Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
39 results about "Chaetomium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Chaetomium is a genus of fungi in the Chaetomiaceae family. It is a dematiaceous (dark-walled) mold normally found in soil, air, cellulose and plant debris. According to the Dictionary of the Fungi (10th edition, 2008), there are about 95 species in the widespread genus.
Nano silver antibacterial latex pillow or mattress and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102010528AUnique antibacterial propertiesAntimicrobial properties provide unique antimicrobial properties uniquePillowsStuffed mattressesChaetomiumPaecilomyces
The invention discloses a nano silver antibacterial latex pillow or mattress and a preparation method thereof. Tiny air holes are fully distributed on the surface of the nano silver antibacterial latex pillow or mattress, and air is filled into the tiny air holes; and the silver antibacterial latex pillow or mattress has bacterial resistance on aspergillus niger, aspergillus flavus, discolored aspergillus, penicillium citrinum, paecilomyces varioti, herbarium cladosporium, trichoderma viride and chaetomium globasum. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: uniformly mixing nano sliver with natural latex; then respectively adding sulphur, bi(triethoxy propylsilane)tetrasulfide and 2,6-butylethylene-4-methylphenol; uniformly stirring; adding soap and air to generate foams; then adding gelatin; and compressing for moulding. The nano silver antibacterial latex pillow or mattress of the invention combines air permeability, high elasticity and soft touch feeling of the latex with efficient bacterial resistance and broad spectrum sterilizing performance of nano silver and can effectively overcome the defects of easy bacterial generation, difficult air permeation, and the like of a common pillow on the market.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Biological organic fertilizer with insect expelling function and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101913956AIncrease contentHigh in nutrientsBio-organic fraction processingOrganic fertiliser preparationThermomonospora fuscaPeat
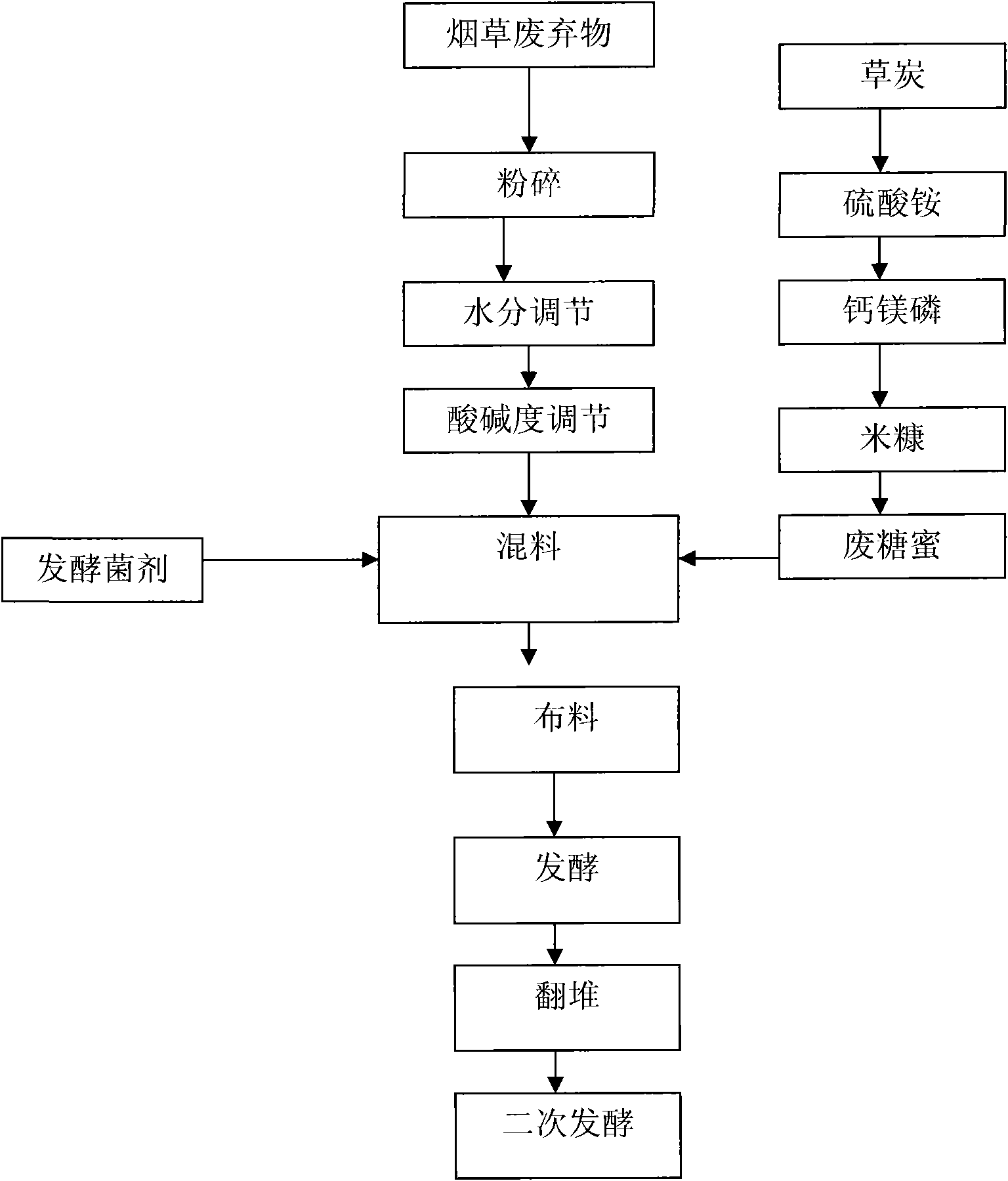
The invention discloses a biological organic fertilizer with an insect expelling function and a preparation method thereof. The fertilizer comprises the following components: tobacco waste, 1 to 2 percent of calcium-magnesium phosphate, 1 to 2 percent of ammonium sulfate, 3 to 5 percent of waste molasses and 0.3 to 0.5 percent of zymocyte based on the total weight of the tobacco waste; and the zymocyte comprises 20 to 35 weight percent of trichoderma viride, 20 to 35 weight percent of bacillus subtilis, 10 to 20 weight percent of rhizopus oryzae, 10 to 20 weight percent of chaetomium and 10 to 20 weight percent of thermomonospora fusca. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: pretreating the tobacco waste; smashing tobacco waste raw materials into sawdust-like grains of 40 to 60 meshes; then adjusting the carbon-to-nitrogen ratio of the raw materials to 20 to 30:1 with grass peat or straw powder; and then adjusting the pH value to 6.5 to 7.5 with Ga(OH)2 and the water content to 40 to 50 weight percent. Due to the adoption of the biological organic fertilizer with the insect expelling function, nicotine in the raw materials can be preserved to the greatest extent, insect damage degree is lowered, the using amount and times of agricultural chemicals are reduced, the application of the agricultural chemicals is effectively reduced, and the production is environmentally friendly.
Owner:MICROBIAL FERMENTATION ENG RES CENT CO LTD OF YUNNAN PROVINCE
Rhodotorula glutinis oil genetic engineering strain and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN102796675AImprove the lubrication effectImprove securityFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyLipid formation
The invention relates to a rhodotorula glutinis oil genetic engineering strain and a construction method and an application thereof. The construction method of the genetic engineering strain is mainly as follows: utilizing rDNA (recombinant deoxyribonucleic acid) of rhodotorula glutinis as a target sequence for homologous integration, using strong promoter genes PGK1 of saccharomyces cerevisiae and malate dehydrogenase genes ME of chaetomium cochloides to construct an expression vector to be introduced into rhodotorula glutinis, and enabling ME genes to obtain high-efficient expression in a rhodotorula glutinis body, wherein the content of lipid in a transformant is improved by 2.5 times in comparison with a wild strain. According to the construction method disclosed by the invention, key enzyme genes and a strong promoter for anabolism of the lipid are introduced on the basis that the anabolism of microbial oil is known, so that the lipid metabolism is regulated and controlled, and the yield of oil is improved. The genetic engineering strain can be applied to production of the microbial oil and development of functional oil related products, such as medicaments, health care products and the like.
Owner:广州溯原生物科技股份有限公司
Animal feed additives
InactiveUS7217433B2Improve feed utilizationReduce chyme viscosityMicroorganismsMicroorganism based processesDNA constructMucor species
The present invention relates to animal feed additives, which additives comprise a monocomponent xylanase derived from a strain of Byssochlamus, Chaetomium, Humicola, Malbranchea, Mucor, Myceliophthora, Paecilomyces, Talaromyces, Thermoascus, or Thielavia. In other aspects, the invention relates to monocomponent xylanase preparations, DNA constructs, recombinant expression vectors, host cells, and methods of producing monocomponent xylanase preparations.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
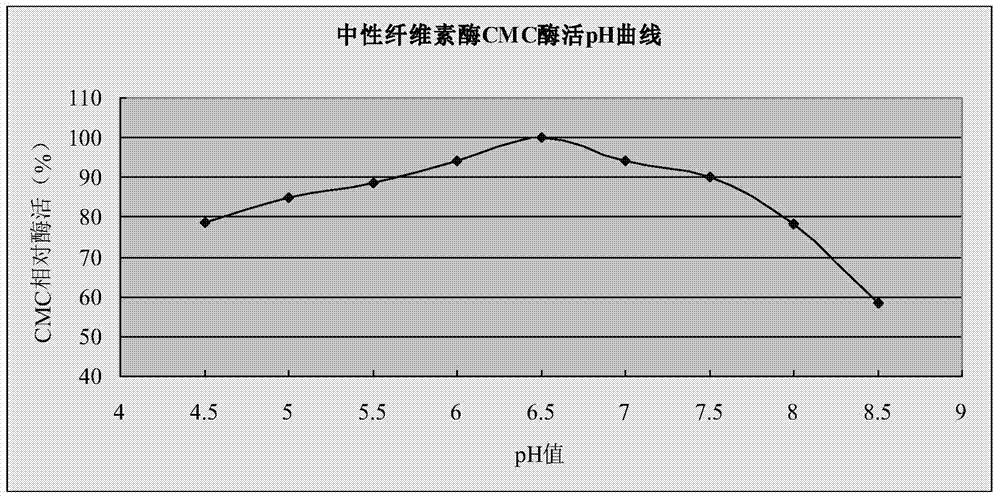
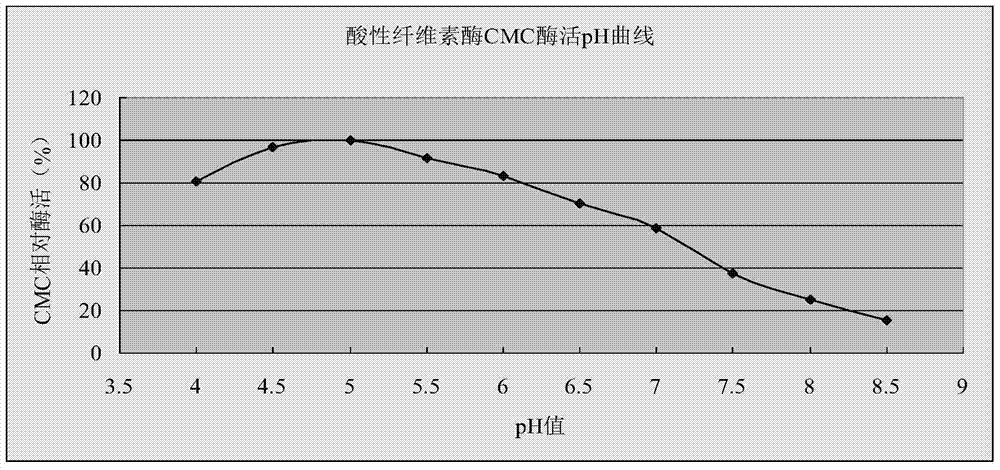
Application of thermophilic Chaetomium cellulose to polishing, dyeing and one-bat technology
ActiveCN105155167AImprove polishing effectReduce dosageTextile treatment machine arrangementsEnzymesHigh concentrationChaetomium
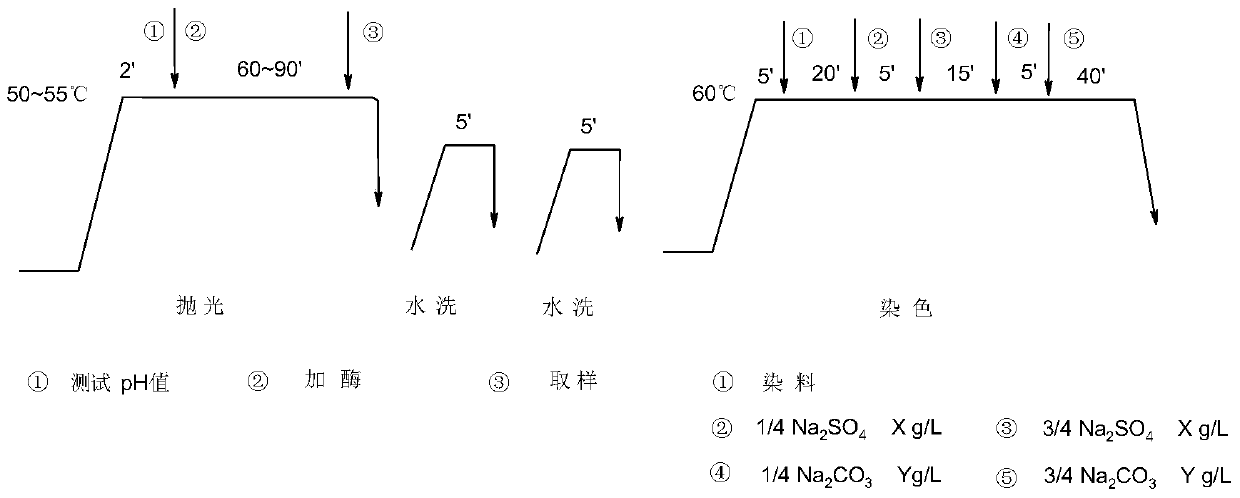
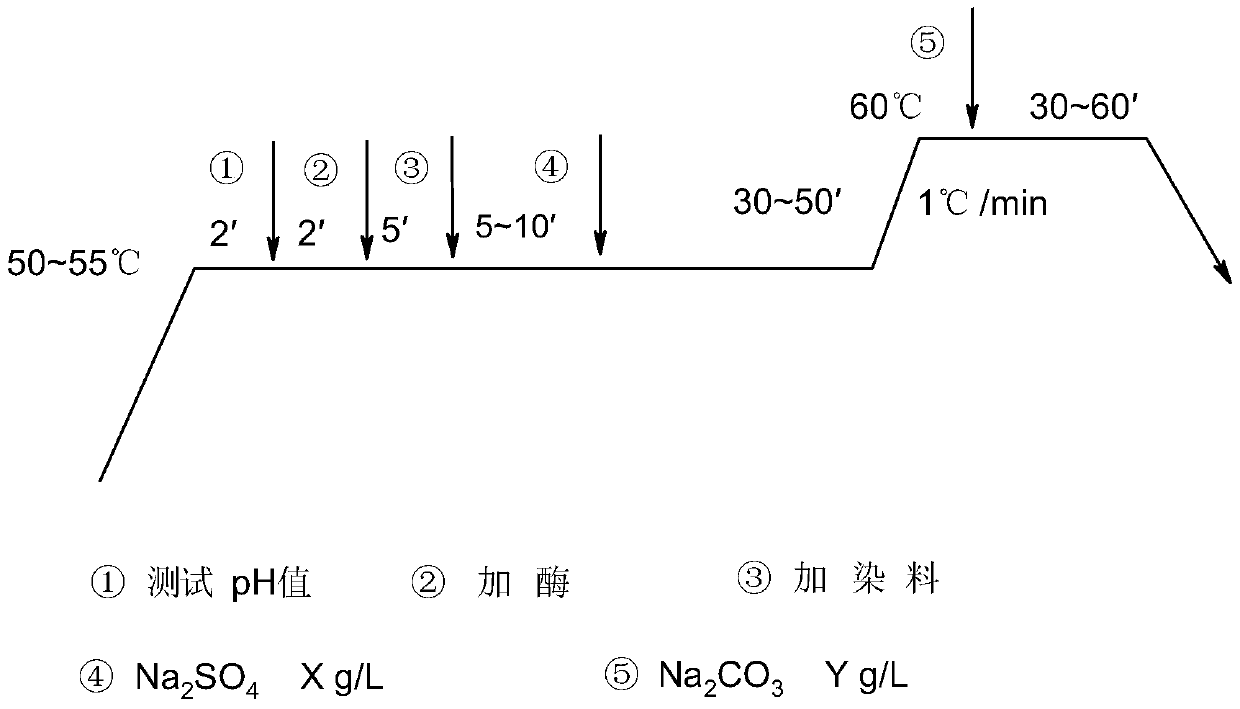
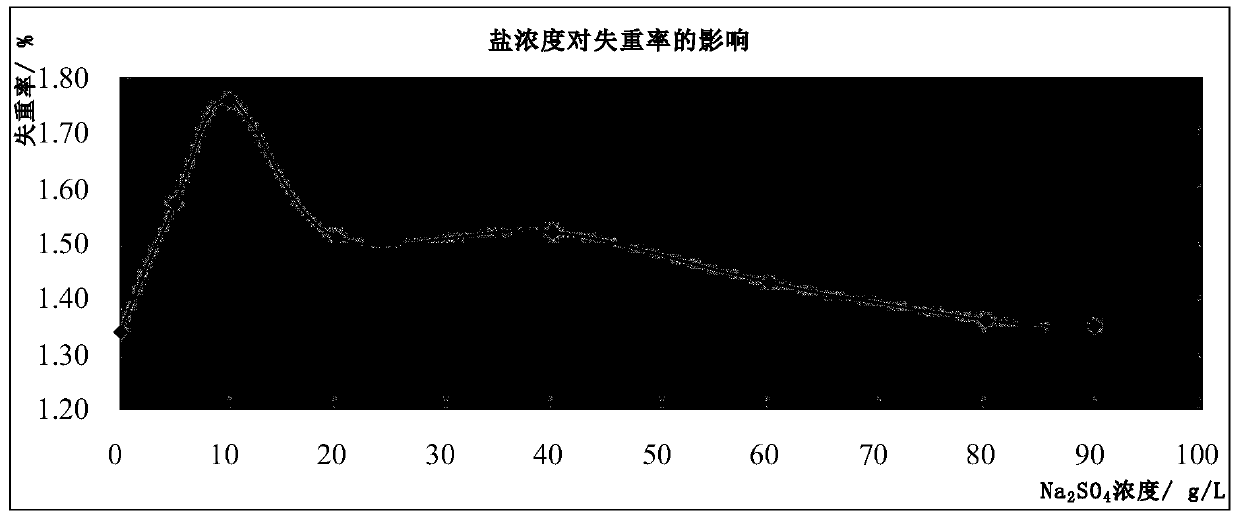
The invention discloses an application of thermophilic Chaetomium cellulose to polishing, dyeing and one-bat technology. The thermophilic Chaetomium cellulose is expressed via Trichoderma reesei or pichia pastoris; the thermophilic Chaetomium cellulose is neutral cellulose having a halophilic function; salt with high concentration has obvious lifting action on activity of neutral cellulose; the optimal action temperature of the neutral cellulose is 57 to 63 DEG C, so polishing temperature and dyeing temperature are the same; during the polishing, even dyeing can be achieved and guaranteed.
Owner:希杰尤特尔(湖南)生物科技有限公司 +1
Decomposing agent for rapidly decomposing straws
InactiveCN105316247ASimple structureHigh organic contentBio-organic fraction processingFungiBacillus licheniformisAspergillus flavus
A decomposing agent for rapidly decomposing straws is characterized in that the decomposing agent comprises 20% of aerobic Bacillus subtilis, 10% of Bacillus licheniformis, 20% of Aspergillus flavus, 20% of Chaetomium seminudum, 20% of Absidia corymbifera and 10% of yeast. A production technology of the decomposing agent comprises the following steps: extracting different organic matter beneficial decomposing bacteria from different environments, and respectively carrying out purification, rejuvenation, propagation and culture; inoculating all cultured single strains into a disinfected solid medium in proportion, fermenting at 25-50DEG C for 4-5d, and carrying out air drying until the water content reaches 25%; and proportioning the air-dried single solid strains according to the above formula, uniformly stirring, and packaging to obtain the solid decomposing agent.
Owner:高云
Biopesticide for preventing cydia pomonella
InactiveCN104872217ANo pollution in the processNo harmBiocideAnimal repellantsPesticide residueFusarium
The invention relates to biopesticide for preventing cydia pomonella. The biopesticide is harmless to people and livestock, generates no phytotoxicity on crops and is free of pesticide residue and environment pollution. The biopesticide comprises following extracts, auxiliaries and synergists including, wherein the extracts include, by weight, 150-200 parts of matrine, 100-150 parts of nicotine, 150-200 parts of cynanchum komarovii, 50-70 parts of tripterygium wilfordii, 80-120 parts of saponin, 50-80 parts of agrimonia pilosa, 40-60 parts of stellera chamaejasme, 80-120 parts of melia azedarach fruit, 40-60 parts of melia azedarach bark, 80-100 parts of pyrethrum flower, 50-80 parts of radix stemonae, 50-80 parts of geranium wilfordii, 200-500 parts of euphorbic acid; the auxiliaries are penetrant, emulgator and stabilizer; the synergists are fungal biocontrol agents composed of trichoderma, penicillium, chaetomium, cylindrocarpon tonkinense, fusarium, beauveria bassiana and metarrhizium anisopliae.
Owner:吴迪
Saccharomyce engineering strain for expressing cbh2 gene and its construction method
A genetically engineered yeast Pichia pastoris GS-D is prepared through screening the thermophilic chaetomium CT2 by PCR method to obtain cellobiohydrolase II gene, cloning it, inserting it in the expression carrier of Pichia yeast, introducing it to Pichia yeast and screening said genetically engineered yeast. It can generate a great deal of active cbh2 protein to convert the rejected fiber material.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Novel Iaccase Enzymes and Their Uses
InactiveUS20080248016A1Eliminate the problemSave energyCosmetic preparationsBacteriaBiotechnologyChaetomium
The present invention relates to novel laccase enzymes obtainable from the strains of the genus Thielavia or from the strains of the genus Chaetomium. The invention relates also to nucleic acid sequences encoding the enzymes, recombinant hosts into which the nucleic acid sequences have been introduced and to methods for the production of the enzymes in recombinant hosts. The enzymes of the invention are suitable for several applications, for example for treating denim and for strain removal.
Owner:AB ENZYMES OY
Broad-spectrum chaetomium strain applied to biological control of plant diseases and applications of broad-spectrum chaetomium strain
InactiveCN105524841ASolve pollutionHigh-quality and pollution-free developmentFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologySequence analysis
The invention provides a broad-spectrum chaetomium strain applied to biological control of plant diseases. The broad-spectrum chaetomium strain is separated and screened from scale-leaf branches of sabina chinensis; through the morphological observation and the ITS sequence analysis, the broad-spectrum chaetomium strain is identified to be C.subaffine in the Chaetomium spp fungus, the broad-spectrum chaetomium strain is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on Oct 19, 2015, and the preservation number of the broad-spectrum chaetomium strain is CGMCC No.11400. The broad-spectrum chaetomium strain can be applied to the biological control of plant diseases, has good inhibiting effects for various common phytopathogens (wilt fusarium oxysporum, botrytis cinerea and root rot fungus) in production, and particularly has obvious inhibiting effects for intractable soil-borne plant pathogens (verticillium dahliae and fusarium oxysporum), the successive cropping obstacle caused by root diseases under the planting mode of the facility can be overcome, and the high-quality and pollution-free development of the agricultural industry is promoted.
Owner:WEIFANG UNIVERSITY
Microbial preparation for treatment of livestock and poultry manure and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107586733AImprove the living environmentHigh activityFungiBio-organic fraction processingFecesDecomposition
The invention discloses a microbial preparation for treatment of livestock and poultry manure. The microbial preparation comprises the following raw materials by weight: 1-5 parts of actinomycetes, 1-4 parts of Chaetomium torulosum freeze-dried powder, 1-3 parts of rhizobium, 1-3 parts of Trichoderma viride freeze-dried powder, 2-6 parts of geotrichum candidum freeze-dried powder, 20-40 parts of coconut shell powder, 1-2 parts of Chinese fir charcoal, 1-2 parts of bagasse, 1-2 parts of brown sugar, 5-15 parts of kaolin, and 100-150 parts of water. The microbial preparation obtained by the method provided by the invention can effectively regulate the microflora structure of livestock and poultry manure, improve the activity of beneficial microorganism, can form a complex and stable ecological system through the interaction of strains, can rapidly decompose organic matters in livestock and poultry manure to produce heat energy, rapidly raise the material temperature, inhibit or kill germs, worm eggs and other harmful organisms, and improve the decomposition degree.
Owner:WEIFANG SHENGQUAN BIOTECH CO LTD
Soybean root rot disease composite biocontrol fungi granule and preparation method thereof
The invention belongs to the field of agricultural production technologies. It is a composite biocontrol fungi particles agent of soybean root rot and its preparation method. The invention is granular formulations and its production process which takes the four Trichoderma and Chaetomium fungi separated from natural soil as the mainly effective ingredients and is mainly used for the prevention and treatment of bean root rot. The present invention changes the disorder prevention and cure limits of applying biocontrol agents made of a single Trichoderma, in the invention there are multiple biocontrol fungi which has preventing and curing effect on the crop root rot, and compared with agent with single biocontrol fungi it has a lot advantages such as wide control scope and complementary role. The granules agent is proper for controlling root rot of plants, crops, trees and flowers, and it is also has promoting effect on crops, meanwhile it is right for people and livestock and crop safety, with advantages such as long-term action, no pollution to the environment, easy application and low-cost.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
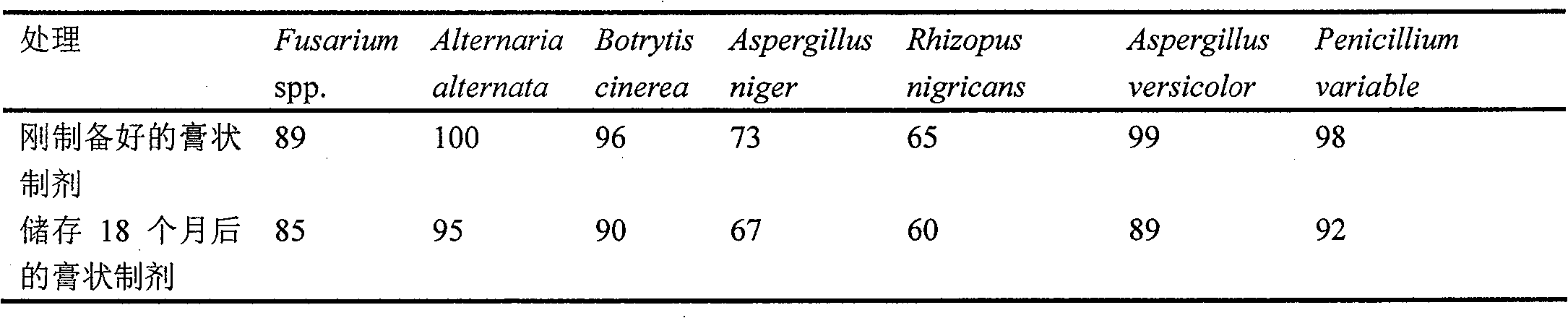
Pasty biological pesticide composite and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a pasty biological pesticide composite and a preparation method thereof. The biological pesticide composite comprises pesticide components and an auxiliary component. The pesticide components are biological prevention funguses. The biological pesticide composite is characterized in that the auxiliary material is starch which accounts for 5%-10% of the total weight of the composite. The biological prevention funguses refer to trichoderma, penicillium, chaetomium, cylindrocarpon, fusarium, Beauveria bassiana and / or metarhiziumanisopliae; a copper ion inhibitor, the addition amount of which is 0.001%-0.05% of the total weight of the composite, is added in the composite; in addition, hydrochloric acid, the addition amount of which is suitable for adjusting the pH valueto 3.0-4.0, is also added in the composite. The composite and biological pesticides prepared by using the method have the greatest advantages of stable product quality, long preservation time (18 months at normal temperature with high activity and 3 years in refrigeration condition); in addition, the invention has fastidious formula and advanced process, does not generate any wastewater, waste gas or waste residues, and is beneficial to environmental protection.
Owner:JIANGSU GENGYUN CHEM CO LTD
Laccase enzymes and their uses
Owner:AB ENZYMES OY
Cationic surfactant and application thereof
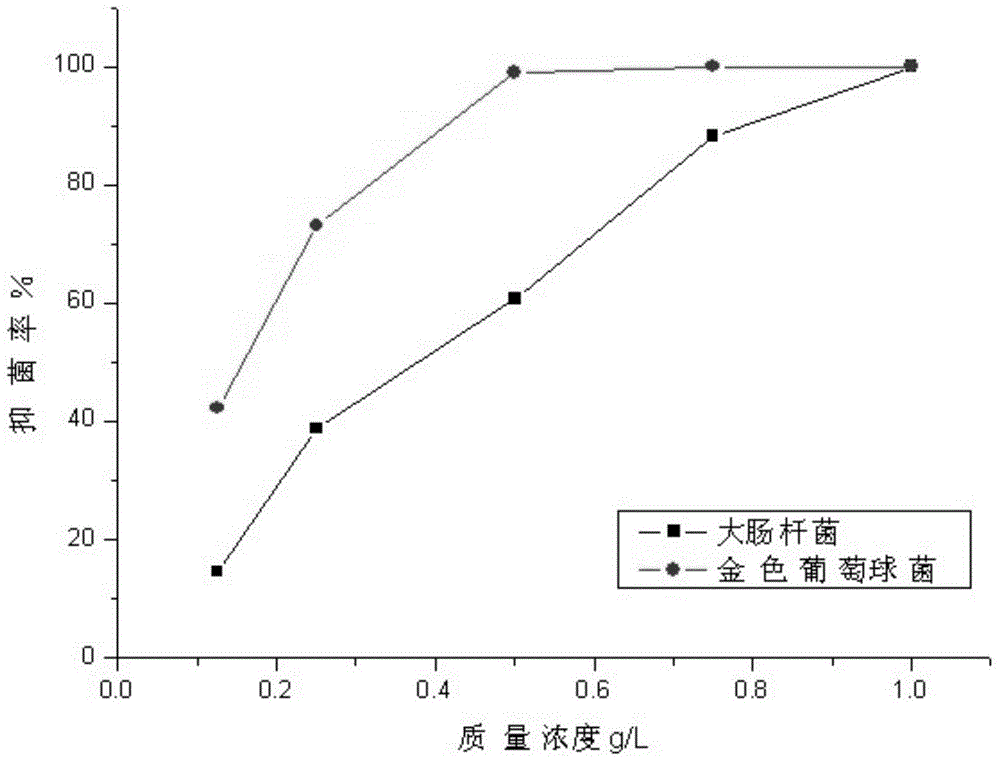
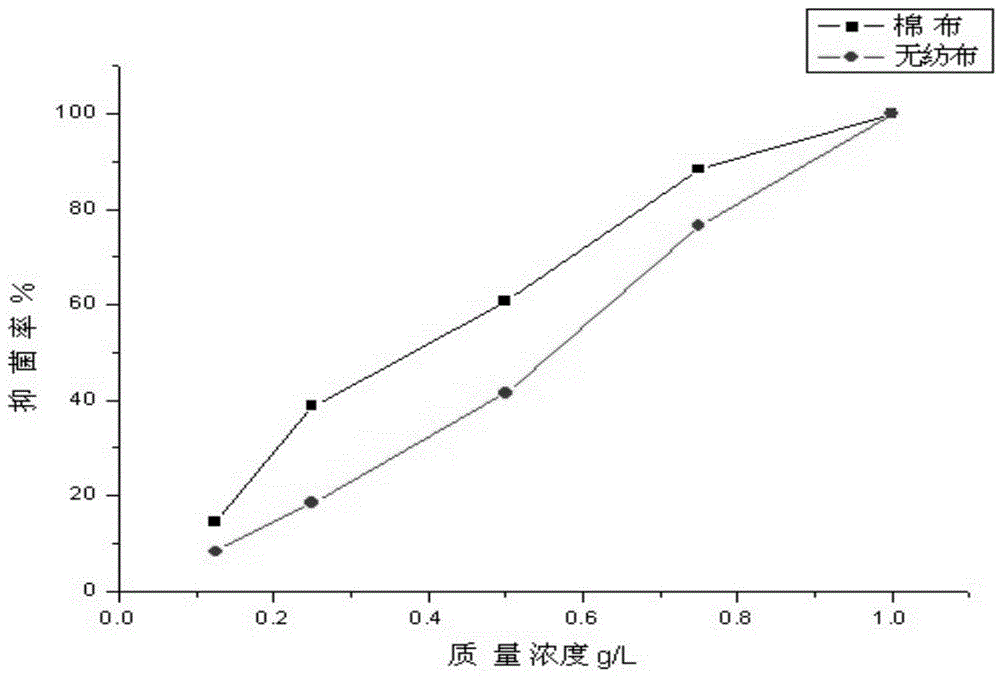
ActiveCN104060463AImprove the bactericidal effectGood anti-yellowing performanceVegetal fibresEscherichia coliStaphylococcus aureus
The invention discloses a cationic surfactant and application thereof and discloses the antibacterial property, mildew resistance, flexibility and anti-yellowing property of cationic quaternary ammonium myristylmethyl dihydroxyethyl ammonium bromide which is used as a clothing antibacterial finishing agent of cotton fabrics and non-woven fabrics. Antibacterial experiments performed on the cotton fabrics and the non-woven fabrics processed by the cationic surfactant with different mass concentration prove that the novel cationic surfactant has the remarkable effect of killing escherichia coli and staphylococcus aureus and also has a certain suppression effect on aspergillus niger, penicillium funiculosum and chaetomium globasum when the mass concentration of the surfactant is 1.0g / L; tests on the flexibility and anti-yellowing property of cotton fabrics processed by the surfactant with different mass ratios prove that the flexibility of the fabrics is most excellent when the mass ratio is 0.25%, and the fabric finished by quaternary ammonium is good in anti-yellowing property.
Owner:广州市金浪星非织造布有限公司
Method for preparing glycyrrhetinic acid monoglucuronide by liquorice fermentation
ActiveCN111485012ALow costSimple operating parametersCosmetic preparationsFungiBiotechnologyChaetomium
The invention discloses a method for preparing glycyrrhetinic acid monoglucuronide (GAMG) by solid-state fermentation of liquorice. The method comprises the following steps of: with Glycyrrhiza uralensis as a main component of a solid culture medium. inoculating Chaetomium globosumTHS3 to carry out solid-state culture, wherein after fermentation is finished, the conversion rate of glycyrrhizic acid (GL) in liquorice can reach 90% or above, so that a mixture containing the GAMG and GL is formed and can be used for preparing a mixed sweetening agent containing GAMG or a GAMG monomer sweetening agent, wherein higher sweetness and solubility are achieved. According to the method, cheap and medicinally and edibly homologous liquorice is directly used as a raw material for solid-state fermentation; the high-yield and high-purity GAMG can be obtained through extraction, separation and purification and concentration and drying of a fermentation product, a target product can be prepared withoutfirstly extracting and separating to obtain GL or preparing beta-D-glucuronidase in advance, the process steps are few, the production cost is low, no pollution is caused, and the method is suitablefor large-scale production.
Owner:JIANGXI SCI & TECH NORMAL UNIV
Uniseriate chaetomium, microbial agent including same, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110747134AEcologically safeEasy to operateFungiAgriculture tools and machinesMicrobial agentEngineering
The invention discloses uniseriate chaetomium, a microbial agent including the same, a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of microbial agents. The preservation number of the uniseriate chaetomium is CGMCC No.18156. The uniseriate chaetomium promotes improvement of soil fertility by promoting effective degradation of straws, adding a nitrogen content of organic carbon and soluble carbon in soil and resisting to pathogenic bacteria. The uniseriate chaetomium disclosed by the invention comes from farmland soil where straw recycling is carried out for along time and can realize green ecological agriculture, thereby ensuring food quality and safety. The enlarged culture process of the uniseriate chaetomium is simple to operate and low in cost and canprepare microbial agents to be generalized and applied in the agricultural field.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Novel laccase enzymes and their uses
InactiveCN101023166AReduce harmful effects on the environmentReduce or even avoid harmful environmental impactsCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsBiotechnologyChaetomium
The present invention relates to novel laccase enzymes obtainable from the strains of the genus Thielavia or from the strains of the genus Chaetomium. The invention relates also to nucleic acid sequences encoding the enzymes, recombinant hosts into which the nucleic acid sequences have been introduced and to methods for the production of the enzymes in recombinant hosts. The enzymes of the invention are suitable for several applications, for example for treating denim and for strain removal.
Owner:AB ENZYMES GMBH
Application of microbial preparation for quickly decomposing cattle faeces
InactiveCN103642701BImprove filtration efficiencyImprove fermentation qualityBio-organic fraction processingFungiCelluloseFeces
The invention discloses a microbial preparation of quickly decomposing cattle faeces as well as a preparation method and an application of the microbial preparation, and relates to a microbial preparation capable of decomposing cattle faeces as well as a preparation method and application of the microbial preparation. The invention aims to solve the problem that in the existing decomposing and fermenting process of cattle faeces, the manure is quick to warm, the degradative rate for cellulose is low, the decomposing degree is not high and the fermenting period is long. The microbial preparation is prepared from long thorned chaetomium, trichoderma koningii, chaetomium torulosum Bainier, Trichoderma viride and cryytococcus neoformans. The preparation method comprises the following steps: I, inoculating a strain on a culture medium; II, preparing a skimmed milk emulsion, inoculating after sterilization and producing a leavening agent on a table; III, carrying out quick freezing on the leavening agent and freezing and drying to obtain the freeze-drying culture powder; and IV, proportioning the freeze-drying culture powder according to weight part to prepare the microbial preparation after uniformly mixing. By fermenting cattle faeces with the microbial preparation, the microbial preparation is quick to warm, and can improve the degree of cellulose degradation and the degree of decomposition of organic fertilizer products and shorten the fermenting period.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
Method for increasing content of ginsenoside in ginseng adventitious roots by utilizing immobilized chaetomium globosum spores
ActiveCN111096222APromote accumulationIncrease contentPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsBiotechnologySporeling
The invention discloses a method for increasing the content of ginsenoside in ginseng adventitious roots by utilizing immobilized chaetomium globosum spores. The method comprises the following steps:(1) preparing a liquid culture medium; (2) culturing the ginseng adventitious roots in the liquid culture medium; (3) preparing a sodium alginate aqueous solution; (4) preparing a chaetomium globosumspore suspension; (5) uniformly mixing the sodium alginate aqueous solution with the chaetomium globosum spore suspension in an isopyknic manner so as to obtain a mixed solution, dropwise adding the mixed solution into a CaCl2 aqueous solution until particles are generated, carrying out filtering to obtain the particles, cleaning the particles with normal saline, and carrying out filtering so as to obtain immobilized chaetomium globosum spores; and (6) adding the immobilized chaetomium globosum spores into the culture medium in the step (2), continuing culturing for 5 days at 25 DEG C under adark condition, and carrying out harvesting. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of simple operation, short growth period, low production cost and the like. According to the method, accumulation of the ginsenoside is effectively promoted; the content of the ginsenoside in the ginseng adventitious roots is remarkably increased; and industrial large-scale production of the ginsenoside is facilitated.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Sodium alginate coated biological agent for preventing clubroot and preparation method of sodium alginate coated biological agent
InactiveCN107136123AHigh compressive strengthEffective controlBiocidePlant growth regulatorsPalygorskiteSalicylic acid
The invention discloses a sodium alginate coated biological agent for preventing clubroot and a preparation method of the sodium alginate coated biological agent. The sodium alginate coated biological agent comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 34-47 parts of a chaetomium liquid, 18-26 parts of potatoes, 2-6 parts of brown sugar, 38-51 parts of palygorskite, a proper amount of distilled water, 19-26 parts of sodium alginate, 13-21 parts of calcium chloride, 4-12 parts of salicylic acid, and proper amount of absolute ethyl alcohol. The palygorskite is used to adsorb and fix a chaetomium spore, then the sodium alginate loaded with the salicylic acid is used to coat the chaetomium spore, the compressive strength of the particle microorganism agent is improved, the particle microorganism agent is not easy to break in the processes of transporting and applying the product so as to be beneficial for the use of the product, the effect of efficiently preventing the clubroot of the crop is realized, the prevention time is greatly prolonged, moreover, the germination of seeds and the growth of seedlings are effectively promoted, and the cold resistance of the seedlings is improved.
Owner:MINGGUANG NONGYUAN CROPS SPECIALIZED COOP
Saccharomyce engineering strain for expressing cbh1 gene and its construction method
A genetically engineered yeast Pichia pastoris GS-H is prepared through screening the thermophilic Chaetomium CT2 by PCR method to obtain cellobiohydrolase II gene, cloning it, inserting it in the expression carrier of Pichia yeast, introducing it to Pichia yeast, and screening said genetically engineered yeast. It can generate a great deal of active cbhl protein to convert the rejected fiber material.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Yeast engineering strain expressing chaetomium thermophilum gla gene and constitution method
InactiveCN101070524AHigh expressionHigh activityFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPichia pastoris
This invention is a genetically engineered strain of yeast Pichia pastoris GS-GLA-22, RT-PCR and RACE Chaetomium from thermophilic bacteria chaetomium thermophilum was glucoamylase gla gene fragment was cloned into the Pichia pastoris secreted expression vector pPIC9K One of recombinant GS-GLA-22 by 6 days induction, glucoamylase protein expression levels of 0.86 mg / mL, its activity is 16.73 U / mL for starch processing and other industrial areas, has a very significant social and economic value.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation and application of a strain of Chaetomium globosa and its metabolite aflatoxin
The invention provides preparation and application of chaetomium globosum and metabolite flavipin thereof. The strain is endophytic fungi obtained by separating gingko leaves, is identified to be chaetomium globosum with a number of CDW7, and is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center with the register number of CGMCC No. 6658. The invention relates to preparation and application of CDW7 metabolite flavipin at the same time. The preparation method comprises the step that the organic solvent extract of the strain CDW7 fermentation broth is subjected to gel column chromatography and recrystallization. The flavipin has strong anti-oxidation activity, and can be used as an antioxidant for application.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Glucoamylase producing method
The invention discloses a glucoamylase producing method and belongs to the technical field of biology. The glucoamylase producing method includes: firstly, cloning glucoamylase genes of aspergillus, chaetomium and yeast; secondly, constructing a pichia pastoris expression vector, a saccharomyces cerevisiae expression vector and a bacillus subtilis expression vector which include three glucoamylase gene expression cassettes, and transforming the vectors to corresponding host bacteria respectively; thirdly, respectively screening recombinants of over-expression glucoamylases as engineering bacteria; and finally, fermenting the pichia pastoris engineering bacteria, the saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacteria and the bacillus subtilis engineering bacteria to produce a recombinant mixed glucoamylase. Different from a traditional single-gene-coded glucoamylase, the recombinant mixed glucoamylase is wide in suitable reaction temperature and pH (potential of hydrogen) range and suitable for various purposes, and yield of the glucoamylase is remarkably increased by the aid of implementation of expression of the three glucoamylase genes in the engineering bacteria, so that production cost is reduced.
Owner:INST OF TROPICAL BIOSCI & BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Straw fiber seedling raising substrate for colonization and bacteria prevention and its production method and two-step colonization and bacteria control method
ActiveCN111727847BVigorousConvenient sourceGrowth substratesSewage/sludge fertilisersBiotechnologyChaetomium
The invention discloses a straw fiber seedling raising substrate for colonization and bacteria prevention, a production method and a two-step colonization and bacteria control method, and belongs to the technical field of crop colonization and bacteria control. Specifically include: the first step is the colonization of biocontrol bacteria powder mixed with matrix, the spraying and colonization of biocontrol bacteria water, or the spraying and colonization of biocontrol bacteria liquid; the second step is the colonization of straw fiber matrix after 10- 15 days, the straw fiber matrix colonized with biocontrol bacteria and the crop seedlings were transplanted to the field synchronously, and the biocontrol bacteria of the matrix and crop seedlings were colonized in the field; One or more mixtures of Streptomyces, Talaromyces flavus and Chaetomium. The above-mentioned straw fiber seedling-raising substrate for colonization and bacteria prevention, its production method and the two-step colonization and bacteria prevention method can effectively colonize and control bacteria, thereby improving the disease resistance of seedlings, and significantly improving the stress resistance of seedling transplanting.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES +1
Application of a thermophilic Chaetomium cellulase in one-bath polishing and dyeing process
ActiveCN105155167BImprove polishing effectReduce dosageTextile treatment machine arrangementsEnzymesChaetomiumHigh concentration
The invention discloses an application of thermophilic Chaetomium cellulose to polishing, dyeing and one-bat technology. The thermophilic Chaetomium cellulose is expressed via Trichoderma reesei or pichia pastoris; the thermophilic Chaetomium cellulose is neutral cellulose having a halophilic function; salt with high concentration has obvious lifting action on activity of neutral cellulose; the optimal action temperature of the neutral cellulose is 57 to 63 DEG C, so polishing temperature and dyeing temperature are the same; during the polishing, even dyeing can be achieved and guaranteed.
Owner:希杰尤特尔(湖南)生物科技有限公司 +1
A strain of Chaetomium monocele, bacterial agent including Chaetomium monocele, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110747134BEcologically safeEasy to operateBio-organic fraction processingAgriculture tools and machinesBiotechnologyChaetomium
The invention provides a strain of Chaetomium monocele, its preparation method and application including Chaetomium monocele, and belongs to the technical field of microbial inoculum; the preservation number of the Chaetomium monocele is: CGMCC No.18156. The chaetomium monolezee of the invention promotes the improvement of soil fertility by promoting the effective degradation of straw, increasing the content of organic carbon and soluble carbon and nitrogen in the soil, and resisting pathogenic bacteria. The chaetomium monolectus of the present invention can grow and reproduce by itself in the soil, and reach an ecologically stable balance with the indigenous microbial community without repeated addition. The chaetomium monorow of the invention is derived from farmland soil where straws have been returned to the field for a long time, and can realize green ecological agriculture to ensure the high quality and safety of food. The enlarged culture process of the chaetomium monorow of the present invention is simple to operate and low in cost, and can be prepared into a microbial agent for popularization and application in the agricultural field.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Application of a thermophilic chaetomium cellulase in pulp and papermaking process
ActiveCN105155324BImprove application efficiencyReduce use costEnzymesPaper material treatmentChaetomiumPichia pastoris
The invention discloses application of chaetomium thermophilum cellulase in the pulping and papermaking process. The chaetomium thermophilum cellulase is expressed through trichoderma reesei or pichia pastoris. The chaetomium thermophilum cellulase is neutral cellulase. In the pulping and papermaking process, the optimal effect pH range of the chaetomium thermophilum cellulase is 6.0 to 7.0, and use cost is reduced. The influences of normal fluctuation of the pH of a neutral papermaking system on the chaetomium thermophilum cellulase are low. Frame needle pulp and frame width pulp are pre-treated before pulping of the chaetomium thermophilum cellulase, frame needle pulp and frame width pulp fibers can be modified, and therefore the binding force between the fibers is improved; the interlayer bonding strength of finished paper and the tensile strength are remarkably improved, and the bulkness and stiffness are not obviously changed.
Owner:SHANDONG YOUTELL BIOCHEM +1
Pasty biological pesticide composite and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a pasty biological pesticide composite and a preparation method thereof. The biological pesticide composite comprises pesticide components and an auxiliary component. The pesticide components are biological prevention funguses. The biological pesticide composite is characterized in that the auxiliary material is starch which accounts for 5%-10% of the total weight of the composite. The biological prevention funguses refer to trichoderma, penicillium, chaetomium, cylindrocarpon, fusarium, Beauveria bassiana and / or metarhiziumanisopliae; a copper ion inhibitor, the addition amount of which is 0.001%-0.05% of the total weight of the composite, is added in the composite; in addition, hydrochloric acid, the addition amount of which is suitable for adjusting the pH value to 3.0-4.0, is also added in the composite. The composite and biological pesticides prepared by using the method have the greatest advantages of stable product quality, long preservation time (18 months at normal temperature with high activity and 3 years in refrigeration condition); in addition, the invention has fastidious formula and advanced process, does not generate any wastewater, waste gas or waste residues, and is beneficial to environmental protection.
Owner:JIANGSU GENGYUN CHEM CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com