Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
47 results about "Clotrimazole" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Clotrimazole is used to treat skin infections such as athlete's foot, jock itch, ringworm, and other fungal skin infections (candidiasis). This medication is also used to treat a skin condition known as pityriasis (tinea versicolor), a fungal infection that causes a lightening or darkening of the skin of the neck, chest, arms, or legs.
Gum resin as a carrier for topical application of pharmacologically active agents
InactiveUS6899897B2Improve the effectiveness of treatmentSustained releaseAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryBENZOIN TINCTUREDisease
The invention provides a biological dressing for treatment of a dermatological disease comprised of a gum resin, a topically acceptable volatile solvent, and a pharmacologically active agent. The gum resin is present in a suitable amount that the composition, when the solvent evaporates, will dry to form a solid coating that sticks to the skin or mucosal membrane to which the composition is applied and maintain the pharmacologically active agent over a sustained period of time in contact with sites on the skin or mucosal membranes exhibiting symptoms of the disease. Methods are provided for treating symptoms of dermatological diseases with such a pharmacological composition. Biological dressings including tincture of benzoin and clotrimazole are shown to be efficacious for the long-term amelioration of symptoms of athlete's foot.
Owner:ADVANCED RESIN THERAPEUTICS INC
Method for preparing metronidazole, clotrimazole and chlorhexidime vaginal acetate effervescent tablet and quality control method
InactiveCN101406463AEasy to useUse cleanOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismDiseasePolyethylene glycol
The invention relates to a method for preparing a new gynecological anti-bacterial anti-inflammatory drug, namely dithiazole vaginal effervescent tablet and a method for quality control. The dithiazole vaginal effervescent tablet is used for treating gynecopathy, anorectal diseases and skin commonly-encountered diseases such as pelvic inflammatory disease, cervical erosion, vaginitis and the like caused by anaerobic bacteria, aerobic bacteria, trichomoniasis, pure or mixed fungal infections. The dithiazole vaginal effervescent tablet is characterized in that lactic acid and a calcium lactate buffer system are added to the formulation so that the pH value of the drug is between 3.5 and 4.0 similar to the vaginal physiological pH and is advantageous to remove pathogen and infusorian, provide living conditions suitable for vaginal beneficial bacterium group of lactic acid bacteria, and promote the illness rehabilitation. Besides, the dithiazole vaginal effervescent tablet uses pharmaceutical acceptable water-soluble polymer materials such as water-soluble polymer polyethylene glycol, polyvidone K30 and the like to enwrap acidic or alkaline components of an effervescent disintegrant so as to avoid the occurrence of hidden spots or even collapsing phenomenon on the surface of the tablet caused by gas production reaction resulted from small amount of water in the storage process, and uses a ethanol solution with adhesives and surface-active agents for granulation so that the hydrolysis of clotrimazole can be prevented, the infiltration of moisture is promoted in use, the uniform collapse is accelerated, and gas bubbles are homogeneous and stable.
Owner:DAKANG JUNBISHA XIANYANG SHAANXI PROV
Clotrimazole gel, and its prepn. method
ActiveCN1903174AGood curative effectImprove transdermal absorption rateOrganic active ingredientsAntimycoticsClotrimazole Vaginal TabletChemistry
A mycosporin gel with high percutaneous absorptivity and stability and its preparing process are disclosed.
Owner:北京科信聚润医药科技有限公司
Metronidazole effervescence patch and technique of preparing the same
ActiveCN101152176AImprove the bactericidal effectGood synergyOrganic active ingredientsAntimycoticsChlorhexidine AcetateTalc
The invention discloses a Metronidazole, Clotrimazole and Chlorhexidine Acetate Effervescent Tablet and the preparation method. Each tablet has the following proportion of contents: metronidazole 0.2 gram, clotrimazole 0.16 gram, acetic acid chlorhexidine acetate 0.008 gram, fumaric acid 0.108 to 0.162 gram, tartaric acid 0.012 to 0.018 gram, solium bicarbonate 0.12 to 0.18 gram, starch 0.02 to 0.04 gram, dextrin 0.003 to 0.007 gram, hydroxypropyl cellulose 0.007 to 0.013 gram, talc 0.01 to 0.017 gram, sodium dodecyl sulfate 0.01to 0.02 gram, and proper proportion of povidone K30 water solution. According to the preparation method, the components are mixed to produce granule (1) and granule (2); the talc, sodium dodecyl sulfate and the granule (1) and granule (2) are mixed uniformly; granule content is tested and according to the granule content, the tablet weight is identified for tabletting. The invention overcomes the shortages with prior art, enables the acetic acid chlorhexidine acetate to perform functions normally, performs synergistic effects of the three drugs, and greatly enhances the cure rate. Besides, the frothing volume is high, and within storage period, the quality is stable and the drug effects are not affected.
Owner:SHANDONG SBOND PHARMA
Nanometer clotrimazole emulsion medicine and its prepn process
InactiveCN1931163AEnhanced inhibitory effectHigh thermodynamic stabilityOrganic active ingredientsAntimycoticsSkin permeabilityDistilled water
The nanometer clotrimazole emulsion medicine consists of surfactant, oil, clotrimazole and distilled water. Its preparation process includes the following steps: weighing surfactant with or without co-surfactant; calculating HLB value and selecting oil for reaching emulsifying HLB value near that of the surfactant phase; dissolving clotrimazole into surfactant; changing the ratio between the surfactant phase and the oil phase regularly; adding distilled water slowly at 20-25 deg.c to form clear and flowing O / W type stable nanometer emulsion liquid. The nanometer clotrimazole emulsion has high skin permeability, no contamination to clothing, high dissolubility of clotrimazole, raised bioavailability of clotrimazole, delayed metabolism time and wide medicine market foreground.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Method for preparing clotrimazole buccal tablets on basis of all-powder direct pressing of modified glucose
ActiveCN105030707AGood compressibilityHigh dissolution rateOrganic active ingredientsAntimycoticsDextrose MonohydrateAlcohol
The invention belongs to the technical field of pharmaceuticals and relates to a method for preparing clotrimazole buccal tablets on basis of all-powder direct pressing of modified glucose. The clotrimazole buccal tablets are composed of the modified glucose, filler, lubricant and disintegrant. The modified glucose is prepared from dextrose monohydrate and binder; the binder is povidone K30. The percentage by weight of the povidone K30 is 0.1% to 0.1% of that of the modified glucose, preferably 0.1% to 0.5% and more preferably 0.1% to 0.3%. Water and ethyl alcohol are used as solvents for the povidone K30 and are subjected to granulating, drying and size stabilizing with the dextrose monohydrate, and water content of the modified glucose is 0.5% to 3%. A single dose of the clotrimazole buccal tablets contains 10mg of an active ingredient, clotrimazole.
Owner:南京泽恒医药技术开发有限公司
Filming aerosol for treating tinea coporis, tinea manuum and tinea pedis
ActiveCN1608669AGood film formingPrevent volatilizationSalicyclic acid active ingredientsAntimycoticsHealing ratePhenols
The filming aerosol for treating tinea coporis, tinea manuum and tinea pedis is prepared with salicylic acid, Clotrimazole, phenol, camphor, wintergreen oil, glycerin and alcohol, and through conventional preparation process. The present invention has the advantages of being convenient, clean and high in healing rate. The medicine liquid forms film on skin, and this can prevent volatilization of medicine component, last effect and avoid contamination to clothing. In addition, the medicine liquid has lauryl azatroketone as transdermal promoter added and has thus fast release of medicine component, strengthened absorption of skin to medicine and high curative effect.
Owner:GUIZHOU JINGCHENG PHARMA
Metronidazole vaginal tablet process and quality control method
InactiveCN101283989AEasy to useUse cleanOrganic active ingredientsPill deliveryDiseaseChlorhexidine Acetate
The invention relates to a preparation method and a quality control method of a new gynecologic drug, Metronidazole, Clotrimazole and Chlorhexidine Acetate Vaginal Tablets, with antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects. The added lactic acid-calcium lactate buffer system results in a drug with pH of 3.5-4.0 t that is similar to the physiological pH in vagina, so as to effectively retain physiological environment in vagina, provide existing conditions suitable for vaginal beneficial bacteria, and promote rehabilitation. The main preparation method comprises the steps of compounding, granulating, grading, mixing, and tabletting. The quality control method comprises the steps of collecting one dosage unit of the product, grinding, adding 100mL water, shaking for 10min, and testing pH (should be 3.5-4.0); testing melting time limit (should be 30min); and measuring the nominal content of the three components by high performance liquid chromatography (should be both in the range of 90.0-110.0%).
Owner:何文健
Dental medicinal membrane and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103919786ALow costEasy to prepareAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsClotrimazoleAnti bacterial
The invention discloses a dental medicinal membrane. The dental medicinal membrane comprises the following components by weight: 3-8g of clotrimazole, 3-8g of dyclonine, 1-3g of metronidazole, 0.3-0.6g of dexamethasone, 10-18g of CMC-Na (sodium carboxymethylcellulose), 40-60g of sodium alginate, 12-18g of tragacanth, 100-150g of ethanol and 1,000-1,500g of purified water. The invention also provides preparation of the dental medicinal membrane, which comprises the following steps: (1) soaking the sodium alginate with ethanol, and grinding in a mortar for later use; (2) naturally peptizing the tragacanth and CMC-Na in the purified water; (3) dissolving the clotrimazole and metronidazole in ethanol, and slowly adding the solution into the mortar in the step (1); dissolving the dexamethasone and metronidazole in the purified water, mixing with the solution in the step (2), slowly adding the mixture into the mortar in the step (1), and constantly grinding to obtain a colloidal liquid; and (4) preparing a membrane from the colloidal liquid, drying and subpackaging. The dental medicinal membrane is low in cost, simple in preparation method and remarkable in treatment effect, and has the effects of inhibiting bacteria and diminishing inflammation; and the dental medicinal membrane is an external application, and is applied to an affected part.
Owner:QINGDAO MUNICIPAL HOSPITAL
Method for determining influence of pollutants on content of active oxygen in green alga cells
PendingCN112033878AAccurate judgment of active oxygen contentJudgment of active oxygen contentMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesPyrenoidCell
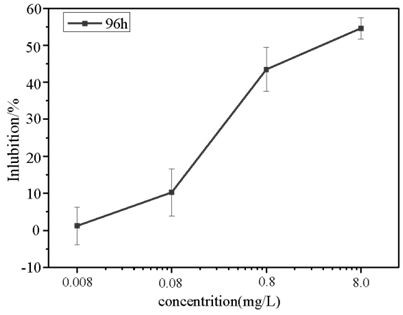
The invention discloses a method for determining the influence of pollutants on the content of active oxygen in green alga cells. Chlorella pyrenoidosa is used for evaluating the influence of a typical pollutant azole bactericide (clotrimazole) on the content of active oxygen in green alga cells; and evaluating the influence of pollutants on active oxygen in the green alga cells according to the DCF fluorescence intensity of the single green alga cells under the action of the azole bactericide pesticide. According to the method, the detection result of the change of the content of the active oxygen in the green alga cells is more accurate, and the problem that the fluorescence intensity measurement is inaccurate due to the change of the number of the cells caused by exposure of pollutantsat different concentrations is solved. The fluorescence intensity of DCF is in direct proportion to the content of active oxygen in cells, so that the influence of pollutants on the content of activeoxygen in cells under a certain concentration can be reflected more intuitively. The method is simple, convenient and rapid in test, low in detection system background, high in sensitivity and good inrepeatability.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry detection method for clotrimazole residues in animal-derived food
ActiveCN110887911AQuick extractionReduce usageComponent separationBiotechnologyGas liquid chromatographic
The invention discloses a gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry detection method for clotrimazole residues in animal-derived food. According to the method, the clotrimazole residues in animal muscle, fat and viscera samples are extracted with a cyclohexane / ethyl acetate mixed solvent accelerated solvent, an extracting solution is purified through gel permeation chromatography and then detected in a gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry multi-reaction monitoring mode and quantification is conducted through an isotope internal standard method. Under optimized conditions, clotrimazolehas a good linear relationship within the range of 1.0-100 [mu] g / L, the correlation coefficient is 0.9995 and the limit of quantitation of the method is 1.0 [mu] g / kg. The average recovery rate of the method is 76.5%-107.4% and the relative standard deviation is not greater than 6.2%. The method is high in extraction efficiency, good in purification effect, high in sensitivity and good in repeatability and can be used for measuring the residual quantity of clotrimazole in animal muscles, fat and viscera.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SHUREN COLLEGE ZHEJIANG SHUREN UNIV
Preparation method of clotrimazole
ActiveCN111423380AReduce the risk of drug quality impactsEmission reductionOrganic chemistryDiphenylmethanolClotrimazole
The invention provides a preparation method of clotrimazole. The preparation method comprises the following steps: step 1, chlorinating (2-chlorphenyl) diphenyl methanol into (2-chlorphenyl) diphenylchloromethane; 2, subjecting (2-chlorphenyl) diphenyl chloromethane and imidazole to condensation to form clotrimazole; the total reaction flow formula is shown in the specification. The invention provides a preparation method of clotrimazole. The initial raw materials (2-chlorphenyl) diphenyl methanol and imidazole are easy to obtain and stable in performance; reaction condition mildness, a product which is unstable when meeting water and synthesized in step 1 does not need to be separated and purified, and can be applied directly in step 2, not only are the requirements on equipment and operation reduced, but also the risk of influencing the quality of the raw material medicine is reduced; the preparation method is simple in operation, short in process period, high in product purity andsuitable for industrial production, , in addition, the reaction solvent in the step 1 is also the reaction solvent in the step 2, emission of three wastes is reduced, and environmental protection is better facilitated.
Owner:无锡富泽药业有限公司
Foam shampoo capable of removing dandruff, relieving itching and controlling oil and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110787114ARelieve itchingPromote blood circulationAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsBiotechnologyBenzoic acid
The invention discloses foam shampoo capable of removing dandruff, relieving itching and controlling oil and a preparation method of the foam shampoo, and belongs to the technical field of shampoo. The shampoo is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 1-3 parts of fructus cnidii, 1-3 parts of polygonum multiflorum, 3-5 parts of mint, 3-4 parts of raw ginger, 2-4 parts of cacumen biotae, 2.5-4 parts of Chinese honeylocust fruit, 1-2 parts of herba ecliptae, 1-3 parts of radix stephaniae tetrandrae, 0.8-3 parts of salicylic acid, 0.5-1.5 parts of benzoic acid, 1-3 parts ofclotrimazole, 0.6-1.5 parts of pyridinone ethanolamine salt, 0.5-2 parts of climbazole, 10-14 parts of lauryl sodium sulfate, 15-20 parts of fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether sulfate, 40-60 parts of distilled water, 4-8 parts of wool fat and 0.4-0.8 part of essence. The shampoo has the beneficial effects that: the shampoo is prepared from a traditional Chinese medicine plant extracting solutionand skin-friendly raw materials, is healthy and free of toxic and side effects, has the effects of killing insects, inhibiting bacteria, removing dandruff and relieving itching, can inhibit growth ofscalp bacteria and fungi, relieve scalp itching, promote scalp blood circulation, remove scalp grease and improve nutrient absorption of hair follicles, and can relieve tinea capitis, dandruff, scalpoil and scalp itching after being used for a long time.
Owner:施建有
Method for detecting 15 forbidden azoles in children cosmetics
PendingCN114594183AMeet the banned ingredient monitoring requirementsMulti-sensitivityComponent separationMicronazoleLiquid chromatography mass spectroscopy
The invention relates to a method for detecting 15 forbidden azoles in children cosmetics. According to the method, 15 azole substances such as econazole, clotrimazole, ketoconazole, fluconazole, miconazole, neoconazole, benznidazole, metronidazole, metronidazole, ornidazole, tinidazole, isometronidazole, lornidazole, hydroxy metronidazole and bifonazole in the children cosmetics can be efficiently and rapidly detected by adopting a liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry method. The detection method fills the blank of children cosmetic detection standards, is high in pertinence, high in sensitivity and multiple in detection types, and protects children cosmetics.
Owner:GUANGDONG TESTING INST OF PROD QUALITY SUPERVISION
Pharmaceutical composition containing metronidazole
The invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition containing metronidazole and particularly relates to a pharmaceutical composition. The pharmaceutical composition contains metronidazole, clotrimazole, chlorhexidine acetate, sodium carboxymethyl starch, sodium carboxymethylcellulose, glycerine and water. The pharmaceutical composition disclosed by the invention has favorable pharmaceutical properties.
Owner:BEIZHEN SHANQING PHARMA
Textile mold reagent as well as preparation method and use method thereof
InactiveCN108677529AEasy to operateReduce manufacturing costBiochemical fibre treatmentChemistryEssence oil
The invention provides a textile mold reagent which comprises 0.015-150g of analytically pure-grade clotrimazole, 45-150 ml of absolute ethyl alcohol, 0.5-50 ml of lavender essential oil and 150-850 ml of deionized water. By adopting the textile mold reagent, a textile can be effectively prevented from mildew stain or insect stain in long-term preservation, without impacting the quality and the color of the textile, and the textile mold reagent is convenient to operate and low in production cost, and the cost of production companies can be reduced.
Owner:丁爱军
Single-dose packaged clotrimazole liquid composition
PendingCN113423382AImprove complianceReduce Medication ErrorsOrganic active ingredientsAntimycoticsClotrimazolePharmacy
It relates to a single-dose packaging unit which is a blow-fill-seal (BFS) container which comprises a sterile pharmaceutical or veterinary liquid composition which is a solution, wherein a) the composition comprises a therapeutically effective amount of clotrimazole or a pharmaceutically or veterinary acceptable salt thereof, together with one or more pharmaceutically or veterinary acceptable excipients or carriers, and b) the container has a volume from 0.05 to 8 mL, with the condition that the water content of the composition is equal to or lower than 4% by weight with respect to the total composition weight. It also relates to a secondary packaging comprising one or more single-dose packaging units.
Owner:LAB SALVAT
Treatments for free-living amoebic infections
ActiveUS10806741B2Effective treatmentReduce adverse side effectsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPhosphorous compound active ingredientsAmoebic encephalitisSappinia
Methods of treating infections caused by free-living amoeba are disclosed. The methods generally include systemic administration of an effective amount of miltefosine, such as an oral or intravenous formulation, and optionally local administration of an effective amount of miltefosine, such as a topical formulation of miltefosine. The methods may further include administration of one or more secondary agents. Exemplary secondary agents include steroids, polyhexamethylene biguanide (PHMB), chlorhexidine, propamidine isethionate, dibromopropamidine isethionate, neomycin, paromomycin, polymyxin B, clotrimazole, ketoconazole, miconazole, and itraconazole. The methods may be used to treat patients with infections caused by a free-living amoeba such as Naegleria fowleri, Balamuthia mandrillaris, Sappinia diploidea, and Acanthamoeba species. Exemplary infections include Acanthamoeba keratitis, granulomatous amoebic encephalitis, cutaneous acanthamoebiasis, primary amoebic meningoencephalitis, Sappinia amoebic encephalitis, or a disseminated disease associated with a free-living amoeba.
Owner:PROFOUNDA
Shuangzotai vaginal expansion suppository and its preparation method and detection method
ActiveCN103284996BImprove bioavailabilityPrevent outflowOrganic active ingredientsSuppositories deliveryChlorhexidine AcetateImmediate release
The invention relates to a Shuangzotai vaginal expansive suppository. The expansive suppository includes an active ingredient composed of clotrimazole, metronidazole and chlorhexidine acetate, a fat-soluble matrix and an expansive carrier. The drug layer is in full contact with the inner wall of the vagina to prevent the drug liquid from flowing out; the expansion plug is an inner and outer layer expansion plug, and the active ingredient is mixed with different substrates to form two layers, which can achieve dual effects of quick release and sustained release; The Shuangzotai vaginal expansion suppository provided by the present invention adopts seven original leading technologies, and the Shuangzotai vaginal expansion suppository has the functions of preventing the outflow of medicinal liquid, quick effect, long drug action time, and prevention of secondary infection, etc. Beneficial effect.
Owner:哈尔滨田美药业股份有限公司
A kind of mixing device and method for clotrimazole cream production
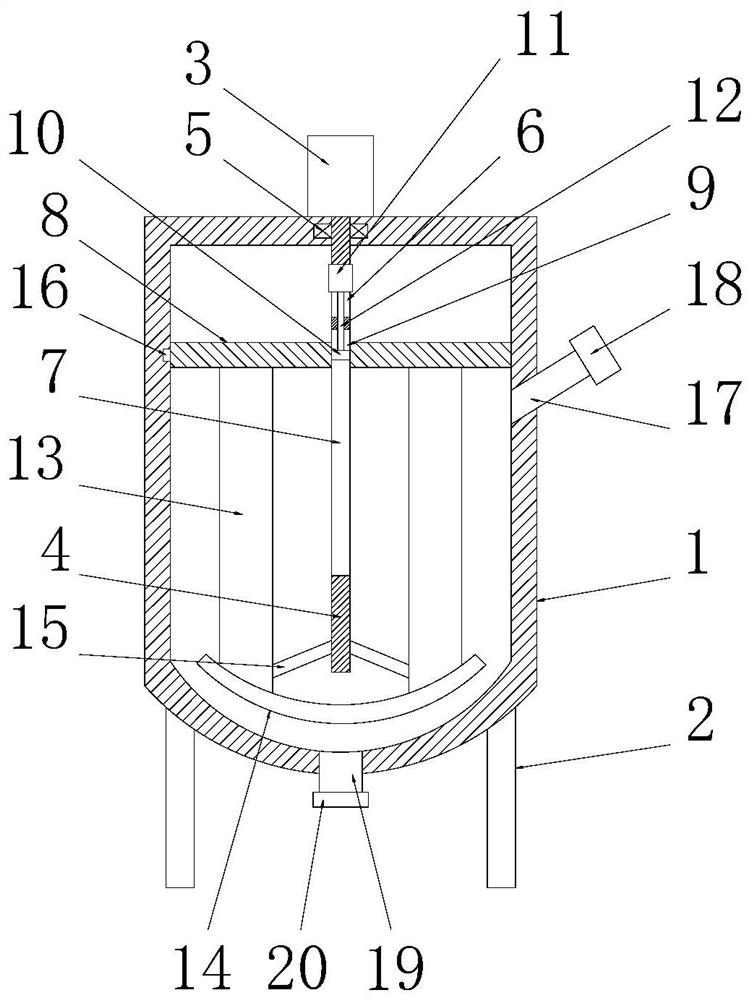
ActiveCN112221411BAvoid stickingGuaranteed outputRotary stirring mixersTransportation and packagingClotrimazoleElectric machinery
The invention discloses a mixing device and method for clotrimazole cream production, comprising a kettle body, the top of the kettle body is fixedly connected with a mixing motor, the inner cavity of the kettle body is provided with a stirring rod, and the stirring rod is provided with a power chamber and the chute, the outer side of the stirring rod is provided with a stirring plate matched with the kettle body, the stirring plate is provided with a sleeve hole, and the sleeve hole is provided with a slide bar matched with the chute, the The top wall of the inner cavity of the power chamber is fixedly connected to the electric telescopic device, and the bottom end of the telescopic rod on the electric telescopic device penetrates the bottom wall of the power chamber and is fixedly connected to the slide rod; the present invention stretches out the telescopic rod through the electric telescopic device, Then use the telescopic rod to push the slide bar down along the chute, and then push the stirring plate down along the inner cavity wall of the kettle body, and then use the stirring plate to squeeze the cream in the inner cavity of the kettle body and discharge it from the discharge pipe, which can effectively It prevents the cream from adhering to the inner wall of the kettle body, can completely discharge the cream in the kettle body, and can effectively ensure the output of the cream.
Owner:河南大新药业有限公司
Pharmaceutical composition containing metronidazole
The invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition containing metronidazole and particularly relates to a pharmaceutical composition. The pharmaceutical composition contains metronidazole, clotrimazole, chlorhexidine acetate, sodium carboxymethyl starch, sodium carboxymethylcellulose, glycerine and water. The pharmaceutical composition disclosed by the invention has favorable pharmaceutical properties.
Owner:BEIZHEN SHANQING PHARMA
External skin ointment and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110638835AUnique effectNo side effectsHeavy metal active ingredientsAntimycoticsSkin OintmentDrug ointment
The invention provides an external skin ointment and a preparation method thereof, and relates to the technical field of traditional Chinese medicine. The external skin ointment is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by mass: 8-12 parts of triamcinolone acetonide acetate and miconazole nitrate and neomycin sulfate cream, 18-22 parts of urea cream, 18-22 parts of clotrimazole cream,8-12 parts of erythromycin cream, 8-12 parts of badger fat, 1-1.4 parts of chloramphenicol injection, 2.2-2.6 parts of metronidazole tablets, 2-4 parts of borneol and 4-8 parts of mercurous chloride.The external ointment has peculiar effects and no toxic and side effects and has a skin-care effect, and the skin can be more delicate after use.
Owner:李生林
Metronidazole-clotrimazole-chlorhexidine acetate vaginal expansive suppository controlled-release preparation and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103735547AImprove stabilityStable drug releaseOrganic active ingredientsAntisepticsClotrimazoleChlorhexidine Acetate
The invention relates to a metronidazole-clotrimazole-chlorhexidine acetate vaginal expansive suppository controlled-release preparation and a preparation method thereof. The metronidazole-clotrimazole-chlorhexidine acetate vaginal expansive suppository controlled-release preparation comprises a suppository core and a controlled-release coating at the outer layer of the suppository core, wherein the controlled-release coating consists of a special coating material and a plasticizer, so that the expansive suppository controlled-release preparation has a zero-order stable release effect; moreover, by using the controlled-release coating, the expansive suppository controlled-release preparation can be stabilized, and the irritation of the controlled-release preparation on the vagina can be lowered; furthermore, by adopting seven types of unique leading technologies, the metronidazole-clotrimazole-chlorhexidine acetate vaginal expansive suppository controlled-release preparation has the beneficial effects of preventing a liquid medicament from flowing outwards, preventing secondary infection, and the like.
Owner:哈尔滨田美药业股份有限公司
Mixing device and method for clotrimazole cream production
ActiveCN112221411AImprove mix qualityEnsure mixing qualityRotary stirring mixersTransportation and packagingClotrimazoleElectric machinery
The invention discloses a mixing device and method for clotrimazole cream production. The mixing device comprises a kettle body, a mixing motor is fixedly connected to the top end of the kettle body,a stirring rod is arranged in an inner cavity of the kettle body, a power cavity and a sliding groove are formed in the stirring rod, a stirring plate matched with the kettle body is arranged on the outer side of the stirring rod in a sleeving mode, and a sleeve hole is formed in the stirring plate; and a sliding rod matched with the sliding groove is arranged in the sleeve hole, the top wall of an inner cavity of the power cavity is fixedly connected with an electric telescopic device, and the bottom end of a telescopic rod on the electric telescopic device penetrates through the bottom wallof the power cavity and is fixedly connected to the sliding rod. The telescopic rod extends out of the electric telescopic device, then the telescopic rod is used for pushing the sliding rod to descend along the sliding groove, then a stirring plate is pushed to descend along the inner cavity wall of the kettle body, cream in the inner cavity of the kettle body can be extruded by the stirring plate to be discharged from a discharging pipe, and the cream can be effectively prevented from adhering to the inner cavity wall of the kettle body; and thus the cream in the kettle body can be completely discharged, and the yield of the cream can be effectively guaranteed.
Owner:河南大新药业有限公司
Ear drops for treating otomycosis externa and preparation method of ear drops
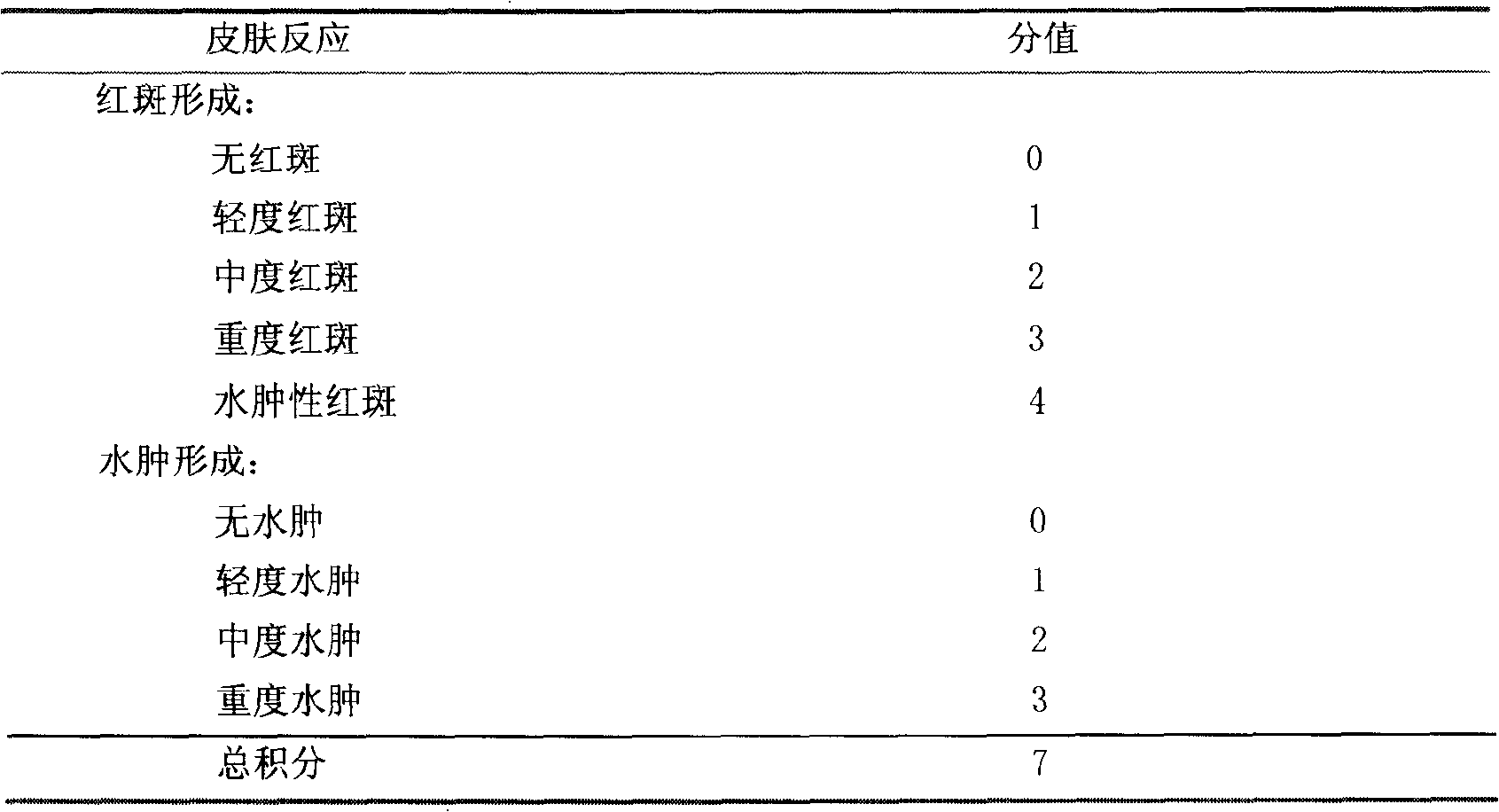
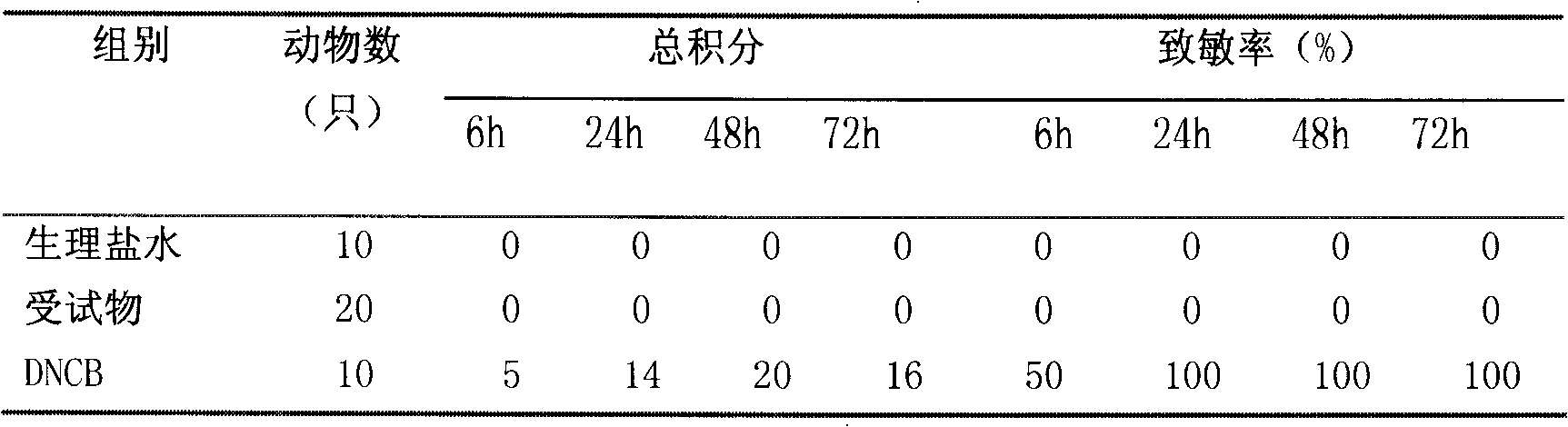
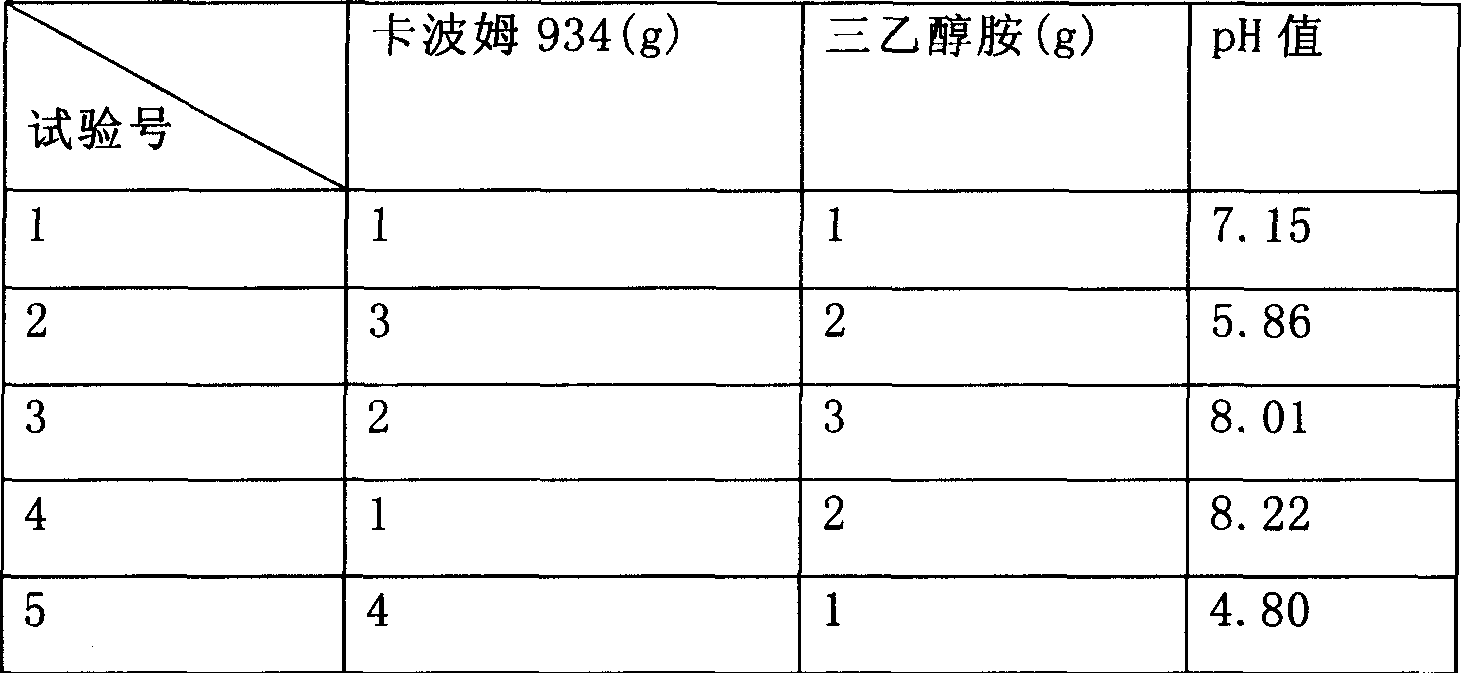
ActiveCN111249219AGood antibacterial effectGood treatment effectOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderClotrimazoleItraconazole
The invention discloses ear drops for treating otomycosis externa and a preparation method of the ear drops. The ear drops for treating otomycosis externa comprise components in percentage by mass asfollows: 3%-20% of itraconazole, 2%-10% of clotrimazole, 0.8%-2.3% of Carbomer-940, 5%-15% of glycerin, 0.5%-1.5% of triethanolamine and the balance purified water. The preparation method comprises steps as follows: glycerin and Carbomer-940 are dissolved by the purified water, triethanolamine is added during stirring, transparent gel is obtained after the components are stirred uniformly, itraconazole and clotrimazole are added to the transparent gel to be stirred, the purified water is added until the overall mass fraction is 100%, all the components are stirred uniformly, and the ear dropsare obtained. The ear drops have the advantages of being good in antibacterial effect, high in cure rate, convenient and simple to administrate and capable of realizing uniform spraying, producing little stimulation to ears, being easy to store and the like, the preparation method is simple and convenient, and the cost is low.
Owner:THE THIRD XIANGYA HOSPITAL OF CENT SOUTH UNIV
Clotrimazole cream and preparation method thereof
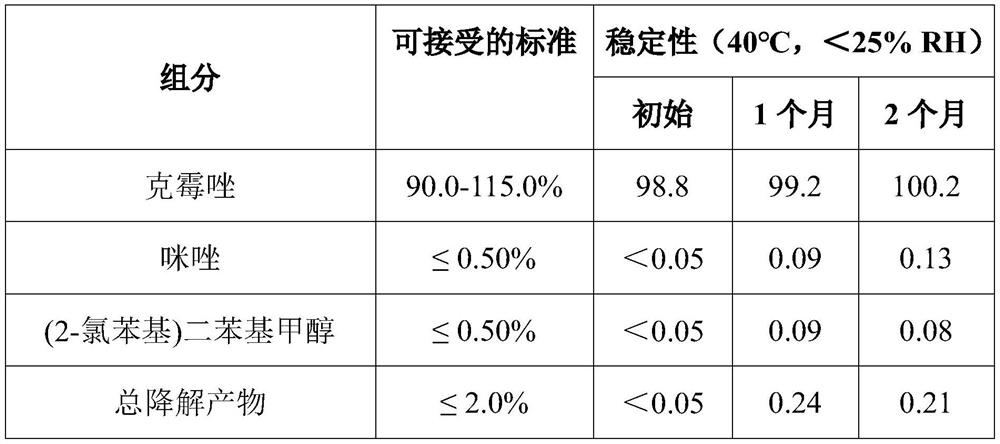
InactiveCN110237025ASmooth releaseSudden releaseOrganic active ingredientsAntimycoticsReduced doseOil phase
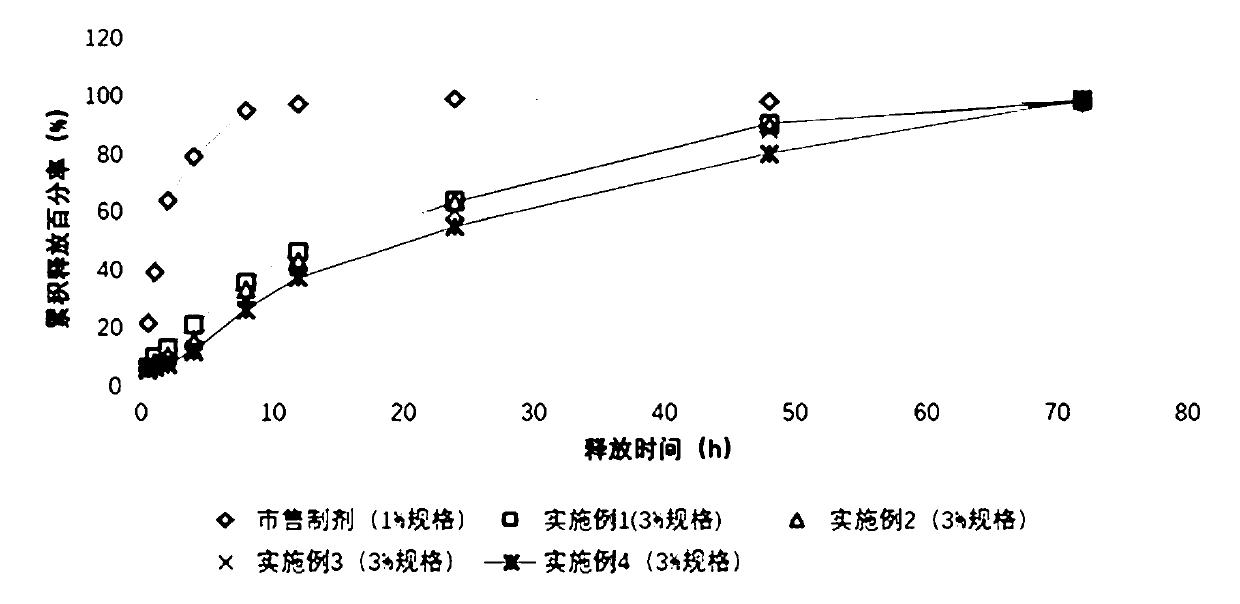
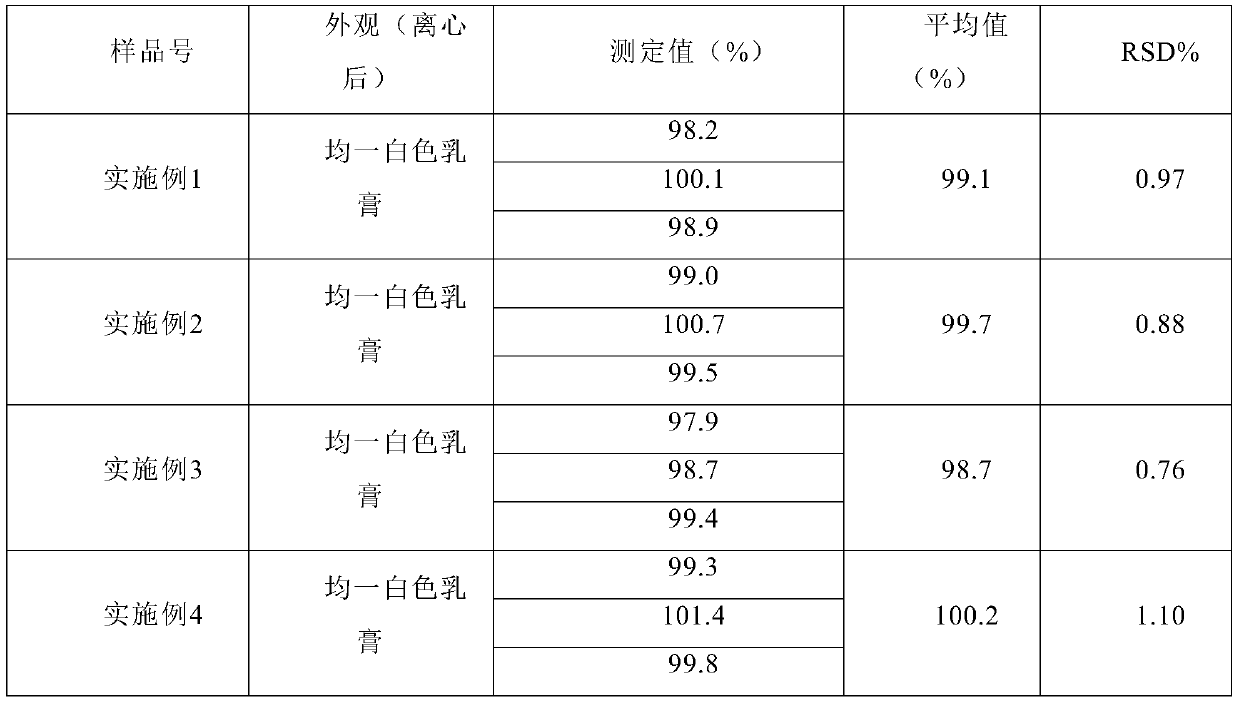
The present invention relates to a quality-stable clotrimazole cream (3%) and a preparation method thereof. The clotrimazole cream is prepared from the following components: clotrimazole, isopropyl myristate, cetanol, octadecanol, Tween 60, Span 60, benzyl alcohol and purified water; and the clotrimazole cream is prepared by heating and melting an oil phase (including the cetanol, octadecanol, isopropyl myristate, partial Tween 60, and Span 60), homogenizing and mixing with an aqueous phase (including the purified water and benzyl alcohol) and a drug phase (including the purified water, Tween 60 and clotrimazole) at a certain temperature, and then conducting rapid cooling. The clotrimazole cream can be slowly and smoothly released in a medium of pH 4.5 (in simulated vaginal conditions) to reduce dose risks, besides, physicochemical stability of the clotrimazole cream is superior to that of other clotrimazole cream products, and the preparation process is simple, short in time consumption, low in energy consumption, and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:HARVEST PHARMA HUNAN CO LTD
Prescription and preparation method of compound ornidazole suppository for treating vaginitis
InactiveCN105663125AExtract completelySimple preparation processOrganic active ingredientsSuppositories deliveryGelatin matrixMedicine
The invention relates to technical field of gynecology medical treatment, in particular to a prescription and preparation method of a compound ornidazole suppository for treating vaginitis.The compound ornidazole suppository is prepared by, by weight, 20-30 parts of ornidazole, 15-20 parts of clotrimazole and 365-375 parts of glycerin gelatin.The preparation method includes: evenly grinding the ornidazole, the clotrimazole and the glycerin gelatin, then adding into glycerin gelatin matrix melt by heat, pouring into a suppository die while the mixture is hot, and solidifying, smoothing and packaging to obtain the compound ornidazole suppository.The preparation method has the advantages that the influence of the matrix on content measuring can be eliminated, complete medicine extraction is achieved, the content measuring of the ornidazole and the clotrimazole is unaffected, and the absorbance of the ornidazole and the clotrimazole in a certain time is constant.The compound ornidazole suppository is simple in preparation process and stable in curative effect.The compound ornidazole suppository is sensitive and accurate, good in repeatability and easy to master when high performance liquid chromatography is used for measuring main components.
Owner:李达
Otic formulations, methods and devices
PendingUS20210106597A1Significant pain reliefLess bacterial community resistanceOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENTAntibiotic drug
The present invention relates to a formulation and method for treating an ear infection, especially otomycosis and otitis externa, by administering a one-time only treatment comprising an antibiotic, antifungal, and an anti-inflammatory in a thick, otic carrier. In one embodiment, the formulation comprises a therapeutically effective amount of active ingredients including a marbofloxacin, terbinafine and / or clotrimazole and dexamethasone.
Owner:DECHRA VETERINARY PROD
Plaster for treating dermatophytosis and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a plaster for treating dermatophytosis and a preparation method thereof, and relates to the technical field of plasters. The plaster for treating dermatophytosis is prepared from the following components: econazole nitrate, triamcinolone acetonide, glycerin, triethanolamine, clotrimazole, albolene, lauryl sodium sulfate, butylated hydroxytoluene, purified water, fluocinoloneacetonide, disodium edetate, Kathon and auxiliary Chinese herbal medicines, can effectively kill and inhibit fungi, treat dermatophytosis and other various skin diseases, is quick and convenient to use, and has good use experience and high treatment effect. Furthermore, the invention provides a preparation method of the plaster for treating dermatophytosis. The preparation method comprises the steps of auxiliary Chinese herbal medicine preparation and plaster preparation, and the whole preparation method is simple in process, and the prepared plaster product has a good treatment effect and excellent use experience.
Owner:张德斌
Compound salicylic acid and clotrimazole aerosol
InactiveCN102626414ANot destructiveEasy to retrofitSalicyclic acid active ingredientsAntimycoticsAlkaneHydrocotyle bowlesioides
The invention discloses a compound salicylic acid and clotrimazole aerosol. Formula raw materials of the aerosol comprise salicylic acid, clotrimazole, phenol, camphor, methyl salicylate, glycerin, and ethanol, and a propellent adopts a hydrofluoroalkane of tetrafluoroethane or heptafluoropropane (HFA227), dimethyl ether (DME), a hydrocarbon or a compressed gas. The volume or weight ratio of the propellent to the formula raw materials is 1:1. The aerosol which uses HFA134a to substitute F-12 as the propellent can avoid the destroy to the atmospheric ozone layer, can realize energy saving and consumption reduction in the medicinal preparation process, and has substantial economic benefits.
Owner:GUIZHOU JINGCHENG PHARMA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com