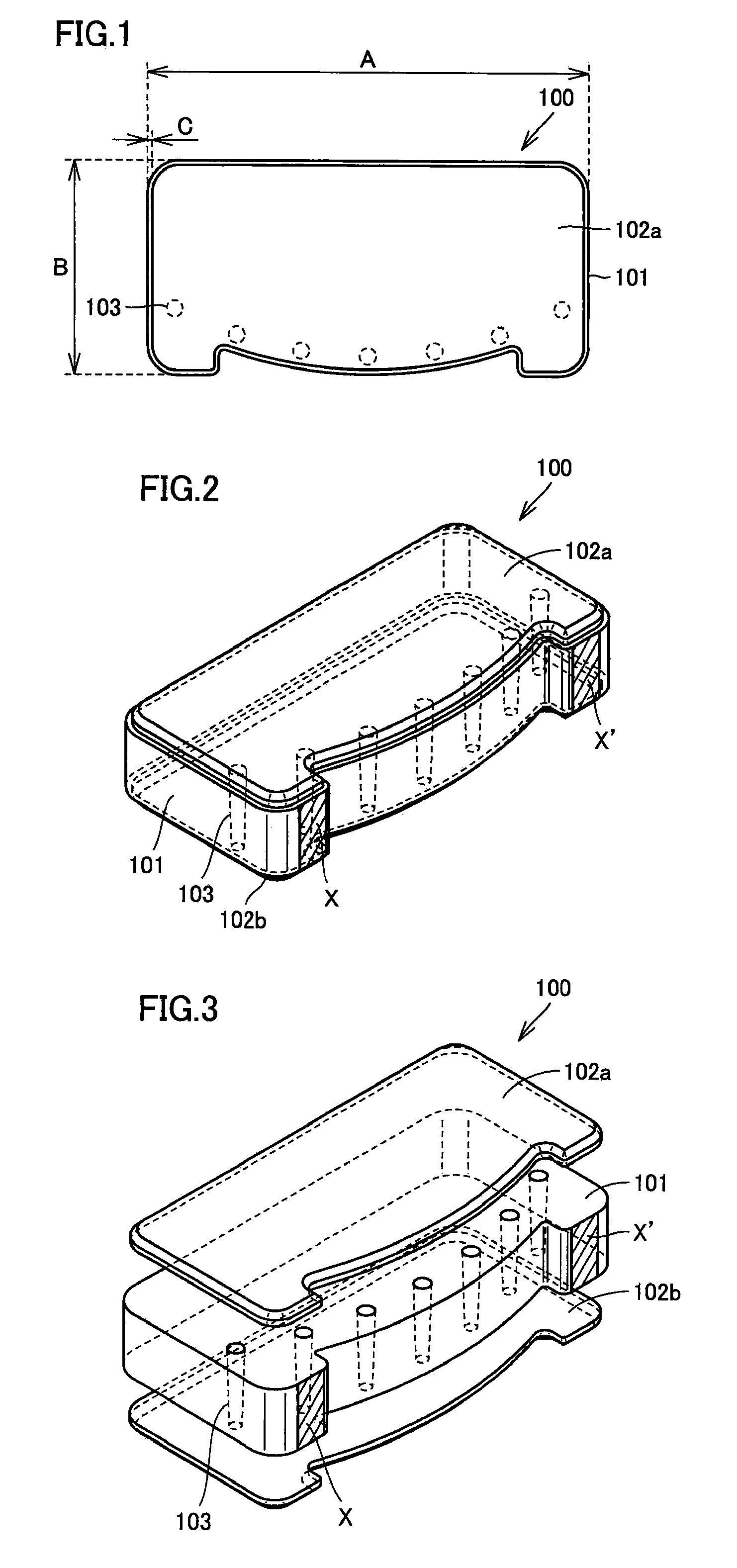
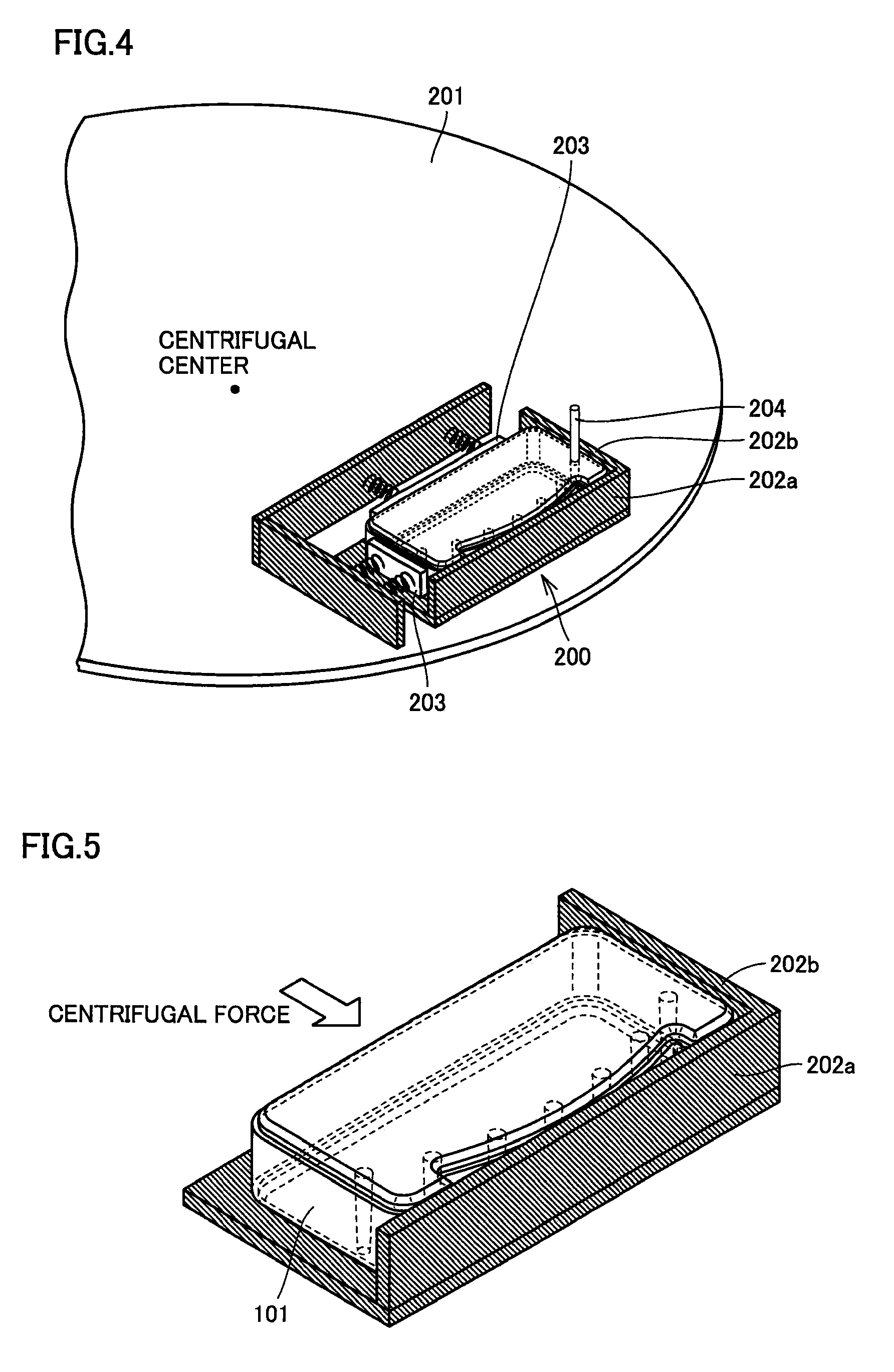
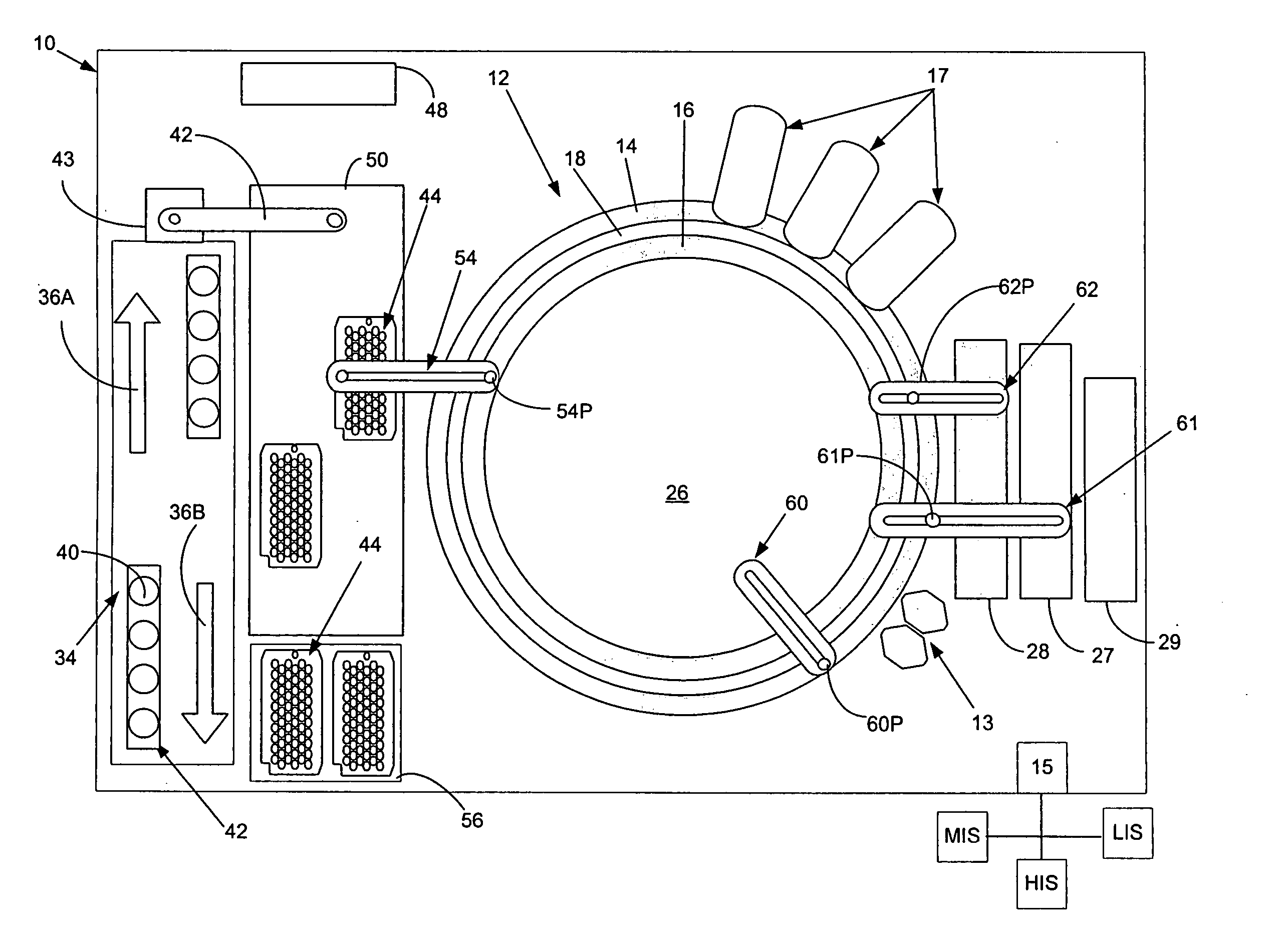
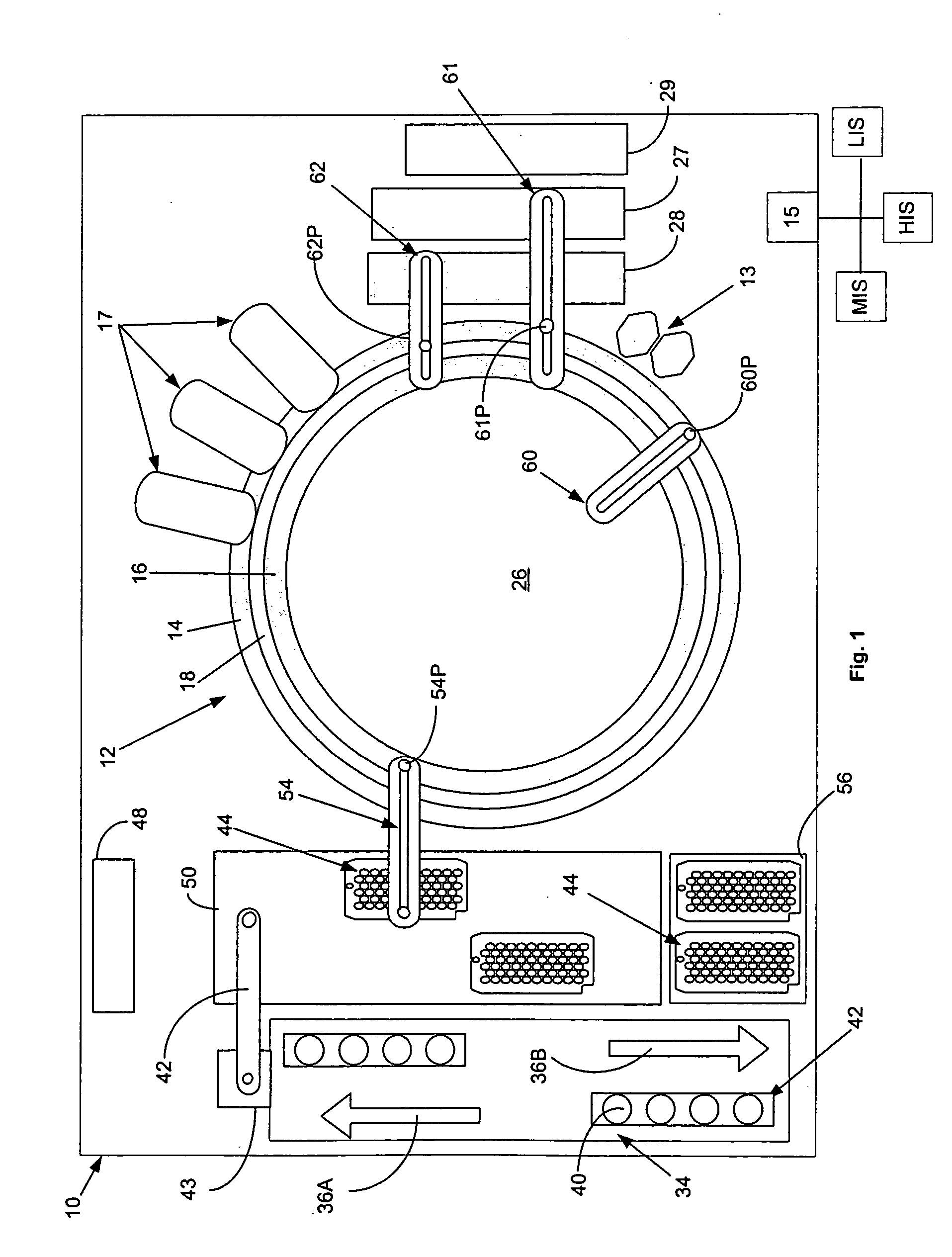
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1306 results about "Cuvette" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A cuvette (French: cuvette = "little vessel") is a small tube-like container with straight sides and a circular or square cross section. It is sealed at one end, and made of a clear, transparent material such as plastic, glass, or fused quartz. Cuvettes are designed to hold samples for spectroscopic measurement, where a beam of light is passed through the sample within the cuvette to measure the absorbance, transmittance, fluorescence intensity, fluorescence polarization, or fluorescence lifetime of the sample. This measurement is done with a spectrophotometer.
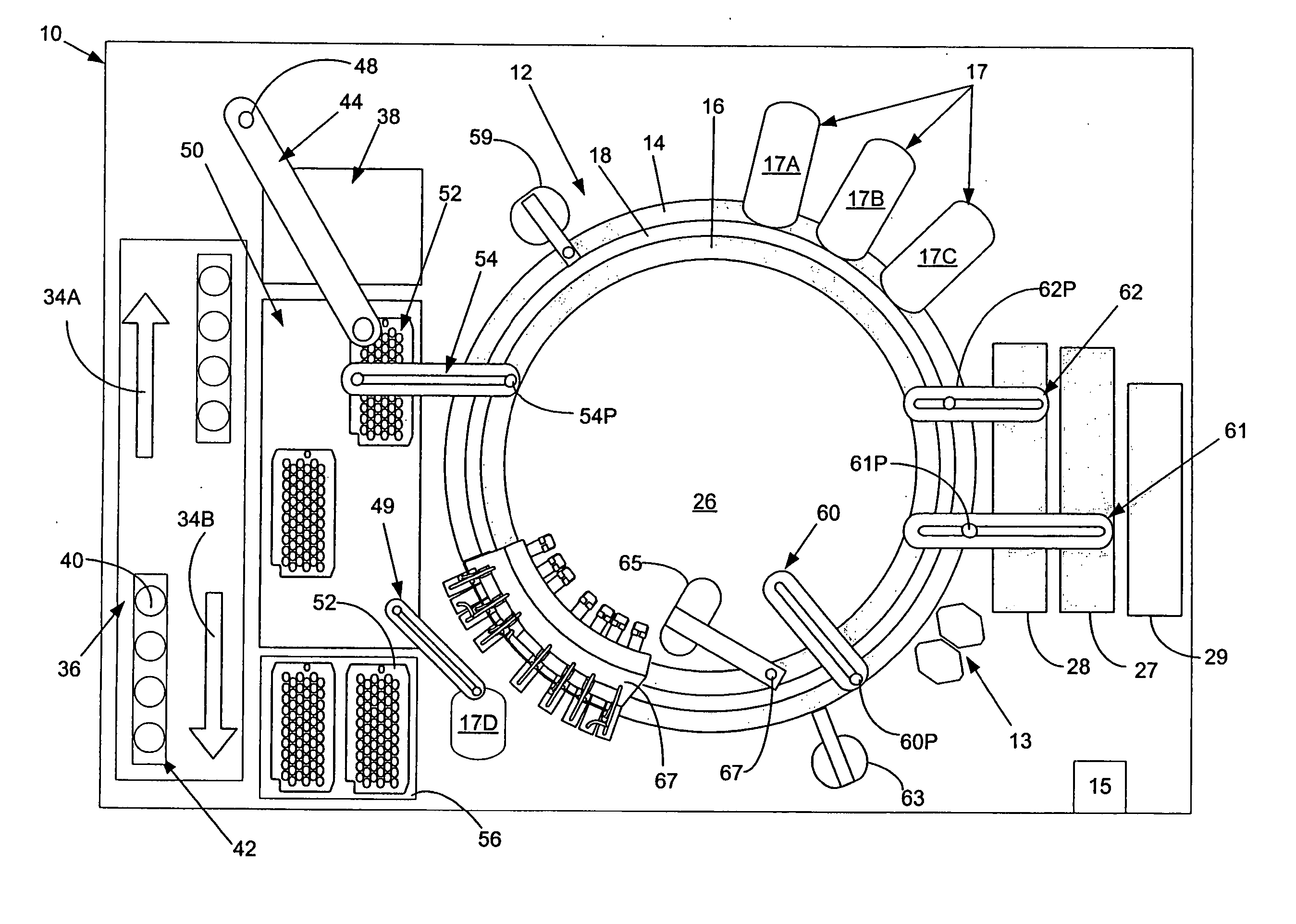
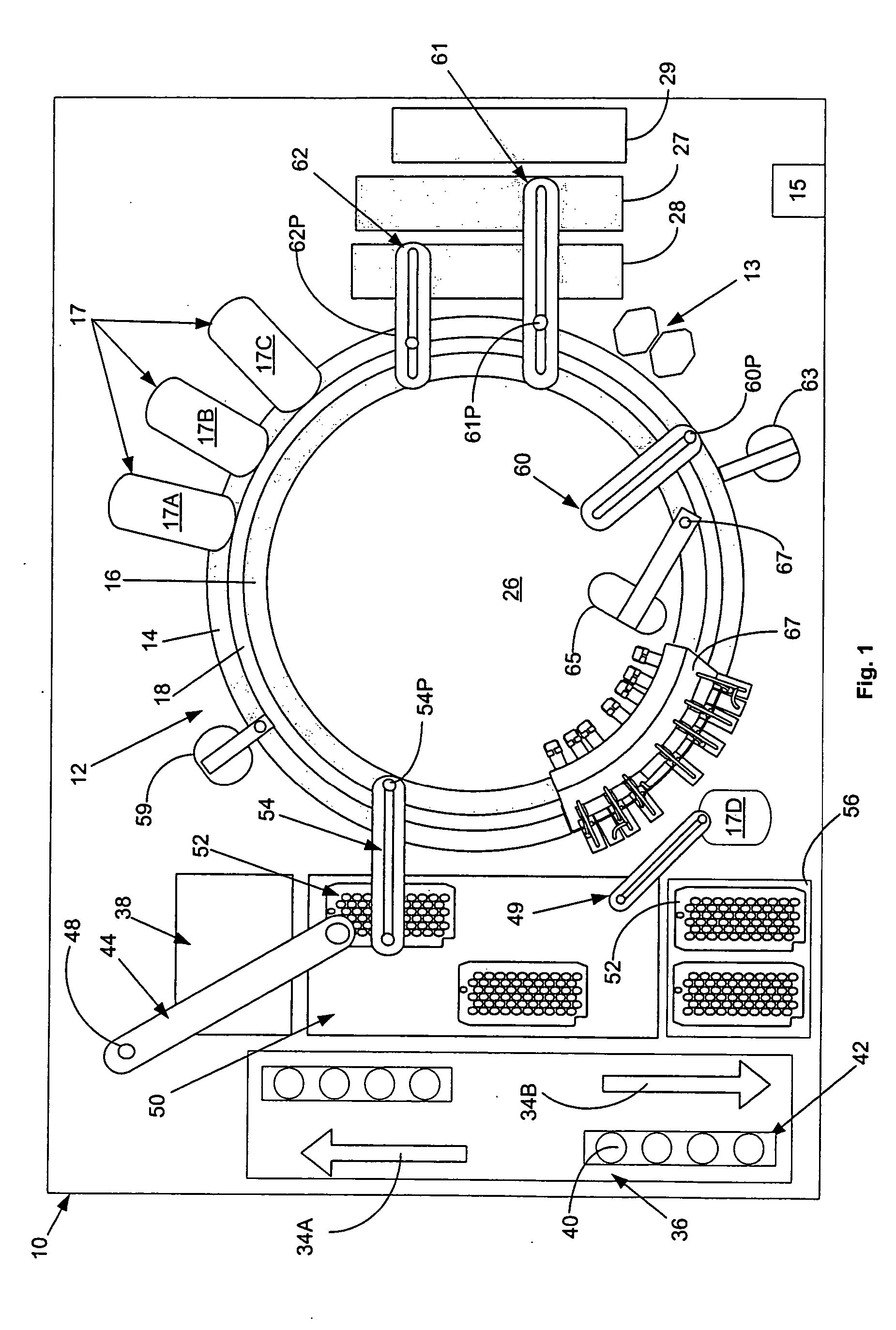
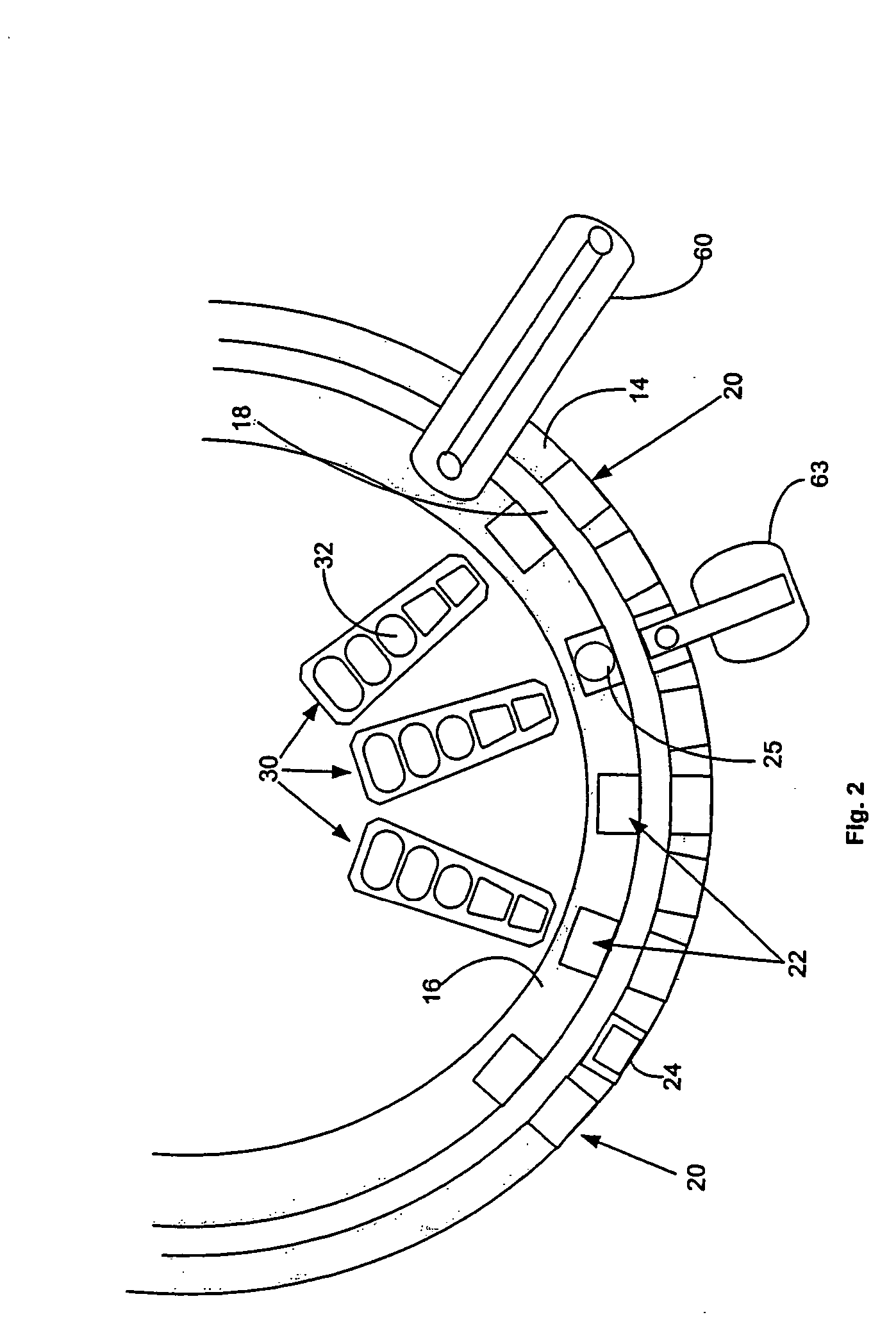
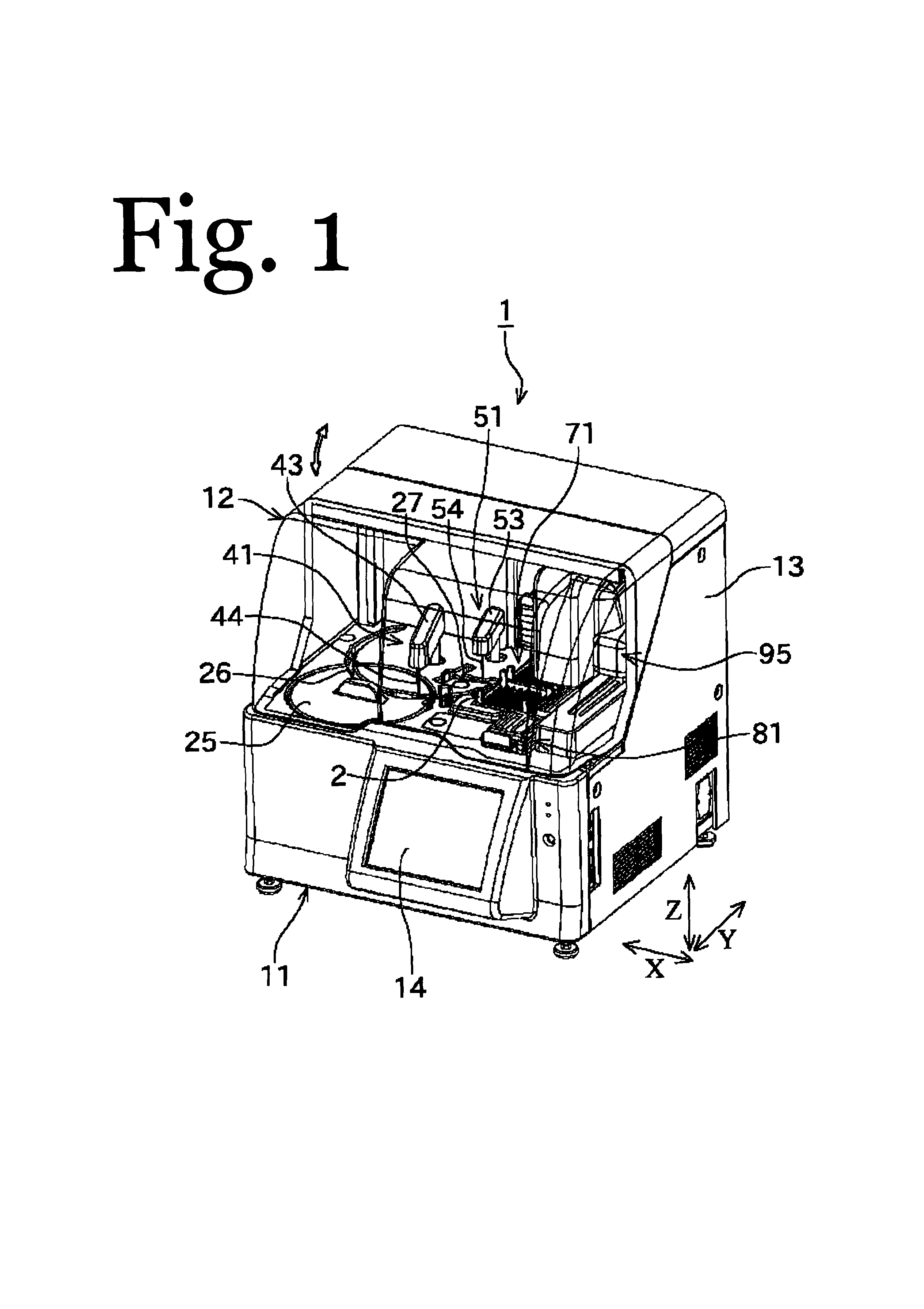
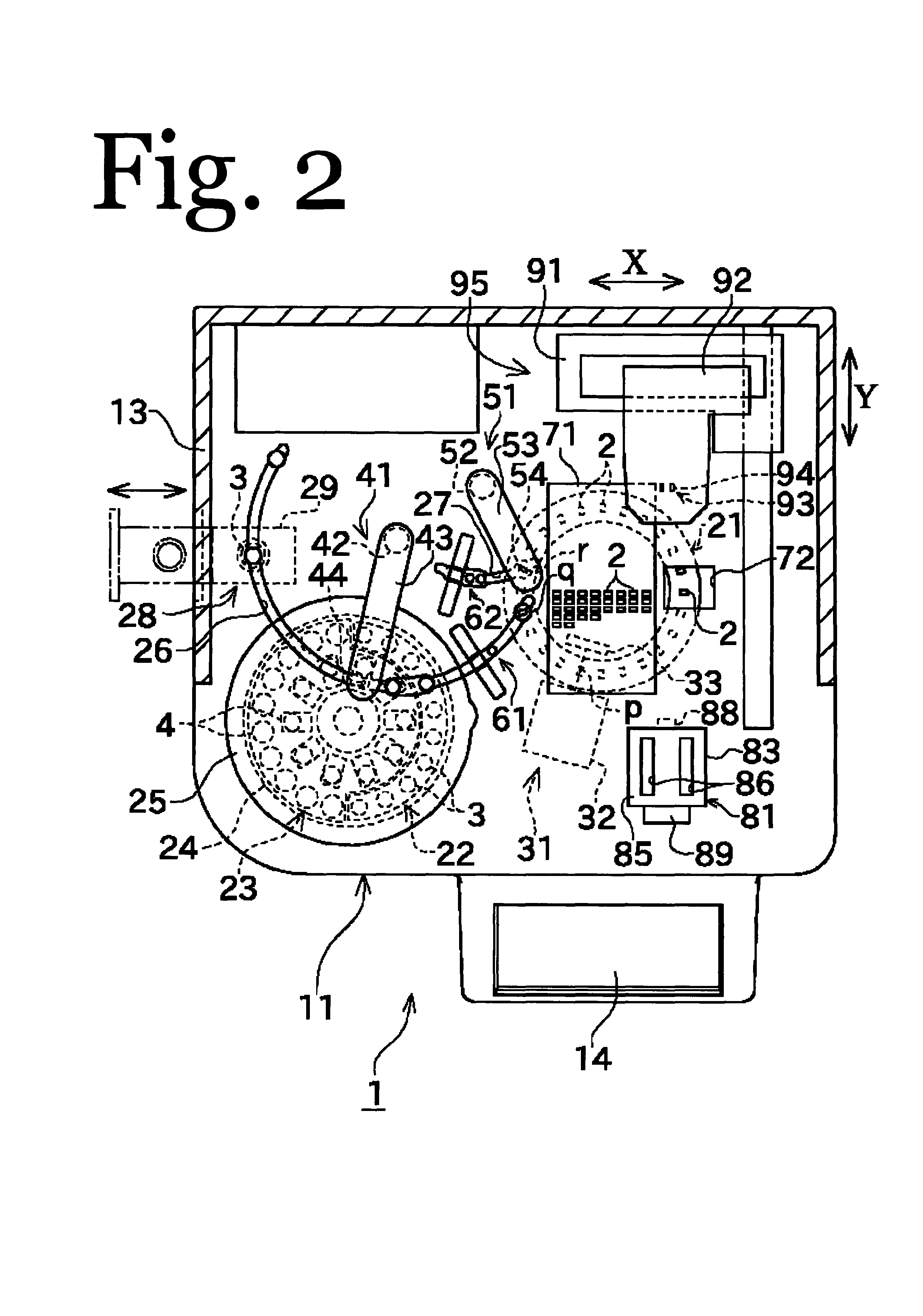
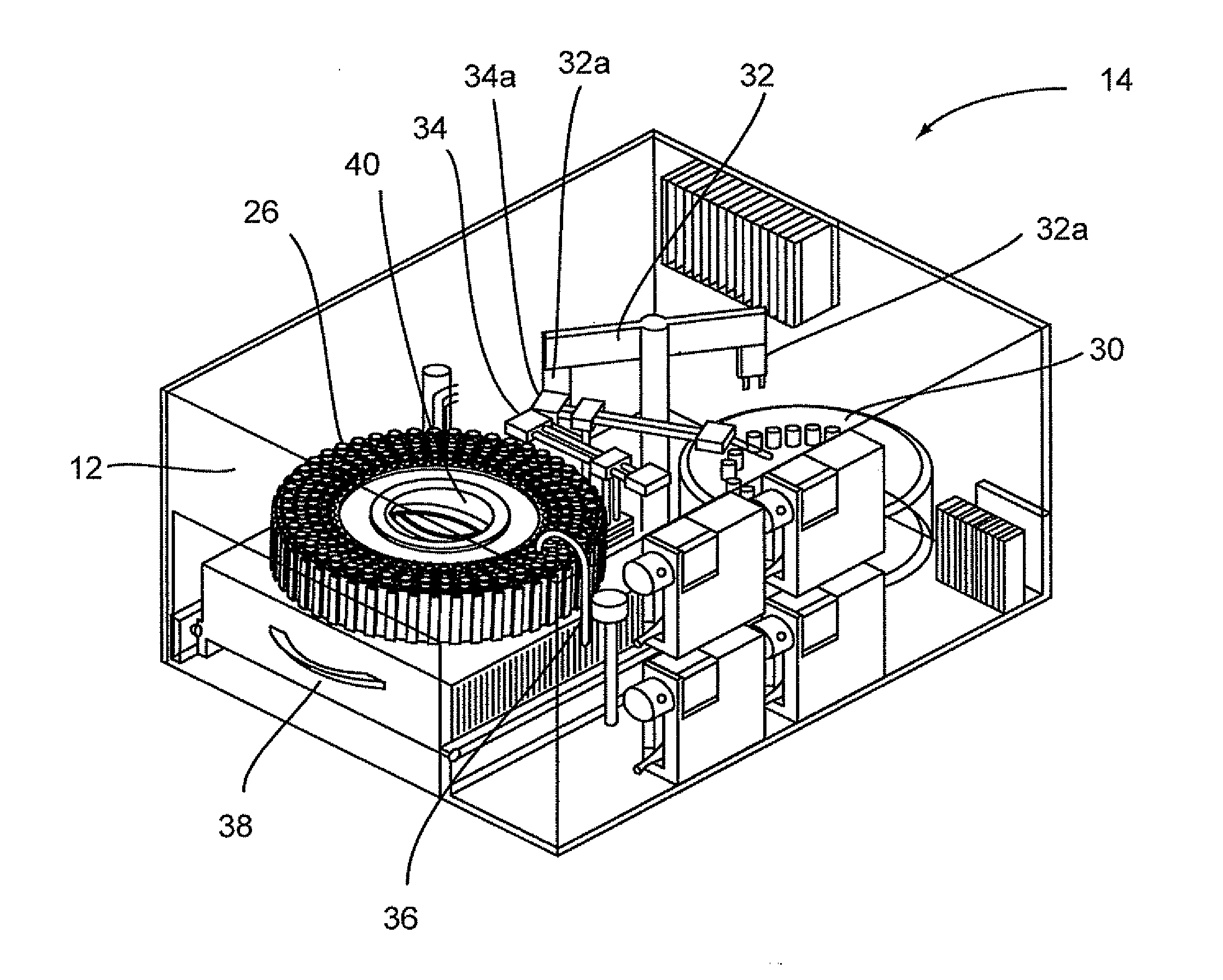
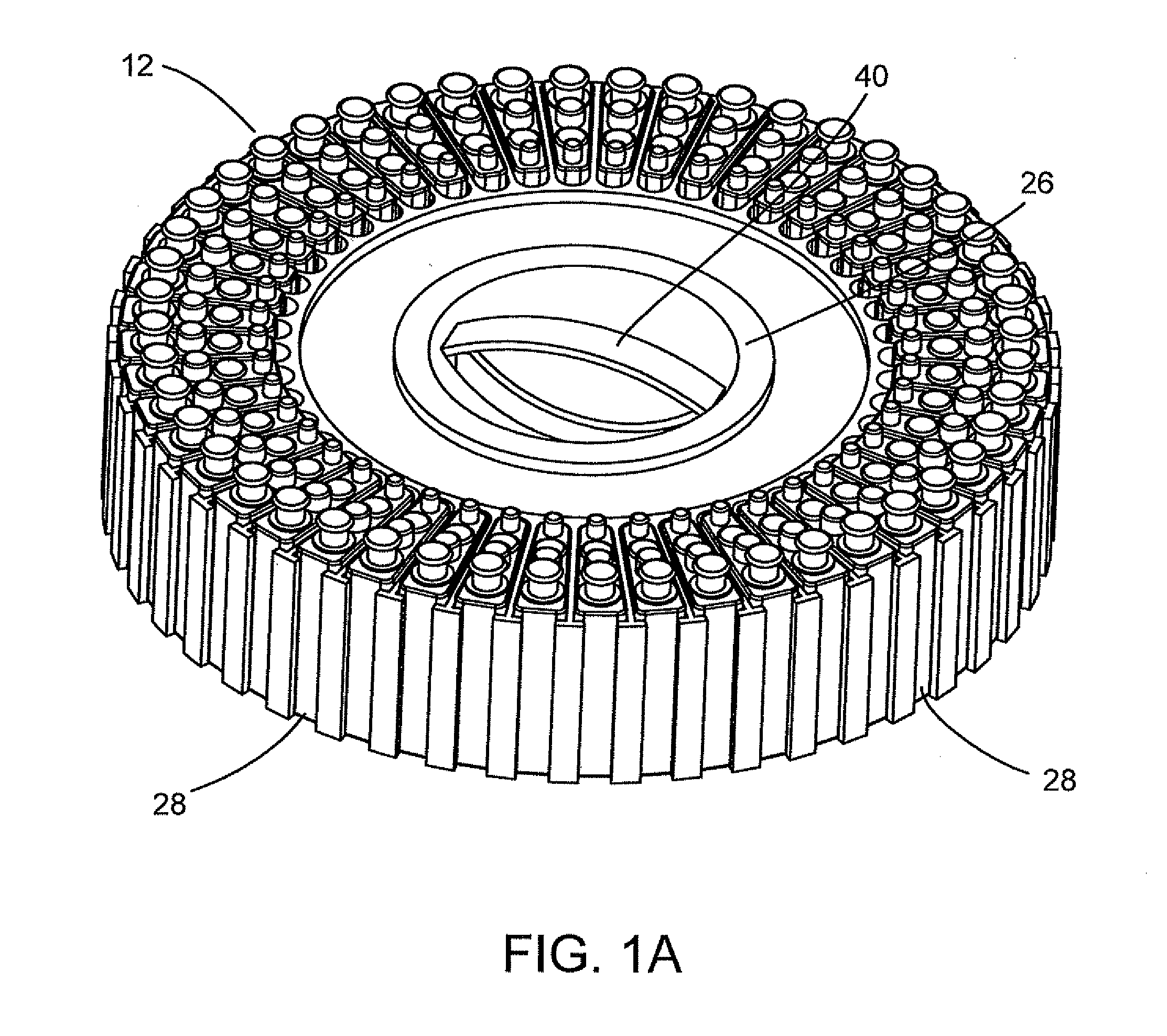
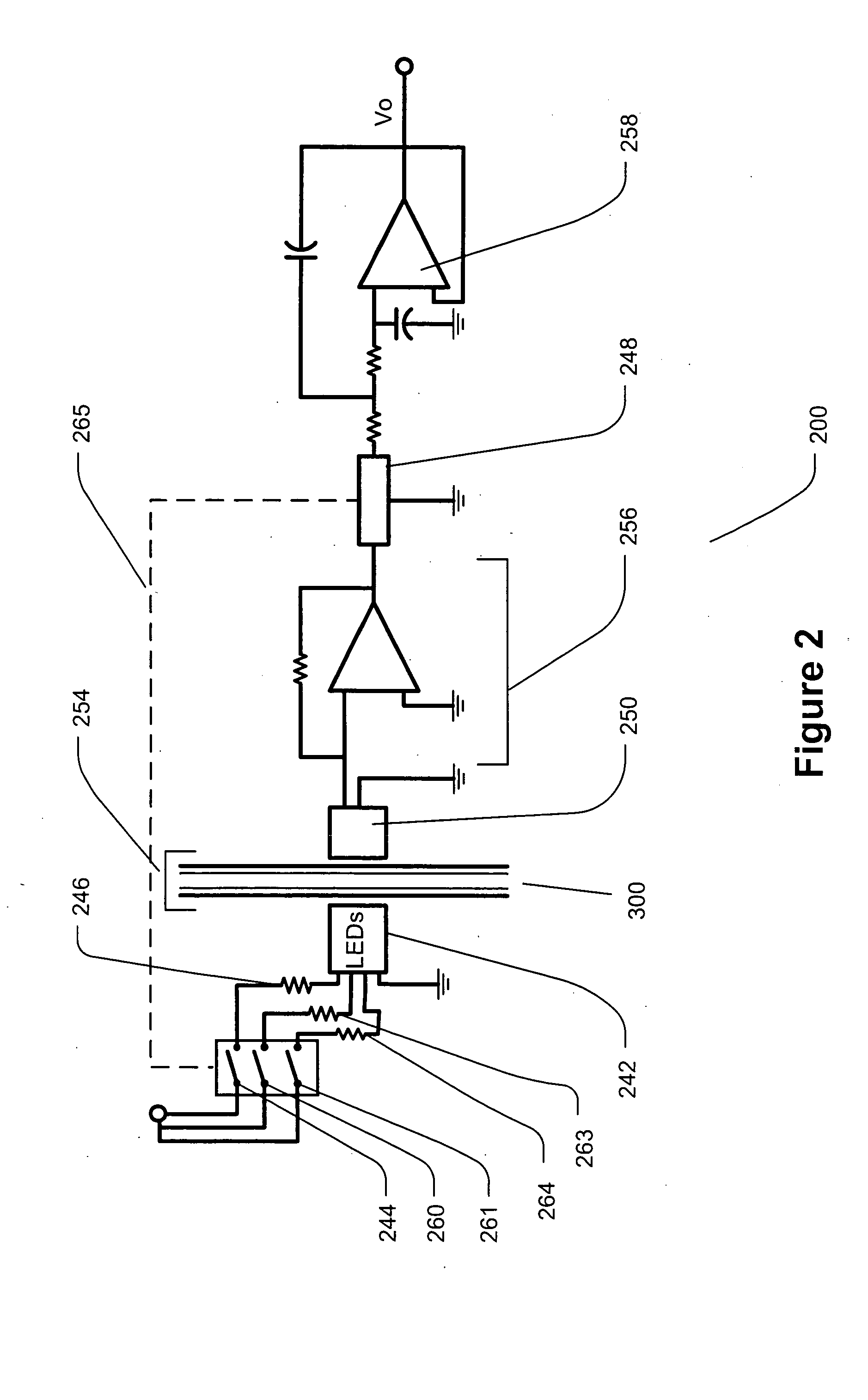
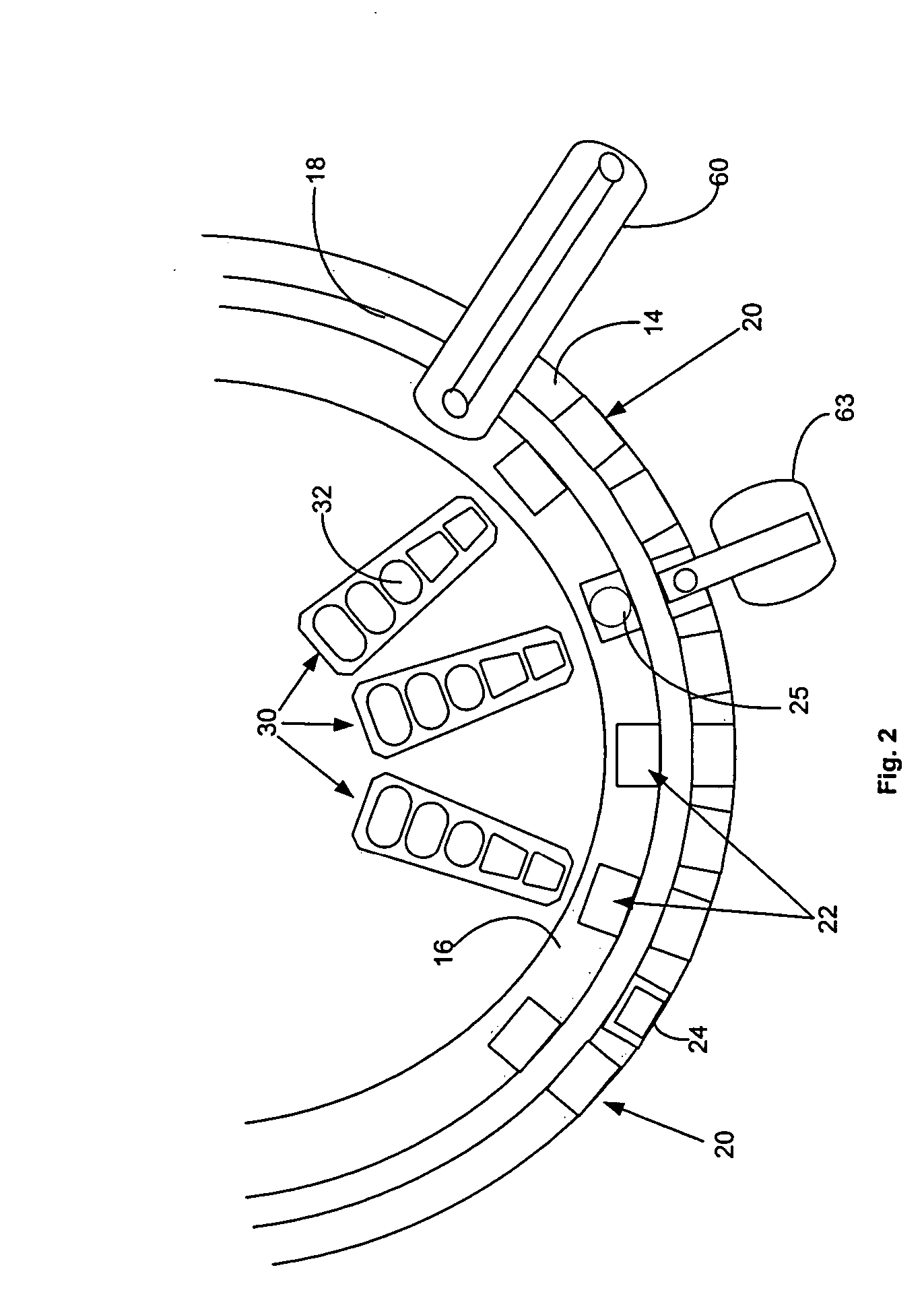
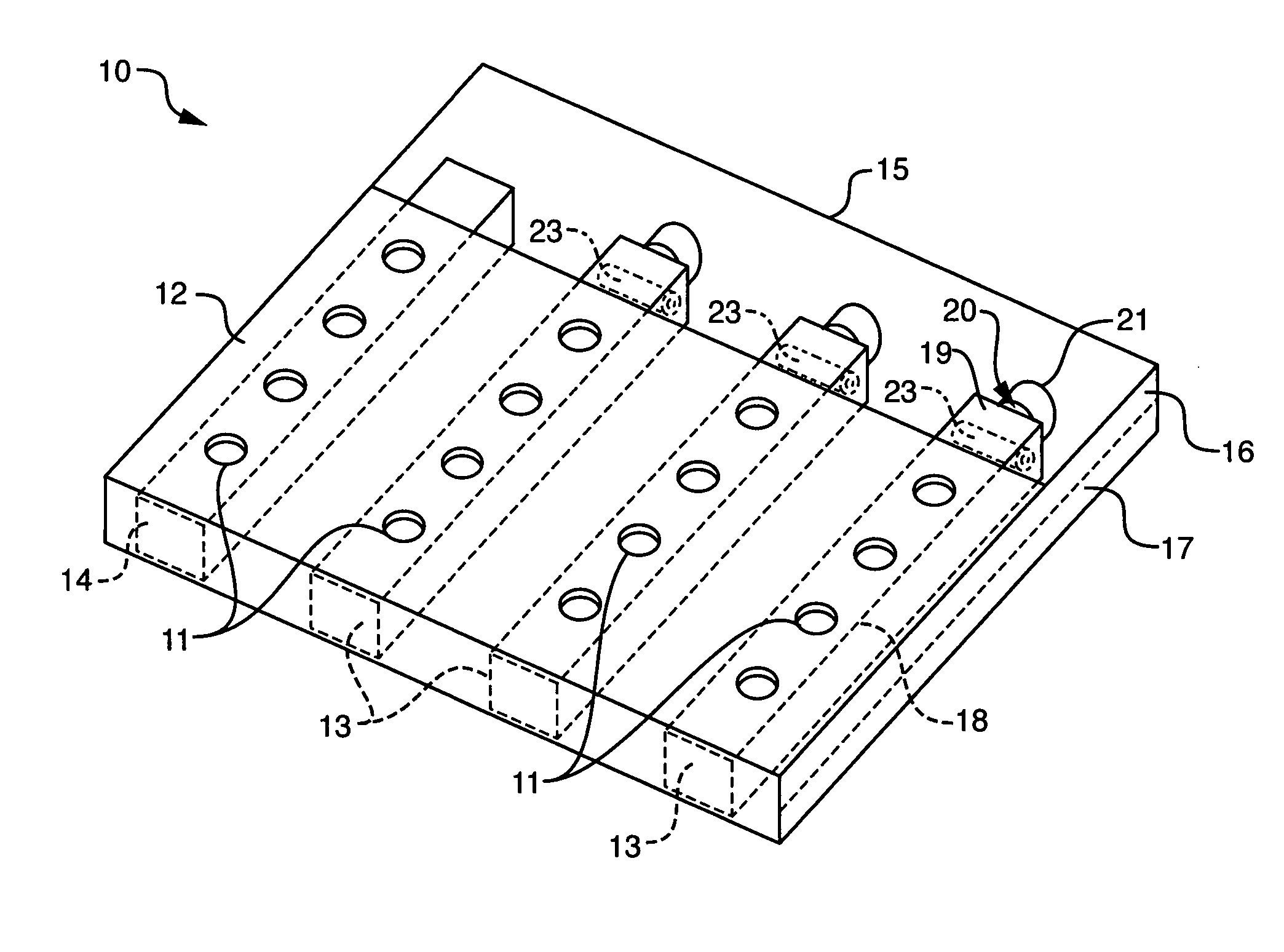
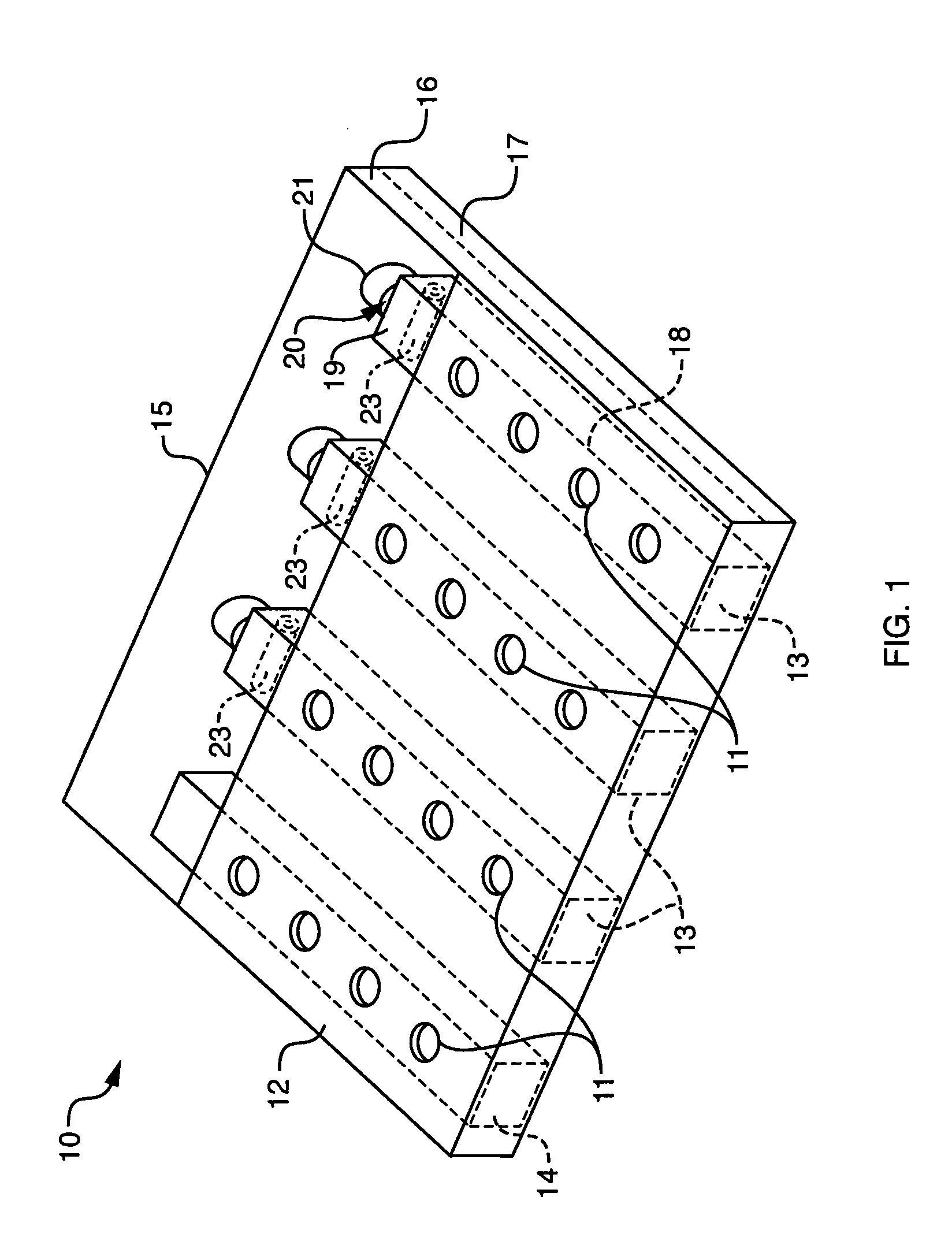
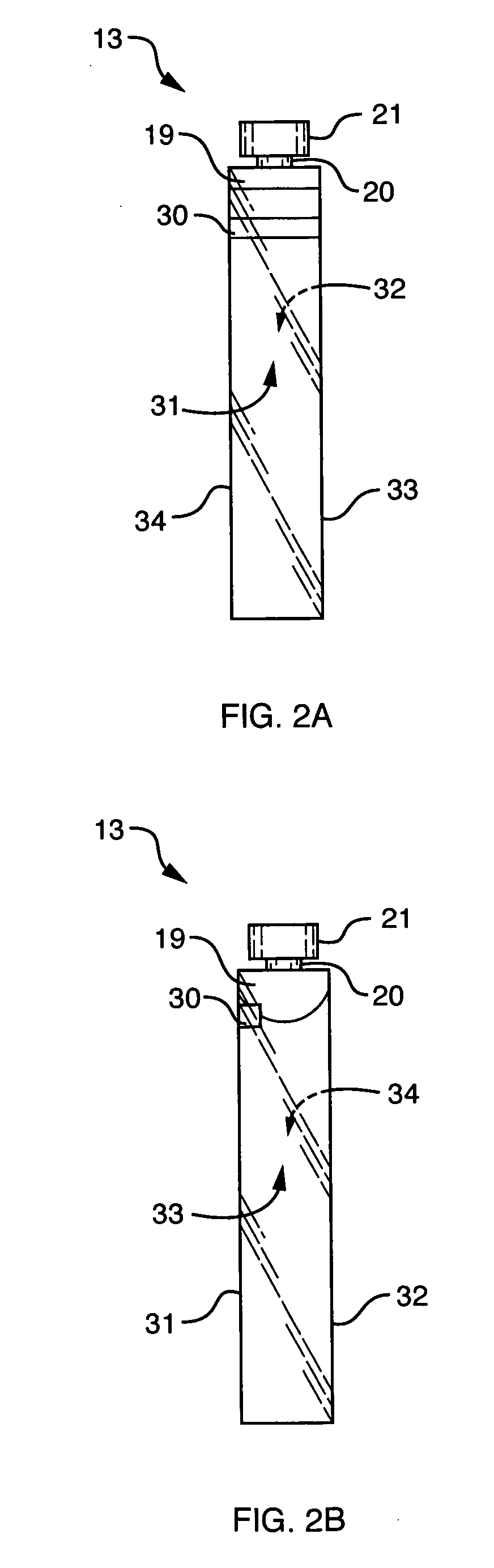
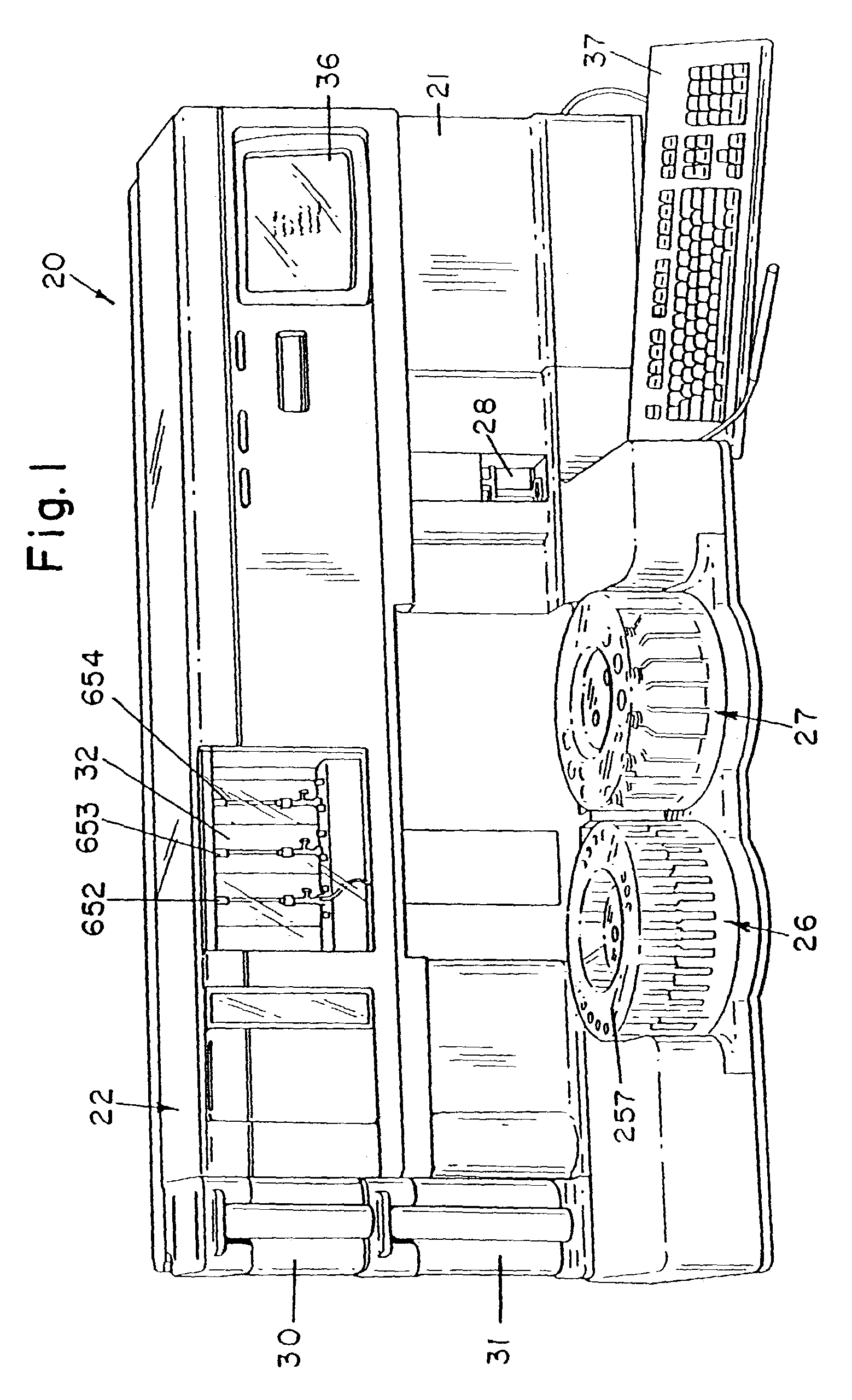
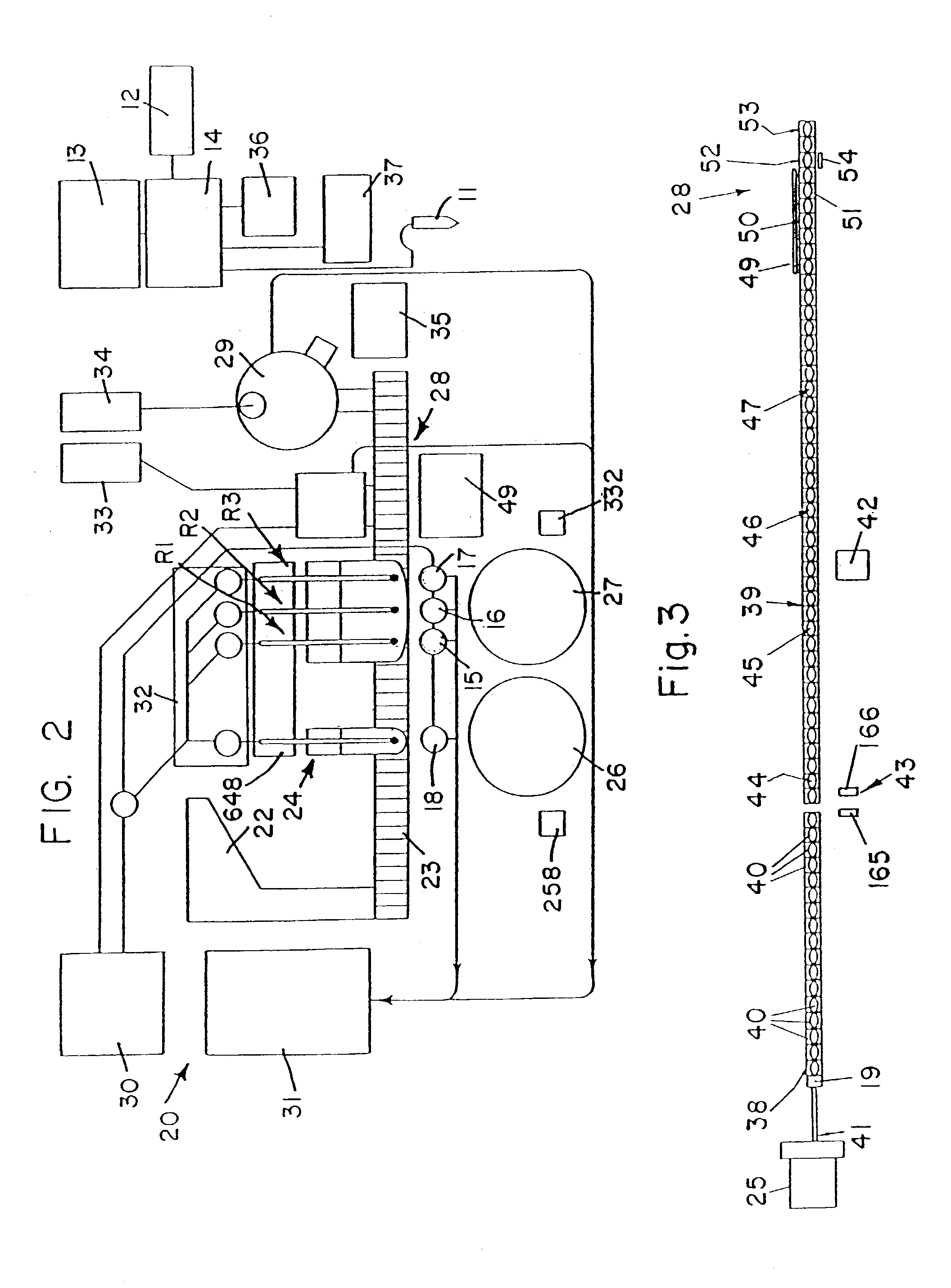
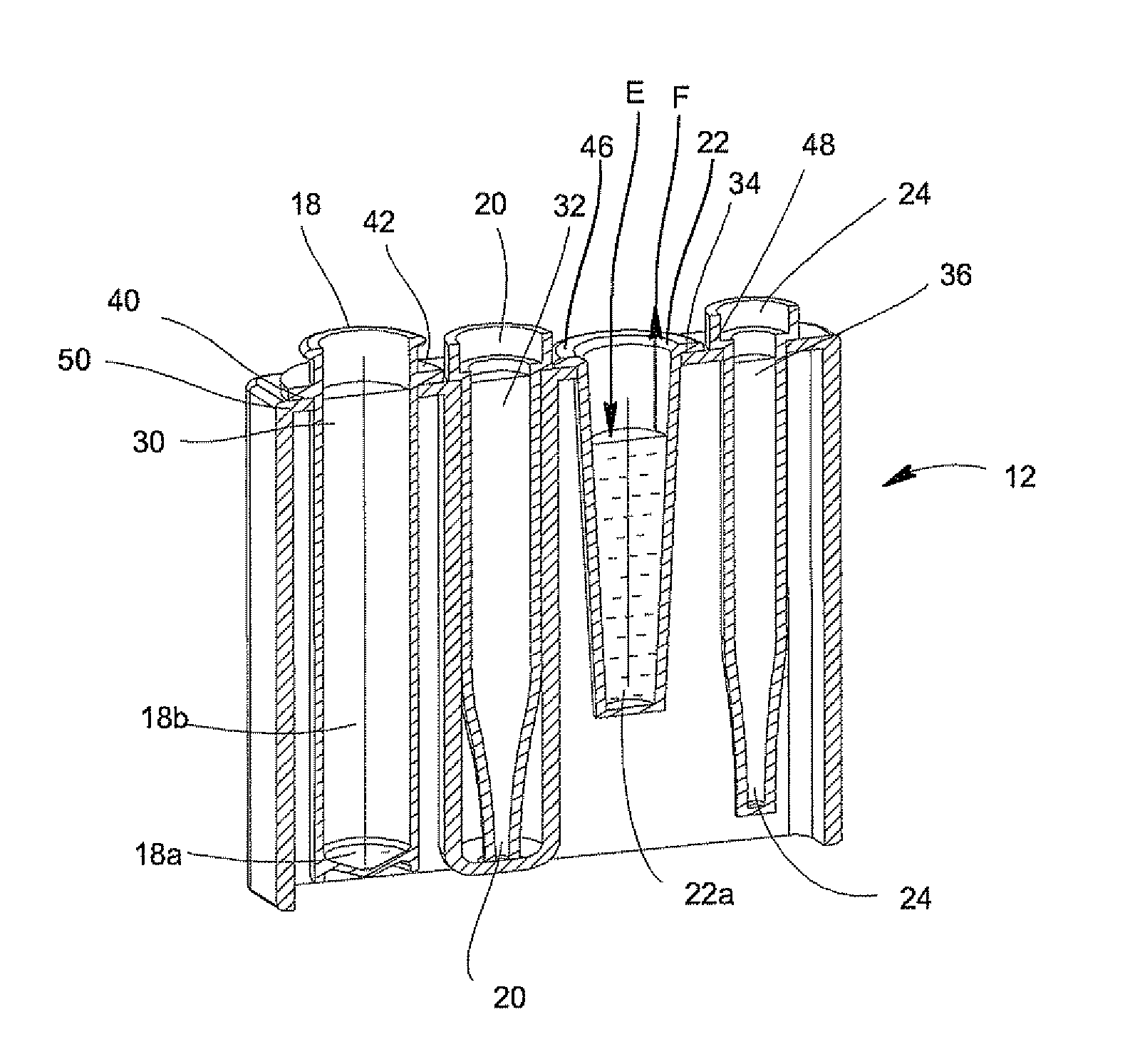
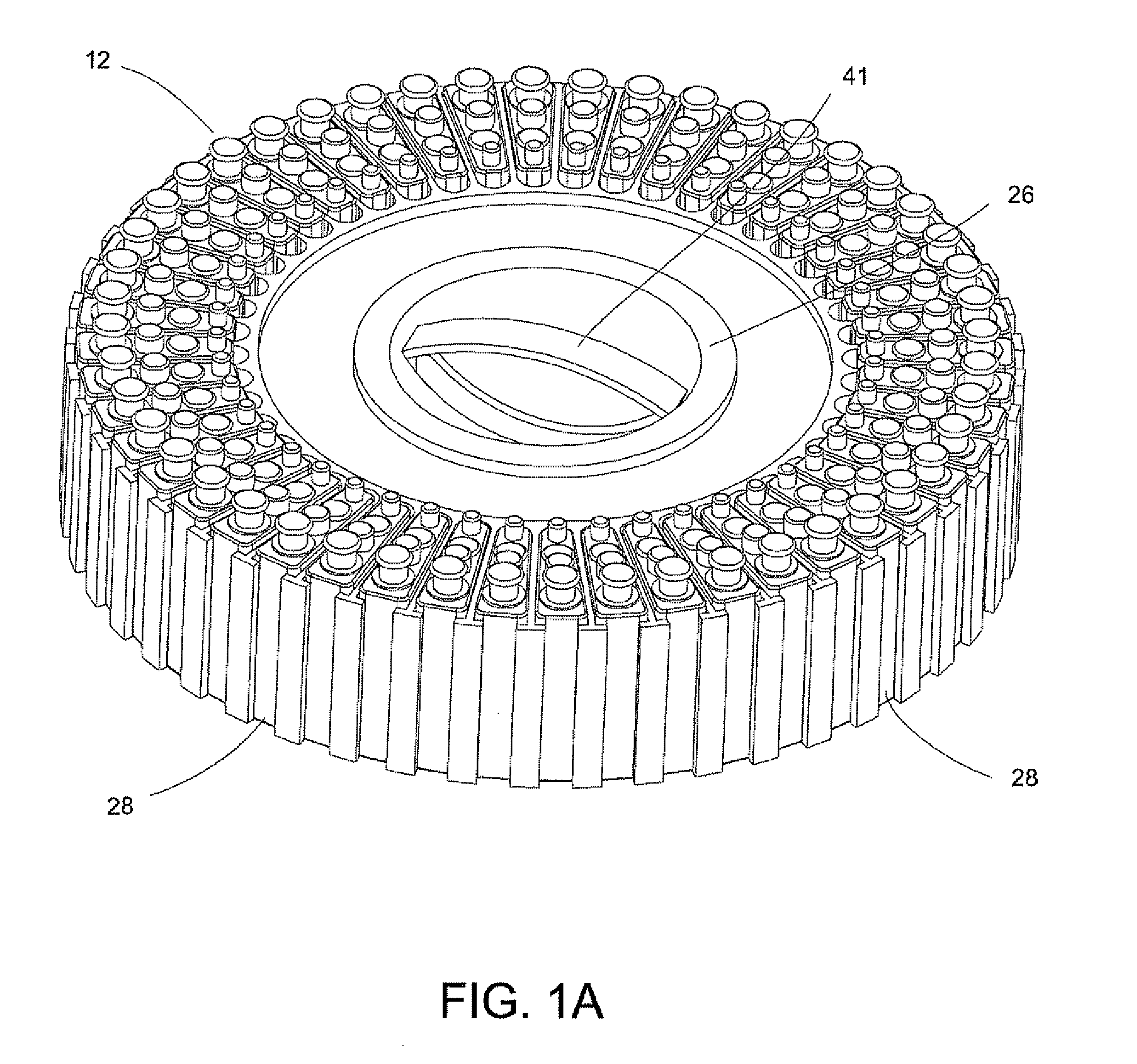
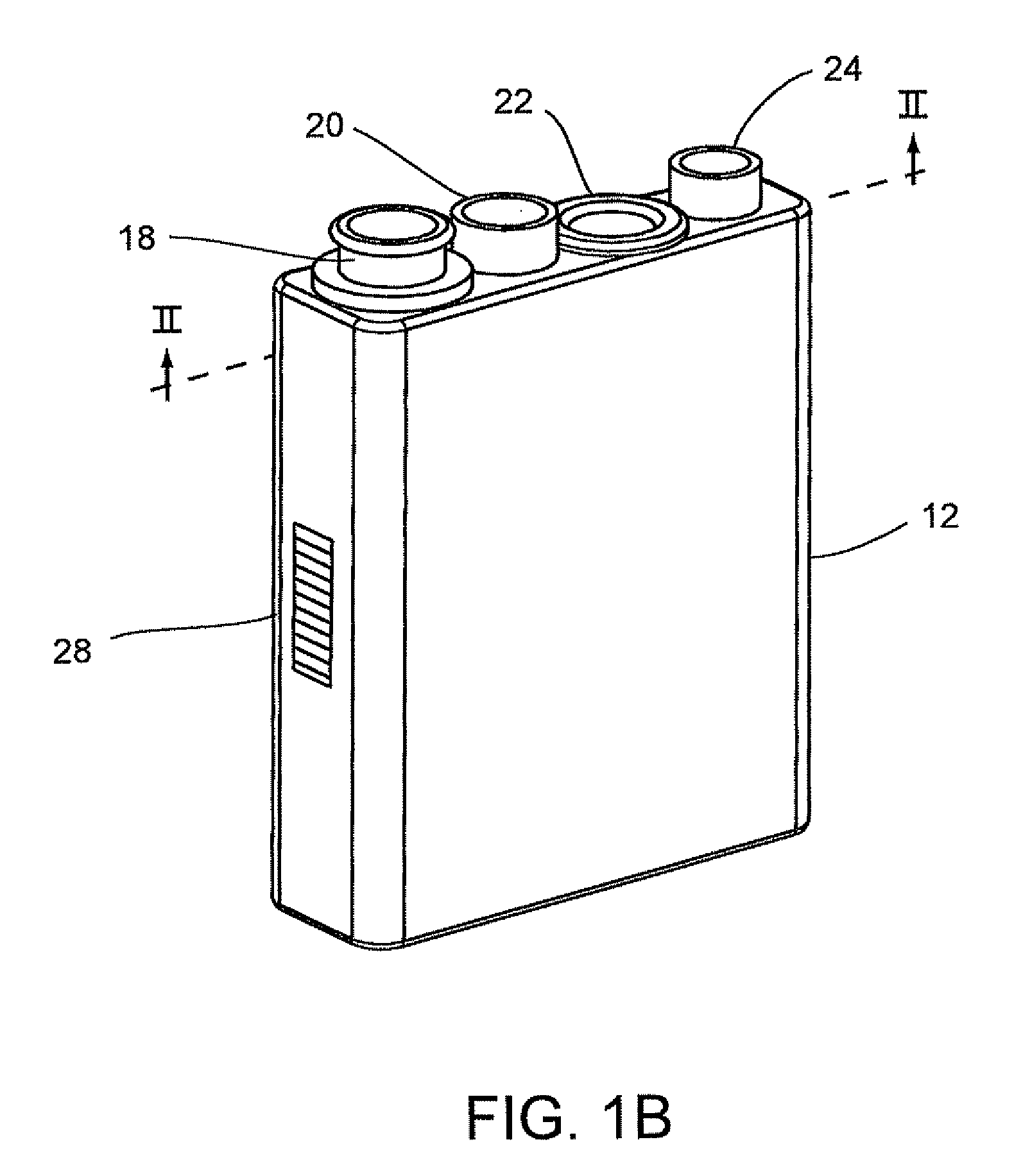
Automated analyzer
InactiveUS20050013737A1High sensitivityImprove processing speedChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceBiological testingCuvetteAutomated analyzer
An automated analyzer for analyzing patient samples. The analyzer includes a plurality of cuvettes, which allow the samples to be mixed with various reagents. The analyzer includes one or more detectors, including a detector adapted to detect luminescence of the reaction mixture in the cuvettes. The analyzer allows for various diagnostic assays to be performed on a single system, and provides for high-sensitivity analysis at faster speeds.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
Automatic analyzer
ActiveUS8043560B2High measurement accuracyLittle changeAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMicrobiological testing/measurementCuvetteAutoanalysis
An automatic analyzer using a reaction vessels of disposable type is provided which is compact in construction and with high accuracy of measurement.The analyzer is comprised with a reaction container which is capable of having a plurality of cuvettes of disposable type set therein, an extracting and injecting unit for injecting a first reagent, a specimen and a second reagent into a disposable cuvette, a light measuring unit for emitting light to the cuvette, and for measuring absorbance thereof and a CPU for producing a calculated value based on outputs of the light measuring unit.The light measuring unit measures absorbance of the first reagent, specimen and second reagent injected into and reacted with each other in a disposable cuvette, and also measures an air blank value representing absorbance of an empty disposable cuvette and a first reagent blank value representing absorbance of a disposable cuvette having first reagent in the cuvette (S104, S106). The CPU compensates the absorbance based on at least one of the air blank value and the first reagent blank value (S112, S113).
Owner:FURUNO ELECTRIC CO LTD
System for Conducting the Identification of Bacteria in Urine
ActiveUS20110008825A1Rapid diagnosisImprove efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCuvettePipette
A system for conducting the identification and quantification of micro-organisms, e.g., bacteria in urine samples which includes: 1) several disposable cartridges for holding four disposable components including a centrifuge tube, a pipette tip having a 1 ml volume, a second pipette tip having a 0.5 ml volume, and an optical cup or cuvette; 2) a sample processor for receiving the disposable cartridges and processing the urine samples including transferring the processed urine sample to the optical cups; and 3) an optical analyzer for receiving the disposable cartridges and configured to analyze the type and quantity of micro-organisms in the urine sample. The disposable cartridges with their components including the optical cups or cuvettes are used in the sample processor, and the optical cups or cuvettes containing the processed urine samples are used in the optical analyzer for identifying and quantifying the type of micro-organism existing in the processed urine samples.
Owner:POCARED DIAGNOSTICS
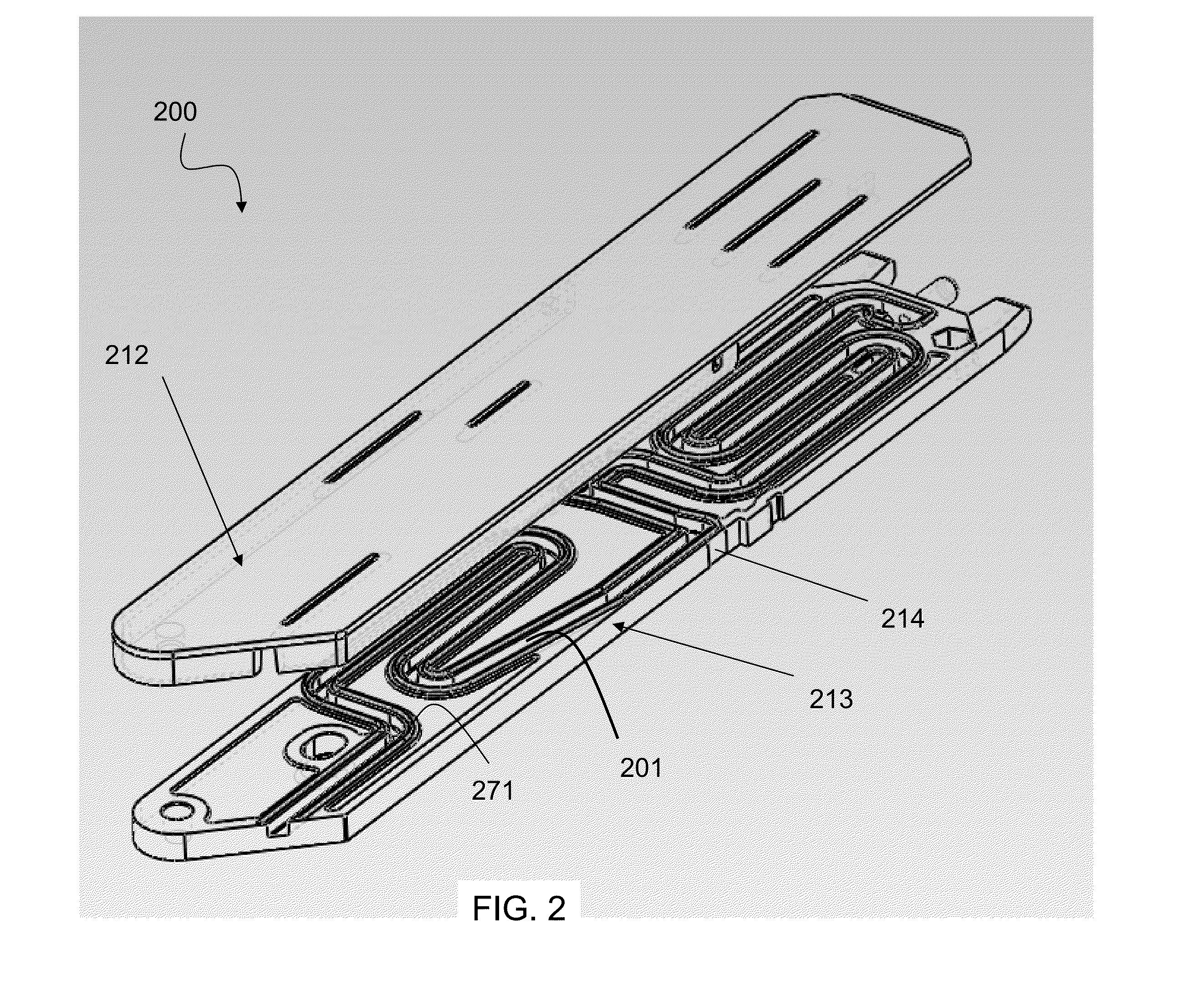
Sealed sample storage element system and method
A system and method operative in accordance with the present disclosure facilitate storage and retrieval of individual or discrete samples of biological, non-biological, and chemical material stored on dry media. Sample material may be disposed upon or within a porous or solid (i.e., non-porous) sample storage medium and subsequently archived in, and retrieved from, storage elements such as multi-well plates, for example, using robotic devices or other automated apparatus. The disclosed system and method enable ejection of sample material from a sealed storage element into a specific well of a multi-well daughter plate, or into a specific cuvette, test tube, or similar container. In some embodiments, a sample carrier comprising a storage medium may be punched or ejected through a first seal of the storage element with an apparatus or implement such as a disposable piercing tip, for instance, inserted through a second seal of the storage element.
Owner:GENTEGRA
Cuvette for flow-type particle analyzer
ActiveUS8233146B2Easy to replaceVibration minimizationWithdrawing sample devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansCuvettePhysics
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Method, system, and compositions for cell counting and analysis
ActiveUS7738094B2Low costEfficient detection and countingLibrary tagsWithdrawing sample devicesData setRed blood cell
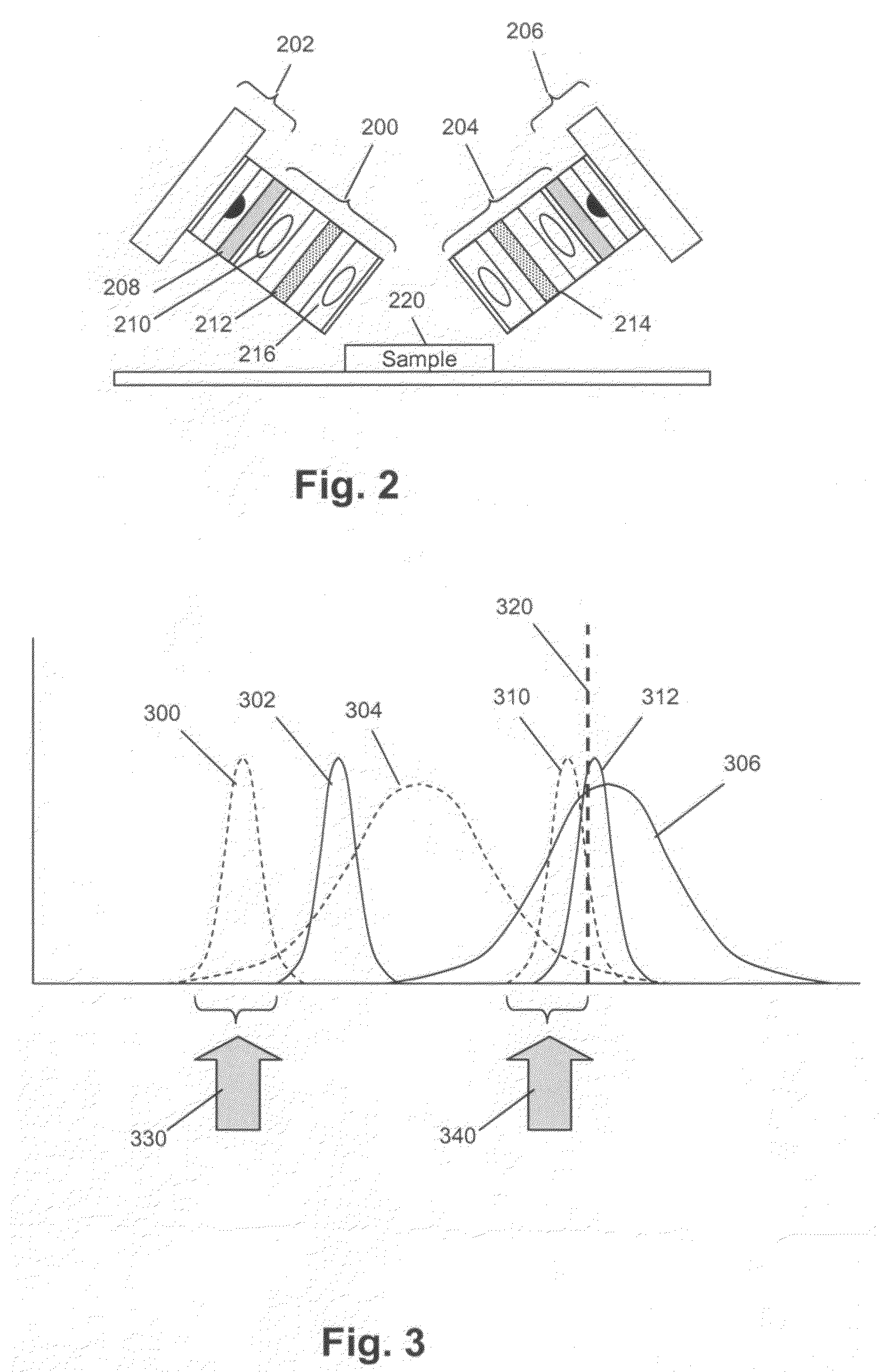
The present invention provides a low cost imaged-based system for detecting, measuring and / or counting labeled features of biological samples, particularly blood specimens. In one aspect, the invention includes a system for imaging multiple features of a specimen that includes one or more light sources capable of successively generating illumination beams each having a distinct wavelength band and a plurality of differentially excitable labels capable of labeling a specimen comprising multiple features, such that each different feature is labeled with a different differentially excitable label. System of the invention may further include a controller operationally associated with the one or more light sources for successively directing illumination beams onto the specimen so that each of the different differentially excitable labels is successively caused to emit an optical signal within the same wavelength band, an optical system capable of collecting such emitted optical signals and forming successive images corresponding to the labeled features of the specimen on a light-responsive surface to form successive sets of image data thereof, and a disposable cuvette for collection and optical analysis of non-red blood cells.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Method and a device for monitoring nucleic acid amplification reactions
InactiveUS6310354B1Continuous measurementSimply performedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCuvetteMicroparticle
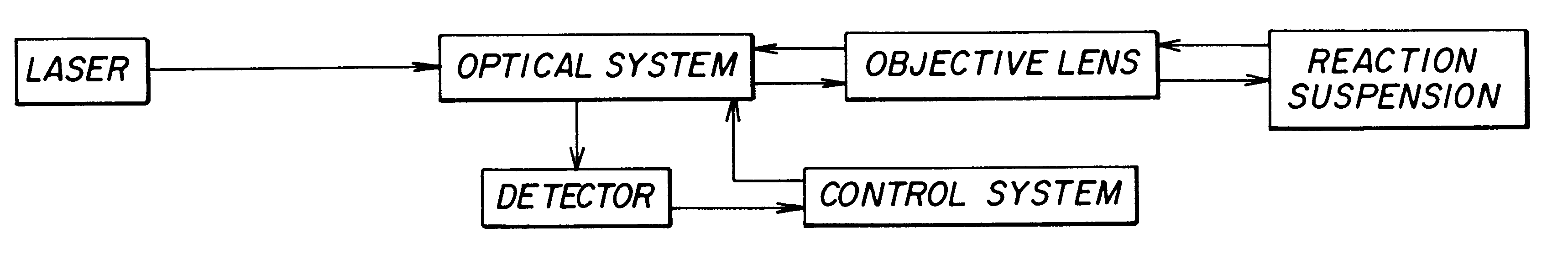
A method for quantitatively measuring nucleic acid amplification reactions, especially the polymerase chain reaction, employing microparticles as hybridization solid phase, a probe sequence labeled with a fluorescent label and a fluorescence detection system which is based on two-photon fluorescence excitation, contacting all the amplification reaction components and the solid phase simultaneously in a closed cuvette, performing the amplification reactions in the same cuvette, focusing a two-photon exciting laser beam into the cuvette during the amplification cycles and measuring the fluorescence signal emitted by the microparticles from one particle at a time when they randomly float through the focal volume of the laser beam. The features of this invention allow a method and device for performing a fast quantitative nucleic acid amplification assay of single or multiple target sequences in a very small closed sample volume.
Owner:SOINI ERKKI
Fixed mounted sorting cuvette with user replaceable nozzle
ActiveUS7201875B2Efficient collectionEfficient productionMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorLaboratory glasswaresCuvetteFlow cell
A flow cell and flow cytometer in which a nozzle at the end of a flow channel is disposed on a removable substrate held at a registered location on a flow cell. Other elements including illumination optics, light collection optics, and the flow cell may then be positioned at fixed locations and would not require subsequent periodic adjustment. The registered location for positioning the nozzle allows removal and replacement of the nozzle key with the nozzle subsequently positioned in the identical location.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Assessment of Biological or Chemical Samples
ActiveUS20090029402A1Improve analytical performanceGreat oxygen gradientBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCuvetteAnalyte
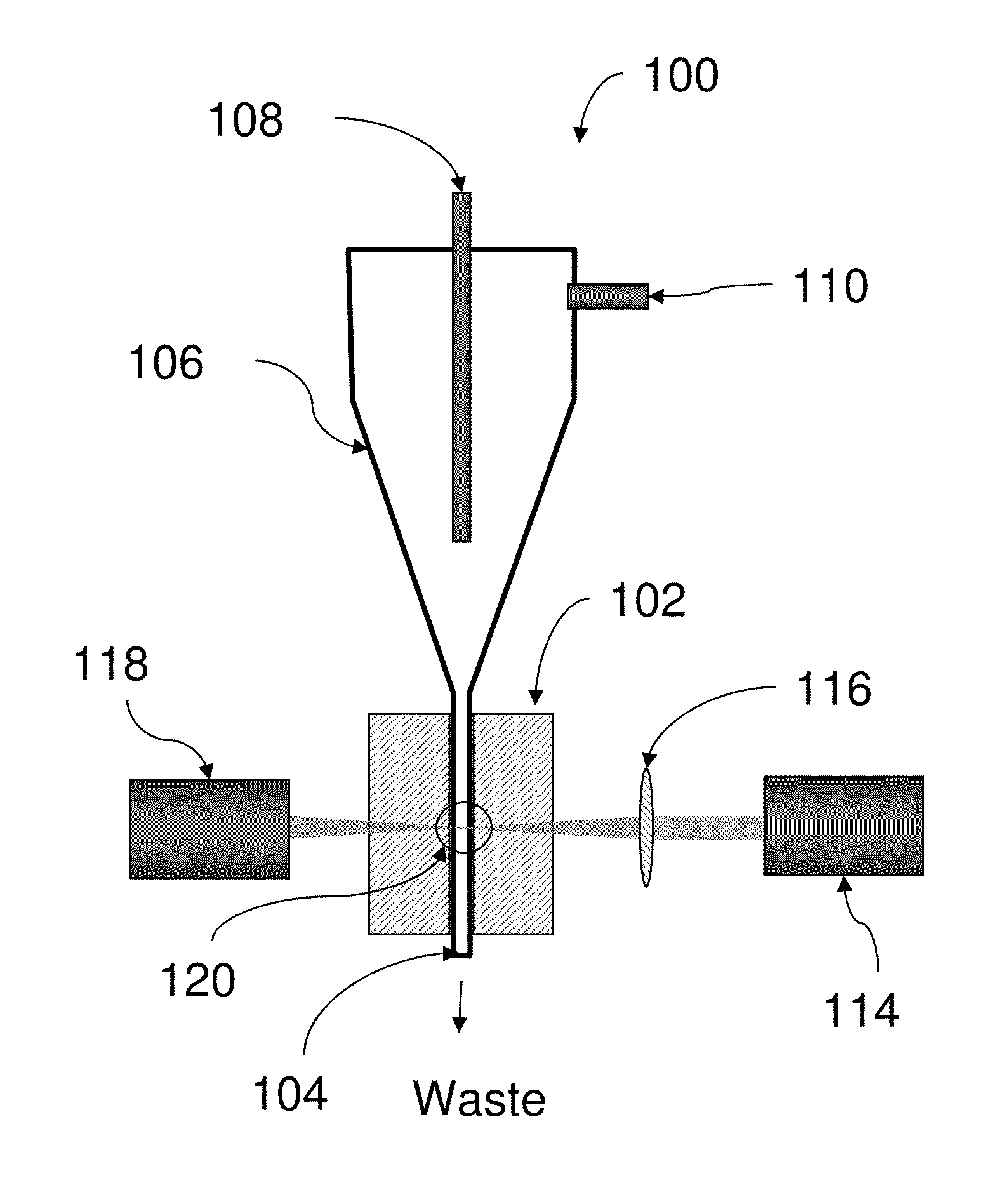
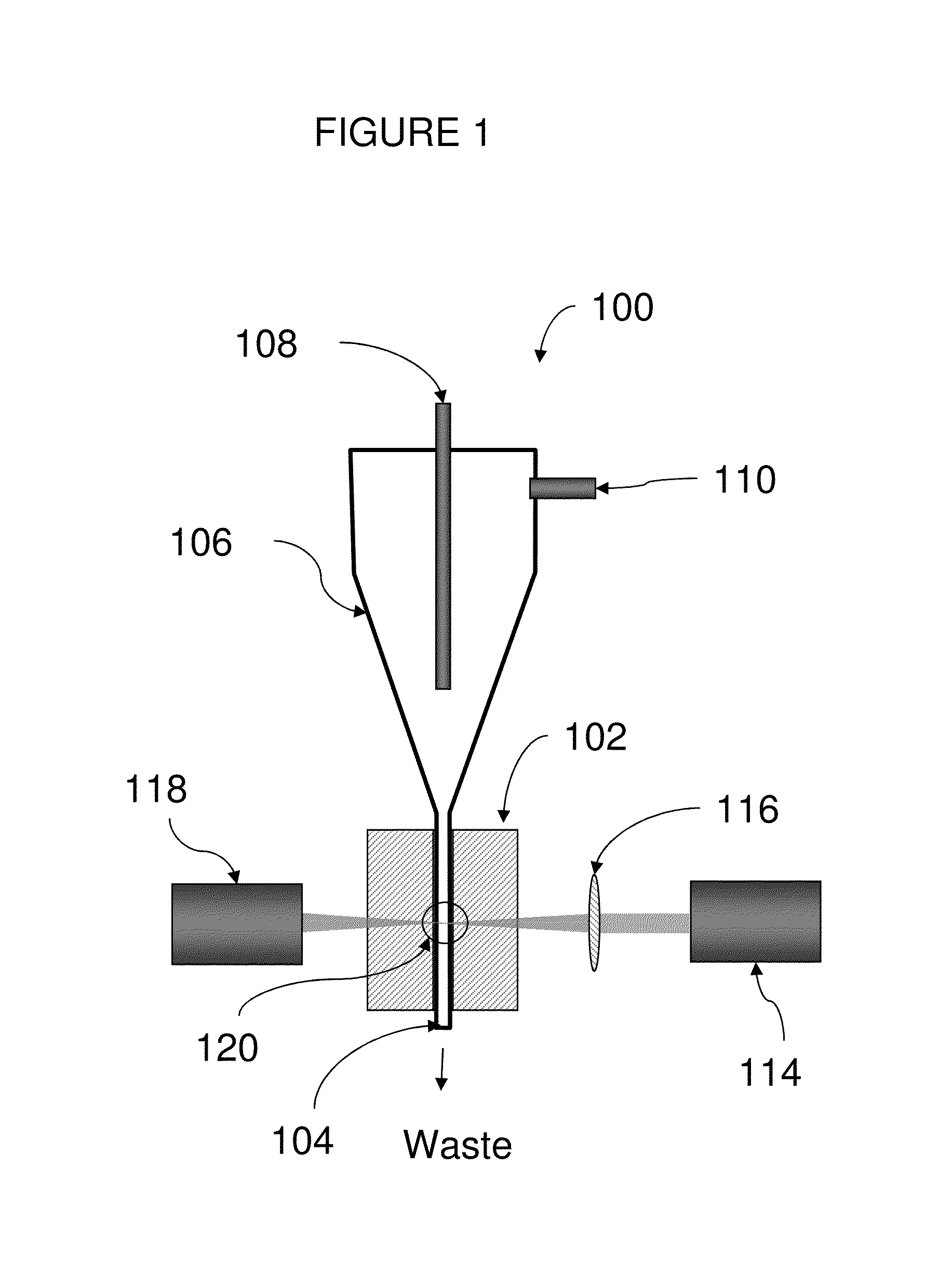
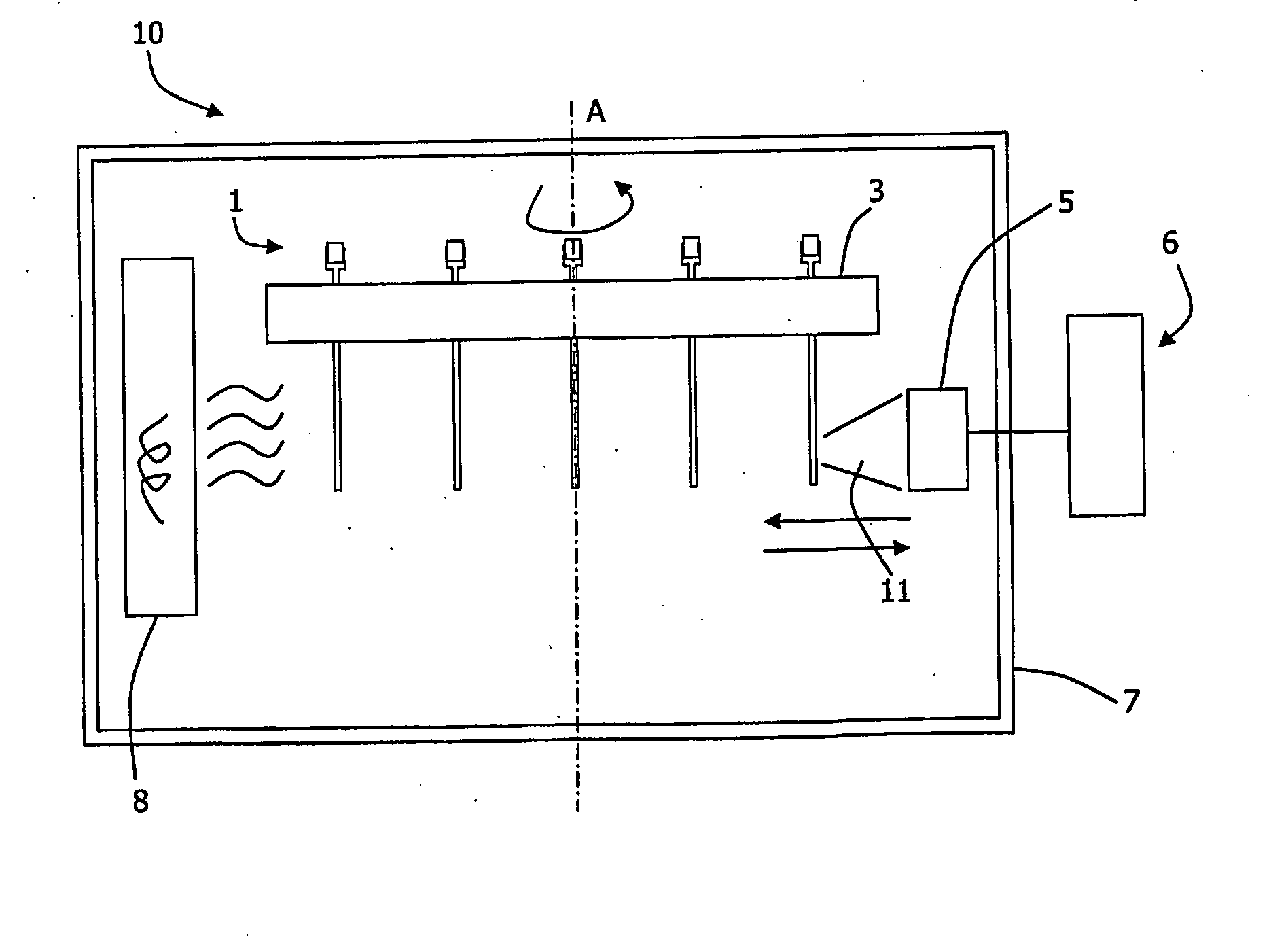
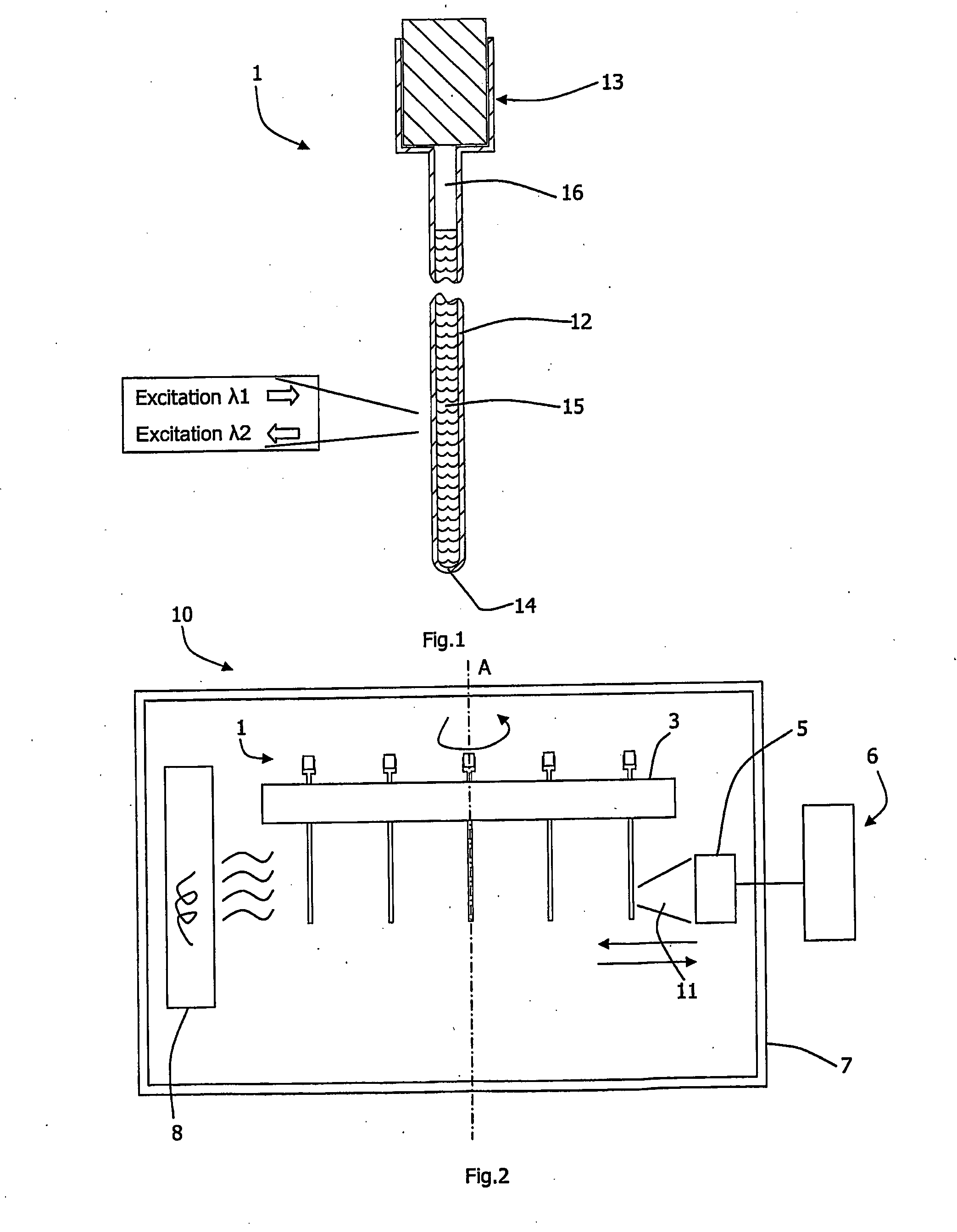
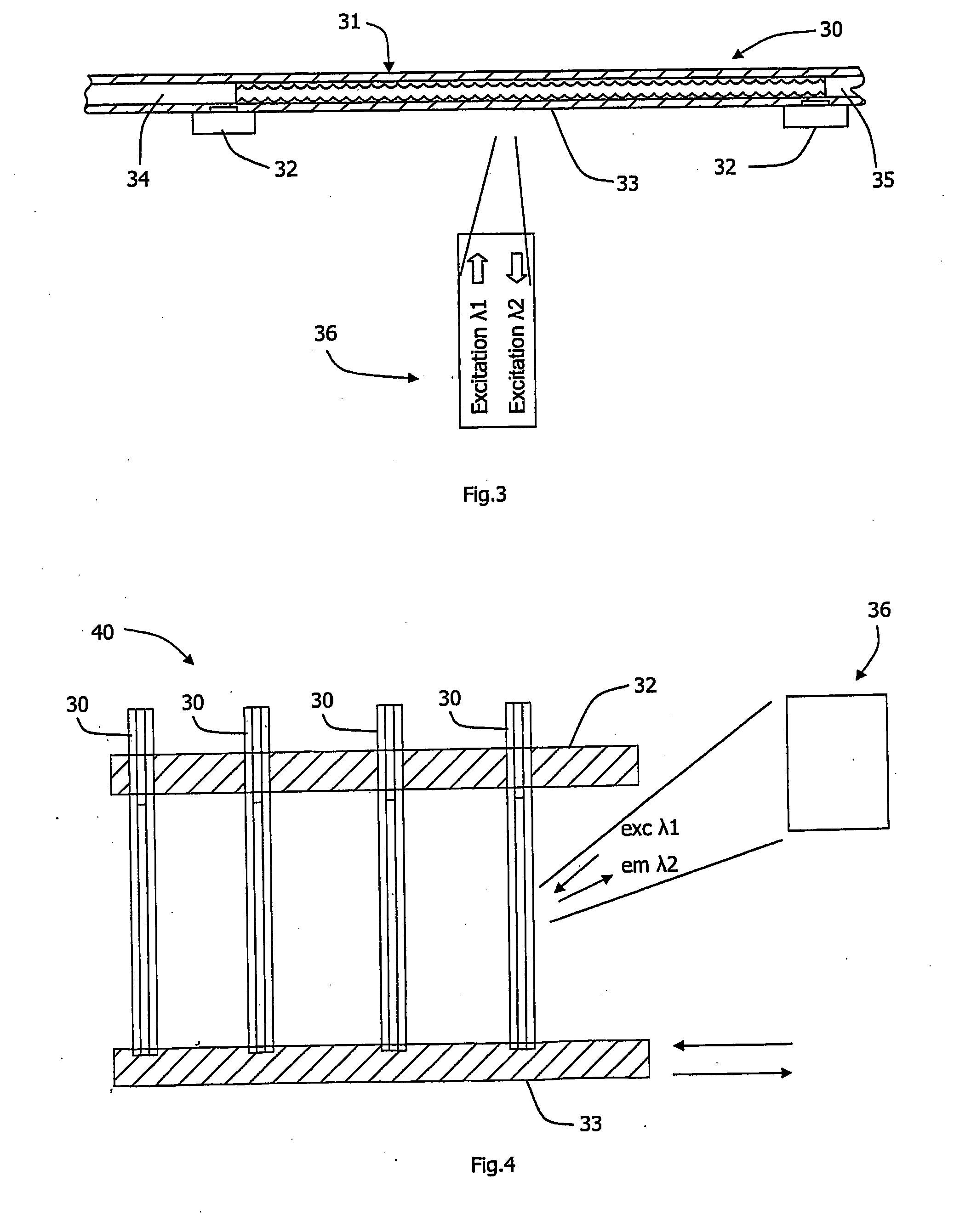
A method for monitoring consumption or release of a gaseous analyte such as oxygen by a liquid sample under investigation includes providing a cuvette (1) having an elongate narrow tube (12) of a material which is substantially gas impermeable and which is at least partly transparent to measurement excitation radiation and emission radiation along some of the length of the tube. The tube (12) has a cross-sectional area of under 1 mm2. The sample (15) is loaded into the cuvette (1), the sample being in contact with a probe in the tube (12), the probe being sensitive to the gaseous analyte, and the liquid having at least one surface and an associated headspace (16). The cuvette, the sample, and the probe are equilibrated at a target measurement temperature. Excitation radiation is directed at a sampling zone of the tube (12) and which is distal from the headspace (16), while maintaining the cuvette at the measurement temperature. The emitted radiation is measured and analysed to determine consumption or release by the sample of the gaseous analyte.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Optical Cup
ActiveUS20120105837A1Rapid diagnosisFast resultsWithdrawing sample devicesBiochemistry apparatusCuvetteEngineering
The present invention relates to a system for conducting the identification and quantification of micro-organisms, e.g., bacteria in biological samples. More particularly, the invention relates to a system comprising a disposable cartridge and an optical cup or cuvette having a tapered surface; wherein the walls are angled to allow for better coating and better striations of the light, an optics system including an optical reader and a thermal controller; an optical analyzer; a cooling system; and an improved spectrometer. The system may utilize the disposable cartridge in the sample processor and the optical cup or cuvette in the optical analyzer.
Owner:POCARED DIAGNOSTICS
Cuvette apparatus and system for measuring optical properties of a liquid such as blood
ActiveUS20050094127A1Withdrawing sample devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringCuvetteOptical property
A optical sensor for measuring tranmissive properties of a solution having: a cuvette body with an enclosed flow passage for the solution, wherein the flow passage further includes a solution inlet and a solution outlet and a cuvette between the inlet and outlet; a light source projecting light of a predetermined wavelength through the cuvette and solution flowing through the cuvette and to a light sensor, wherein the cuvette has inner wall surfaces opaque to the light of said predetermined wavelength, and the inner wall is in contact with the solution.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
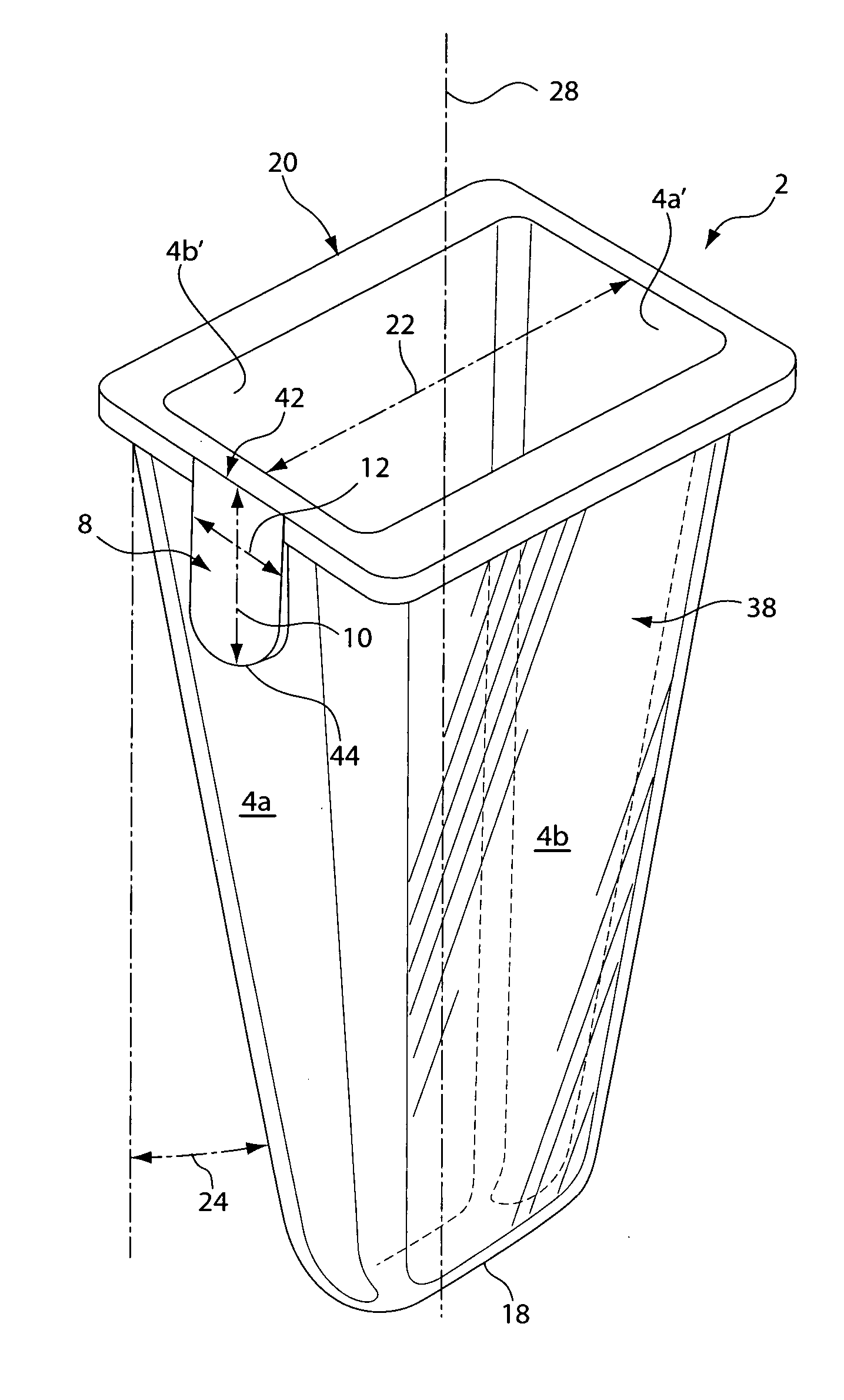
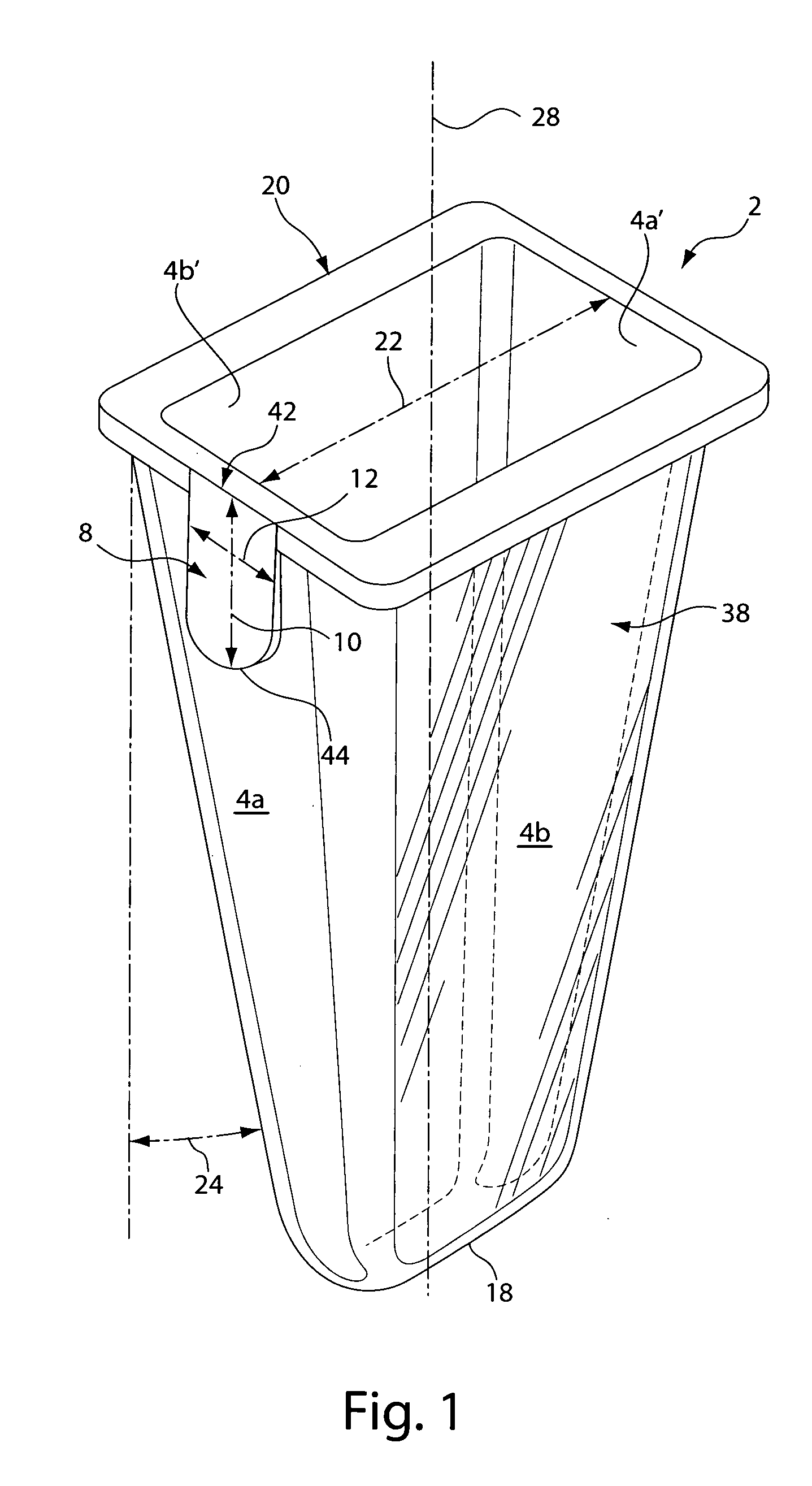
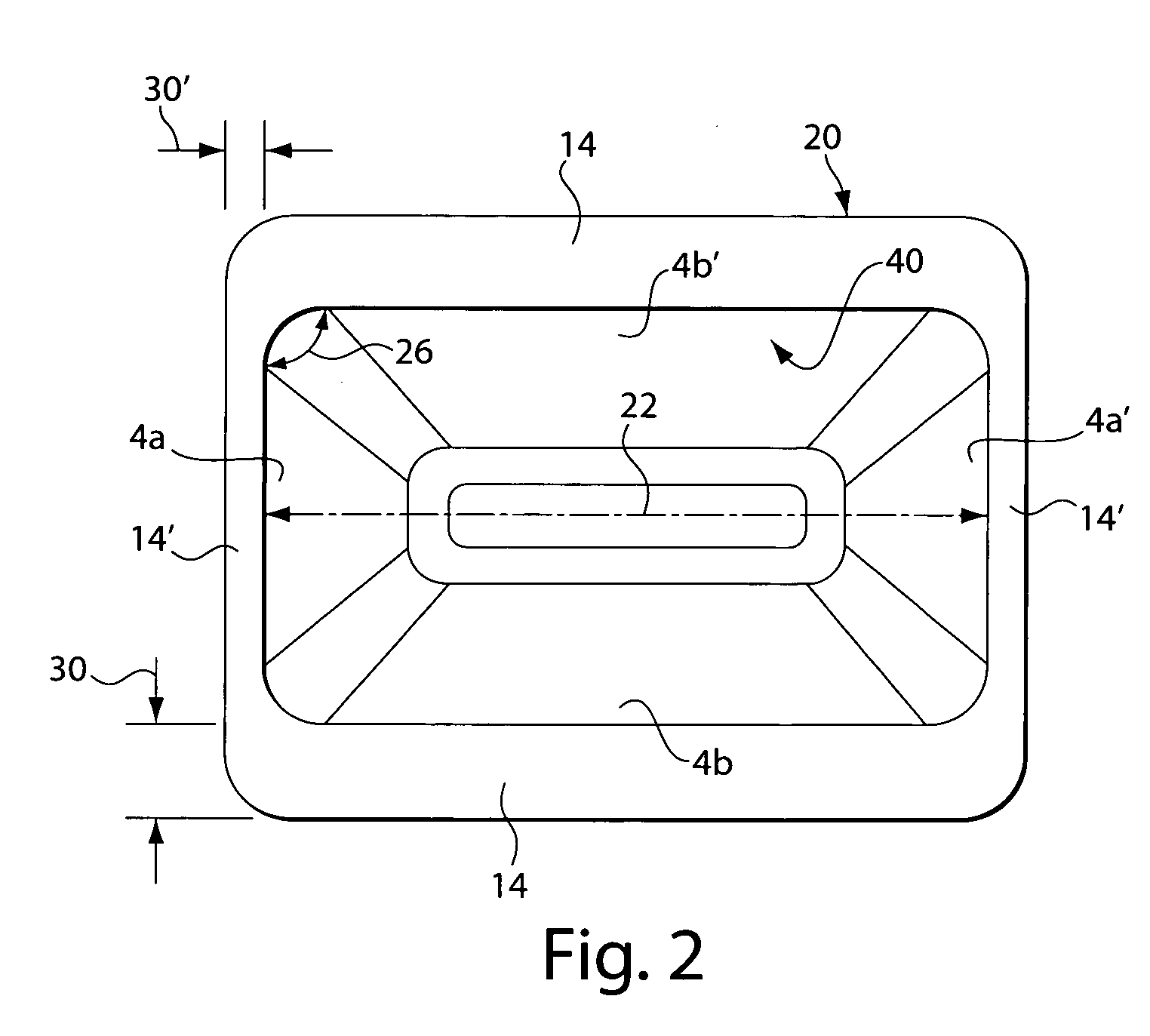
Tapered cuvette and method of collecting magnetic particles
ActiveUS20050271550A1Analysis material containersAnalysis using chemical indicatorsCuvetteParticle physics
A vessel for use in clinical analysis including an open top, a closed bottom, and at least four tapered sides. A method for collecting magnetic particles in a fluid comprising the steps of providing a magnet and a vessel containing magnetic particles in a fluid, attracting the magnetic particles to the magnet, and moving the magnetic particles with the magnet out of the fluid.
Owner:BIOKIT
Optical reader for diffraction grating-based encoded optical identification elements
ActiveUS20060071075A1Increase the number ofMinimizing sensitivityPaper-money testing devicesRecord carriers used with machinesCuvetteFluorescence
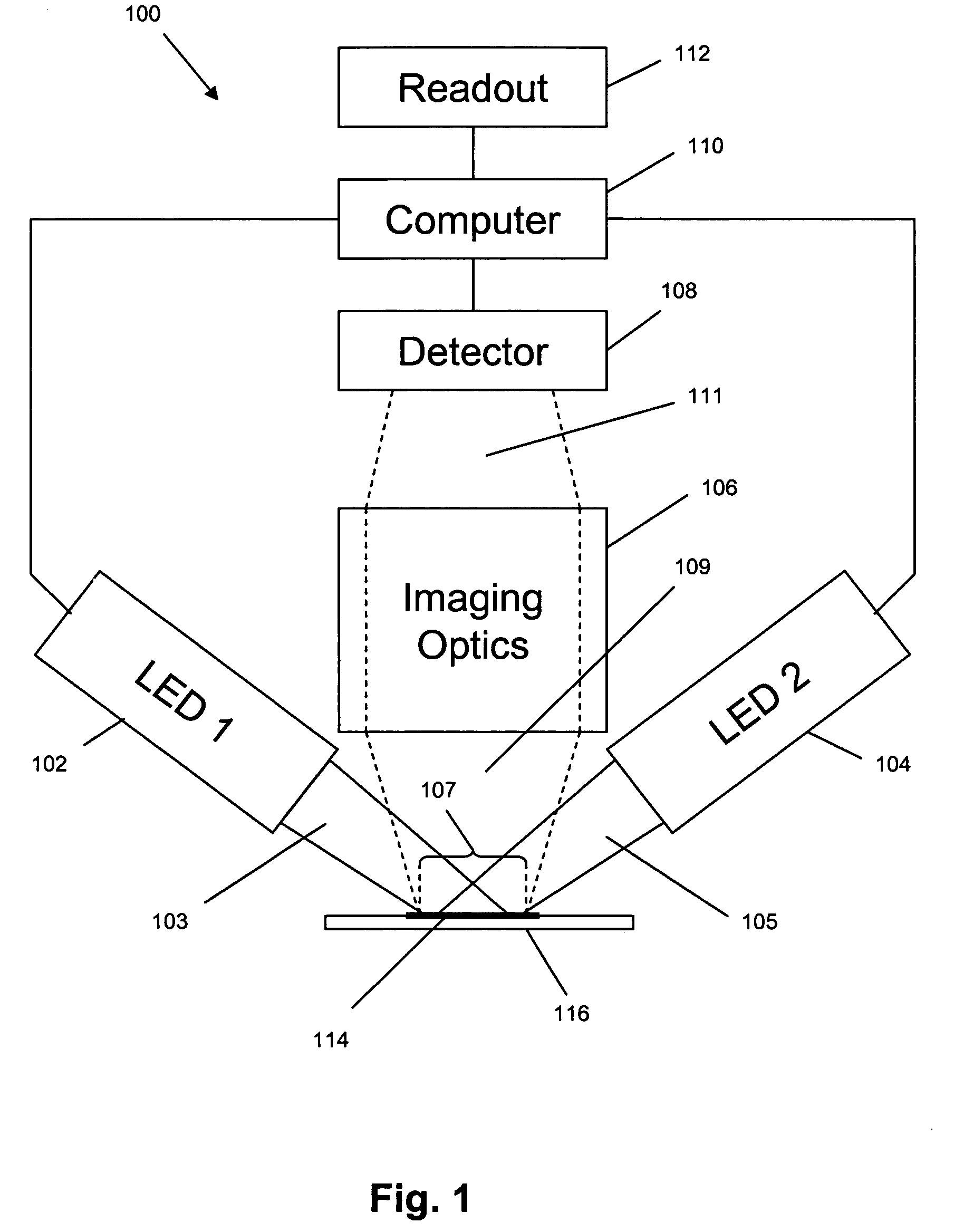
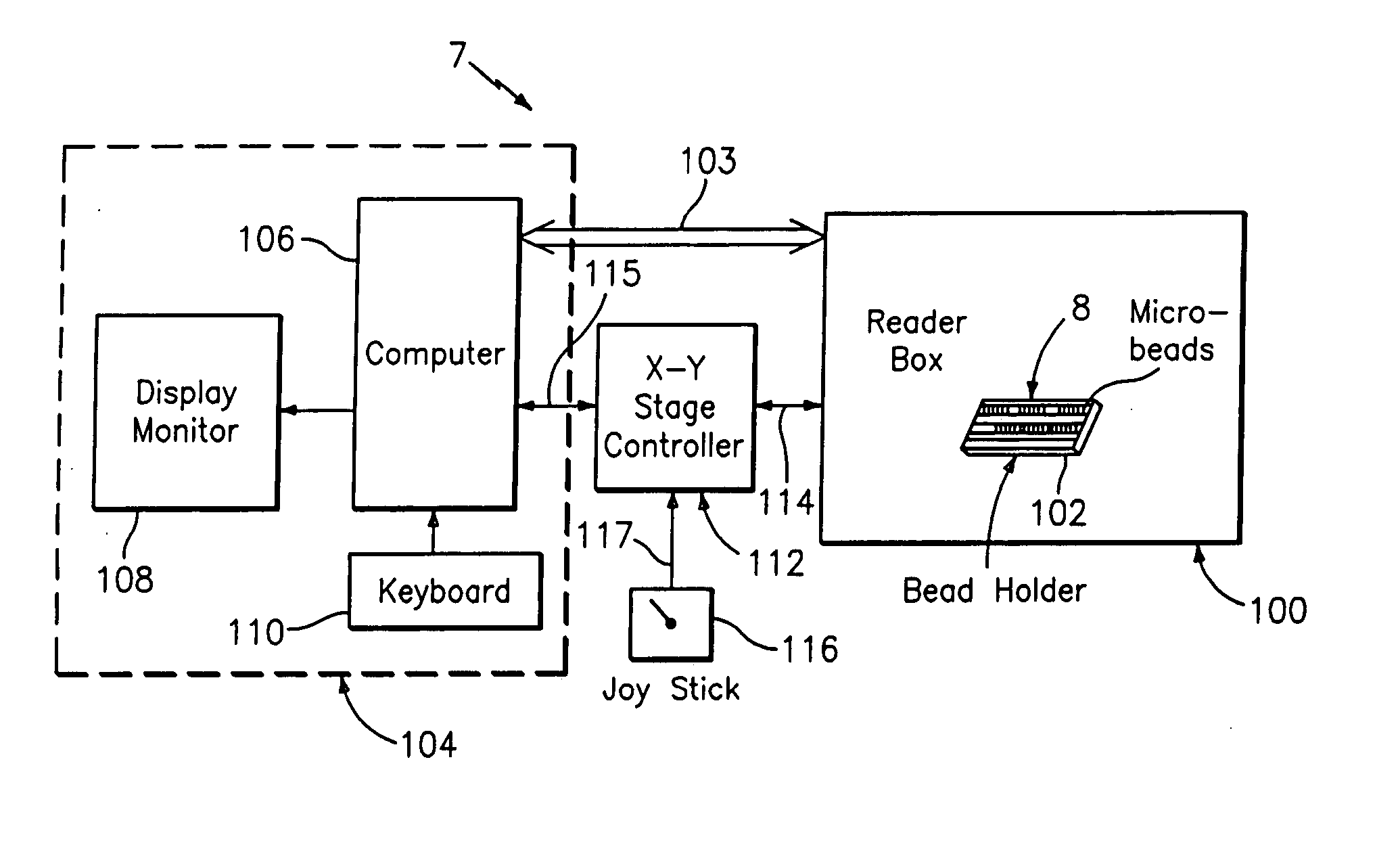
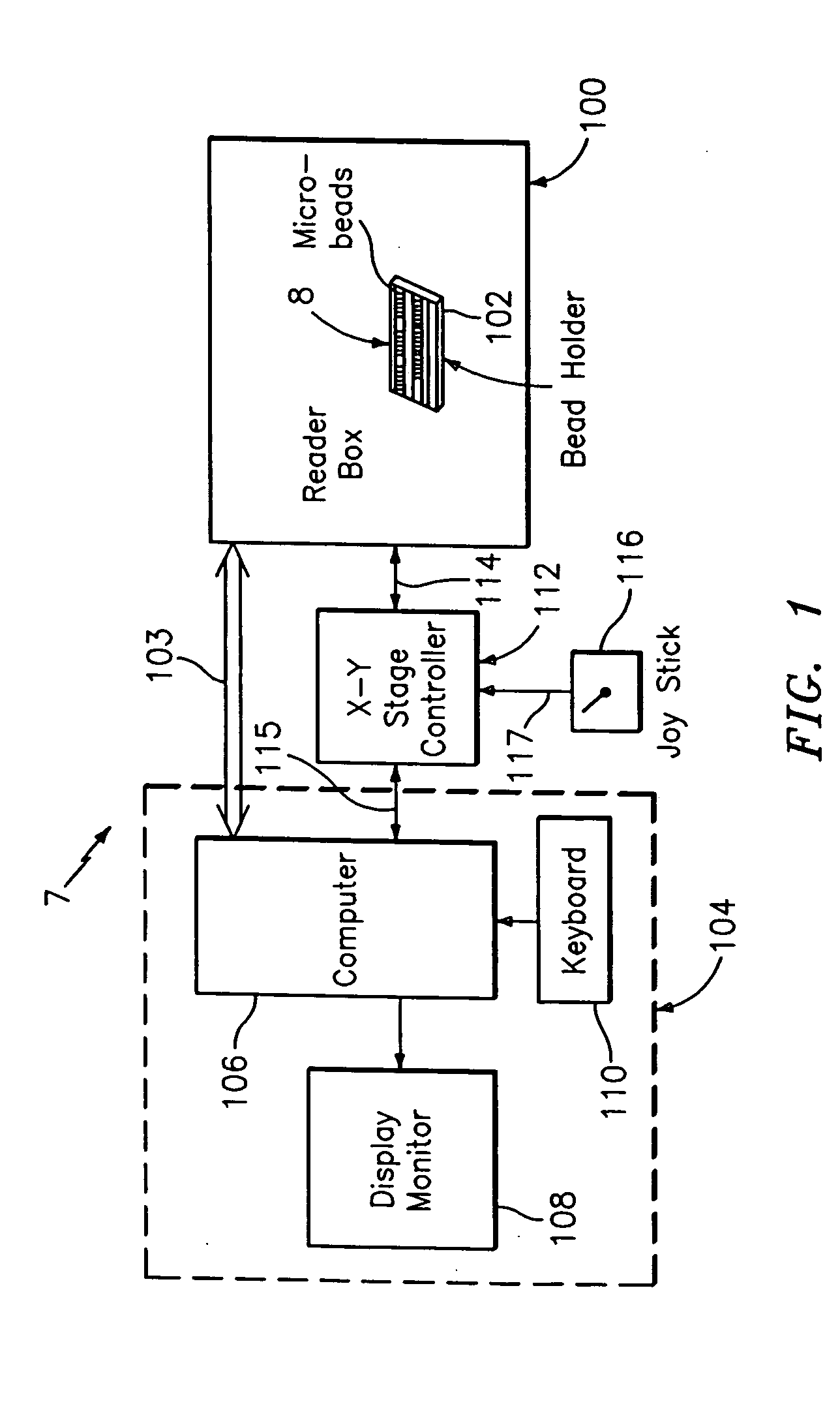
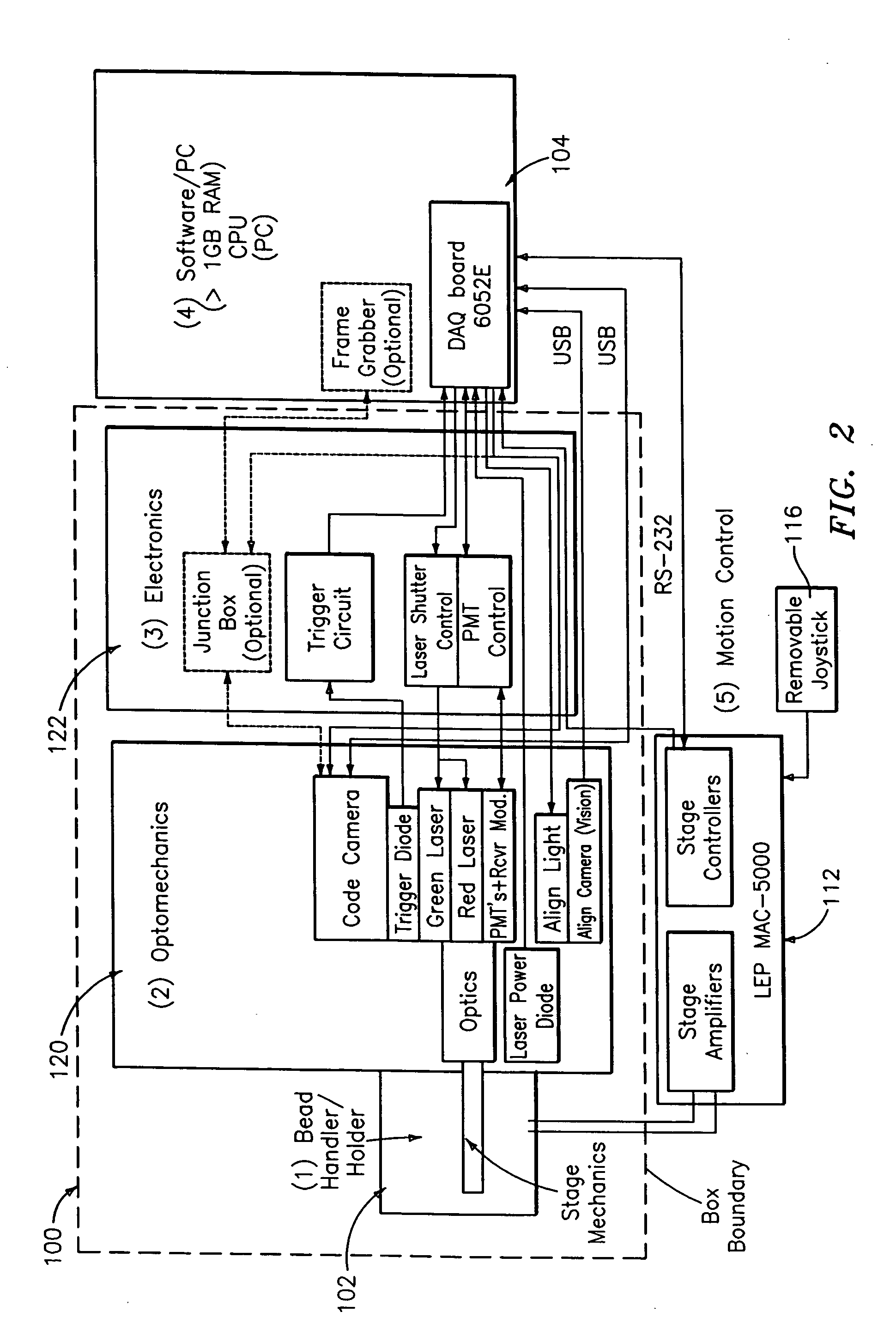
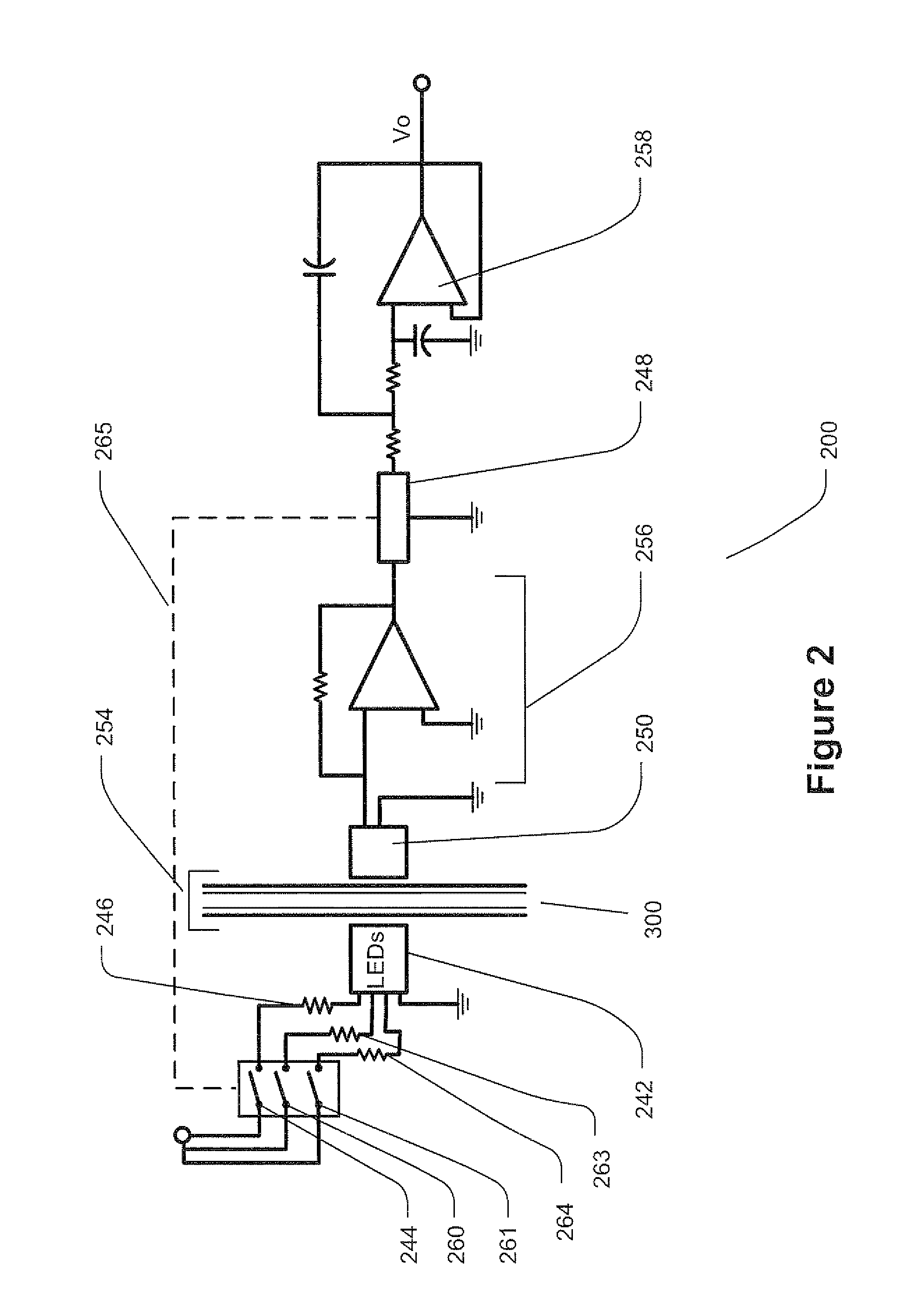
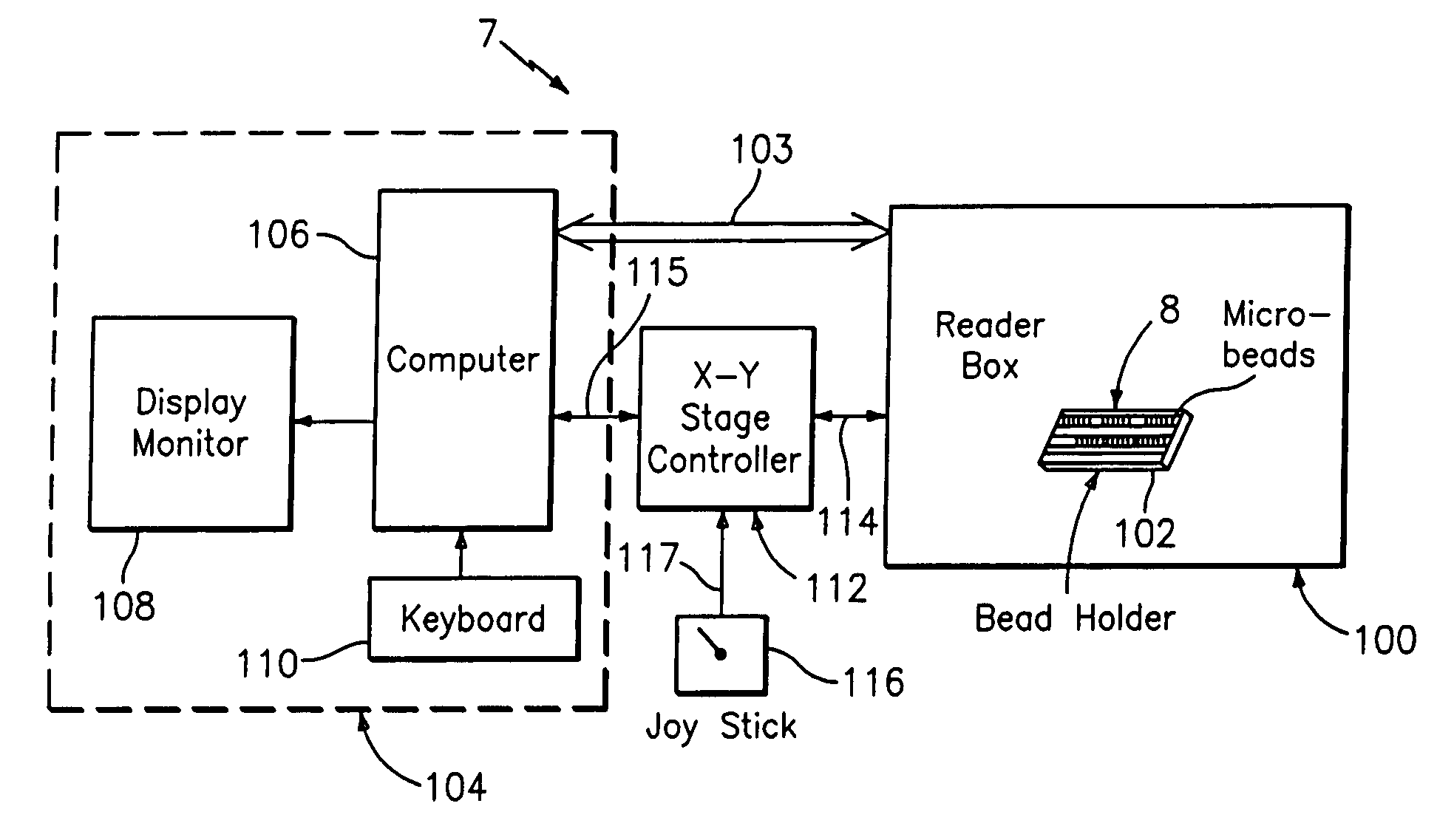
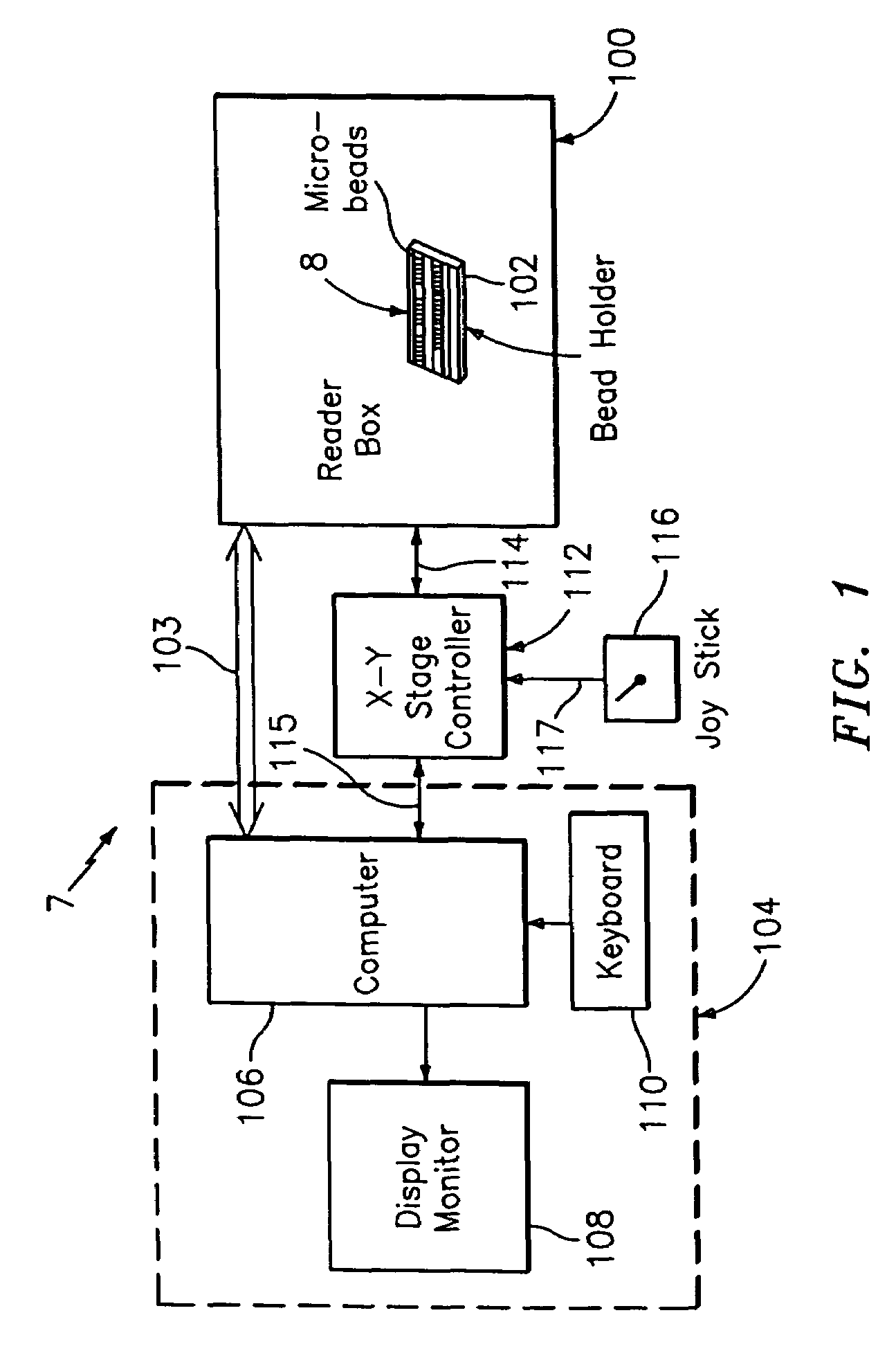
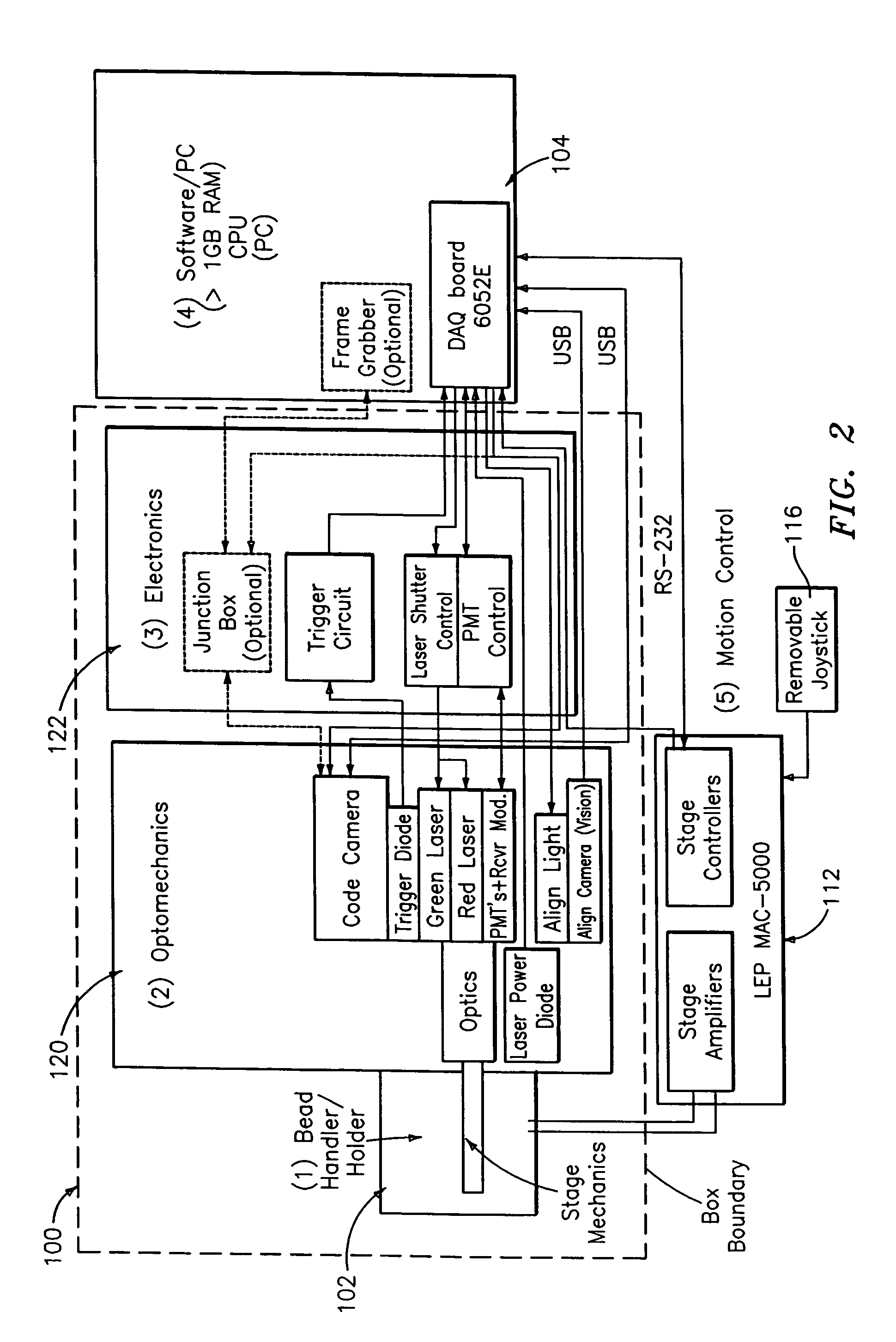
An optical reader system 7 for diffraction grating-based encoded microbeads (or bead reader system), comprises a reader box 100, which accepts a bead cell (or cuvette) 102 that holds the microbeads 8, having an embedded code therein. The reader box 100 interfaces along lines 103 with a known computer system 104. The reader box 100 interfaces with a stage position controller 112 and the controller 112 interfaces along a line 115 with the computer system 104 and a manual control device (or joy stick) 116 along a line 117. The reader interrogates the microbeads to determine the embedded code and / or the fluorescence level on the beads. The reader provides information similar to a bead flow cytometer but in a planar format, i.e., a virtual cytometer.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Automated endoscope reprocessor germicide concentration monitoring system and method
ActiveUS8246909B2Avoid accumulationOptical radiation measurementDispersed particle filtrationCuvetteReprocessor
A method measures a property of a germicidal solution in an endoscope processor spectroscopically by placing a quantity of the solution into a cuvette and passing a light therethrough. A reservoir receives a quantity of the solution and bubbles are filtered out via a cross-flow filter prior to putting a sample therefrom into the cuvette for measuring.
Owner:ASP GLOBAL MFG GMBH
Cuvette apparatus and system for measuring optical properties of a liquid such as blood
A optical sensor for measuring tranmissive properties of a solution having: a cuvette body with an enclosed flow passage for the solution, wherein the flow passage further includes a solution inlet and a solution outlet and a cuvette between the inlet and outlet; a light source projecting light of a predetermined wavelength through the cuvette and solution flowing through the cuvette and to a light sensor, wherein the cuvette has inner wall surfaces opaque to the light of said predetermined wavelength, and the inner wall is in contact with the solution.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
Method and flow system for spectrometry and a cuvette for the flow system
InactiveUS6297505B1Easy to produceRadiation pyrometryScattering properties measurementsCuvetteHigh pressure
The present invention relates to an on-line method and a flow system as well as a cuvette for carrying out IR spectrometry for analysis of liquid food products, possibly containing dissolved gases, in a process line in a liquid food product processing plant, especially a dairy processing milk and milk products. A liquid sample is extracted from the process line to a measuring branch, the sample is thermostated and passed to a measurement cuvette. The IR-absorbance spectrum is measured, e.g. in the MID-IR or NIR-range. In order to obtain an on-line monitoring of the process line the liquid food sample is extracted directly from the process line into the measurement branch, in which the pressure is maintaining at least as high as in the adjacent process line. The high pressure ensures that dissolved air will stay dissolved in the liquid food. Before each new sample the measurement branch and cuvette are flushed by high flow rates with a part of the new sample to clean the cuvette. The measurement cuvette has strong windows, preferably diamond windows to stand a high pressure and high flow rates. The on-line system is arranged to carry out eg. 120 measurements per hour.
Owner:FOSS ELECTRIC
Tapered cuvette and method of collecting magnetic particles
ActiveUS8211386B2Analysis material containersAnalysis using chemical indicatorsCuvetteParticle physics
A vessel for use in clinical analysis including an open top, a closed bottom, and at least four tapered sides. A method for collecting magnetic particles in a fluid comprising the steps of providing a magnet and a vessel containing magnetic particles in a fluid, attracting the magnetic particles to the magnet, and moving the magnetic particles with the magnet out of the fluid.
Owner:BIOKIT
Microchip and Method of Using the Same
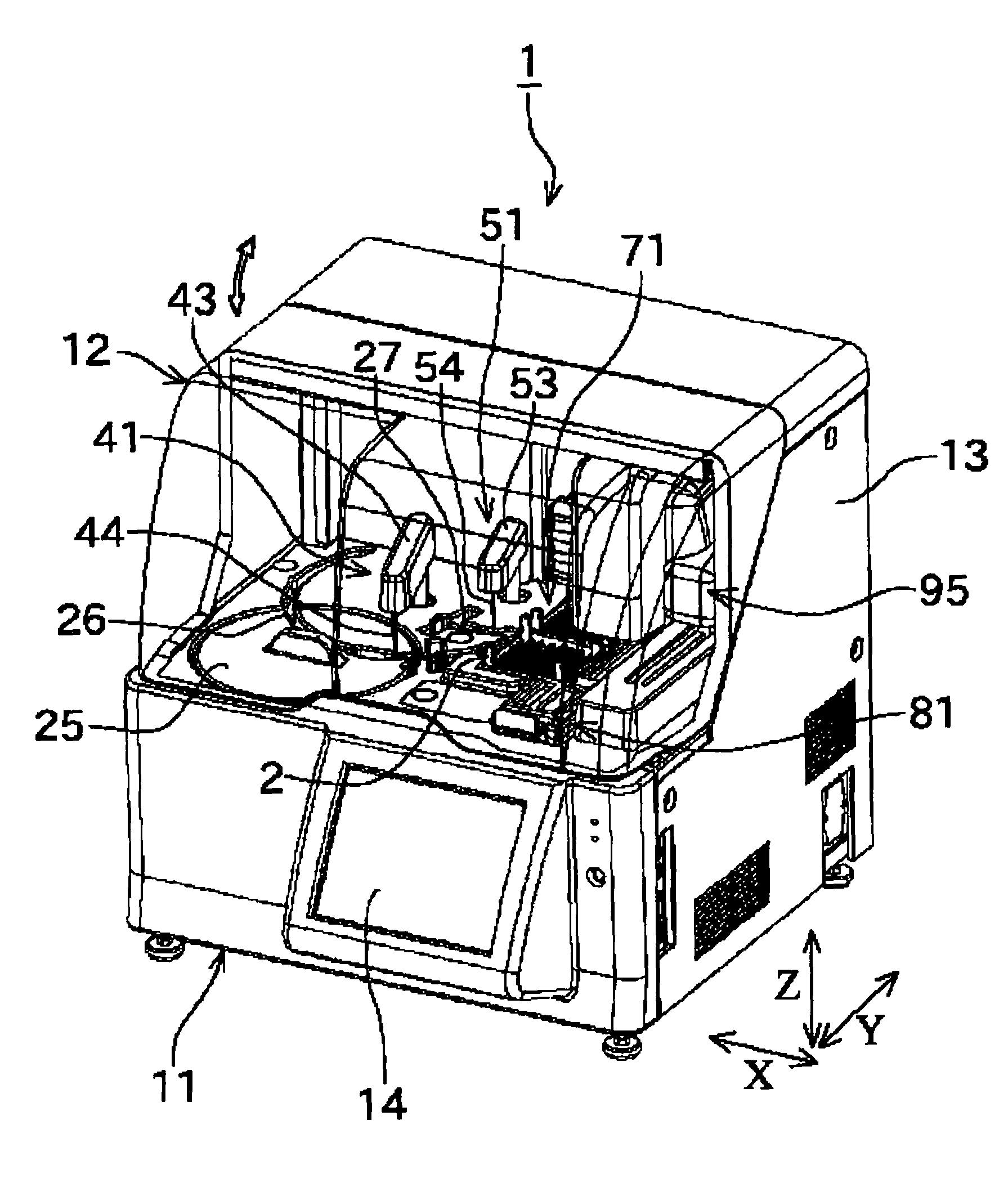
ActiveUS20090111675A1Increase the cross-sectional areaOptical axis alignment is facilitatedSamplingCircuit elementsCuvetteEngineering
A microchip including a first substrate with a groove formed on a substrate surface or a pass-through hole passing in a thickness direction of the substrate, and one or more second substrates laminated on a surface of the first substrate; the microchip including an optical measurement cuvette consisting of a space configured by the groove or the pass-through hole, and a substrate surface of the second substrate; wherein a side wall surface of the second substrate is positioned on an inner side than a side wall surface of the first substrate in at least one part of a side wall surface of the microchip, and a method of using the same are provided.
Owner:HORIBA LTD
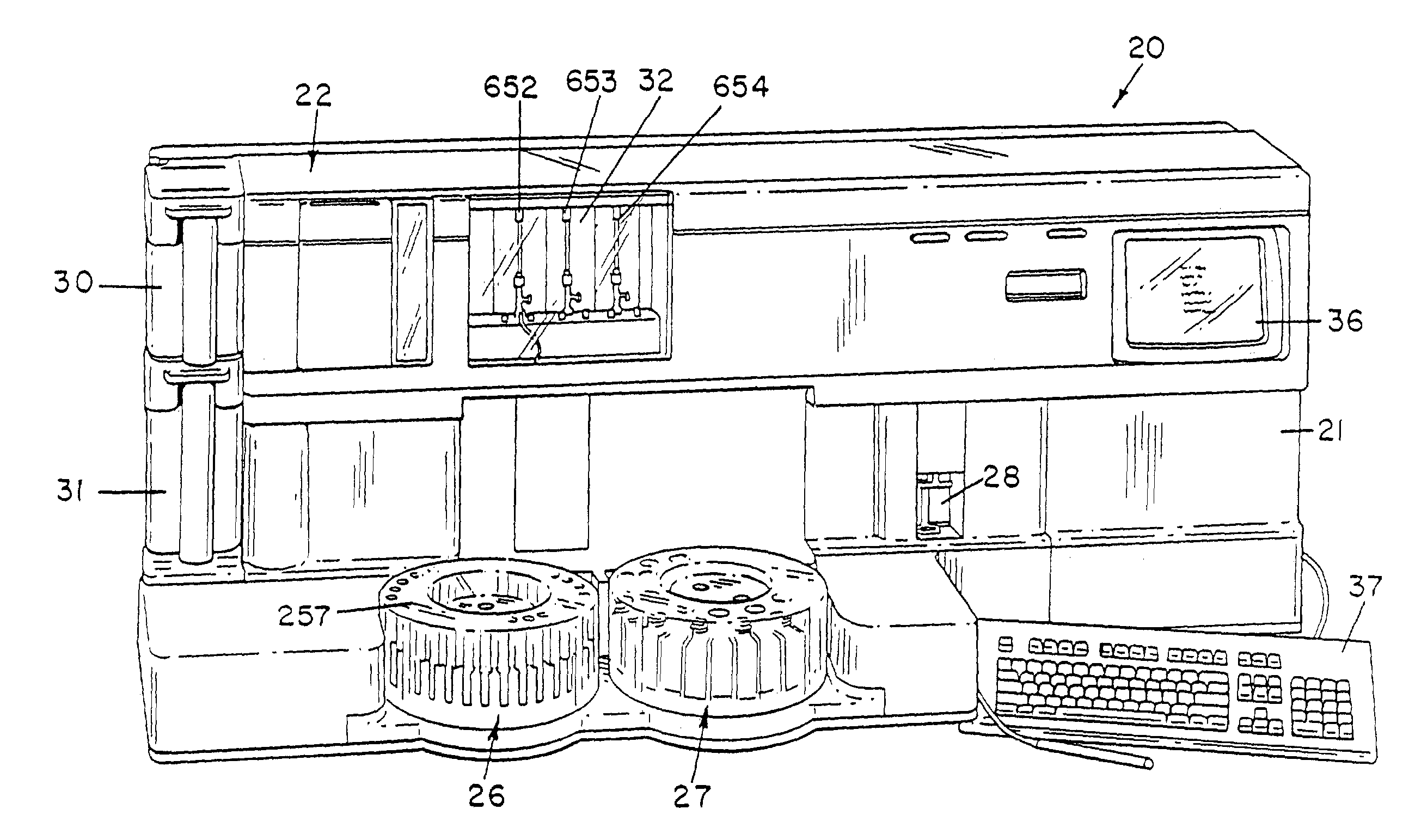
Calibration solution system for use in an automatic clinical analyzer
InactiveUS20050249634A1Eliminate needMaterial analysis by optical meansChemical methods analysisCuvetteBiochemical engineering
A biochemical analyzer adapted to automatically perform calibration and quality control protocols using shuttles adapted to remove calibration and quality control solution vials from a loading tray and to inventory said solution vials on board the biochemical analyzer in a calibration and quality control solution server. In addition, the analyzer is adapted to automatically penetrate the closure covering the opening of the calibration and quality control solution vials, aspirate an amount of solution therefrom and dispense said solution into a test cuvette, thereby eliminating the previous need for operator intervention.
Owner:DADE BEHRING
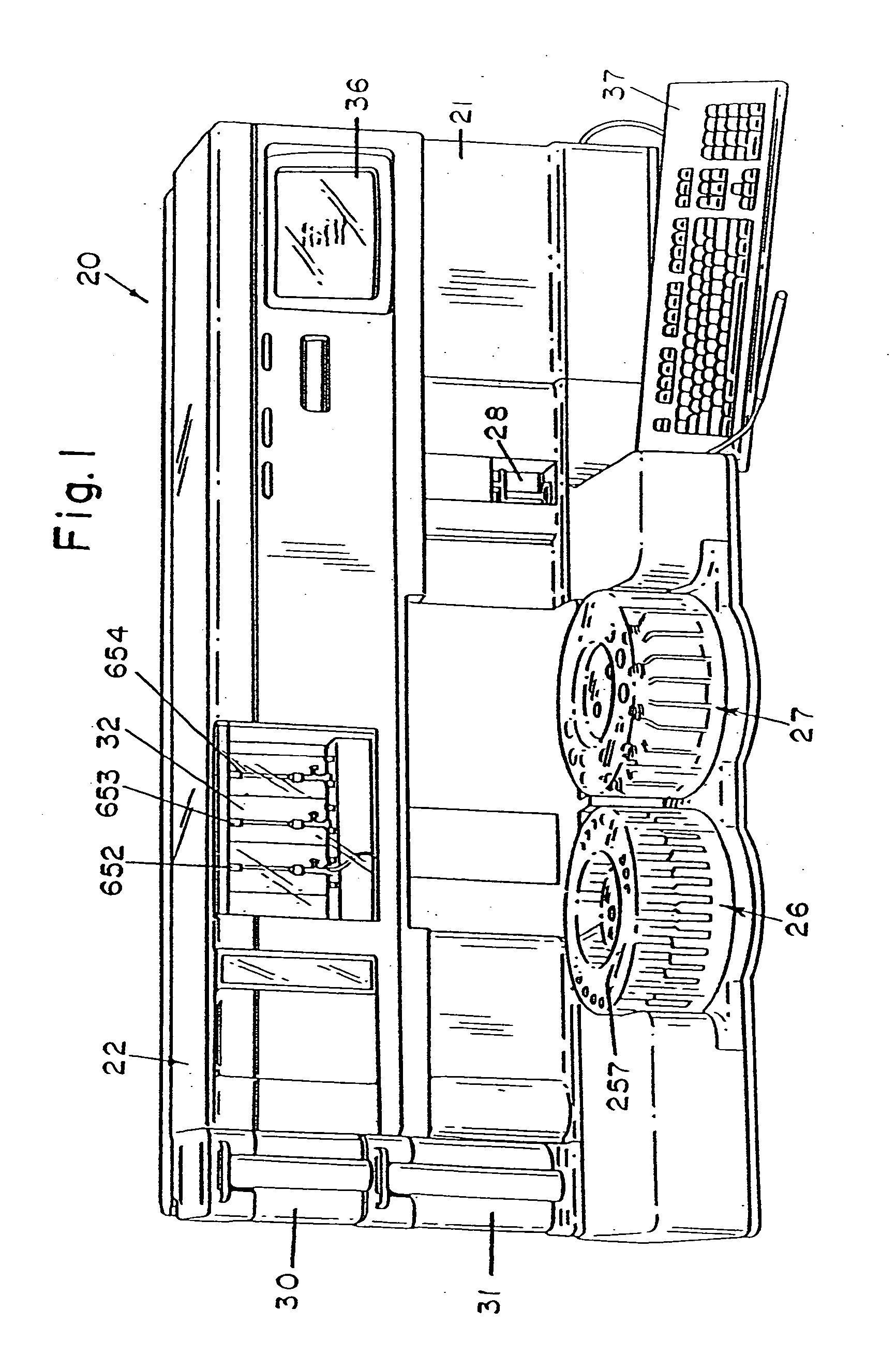
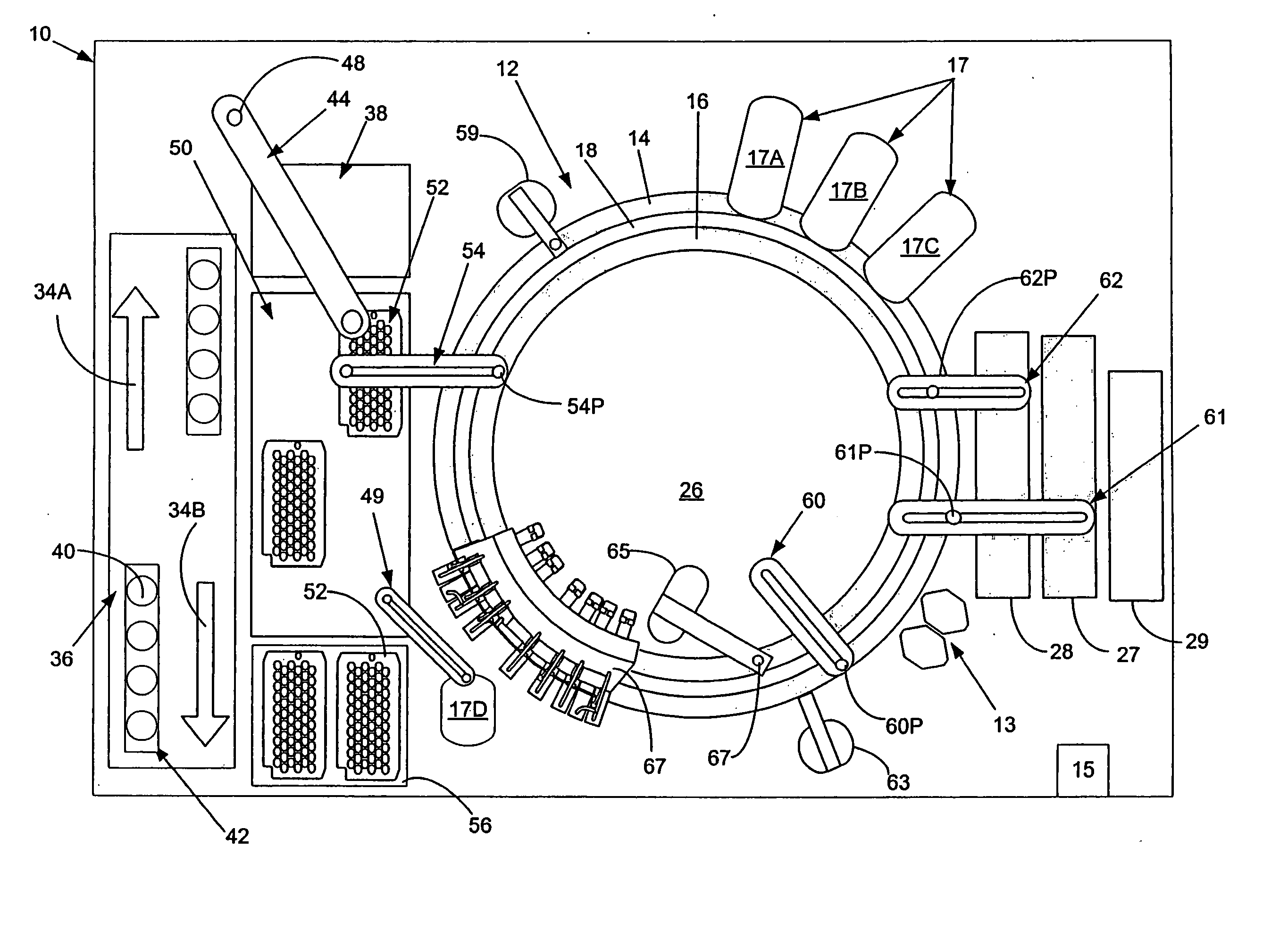
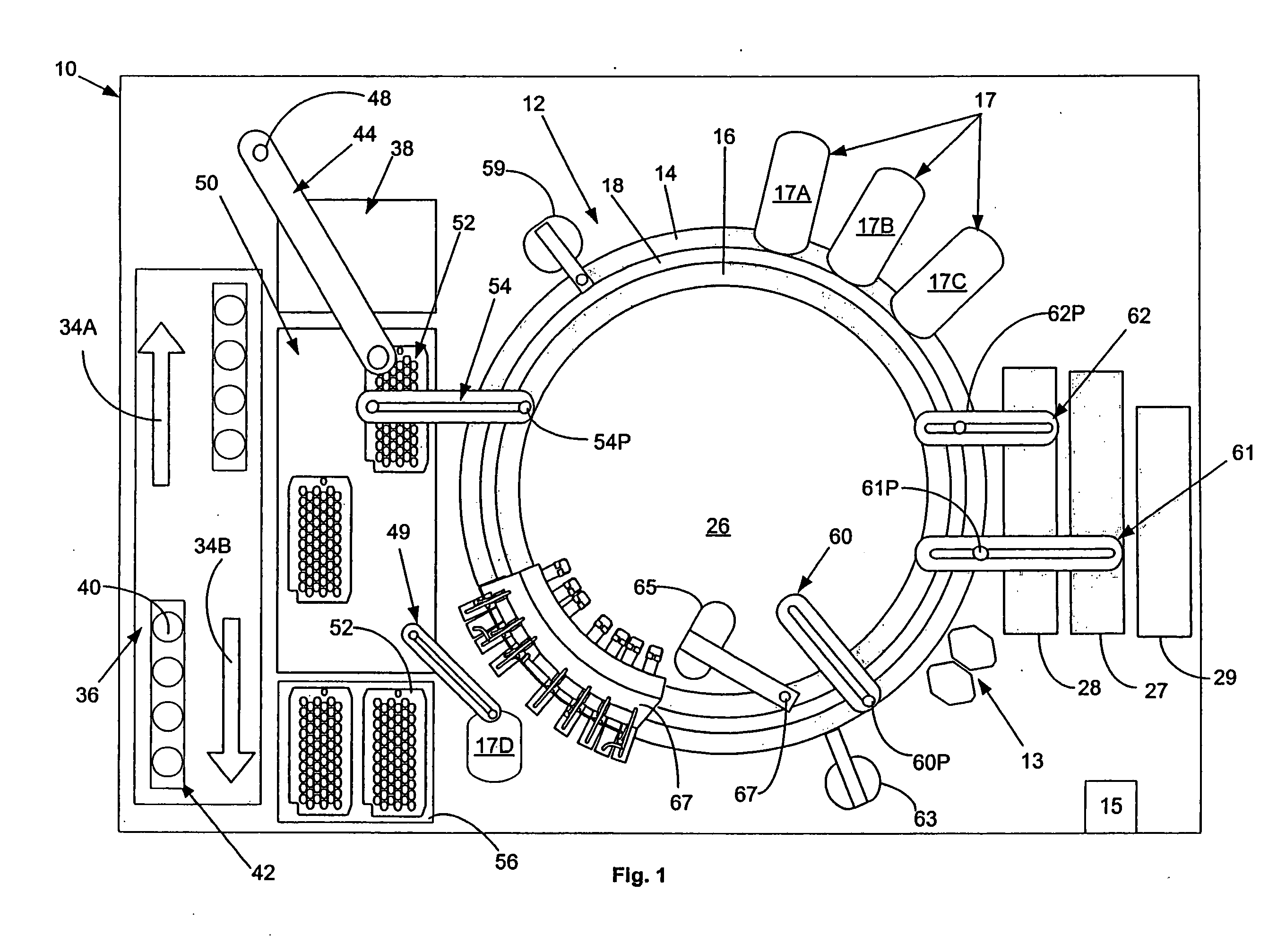
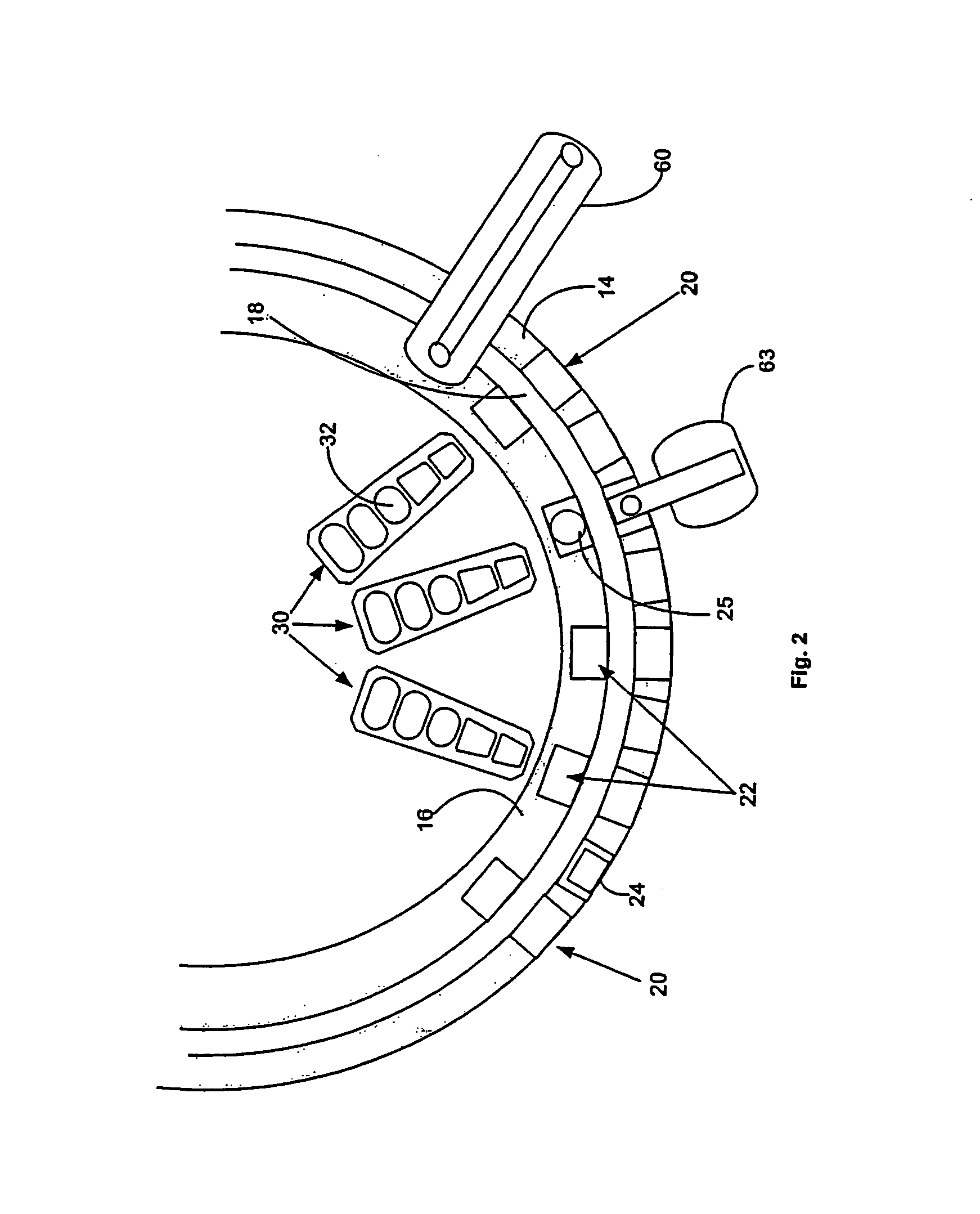
Cuvette for an automated analyzer
An analyzer for performing automated assay testing. The analyzer includes a storage and conveyor system for conveying cuvettes to an incubation or processing conveyor, a storage and selection system for test sample containers, a storage and selection system for reagent containers, sample and reagent aspirating and dispensing probes, a separation system for separating bound from unbound tracer or labeled reagent, a detection system and date collection / processing system. All of the sub-units of the machine are controlled by a central processing unit to coordinate the activity of all of the subunits of the analyzer. The analyzer is specifically suited for performing heterogeneous binding assay protocols, particularly immunoassays.
Owner:ALUMINUM PECHINEY
Apparatus and method for calibration of spectrophotometers
ActiveUS20050168737A1Easy to controlEliminates meniscus errorPhotometry using reference valueRadiation pyrometryCuvetteEvaporation
An apparatus and related method for optical calibration of spectrophotometers is described. The apparatus is a calibration plate including one or more cuvettes filled with solutions of interest. The cuvettes are sealed to prevent evaporation. The cuvettes also possess a compressible component to allow for expansion of the solution and a bubble control apparatus to ensure that the compressible component does not intersect the beam path. A piece of neutral density glass is optionally included in the apparatus to track optical changes of the solutions over time.
Owner:ARTEL
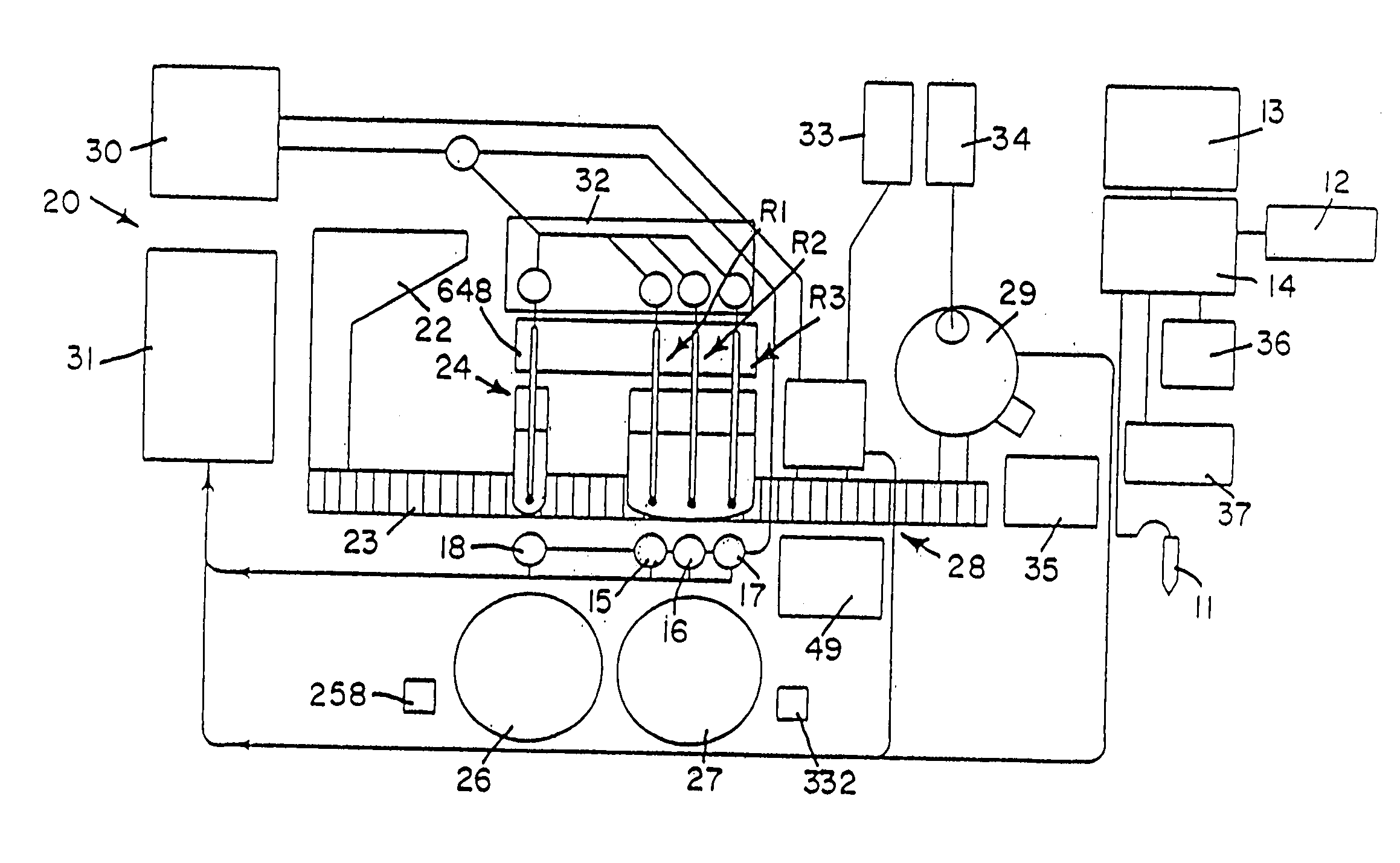
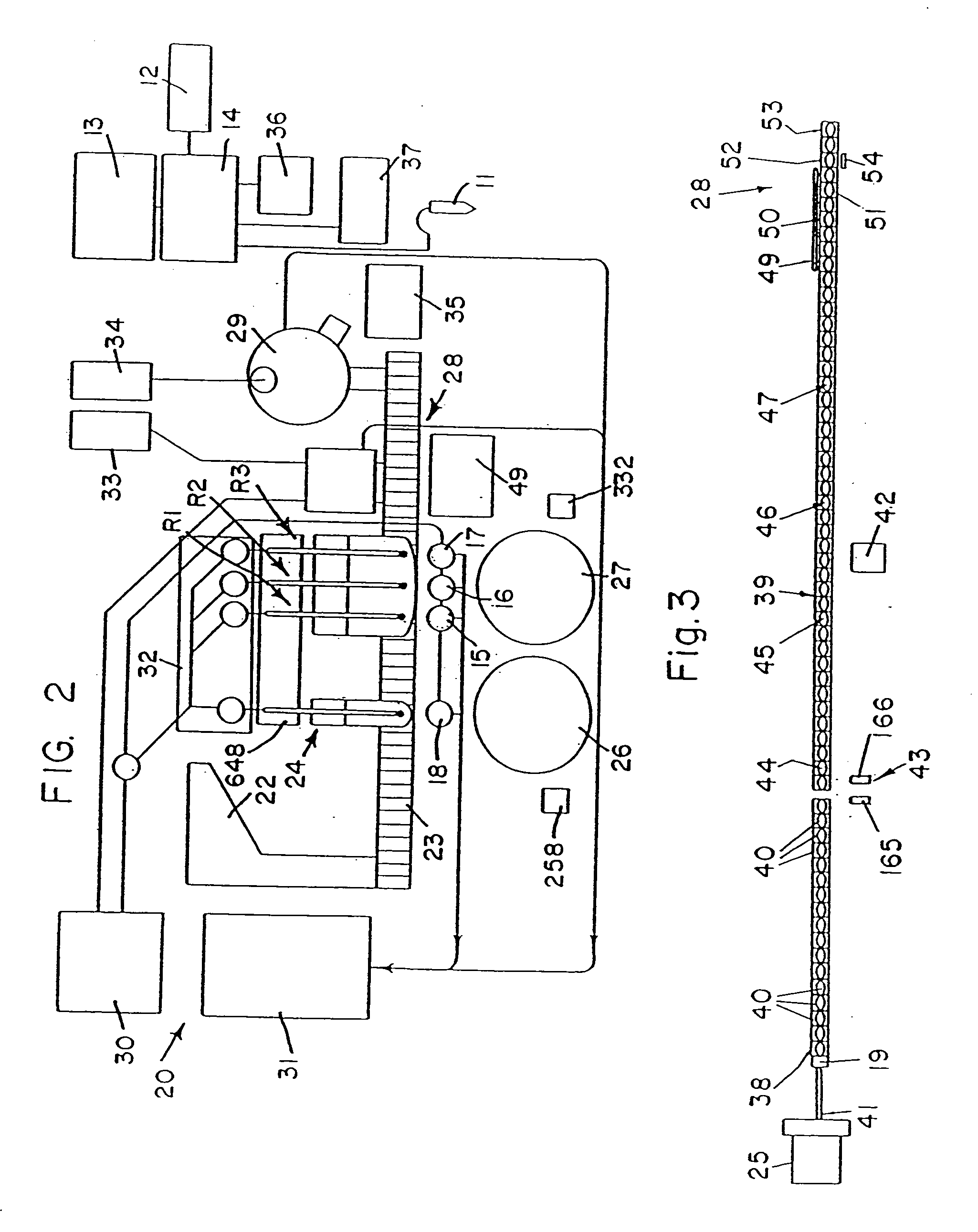
Fluid handling apparatus for an automated analyzer
InactiveUS7182912B2Improve versatilityChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceLaboratory glasswaresEngineeringSelection system
An analyzer for performing automated assay testing. The analyzer includes a storage and conveyor system for conveying cuvettes to an incubation or processing conveyor, a storage and selection system for test sample containers, a storage and selection system for reagent containers, sample and reagent aspirating and dispensing probes, a separation system for separating bound from unbound tracer or labeled reagent, a detection system and date collection / processing system. All of the subunits of the machine are controlled by a central processing unit to coordinate the activity of all of the subunits of the analyzer. The analyzer is specifically suited for performing heterogeneous binding assay protocols, particularly immunoassays.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
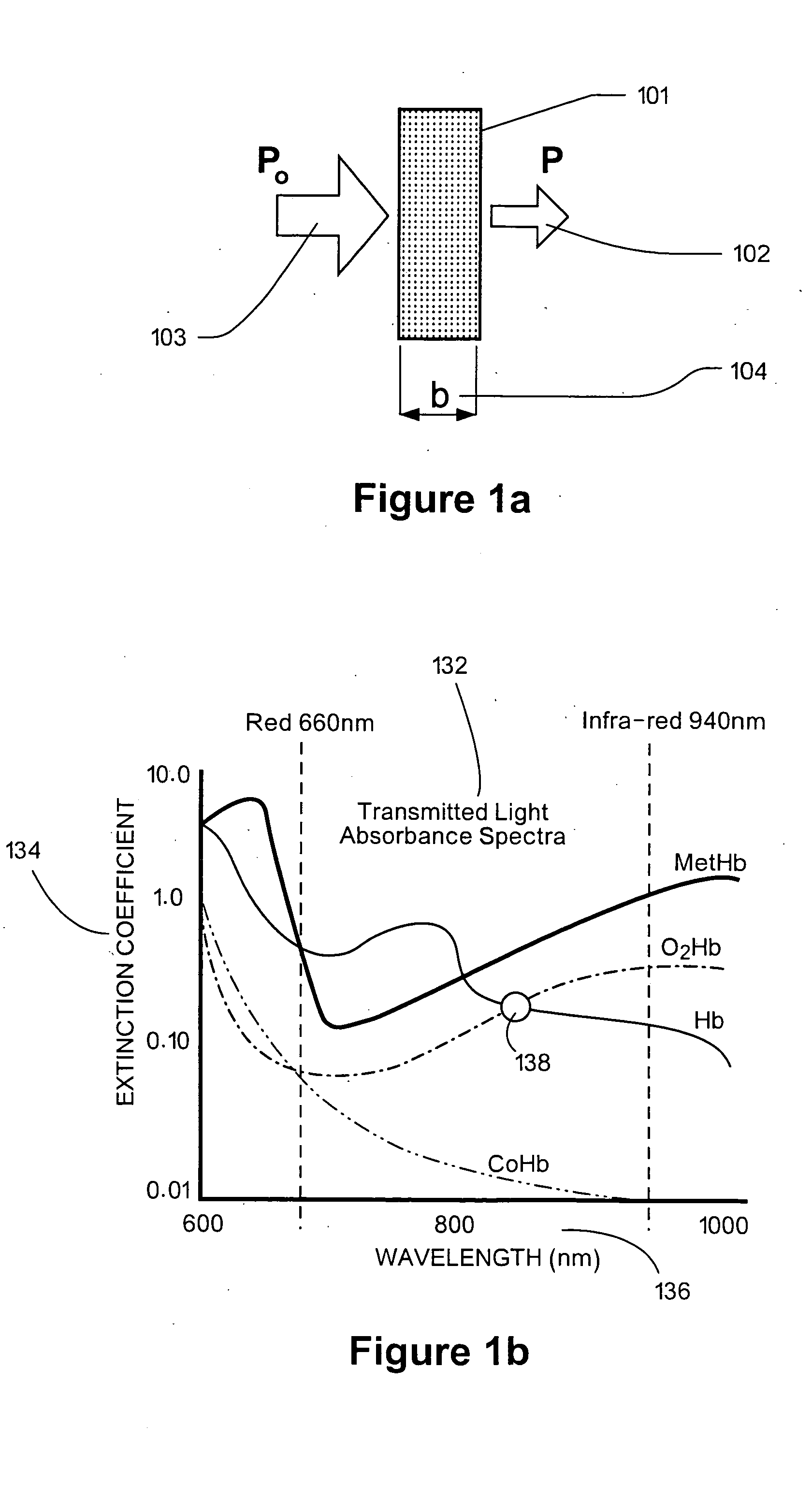
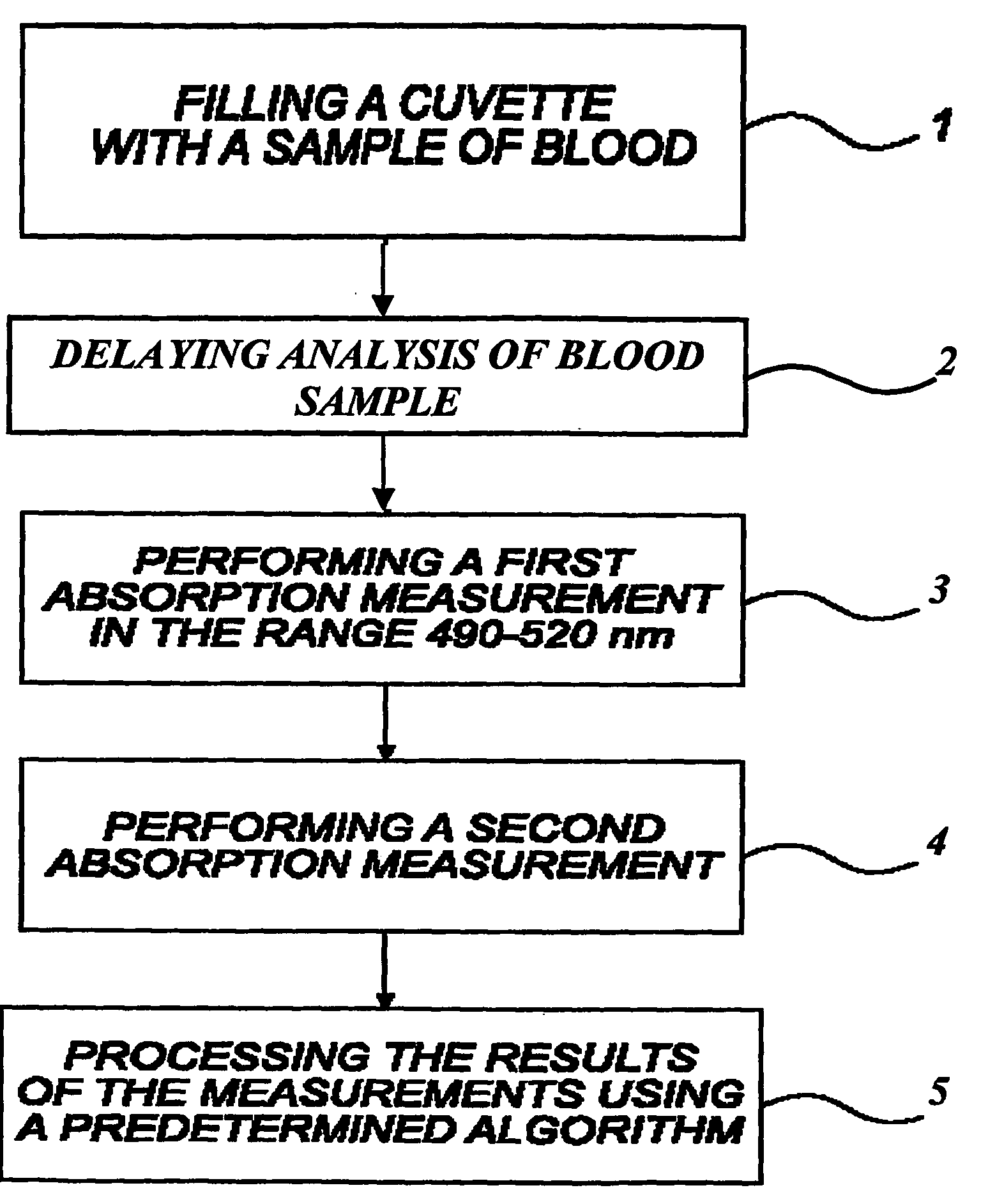
Method and System for Quantitative Hemoglobin Determination
InactiveUS20090075324A1Method is fastBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCuvetteHemoglobin determination
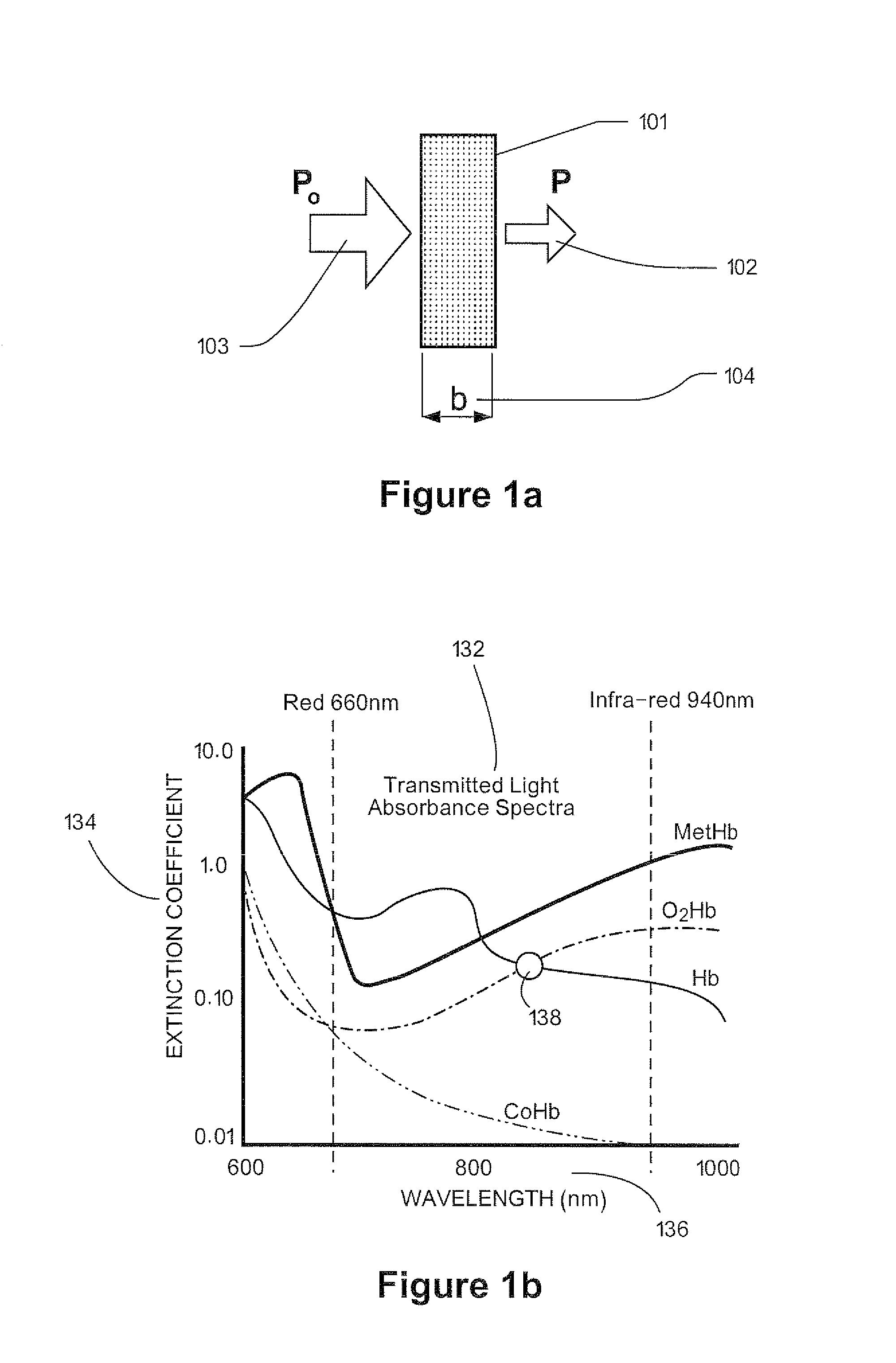
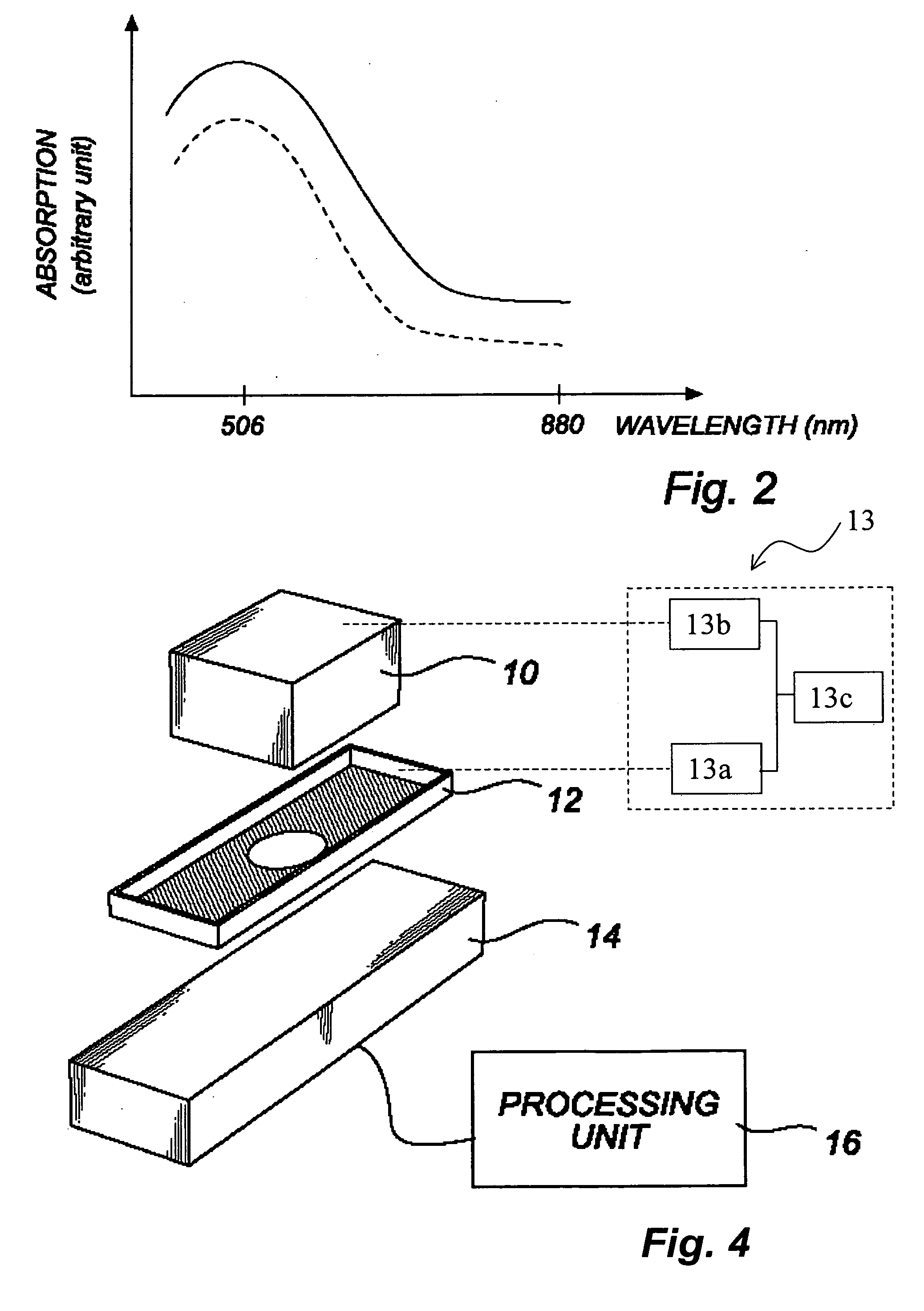
A method for quantitative hemoglobin determination in undiluted, unhemolyzed whole blood is provided which comprises: acquiring a sample of unaltered whole blood into a capillary cuvette, presenting the cuvette to a set-up for an absorption measurement, delaying absorption measurement for a determined period of time, performing a first absorption measurement at a first wavelength in the range 490-520 nm directly on the sample in the cuvette, further conducting a second absorption measurement at a second wavelength different from the first wavelength and at which the absorption is substantially smaller than at the first wavelength, and processing results of the first and second absorption measurements to determine the concentration of hemoglobin in the sample. A system for implementing the method also is provided.
Owner:HEMOQUE AB
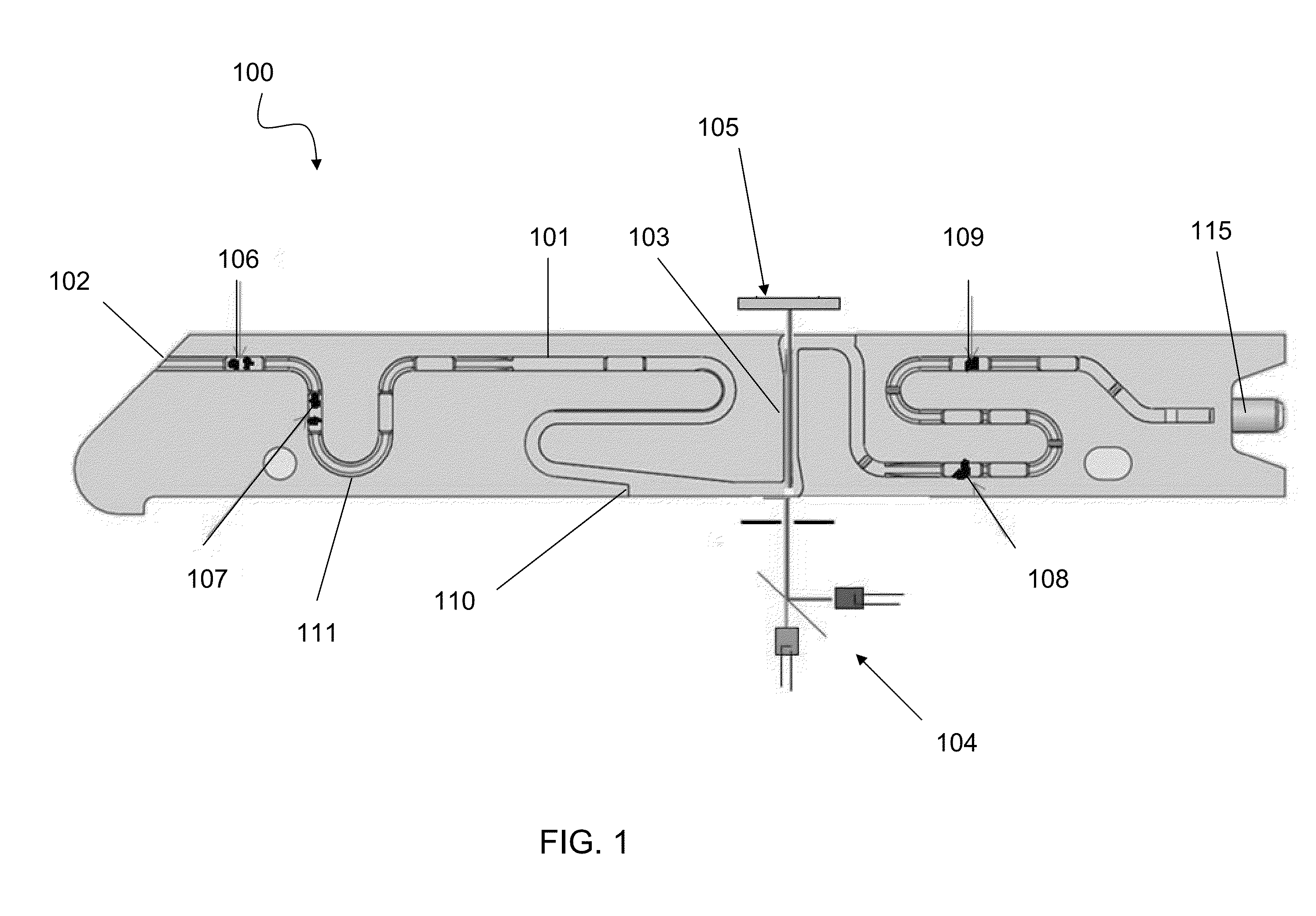
System and method for a composite lens for a flow cytometer
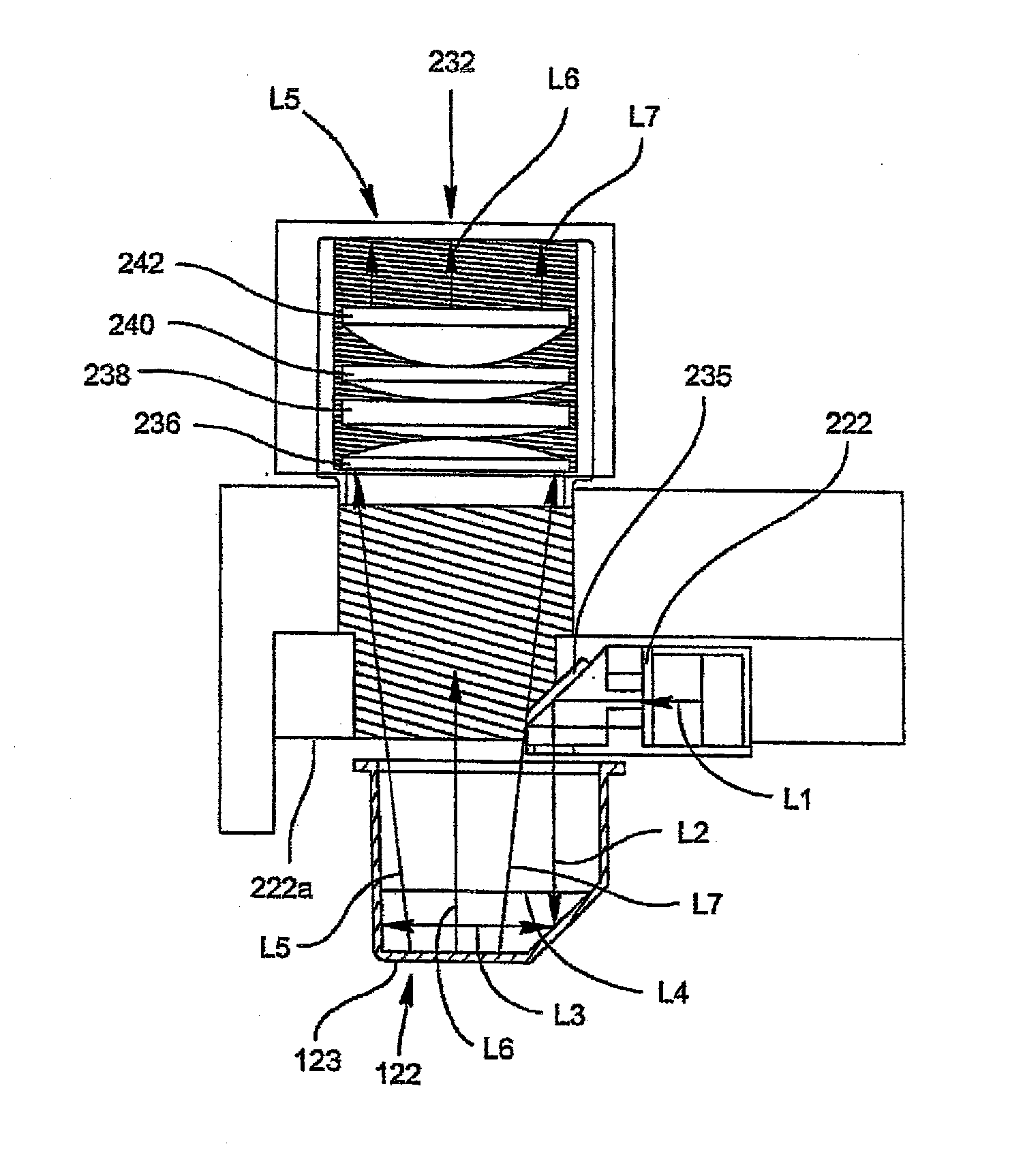
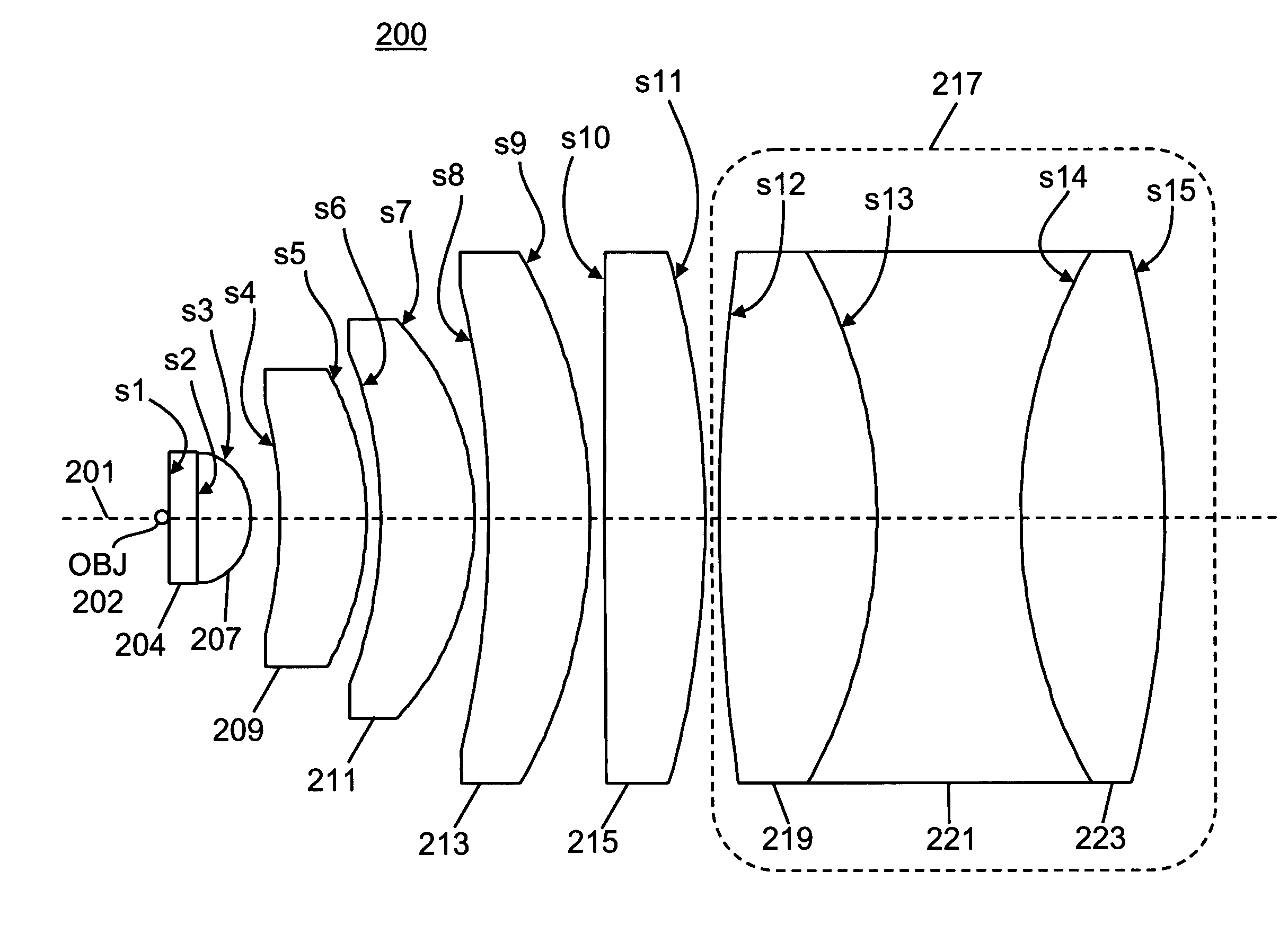
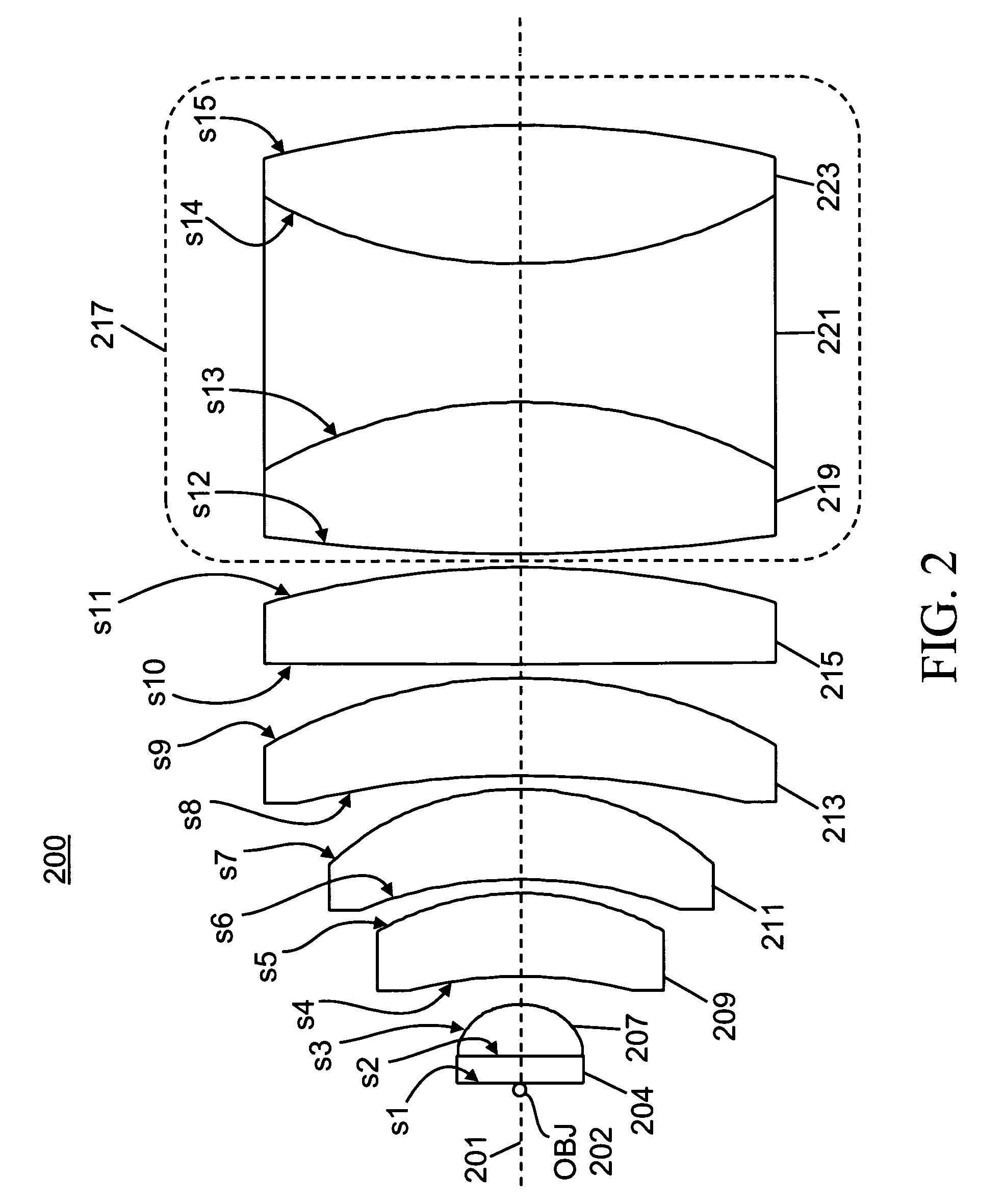
A lens system for collecting and focusing light emanating from an object has a cuvette housing the object and having a wall of thickness not greater than 1.5 millimeters; a plano-convex lens having a planar surface affixed to the wall; a sequence of at least three meniscus lenses, each meniscus lens having a concave surface toward the object and a convex surface, each successive meniscus lens receiving the light from the immediately preceding meniscus lens and having radii of curvature of its concave and convex surfaces greater than corresponding radii of the preceding meniscus lens; and at least one compound lens that may be a doublet lens or a triplet lens, the compound lens receiving the light from a last meniscus lens, wherein an image of a geometrical point on the object has a root-mean square spot size equal to or less than 63 μm.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
System for Conducting the Identification of Bacteria in Biological Samples
ActiveUS20110042582A1Rapid diagnosisFast resultsWithdrawing sample devicesPhotometryCuvetteEngineering
The present invention relates to a system for conducting the identification and quantification of micro-organisms, e.g., bacteria in biological samples. More particularly, the invention relates to a system comprising a disposable cartridge and an optical cup or cuvette having a tapered surface; an optics system including an optical reader and a thermal controller; an optical analyzer; a cooling system; and an improved spectrometer. The system may utilize the disposable cartridge in the sample processor and the optical cup or cuvette in the optical analyzer.
Owner:POCARED DIAGNOSTICS
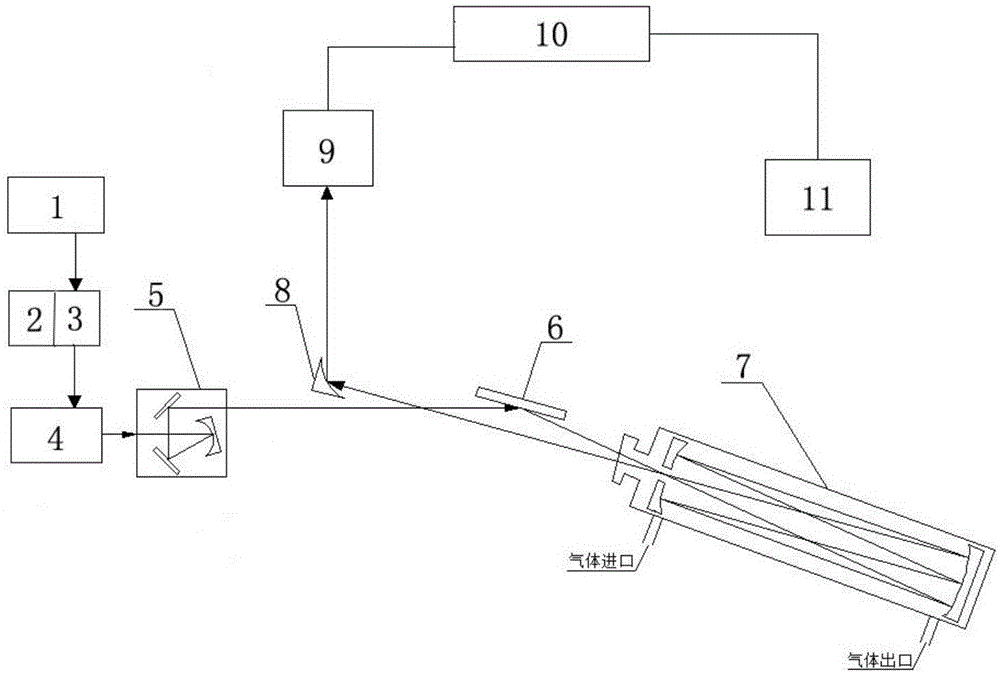
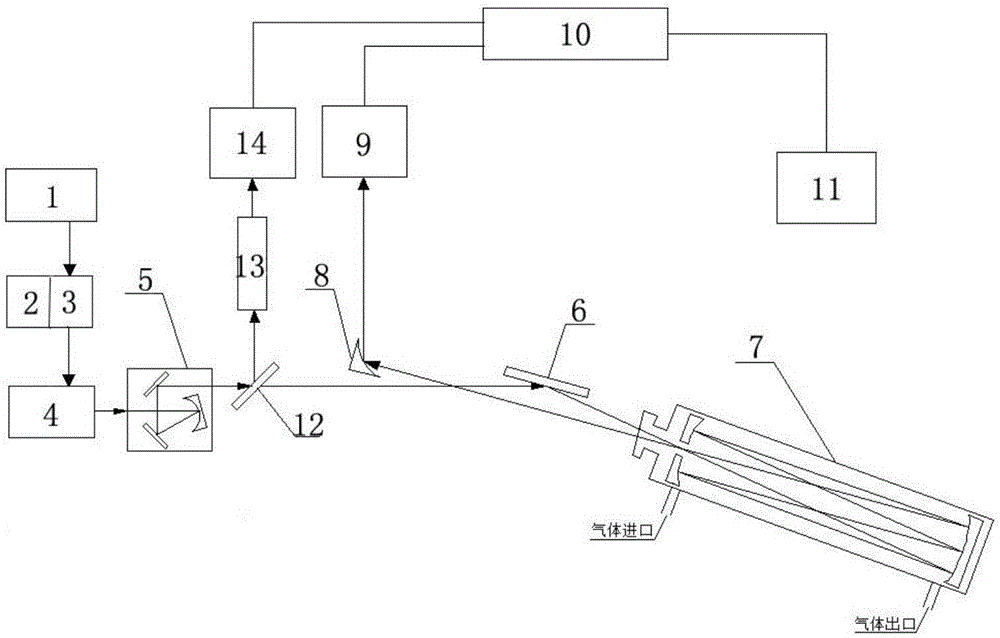
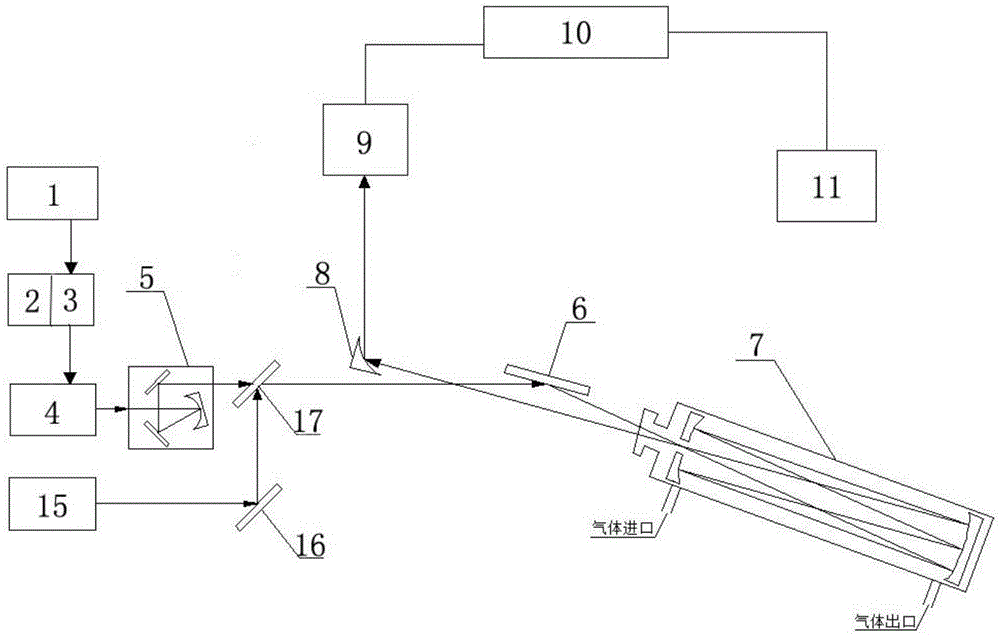
Two quantum cascade laser spectrum-based multicomponent gas simultaneous detection device and method
ActiveCN105277503AEfficient detectionAvoid absorbing interference effectsMaterial analysis by optical meansOptoelectronicsQuantum cascade laser
The present invention relates to the technical field of laser spectrum detection and gas detection, and in particular relates to a two quantum cascade laser spectrum-based multicomponent gas simultaneous detection device and method. An arbitrary waveform function generator outputs a periodic signal which only superposes high-frequency modulation signals in any half period to be used as a laser current signal, a room temperature continuous mode mid-infrared quantum cascade laser is driven by a current control unit, the laser emits a laser signal, the laser signal passes sequentially through a focusing collimating three-dimensional adjustment system, a first mirror, a sample absorption pool and a off-axis parabolic mirror to be reflected to a first detector, the first detector passes the laser signal through a data acquisition unit to convert into an electrical signal and transmit to a computer, and information of the gas to be measured can be obtained by analysis and processing of the electrical signal by the computer. The devices simultaneously utilizes two spectrums for gas detection, and has the advantages of high detection sensitivity, high detection accuracy, no need of external standard gas calibration, simple optical path adjustment, fast response, and stability, and the like.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Mobile water analysis
ActiveUS20130330245A1Increase alkalinityFacilitate in-field chemical analysisAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorCuvettePartial alignment
An embodiment provides a cuvette apparatus including: a lid and a body, the body including a fluid channel disposed therein; and the lid including at least one opening aligned with a portion of the fluid channel, thereby providing access to the fluid channel in the body. Other aspects are described and claimed.
Owner:HACH CO
Automated analyzer
InactiveUS20060051243A1Chemiluminescene/bioluminescenceAnalysis by electrical excitationCuvetteAutomated analyzer
An automated analyzer for analyzing patient samples. The analyzer includes a plurality of cuvettes, which allow the samples to be mixed with various reagents. The analyzer includes one or more detectors, including a detector adapted to detect luminescence of the reaction mixture in the cuvettes. The analyzer allows for various diagnostic assays to be performed on a single system, and provides for high-sensitivity analysis at faster speeds.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
Optical reader for diffraction grating-based encoded optical identification elements
ActiveUS7441703B2Increase the number ofMinimizing sensitivityPaper-money testing devicesRecord carriers used with machinesCuvetteFluorescence
An optical reader system 7 for diffraction grating-based encoded microbeads (or bead reader system), comprises a reader box 100, which accepts a bead cell (or cuvette) 102 that holds the microbeads 8, having an embedded code therein. The reader box 100 interfaces along lines 103 with a known computer system 104. The reader box 100 interfaces with a stage position controller 112 and the controller 112 interfaces along a line 115 with the computer system 104 and a manual control device (or joy stick) 116 along a line 117. The reader interrogates the microbeads to determine the embedded code and / or the fluorescence level on the beads. The reader provides information similar to a bead flow cytometer but in a planar format, i.e., a virtual cytometer.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
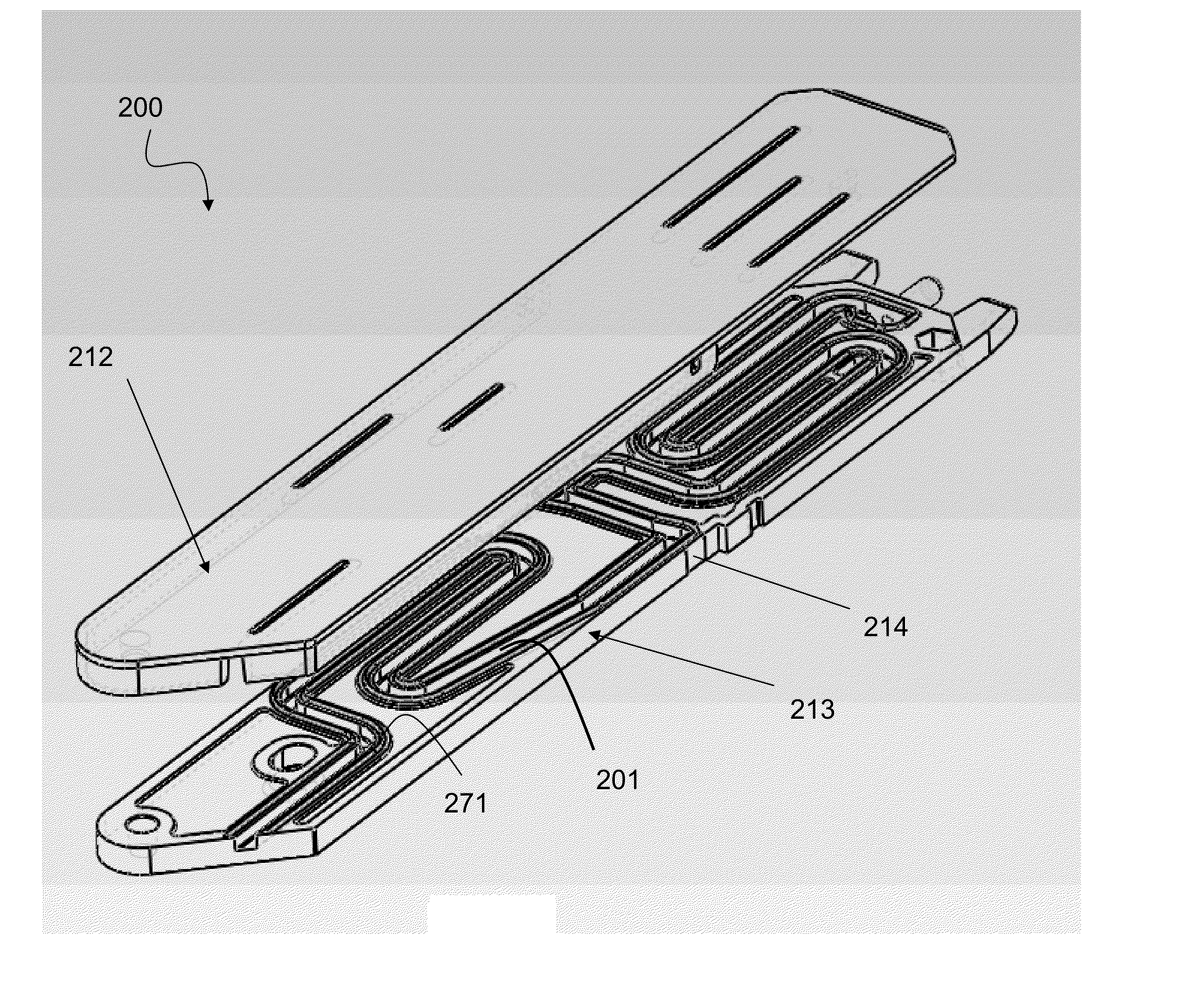
Apparatus for electroporation
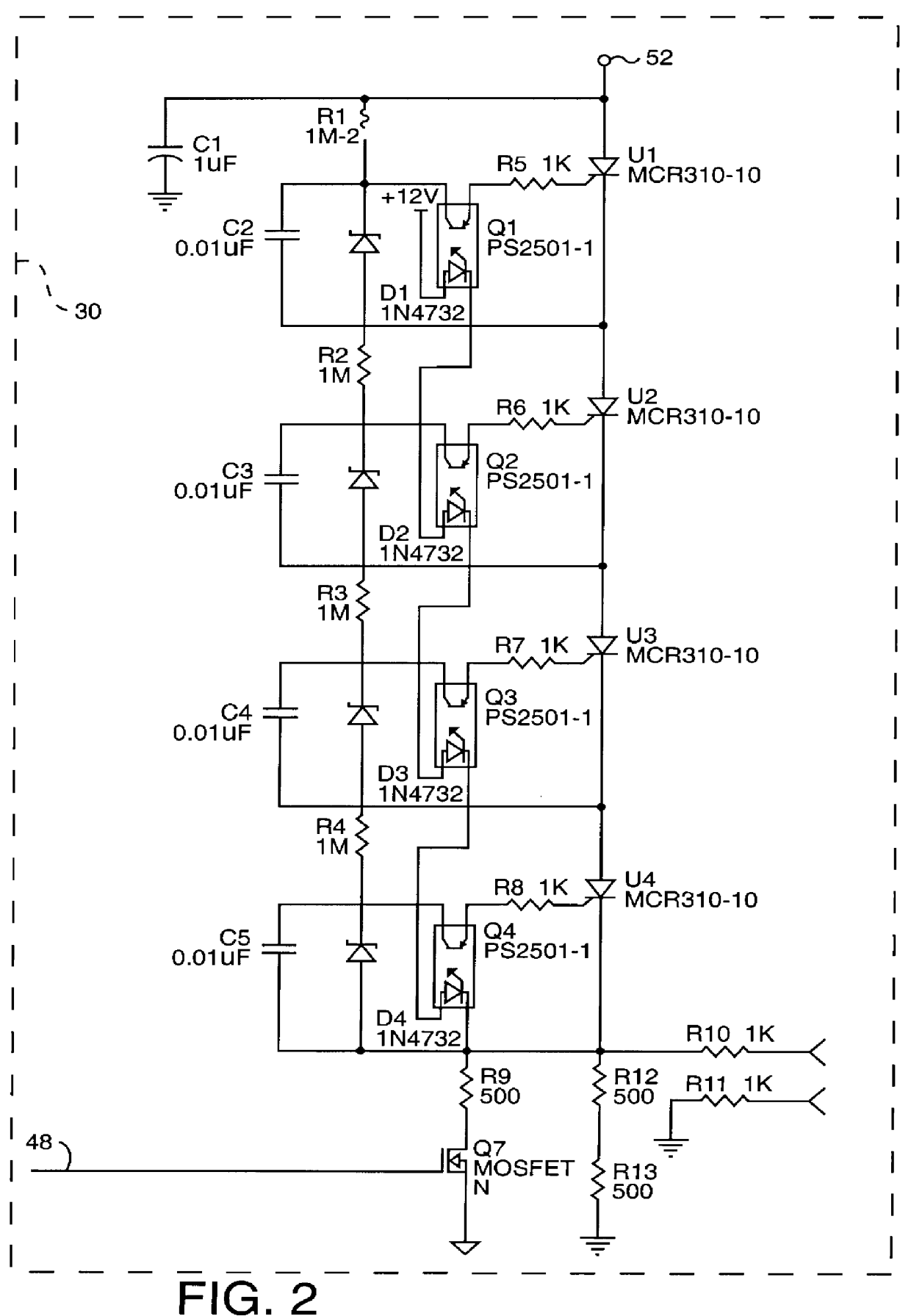
InactiveUS6103084AAvoid delayImprove transformation efficiencySludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementMicrocontrollerTransformer
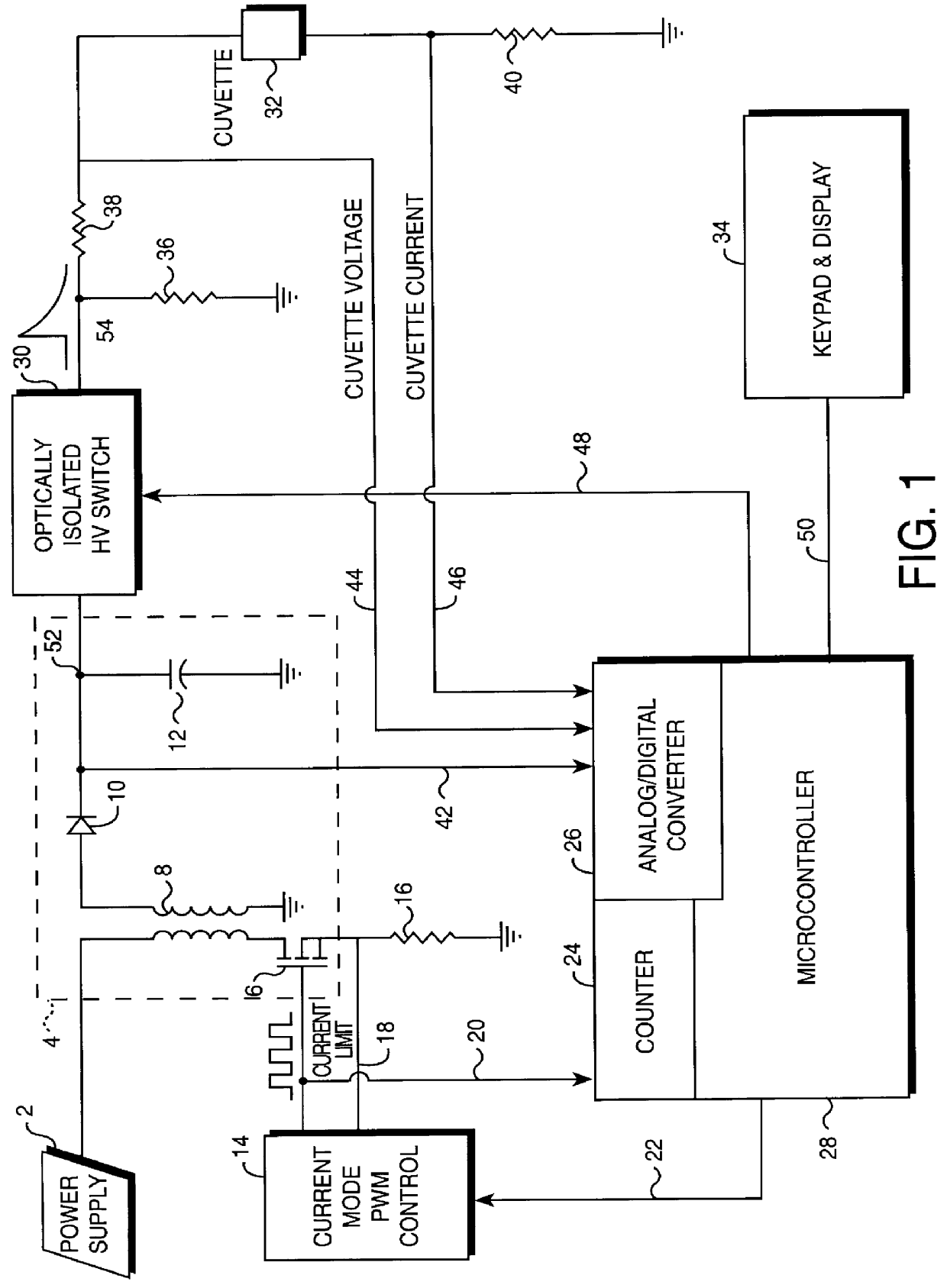
An apparatus for electroporation stores a level of charge, specified by a user, on a capacitor, which is delivered to a cuvette through an optically isolated high voltage switch. The capacitor is charged through a charging system, including a current mode pulse width modulation control circuit, which monitors the current in the primary winding of a transformer and supplies a pulse width modulated signal, limiting the current on every pulse to a level set by the microcontroller, to the controlling transistor in order to generate the drive to the primary winding of the transformer. A controlled amount of energy is transferred through each pulse to the capacitor. The microcontroller monitors the voltage on the capacitor up to a threshold level to predict the number of pulses necessary to store the requested amount of charge on the capacitor. The microcontroller will then count the number of pulses until the number of pulses necessary to store the requested amount of charge on the capacitor has been reached. At this point the requested voltage is delivered to the cuvette through the optically isolated high voltage switch comprised of sensitive gate SCRs coupled together in series. The voltage and current at the cuvette are monitored and input to the microcontroller so that the impedance at the cuvette is calculated by the microcontroller and errors in the composition of the solution within the cuvette are detected.
Owner:EPPENDORF NETHELER HINZ GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com