Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
324 results about "Automated analyzer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
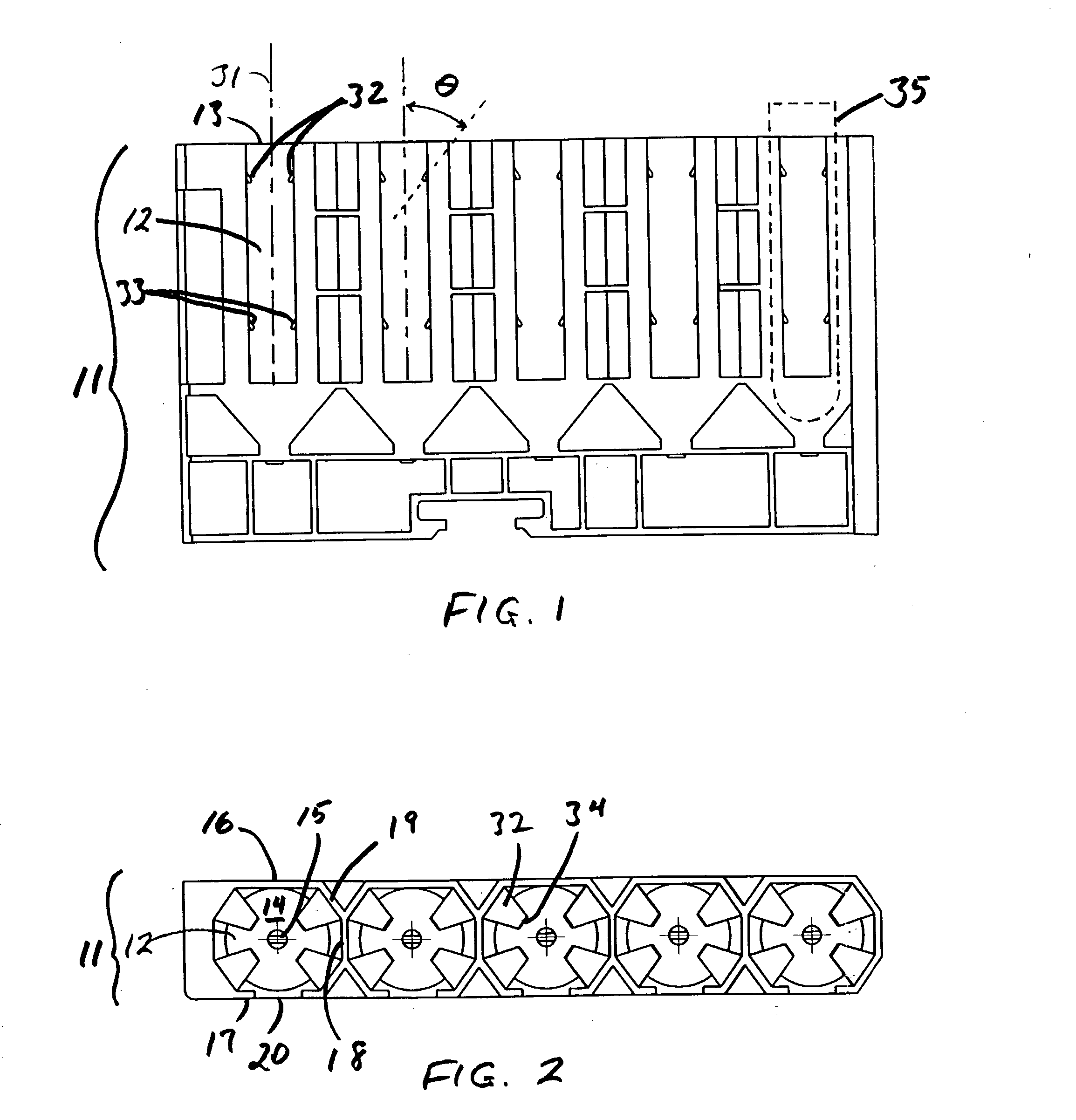
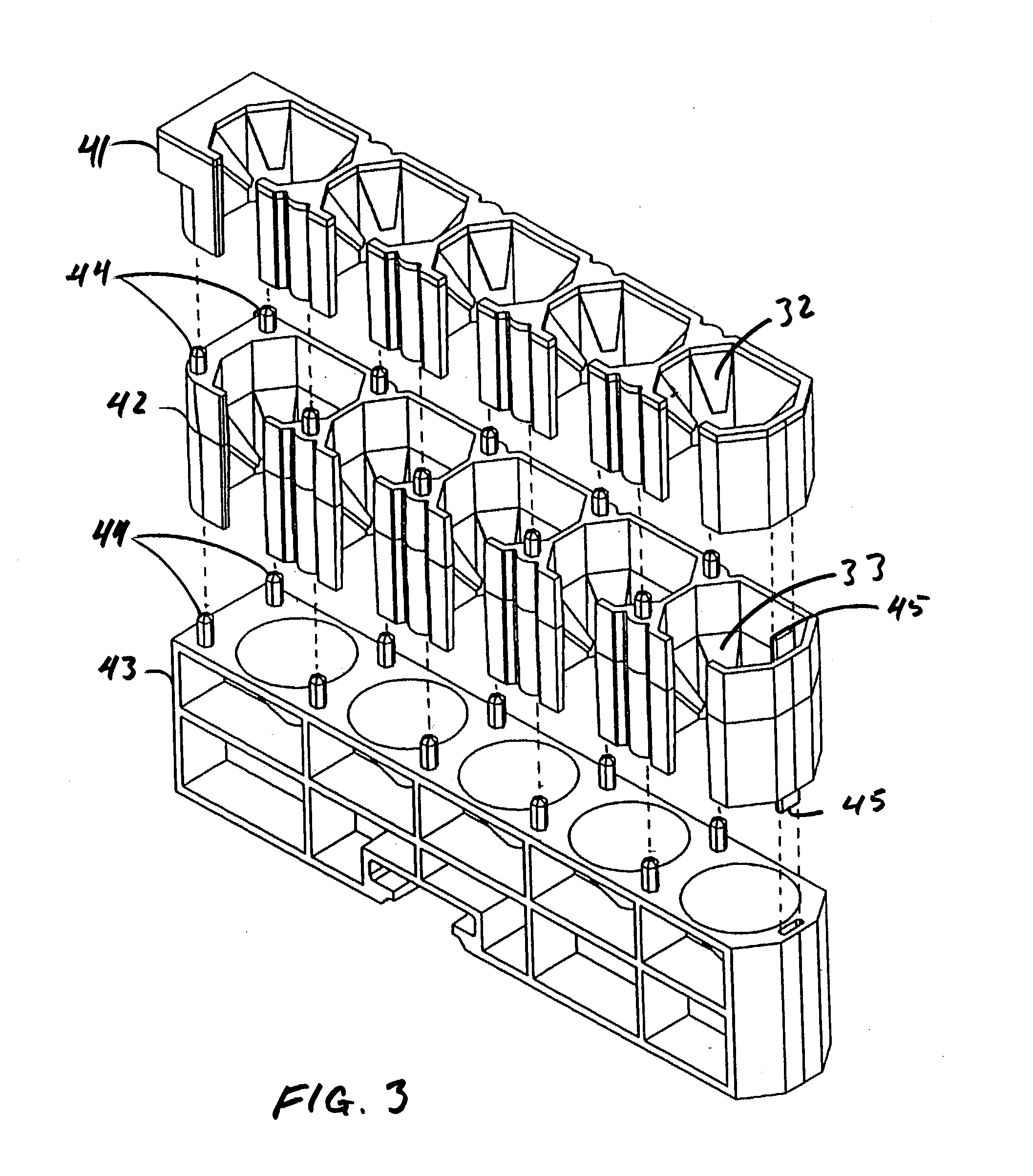
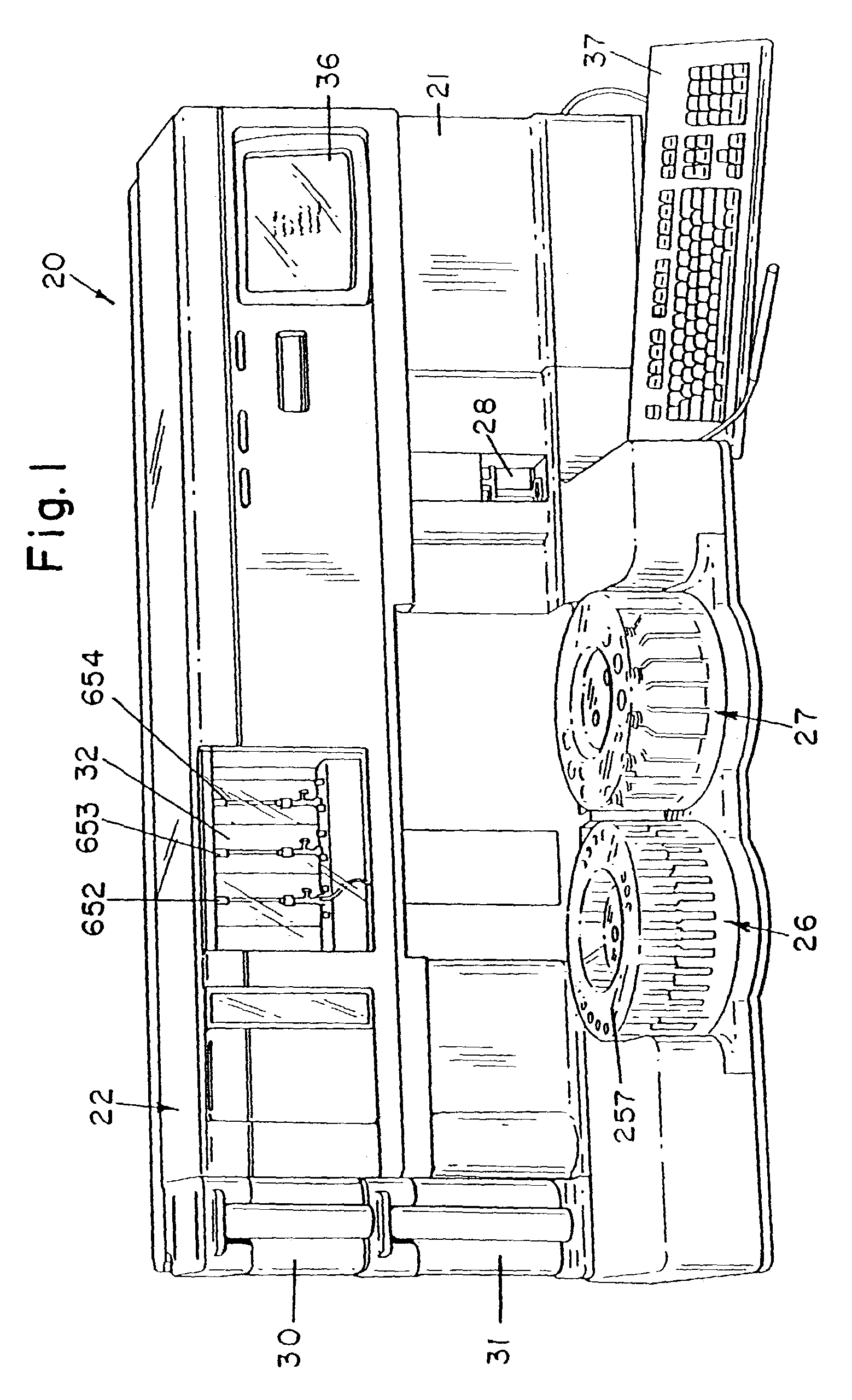
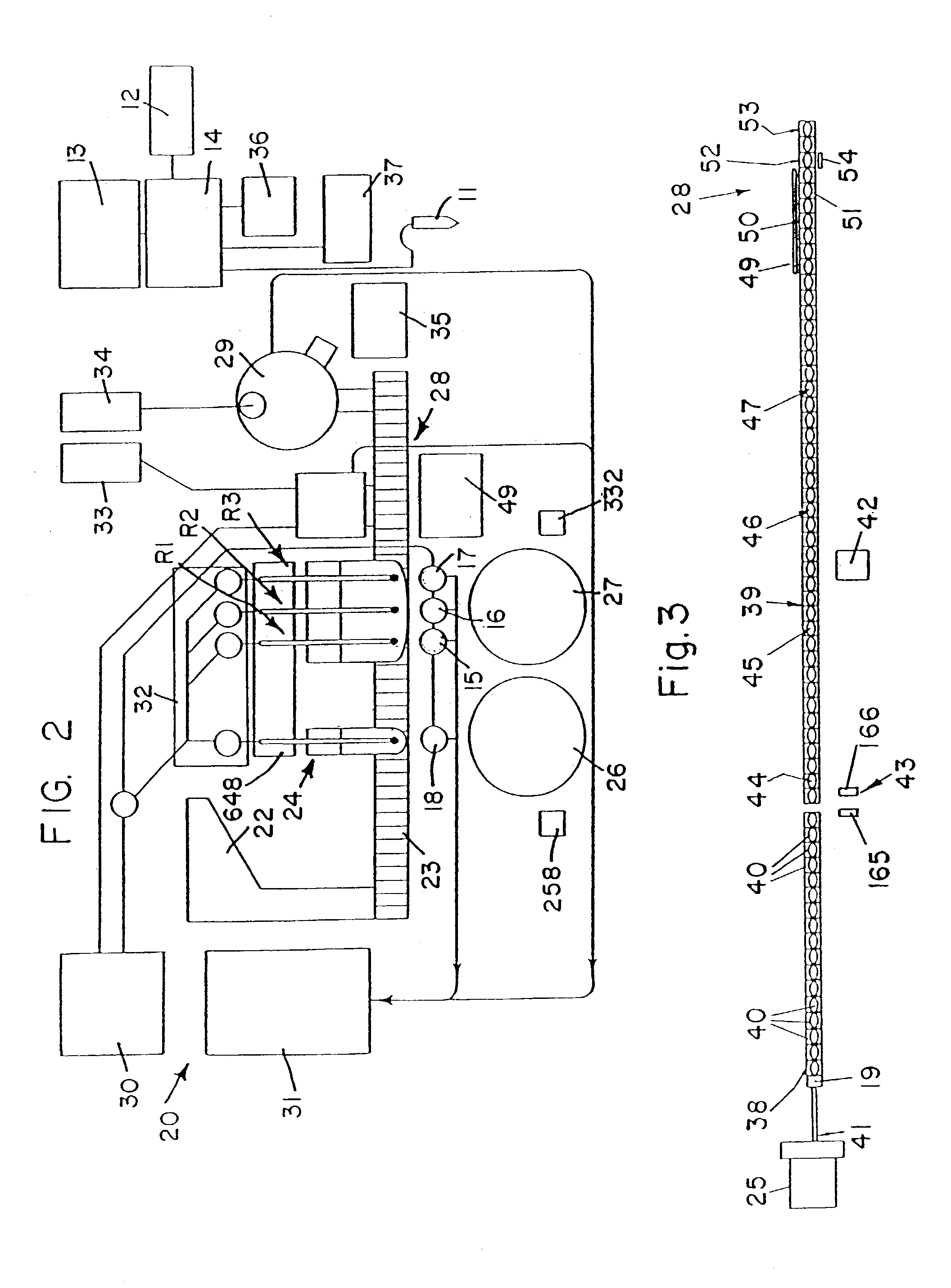
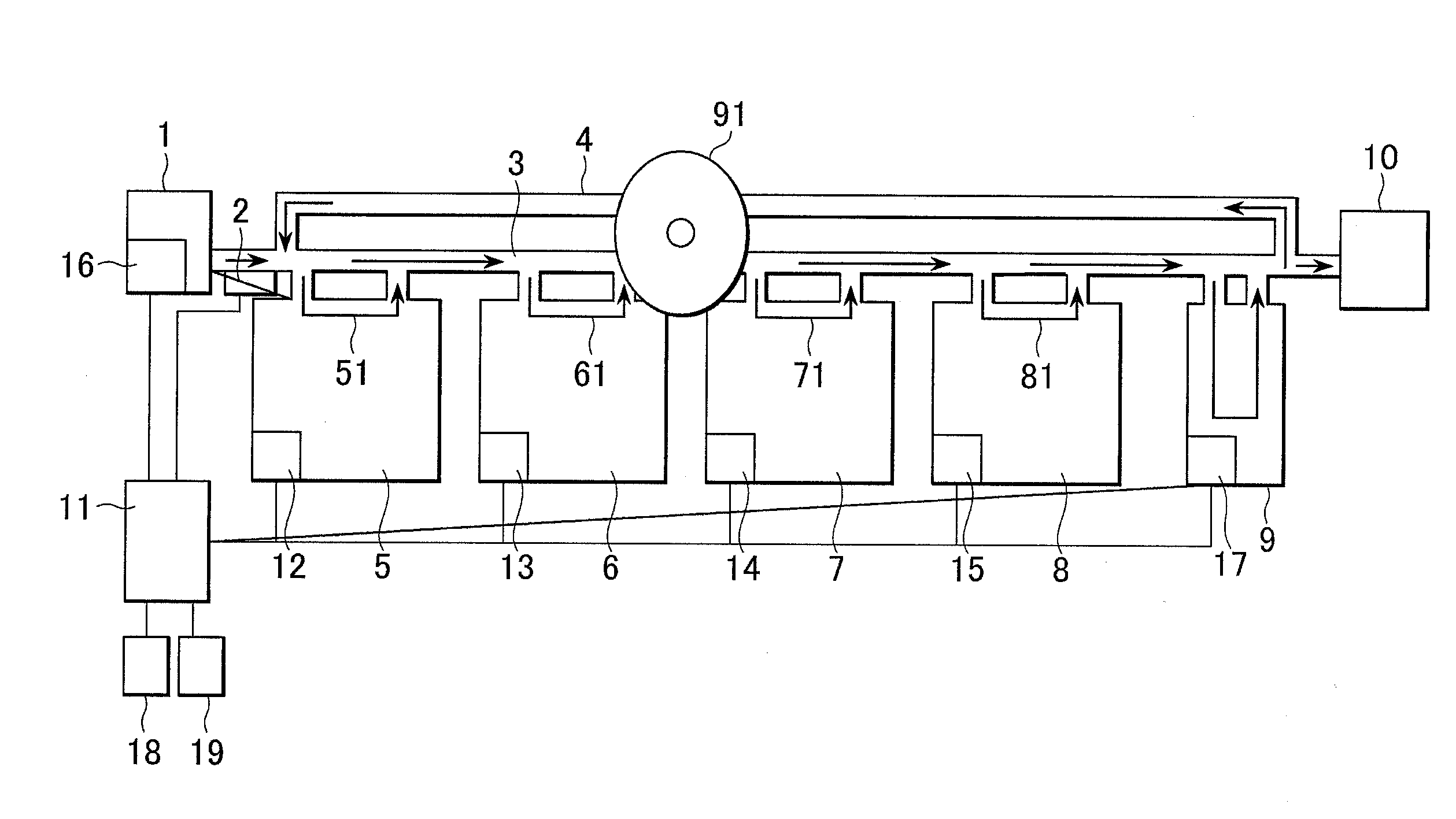
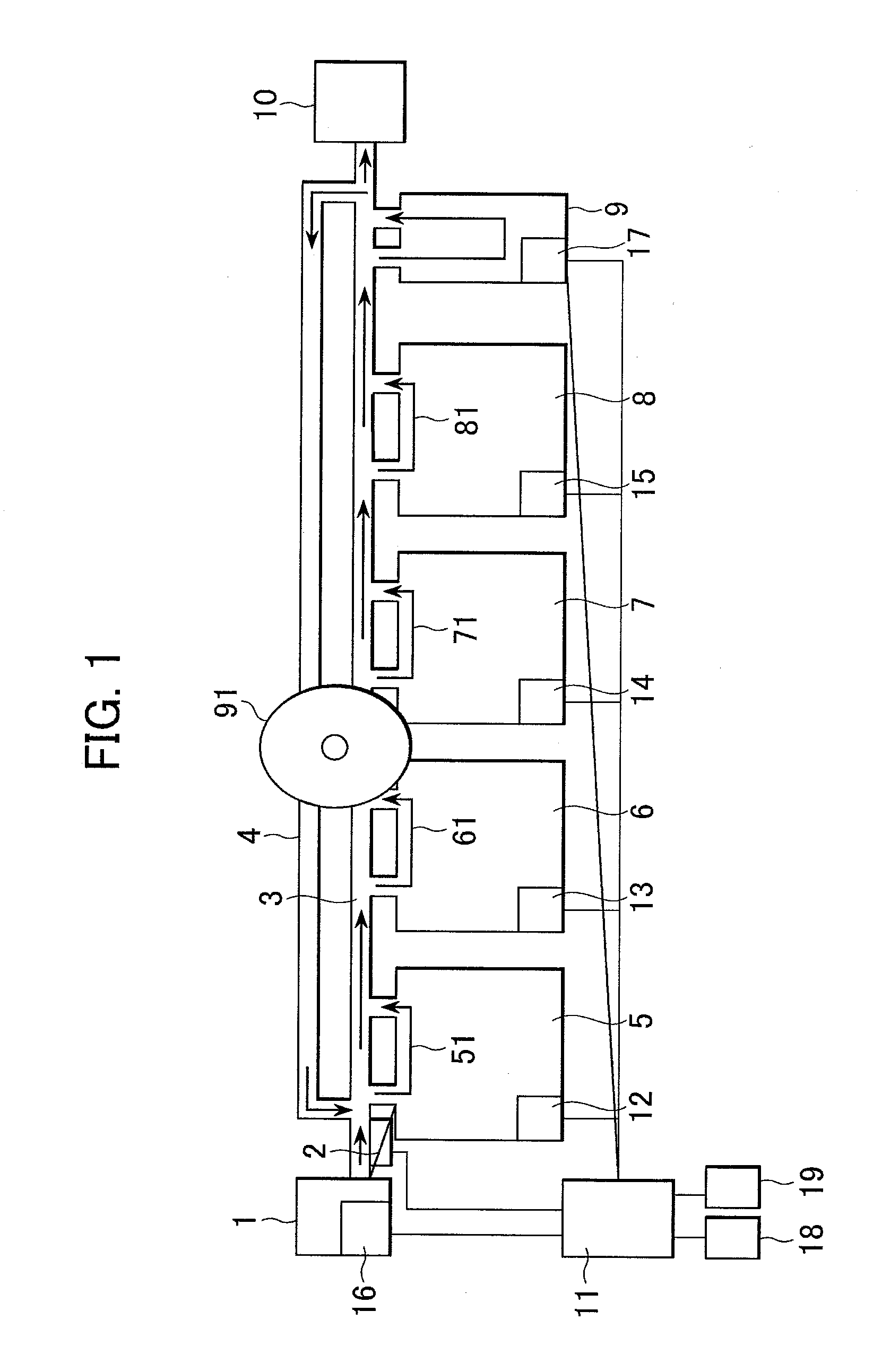
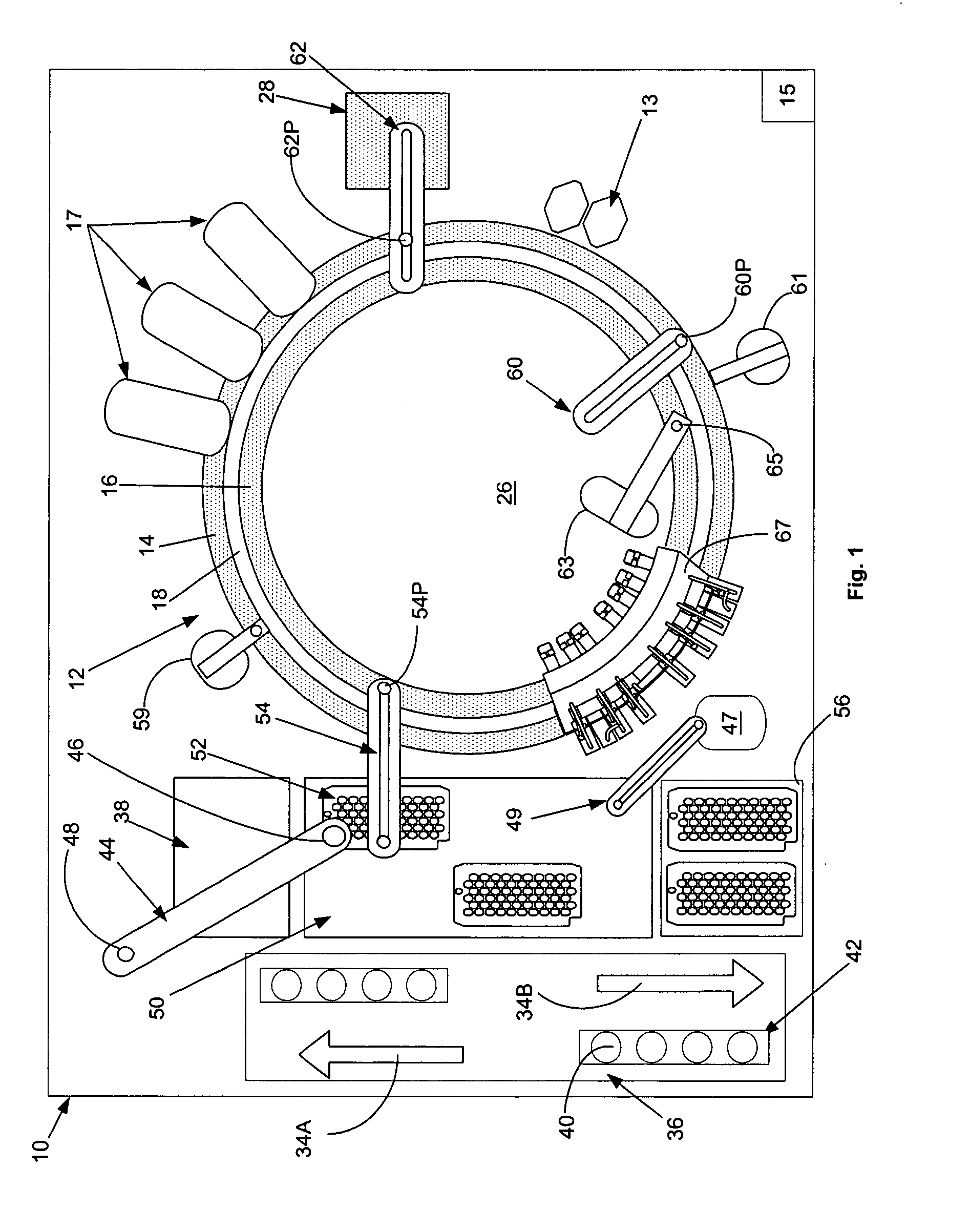
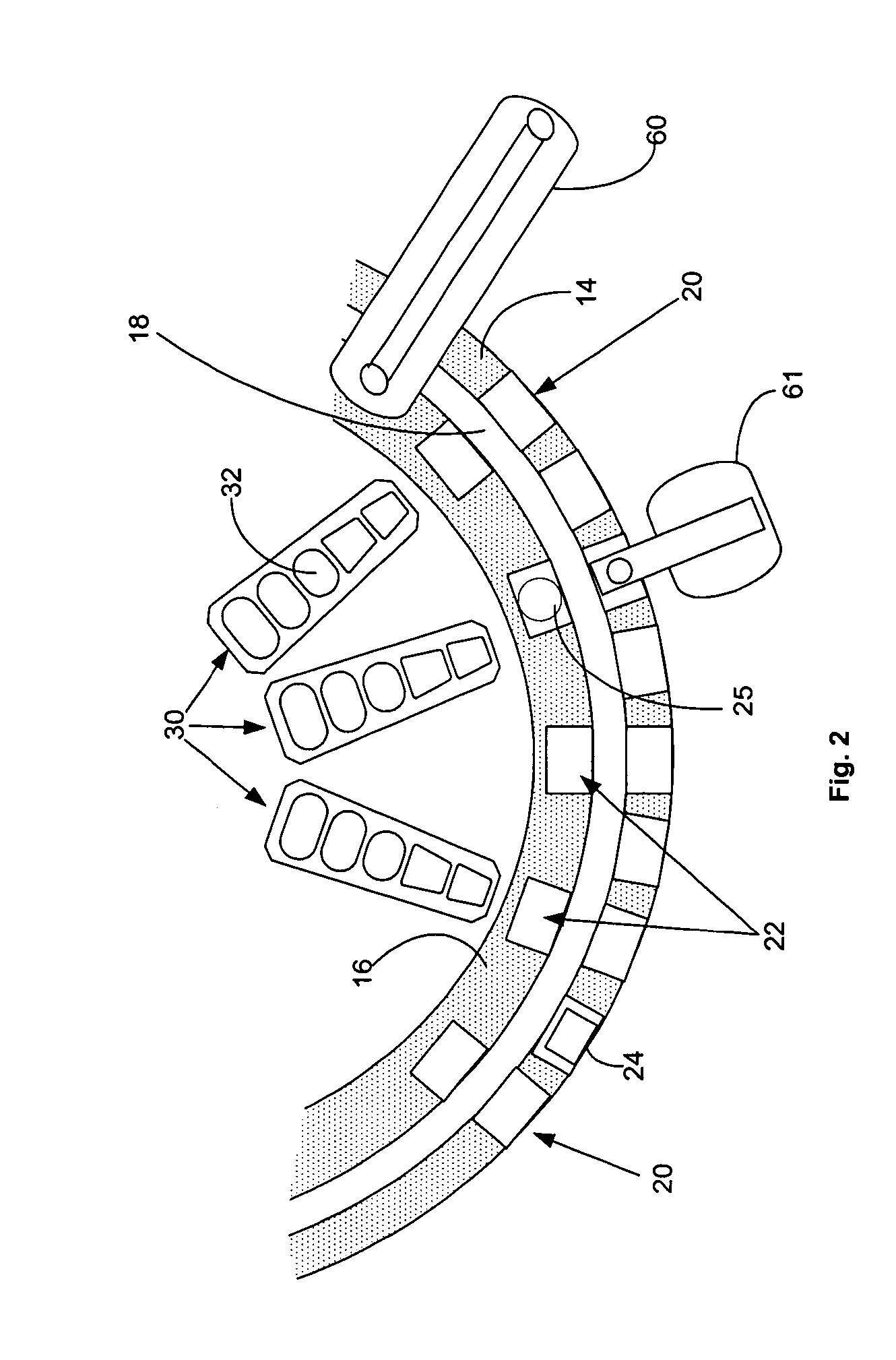
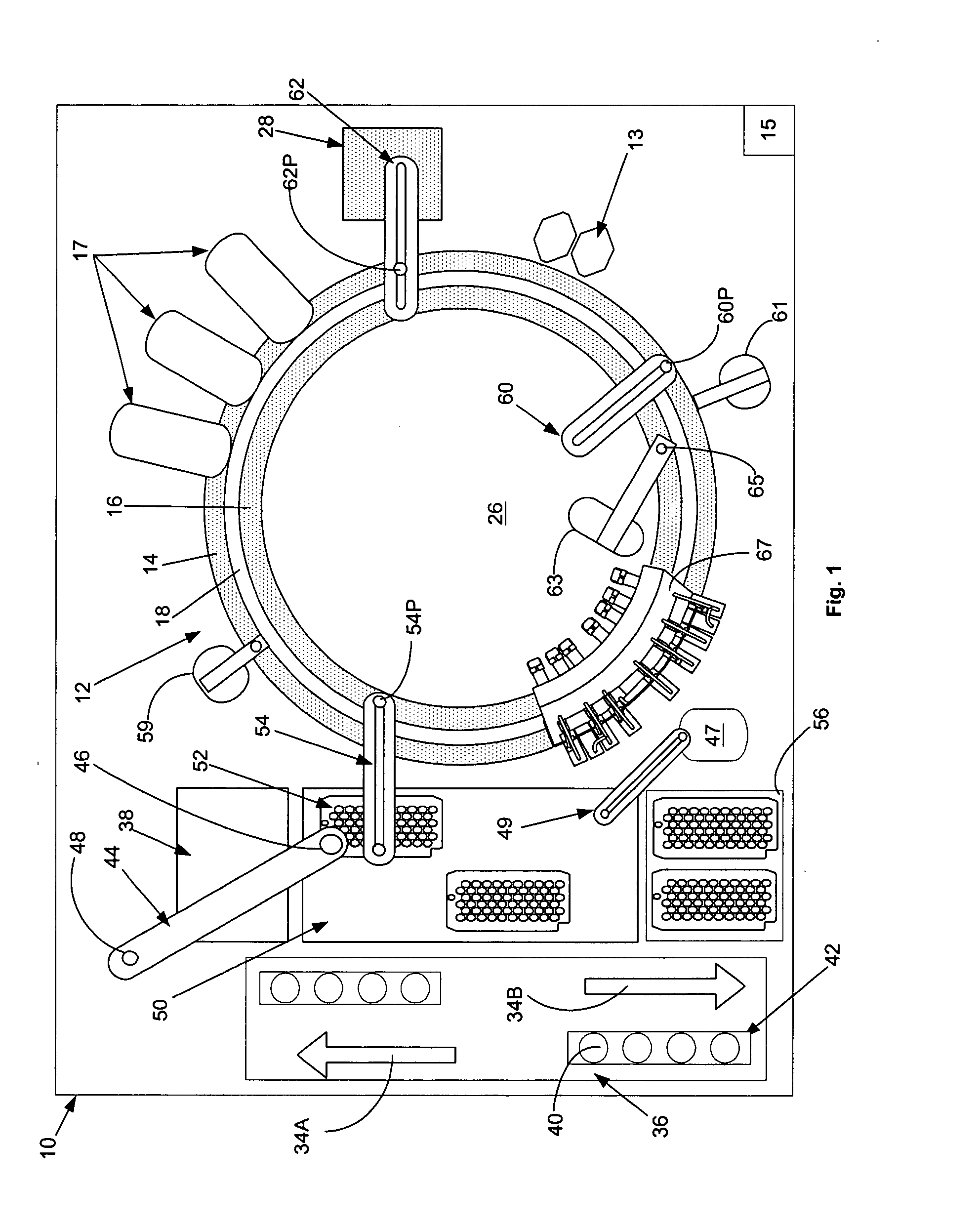
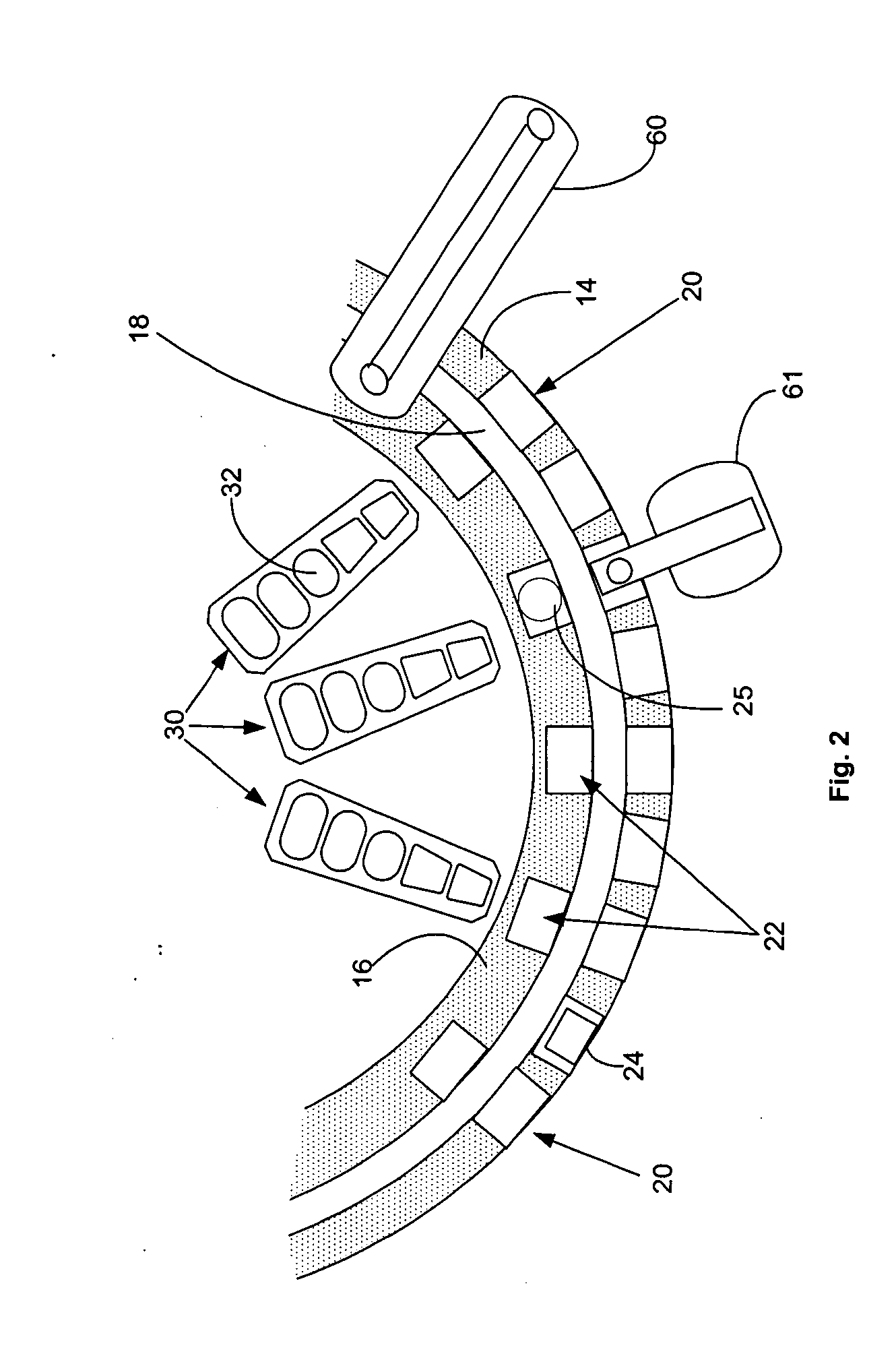
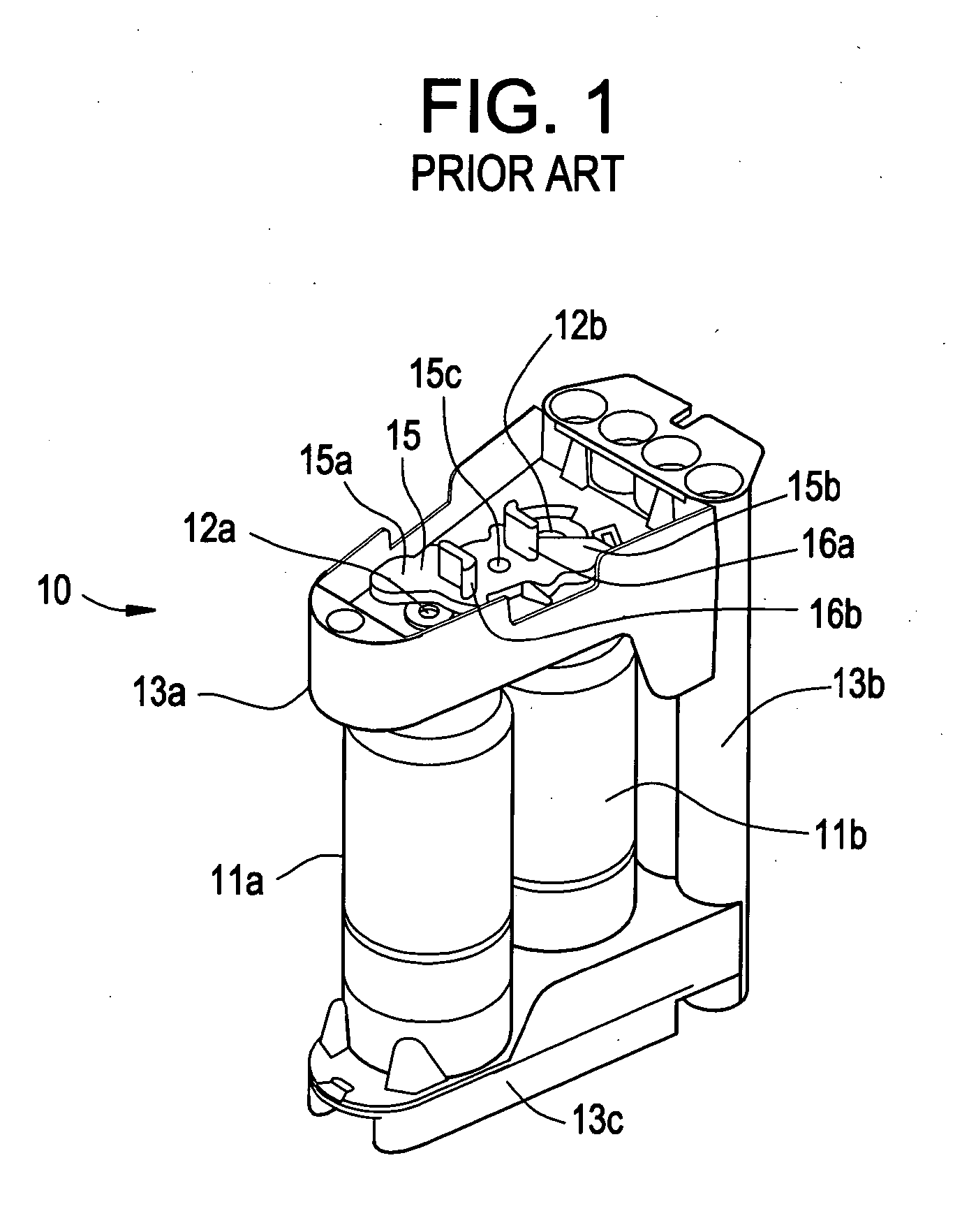
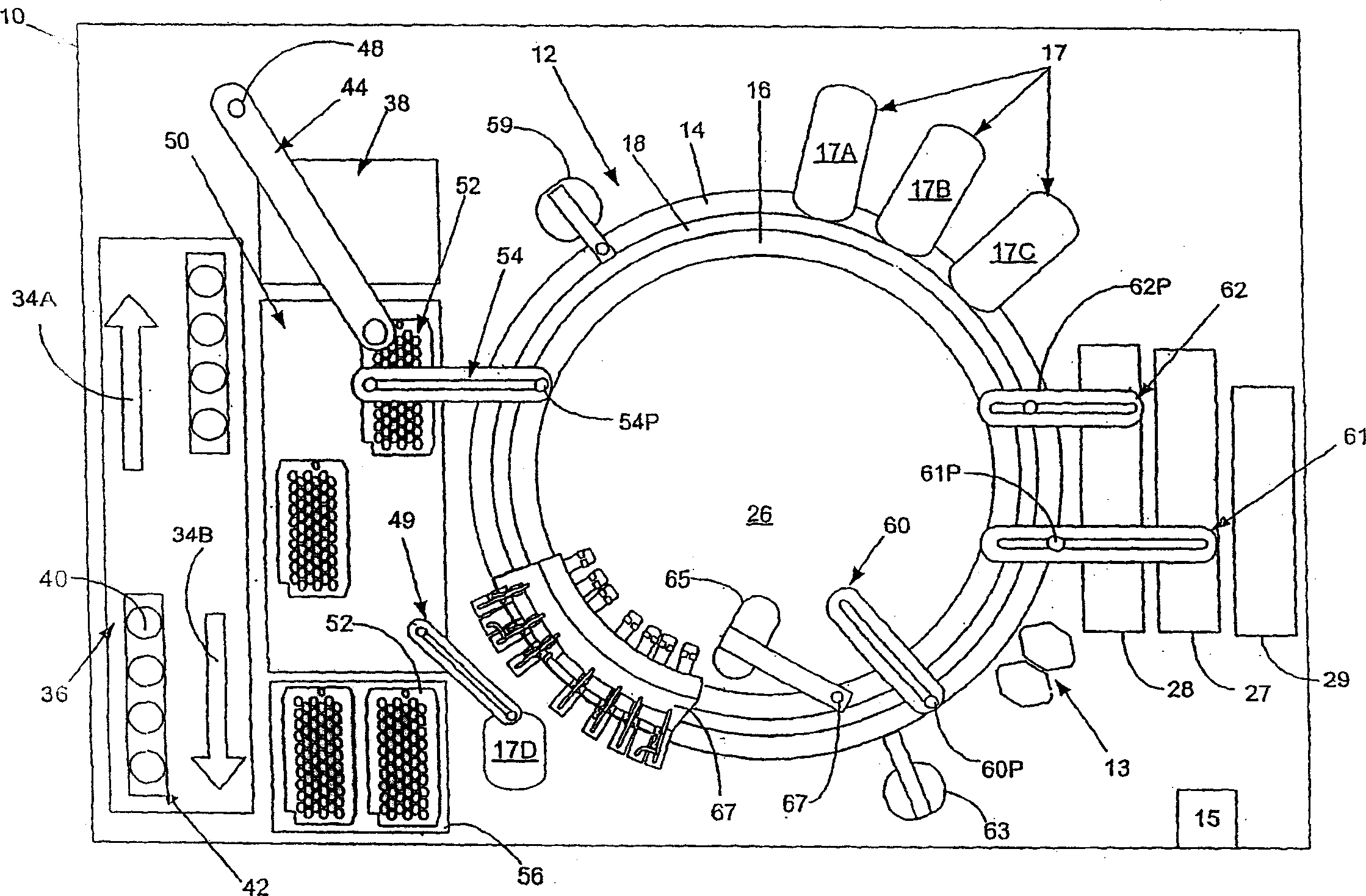
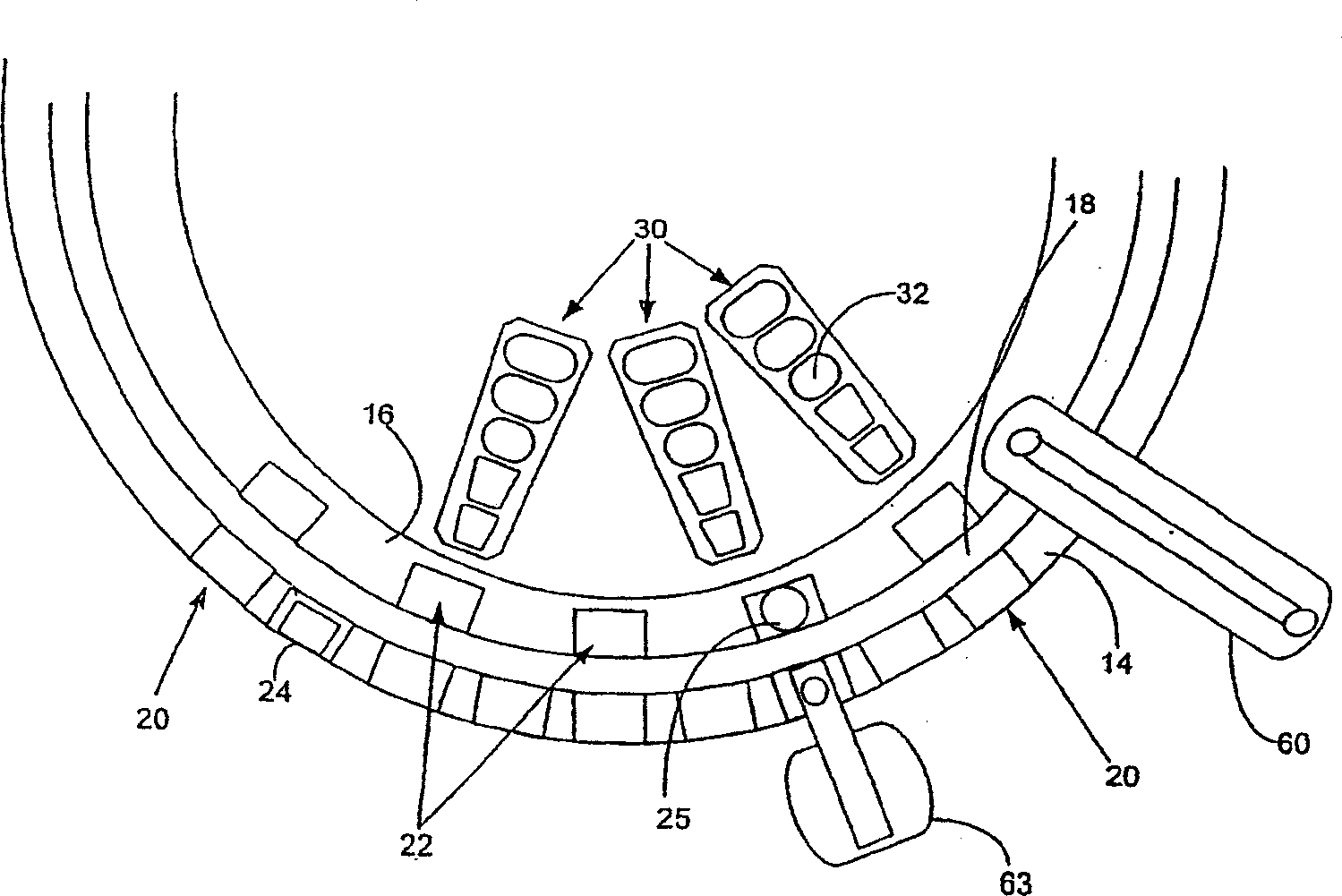
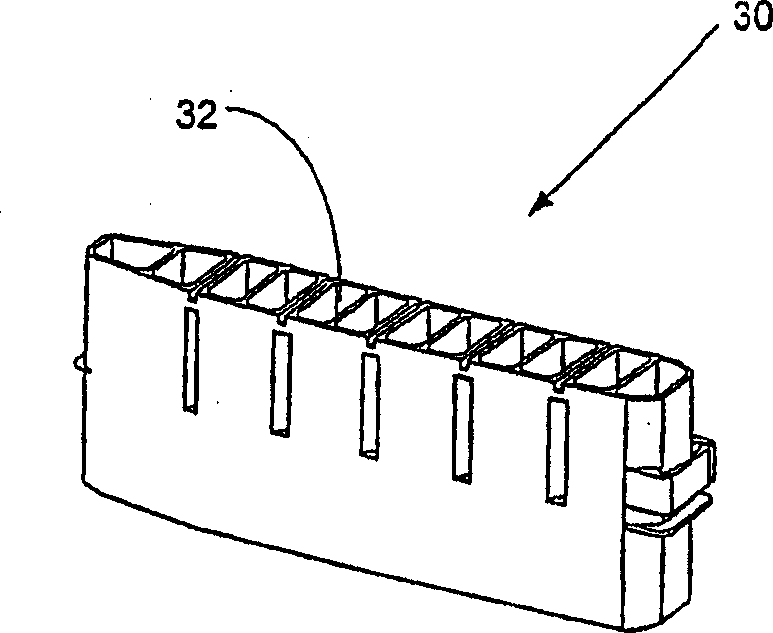
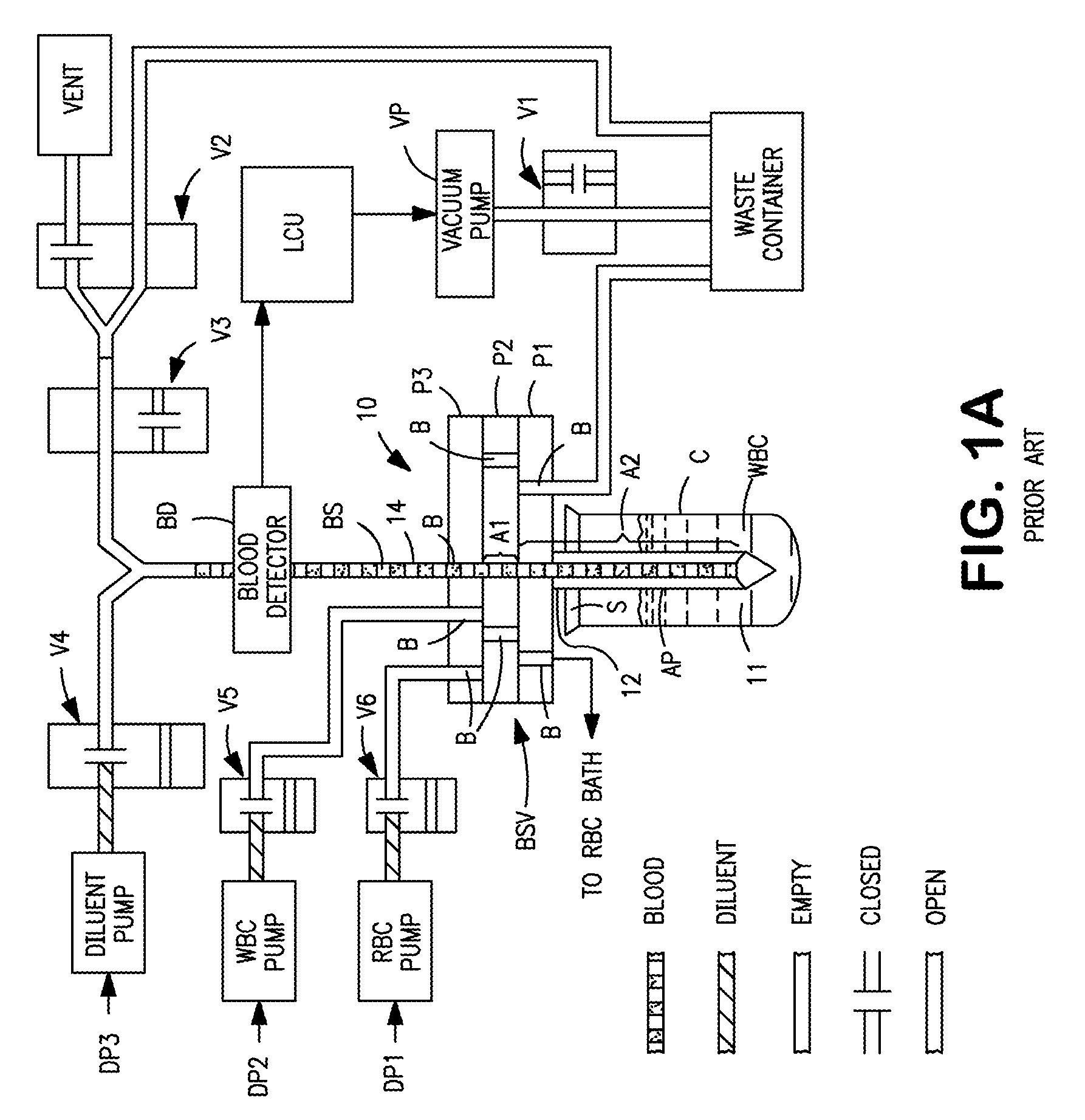
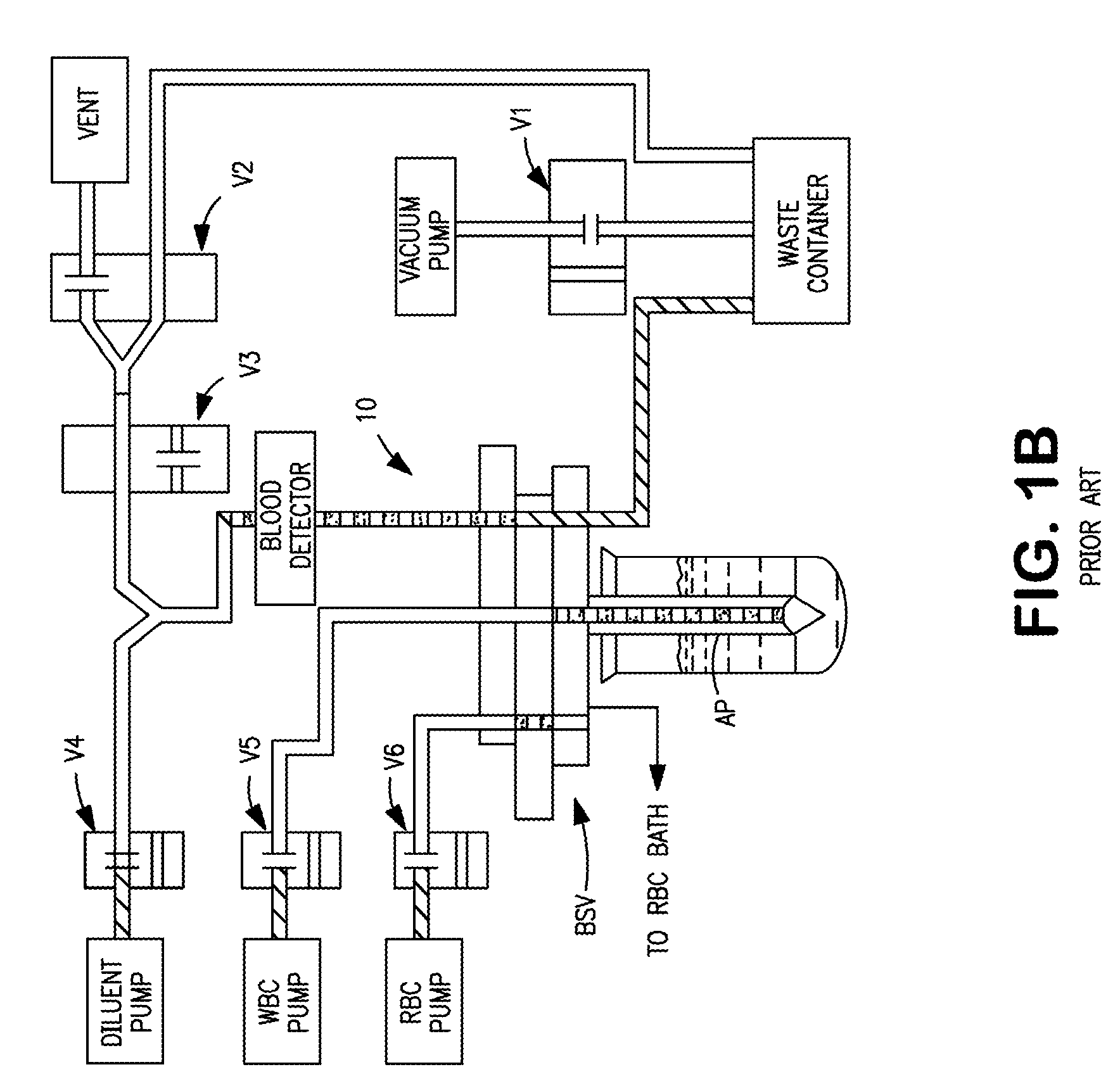
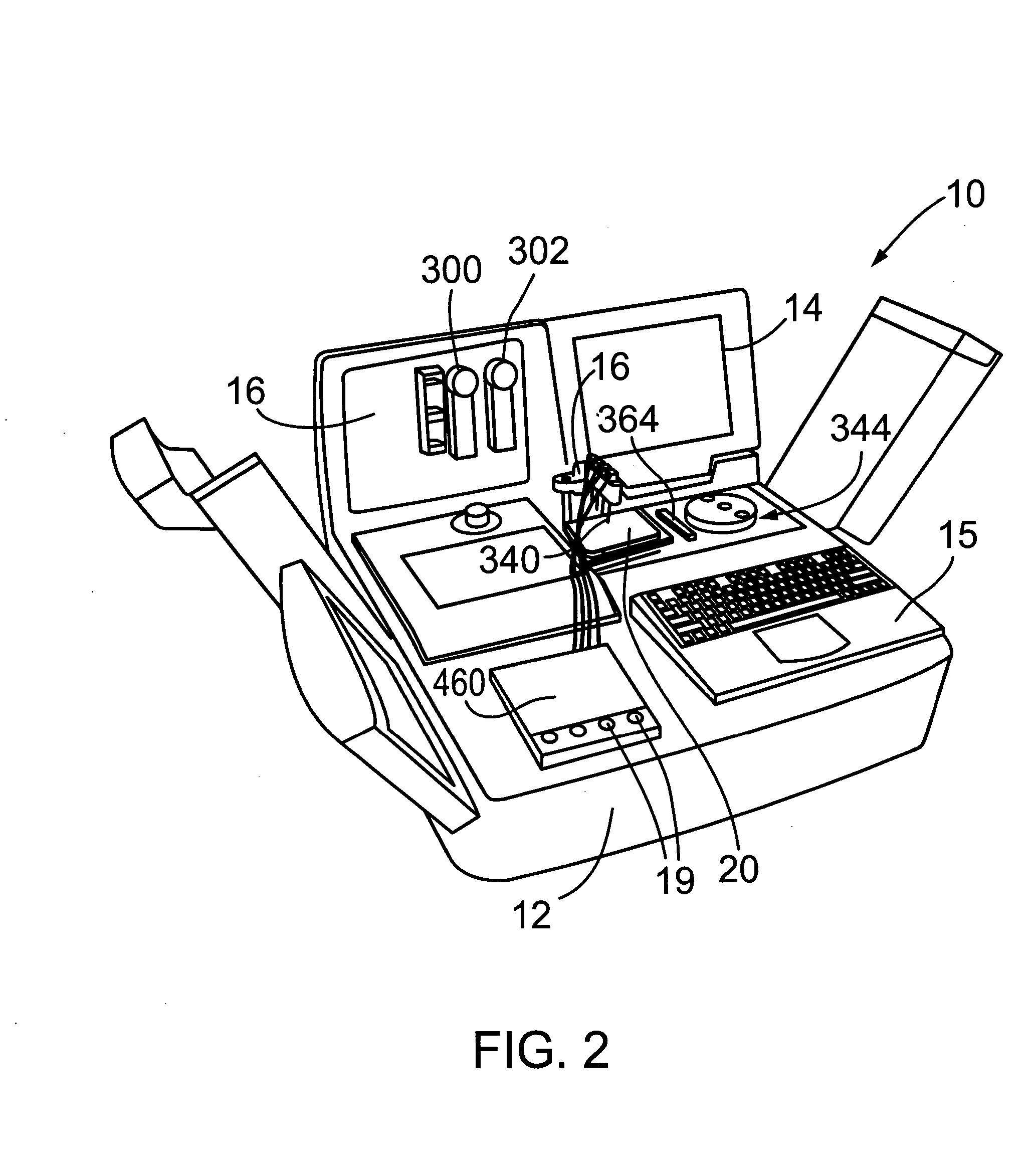
Automated analyzer
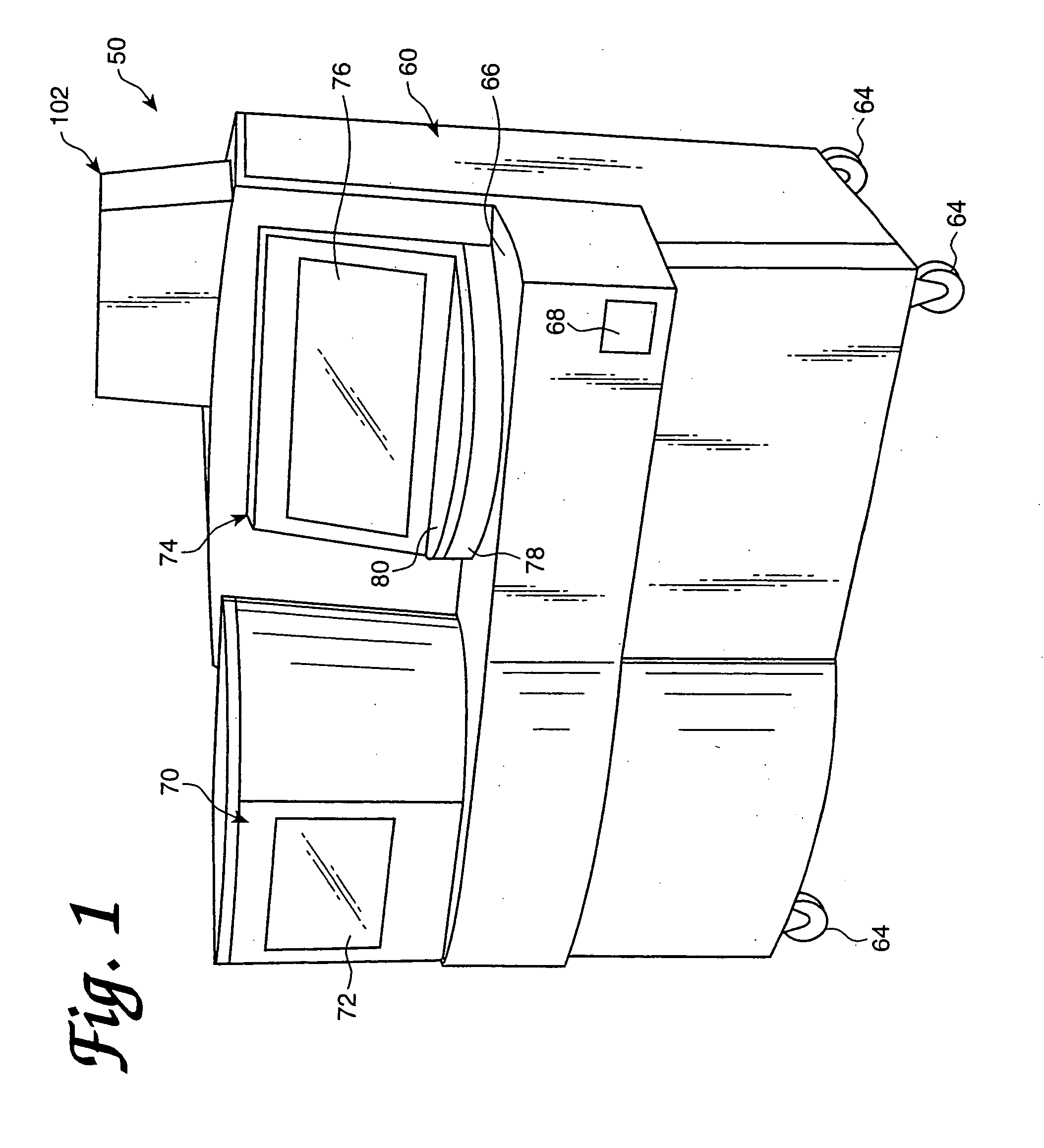
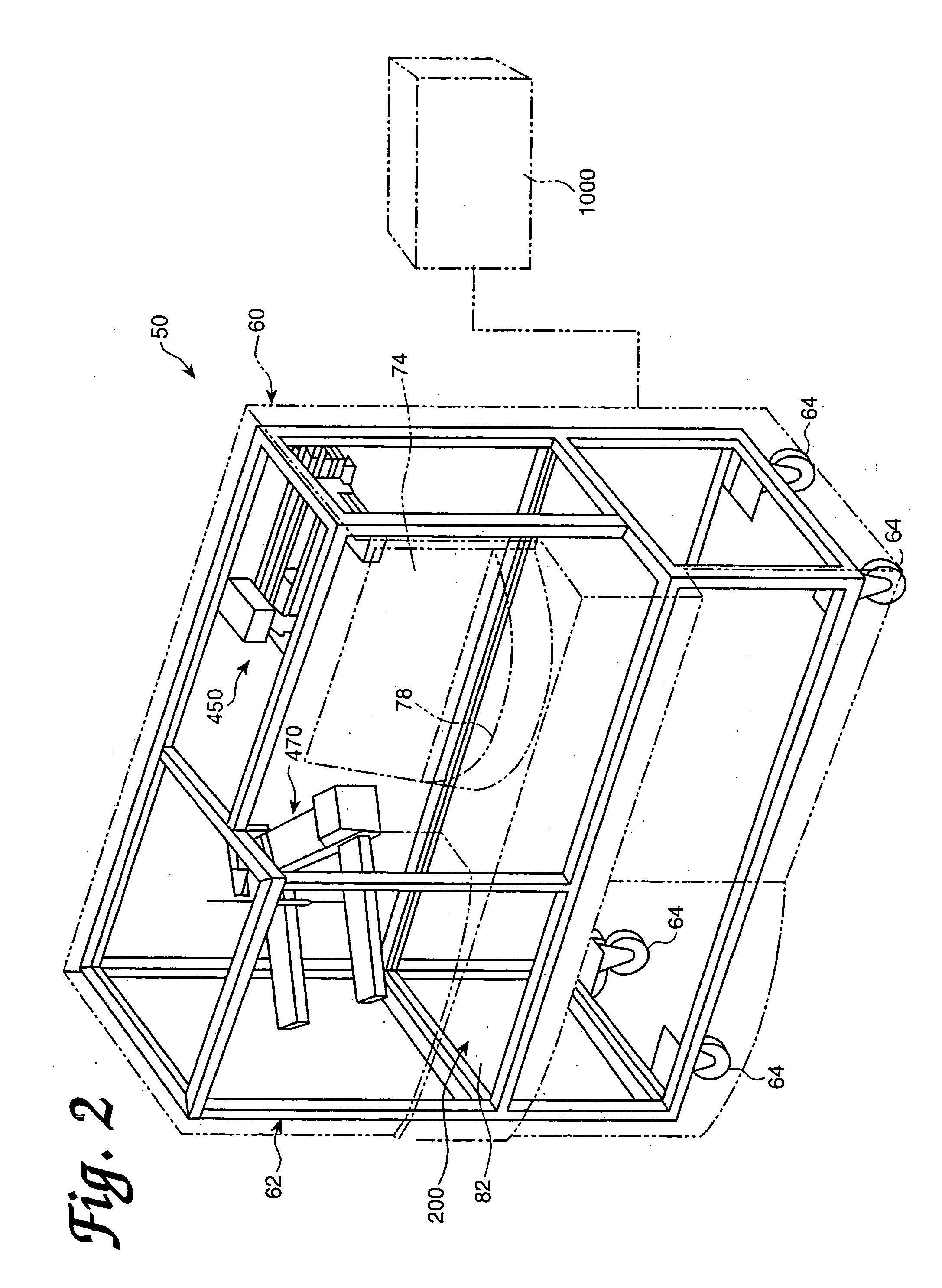
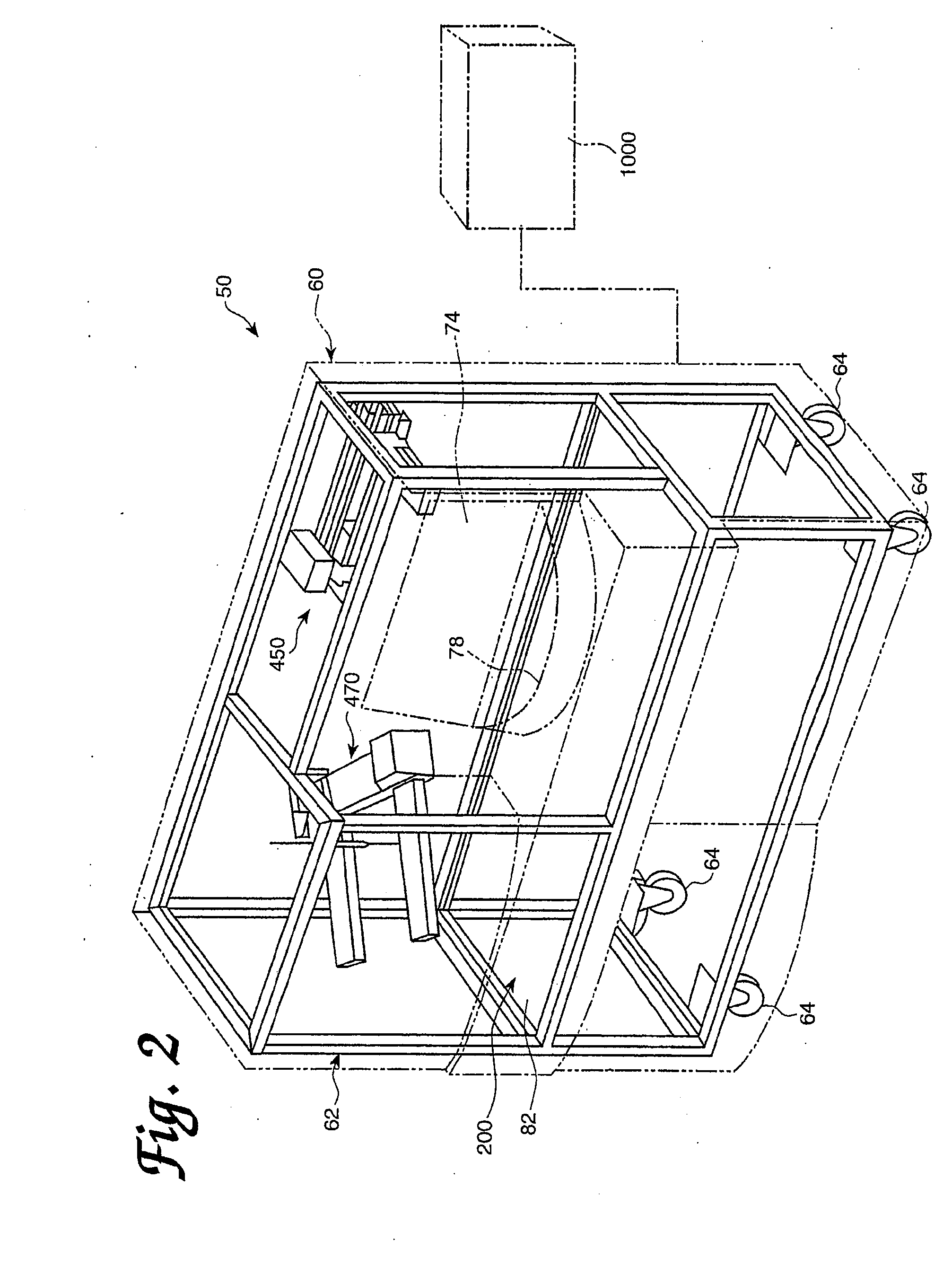
InactiveUS20060210435A1Minimal operator involvementEasy loadingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLiquid-crystal displayBarcode
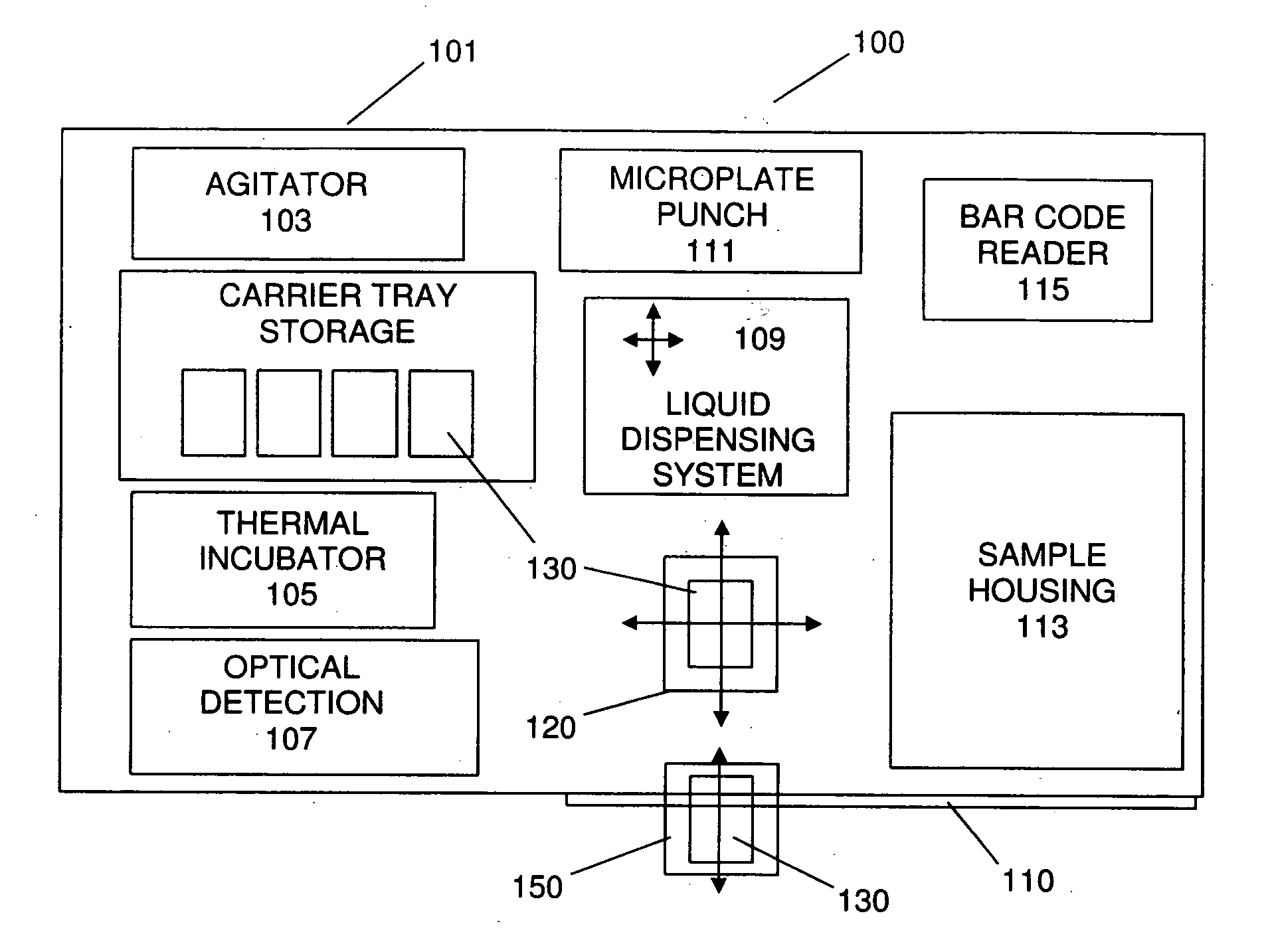
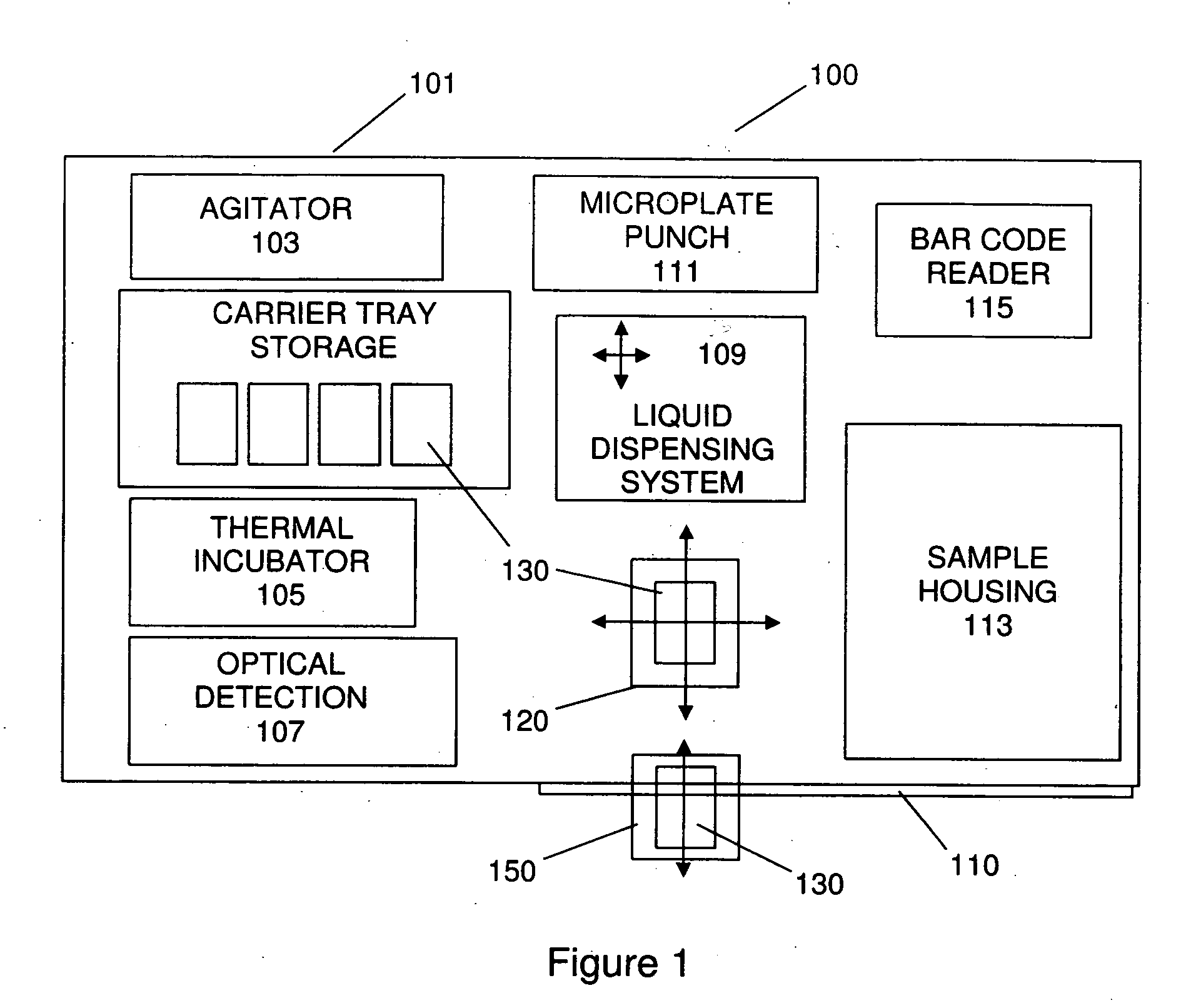
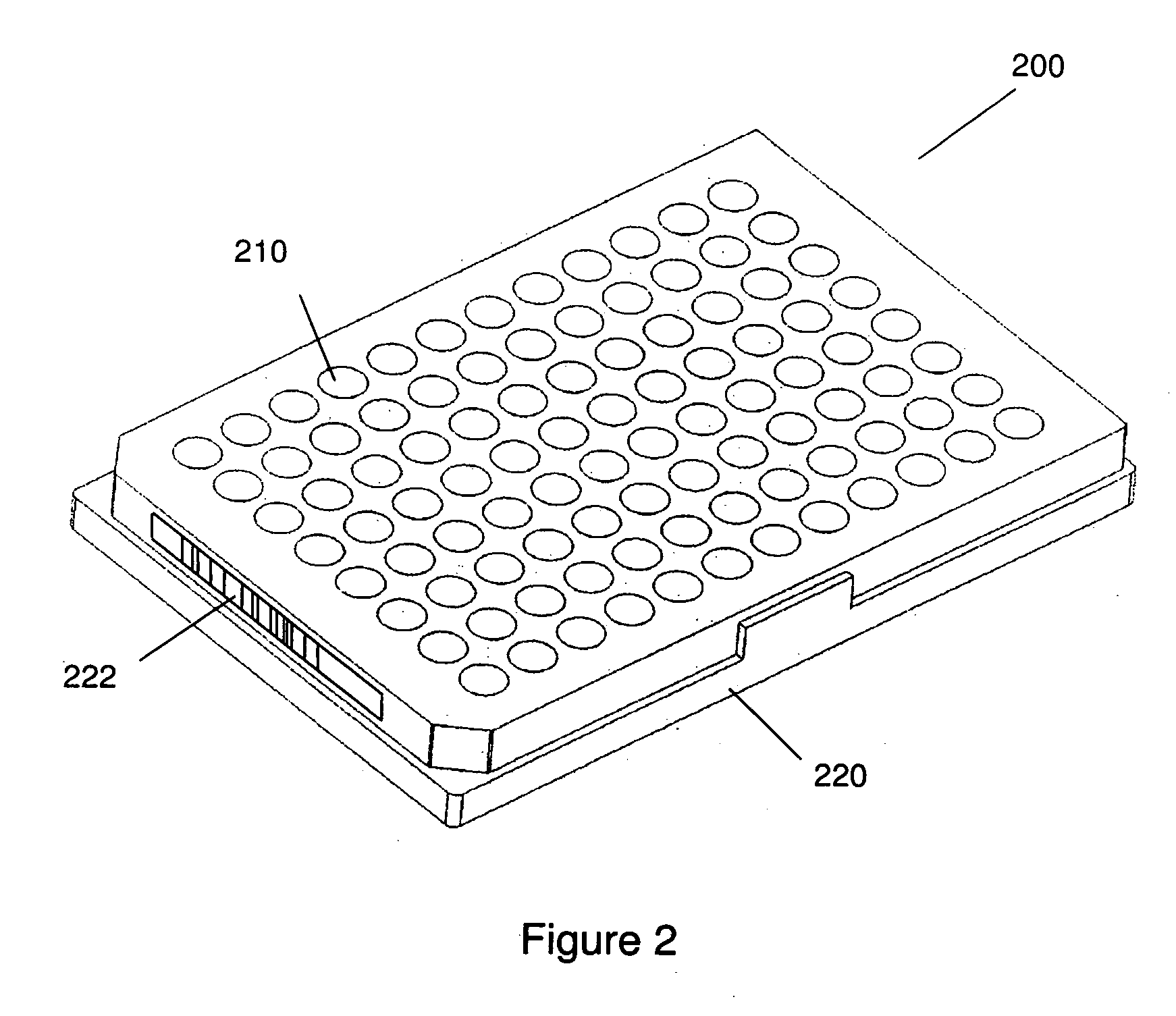
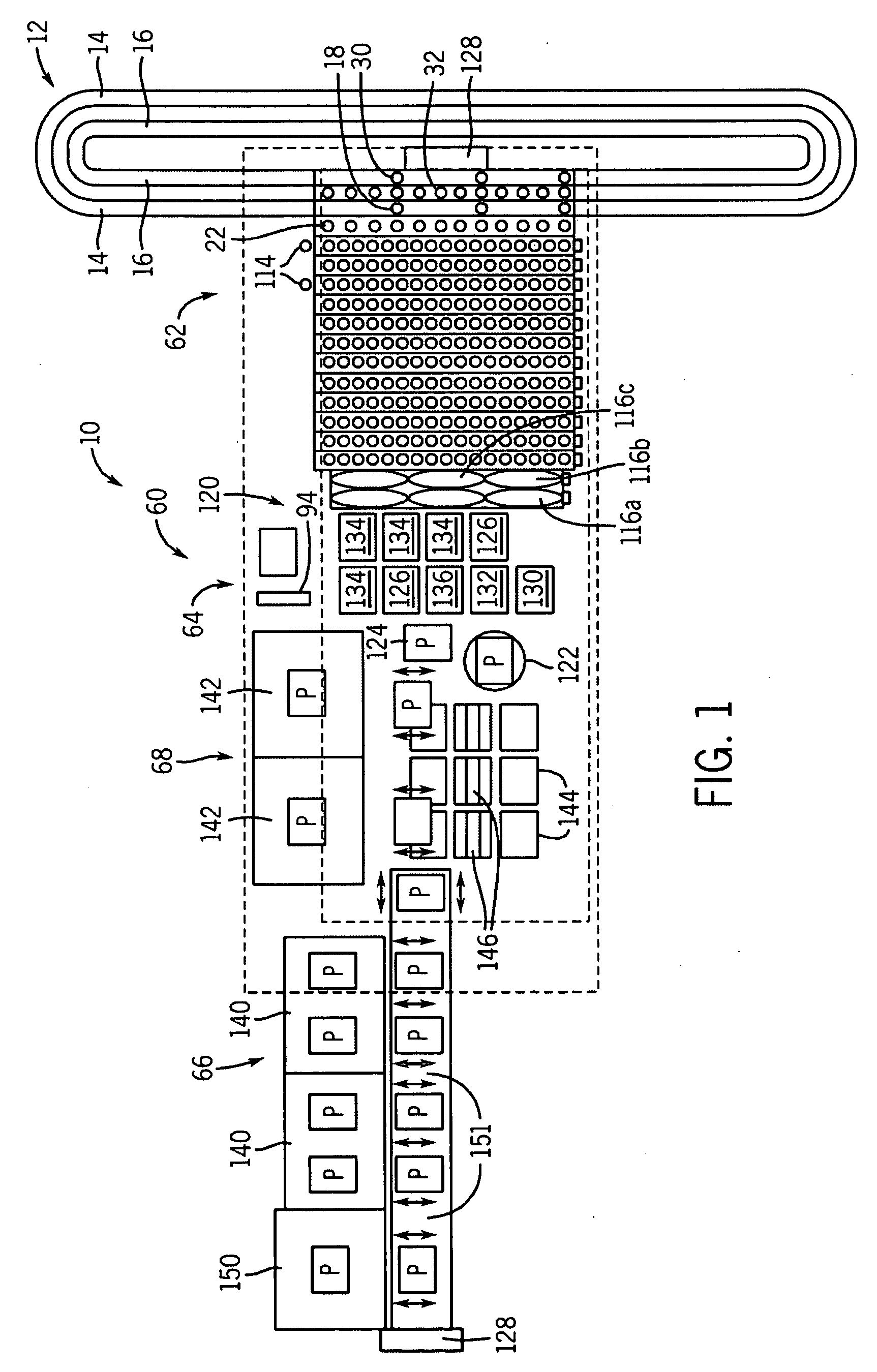
The present invention provides a bar-code driven, completely automated, microplate-based analyzer system for performing chemical, biochemical or biological assays. The analyzer is a modular, bench-top instrument that compactly integrates subsystems for sample dispensing, liquid handling, microplate transport, thermal incubation, vortexing, solid phase separation and optical reading. An internal processor is included for automating the instrument, and a user interface to facilitate communication with the operator via a touch-sensitive liquid-crystal display (LCD), and communicating with a remote network via multiple protocols. The analyzer includes firmware resident within the processing system and the user interface allows the operator to select pre-defined assay batch protocols and the user interface is configured in such as way so as to restrict an operator from programming the firmware.
Owner:NOVX SYST CANADA
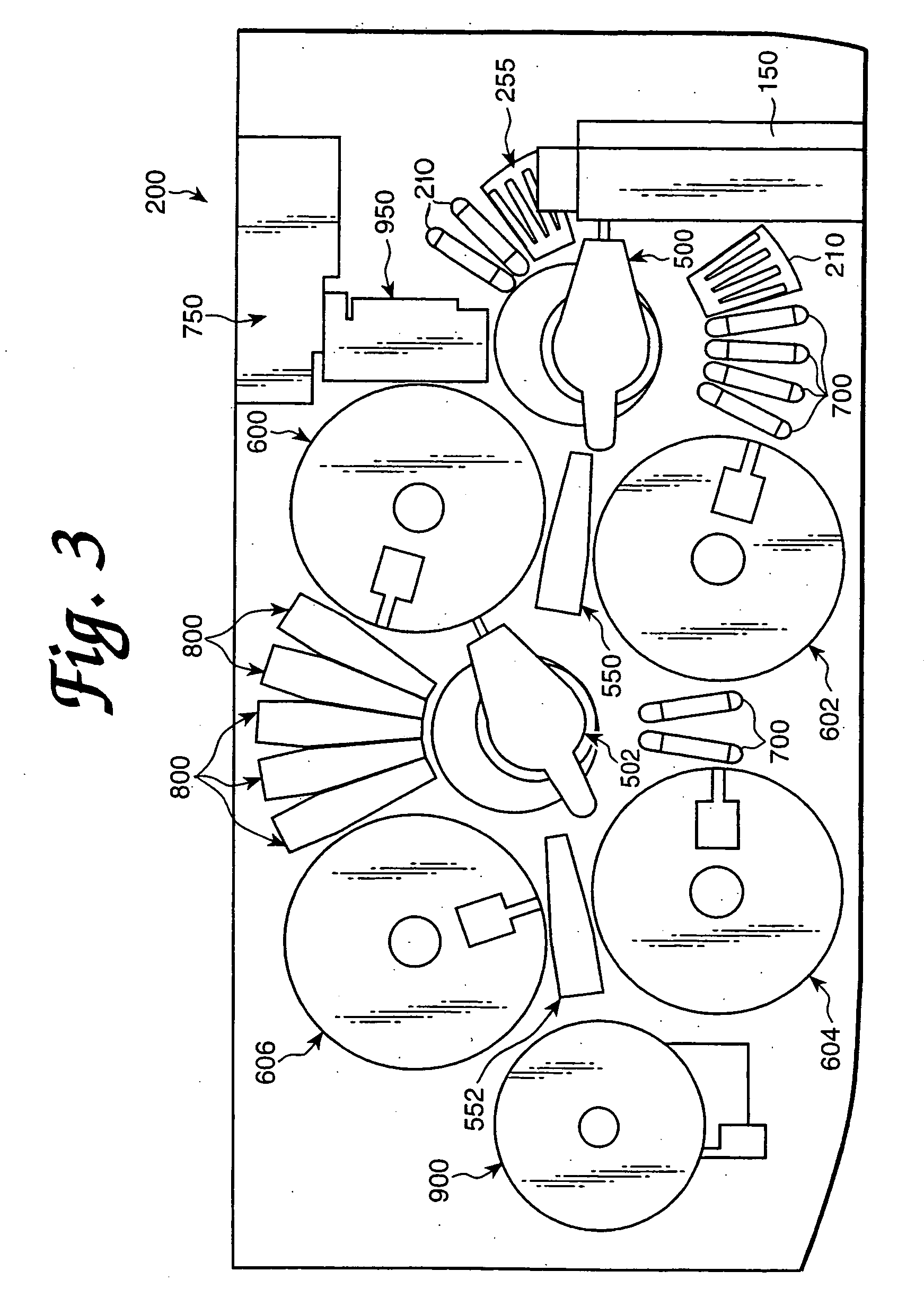
Automated analyzer for clinical laboratory
InactiveUS20090117620A1Manual loadingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsClinical chemistryMicro perforated plate
A laboratory automation system that is capable of carrying out clinical chemistry assays, immunoassays, amplification of nucleic acid assays, and any combination of the foregoing, said laboratory automation system employing at least one of micro-well plates and deep multi-well plates as reaction vessels. The use of micro-well plates as reaction vessels enables the laboratory automation system to assume a variety of arrangements, i.e., the laboratory automation system can comprise a variety of functional modules that can be arranged in various ways. In order to effectively carry out immunoassays by means of micro-well plates, a technique known as inverse magnetic particle processing can be used to transfer the product(s) of immunoassays from one micro-well of a micro-well plate to another.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Automated analyzer
InactiveUS20050013737A1High sensitivityImprove processing speedChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceBiological testingCuvetteAutomated analyzer
An automated analyzer for analyzing patient samples. The analyzer includes a plurality of cuvettes, which allow the samples to be mixed with various reagents. The analyzer includes one or more detectors, including a detector adapted to detect luminescence of the reaction mixture in the cuvettes. The analyzer allows for various diagnostic assays to be performed on a single system, and provides for high-sensitivity analysis at faster speeds.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
Automated process for isolating and amplifying a target nucleic acid sequence
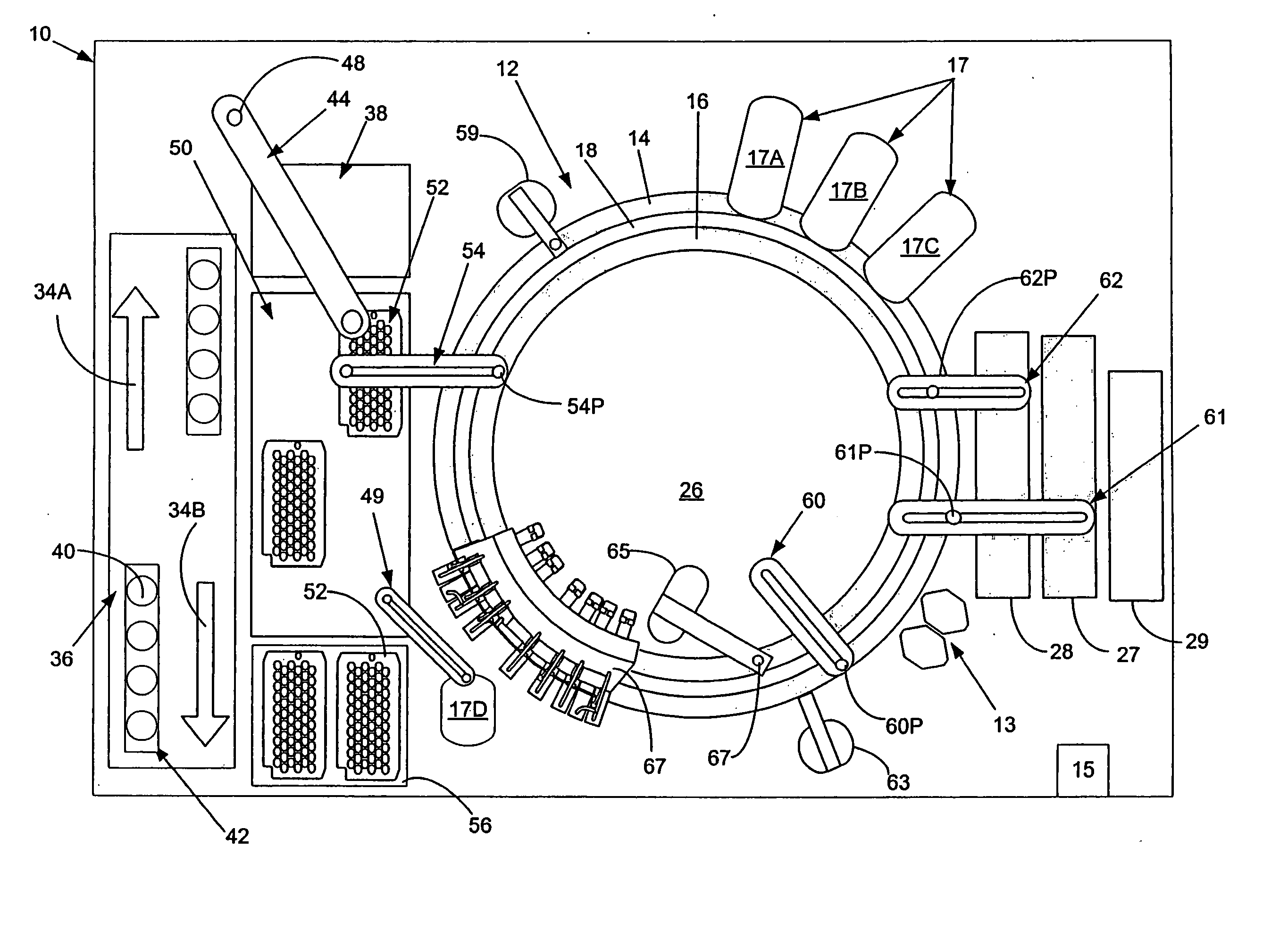
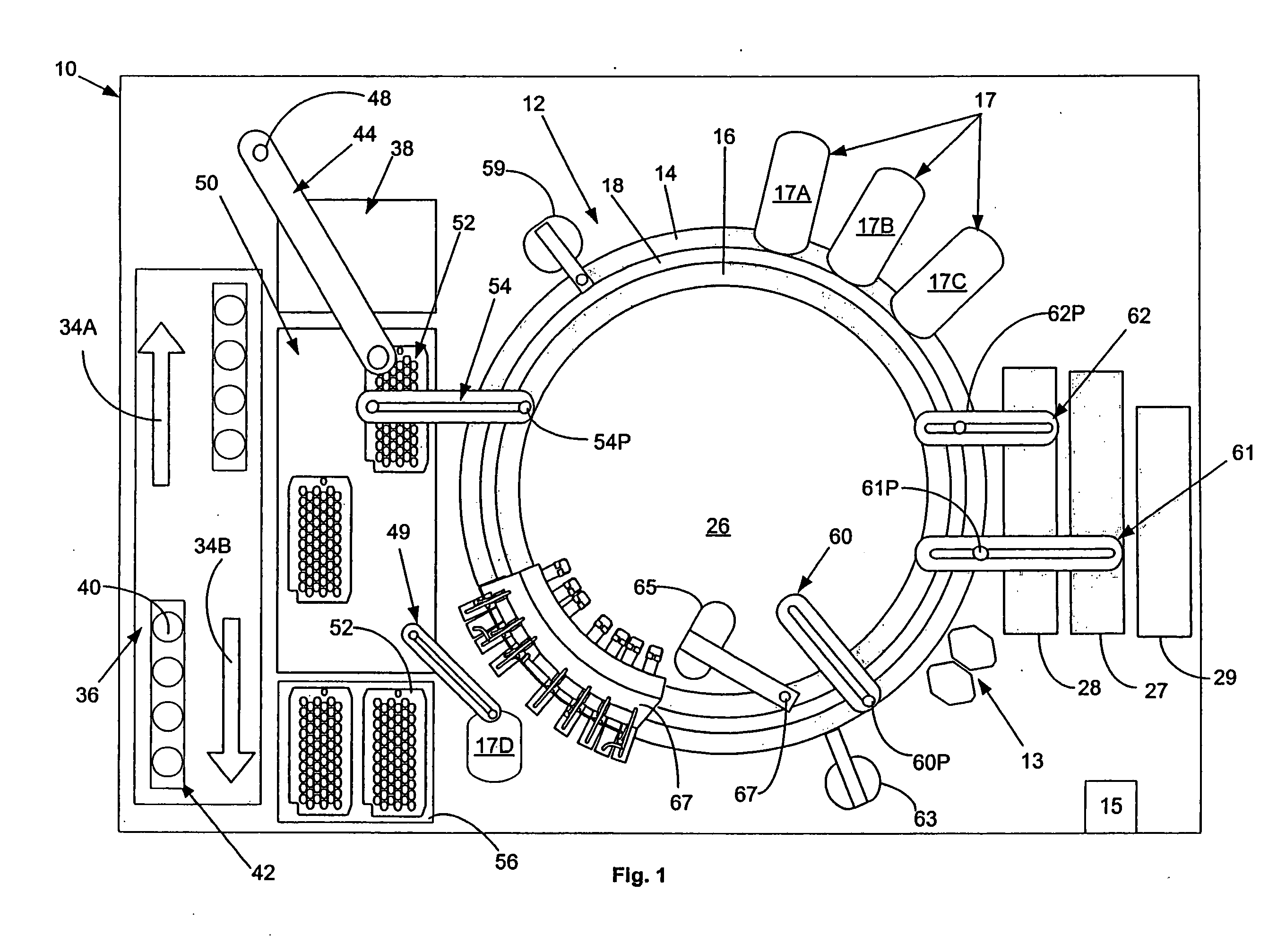
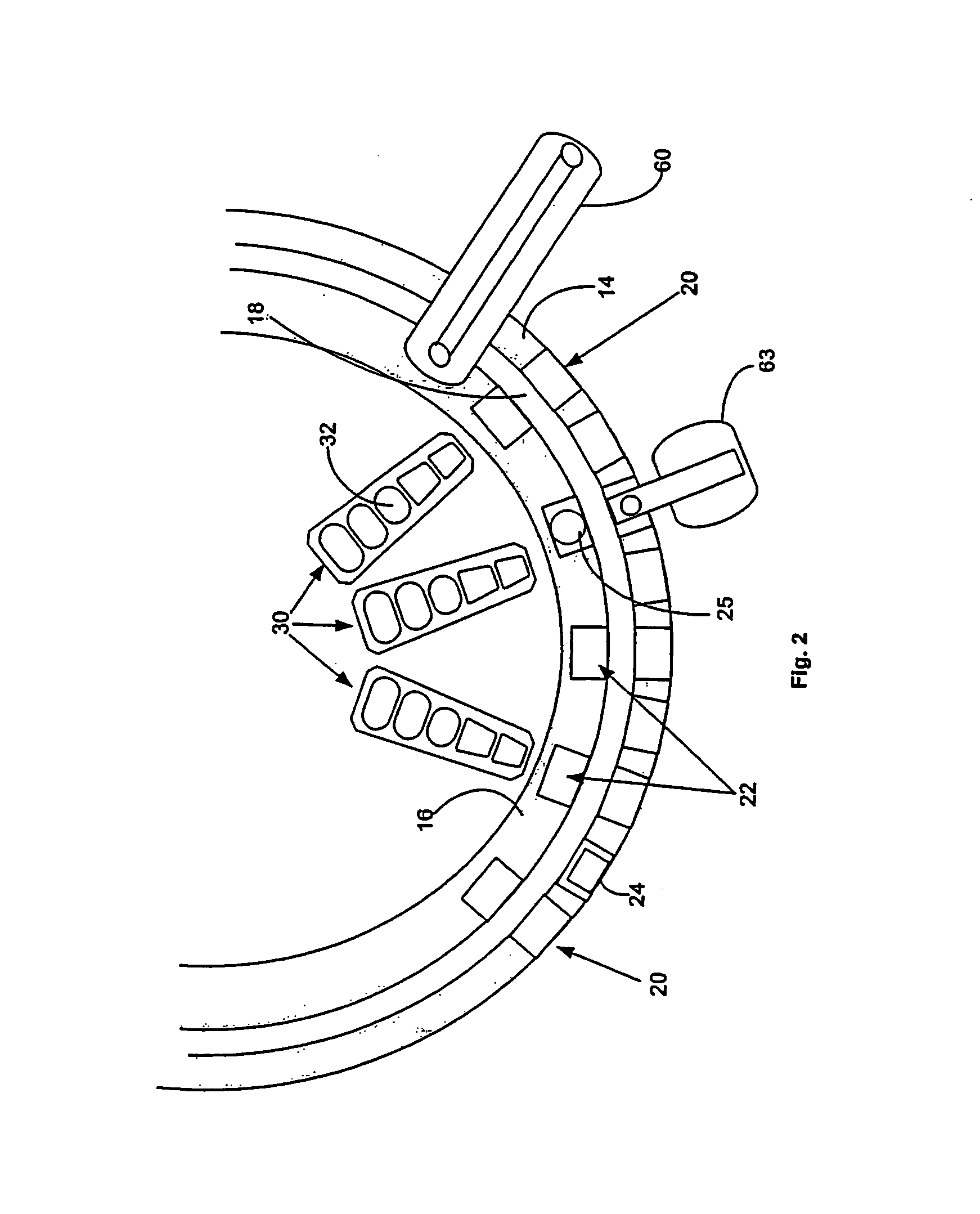
InactiveUS6890742B2Efficient and high through-put operationEfficient space utilizationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsRotating receptacle mixersIsolation proceduresTemperature control
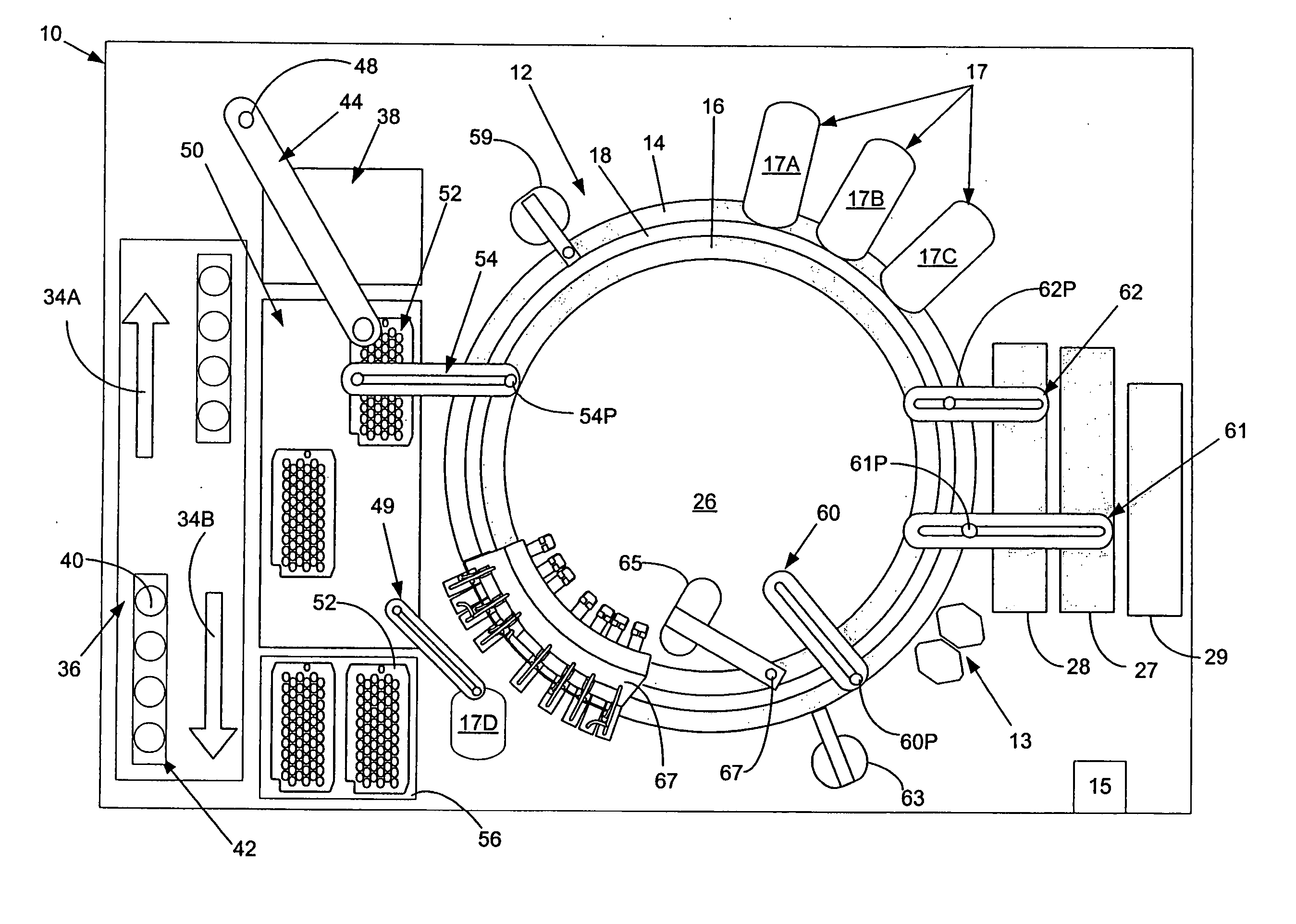
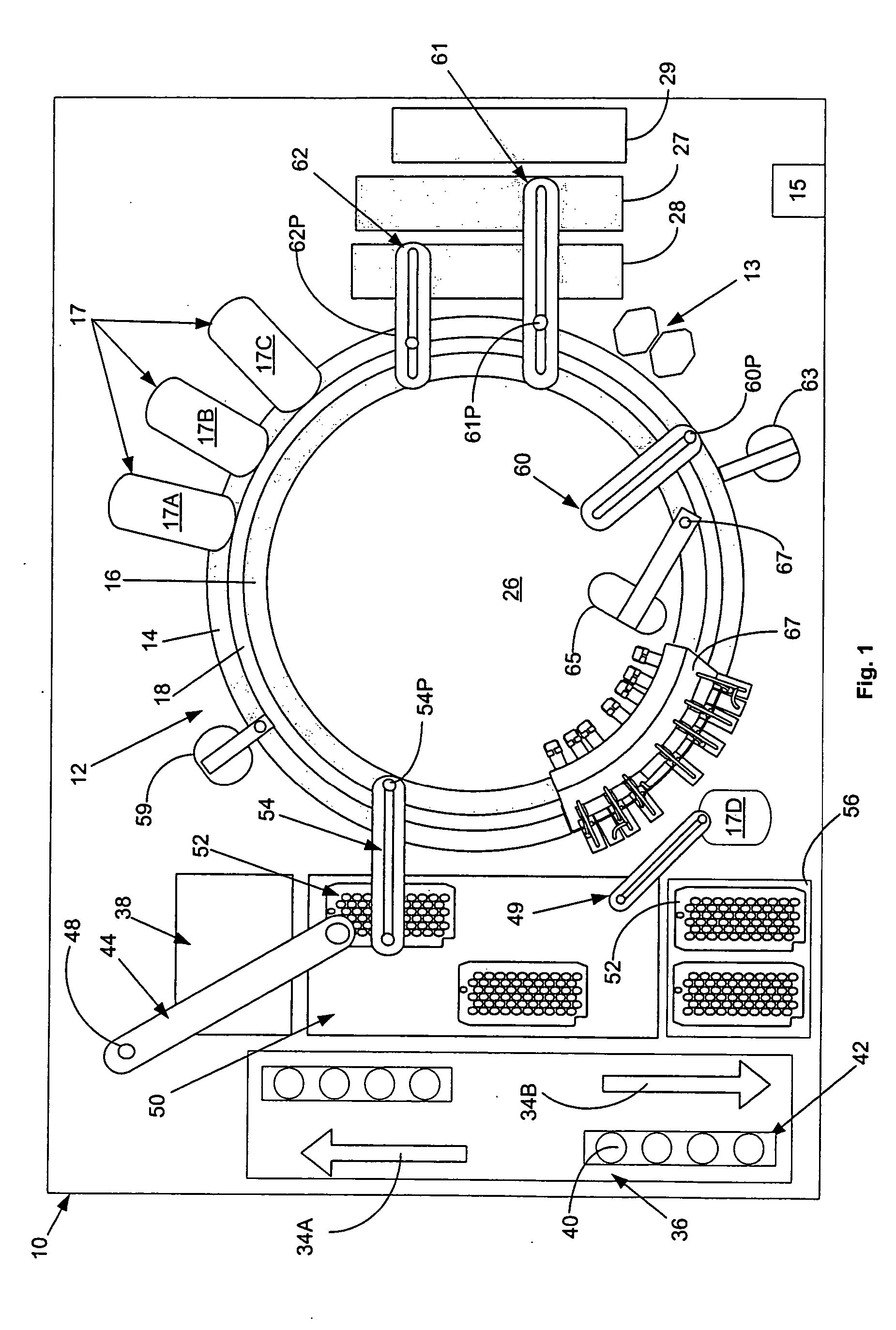
An automated analyzer for performing multiple diagnostic assays simultaneously includes multiple stations, or modules, in which discrete aspects of the assay are performed on fluid samples contained in reaction receptacles. The analyzer includes stations for automatically preparing a specimen sample, incubating the sample at prescribed temperatures for prescribed periods, preforming an analyte isolation procedure, and ascertaining the presence of a target analyte. An automated receptacle transporting system moves the reaction receptacles from one station to the next. The analyzer further includes devices for carrying a plurality of specimen tubes and disposable pipette tips in a machine-accessible manner, a device for agitating containers of target capture reagents comprising suspensions of solid support material and for presenting the containers for machine access thereto, and a device for holding containers of reagents in a temperature controlled environment and presenting the containers for machine access thereto. A method for performing an automated diagnostic assay includes an automated process for isolating and amplifying a target analyte. The process is performed by automatically moving each of a plurality of reaction receptacles containing a solid support material and a fluid sample between stations for incubating the contents of the reaction receptacle and for separating the target analyte bound to the solid support from the fluid sample. An amplification reagent is added to the separated analyte after the analyte separation step and before a final incubation step.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Automated process for isolating and amplifying a target nucleic acid sequence
InactiveUS20050130198A1Efficient and high through-put operationEfficient comprehensive utilizationRotating receptacle mixersBioreactor/fermenter combinationsIsolation proceduresTemperature control
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
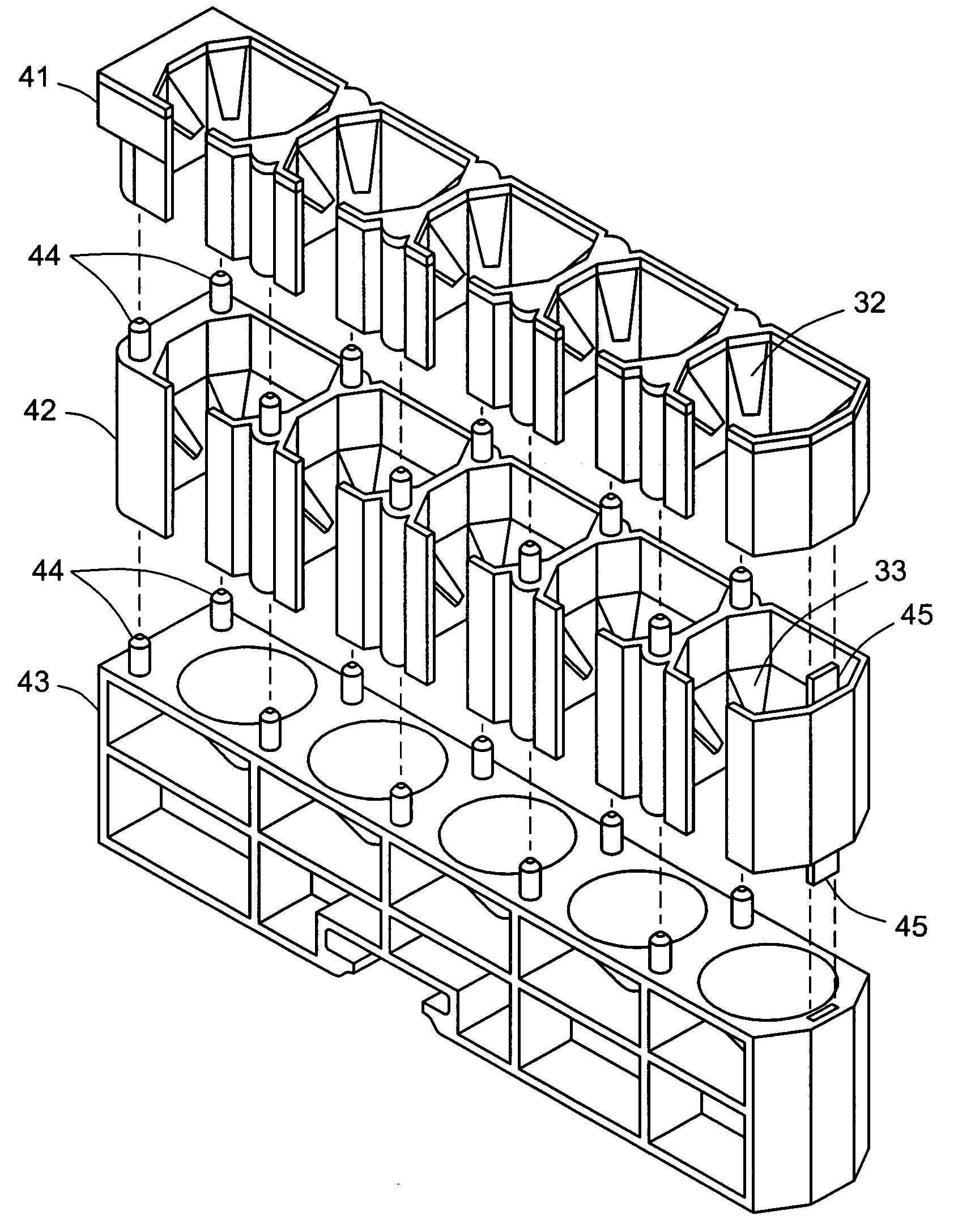
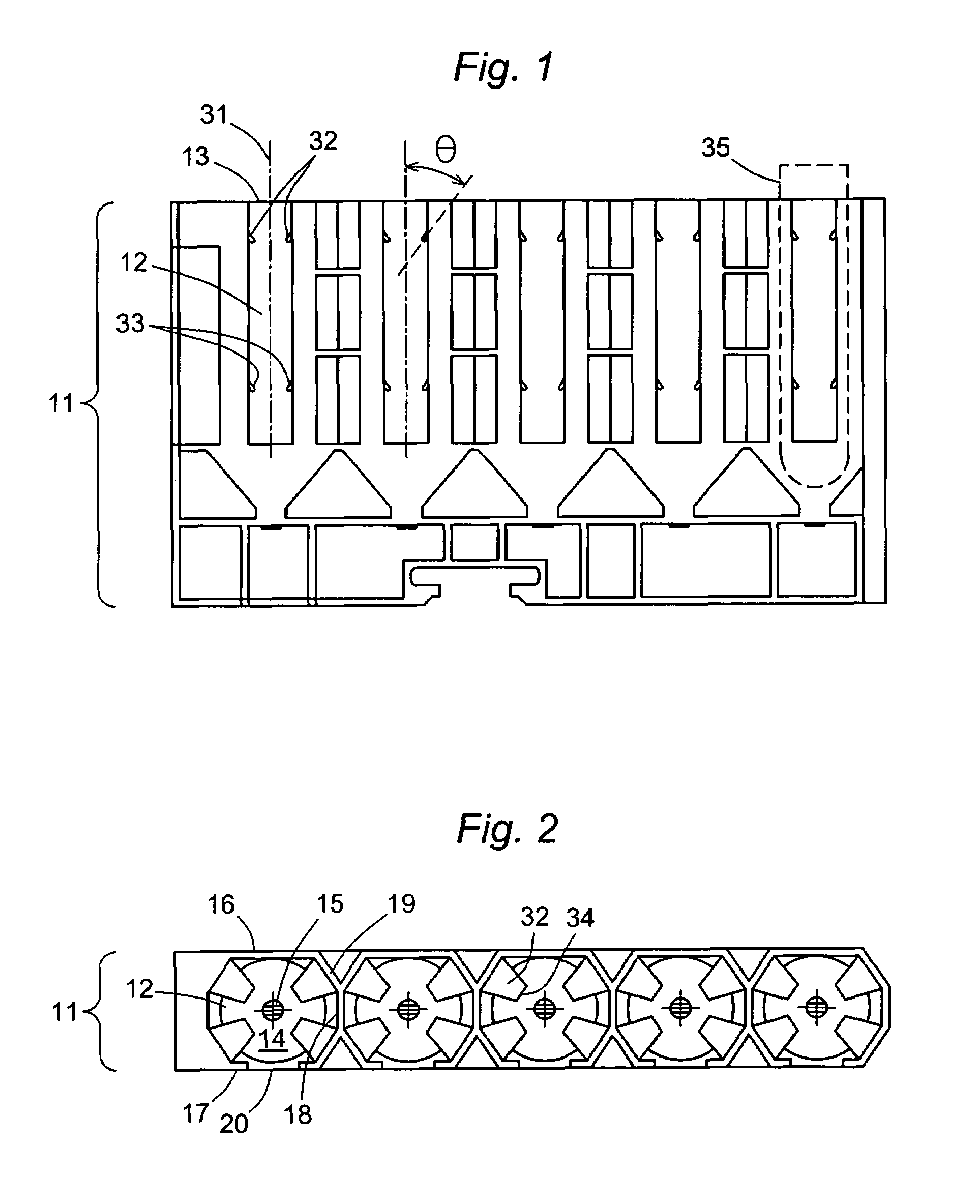
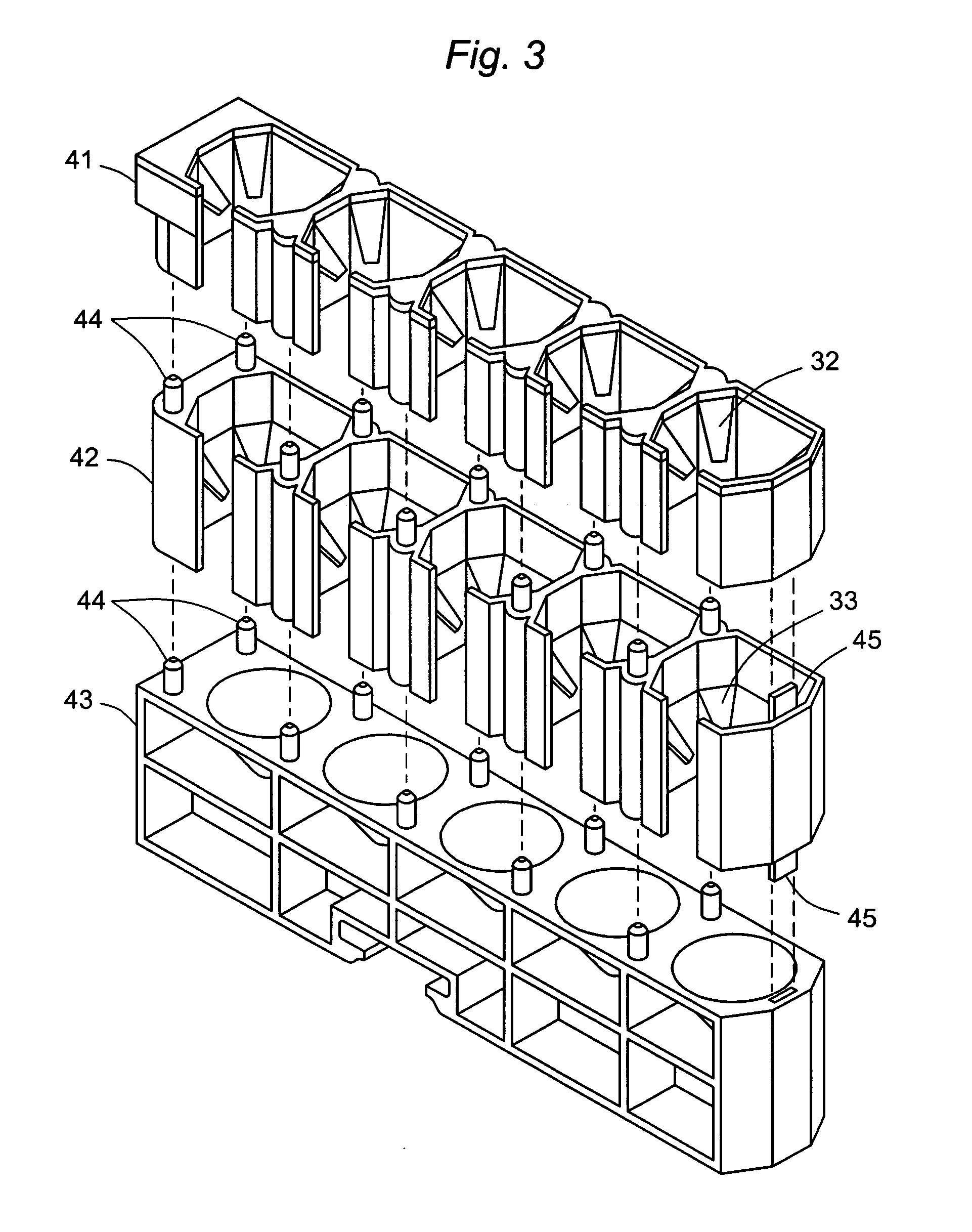
Tube rack accommodating a range of tube diameters
A tube rack for holding and transporting sample tubes or other liquids in an automated analyzer is built to accommodate tubes of different sizes in a stable aligned configuration, the rack containing a row of parallel open-top tube chambers, each chamber containing two sets of resilient tabs integrally molded with the chamber walls and at different heights in the chamber.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Automated analyzer
InactiveUS7666355B2Easy loadingImprove automationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLiquid-crystal displayBarcode
The present invention provides a bar-code driven, completely automated, microplate-based analyzer system for performing chemical, biochemical or biological assays. The analyzer is a modular, bench-top instrument that compactly integrates subsystems for sample dispensing, liquid handling, microplate transport, thermal incubation, vortexing, solid phase separation and optical reading. An internal processor is included for automating the instrument, and a user interface to facilitate communication with the operator via a touch-sensitive liquid-crystal display (LCD), and communicating with a remote network via multiple protocols. The analyzer includes firmware resident within the processing system and the user interface allows the operator to select pre-defined assay batch protocols and the user interface is configured in such as way so as to restrict an operator from programming the firmware.
Owner:NOVX SYST CANADA
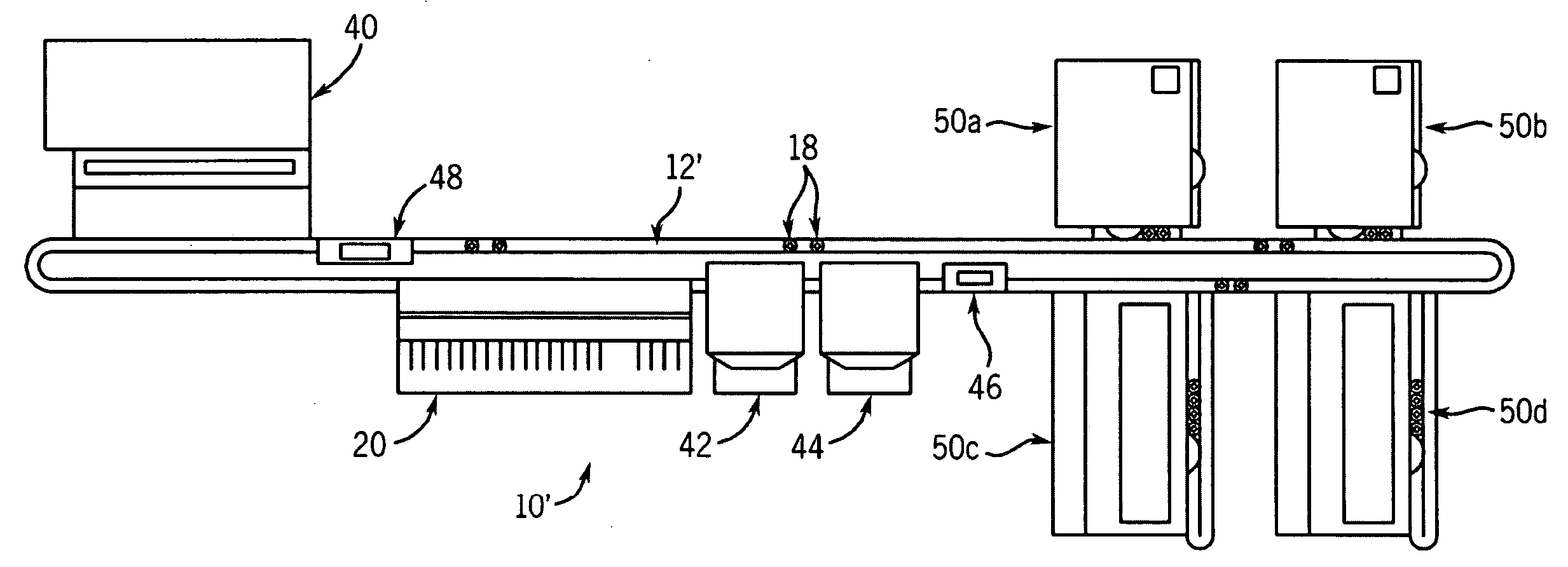
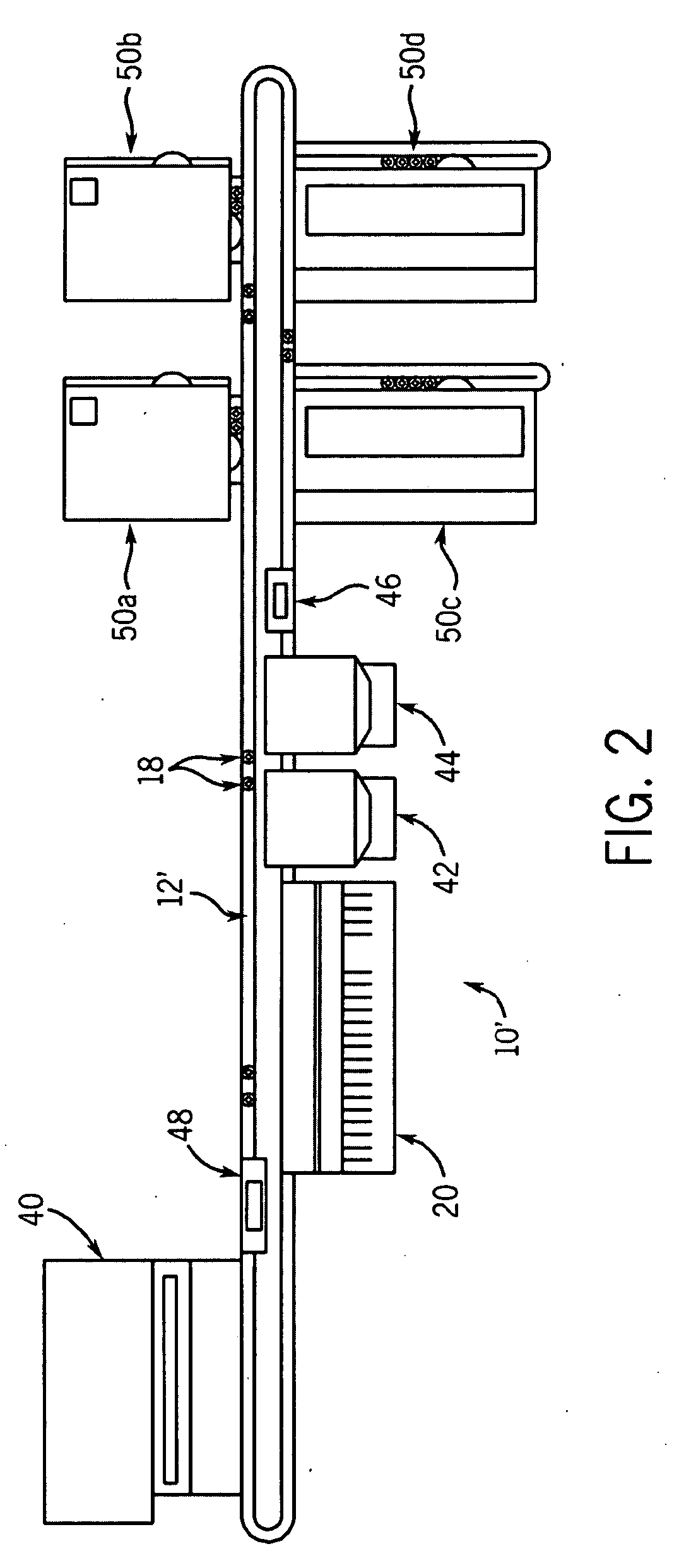
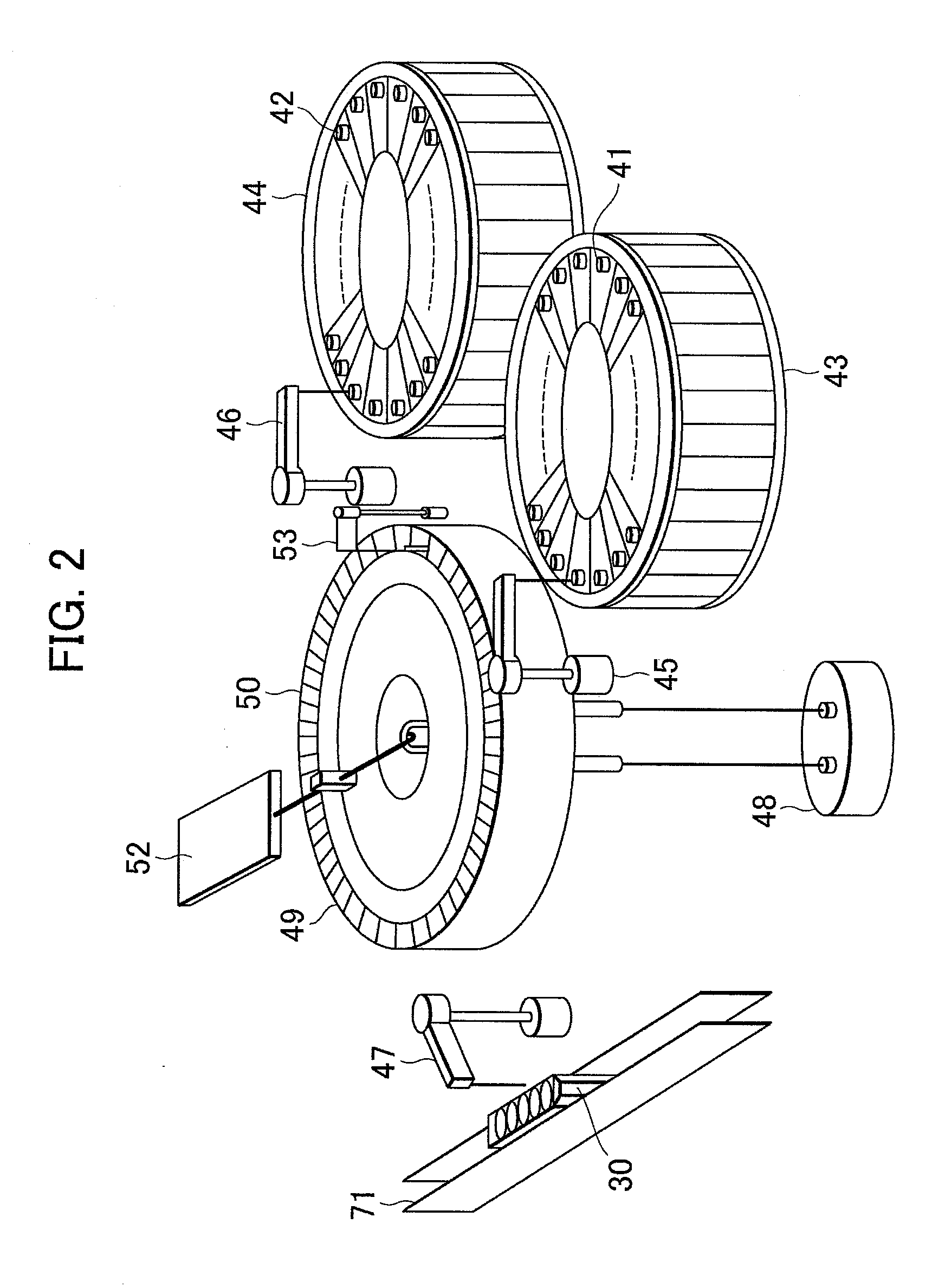
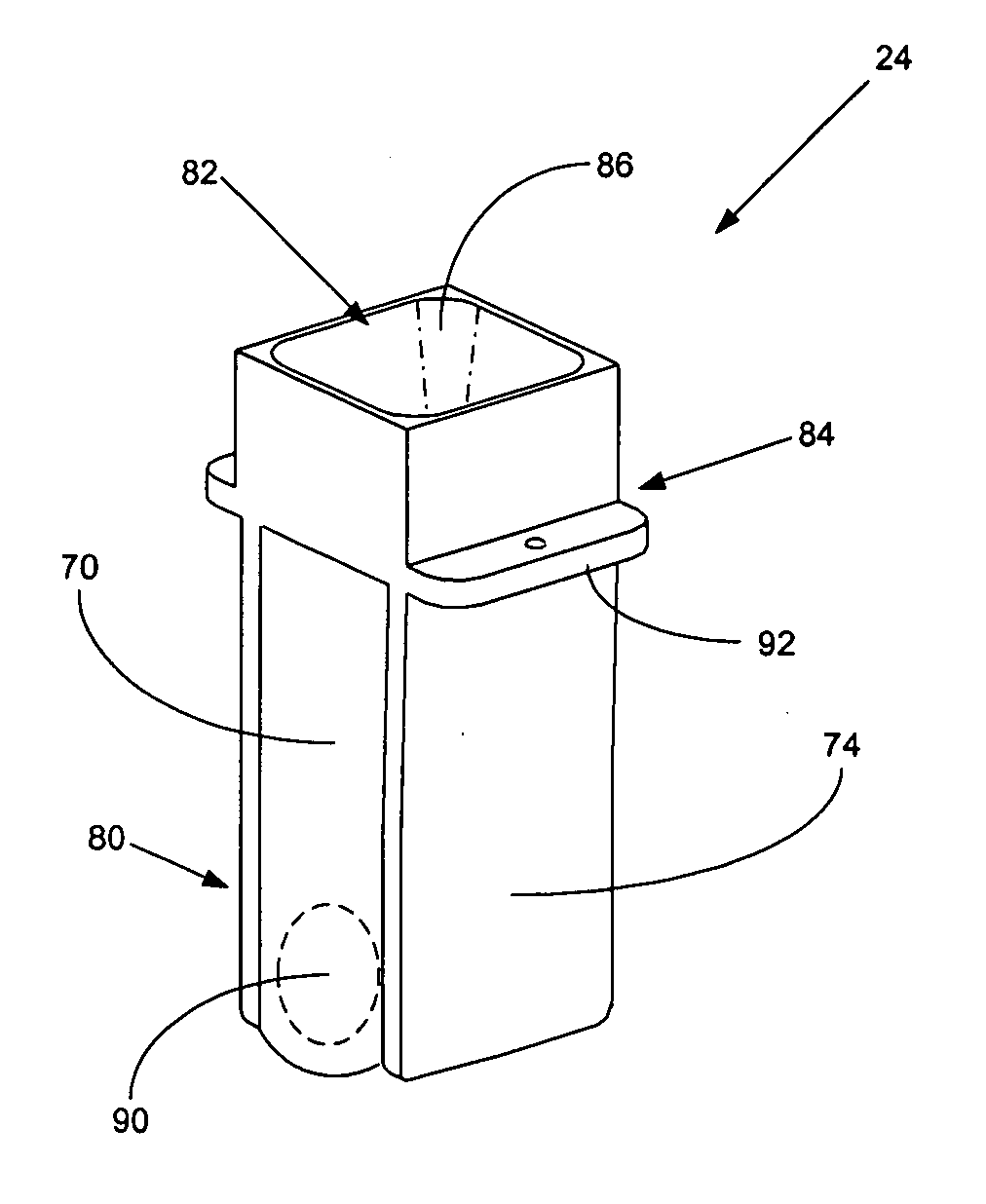
Cuvette for an automated analyzer
An analyzer for performing automated assay testing. The analyzer includes a storage and conveyor system for conveying cuvettes to an incubation or processing conveyor, a storage and selection system for test sample containers, a storage and selection system for reagent containers, sample and reagent aspirating and dispensing probes, a separation system for separating bound from unbound tracer or labeled reagent, a detection system and date collection / processing system. All of the sub-units of the machine are controlled by a central processing unit to coordinate the activity of all of the subunits of the analyzer. The analyzer is specifically suited for performing heterogeneous binding assay protocols, particularly immunoassays.
Owner:ALUMINUM PECHINEY
Tube rack accommodating a range of tube diameters
A tube rack for holding and transporting sample tubes or other liquids in an automated analyzer is built to accommodate tubes of different sizes in a stable aligned configuration, the rack containing a row of parallel open-top tube chambers, each chamber containing two sets of resilient tabs integrally molded with the chamber walls and at different heights in the chamber.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
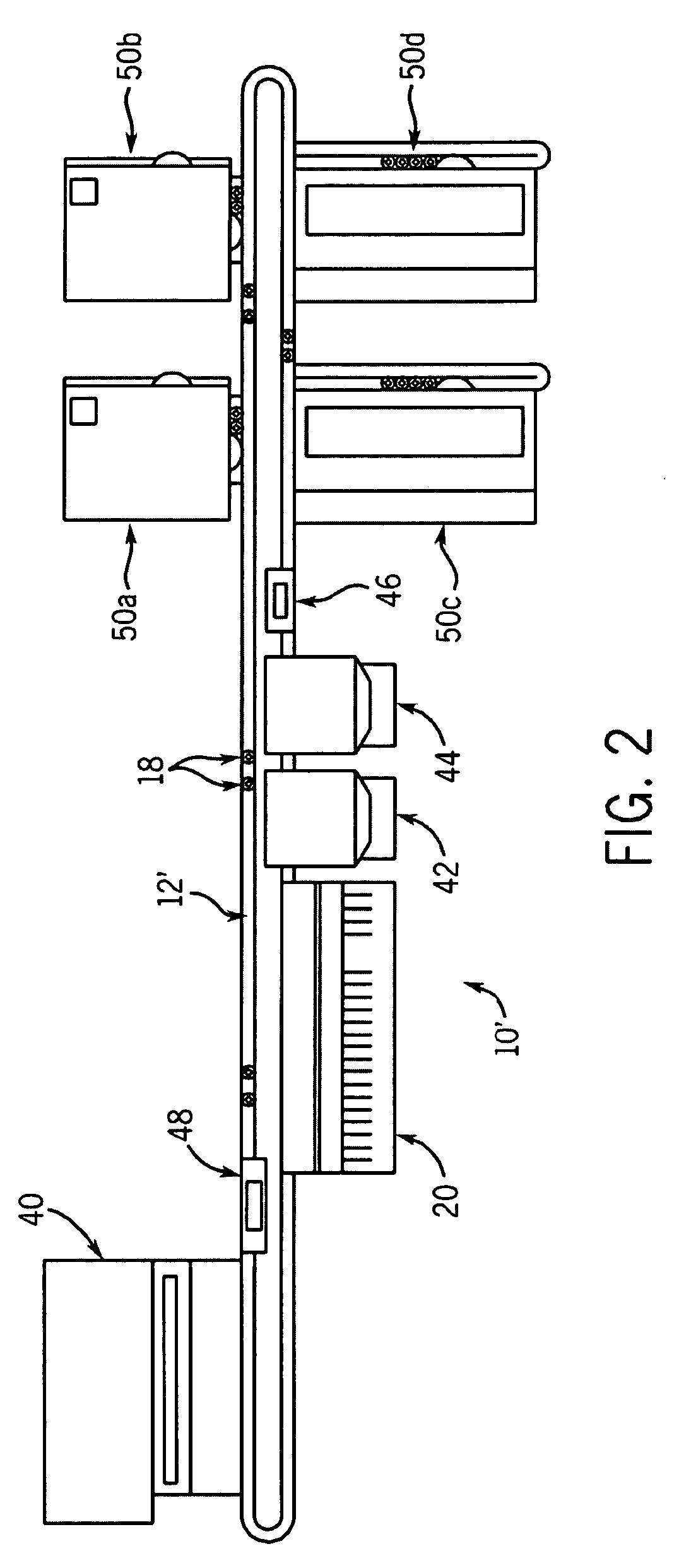
Fluid handling apparatus for an automated analyzer
InactiveUS7182912B2Improve versatilityChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceLaboratory glasswaresEngineeringSelection system
An analyzer for performing automated assay testing. The analyzer includes a storage and conveyor system for conveying cuvettes to an incubation or processing conveyor, a storage and selection system for test sample containers, a storage and selection system for reagent containers, sample and reagent aspirating and dispensing probes, a separation system for separating bound from unbound tracer or labeled reagent, a detection system and date collection / processing system. All of the subunits of the machine are controlled by a central processing unit to coordinate the activity of all of the subunits of the analyzer. The analyzer is specifically suited for performing heterogeneous binding assay protocols, particularly immunoassays.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
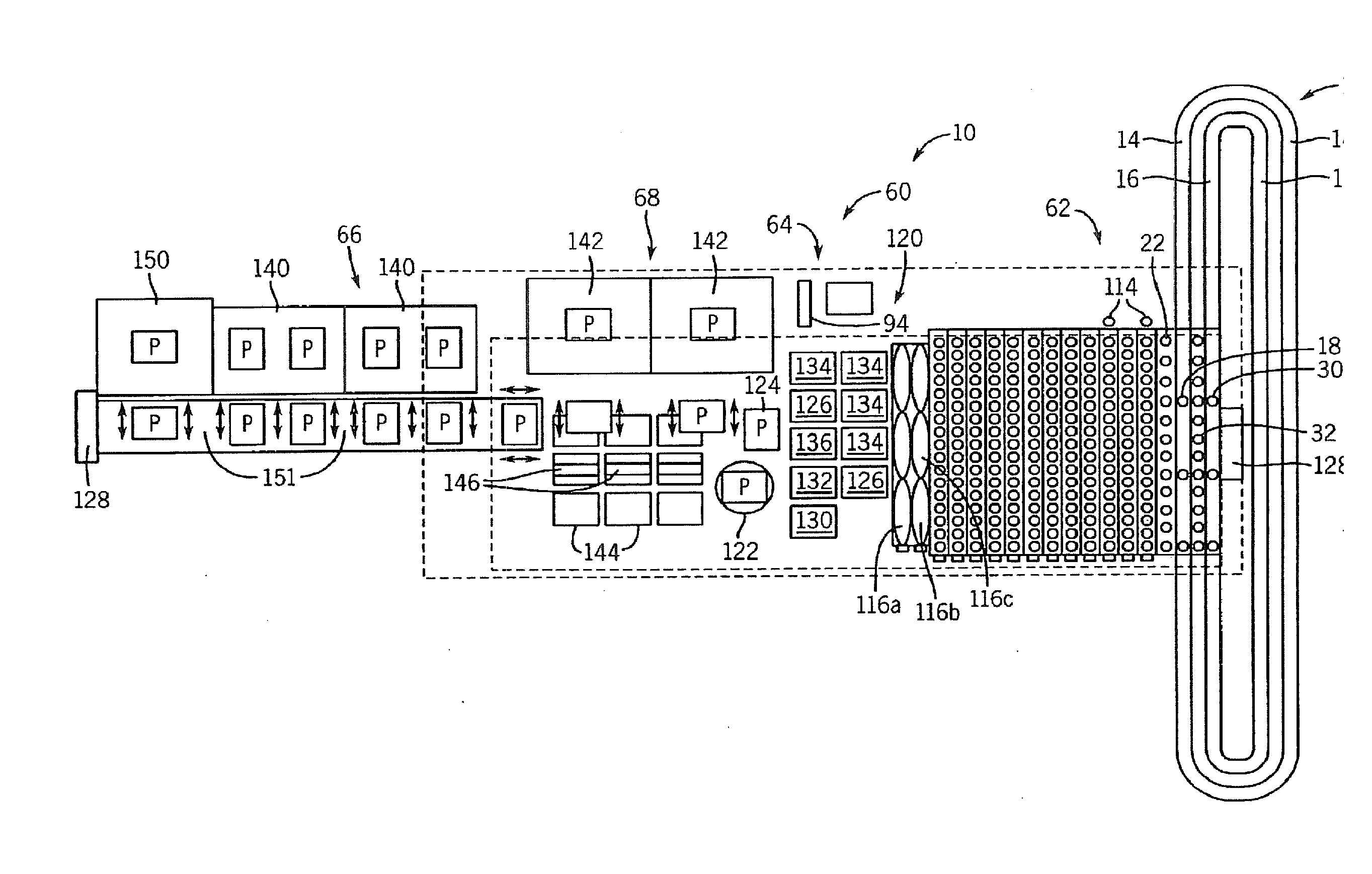
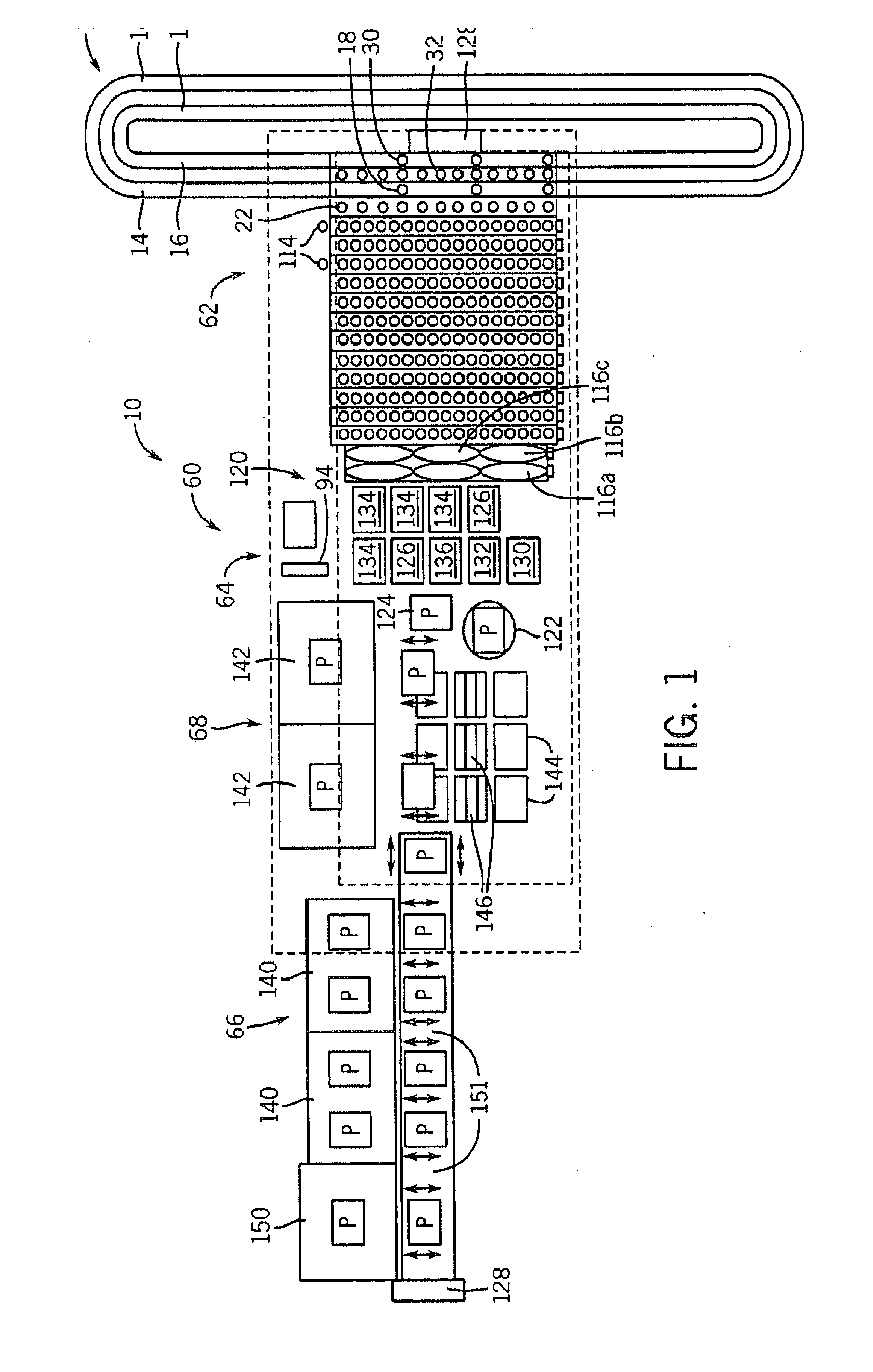
Temperature-Controlled Incubator Having A Receptacle Mixing Mechanism
InactiveUS20080063573A1Efficient and high through-put operationEfficient space utilizationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusIsolation proceduresTemperature control
An automated analyzer for performing multiple diagnostic assays simultaneously includes multiple stations, or modules, in which discrete aspects of the assay are performed on fluid samples contained in reaction receptacles. The analyzer includes stations for automatically preparing a specimen sample, incubating the sample at prescribed temperatures for prescribed periods, performing an analyte isolation procedure, and ascertaining the presence of a target analyte. An automated receptacle transporting system moves the reaction receptacles from one station to the next. The analyzer further includes devices for carrying a plurality of specimen tubes and disposable pipette tips in a machine-accessible manner, a device for agitating containers of target capture reagents comprising suspensions of solid support material and for presenting the containers for machine access thereto, and a device for holding containers of reagents in a temperature controlled environment and presenting the containers for machine access thereto. A method for performing an automated diagnostic assay includes an automated process for isolating and amplifying a target analyte. The process is performed by automatically moving each of a plurality of reaction receptacles containing a solid support material and a fluid sample between stations for incubating the contents of the reaction receptacle and for separating the target analyte bound to the solid support from the fluid sample. An amplification reagent is added to the separated analyte after the analyte separation step and before a final incubation step.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Automated analyzer
InactiveUS20060051243A1Chemiluminescene/bioluminescenceAnalysis by electrical excitationCuvetteAutomated analyzer
An automated analyzer for analyzing patient samples. The analyzer includes a plurality of cuvettes, which allow the samples to be mixed with various reagents. The analyzer includes one or more detectors, including a detector adapted to detect luminescence of the reaction mixture in the cuvettes. The analyzer allows for various diagnostic assays to be performed on a single system, and provides for high-sensitivity analysis at faster speeds.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
Automated analyzer
InactiveUS20080056944A1Highly reliable measurementAvoid disturbanceMaterial analysis by optical meansLaboratory analysis dataQuality controlAutomated analyzer
A set standard sample is identified, and a quality control material relevant to a reagent requested by the standard sample and stored in a buffer is fed automatically to an analyzer module. The measurement of the quality control material is performed immediately after the measurement of the standard sample for the reagent. A warning signal is generated to prompt the operator to replenish the quality control material when it is decided from the amount of the residual quality control material stored in the buffer that the quality control material is insufficient.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC +1
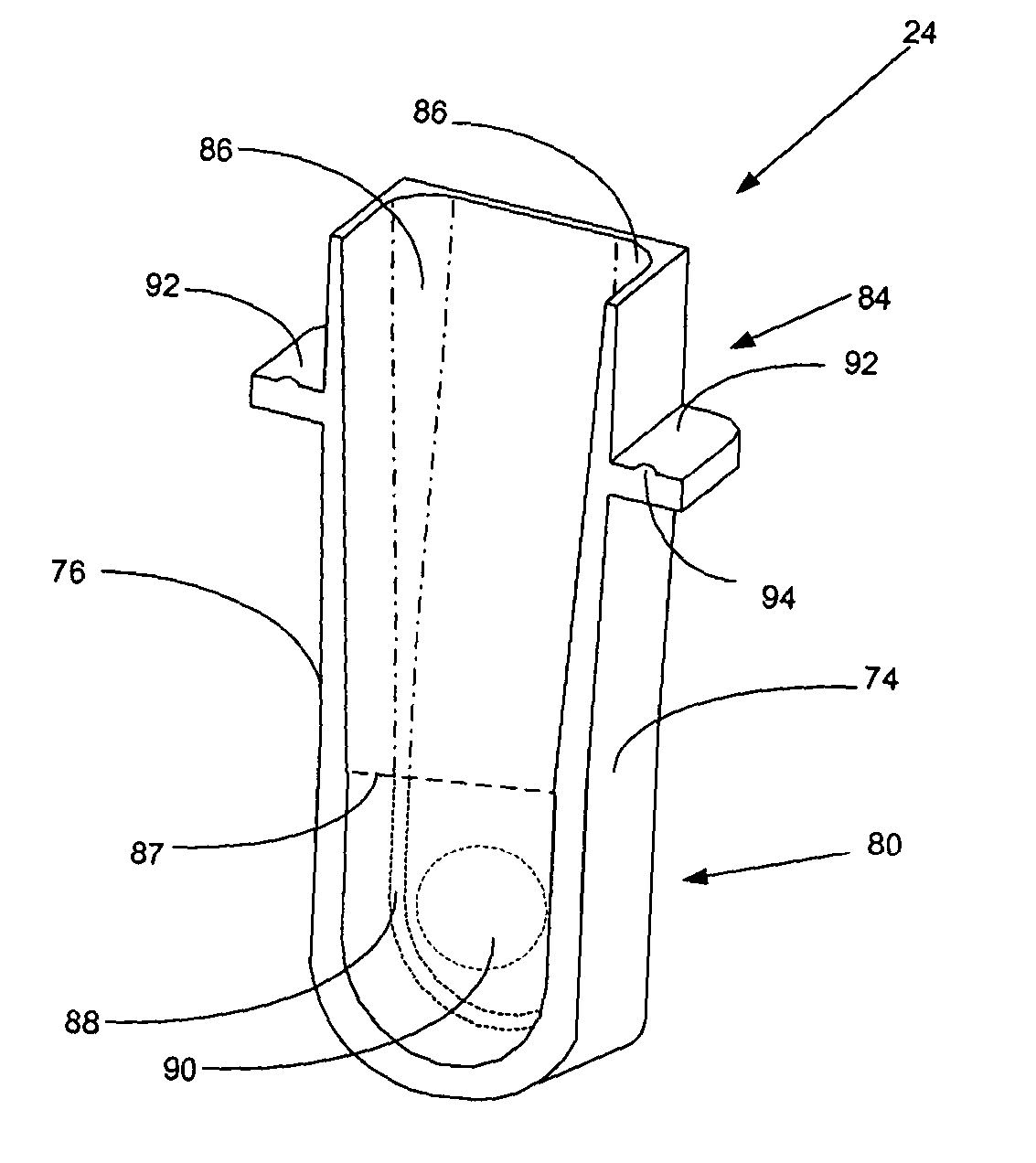
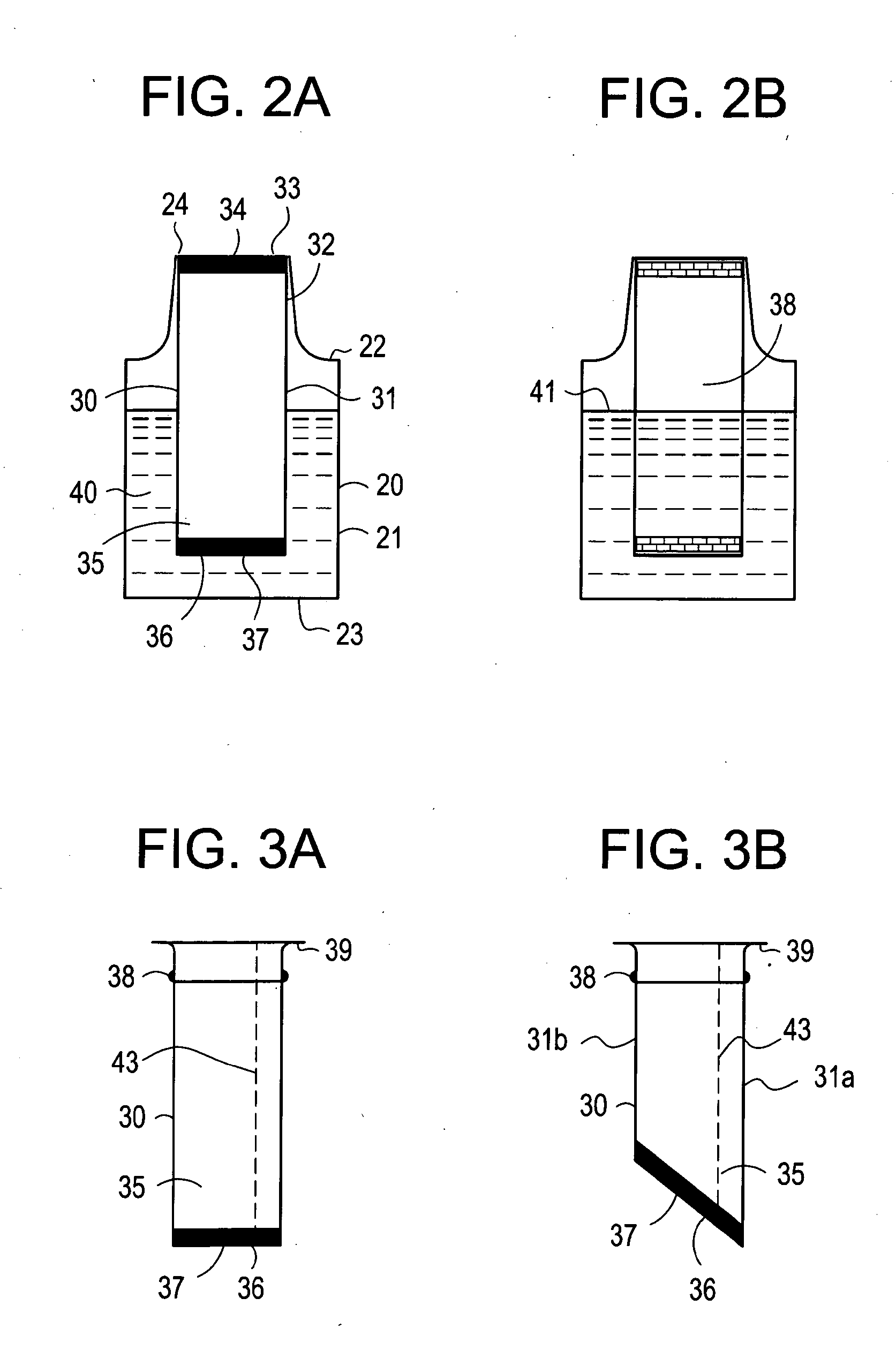
Reaction cuvette having anti-wicking features for use in an automatic clinical analyzer
ActiveUS7138091B2Easy to automateWithdrawing sample devicesChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceCuvetteAutomated analyzer
A reaction cuvette having anti-wicking wall fillets that inhibit liquid wicking along an interior wall surface so that the reaction cuvette may be used in a cuvette-rewashing system in an automated analyzer and not be adversely affected by any reagent contaminants remaining from assays previously performed in said reaction cuvette. The anti-wicking wall fillets comprise a curvilinear taper extending from an open top downwards into the cuvette to form a rounded concave blend between the cuvette's front and back walls and side walls.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
Reaction cuvette having anti-wicking features for use in an automatic clinical analyzer
ActiveUS20050013746A1Easy to automateChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceWithdrawing sample devicesCuvetteAutomated analyzer
A reaction cuvette having anti-wicking wall fillets that inhibit liquid wicking along an interior wall surface so that the reaction cuvette may be used in a cuvette-rewashing system in an automated analyzer and not be adversely affected by any reagent contaminants remaining from assays previously performed in said reaction cuvette. The anti-wicking wall fillets comprise a curvilinear taper extending from an open top downwards into the cuvette to form a rounded concave blend between the cuvette's front and back walls and side walls.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
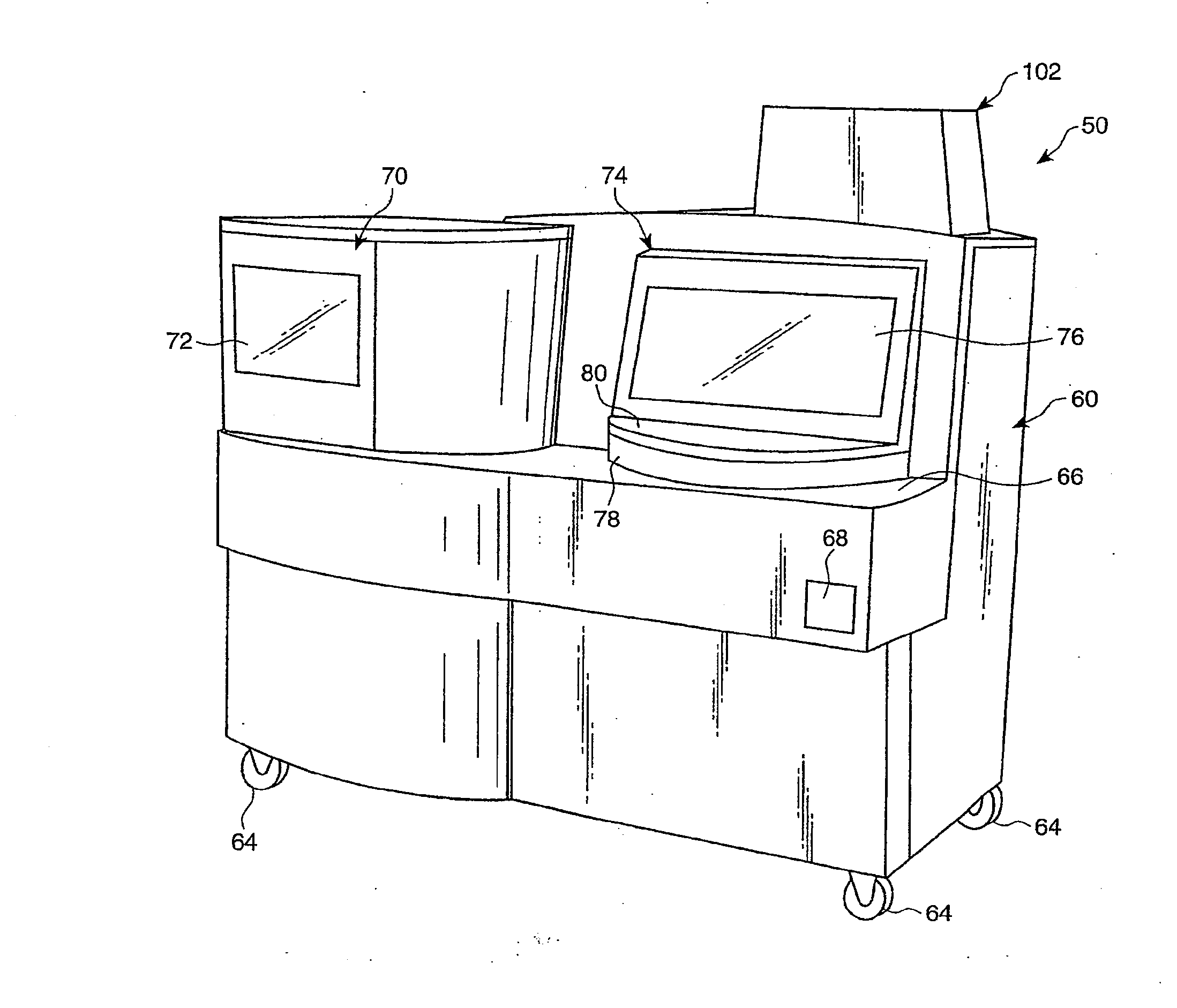
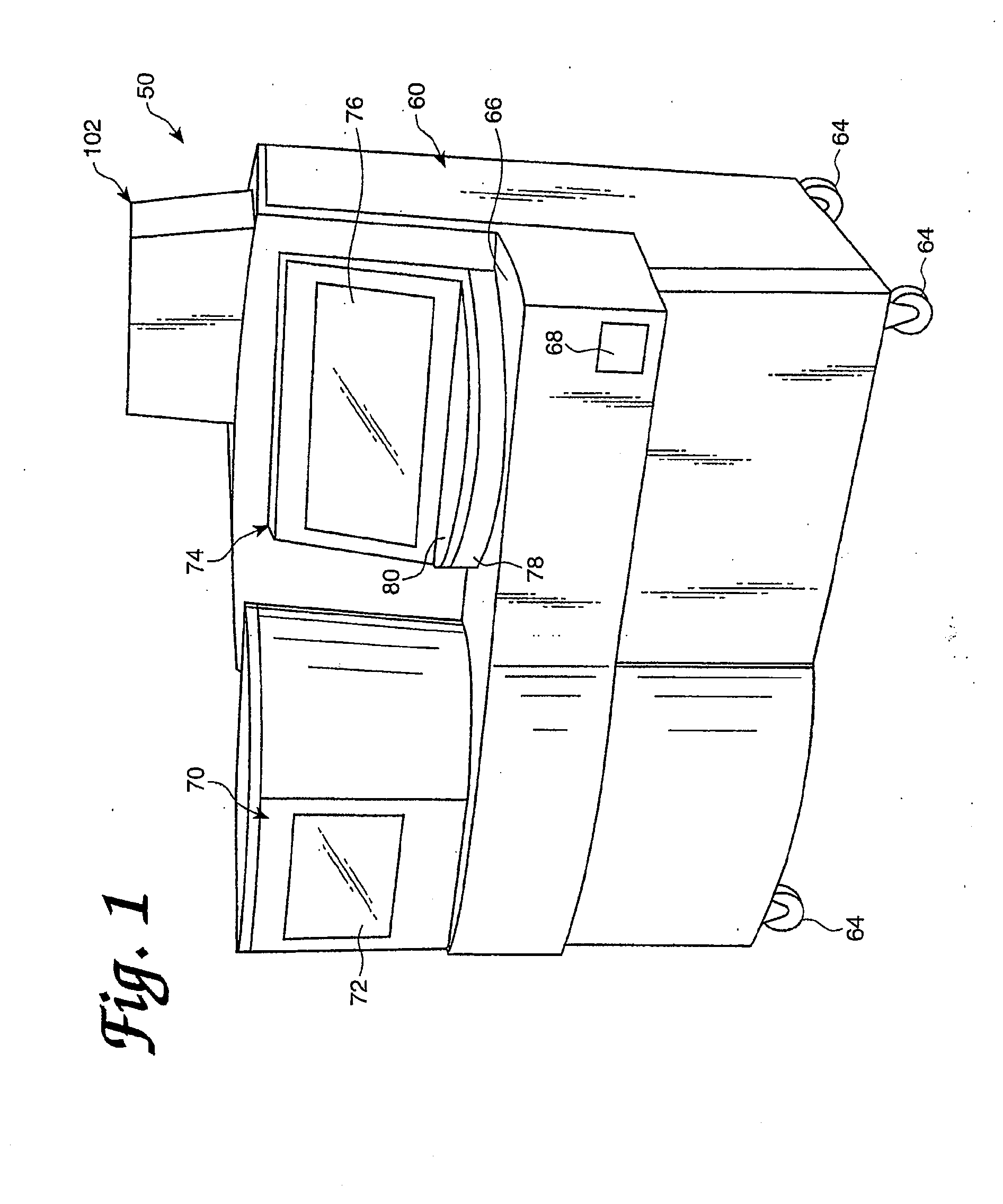
Automated analyzer for clinical laboratory
ActiveUS20120282684A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicro perforated plateClinical chemistry
A laboratory automation system that is capable of carrying out clinical chemistry assays, immunoassays, amplification of nucleic acid assays, and any combination of the foregoing, said laboratory automation system employing at least one of micro-well plates and deep multi-well plates as reaction vessels. The use of micro-well plates as reaction vessels enables the laboratory automation system to assume a variety of arrangements, i.e., the laboratory automation system can comprise a variety of functional modules that can be arranged in various ways. In order to effectively carry out immunoassays by means of micro-well plates, a technique known as inverse magnetic particle processing can be used to transfer the product(s) of immunoassays from one micro-well of a micro-well plate to another.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
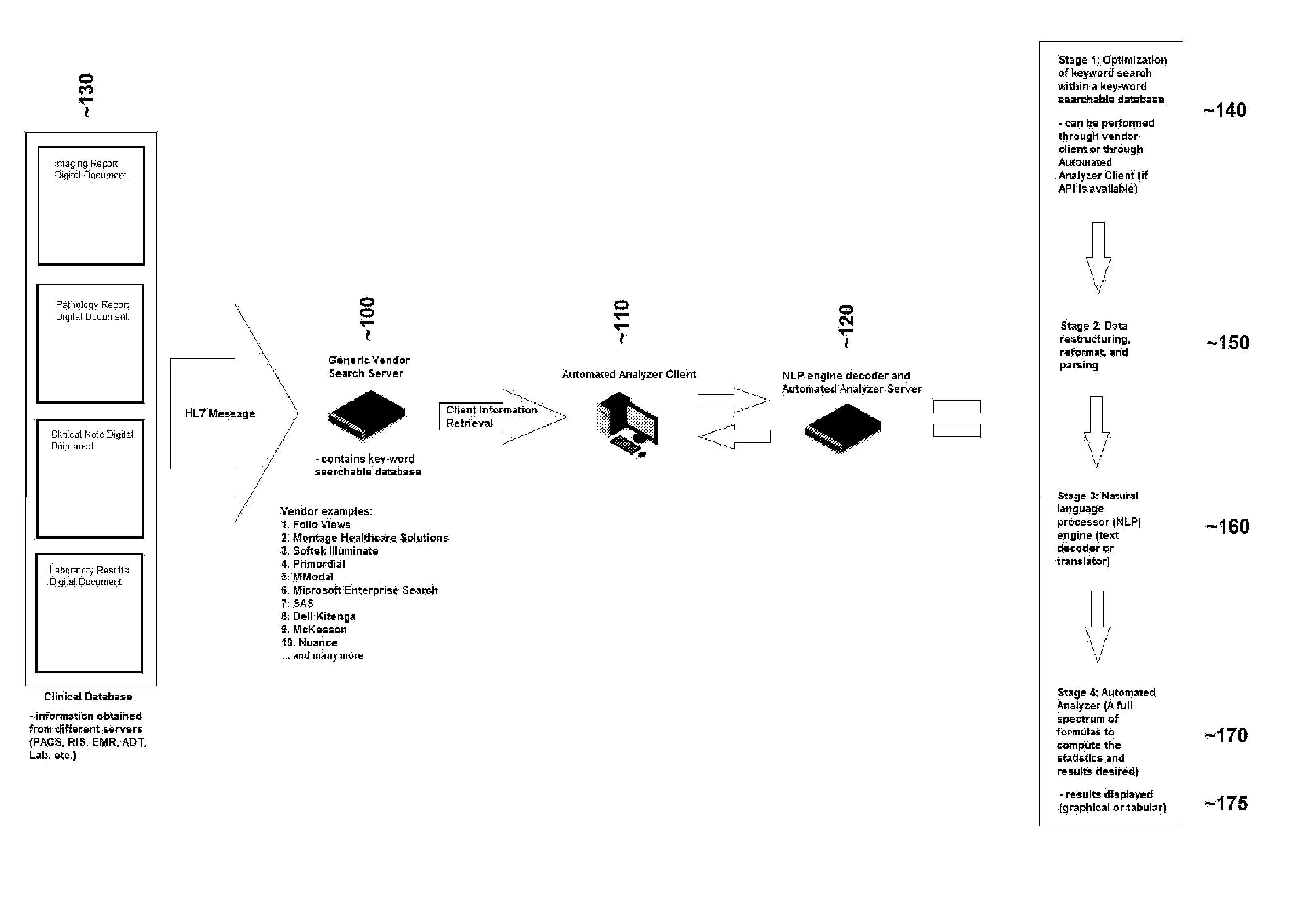
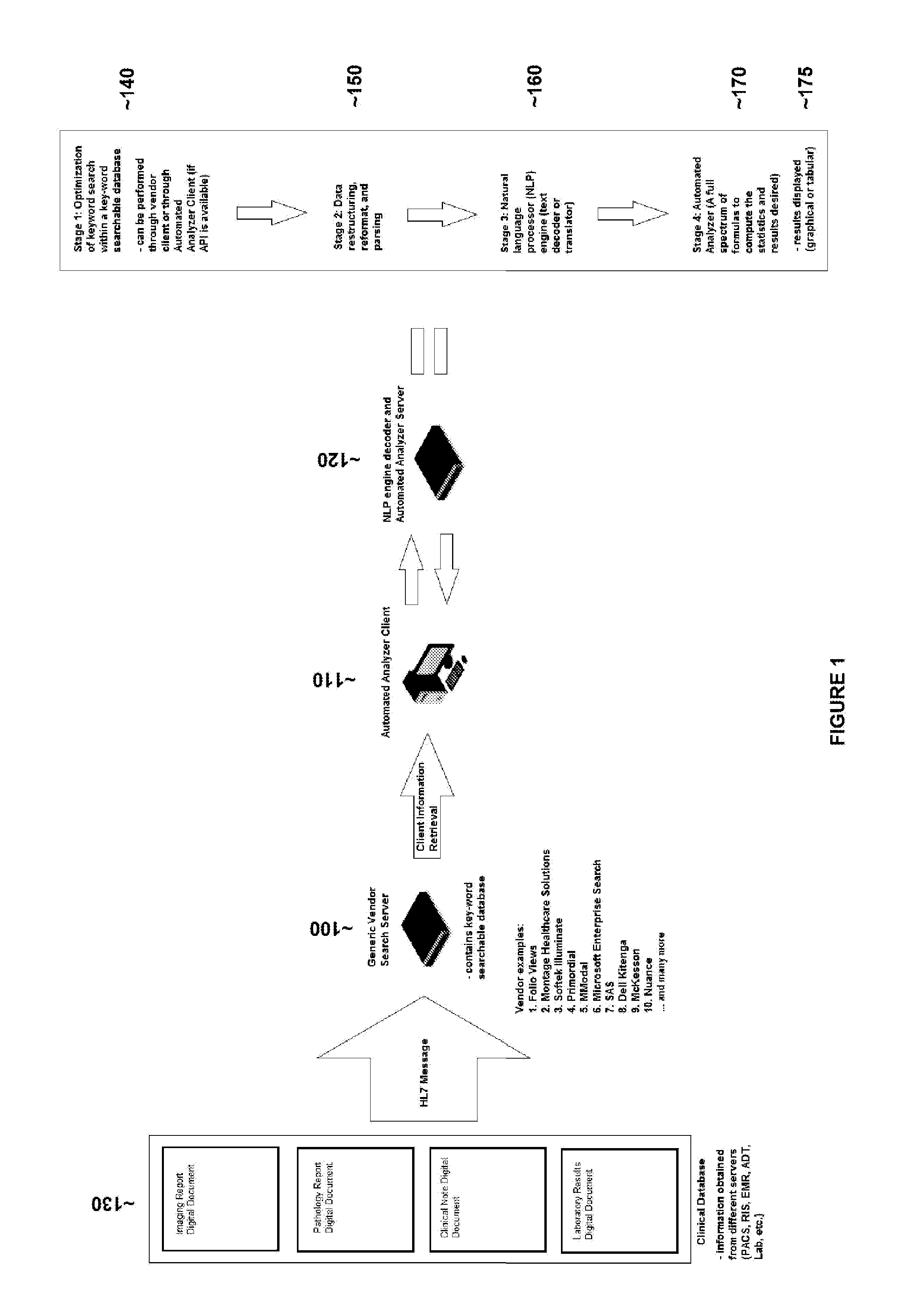
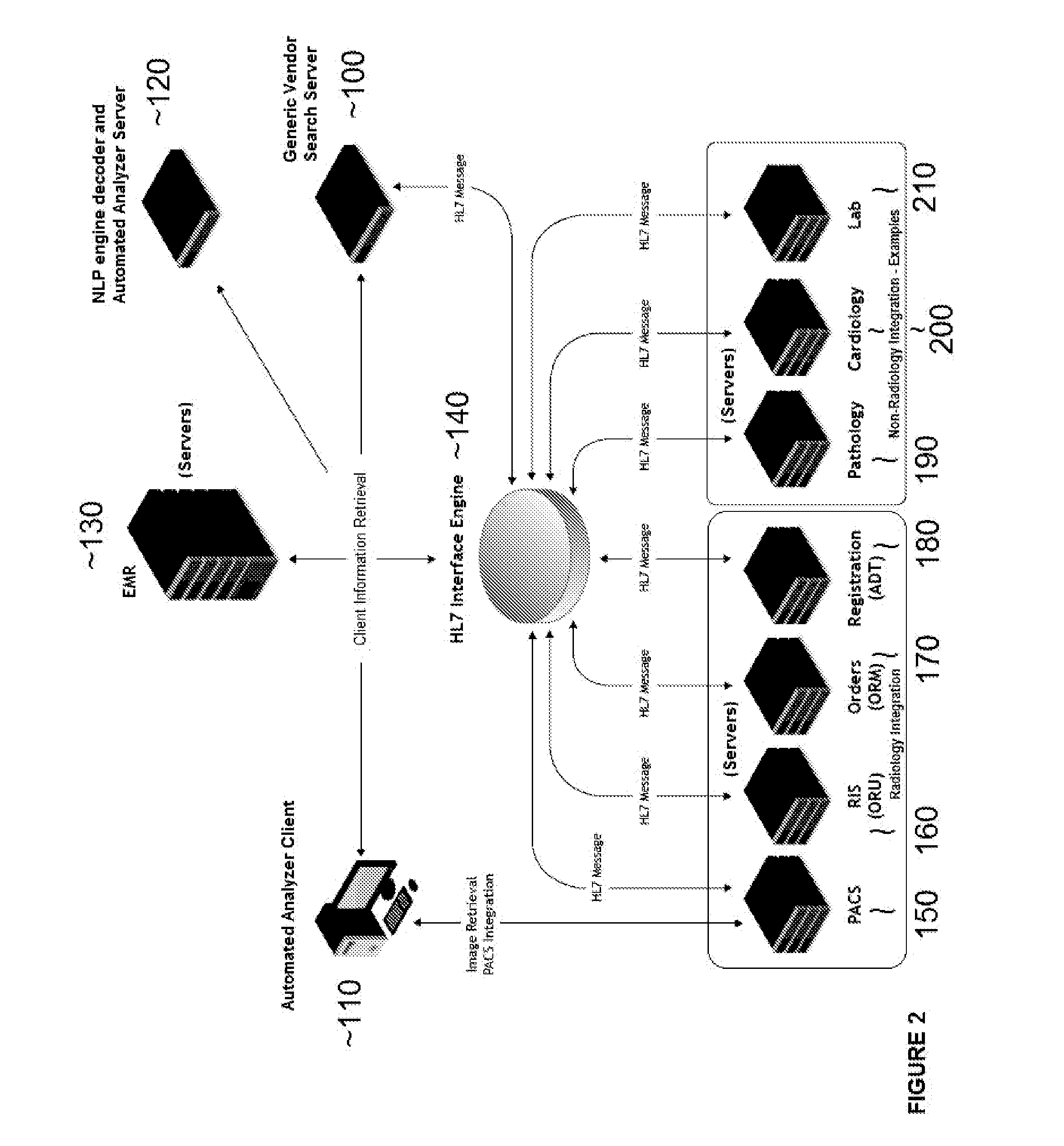
Method for searching a text (or alphanumeric string) database, restructuring and parsing text data (or alphanumeric string), creation/application of a natural language processing engine, and the creation/application of an automated analyzer for the creation of medical reports
A sequential series of methods for optimized searching within a text (or alphanumeric string) database to retrieve specific and relevant results, followed by optimized restructuring and parsing of text data (or alphanumeric string), followed by creation / application of a natural language processing engine, followed by the creation / application of an automated analyzer is presented.
Owner:HAYTER II ROBERT G
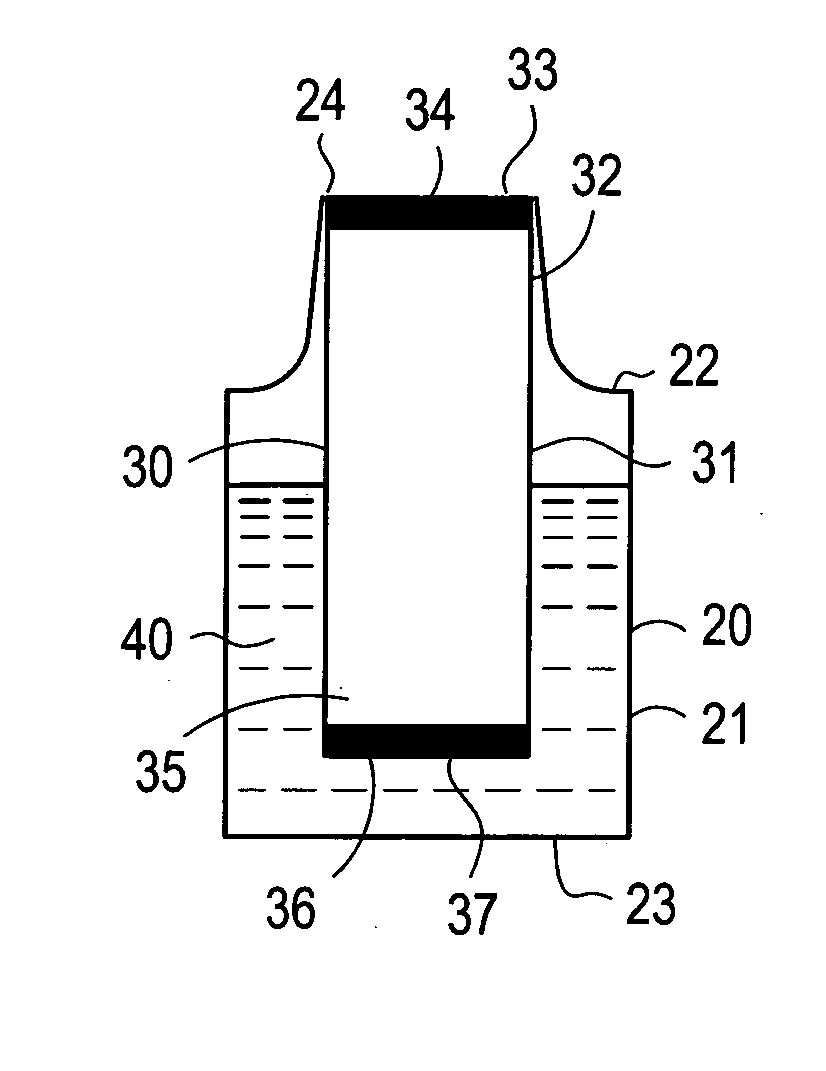
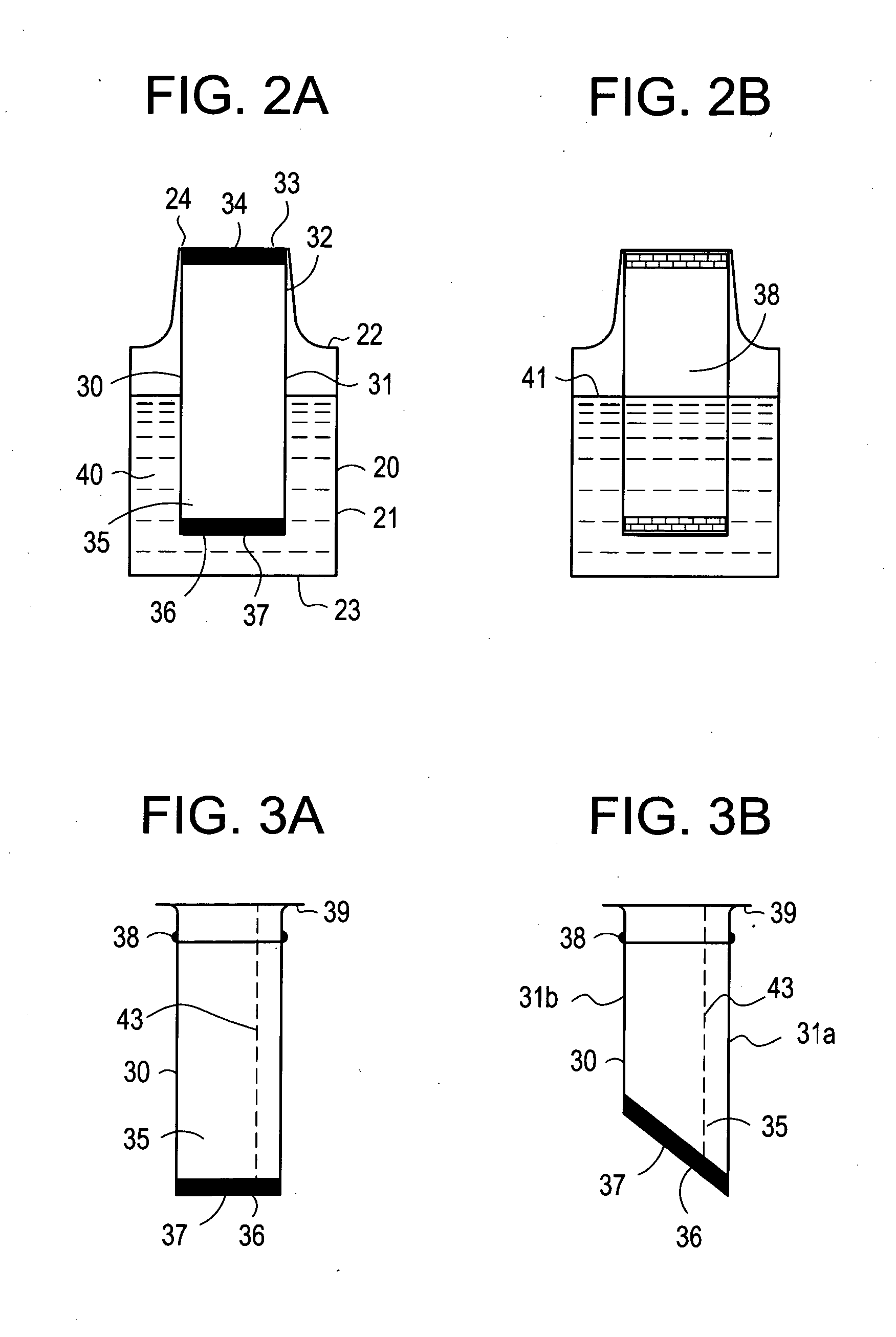
Containers for reducing or eliminating foaming
InactiveUS20100276445A1Opening closed containersBottle/container closureAutomated analyzerMechanical engineering
A foam reducing or eliminating container for containing a liquid includes: a container body having a top portion, a bottom portion and an opening for adding a liquid to or removing a liquid from the container body; and a hollow baffle located within the container with first and second openings therein. The first and second openings are covered with a pierceable seal, wherein the first opening of the baffle is at least partially aligned with the opening of the container. In a preferred embodiment, the container is a reagent supply container for an automated analyzer, which includes: a container as described above; and a closure which is movable away from the opening of the container to be in an open position and movable into contact with the opening to be in a closed position. In another preferred embodiment a reagent supply for an automated analyzer includes: the reagent supply container as described above; and a liquid reagent therein. The second opening of the baffle is submerged in liquid. A method for reducing or eliminating the aspiration of foam into a metering probe includes: providing a reagent supply as described above; providing a metering probe movable in a direction toward and away from the reagent supply; moving the closure away from the opening of the container; piercing both seals covering the first and second openings of the baffle allowing liquid to enter the baffle from the end of the baffle submerged in the liquid, wherein the seals may or may not be pierced with the metering probe; moving the metering probe into the first opening of the baffle and into contact with the liquid in the baffle; aspirating a selected amount of liquid in the baffle; and moving the metering probe out of the baffle.
Owner:ORTHO-CLINICAL DIAGNOSTICS
Automated analyzer for clinical laboratory
InactiveUS8222048B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsClinical chemistryMicrowell Plate
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Containers for reducing or eliminating foaming
InactiveUS20060286004A1Reducing and eliminating aspirationAnalysis using chemical indicatorsAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionEngineeringAutomated analyzer
A foam reducing or eliminating container for containing a liquid includes: a container body having a top portion, a bottom portion and an opening for adding a liquid to or removing a liquid from the container body; and a hollow baffle located within the container with first and second openings therein. The first and second openings are covered with a pierceable seal, wherein the first opening of the baffle is at least partially aligned with the opening of the container. In a preferred embodiment, the container is a reagent supply container for an automated analyzer, which includes: a container as described above; and a closure which is movable away from the opening of the container to be in an open position and movable into contact with the opening to be in a closed position. In another preferred embodiment a reagent supply for an automated analyzer includes: the reagent supply container as described above; and a liquid reagent therein. The second opening of the baffle is submerged in liquid. A method for reducing or eliminating the aspiration of foam into a metering probe includes: providing a reagent supply as described above; providing a metering probe movable in a direction toward and away from the reagent supply; moving the closure away from the opening of the container; piercing both seals covering the first and second openings of the baffle allowing liquid to enter the baffle from the end of the baffle submerged in the liquid, wherein the seals may or may not be pierced with the metering probe; moving the metering probe into the first opening of the baffle and into contact with the liquid in the baffle; aspirating a selected amount of liquid in the baffle; and moving the metering probe out of the baffle.
Owner:ORTHO-CLINICAL DIAGNOSTICS
Automated multi-detector analyzer
An automated analyzer for analyzing patient samples. The analyzer includes a plurality of cuvettes, which allow the samples to be mixed with various reagents. The analyzer includes one or more detectors, including a detector adapted to detect luminescence of the reaction mixture in the cuvettes. The analyzer allows for various diagnostic assays to be performed on a single system, and provides for high-sensitivity analysis at faster speeds.
Owner:DADE BEHRING
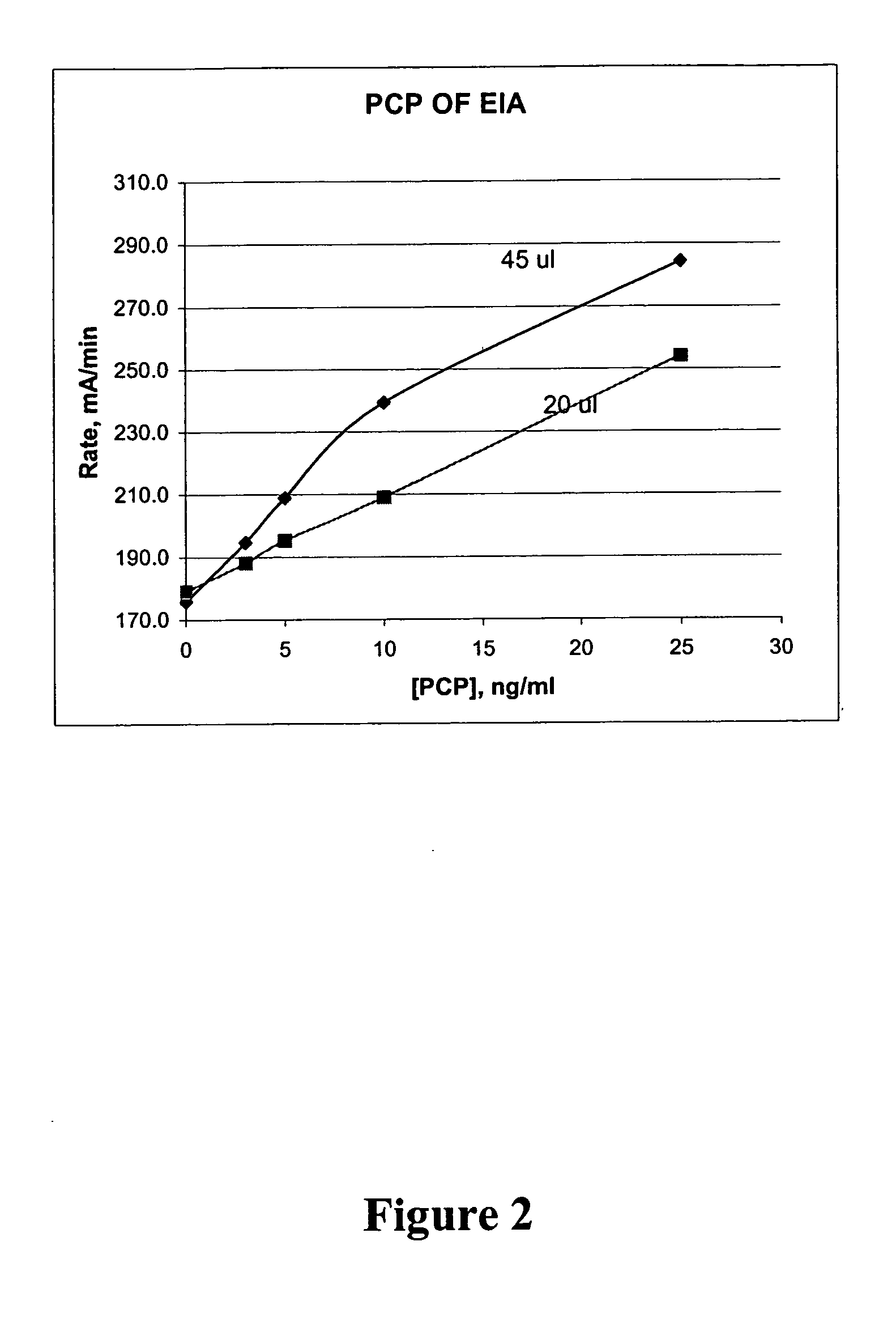
Homogeneous enzyme immunoassay for oral fluid
The present invention discloses homogeneous enzyme immunoassay systems, methods and kits useful for the qualitatively and quantitatively determination of analytes in oral fluid samples. The system involves a competitive enzyme immunoassay employing a conjugate comprising glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PDH) and an analyte. The methods and kits are particularly useful in the detection of recent drug use and for fast determination of analytes using auto-analyzers.
Owner:LIN ZHI INT
Video monitoring system detection method and apparatus thereof
InactiveCN101500177AObjective evaluationEvaluation scienceClosed circuit television systemsDigital videoVideo monitoring
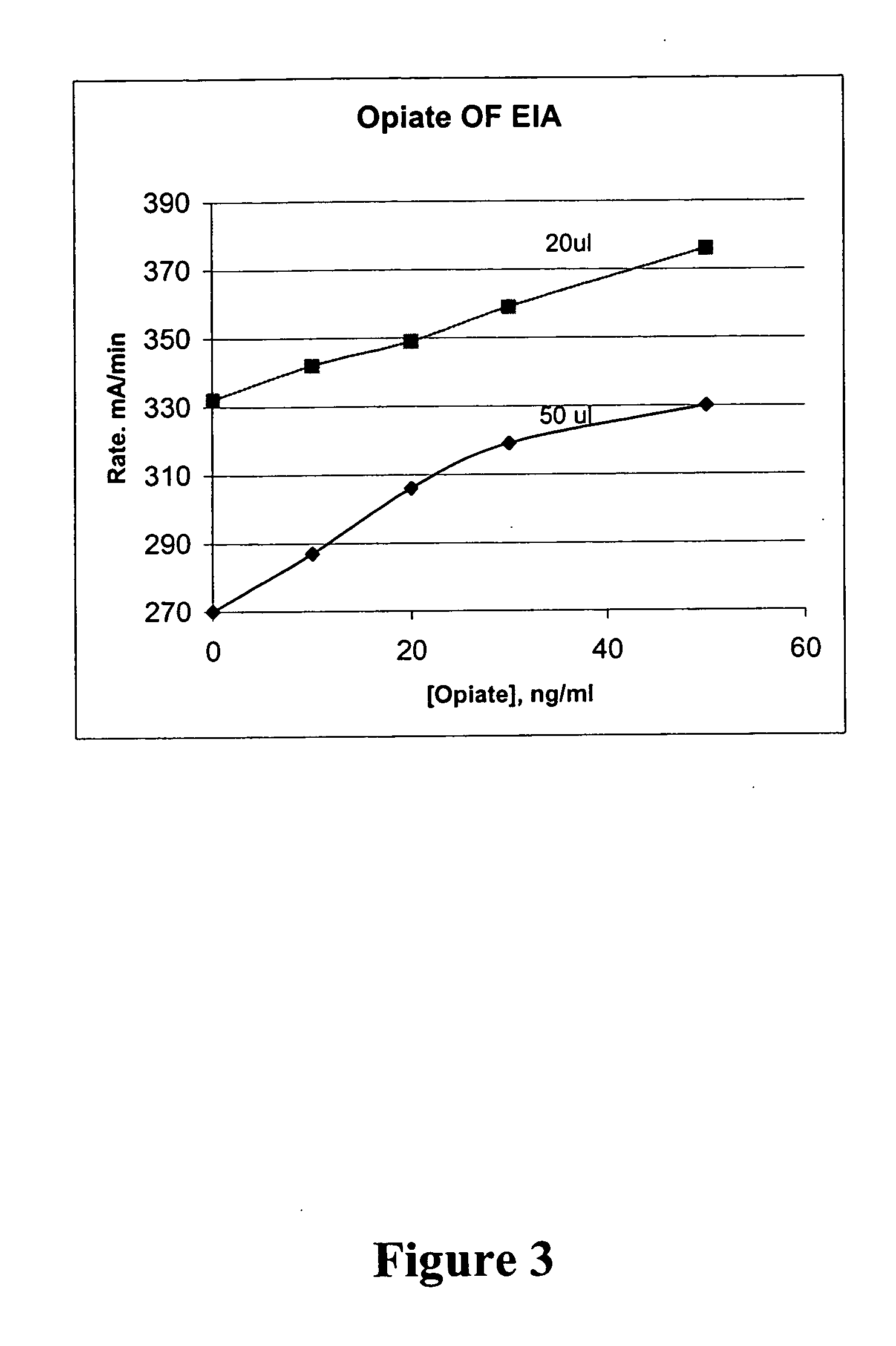
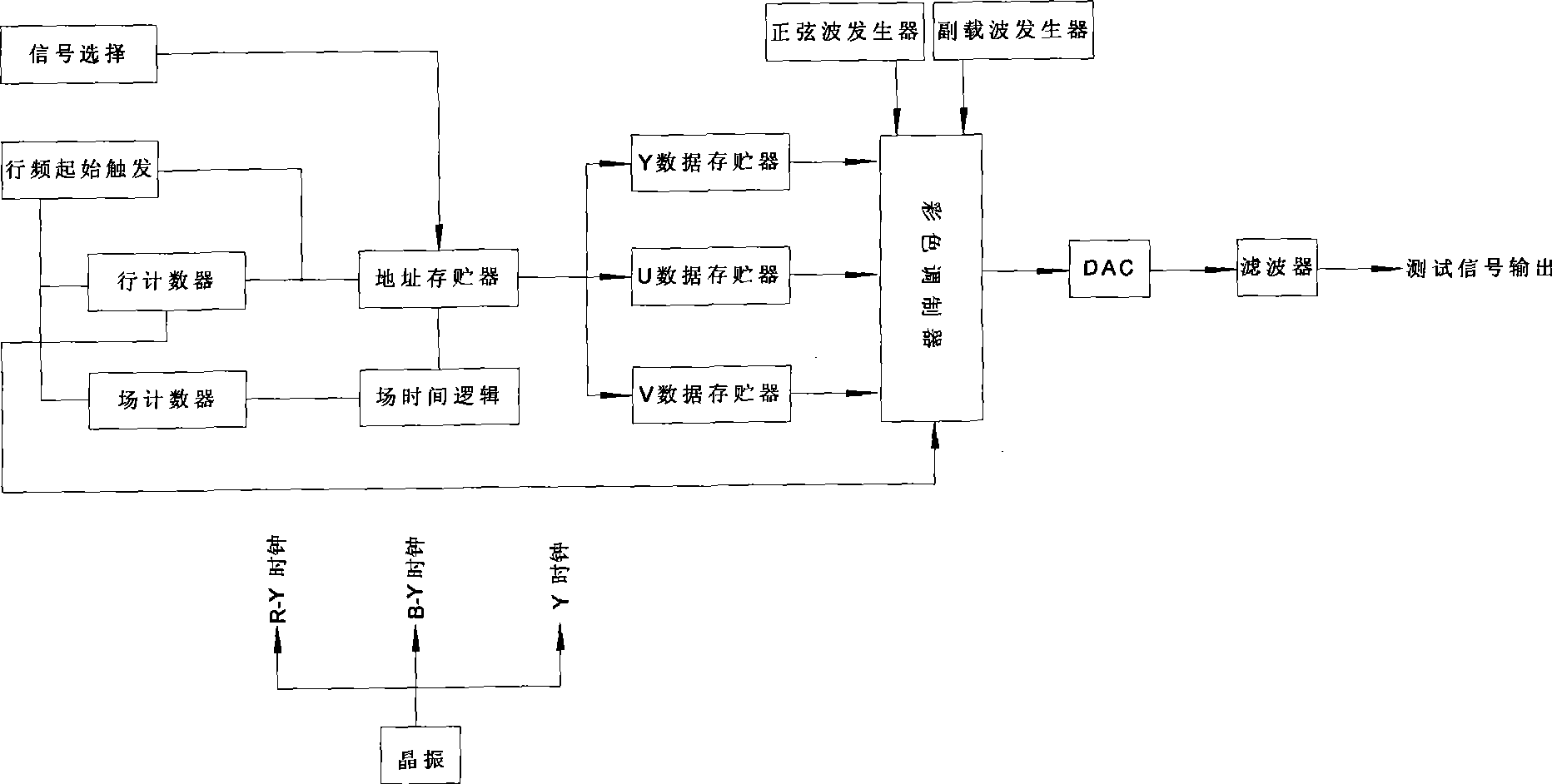
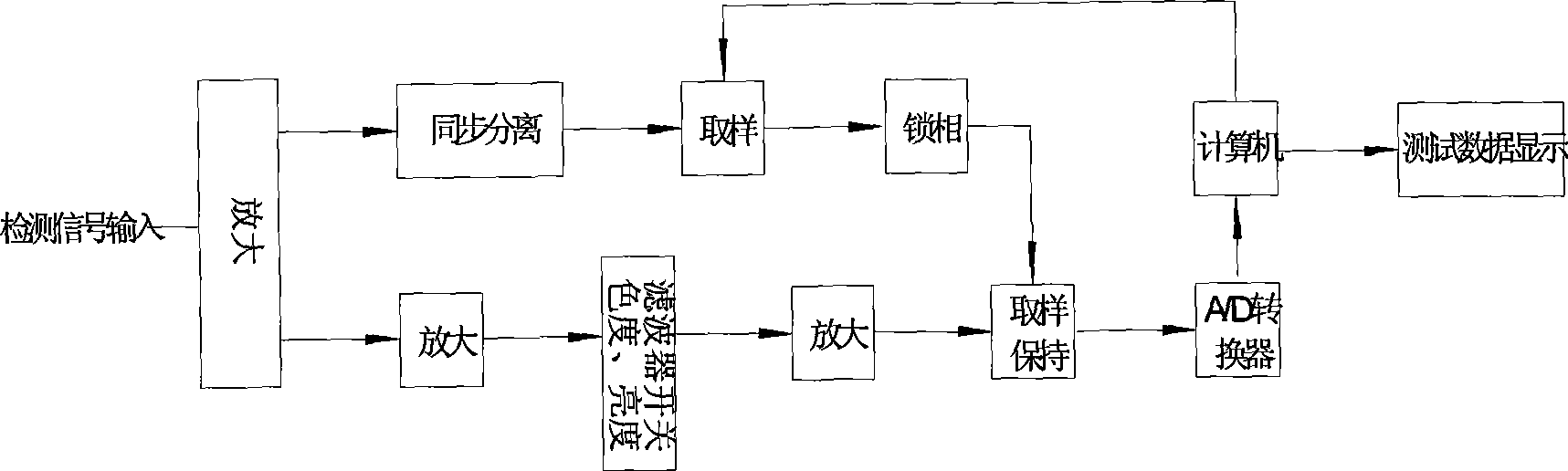
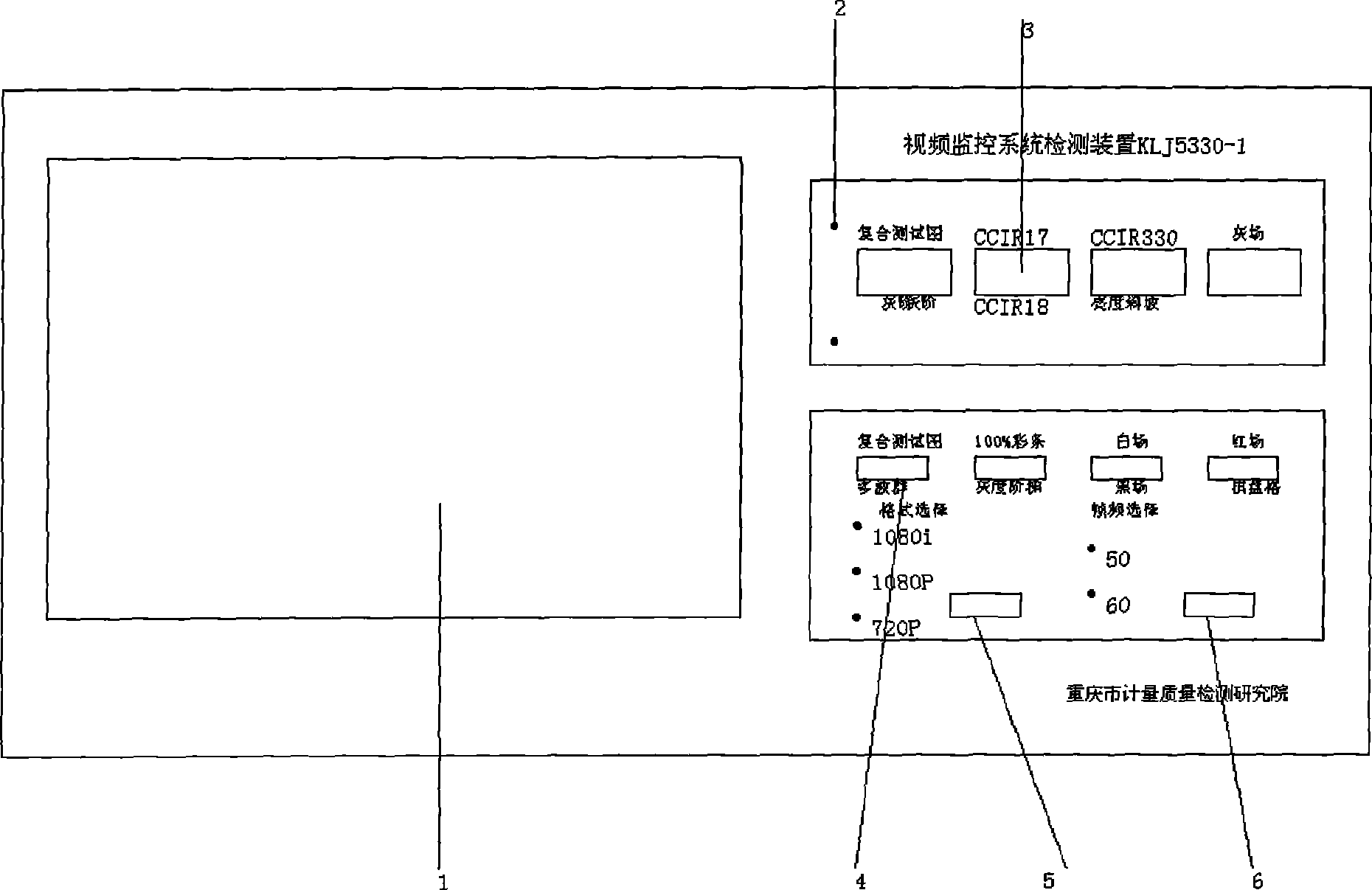
The invention provides a method for detecting a video monitoring system and a device thereof; a standard definition television test signal and a high definition television test signal are generated by a signal source generator; the test signals are accessed in a video channel of a video monitoring system to be detected, and with a video index of the video monitoring system to be detected, video data is collected, analyzed and tested by an automatic analyzer based on the control of a single board computer of a computer; and the test result is displayed in the form of graphic and data. The invention can more scientifically and objectively assess the signal index of digital television video equipment, can carry out the test on video indexes of random signal-to-noise ratio, synchronization amplitude, white strip amplitude, luminance nonlinearity, amplitude frequency characteristic and the like of the video monitoring system, simultaneously has the function of image display of the video to be detected, can generate gray scale signals of 11 grade, and meets the detecting requirement of the field of video monitoring; furthermore, the invention has simple structure, convenient use, lower detecting cost, and is applicable to on-site detection and fill the emptiness of special detection instrument in the detection field of domestic and foreign video monitoring project.
Owner:CHONGQING ACAD OF METROLOGY & QUALITY INST
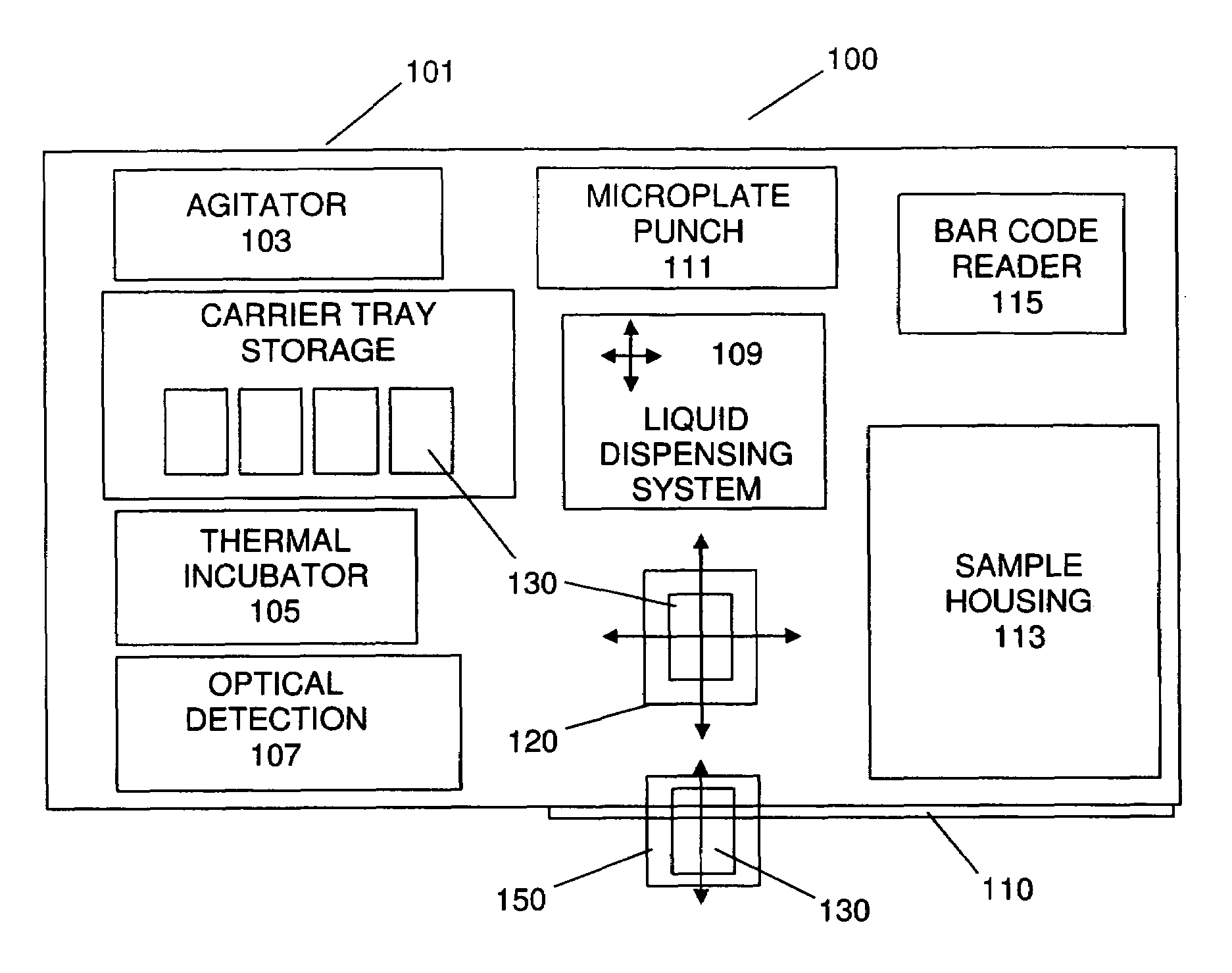
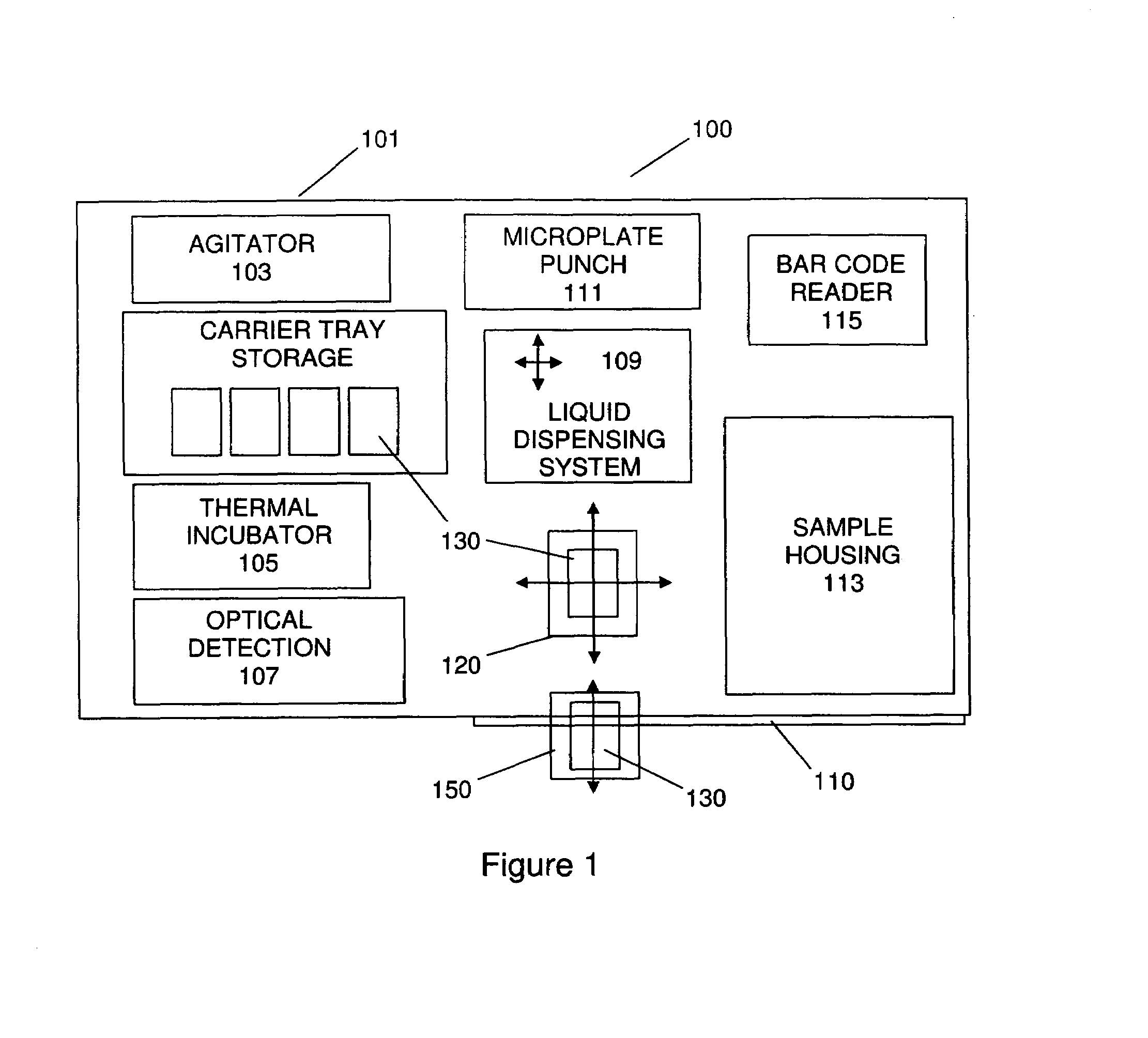
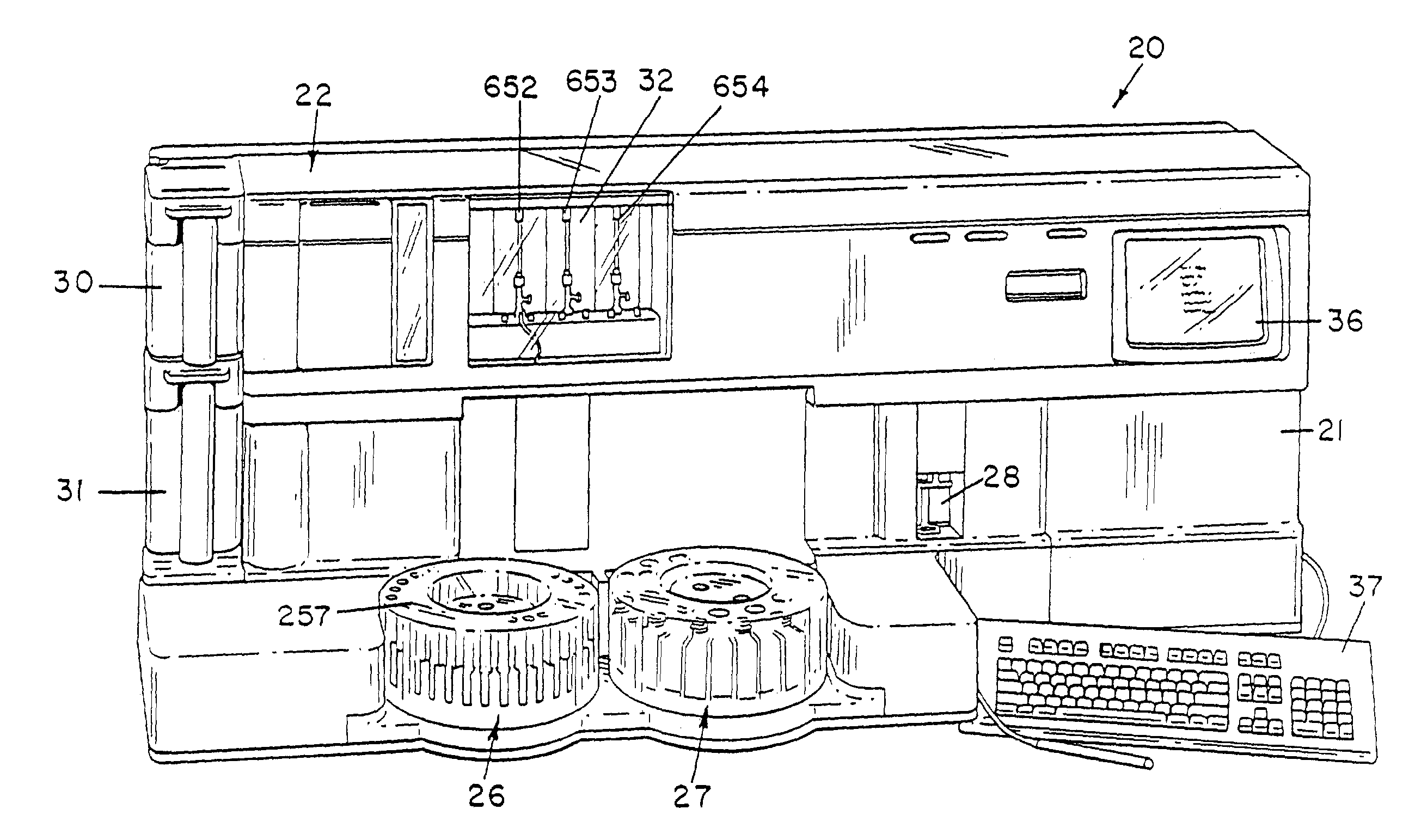
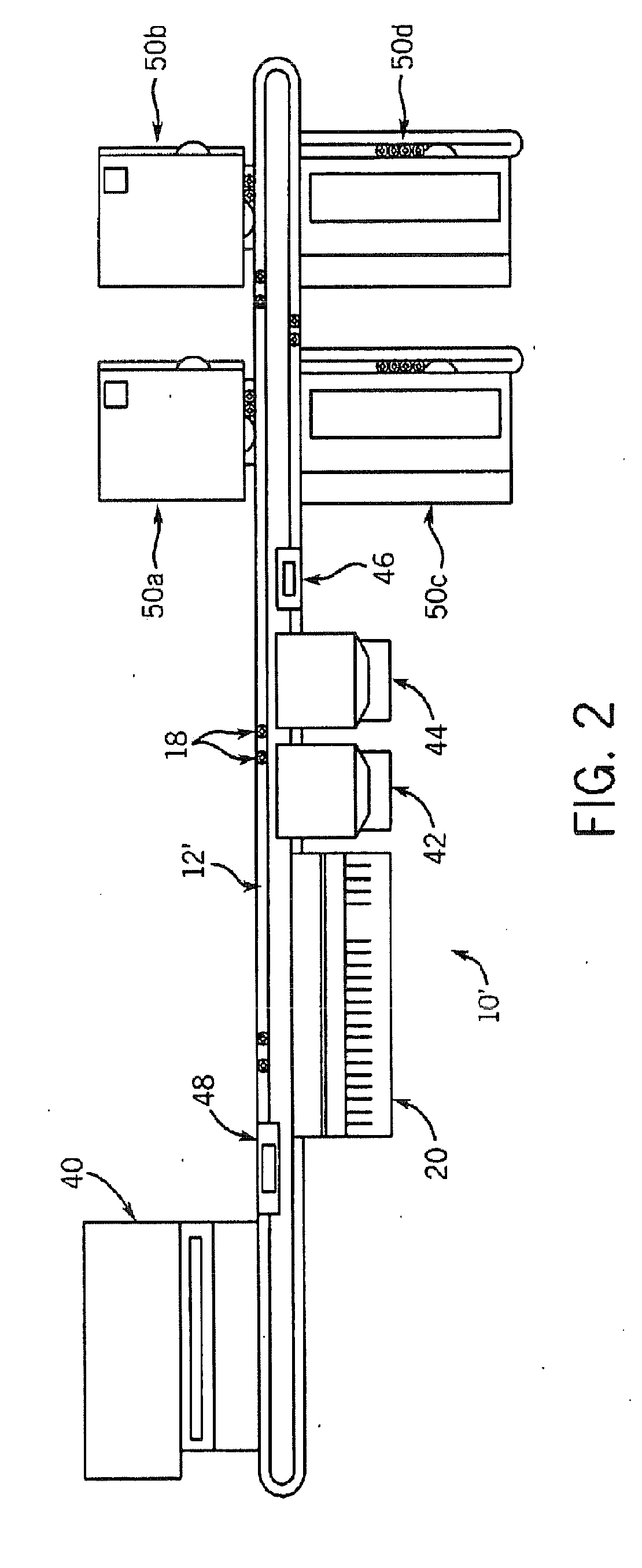
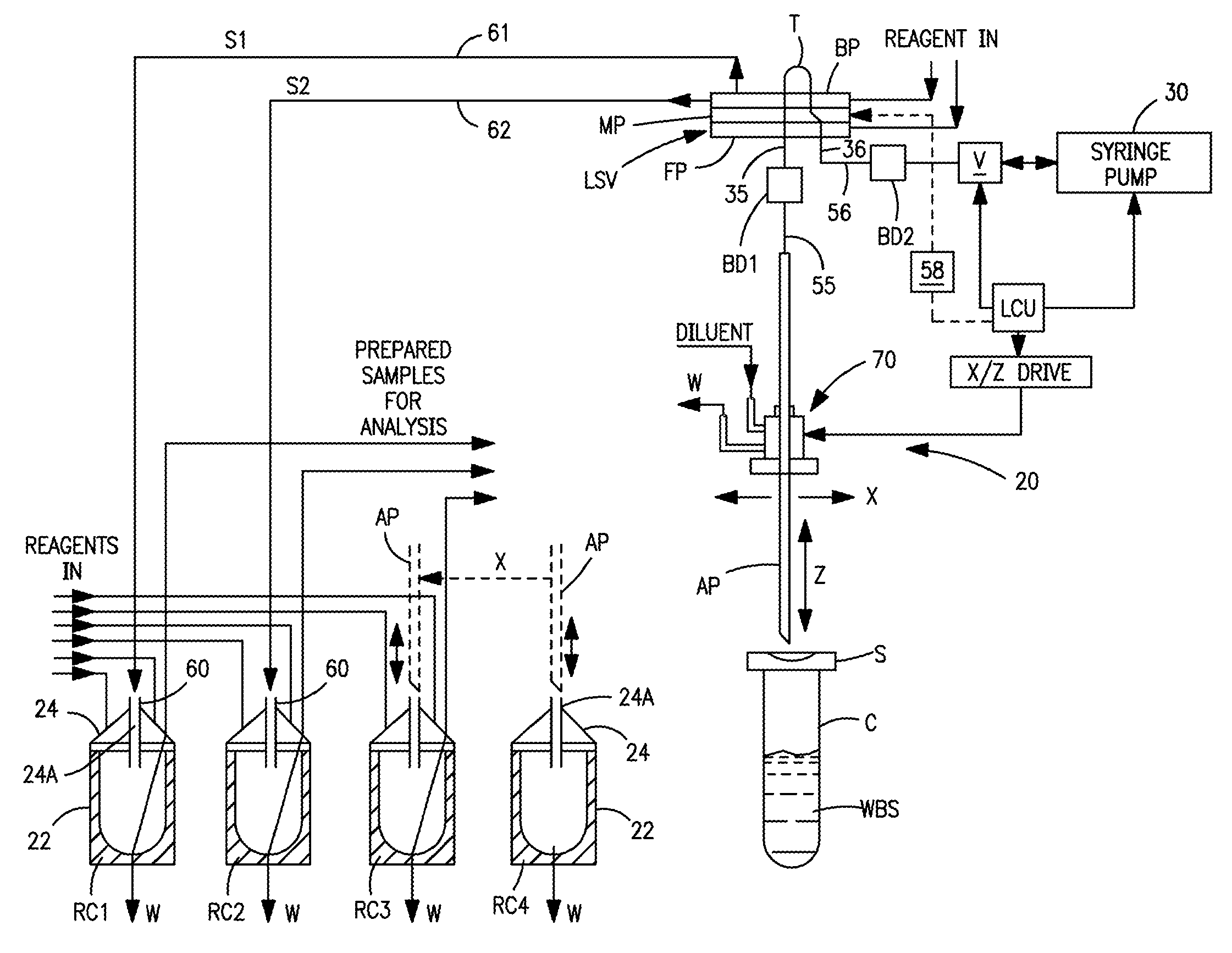
Apparatus for Aspirating and Dispensing Liquids in an Automated Analyzer
Apparatus for aspirating and dispensing liquid samples in an analytical instrument, e.g., a hematology instrument, includes a liquid-sampling valve that, while operating to segment and position for dispensing one or more precise volumes of a liquid sample that has been aspirated into the valve by a pump, simultaneously enables the apparatus to be operated in an aspirate / dispense (suck-and-spit) mode in which a liquid sample can be selectively driven through the valve in opposite directions by a pump, e.g., a syringe pump.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Automated analyzer using light diffraction
InactiveUS20070264707A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteLight diffraction
The present invention provides an automated analyzer system for performing chemical, biochemical or biological assays using changes / no changes in diffraction of light by the presence / absence of analytes which may or may not be present in a sample binding to their analyte specific receptors laid out in a preselected pattern in a disposable sensor. The analyzer is a modular, bench-top instrument that compactly integrates subsystems for sample dispensing, liquid handling, and optical generation of laser light beams and detectors for detecting for diffracted light. An internal processor is included for automating the instrument, and a user interface to provide communication with the operator.
Owner:ANGLE EURO LTD
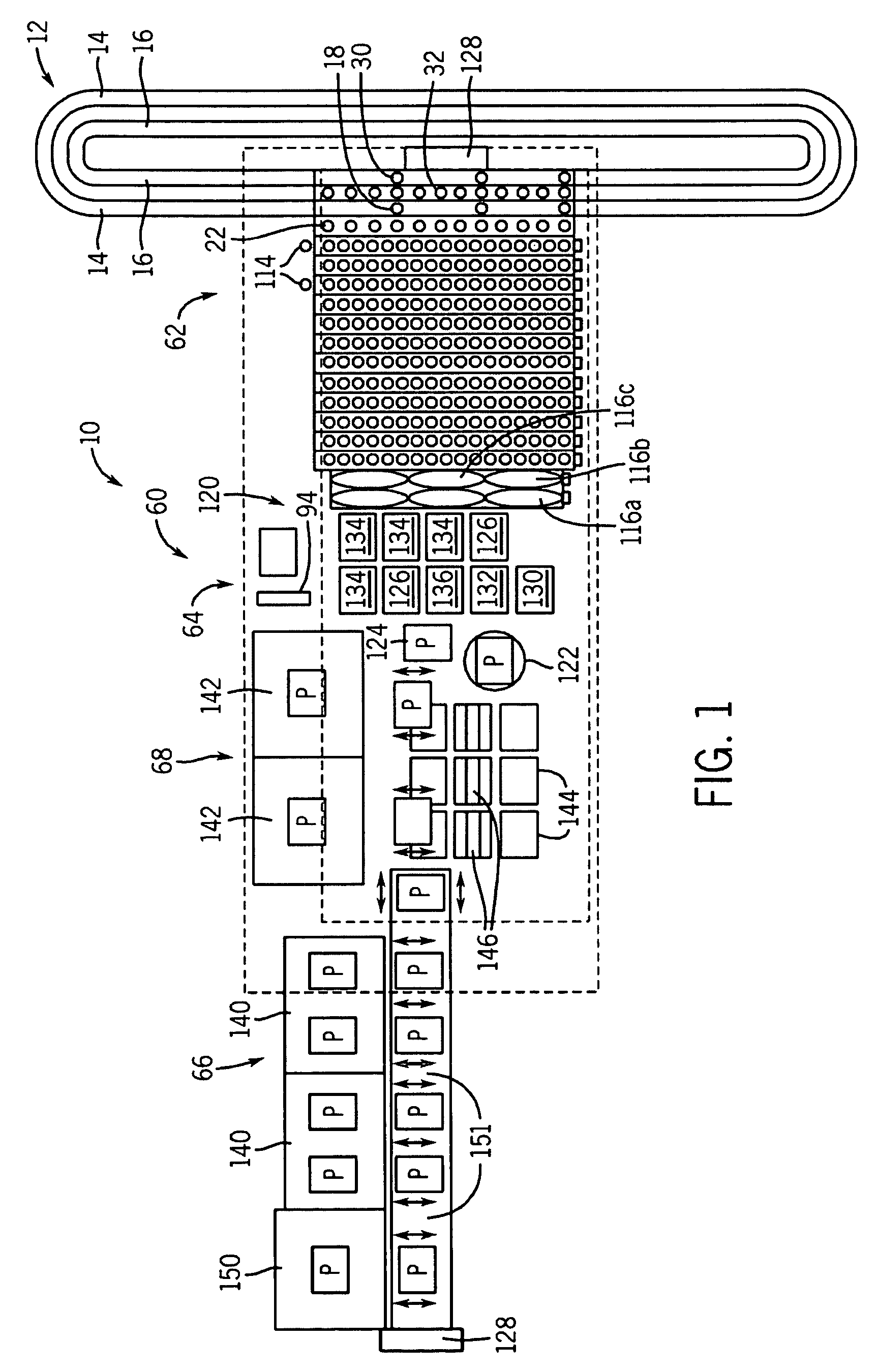
Automatic analysis device and automatic analysis method
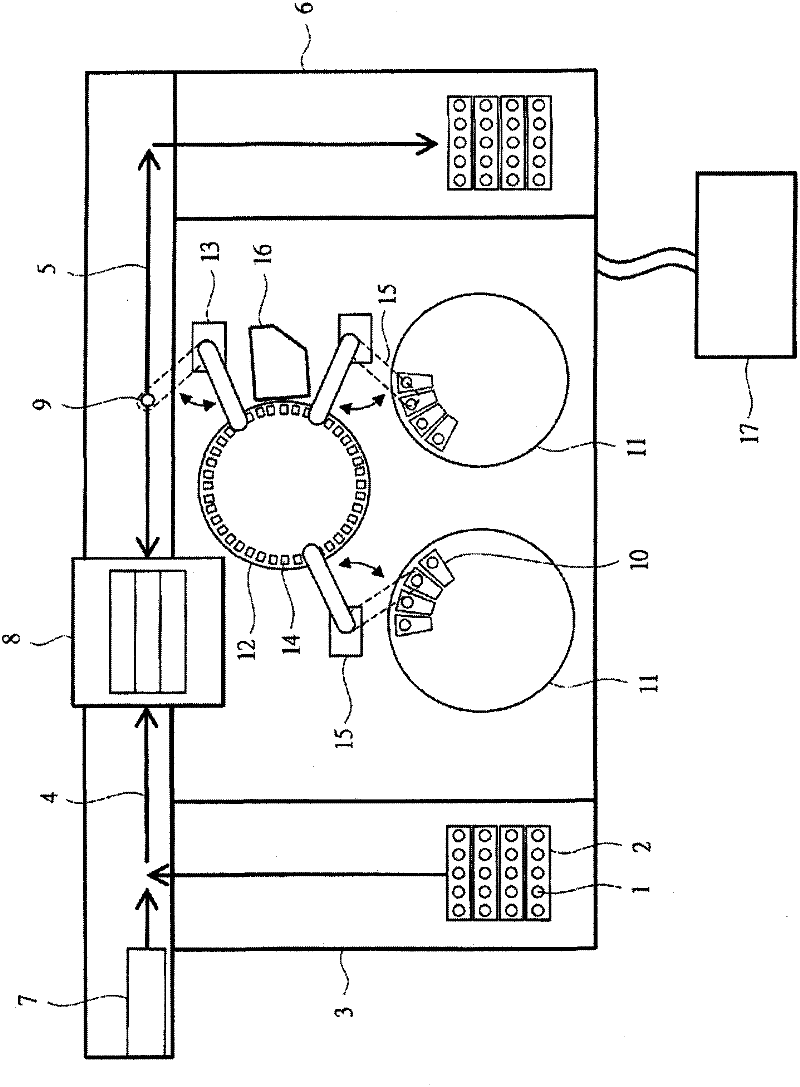
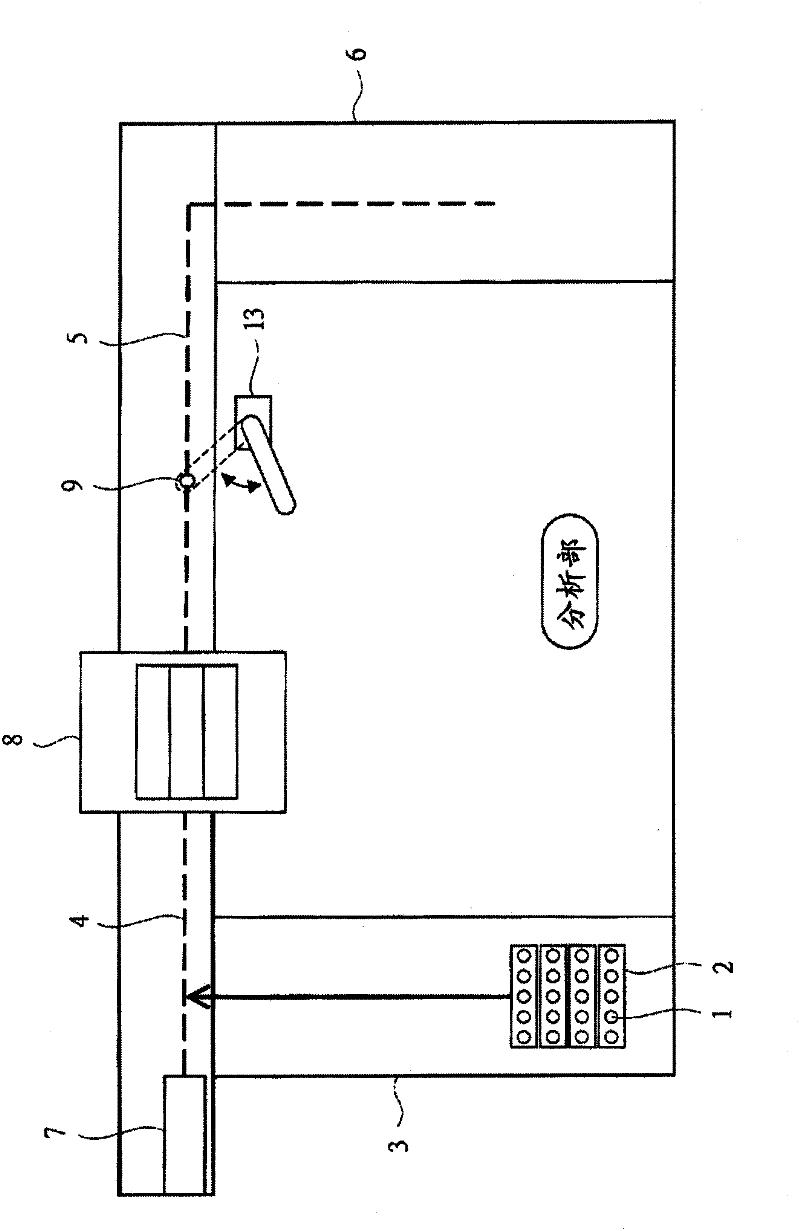
Provided is a technology pertaining to the transport of samples in an automated analyzer, which allows a sample container containing a sample having a high degree of urgency and priority for analysis to be moved quickly to a sample dispensing position. The analyzer is provided with a rack buffer unit (8) serving as a sample container switching section is provided between a rack transport module (4) and a rack transport module (5) that transport racks (2) carrying sample containers (1), and an urgent sample loading module (7) on which is placed a rack (2) carrying a sample container (1) containing a sample which has priority for analysis. The rack (2) carrying the sample currently being dispensed and a rack (2) which has priority for analysis are switched at the rack buffer unit (8), and the sample container (1) carried on the rack (2) which has priority for analysis is quickly moved to the sample dispensing position.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
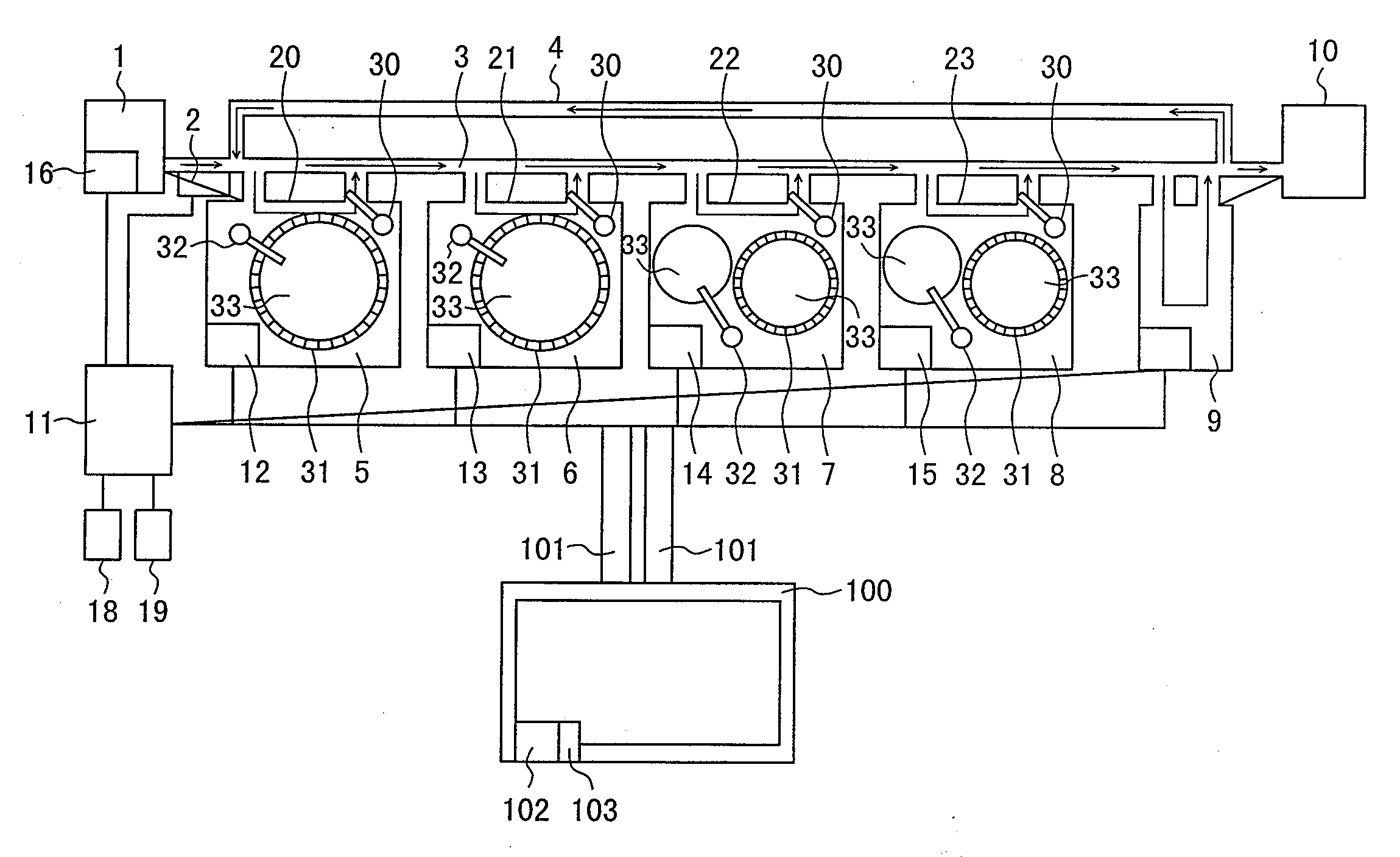
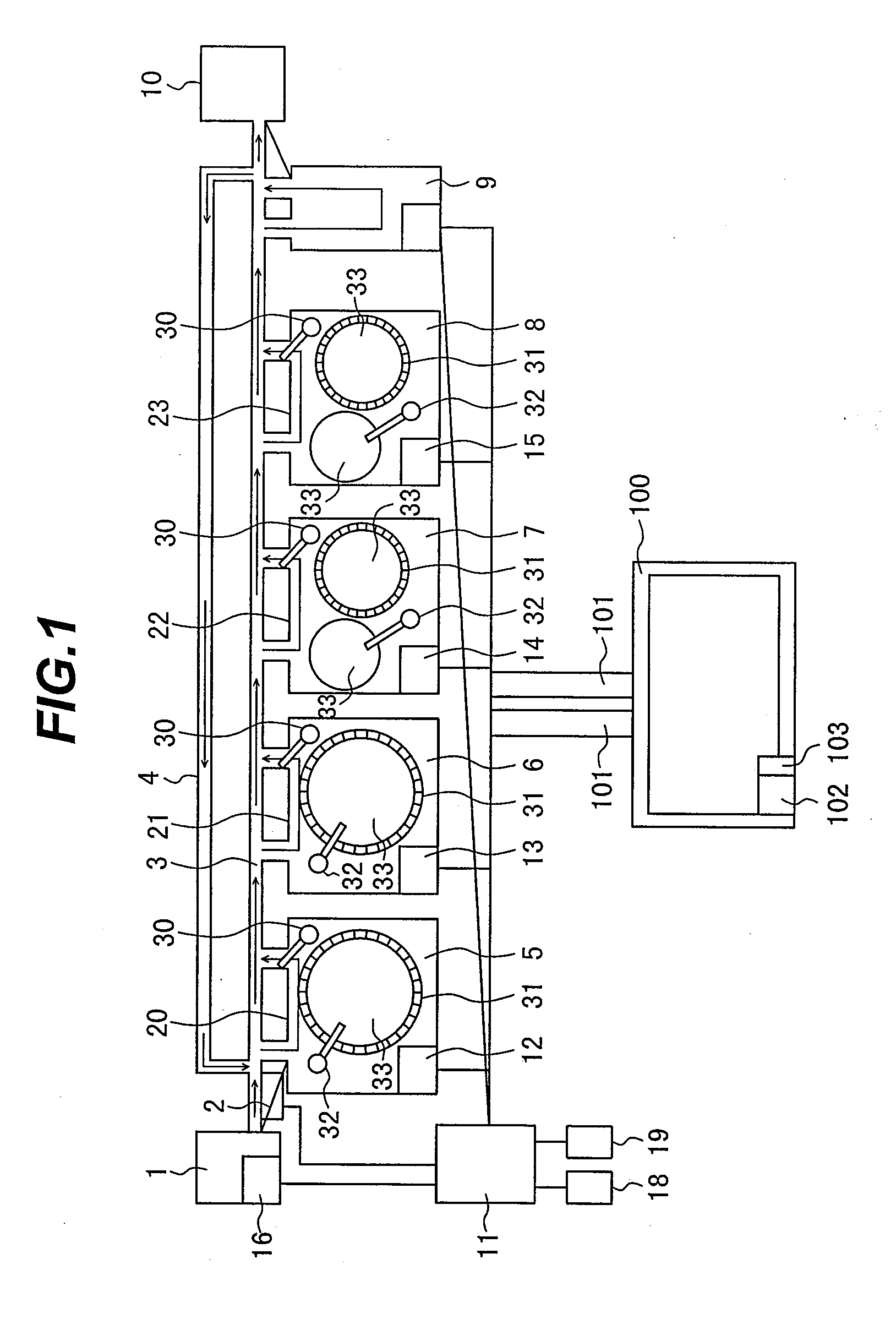
Automatic analyzer and method for using the same
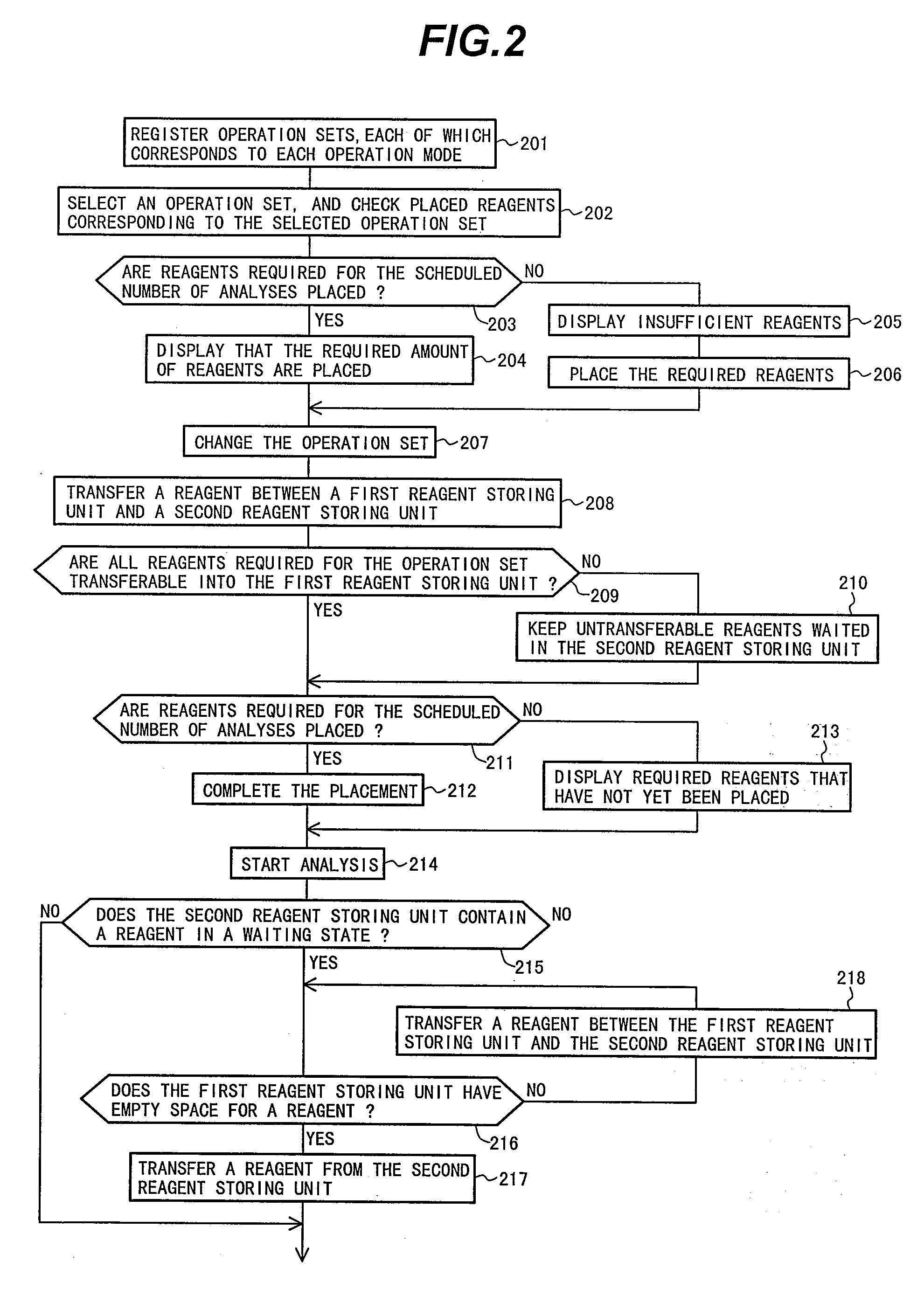
ActiveUS20090035867A1Reduce loadReducing a user's workloadMaterial analysis by optical meansBiological testingAutomated analyzerOperation mode
Disclosed herein is an automatic analyzer that is capable of reducing a user's workload required when a reagent is placed, and thereby facilitating change of the operation mode of the automatic analyzer.An automatic analyzer comprises: a reaction unit including a plurality of vessels; a first reagent storing unit that is capable of storing a plurality of reagent cassettes; a sample dispenser for dispensing a sample into the reaction unit; a reagent dispenser for dispensing a reagent corresponding to an analysis item from the first reagent storing unit into the reaction unit; a second reagent storing unit that is capable of storing a plurality of reagent cassettes; and reagent cassette transfer means that is capable of transferring a reagent between the first reagent storing unit and the second reagent storing unit, the automatic analyzer further comprising reagent selection means for selecting a reagent to be used for analysis operation based an operation set, wherein the operation set specifies a combination of an analysis item and the scheduled number of analyses corresponding to the analysis item.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
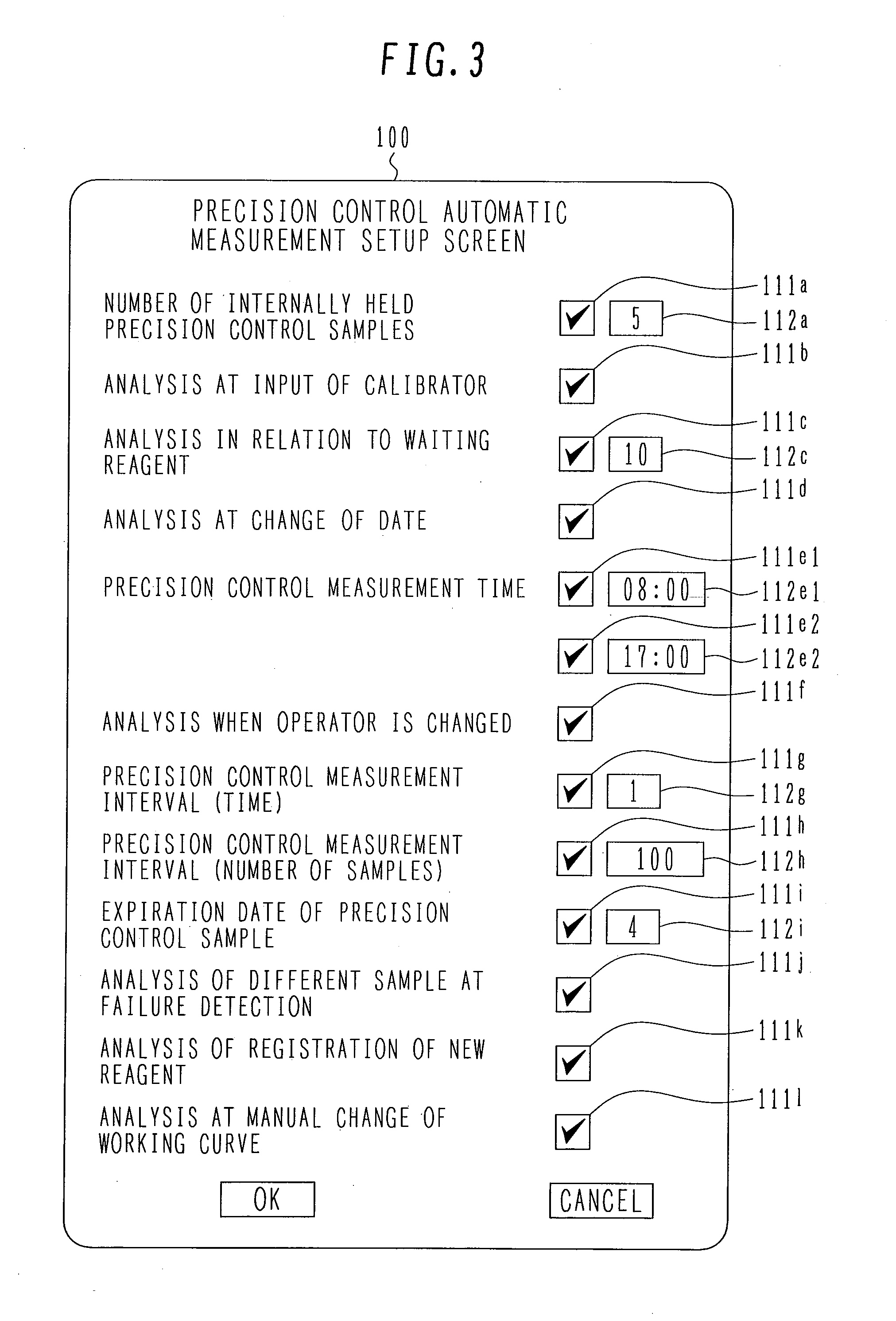
Automatic analyzer
InactiveUS20080219887A1Avoid analysisEasy to controlSamplingMaterial analysis by optical meansAutomated analyzerMeasurement precision
An automatic analyzer is capable of performing analysis of a precision control sample in response to an external factor to alleviate the burden on the operator and surely performing precision control at appropriate timing at which precision control must be performed, thereby allowing automatic maintenance of the measurement precision. Analysis of a precision control sample is performed by creating an analysis request for the internally held precision control sample and then transferring the precision control sample in response to an external factor occurring, for example, when a calibrator is inputted in the analyzer, the number of remaining reagents under analysis satisfies a predetermined condition (becomes zero or falls below a specified value), the date changes, a specified time runs out, the operator is changed, the number of analyzed samples exceeds a specified value, a specified time period has elapsed, a new reagent is registered, a measurement failure is detected, etc.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
System and Method for Incubating the Contents of A Reaction Receptacle
InactiveUS20080089818A1Efficient and high through-put operationEfficient comprehensive utilizationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusIsolation proceduresTemperature control
An automated analyzer for performing multiple diagnostic assays simultaneously includes multiple stations, or modules, in which discrete aspects of the assay are performed on fluid samples contained in reaction receptacles. The analyzer includes stations for automatically preparing a specimen sample, incubating the sample at prescribed temperatures for prescribed periods, performing an analyte isolation procedure, and ascertaining the presence of a target analyte. An automated receptacle transporting system moves the reaction receptacles from one station to the next. The analyzer further includes devices for carrying a plurality of specimen tubes and disposable pipette tips in a machine-accessible manner, a device for agitating containers of target capture reagents comprising suspensions of solid support material and for presenting the containers for machine access thereto, and a device for holding containers of reagents in a temperature controlled environment and presenting the containers for machine access thereto. A method for performing an automated diagnostic assay includes an automated process for isolating and amplifying a target analyte. The process is performed by automatically moving each of a plurality of reaction receptacles containing a solid support material and a fluid sample between stations for incubating the contents of the reaction receptacle and for separating the target analyte bound to the solid support from the fluid sample. An amplification reagent is added to the separated analyte after the analyte separation step and before a final incubation step.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Method of determining substrate contained in hemoglobin-containing sample
InactiveUS20070154976A1Accurate measurementReduce distractionsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingActive agentSuccinic acid
The present invention provides a convenient, efficient method for determining a substrate contained in a hemoglobin-containing sample and a reagent therefor, which can be employed for a variety of automatic analyzers while reducing interference of hemoglobin contained in the sample. A method for determining a substrate contained in a hemoglobin-containing sample through reaction of an oxidase with the substrate and optical measurement of the produced hydrogen peroxide by use of a peroxidase and an oxidizable color producing reagent, characterized in that the hemoglobin-containing sample is treated with an anionic surfactant selected from among a polyoxyethylene alkyl ether sulfate salt, a polyoxyethylene alkylphenyl ether sulfate salt, a polyoxyethylene alkyl ether phosphate, a polyoxyethylene alkyl sulfosuccinate, a polyoxyethylene alkyl ether carboxylate salt, a polyoxyethylene alkyl ether sulfonate salt, triethanolamine lauryl sulfate, an alkyl sulfosuccinate, and an alkylphenyl ether sulfonate salt.
Owner:SEKISUI MEDICAL CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com