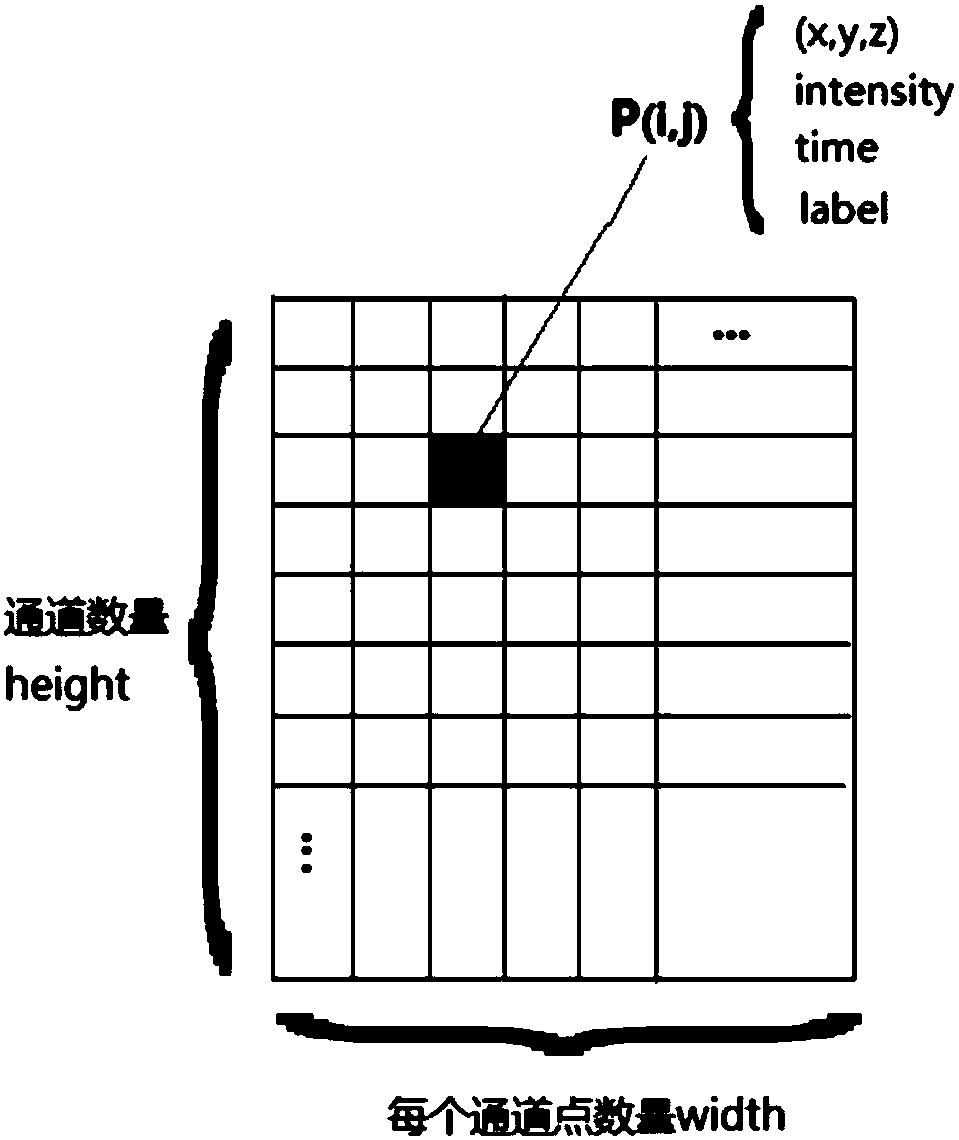
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
727 results about "Global coordinate system" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
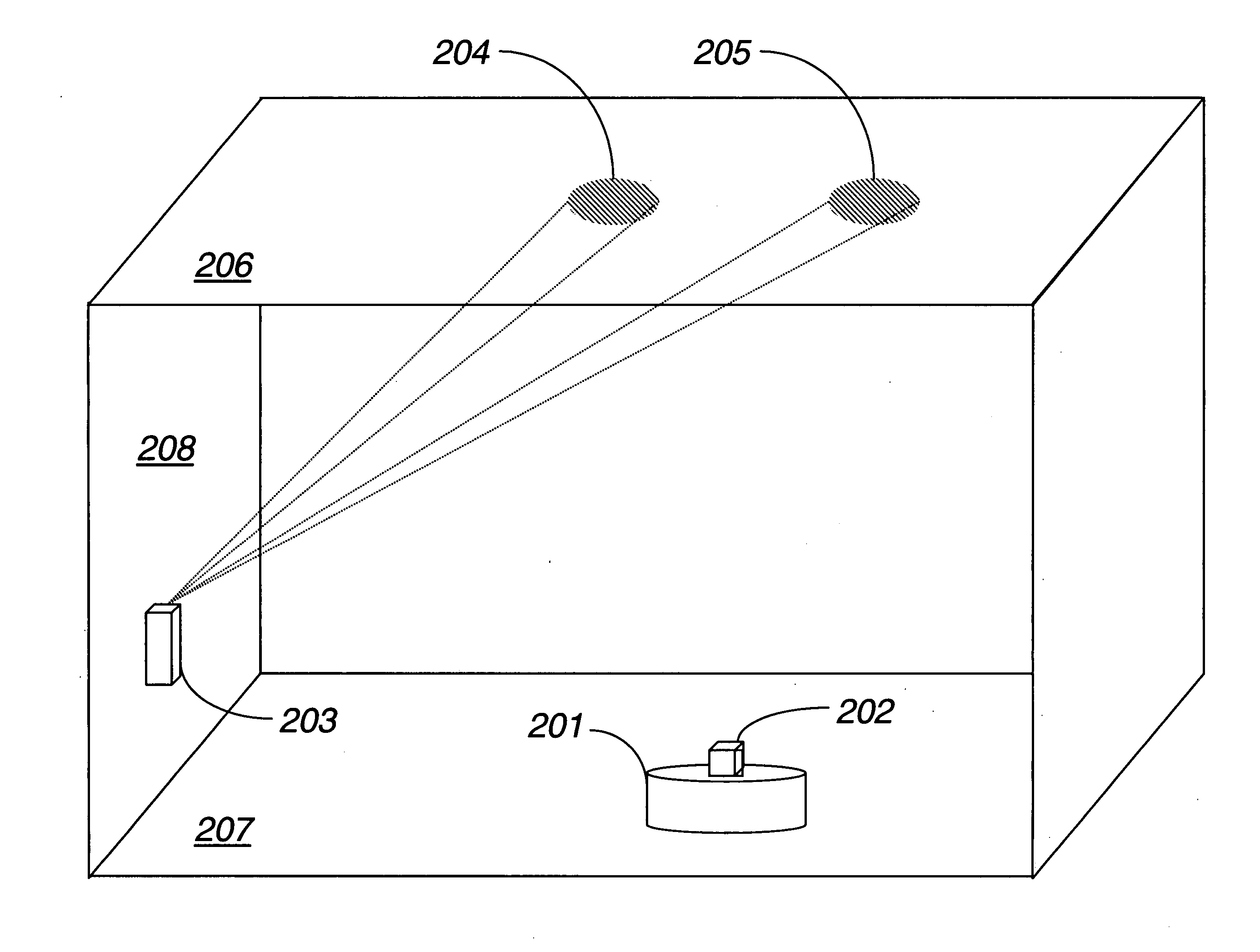
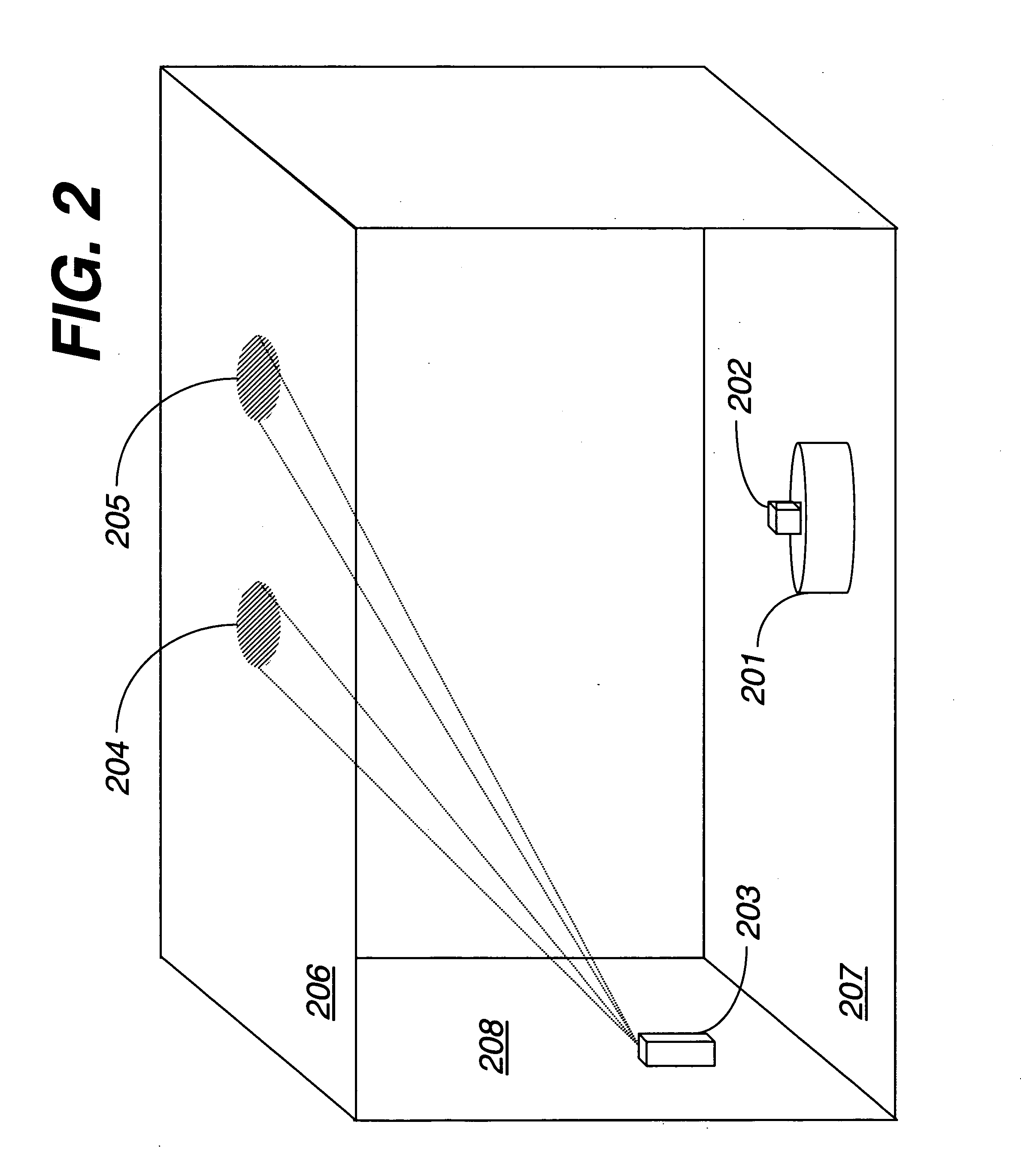
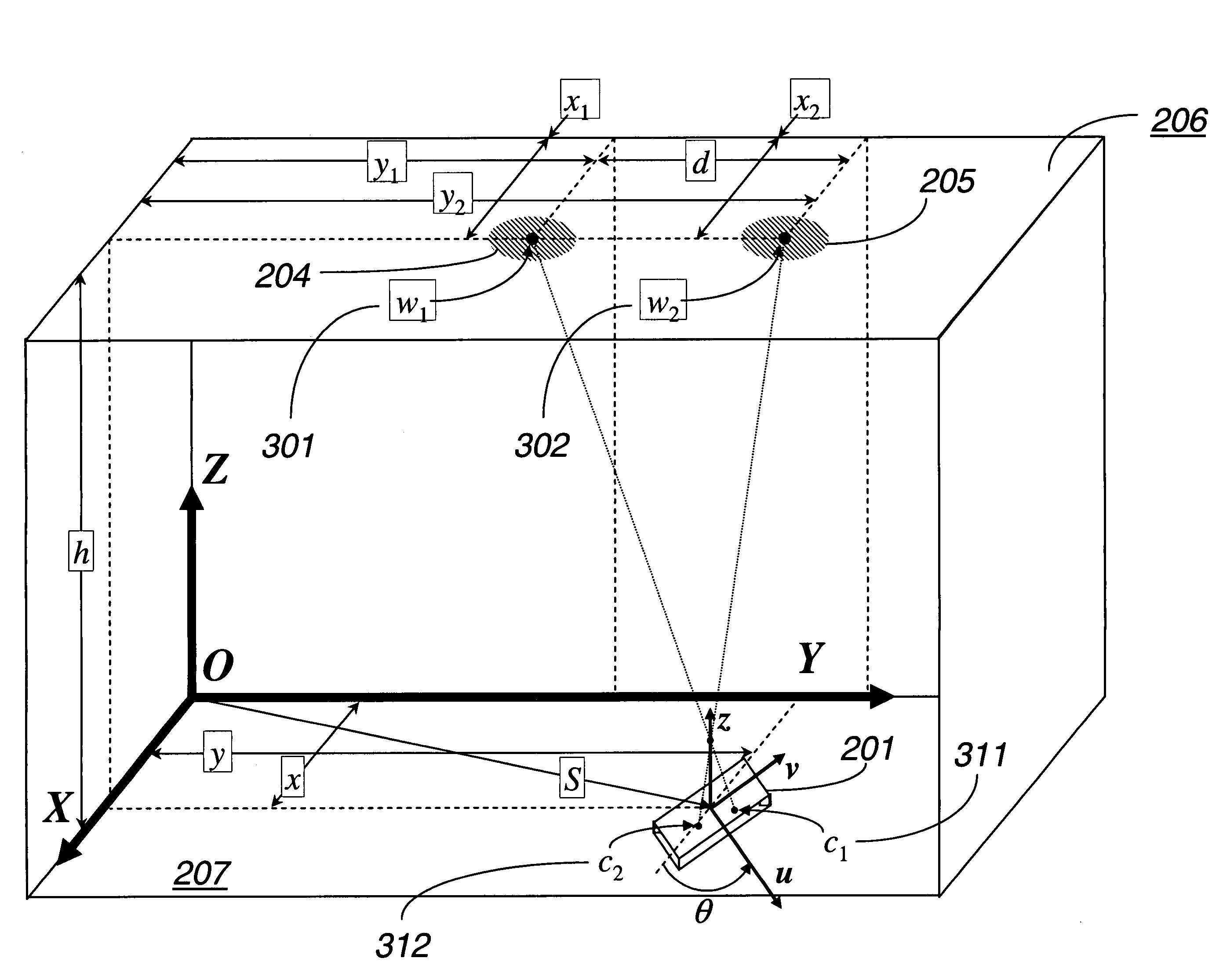
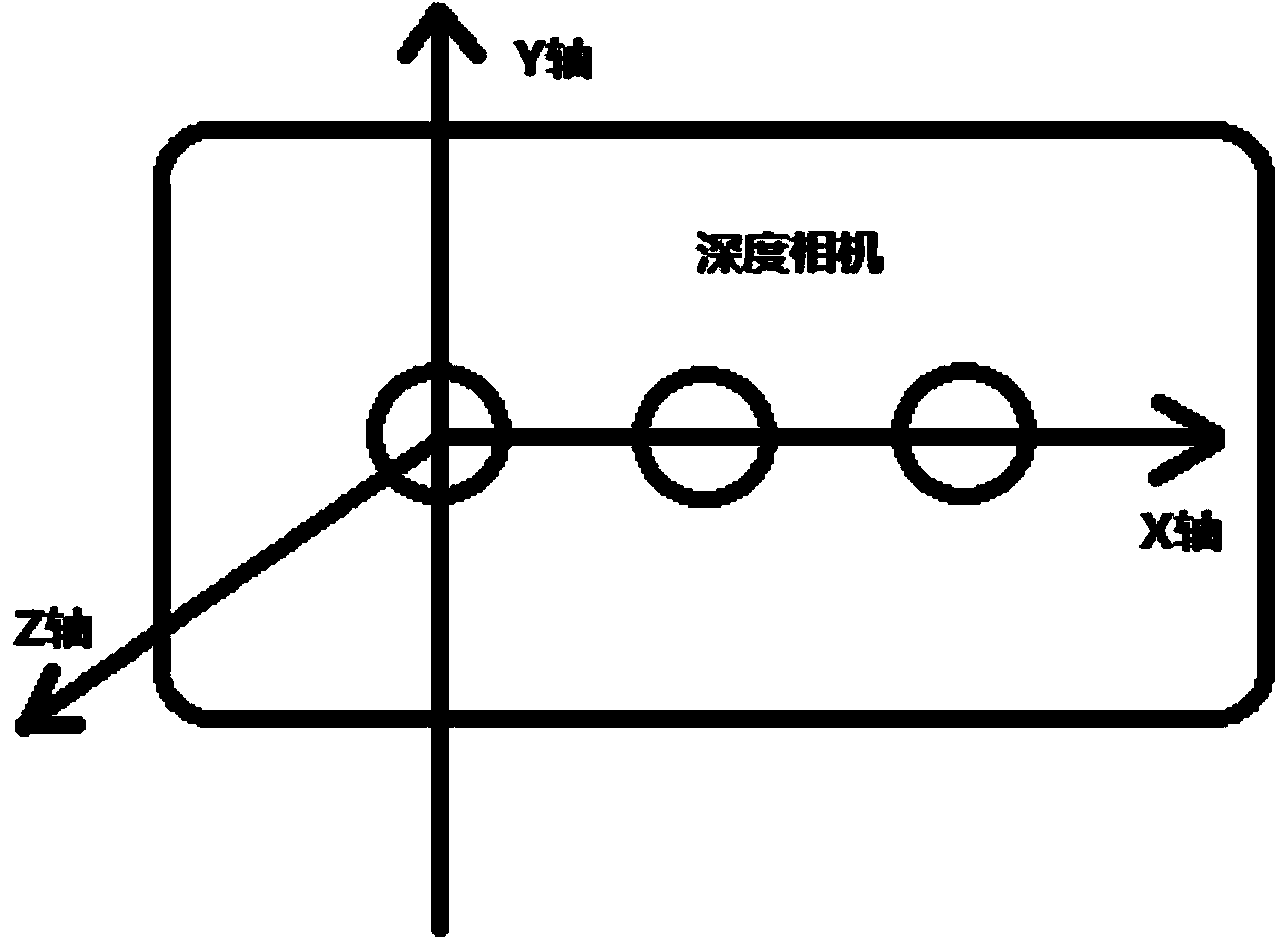
Global Coordinate System. The global coordinate system describes the arena in which your radar or sonar simulation takes place. Within this arena, you can place radar or sonar transmitters and receivers, and targets. These objects can be either stationary or moving.
Methods and apparatus for position estimation using reflected light sources
InactiveUS20050213082A1Angle measurementOptical rangefindersSignal processing circuitsCompanion animal
The invention is generally related to the estimation of position and orientation of an object with respect to a local or a global coordinate system using reflected light sources. A typical application of the method and apparatus includes estimation and tracking of the position of a mobile autonomous robot. Other applications include estimation and tracking of an object for position-aware, ubiquitous devices. Additional applications include tracking of the positions of people or pets in an indoor environment. The methods and apparatus comprise one or more optical emitters, one or more optical sensors, signal processing circuitry, and signal processing methods to determine the position and orientation of at least one of the optical sensors based at least in part on the detection of the signal of one or more emitted light sources reflected from a surface.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
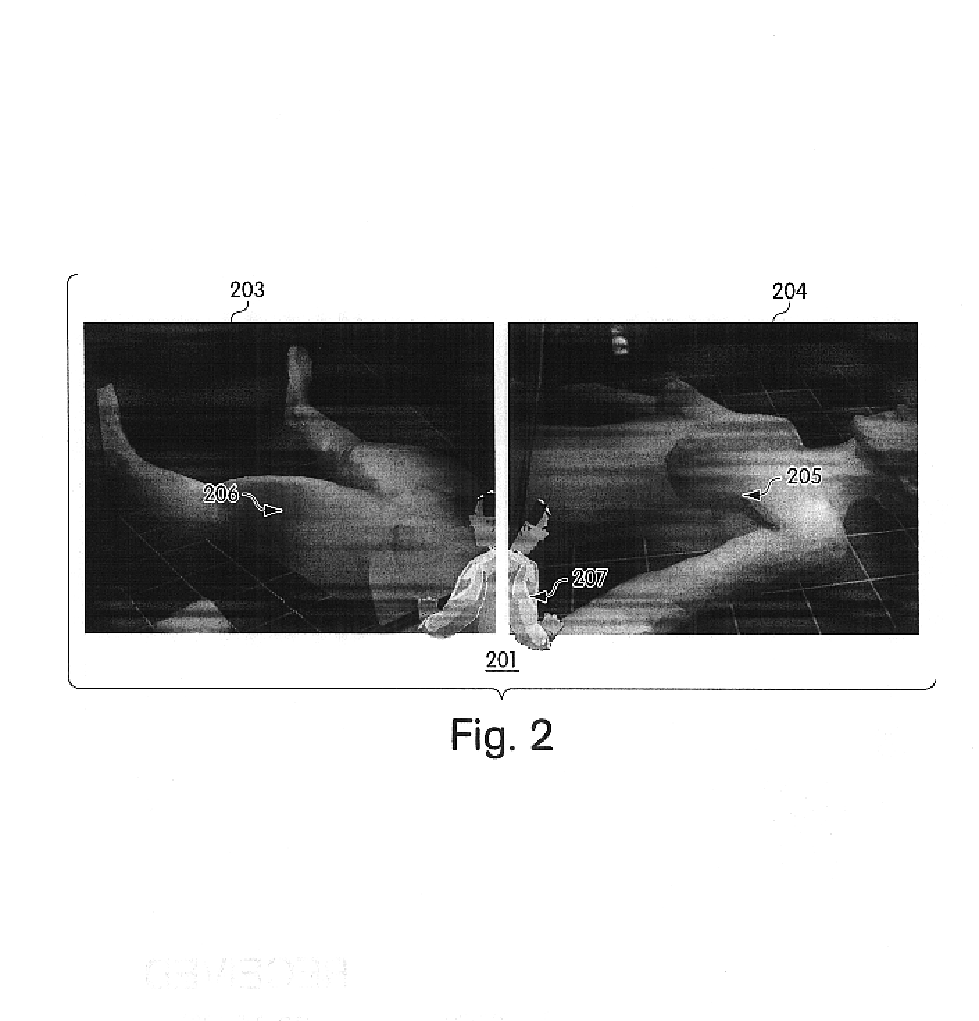
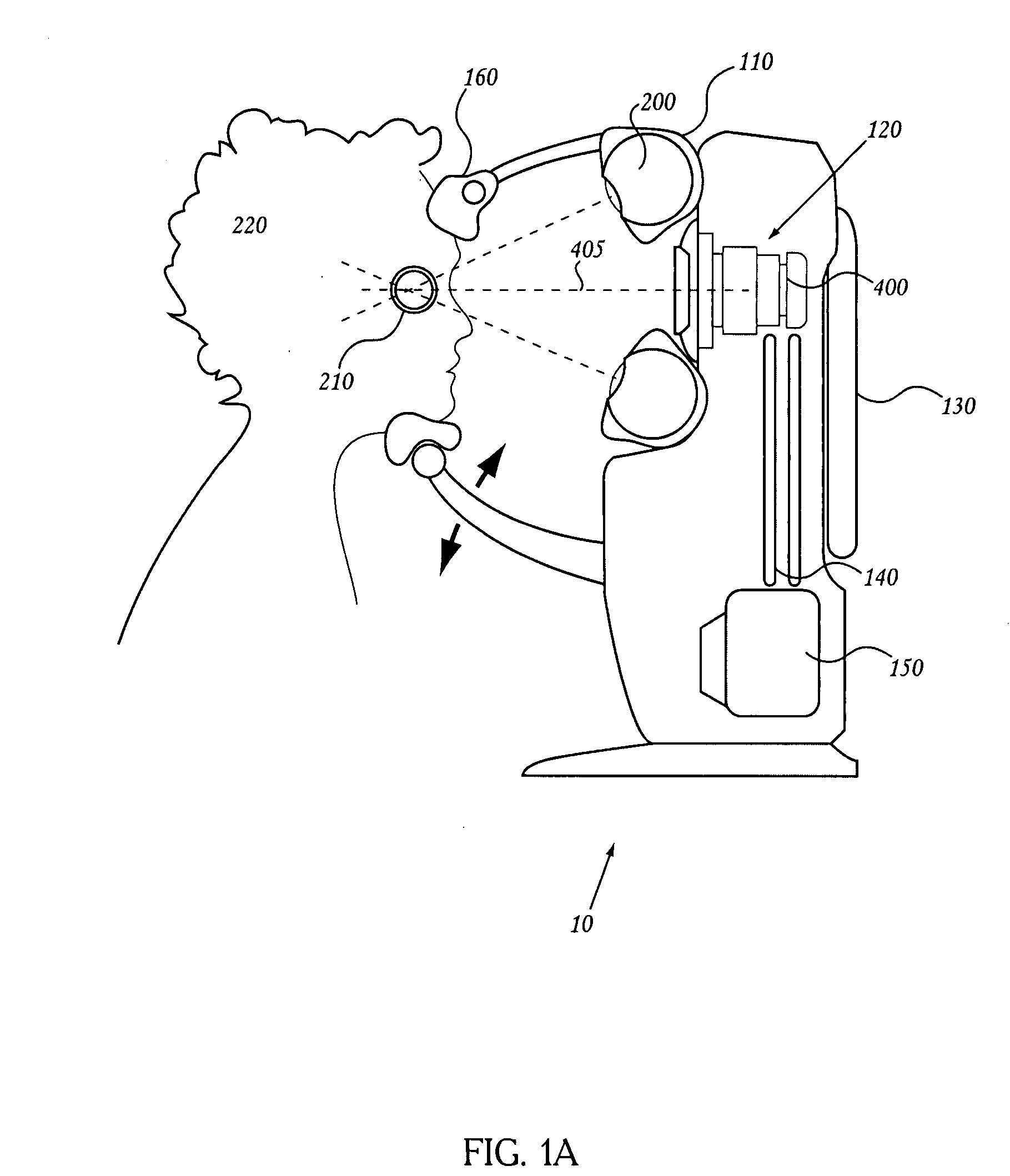
Apparatus and method for a global coordinate system for use in robotic surgery
ActiveUS20150335480A1Facilitating robotic surgeryDiagnostics using lightEye surgeryKinematicsEngineering
An apparatus and method for establishing a global coordinate system to facilitate robotic assisted surgery. The coordinate system may be established using a combination of the robotic data, i.e., kinematics, and optical coherence tomographic images generated by an overhead optical assembly and a tool-based sensor. Using these components, the system may generate a computer-registered three-dimensional model of the patient's eye. In some embodiments, the system may also generate a virtual boundary within the coordinate system to prevent inadvertent injury to the patient.
Owner:AURIS HEALTH INC
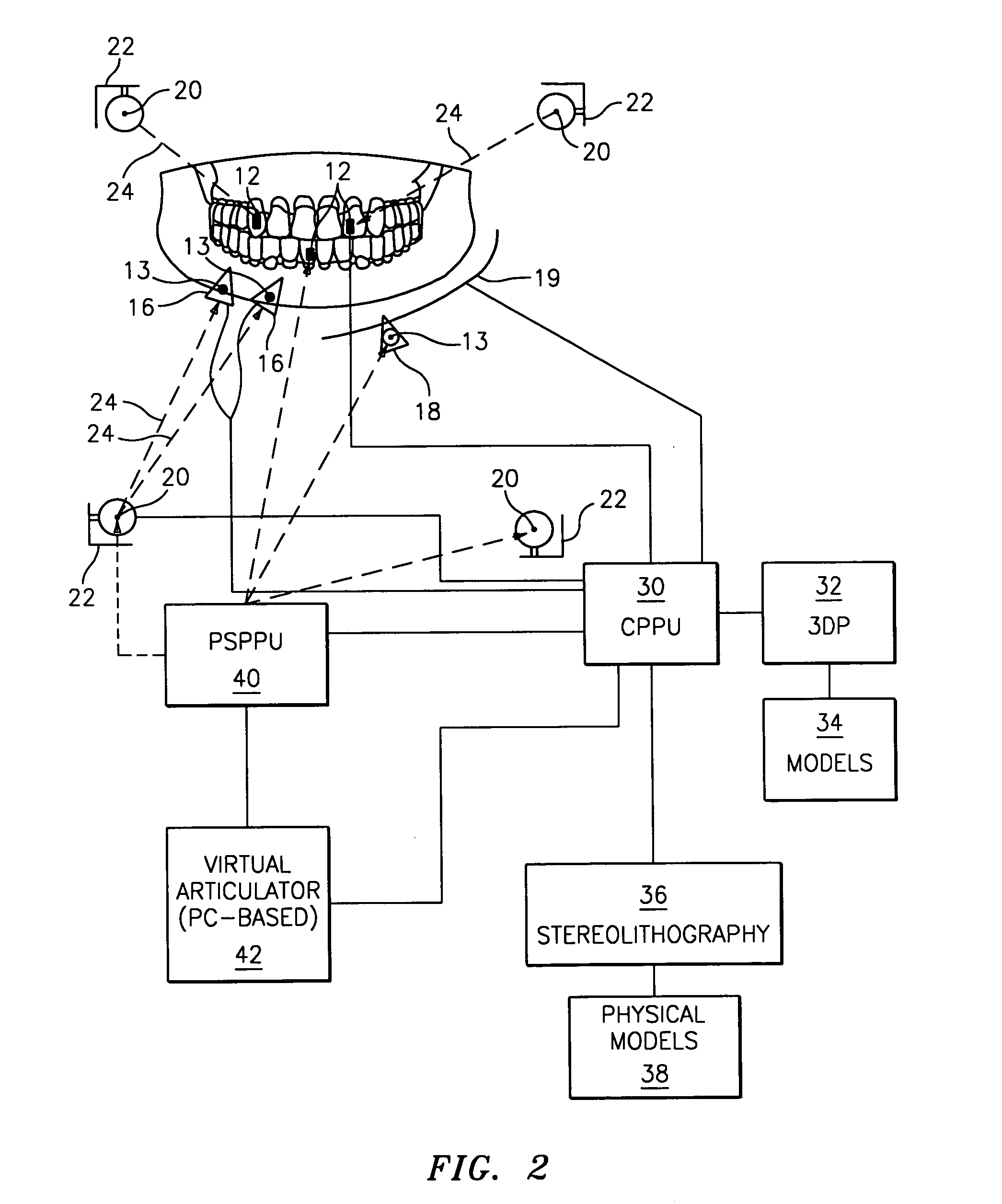
Digital technologies for planning and carrying out dental restorative procedures
A method and system for the fabrication of dental articles includes at least two imaging and measuring devices, which measure and provide images of the internal and external structure of intra-oral objects in a patient's oral cavity. The outputs from these devices are linked so that the descriptions of the intra-oral objects and features, oral cavity and surrounding bone structure are stored in a system of reference positions. The system of reference positions functions as a “global positioning device” registering locations and orientations of the measuring and imaging device or probe relative to the intra-oral objects and bone structure and orientations of the resulting individual frames or scans in the global system of coordinates. Three-dimensional images, scans and / or maps of the oral cavity obtained from each device are pieced together to generate solid three-dimensional models of the intra-oral objects.
Owner:PENTRON LAB TECH
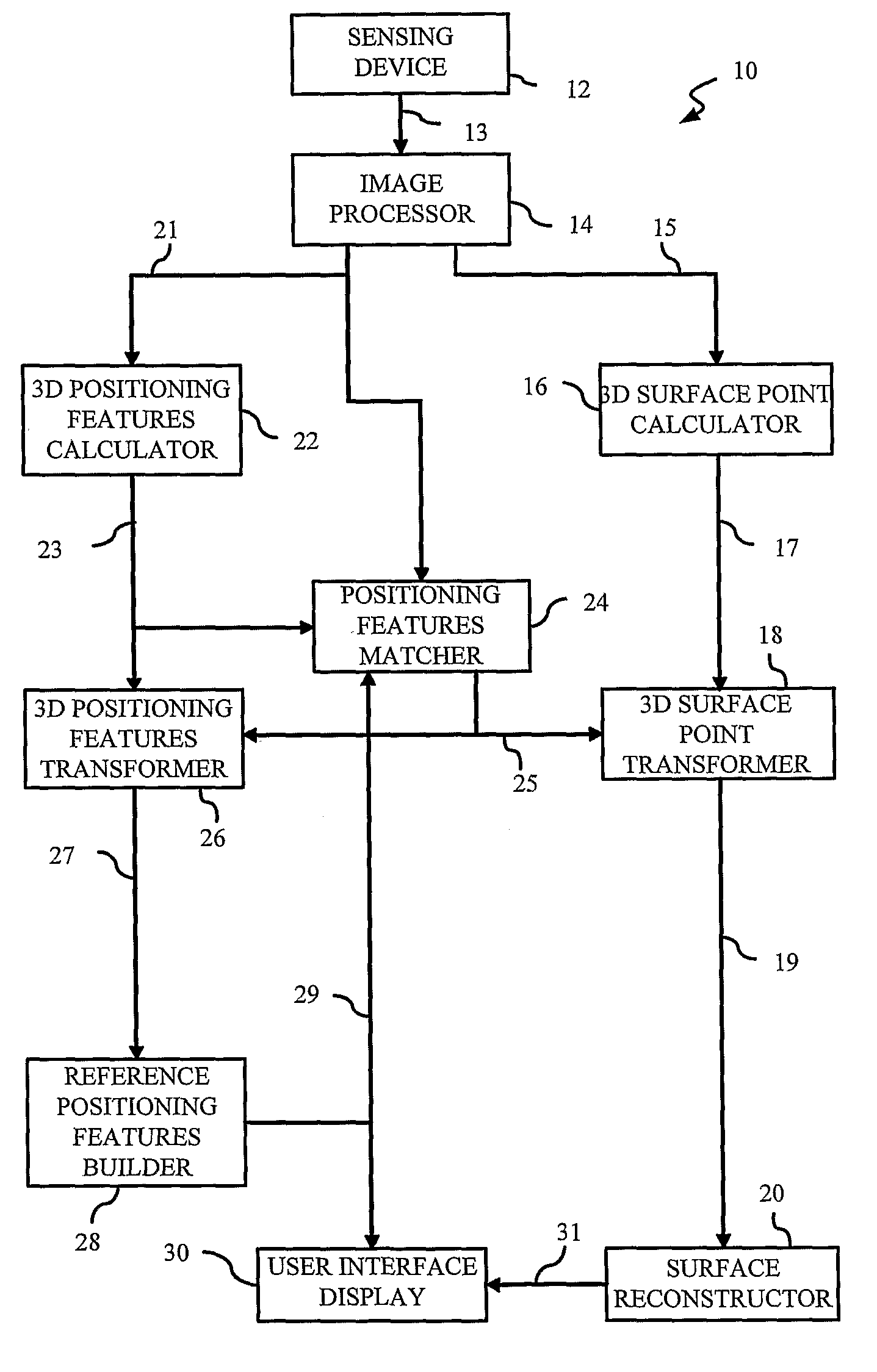
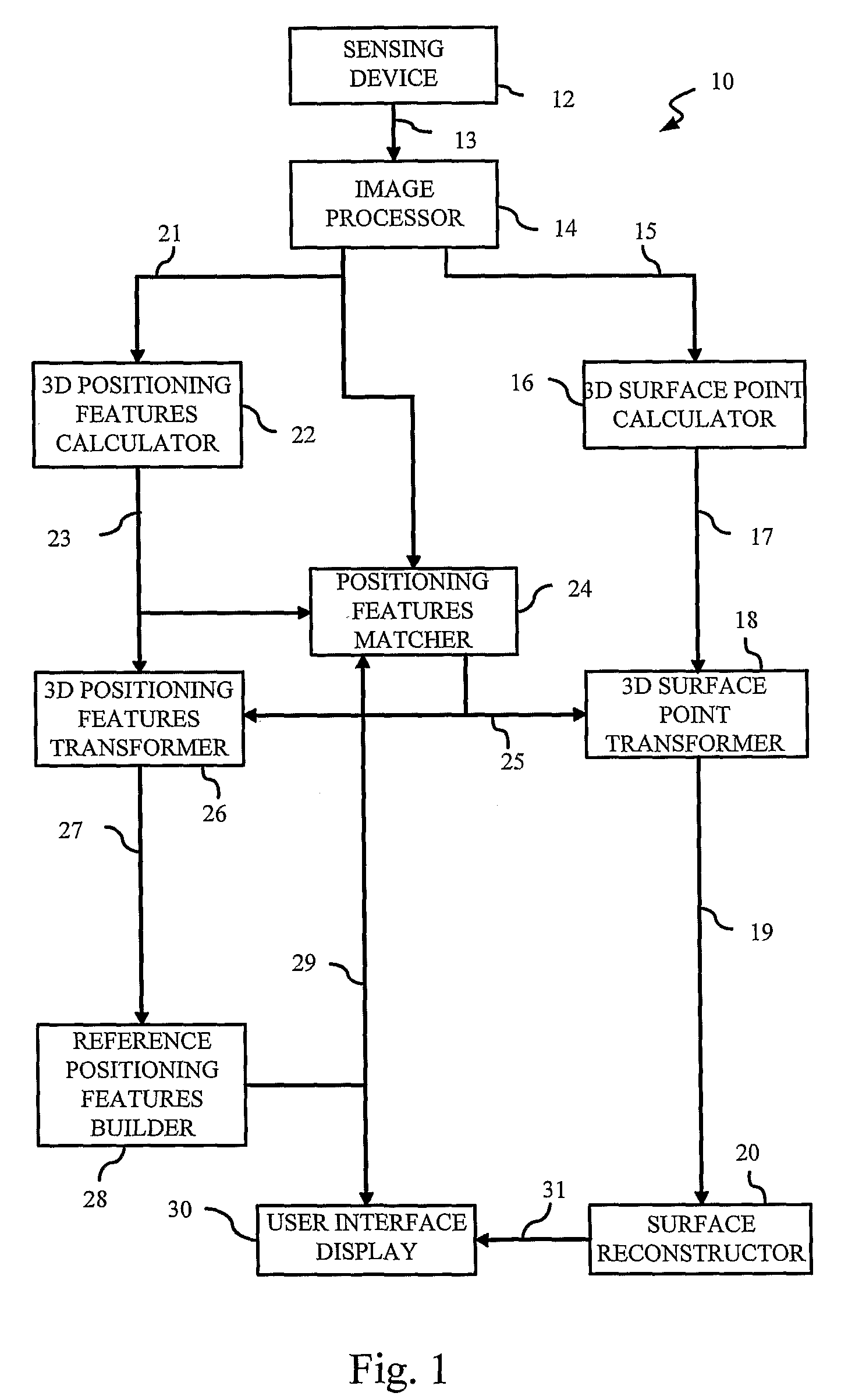
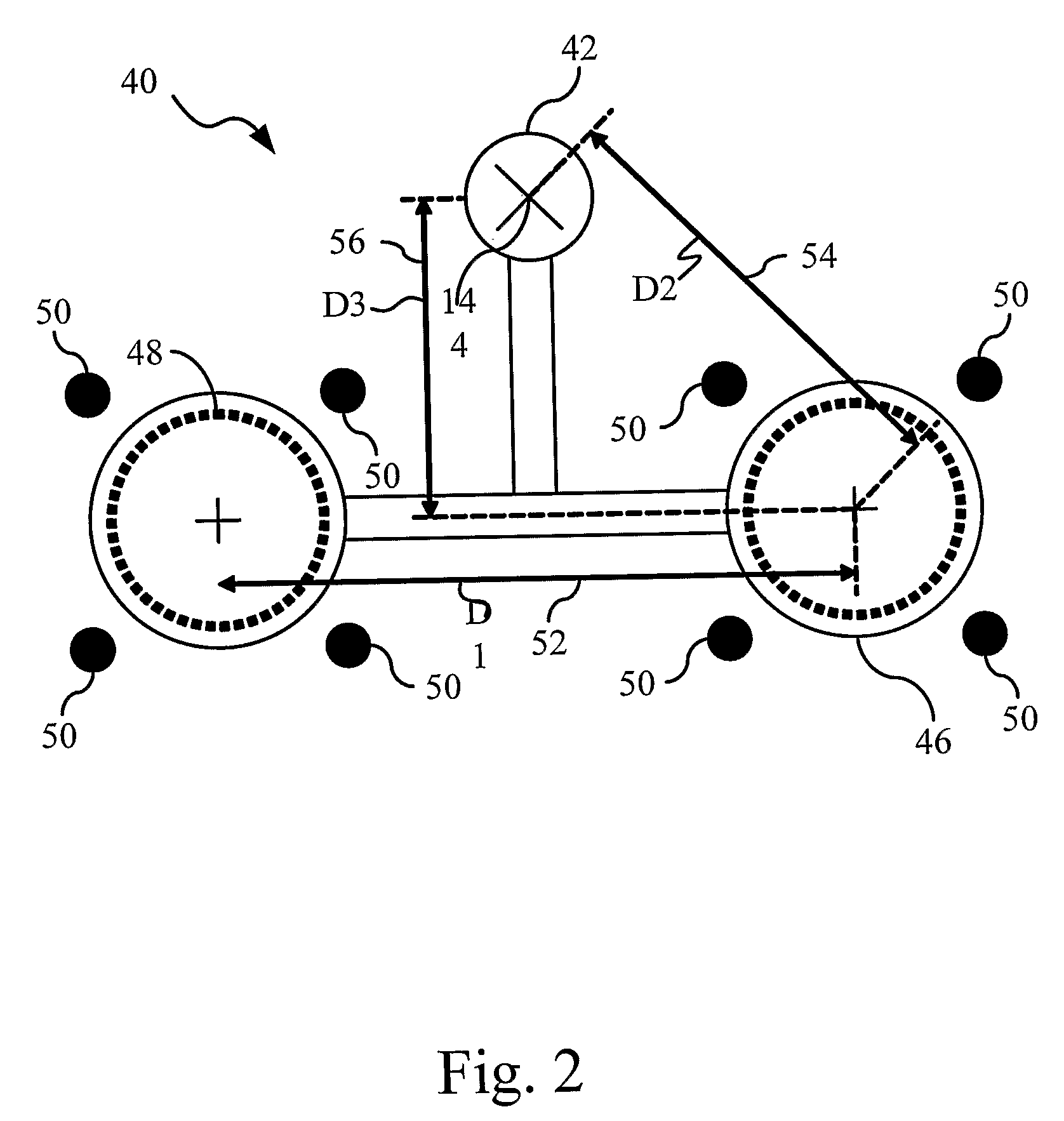
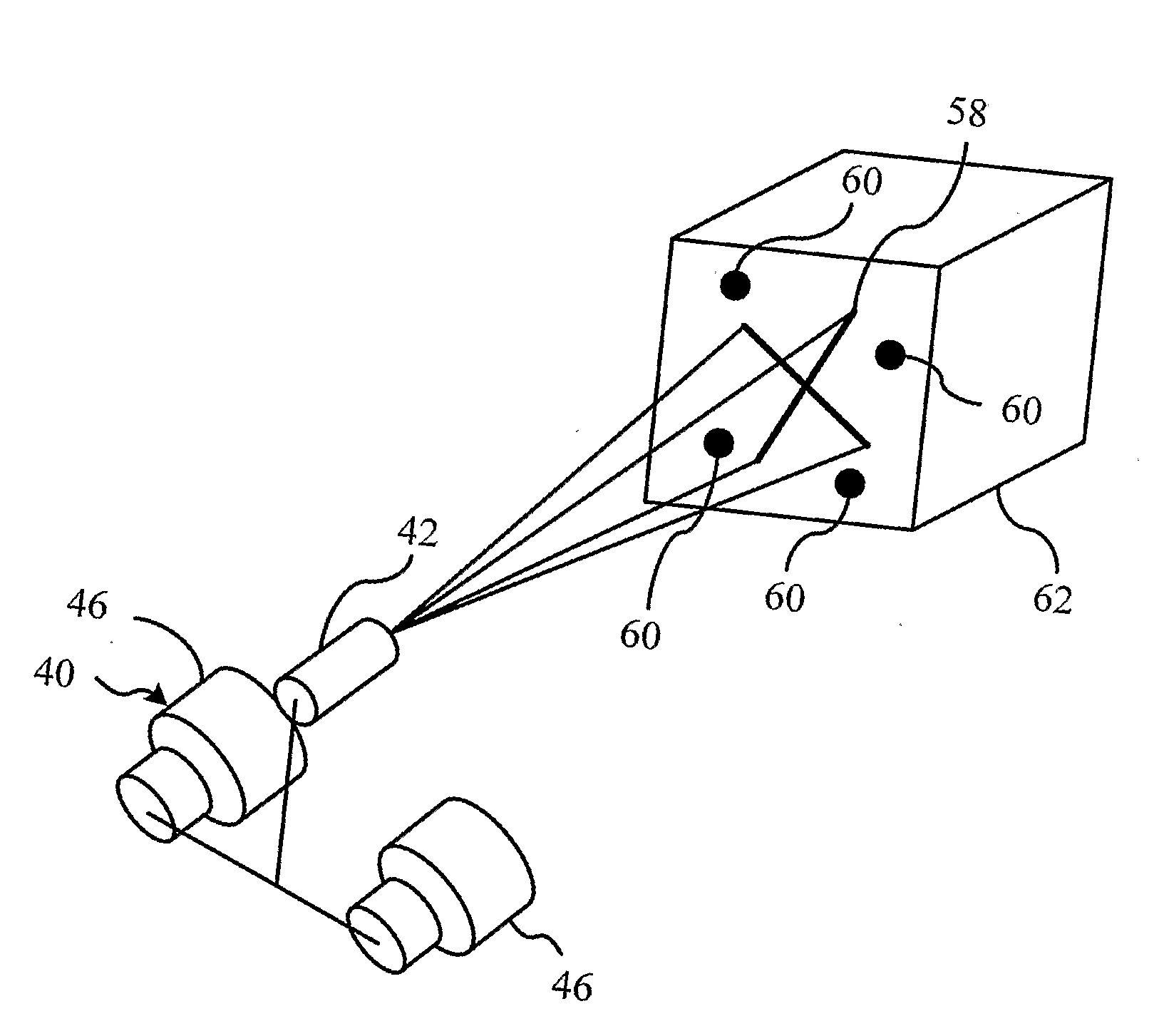
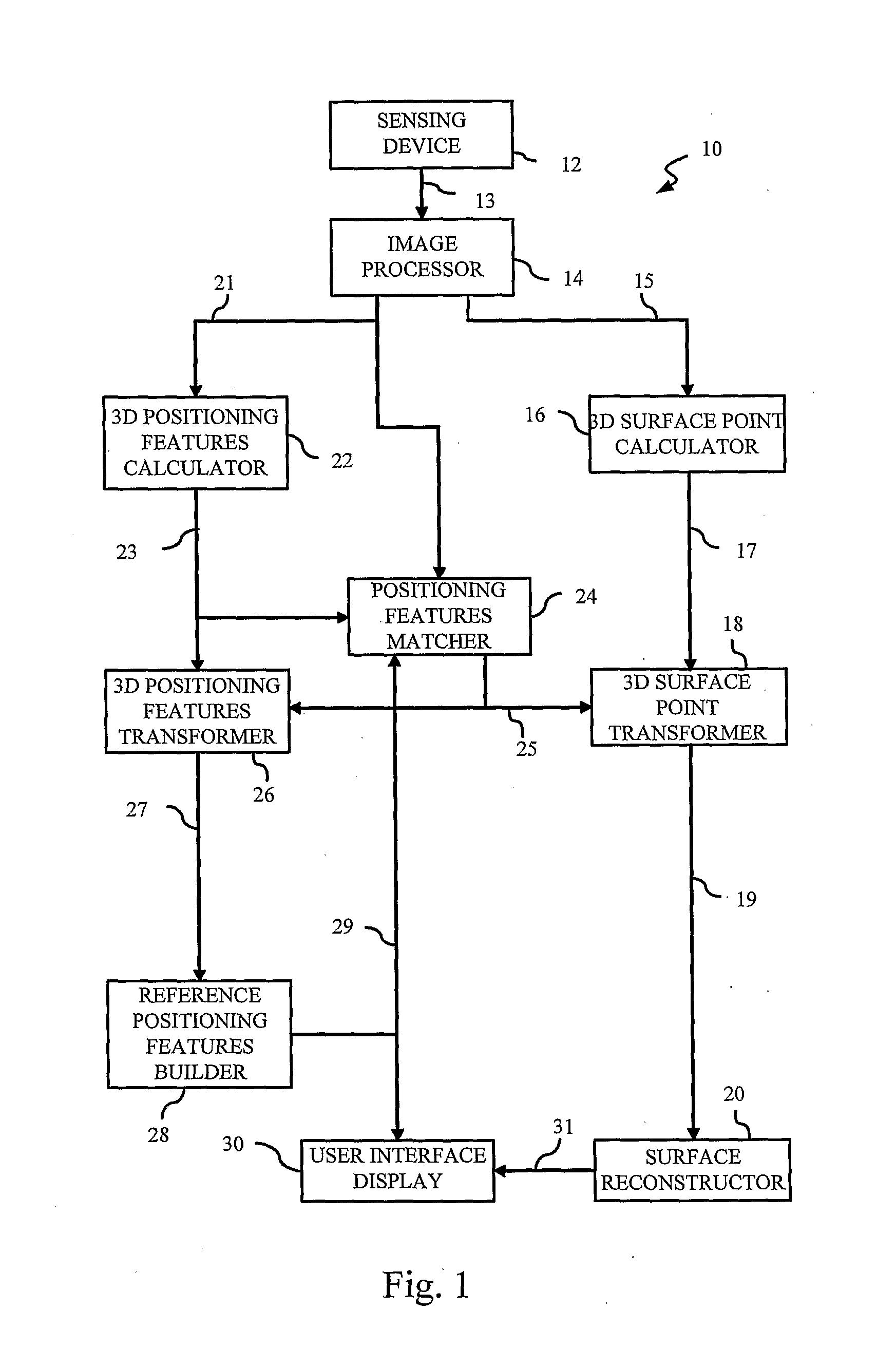
Auto-referenced system and apparatus for three-dimensional scanning
A system, apparatus and method for three-dimensional scanning and digitization of the surface geometry of objects are claimed. The system includes a hand-held apparatus that is auto-referenced. The system is auto-referenced since it does not need any positioning device to provide the 6 degree of freedom transformations that are necessary to integrate 3D measurements in a global coordinate system while the apparatus is manipulated to scan the surface. The system continuously calculates its own position and orientation from observation while scanning the surface geometry of an object. To do so, the system exploits a triangulation principle and integrates an apparatus that captures both surface points originating from the reflection of a projected laser pattern on an object's surface and 2D positioning features originating from the observation of target positioning features.
Owner:CREAFORM INC
Sensing device and method for measuring position and orientation relative to multiple light sources
InactiveUS20050213109A1Low costPosition fixationUsing optical meansComputer scienceGlobal coordinate system
A sensing device and method of estimating the position and orientation of an object with respect to a local or a global coordinate system is disclosed. The method and device include one or more optical sensor, a signal processing circuitry and a signal processing algorithm to determine the position and orientation. A sensor is positioned within the housing. At least one of the optical sensors used in the method and system outputs information based at least in part on the detection of the signal of one or more light sources.
Owner:EVOLUTION ROBOTICS
Methods and apparatus for position estimation using reflected light sources
The invention is generally related to the estimation of position and orientation of an object with respect to a local or a global coordinate system using reflected light sources. A typical application of the method and apparatus includes estimation and tracking of the position of a mobile autonomous robot. Other applications include estimation and tracking of an object for position-aware, ubiquitous devices. Additional applications include tracking of the positions of people or pets in an indoor environment. The methods and apparatus comprise one or more optical emitters, one or more optical sensors, signal processing circuitry, and signal processing methods to determine the position and orientation of at least one of the optical sensors based at least in part on the detection of the signal of one or more emitted light sources reflected from a surface.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
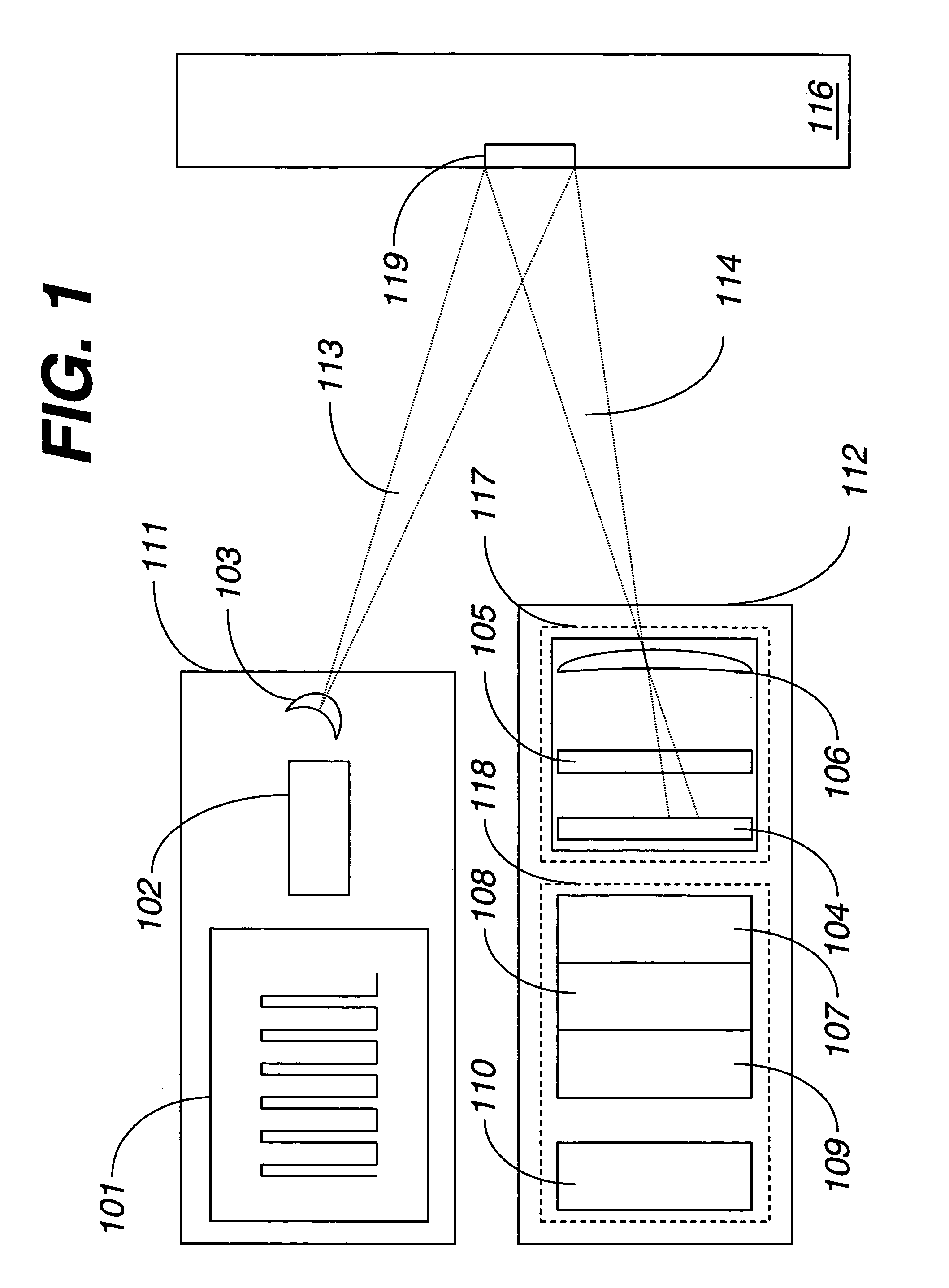
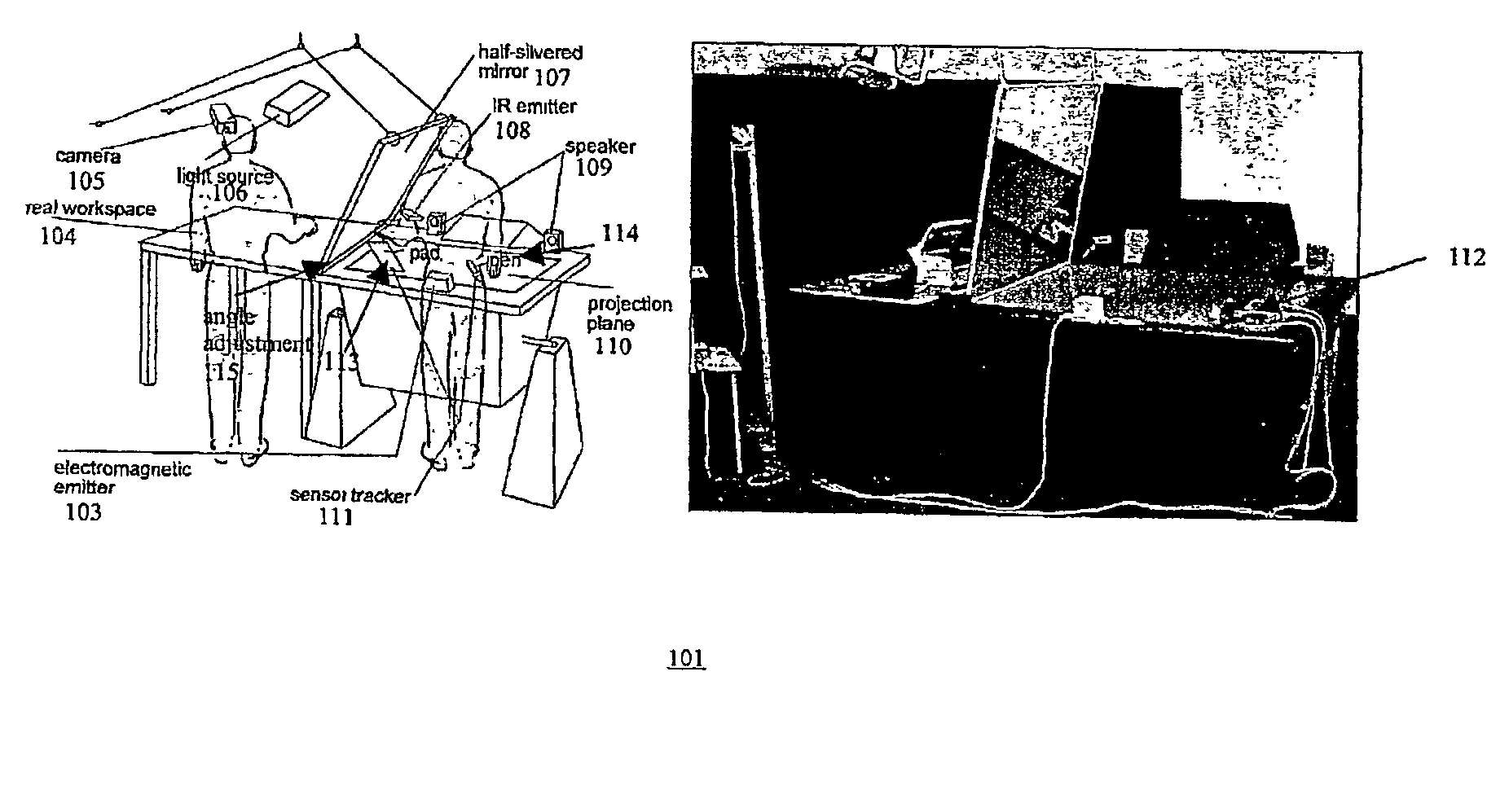
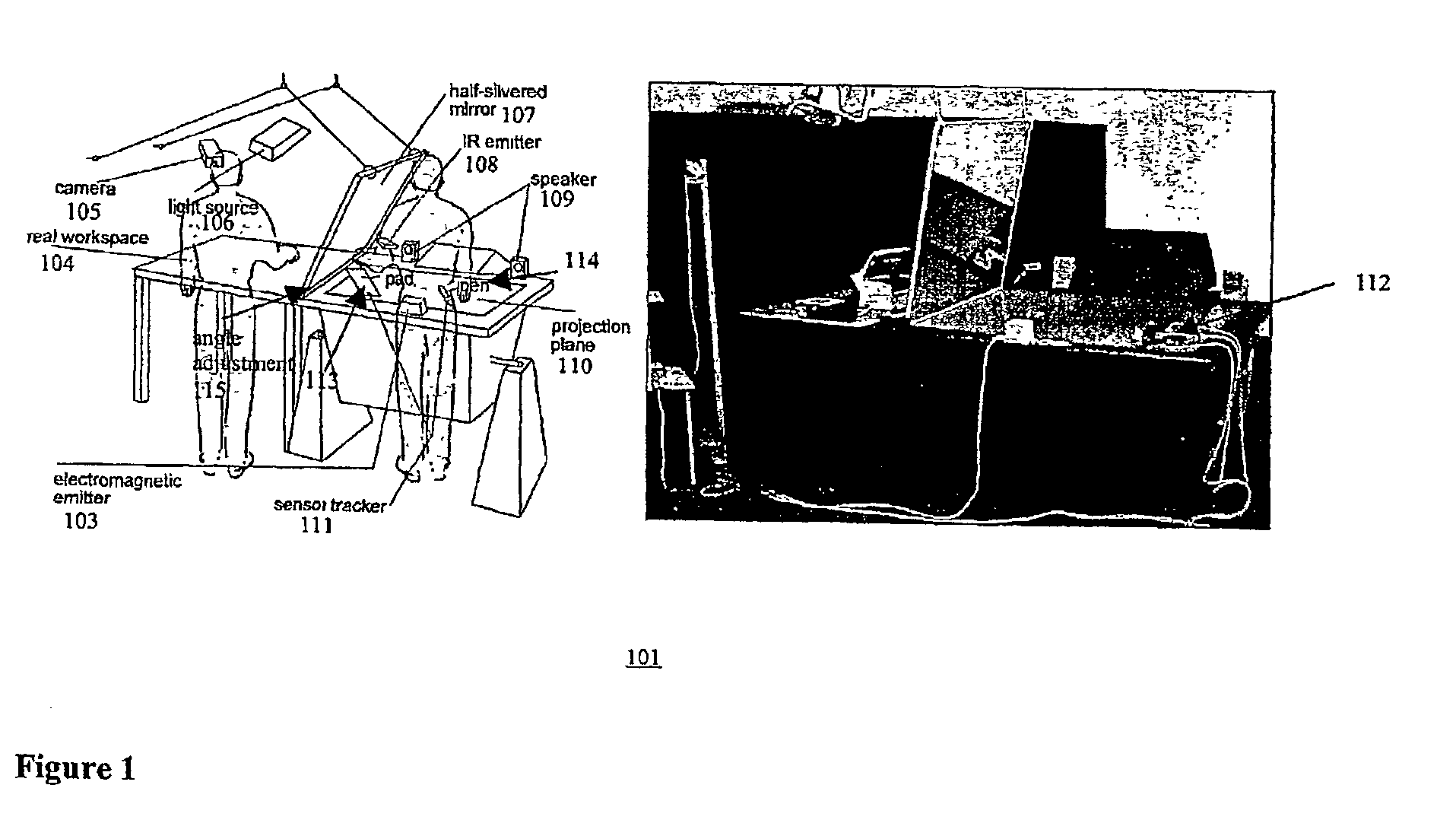
Extended virtual table: an optical extension for table-like projection systems
InactiveUS6803928B2Input/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer graphics (images)Projection system
Apparatus that uses a large transflective mirror to extend a virtual reality system such as a virtual table that employs a projection plane to produce the virtual reality. The transflexive mirror is positioned relative to the projection plane such that the plane of the mirror intersects the projection plane and the angle of the mirror relative to the projection plane is such that the user of the system who looks at the mirror sees the projection plane reflected in the mirror. The virtual reality system is responsive to the position of the mirror and the direction in which a user is looking and produces separate virtual realities on the projection plane: one when the user is looking at the mirror and another when the user is looking at the projection plane. The virtual reality that the user sees when looking at the mirror may or may not be coherent with the virtual reality that the user sees when looking at the projection plane. The two virtual realities may share a global coordinate system that is divided into two parts by the plane of the mirror, and what the user sees when looking into the mirror may be what the user would see looking through a window into the part of the global coordinate system behind the mirror. Because the mirror is transflective, real objects whose locations are known to the virtual reality system can he placed behind the mirror and the virtual reality reflected in the mirror may be used to augment the real objects. One use of such augmentation is virtual trial assembly of a virtual mockup with a physical mockup.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
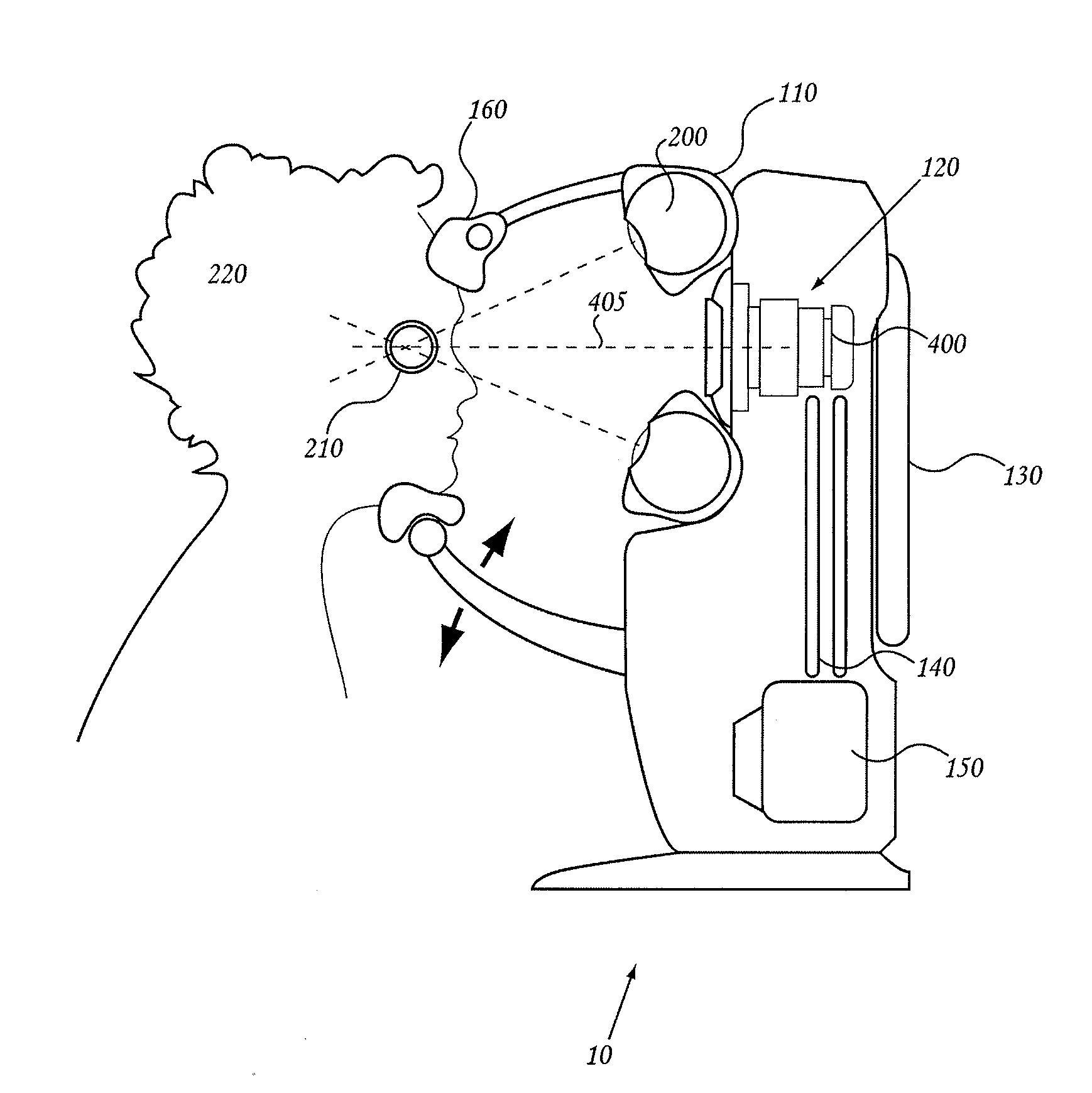
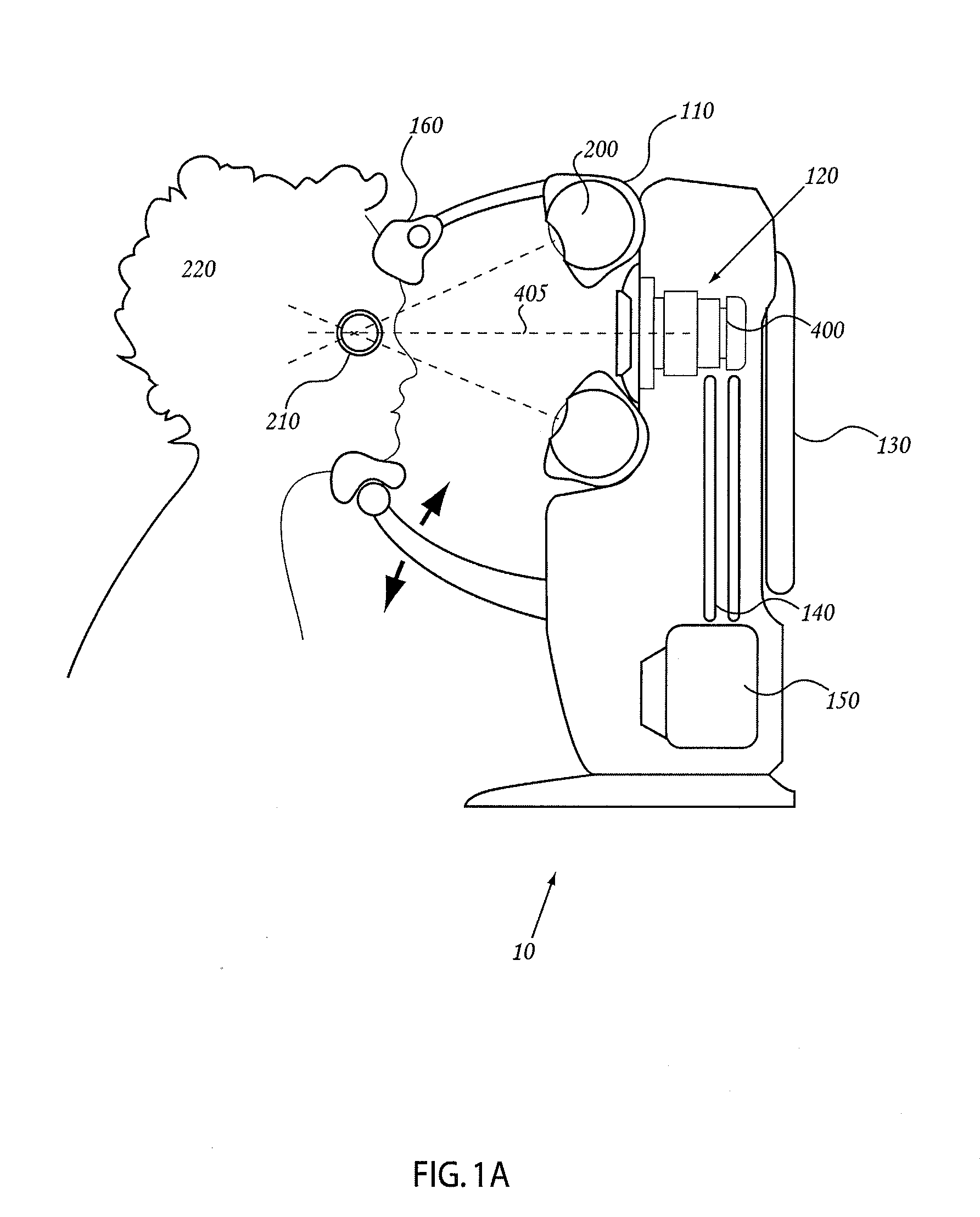
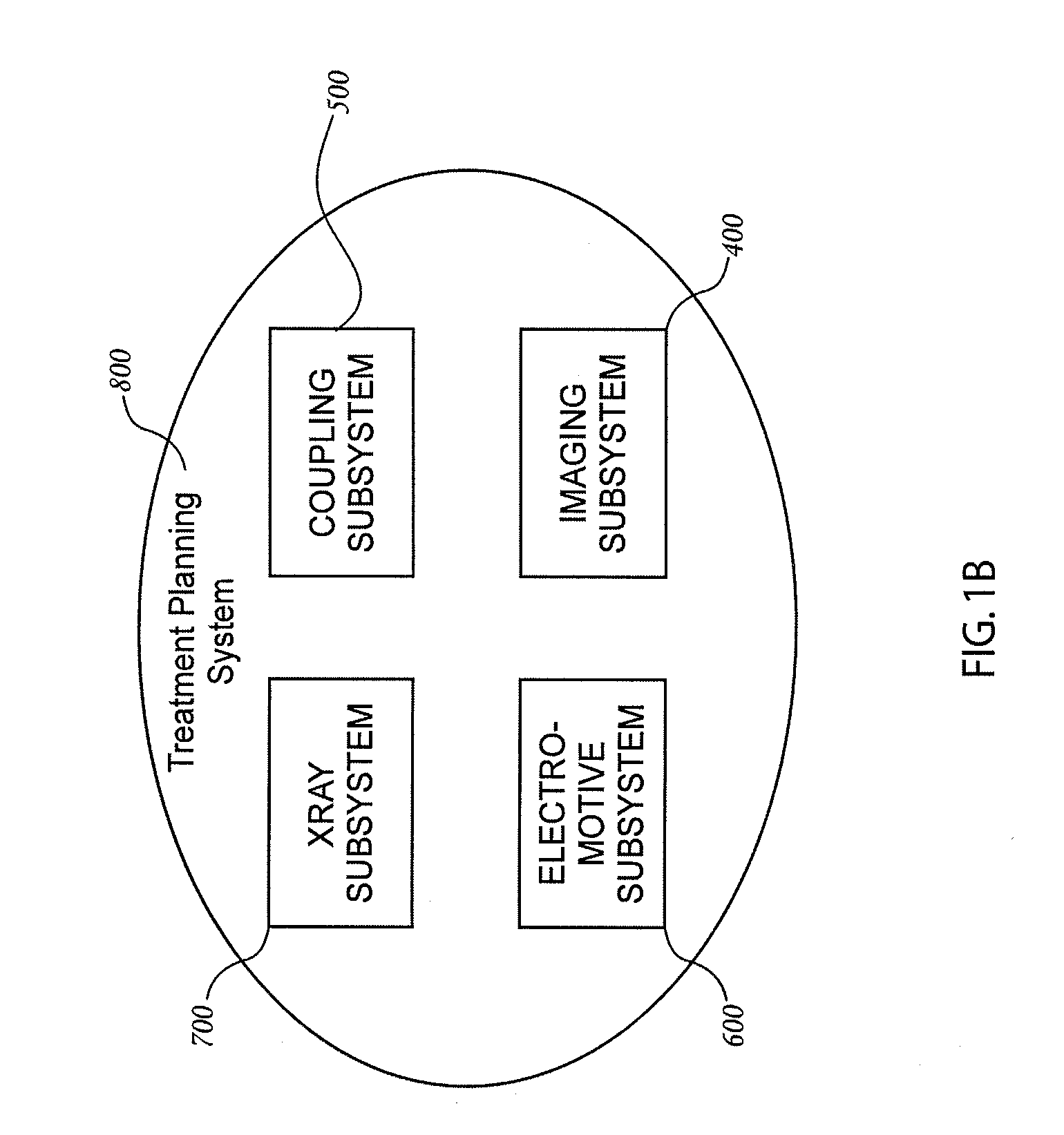
Orthovoltage radiotherapy
ActiveUS20080212738A1Dry up neovascular membraneStabilized and improved acuityHandling using diaphragms/collimetersRadiation beam directing meansRadiosurgeryBeam energy
A radiosurgery system is described that is configured to deliver a therapeutic dose of radiation to a target structure in a patient. In some embodiments, inflammatory ocular disorders are treated, specifically macular degeneration. In some embodiments, other disorders or tissues of a body are treated with the dose of radiation. In some embodiments, the target tissues are placed in a global coordinate system based on ocular imaging. In some embodiments, the target tissues inside the global coordinate system lead to direction of an automated positioning system that is directed based on the target tissues within the coordinate system. In some embodiments, a treatment plan is utilized in which beam energy and direction and duration of time for treatment is determined for a specific disease to be treated and / or structures to be avoided. In some embodiments, a fiducial marker is used to identify the location of the target tissues. In some embodiments, radiodynamic therapy is described in which radiosurgery is used in combination with other treatments and can be delivered concomitant with, prior to, or following other treatments.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC INC
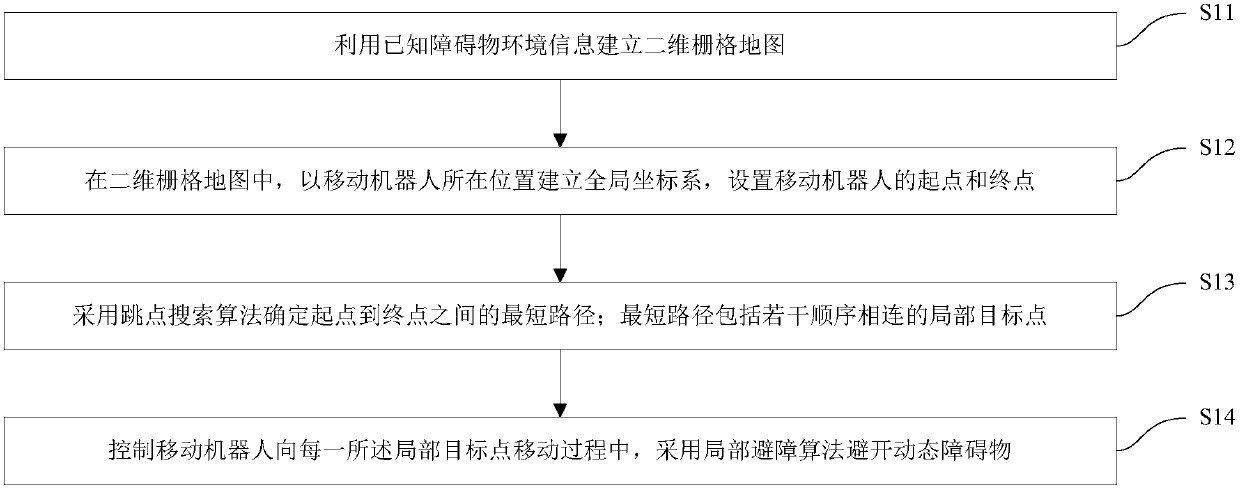
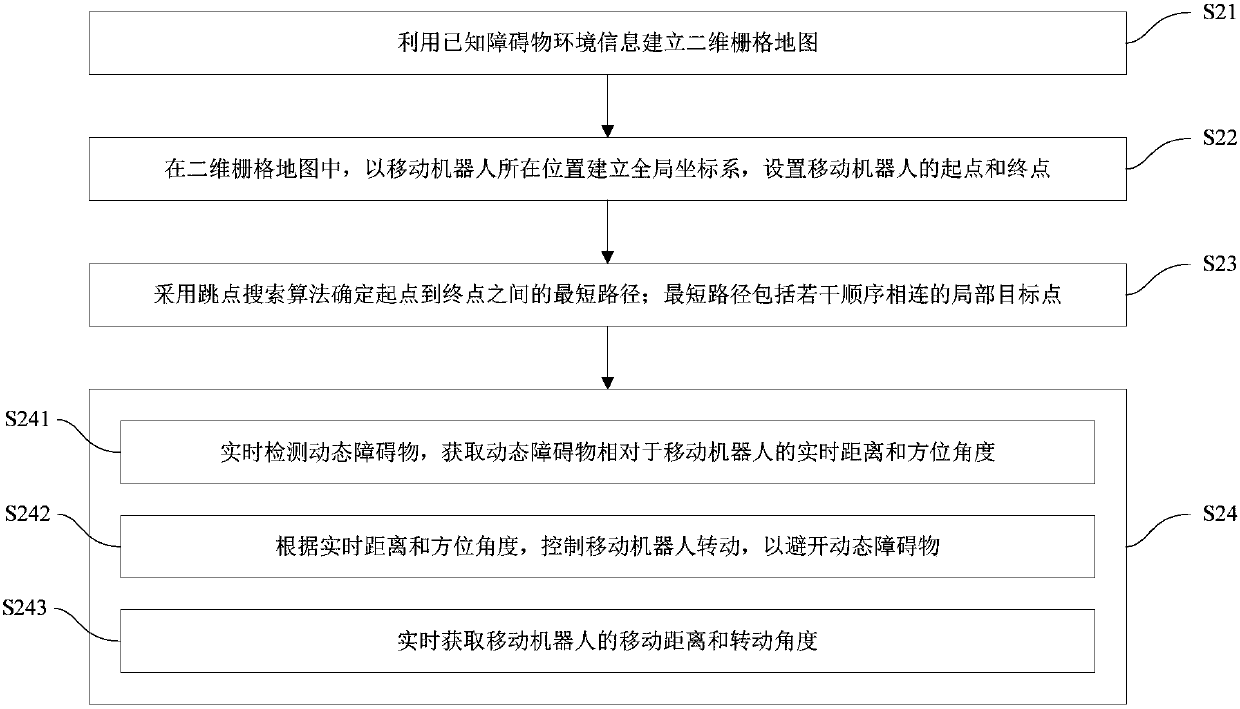
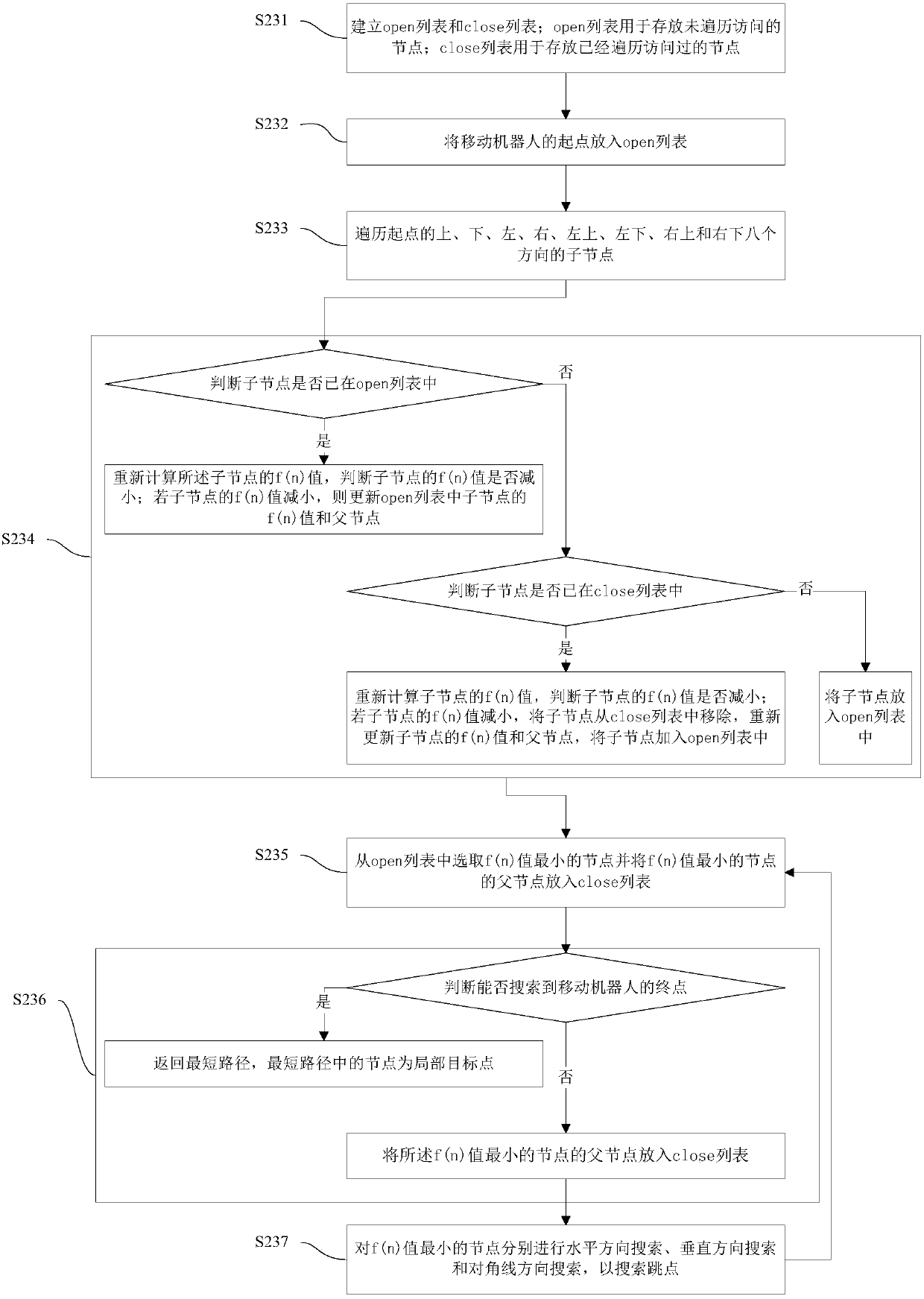
Mobile robot path planning and obstacle avoidance method and system
InactiveCN105955280AReduce path planning timeGuaranteed accuracyPosition/course control in two dimensionsObstacle avoidance algorithmMobile robots path planning
The invention discloses a mobile robot path planning and obstacle avoidance method and system. The mobile robot path planning method comprises the following steps: establishing a two-dimensional grid map by utilizing known obstacle environment information; in the two-dimensional grid map, establishing a global coordinate system at the place of a mobile robot, and setting a starting point and a terminal point of the mobile robot; determining the shortest path between the starting point and the terminal point through a jump point search algorithm, wherein the shortest path comprises a plurality of local target points connected in sequence; and in the process of controlling the mobile robot to move to each of the local target points, utilizing a local obstacle avoidance algorithm to avoid a dynamic obstacle. The mobile robot path planning and obstacle avoidance method adopts the jump point search algorithm to obtain the shortest path quickly, so that path search efficiency can be improved, and storage space is saved; and through the local obstacle avoidance algorithm, accuracy and real-time performance of mobile robot path planning and obstacle avoidance can be ensured, and autonomous navigation of the mobile robot is realized.
Owner:TCL CORPORATION
Extended virtual table: an optical extension for table-like projection systems
InactiveUS20030085866A1Input/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer graphics (images)Projection plane
Apparatus that uses a large transflective mirror to extend a virtual reality system such as a virtual table that employs a projection plane to produce the virtual reality. The transflexive mirror is positioned relative to the projection plane such that the plane of the mirror intersects the projection plane and the angle of the mirror relative to the projection plane is such that the user of the system who looks at the mirror sees the projection plane reflected in the mirror. The virtual reality system is responsive to the position of the mirror and the direction in which a user is looking and produces separate virtual realities on the projection plane: one when the user is looking at the mirror and another when the user is looking at the projection plane The virtual reality that the user sees when looking at the mirror may or may not be coherent with the virtual reality that the user sees when looking at the projection plane. The two virtual realities may share a global coordinate system that is divided into two parts by the plane of the mirror, and what tile user sees when looking into the mirror may be what the user would see looking through a window Into the part of the global coordinate system behind the mirror. Because the mirror is transflective, real objects whose locations are known to the virtual reality system can he placed behind the mirror and the virtual reality reflected in the mirror may be used to augment the real objects. One use of such augmentation is virtual trial assembly of a virtual mockup with a physical mockup.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Auto-Referenced System and Apparatus for Three-Dimensional Scanning
A system, apparatus and method for three-dimensional scanning and digitization of the surface geometry of objects are claimed. The system comprises a hand-held apparatus that is auto-referenced. The system is auto-referenced since it does not need any positioning device to provide the 6 degree of freedom transformations that are necessary to integrate 3D measurements in a global coordinate system while the apparatus is manipulated to scan the surface. The system continuously calculates its own position and orientation from the reflection of a projected laser pattern on an object's surface and 2D positioning features originating from the observation of target positioning features. Using the described system, it is possible to simultaneously build and match a 3D representation of the positioning features while accumulating the 3D surface points describing the surface geometry.
Owner:CREAFORM INC
Apparatus and method for a global coordinate system for use in robotic surgery
ActiveUS10383765B2Facilitating robotic surgeryDiagnostics using lightEye surgeryKinematicsEngineering
An apparatus and method for establishing a global coordinate system to facilitate robotic assisted surgery. The coordinate system may be established using a combination of the robotic data, i.e., kinematics, and optical coherence tomographic images generated by an overhead optical assembly and a tool-based sensor. Using these components, the system may generate a computer-registered three-dimensional model of the patient's eye. In some embodiments, the system may also generate a virtual boundary within the coordinate system to prevent inadvertent injury to the patient.
Owner:AURIS HEALTH INC
Accessing positional information for a mobile station using a data code label
InactiveUS20110039573A1Navigational calculation instrumentsParticular environment based servicesDisplay deviceMobile station
Positional information for a mobile station is acquired using a data code label and the positional information is updated as the mobile station moves without the need for signals from a Satellite Positioning System (SPS), such as the Global Positioning System (GPS). The data code label is read and information encoded within the data code label is used to obtain positional information, which may be, e.g., a digital map, directions, or non-navigational information, which may be provided via a display or speakers. The positional information may be referenced to a local coordinate system or a global coordinate system. The position of the mobile station is updated using inertial sensors within the mobile station and / or using a measured radio signal and a wireless access point almanac that may be obtained using the information encoded within the data code label. Updated positional information for the mobile station is then provided.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
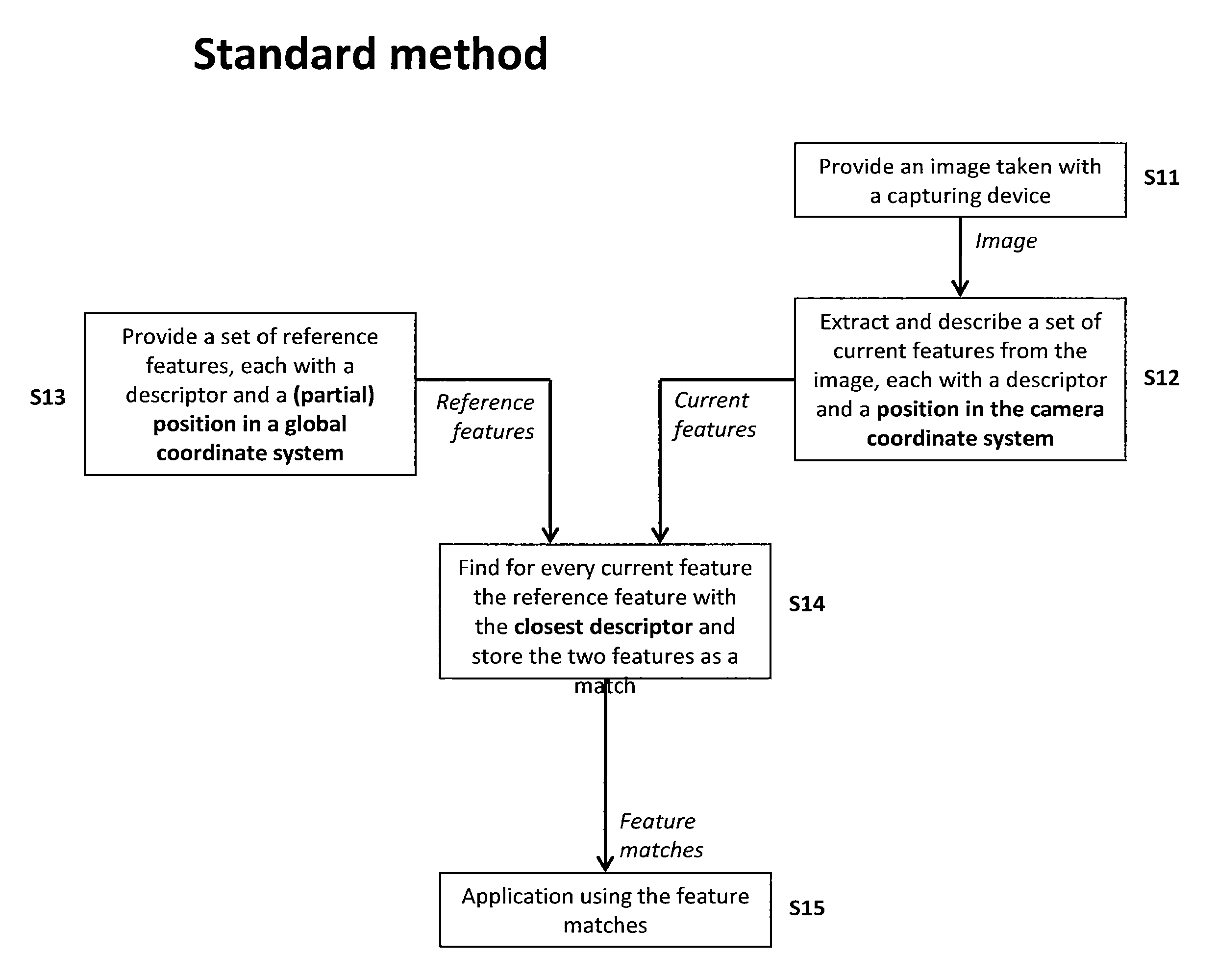
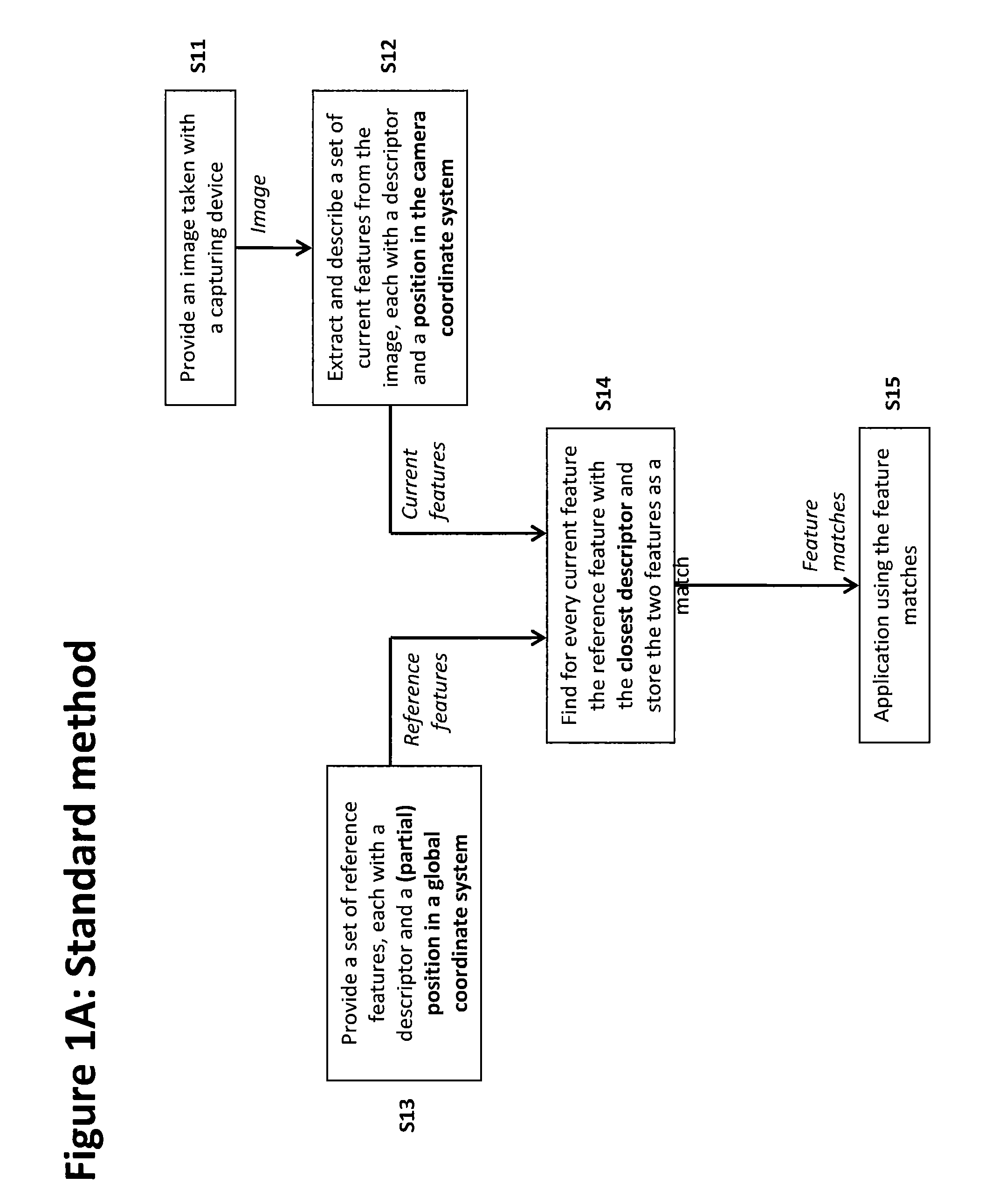
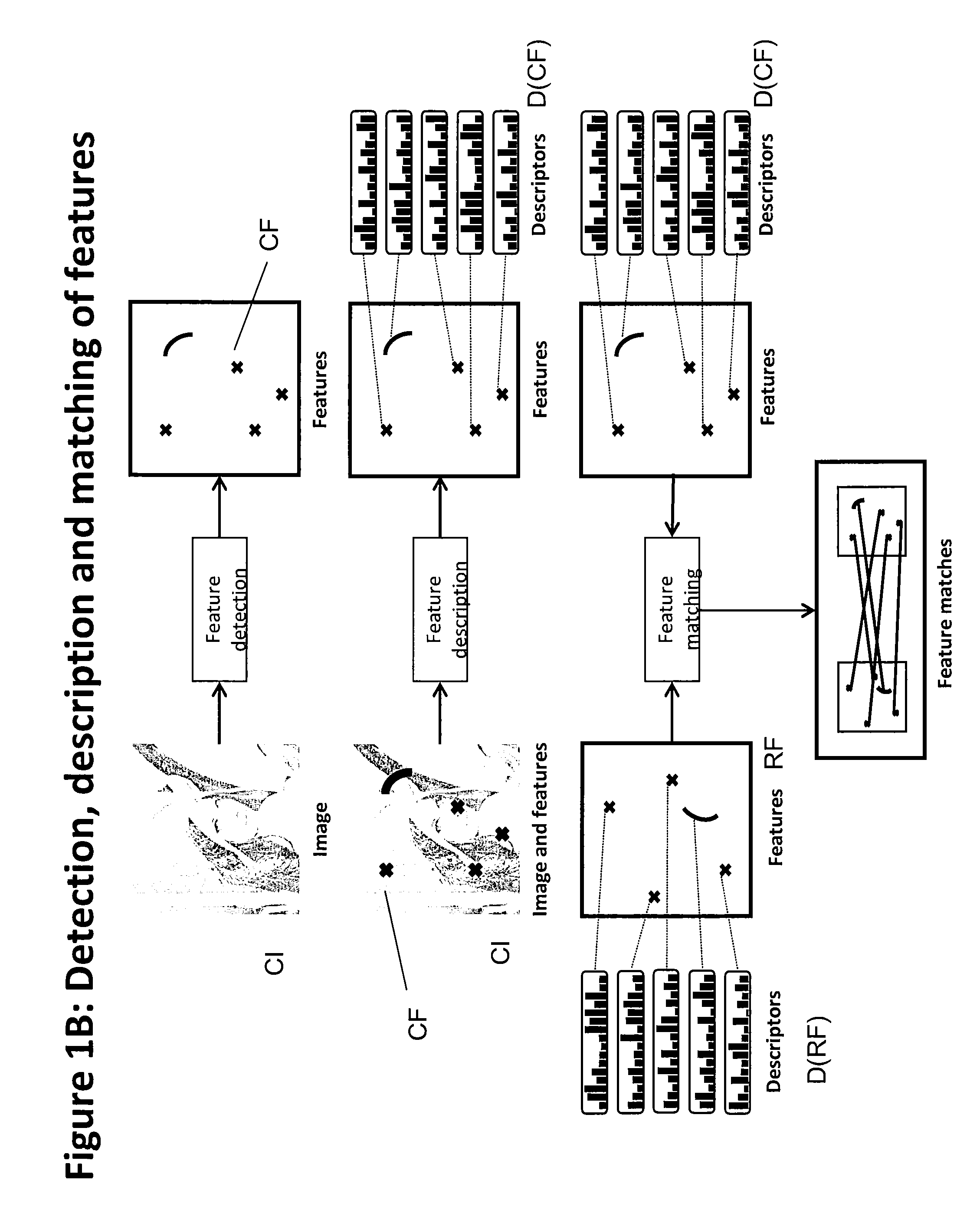
Method of matching image features with reference features
ActiveUS9400941B2Increase weightReduce uncertaintyImage enhancementImage analysisImaging FeatureSimilarity measure
A method of matching image features with reference features comprises the steps of providing a current image, providing a set of reference features, wherein each of the reference features comprises at least one first parameter which is at least partially indicative of a position and / or orientation of the reference feature with respect to a global coordinate system, wherein the global coordinate system is an earth coordinate system or an object coordinate system, or at least partially indicative of a position of the reference feature with respect to an altitude, detecting at least one feature in the current image in a feature detection process, associating with the detected feature at least one second parameter which is at least partially indicative of a position and / or orientation of the detected feature, or which is at least partially indicative of a position of the detected feature with respect to an altitude, and matching the detected feature with a reference feature by determining a similarity measure.
Owner:APPLE INC
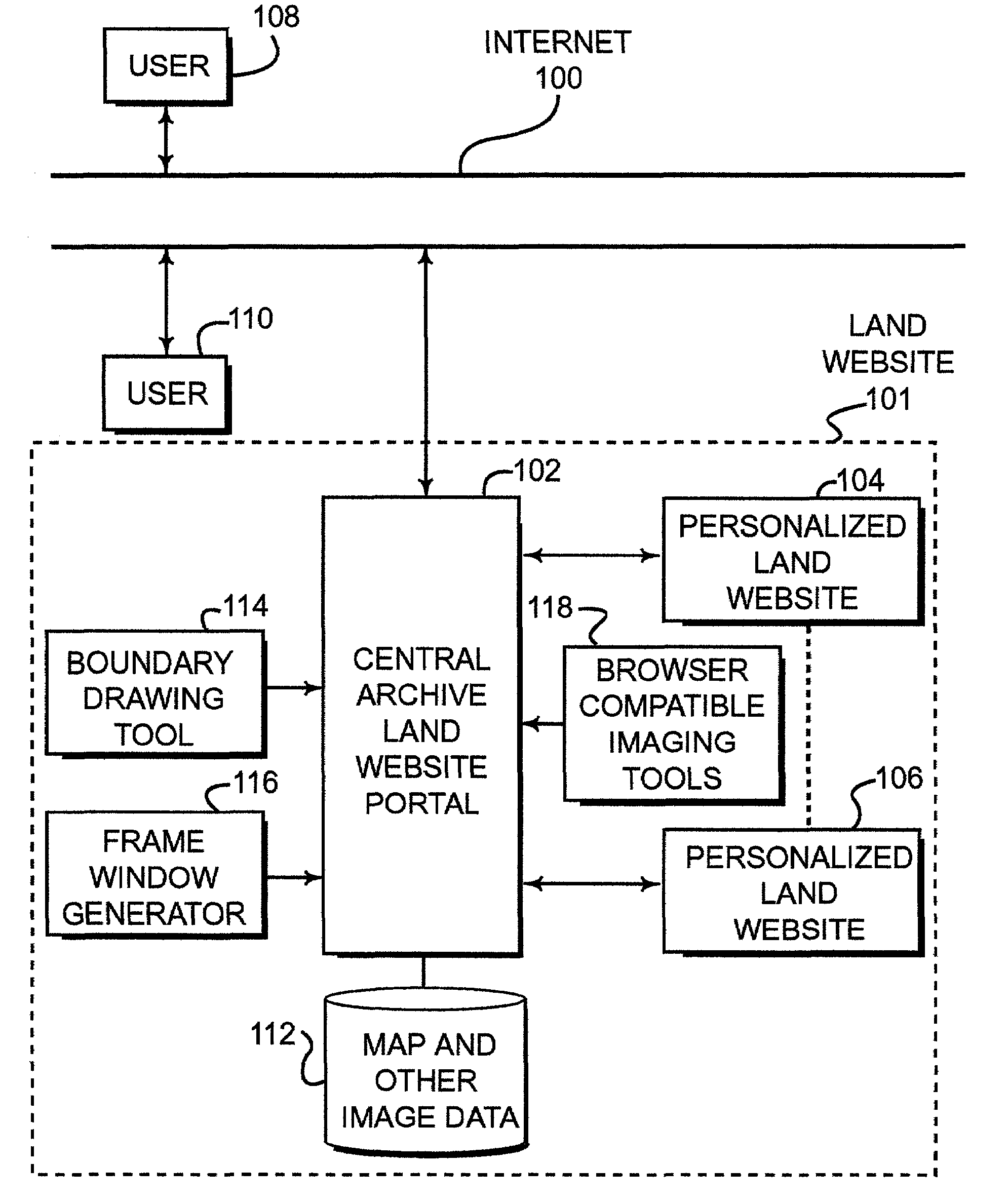
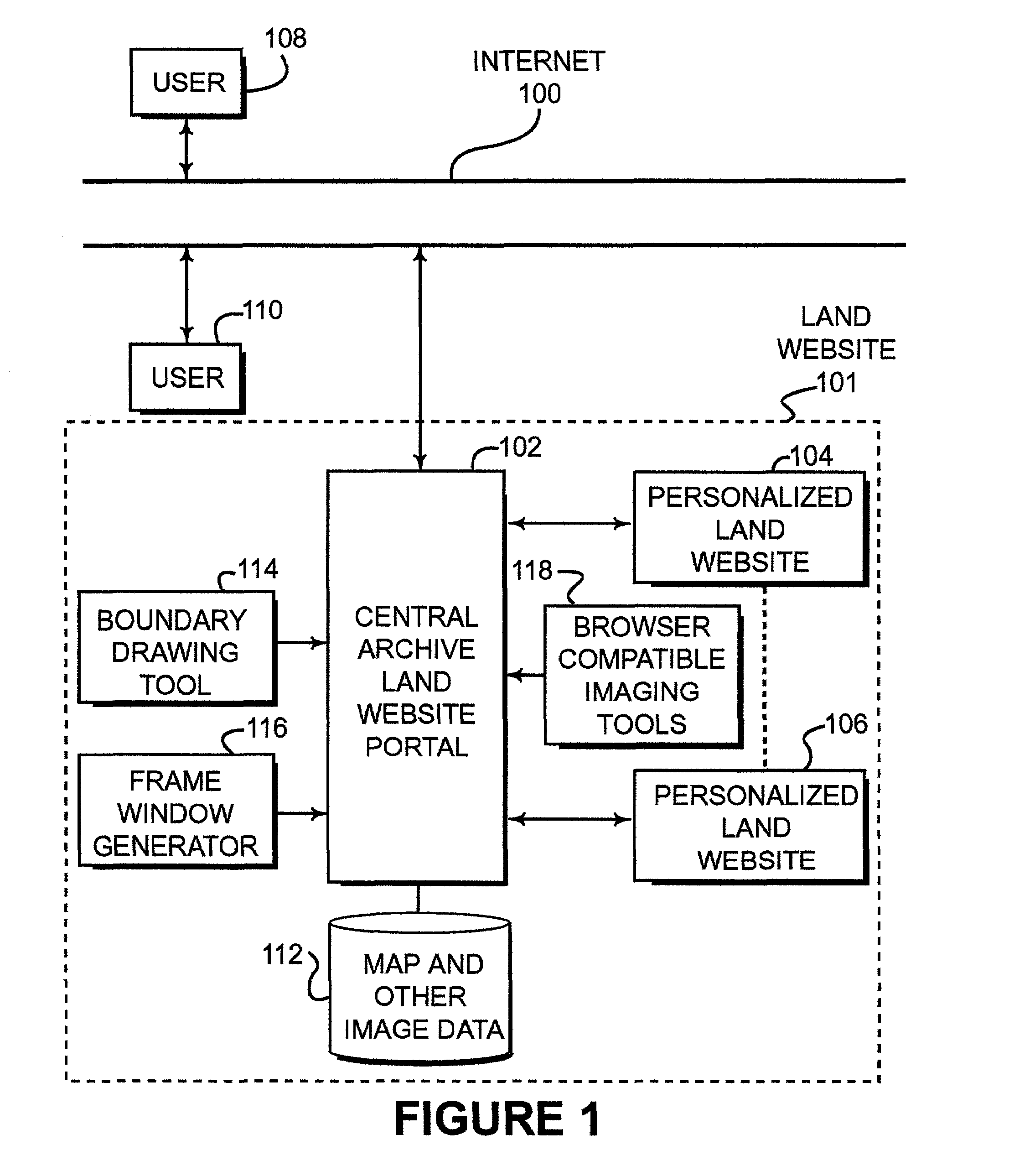
Identification, storage and display of land data on a website
ActiveUS7171389B2Optimize locationLimited accessInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlPersonalizationDocument preparation
Disclosed is a land website that provides a personalized database on which data can be stored, retrieved, customized and communicated (e.g., by e-mail) relating to a particular piece of property. The database can be accessible via a password and a security code over the Internet and may be encrypted for transmission. Land websites can be established that contain image data, map libraries, virtual tours, legal descriptions, title information, e-documents, actual pictures of property and various other information. Unique 3-D imaging of composite images can be provided on the land website as well as fly-around composite 3-D images. The land website provides a unique way of packaging information relating to a piece of land in a single, accessible location. A boundary applet tool is provided on the land website portal that allows a user to simply and easily draw boundaries around the property of interest and then submit an order for more detailed information about the property of interest. Various map data and image data are provided to assist the user in drawing the boundaries. Acreage amounts are automatically calculated based upon the size and area drawn by the user. Properties of interest can be easily accessed by a global coordinate system or by searching on map data that is provided on a wide range of scales.
Owner:LANDNET CORP
Method of matching image features with reference features
ActiveUS20150161476A1Increase weightWeight increaseImage enhancementImage analysisImaging FeatureSimilarity measure
A method of matching image features with reference features comprises the steps of providing a current image, providing a set of reference features, wherein each of the reference features comprises at least one first parameter which is at least partially indicative of a position and / or orientation of the reference feature with respect to a global coordinate system, wherein the global coordinate system is an earth coordinate system or an object coordinate system, or at least partially indicative of a position of the reference feature with respect to an altitude, detecting at least one feature in the current image in a feature detection process, associating with the detected feature at least one second parameter which is at least partially indicative of a position and / or orientation of the detected feature, or which is at least partially indicative of a position of the detected feature with respect to an altitude, and matching the detected feature with a reference feature by determining a similarity measure.
Owner:APPLE INC
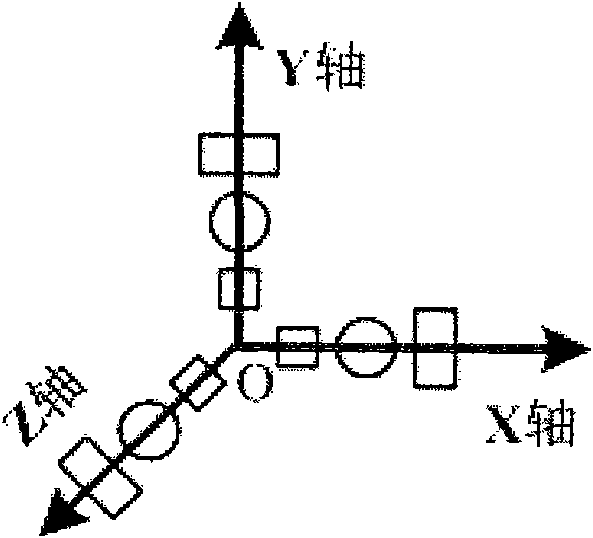
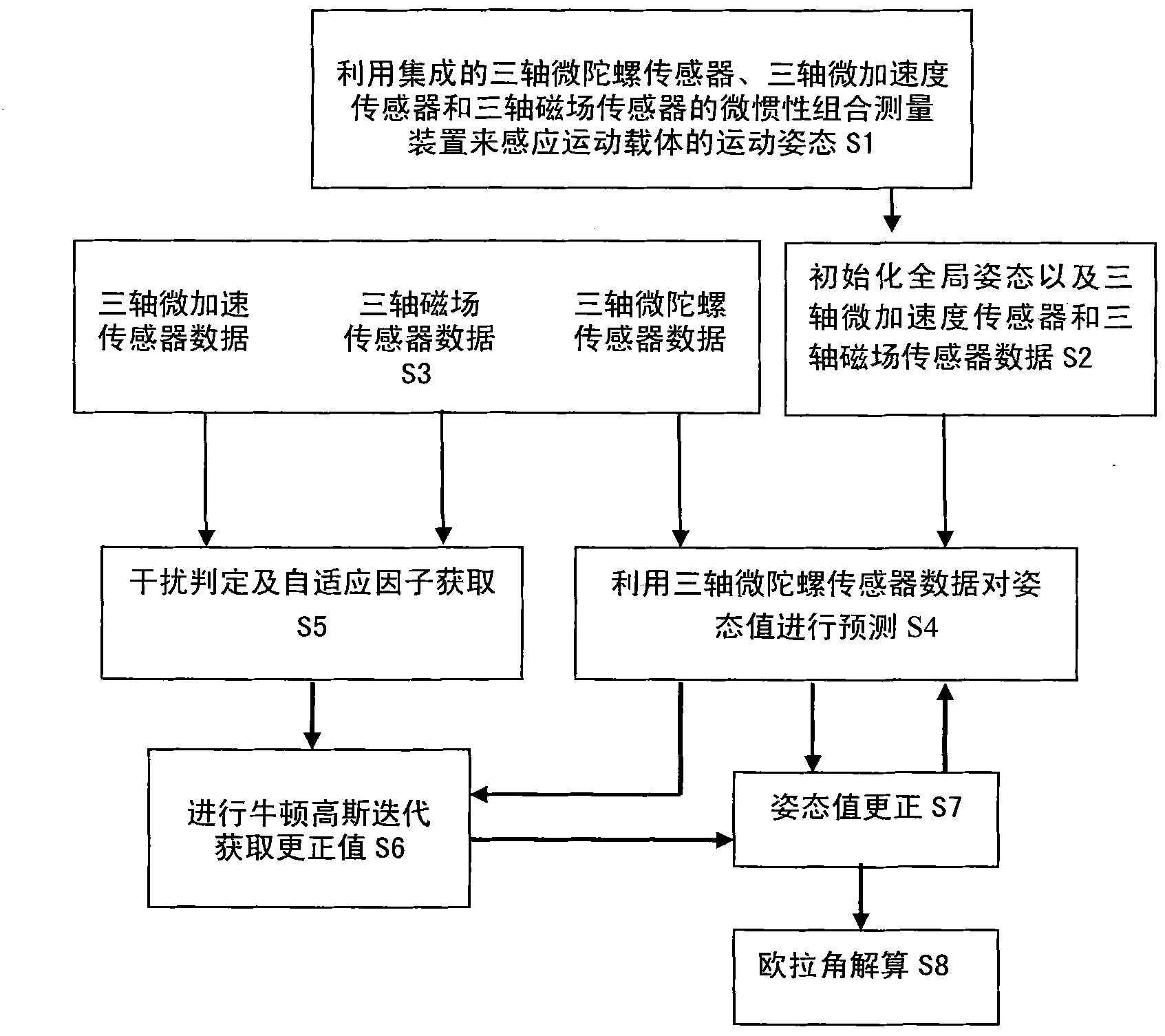
Self-adaptation three-dimensional attitude positioning method based on microinertia and geomagnetic technology
InactiveCN101915580AReduce complexityImprove accuracyNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by terrestrial meansGyroscopeSimulation
The invention discloses a self-adaptation three-dimensional attitude positioning method based on microinertia and a geomagnetic technology, comprising the following steps of: (1) inducing a motion attitude of a carrier by utilizing a sensor of a microinertia measuring device; (2) setting an initial attitude of the microinertia measuring device and accelerated speed and geomagnetic field information under a global coordinate system; (3) solving the attitude value of the microinertia measuring device; (4) predicting the attitude value of the microinertia measuring device by utilizing triaxial micro-gyroscope sensor data; (5) carrying out confidence judgment on the triaxial micro-acceleration sensor data and triaxial magnetic field sensor data, detecting the interference of a surrounding environment, and setting self-adaptation parameters; (6) obtaining the attitude error value of the microinertia measuring device by utilizing the triaxial micro-acceleration sensor data and the triaxial magnetic field sensor data which are processed in the step (5); (7) fusing the attitude predictive value obtained from the step (4), corrected information obtained from the step (6) and the self-adaptation parameters obtained from the step (5) to obtain the attitude value of the microinertia measuring device; and (8) outputting attitude information.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for measuring positioning points based on laser tracker in docking process of airplane parts
InactiveCN102519441AImprove assembly measurement accuracyReduce work intensitySurveying instrumentsUsing optical meansJet aeroplaneObservation point
The invention discloses a method for measuring positioning points based on a laser tracker in a docking process of airplane parts. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of 1, establishing a model of transformation between an airplane global coordinate system and a laser tracker measure coordinate system according to common observation points, 2, acquiring current calculating positions of positioning measure points of airplane parts according to a process joint sphere centre position, and 3, controlling and driving a laser tracker to search current accurate positions of the positioning measure points of the airplane parts from the current calculating positions according to a cross helical search method and to carry out automatic measure. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that 1, an advanced laser measure technology is adopted so that the airplane assembling measure precision is improved; and 2, a measure process does not need artificial light introduction and full automatic search measure of a docking assembling process is realized according to an algorithm so that working efficiency and measure precision are greatly improved and working strength of workers is reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Accurate positioning and parking method of trackless navigation AGV
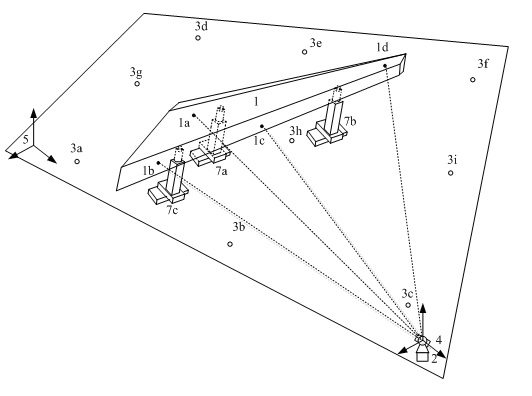
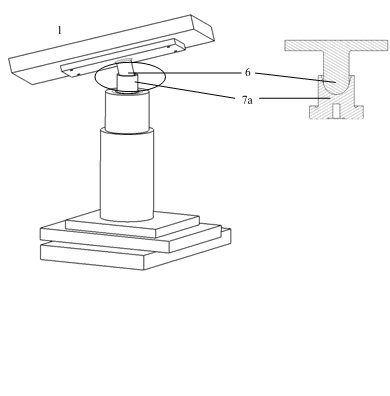
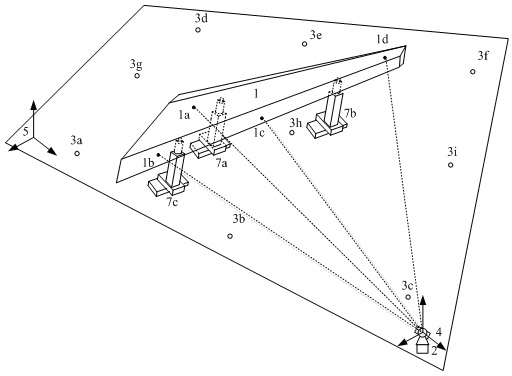
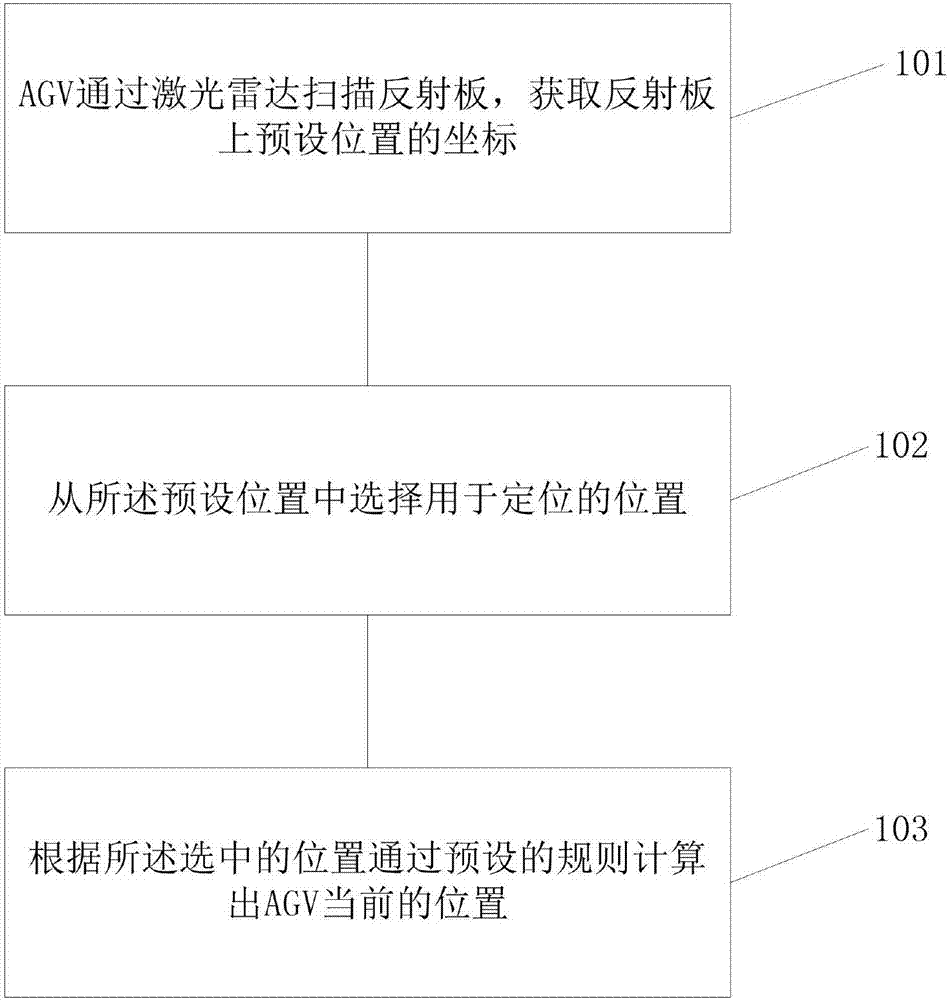
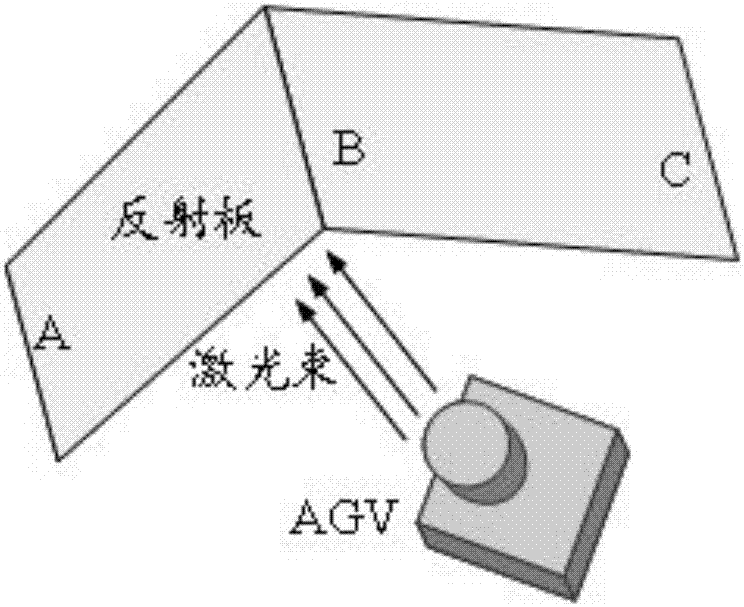
ActiveCN106969768AImprove reliabilityHigh precisionNavigational calculation instrumentsPosition fixationRadarGlobal coordinate system
The embodiment of the invention provides an accurate positioning and parking method of a trackless navigation AGV. The accurate positioning and parking method comprises the steps that the AGV scans a reflection plate through laser radar to obtain coordinates of preset positions on the reflection plate; a position for positioning is selected from the preset positions; the current position of the AGV is calculated according to preset rules and the selected position. According to the method, three special reflection points are extracted to achieve three-point positioning, the coordinate orientation of the AGV under a global coordinate system is determined mainly through a least square method, and then the direction angle of the AGV is calculated through multiple quadrants. The relative position and the direction angle of the AGV with respect to the reflection plate can be also calculated through outline detection so that the AGV can be accurately parked at the designated of the reflection plate. By adopting the method, the defect of poor positioning accuracy of an SLAM technology is overcome to the most degree, and a reliable solution is also provided for automatic charging of the trackless navigation AGV.
Owner:SHENZHEN ZHUMANG TECH CORP
Splicing measuring method and system based on three-dimensional target
InactiveCN102155923ALarge measuring rangeEasy to operateMeasuring points markingUsing optical meansThree dimensional measurementVision sensor
The invention provides a splicing measuring method and system based on a three-dimensional target. The splicing measuring method comprises the following steps: (a) arranging two cameras in positions where a measured object can be observed, calibrating the parameters of the two cameras and setting a global coordinate system; (b) determining the coordinate value of a mark point on a three-dimensional target fixed on a vision sensor in a vision sensor coordinate system; (c) moving the vision sensor to the position where an area to be measured of the measured object can be measured, and carrying out three-dimensional measurement on the area to be measured of the measured object by using the vision sensor to obtain the three-dimensional data of the area to be measured of the measured object inthe vision sensor coordinate system; (d) determining the transformation relation between the vision sensor coordinate system in the current position and the global coordinate system; (e) transformingthe three-dimensional data obtained in the step (c) to the global coordinate system by using the transformation relation determined in the step (d); and (f) repeating the steps (c), (d) and (e) to complete the splicing of the three-dimensional measurement data of the measured object in the global coordinate system.
Owner:BEIJING INFORMATION SCI & TECH UNIV
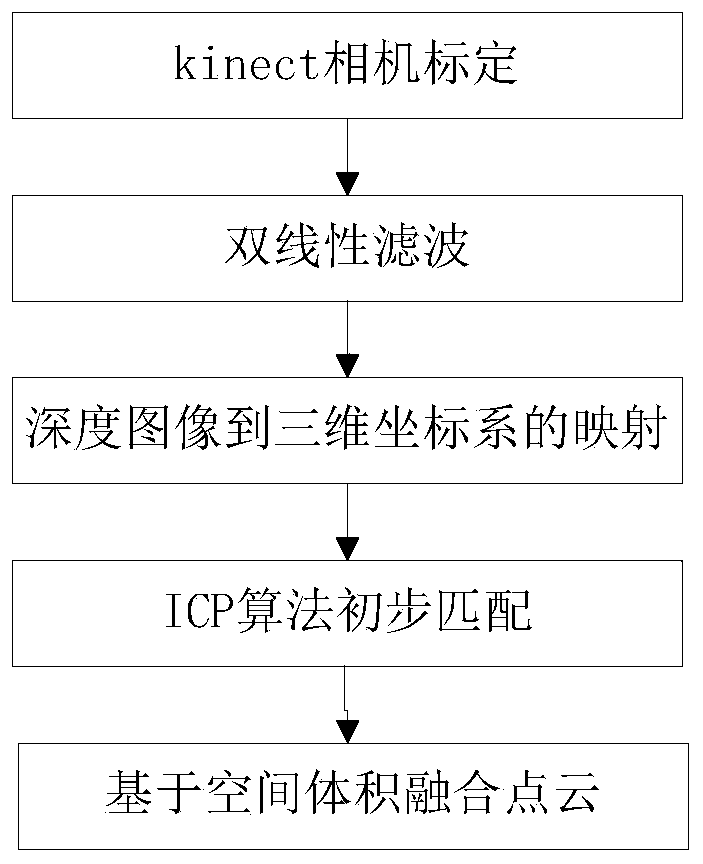
Method for rebuilding three-dimensional scene of downhole environment
InactiveCN103456038ARealize 3D scene reconstructionImage analysis3D modellingMatch algorithmsGlobal coordinate system
The invention provides a method for rebuilding a three-dimensional scene of a downhole environment. The method includes the steps that S1, a depth camera is calibrated to determine internal parameters of the camera; S2, bilinearity filtering is carried out on the depth of a current frame to reduce noise interference; S3, a depth image of the current frame is mapped to a three-dimensional coordinate system of the depth camera; S4, primary registering is carried out through an ICP matching algorithm to obtain a transformation matrix between the depth image of the current frame and a depth image of a previous frame of the depth camera, and the depth image of the current frame can be converted to a global coordinate system through accumulation of the transformation matrixs; S5, the scene is rebuilt through a volume space fusion algorithm. According to the technical scheme, the three-dimensional scene of the downhole environment can be rebuilt economically and rapidly.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Three-dimensional shape vision measuring method and system for large component surface
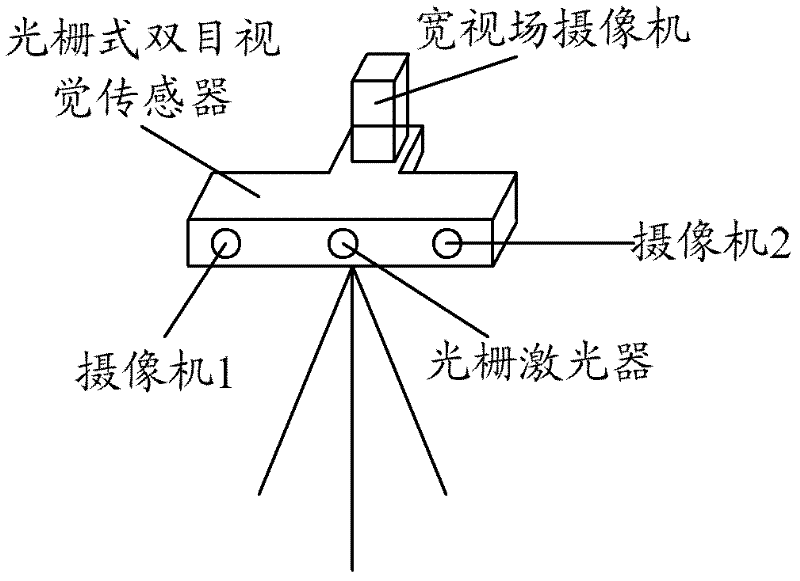
InactiveCN102445164ARealize 3D shape visual measurementFlexible emissionsUsing optical meansWide fieldThree dimensional shape
The invention provides a three-dimensional shape vision measuring method and system for a large component surface. The system comprises an image acquiring system, a controller, a computer, a three-dimensional optical measuring head, and a plurality of plane targets, wherein the plane targets are distributed around a measured objected; the three-dimensional optical measuring head and the plane targets are connected with the controller and the image acquiring system; the controller and the image acquiring system are connected with the computer; the three-dimensional optical measuring head comprises a grating binocular vision sensor and a wide-field camera, wherein the grating binocular vision sensor is used for measuring the three-dimensional shape of different sub regions of the large component surface; and the wide-field camera is used for measuring the plane targets; the computer uses the plane targets measured by the wide-field camera as medium, so that the three-dimensional shape data of different sub regions is integrated to a global coordinate system. The plane targets are used as medium, marks are not needed to be pasted on the measured object, and the global integrating device is not needed; simultaneously, the positions of the plane targets can be flexibly arranged according to the shape of the measured object without a measuring dead angle.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for creating 3D map based on 3D laser
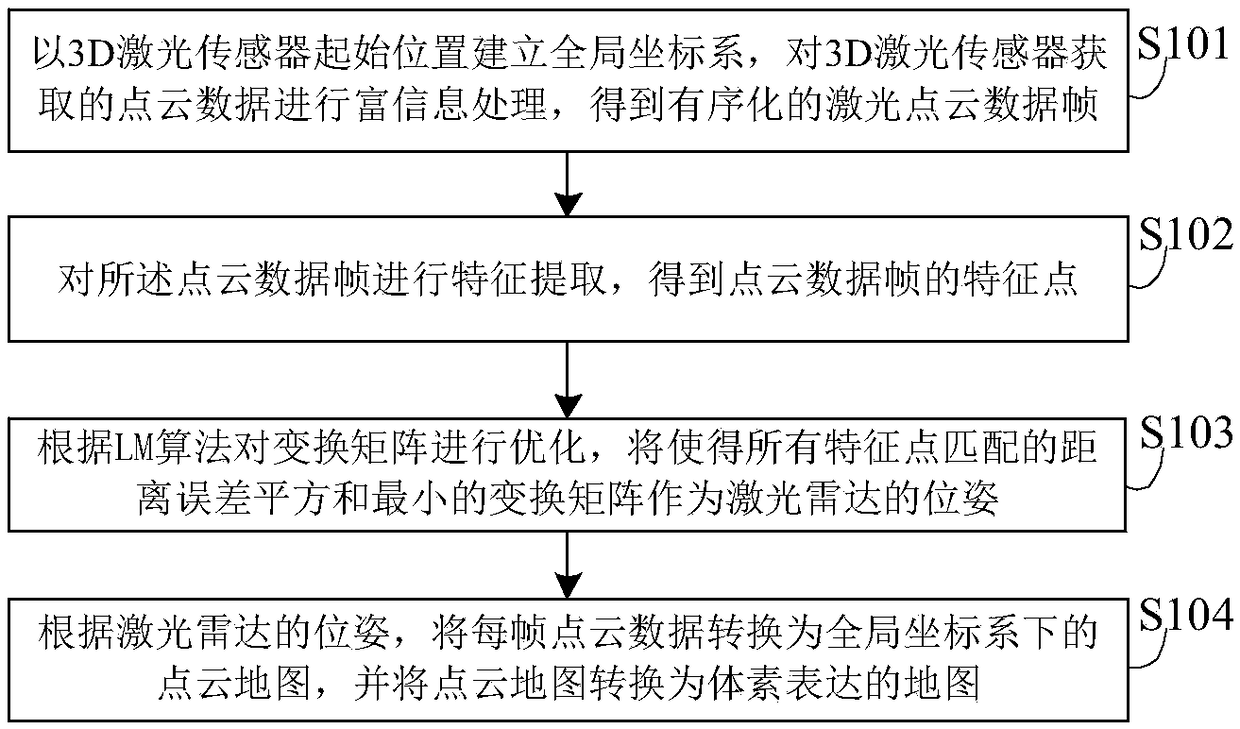
ActiveCN108320329AHigh precisionAvoid the problem of inconvenient filtering and denoisingImage enhancementDetails involving processing stepsInformation processingVoxel
The invention discloses a method for creating a 3D map based on a 3D laser, and belongs to the technical field of data processing. The method comprises the steps of performing rich information processing on point cloud data obtained by a 3D laser sensor to obtain an ordered laser point cloud data frame; performing feature extraction on the point cloud data frame to obtain feature points of the point cloud data frame; optimizing a transformation matrix according to an LM algorithm, and enabling the transformation matrix capable of enabling the sum of squares of distance errors of the matching of all feature points to be the minimum to serve the pose of radar; transforming each frame of the point cloud data into a point cloud map under a global coordinate system according to the pose of theradar, and transforming the point cloud map into a map expressed by voxels. According to the invention, rich information processing is performed on the original laser data, thereby providing a data basis for the creation of the 3D map. The method avoids a problem that it is inconvenient to perform filtering and denoising by adopting a point cloud map through adopting an expression mode of the voxel map, and the definition of the 3D map is improved.
Owner:维坤智能科技(上海)有限公司 +1
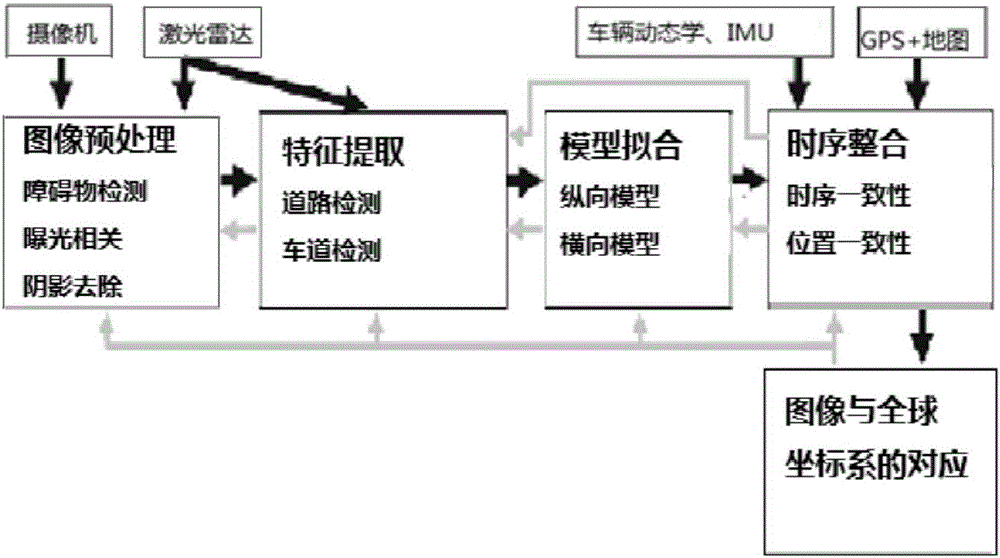
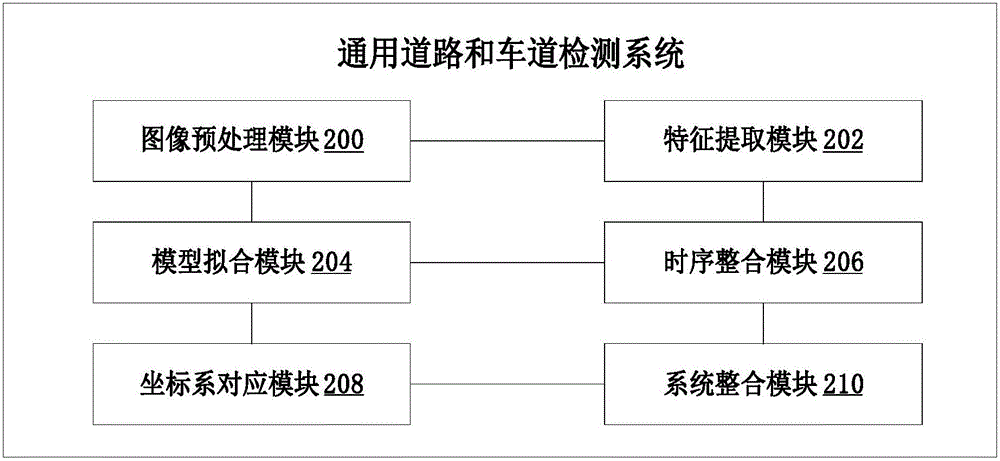
Universal road and lane detection system and method
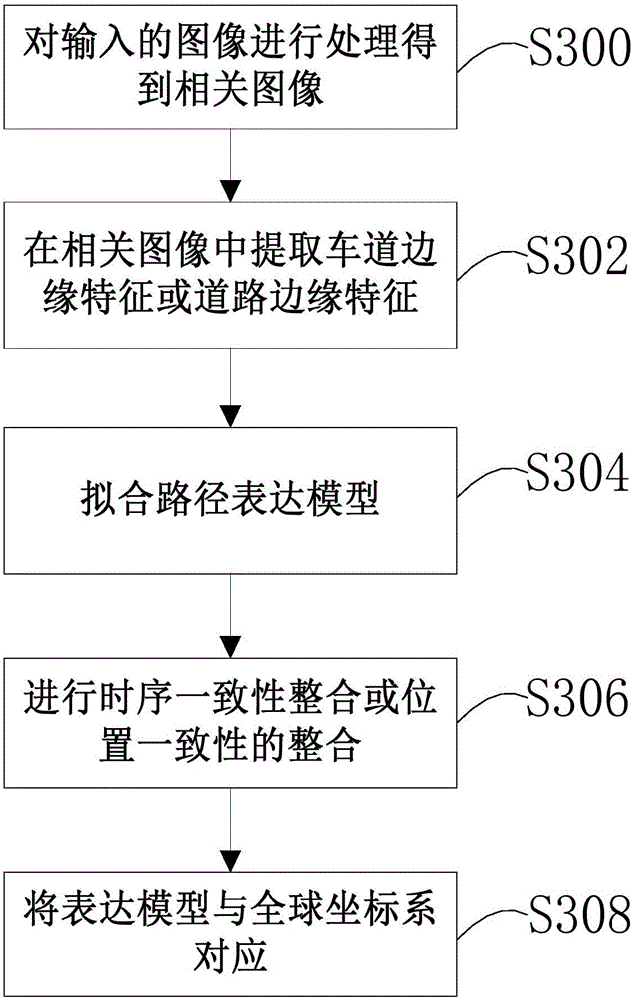
ActiveCN105825173AThe solution function is not perfectCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionInterference elimination
The invention relates to a universal road and lane detection system and method. The method comprises: S300, interference elimination and image artifact and irrelevant image part removing are carried out on an input image to obtain a relevant image; S302, lane edge feature or road edge feature is extracted from the relevant image; S304, according to the lane edge feature or road edge feature, fitting is carried out to obtain a synthesized path expression model; S306, the path expression model is tracked to carry out time sequence consistency integration or position consistency integration; and S308, the path expression model corresponds to a global coordinate system. On the basis of the module design, pretreatment is carried out on the image inputted by the camera, the interested relevant image is selected; lane detection or road detection is carried out by combining input information of the laser radar; model fitting is carried out to estimate a road path and the accuracy of path estimation is improved by using the time sequence integration module; and then the image corresponds to the global coordinate system in real time by using a coordinate system correspondence module to improving path estimation accuracy. Therefore, a problem that the existing road estimation model has imperfect functions can be solved.
Owner:FUZHOU HUAYING HEAVY IND MACHINERY
Synergetic control method of aircraft part pose alignment based on four locater
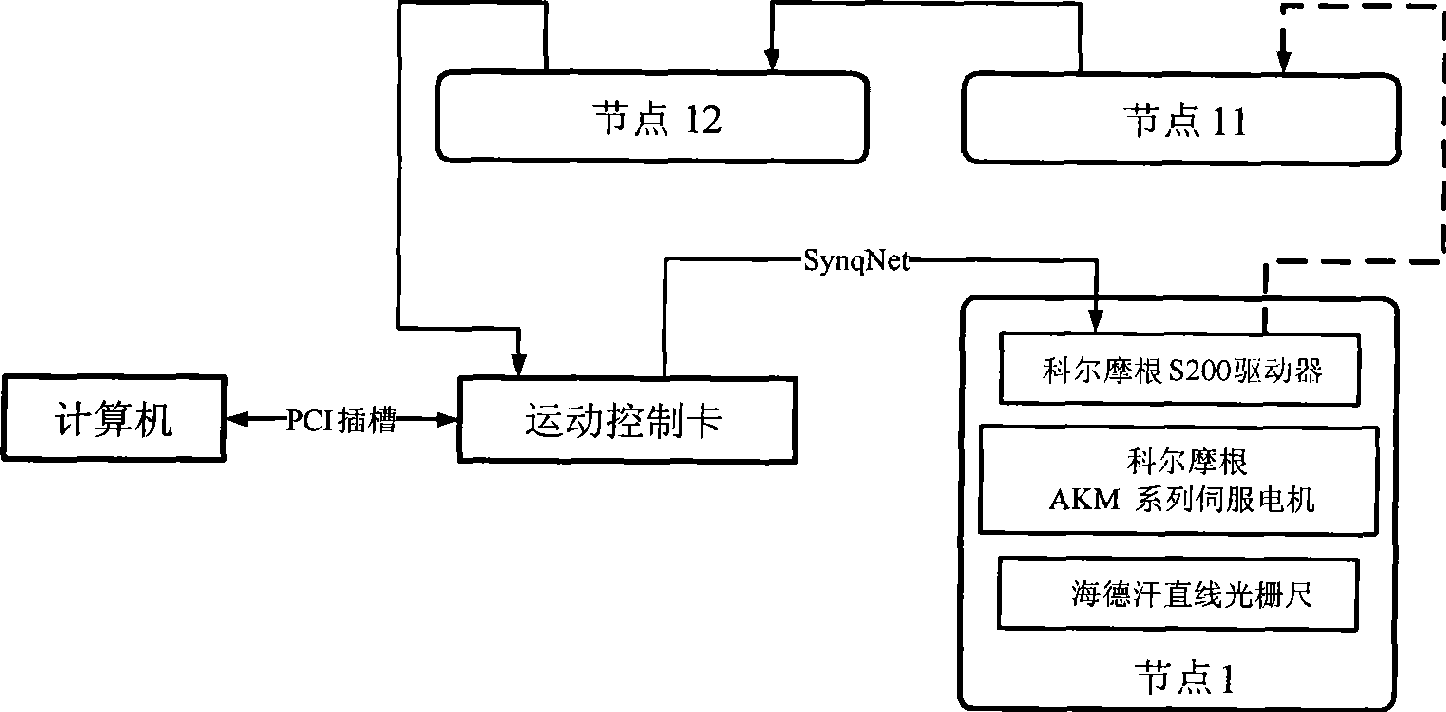
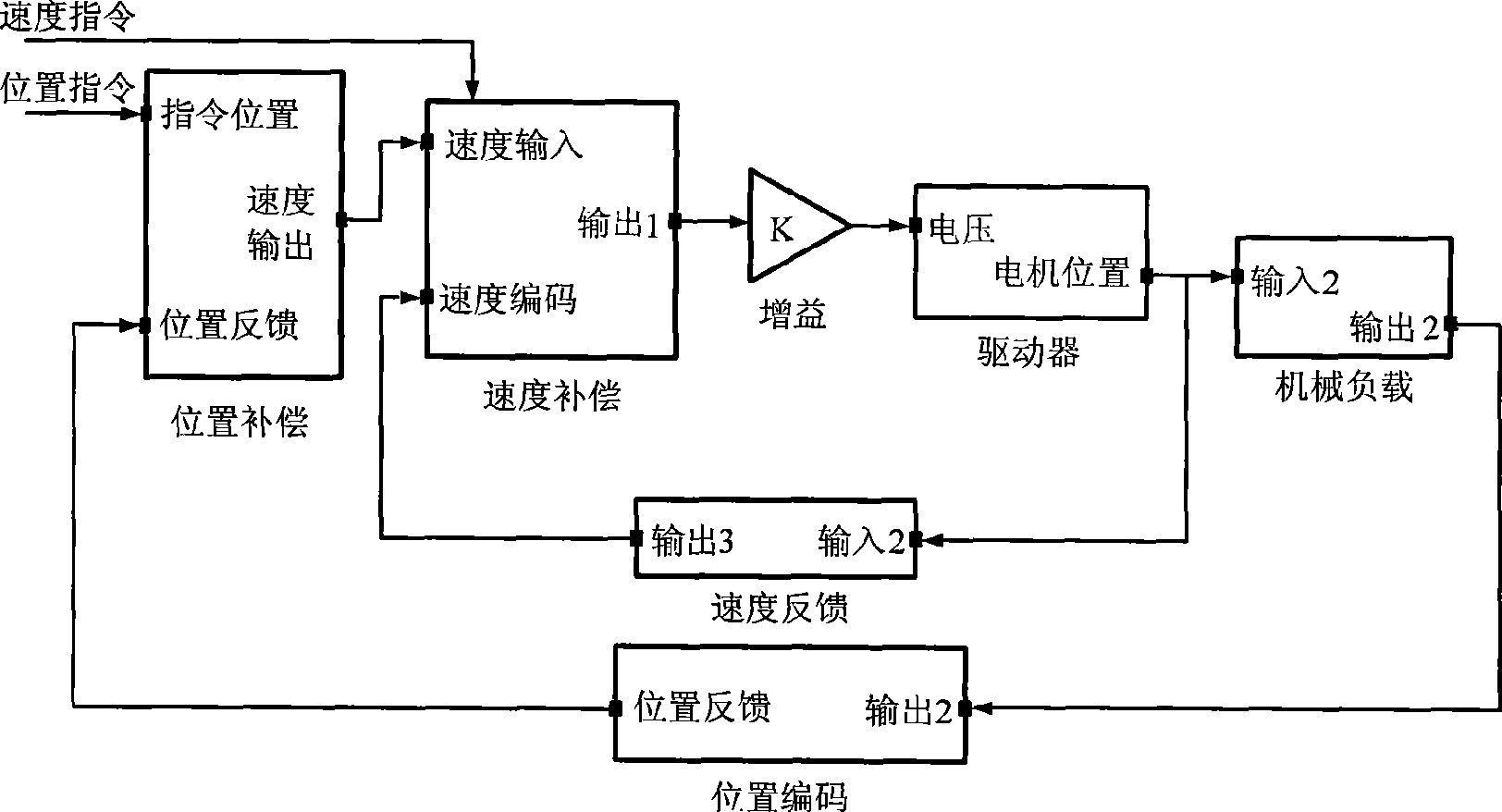
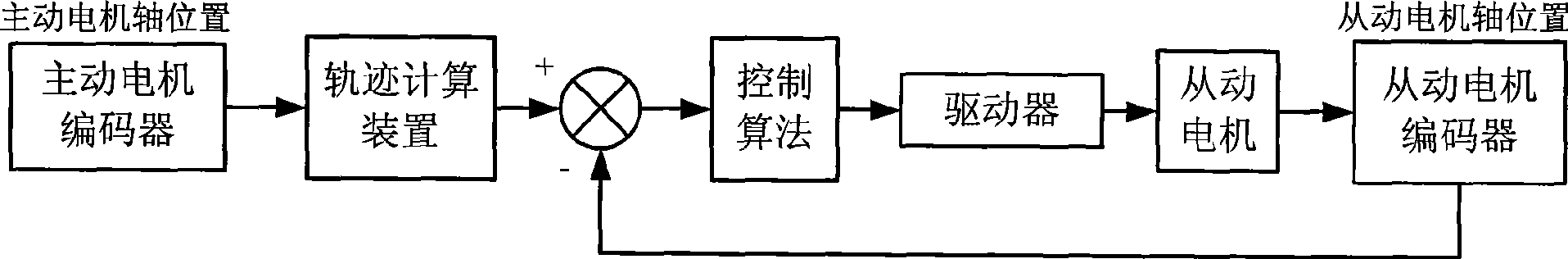
The invention discloses a method for adjusting and synergetically controlling the position and pose of an aircraft component based on four locators. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, a global coordinate system OXYZ is established, and the current position and pose and the target position and pose of the aircraft component are calculated under the global coordinate system; secondly, the automatic adjusting path and the inch adjusting path of the aircraft component are formed; thirdly, the track of the sphere pivot wiring point between the locator and the aircraft component is planed according to the automatic adjusting path and the inch adjusting path; fourthly, the track of the sphere pivot wiring point is inverted into the driving parameter of a 12 motor axle synchronous control network; fifthly, the 12 motor axle synchronous control network is built based on a SynqNet bus, and the position servo of single motor axle adopts the full-closed loop digit controlling; and sixthly, two locators are selected, and the collocated relation between the locators is the master-slave motion mode. The method has the following advantages: firstly, the path for adjusting the position and pose of the aircraft component can be planed; secondly, the full-closed loop controlling of the single axle motion of the locator can be realized; and thirdly, the 12 axle synchronous motion of the position and pose adjusting system can be realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Portable orthovoltage radiotherapy
InactiveUS20080089480A1Dry up neovascular membraneStabilized and improved acuityLaser surgeryDiagnostic recording/measuringOcular structureOcular imaging
A portable orthovoltage radiotherapy system is described that is configured to deliver a therapeutic dose of radiation to a target structure in a patient. In some embodiments, inflammatory ocular disorders are treated, specifically macular degeneration. In some embodiments, the ocular structures are placed in a global coordinate system based on ocular imaging. In some embodiments, the ocular structures inside the global coordinate system lead to direction of an automated positioning system that is directed based on the ocular structures within the coordinate system.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC INC
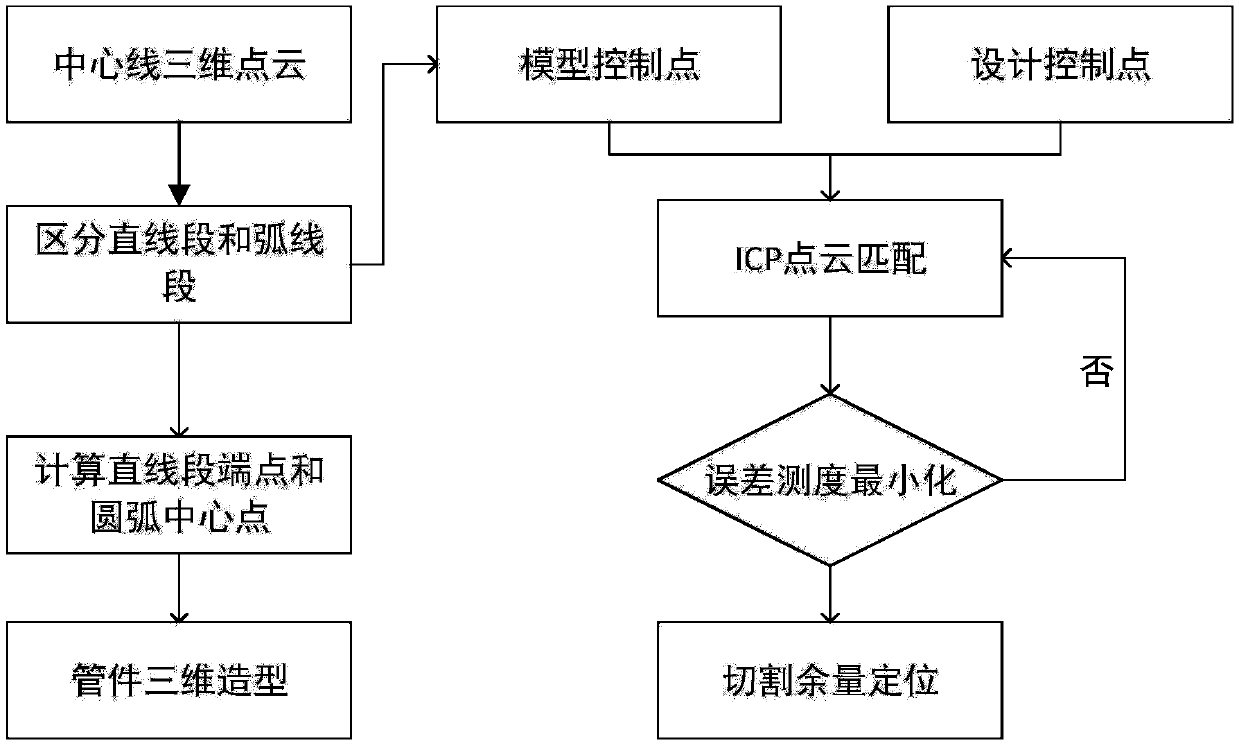
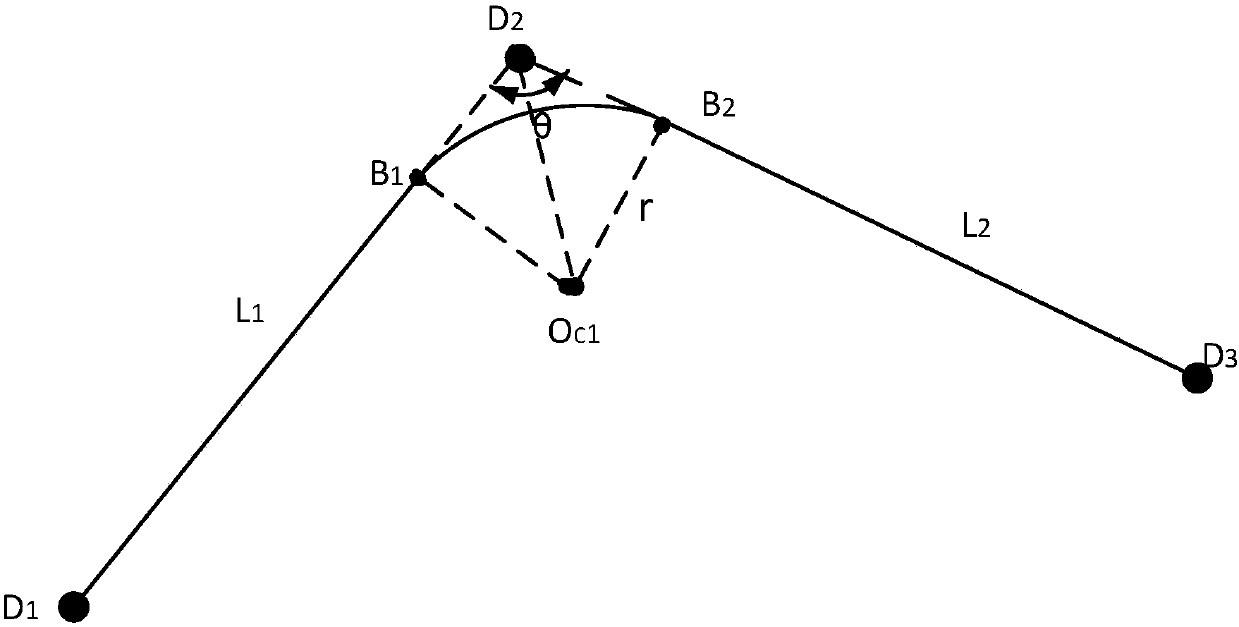
Bend pipe measuring and allowance locating method facing digital manufacture
ActiveCN108074277ARealize 3D reconstructionRealization of self-seeking cuttingImage enhancementImage analysisMatch algorithmsMultiple sensor
The invention relates to a bend pipe measuring and allowance locating method facing digital manufacture. The method comprises the following steps that multiple sensors are calibrated globally by meansof a laser tracker and a target, and coordinate systems of the sensors are unified into a global coordinate system; the sensors collect bend-pipe images and carry out edge detection and morphologicalrefinement to obtain a center line of the bend pipe in a strictly synchronous way, and 3D reconstruction of the center line is carried out in a bidirectional polar line matching algorithm; the centerline is dispersed into space point cloud, a control point, straightway end points and an arc center point of an arc segment are calculated, and 3D molding is carried out by taking the center line asa guiding line; and a design model matches a measurement model via a nearest point iteration method, the allowance position is calculated. Thus, self-locating cutting and welding of the bend pipe is realized, and the digital manufacturing process of the bend pipe is accelerated.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method, an apparatus and a computer-readable medium for processing a night vision image dataset
ActiveUS20100284626A1Enhancing dynamic levelReduce noiseImage enhancementImage analysisNight visionFeature vector
A method is disclosed for enhancing the quality of an image dataset, such as, e.g., reducing the noise in a noisy image data set and increasing the contrast in the image data set. The method may be used for processing a sequence of image datasets, e.g. night vision image datasets, wherein said sequence comprises at least two image datasets each having at least two pixels, and wherein each pixel has an intensity value. The method comprises calculating a structure tensor for each pixel in an image dataset comprised in the sequence of image datasets; calculating values in a summation kernel based on said structure tensor for each pixel in said image dataset; calculating a weighted intensity value for each pixel in said first image dataset, using as weights the values in said summation kernel; storing said weighted intensity value for each pixel in said image dataset as a processed intensity value for each corresponding pixel in a processed output image dataset; rotating a local coordinate system in which the summation kernel is described resulting in that the coordinate axes of said local coordinate system coincide with the directions of the eigenvectors of said structure tensor, where said eigenvectors are described in the global coordinate system of the image dataset, and scaling the coordinate axes of the local coordinate system in which the summation kernel is described by an amount related to the eigenvalues of the structure tensor via a width function W(λi)=σi, and wherein said eigenvalues depend on the amount of intensity variation in the direction of their corresponding eigenvectors, the width function being a decreasing function such that w(0)=σmax and lima→∞w=σmin. An apparatus and a computer readable medium are also provided.
Owner:MALM +3
Personal robotic system and method
InactiveUS20160207193A1Minimize destabilizing momentProgramme-controlled manipulatorDigital data processing detailsRobotic systemsRobotic arm
One embodiment is directed to a personal robotic system, comprising: an electromechanical mobile base configured to be controllably movable upon a substantially planar surface in a global coordinate system wherein a Z axis is defined perpendicular to the substantially planar surface; a torso assembly movably coupled to the mobile base such that the torso may be controllably moved in a direction substantially parallel to the Z axis and also controllably rotated about an axis substantially perpendicular to the Z axis; a head assembly movably coupled to the torso assembly; a robotic arm operatively coupled to the torso assembly; and a controller operatively coupled to the mobile base, torso assembly, head assembly, and robotic arm, and configured to controllably manipulate nearby objects while also automatically minimizing destabilizing moments applied to the mobile base through movement of at least one of the mobile base, torso assembly, head assembly, and robotic arm.
Owner:WILLOW GARAGE
System for object detection and recognition in videos using stabilization
ActiveUS8885887B1Reduce and eliminate apparent image motionImage enhancementImage analysisFeature vectorObject Class
Described is a system for stabilizing, detecting, and recognizing objects in video captured from a mobile platform. The system first receives a video (with a plurality of image frames) captured from a mobile platform. The video is stabilized by registering the image frames to a global coordinate system to generate stabilized image frames. A bio-inspired attention algorithm is applied to the stabilized image frames to produce a set of locations in the stabilized image frames that are salient points representative of an object of interest. An image chip is generated that surrounds each salient point. High-dimensional feature vectors are extracted from the image chip. The feature vectors are then classified as an object class. Thus, through classifying the feature vectors, an object of interest can be identified in the video as captured from the mobile platform.
Owner:HRL LAB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com