Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
350 results about "Hematology" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Hematology, also spelled haematology, is the branch of medicine concerned with the study of the cause, prognosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases related to blood. It involves treating diseases that affect the production of blood and its components, such as blood cells, hemoglobin, blood proteins, bone marrow, platelets, blood vessels, spleen, and the mechanism of coagulation. Such diseases might include hemophilia, blood clots, other bleeding disorders and blood cancers such as leukemia, multiple myeloma, and lymphoma. The laboratory work that goes into the study of blood is frequently performed by a medical technologist or medical laboratory scientist.
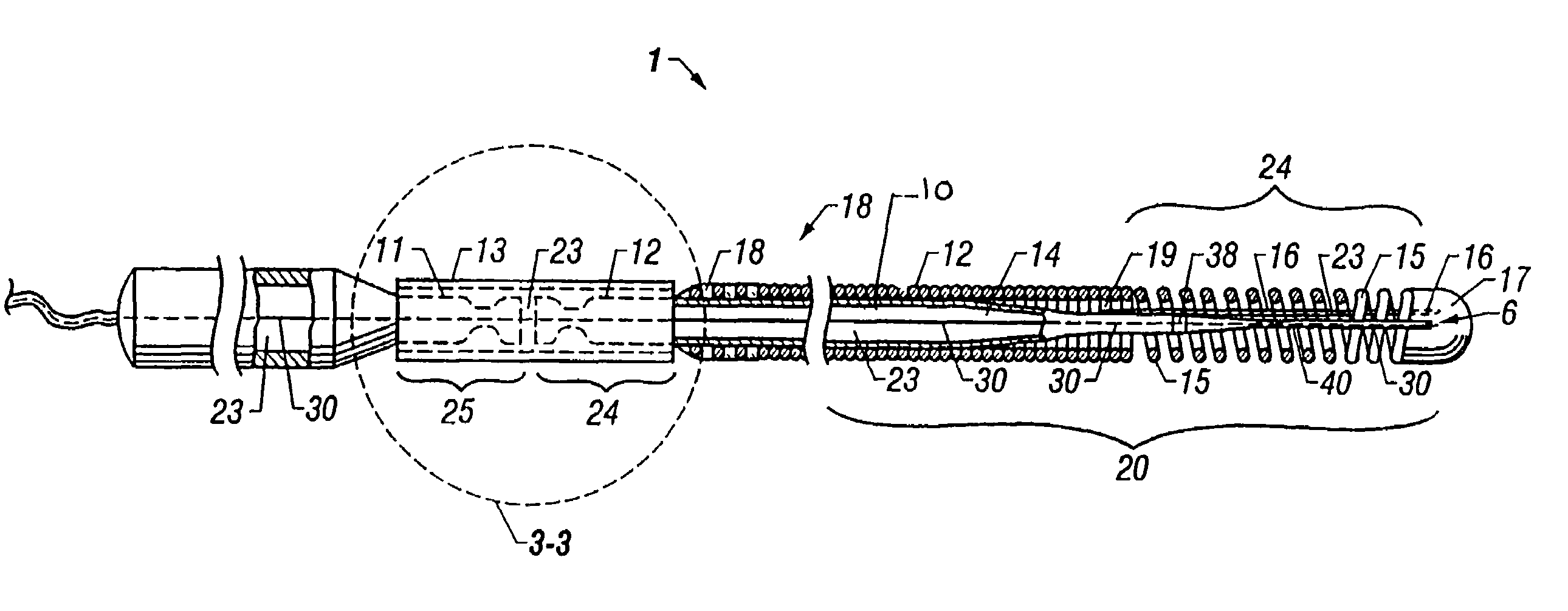
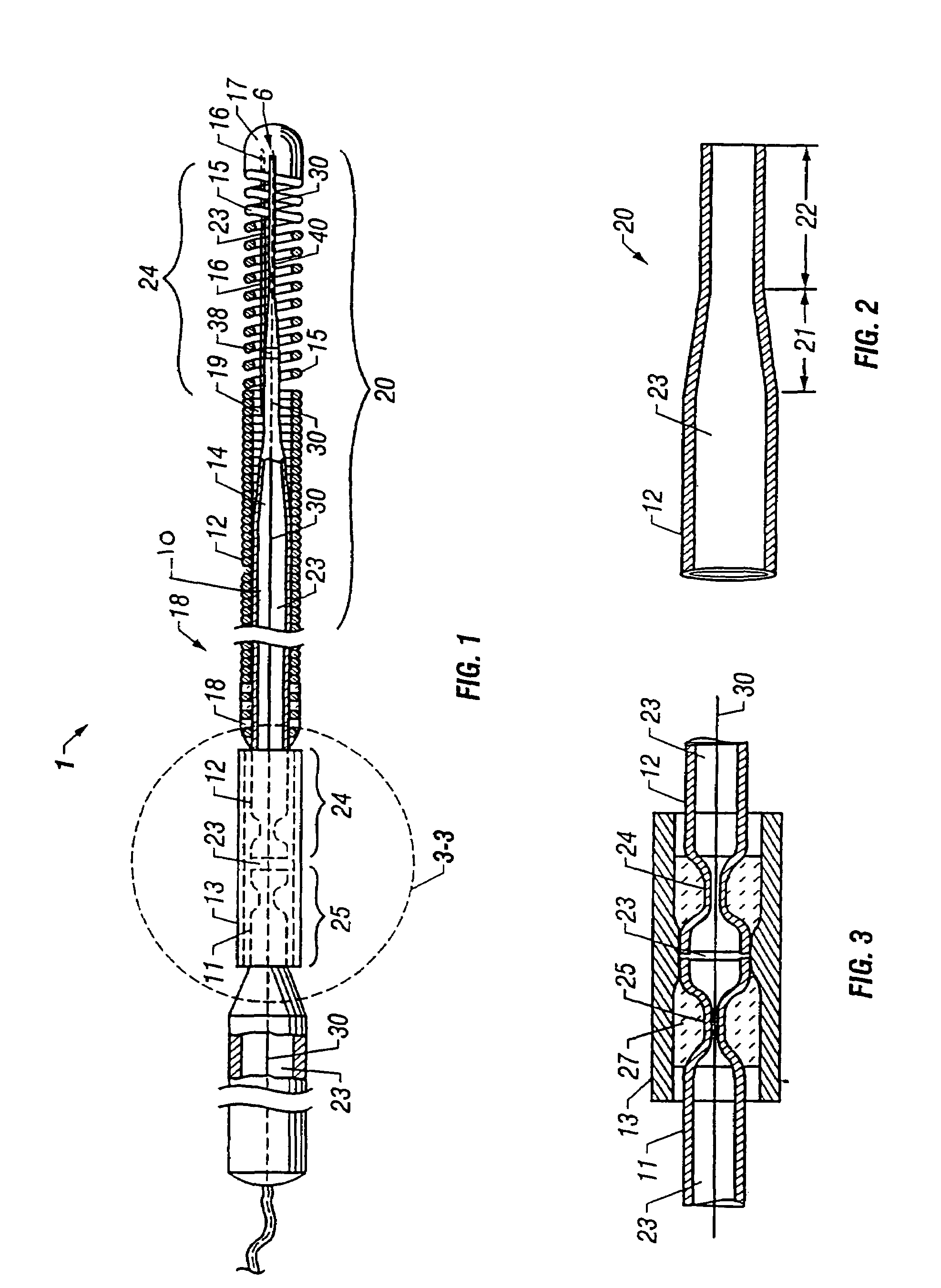
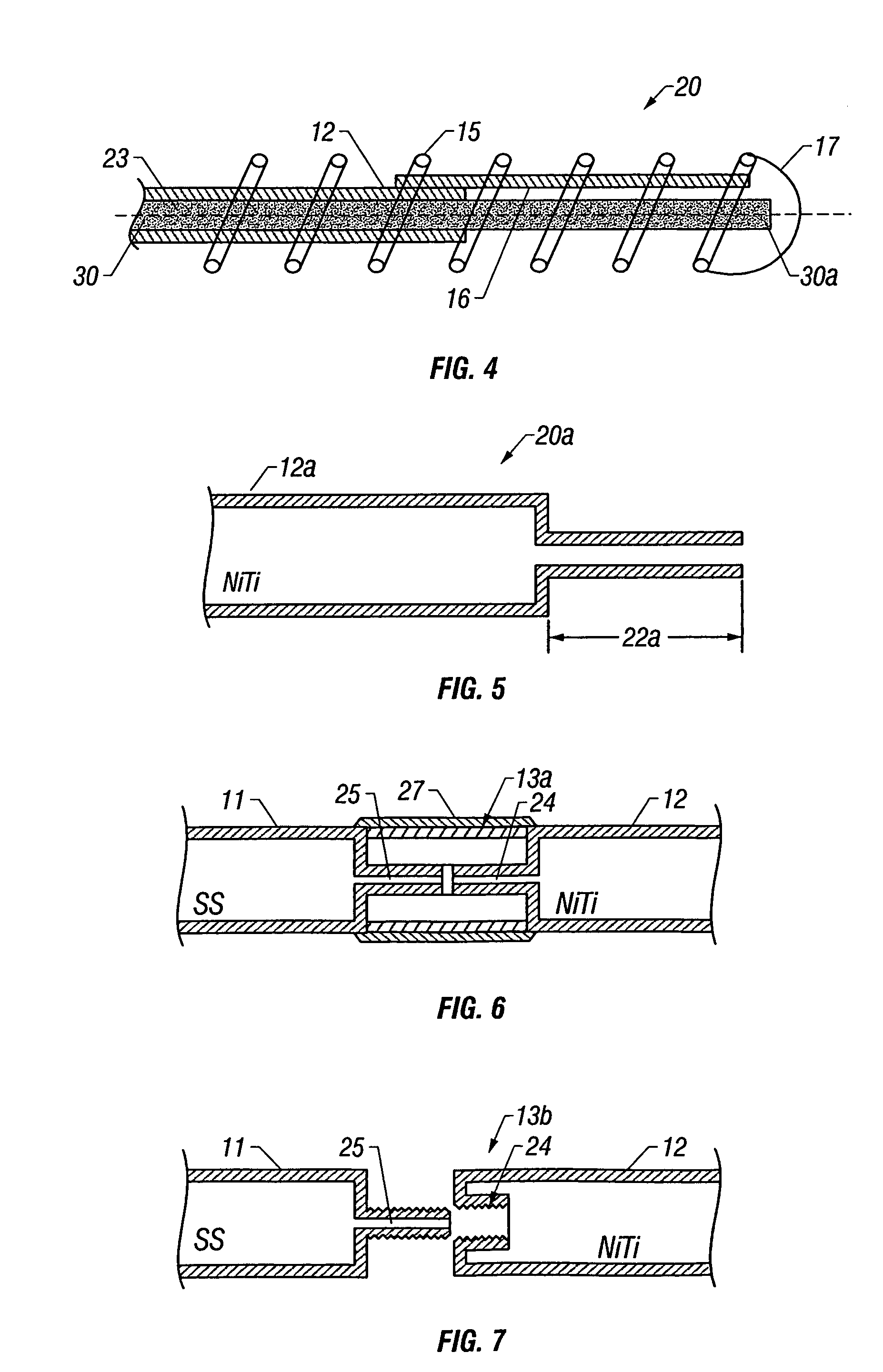
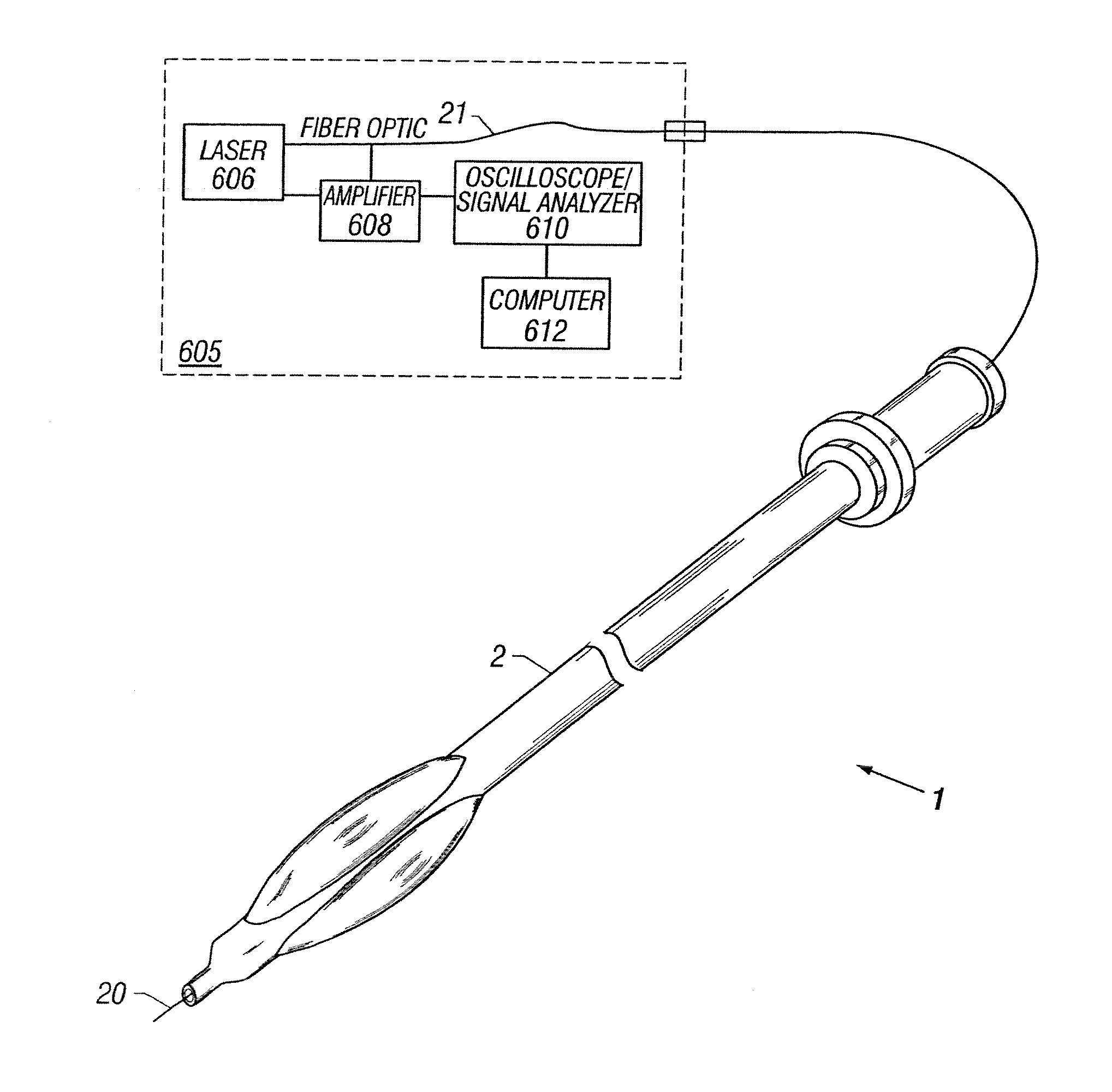
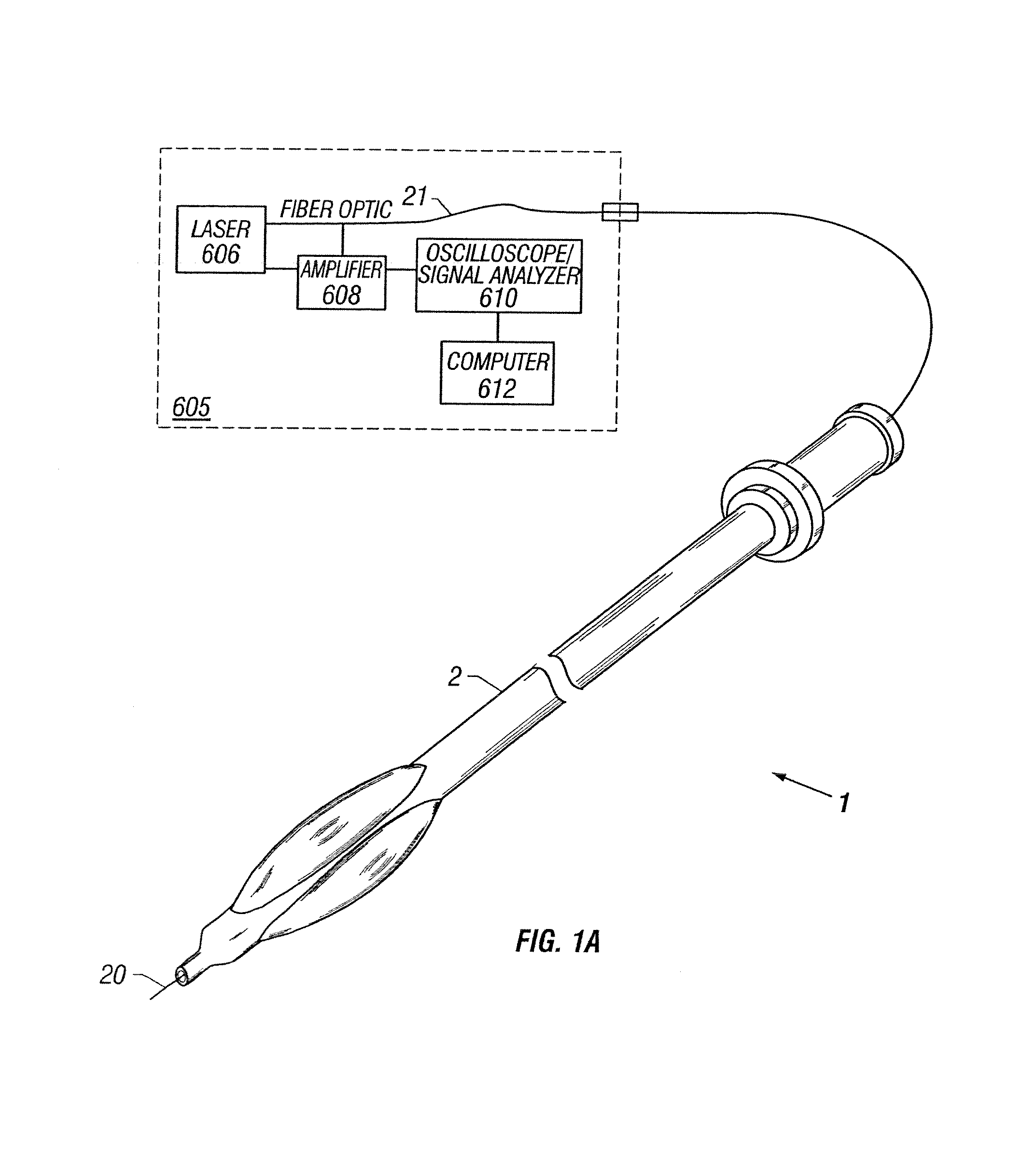
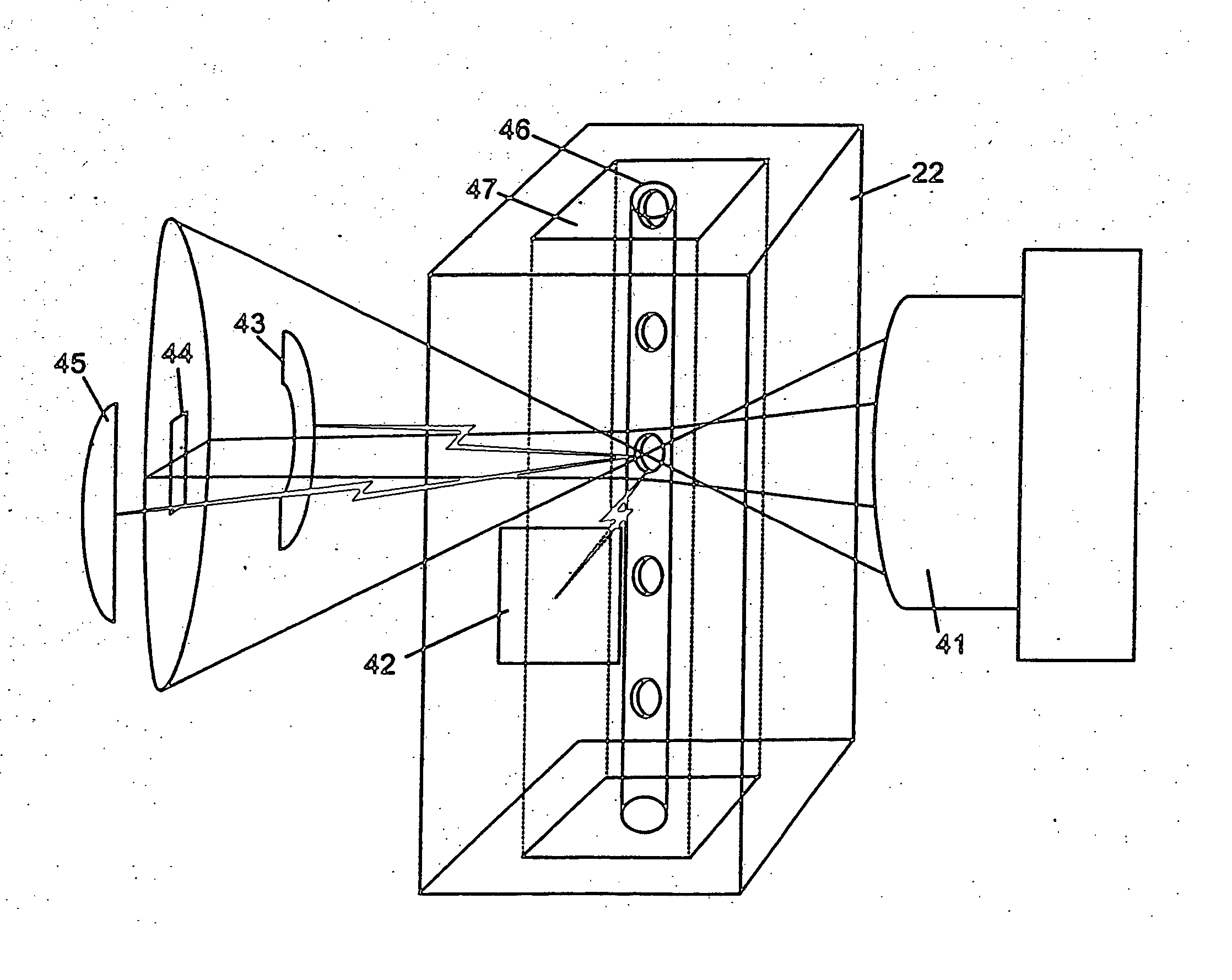
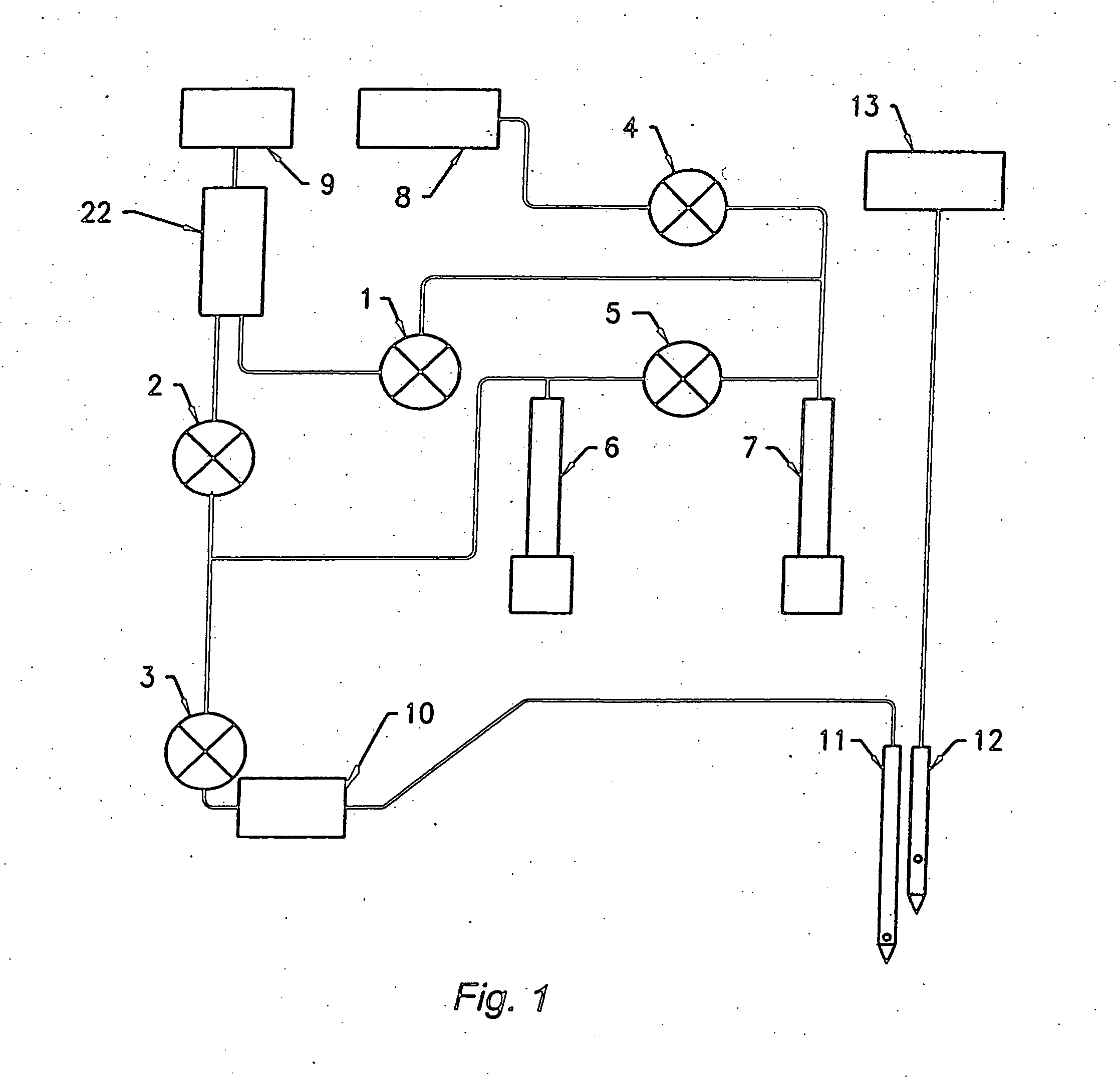
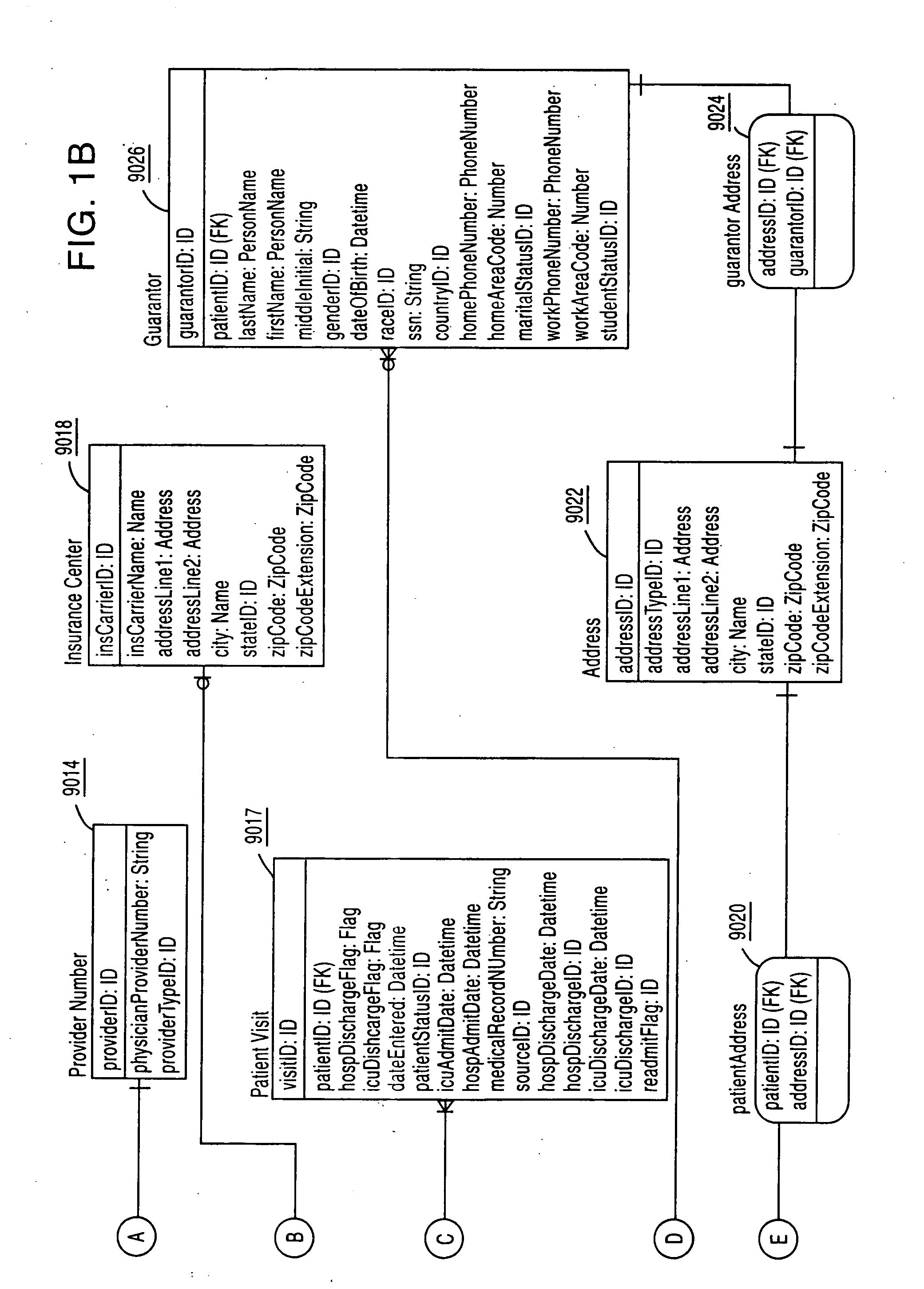
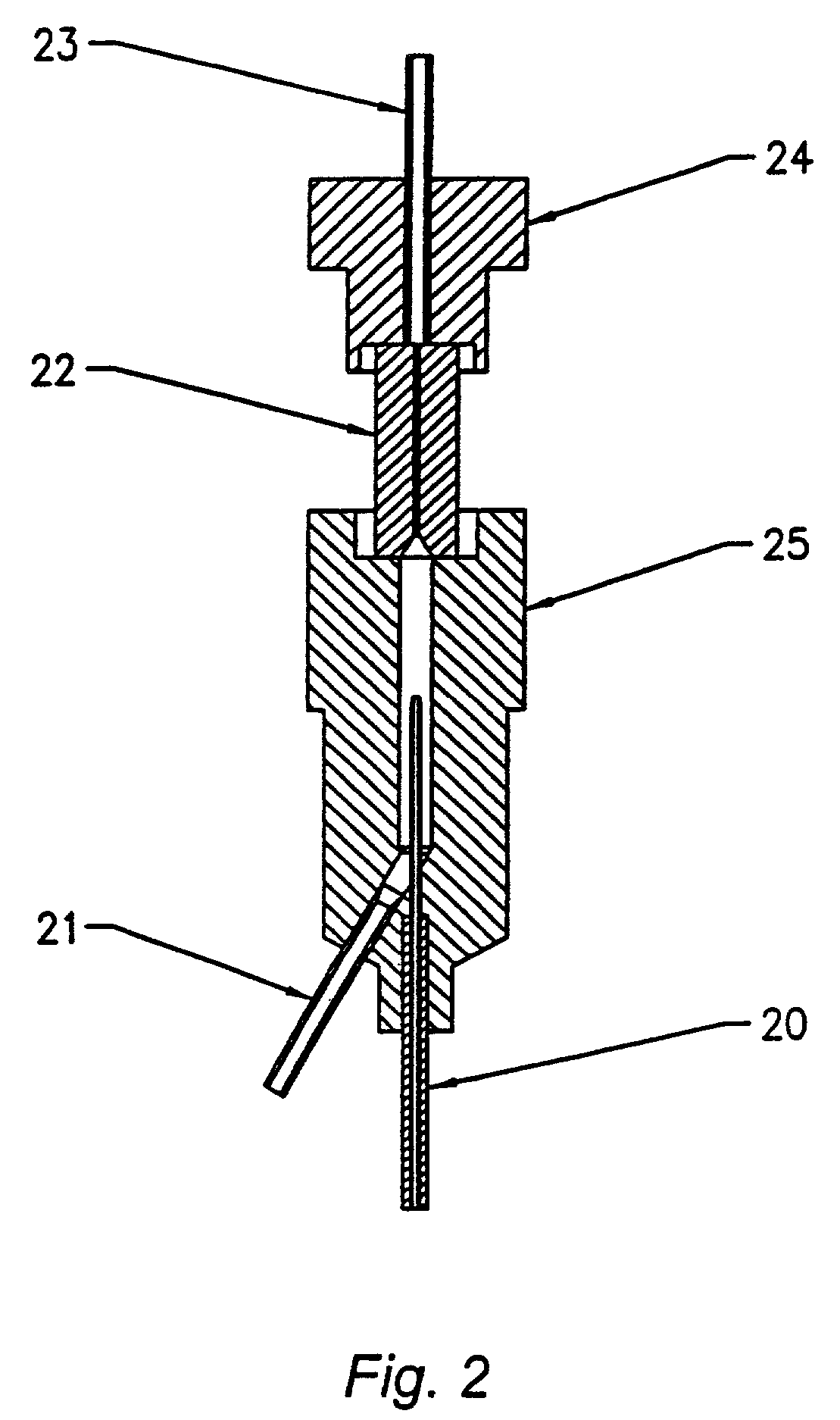
Guidewire with optical fiber
Apparatus and method to perform therapeutic treatment and diagnosis of a patient's vasculature through the use of an intravascular device having an optical fiber disposed therein. In an embodiment of this invention, the apparatus includes a therapeutic guidewire and at least one optical fiber disposed through the therapeutic guidewire, the optical fiber capable of providing diagnostic information before, during, and after the therapeutic treatment. In an embodiment, diagnostic information includes vessel and blood characteristics such as hemodynamic characteristics, hematological parameters related to blood and blood components, and thermal parameters of the vasculature.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
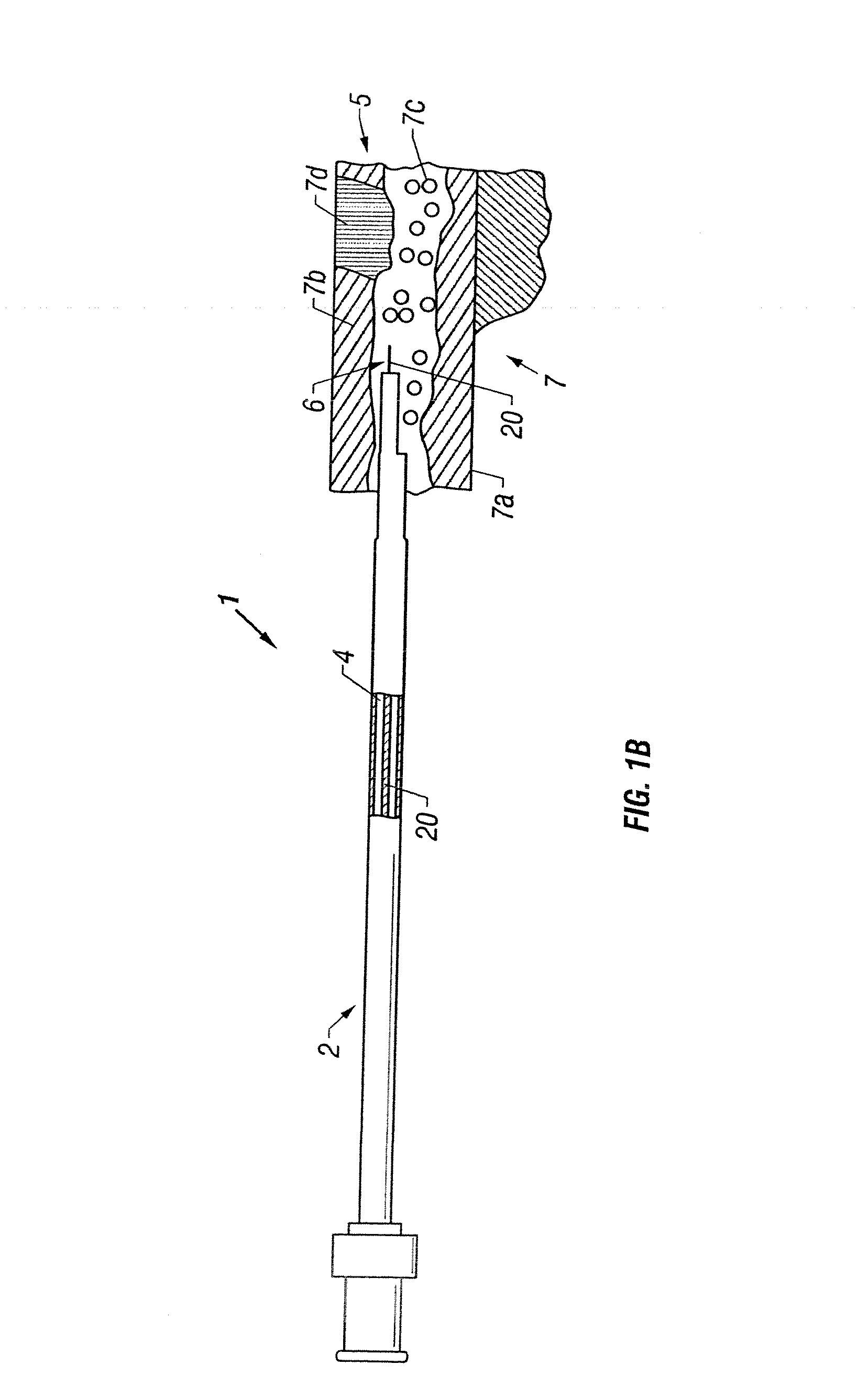
Catheter with optical fiber sensor
An apparatus and method to perform therapeutic treatment and diagnosis of a patient's vasculature through the use of an intravascular device having an optical fiber disposed therein. In an embodiment, the apparatus includes an intravascular device to perform a therapeutic treatment and at least one optical fiber disposed through the intravascular device. The optical fiber is configured to provide diagnostic information before, during, and after the therapeutic treatment. In an embodiment, diagnostic information includes vessel and blood characteristics such as hemodynamic characteristics, hematological parameters related to blood and blood components, and thermal parameters of the vasculature.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
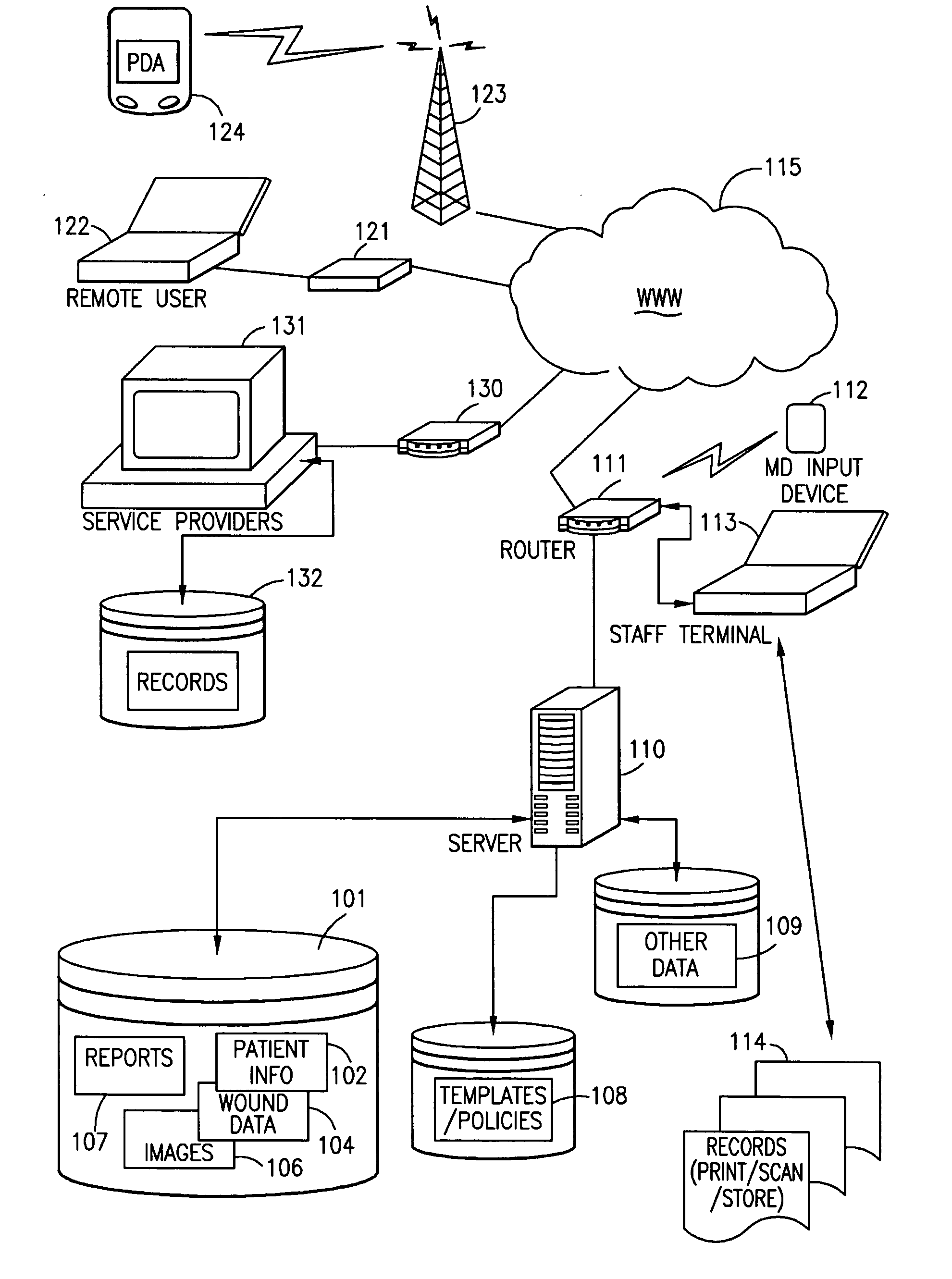
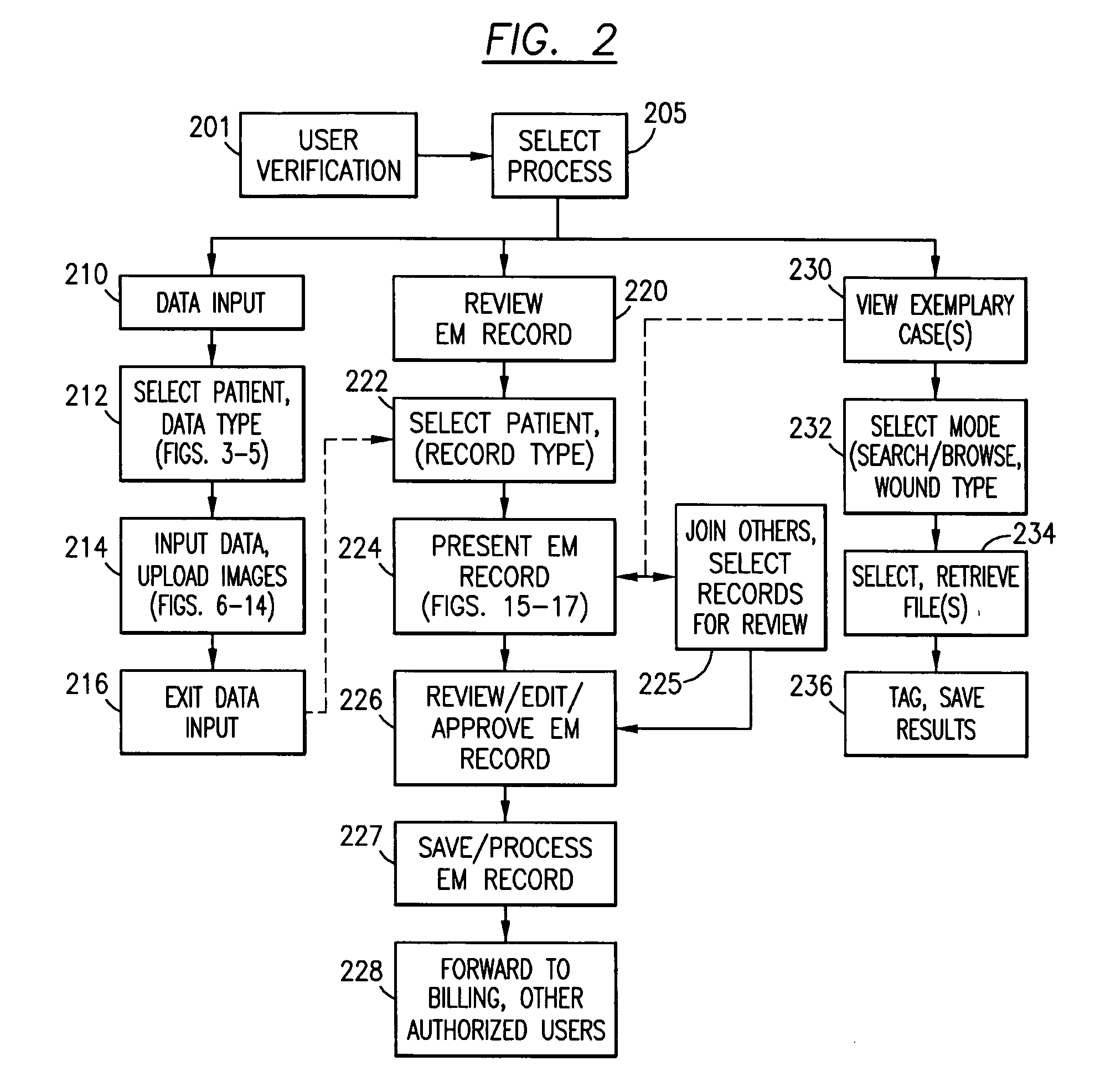
Wound electronic medical record system
InactiveUS20060116904A1Easy to learnEliminate the problemMedical data miningMedical report generationMedical recordMedicine.hematology
Methods and apparatus for storing and reviewing wound data are shown using a digital datasheet, or wound electronic medical record (WEMR). The WEMR is preferably presented via a single page containing all data that should be considered by a wound healing provider, as predetermined by protocol. This includes, but is not limited to, fields for: a digital photograph of the wound; a graph of the wound healing rate (length, width, depth and area over time); wound and other treatments including current systemic medications, along with a patient identifier and review / approval indicator. This may also include hematology and chemistry laboratory data; radiology and pathology images along with their associated reports; ambulation status and other history; and microbiology data including sensitivities. The WEMR is implemented via a wound database system, which includes templates and policies for rapid report generation and tools for protocol mapping. A particular WEMR page may be designed for electronic or paper review and approval by a treating physician, thus permitting comprehensive but efficient review of all relevant wound data, whether for a personal or remote consult, real-time or otherwise. When teaching or doing studies, patient identifier information can be masked while still enabling review of large but detailed data sets for a variety of wound and patient criteria.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
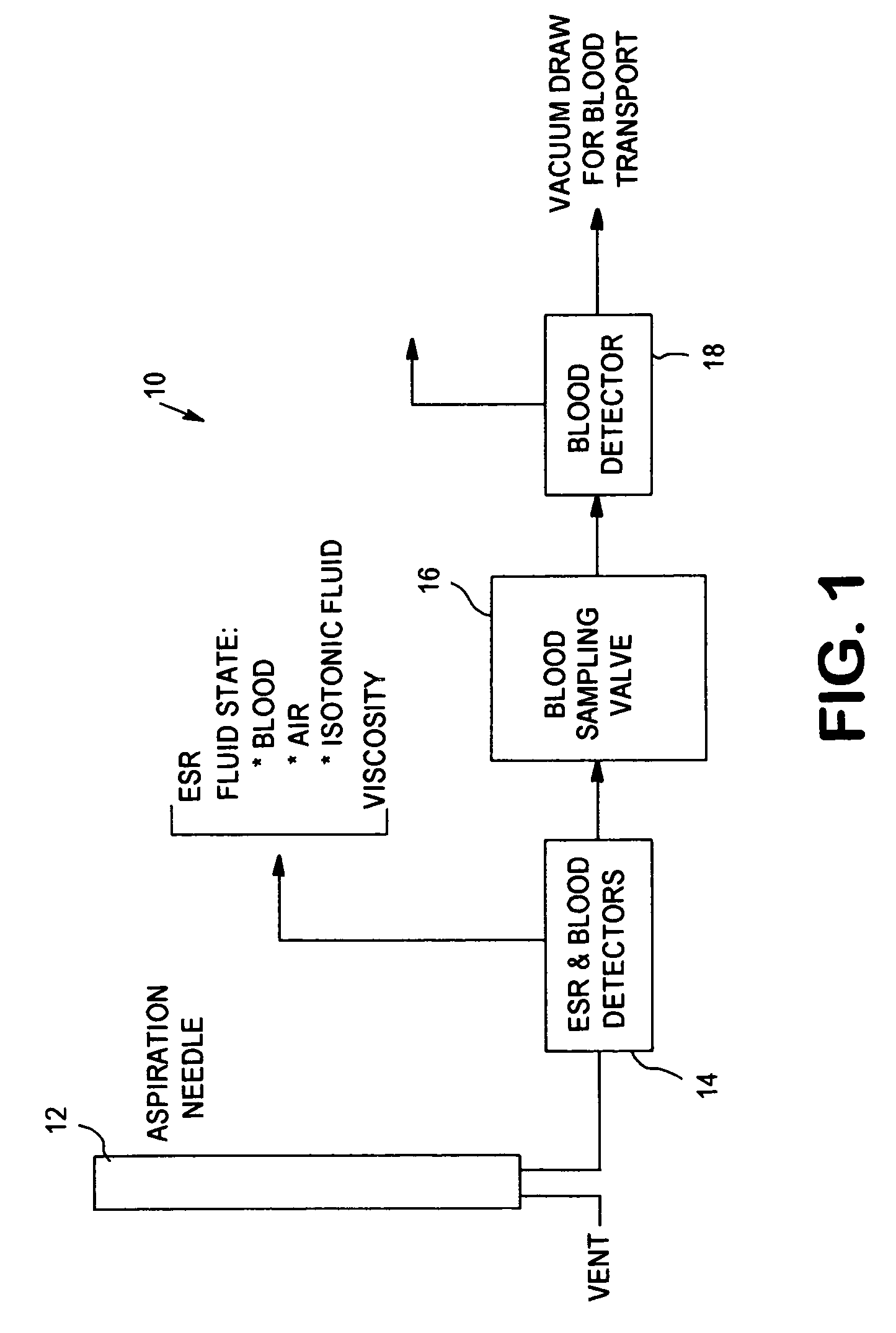
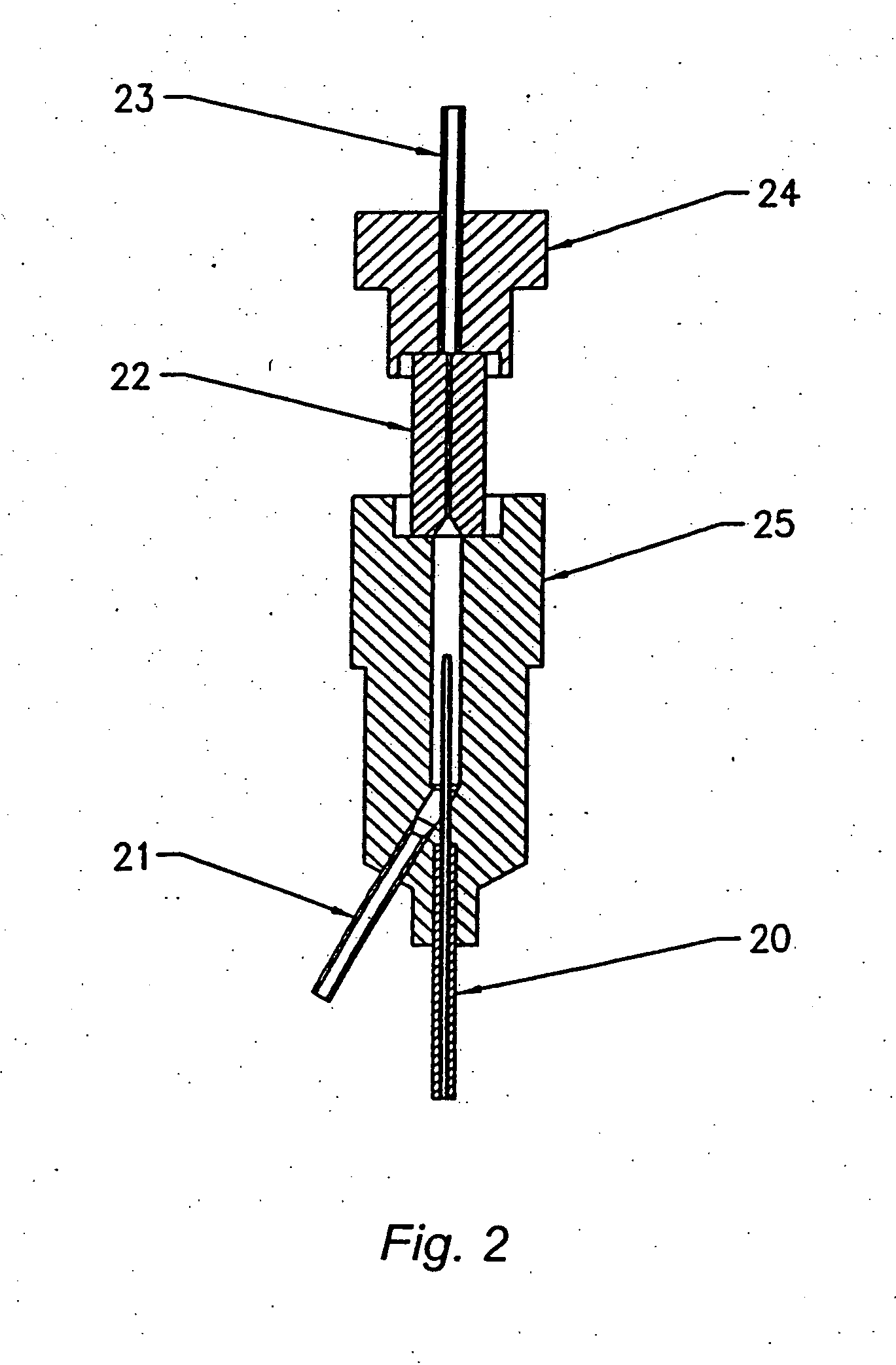
Apparatus and method for analyzing a liquid in a capillary tube of a hematology instrument
InactiveUS7207939B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesBlood capillaryHematology
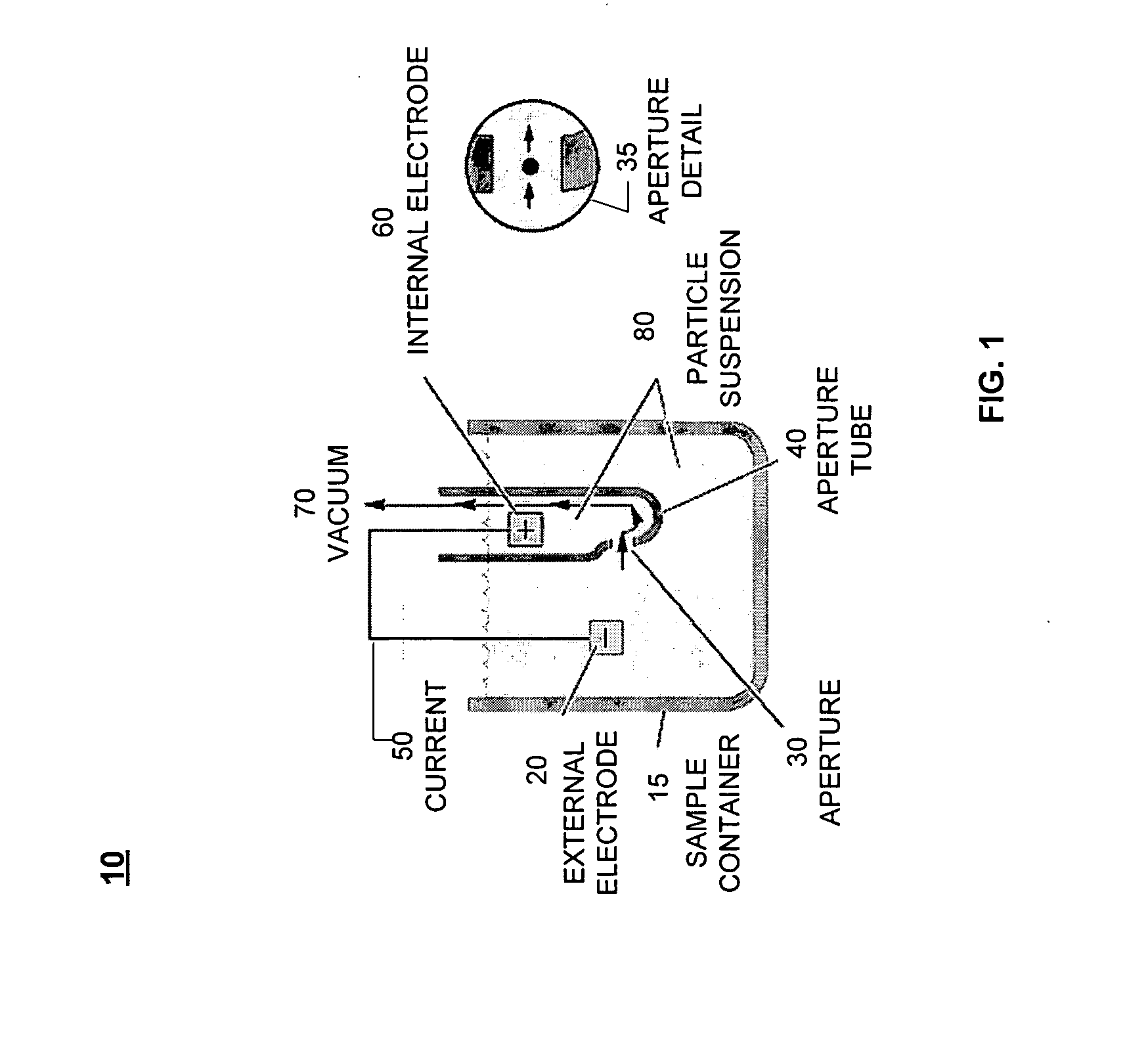
An apparatus and method for determining the density and fluid-type of a fluid flowing in a capillary tube, the velocity and viscosity of a blood sample flowing in a capillary tube, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) of a blood sample after flow has been brought to an abrupt stop in a capillary tube, and / or the zeta sedimentation rate (ZSR) of a blood sample after flow has been brought to an abrupt stop in a capillary tube. These measurements are accomplished by directing a waveform pulse, such as an ultrasound pulse, at a pre-determined frequency transversely across the capillary tube and sample fluid, and by determining the flight of time of the pulse through the capillary tube and sample fluid and / or the Doppler shift of the echo signals reflecting off cells moving forwardly or transversely within a flowing, or stationary, blood sample.
Owner:COULTER INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
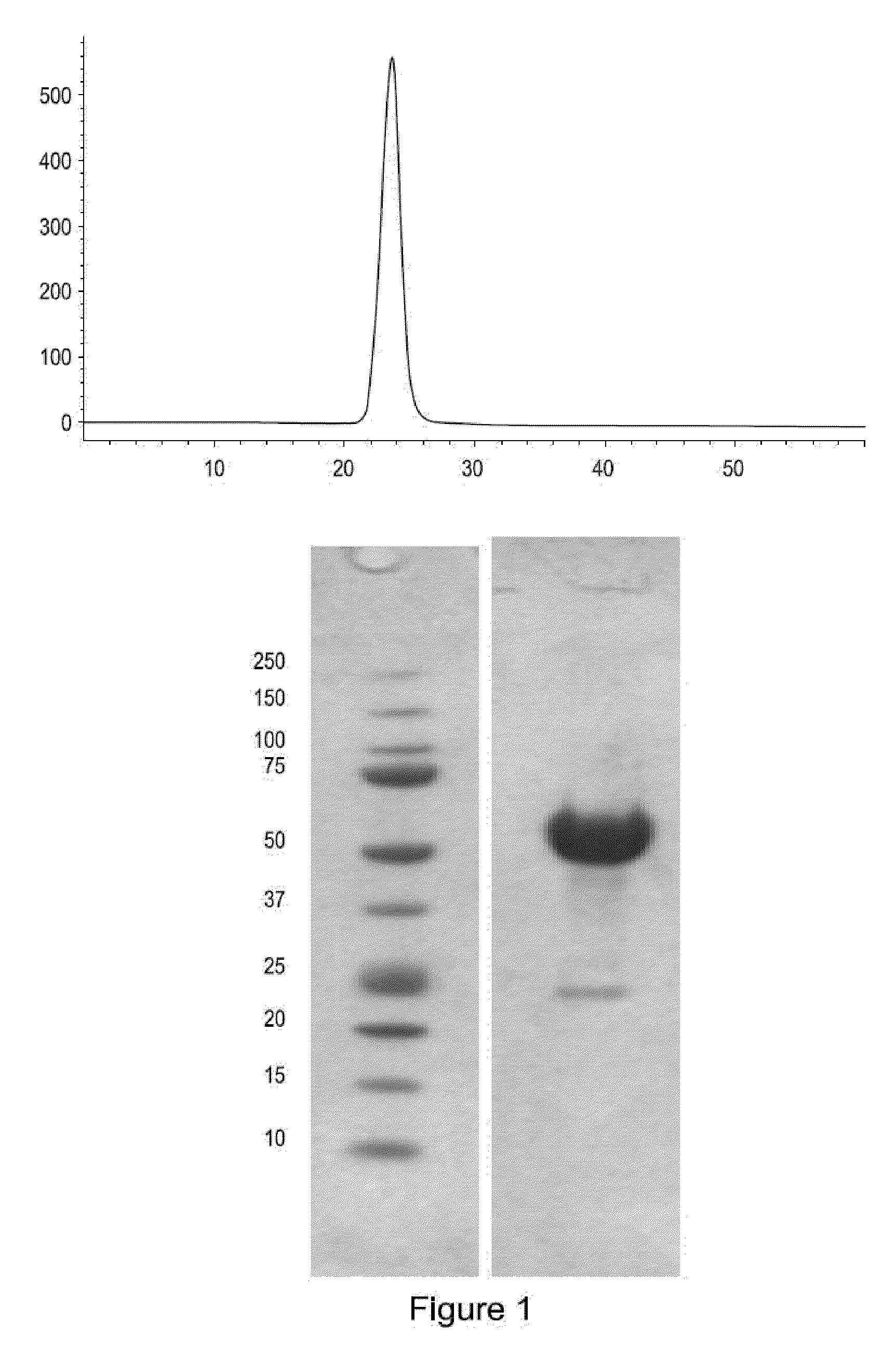
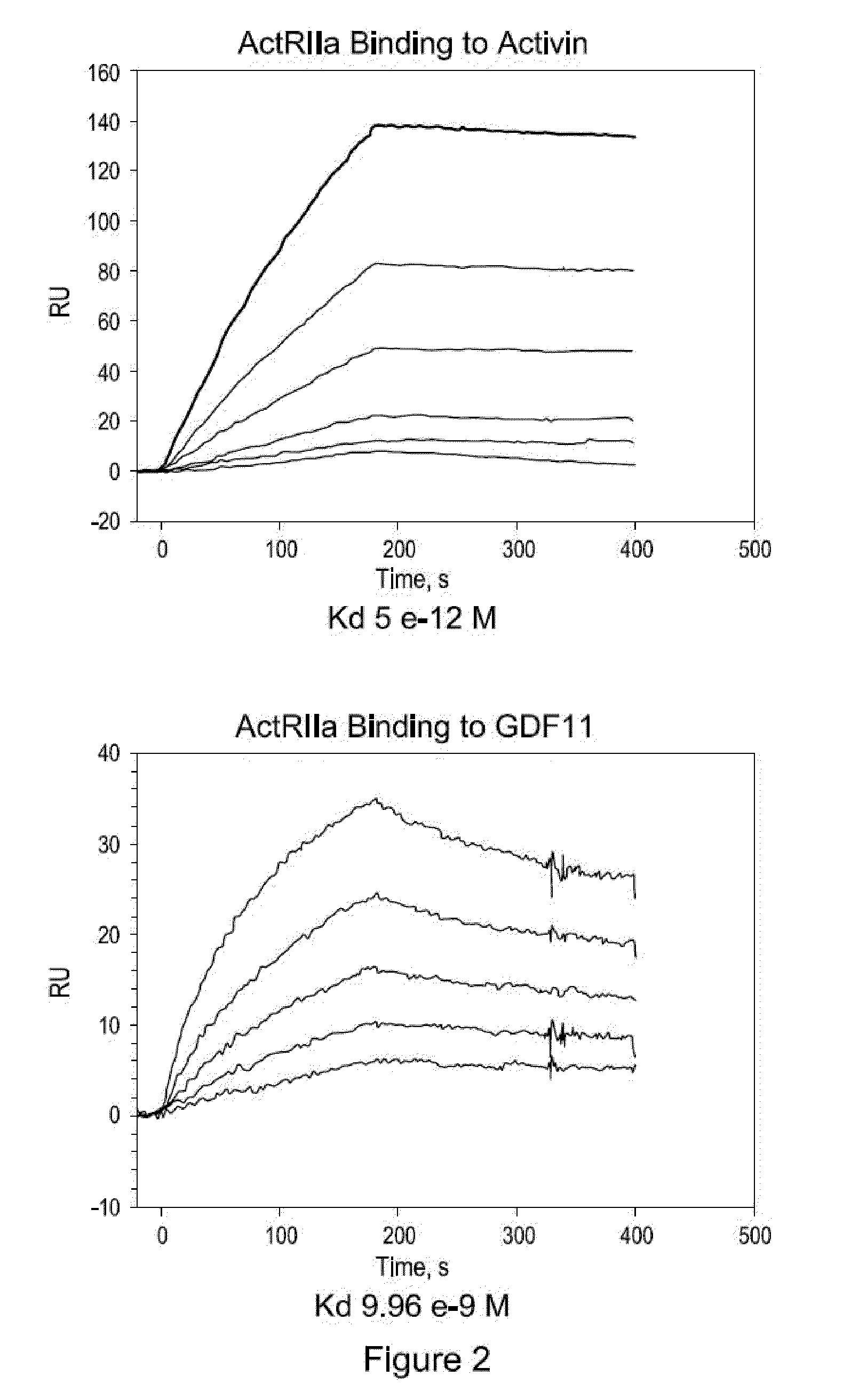
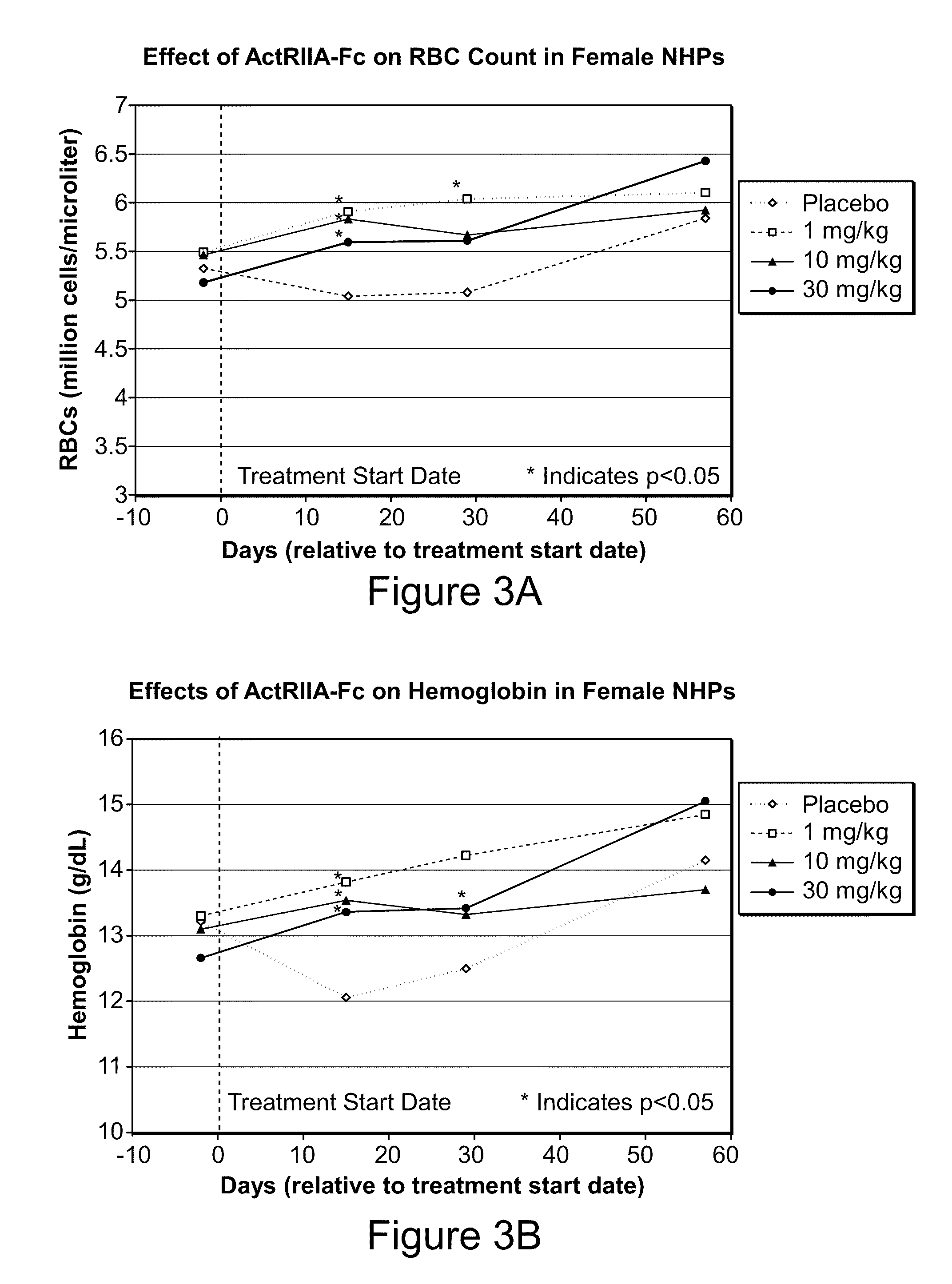
Methods for dosing an activin-actriia antagonist and monitoring of treated patients
InactiveUS20100015144A1Undesired effectImprove the level ofPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHematologyAntagonist
In certain aspects, the present invention provides methods for dosing a patient with an activin-ActRIIa antagonist and methods for managing patients treated with an activin-ActRIIa anatagonist. In certain aspects, the methods involve measuring one or more hematologic parameters in a patient.
Owner:ACCELERON PHARMA INC
Flow-cytometry-based hematology system
InactiveUS20060203226A1Reduce wasteLow costWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationMedicine.hematologyFlow cell
Owner:IDEXX LABORATORIES
System and method for standardizing care in a hospital environment
InactiveUS20050159987A1Minimizing adverse eventMinimizing complicationAlarmsSpecial data processing applicationsMedicine.hematologyGuideline
A system and method for standardizing care in a hospital environment. Information concerning the latest care and practice standards for a given condition is provided to a decision support module. The decision support module comprises decision support algorithms that reflect a standardize guideline of practice for a particular medical condition. The general categories of cardiovascular, endocrinology, general, gastrointestinal, hematology, infectious diseases, neurology, pharmacology, pulmonary, renal, surgery, toxicology, trauma all have guidelines and practice standards associated with them. Patient data and user input are inputted to the decision support algorithm. The user may be prompted for user input, and an assessment is made of the patient so as provide patient care advice for the patient. Examples of patient care advice are a diagnosis, a method of treatment, and a laboratory protocol.
Owner:VISICU
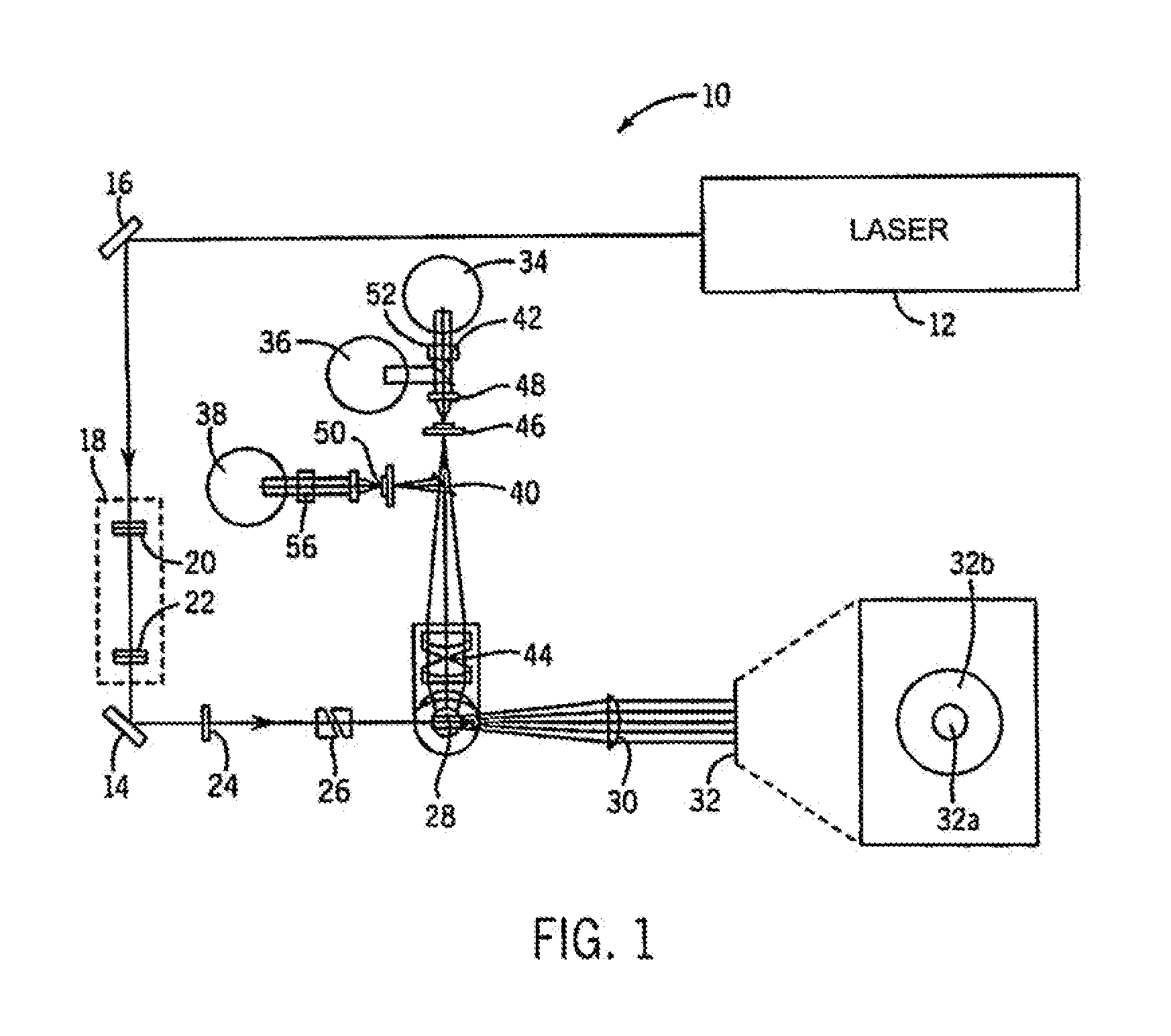
Method and apparatus for performing platelet measurement
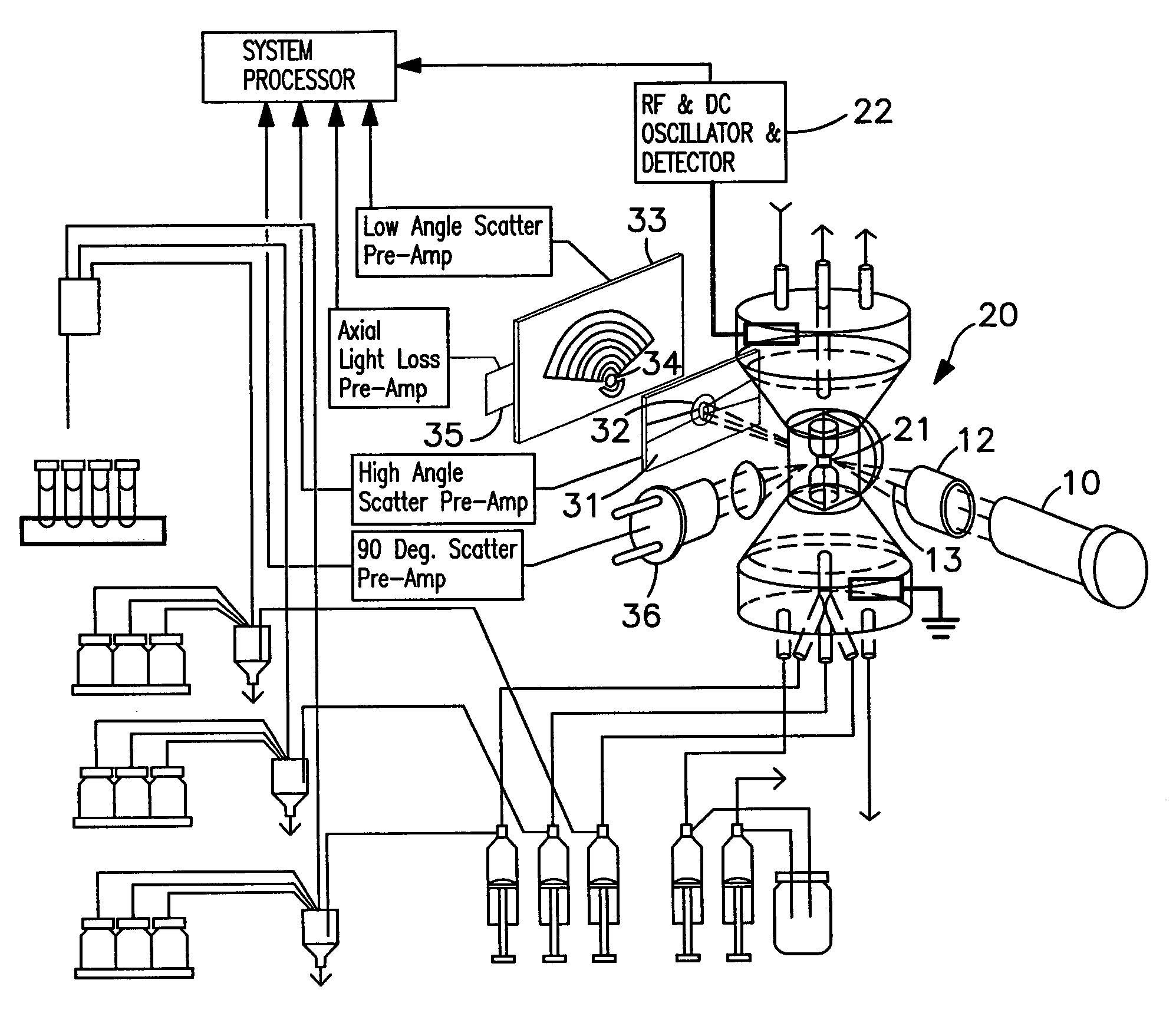
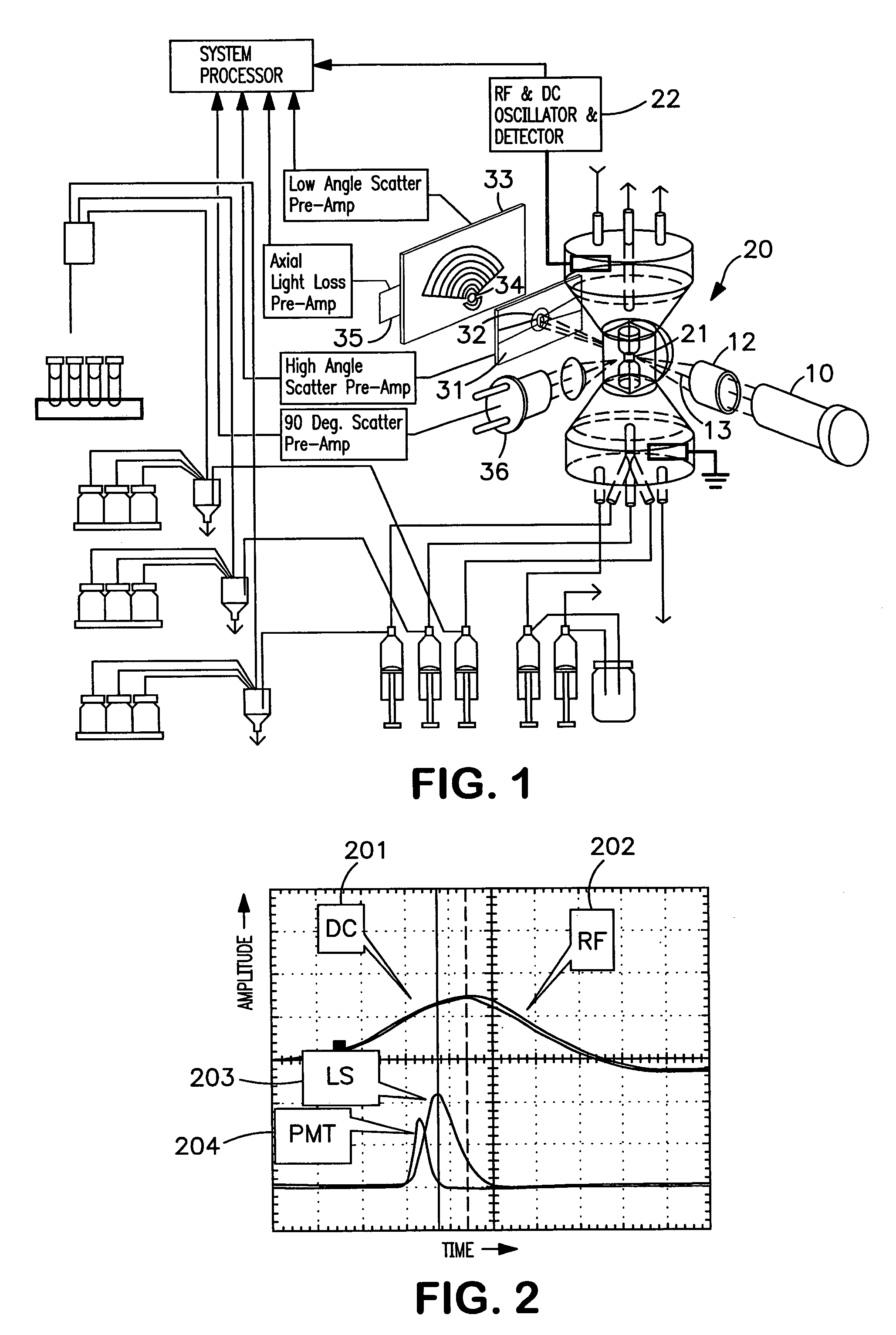
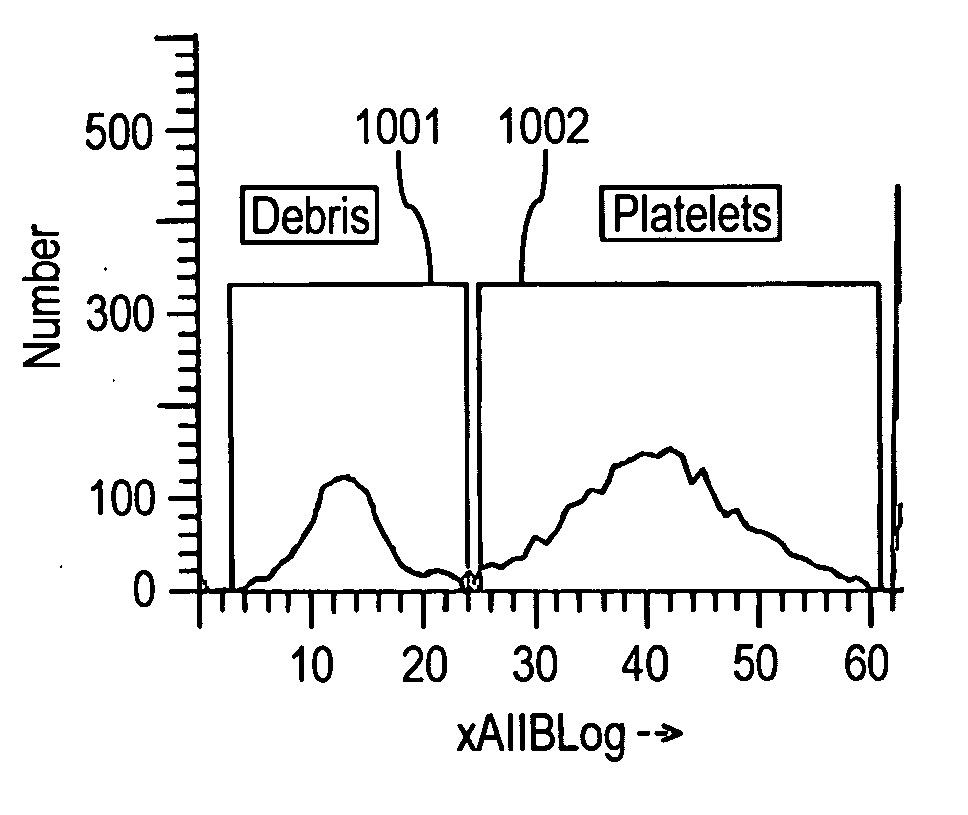
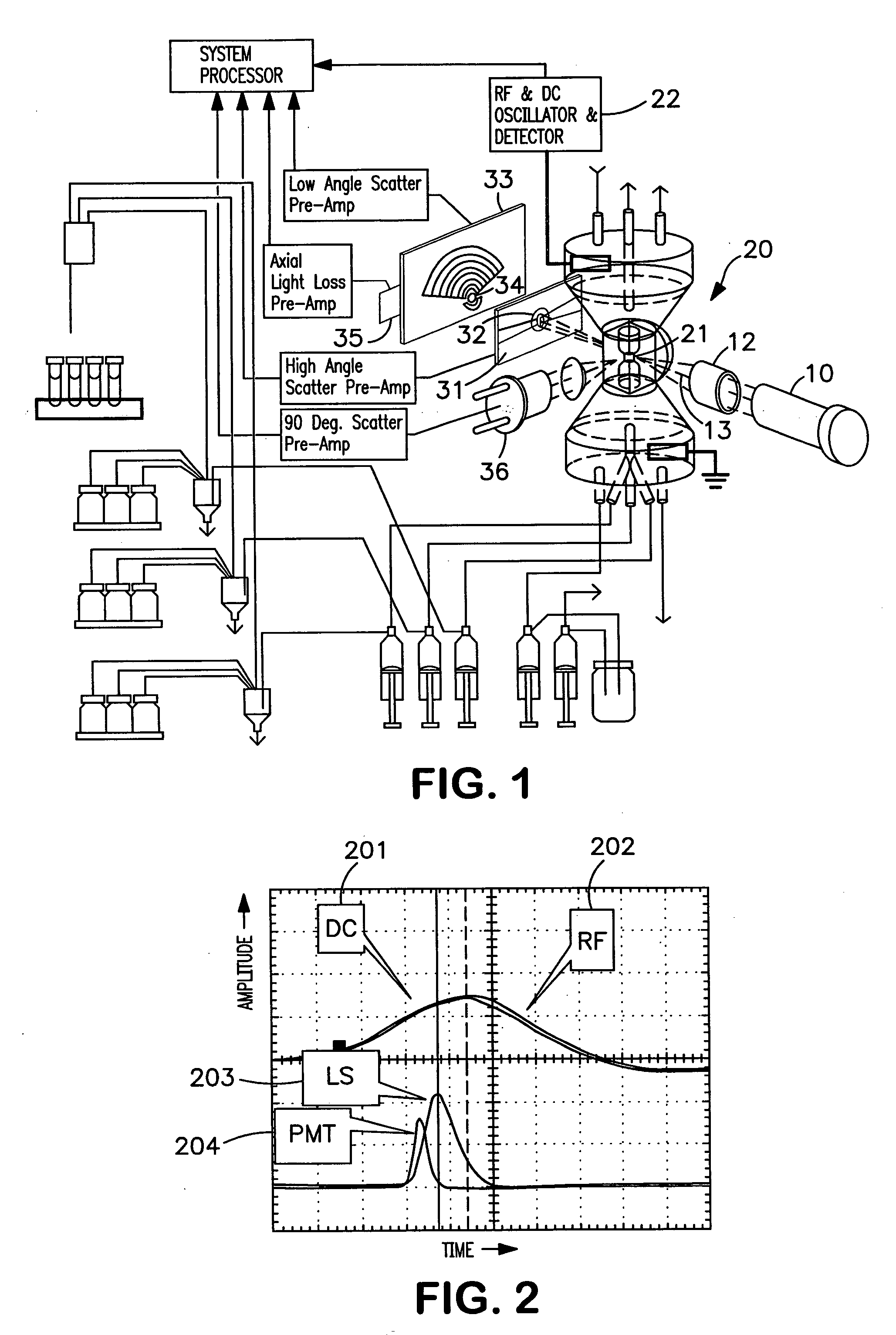
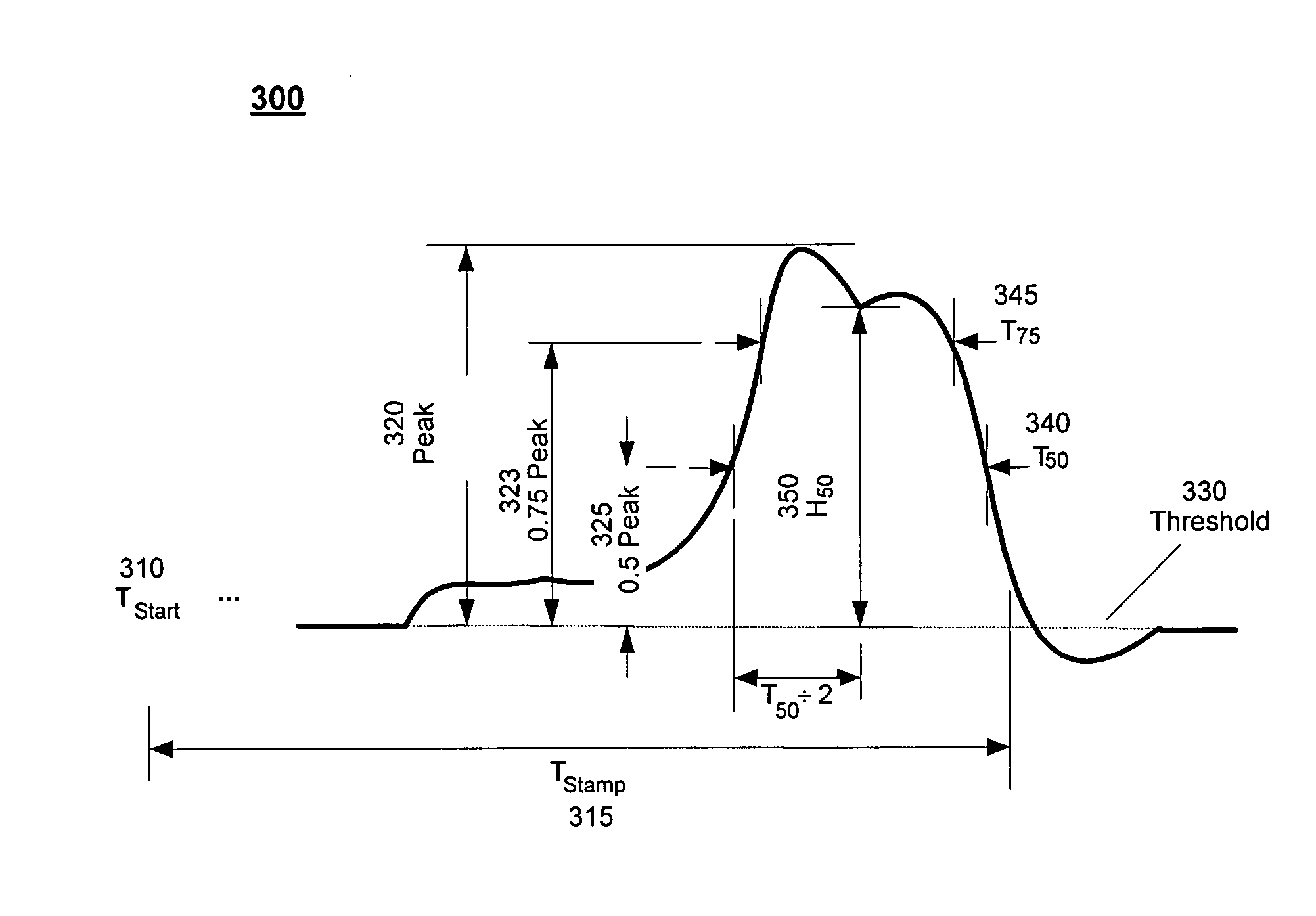
The present invention relates to a hematology instrument system that discriminates platelets from red blood cells, debris and other particles within a blood sample. The instrument system uses an optical trigger and collects data at optical sensor locations relative to a flow cell-illuminating laser beam's optical axis. An axial sensor measures axial light loss due to a particle in the flow cell's illumination aperture. In addition, the instrument system can include an RF unit generates electrical parameters, such as DC and RF parameters, within the flow cell. Blood specimens can be prepared with and without a sphering agent.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
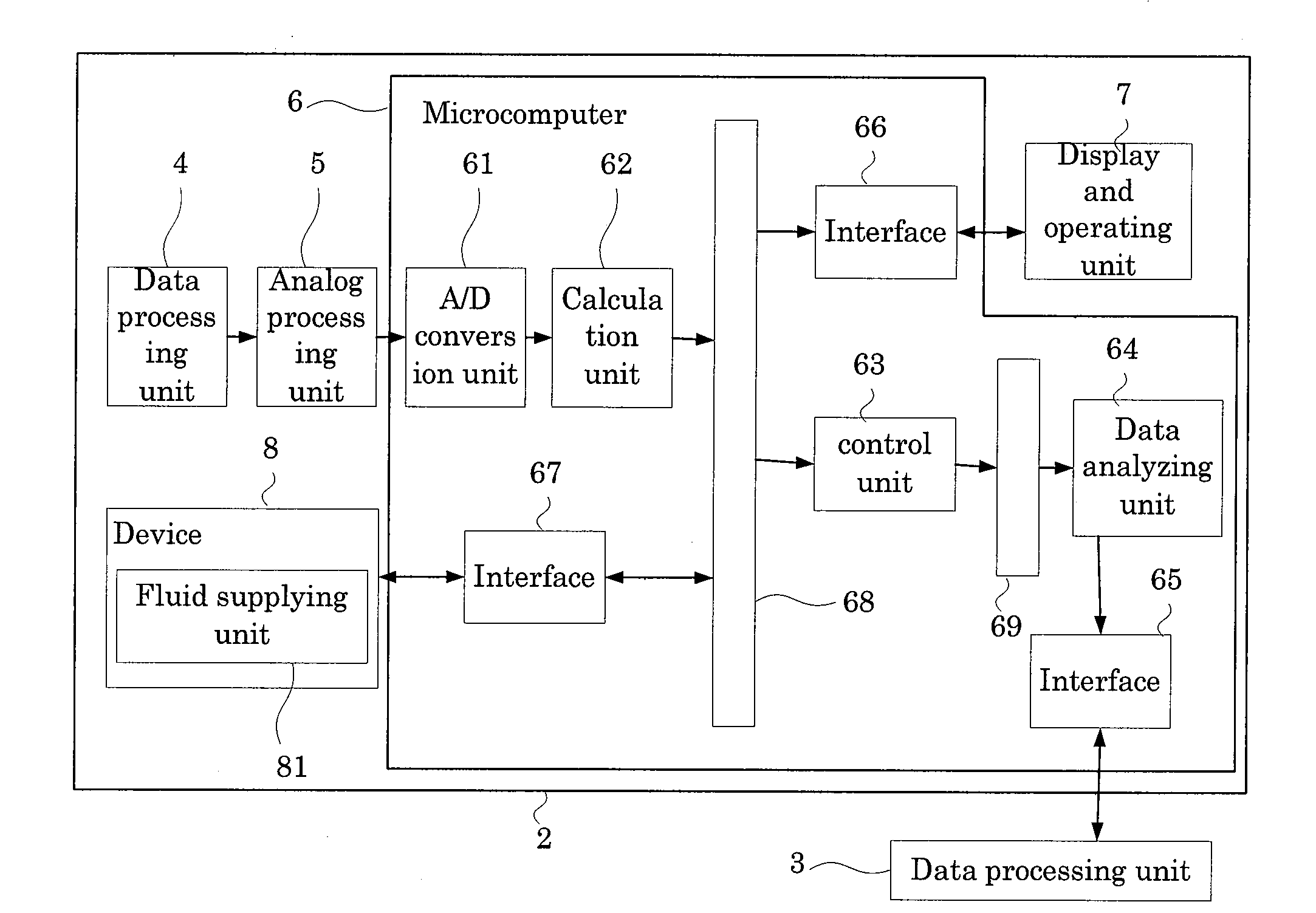
Hematology analyzer, hematology analyzing method, and computer program product
InactiveUS20080268494A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMedicine.hematologyInformation support
A hematology analyzer, obtains red blood cell scattered light information which is scattered light information related to red blood cells contained in a blood sample and reticulocyte scattered light information which is scattered light information related to reticulocytes contained in the blood sample; obtains a value equivalent to the amount of hemoglobin in the red blood cells from the red blood cell scattered light information; obtains a value equivalent to the amount of hemoglobin in the reticulocytes from the reticulocyte scattered light information; obtains difference between the hemoglobin amounts which is the difference between the value equivalent to the amount of hemoglobin in the red blood cells and the value equivalent to the amount of hemoglobin in the reticulocytes; and obtains information supporting clinical examination based on the value equivalent to the amount of hemoglobin in the reticulocytes and the difference between the hemoglobin amounts, is disclosed. A hematology analyzing method and a computer program product are also disclosed.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
Molecular detection of chromosome aberrations
InactiveUS7034144B2High sensitivitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementComparable sizeNucleic Acid Probes
The invention relates to the field of cytogenetics and the application of genetic diagnostic techniques in pathology and hematology. Specifically, the invention relates to nucleic acid probes that can be used in hybridization techniques for the detection of chromosomal aberrations and other gene rearrangements such as immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor gene rearrangements. The probes provided by the invention are a distinct and balanced set of probes of comparable size, each preferably being from 1 to 100 kb, or smaller, and flanking a potential breakpoint in a chromosome.
Owner:DAKOAS
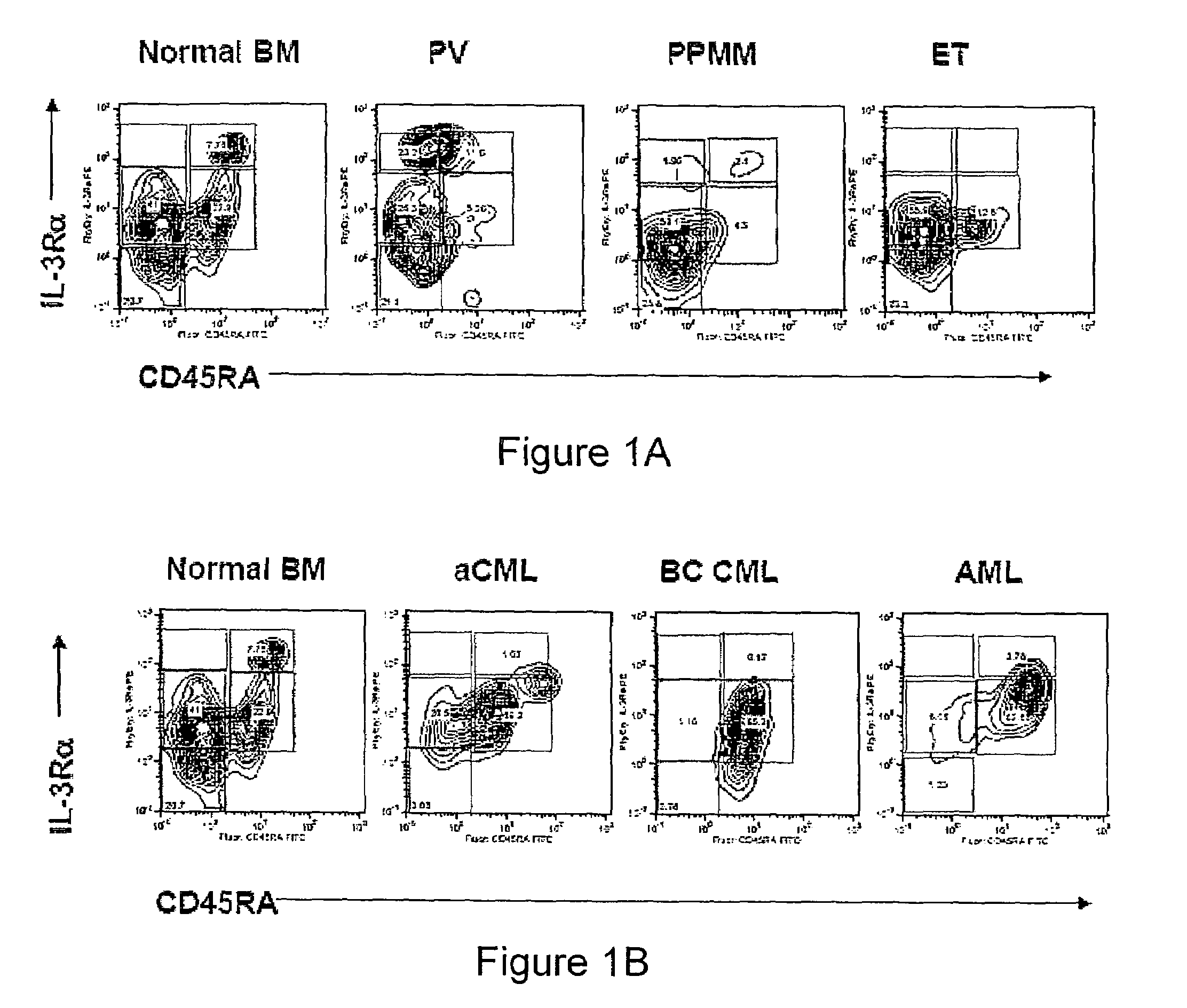
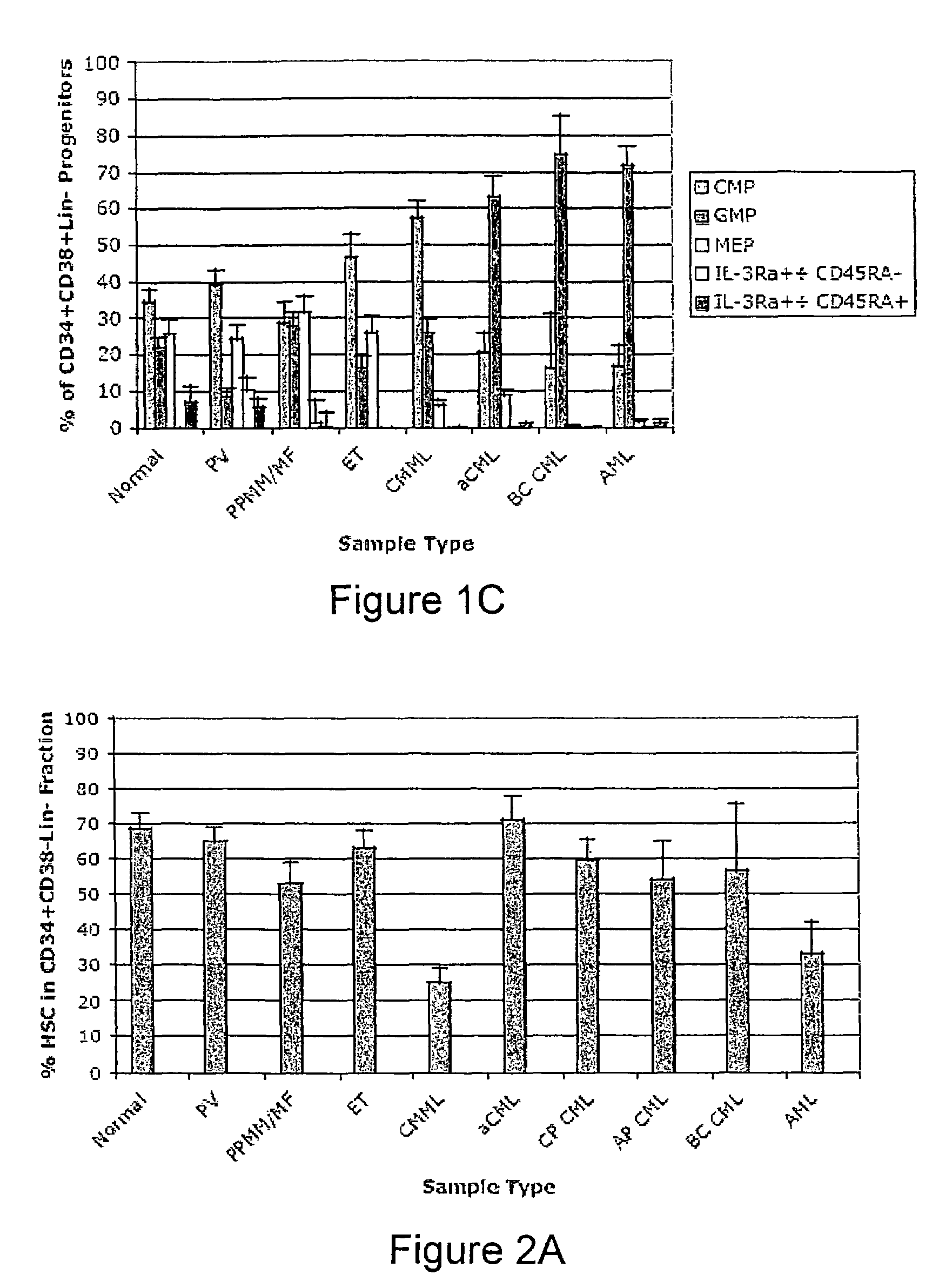
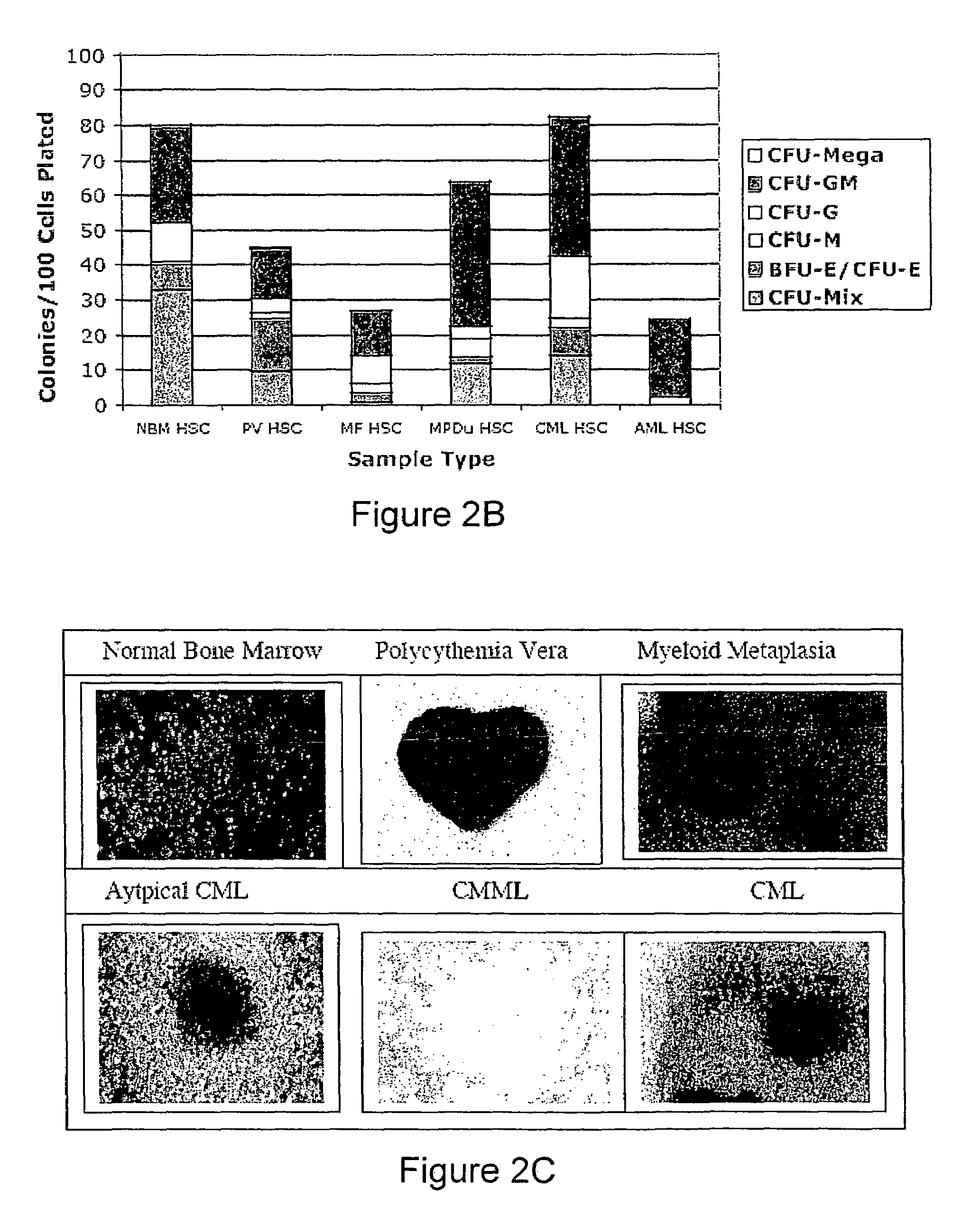
Methods for diagnosing and evaluating treatment of blood disorders
Methods, systems and kits are provided for the clinical staging of blood disorders including myelodysplastic syndrome, myeloproliferative diseases and leukemias by differential analysis of hematologic samples for the distribution of one or more hematopoietic stem or progenitor cell subsets. Additional functional, genetic, gene expression, proteomic or other molecular analyses of the hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells from the patients can also be employed in the staging methods of the invention.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
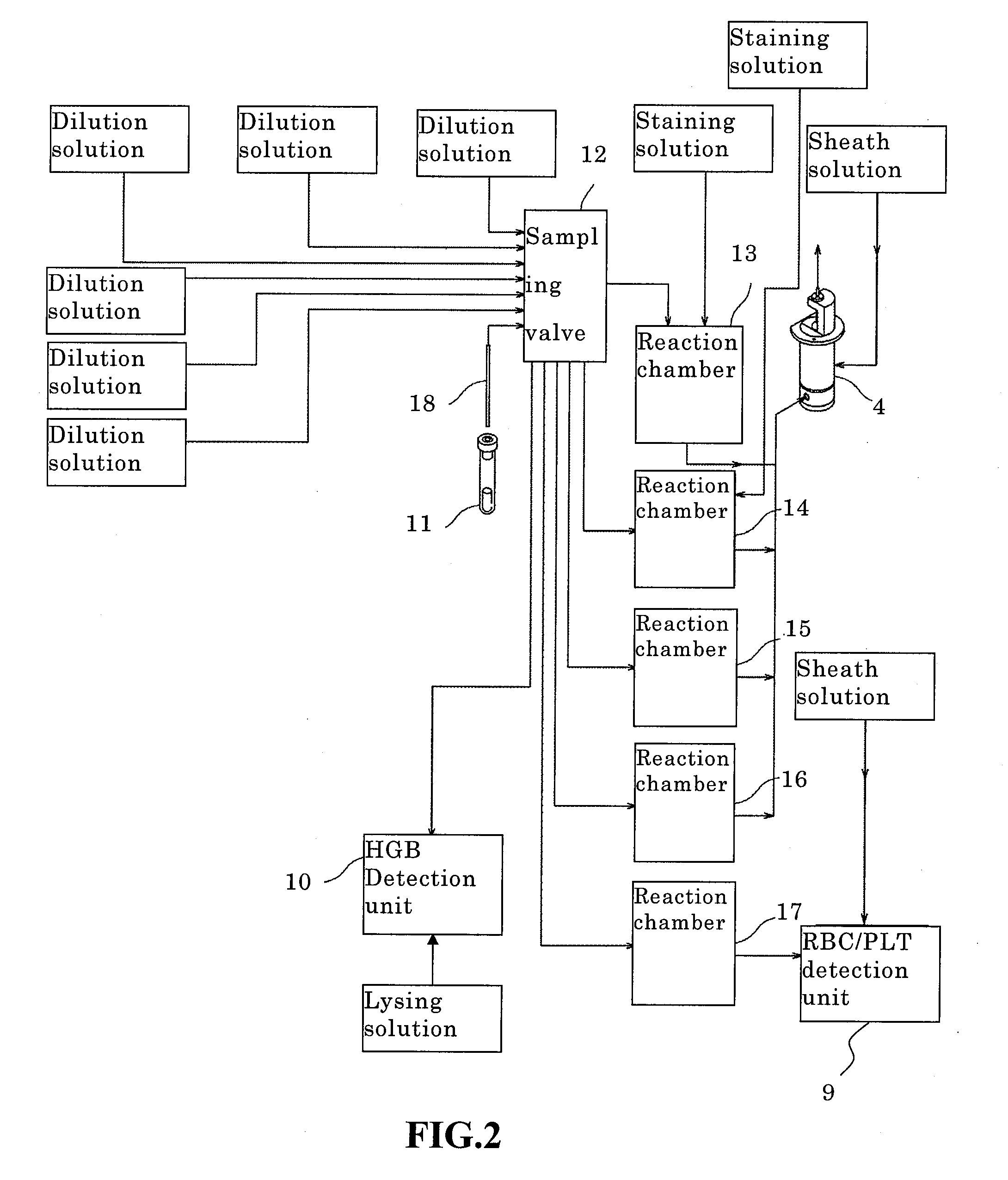
Consumable tube for use with a flow cytometry-based hematology system
InactiveUS7064823B2Minimizes reagent wasteReduces systemWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationMedicine.hematologyFlow cell
The present invention is a flow cytometry-based hematology system useful in the analysis of biological samples, particularly whole blood or blood-derived samples. The system is capable of determining at least a complete blood count (CBC), a five-part white blood cell differential, and a reticulocyte count from a whole blood sample. The system preferably uses a laser diode that emits a thin beam to illuminate cells in a flow cell and a lensless optical detection system to measure one or more of axial light loss, low-angle forward scattered light, high-angle forward scattered light, right angle scattered light, and time-of-flight measurements produced by the cells. The lensless optical detection system contains no optical components, other than photoreactive elements, and does not include any moving parts. Finally, the system uses a unique system of consumable reagent tubes that act as reaction chambers, mixing chambers, and waste chambers for the blood sample analyses. The consumable tubes incorporate reference particles, which act as internal standards to ensure that the dilutions made during processing of the samples have been carried out correctly, and to ensure that the instrument is working properly. The present invention also relates to methods for using the system.
Owner:IDEXX LABORATORIES
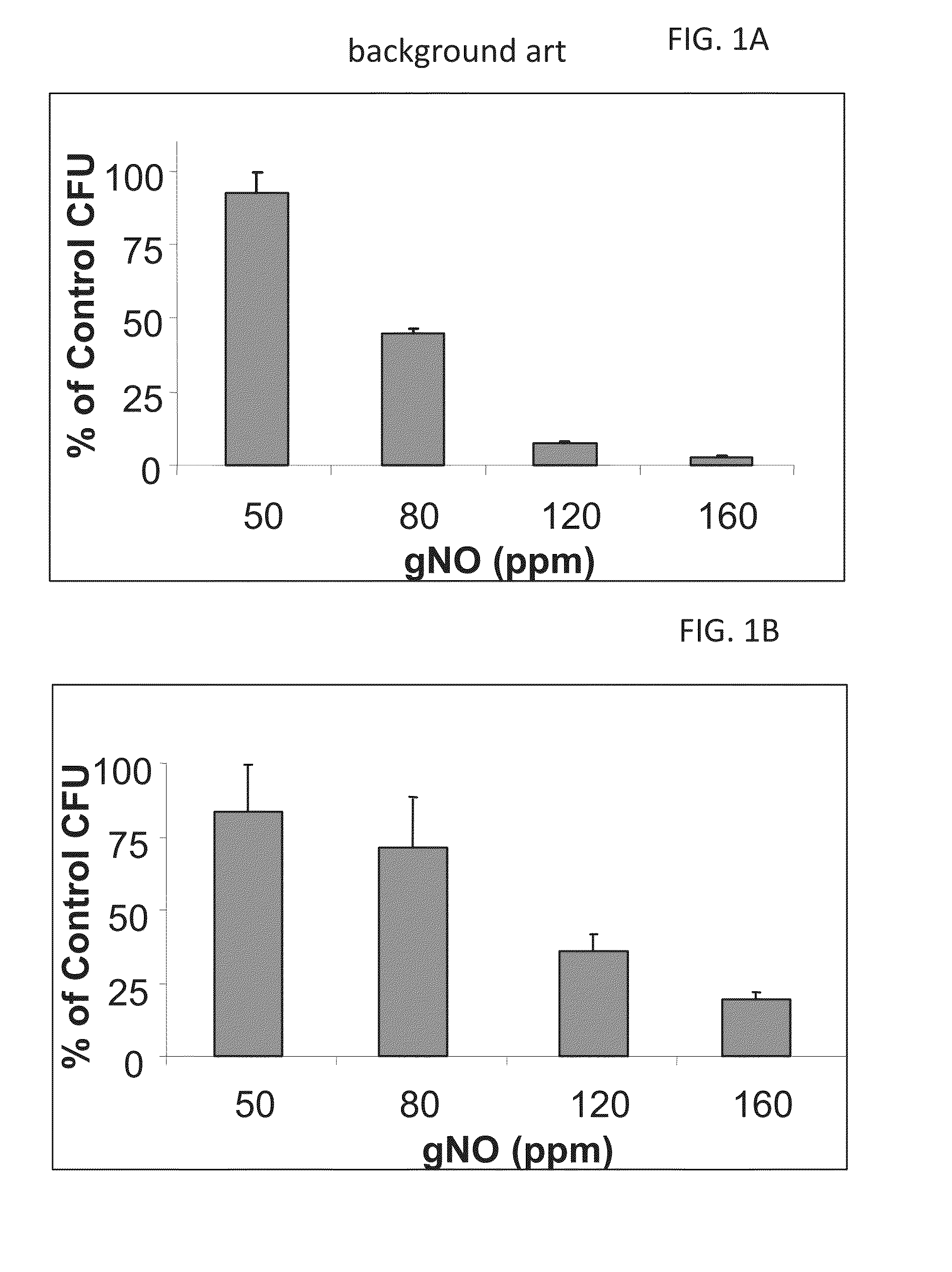
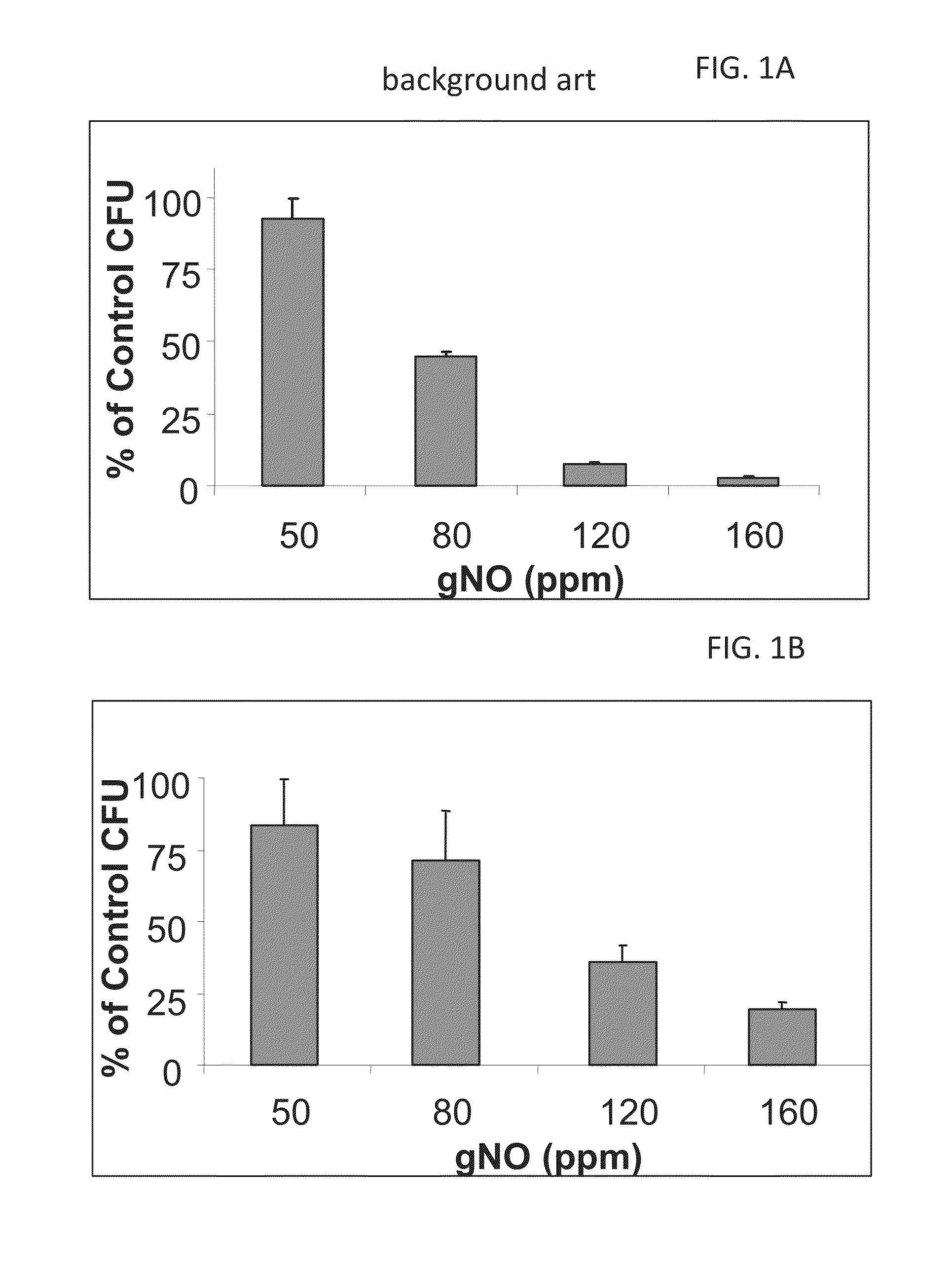
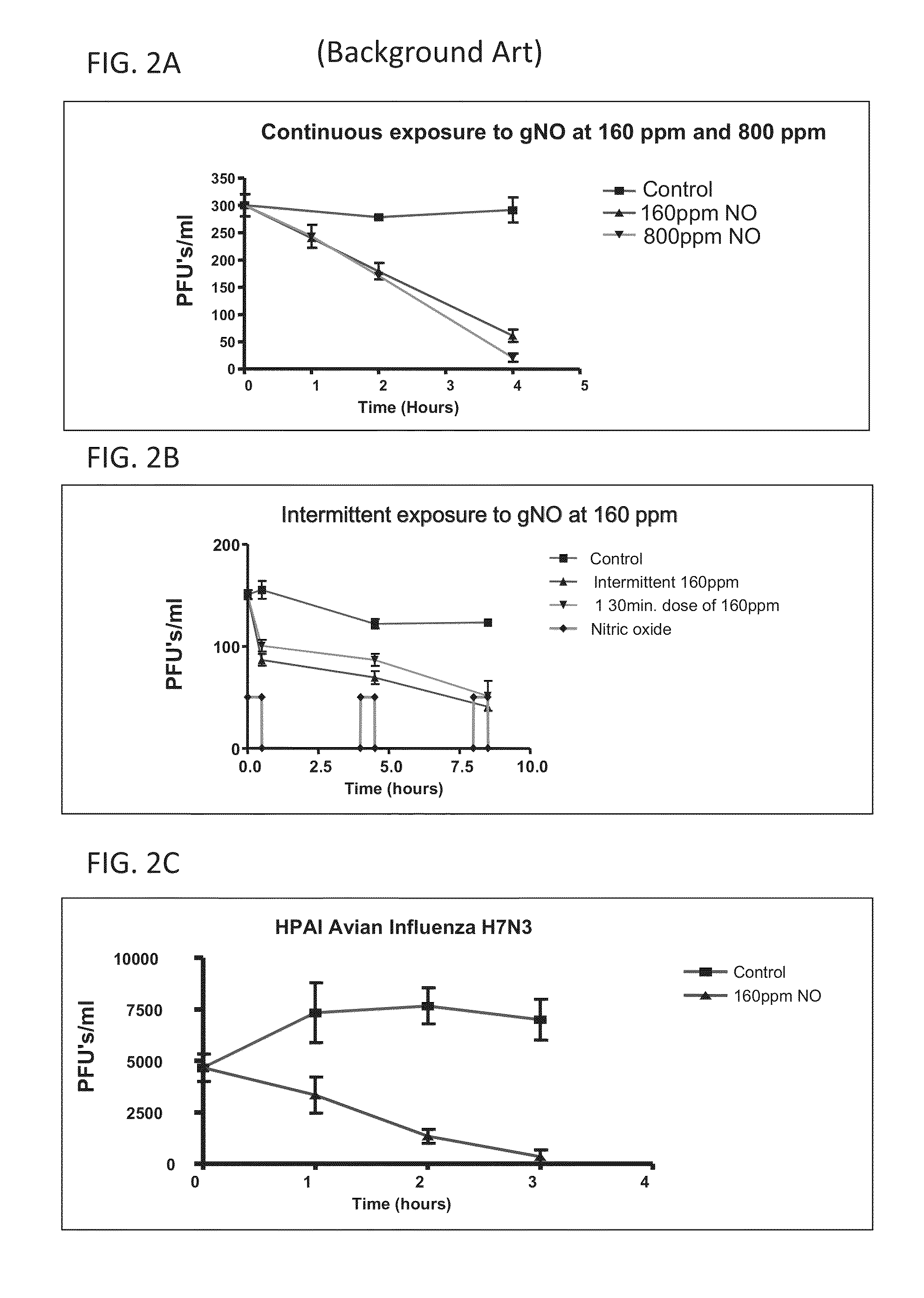
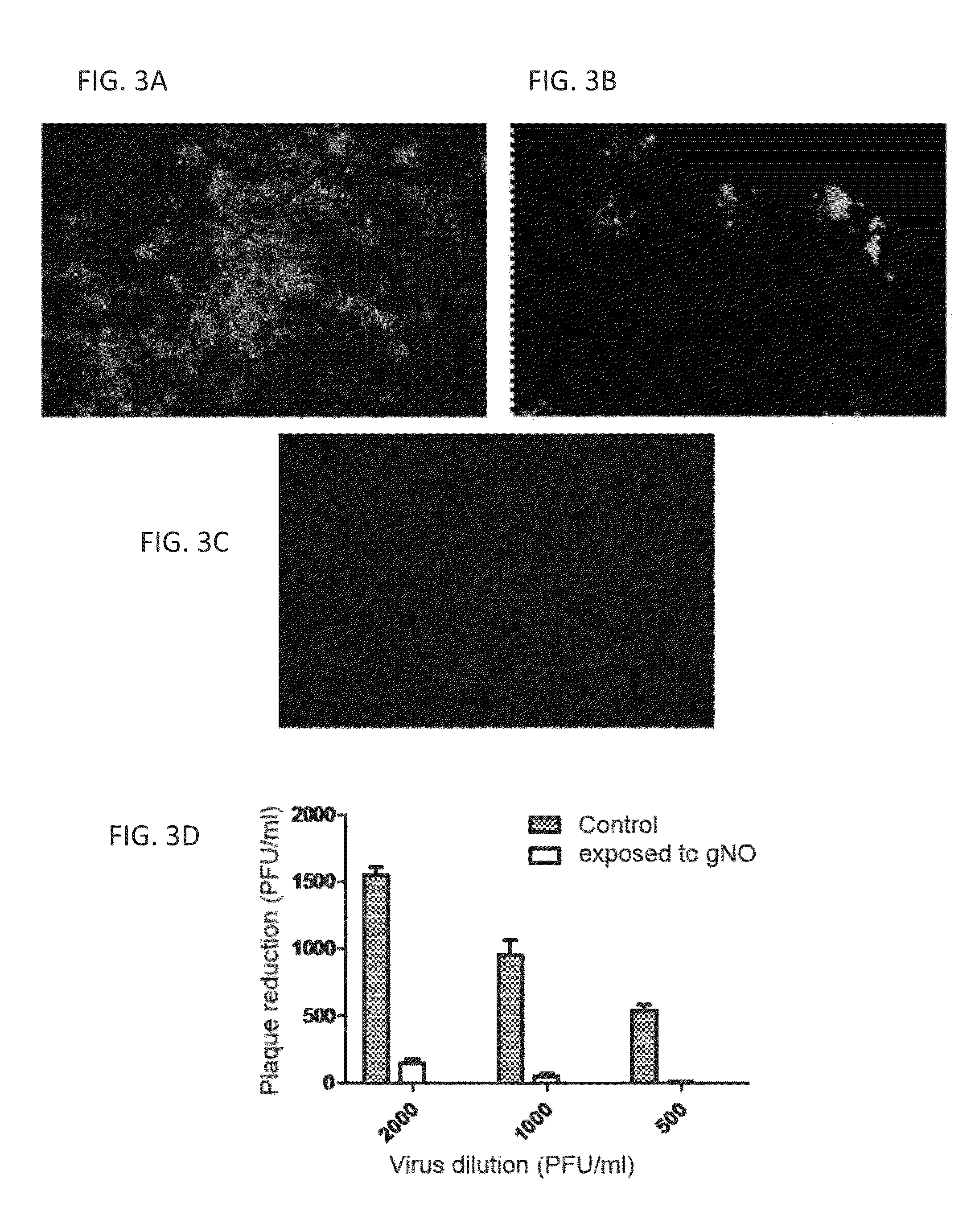
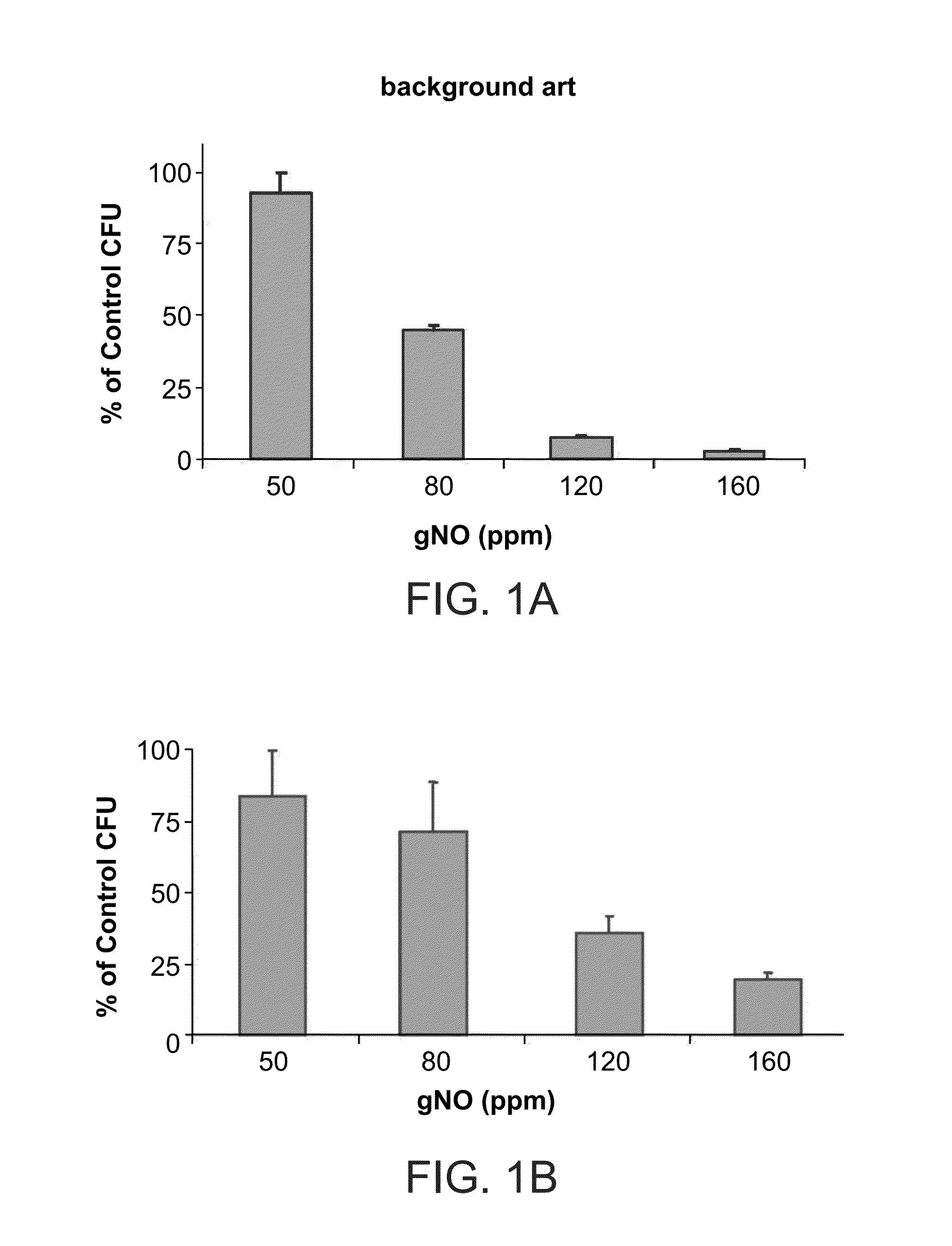
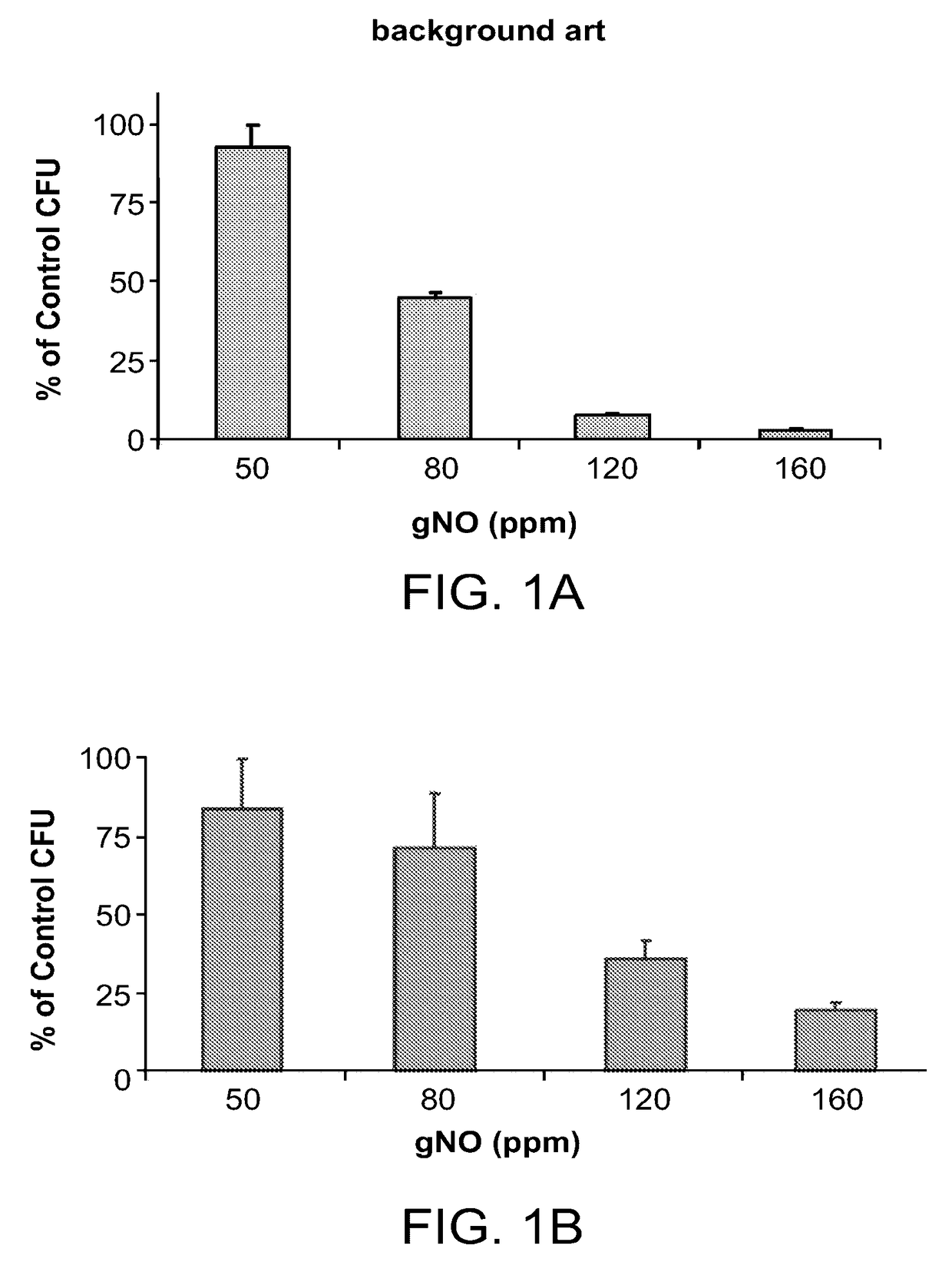
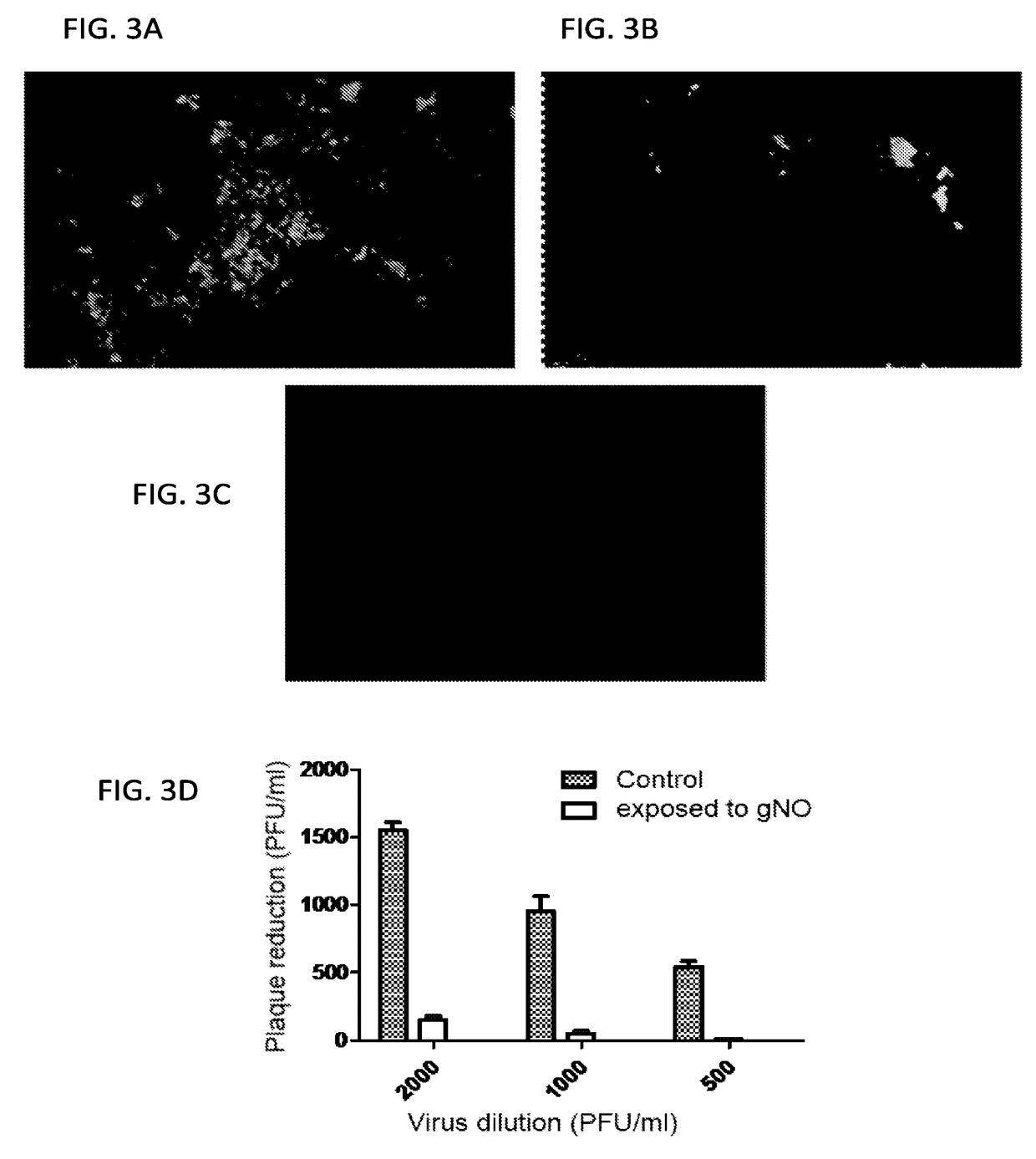
Inhalation of nitric oxide for treating respiratory diseases
InactiveUS20150034084A1Effected safelyRespiratorsInorganic active ingredientsLiver and kidneyVascular endothelium
A method of treating a human subject which is effected by intermittent inhalation of gaseous nitric oxide at a concentration of at least 160 ppm is disclosed. The method can be utilized for treating a human subject suffering from, or prone to suffer from, a disease or disorder that is manifested in the respiratory tract, or from a disease or disorder that can be treated via the respiratory tract. The disclosed method can be effected while monitoring one or more of on-site and off-site parameters such as vital signs, methemoglobin levels, pulmonary function parameters, blood chemistry and hematological parameters, blood coagulation parameters, inflammatory marker levels, liver and kidney function parameters and vascular endothelial activation parameters, such that no substantial deviation from a baseline in seen in one or more of the monitored parameters.
Owner:ADVANCED INHILATION THERAPIES AIT LTD
Method and apparatus for performing platelet measurement
InactiveUS20070105231A1Withdrawing sample devicesDead animal preservationMedicine.hematologyFlow cell
The present invention relates to a hematology instrument system that discriminates platelets from red blood cells, debris and other particles within a blood sample. The instrument system uses an optical trigger and collects data at optical sensor locations relative to a flow cell-illuminating laser beam's optical axis. An axial sensor measures axial light loss due to a particle in the flow cell's illumination aperture. In addition, the instrument system can include an RF unit generates electrical parameters, such as DC and RF parameters, within the flow cell. Blood specimens can be prepared with and without a sphering agent.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Combined use of anti-cytokine antibodies or antagonists and anti-CD20 for treatment of B cell lymphoma
InactiveUS20050180975A1Avoiding and decreasing and resistanceIncrease ratingsBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsBiological activationHematologic malignancy
The present invention discloses combined therapies for treating hematologic malignancies, including B cell lymphomas and leukemias or solid non-hematologic tumors, comprising administration of anti-cytokine antibodies or antagonists to inhibit the activity of cytokines which play a role in perpetuating the activation of B cells. The administration of such antibodies and antagonists, particularly anti-IL10 antibodies and antagonists, is particularly useful for avoiding or decreasing the resistance of hematologic malignant cells or solid tumor cells to chemotherapeutic agents and anti-CD20 or anti-CD22 antibodies. The invention also provides combination therapies for solid tumors having B cell involvement comprising the administration of an anti-cytokine antibody and a B cell depleting antibody such as RITUXAN®.
Owner:BIOGEN INC
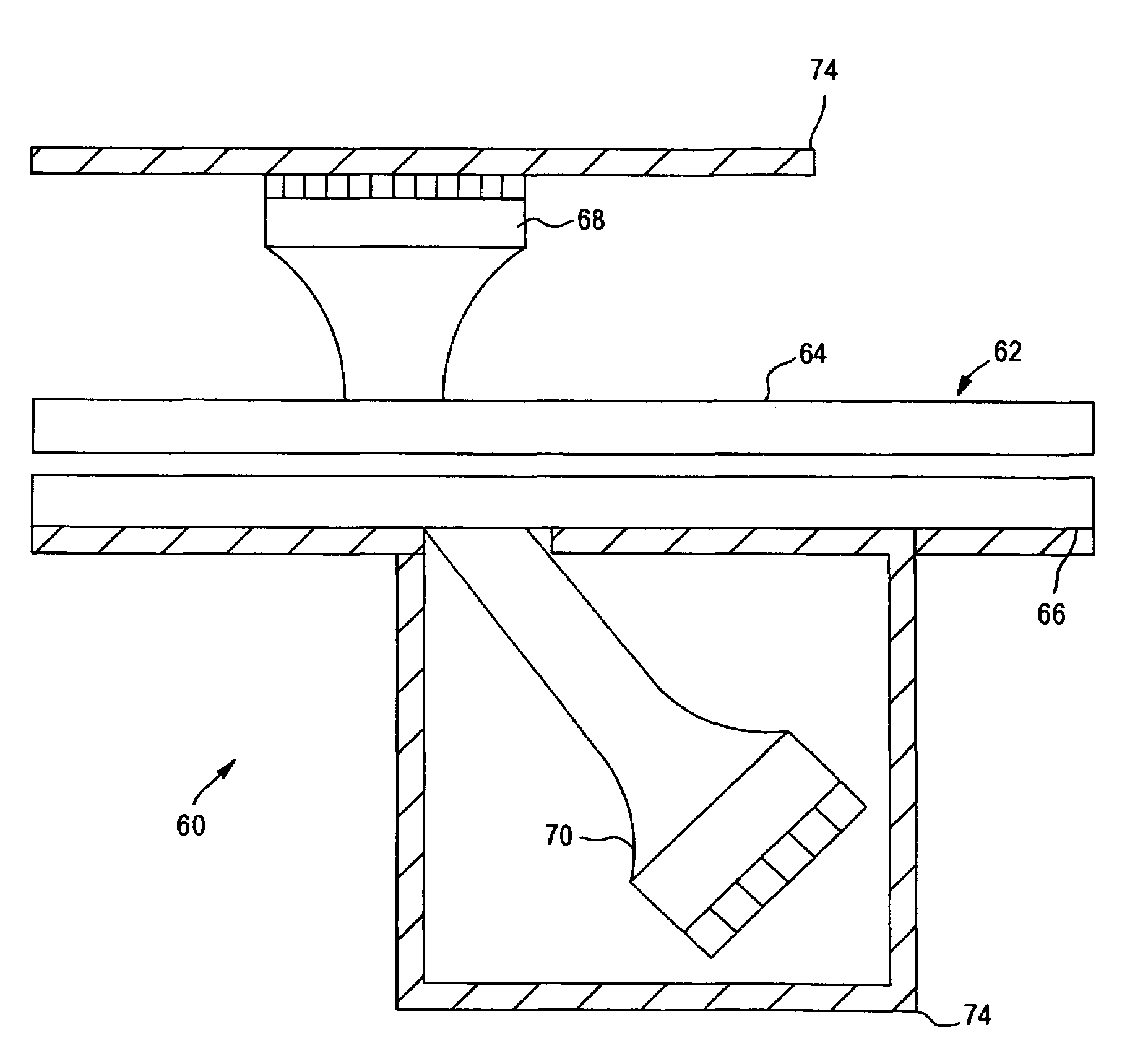
Disposable cassette and method of use for blood analysis on blood analyzer
ActiveUS20100120083A1Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMedicine.hematologyBlood gas analysis
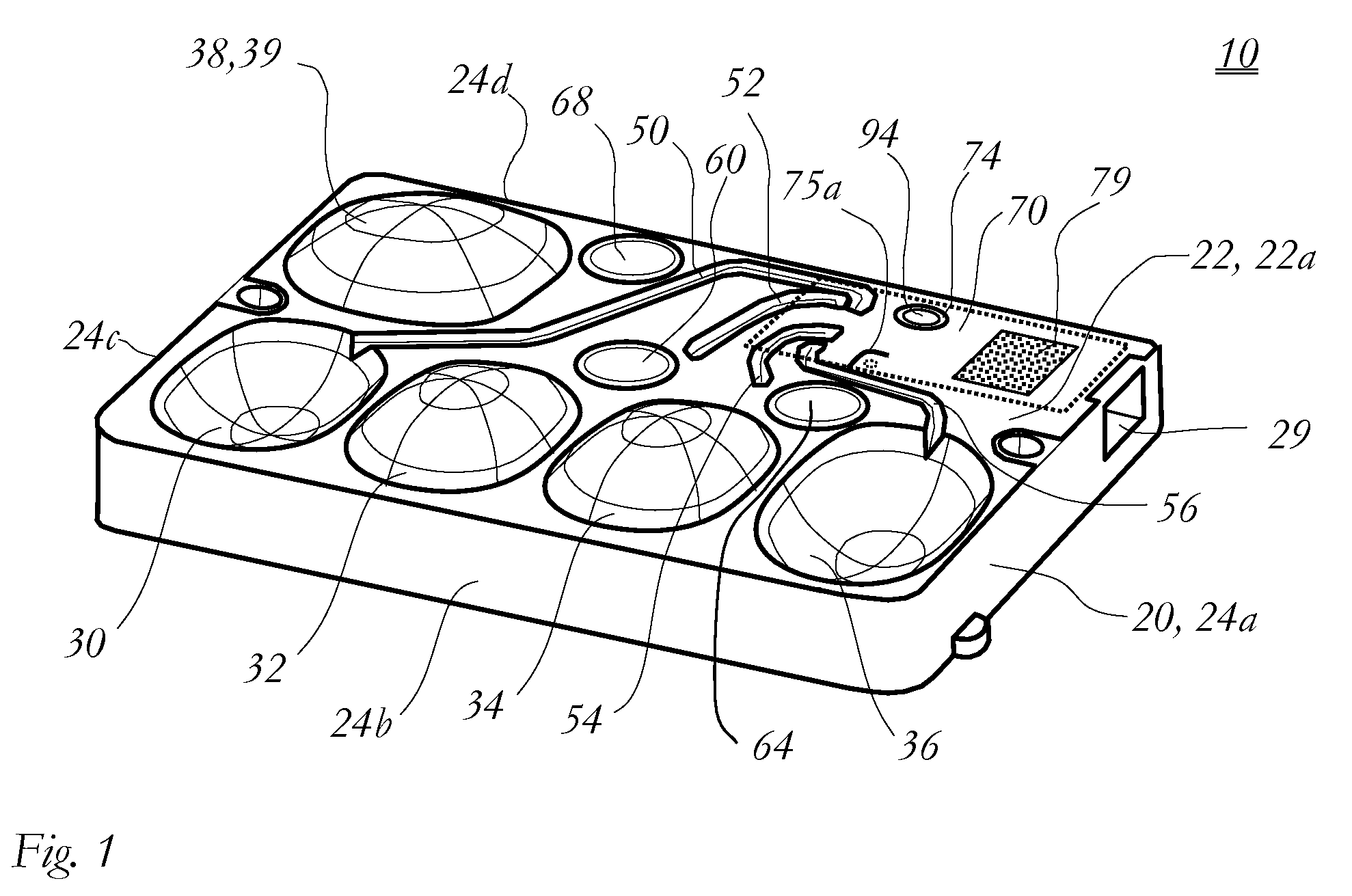
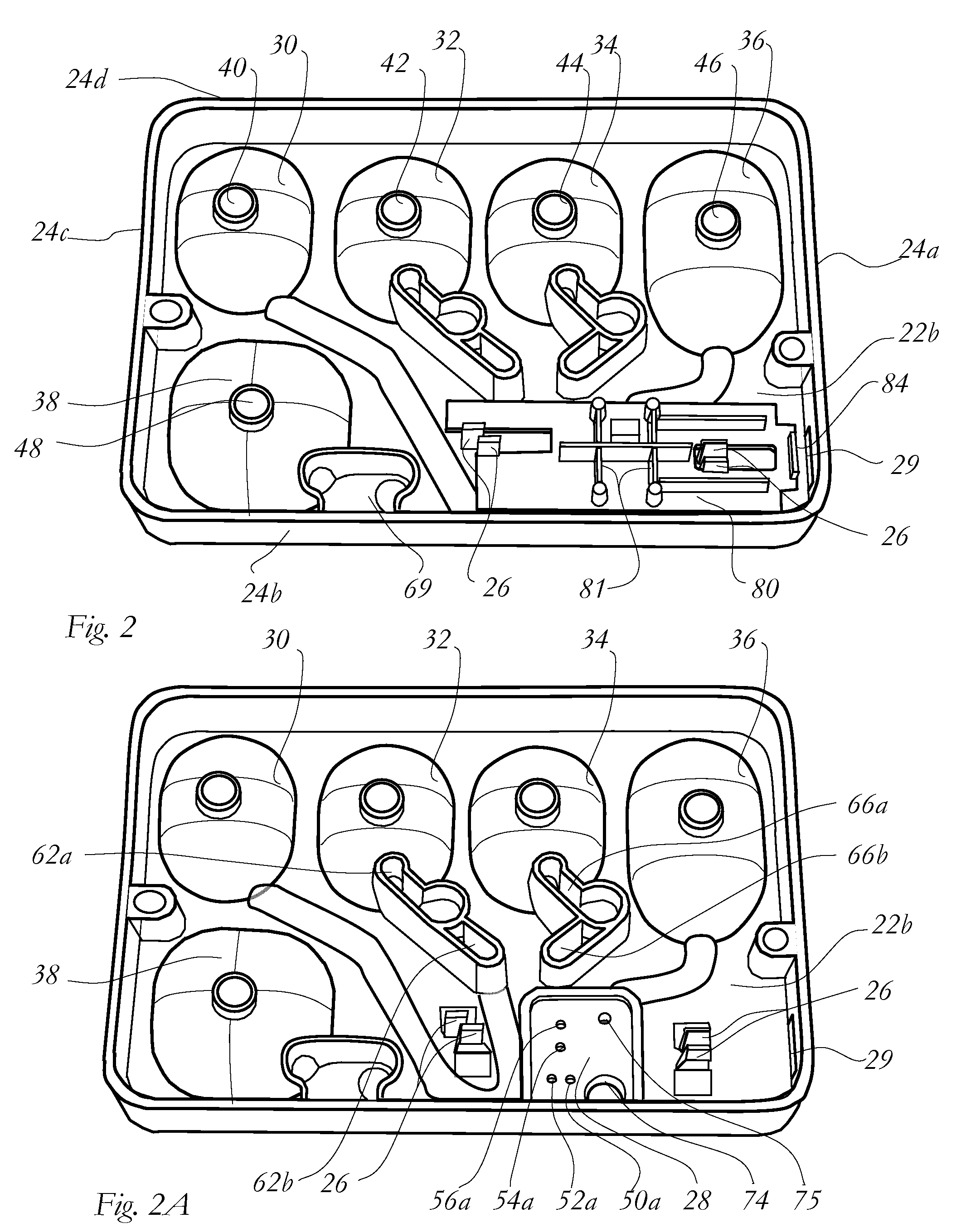
A disposable cassette for blood analysis includes a housing having an upper panel and a sampling section having a filling inlet; at least one pair of chambers in a form of depression of the upper panel of the housing and sealed by a diaphragm; portions of the diaphragm over the chambers being flexible; and one or more channels adapted to interconnect the pair of chambers; one of the chambers containing a predetermined amount of a reagent for blood analysis; and a sample outlet disposed next to and connected to the chamber containing the reagent, the sample outlet including an outlet cavity recessed from the upper panel, a divider disposed therein, and a cover covering the outlet cavity; the sample outlet sealing the reagent to the chamber containing the reagent. Further disclosed is the method of using the disposable cassette for measurements of hematology parameters on a blood analyzer.
Owner:BOULA MEDICAL AB
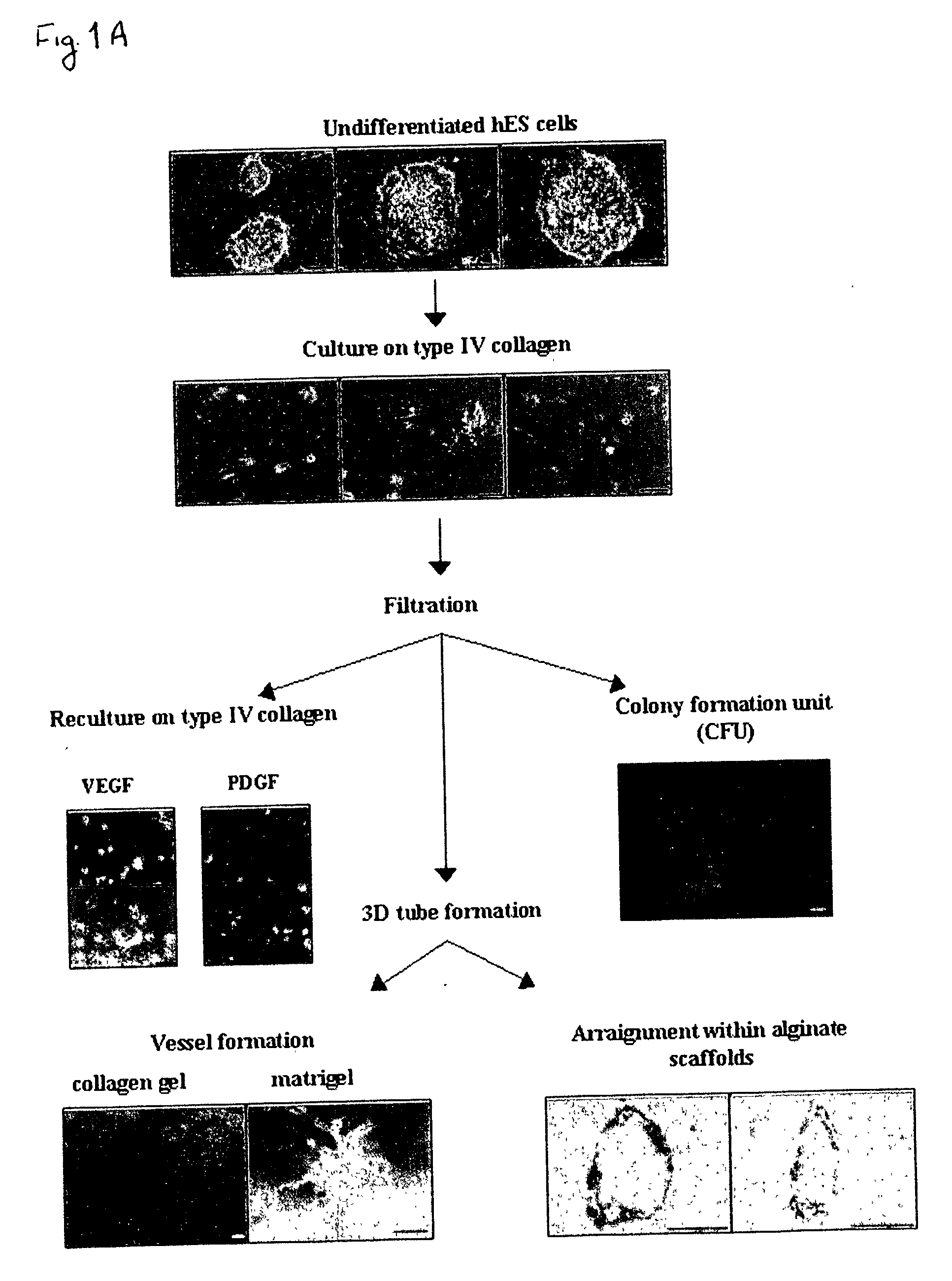
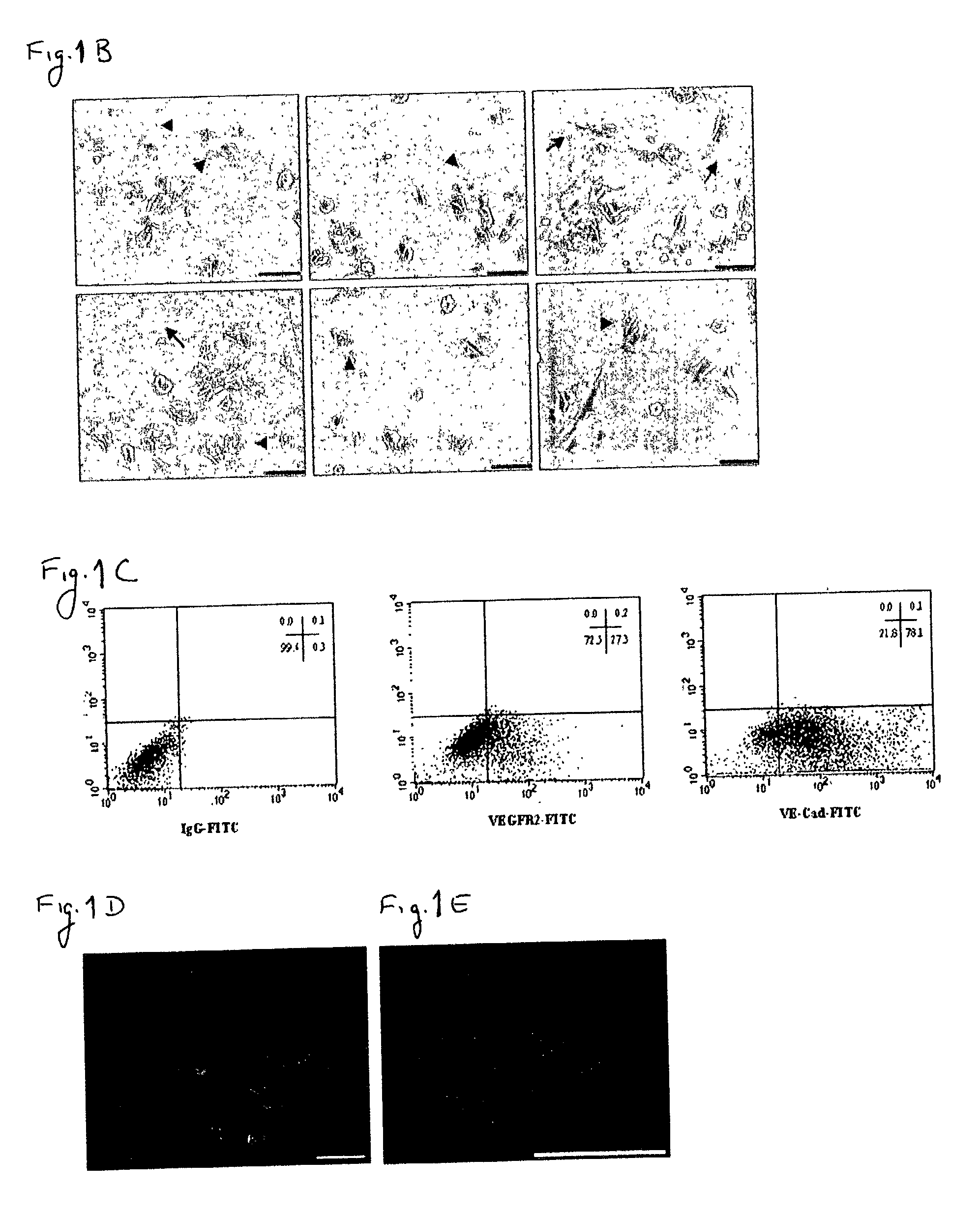
Novel methods for the in-vitro identification, isolation and differentiation of vasculogenic progenitor cells
InactiveUS20030194802A1Avoid adjustmentBiocideGenetic material ingredientsPharmaceutical drugTissue Differentiation
There is provided a simplified and inexpensive method for the in-vitro identification, isolation and culture of human vasculogenic progenitor cells. The method and the progenitor cells isolated thereby can be used for in-vitro vascular engineering, treatment of congenital and acquired vascular and hematological abnormalities, for evaluation and development of drugs affecting vasculo- and angiogenic processes, and for further investigation into tissue differentiation and development.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Detection and measurement of hematological parameters characterizing cellular blood components
InactiveUS20060257883A1Improve concentrationEasy diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingDiseaseBlood component
Systems and methods for the diagnostic analysis of blood samples. The present invention uses sensor technology useful in the analysis of headspace sample from blood to provide an efficient and accurate means for identifying the presence of a volatile marker associated with hematological diseases or conditions. In a preferred embodiment, the sensor technology of the present invention includes detecting means such as RNA oligonucleotide chains or aptamers.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Inhalation of nitric oxide for treating respiratory diseases
A method of treating a human subject which is effected by intermittent inhalation of gaseous nitric oxide at a concentration of at least 160 ppm is disclosed. The method can be utilized for treating a human subject suffering from, or prone to suffer from, a disease or disorder that is manifested in the respiratory tract, or from a disease or disorder that can be treated via the respiratory tract. The disclosed method can be effected while monitoring one or more of on-site and off-site parameters such as vital signs, methemoglobin levels, pulmonary function parameters, blood chemistry and hematological parameters, blood coagulation parameters, inflammatory marker levels, liver and kidney function parameters and vascular endothelial activation parameters, such that no substantial deviation from a baseline in seen in one or more of the monitored parameters.
Owner:ADVANCED INHILATION THERAPIES AIT LTD
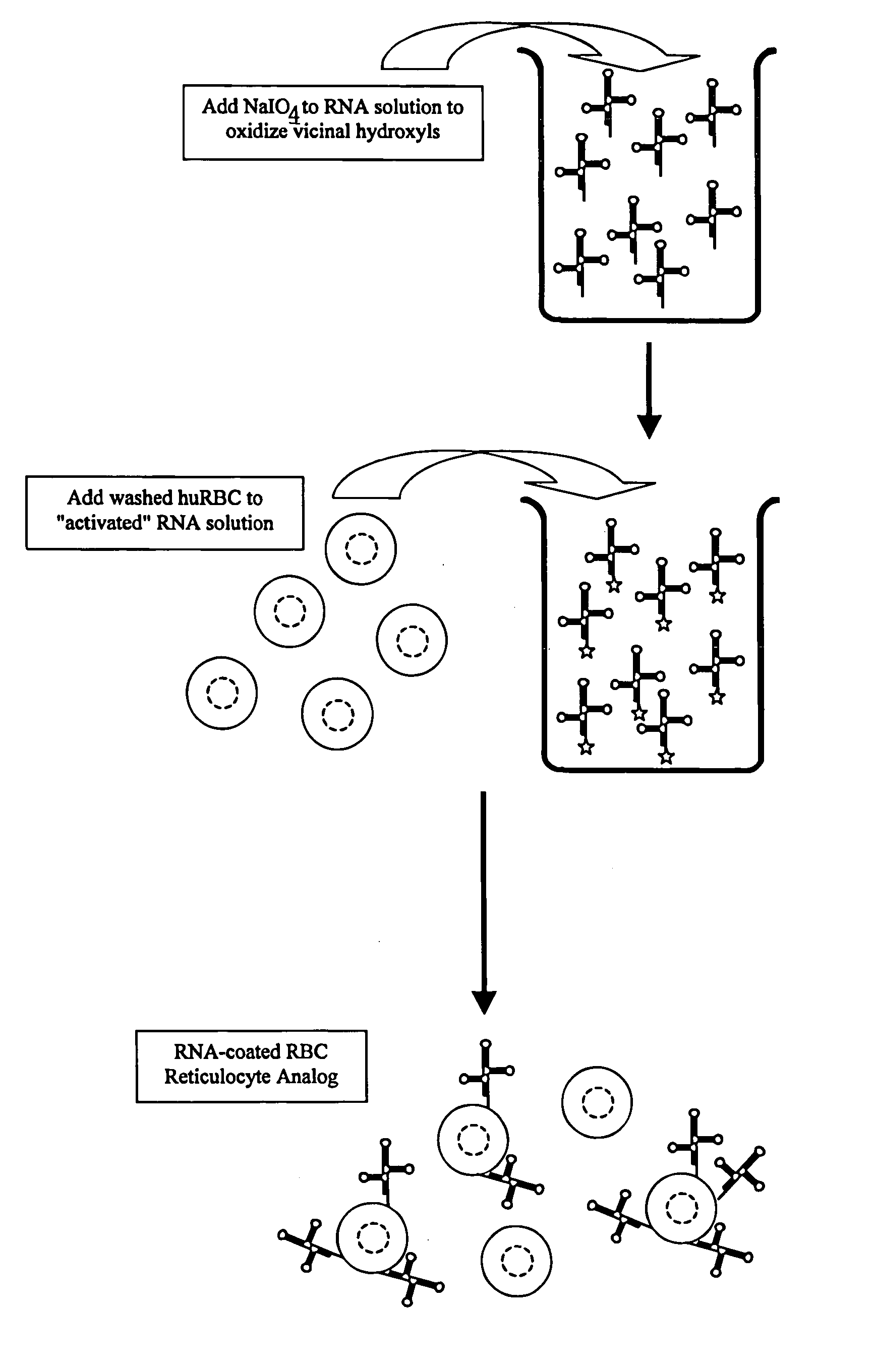
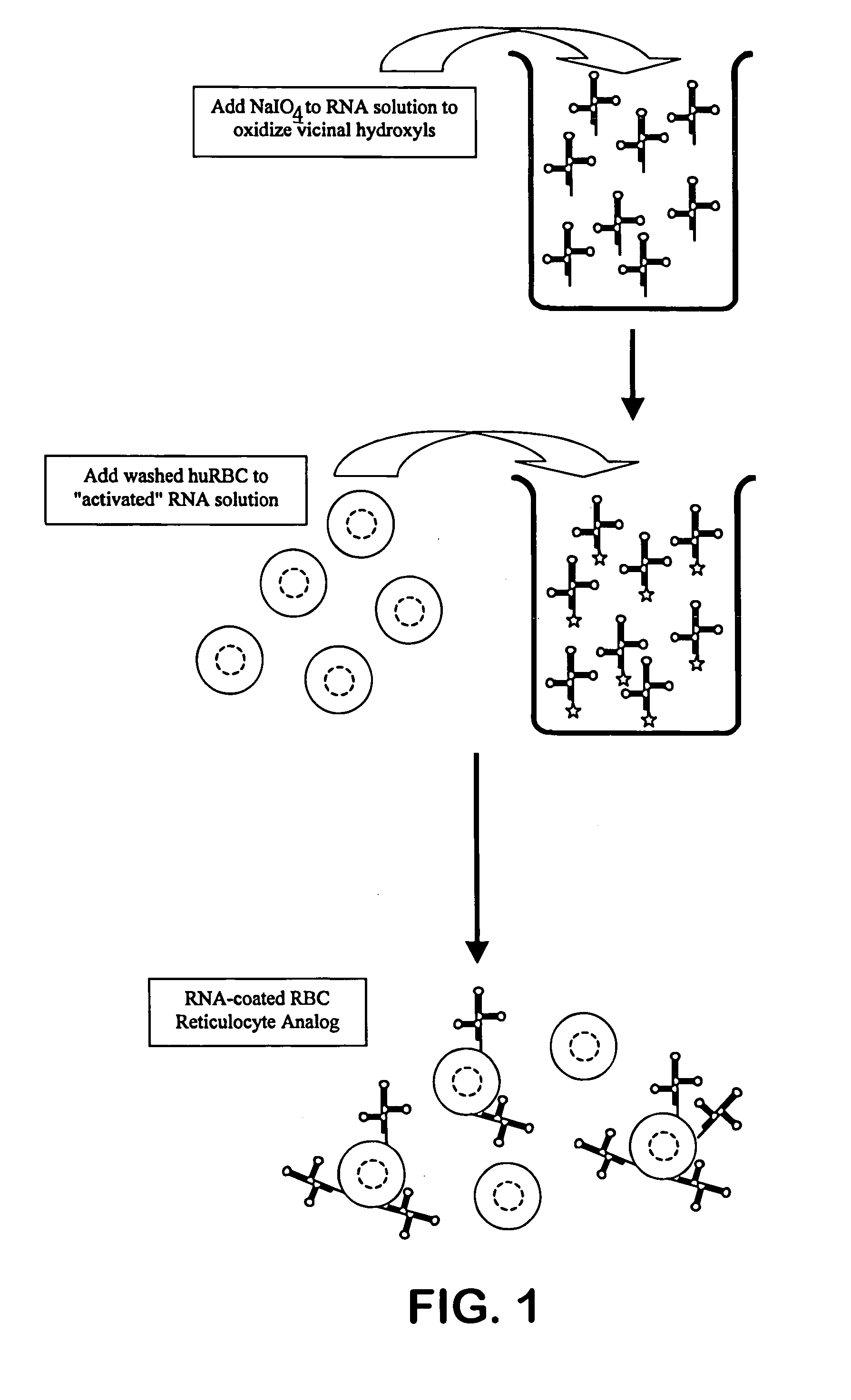
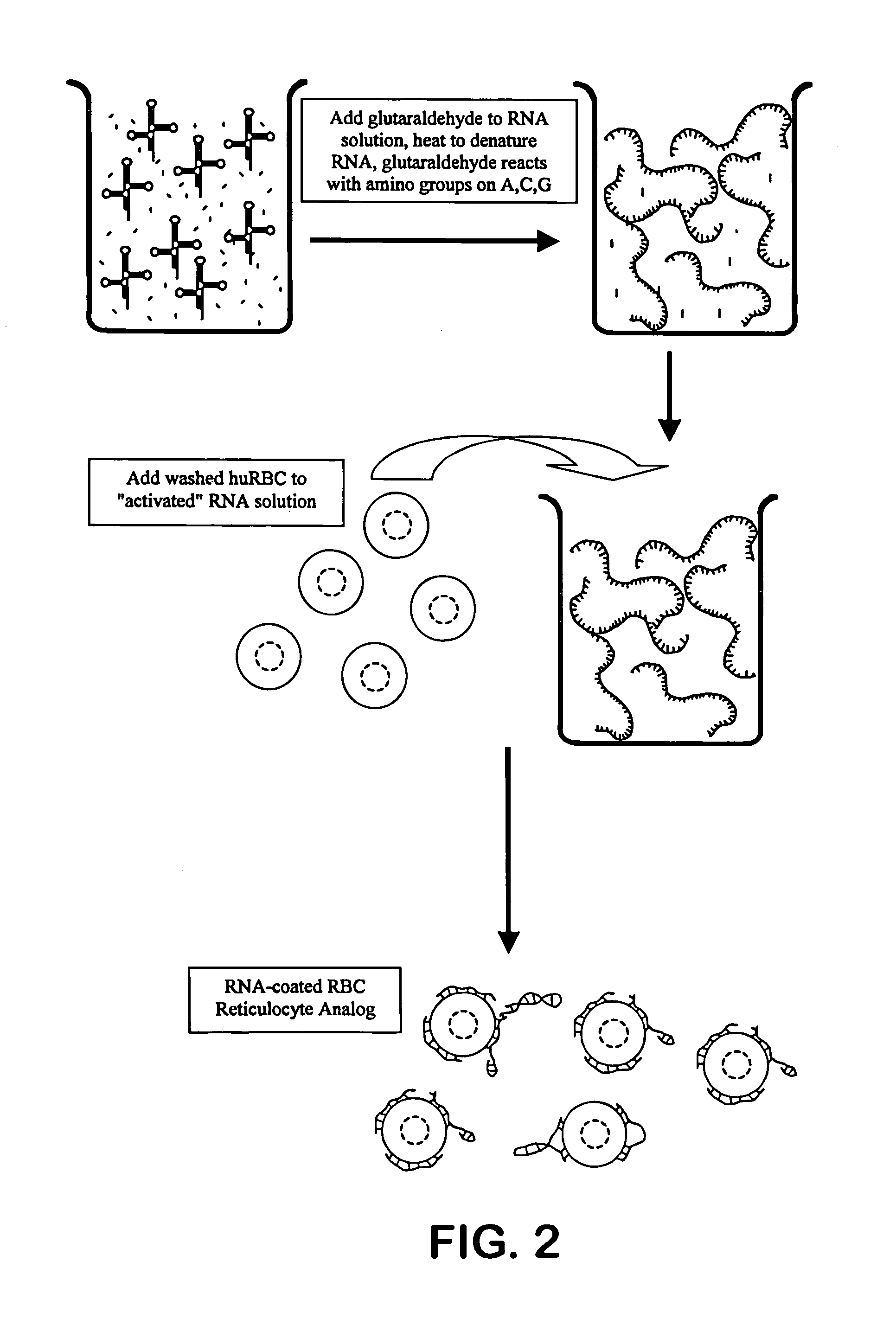
Hematology controls for reticulocytes and nucleated red blood cells
ActiveUS7195919B2Microbiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsMedicine.hematologyBiopolymer
The present invention is drawn to a hematology control made from particles a particle having a biopolymer attached to a surface of the particle. The particle simulates a component of a blood sample, such as a reticulocyte or nucleated red blood cell component of a blood cell sample in a flow cytometer or hematology analysis instrument. The present invention is further drawn to methods of making and using the hematology control.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Systems and methods for particle counting
ActiveUS20070143033A1Accurate measurementDigital computer detailsVolume indication and recording devicesMedicine.hematologyParticle physics
Systems and methods consistent with embodiments of the present invention provide a method for the measurement and analysis of particle counts in flow cytometry and hematology instruments. In some methods for the measurement and analysis of particle counts, a corrected histogram of particle distributions is calculated and used to obtain an accurate count of particles and an accurate measurement of other particle parameters.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
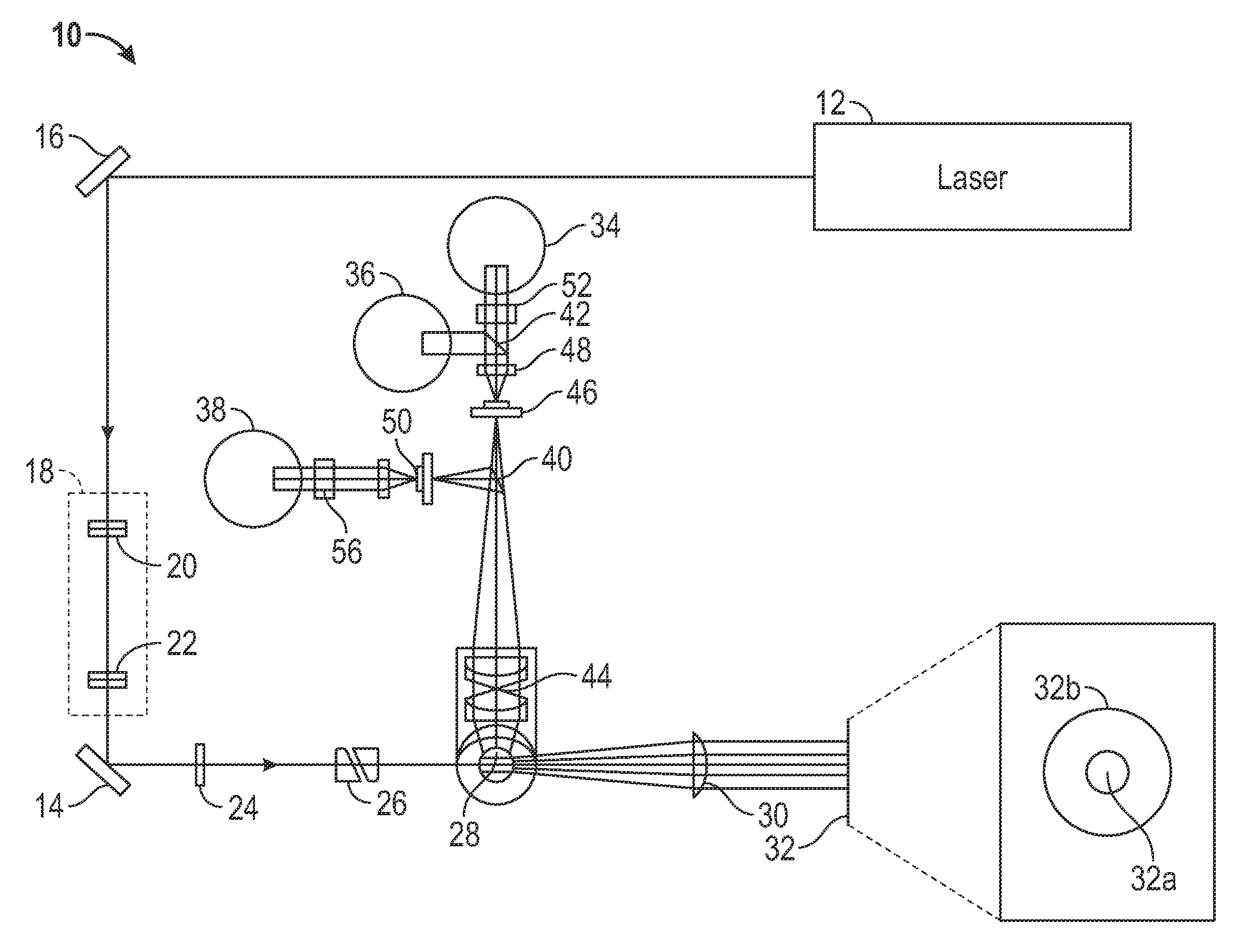
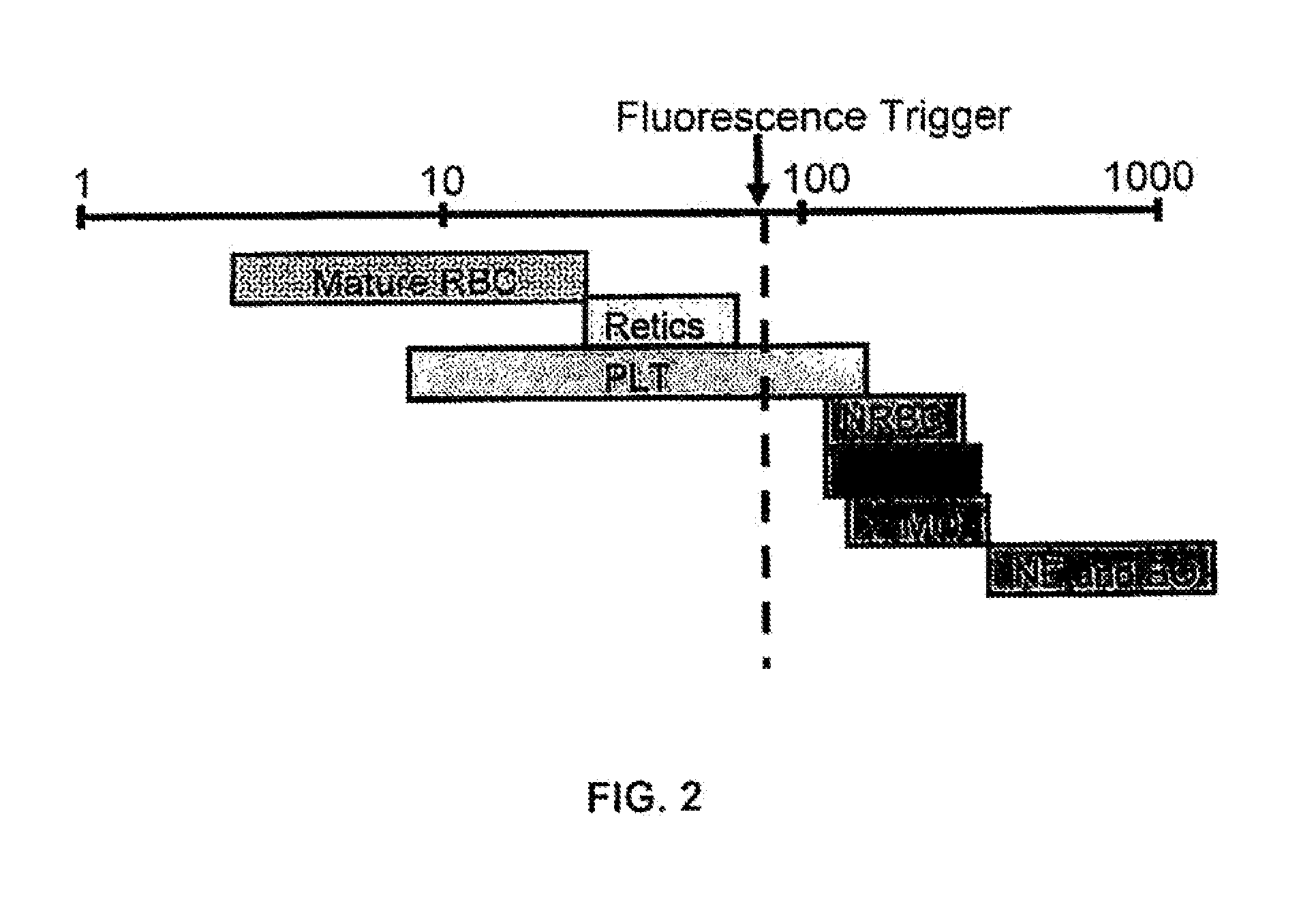
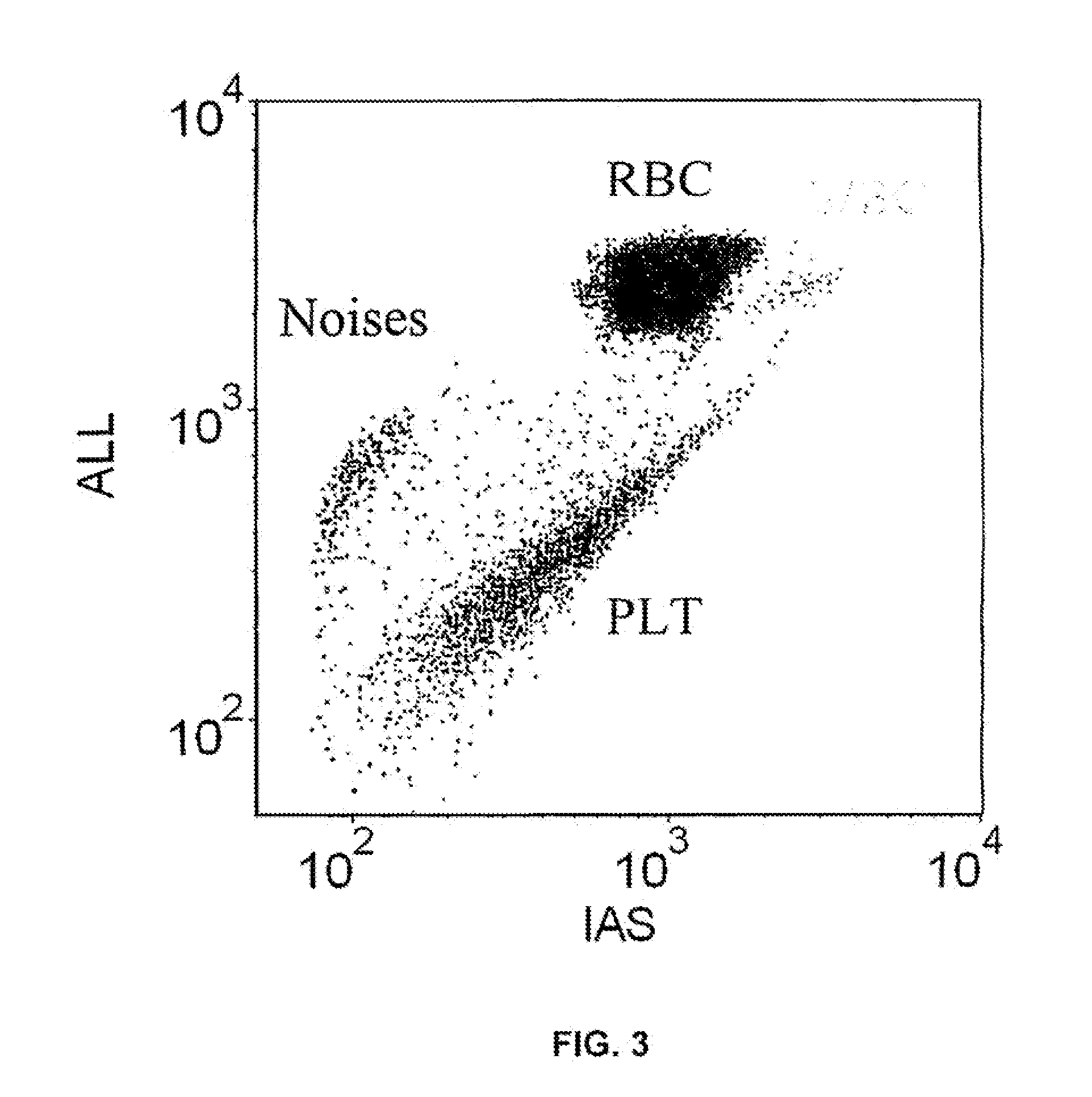
White Blood Cell Analysis System and Method
ActiveUS20120282598A1Accurate distinctionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFluorescent stainingAssay
Systems and methods for analyzing blood samples, and more specifically for performing a white blood cell (WBC) differential analysis. The systems and methods screen WBCs by means of fluorescence staining and a fluorescence triggering strategy. As such, interference from unlysed red blood cells (RBCs) and fragments of lysed RBCs is substantially eliminated. The systems and methods also enable development of relatively milder WBC reagent(s), suitable for assays of samples containing fragile WBCs. In one embodiment, the systems and methods include: (a) staining a blood sample with an exclusive cell membrane permeable fluorescent dye, which corresponds in emission spectrum to an excitation source of a hematology instrument; (b) using a fluorescence trigger to screen the blood sample for WB Cs; and (c) using measurements of (1) axial light loss, (2) intermediate angle scatter, (3) 90° polarized side scatter, (4) 90° depolarized side scatter, and (5) fluorescence emission to perform a differentiation analysis.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
System and method for standardizing care in a hospital environment
InactiveUS20060122869A9Minimizing adverse eventsMinimize complicationsAlarmsSpecial data processing applicationsMedicine.hematologyGuideline
A system and method for standardizing care in a hospital environment. Information concerning the latest care and practice standards for a given condition is provided to a decision support module. The decision support module comprises decision support algorithms that reflect a standardize guideline of practice for a particular medical condition. The general categories of cardiovascular, endocrinology, general, gastrointestinal, hematology, infectious diseases, neurology, pharmacology, pulmonary, renal, surgery, toxicology, trauma all have guidelines and practice standards associated with them. Patient data and user input are inputted to the decision support algorithm. The user may be prompted for user input, and an assessment is made of the patient so as provide patient care advice for the patient. Examples of patient care advice are a diagnosis, a method of treatment, and a laboratory protocol.
Owner:VISICU
Inhalation of nitric oxide for treating respiratory diseases
A method of treating a human subject which is effected by intermittent inhalation of gaseous nitric oxide at a concentration of at least 160 ppm is disclosed. The method can be utilized for treating a human subject suffering from, or prone to suffer from, a disease or disorder that is manifested in the respiratory tract, or from a disease or disorder that can be treated via the respiratory tract. The disclosed method can be effected while monitoring one or more of on-site and off-site parameters such as vital signs, methemoglobin levels, pulmonary function parameters, blood chemistry and hematological parameters, blood coagulation parameters, inflammatory marker levels, liver and kidney function parameters and vascular endothelial activation parameters, such that no substantial deviation from a baseline in seen in one or more of the monitored parameters.
Owner:ADVANCED INHILATION THERAPIES AIT LTD
Methods of Using Interleukin-10 for Treating Diseases and Disorders
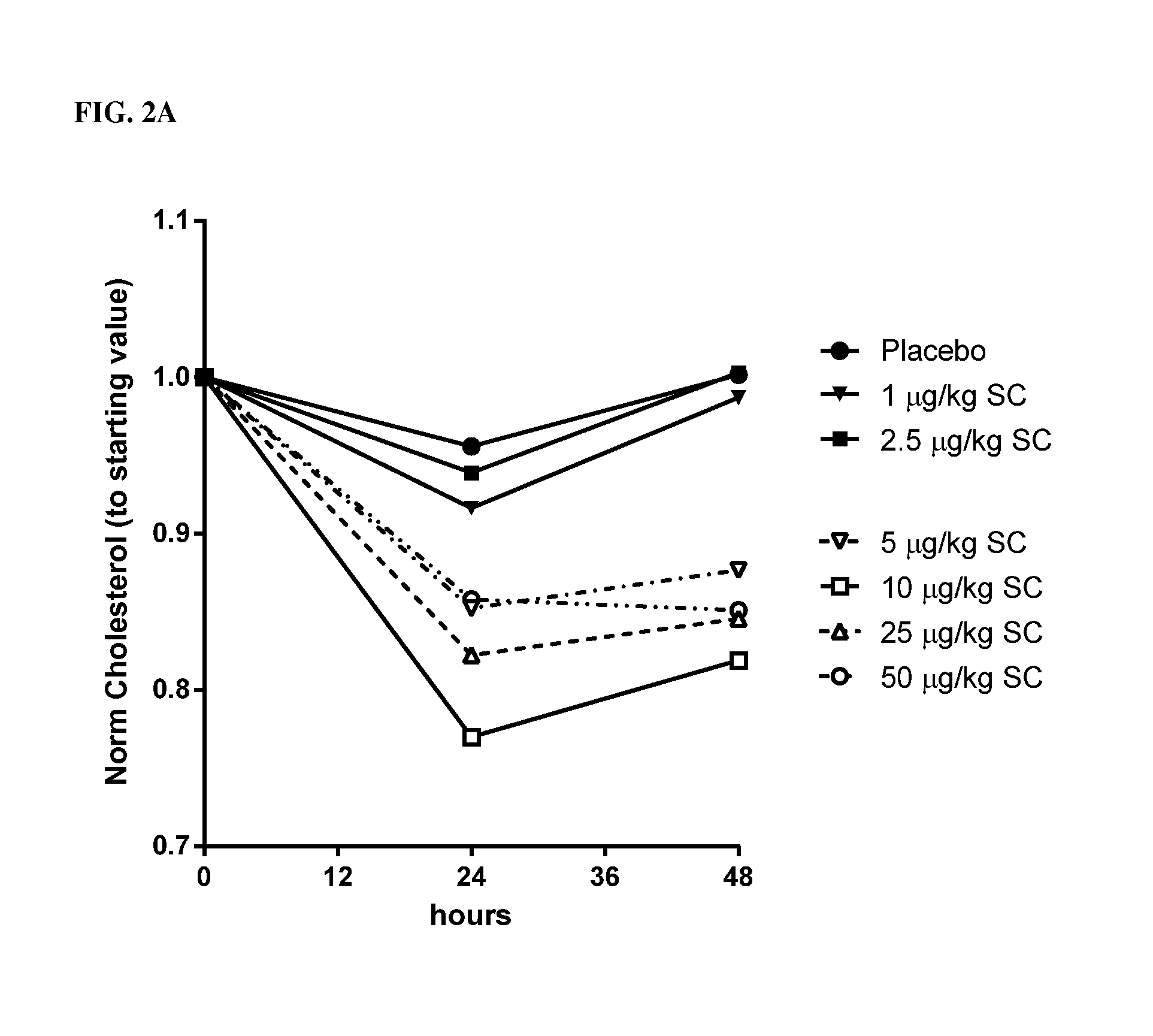
InactiveUS20160375101A1Reduction in total serum cholesterolPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismDrugAdverse effect
Methods for determining dosing parameters associated with subcutaneous administration of IL-10 useful for the treatment and / or prevention of a cholesterol-related disease, disorder or condition, and pharmaceutical compositions associated therewith, are provided herein. Certain embodiments are directed to means for establishing a therapeutic range of an IL-10 agent in a subject. In some embodiments, particular parameters (e.g., hematological parameters) are monitored to provide an indication of the upper limit of the therapeutic range such that any untoward adverse effects are avoided.
Owner:ARMO BIOSCI
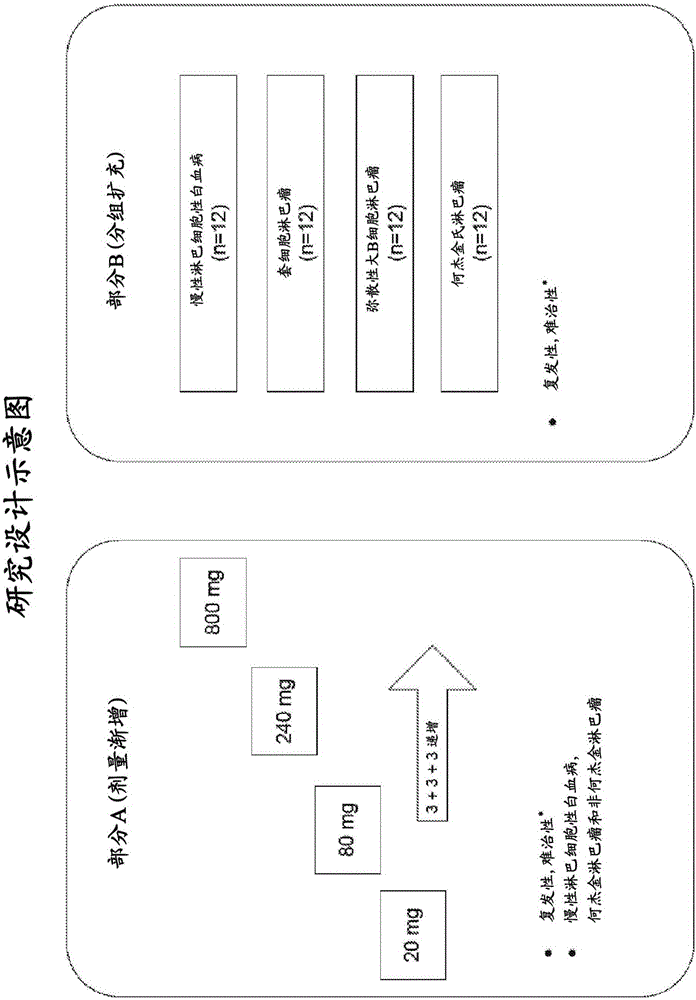
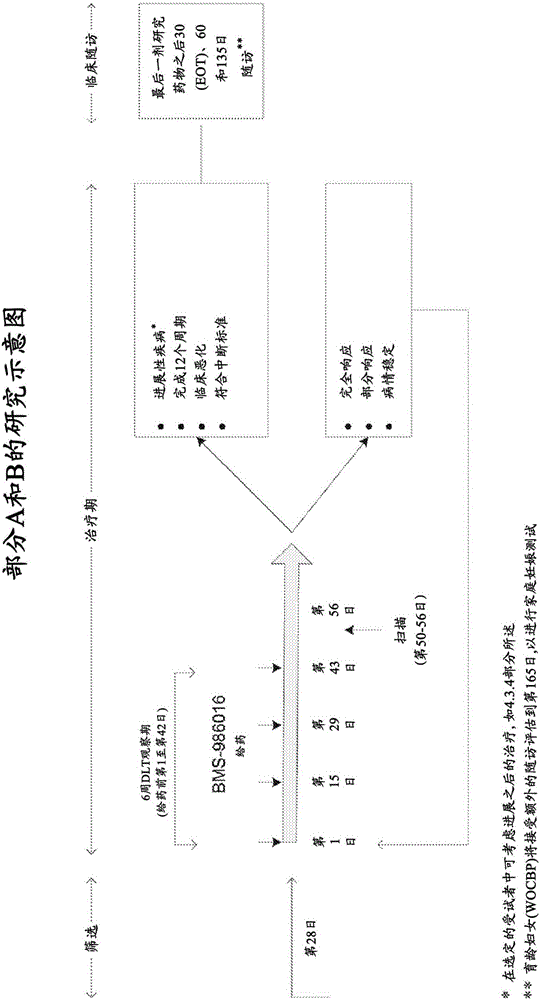
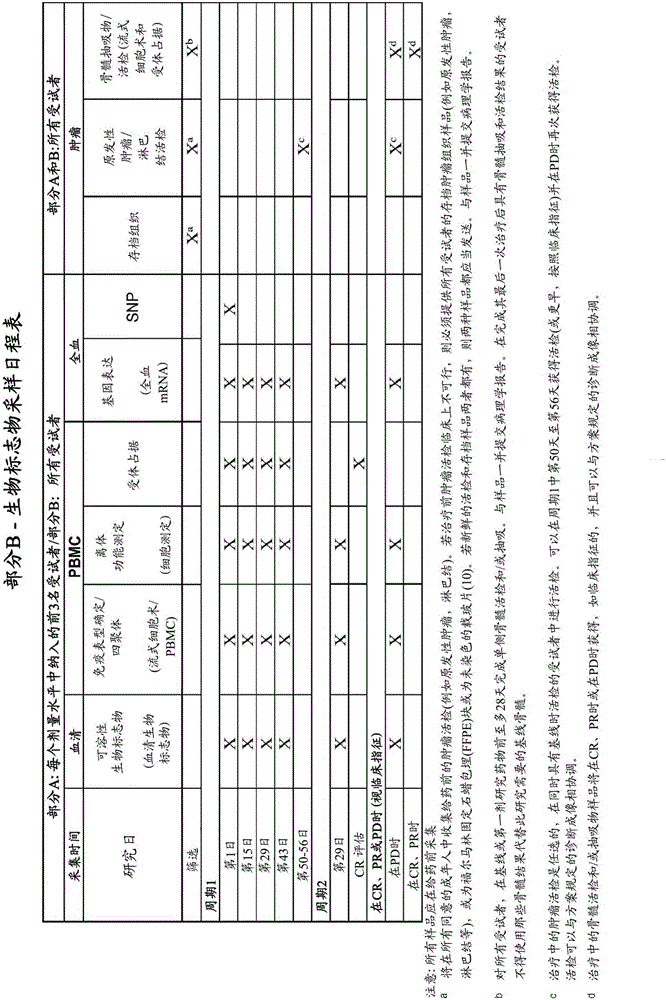
Anti-lag-3 antibodies to treat hematological malignancies
Provided are methods for clinical treatment of hematological malignancies, such as relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia or lymphoma using an anti-LAG-3 antibody. Particular malignancies include, e.g., chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), Hodgkin lymphoma (HL), or non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL).
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Method for hematology analysis
InactiveUS20110275064A1Reduce complexityLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansMedicine.hematologyFluorescence
A method whereby one or more fluorescent dyes are used to bind and stain nucleic acids in certain blood cells, such as, for example, white blood cells, nucleated red blood cells, and reticulocytes, and to induce fluorescent emissions upon excitation of photons from a given source of light, such as, for example, a laser, at an appropriate wavelength. More particularly, this invention provides a method whereby a fluorescent trigger is used in a data collection step for collecting events that emit strong fluorescence, in order to separate white blood cells and nucleated red blood cells from red blood cells and platelets without the need for using a lysing agent.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Cytological and histological fixative composition and methods of use
InactiveCN1310797AReduce pollutionImmobilised enzymesPreparing sample for investigationMedicine.hematologyParticulates
The present invention is directed to a fixative composition, the use of the fixative composition in preparing cytological or histological specimens, and a method of preparing particulate matter, such as cytology, hematology and microbiology specimens, for examination by collecting the particulate matter in a uniform layer, preferably a monolayer, and fixing the particles in a composition according to the present invention. The cytological, hematological, microbiological and histological fixative composition of the present invention contains an aldehyde cross-linker, a polyol and a detergent. The method of the present invention for preserving the particulate or histological specimen uses the fixative composition containing an aldehyde cross-linker, a polyol and a detergent.
Owner:莱密纳股份有限公司
Inhalation of nitric oxide for treating respiratory diseases
Owner:ADVANCED INHILATION THERAPIES AIT LTD
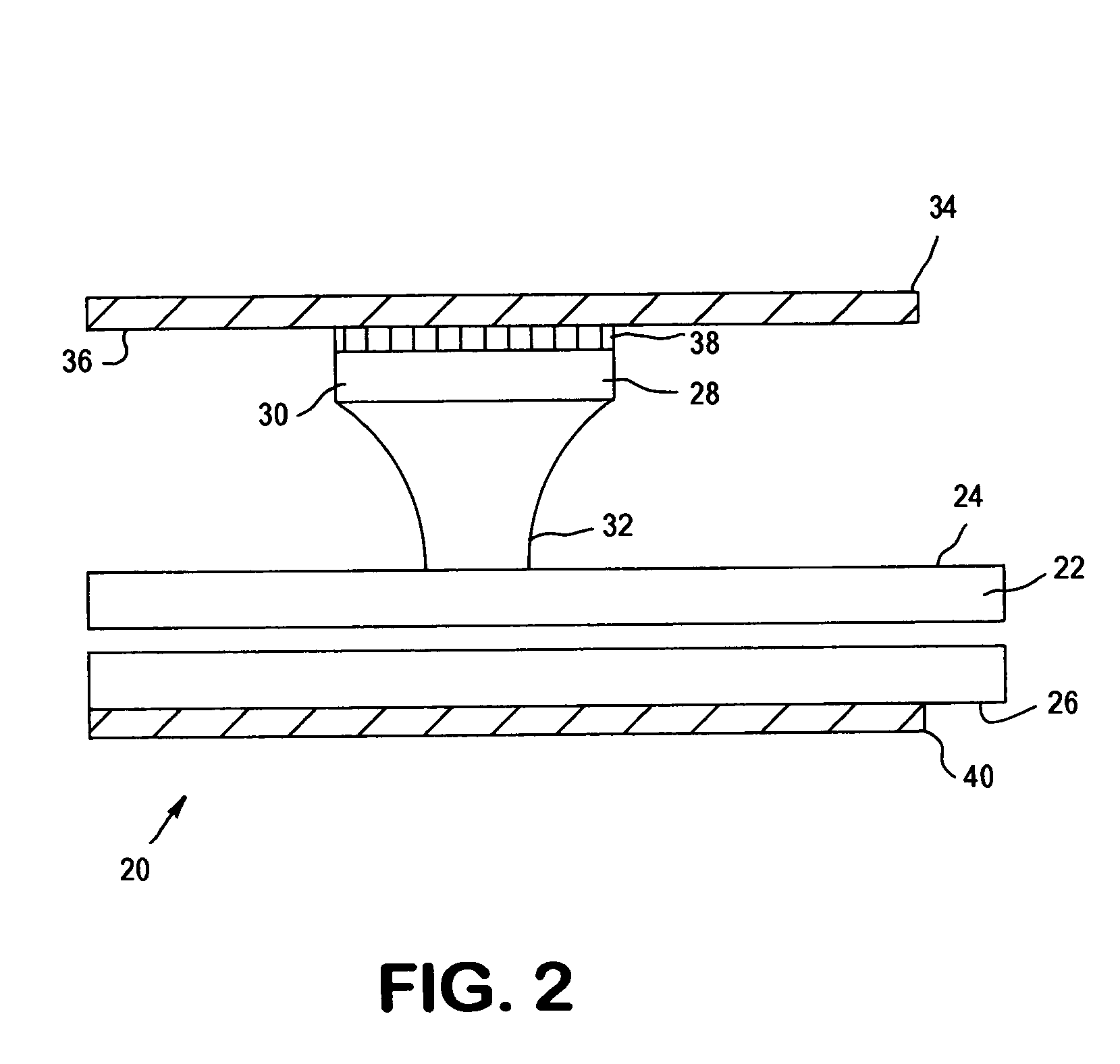
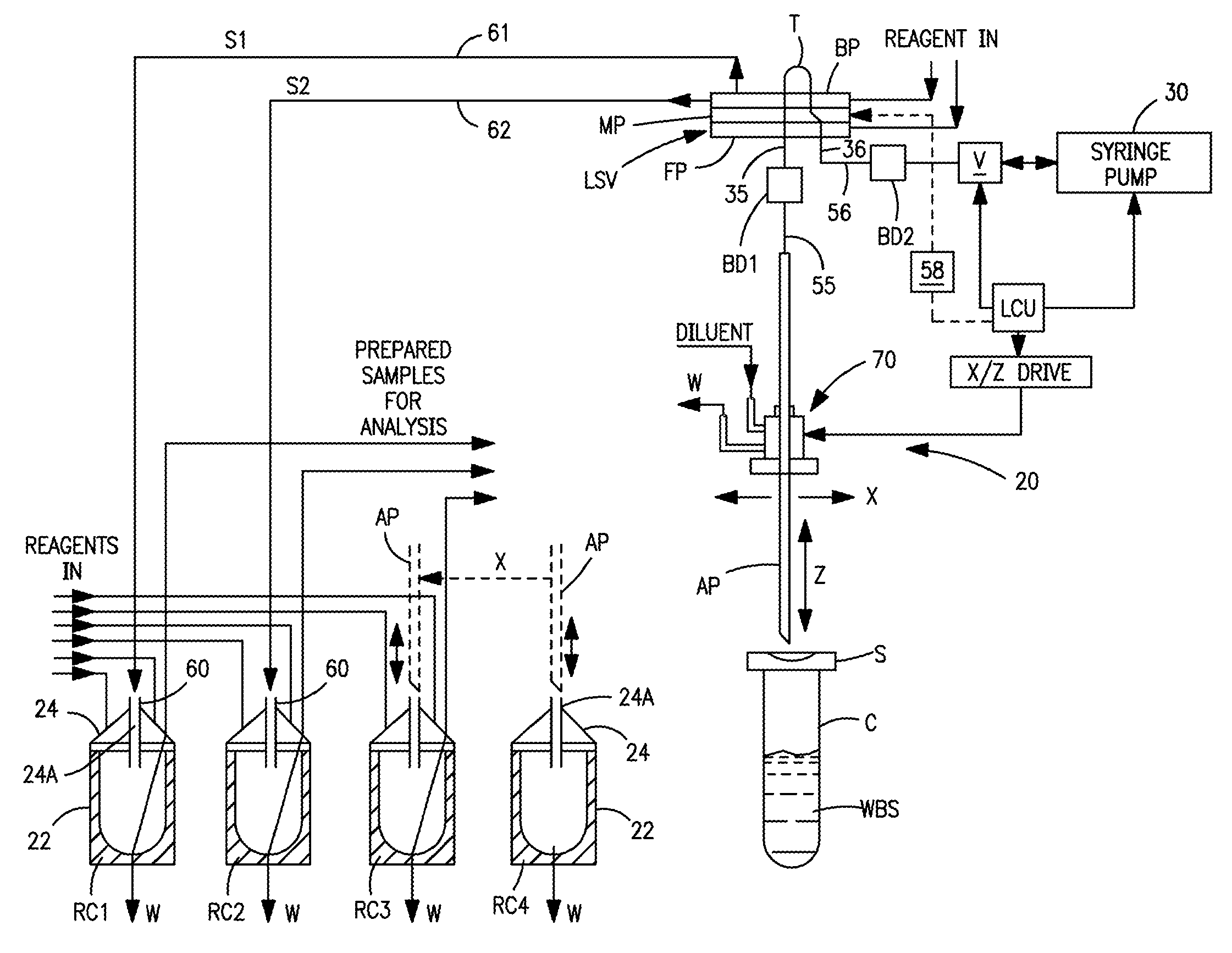
Apparatus for Aspirating and Dispensing Liquids in an Automated Analyzer
Apparatus for aspirating and dispensing liquid samples in an analytical instrument, e.g., a hematology instrument, includes a liquid-sampling valve that, while operating to segment and position for dispensing one or more precise volumes of a liquid sample that has been aspirated into the valve by a pump, simultaneously enables the apparatus to be operated in an aspirate / dispense (suck-and-spit) mode in which a liquid sample can be selectively driven through the valve in opposite directions by a pump, e.g., a syringe pump.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com