Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
350 results about "Amniotic fluid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The amniotic fluid is the protective liquid contained by the amniotic sac of a gravid amniote. This fluid serves as a cushion for the growing fetus, but also serves to facilitate the exchange of nutrients, water, and biochemical products between mother and fetus.
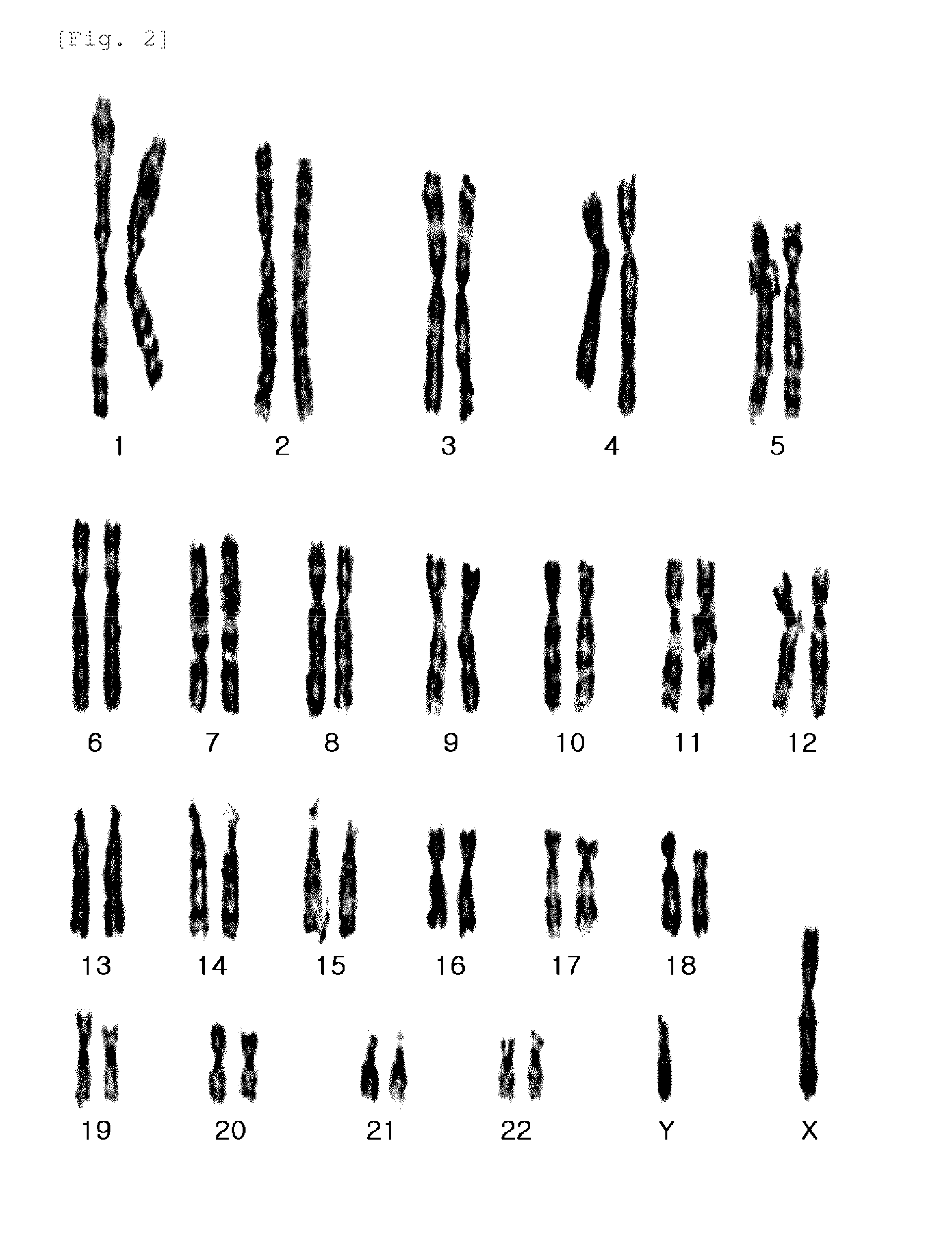
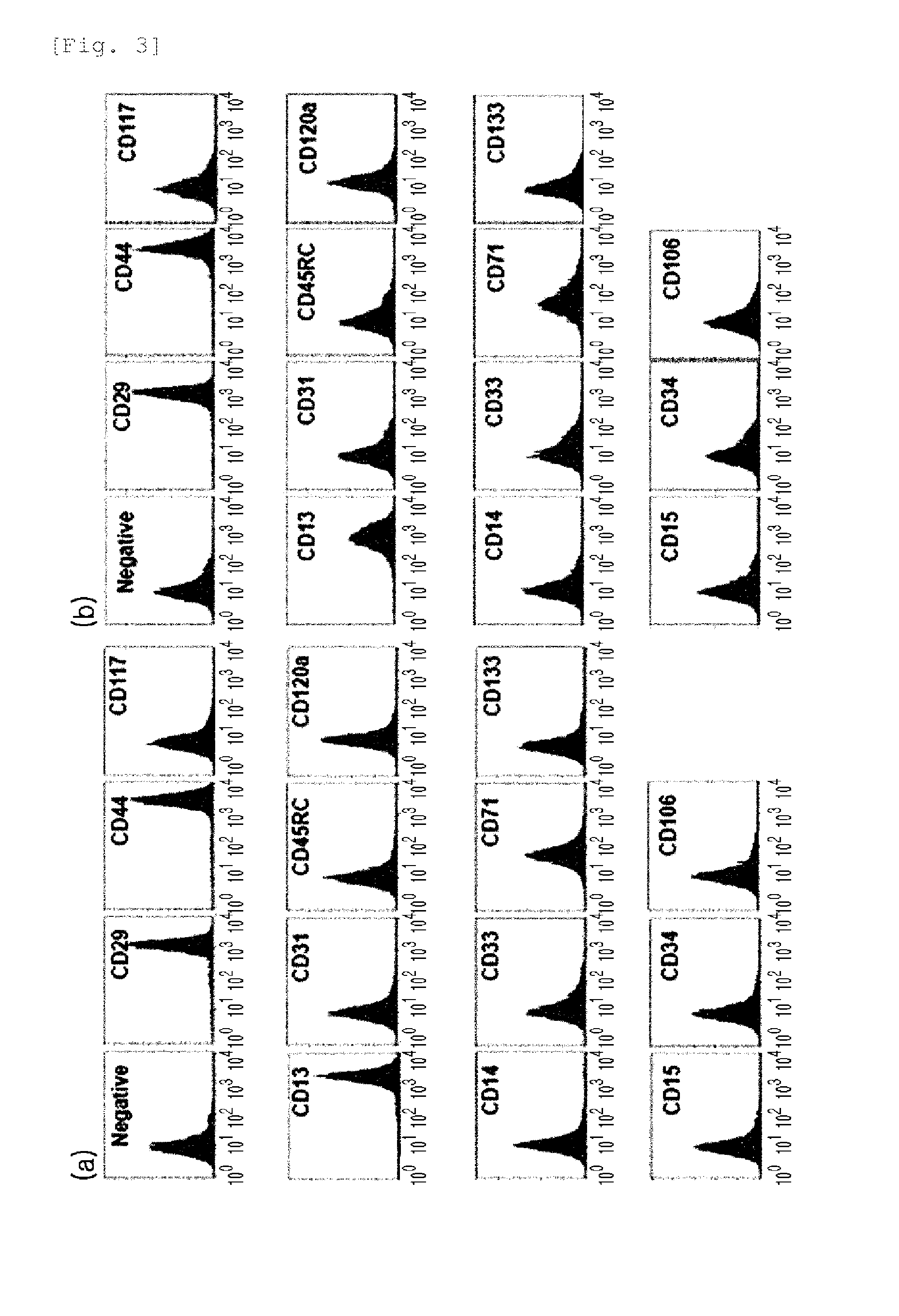
Multipotent amniotic fetal stem cells
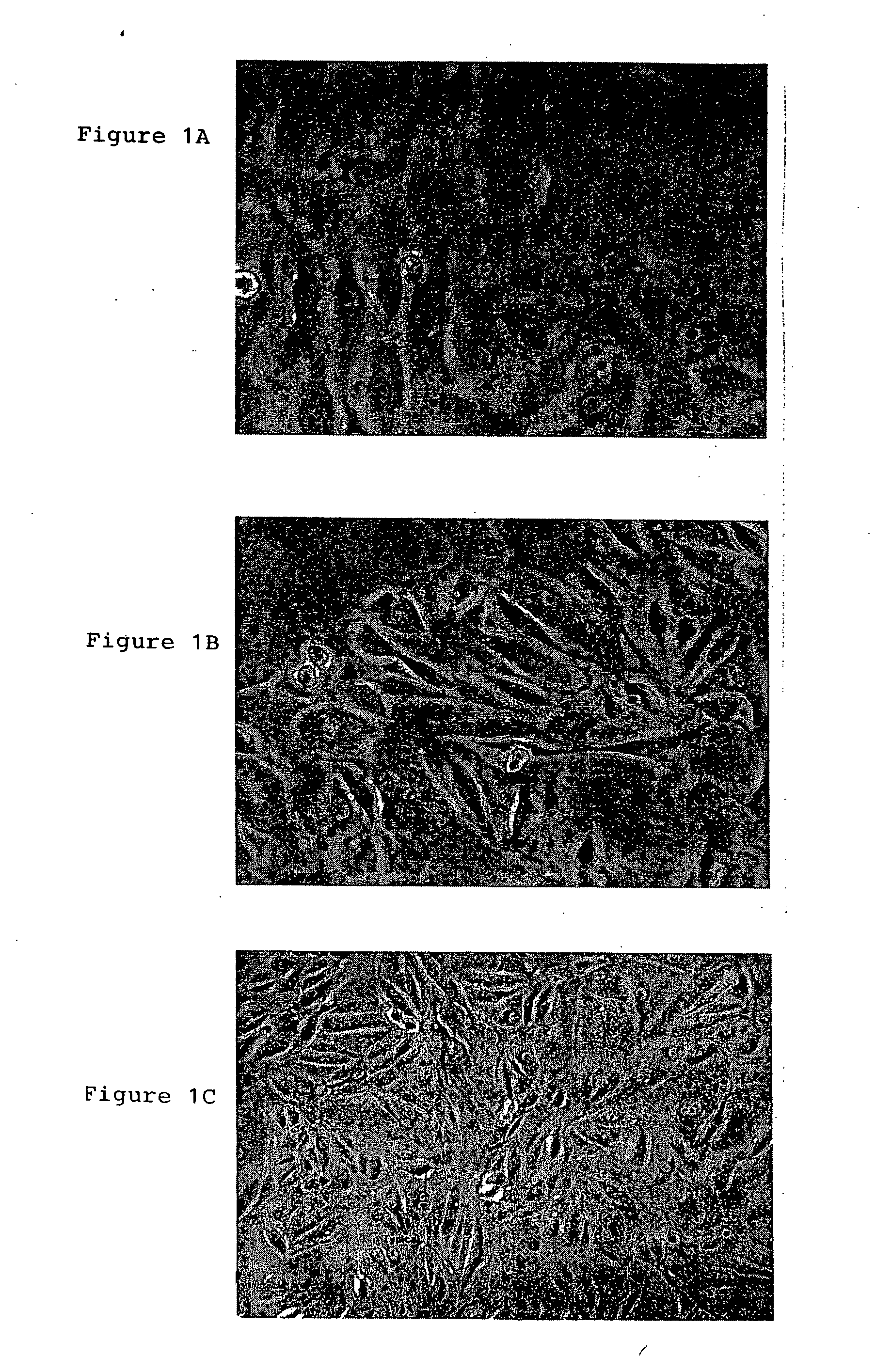
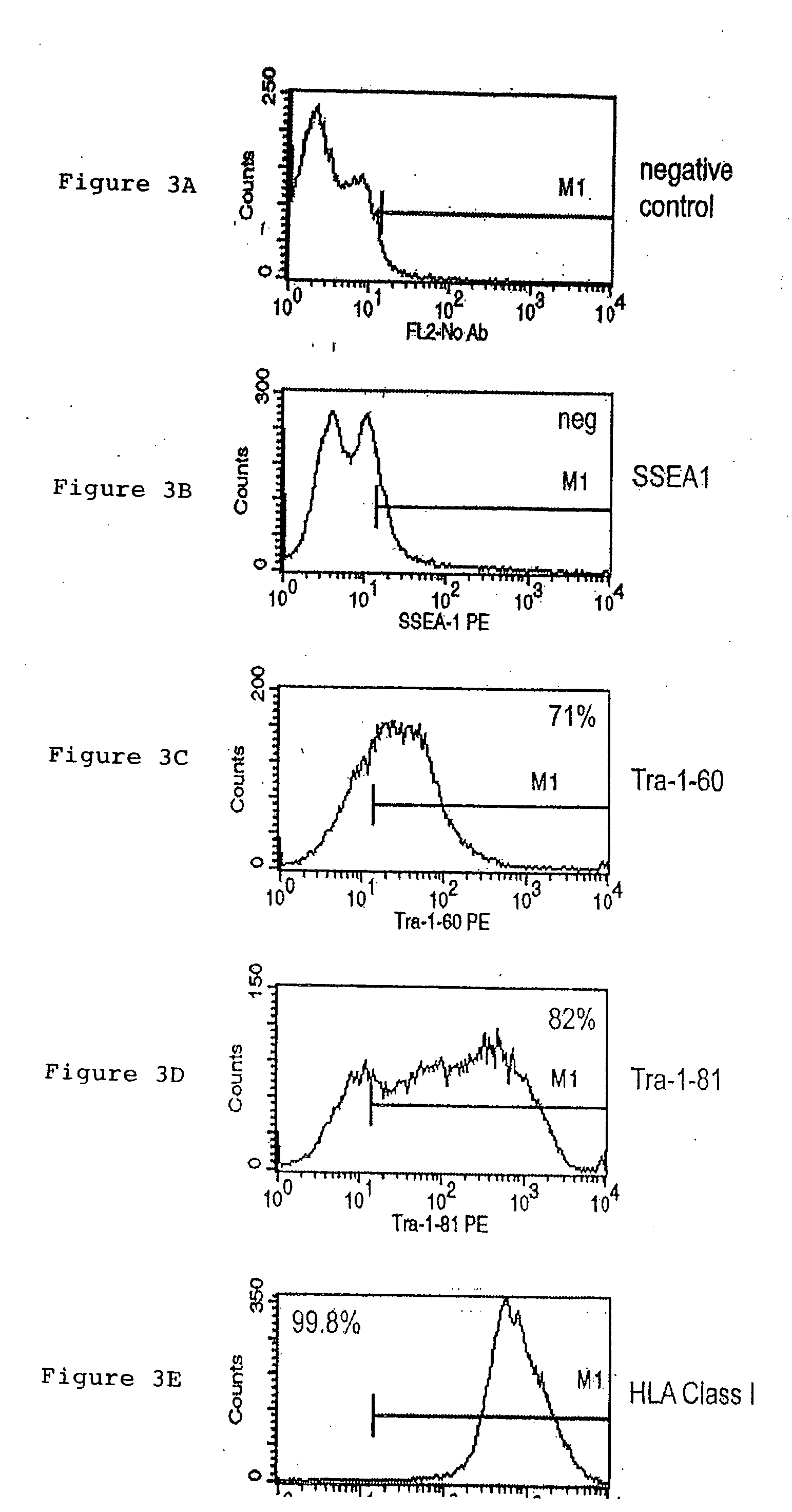
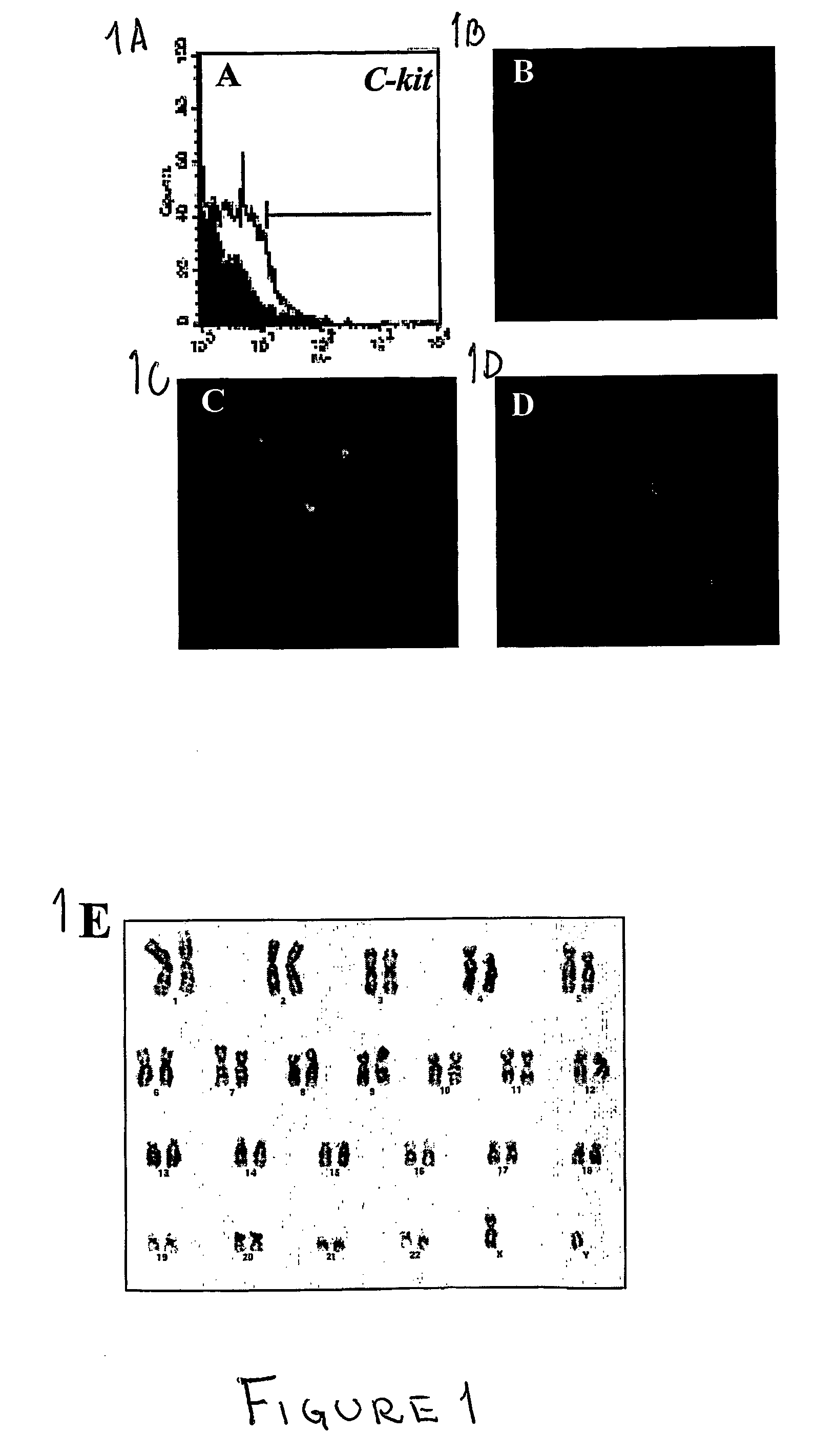
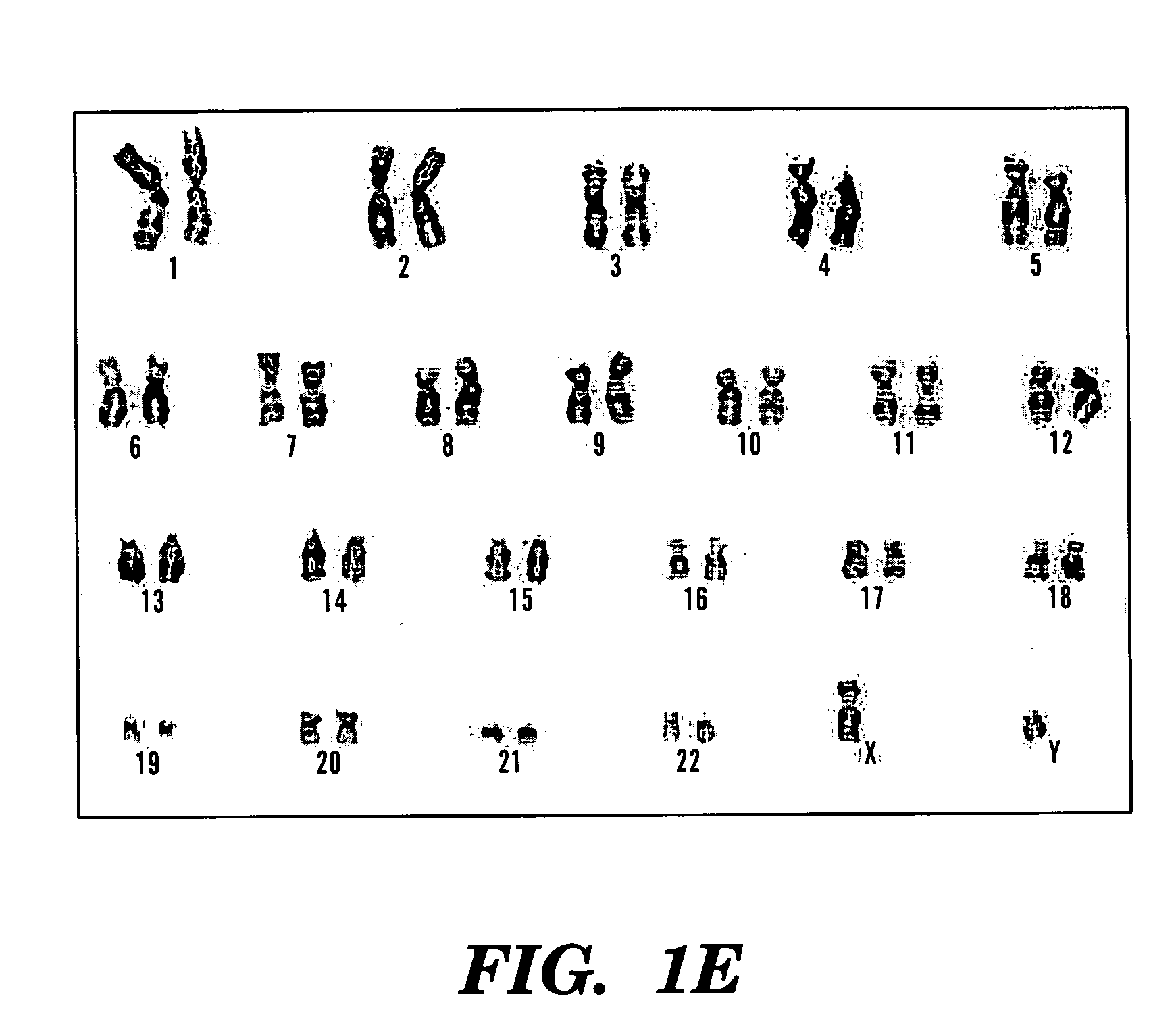
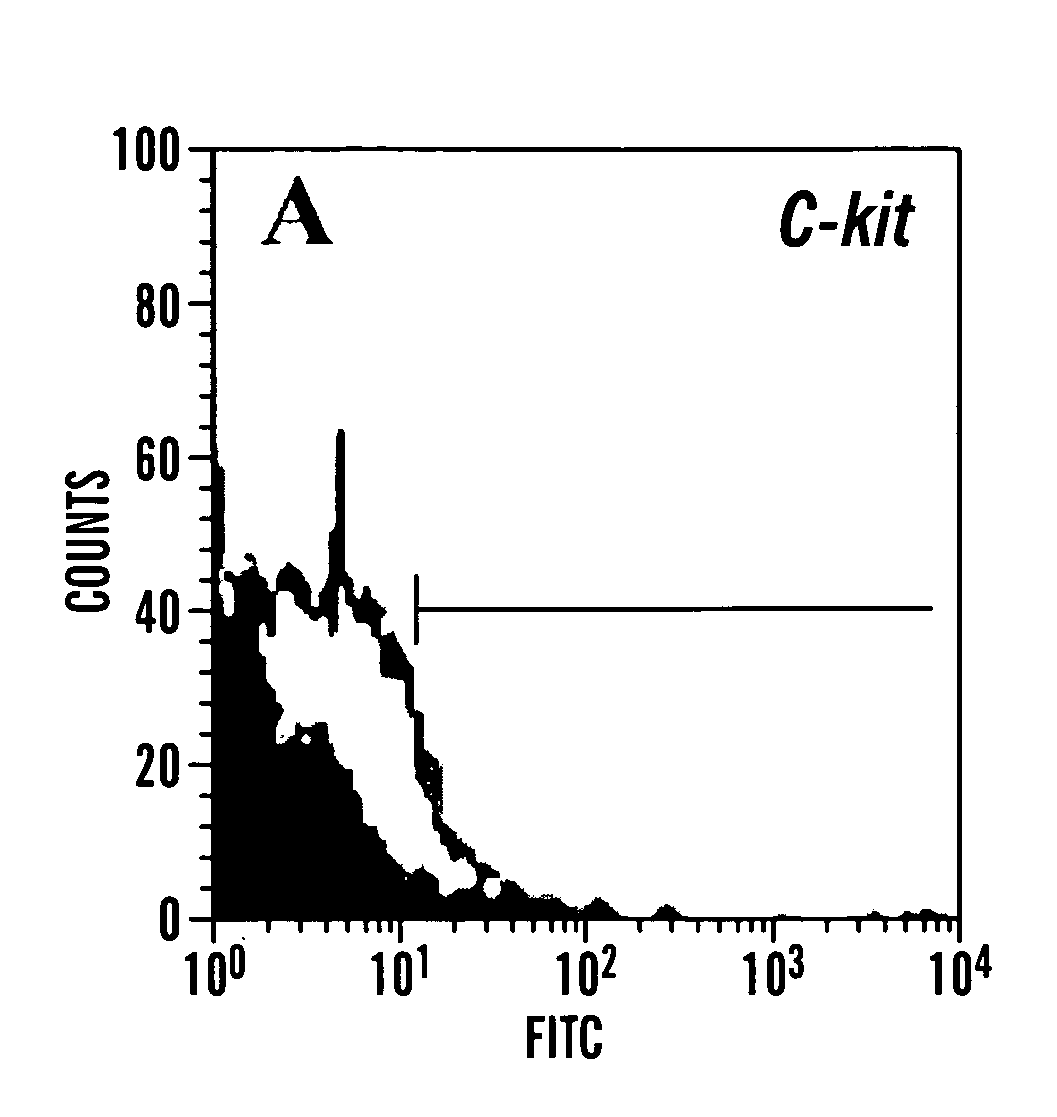
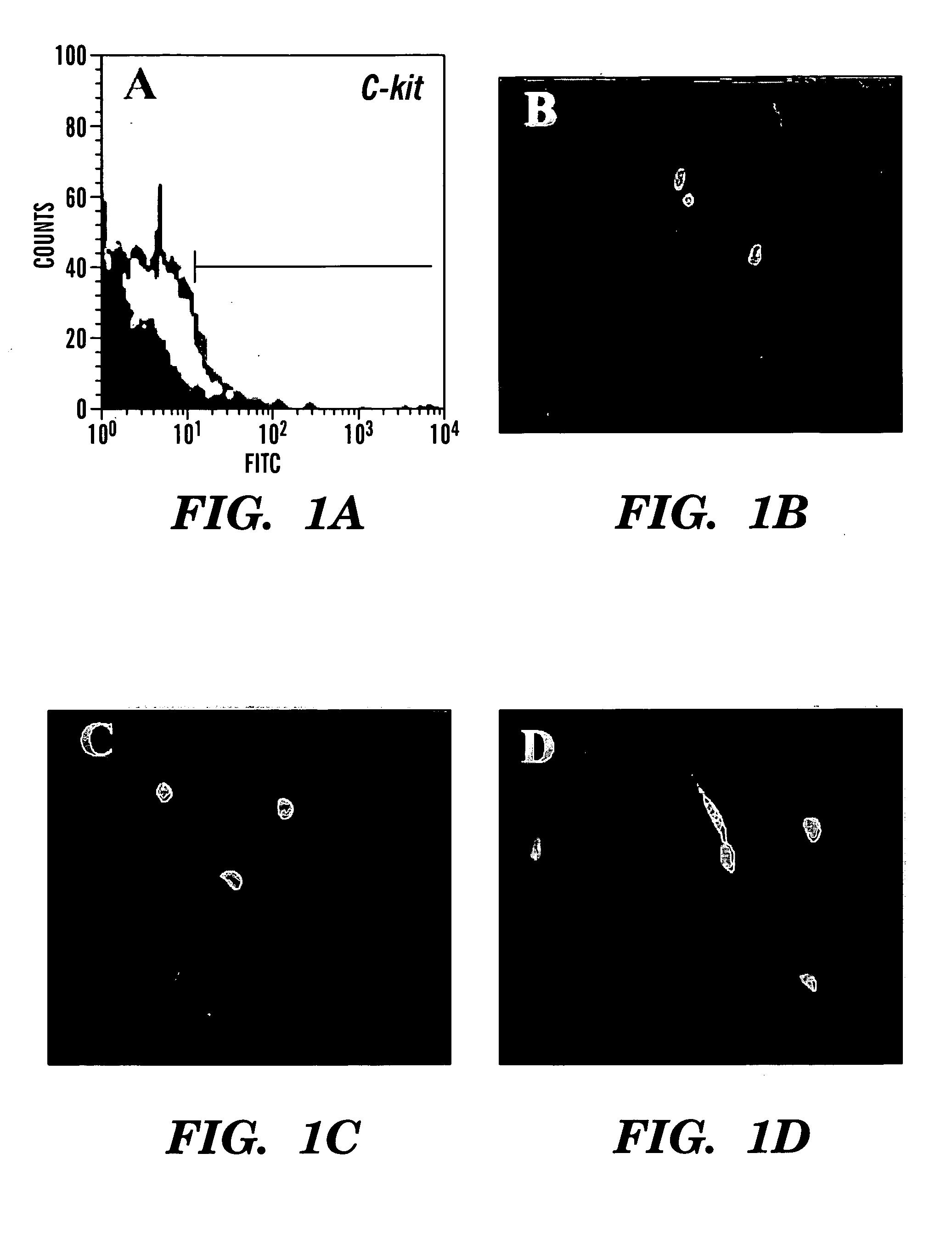
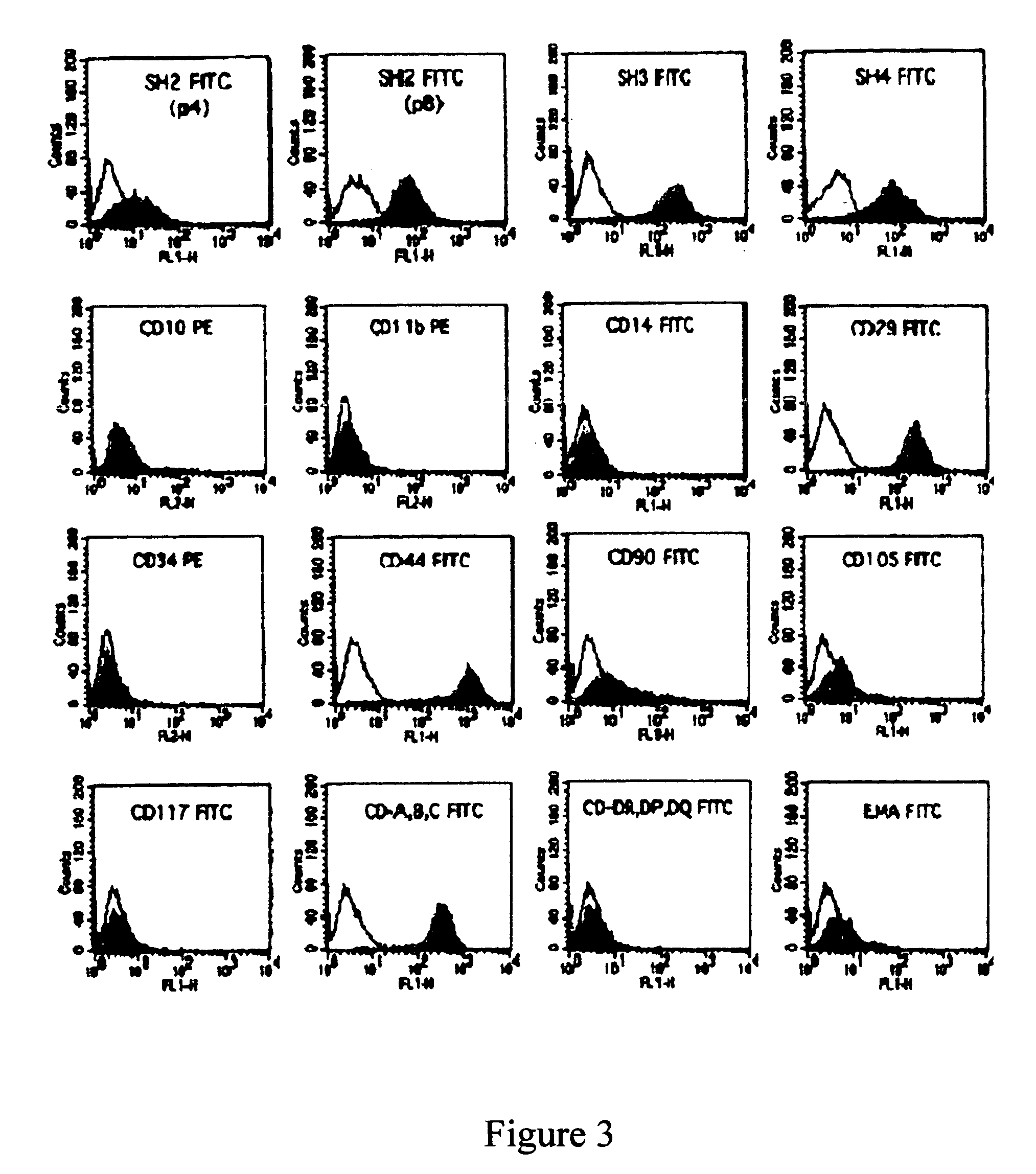
A source of multipotent amniotic fluid / fetal stem cells (MAFSCs) is disclosed. MAFSC are of fetal origin and have a normal diploid karyotype. These cells are characterized by the following cell surface markers: SSEA3, SSEA4, Tra-1-60, Tra-1-81, Tra-2-54, HLA class I, CD13, CD44, CD49b, CD105 and are distinguished by the absence of the antigen markers CD34, CD45, and HLA Class II, but are distinguished from mouse embryonic stem cells in that these cells do not express the cell surface marker SSEA1. MAFSC express the stem cell transcription factor Oct-4. MAFSC cells can be propagated for an indefinite period of time in continuous culture in an undifferentiated state. The MAFSCs have the ability to differentiate in culture in a regulated manner, into three or more subphenotypes. Cells can then be differentiated into endodermal, mesodermal and ectodermal derived tissues in vitro and in vivo. A method for isolating, identifying, expanding and differentiating MAFSCs is disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods of isolation, expansion and differentiation of fetal stem cells from chorionic villus, amniotic fluid, and placenta and therapeutic uses thereof
InactiveUS20050124003A1Sufficient supplyRaise the potentialNervous disorderMuscular disorderBiologyAmniotic fluid
The present invention is directed to pluripotent fetal stem cells derived from chorionic villus, amniotic fluid, and placenta and the methods for isolating, expanding and differentiating these cells, and their therapeutic uses such as manipulating the fetal stem cells by gene transfection and other means for therapeutic applications.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Prenatal Diagnosis Using Cell-Free Fetal DNA in Amniotic Fluid
InactiveUS20070212689A1Rapid determinationAddressing slow performanceMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansCell-free fetal DNAAmniotic fluid
The present invention relates to improved methods of prenatal diagnosis, screening, monitoring and / or testing. The inventive methods include the analysis by array-based hybridization of cell-free fetal DNA isolated from amniotic fluid. In addition to allowing the prenatal diagnosis of a variety of diseases and conditions, and the assessment of fetal characteristics such as fetal sex and chromosomal abnormalities, the new inventive methods provide substantially more information about the fetal genome in less time than it takes to perform a conventional metaphase karyotype analysis. In particular, the enhanced molecular karyotype methods provided by the present invention allow the detection of chromosomal aberrations that are not often detected prenatally such as microdeletions, microduplications and subtelomeric rearrangements.
Owner:BIANCHI DIANA W +2
Banking of multipotent amniotic fetal stem cells
Stem cells, including those designated as multipotent amniotic fluid stem cells (MAFSC) cells are found in the amniotic fluid of mammals, including humans. MAFSCs are fetal, multipotent stem cells that can be used for any desired stem cell utility, including treatment of individuals in need of tissue replacement or gene therapy. Methods of banking MAFSCs derived from the amniotic fluid cells of pregnant individuals are disclosed. Amniotic fluid-derived cells are banked for the purpose of access to transplantation antigen-compatible or syngeneic multipotent stem cells.
Owner:HAAS MARTIN
Prenatal diagnosis using cell-free fetal DNA in amniotic fluid
InactiveUS20070111233A1Improved and rapid methodHigh recovery rateSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCell-free fetal DNAAmniotic fluid
The present invention relates to improved methods of prenatal diagnosis, screening, monitoring and / or testing. The inventive methods include the analysis by array-based hybridization of cell-free fetal DNA isolated from amniotic fluid. In addition to allowing the prenatal diagnosis of a variety of diseases and conditions, and the assessment of fetal characteristics such as fetal sex and chromosomal abnormalities, the new inventive methods provide substantially more information about the fetal genome in less time than it takes to perform a conventional metaphase karyotype analysis. In particular, the enhanced molecular karyotype methods provided by the present invention allow the detection of chromosomal aberrations that are not often detected prenatally such as microdeletions, microduplications and subtelomeric rearrangements. Also provided are improved methods of extraction of fetal DNA from amniotic fluid.
Use of a human amniotic membrane composition for prophylaxis and treatment of diseases and conditions of the eye and skin
InactiveUS7871646B2Improve the level ofMammal material medical ingredientsDead animal preservationDiseaseEmulsion
A method of preparing an amniotic membrane extract including the steps of obtaining a healthy amniotic membrane from a pregnant mammal, such as a pig, cow, horse or human, homogenizing the membrane to obtain a homogenate solution, freezing the homogenate solution, and lyophilizing the frozen homogenate solution to dryness is disclosed. Preferably, the lyophilized homogenate is pulverized to a powder. The lyophilized homogenate is then reconstituted before use, e.g., in a liquid, such as a balanced salt solution or fresh amniotic fluid, or in another substance, such a gel, an ointment, a cream or a soap, depending on the intended use. Also disclosed is a pharmaceutical composition prepared according to the method of the invention, for prophylaxis and / or treatment of a disease or condition, especially of the eye or the skin. Exemplary pharmaceutically acceptable carriers for the composition of the invention include an ophthalmic solution for eye drops, a gel, an ointment, an emulsion, a cream, a powder and a spray.
Owner:REPSCO
Diagnosis of fetal aneuploidy
The invention relates to a method for the early non-invasive diagnosis of fetal aneuploidy. In particular, the invention concerns the diagnosis of fetal aneuploidy by identifying protein expression patterns characteristics of fetal aneuploidy in a maternal biological fluid, such as maternal serum or amniotic fluid.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
Use of a human amniotic membrane composition for prophylaxis and treatment of diseases and conditions of the eye and skin
InactiveUS20080108045A1Improve the level ofDead animal preservationMammal material medical ingredientsEmulsionMedicine
A method of preparing an amniotic membrane extract including the steps of obtaining a healthy amniotic membrane from a pregnant mammal, such as a pig, cow, horse or human, homogenizing the membrane to obtain a homogenate solution, freezing the homogenate solution, and lyophilizing the frozen homogenate solution to dryness is disclosed. Preferably, the lyophilized homogenate is pulverized to a powder. The lyophilized homogenate is then reconstituted before use, e.g., in a liquid, such as a balanced salt solution or fresh amniotic fluid, or in another substance, such a gel, an ointment, a cream or a soap, depending on the intended use. Also disclosed is a pharmaceutical composition prepared according to the method of the invention, for prophylaxis and / or treatment of a disease or condition, especially of the eye or the skin. Exemplary pharmaceutically acceptable carriers for the composition of the invention include an ophthalmic solution for eye drops, a gel, an ointment, an emulsion, a cream, a powder and a spray.
Owner:REPSCO
Topical wound therapeutic compositions
There is provided a composition for healing burns and wounds in mammals, which contains a cromolyn compound or the combination of a cromolyn compound and hyaluronic acid a corticosteroid. Advantageously, elements found in amniotic fluid are also included.
Owner:ALPHAMED PHARMA CORP
Methods of isolation, expansion and differentiation of fetal stem cells from chorionic villus, amniotic fluid, and placenta and therapeutic uses thereof
InactiveUS20070116682A1Sufficient supplyRaise the potentialBiocideNervous disorderAmniotic fluidBiology
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Methods of isolation, expansion and differentiation of fetal stem cells from chorionic villus, amniotic fluid, and placenta and therapeutic uses thereof
InactiveUS20070116684A1Sufficient supplyRaise the potentialBiocideNervous disorderAmniotic fluidBiology
The present invention is directed to pluripotent fetal stem cells derived from chorionic villus, amniotic fluid, and placenta and the methods for isolating, expanding and differentiating these cells, and their therapeutic uses such as manipulating the fetal stem cells by gene transfection and other means for therapeutic applications.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
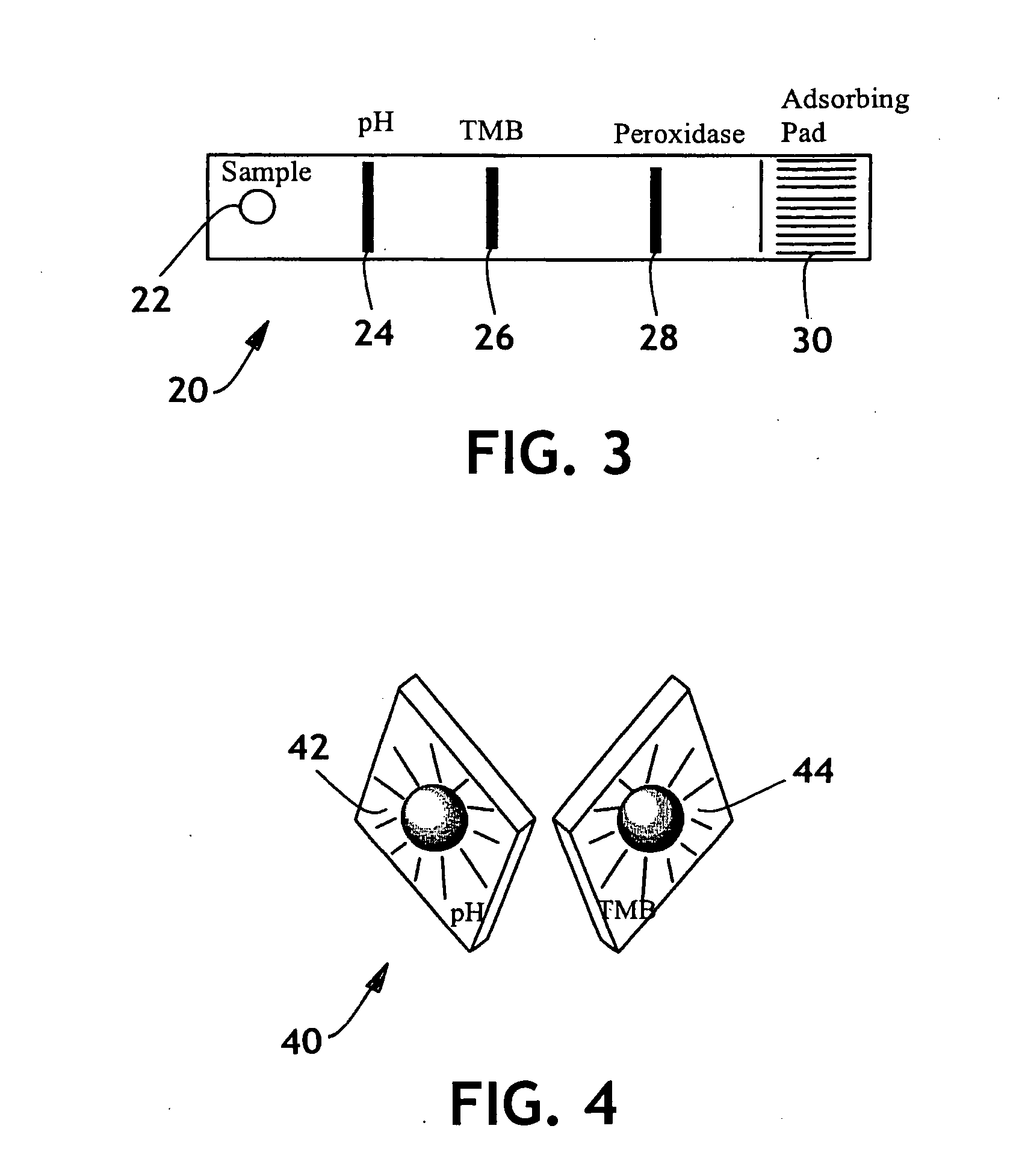
Detection of premature rupture of the amniotic membrane
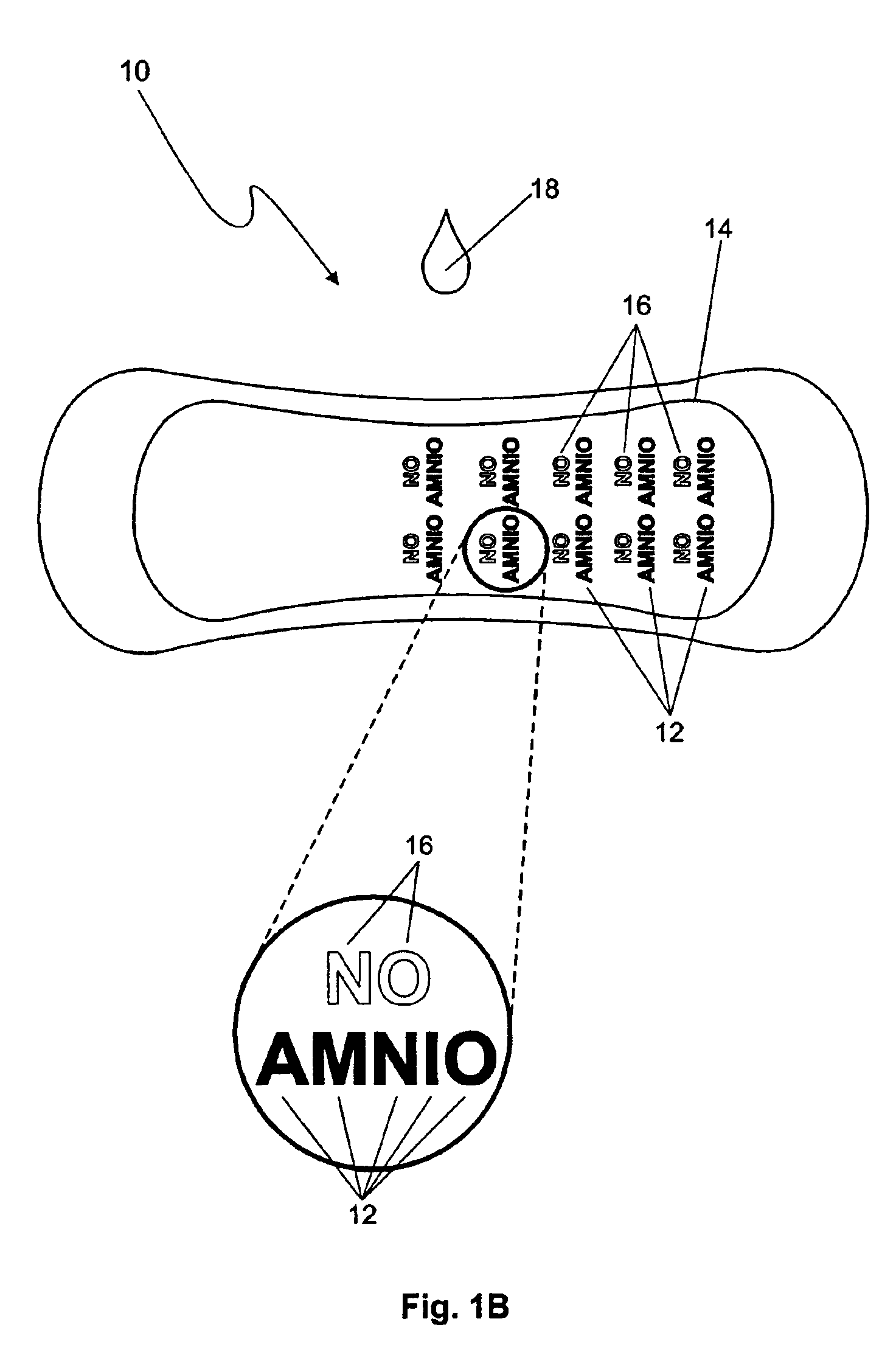
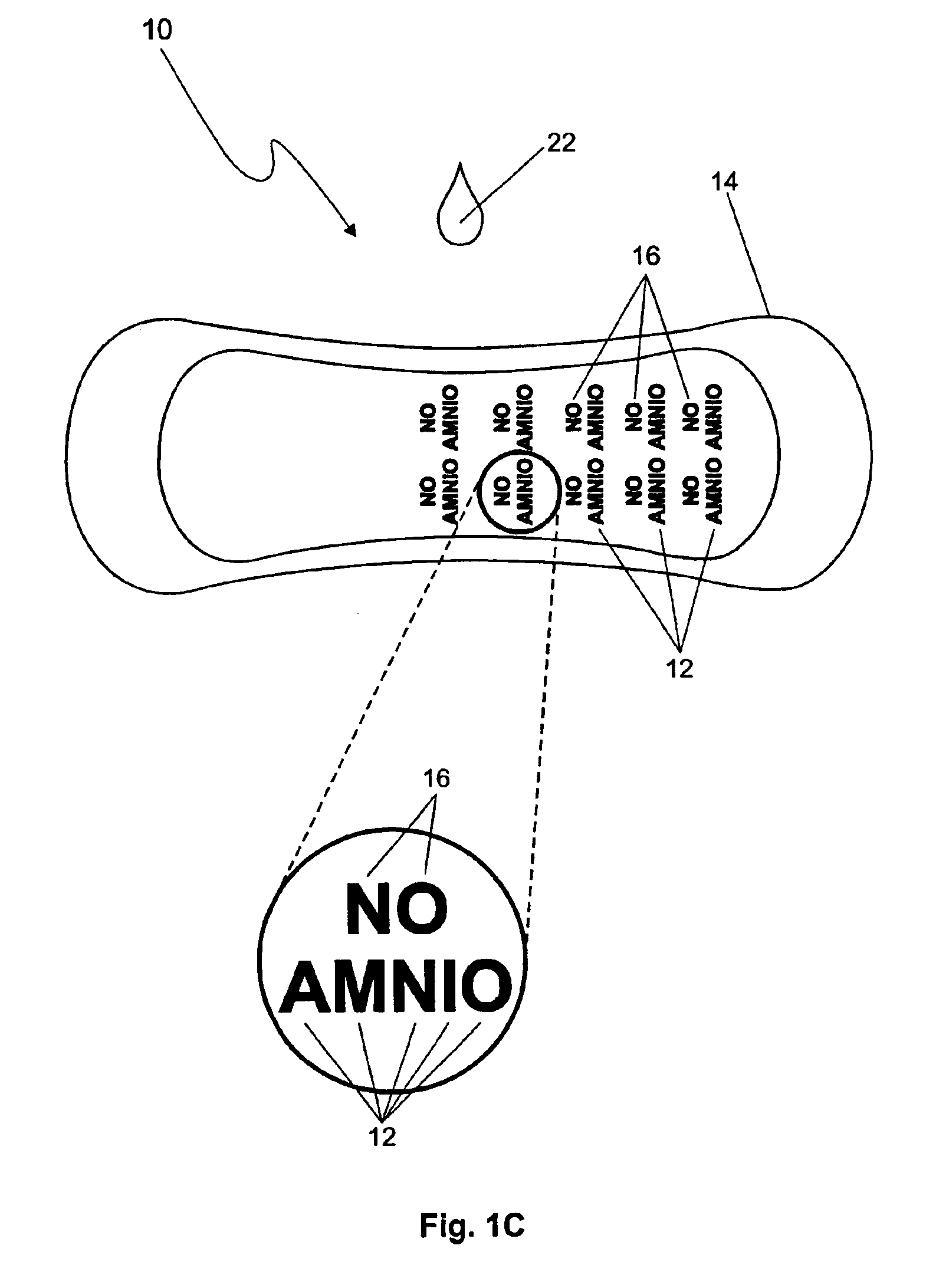
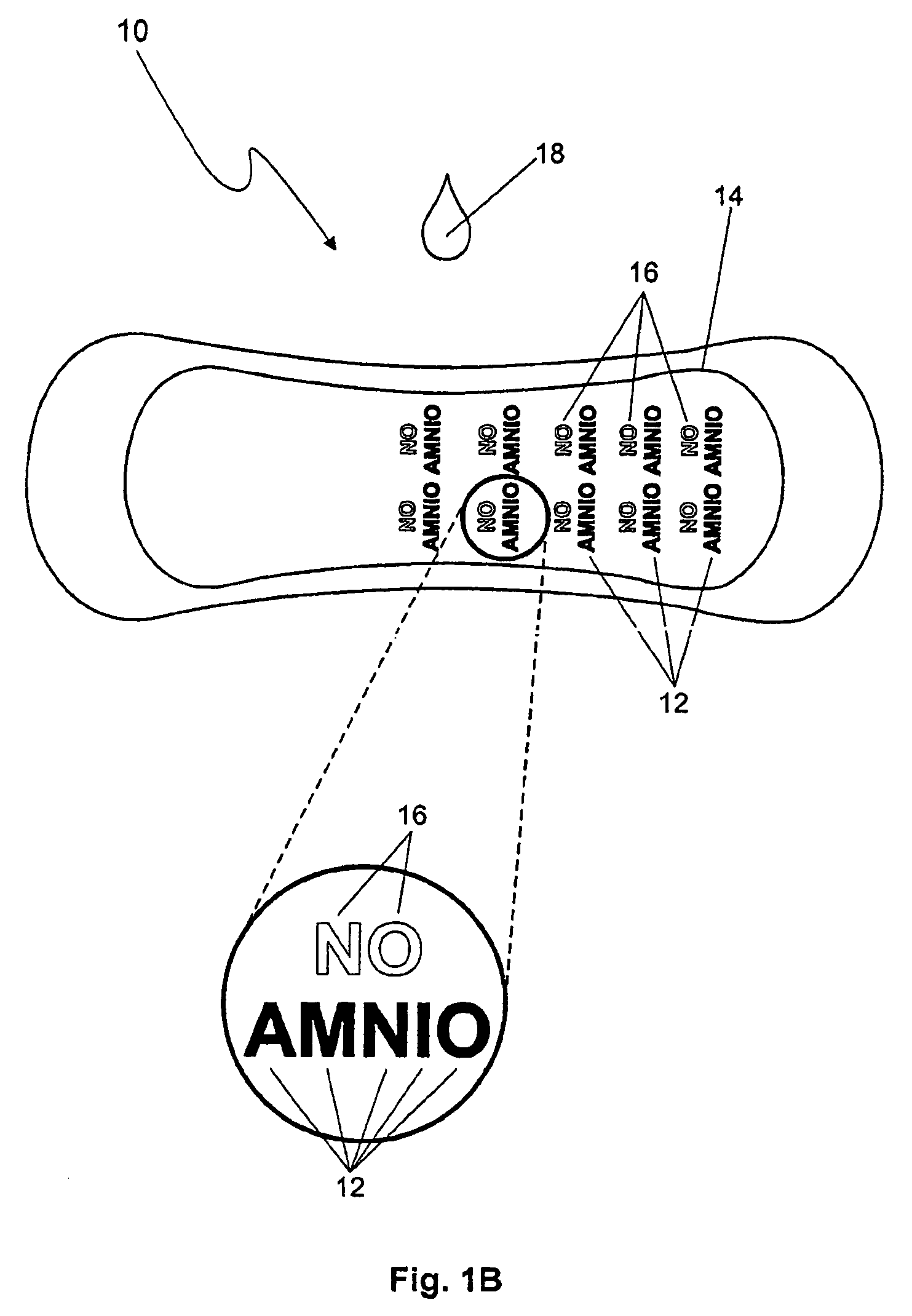
The premature rupture of amniotic fluid (PROM) may be discovered through a number of inventive means. Methods of evaluating whether PROM is present include; a) through the testing of the pH of vaginal fluids using an irreversible pH test; b) through the detection of analytes (e.g. enzymes) specific to amniotic fluid in the vaginal fluids; c) though the detection of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in the vaginal fluid; and d) through the detection of cholesterol in vaginal fluid. While individually indicative of PROM, it is desirable to combine at least two of these techniques to yield a powerful tool of even greater reliability. Test devices and feminine hygiene pads into which the test methods may be incorporated are also included herein.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Amnion and chorion replacement cover and uses thereof in surgical repair of muscles
Improved methods for a surgical repair of a muscle are described. The improvement includes covering a damaged site of muscle with at least one of an amniotic fluid and a replacement cover for muscle sheath prior to wound closing during the surgery. The replacement cover contains at least one layer of human amnion and chorion tissues and is adapted to a shape appropriate for enclosing the muscle. The methods reduce inflammation, inhibit fibrosis, scarring, fibroblast proliferation and post-operative infection, while also promote more rapid healing and smooth gliding of the affected muscle against adjacent structures. Related replacement covers, kits and methods of preparation are also described.
Owner:LIVENTA BIOSCI
Secretion-monitoring article
InactiveUS6921647B2Overcome disadvantagesReliable indicationMicrobiological testing/measurementVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsAmniotic fluidAbsorbent material
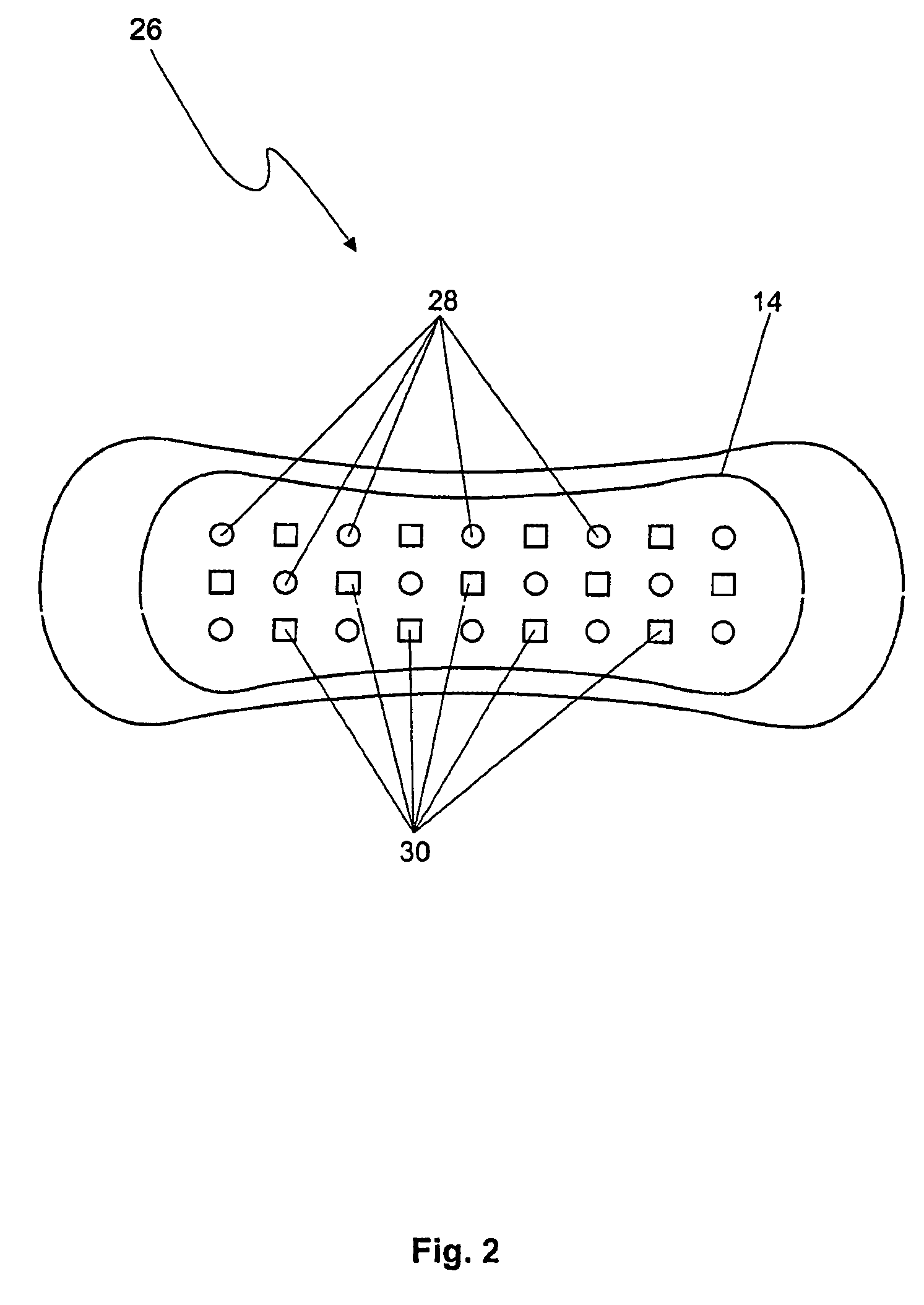
A secretion-monitoring article for identifying a secreted biological fluid having a body with an absorbent material and least one pH determining member and a reagent associated with the absorbent material is disclosed. The article can be embodied as a swab, gauze, panty shield, hygienic napkin, diaper or interlabial absorbent structure and can be used to indicate the presence of amniotic fluid, or secretions associated with bacterial, parasite, fungal, or yeast infections without giving a false positive result upon exposure to urine. The present invention also teaches a pH indicator mixture and method of attaching the indicator to a substrate for use alone or integrated in an absorbent body and further teaches a method for monitoring the health condition of a person using the secretion-monitoring article.
Owner:COMMON SENSE
Secretion-monitoring article
InactiveUS7314752B2Overcome disadvantagesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBacterial vaginosisAmniotic fluid
A secretion-monitoring article for identifying a secreted biological fluid. The article includes a body with an absorbent material for absorbing a biological fluid secreted from a person and an indicator system. The indicator system includes an indicator agent and an ion-balance reagent, wherein the indicator system provides an indication of physiological conditions associated with the pH or the buffer capacities of the biological fluid, which indication is stable for at least 48 and preferably at least 72 hours. The article can be embodied as a swab, gauze, shield, hygienic napkin, diaper or interlabial absorbent structure and can be used to indicate the presence of amniotic fluid, or secretions associated with bacterial vaginosis without giving a false positive result upon exposure to urine or after drying.
Owner:COMMON SENSE
Diagnostic pad
InactiveUS6627394B2Microbiological testing/measurementVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsAmniotic fluidEngineering
An indicator system including two pH sensitive indicators and a reagent is disclosed. The indicator system can be integrated into a number of products such as sanitary napkins or panty shields and thus can indicate the presence of amniotic fluid or secretions associated with vaginosis without giving a false positive result upon exposure to urine.
Owner:COMMON SENSE
Secretion-monitoring article
InactiveUS20070003993A1Overcome disadvantagesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBacterial vaginosisAmniotic fluid
A secretion-monitoring article for identifying a secreted biological fluid comprising a body with an absorbent material for absorbing a biological fluid secreted from a person and an indicator system. The indicator system comprises an indicator agent and an ion-balance reagent, wherein the indicator system provides an indication of physiological conditions associated with the pH or the buffer capacities of the biological fluid, which indication is stable for at least 48 hours, preferably at least 72 hours. The article can be embodied as a swab, gauze, shield, hygienic napkin, diaper or interlabial absorbent structure and can be used to indicate the presence of amniotic fluid, or secretions associated with bacterial vaginosis without giving a false positive result upon exposure to urine or drying out.
Owner:COMMON SENSE
Use of Amniotic Fluid (Af) in Treating Ocular Disease and Injury
InactiveUS20080286378A1Hindering surgical procedureEasy accessSenses disorderMammal material medical ingredientsDiseaseAmniotic fluid
Compositions and methods for the treatment of ocular disease and injury are provided. The methods involve the administration of amniotic fluid directly to the eye, for example, as eye drops. The types of diseases and injuries that can be treated in this manner include chemical burns, dry eye and corneal neovascular disorders, corneal opacities (including corneal haze) and inflammatory diseases of the eye.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Acellular amnion derived therapeutic compositions
ActiveUS9132156B1Reduce in quantityInduce and responsePowder deliveryCosmetic preparationsAmniotic fluidViable cell
Acellular amnion derived therapeutic compositions are described having a number of various compositional embodiments. An acellular amnion derived therapeutic composition has essentially no live or active amniotic stems cells. The amniotic stem cells may be destroyed, and the cells and cell debris may be removed from the acellular amnion derived therapeutic composition. An acellular amnion derived therapeutic composition may comprise micronized amniotic membrane particles, and / or amniotic fluid. An acellular amnion derived therapeutic composition may be a dispersion of micronized amniotic membrane combined with a fluid, such as plasma, saline, amniotic fluid, combinations thereof and the like. An acellular amnion derived therapeutic composition may be combined with a matrix component to form a composite. An acellular amnion derived therapeutic composition may be used in conjunction with a composition comprising viable cells, such as stem cells.
Owner:AMNIO TECH +1
Amnion and chorion constructs and uses thereof in sport injury surgeries
Improved methods for sport injury surgeries are described. The improvement includes covering a damaged site of fascia with at least one of an amniotic fluid and a construct for use in surgical repair of the sport injury prior to wound closing. The construct contains an allograft comprising at least one layer of human amnion and chorion tissues and the construct has a size and shape suitable for covering the damaged site of fascia. The method improves fascial membrane repair, reduces complications and recovery time of sport injury surgeries.
Owner:LIVENTA BIOSCI
Skin formulation, preparation and uses thereof
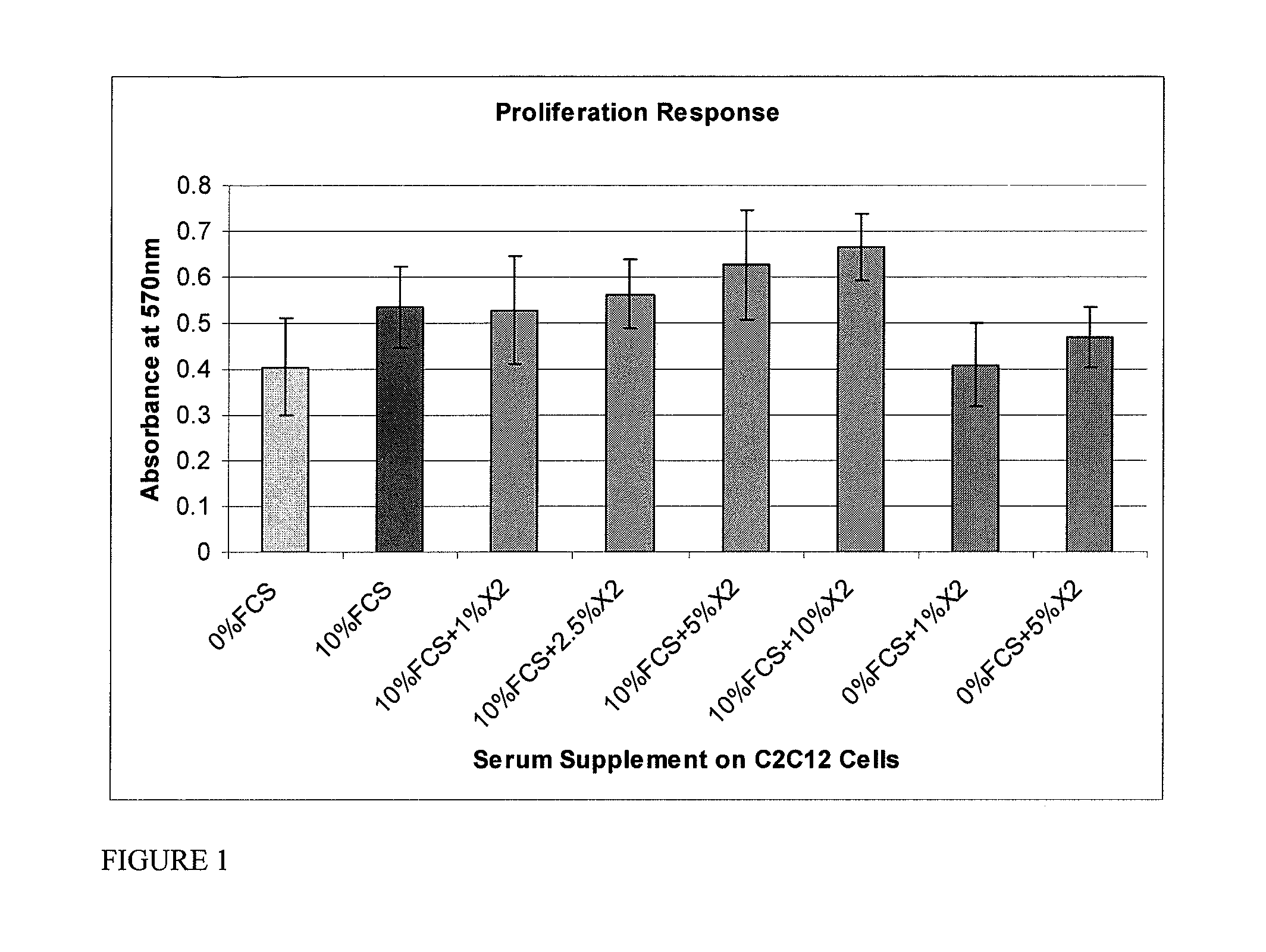
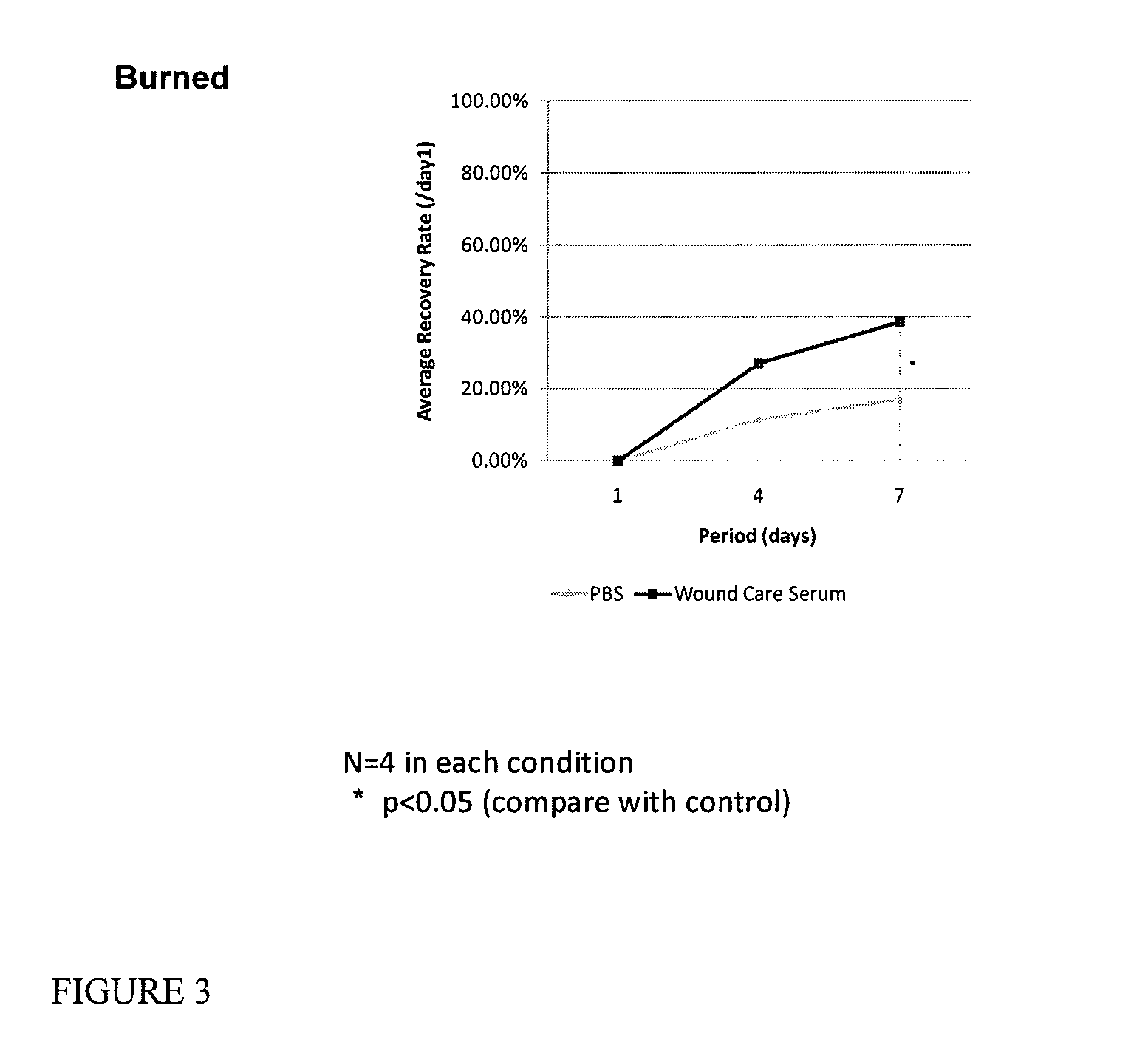
Serum compositions for application to skin are described which contain an amniotic fluid extract in combination with embryonic stem cells. Formulations containing the serum composition are also described. The serum compositions and formulations may be applied to skin for treatment of symptoms of aging, wounds, burns, scars or other skin lesions. Methods of preparing the serum compositions and formulations are also disclosed.
Owner:GOLDEN PEARL INVESTMENT
Method for Obtaining Sterile Human Amniotic Fluid and Uses Thereof
ActiveUS20150025366A1Improve stabilityFacilitating and minimizing costSurgeryMedical devicesWound healingMedicine
Provided herein is a method for sterilely filtering amniotic fluid from selected caesarean sections of an individual. The amniotic fluid is first centrifuged at 5,000 to 10,000 rpm for 30 to 60 minutes and filtered through filters with about 5 to about 10 μm pore size. Next, the fluid is sequentially filtered through a series of membrane filters with the pore sizes 1 μm and 0.45 or / and 0.2 μm. The filtrate is then aseptically transferred to and sealed in syringes or vials. The fluid is subsequently lyophilized to obtain the lyophilisate of amniotic fluid. Amniotic fluid is reconstituted by adding sterile water to the lyophilisate, and the reconstituted fluid is used for wound healing, cosmetic, orthopedic or ophthalmic applications, particularly for the treatment of dry eyes.
Owner:MAM HLDG OF WEST FLORIDA L L C
Devices and methods for detecting amniotic fluid in vaginal secretions
ActiveUS7709272B2Minimizing false positive resultLower and accurately set up the threshold of sensitivity of the deviceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAmniotic fluidVaginal secretion
Owner:QIAGEN SCIENCES LLC
Method for Obtaining Sterile Human Amniotic Fluid and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20140336600A1Reduce riskFree from painMicrobiological testing/measurementMedical devicesIncision SiteAmniotic fluid
Provided herein is a pre-Caesarean method for collecting amniotic fluid from a patient. A needle is inserted into the incision site for the future C-section, which may be under ultrasound guidance, through which the amniotic fluid is drawn under a low level suction and, optionally, gravity to a sterile collection container. The method encompasses filtering and / or irradiating the amniotic fluid to collect biomolecules of interest such as growth factors and / or stem cells. Also provided is the sterile amniotic fluid or filtrates thereof collected by the method described herein
Owner:MAM HLDG OF WEST FLORIDA L L C
Two-stage culture protocol for isolating mesenchymal stem cells from amniotic fluid
ActiveUS7101710B2Encourage illegal terminationRaise the possibilityArtificial cell constructsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsAmniotic fluid cellAmniotic fluid
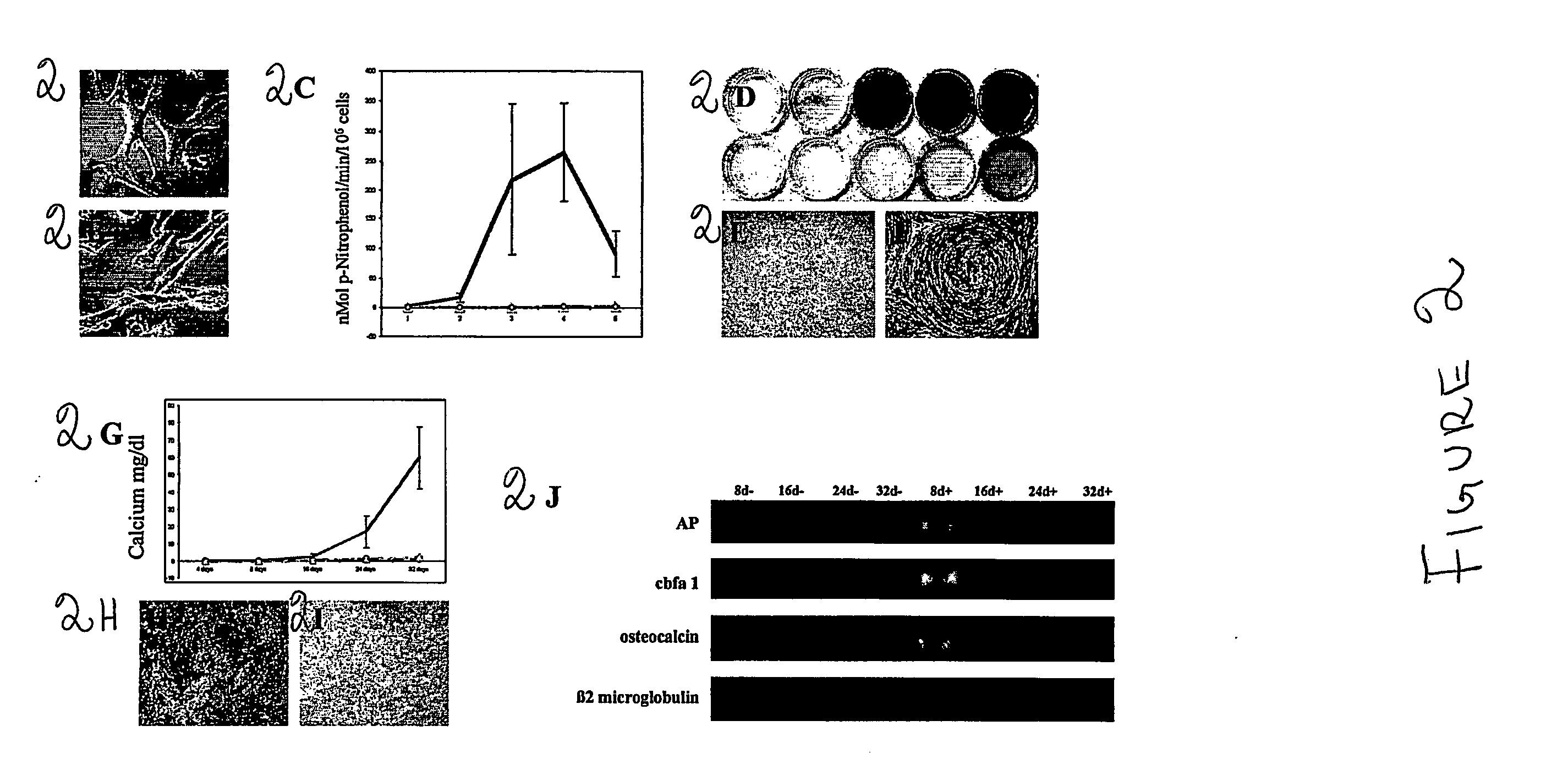
A method of harvesting mesenchymal stem cells from human amniotic fluid uses a two-stage culture protocol comprising culturing human amniocytes and then culturing mesenchymal stem cells. For culturing human amniocytes, primary amniocyte cultures are set up using routine or standard culture protocol in a cytogenetic laboratory. Non-adherent human amniotic fluids cells in the supernatant medium are collected. For culturing mesenchymal stem cells (“MSC”), the non-adherent cells are centrifuged and then plated with an alpha-modified Minimum Essential Medium supplemented with fetal bovine serum. Incubate with humidified CO2 for MSC growth. Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (“RT-PCR”) and immunocytochemical analyses reveal that Oct-4 mRNA and OCT-4 protein expression is detectable in the cultured amniotic fluid mesenchymal stem cells (“AFMSCs”). Under differentiation culture conditions, the AFMSCs can be induced to develop into multi-lineage cells, such as adipocytes, osteocytes, neuronal cells, etc.
Owner:U NEURON BIOMEDICAL INC
Composition for Improving Skin Conditions Using Fetal Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Amniotic Fluid
The present invention relates to a culture medium for the fetus-derived mesenchymal stem cells in amniotic fluid. More particularly, the present invention relates to a composition for improving skin conditions, comprising the culture medium of fetus-derived mesenchymal stem cells in amniotic fluid as an active ingredient, in which the skin conditions to be improved include whitening, wrinkles, skin damages caused by UV rays or skin lifting. Further, the present invention relates to a method for preparing the composition, comprising the steps of culturing the fetus-derived mesenchymal stem cells in amniotic fluid; and collecting the culture medium.
Owner:STEMMEDIENCE
Medical dressing with bioactivity and preparation method of medical dressing
InactiveCN106139230AAvoid immune rejectionImprove mechanical propertiesAbsorbent padsBandagesDiseaseFreeze-drying
The invention relates to a medical dressing with bioactivity and a preparation method of the medical dressing and belongs to the technical field of biomedical engineering and material science. The medical dressing with the bioactivity is used for covering skin defect wounds caused by burning, scalding, operation, wounds and diseases and inducing wound repair and is prepared as follows: one or more of embryonic stem cells, umbilical cord blood stem cells, amniotic fluid stem cells, peripheral blood stem cells and bone mesenchymal stem cells of humans or animals are cultured in vitro, stem cell growth factors secreted in the logarithmic growth phase are collected and mixed in proportion with one or more of I type collagen, III type collagen, chitosan, hyaluronic acid, chondroitin sulfate and sodium alginate, thin-layer sponge is taken as an inner layer, a porous high-polymer material film outer layer prepared from a mixture formed by one or more of PLA (polylactic acid), PGA (polyglycolic acid), PLGA (poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)) and PCL (polycaprolactone) is attached, the product is frozen-dried and cut, and the medical dressing with the bioactivity is formed and used for treating skin defect wounds caused by burning, scalding, operation, wounds and diseases and inducing wound repairing.
Owner:南京天其美生物技术有限公司
Detecting bacteria in fluids
InactiveUS20070211251A1Microbiological testing/measurementScattering properties measurementsLight scatter measurementFiltration
A method for the detection of bacteria in aqueous fluids in the form of solutions, emulsions and or suspensions, such as drinking water, liquid food and drinks and biological fluids such as urine, spinal and / or amniotic fluids and serums by measurement of light scattering The fluid suspected of containing bacteria is filtered, first to exclude particles of sizes larger than the size of the expected bacteria. Other filtration methods are used in addition to exclude different constituents of the examined fluid. Ion exchange chromatography is such a method. The verification of bacterial contamination and the calculation of its level is performed by matching measured scattering profiles with pre-stored calibrated scattering profiles. A system for carrying out the measurements including cuvette units suited for light scattering measurements is provided.
Owner:WEISCHSELBAUM AMNON
Methods of isolation, expansion and differentiation of fetal stem cells from chorionic villus, amniotic fluid, and placenta and therapeutic uses thereof
InactiveUS7968336B2Sufficient supplyRaise the potentialNervous disorderMuscular disorderAmniotic fluidTransfection
The present invention is directed to pluripotent fetal stem cells derived from chorionic villus, amniotic fluid, and placenta and the methods for isolating, expanding and differentiating these cells, and their therapeutic uses such as manipulating the fetal stem cells by gene transfection and other means for therapeutic applications.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Skin formulation, preparation and uses thereof
Serum compositions for application to skin are described which contain an amniotic fluid extract in combination with embryonic stem cells. Formulations containing the serum composition are also described. The serum compositions and formulations may be applied to skin for treatment of symptoms of aging, wounds, burns, scars or other skin lesions. Methods of preparing the serum compositions and formulations are also disclosed.
Owner:GOLDEN PEARL INVESTMENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com