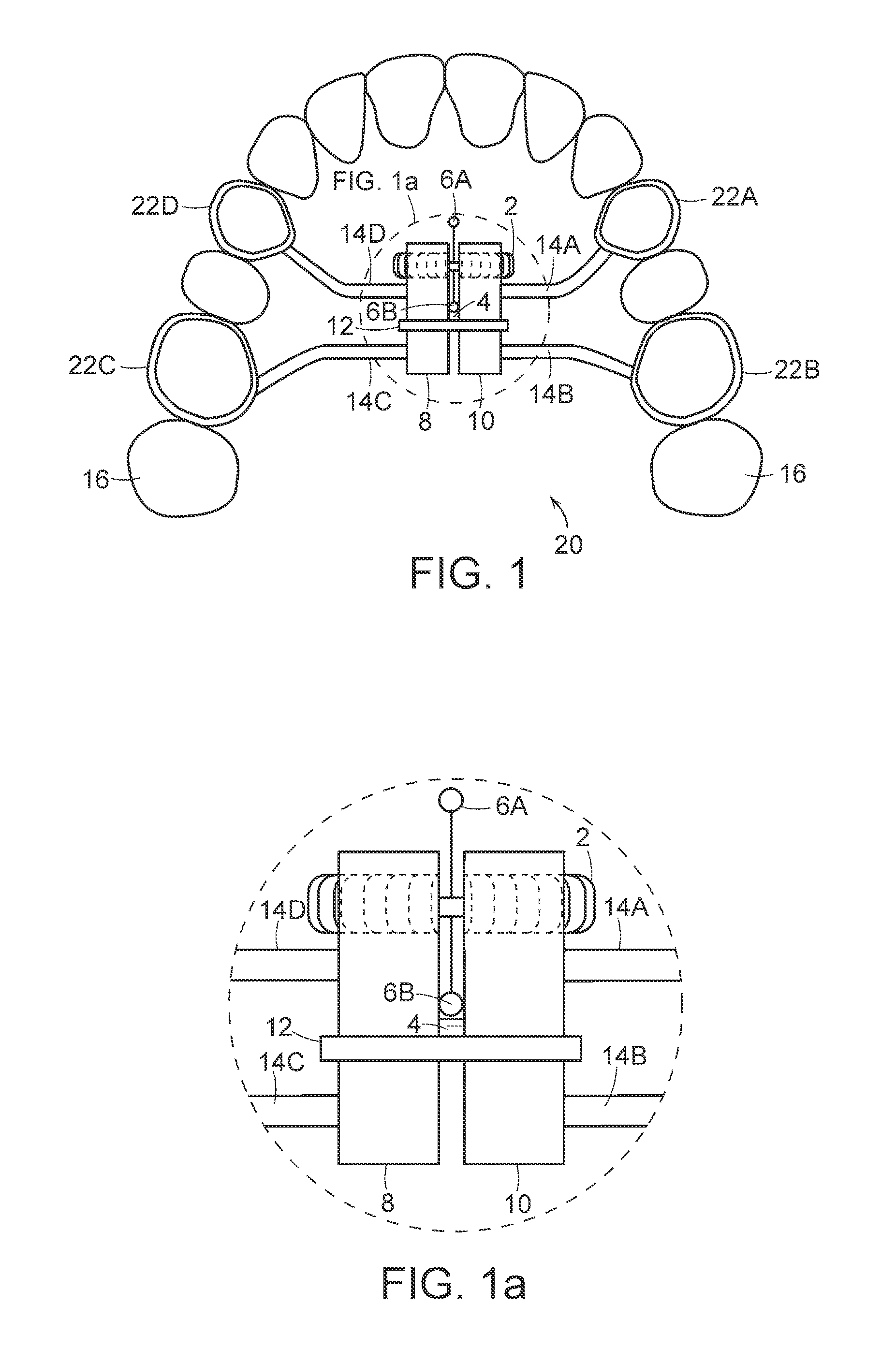
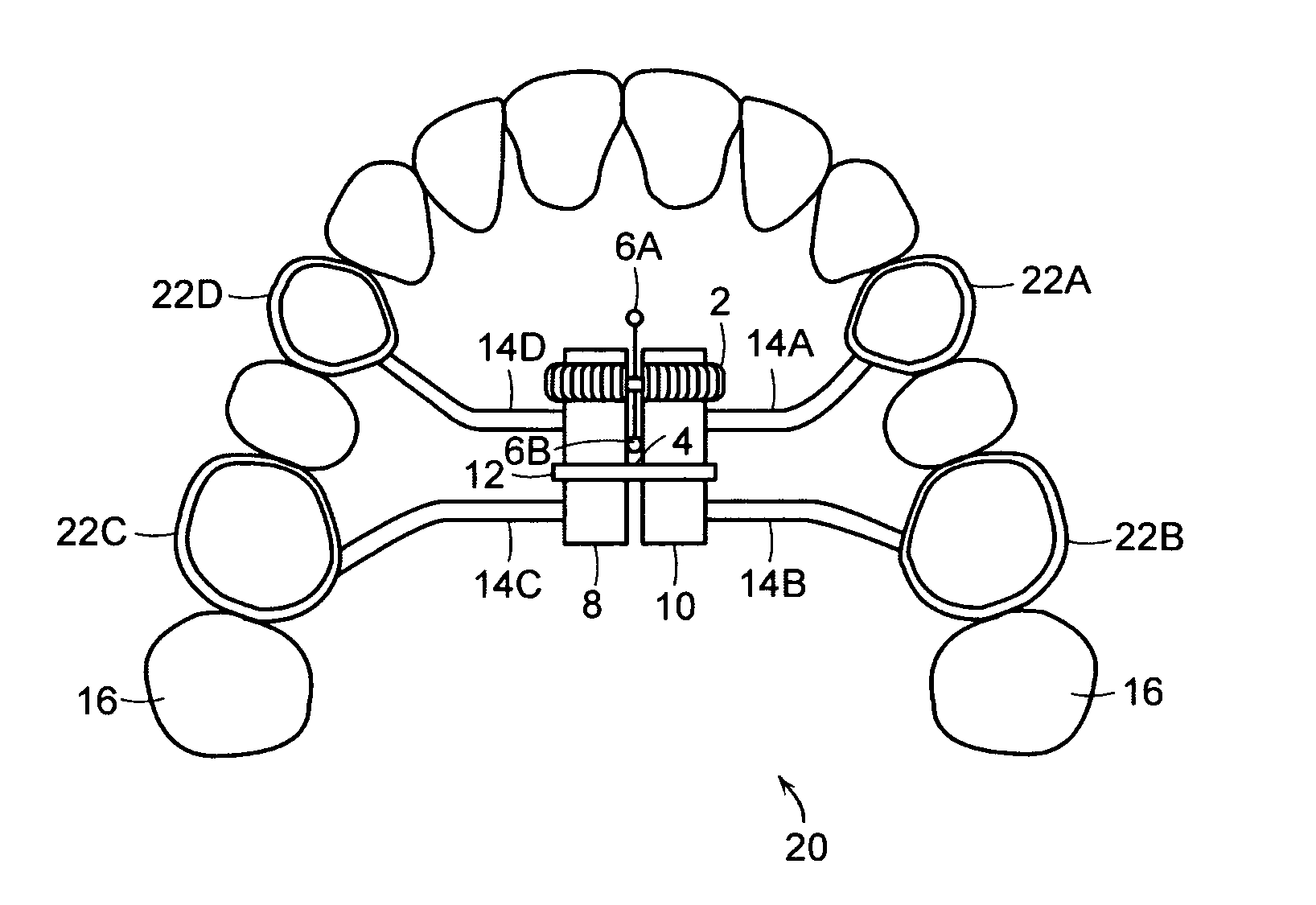
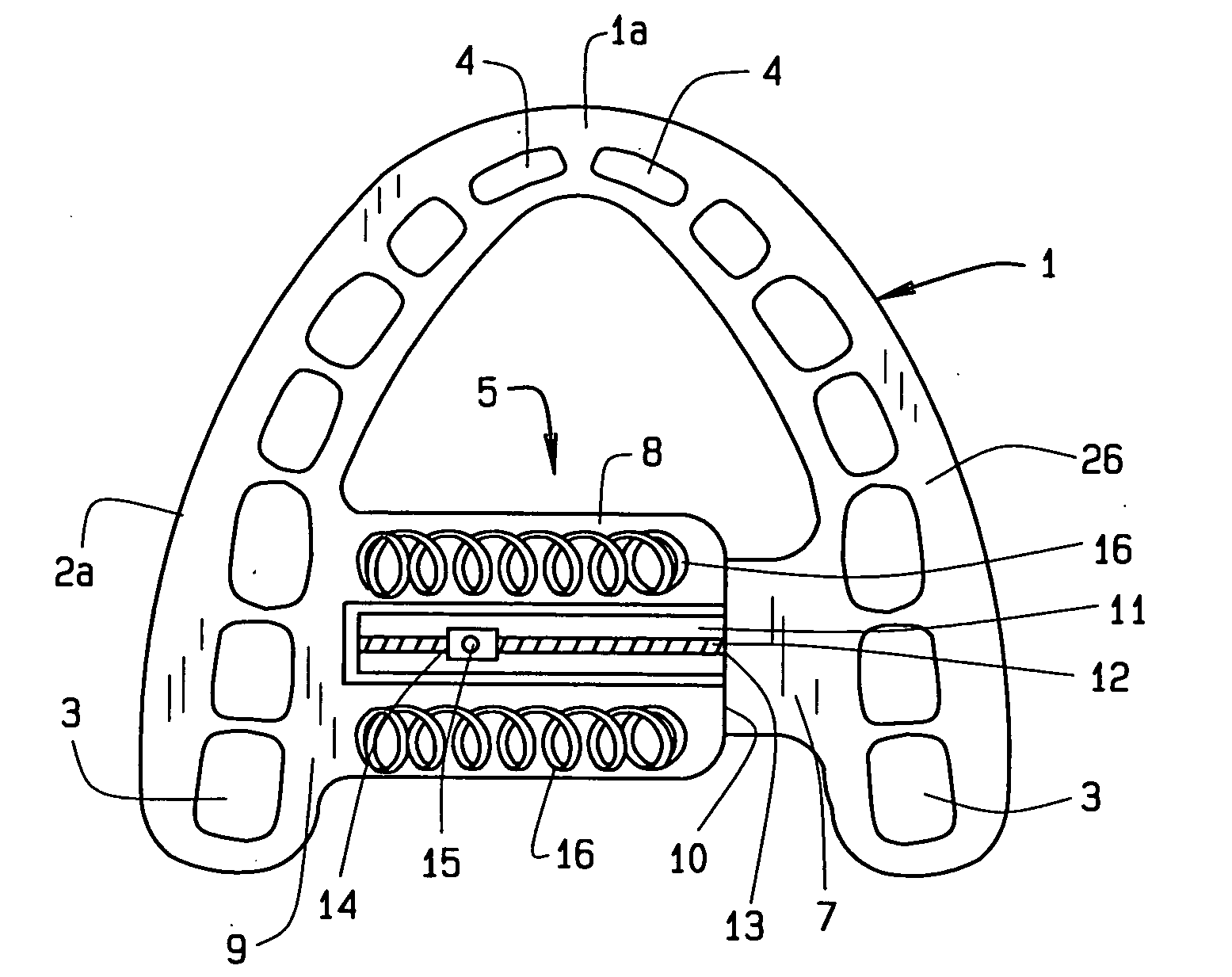
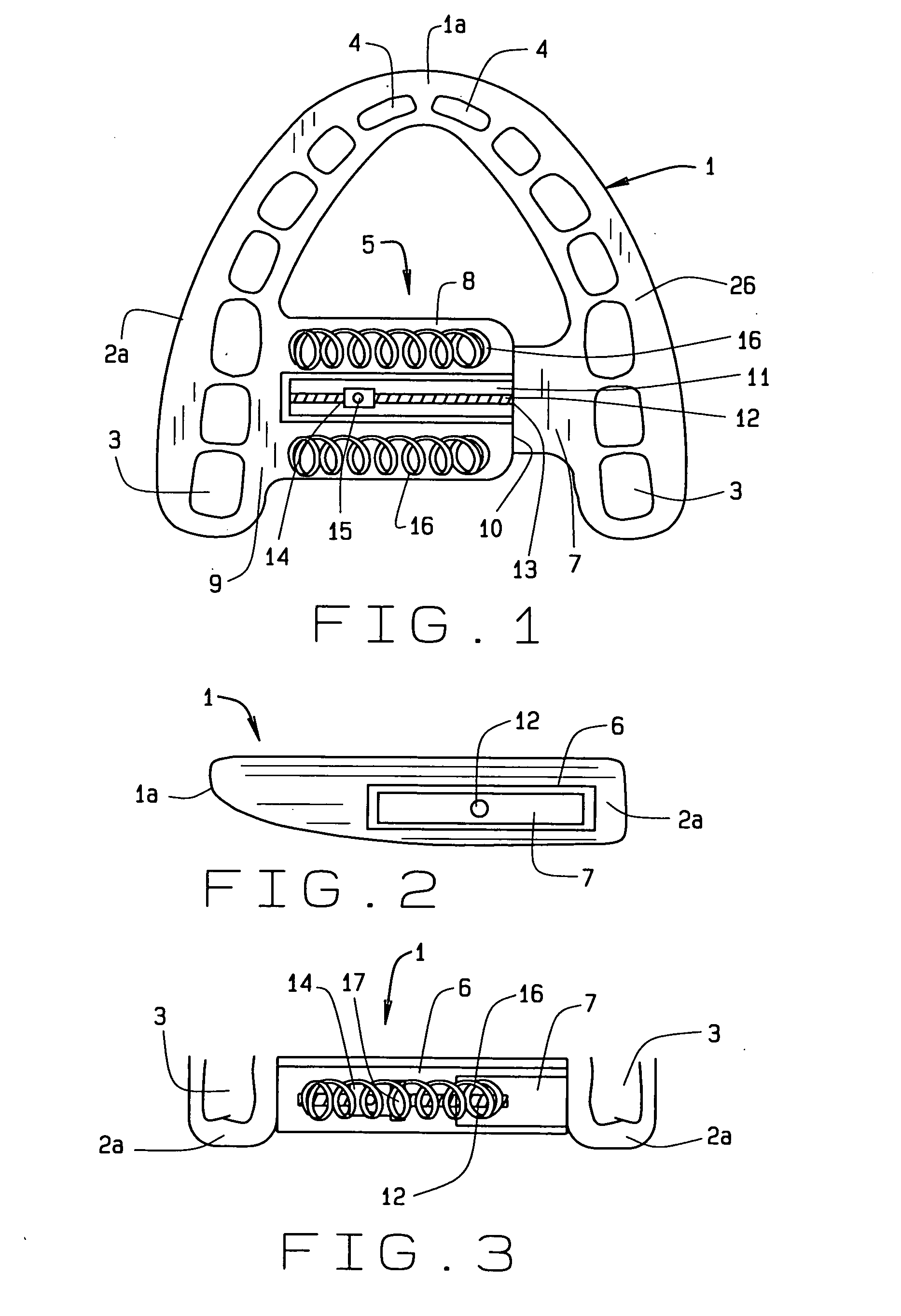
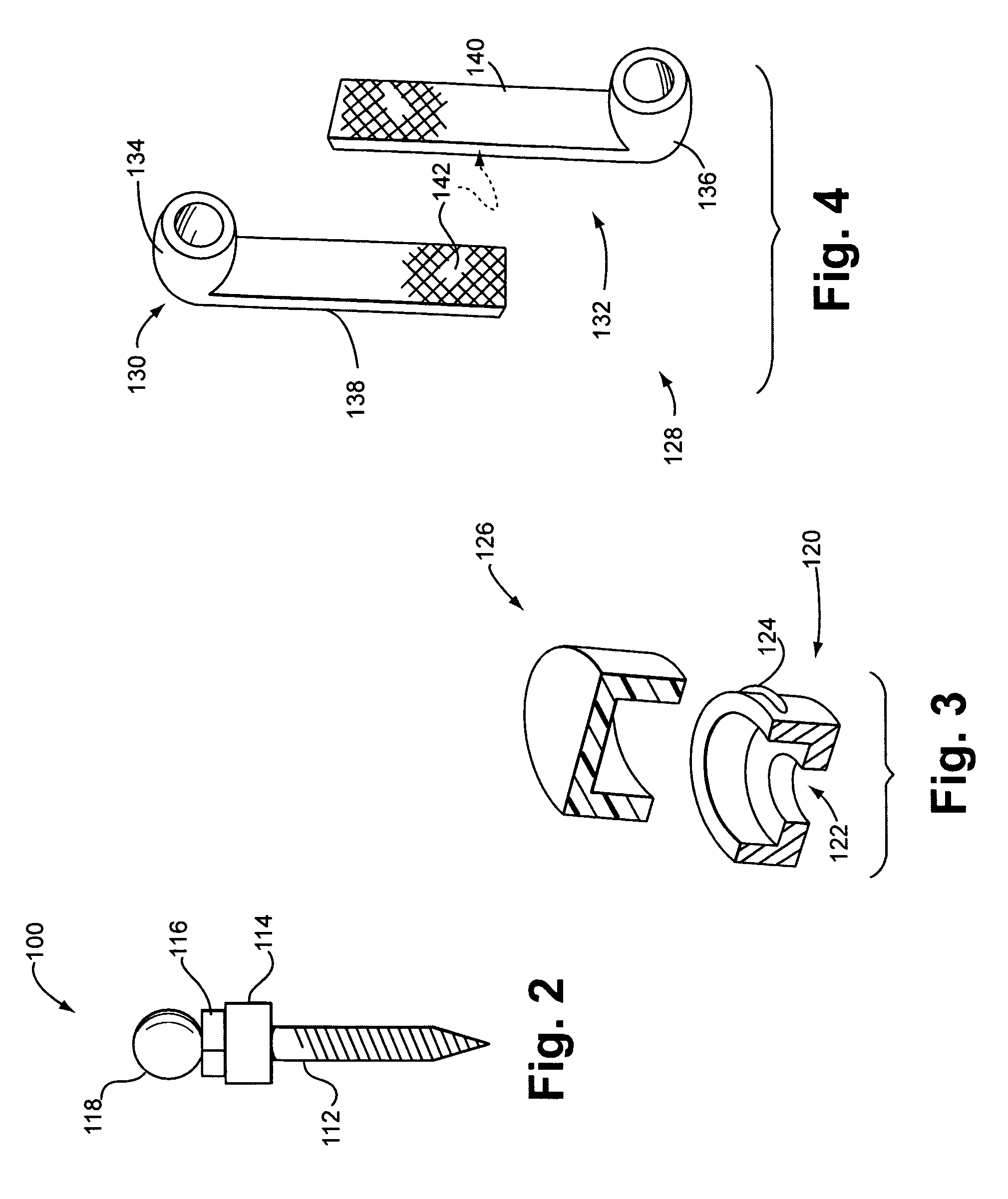
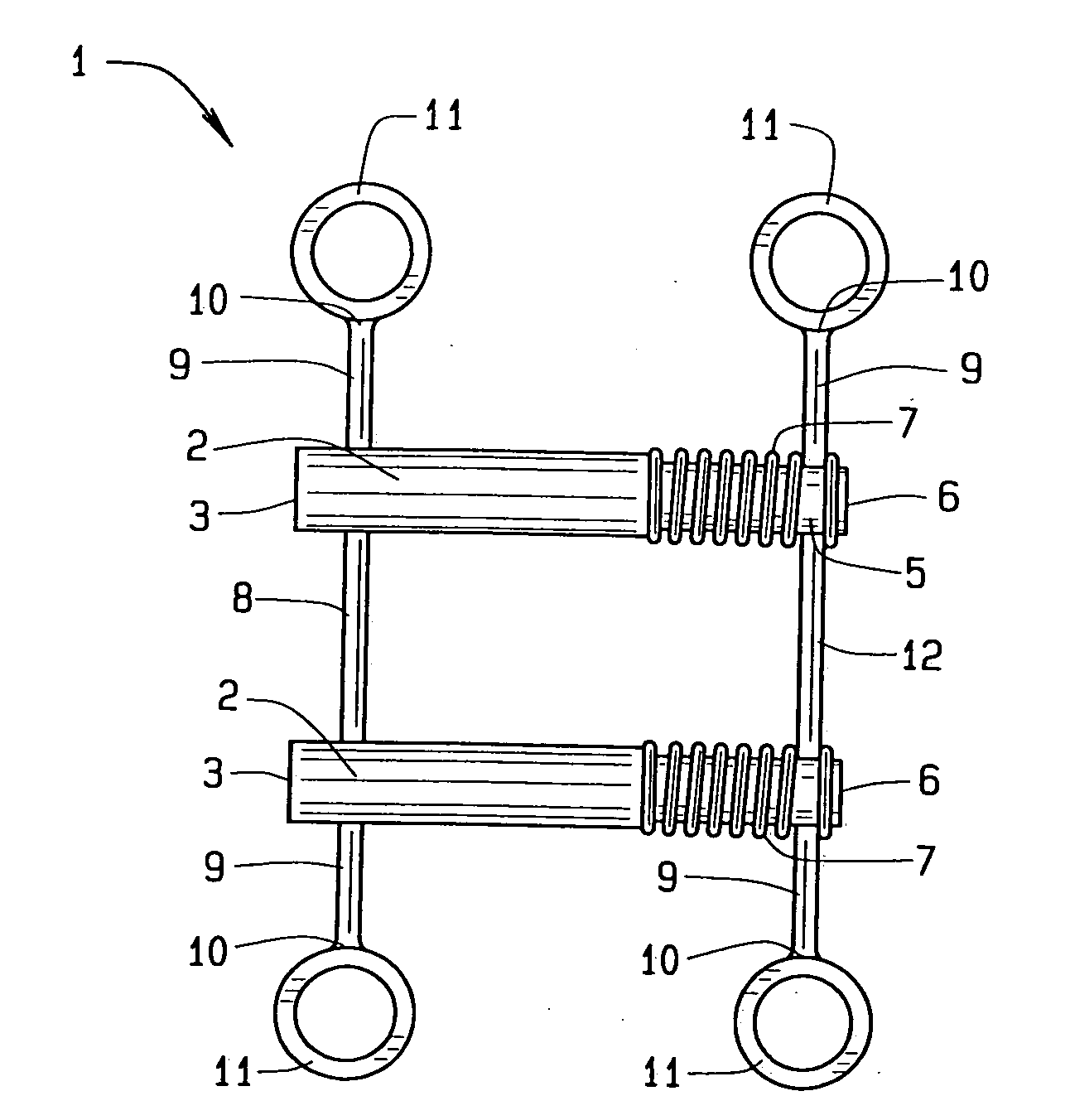
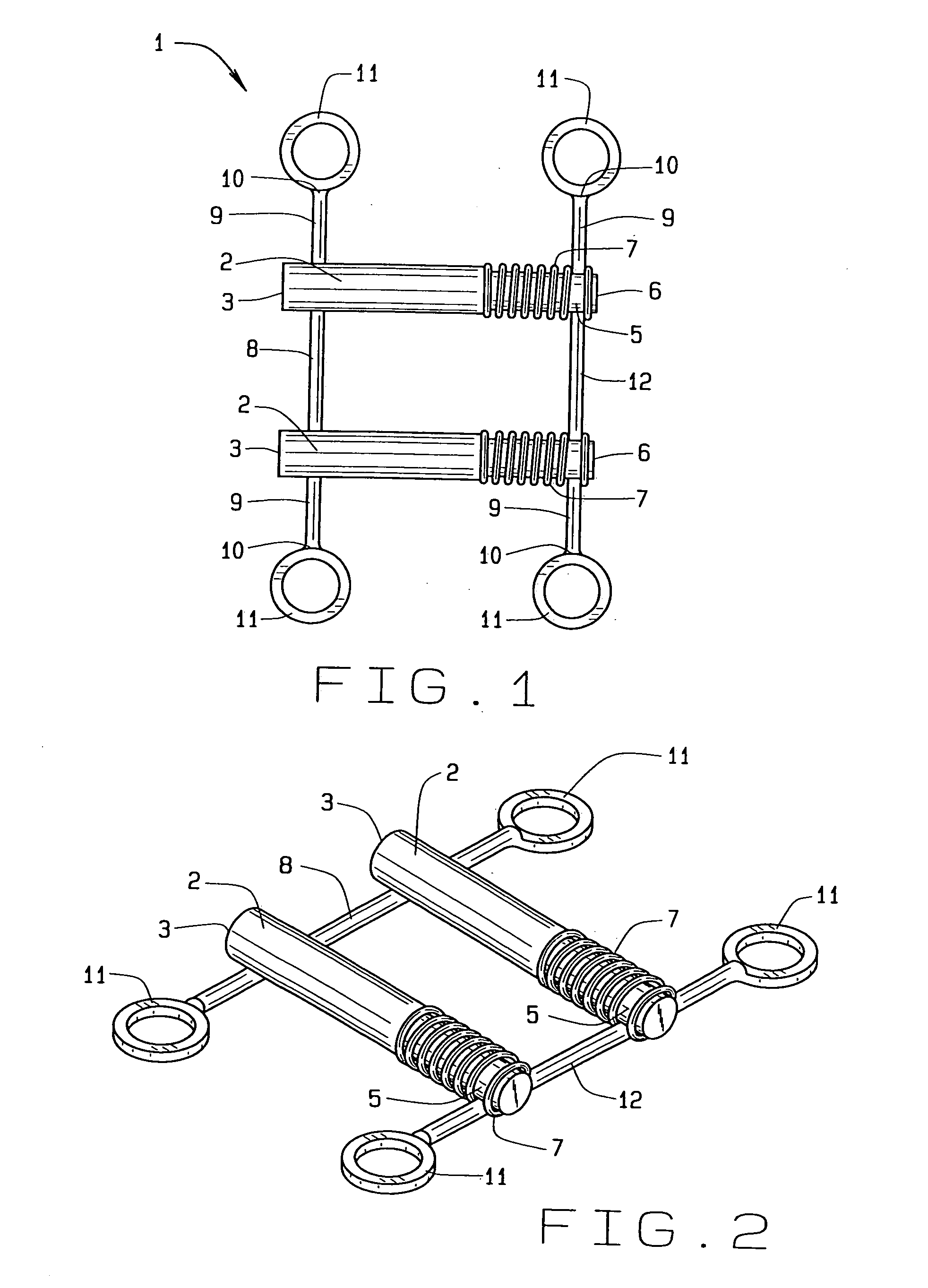
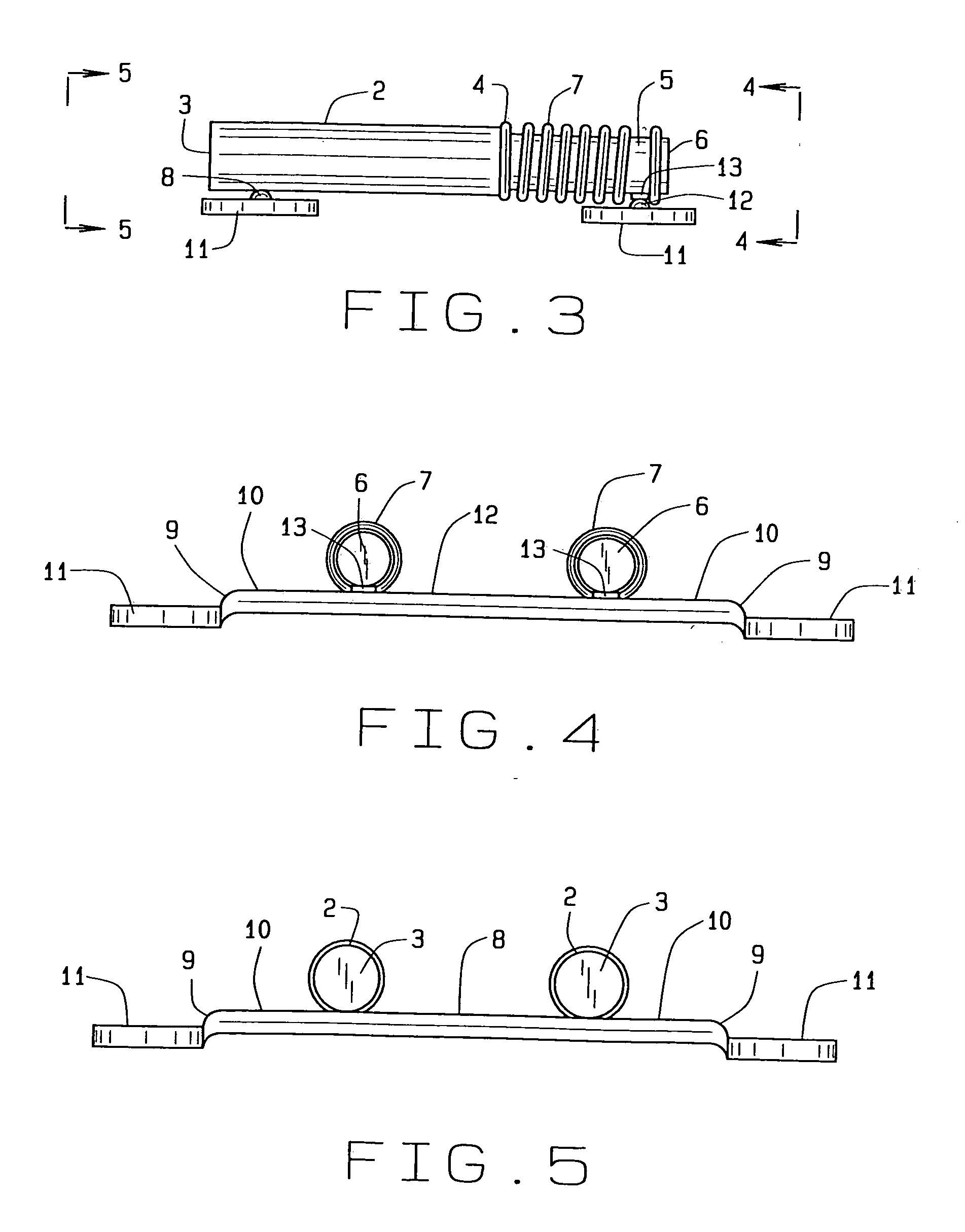
Dental apparatus for treating malocclusion
InactiveCN103945790APrecisely fit the structureAdaptive structureOthrodonticsDental instrumentsMaxillary growth
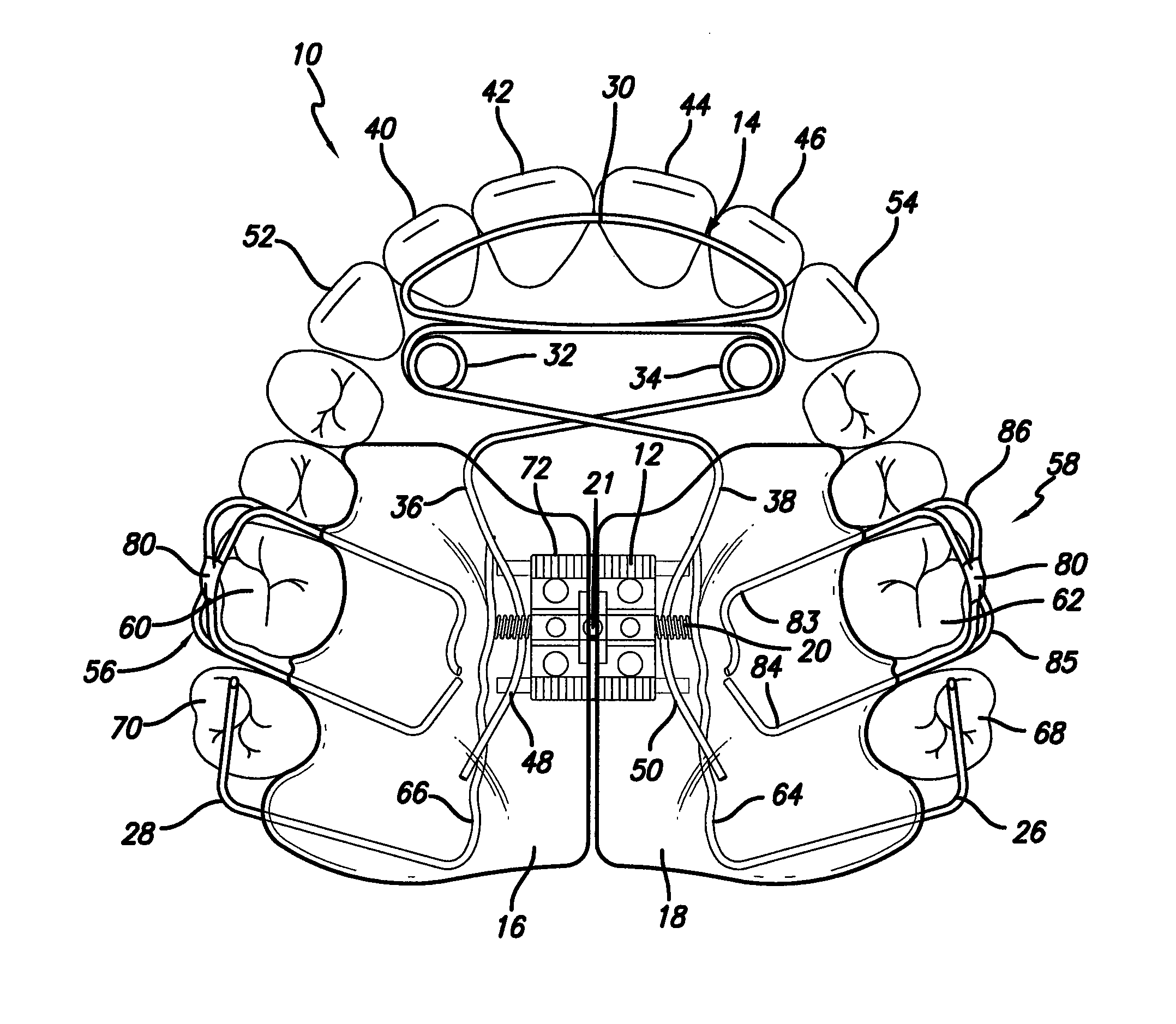
Device for activating mandibular growth, maxillary growth and mandibular advancement, said device comprising: a first rod (3) with a front end (9) and a rear end (10); a second rod (4) with a front end (11) and a rear end (12); said first (3) and second (4) rods being relatively rigid and having mutually different lengths; a first pivoting articulation (6) for connecting the front end (9) of the first rod (3) to a first dental arch of a person; a second pivoting articulation (8) for connecting the front end of the second rod (4) to the second dental arch of the person; a third pivoting articulation (7) interconnecting the rear ends (10, 12) of the rods (3, 4) and allowing the device to chnage from an open position to a closed position and thus follow the movement of opening and closing of the jaws, characterized in that said third pivoting articulation (7) is able to be connected to the dental arch carrying the shortest rod with the aid of elastic means (5) returning the device to the closed position, in such a way that said rods are able to induce a movement of the mandibular arch relative to the maxillary arch in the closed position of the jaws.
Owner:ORTHODONTIE ALLIANCE LAB
Method and device for manufacturing orthodontic bracket
InactiveCN105708565AGood effectImprove efficiencyBracketsAnatomical structuresManufacturing technology
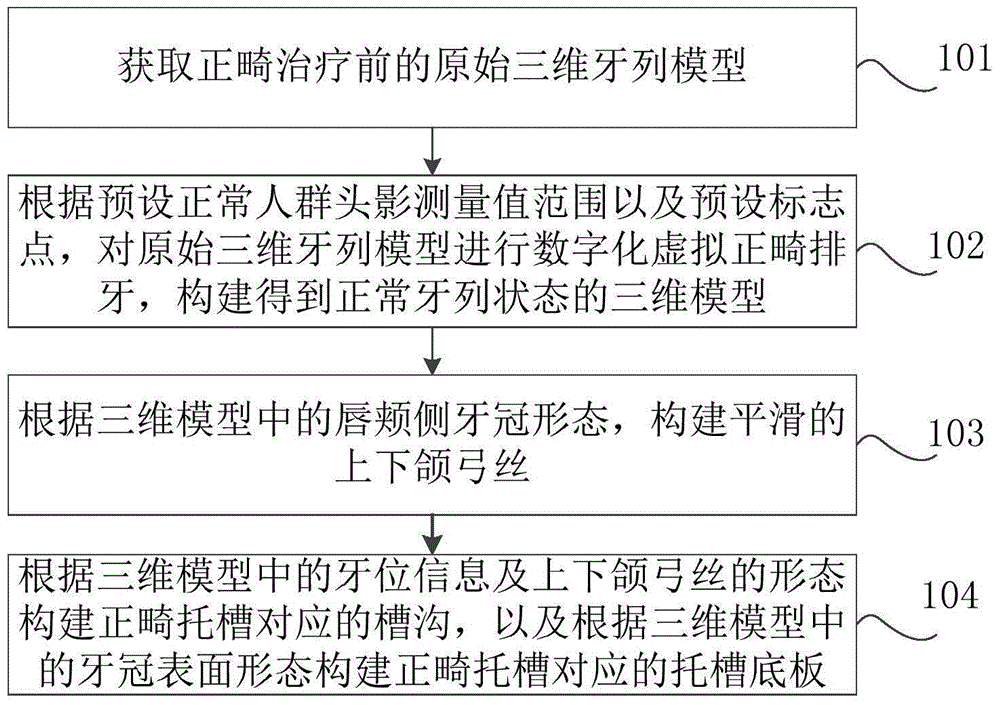
The invention discloses a method and device for manufacturing an orthodontic bracket and relates to the technical field of orthodontic bracket manufacturing, by means of the method and device for manufacturing the orthodontic bracket, the personalized orthodontic bracket can be manufactured according to the unique tooth three-dimensional anatomical structure of each patient, and the effect and efficiency of orthodontic treatment can be improved.The method includes the steps that firstly, an original three-dimensional tooth column model before orthodontic treatment is obtained; then, digital virtual orthodontic tooth arrangement is conducted on the original three-dimensional tooth column model according to the preset head shadow measurement value range of normal people and preset mark points, and a three-dimensional model of a normal tooth column state is constructed; smooth maxillary arch wires and mandibular arch wires are constructed according to the lip buccal side tooth crown state in the three-dimensional model; finally, a bracket gutter corresponding to the orthodontic bracket is constructed according to the tooth position information in the three-dimensional model and the states of the maxillary arch wires and mandibular arch wires, and a bracket bottom plate corresponding to the orthodontic bracket is constructed according to the dental crown surface form in the three-dimensional model.The method and device are suitable for processing the orthodontic bracket.
Owner:北京正齐口腔医疗技术有限公司
Maxillary expansion and advancement orthodontic applicance
InactiveUS9011145B2Effectively and efficiently combineUseful and effective to accomplish craniofacial modificationOthrodonticsDental toolsOrthodonticsMaxillary arch
A palatal expansion orthodontic appliance comprising, an advancer for advancing the upper front teeth, an expansion screw for controlling the expansion of two acrylic halves that each contain a Hang Clasp and optionally a molar intrusion wire. The two acrylic halves share and anchor the wire ends of the advancer, the Hang clasps and any molar intrusion wires. The orthodontic appliance simultaneously expands the maxillary arch and advances the upper front teeth. Methods of manufacture, including kits for the manufacture of the orthodontic appliance are also included.
Owner:HANG WILLIAM M
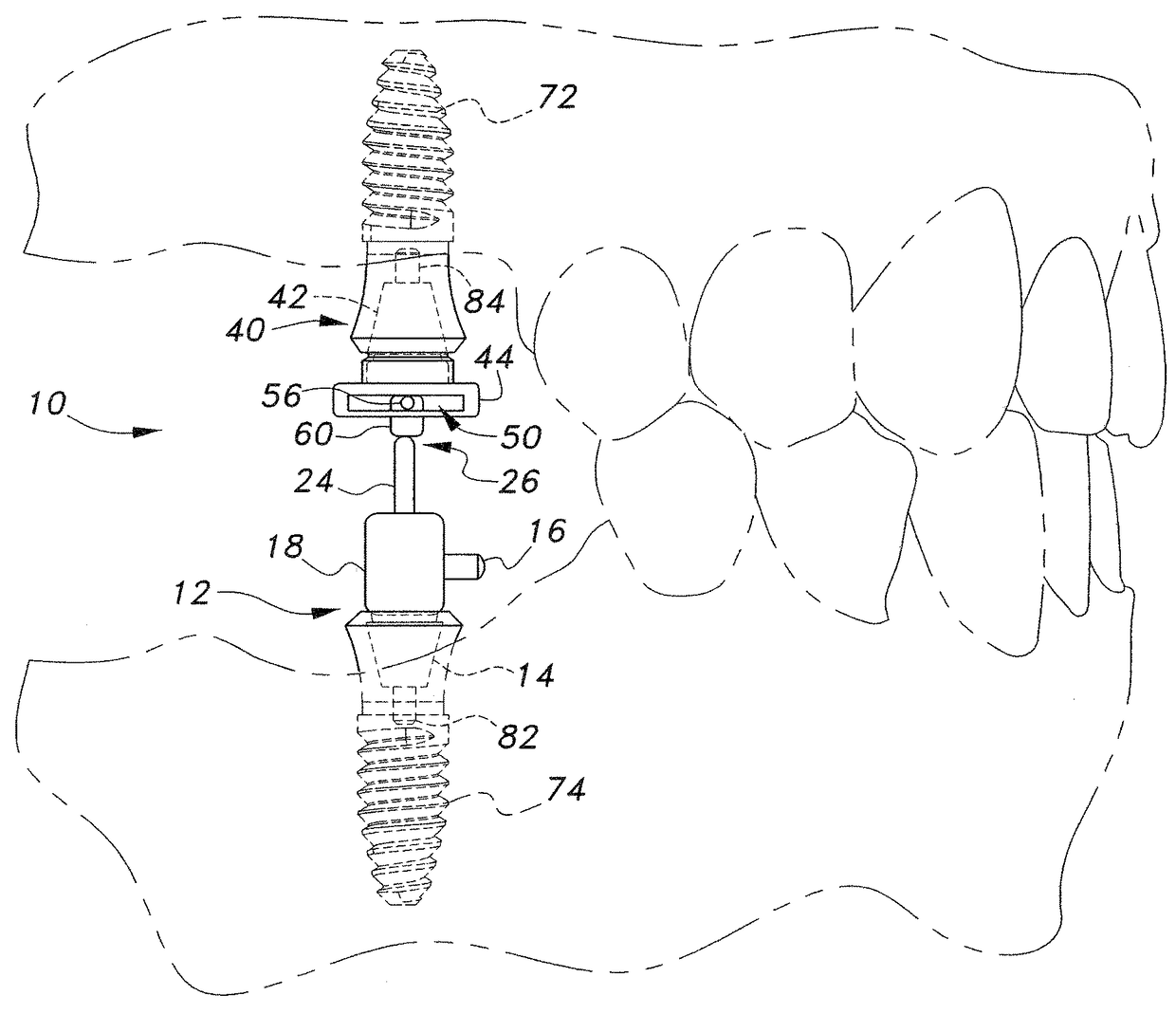
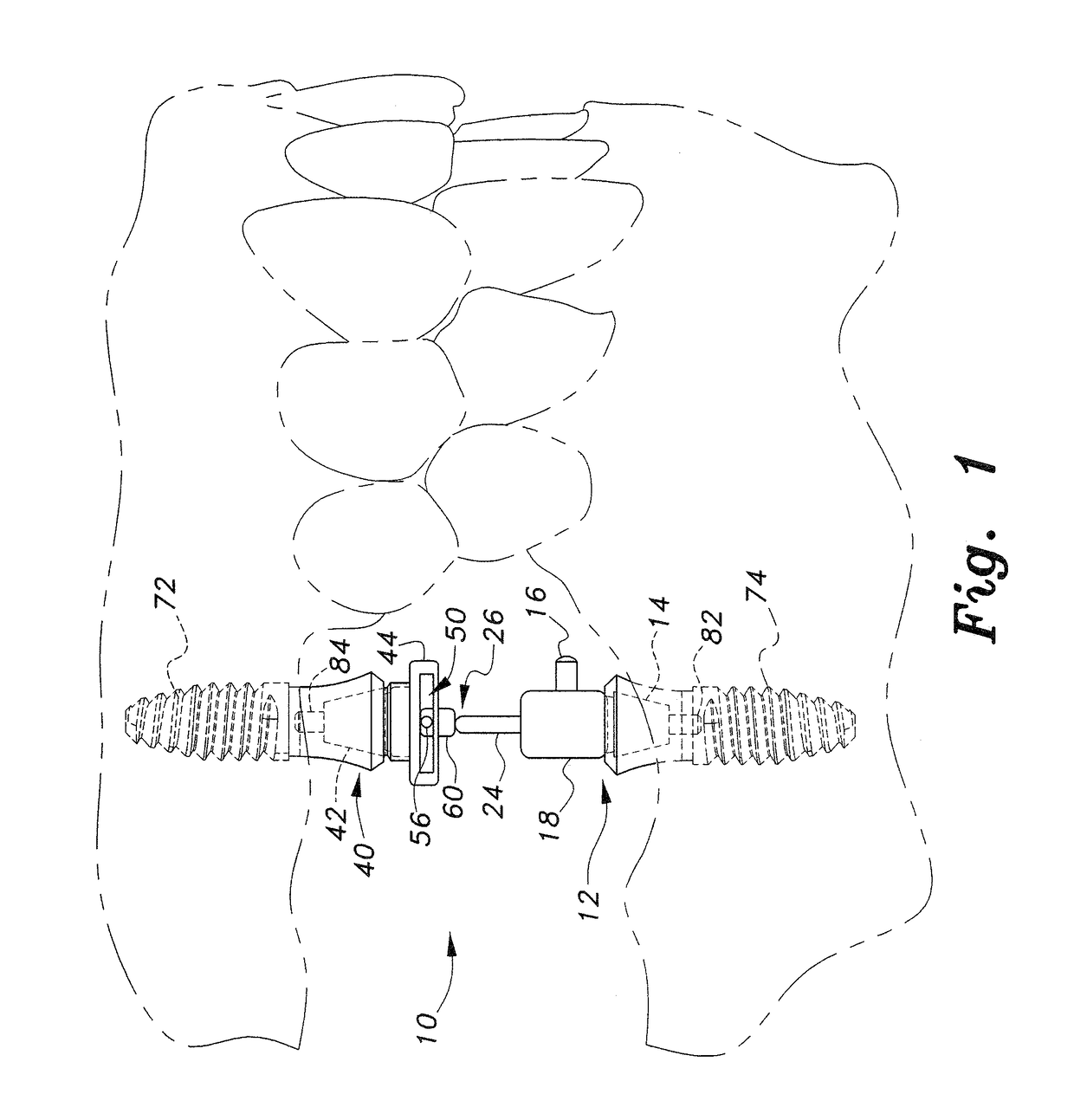
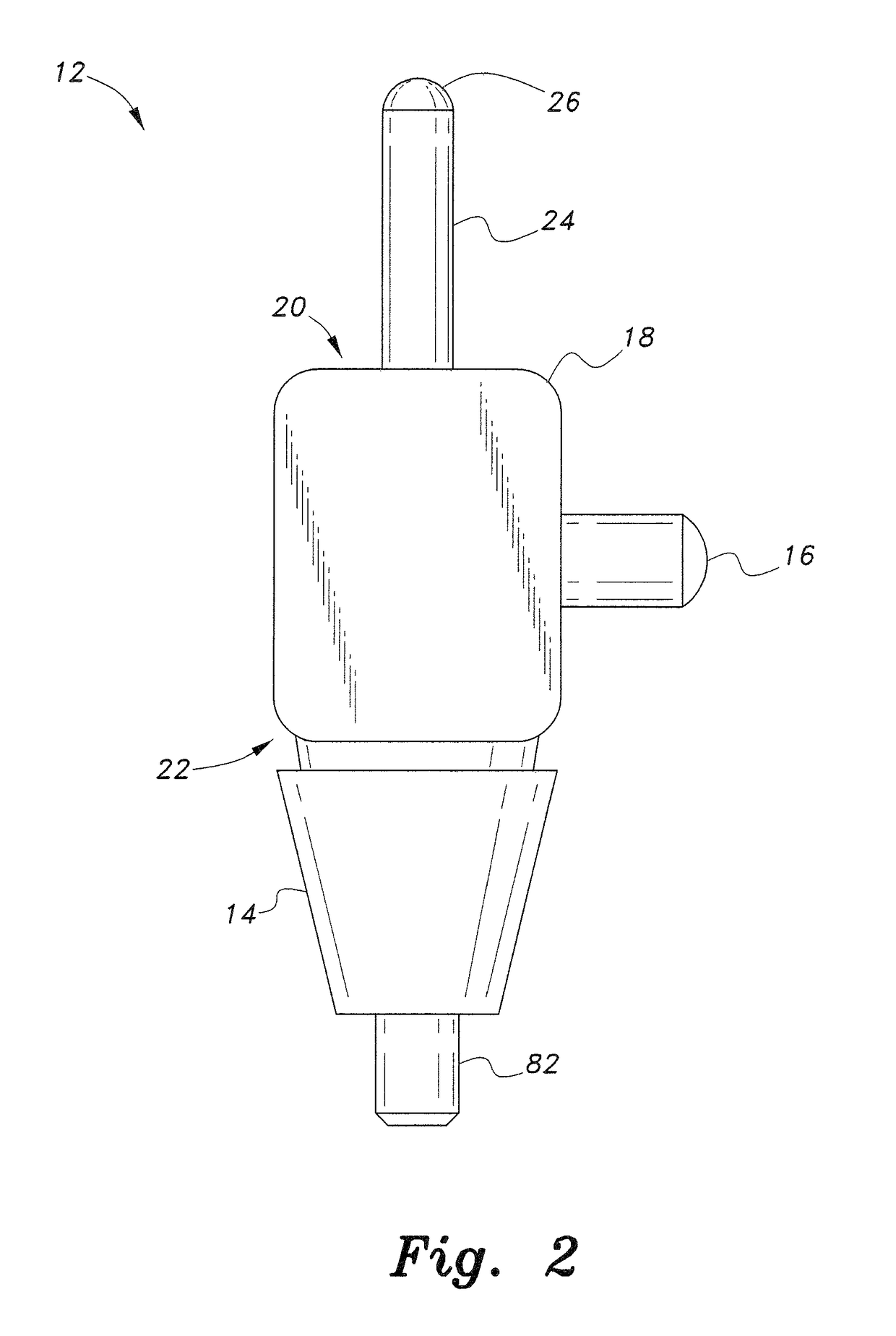
Capture of a planned vertical dimension of occlusion to facilitate simultaneous restoration of both maxillary and mandibular arches using implants
InactiveUS7789664B1Increase professional earningsDental implantsImpression capsAnatomical structuresMechanical models
Apparatus and method enabling implant supported dental prostheses to be fabricated for reconstruction of both maxillary and mandibular arches from a procedure requiring only one surgery. At least three pairs of reference points in the maxillary arch and in the mandibular arch are connected by adjustable members which are subsequently fixed in length and in mutual orientation to enable necessary impressions and casts to be made. The adjustable members engage anchoring members such as ball headed screws which are fixed to the maxillary and mandibular anatomy. Subsequently fabricated mechanical models of the patient anatomy, such as impressions and casts, capture critical geometric relationships from the adjustable members and their associated anchoring members, thereby enabling both maxillary and mandibular implant mountable prostheses to be fabricated from information gathered during only one surgical session.
Owner:TOTH RICHARD W
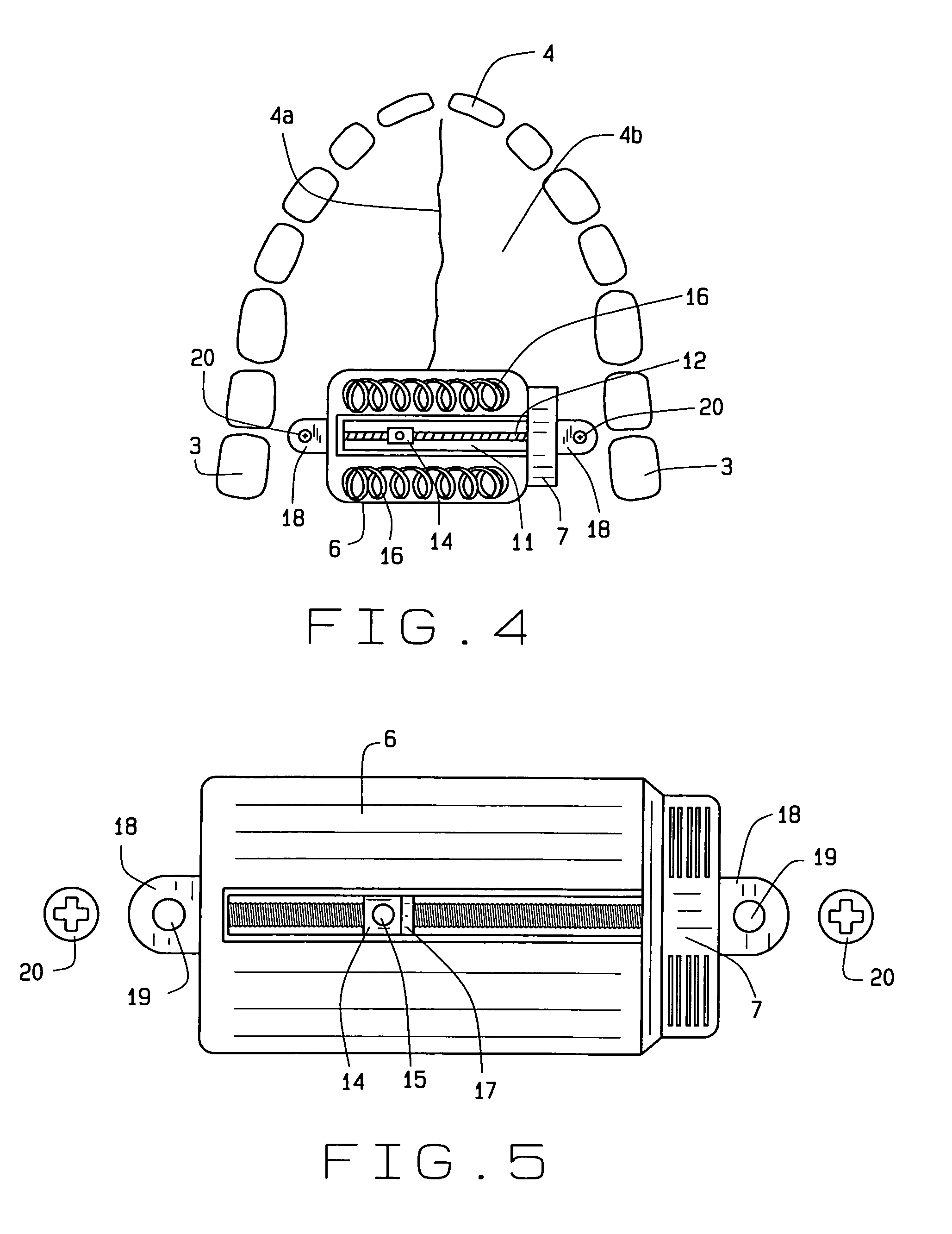
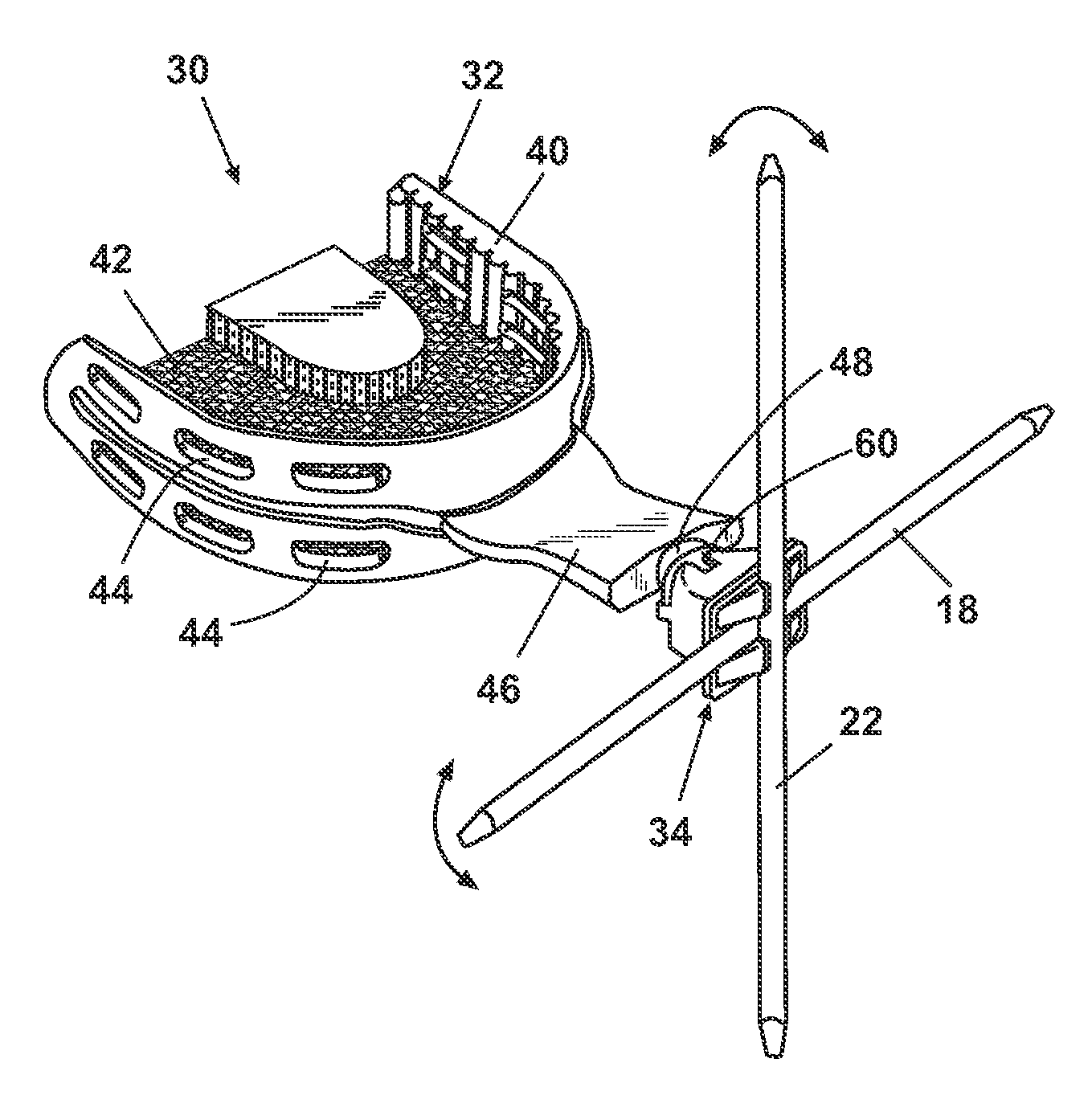
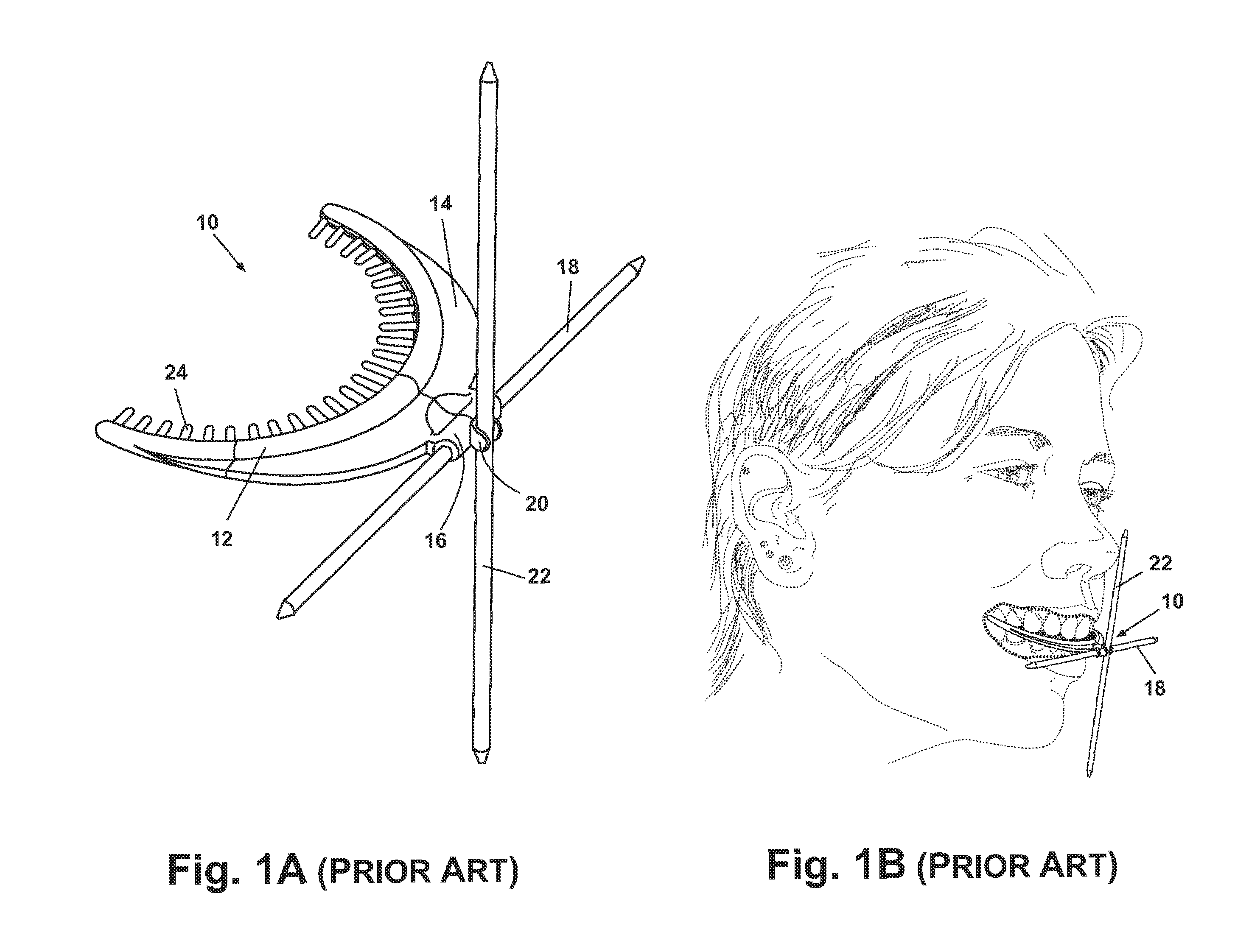
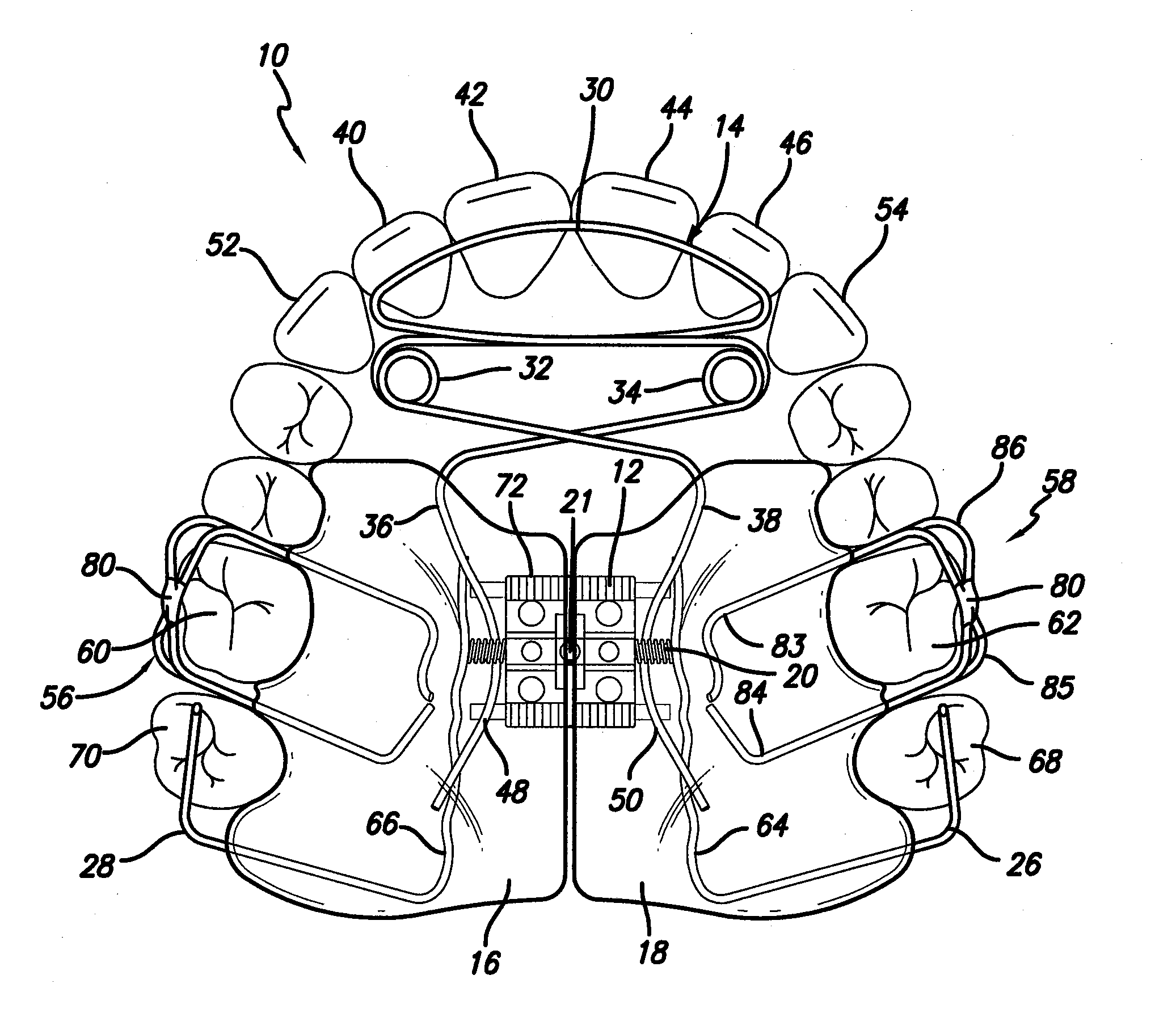
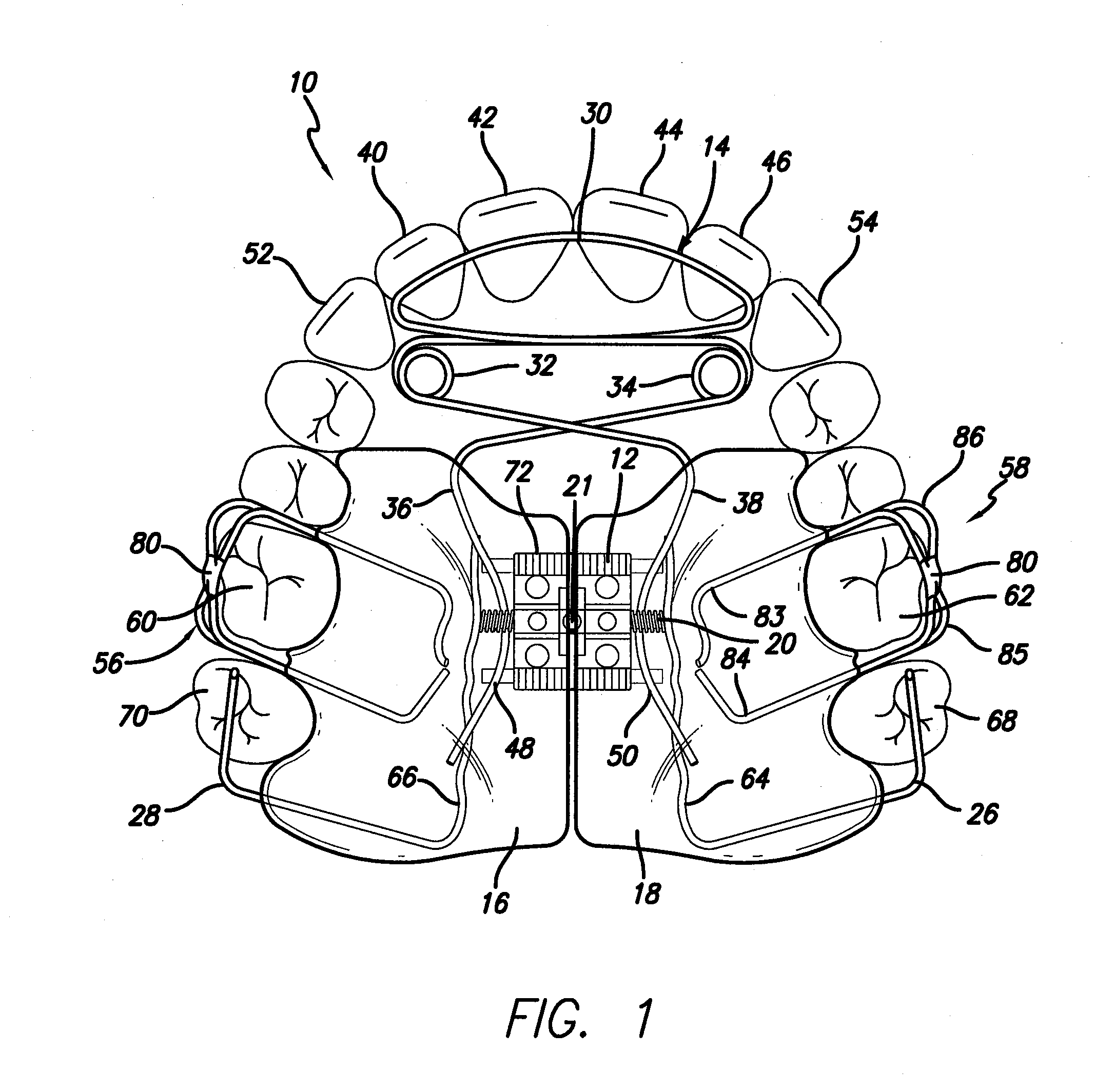
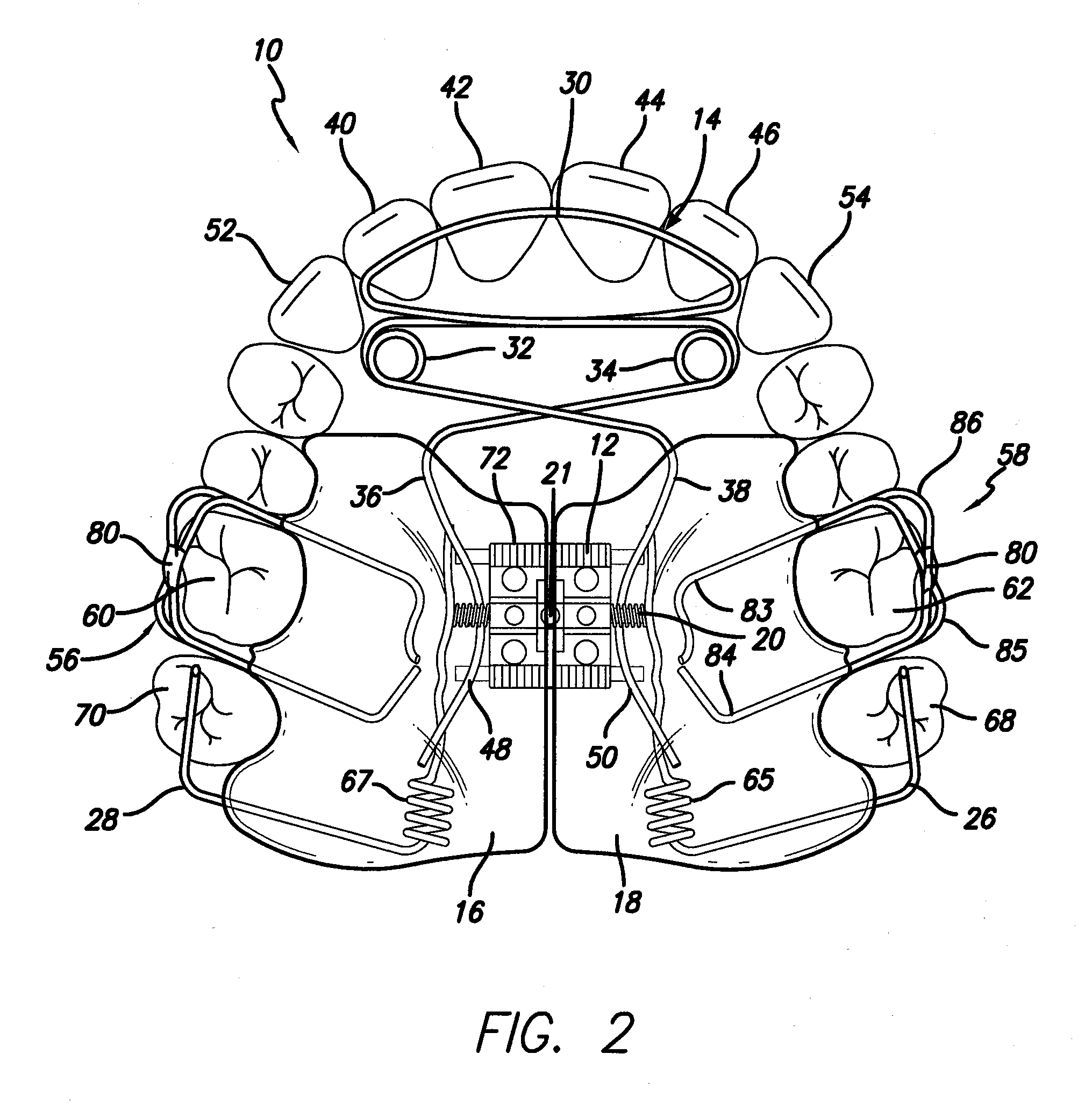
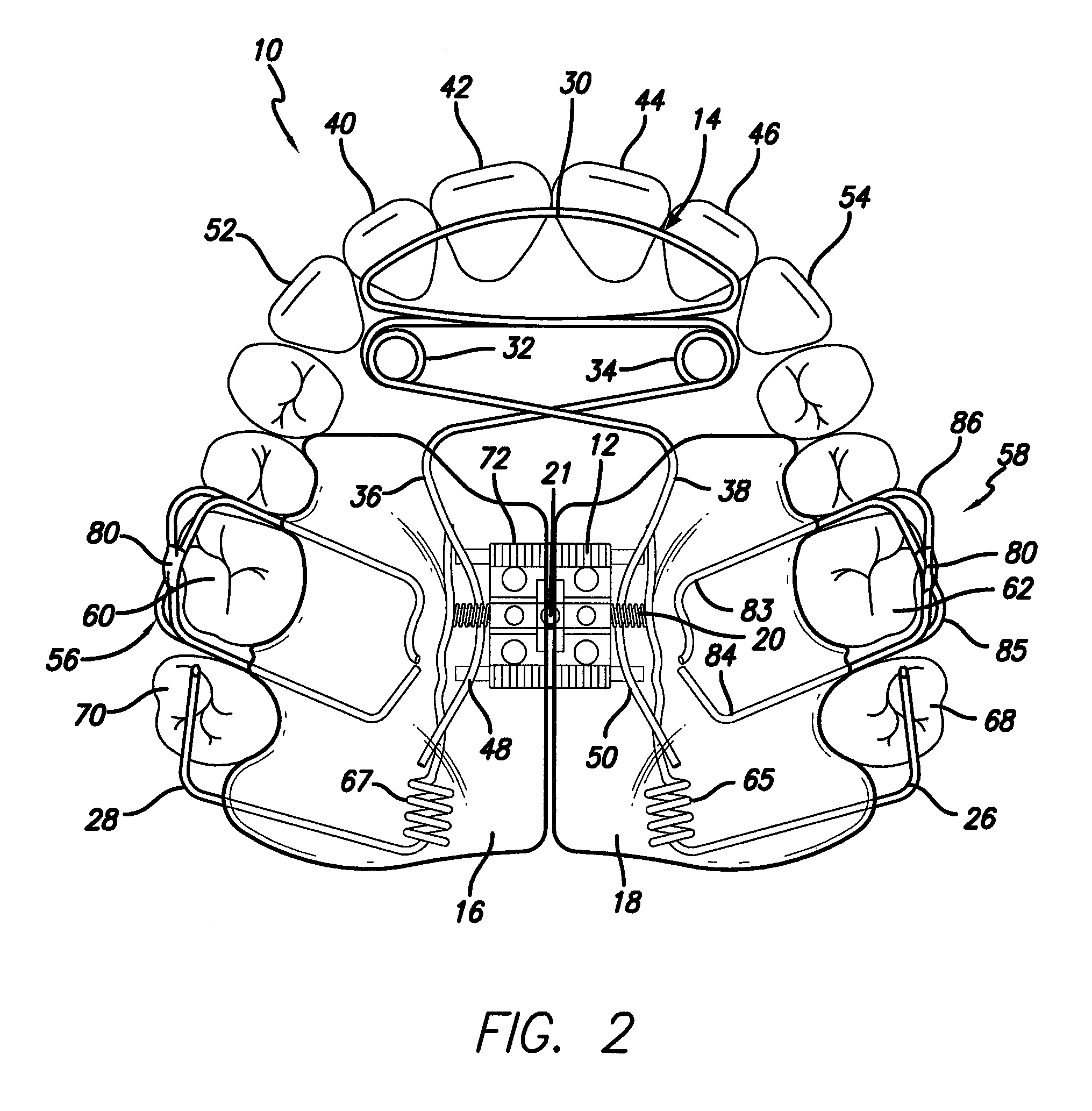
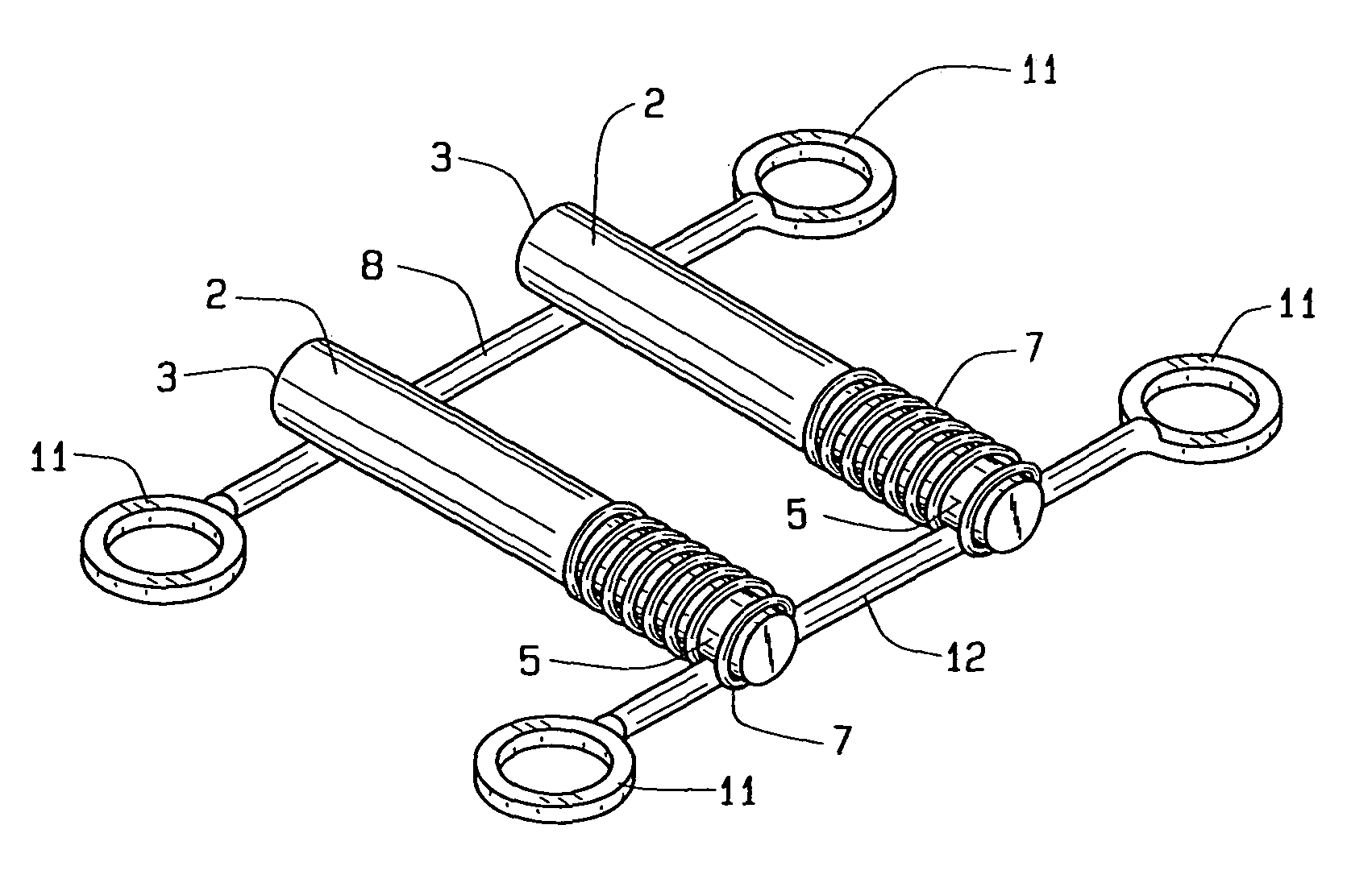
Biased palatal bone expander
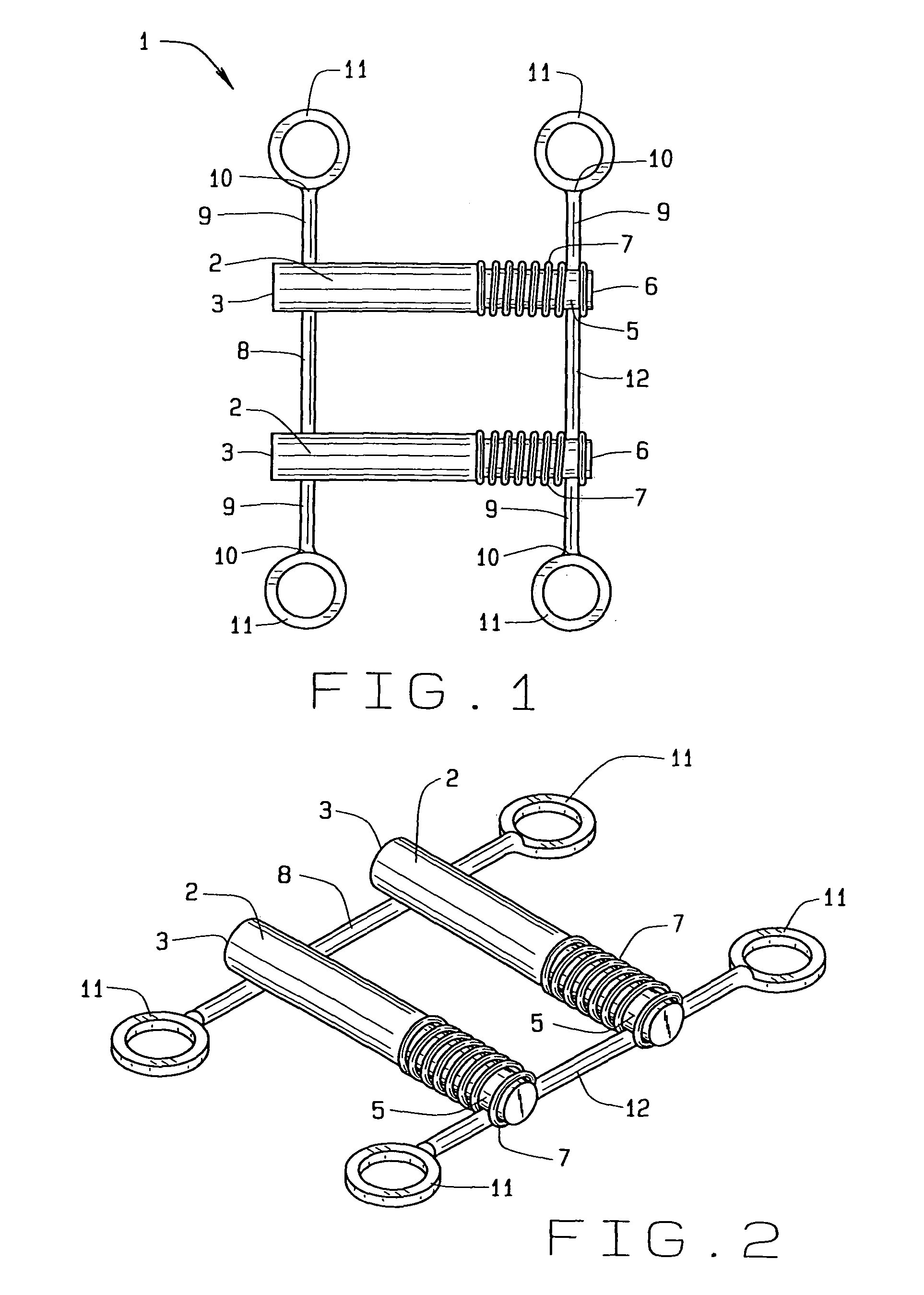
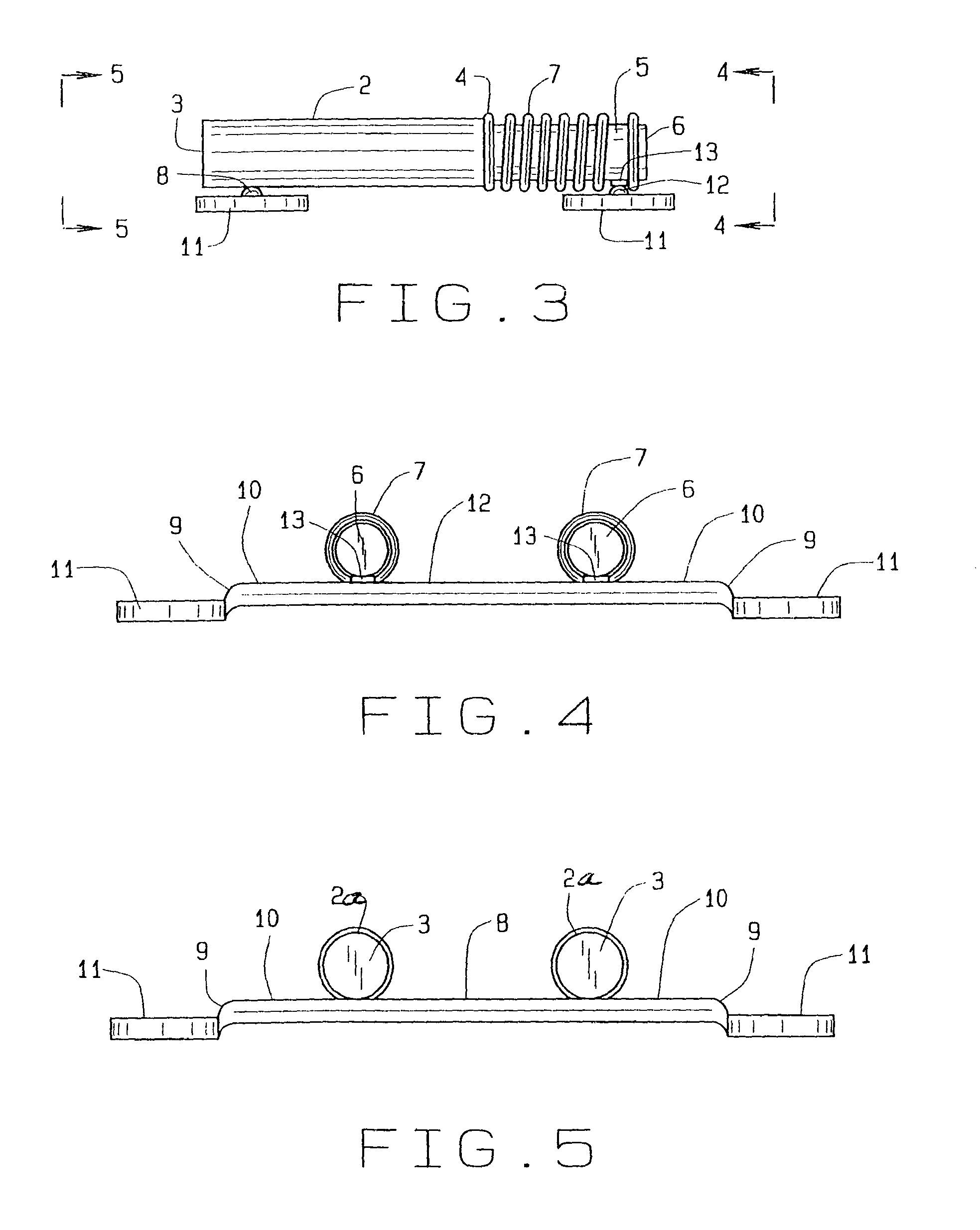
A biased palatal bone expander attaches directly to the palatal bone in the roof of the mouth of a patient. The expander has dual, biased, mutually parallel rods. The rods extend from coaxial tubes and have coaxial springs. The expansion of the springs urges the rod outwardly from the center of the expander thus widening the maxillary arch incrementally without a connection upon the teeth. The tubes and rods each attach to two mutually parallel bars perpendicular to the rods. Each bar has two opposite ends with an eyelet upon each end. The eyelets receive screws for securing the expander to a patient. Additionally, the appliance may include a thermoformed shell that a surgeon or orthodontist uses to guide positioning the appliance for installation.
Owner:WILLIAMS MICHAEL O
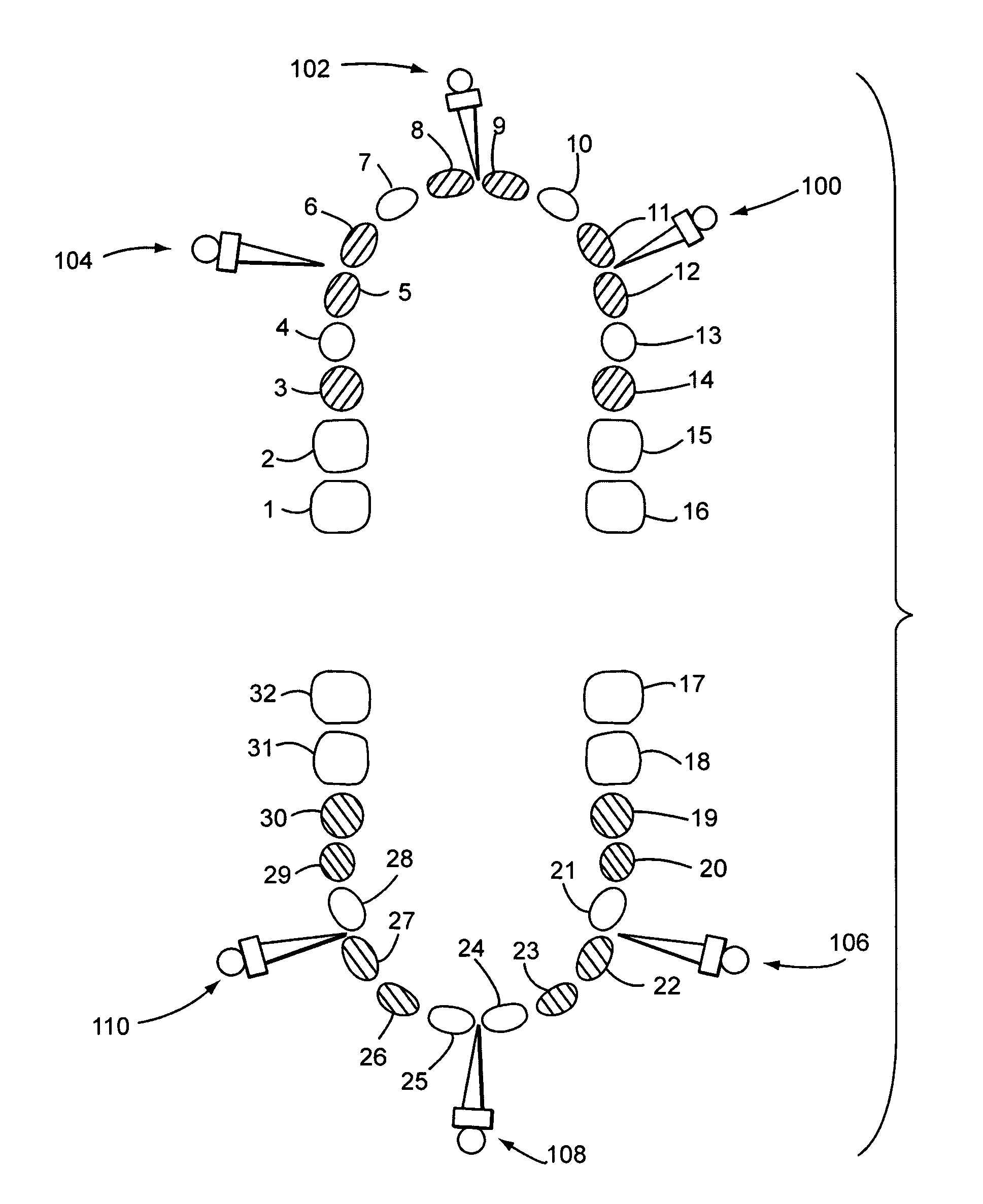
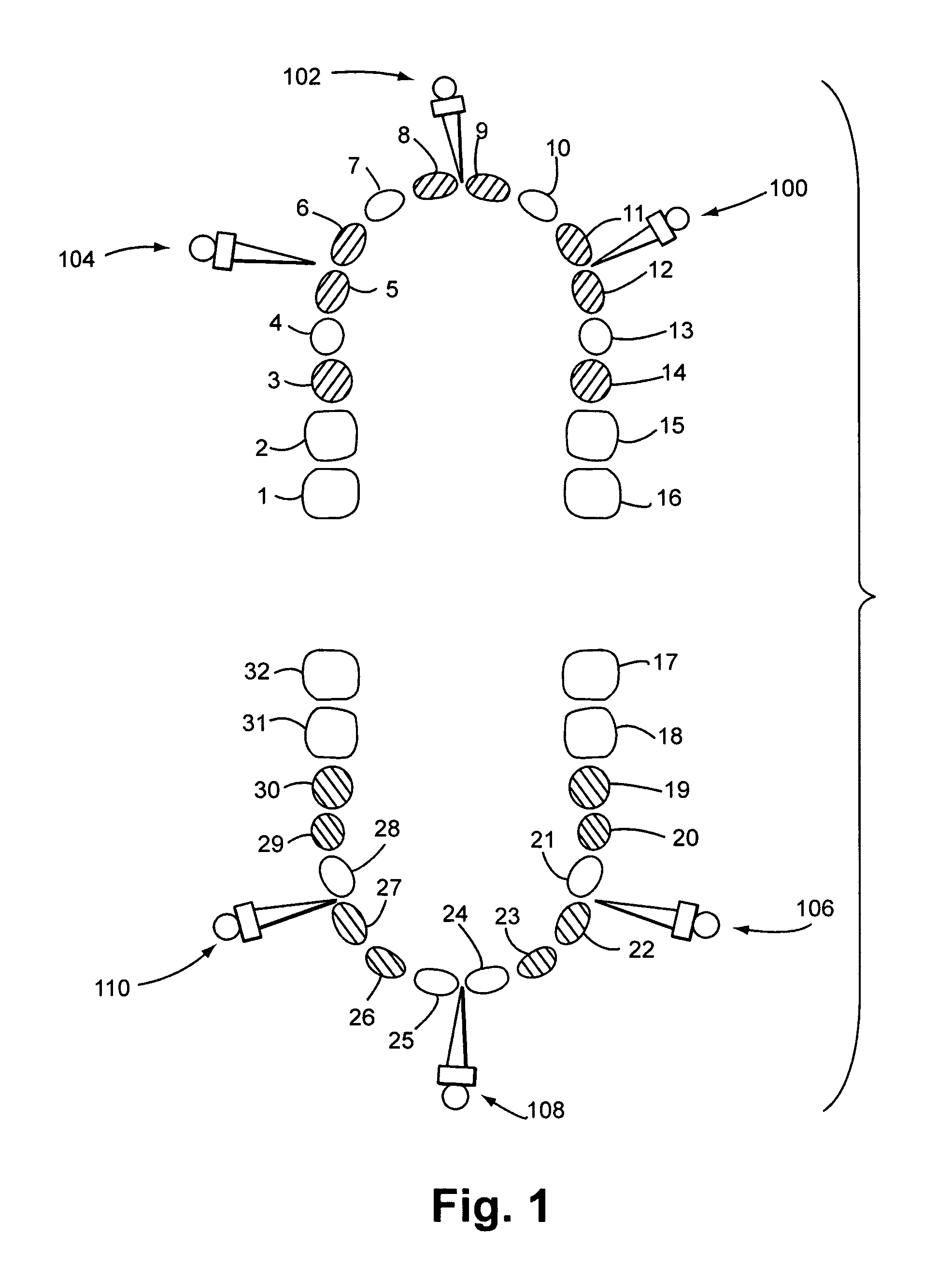
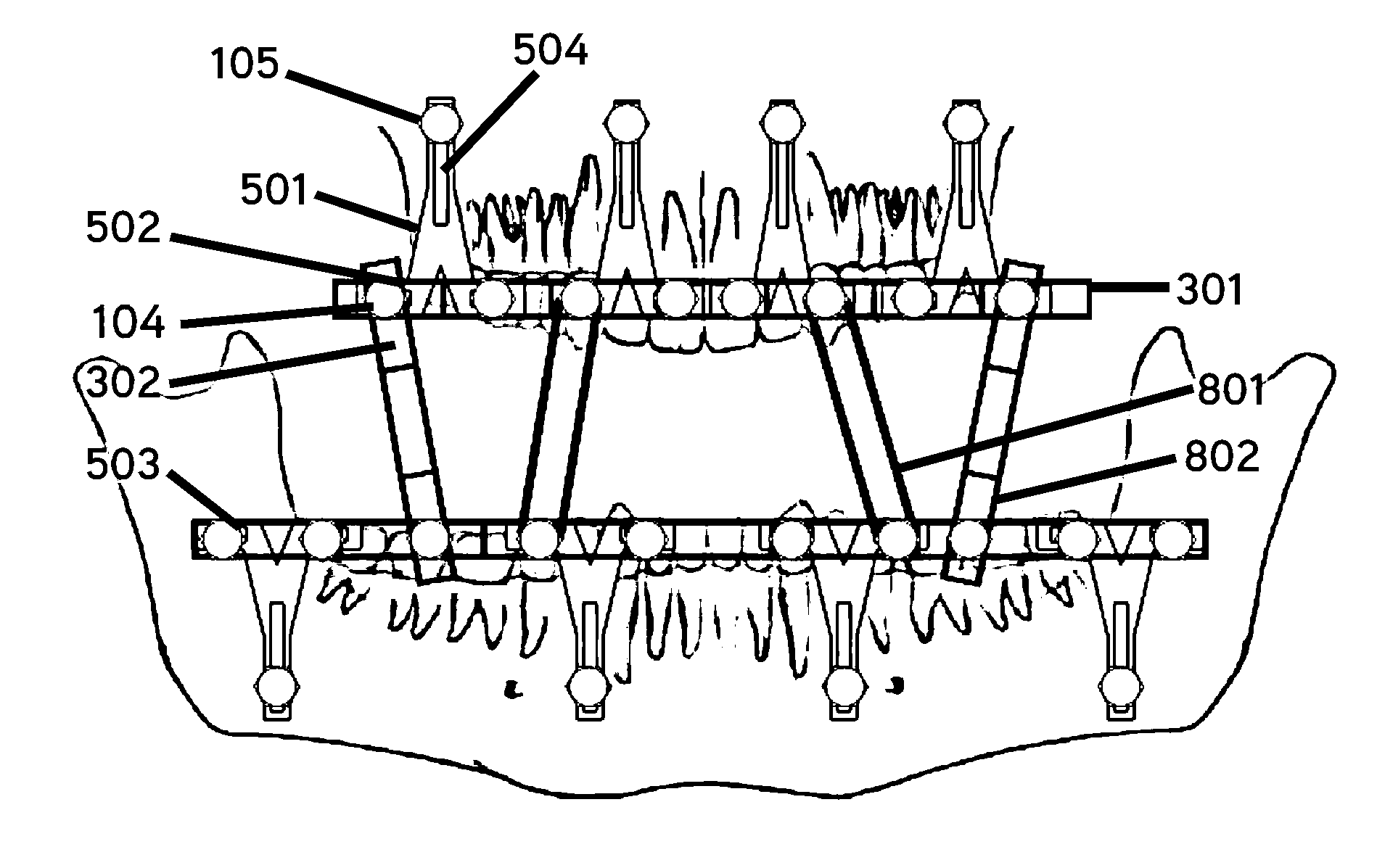
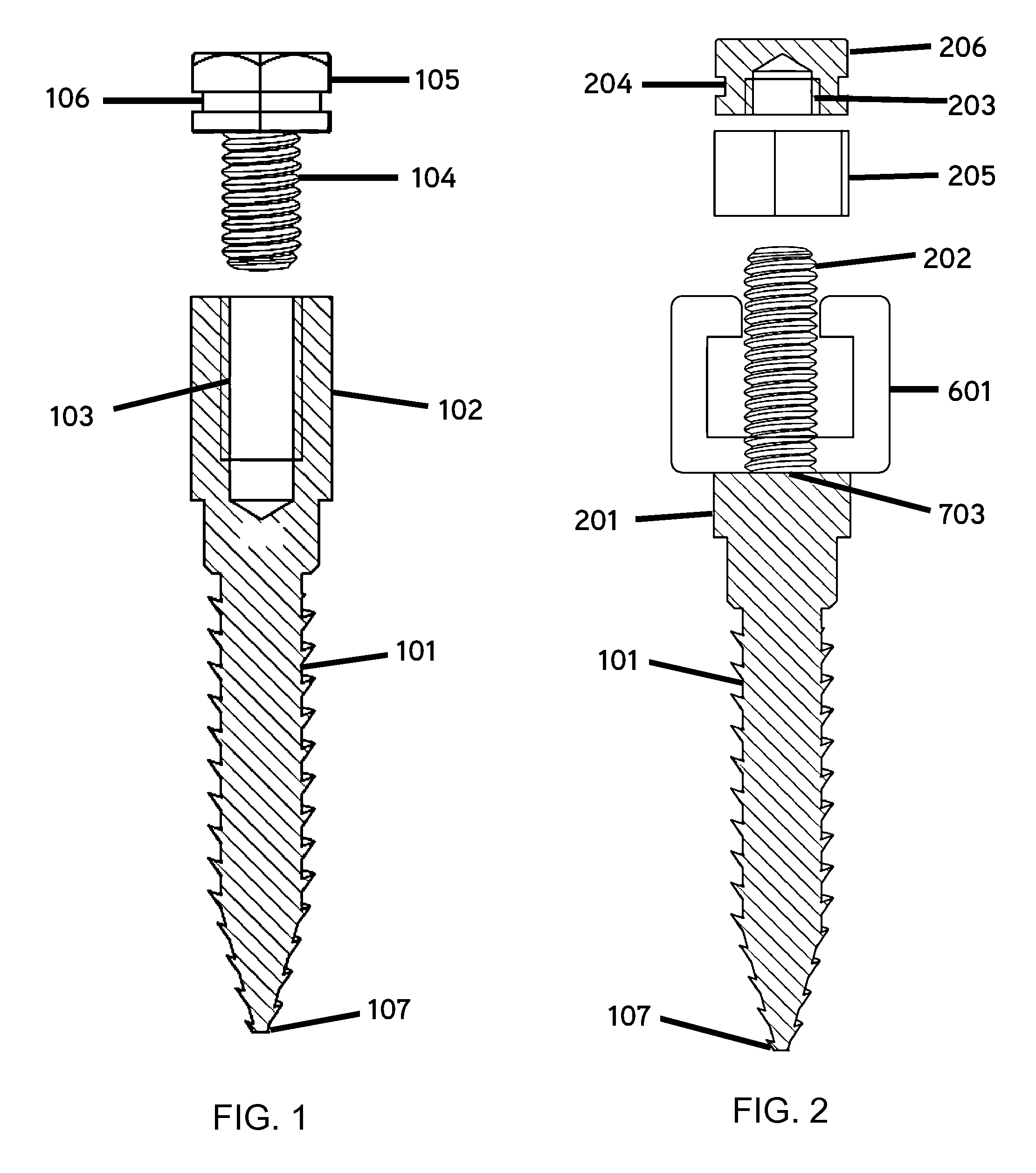
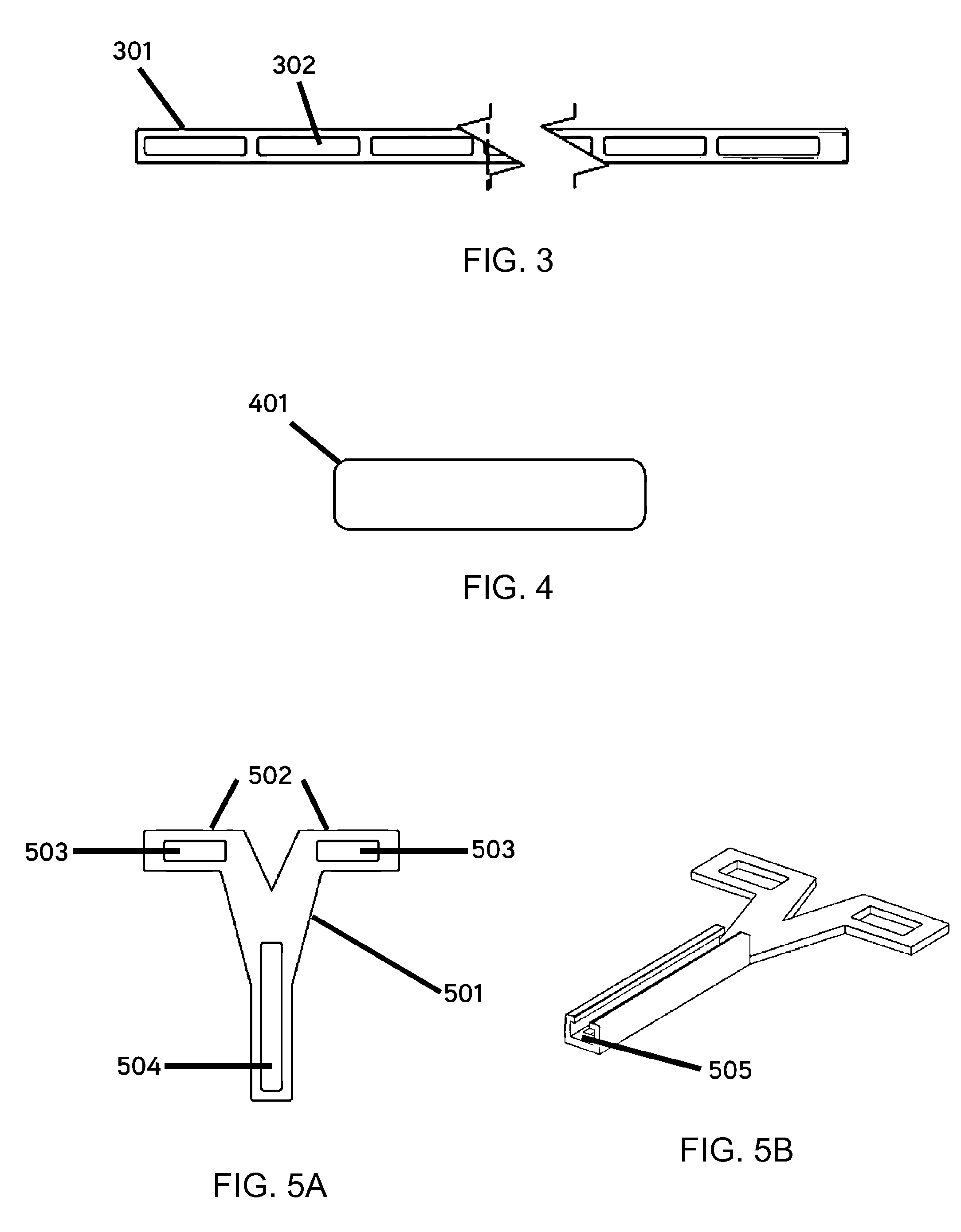
Bone Fixation System And Methods
ActiveUS20150351801A1Improve stabilityReducing periodontal diseaseSuture equipmentsDental implantsBone fixationOrthodontics
An intermaxillary fixation system is provided, including a bone anchorage screw having at least one of an elongated head with internal threading and an externally threaded screw extending from a head of the bone anchorage screw, a fixation system, and a rail bar. A method for the stabilization and fixation of maxillary and mandibular arches is also provided, including setting a plurality of bone anchorage screws to the maxillary and mandibular arch, each bone anchorage screw having a head, fixing one or more T-shaped bars to the bone anchorage screws, bending and connecting a rail bar to heads of the one or more T-shaped bars with orthodontic screws, and wrapping a connector between the heads of the bone anchorage screws located on the mandibular arch and the maxillary arch.
Owner:MONTEJO JAVIER
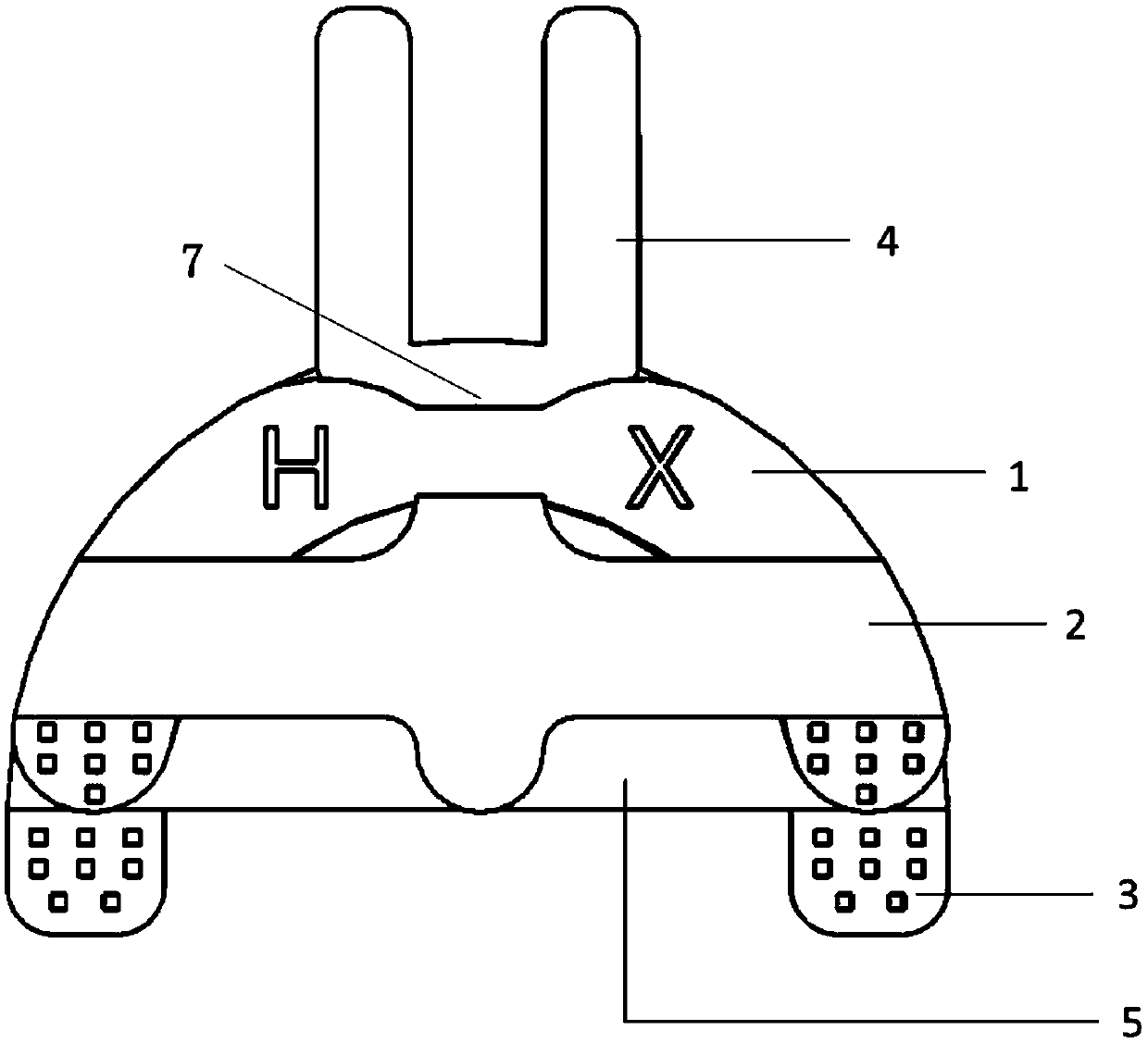
Pluggable gothic arch tracing system used for dental restoration and method thereof
ActiveCN107669359ADetermine scienceEasy to recordDental articulatorsEducational modelsEngineeringUpper lip
The invention discloses a pluggable gothic arch tracing system used for dental restoration and a method thereof. The pluggable gothic arch tracing system comprises an upper jaw arch plate and a lowerjaw arch plate, the upper jaw arch plate is in a U-shaped structure, and a T-shaped upper jaw tracing plate is embedded in an inner side of the upper jaw arch plate; the lower jaw arch plate is in a U-shaped structure, a handle is inserted at a front end of the lower jaw arch plate 3, a T-shaped lower jaw arch plate is embedded in the inner side of the lower jaw arch plate 3, and a tracing needleis connected with the lower jaw arch plate through screw thread. According to the tracing system, a front tooth zone tongue side avoidance groove is arranged at a front end of the upper jaw arch plate, a wax rim space is reserved, and the tracing system is in favor of recording and transferring fullness of a maxillary anterior region through wax addition or reduction during dental restoration forpatient. The handle is a pluggable type, is inserted at a channel section of the lower jaw arch plate while mold taking and facebow using, and the can be removed while the aesthetics information is recorded by wax rim. According to the invention, a fork and a bite silicone rubber are not used for facebow transfer, and an upper lip is not interfered while aesthetics information is transferred.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Removable rapid maxillary expander
A maxillary arch expander, in particular an expander for use with a human patient, is described. Also described are a method of treatment that includes the use of the maxillary arch expander and a method of inserting and removing the maxillary arch expander from the mouth of the patient. All or part of the maxillary arch expander is generally easily removable and reinsertable during use.
Owner:TAYSIDE HEALTH BOARD
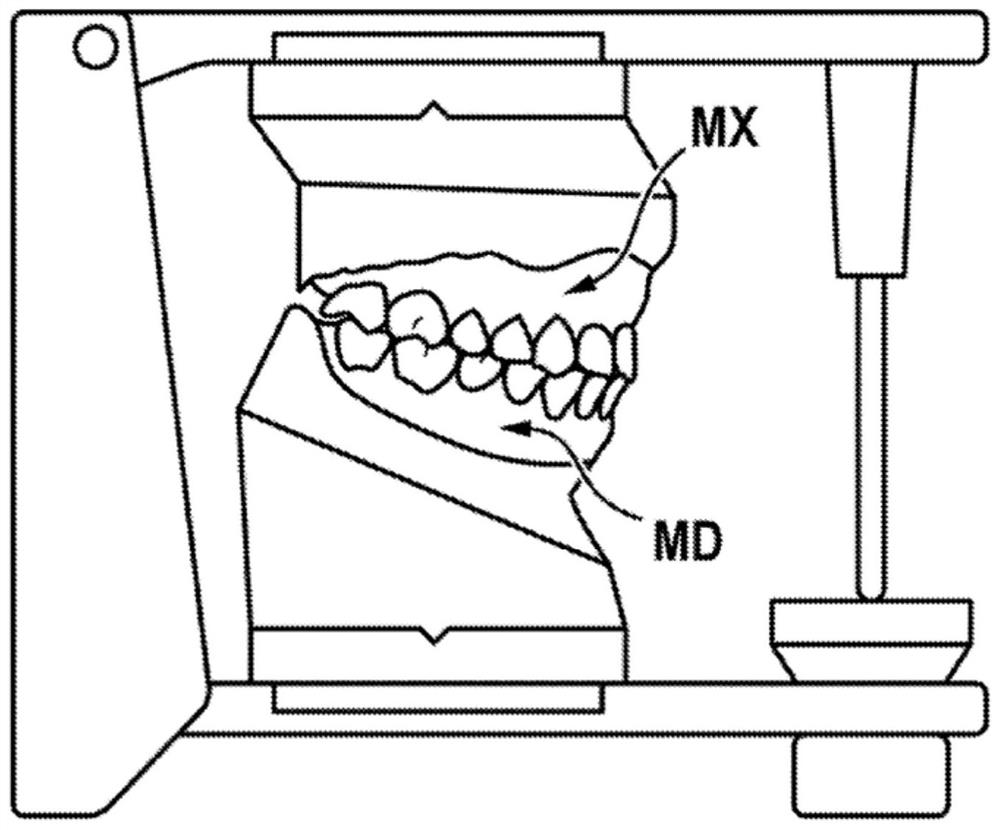
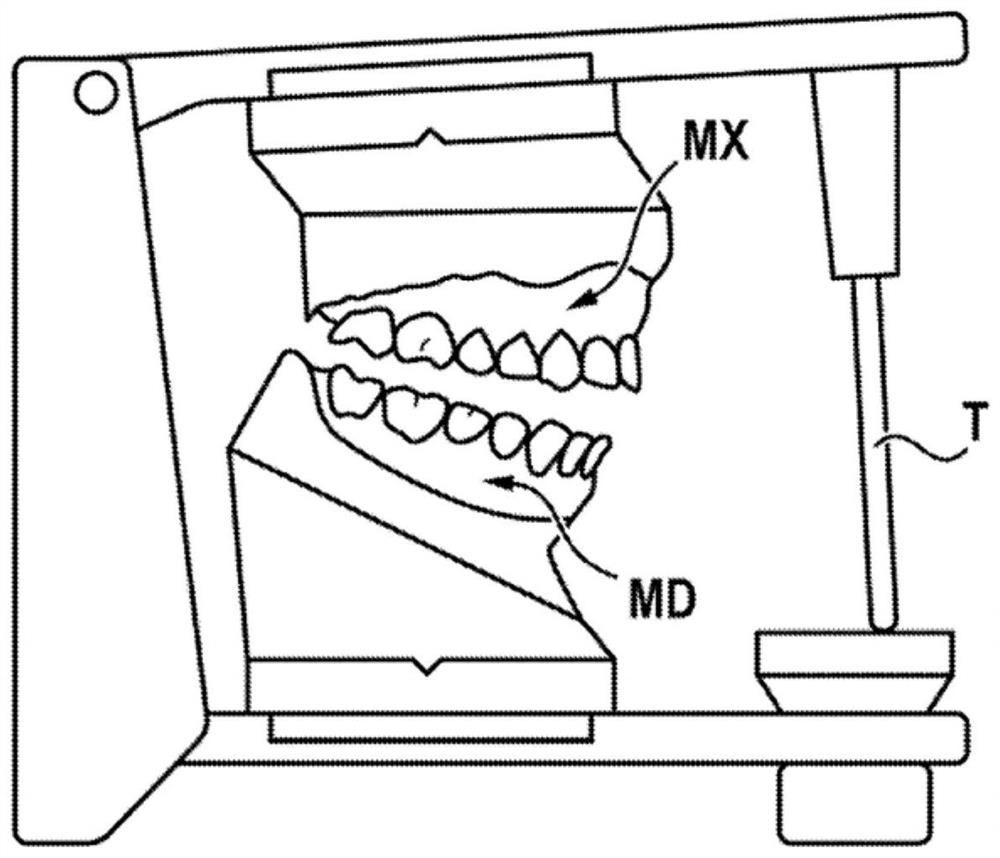
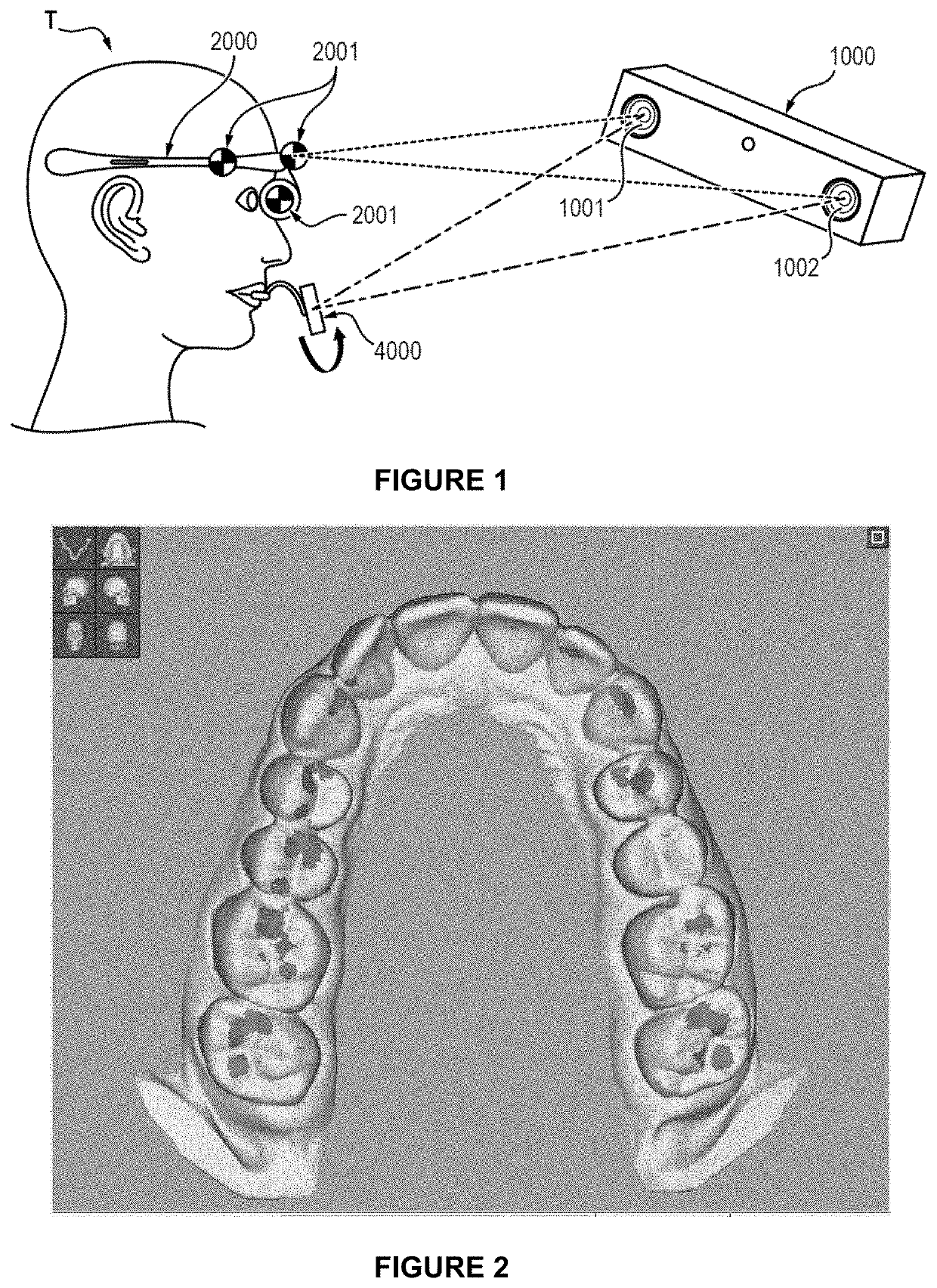
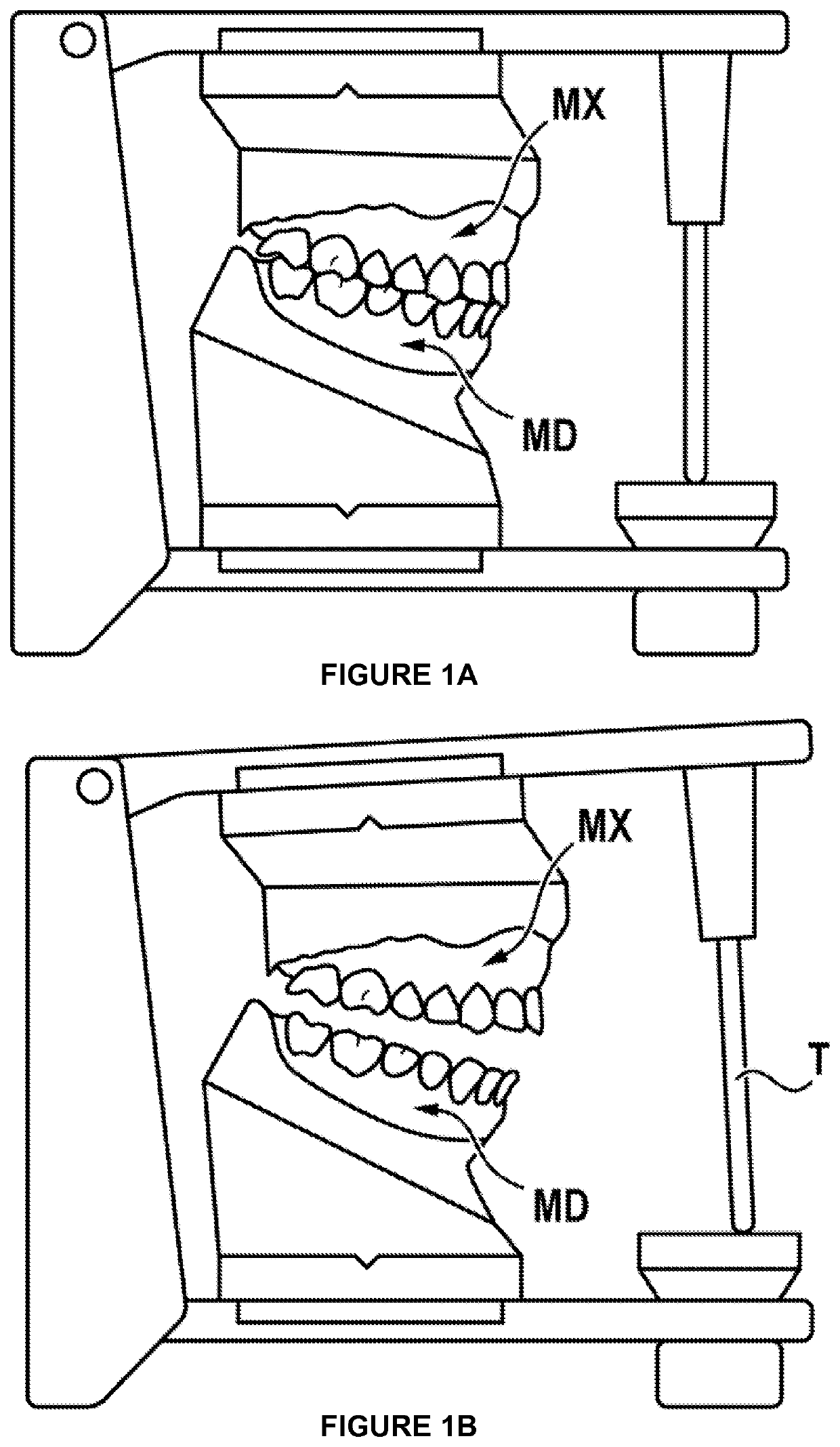
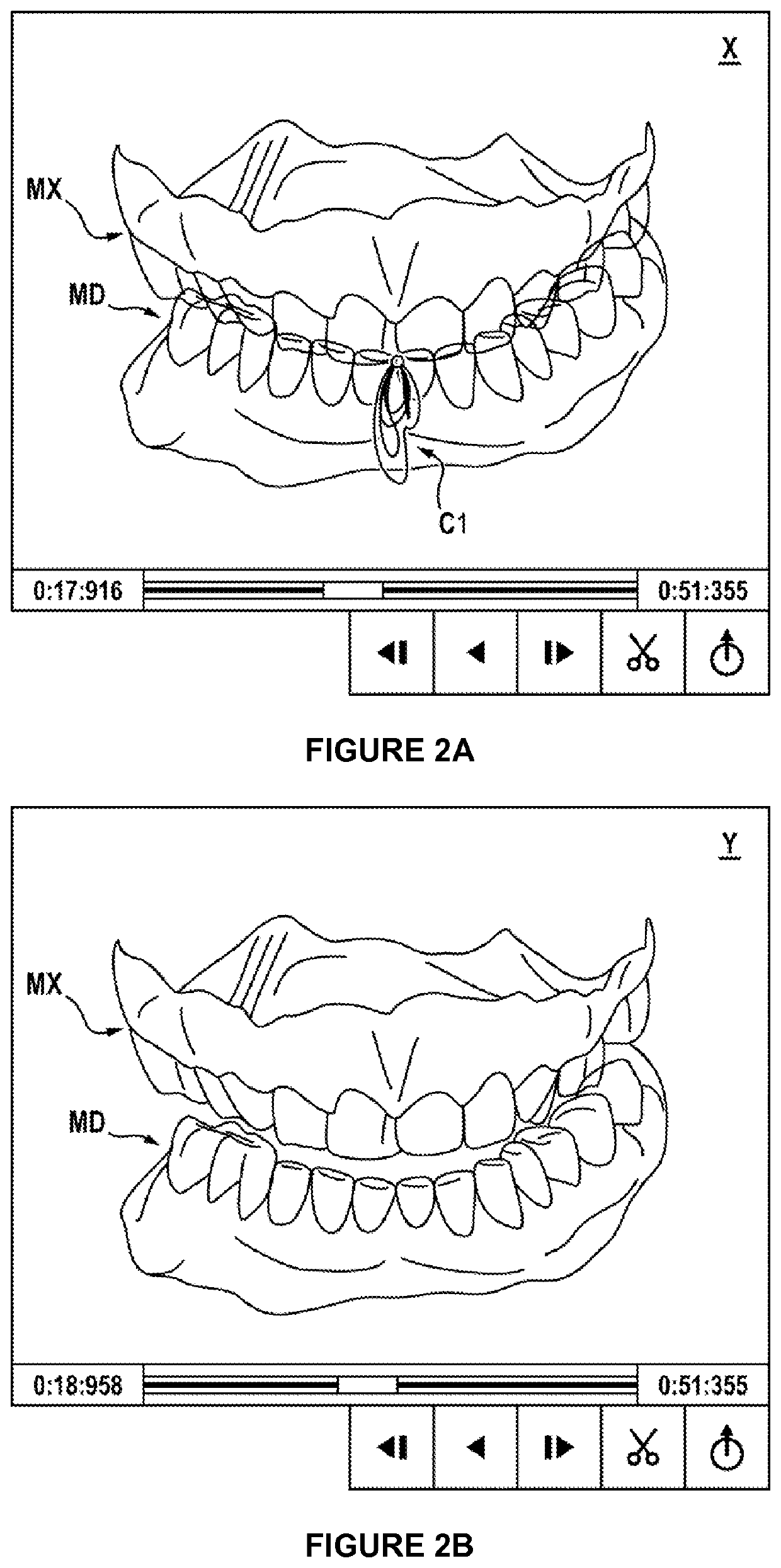
Method for animating models of the mandibular and maxillary arches of a patient in a corrected intermaxillary relationship
The invention relates to a method for animating models of the mandibular and maxillary arches of a patient in a corrected intermaxillary relationship, comprising: providing three-dimensional numerical models (MD, MX) of the mandibular and maxillary arches of the patient; providing a recording of the mandibular motion of the patient, said recording comprising a plurality of relative positions of the mandible of the patient with respect to the maxilla; selecting, from said positions, a reference position (X) of the mandible with respect to the maxilla of the patient; - determining a target position (Y) for the mandible with respect to the maxilla, said target position defining a corrected intermaxillary relationship for the patient; determining a rigid transformation between the reference position (X) and the target position (Y); applying said rigid transformation (i) to the recording of the mandibular motion of the patient in order to animate the three-dimensional numerical models of the mandibular and maxillary arches, or (ii) to the three-dimensional numerical model of the mandible, the delivered recording of the mandibular motion being applied to the three-dimensional numerical models of the mandible and of the maxilla in order to animate said models.
Owner:MODJAW
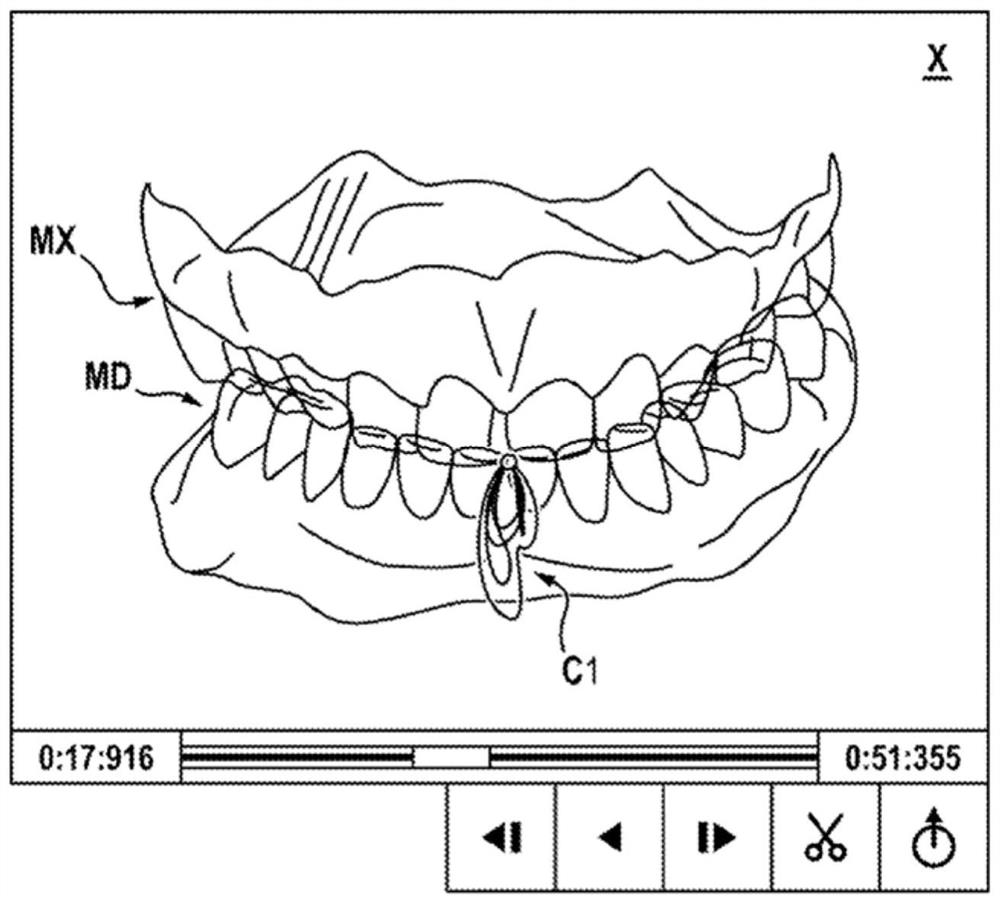
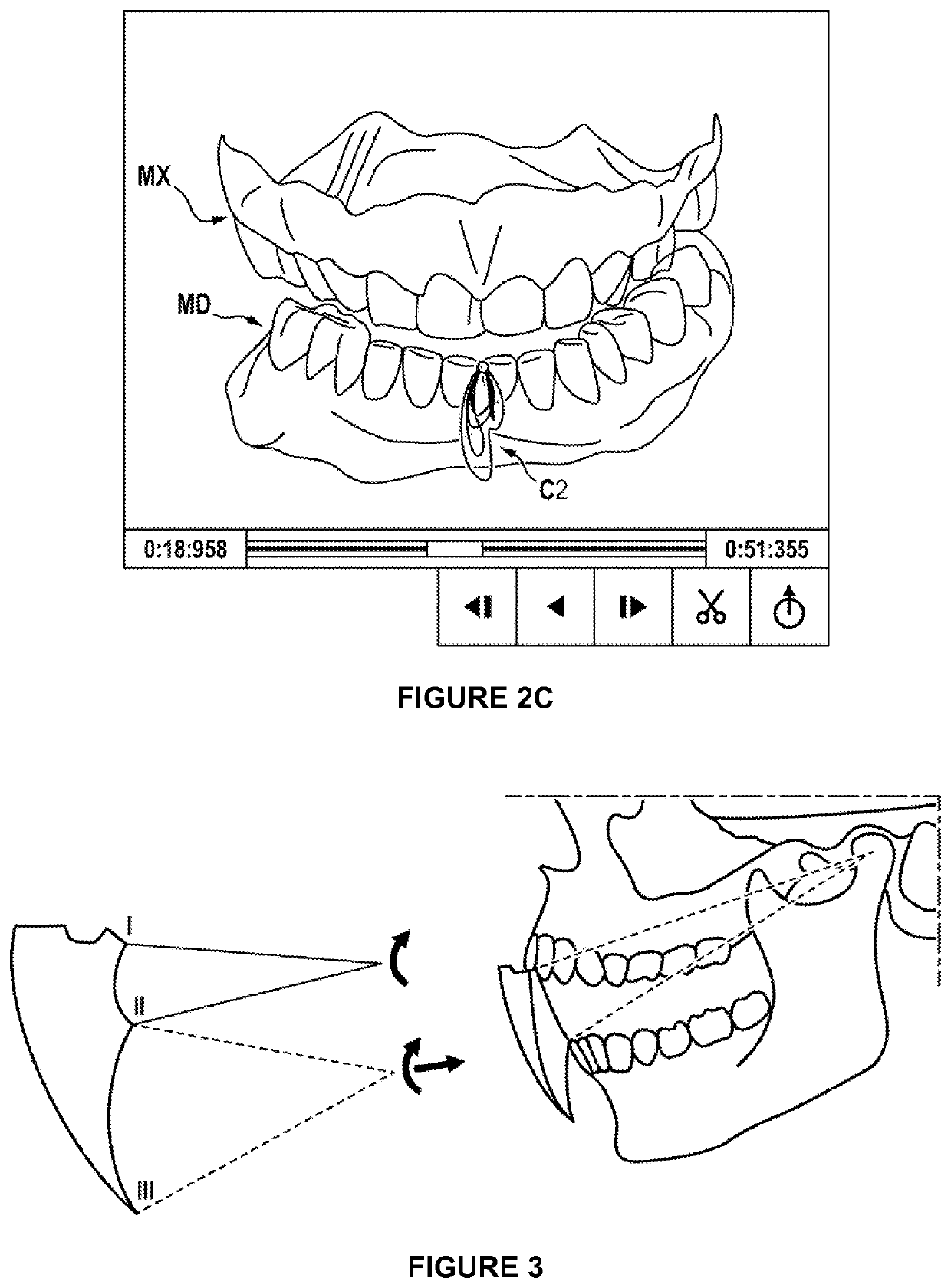
Method for determining a mapping of the contacts and/or distances between the maxillary and mandibular arches of a patient
The invention relates to a method for determining a mapping of the contacts and / or distances between the teeth of the maxillary arch and the mandibular arch of a patient, characterised in that it comprises the following steps:obtaining the mandibular kinematics recorded on the patient;obtaining surface meshes of the maxillary arch and the mandibular arch and registering said meshes relative to one another;creating a reduced mesh of at least one of said arches, comprising the selection, in the mesh of said arch, of the cells in which the nodes are located at a distance of less than 1 cm from the mesh of the opposite arch;creating, for each cell of said reduced mesh, a bounding box comprising a plurality of voxels surrounding said cell;using the mandibular kinematics, calculating a network of contacts comprising, for each voxel of the bounding box, information on the existence of a contact between said voxel and a node of the mesh of the opposite arch during a relative movement of the mandibular arch in relation to the maxillary arch.
Owner:MODJAW
Method for aligning virtual models of dental arches of an individual with a digital model of the face of said individual
The invention relates to a method for aligning non-radiographic virtual models of a mandibular arch and of a maxillary arch of an individual with a non-radiographic digital model of the face of said individual, characterized in that it comprises: fastening a mandibular marker rigidly to the mandibular arch of the individual, said mandibular marker defining a first frame of reference; providing a non-radiographic virtual model of the mandibular arch and a non-radiographic virtual model of the maxillary arch; digitizing at least one portion of the surface of the teeth or of a prosthetic device securely fastened to said arch and at least one rigid portion of said marker by means of an intra- or extra-oral camera, so as to produce a digital record of said portions of the mandibular arch and of the marker in a given second frame of reference; on the basis of said record and of the virtual models of the mandibular arch and of the mandibular marker, matching the digital model of the mandibular marker with the marker, and the virtual model of the mandibular arch with said arch, and locating the virtual model of the mandibular arch in the first frame of reference; acquiring a non-radiographic digital model of the face of the patient; and locating the digital model of the face in the first frame of reference, so as to align the virtual models of the maxillary and mandibular arches with said digital model of the face.
Owner:MODJAW
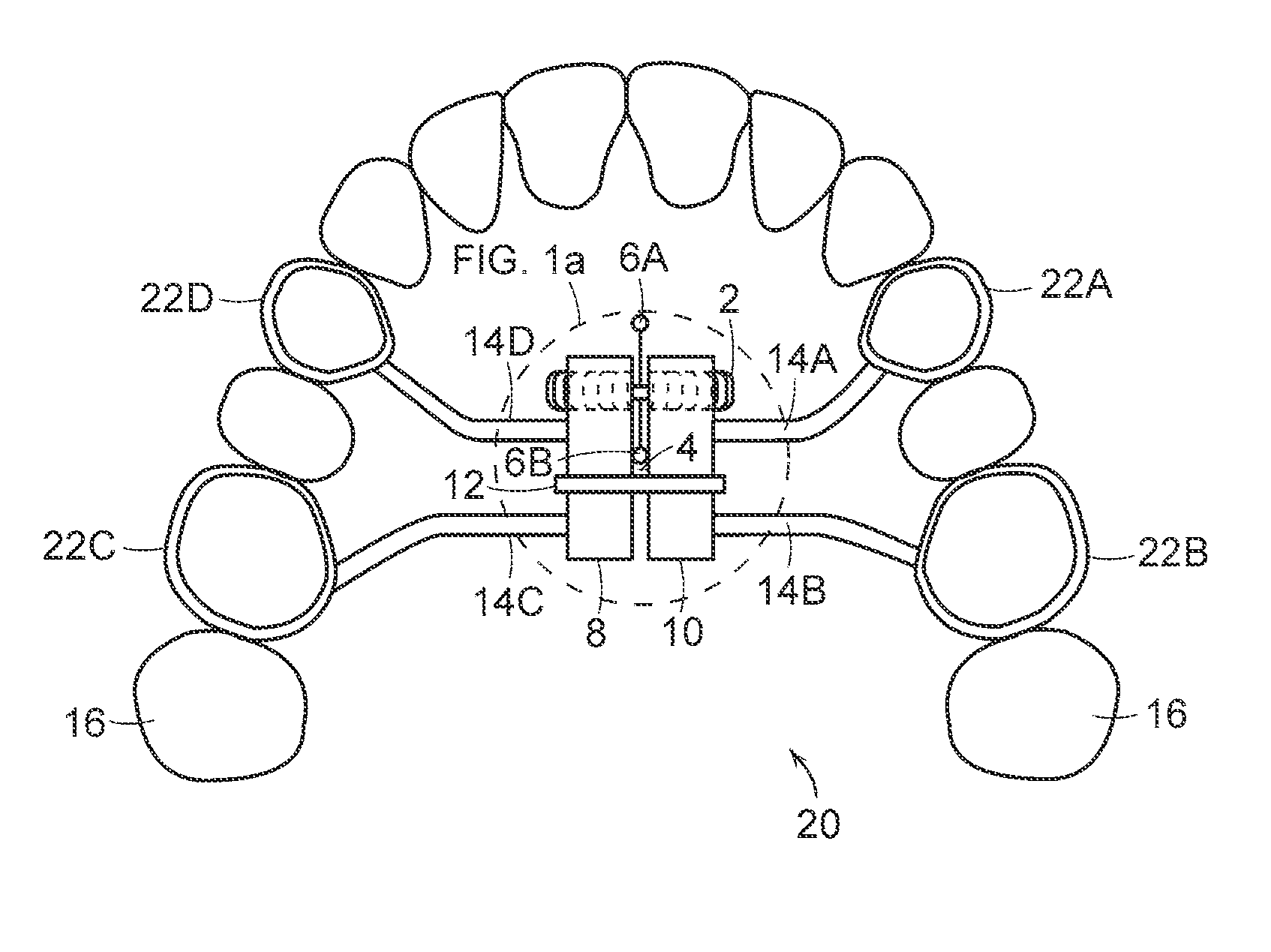
Device for expanding maxillary dental arch through automatic force application
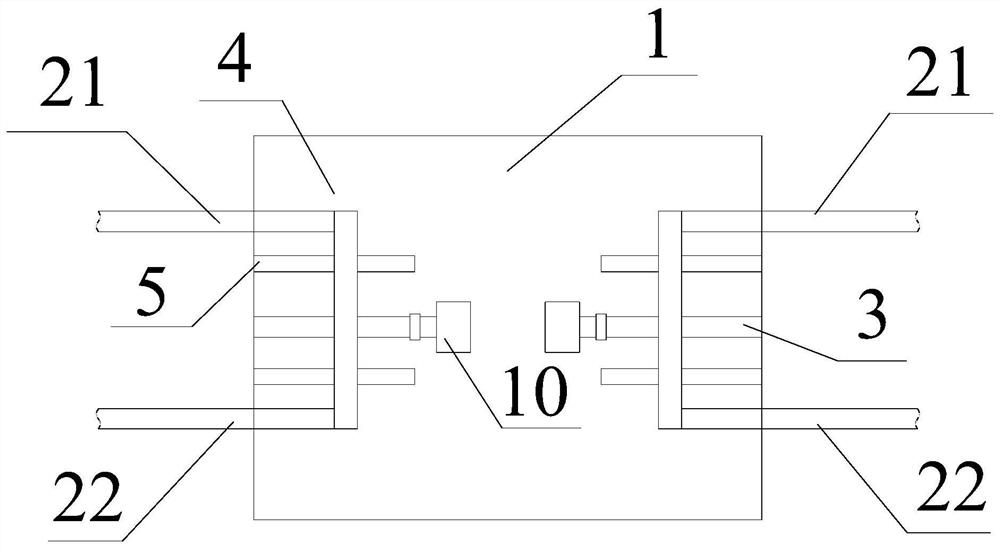
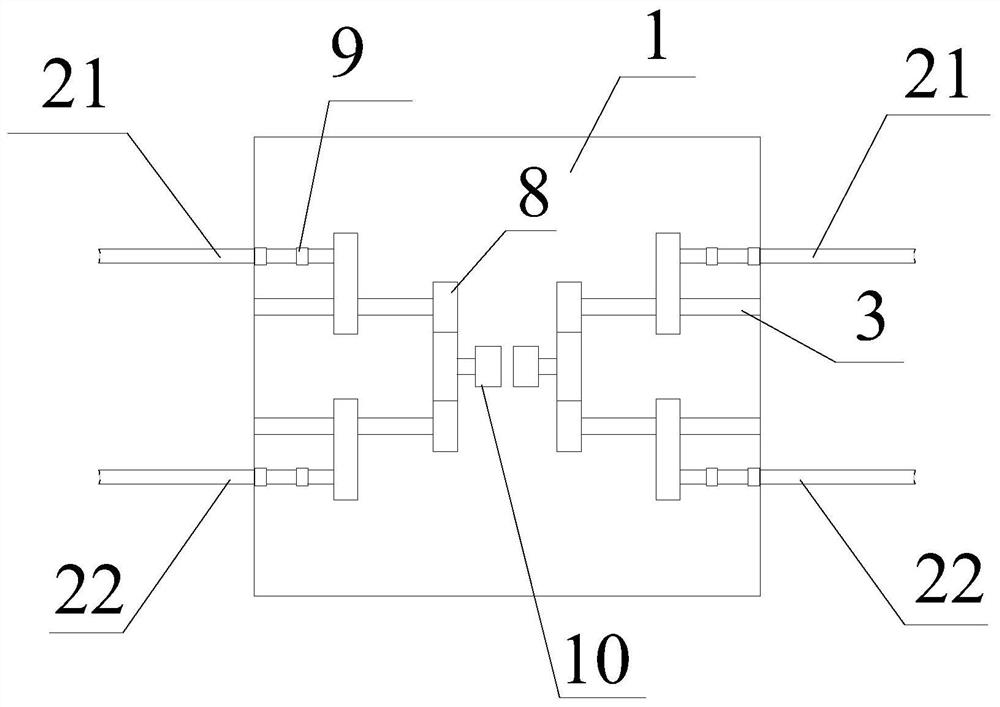
InactiveCN112618068ARealize automatic afterburnerImprove comfortDental implantsOthrodonticsPoor compliancePatient compliance
The invention discloses a device for expanding a maxillary dental arch through automatic force application. The device comprises a support, force application rods, a driving mechanism and a guide mechanism, wherein the force application rods are slidably connected with the guide mechanism, the guide mechanism and the driving mechanism make the force application rods horizontally move towards the outer side or the inner side of the support, the guide mechanism is fixedly arranged on the support, the output end of the driving mechanism is connected with the force input ends of the force application rods, the force application rods are arranged at the two sides of the support, and the guide mechanism and the driving mechanism make the force application rods horizontally move towards the outer side or the inner side of the support; and the guide mechanism comprises a guide rail and a guide sliding block, and the sliding block is slidably arranged on the guide rail and is also connected with the output ends of the force application rods and the output end of the driving mechanism. Automatic force application of an arch expander can be achieved, and the situation is avoided that the treatment progress and effect are influenced due to poor compliance of a patient; force application parameters can be adjusted according to the condition of the patient, and the comfort of the patient in the treatment process can be improved through single small-distance and high-frequency force application; and improvement from traditional maxillary arch expansion to high implementation rate increase is achieved to ensure the clinical arch expansion effect.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF MEDICAL COLLEGE OF XIAN JIAOTONG UNIV
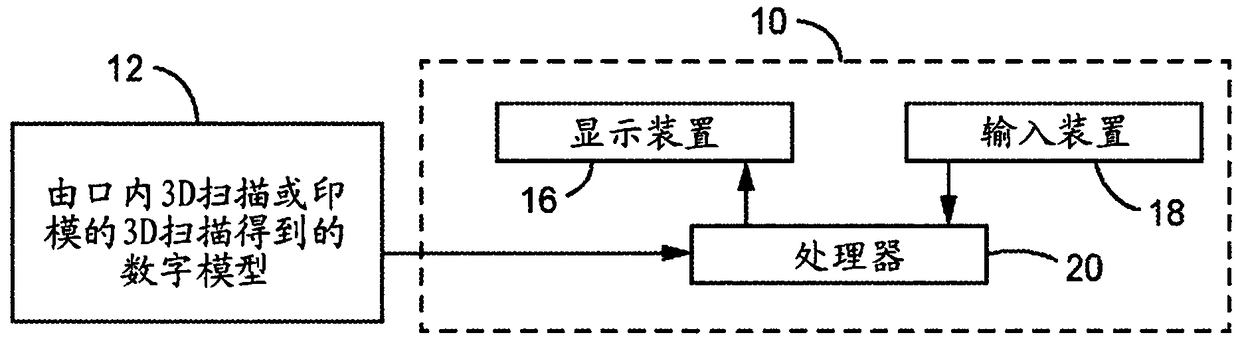
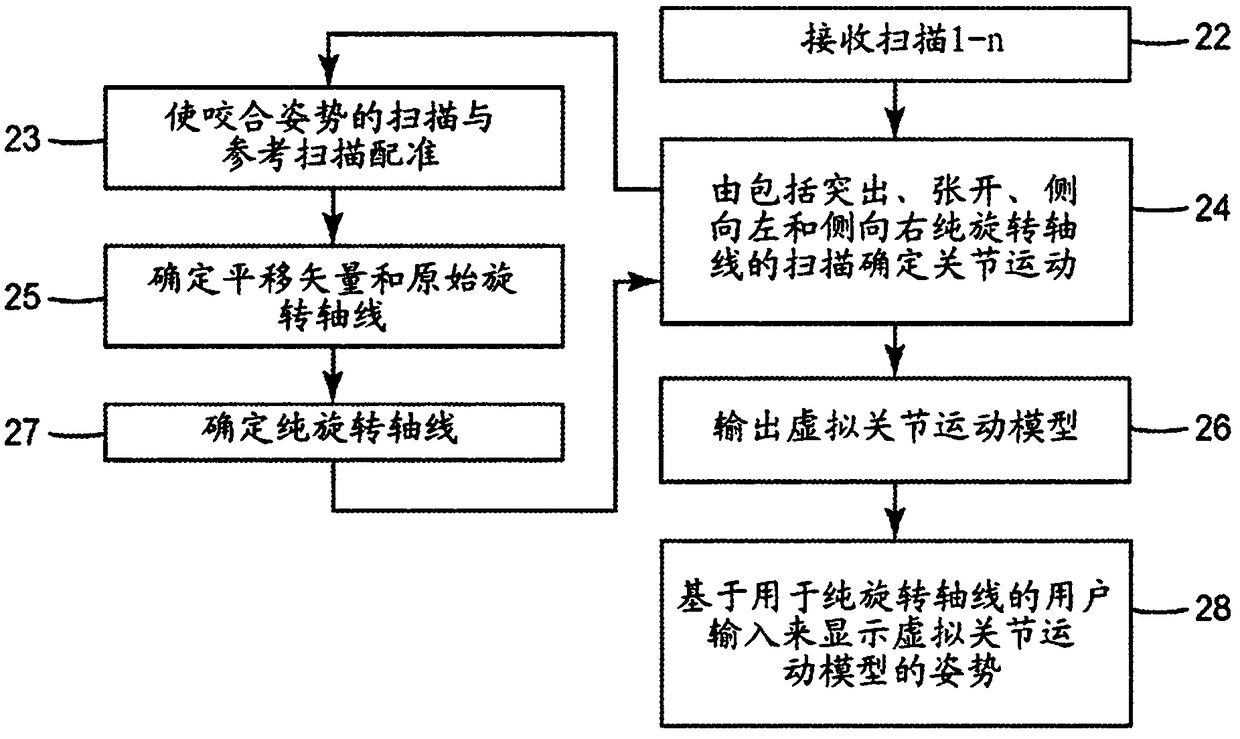
Virtual model of articulation from intra-oral scans
The invention provides a method for determining virtual articulation from dental scans. The method includes receiving digital 3D models of a person's maxillary and mandibular arches, and digital 3D models of a plurality of different bite poses of the arches. The digital 3D models of the maxillary and mandibular arches are registered with the bite poses to generate transforms defining spatial relationships between the arches for the bite poses. Based upon the digital 3D models and transforms, the method computes a pure rotation axis representation for each bite pose of the mandibular arch withrespect to the maxillary arch. The virtual articulation can be used in making restorations or for diagnostic purposes.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Centric relation bite registration tool
The centric relation bite registration tool is a tool for recording the centric relation of a patient's mandible in order to obtain proper occlusion to fabricate a full mouth fixed dental prosthesis. The centric relation bite registration tool includes both a vertically adjustable portion and a horizontally adjustable portion. The vertically adjustable portion is adapted for mounting in a dental implant in the patient's mandibular arch, and the horizontally adjustable portion is adapted for mounting in a dental implant in the patient's maxillary arch. The vertically adjustable portion and the horizontally adjustable portion are releasably secured to one another between the mandibular and maxillary arches providing a single tool which is both horizontally and vertically adjustable for recordation of the proper occlusion between the patient's mandible and maxilla.
Owner:KING SAUD UNIVERSITY
A Digital Alignment Method Based on Tooth Root Information
ActiveCN105147401BIncreased risk of not moving as expected, etc.Improve tooth row efficiencyOthrodonticsSpecial data processing applicationsCollision detectionRoot surface
The invention relates to a digital tooth arrangement method used in the field of orthodontics, which is characterized in that the tooth root position is displayed during the tooth arrangement process through digital technology to ensure that the tooth arrangement result is within the physiological limit and make the tooth arrangement result more accurate and reasonable. The steps include: 1. Establishment of an orthodontic virtual jaw model including tooth root information; 2. Fix a point to parameterize each tooth; 3. Define a global coordinate system; 4. Arrange mandibular teeth: 1) Position the lower incisors, 2. ) Construct the bracket plane, 3) Construct the arch curve and align the teeth, 4) Construct the root plane and root surface curve, 5) Adjust the position of the tooth root; 5, Arrange the maxillary teeth: 1) Position the upper incisor, 2) Adjust the maxillary bracket 3) Construct the maxillary arch curve and arrange the teeth, 4) Adjust the position of the tooth root 6. Fine-tune the tooth arrangement results based on the collision detection.
Owner:北京那雅医疗技术有限公司
Method for animating models of the mandibular and maxillary arches of a patient in a corrected intermaxillary relationship
PendingUS20220008174A1Overcomes drawbackReduce vertical sizeMedical simulationImage enhancementEngineeringIntermaxillary Relationship
The invention relates to a method for animating models of the mandibular and maxillary arches of a patient in a corrected intermaxillary relationship, comprising: —providing three-dimensional numerical models (MD, MX) of the mandibular and maxillary arches of the patient; —providing a recording of the mandibular motion of the patient, said recording comprising a plurality of relative positions of the mandible of the patient with respect to the maxilla; —selecting, from said positions, a reference position (X) of the mandible with respect to the maxilla of the patient; —determining a target position (Y) for the mandible with respect to the maxilla, said target position defining a corrected intermaxillary relationship for the patient; —determining a rigid transformation between the reference position (X) and the target position (Y); —applying said rigid transformation (i) to the recording of the mandibular motion of the patient in order to animate the three-dimensional numerical models of the mandibular and maxillary arches, or (ii) to the three-dimensional numerical model of the mandible, the delivered recording of the mandibular motion being applied to the three-dimensional numerical models of the mandible and of the maxilla in order to animate said models.
Owner:MODJAW
Biased palatal bone expander
A biased palatal bone expander attaches directly to the palatal bone in the roof of the mouth of a patient. The expander has dual, biased, mutually parallel rods. The rods extend from coaxial tubes and have coaxial springs. The expansion of the springs urges the rod outwardly from the center of the expander thus widening the maxillary arch incrementally without a connection upon the teeth. The tubes and rods each attach to two mutually parallel bars perpendicular to the rods. Each bar has two opposite ends with an eyelet upon each end. The eyelets receive screws for securing the expander to a patient. Additionally, the appliance may include a thermoformed shell that a surgeon or orthodontist uses to guide positioning the appliance for installation.
Owner:WILLIAMS MICHAEL O
Virtual joint motion model for dental processing
PendingCN114144841AReduce or eliminate distractionsGood for healthMedical simulationImpression capsDentitionBiomedical engineering
The present invention relates to a method for determining whether a tooth is properly shaped and oriented to avoid hindering another tooth using virtual articulation movement. The method includes a) receiving, by a computing device, data indicative of a virtual dentition of a patient's oral cavity, the data indicative of the virtual dentition including data indicative of at least one of a virtual mandibular arch representing a mandibular arch of the patient or a virtual maxillary arch representing a maxillary arch of the patient; b) receiving data indicative of selected points on the virtual dentition of the oral cavity; and c) determining a tangent vector indicative of the direction of movement of the selected point, and determining, based on the determined tangent vector, whether the orientation of the teeth of the virtual dentition or the shape of the teeth is properly shaped and oriented, where the tangent vector is based on the axis of rotation of the virtual mandibular arch.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com