Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
88 results about "Nucleated Red Blood Cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
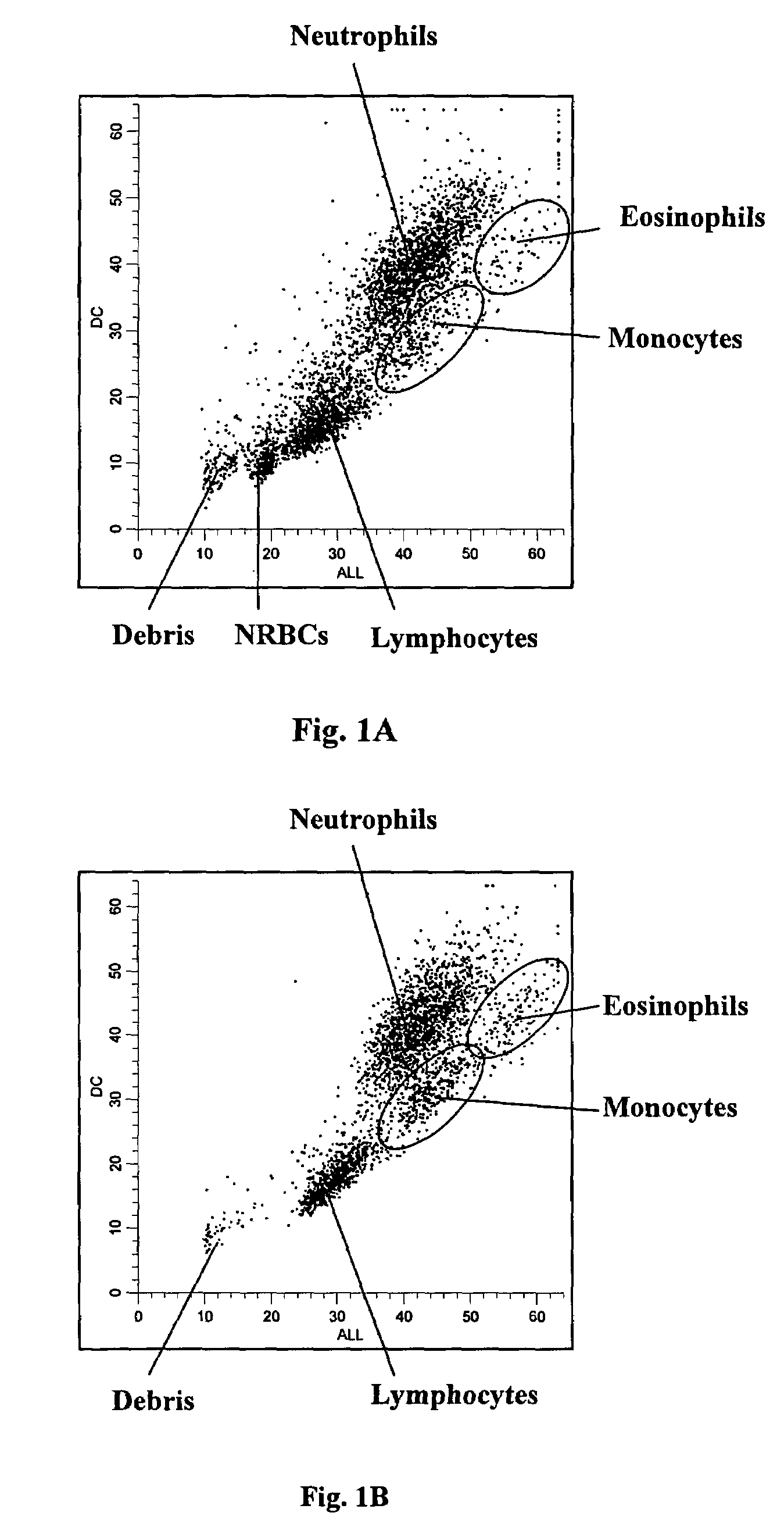
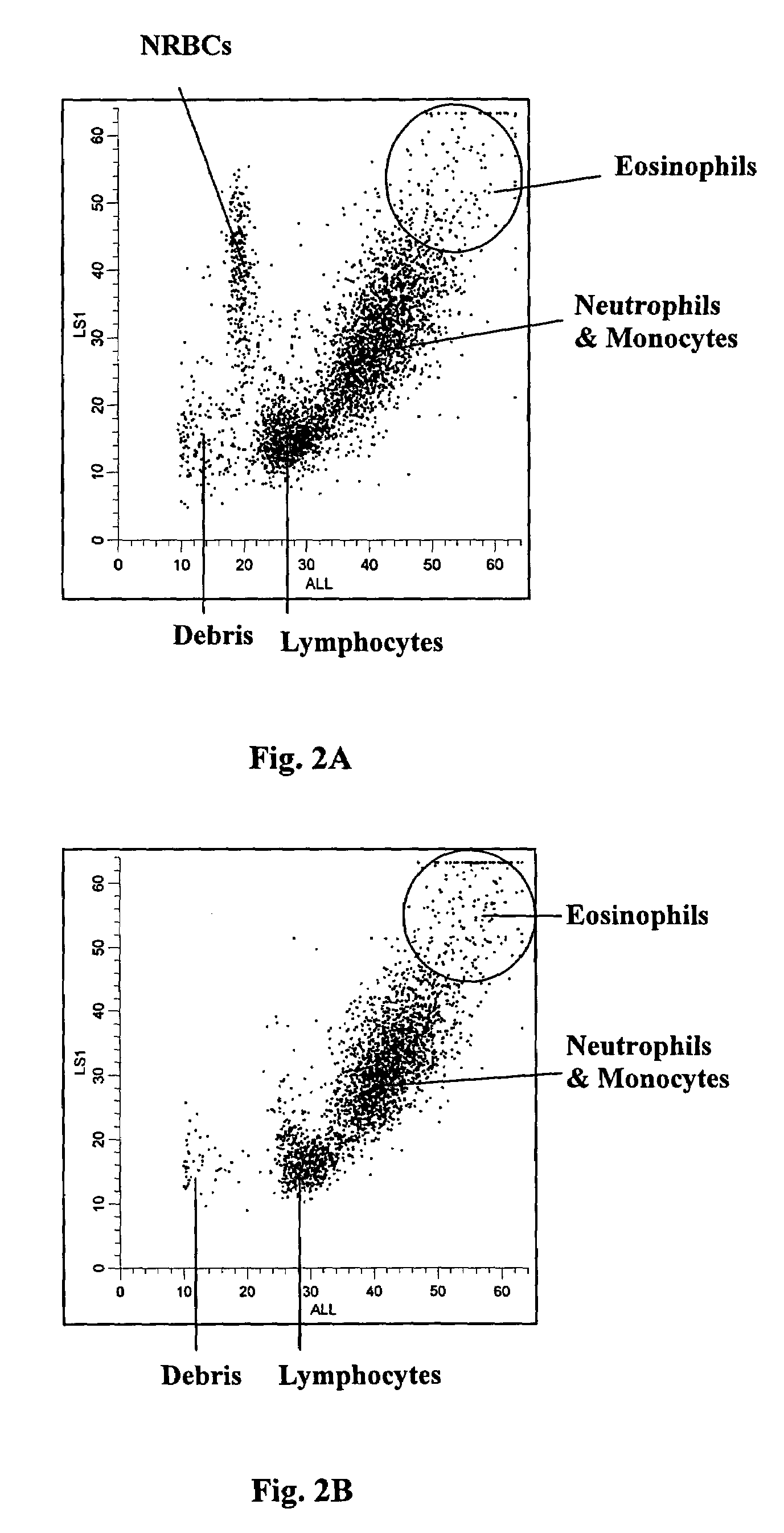
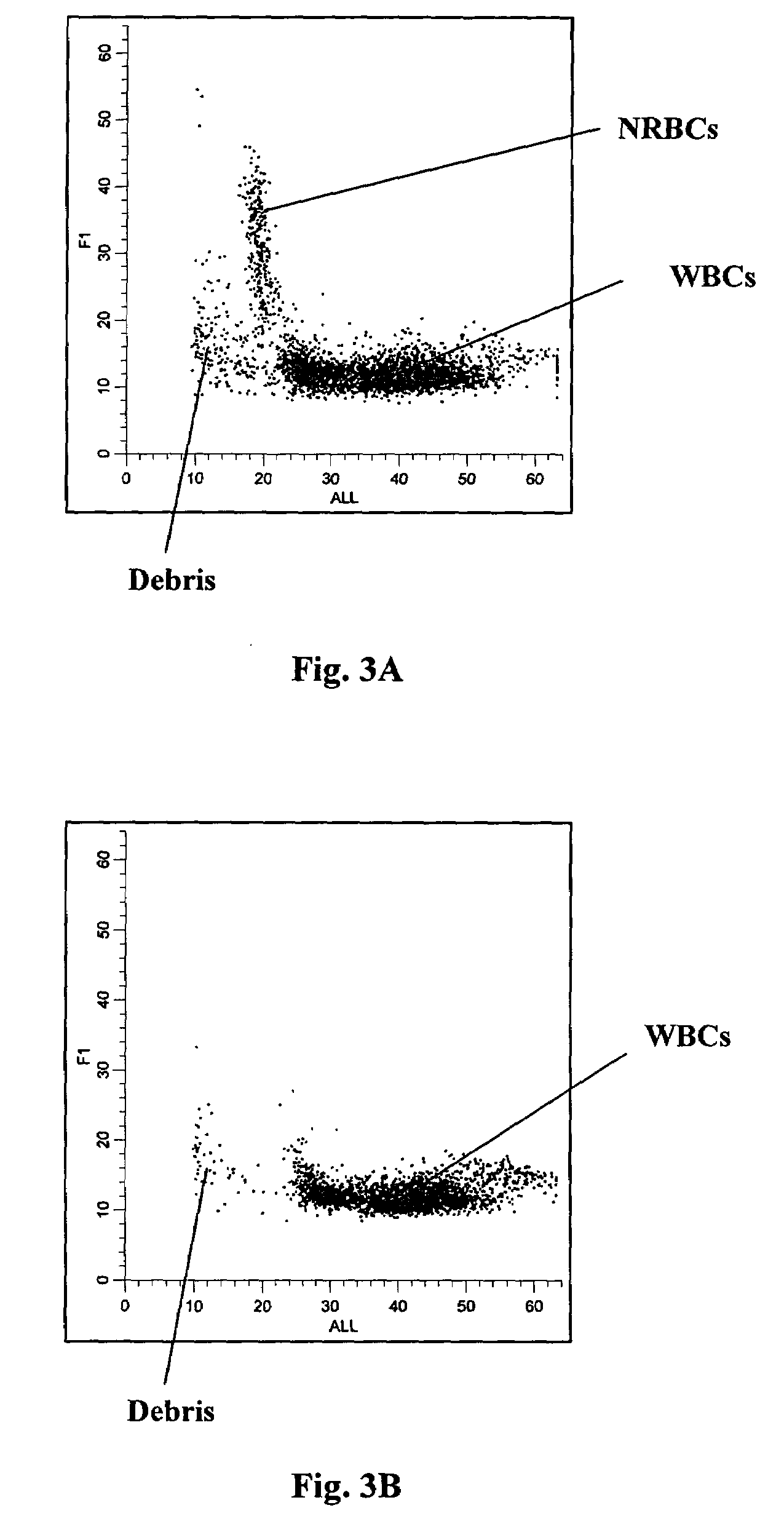
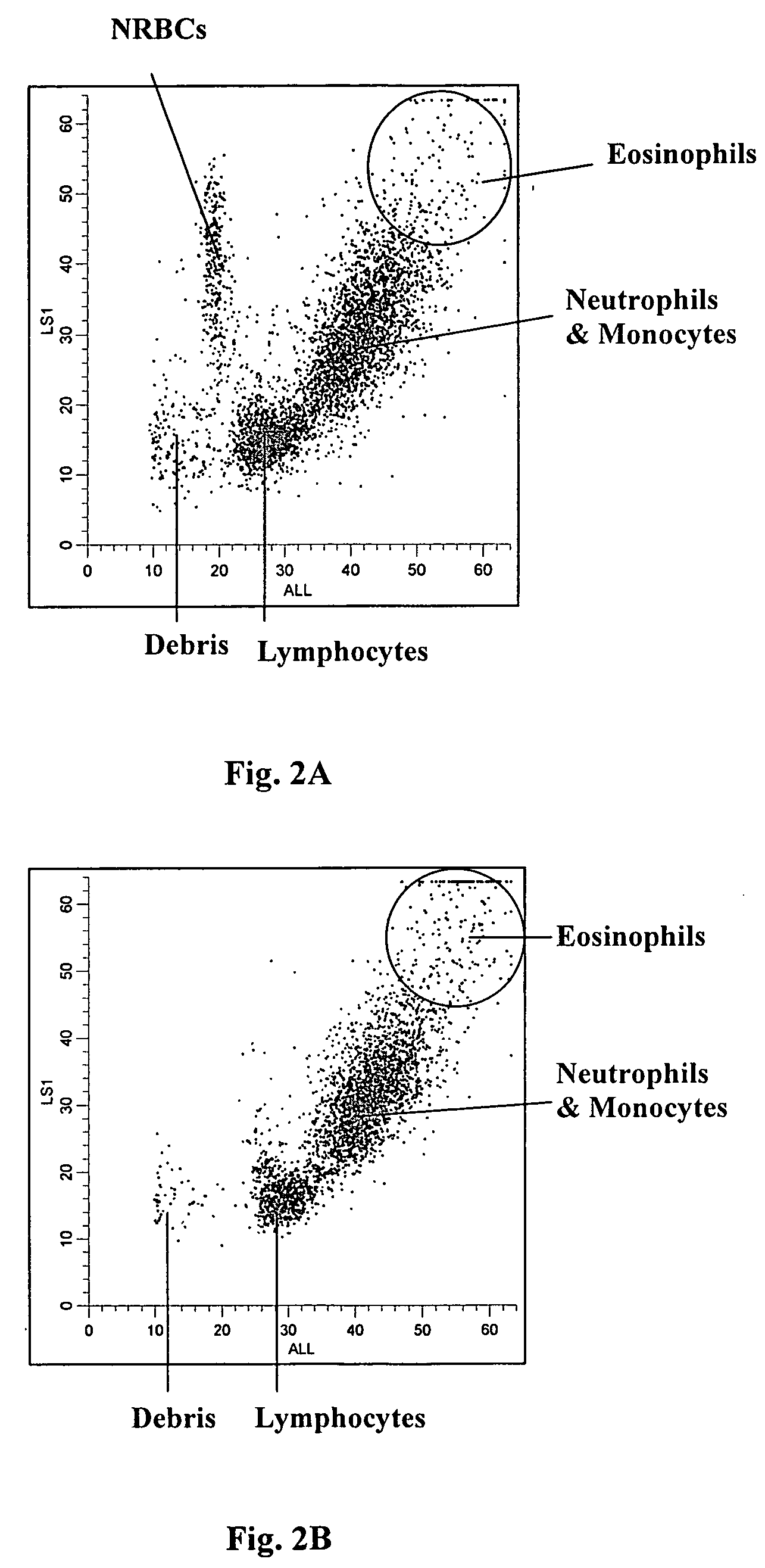
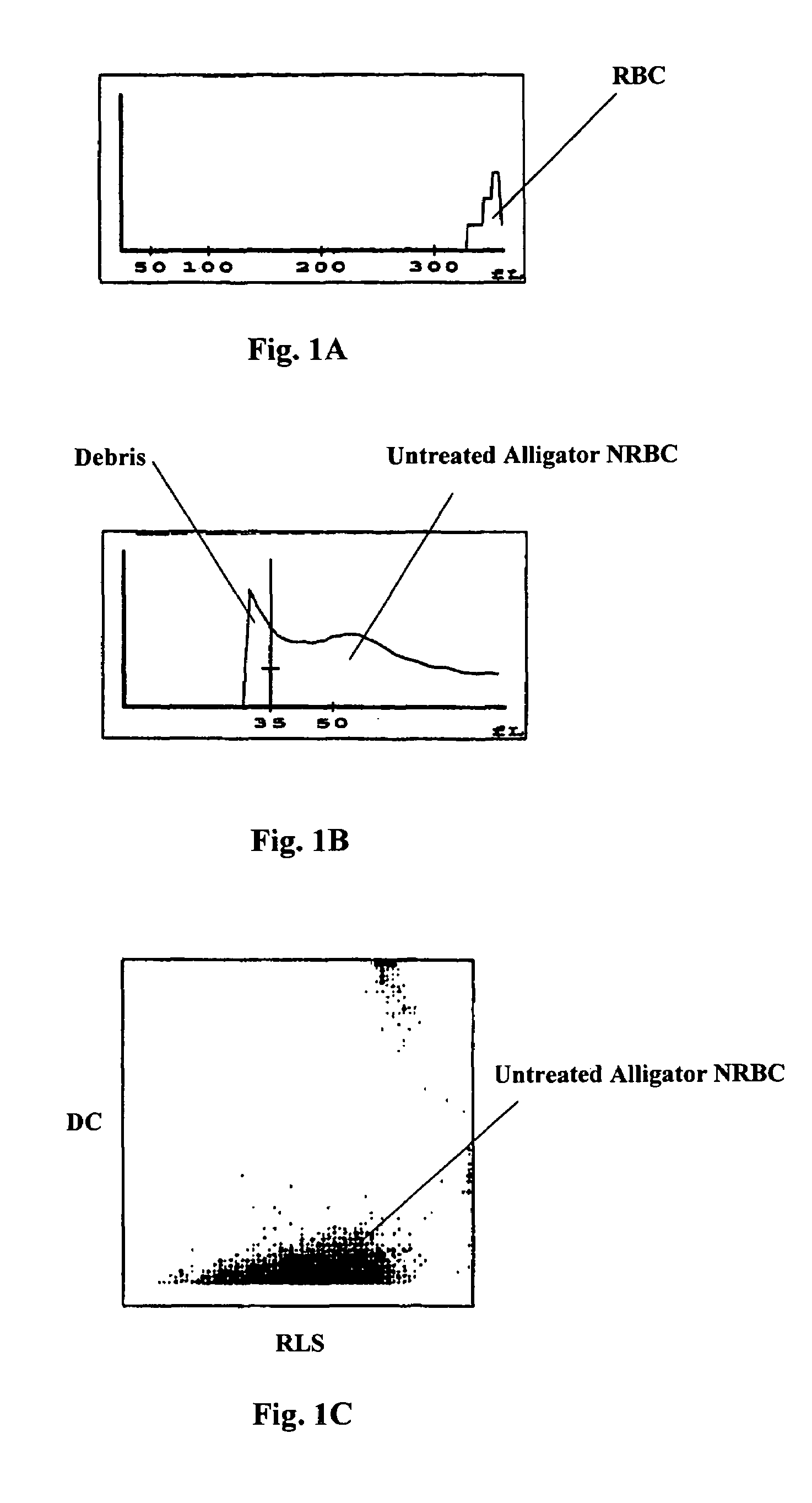
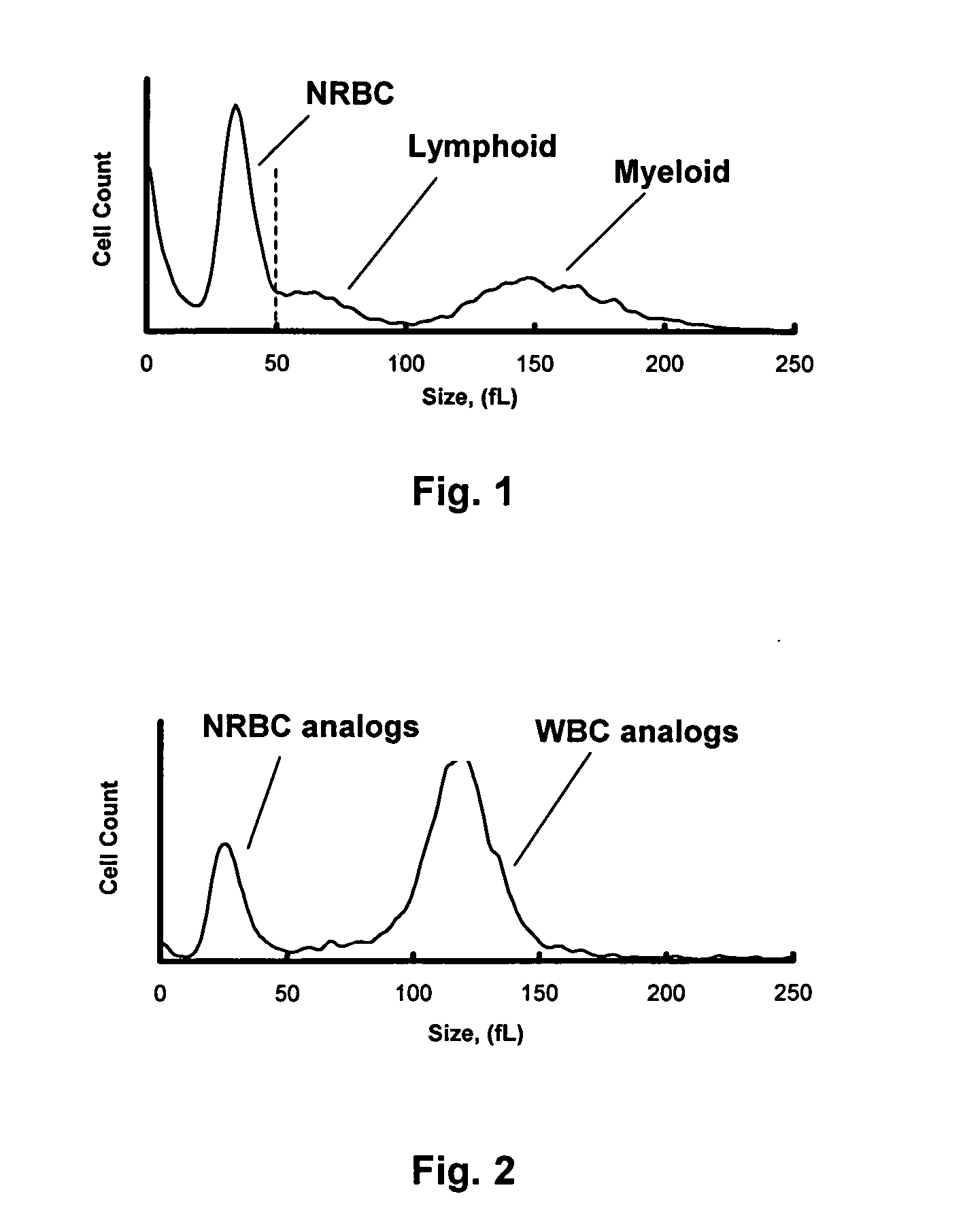
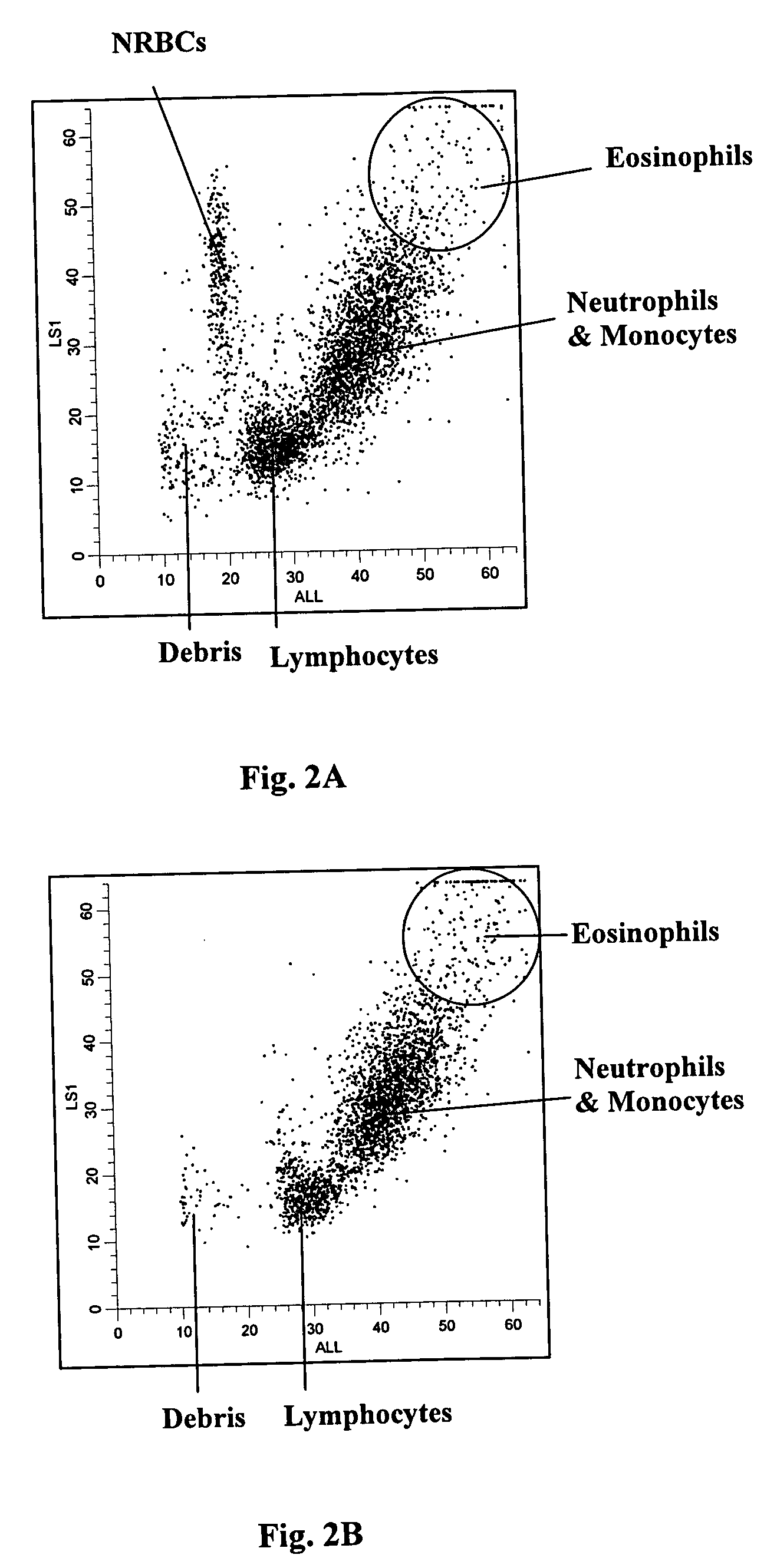
Red blood cells that are at the last stage of development, still containing a nucleus, that are found in the bone marrow and occasionally in the peripheral blood.
Selection of cells using biomarkers
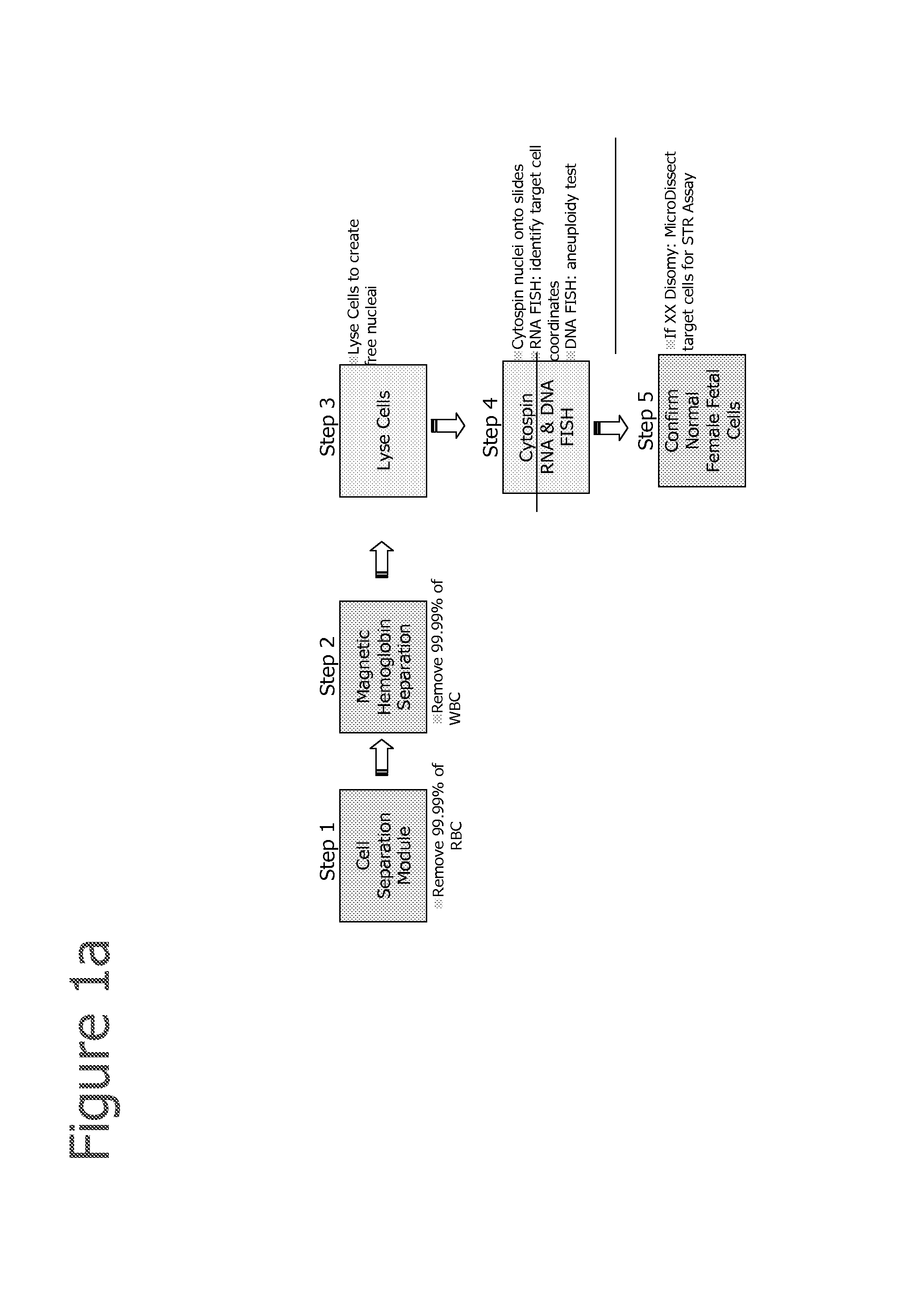
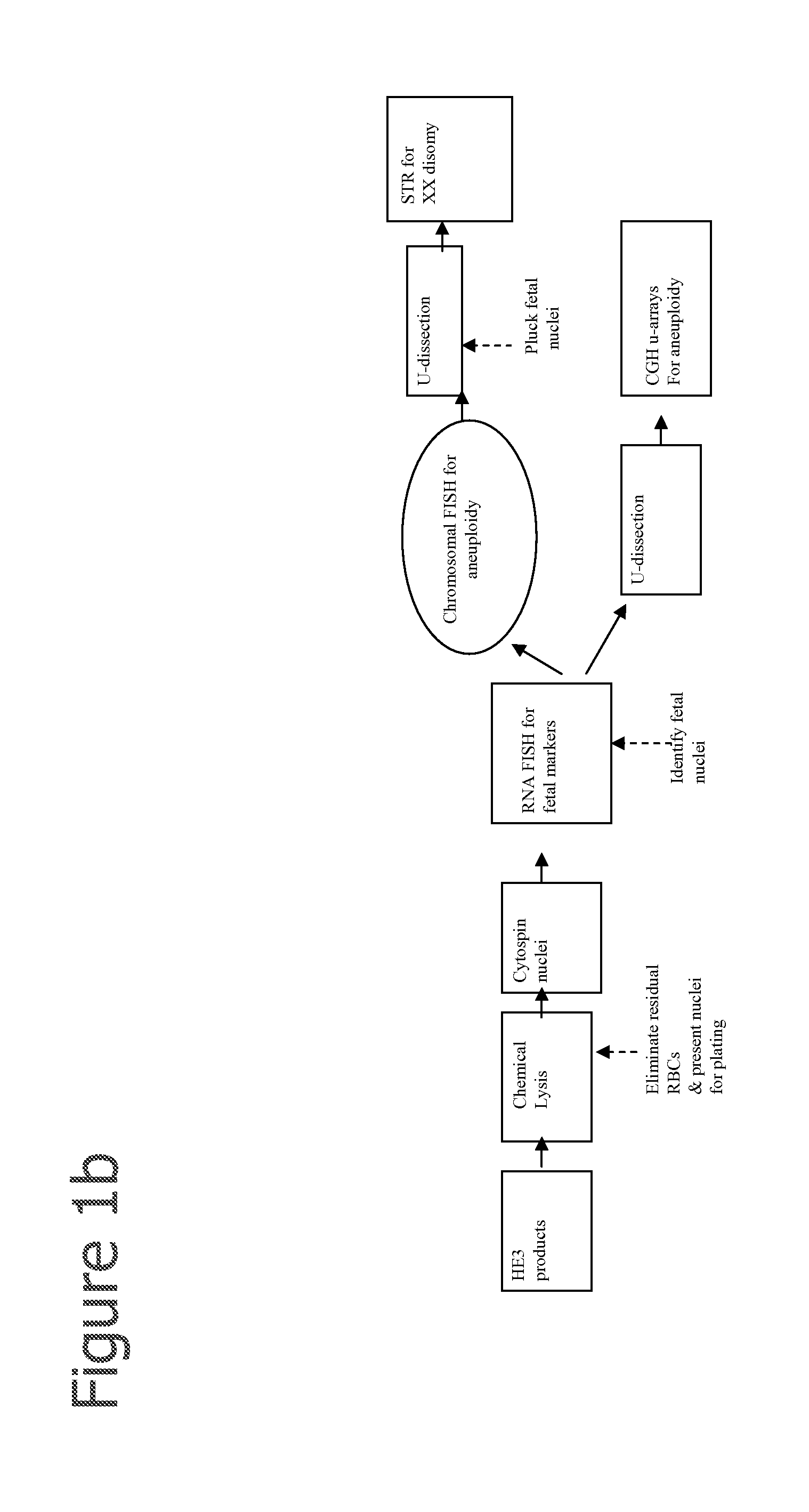
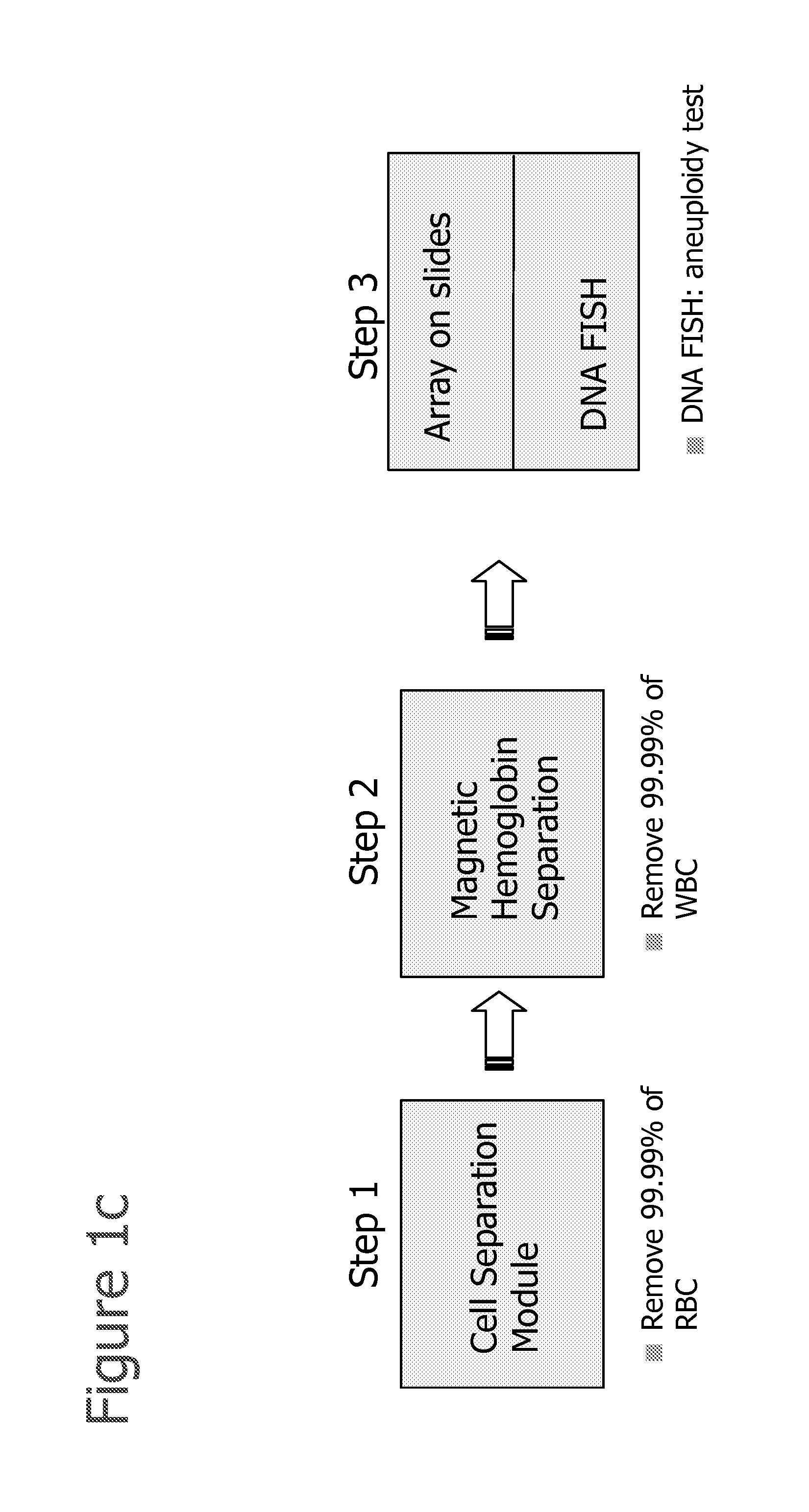
InactiveUS20080113358A1Easy to separateIncrease the number ofMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisFetal abnormalityFetal cell
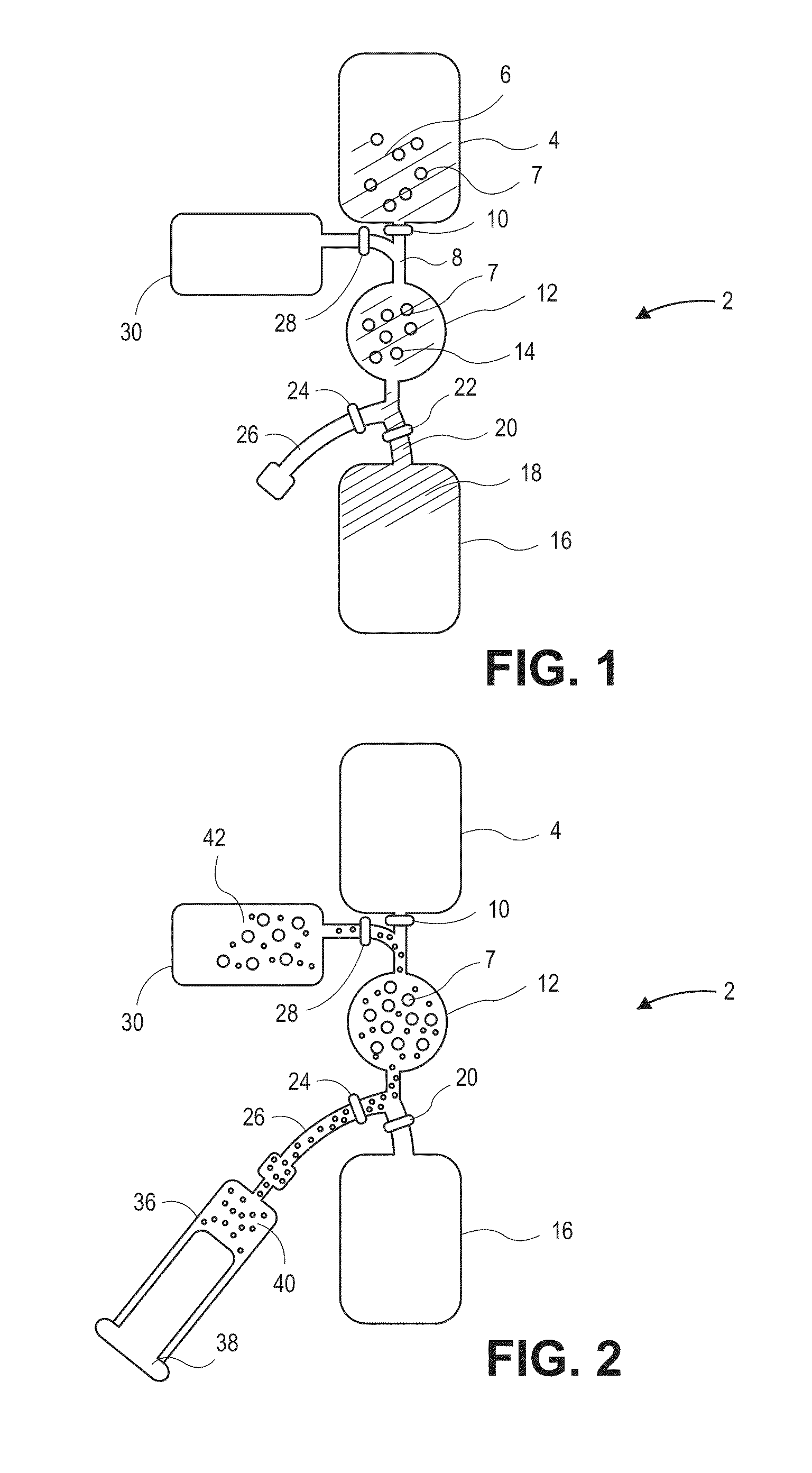
The present invention provides systems, apparatuses, and methods to isolate, select or detect the presence of a target cell (e.g., fetal cells) in a sample comprising mixed populations of cells that vastly outnumber the target cells. Target cells include fetal cells, such as nucleated red blood cells, and methods of selecting such cells include diagnosis of fetal abnormalities, i.e., aneuploidy. Furthermore, methods comprise utilizing fetal biomarkers to select fetal cells in a sample comprising fetal and adult cells.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +2
Methods for detecting fetal abnormality
InactiveUS20070059716A1Material nanotechnologyMicrobiological testing/measurementFetal abnormalityNucleic Acid Probes
The invention relates to a method of identifying fetal abnormality from a maternal blood sample by capturing an image of a fetal nucleated red blood cell obtained from the maternal blood sample; inputting probe intensities for a plurality of nucleic acid probes that bind fetal nucleic acids of interest; analyzing the probe intensities; and generating a diagnostic output according to results of the analysis. In some embodiments, the probes are specific to a chromosome.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +2
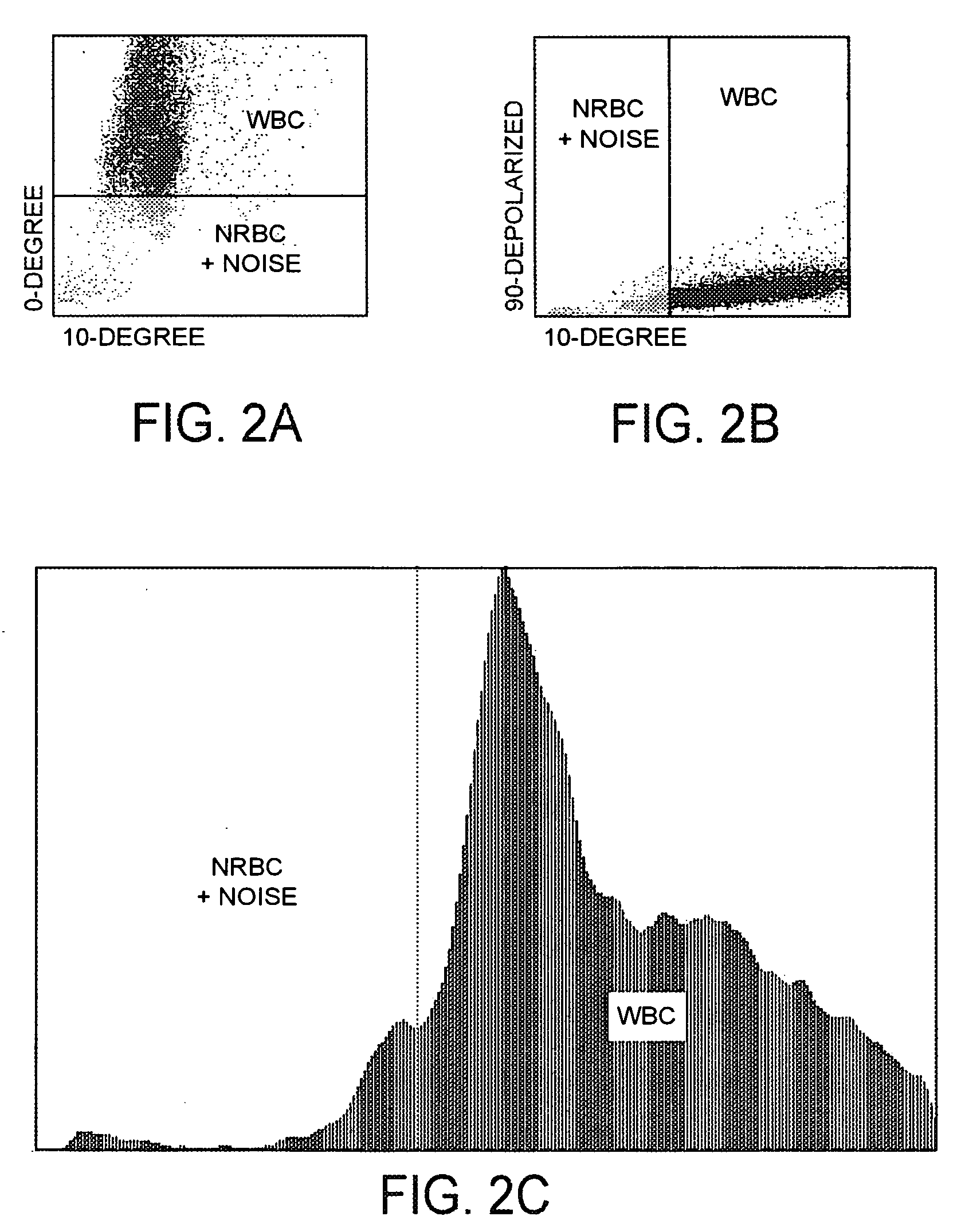
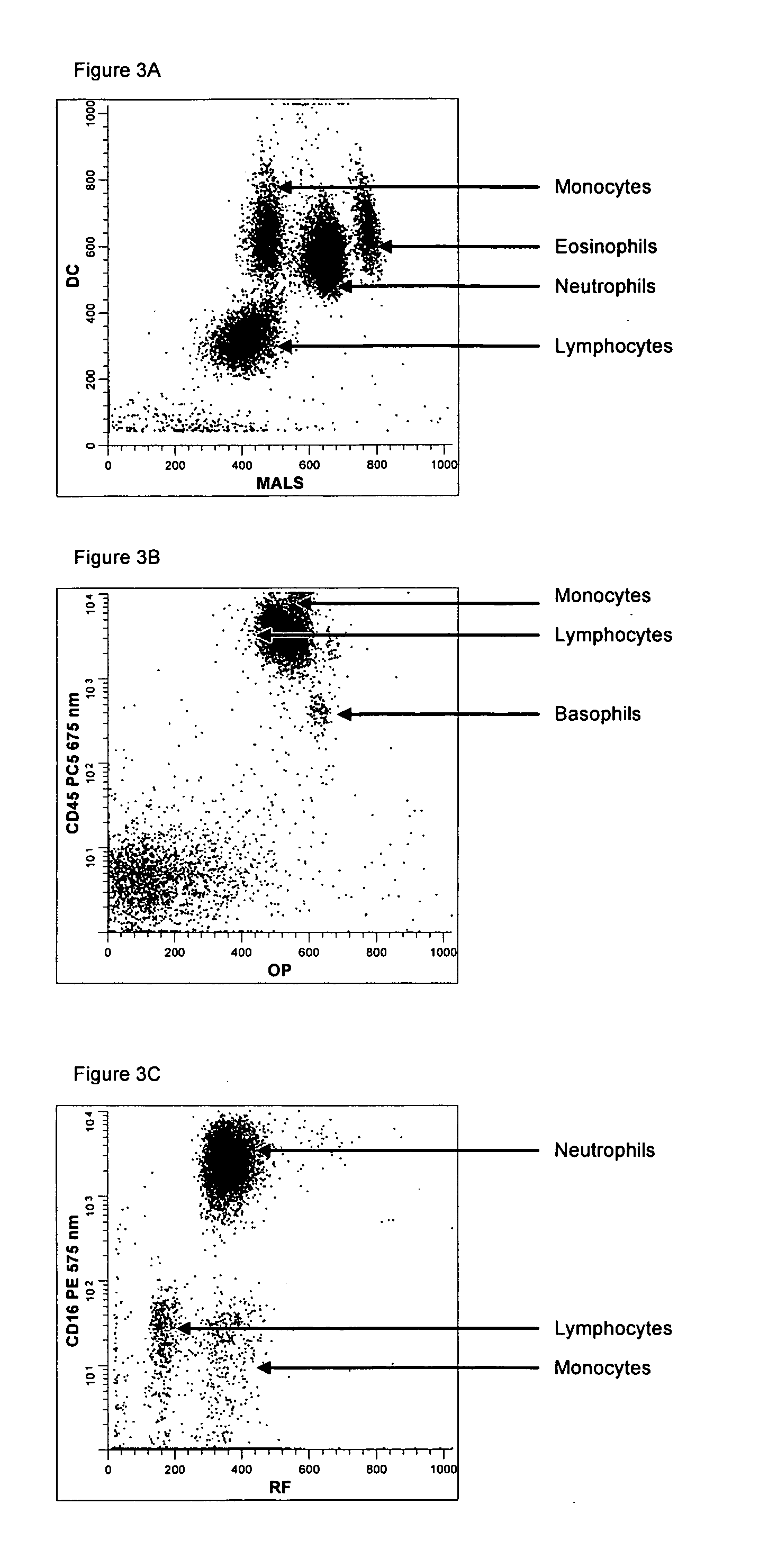
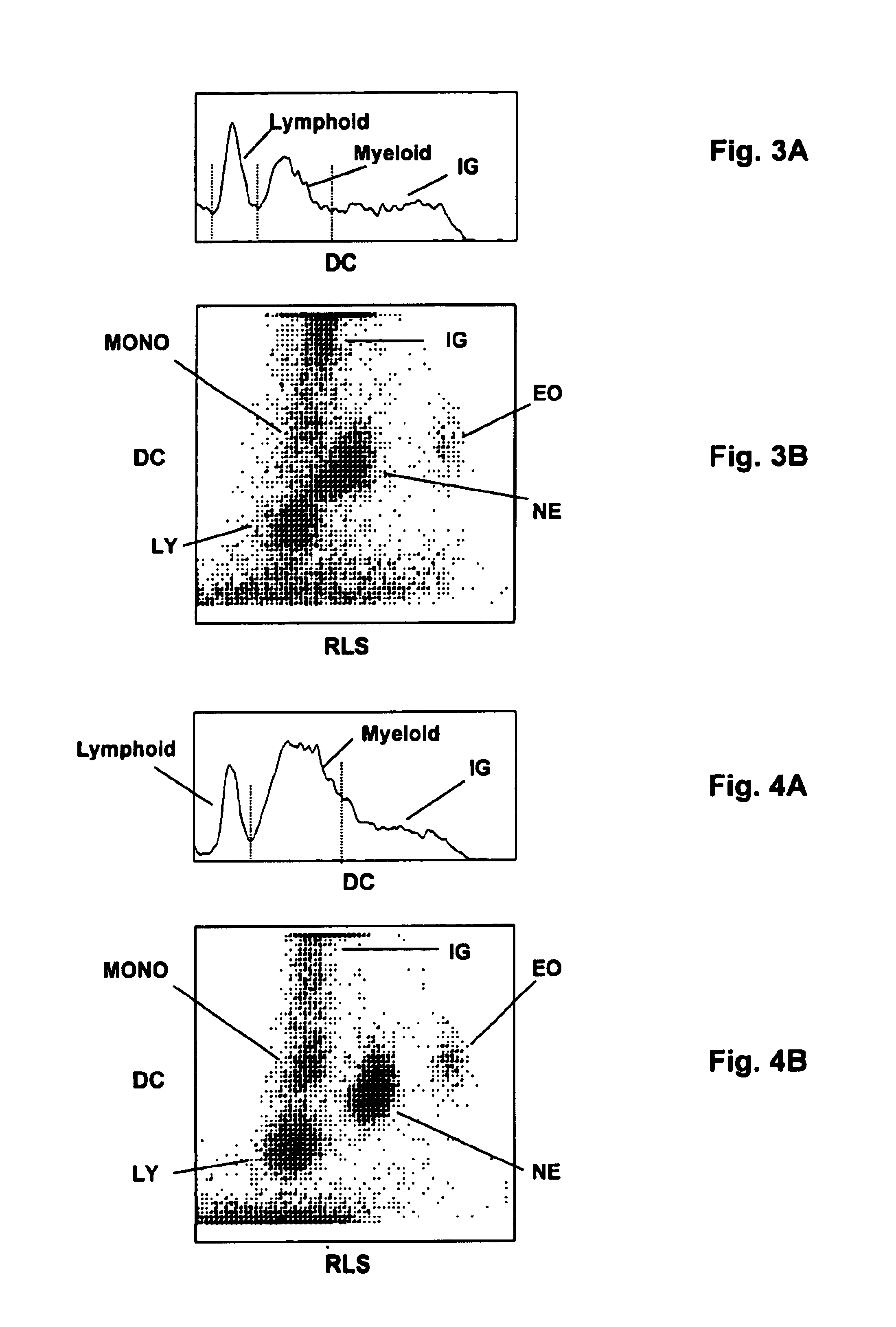
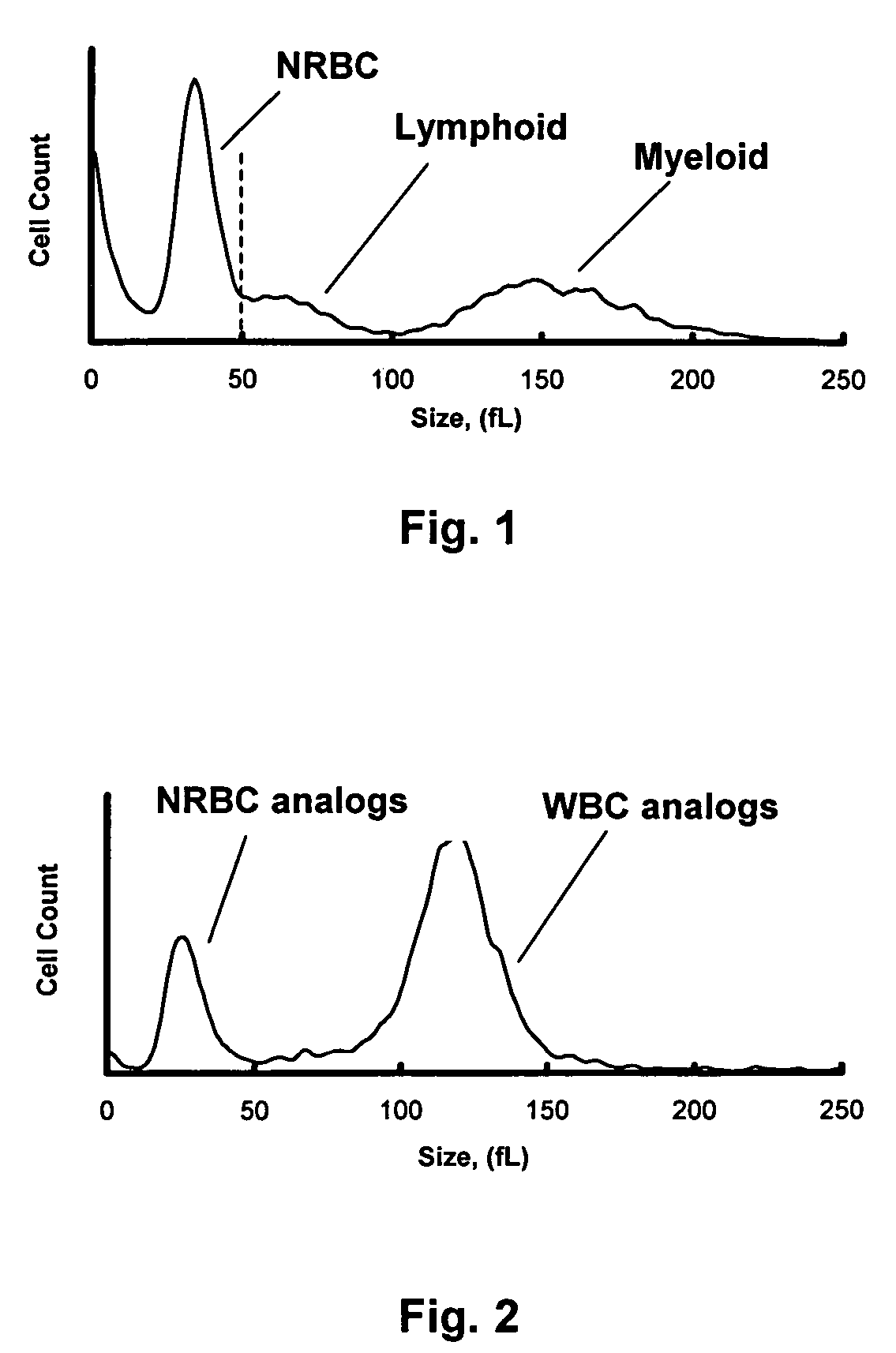
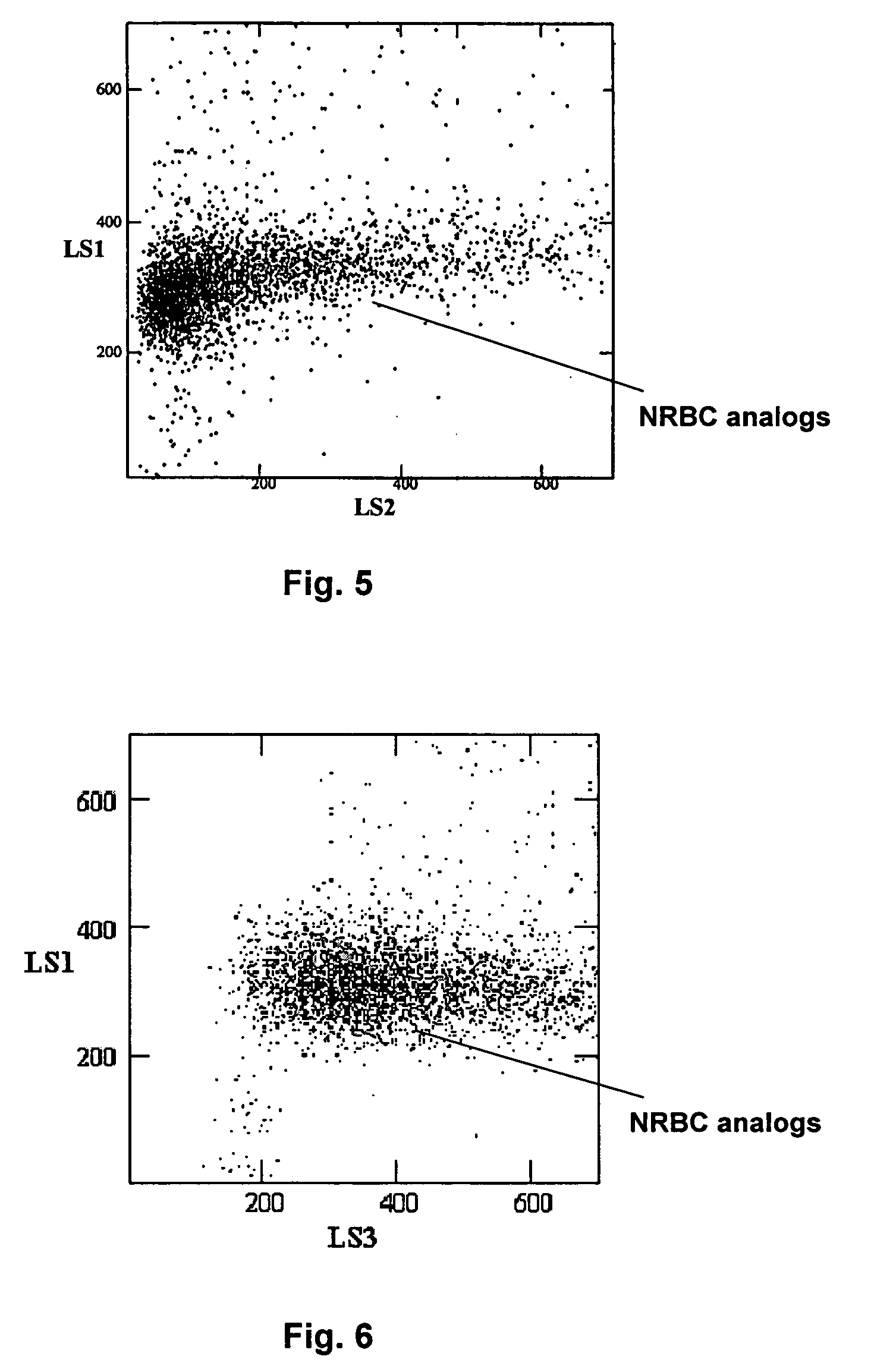
Method for determination of nucleated red blood cells and leukocytes in a whole blood sample in an automated hematology analyzer
ActiveUS20080153170A1Reduce distractionsInterfere with accurateSamplingBiological particle analysisLipid formationRed blood cell
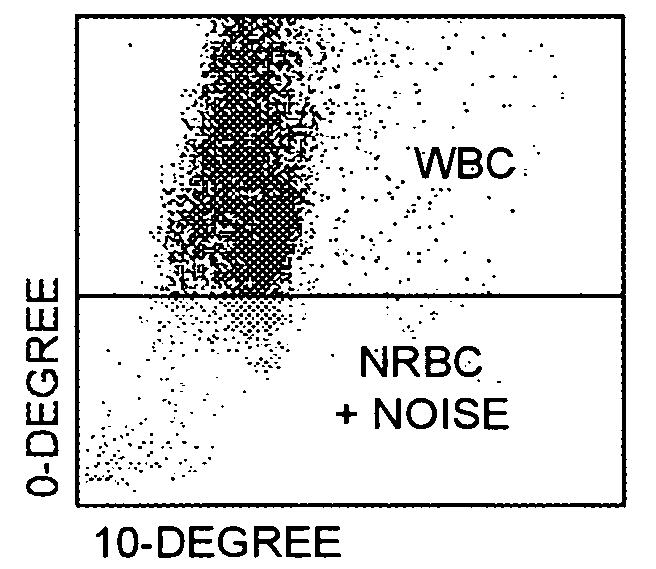
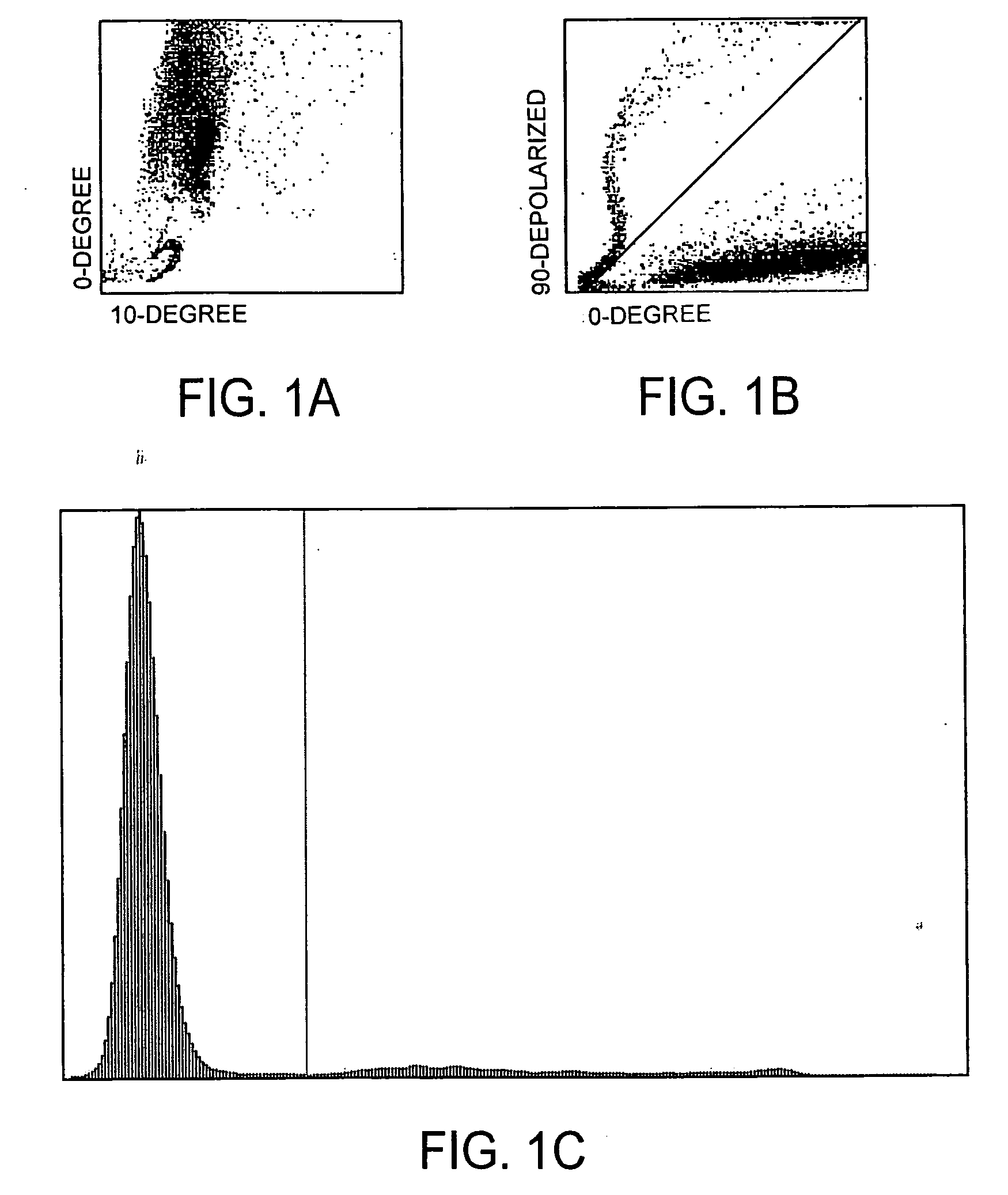
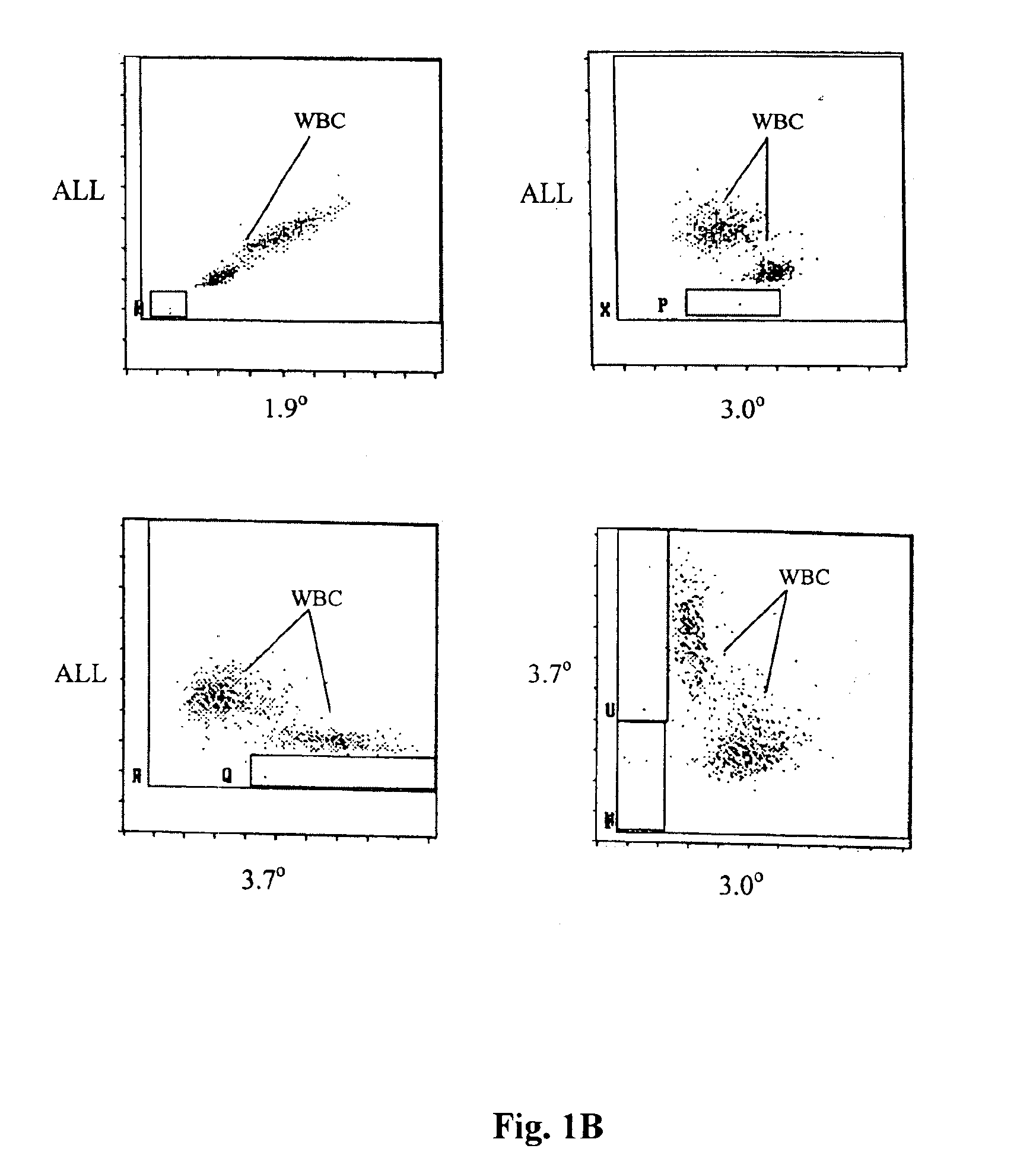
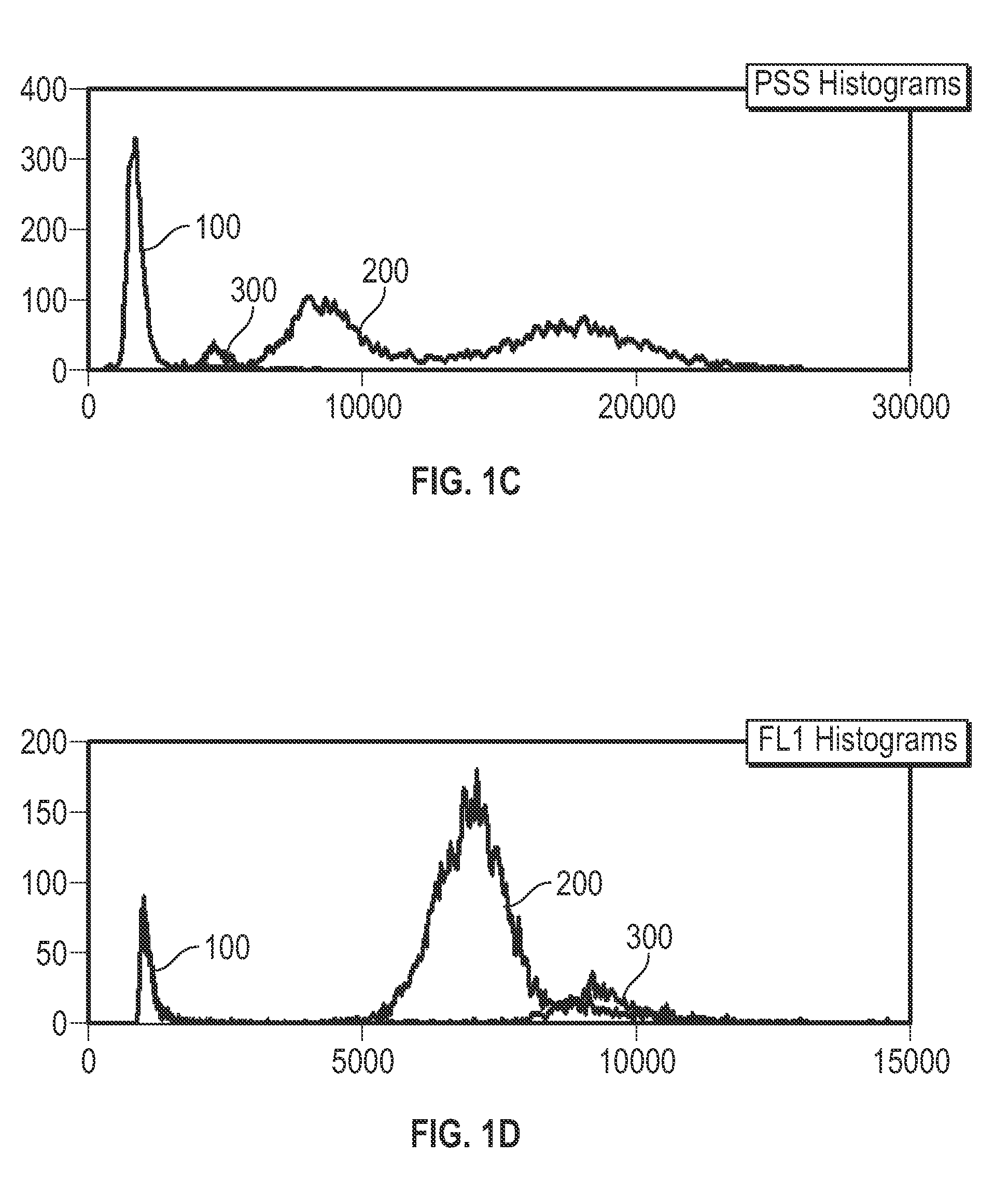
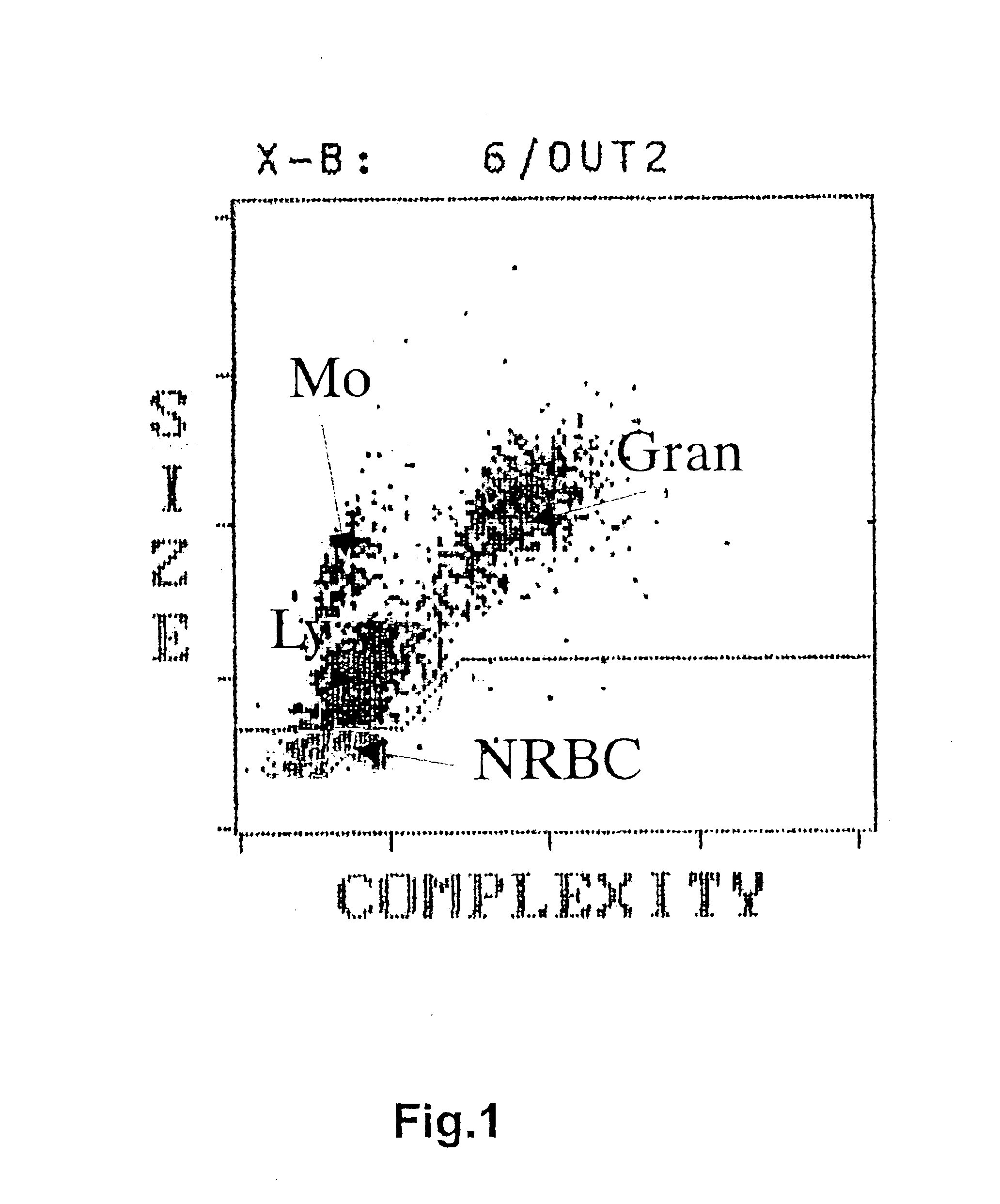
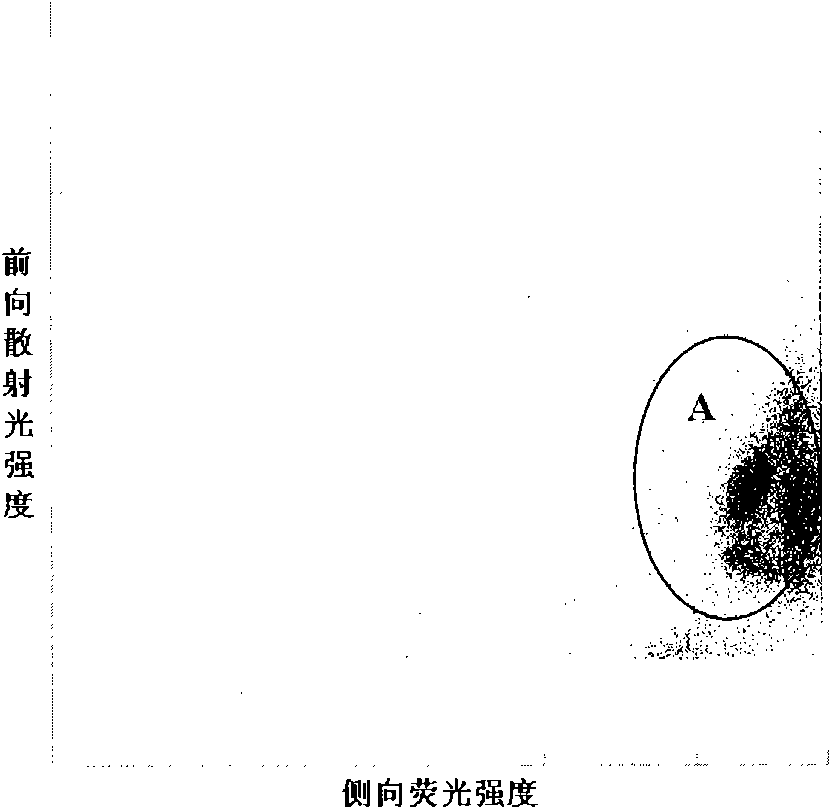
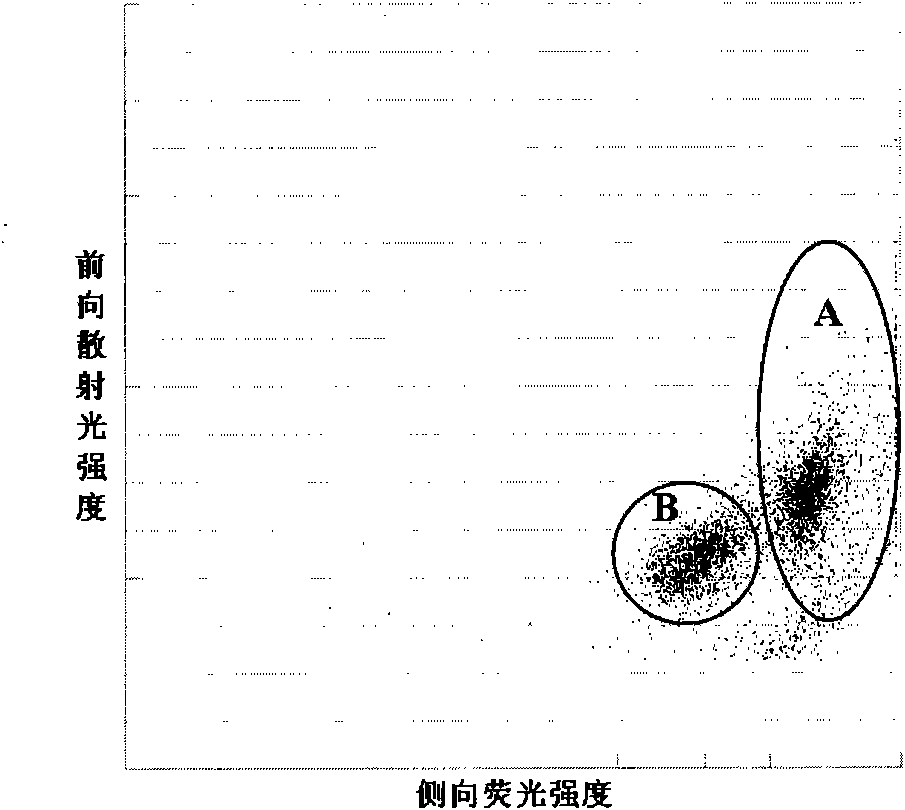
A method for enumerating white blood cells and nucleated red blood cells. The method comprises the steps of:(b) providing a lysed sample of whole blood;(b) introducing the lysed sample to a light-scattering multi-angle depolarizing flow cytometer;(c) removing depolarizing interference, e.g., lipid droplets and other measured particles;(d) differentiating nucleated red blood cells and noise from white blood cells in the absence of depolarizing interference;(e) differentiating nucleated red blood cells from noise in the absence of depolarizing interference and white blood cells; and(f) differentiating possible platelet clumps.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Method of measurement of nucleated red blood cells
Methods are provided for measurement of nucleated red blood cells. The methods include exposing a blood cell sample to a reagent system to lyse mature red blood cells, subsequently analyzing nucleated red blood cells in a flow cell by axial light loss, low angle light scatter and DC impedance measurements, or two selected measurements thereof; and then differentiating nucleated red blood cells from other cell types by using measured signals and / or functions thereof.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Method of measurement of nucleated red blood cells
Methods are provided for measurement of nucleated red blood cells in a blood sample. The methods include exposing a blood cell sample to a reagent system to lyse mature red blood cells, subsequently analyzing nucleated red blood cells in a flow cell by axial light loss, DC impedance, and medium angle light scatter measurements; by axial light loss, low angle light scatter, and medium angle light scatter measurements; or by axial light loss, DC impedance, low angle light scatter, and medium angle light scatter measurements; and then differentiating nucleated red blood cells from other cell types by using measured signals and / or functions thereof.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
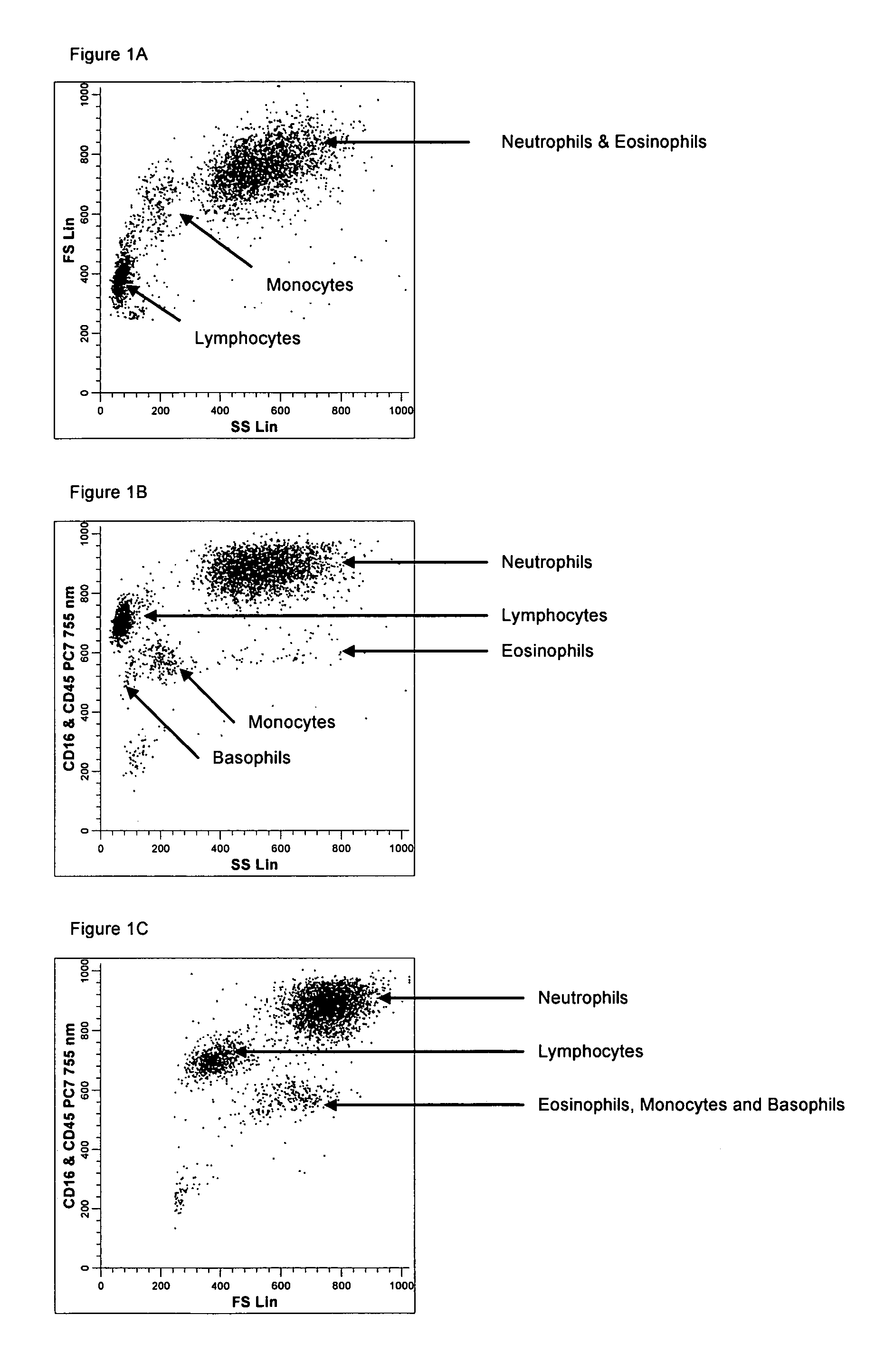
Method for a fully automated monoclonal antibody-based extended differential
ActiveUS20050260766A1Great advanceHigh degree of sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAntigenWhite blood cell
A method useful for the enumeration of cell populations in a biological sample includes the steps of reacting in a single reaction mixture a sample, a first antibody labeled with a fluorochrome having a first emission spectrum and an additional antibody. The first antibody binds to an antigenic determinant differentially expressed on leukocytes and non-leukocytes. The additional antibody binds to an antigenic determinant differentially expressed on mature and immature granulocytes or myeloid cells, and is labeled either with the first fluorochrome or an additional fluorochrome having an emission spectrum distinguishable from the first emission spectrum. The reaction mixture can be mixed with a nucleic acid dye having an emission spectrum that overlaps with one of the first or additional emission spectra. The reaction mixture may be treated with a lytic system that differentially lyses non-nucleated red blood cells and conserves leukocytes. Populations of hematological cells are detected and enumerated using at least two parameters (fluorescence, optical, and electrical) for each population.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Method of measurement of nucleated red blood cells
Methods are provided for measurement of nucleated red blood cells in a blood sample. The methods include exposing a blood cell sample to a reagent system to lyse mature red blood cells, subsequently analyzing nucleated red blood cells in a flow cell by axial light loss, DC impedance, and medium angle light scatter measurements; by axial light loss, low angle light scatter, and medium angle light scatter measurements; or by axial light loss, DC impedance, low angle light scatter, and medium angle light scatter measurements; and then differentiating nucleated red blood cells from other cell types by using measured signals and / or functions thereof.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Method for a fully automated monoclonal antibody-based extended differential
ActiveUS7625712B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFluorescenceWhite blood cell
A method useful for the enumeration of cell populations in a biological sample includes the steps of reacting in a single reaction mixture a sample, a first antibody labeled with a fluorochrome having a first emission spectrum and an additional antibody. The first antibody binds to an antigenic determinant differentially expressed on leukocytes and non-leukocytes. The additional antibody binds to an antigenic determinant differentially expressed on mature and immature granulocytes or myeloid cells, and is labeled either with the first fluorochrome or an additional fluorochrome having an emission spectrum distinguishable from the first emission spectrum. The reaction mixture can be mixed with a nucleic acid dye having an emission spectrum that overlaps with one of the first or additional emission spectra. The reaction mixture may be treated with a lytic system that differentially lyses non-nucleated red blood cells and conserves leukocytes. Populations of hematological cells are detected and enumerated using at least two parameters (fluorescence, optical, and electrical) for each population.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
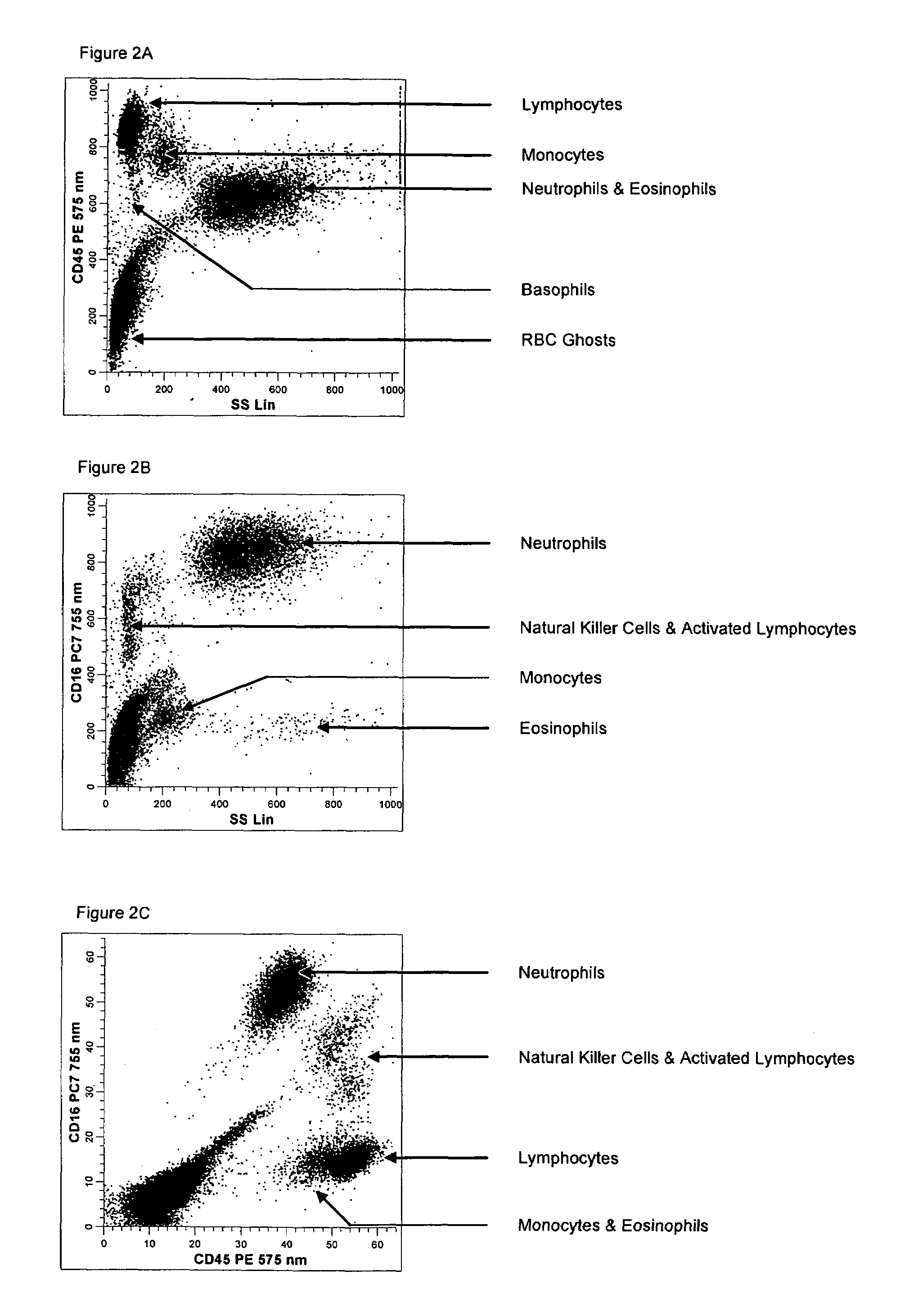
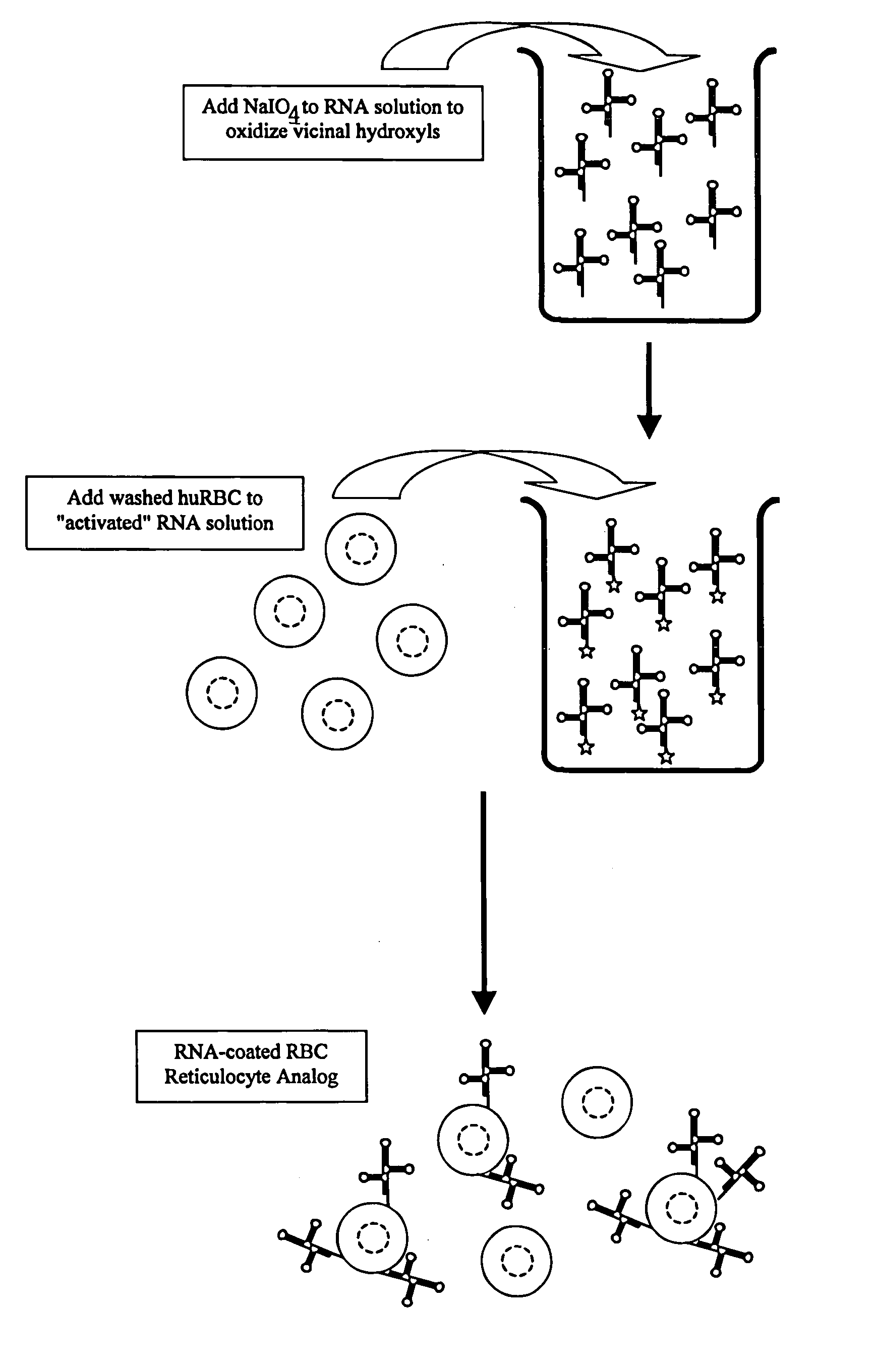
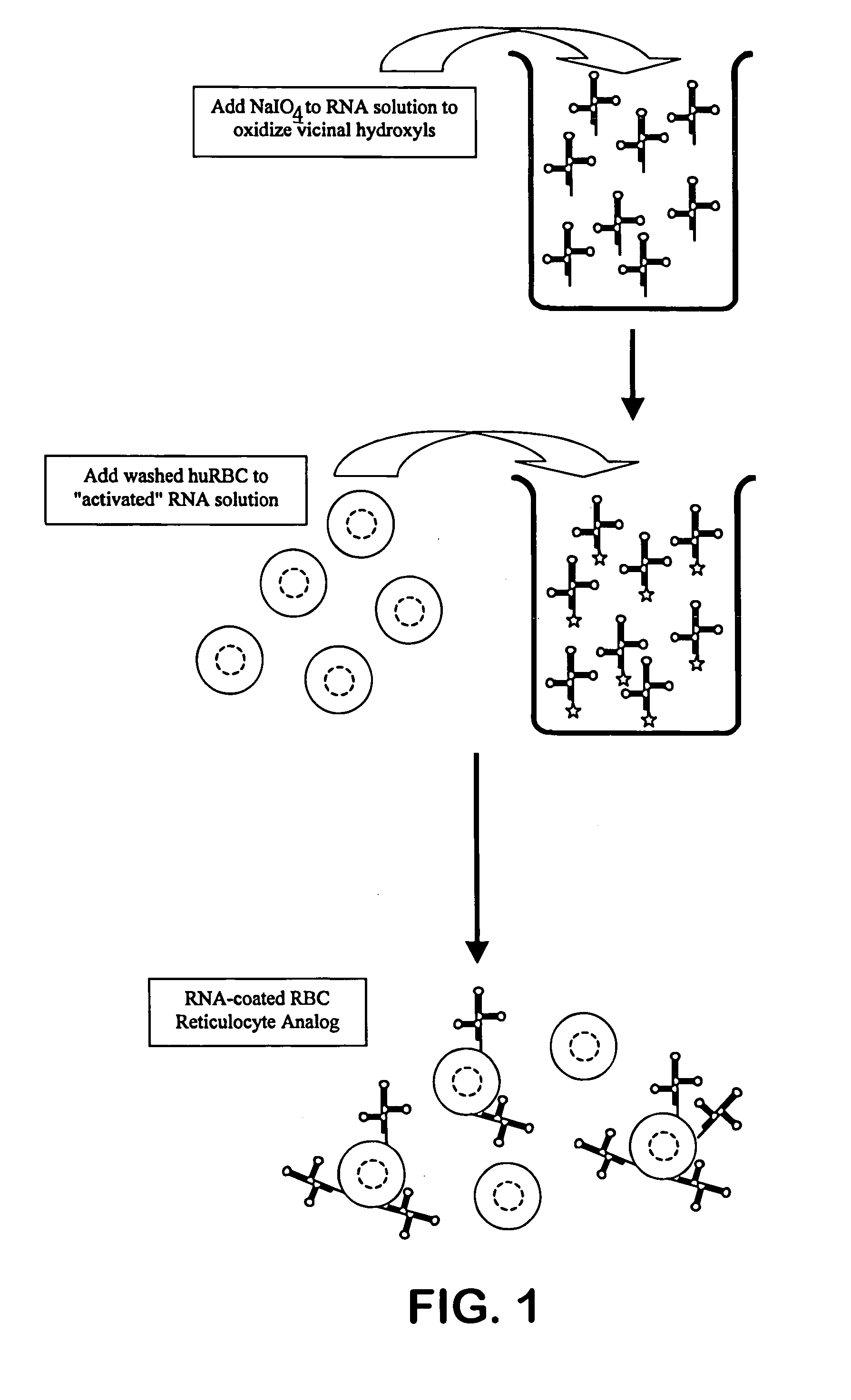
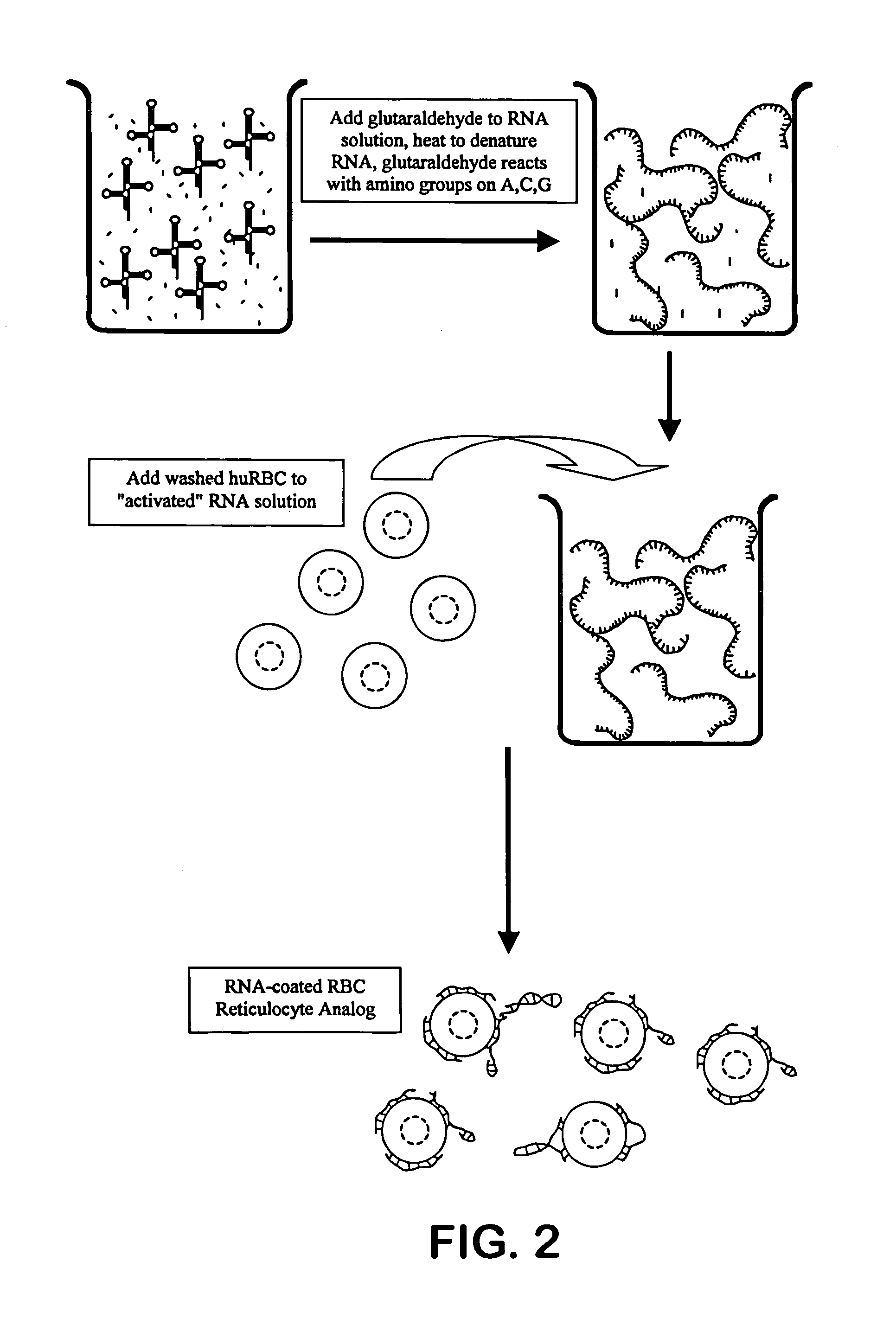
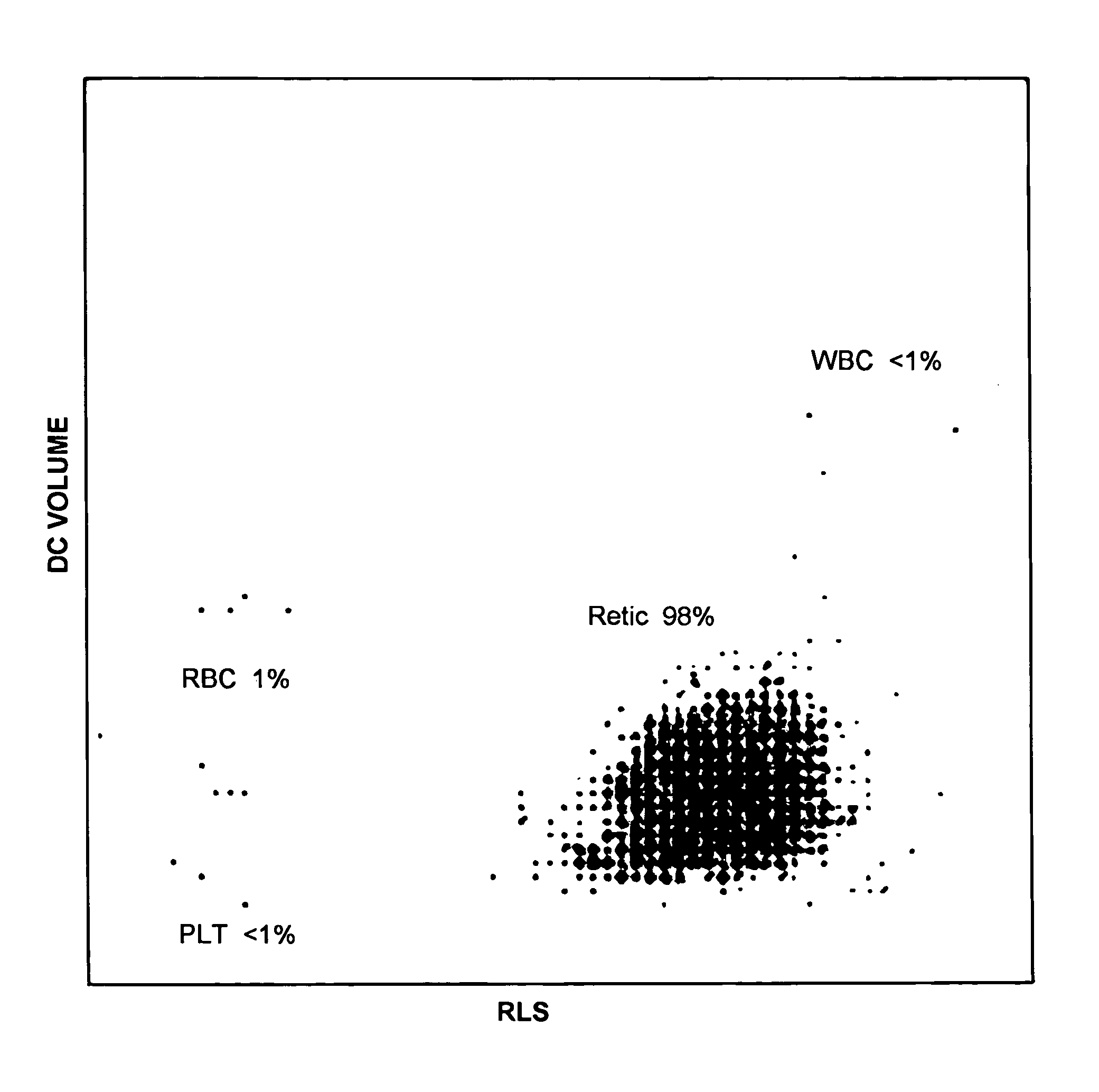
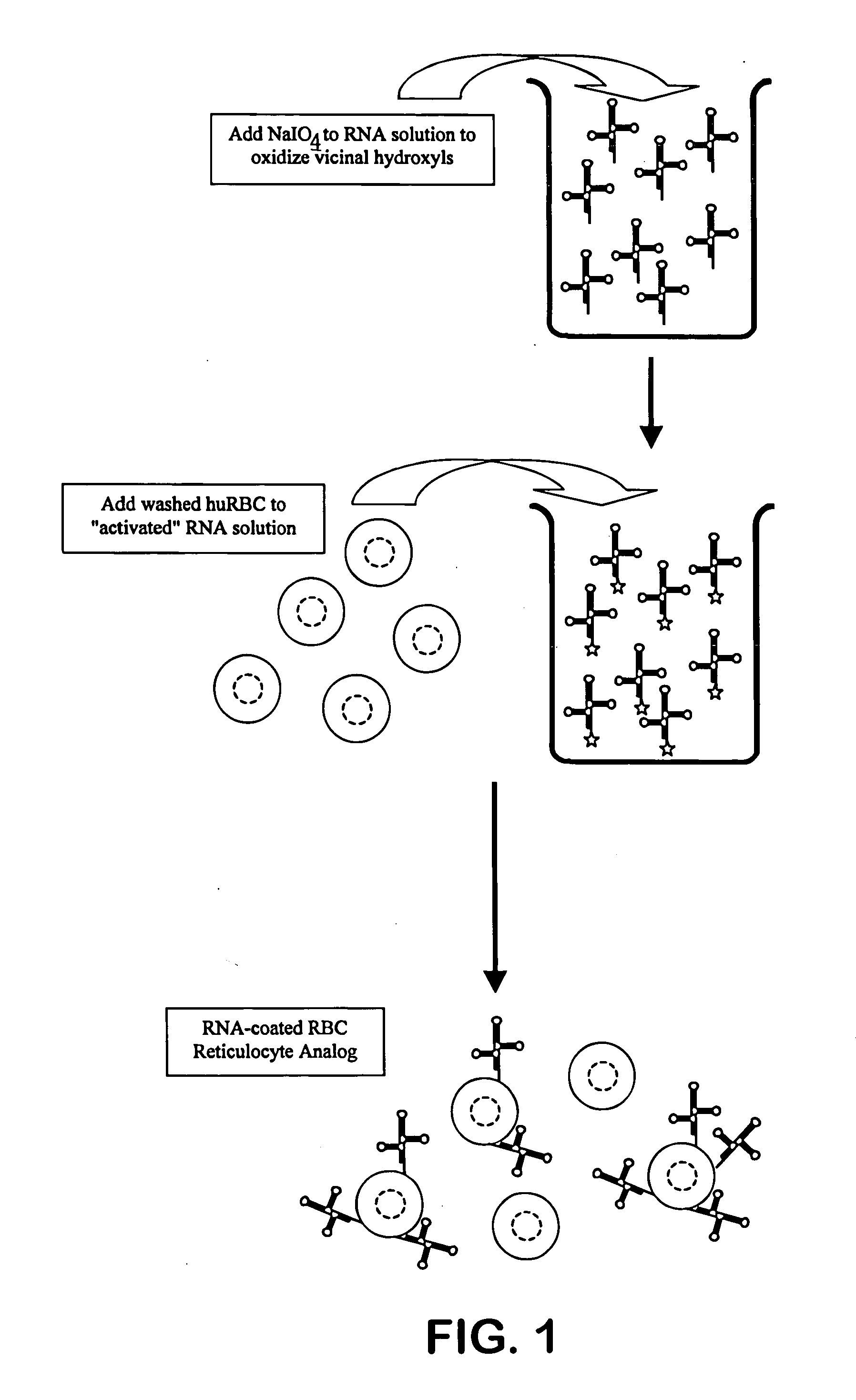
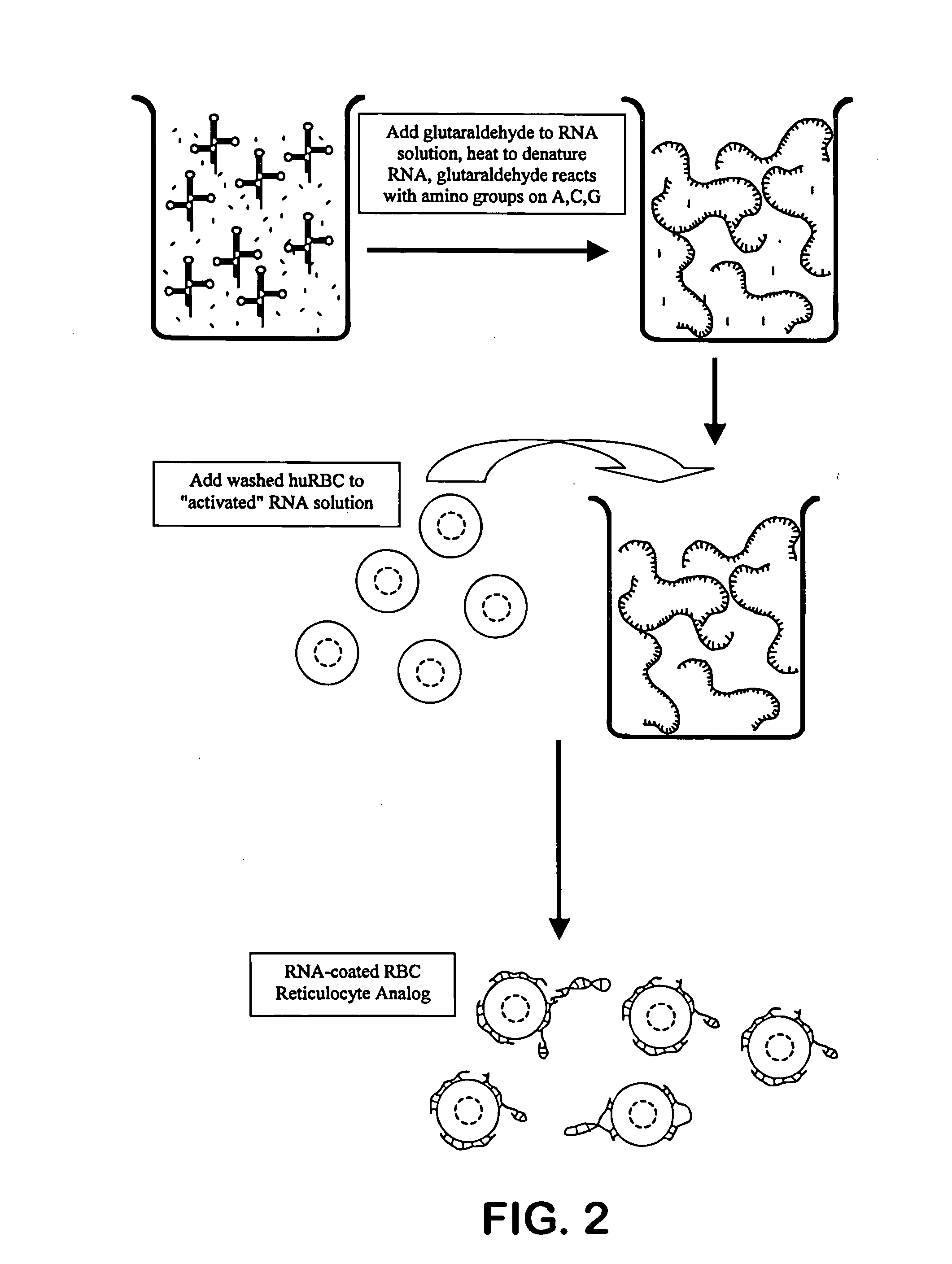
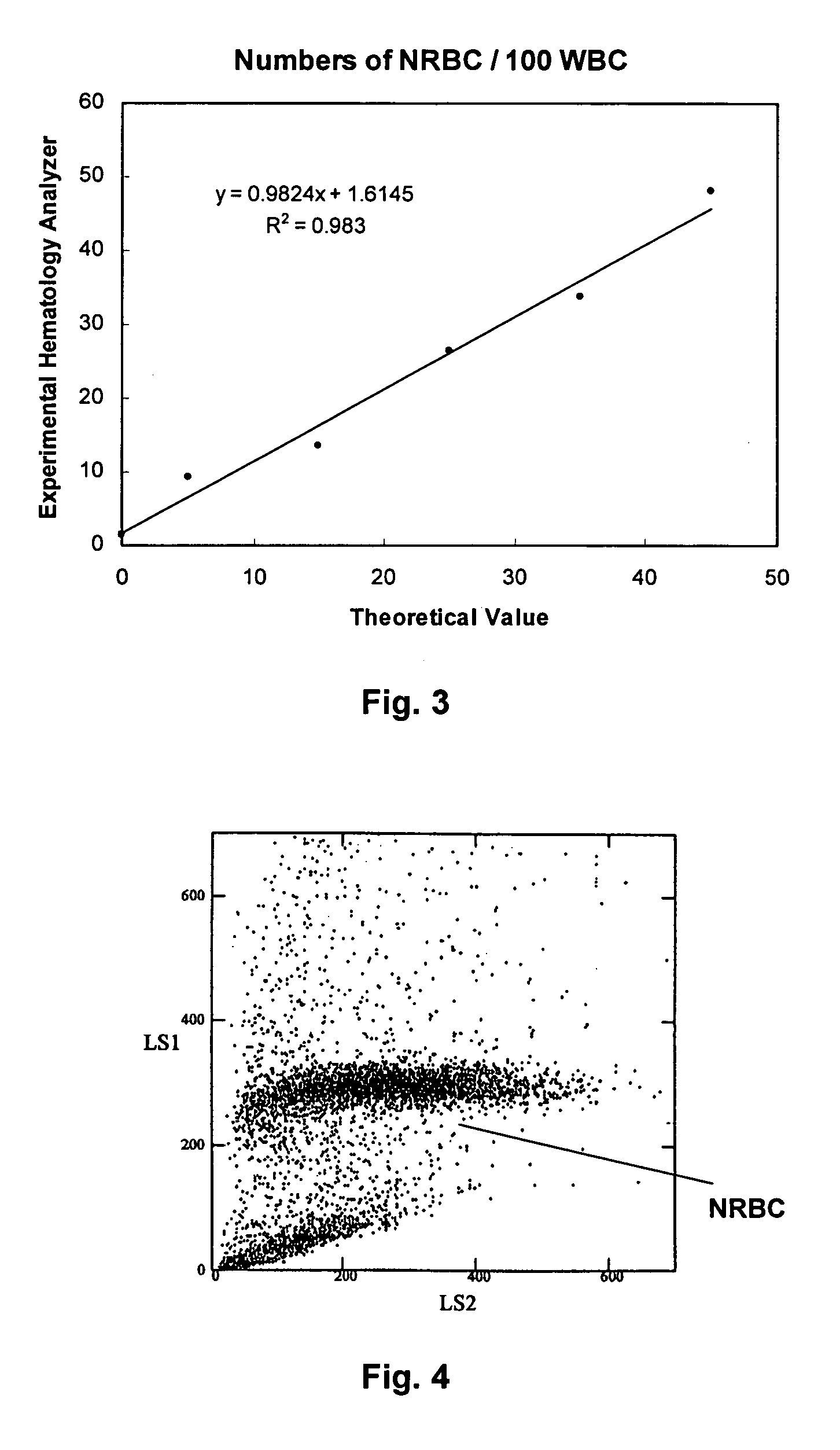
Hematology controls for reticulocytes and nucleated red blood cells
ActiveUS7195919B2Microbiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsMedicine.hematologyBiopolymer
The present invention is drawn to a hematology control made from particles a particle having a biopolymer attached to a surface of the particle. The particle simulates a component of a blood sample, such as a reticulocyte or nucleated red blood cell component of a blood cell sample in a flow cytometer or hematology analysis instrument. The present invention is further drawn to methods of making and using the hematology control.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Reference control containing a nucleated red blood cell component
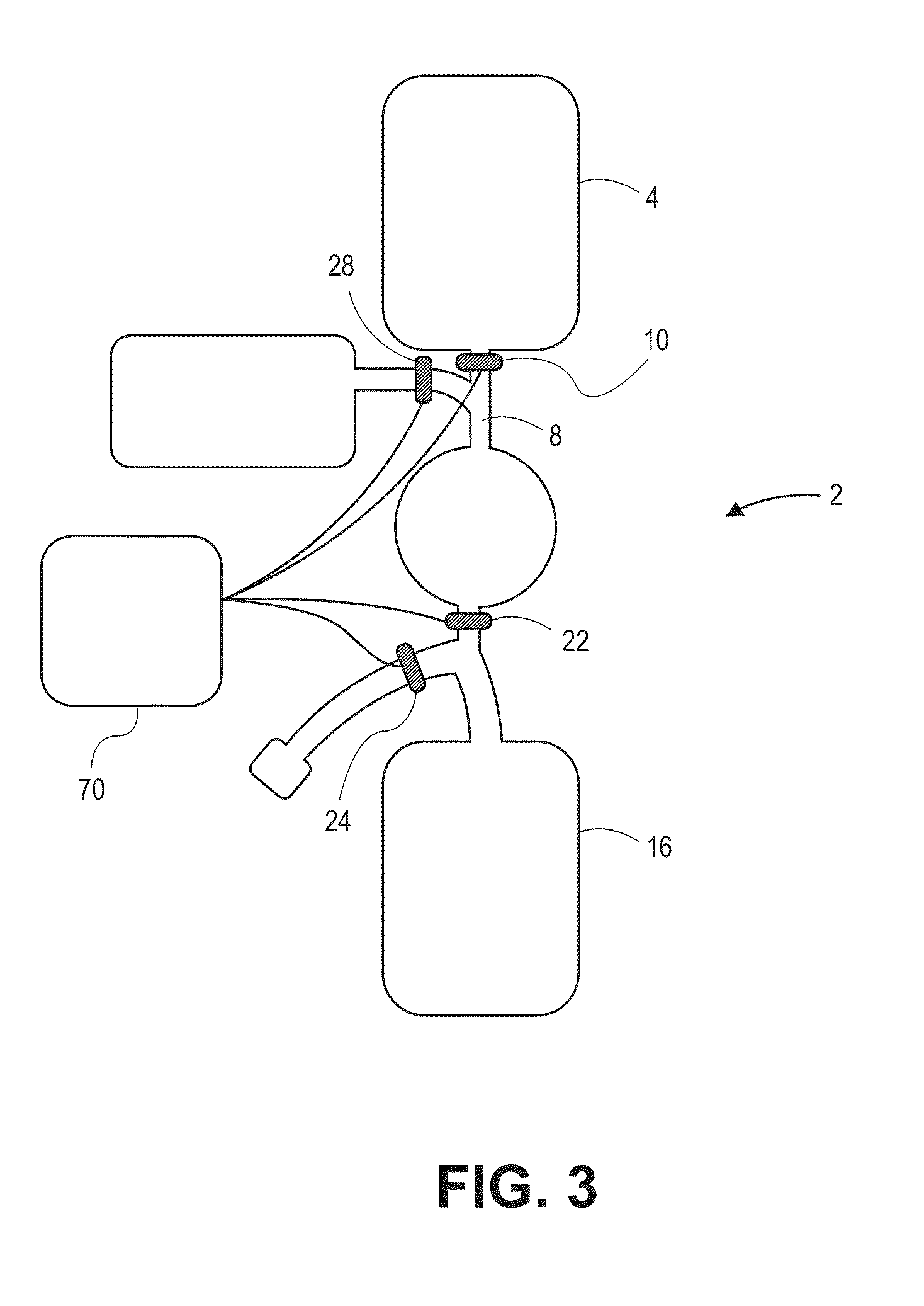
A method of making a reference control containing a nucleated red blood cell component includes providing a blood cell containing a nucleus; treating the blood cell with a treatment solution to alter a nucleus property from a natural value to a target value suitable for simulating nucleated red blood cells on a blood analyzer; and suspending treated blood cell in a suspension medium to form a reference control. The method also includes integrating the nucleated red blood cell component with white blood cell, red blood cell, platelet and reticulocyte components. Further disclosed is a cell treatment composition for altering a nucleus property, which includes a conditioning component, a lytic component for permeating cell membrane, and a fixing component for preserving the cell nucleus. Also disclosed is a method of using the reference control for measurement of nucleated red blood cells on a blood analyzer.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Method of using a reference control composition for measurement of nucleated red blood cells
ActiveUS20050079623A1Analysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionBiological testingRed blood cellOptical measurements
Methods of using a reference control composition containing a nucleated red blood cell component for measurement of nucleated red blood cells are disclosed. The nucleated red blood cell component is made of stabilized or processed nucleated blood cells which have impedance and optical properties simulating the impedance and optical properties of human nucleated red blood cells under a blood lysing condition as measured by a specific measurement. The methods include mixing the reference control composition with a lytic reagent, and analyzing the control sample mixture on a flow cytometric instrument by impedance, impedance and optical measurement, or DC impedance and a multi-dimensional measurement of light scatter, radio frequency and a second DC impedance; and reporting the simulated nucleated red blood cells in the reference control composition.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Reagent for sample analysis, reagent kit for sample analysis and method for sample analysis
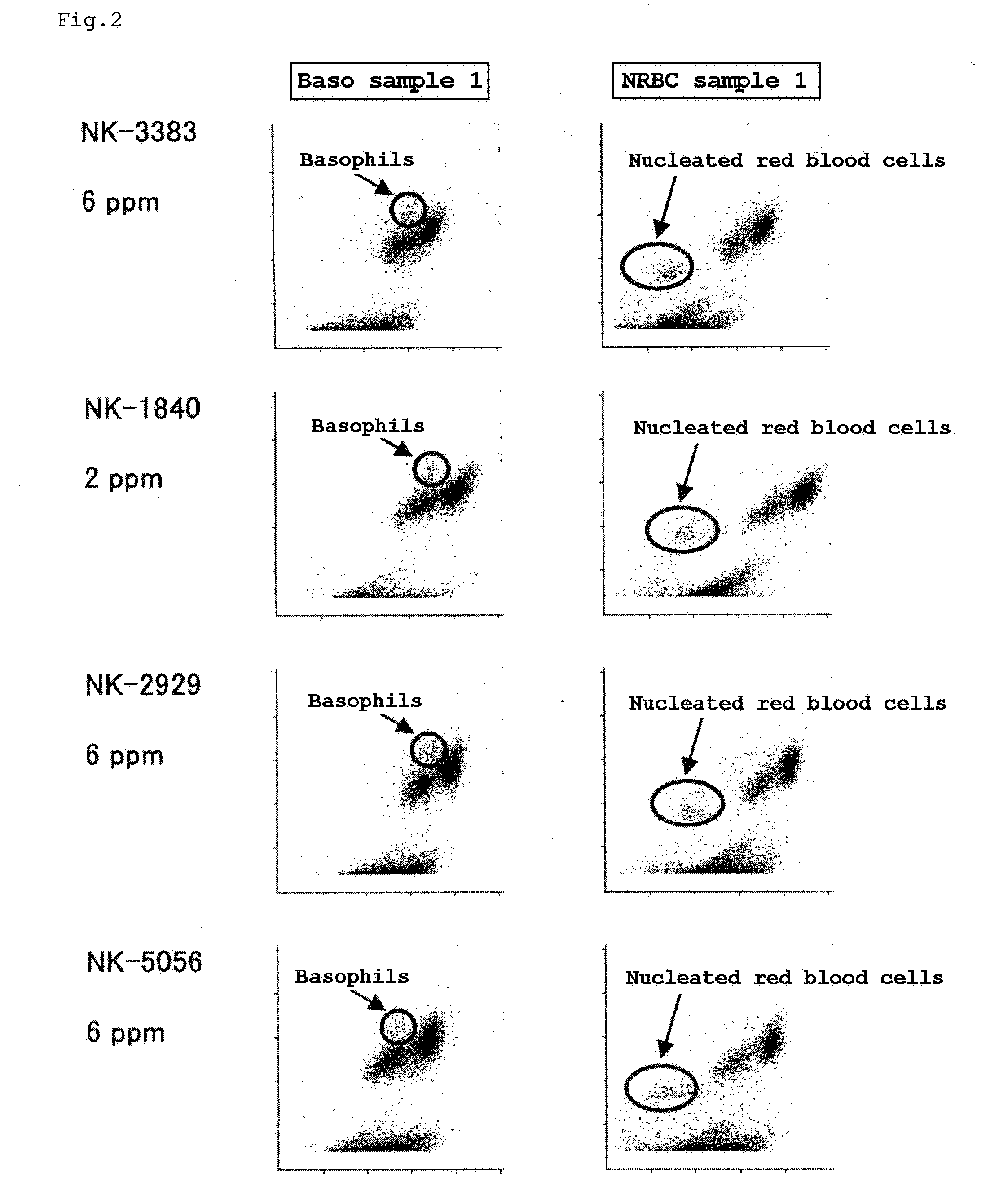
A reagent for measuring a basophil and / or a nucleated red blood cell is described. The reagent comprises (a) an alcohol having 4 to 8 total carbon atoms, and (b) one or more fluorescent dyes selected from the group consisting of a compound of the general formula (I) and a compound of the general formula (II).
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
Reference control containing a nucleated red blood cell component
A method of making a reference control containing a nucleated red blood cell component includes providing a blood cell containing a nucleus; treating the blood cell with a treatment solution to alter a nucleus property from a natural value to a target value suitable for simulating nucleated red blood cells on a blood analyzer; and suspending treated blood cell in a suspension medium to form a reference control. The method also includes integrating the nucleated red blood cell component with white blood cell, red blood cell, platelet and reticulocyte components. Further disclosed is a cell treatment composition for altering a nucleus property, which includes a conditioning component, a lytic component for permeating cell membrane, and a fixing component for preserving the cell nucleus. Also disclosed is a method of using the reference control for measurement of nucleated red blood cells on a blood analyzer.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Reference control for optical measurement of nucleated red blood cells of a blood sample
ActiveUS6962817B2Dead animal preservationAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionSpherical granuleOptical property
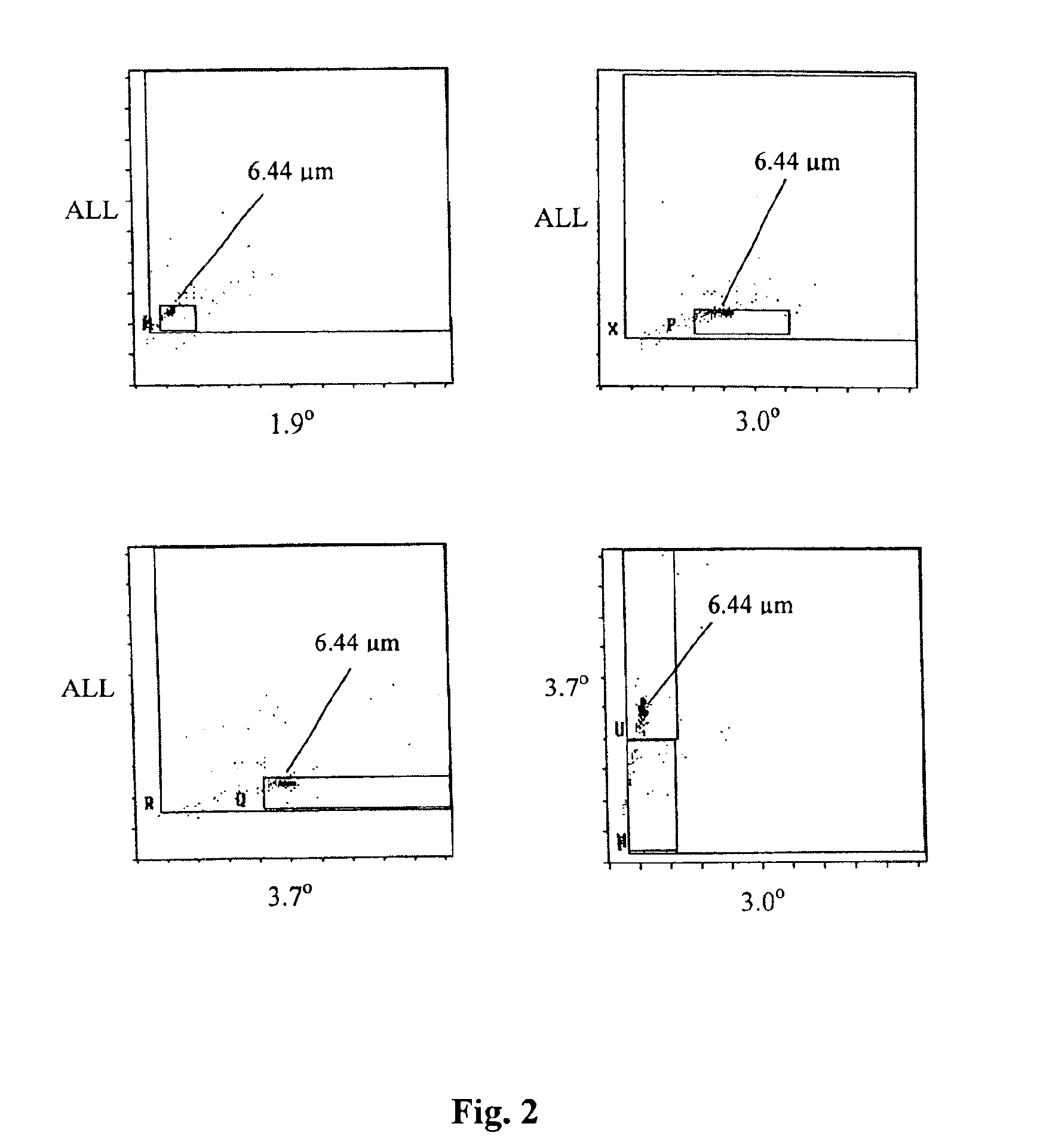
Reference control compositions and the method of use are disclosed for measurement of nucleated red blood cells, which includes one set of synthetic spherical particles having a mean particle diameter ranging from 6.2 μm to 6.8 μm and a refractive index from 1.58 to 1.62 monodispersed in an aqueous suspension medium. The synthetic spherical particles have optical properties simulating optical properties of nucleated red blood cells as measured by optical measurements. The reference control composition can further include a second set of the synthetic spherical particles having optical properties simulating optical properties of white blood cells. Further disclosed is a reference control system which includes a series of reference control compositions, each having an amount of one type of synthetic spherical particles which have optical properties simulating the optical properties of nucleated red blood cells having a specific cell maturity.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Method of measurement of nucleated red blood cells
Methods are provided for measurement of nucleated red blood cells. The methods include exposing a blood cell sample to a reagent system to lyse mature red blood cells, subsequently analyzing nucleated red blood cells in a flow cell by axial light loss, low angle light scatter and DC impedance measurements, or two selected measurements thereof; and then differentiating nucleated red blood cells from other cell types by using measured signals and / or functions thereof.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Method for separating and authenticating erythroblast of blood
InactiveCN101122601AEasy to identifyPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsBiologyGene
The invention discloses a method for separating and appraising nucleated red blood cells in blood, including the following steps: (1) confecting reagent; (2) preparing anti-degumming slide; (3) selecting the staining method for nucleated red blood cells; (4) getting nucleated red blood cells from blood through microoperation. The method for separating and appraising nucleated red blood cells in blood can effectively identify nucleated red blood cells. Nucleated blood cell can be detected in 40 samples and the detection rate is 100 percent. Each sample is detected to have 2*106 to 6*106 / ml nucleated blood cell. In the invention, after the aniline being stained, the nucleated red blood cell is easy to be identified and skilled microoperation can quickly obtain the single nucleated red blood cell, so that the invention lays a good primary foundation to apply the single red blood cell in gene analysis.
Owner:孙艳萍
Method for measurement of immature granulocytes
InactiveUS6916658B2Material thermal conductivityMicrobiological testing/measurementRed CellImmature Granulocyte
A method for measuring immature granulocytes in a blood sample is described. The method includes the steps of lysing red blood cells of a blood sample with a lytic reagent, analyzing the sample mixture by DC impedance measurement, determining immature granulocytes from obtained DC histogram, and reporting immature granulocytes in the blood sample. The method further includes measuring nucleated red blood cells in the blood sample.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Methods and devices for obtaining and analyzing cells
InactiveUS20130130265A1Microbiological testing/measurementOn/in organic carrierGenetic MaterialsGenetic Screening (procedure)
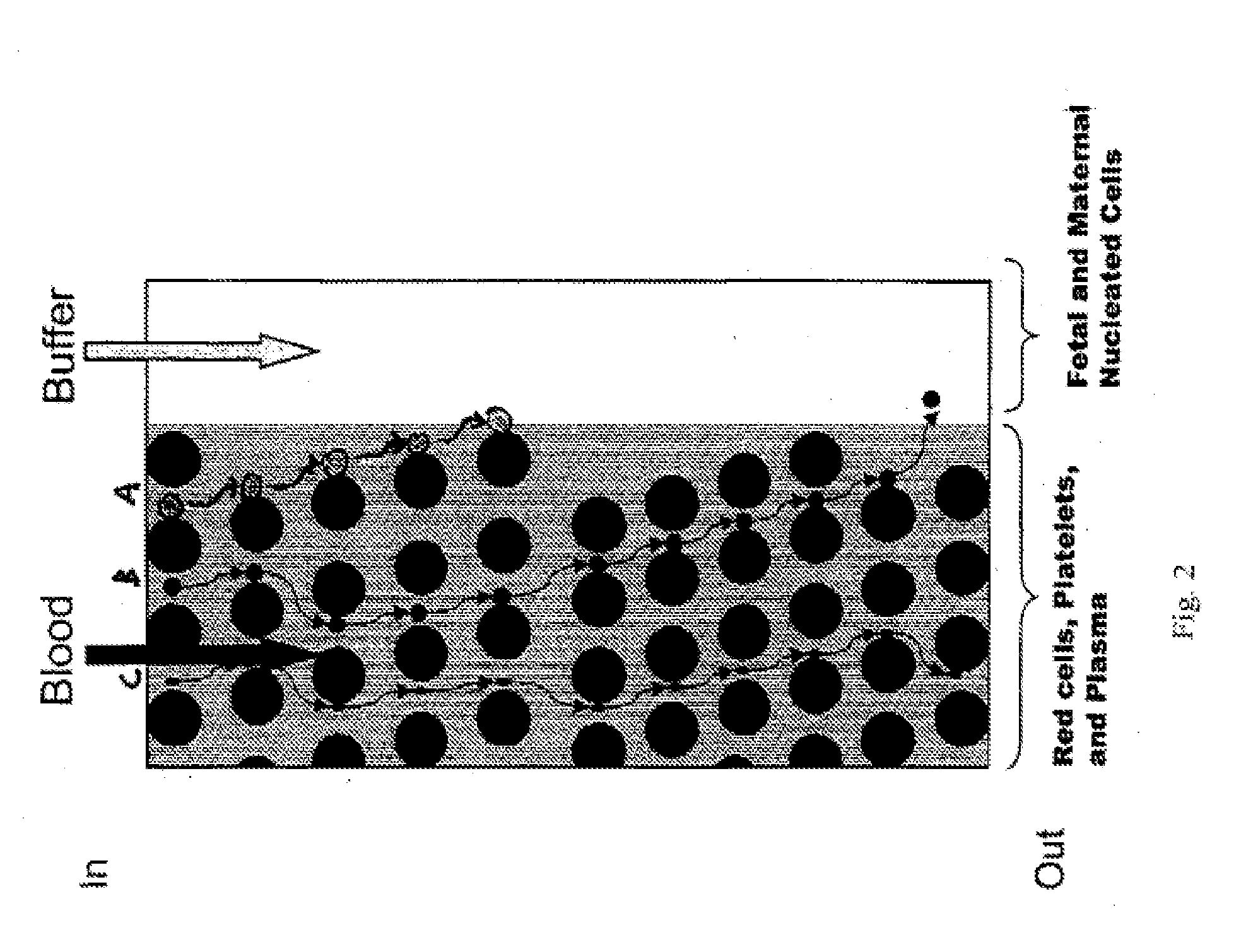
A method for concentrating and isolating nucleated cells, such as maternal and fetal nucleated red blood cells (nRBCs), in a maternal whole blood sample. The invention also provides methods and apparatus for preparing to analyze and analyzing the sample for identification of fetal genetic material as part of prenatal genetic testing. The invention also pertains to methods and apparatus for discriminating fetal nucleated red blood cells from maternal nucleated red blood cells obtained from a blood sample taken from a pregnant woman.
Owner:CELLSCAPE CORP
Hematology controls for reticulocytes and nucleated red blood cells
ActiveUS20050136409A1Microbiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsMedicine.hematologyBiopolymer
The present invention is drawn to a hematology control made from particles a particle having a biopolymer attached to a surface of the particle. The particle simulates a component of a blood sample, such as a reticulocyte or nucleated red blood cell component of a blood cell sample in a flow cytometer or hematology analysis instrument. The present invention is further drawn to methods of making and using the hematology control.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
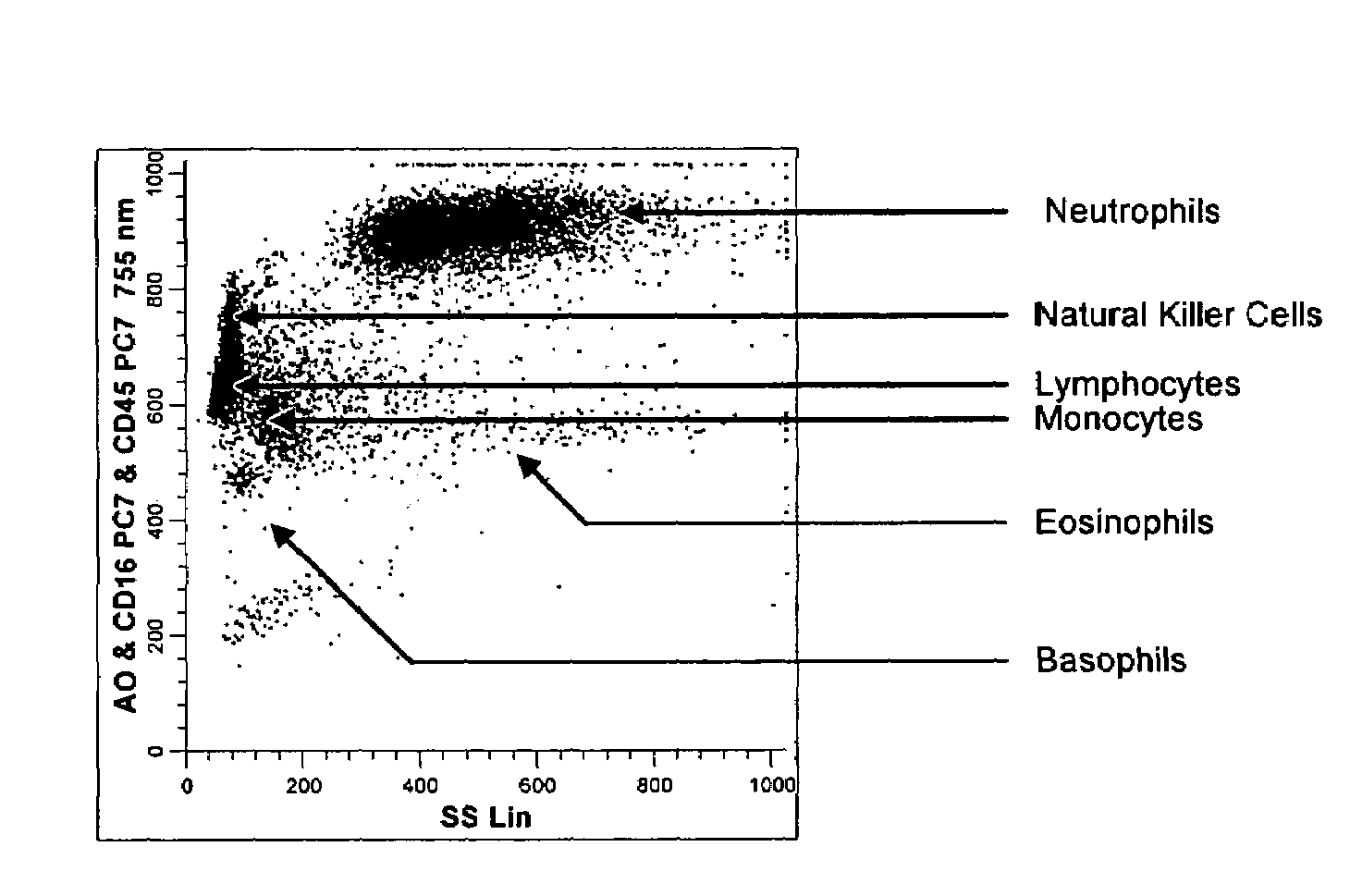
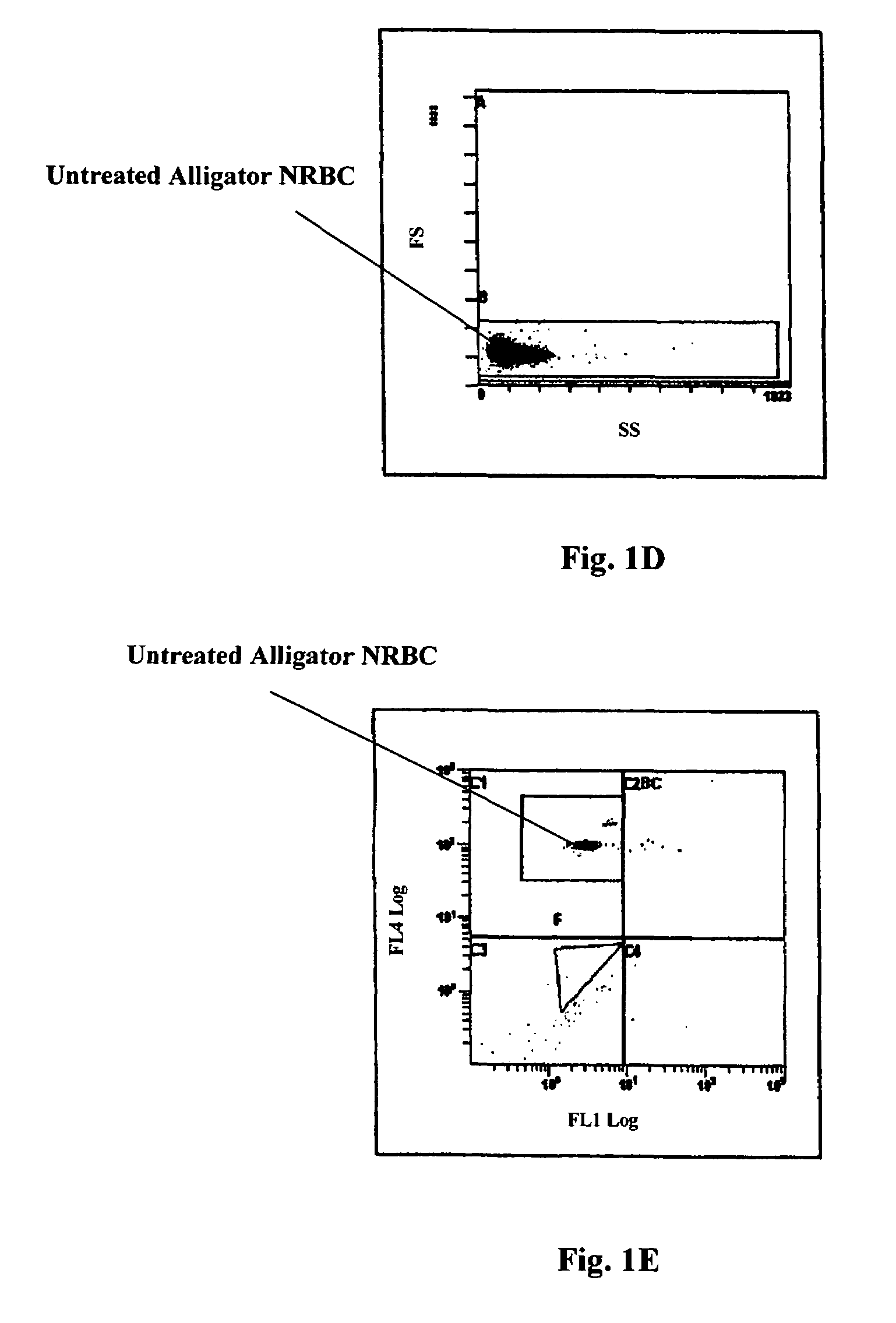
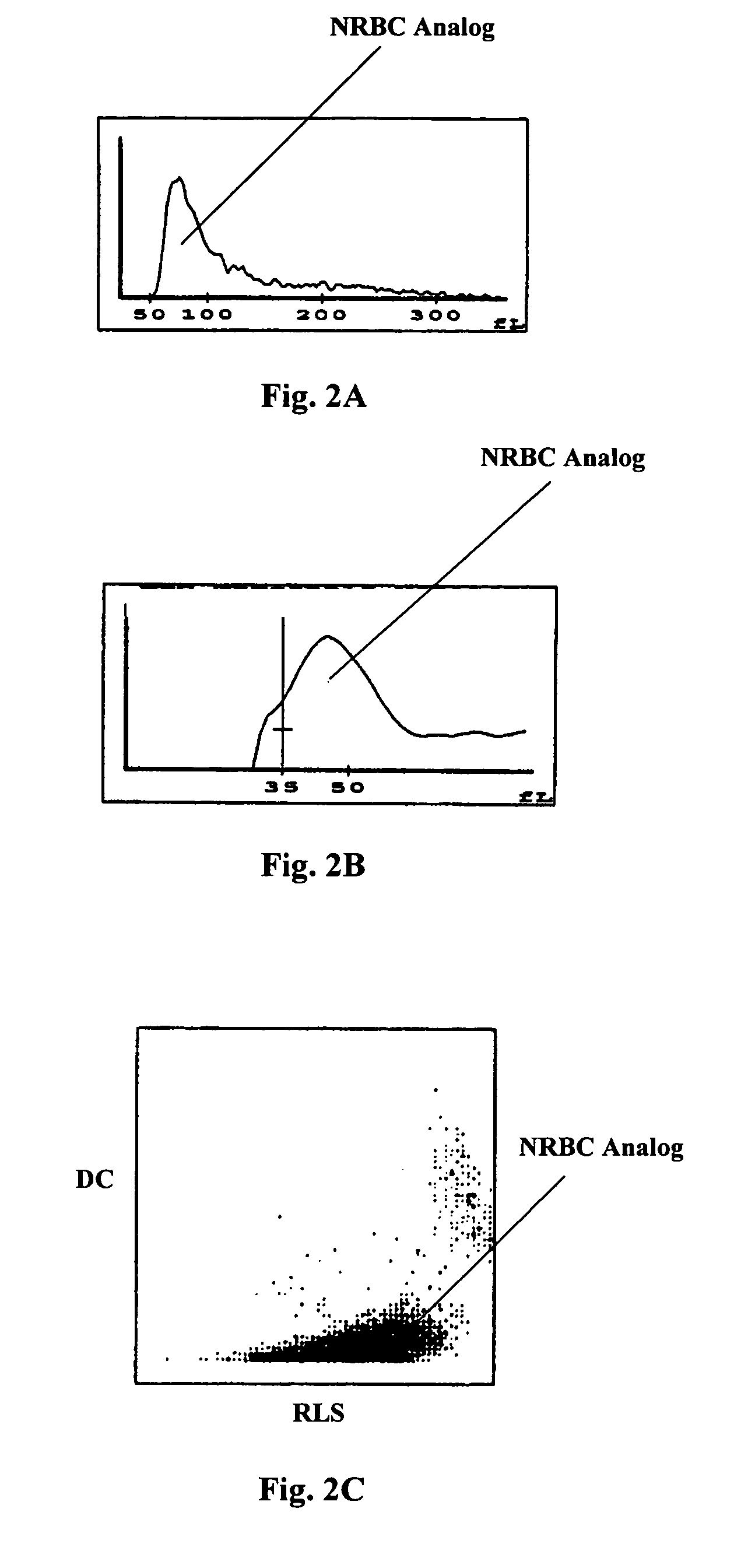
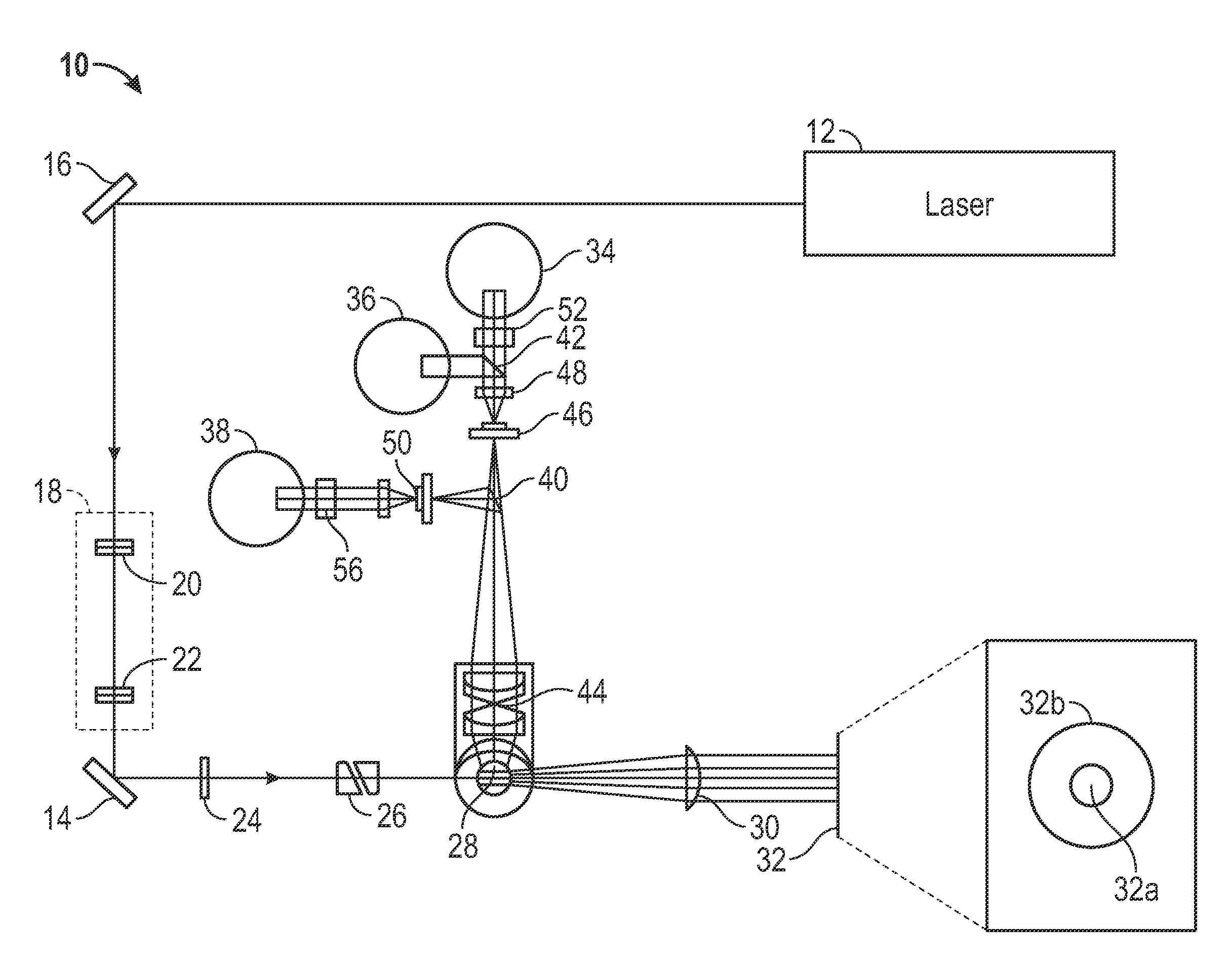
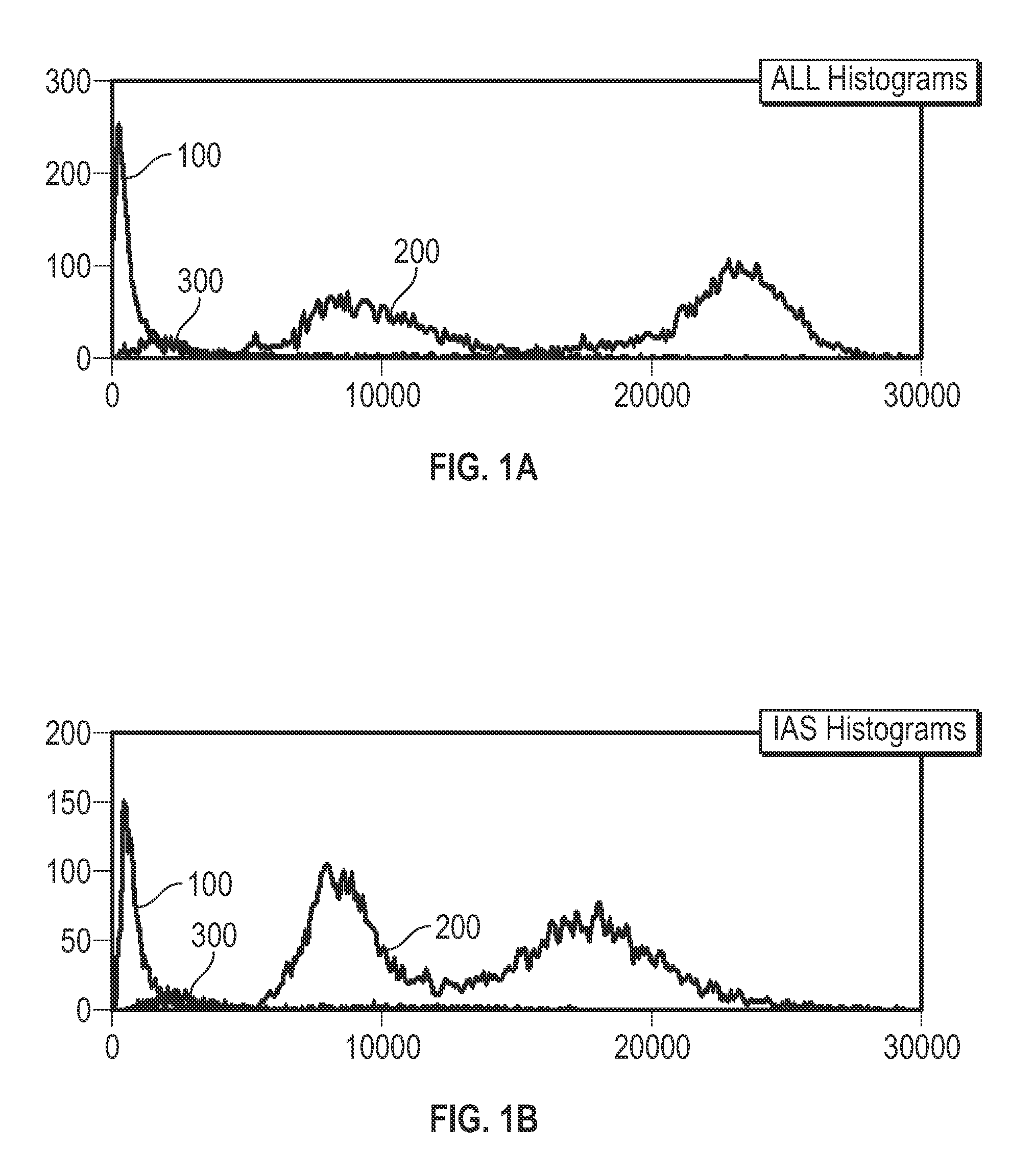
Nucleated Red Blood Cell Analysis System and Method
ActiveUS20120282599A1Eliminate distractionsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRed blood cellFluorescence
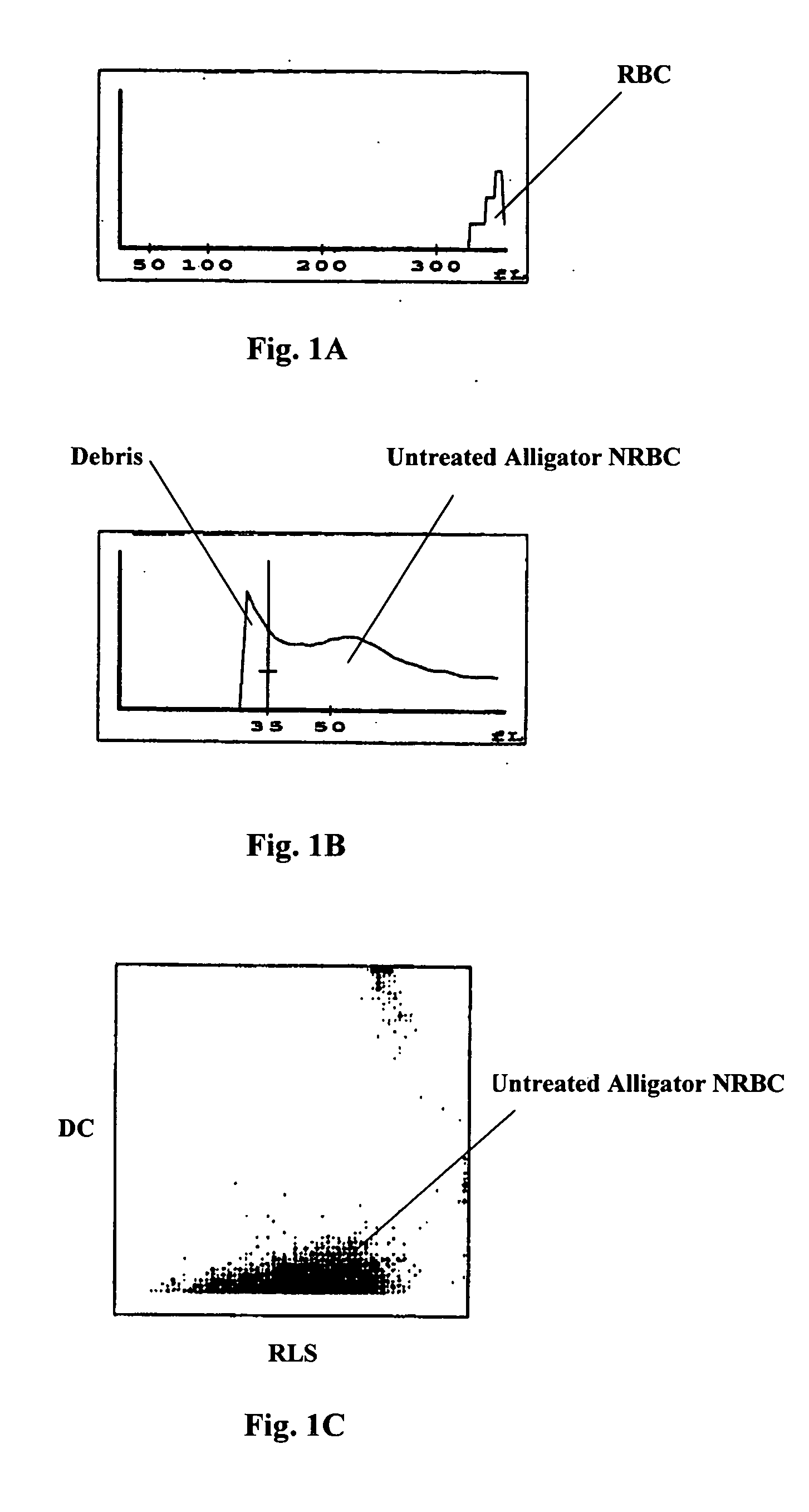
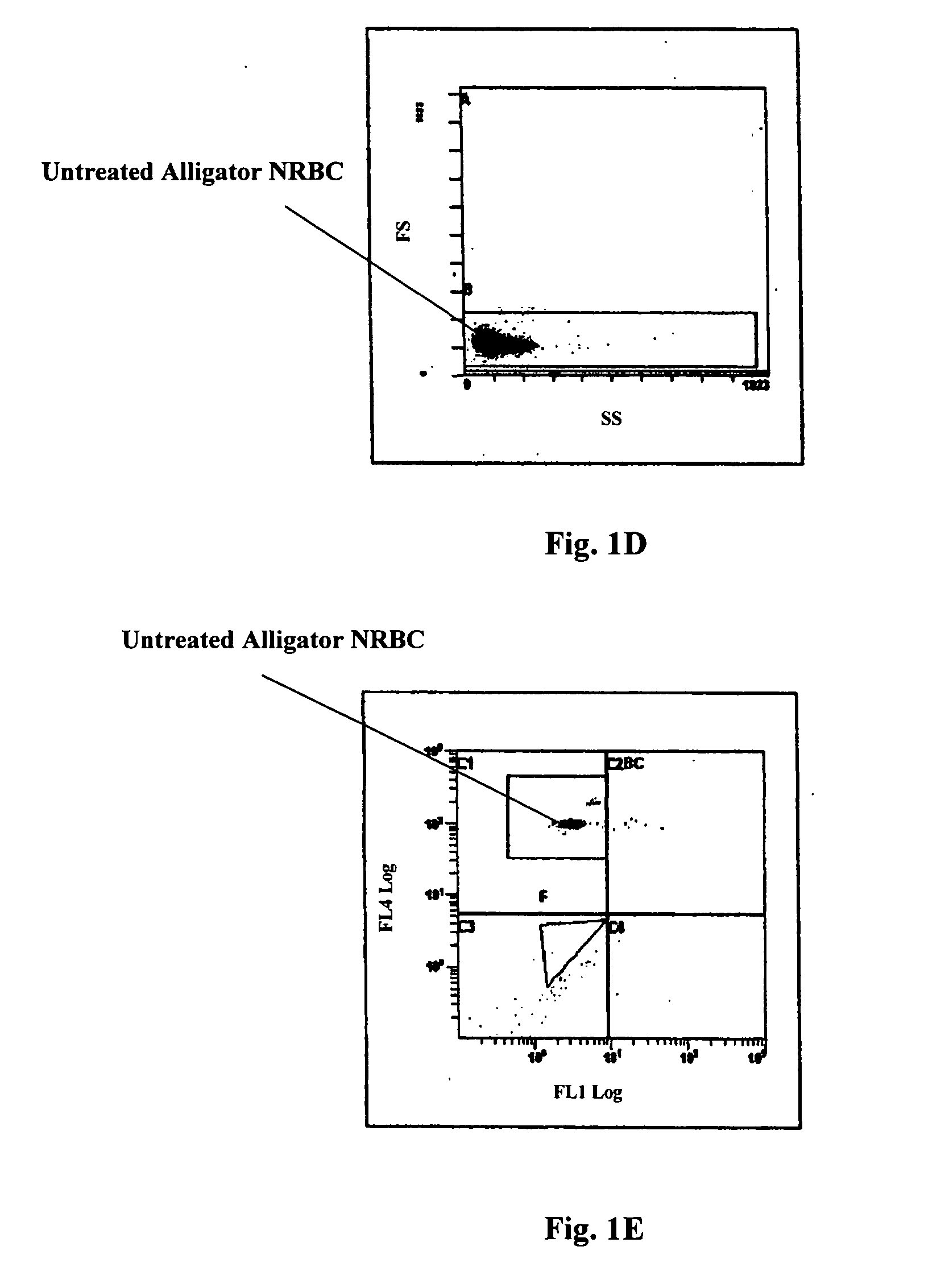
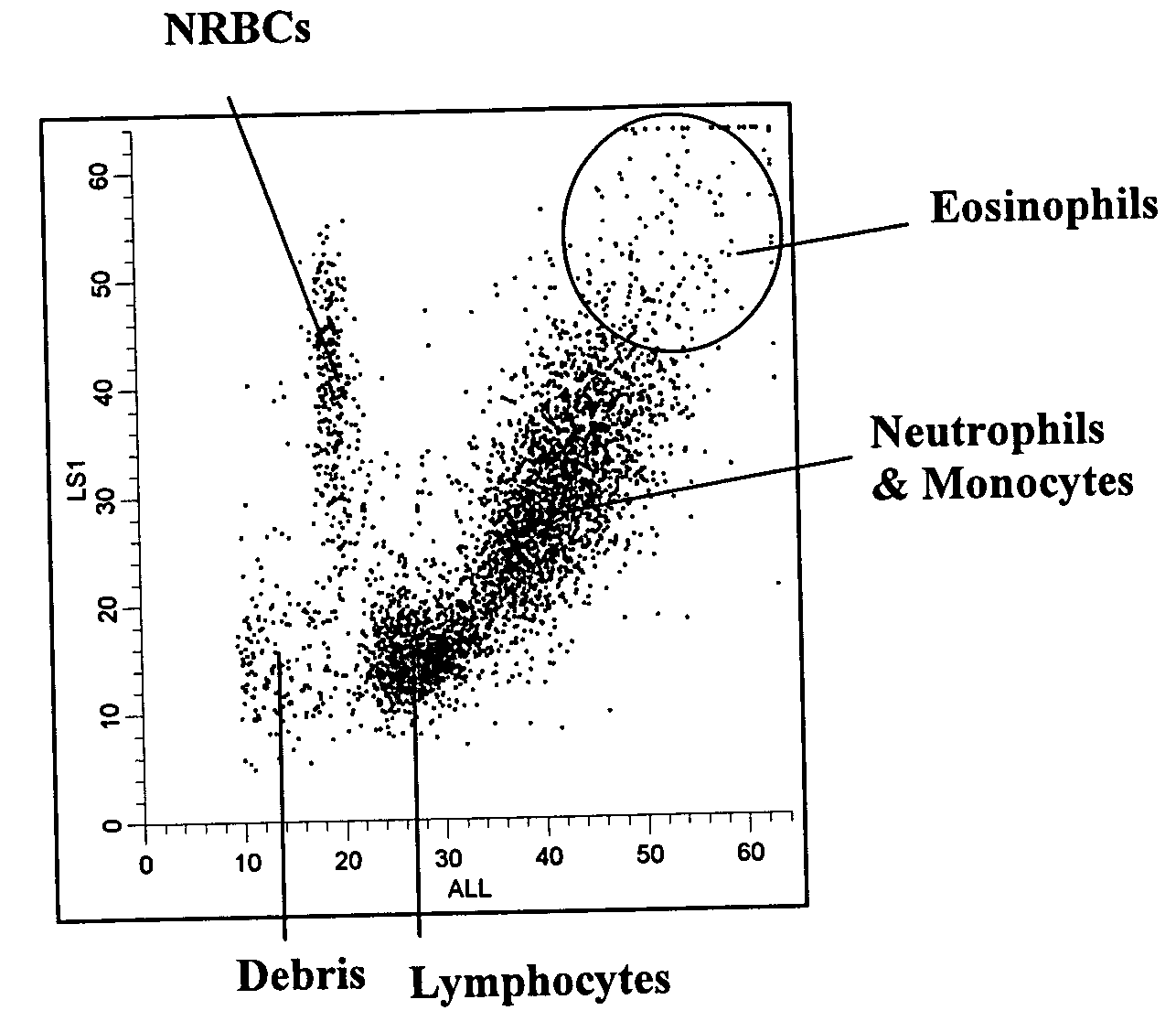
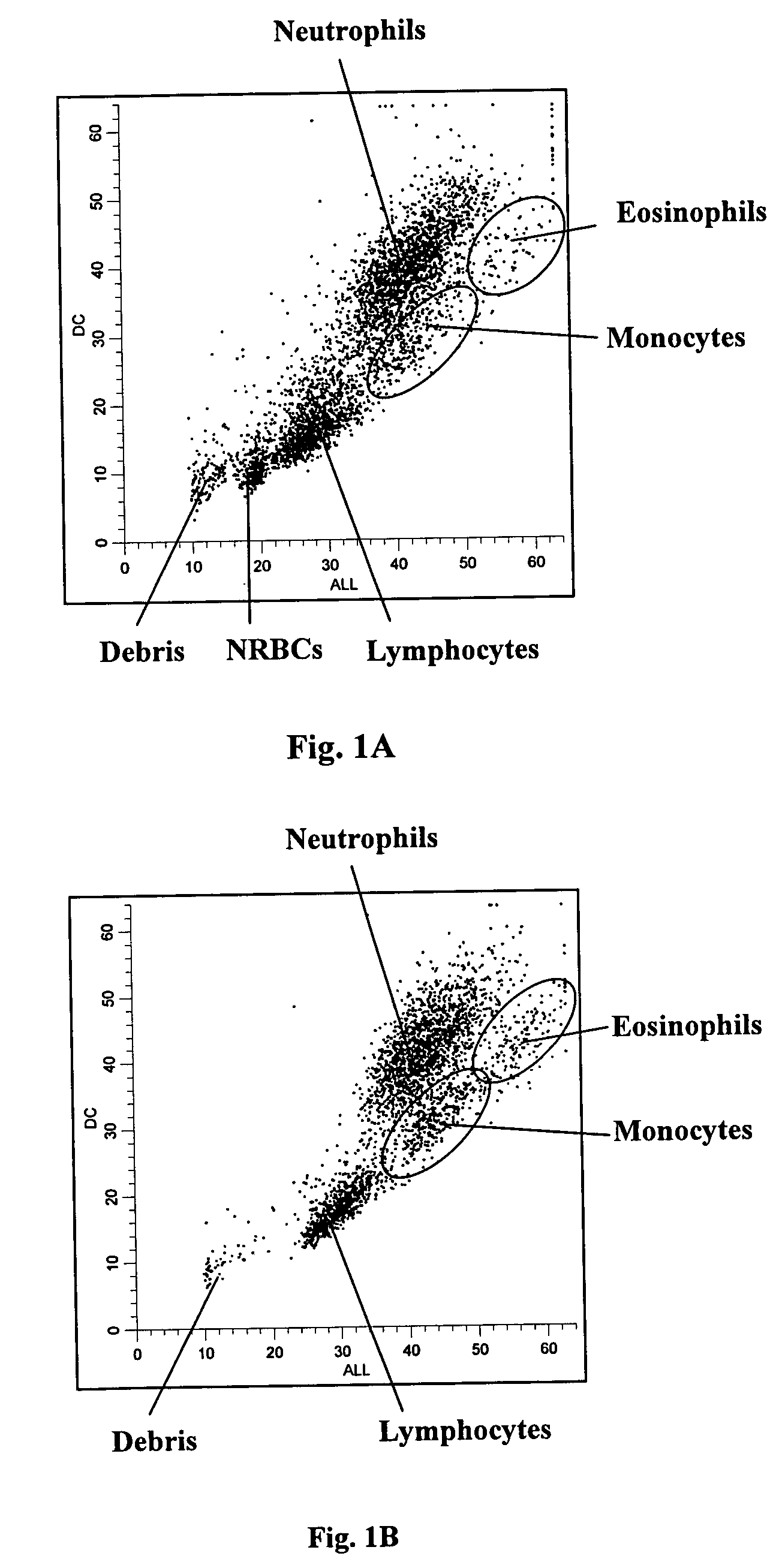
Systems and methods for analyzing blood samples, and more specifically for performing a nucleated red blood cell (nRBC) analysis. The systems and methods screen a blood sample by means of fluorescence staining and a fluorescence triggering strategy, to identify nuclei-containing particles within the blood sample. As such, interference from unlysed red blood cells (RBCs) and fragments of lysed RBCs is substantially eliminated. The systems and methods also enable development of relatively milder reagent(s), suitable for assays of samples containing fragile white blood cells (WBCs). In one embodiment, the systems and methods include: (a) staining a blood sample with an exclusive cell membrane permeable fluorescent dye; (b) using a fluorescence trigger to screen the blood sample for nuclei-containing particles; and (c) using measurements of light scatter and fluorescence emission to distinguish nRBCs from WBCs.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Method to determine an engrafting cell dose of hematopoietic stem cell transplant units
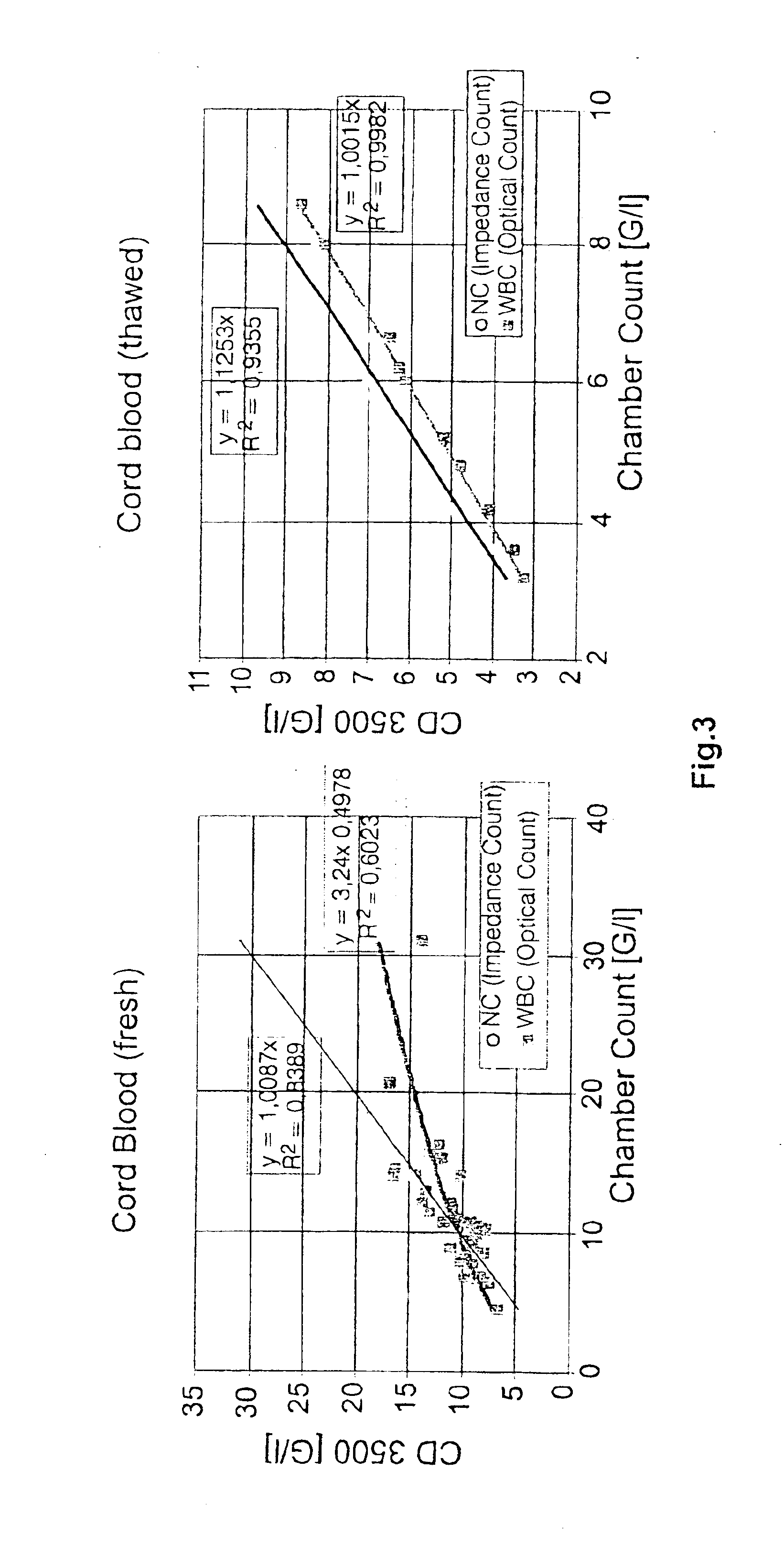
InactiveUS6852534B2Accurate assessmentAutomatically performBiocideDead animal preservationCord blood stem cellCell dose
A method to determine an engrafting cell dose of hematopoietic stem cell transplant units from transplant sources having nucleated cells selected from the group consisting of cord blood, bone marrow, peripheral blood comprising the steps of[0002]subjecting the source to a substantially complete erythrocyte lysis,[0003]measuring in a cell counter a signal corresponding selectively to white blood cells,[0004]assessing essentially quantitatively nucleated red blood cell (NRBC) count as part of the total nucleated cell (NC) count,[0005]and determining the number of white blood cells (WBCs) as transplant relevant cells.
Owner:KOURION THERAPEUTICS
Separation and purification method for fetal nucleated red blood cells and Down syndrome screening kit
InactiveCN103103161AEfficient separationAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementBlood/immune system cellsPurification methodsMagnetic bead
The invention discloses a separation and purification method for fetal nucleated red blood cells and a Down syndrome screening kit and belongs to the detection field of molecular cell biology. The separation and purification method comprises the following steps: firstly, fully mixing maternal peripheral blood and a CD45 antibody labeling magnetic bead to adsorb white blood cells; discarding on a magnetic separator, transferring upper-layer cells to a test tube containing a CD71 antibody labeling magnetic bead, and fully and uniformly mixing; separating on the magnetic separator to obtain nucleated red blood cells; extracting a genome DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) of the nucleated red blood cells; adding SRY (Sexdetermining Region Y), DSCR (Down Syndrome Critical Region) and USC2 specific probes, DSCR and USC2 competitive primers, an SRY specific primer and a DNA to be detected into the same competitive fluorescent quantitation PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) reaction system for multiple competitive real-time fluorescence quantification PCR reactions to obtain Cts of DSCR and USC2; and calculating a difference value between the Cts to judge whether a sample to be detected is highly risk to DS (Down Syndrome).
Owner:SHANDONG YADA PHARMA
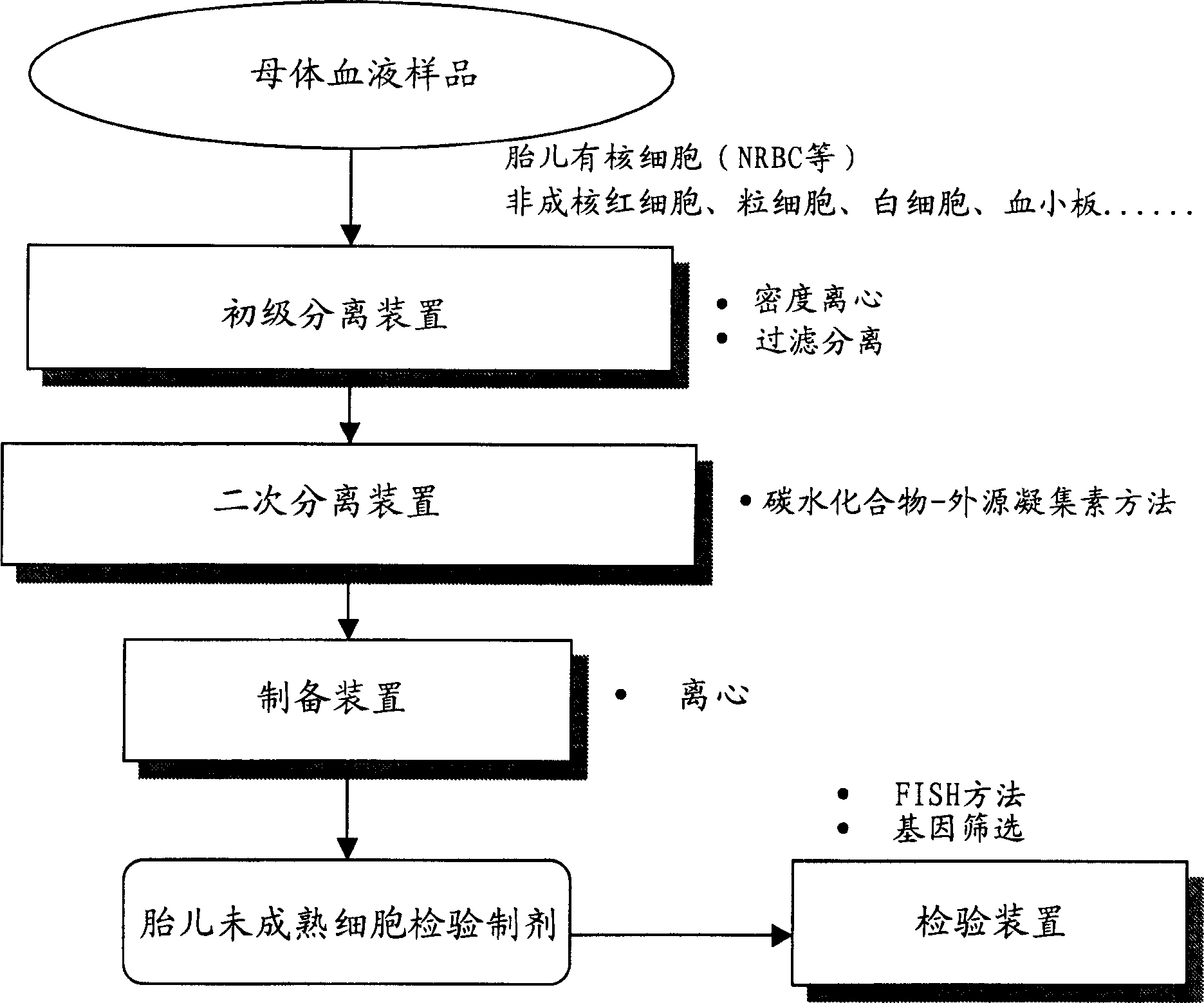
Blood cell separation system
The invention provides a blood cell separation system, which is used for the precise separation and concentration of rare fetal nucleated cells mixed in the blood of pregnant women, so as to facilitate the obtaining of test preparations that can be used for prenatal chromosome / gene diagnosis. The blood cell separation system is characterized in that it includes (1) a primary separation device, which is used to mainly remove non-nucleated red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets from a blood sample taken from a pregnant woman to obtain a primary separation sample, (2) a secondary separation device , for the removal of residual non-nucleated erythrocytes and leukocytes from a primary fraction obtained using the primary fractionation device using the carbohydrate-lectin method to obtain a secondary fraction containing concentrated fetal nucleated cells, and (3) A preparation device for preparing the secondary separation sample obtained by the secondary separation device.
Owner:NETECH
Method of using a reference control composition for measurement of nucleated red blood cells
ActiveUS7198953B2Analysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionBiological testingRed blood cellOptical measurements
Methods of using a reference control composition containing a nucleated red blood cell component for measurement of nucleated red blood cells are disclosed. The nucleated red blood cell component is made of stabilized or processed nucleated blood cells which have impedance and optical properties simulating the impedance and optical properties of human nucleated red blood cells under a blood lysing condition as measured by a specific measurement. The methods include mixing the reference control composition with a lytic reagent, and analyzing the control sample mixture on a flow cytometric instrument by impedance, impedance and optical measurement, or DC impedance and a multi-dimensional measurement of light scatter, radio frequency and a second DC impedance; and reporting the simulated nucleated red blood cells in the reference control composition.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Nucleated red blood cell simulation particle and blood quality control substance and preparation methods and application thereof
ActiveCN102109430AEasy to realize industrial productionHigh simulationPreparing sample for investigationDisease diagnosisCell processingWhite blood cell
The invention provides a nucleated red blood cell simulation particle and a preparation method thereof. The particle is a white blood cell combined with a fluorescent dyeing inhibitor, and the inhibitor is stably combined with a nucleus or nucleic acid in the cell, so that the capacity of the particle of combining with a fluorescent dye during detection is reduced. The method comprises the following steps of: (a) obtaining the washed and purified white blood cell; (b) suspending the white blood cell in fluorescent dyeing inhibitor-containing cell processing liquid, wherein the inhibitor is stably combined with the nucleus or the nucleic acid in the cell; and (c) washing the obtained product. The invention also provides a nucleated red blood cell simulation particle-containing blood quality control substance, and application of the nucleated red blood cell simulation particle and the blood quality control substance thereof to the quality control of a blood cell analyzer.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Methods and devices for obtaining and analyzing cells
InactiveUS20130130930A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningGenetic MaterialsGenetic Screening (procedure)
A method for concentrating and isolating nucleated cells, such as maternal and fetal nucleated red blood cells (nRBCs), in a maternal whole blood sample. The invention also provides methods and apparatus for preparing to analyze and analyzing the sample for identification of fetal genetic material as part of prenatal genetic testing. The invention also pertains to methods and apparatus for discriminating fetal nucleated red blood cells from maternal nucleated red blood cells obtained from a blood sample taken from a pregnant woman.
Owner:CELLSCAPE CORP
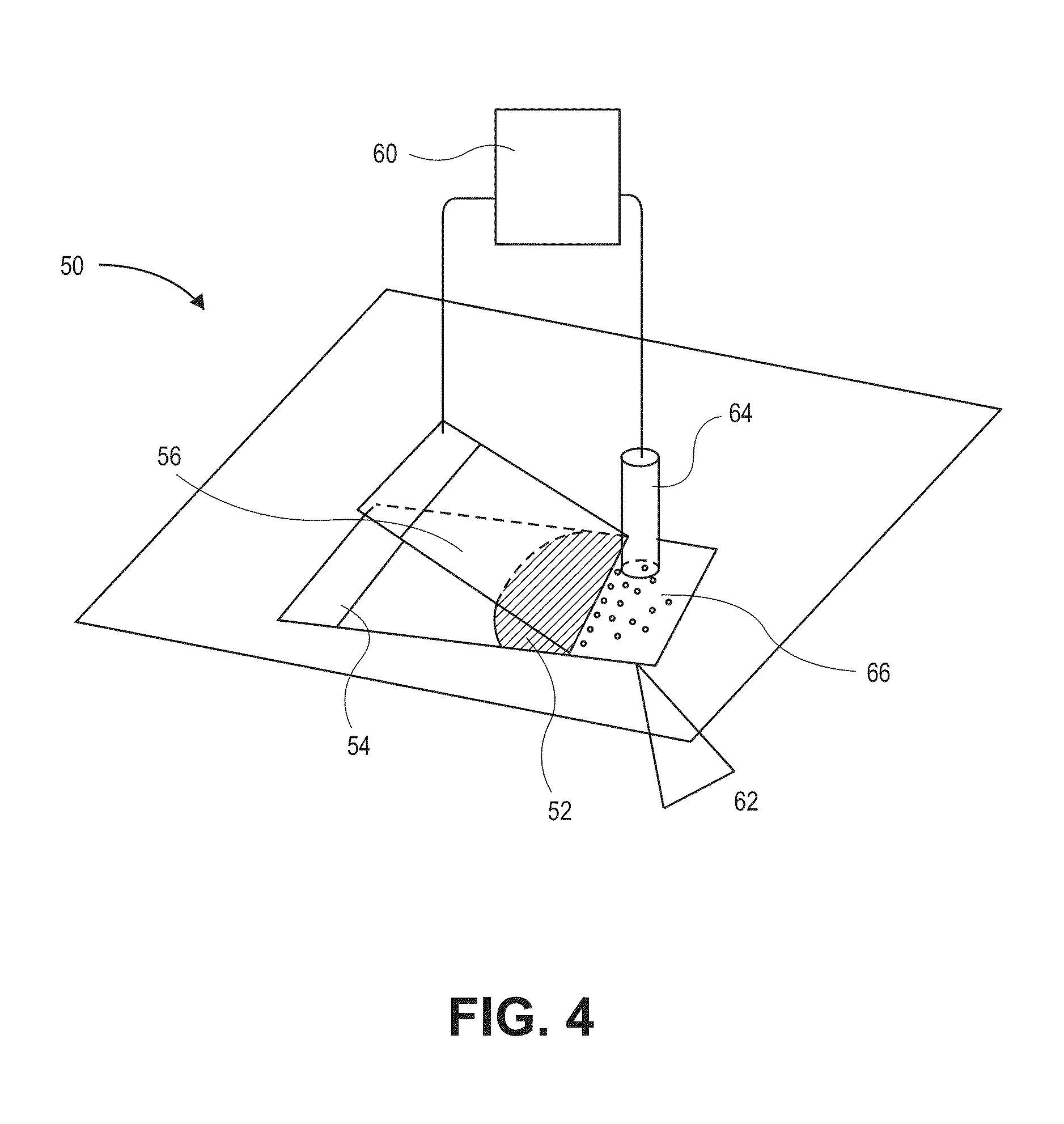
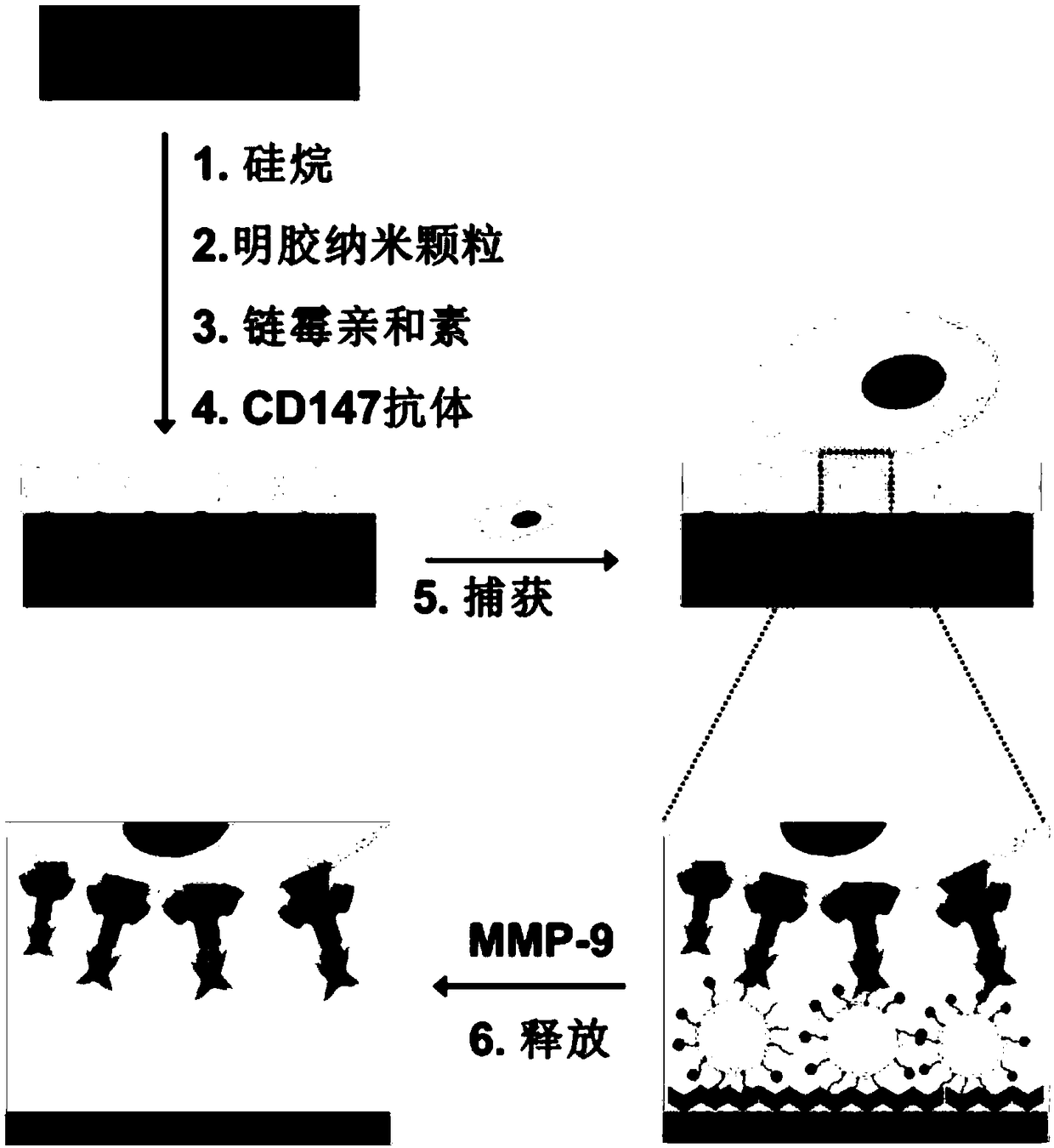
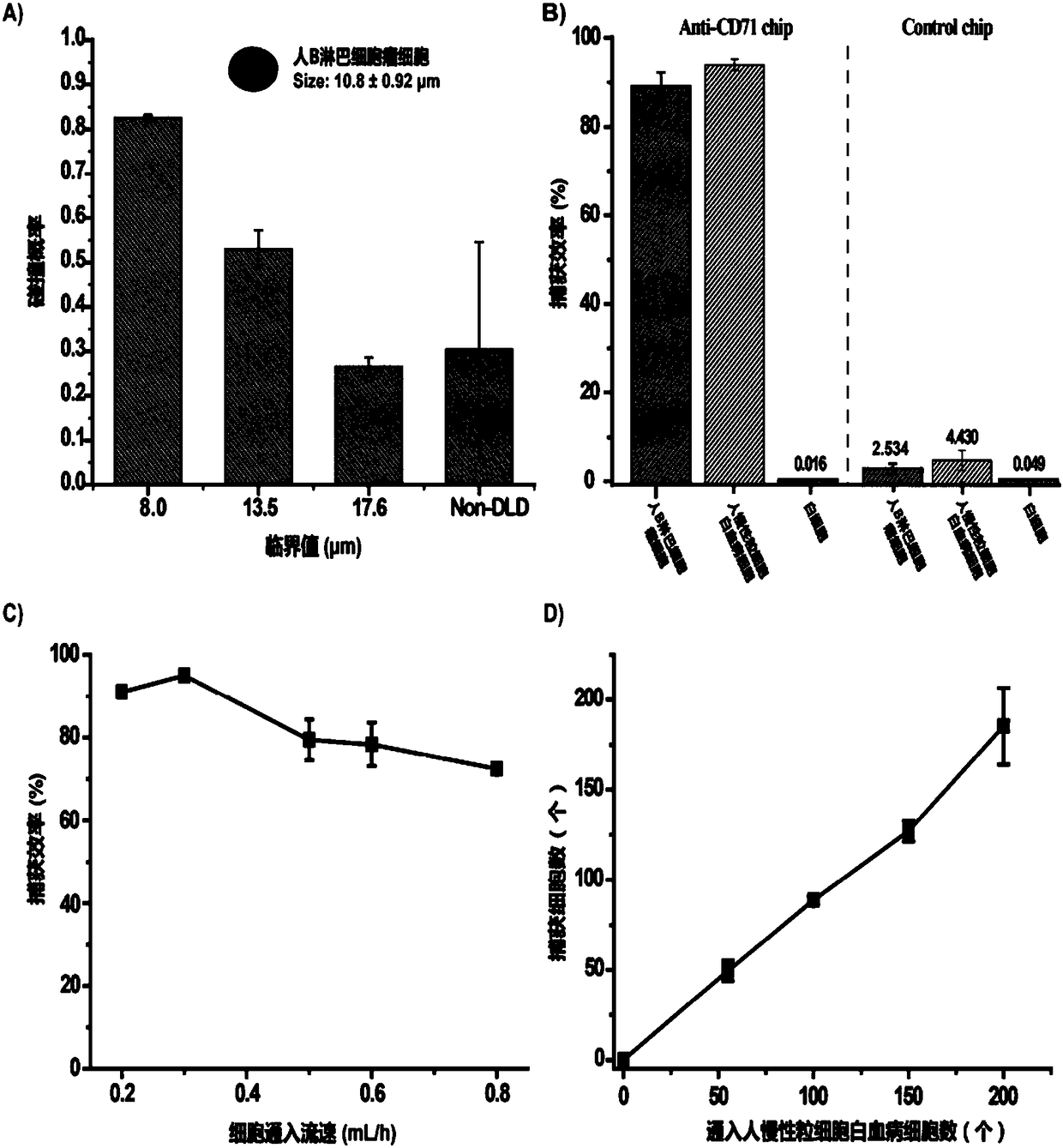
Method for capturing and identifying fetal nucleated red blood cells in a microfluidic chip
InactiveCN108753573AIncreased chance of collisionImprove capture abilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiotin-streptavidin complexCell layer
The invention provides a method for capturing and identifying fetal nucleated red blood cells in a microfluidic chip. The method comprises the following steps: 1, synthesizing gelatin nanoparticles bya two-step solvent removal method and preparing into a precursor liquid, and then introducing into a microfluidic chip to form a nanometer coating on the inner wall thereof, wherein the microfluidicchip comprises a plurality of serpentine main channels and the plurality of fish bone units; 2, modifying streptavidin on the nanometer coating by a chemical modification method, then grafting a biotin-modified antibody; 3, separating a mononuclear cell layer containing fetal nucleated red blood cells from peripheral blood by density-gradient centrifugation; 4, allowing mononuclear cell suspensionto flow into the microfluidic chip at a certain flow rate for capturing; 5, introducing a certain concentration of gelatinase into the microfluidic chip that captures fetal nucleated red blood cells,releasing fetal nucleated red blood cells by degrading the nanometer coating; and 6, identifying captured fetal nucleated red blood cells by using specific antibodies.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
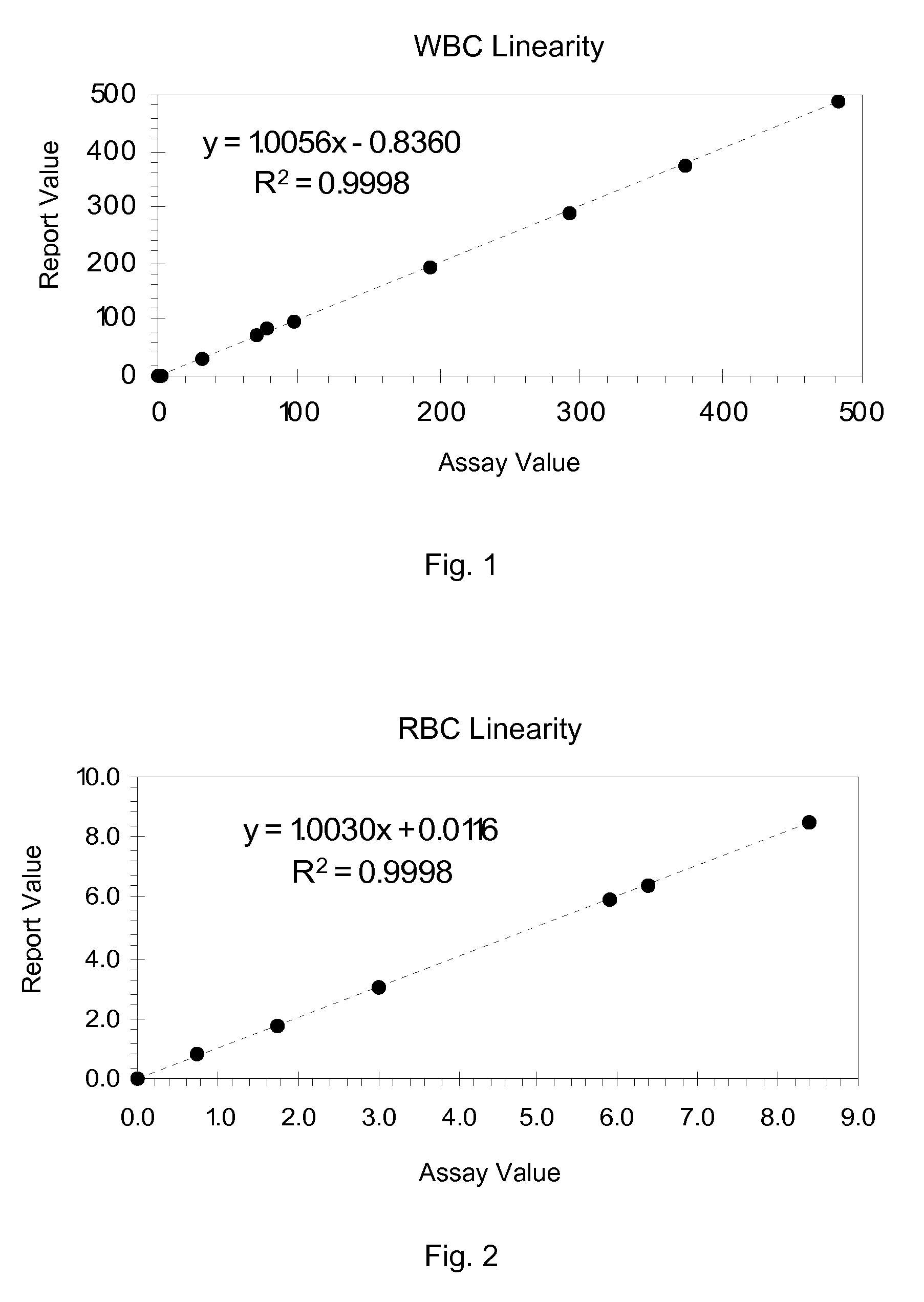
Hematology Linearity Control Composition, System and Method of Use
ActiveUS20080113438A1Affect measurementReduce concentrationDead animal preservationIndividual particle analysisMedicine.hematologyWhite blood cell
A linearity control system includes a series of linearity control compositions, each thereof includes white blood cell analogs and stabilized red blood cells in a suspension medium. The concentration of the white blood cell analogs in the series of control compositions increases from 0.2×103 to 800×103 analogs per microliter, and the concentration of the white blood cell analogs in at least one control composition is greater than 120×103 analogs per microliter. The stabilized red blood cells facilitate mono-dispersion of the white blood cell analogs in the suspension medium by gently mixing. The control compositions further include platelet analogs, or additionally include reticulocyte and / or nucleated red blood cell analogs. The linearity control system allows the verification of the reportable measurement range and linearity of the measurements of hematology analyzers for white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets in extended concentration ranges.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
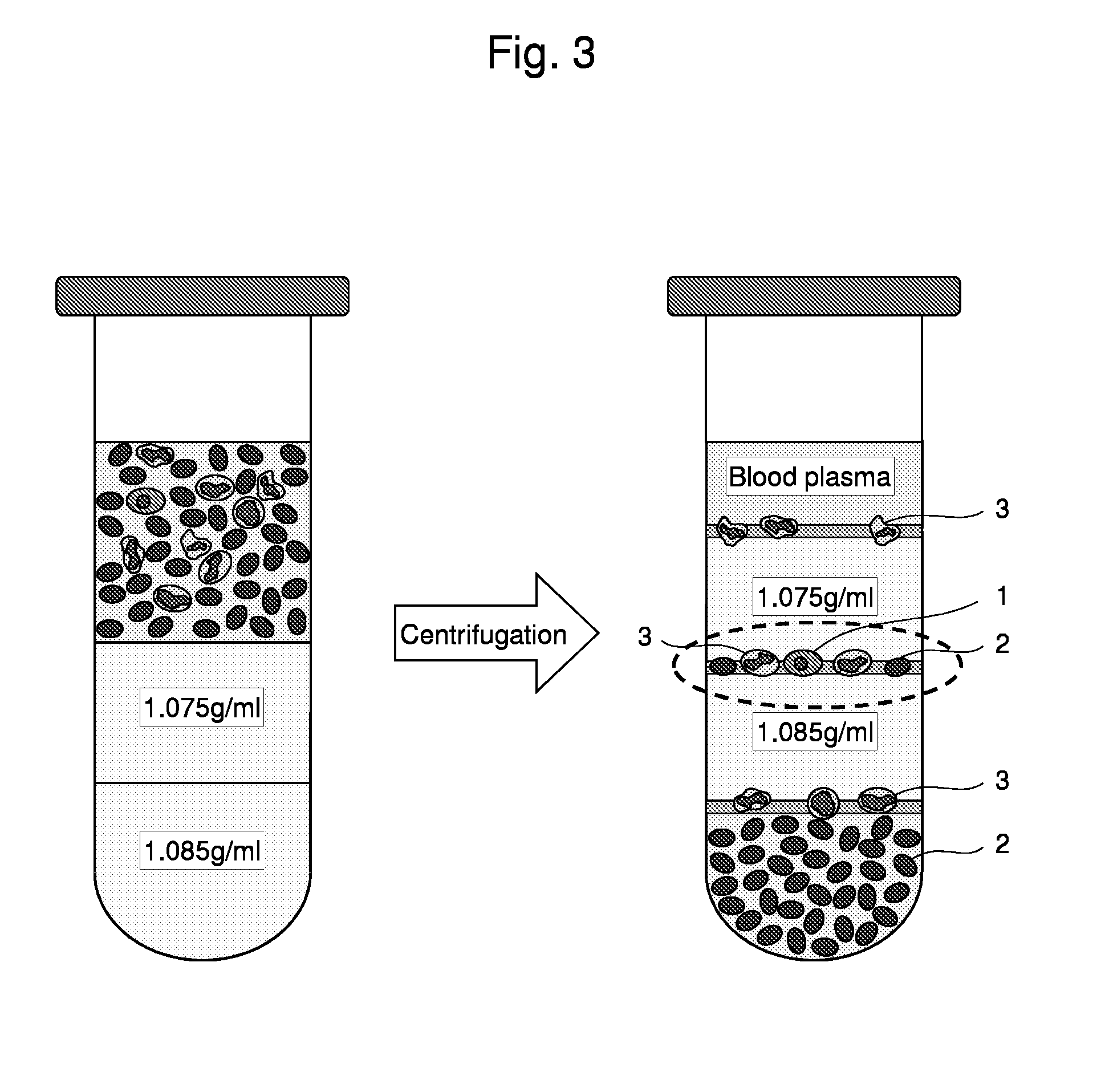
Method for collecting nucleated red blood cells via density-gradient centrifugation utilizing changes in blood cell density
ActiveUS20130072402A1Cell count is reducedIncreased riskMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningCell FractionRed blood cell
This invention provides a method for concentrating and collecting small quantities of fetal nucleated red blood cells contained in the maternal blood. The method for concentrating and collecting nucleated red blood cells from the maternal blood comprises: (i) subjecting the maternal blood to a first density-gradient centrifugation and collecting a cell fraction containing nucleated red blood cells; (ii) treating the cell fraction containing nucleated red blood cells so as to selectively changes the density of the nucleated red blood cells from that of the white blood cells; and (iii) subjecting the treated cell fraction containing the nucleated red blood cells to a second density-gradient centrifugation so as to collect a fraction containing nucleated red blood cells.
Owner:JAPAN ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH +2
Method for separating free fetal cells from peripheral blood of pregnant women
ActiveCN108535228AIncrease the frequency of collisionsImprove capture efficiencyLaboratory glasswaresFluorescence/phosphorescenceFetal cellCell separation
The present invention relates to a method for separating free fetal cells from peripheral blood of a pregnant woman. The method utilizes the cell separation function and the specific affinity recognition principle of a microfluidic chip to realize high-efficiency and high-purity capture and separation of the free fetal cells (fetal nucleated red blood cells, trophoblast cells, and the like) in theperipheral blood of the pregnant woman. Within the microfluidic chip, a microarray structure with a specific geometric arrangement is designed, and the microarray structure is modified with moleculargroups having an affinity recognition function such as a nucleic acid aptamer, an antibody and a polypeptide. By adjusting parameters of the microarray structure, the collision efficiency of different sizes of fetal cells and microarrays can be controlled, and the capture and enrichment of the fetal cells of different sizes can be realized.
Owner:WISDOM HEALTHY BIOTECH XIAMEN CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com