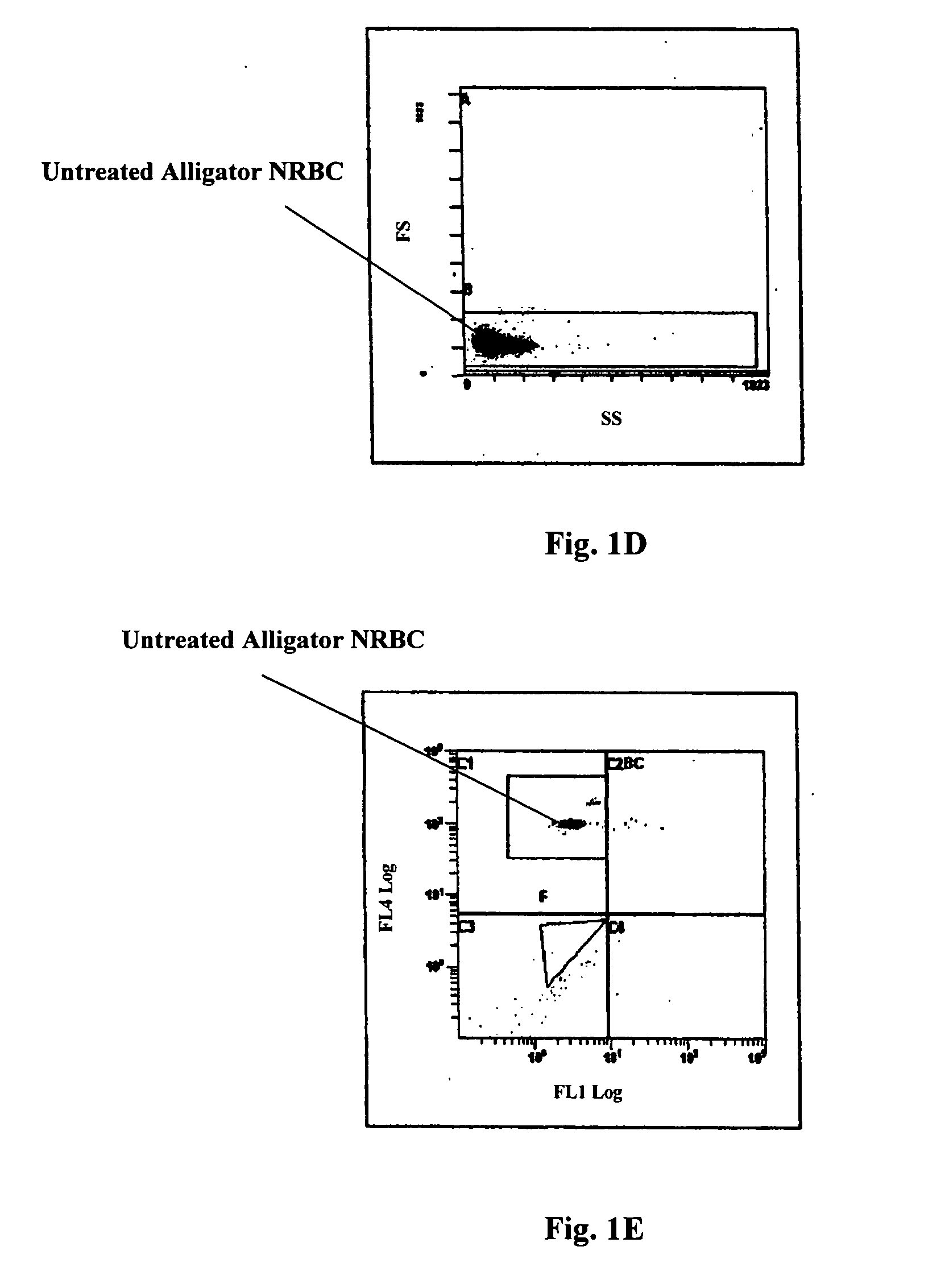
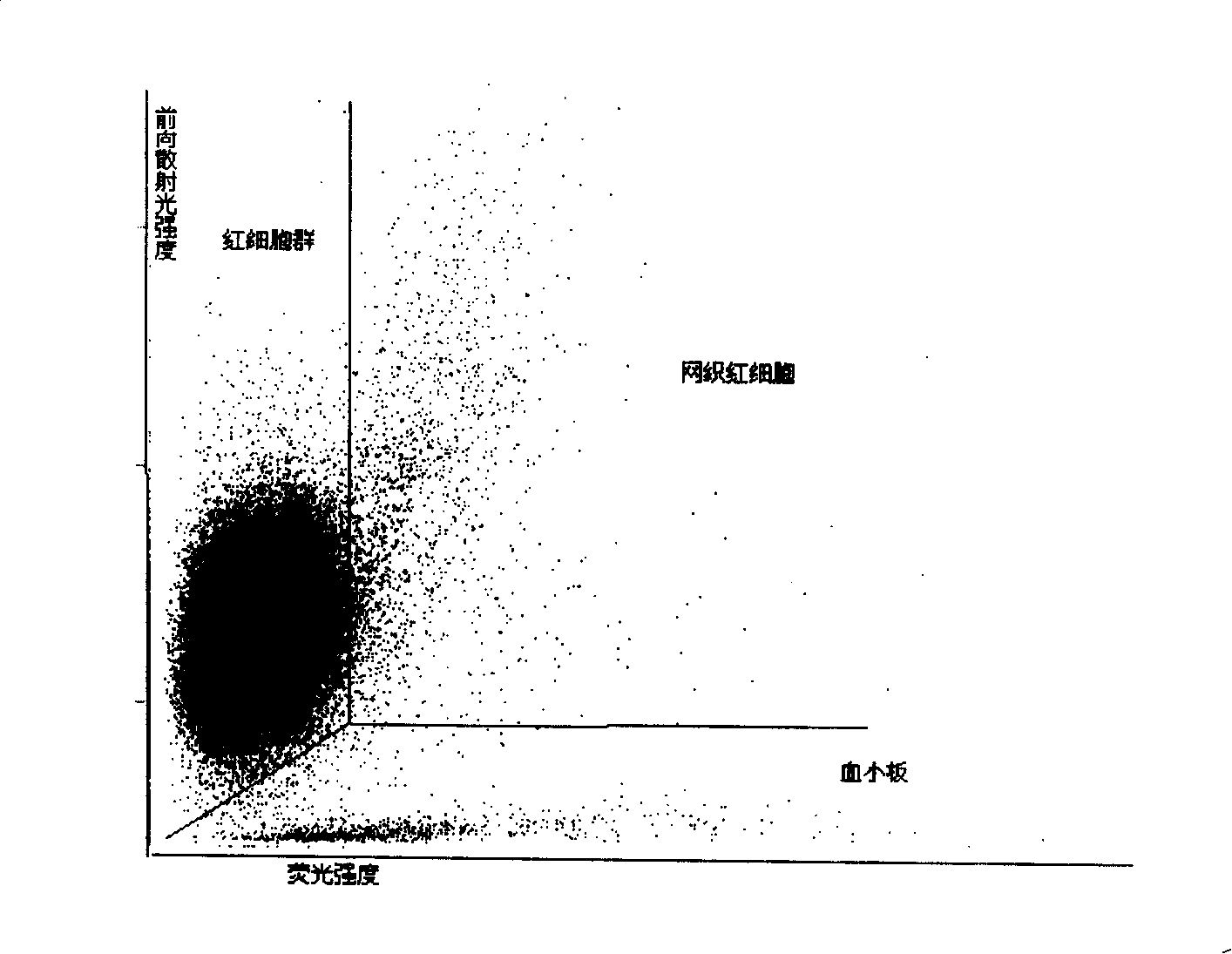
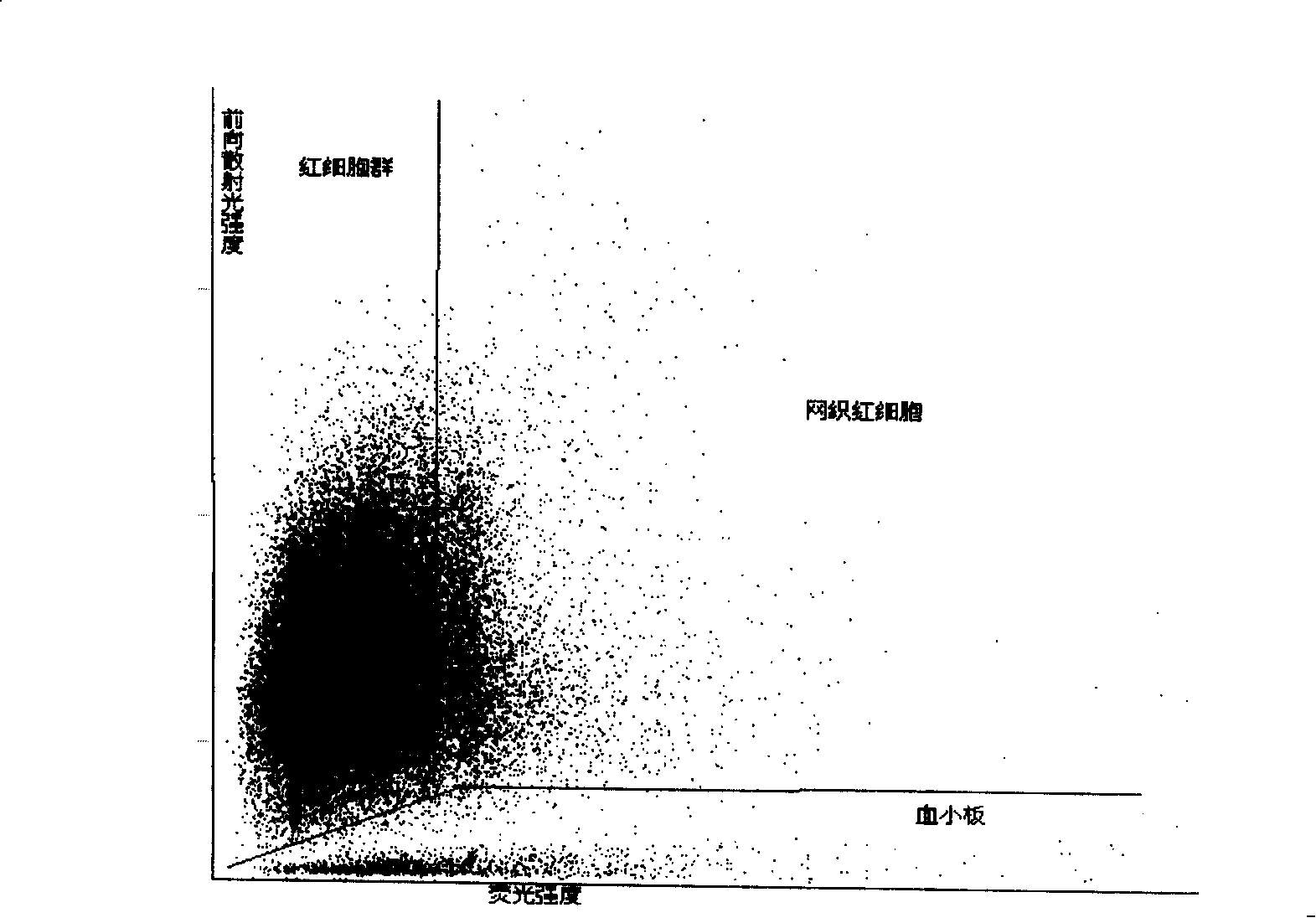
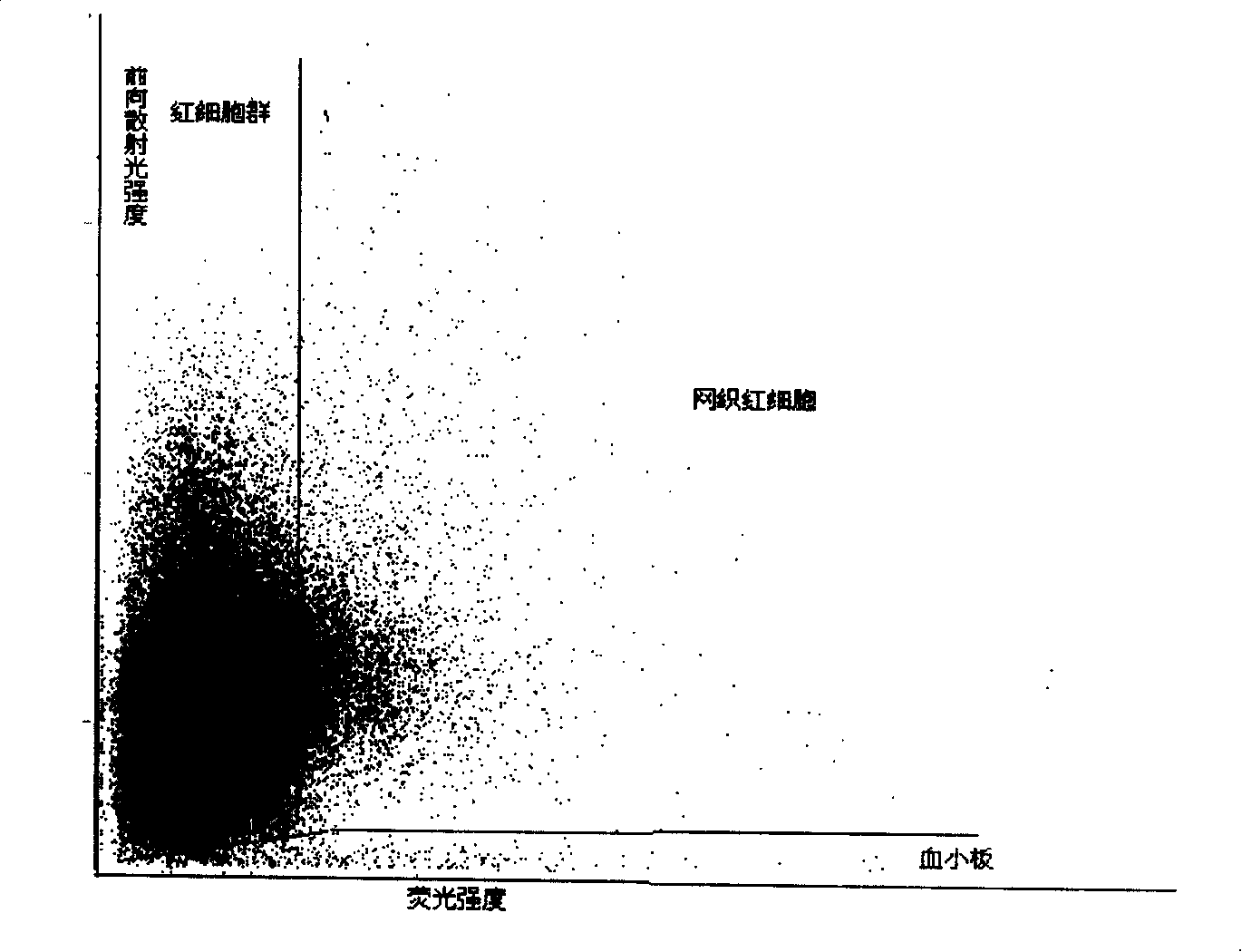
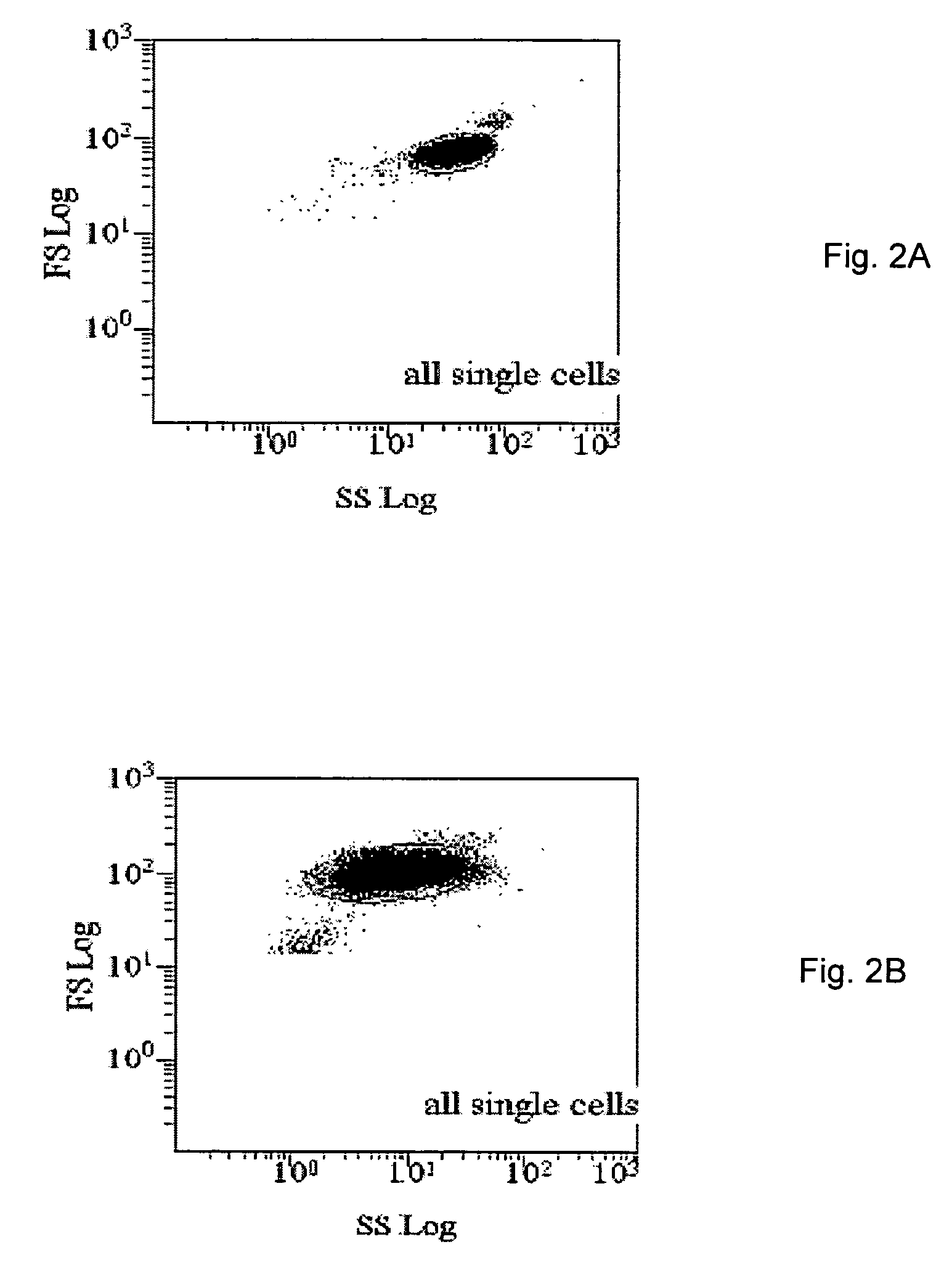
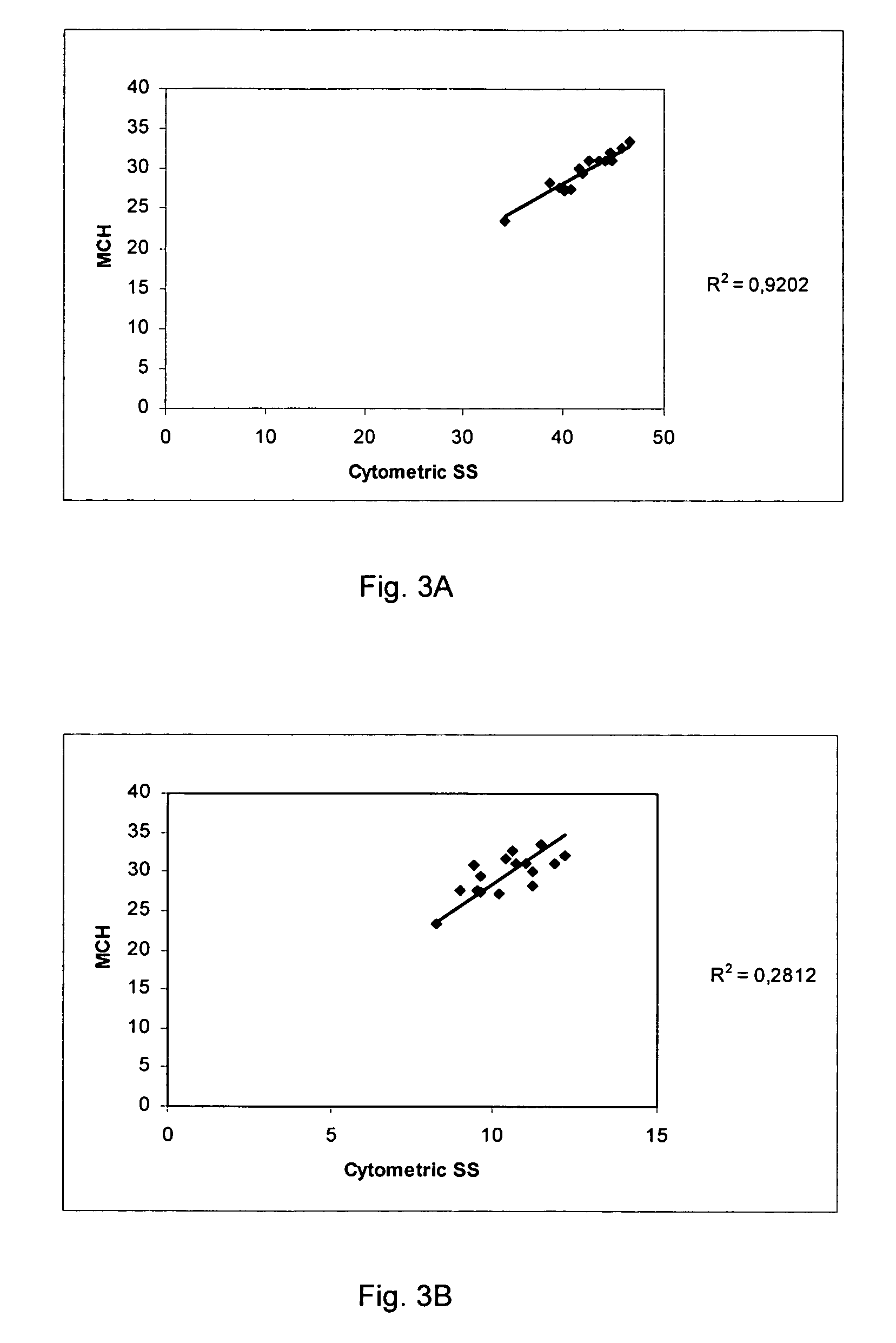
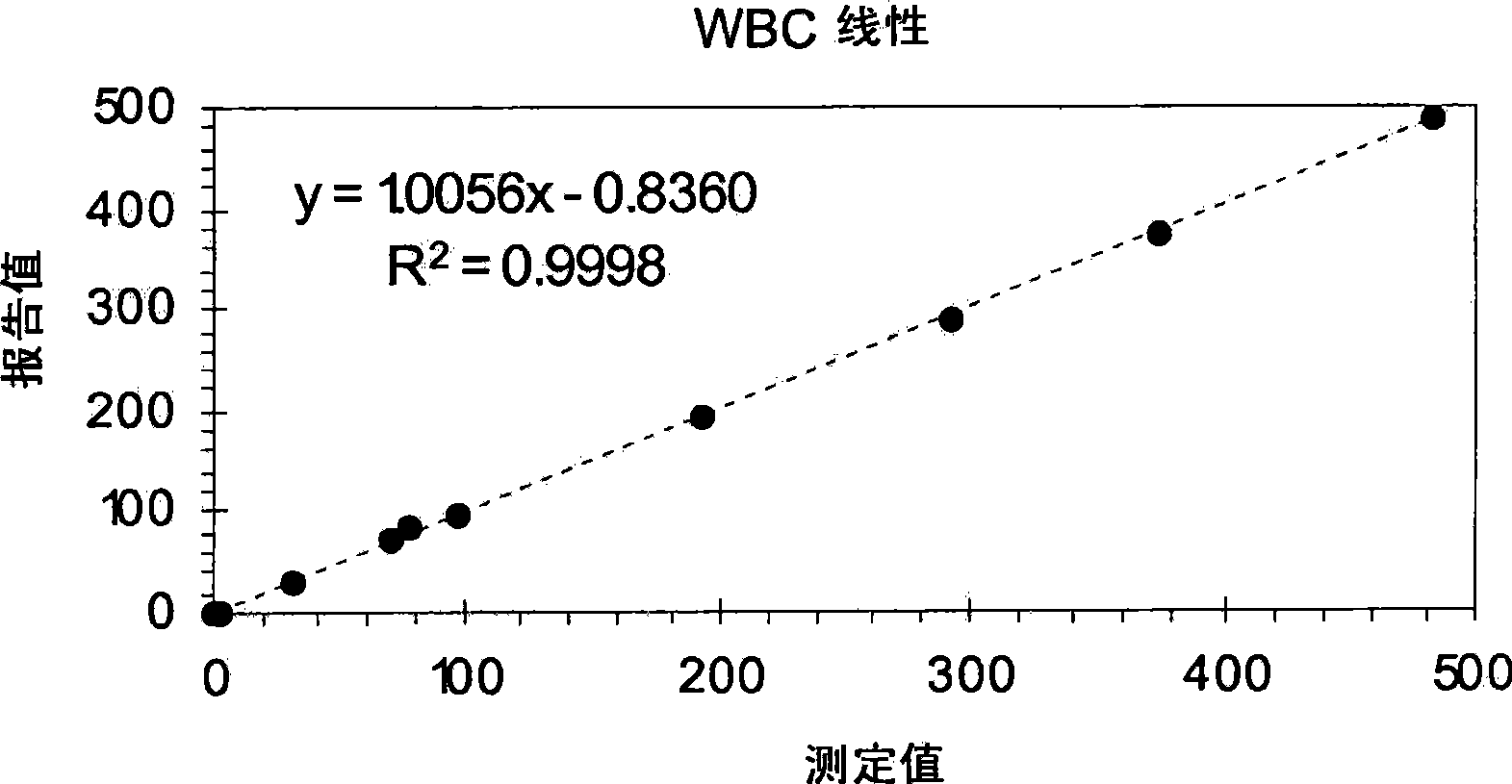
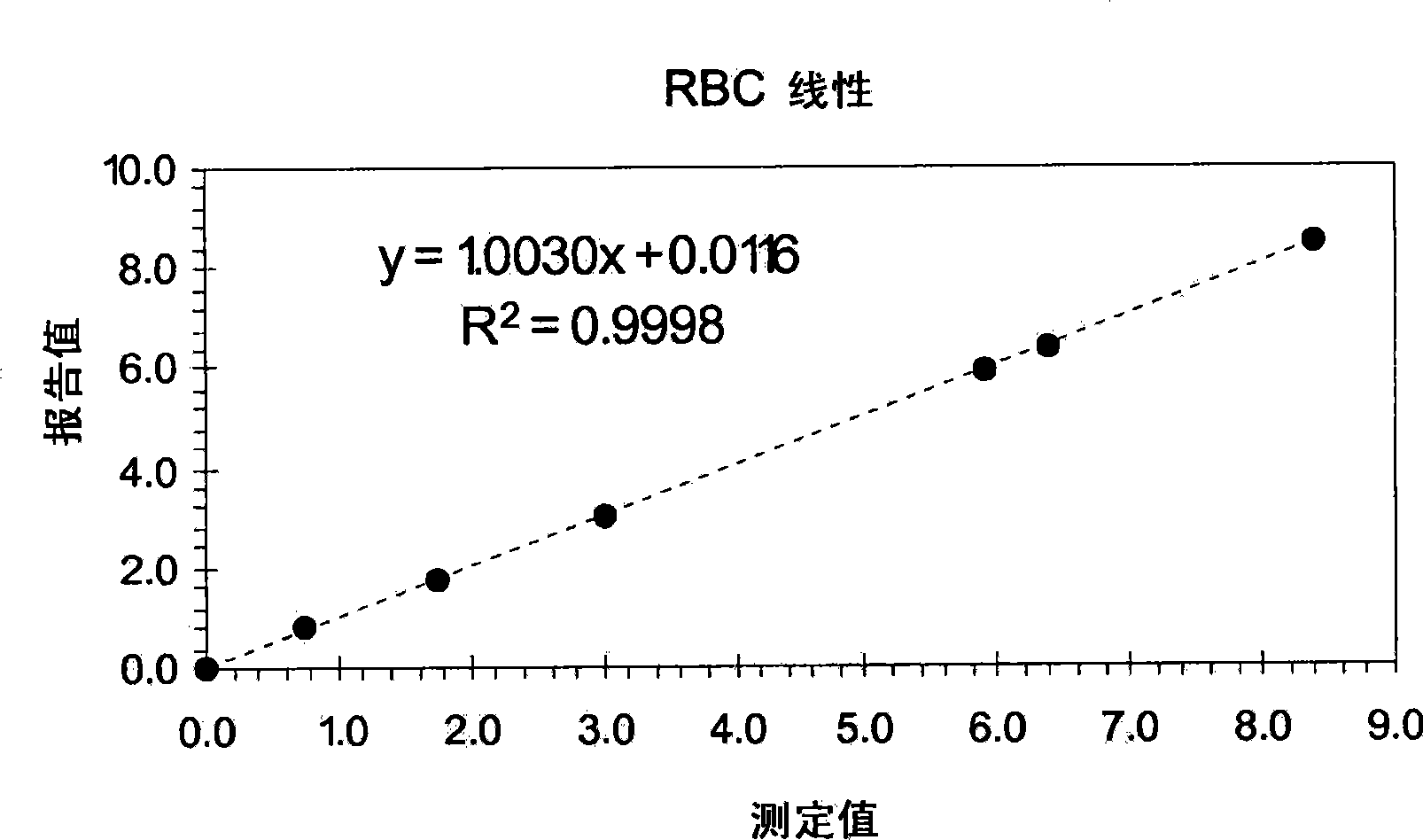
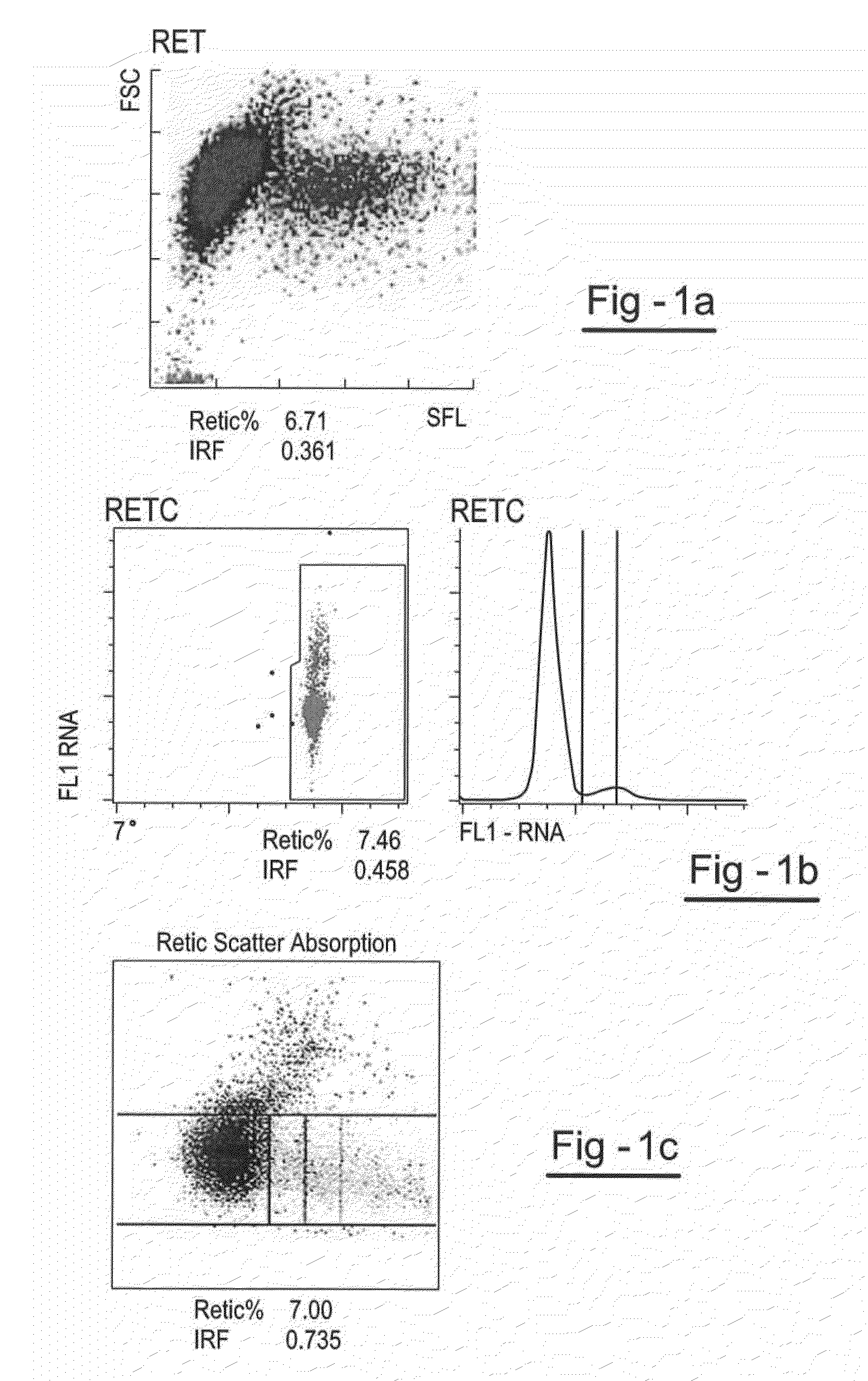
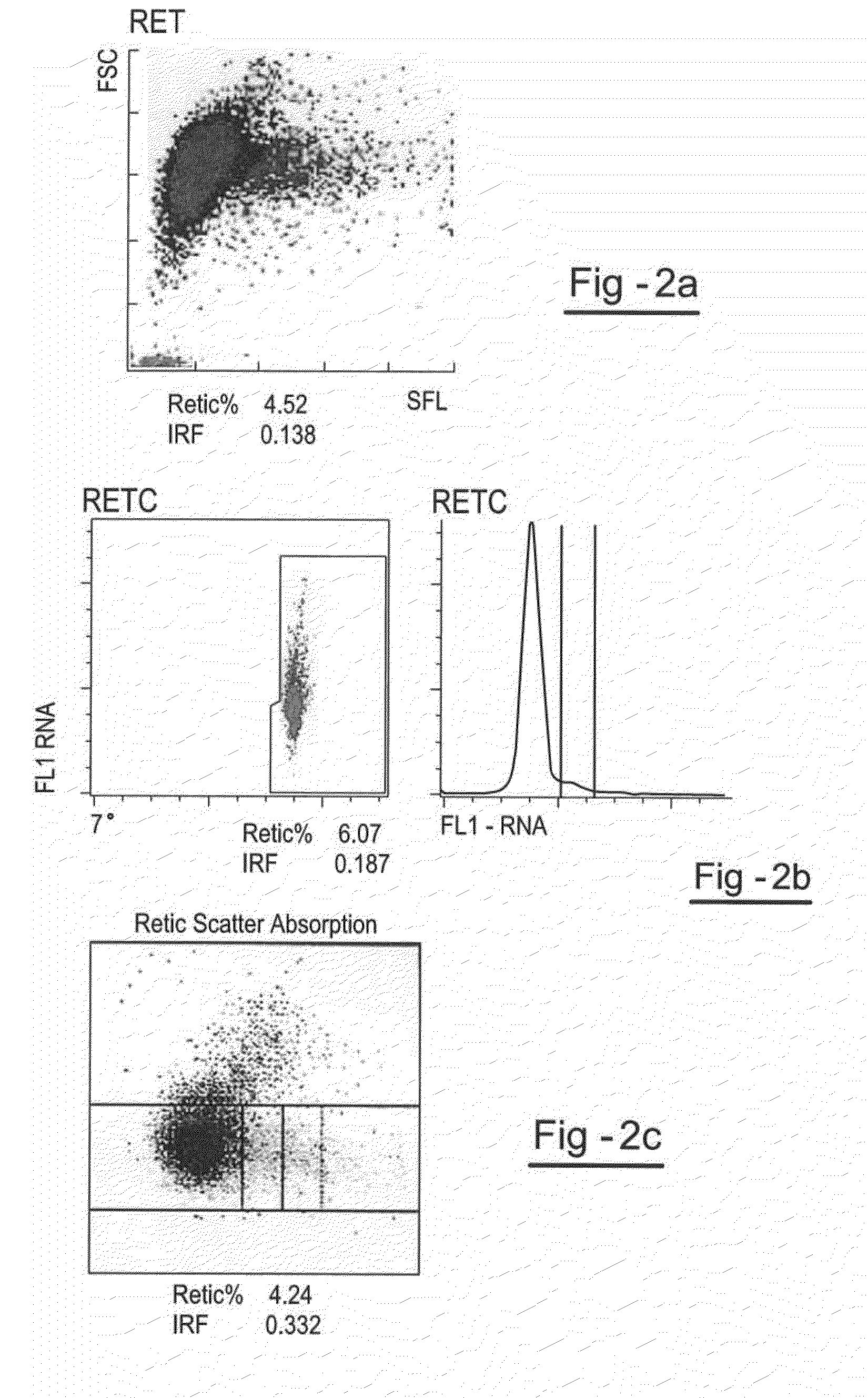
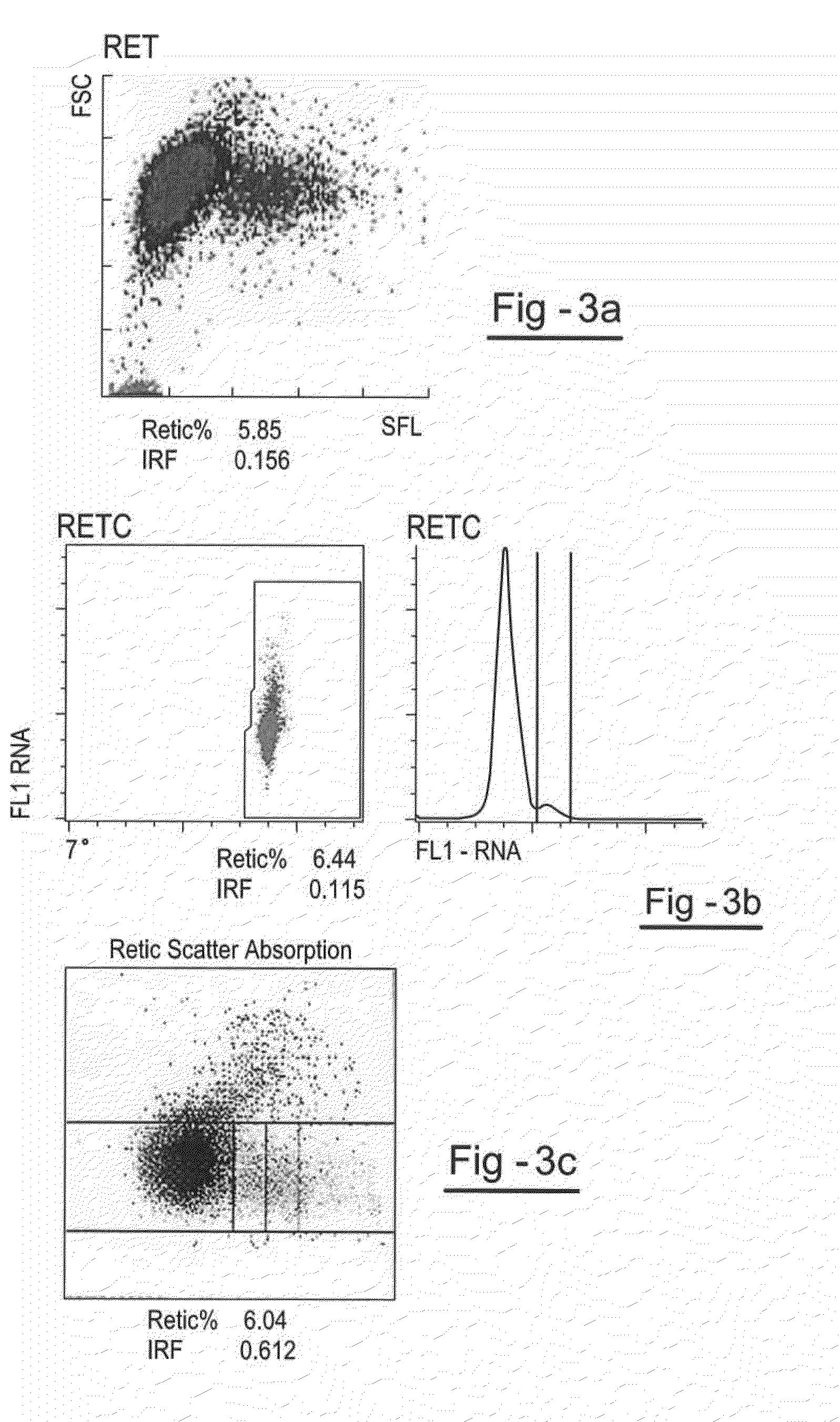
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
103 results about "Reticulocyte" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Reticulocytes are immature red blood cells (RBCs). In the process of erythropoiesis (red blood cell formation), reticulocytes develop and mature in the bone marrow and then circulate for about a day in the blood stream before developing into mature red blood cells. Like mature red blood cells, in mammals, reticulocytes do not have a cell nucleus. They are called reticulocytes because of a reticular (mesh-like) network of ribosomal RNA that becomes visible under a microscope with certain stains such as new methylene blue and Romanowsky stain.
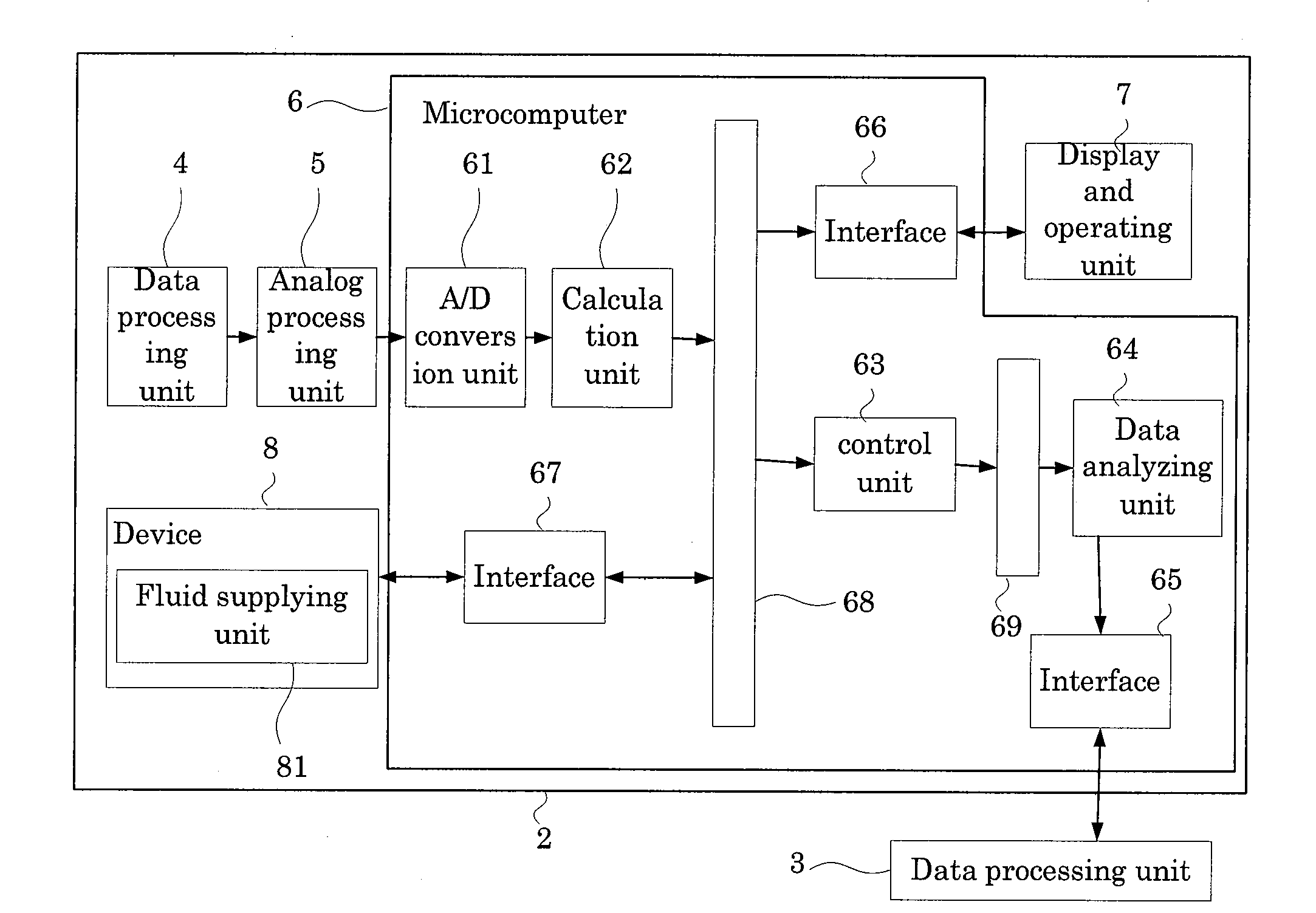
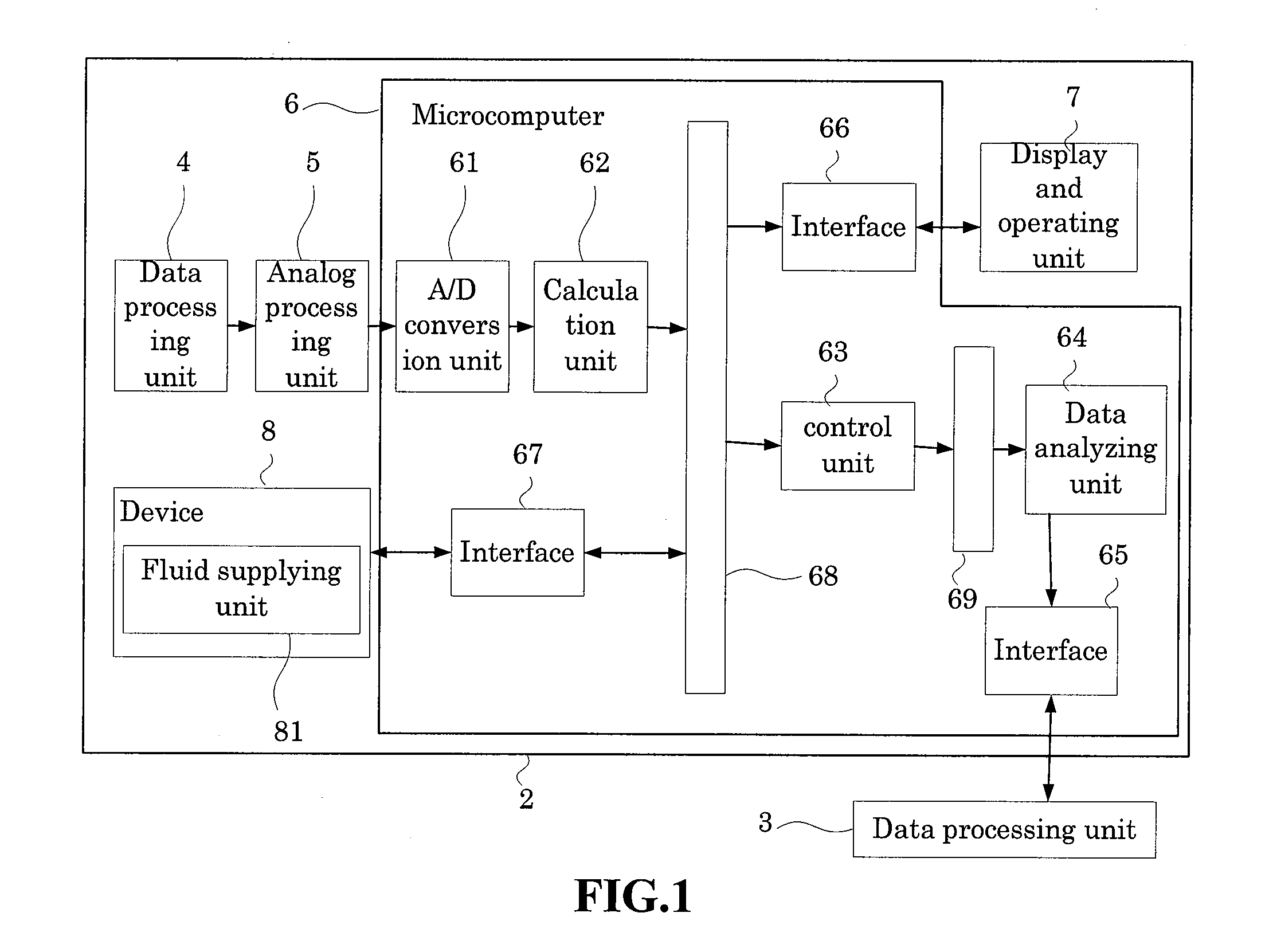
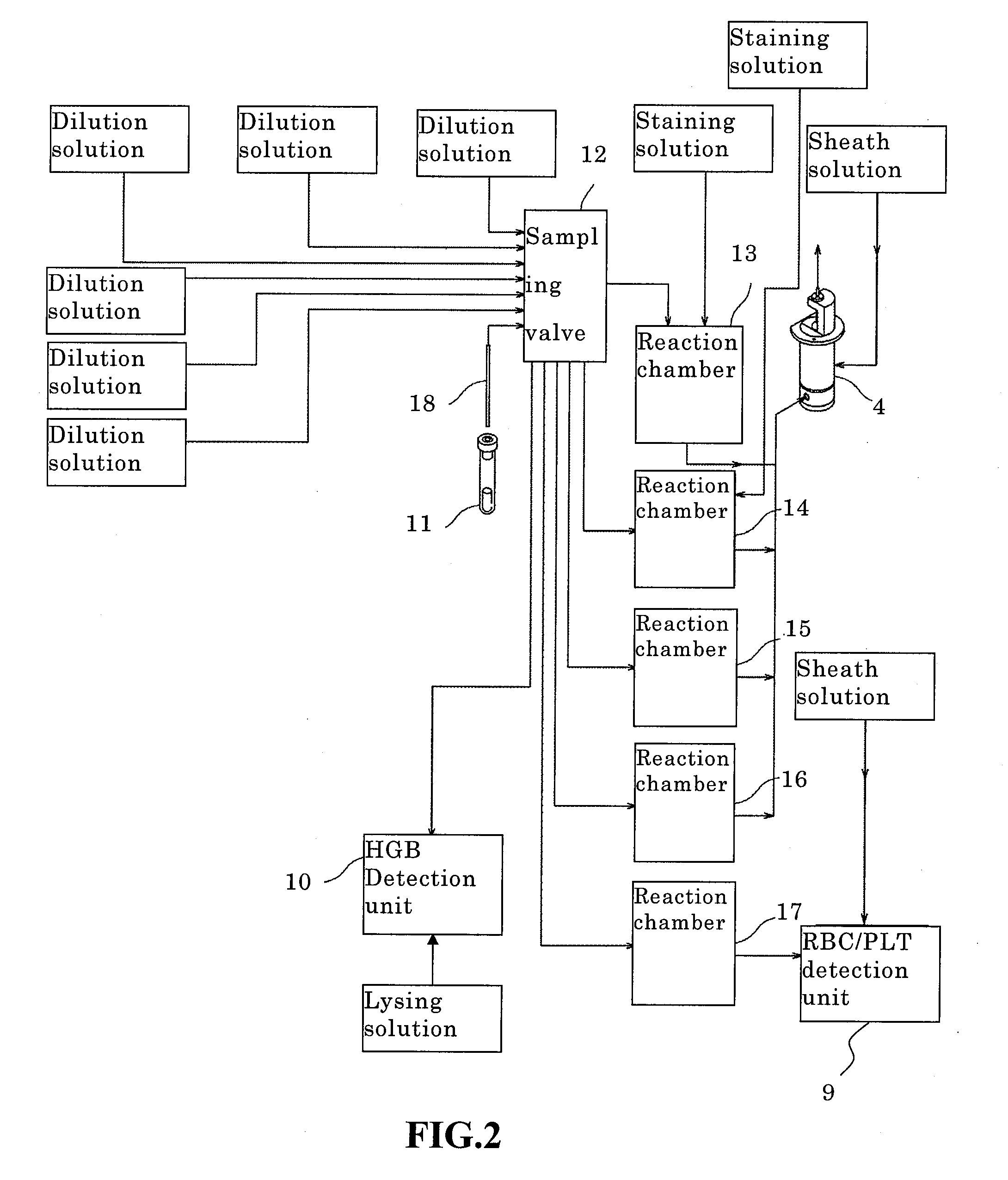
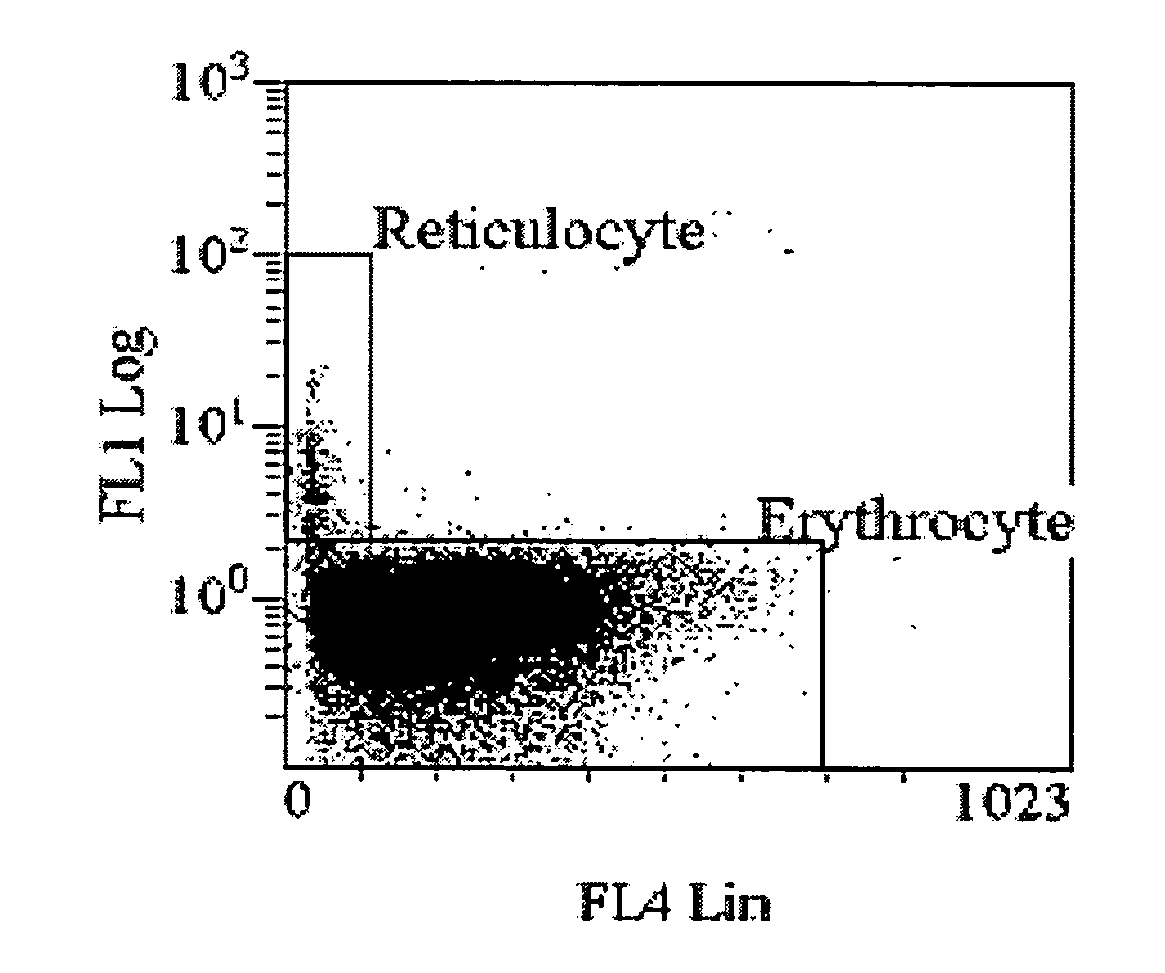
Hematology analyzer, hematology analyzing method, and computer program product
InactiveUS20080268494A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMedicine.hematologyInformation support
A hematology analyzer, obtains red blood cell scattered light information which is scattered light information related to red blood cells contained in a blood sample and reticulocyte scattered light information which is scattered light information related to reticulocytes contained in the blood sample; obtains a value equivalent to the amount of hemoglobin in the red blood cells from the red blood cell scattered light information; obtains a value equivalent to the amount of hemoglobin in the reticulocytes from the reticulocyte scattered light information; obtains difference between the hemoglobin amounts which is the difference between the value equivalent to the amount of hemoglobin in the red blood cells and the value equivalent to the amount of hemoglobin in the reticulocytes; and obtains information supporting clinical examination based on the value equivalent to the amount of hemoglobin in the reticulocytes and the difference between the hemoglobin amounts, is disclosed. A hematology analyzing method and a computer program product are also disclosed.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
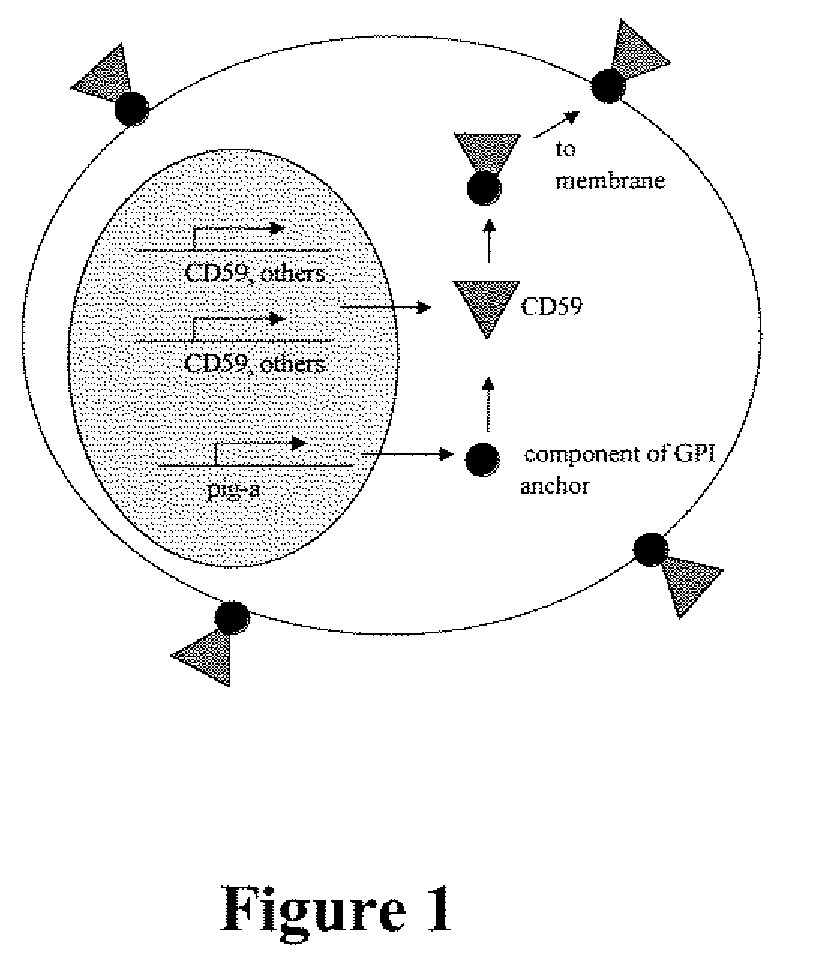
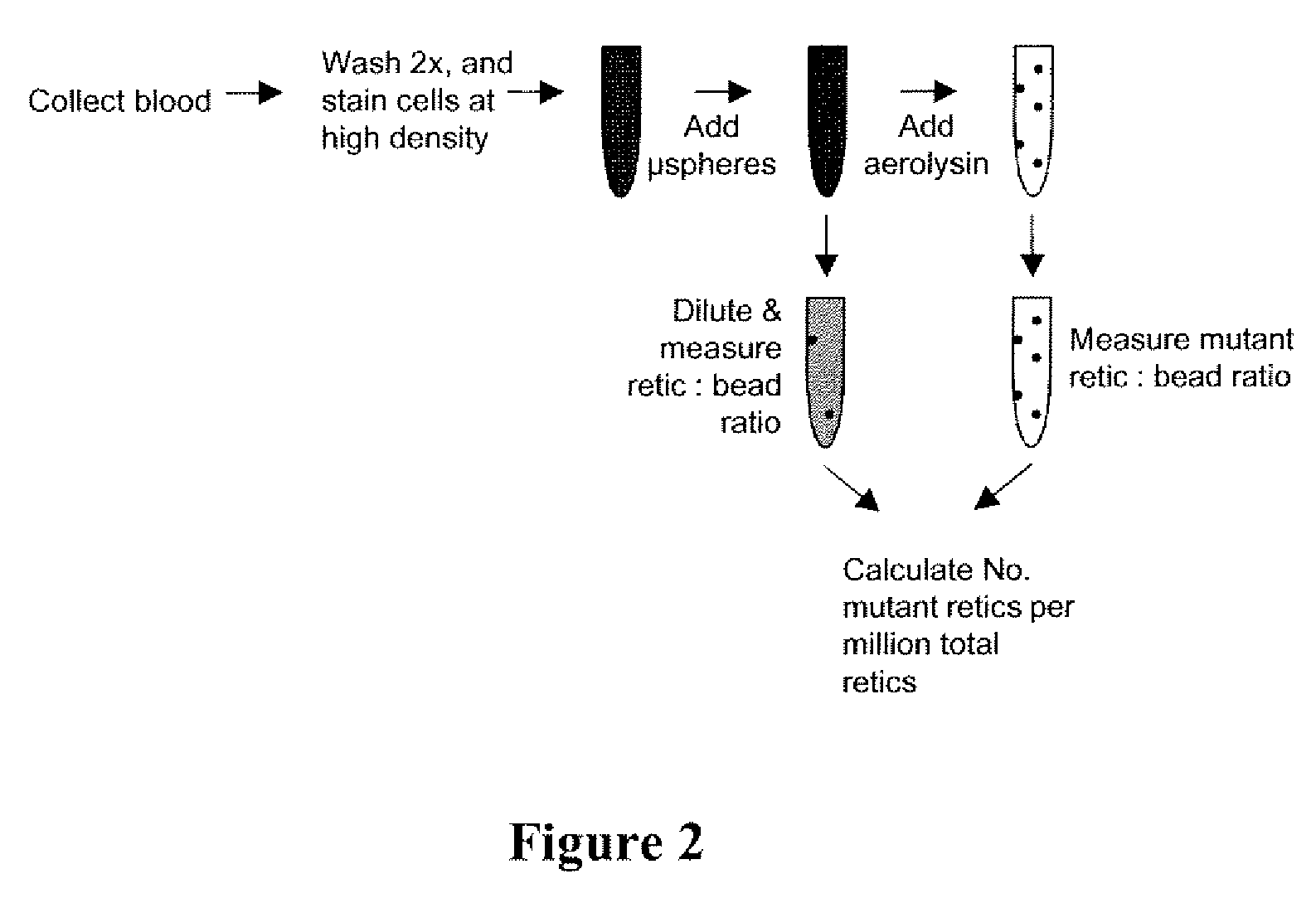
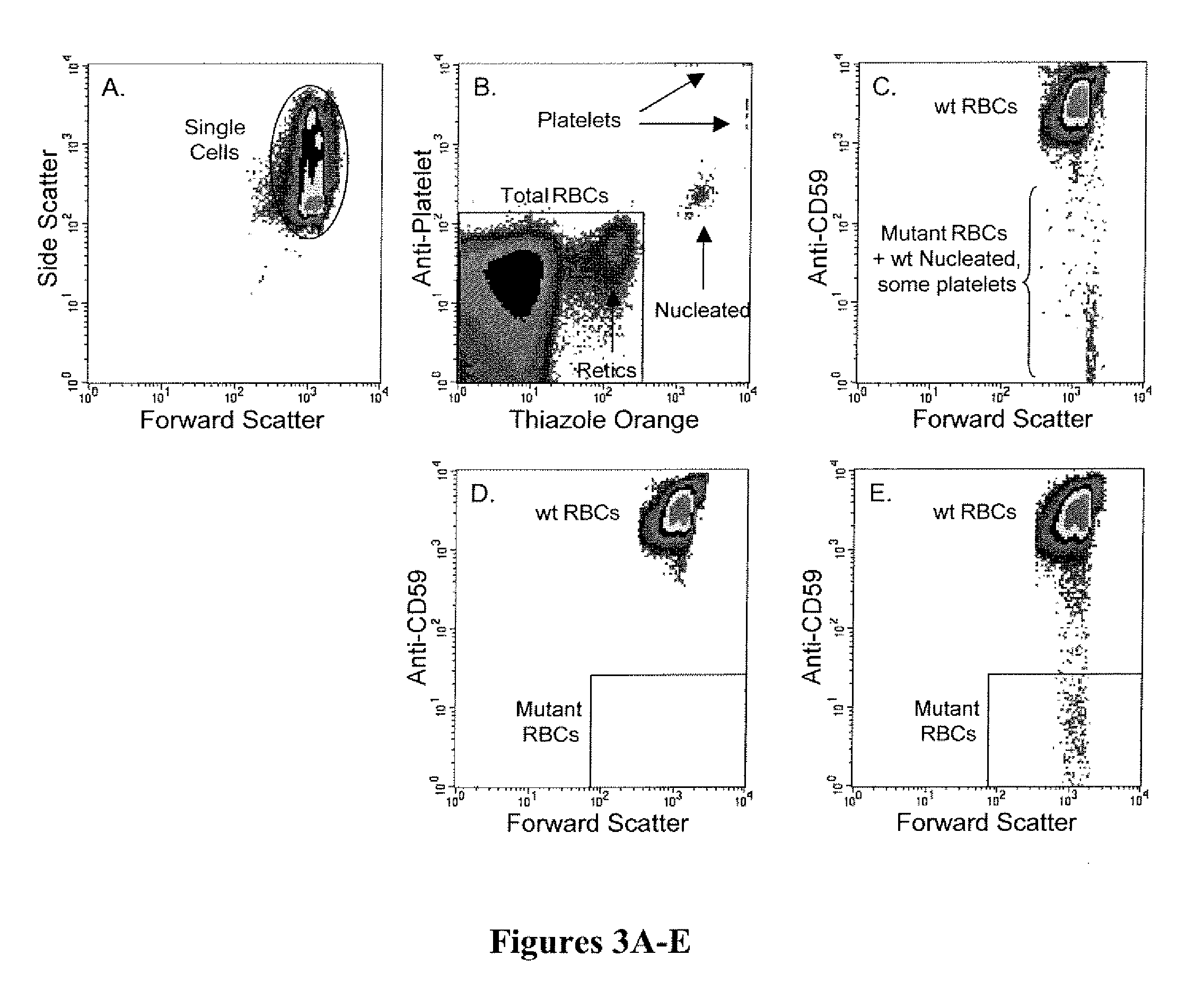
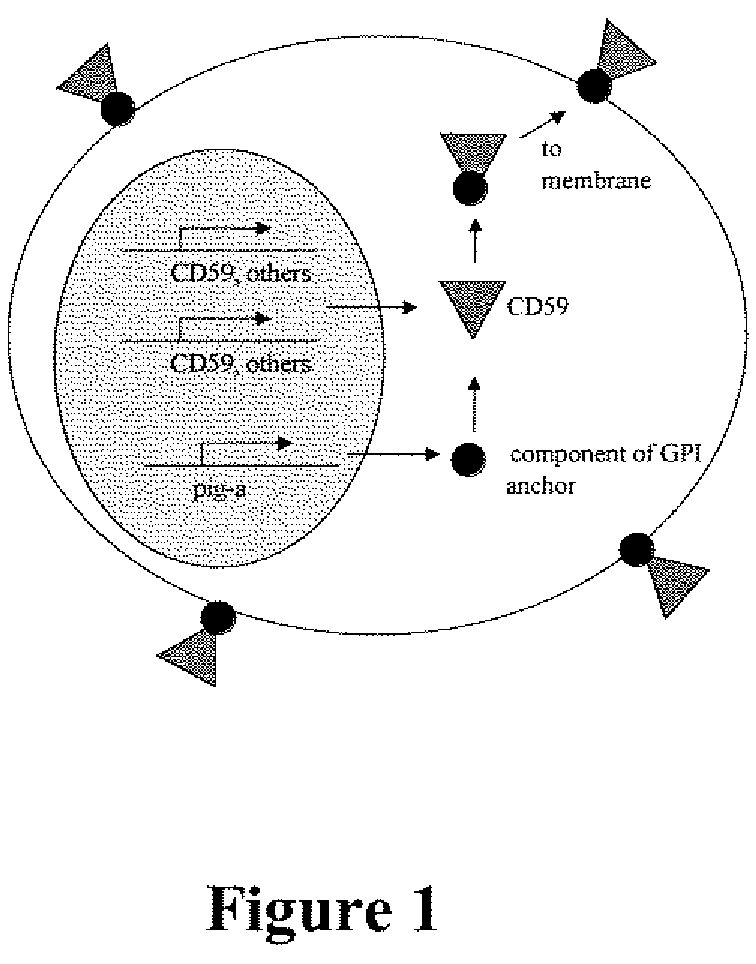
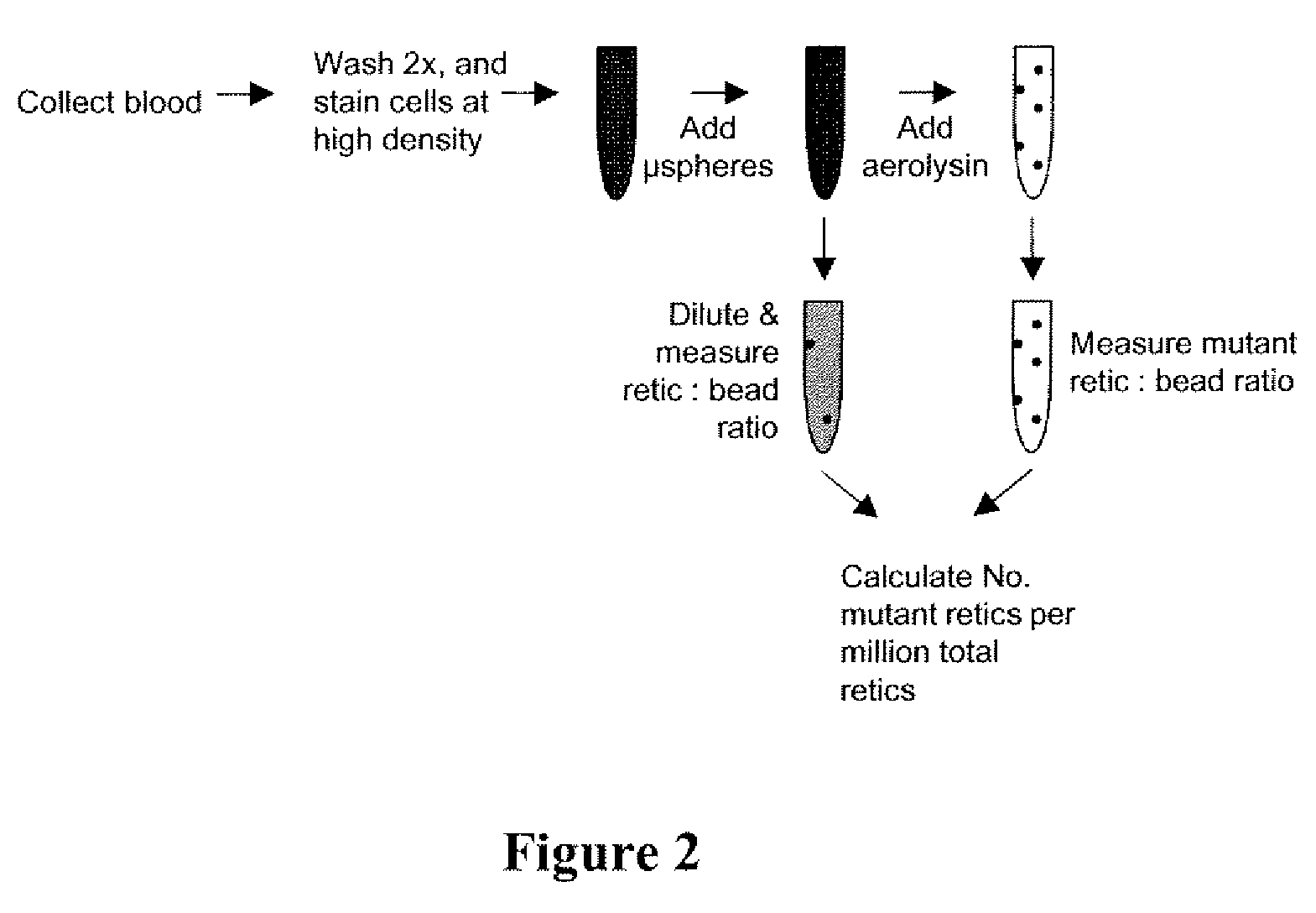
Method for measuring in vivo mutation frequency at an endogenous gene locus
ActiveUS20070274919A1Fast and reliable and accurateUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsStainingRed blood cell
The present invention relates a method for the enumeration of in vivo gene mutation. The method utilizes differential staining of GPI-anchor deficient erythrocyte populations to distinguish between wild-type and pig-a gene mutants. Quantitative analyses can be conducted on erythrocytes and / or reticulocytes, and is based upon fluorescent emission and light scatter following exposure to an excitatory light source. Counting of mutant erythrocytes or reticulcoytes relative to the number of total erythrocytes or reticulocytes can be used to assess the DNA-damaging potential of an exogenous chemical agent, the DNA-damaging potential of an exogenous physical agent, the effects of an exogenous agent which can modify endogenously-induced DNA damage, and the effects of an exogenous agent which can modify exogenously-induced DNA damage. Kits for practicing the invention are also disclosed.
Owner:LITRON LAB
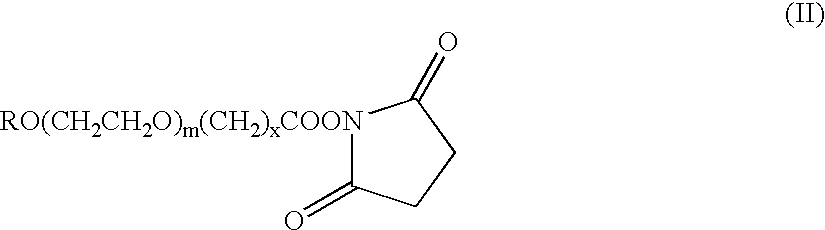
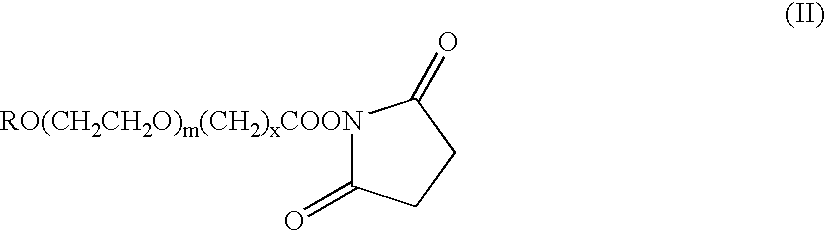
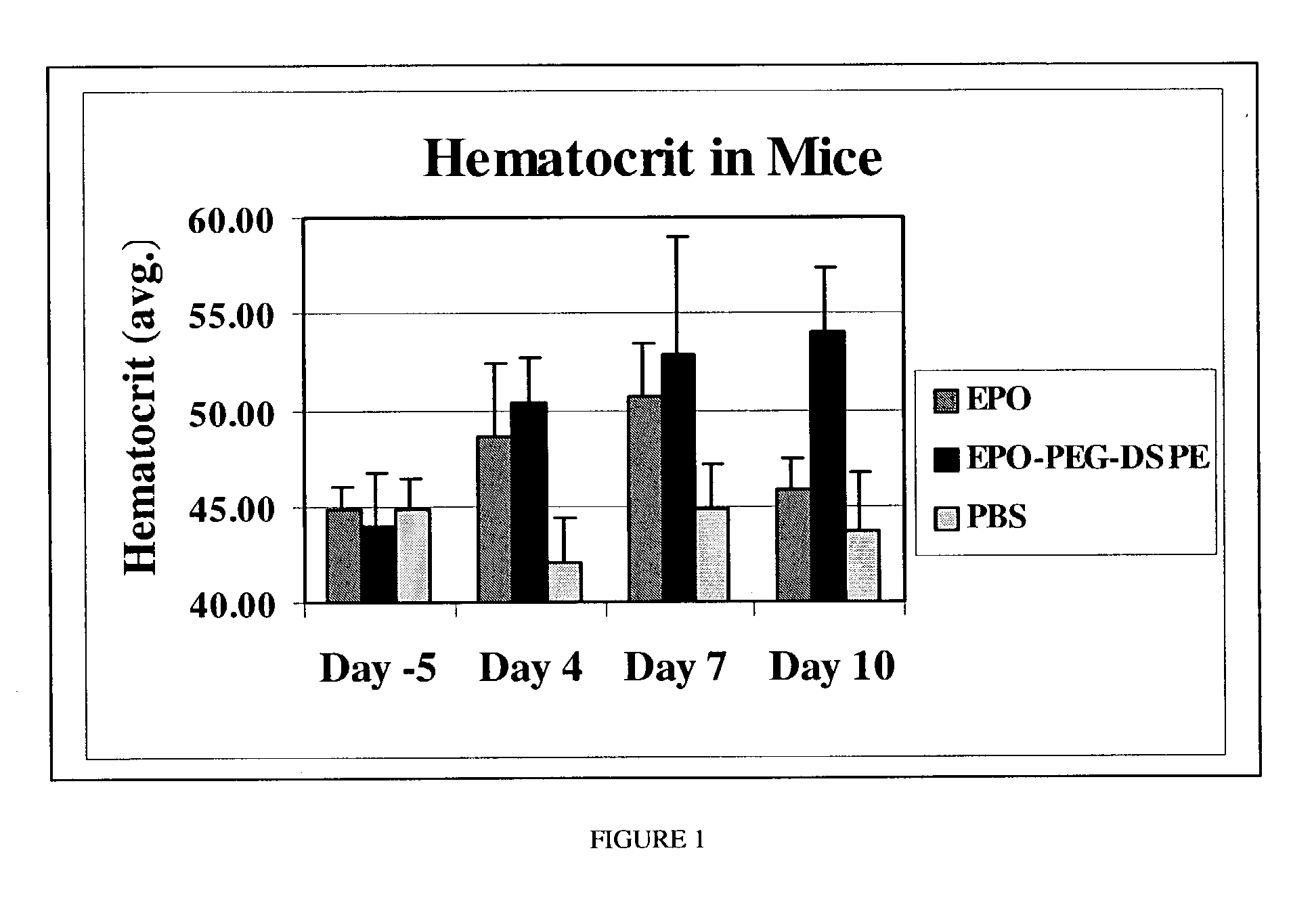
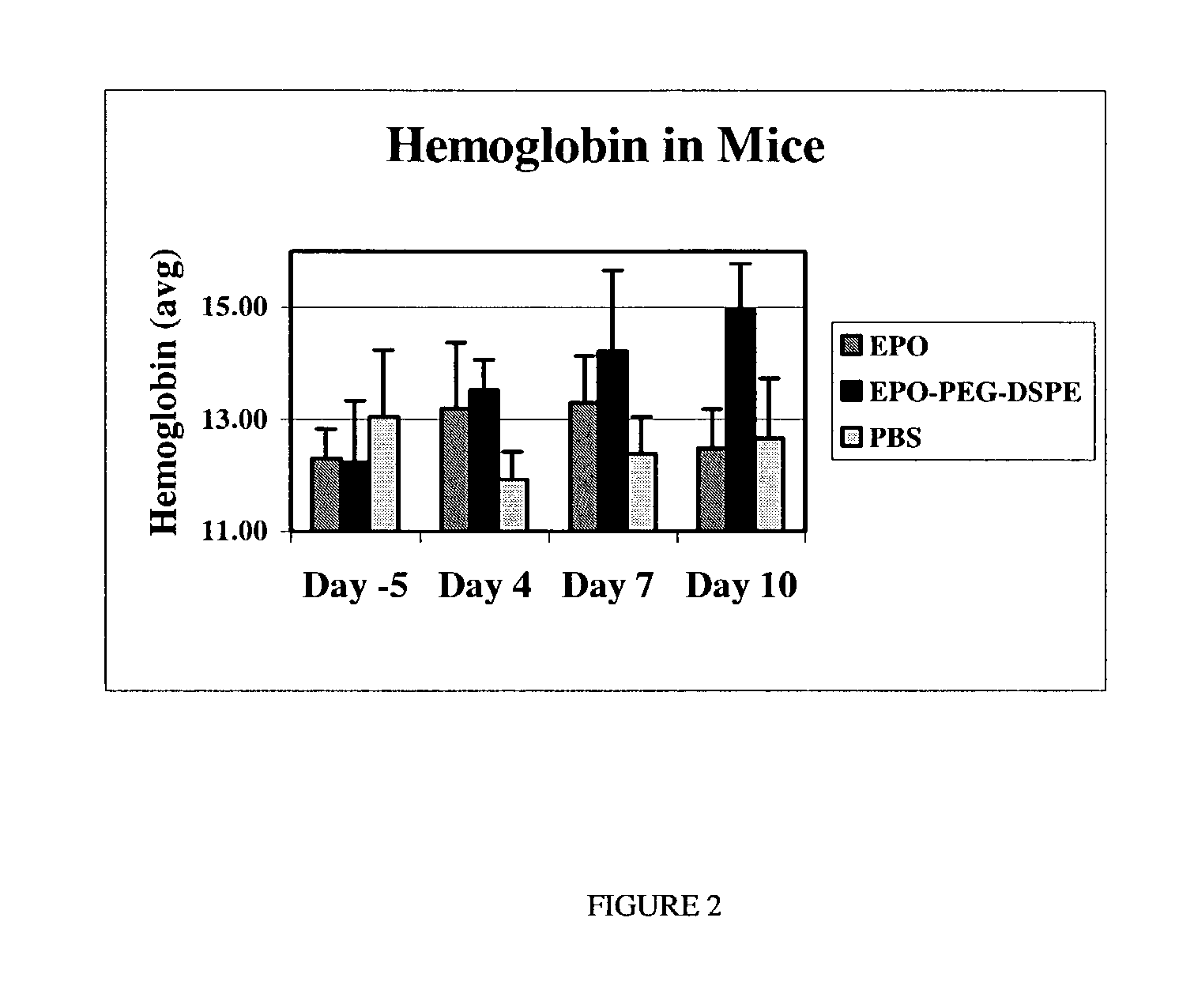
Erythropoietin conjugates
InactiveUS7128913B2Easy to synthesizePeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsRed blood cellBone marrow cell
The present invention refers to conjugates of erythropoietin with poly(ethylene glycol) comprising an erythropoietin glycoprotein having an N-terminal α-amino group and having the in vivo biological activity of causing bone marrow cells to increase production of reticulocytes and red blood cells and selected from the group consisting of human erythropoietin and analogs thereof which have the sequence of human erythropoietin modified by the addition of from 1 to 6 glycosylation sites or a rearrangement of at least one glycosylation site; said glycoprotein being covalently linked to one poly(ethylene glycol) group of the formula—CO—(CH2)x—(OCH2CH2)m—ORwherein the —CO of the poly(ethylene glycol) group forms an amide bond with said N-terminal α-amino group; and wherein R is lower alkyl; x is 2 or 3; and m is from about 450 to about 1350.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE INC
Erythropoietin conjugate compounds with extended half-lives
InactiveUS7074755B2Increases circulating serum half-lifeIncrease productionPeptide/protein ingredientsTissue cultureErythrocyte productionSerum ige
The invention provides biologically active erythropoietin (EPO) conjugate compositions wherein EPO is covalently conjugated to a non-antigenic hydrophilic polymer covalently linked to an organic molecule that increases the circulating serum half-life of the composition. The invention thus relates to EPO derivatives described by the formula EPO-(X-Y)N where EPO is erythropoietin or its pharmaceutical acceptable derivatives having biological properties of causing bone marrow cells to increase production of reticulocytes and red blood cells, X is PEG or other water soluble polymers, Y is an organic molecule that increases the circulating half-life of the construct more than the PEG alone and N is an integer from 1 to 15. Other molecules may be included between EPO and X and between X and Y to provide the proper functionality for coupling or valency.
Owner:CENTOCOR
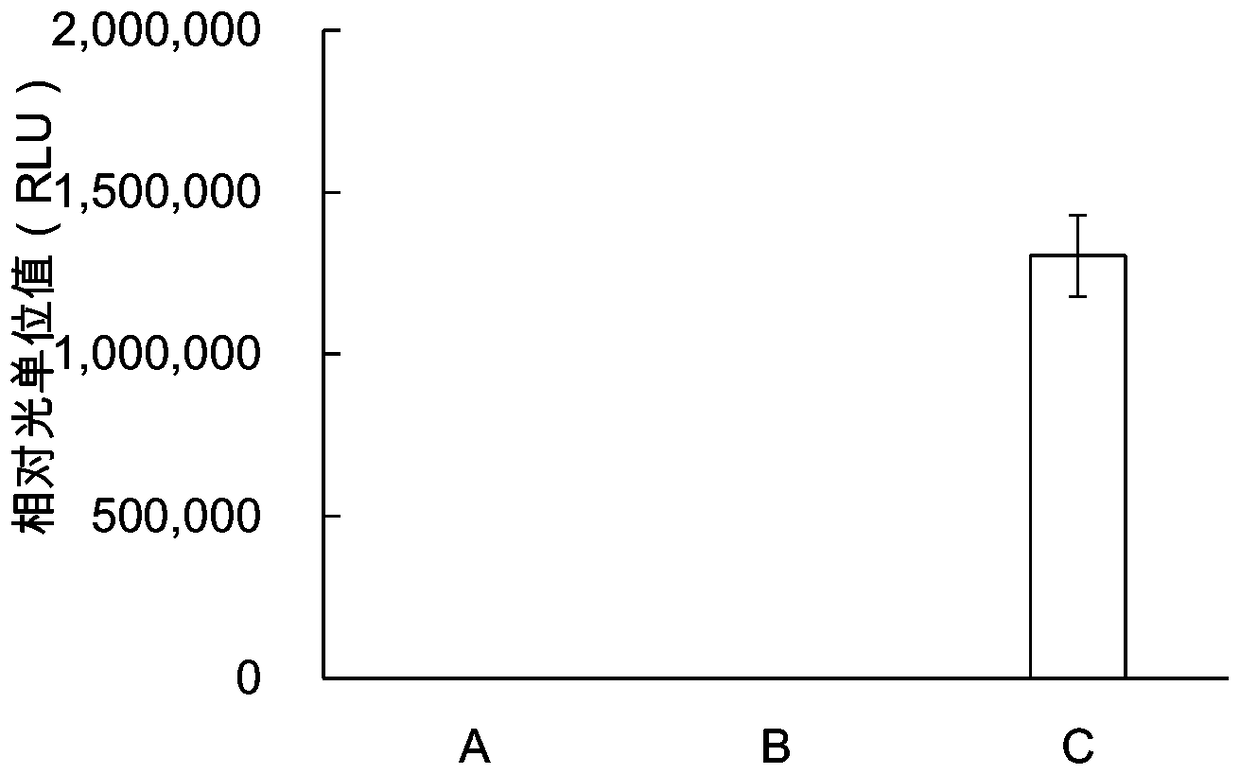
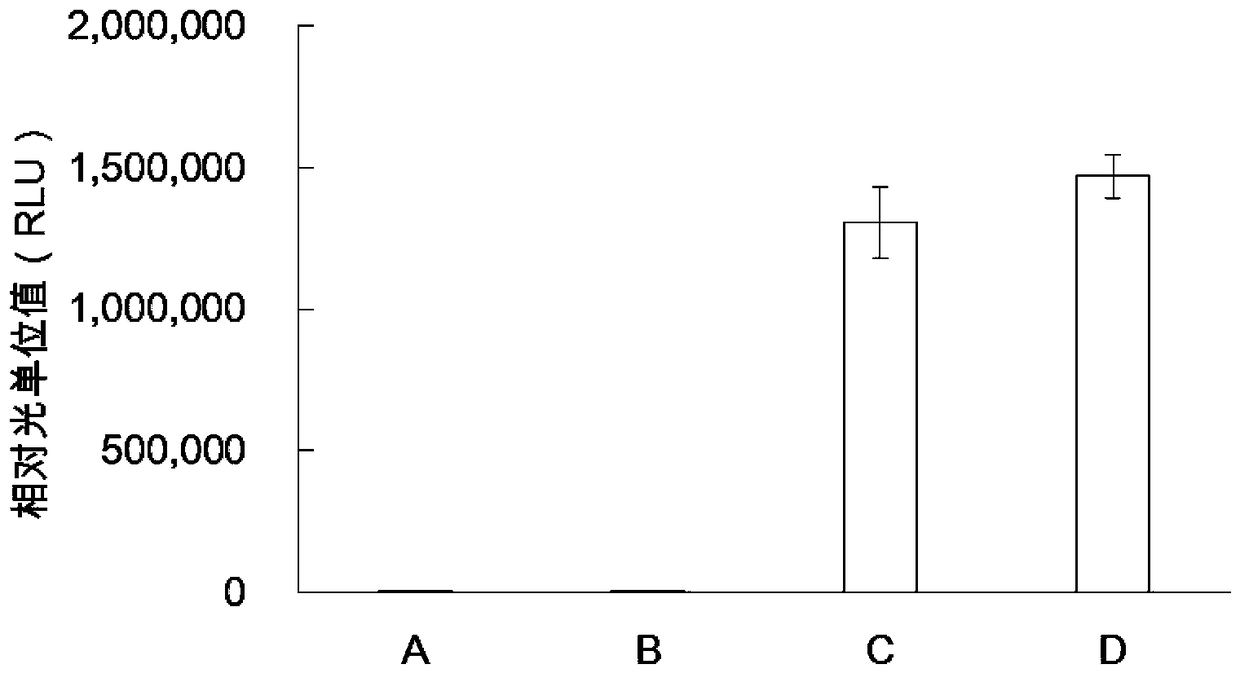
Protein synthesis system for in-vitro protein synthesis, kit and preparation method for protein through in-vitro synthesis
ActiveCN108535489AIncrease productionLow costMicroorganism lysisBiological testingCell freeProtein insertion
The invention provides a protein synthesis system for in-vitro protein synthesis, a kit and a preparation method for a protein through in-vitro synthesis. Specifically, the in-vitro cell-free expression system provided by the invention is capable of extremely efficiently synthesizing proteins and synthesizing complex proteins. Moreover, due to the in-vitro cell-free expression system disclosed bythe invention, the relative light unit value of the activity of the synthesized luciferase is higher than that of the conventional commercial system (such as a rabbit reticulocyte in-vitro expressionsystem) by at least one order of magnitude (more than or equal to 10 times or higher).
Owner:KANGMA SHANGHAI BIOTECH LTD
Diglycosylated erythropoietin
InactiveUS6930086B2Increase productionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsErythrocyte productionBone marrow cell
This invention is directed to an erythropoietin mutein having in vivo biological activity for causing bone marrow cells to increase production of reticulocytes and red blood cells, in that the mutein is N-glycosylated at Asn38 and Asn83 but not N-glycosylated at Asn24. Such muteins have improved pharmaceutical properties.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE INC
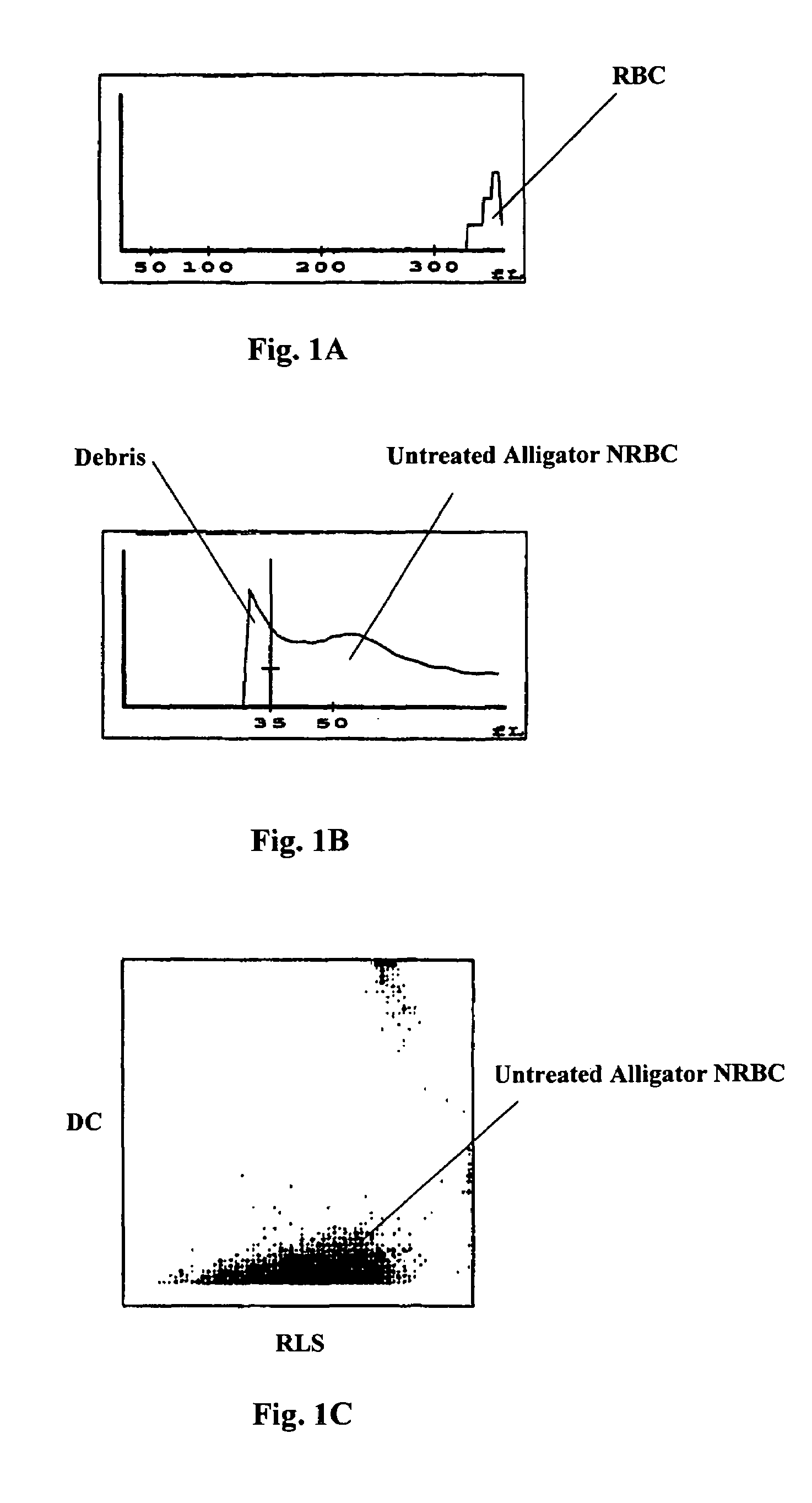
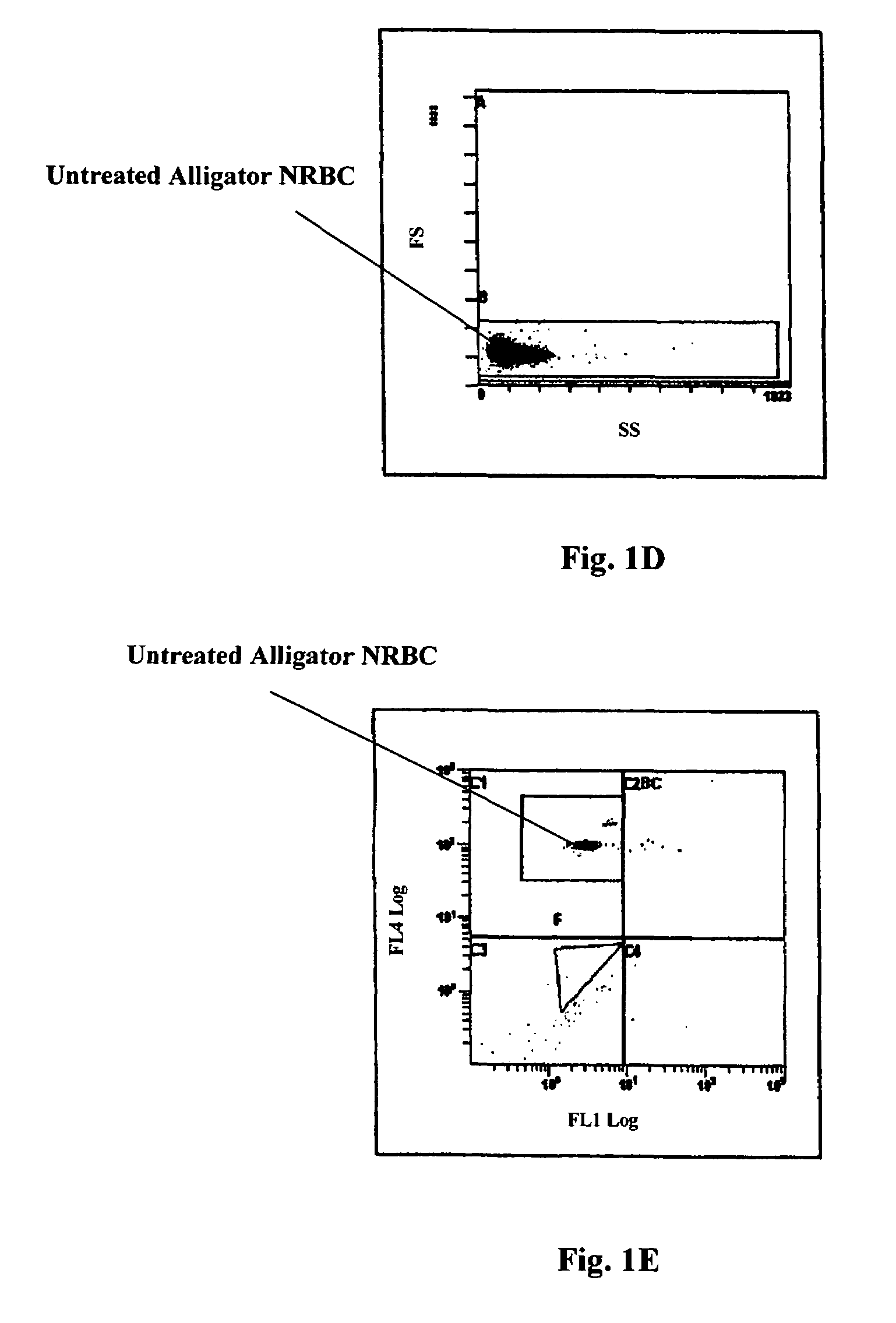
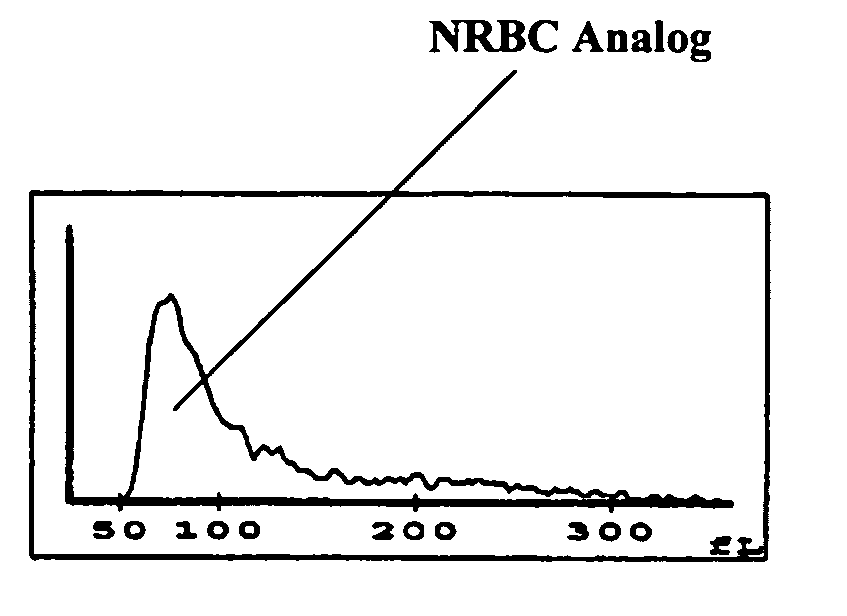
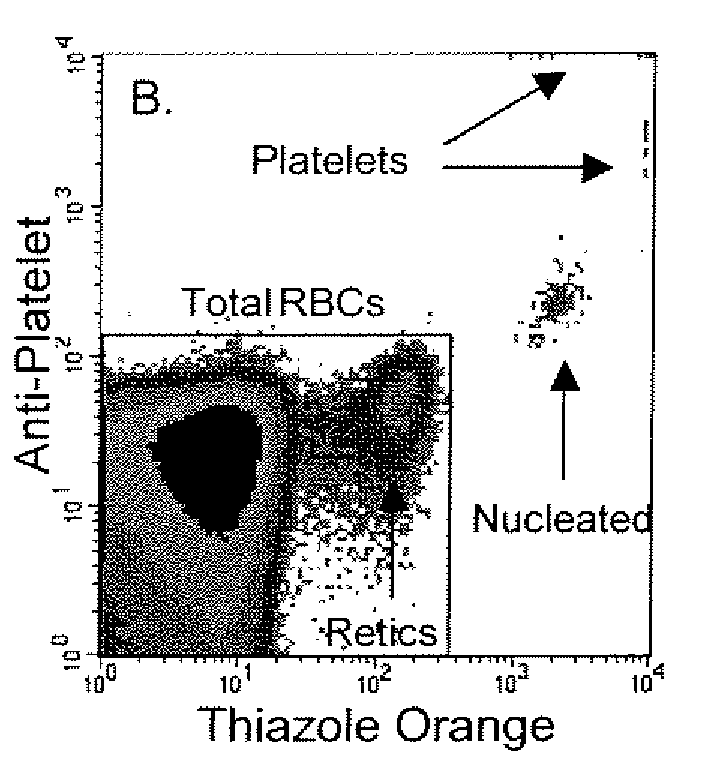
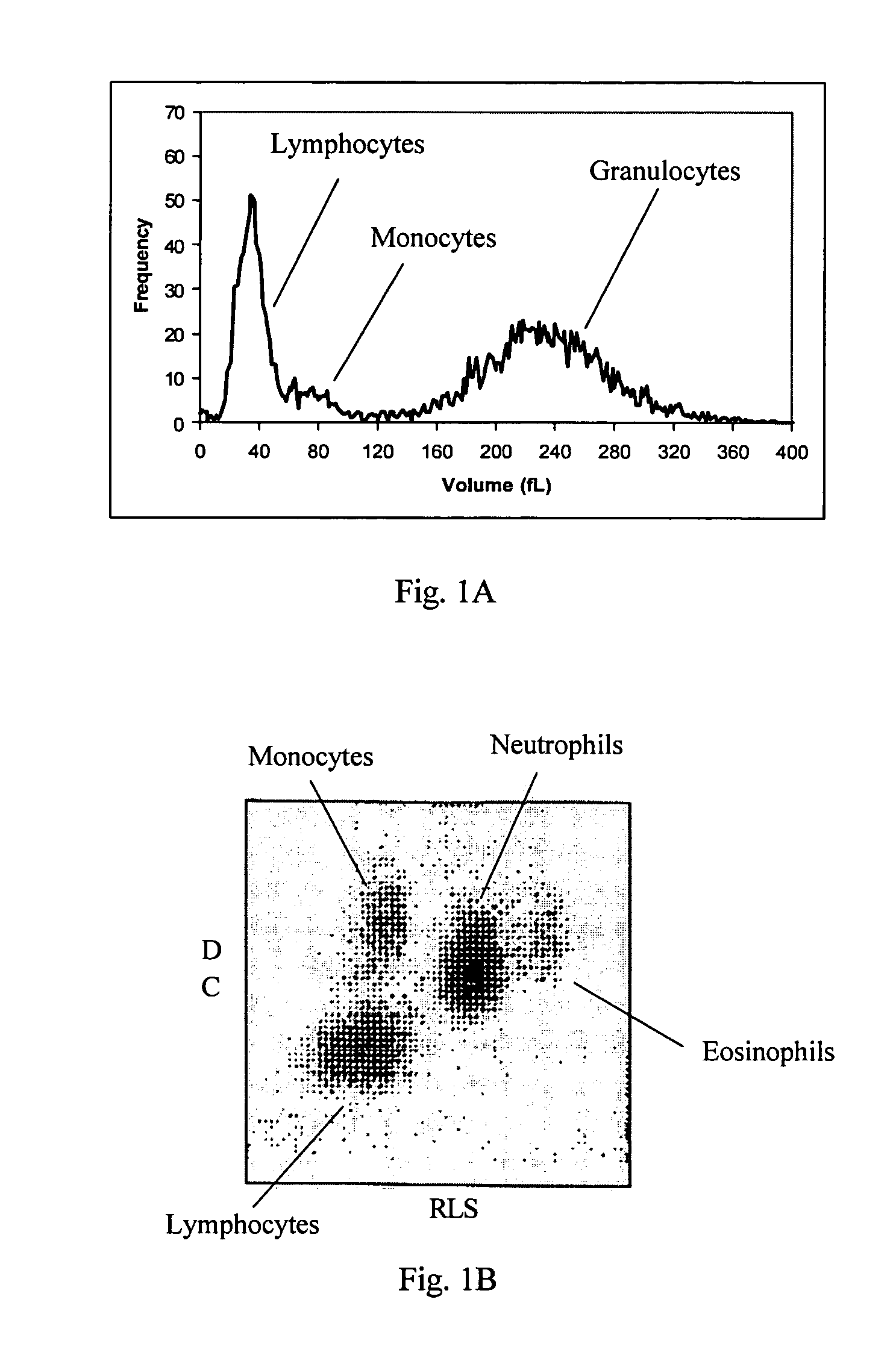
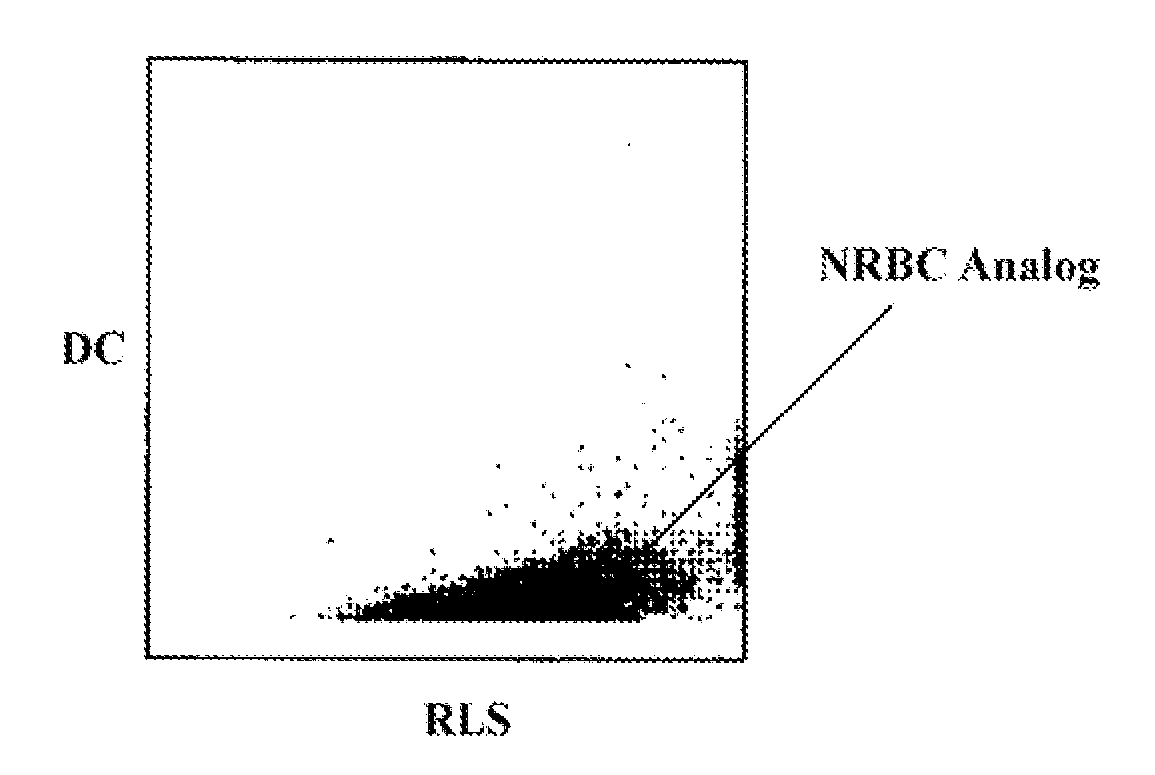
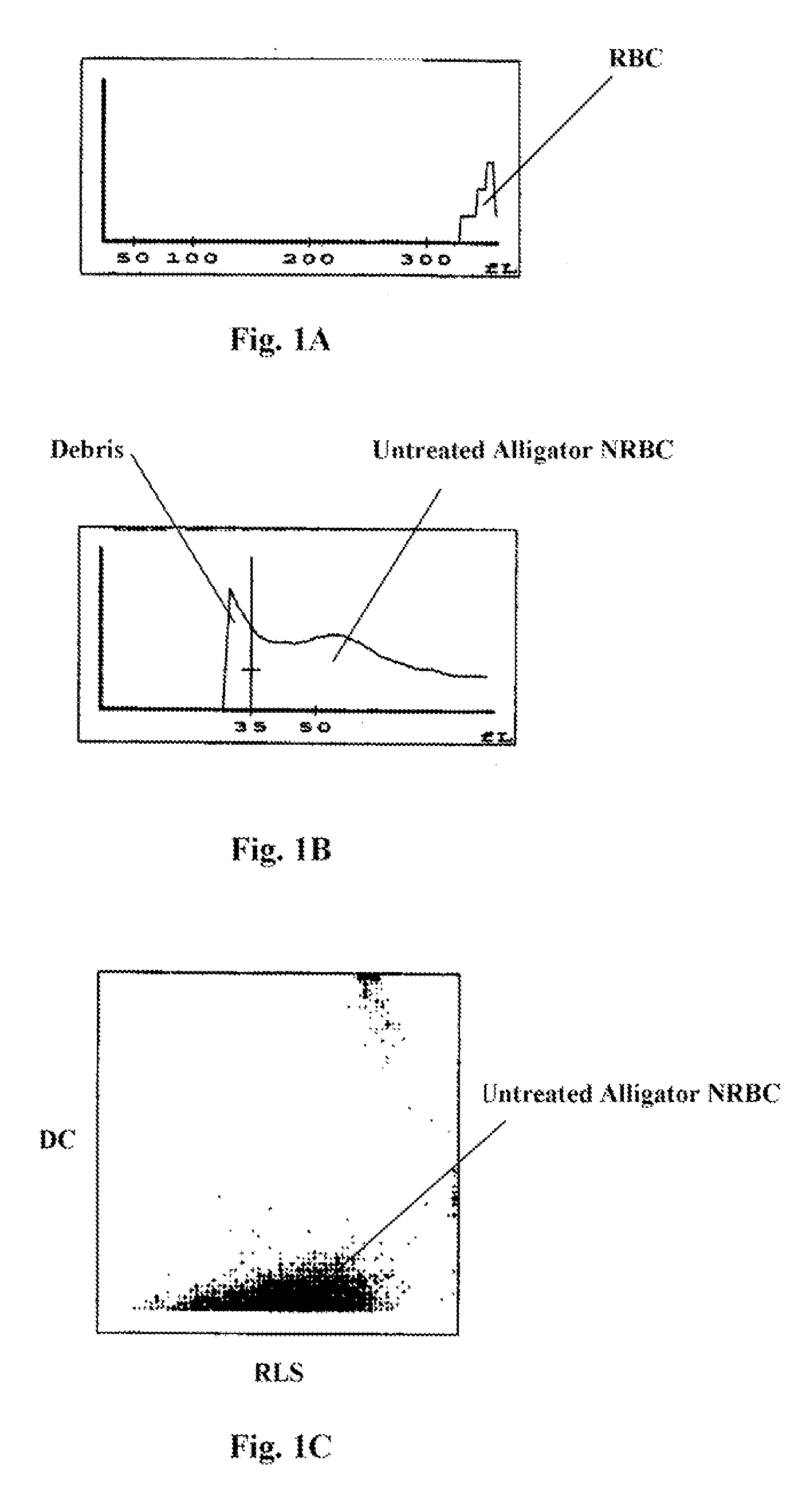
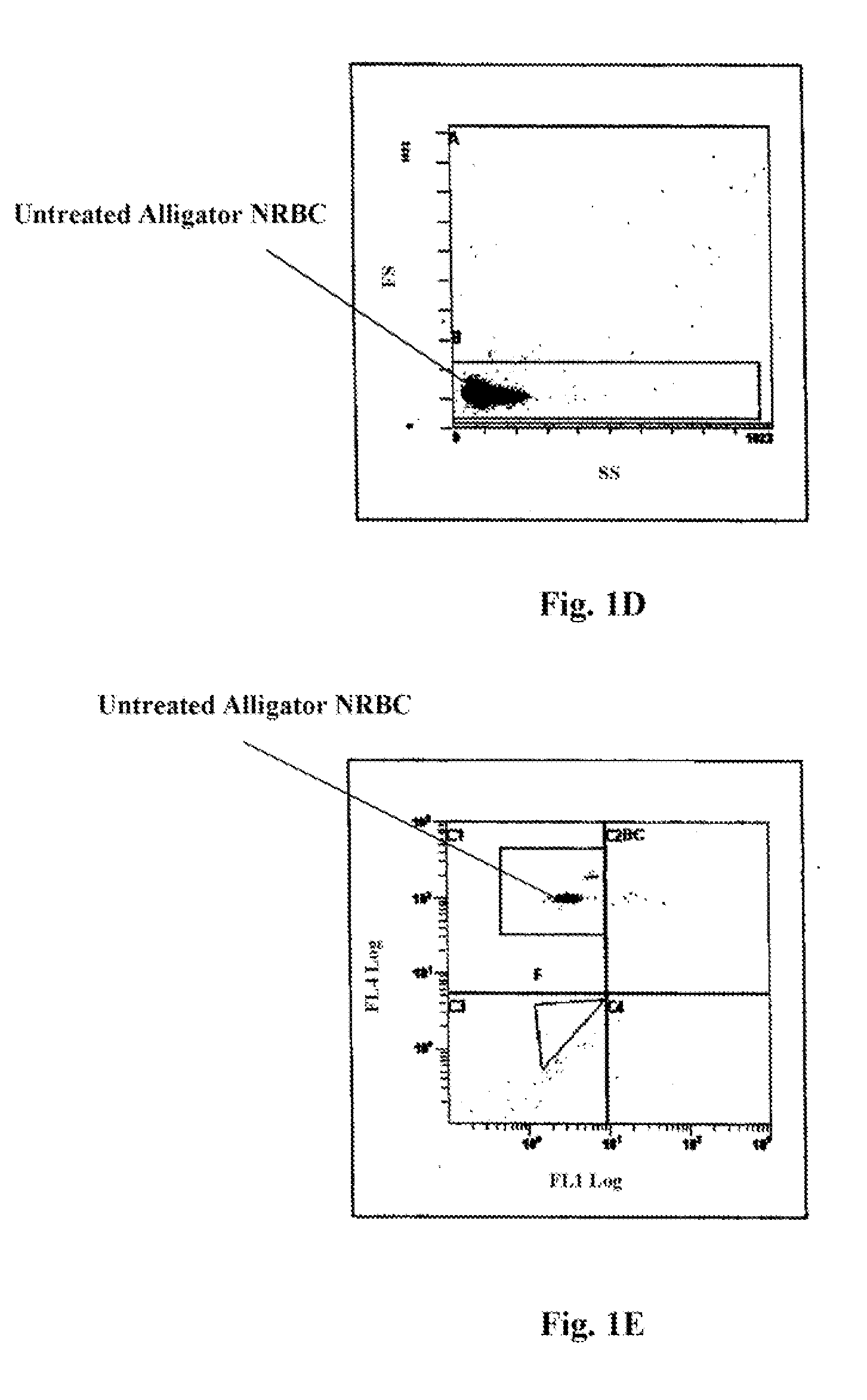
Hematology controls for reticulocytes and nucleated red blood cells
ActiveUS7195919B2Microbiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsMedicine.hematologyBiopolymer
The present invention is drawn to a hematology control made from particles a particle having a biopolymer attached to a surface of the particle. The particle simulates a component of a blood sample, such as a reticulocyte or nucleated red blood cell component of a blood cell sample in a flow cytometer or hematology analysis instrument. The present invention is further drawn to methods of making and using the hematology control.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
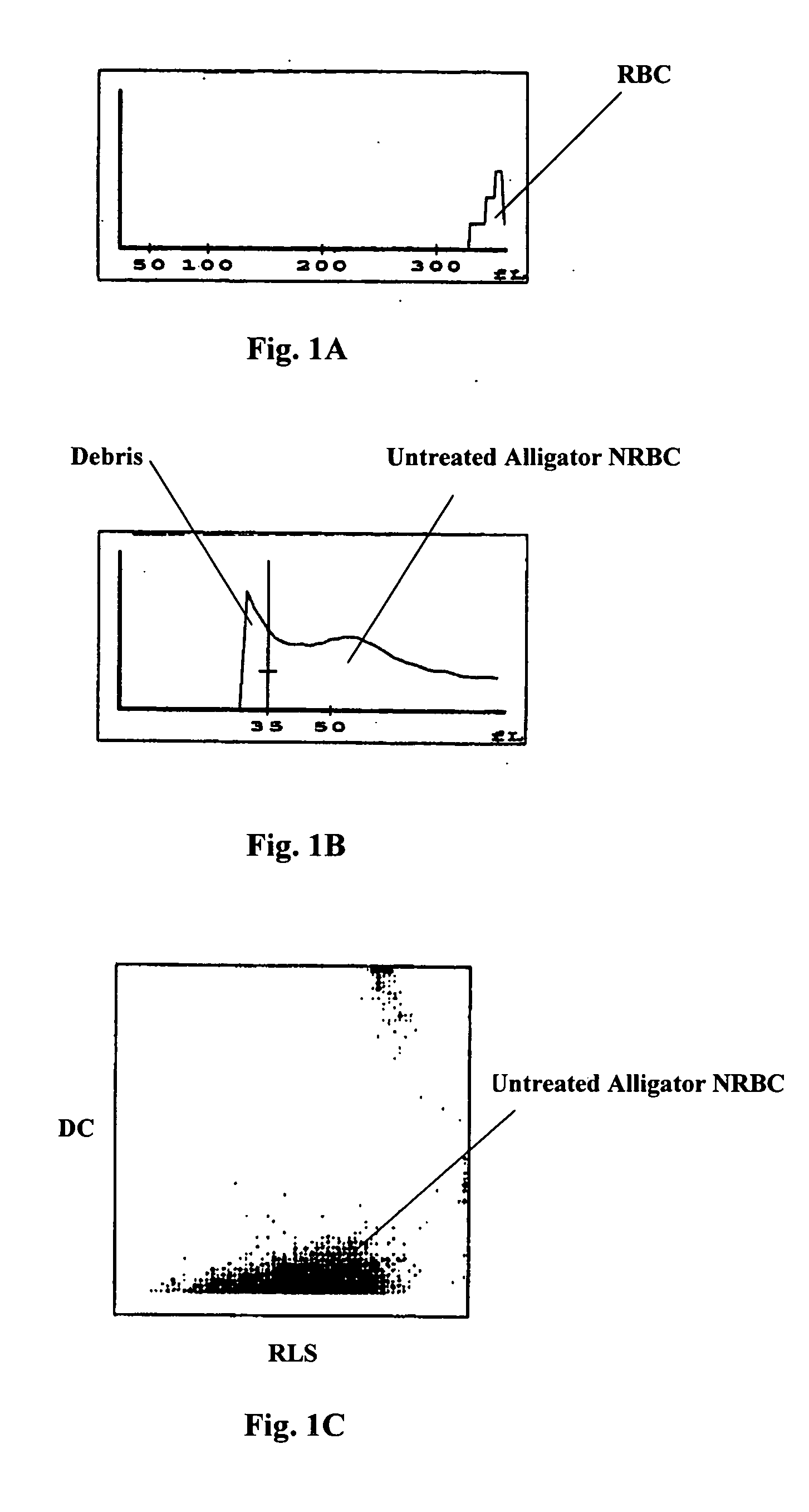
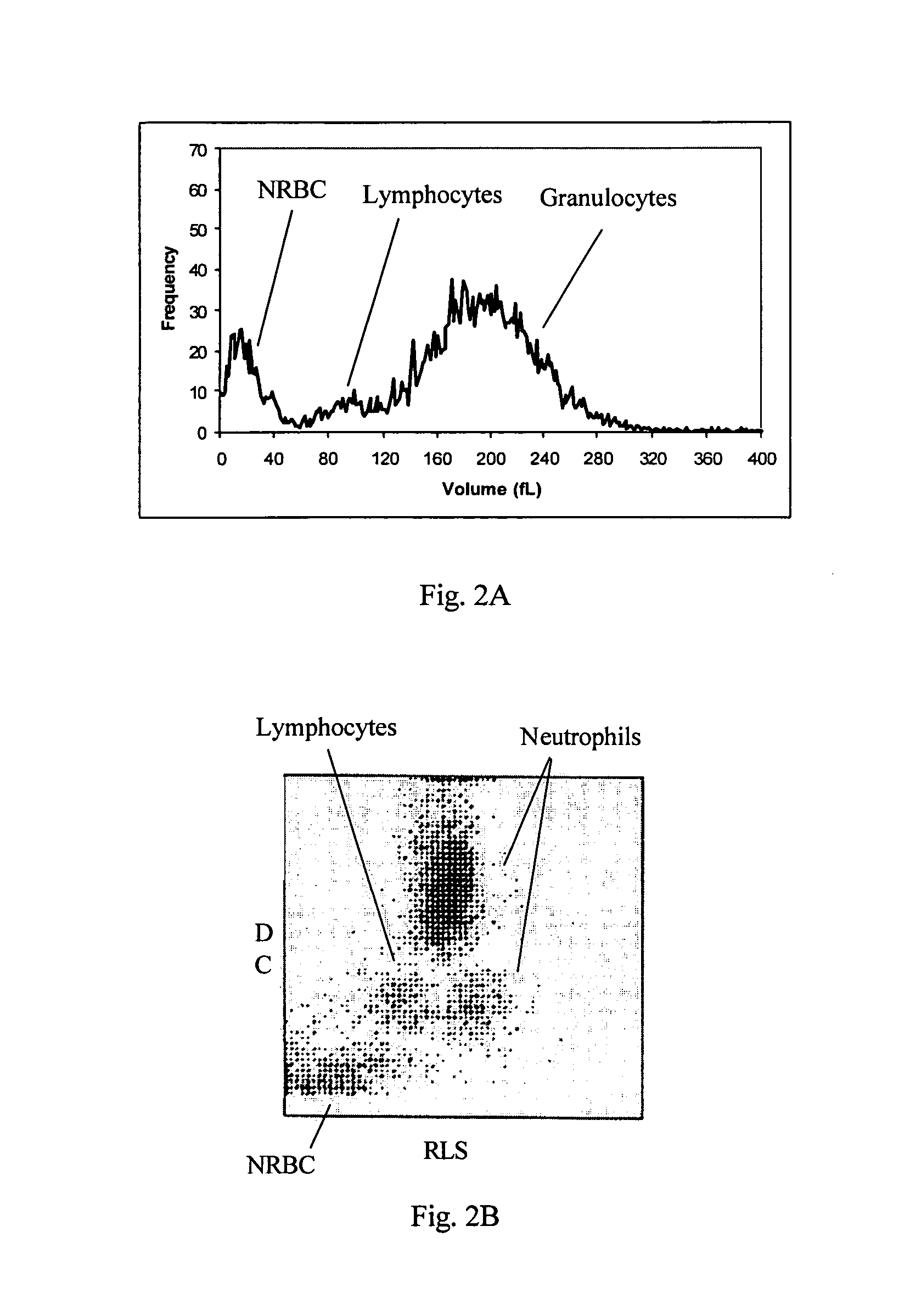
Reference control containing a nucleated red blood cell component
A method of making a reference control containing a nucleated red blood cell component includes providing a blood cell containing a nucleus; treating the blood cell with a treatment solution to alter a nucleus property from a natural value to a target value suitable for simulating nucleated red blood cells on a blood analyzer; and suspending treated blood cell in a suspension medium to form a reference control. The method also includes integrating the nucleated red blood cell component with white blood cell, red blood cell, platelet and reticulocyte components. Further disclosed is a cell treatment composition for altering a nucleus property, which includes a conditioning component, a lytic component for permeating cell membrane, and a fixing component for preserving the cell nucleus. Also disclosed is a method of using the reference control for measurement of nucleated red blood cells on a blood analyzer.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Method for hematology analysis
InactiveUS20110275064A1Reduce complexityLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansMedicine.hematologyFluorescence
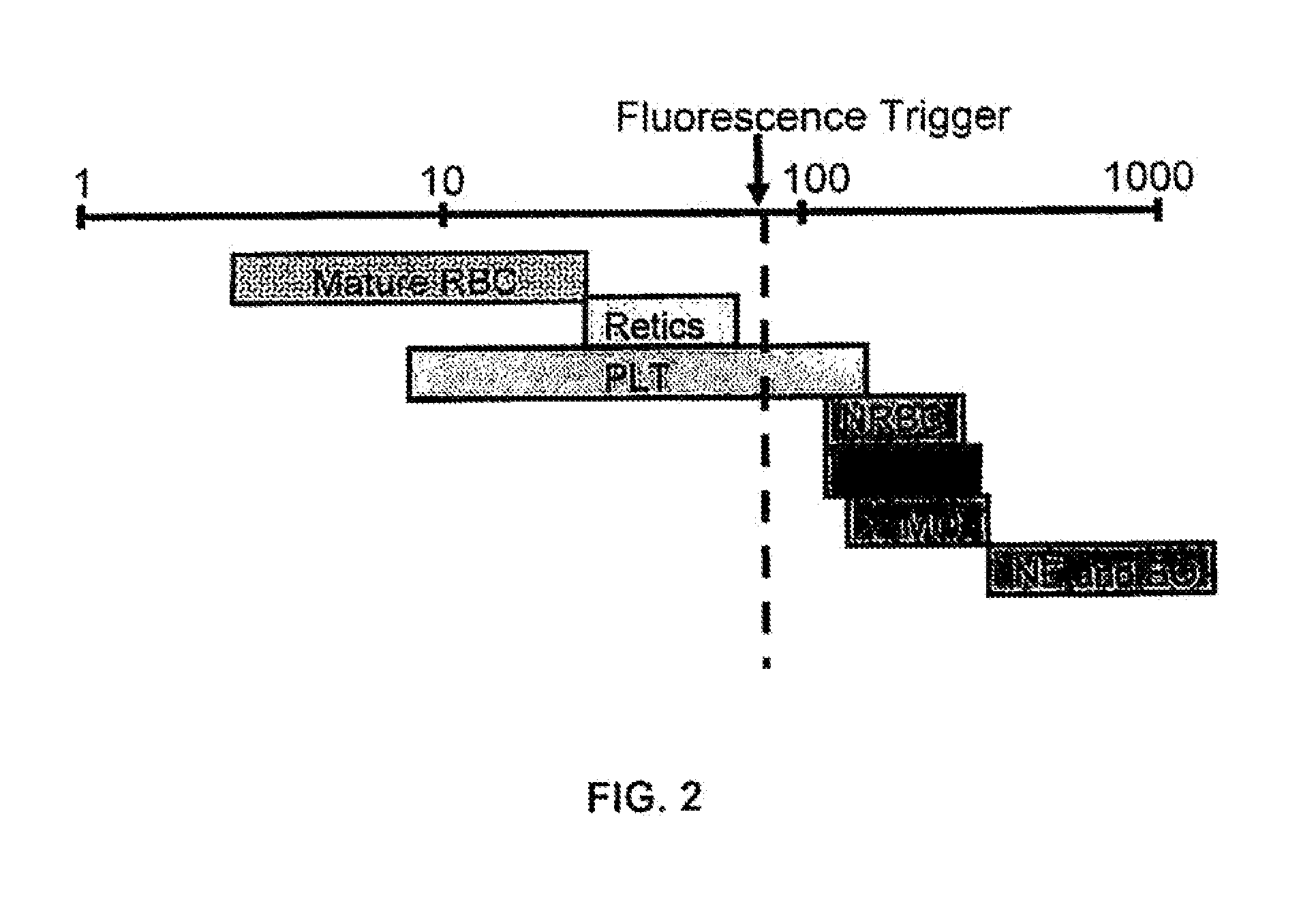
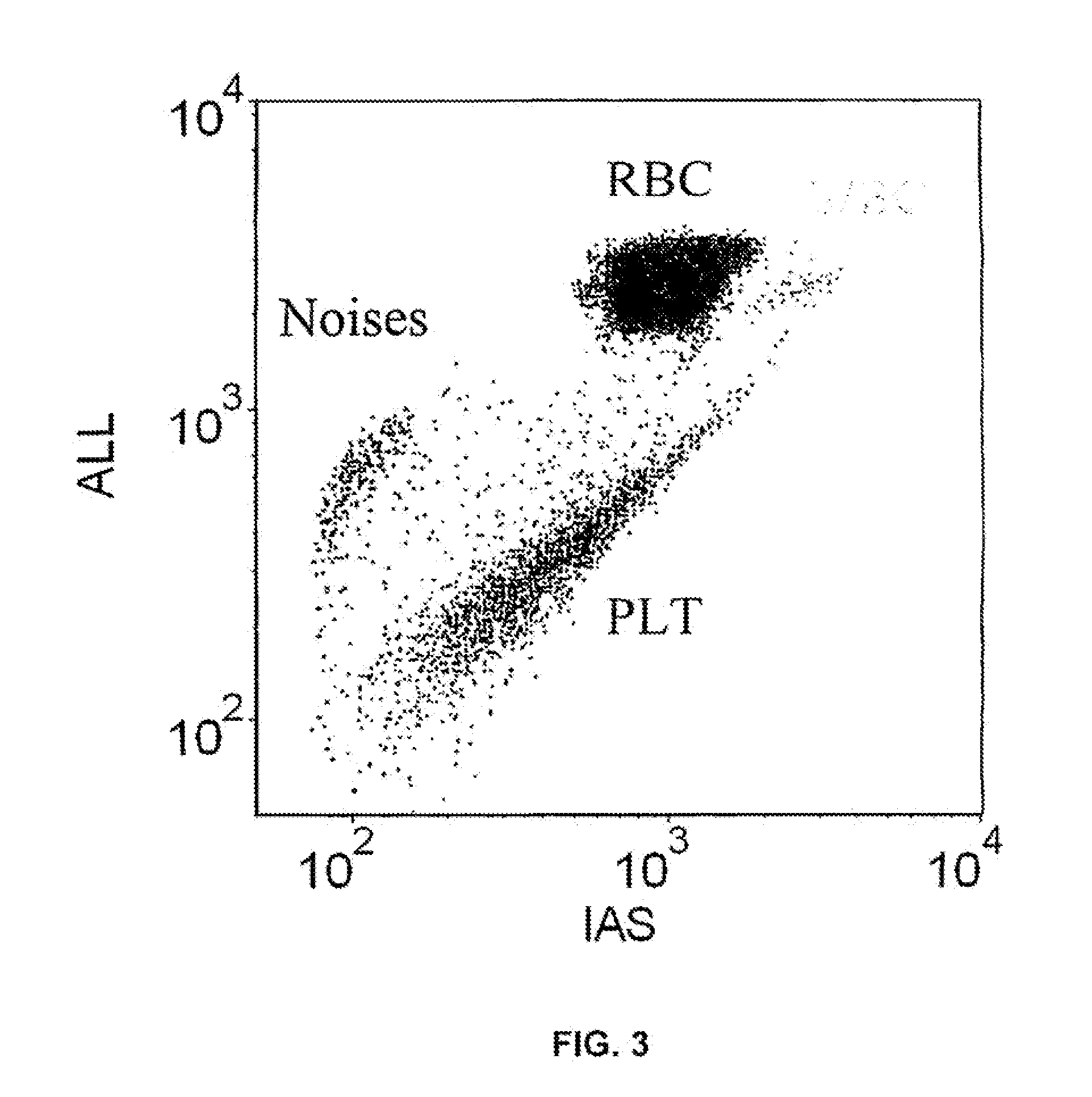
A method whereby one or more fluorescent dyes are used to bind and stain nucleic acids in certain blood cells, such as, for example, white blood cells, nucleated red blood cells, and reticulocytes, and to induce fluorescent emissions upon excitation of photons from a given source of light, such as, for example, a laser, at an appropriate wavelength. More particularly, this invention provides a method whereby a fluorescent trigger is used in a data collection step for collecting events that emit strong fluorescence, in order to separate white blood cells and nucleated red blood cells from red blood cells and platelets without the need for using a lysing agent.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Reference control containing a nucleated red blood cell component
A method of making a reference control containing a nucleated red blood cell component includes providing a blood cell containing a nucleus; treating the blood cell with a treatment solution to alter a nucleus property from a natural value to a target value suitable for simulating nucleated red blood cells on a blood analyzer; and suspending treated blood cell in a suspension medium to form a reference control. The method also includes integrating the nucleated red blood cell component with white blood cell, red blood cell, platelet and reticulocyte components. Further disclosed is a cell treatment composition for altering a nucleus property, which includes a conditioning component, a lytic component for permeating cell membrane, and a fixing component for preserving the cell nucleus. Also disclosed is a method of using the reference control for measurement of nucleated red blood cells on a blood analyzer.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Agent and method for testing reticulocyte
ActiveCN101231243AQuick tagGood repeatabilityOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementBlood specimenRed blood cell
The invention discloses a reticular cell detect reagent and the testing method thereof, and the reagent and the method can be applied to an apparatus based on the streaming technical principle to count accurately the analyzing reticular cell in blood specimen. The reagent and the method of the invention adopt a novel red fluorescence excitation dye which is used for marking RNA in the reticular cell, and the rapid sign of RNA in the reticular cell can be realized under the environmental temperature through a matched sphericize reagent system.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
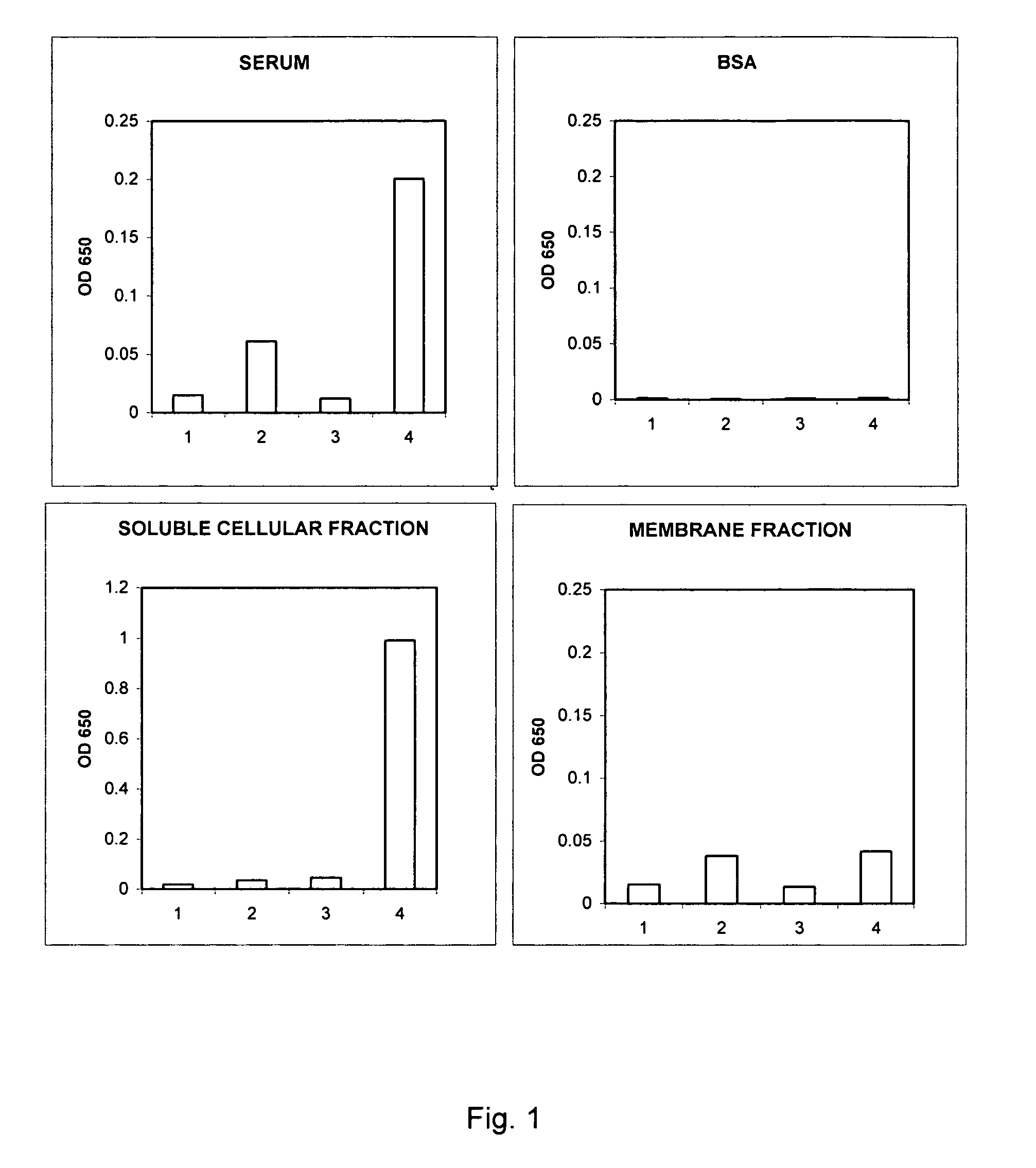
Method of measurement of cellular hemoglobin
ActiveUS20070020612A1Prevent further reactionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingFluorescenceCell membrane
A method of measuring cellular hemoglobin of a blood sample includes mixing a blood sample with a permeation reagent, and incubating the sample mixture to permeate cellular membrane of red blood cells and to cause hemoglobin aggregation within the cells; adding a neutralization reagent to inhibit further reactions of the permeation reagent; performing a cell-by-cell measurement of side scatter signals of the red blood cells in the sample mixture on a flow cytometer; and obtaining cellular hemoglobin (Hgbcell) of each red blood cell using the obtained side scatter signals. The method further includes measuring cellular hemoglobin of reticulocytes (Hgbretic) by differentiating reticulocytes using a simultaneous fluorescence measurement. The method also includes measuring cellular percentage of a hemoglobin variant in mature red blood cells or reticulocytes by adding a fluorescent antibody in the neutralization reagent and detecting fluorescence signals of antibody bound hemoglobin variant.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Hematology controls for reticulocytes and nucleated red blood cells
ActiveUS20050136409A1Microbiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsMedicine.hematologyBiopolymer
The present invention is drawn to a hematology control made from particles a particle having a biopolymer attached to a surface of the particle. The particle simulates a component of a blood sample, such as a reticulocyte or nucleated red blood cell component of a blood cell sample in a flow cytometer or hematology analysis instrument. The present invention is further drawn to methods of making and using the hematology control.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Method and System for Analyzing a Blood Sample
ActiveUS20100240055A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRed blood cellGhost cell
Methods, systems, and computer program products for the analysis of a blood sample are disclosed. One embodiment is a method of detecting and enumerating hard-to-ghost cells in a blood sample. Another embodiments is a method of analyzing reticulocytes in a blood sample. Methods of using blood count parameters are also provided.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Real time method of detecting acute inflammatory conditions
ActiveUS7361517B2Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsDisease diagnosisRed blood cellLupus erythematosus
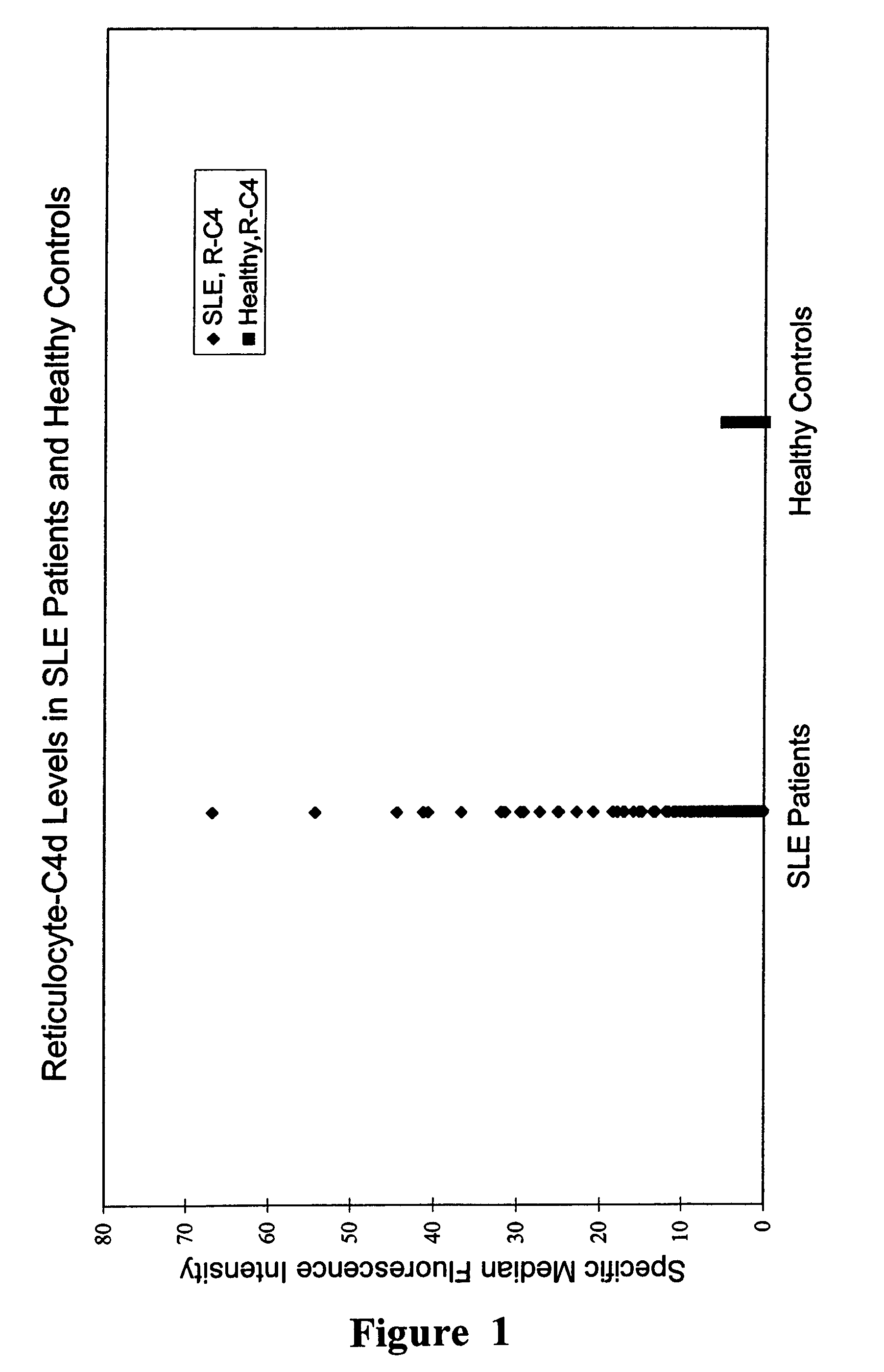
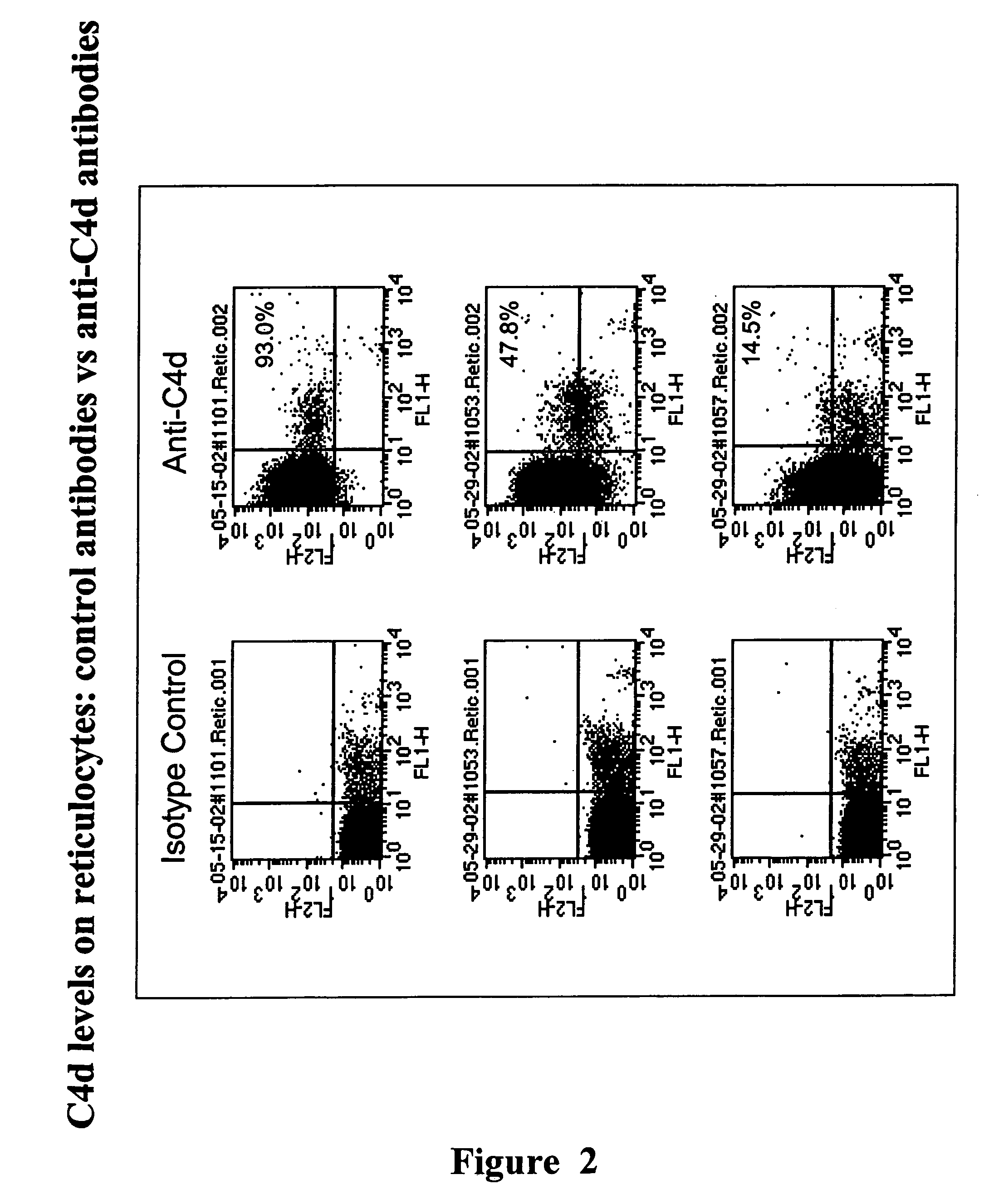
This invention relates to the diagnosis and / or monitoring of patients with inflammatory diseases or conditions, including systemic lupus erythematosus, particularly for diagnosis of the acute stage of the disease, including methods and kits for carrying out this activity. This disclosure presents the surprising discovery that levels of complement pathway components on reticulocytes can be used to diagnose, monitor, or predict the occurrence of acute episodes of chronic inflammatory diseases or conditions.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Application of artemisinin derivative in preparation of medicaments for treating Crohn disease
InactiveCN102048728AFew and mild side effectsAchieving the goal of treating Crohn's diseaseOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemSide effectHepatic dysfunction
The invention discloses an application of an artemisinin derivative in preparation of medicament for treating Crohn disease, and the artemisinin derivative is selected from artesunate or artemether or styrene monomer 905 (SM905). The artemisinin derivative can be used for achieving the purpose of treating the Crohn disease by inhibiting Th1 / Th17 immune response and inhibiting nuclear factor-kB activation. Compared with the existing medicaments, the artemisinin derivative has less and light side effects, in one year of following visits for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, transient reticulocyte decline and hepatic dysfunction only occur in individual cases, and the health can be restored by liver protection treatment without medicament withdrawal. Therefore, the artemisinin derivative can be taken by patients for a long time, the treatment can be maintained, and the purpose of effective treatment can be achieved.
Owner:RENJI HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
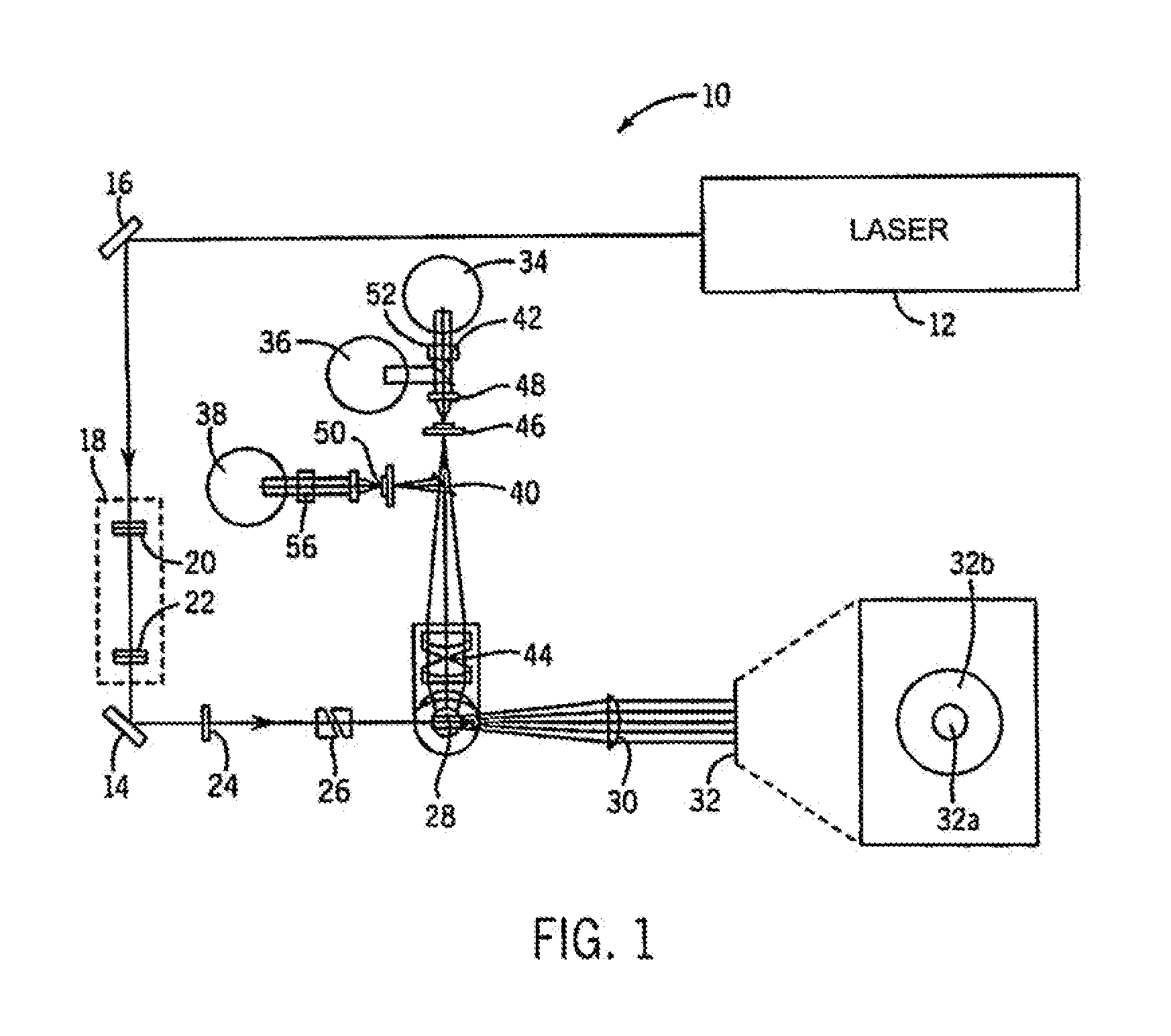
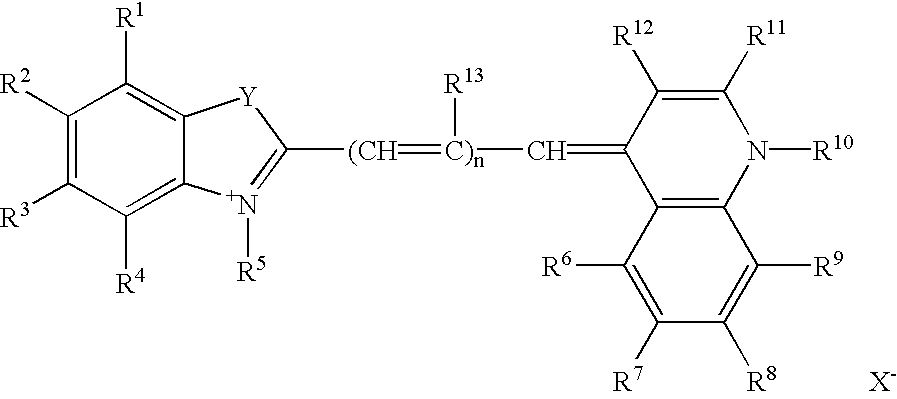
Helium-neon excitable reticulocyte dyes derivable from halolepidines
InactiveUS7083982B2High strengthLow backgroundCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsRed blood cellHelium
A method for synthesizing dyes excitable by a helium-neon laser (excitable at 633 nm) from hololepidines, e.g., 7-halolepidine, which dyes are suitable for detection and enumeration of reticulocytes in human blood samples. In another aspect, the invention provides a method for immunotyping phenocytes. The method is based on the phenomenon that when dyes of certain structure intercalate into DNA or RNA, the intensity of the dye increases. Dyes suitable for this invention can be described as having (a) a first heterocyclic moiety, (b) a second heterocyclic moiety, and (c) a linking group that connects the first and second heterocyclic moieties. Both the first and second heterocyclic moieties must contain at least two rings, preferably fused together. The dye is characterized by conjugation, whereby the first moiety is ethylenically conjugated to the second moiety.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
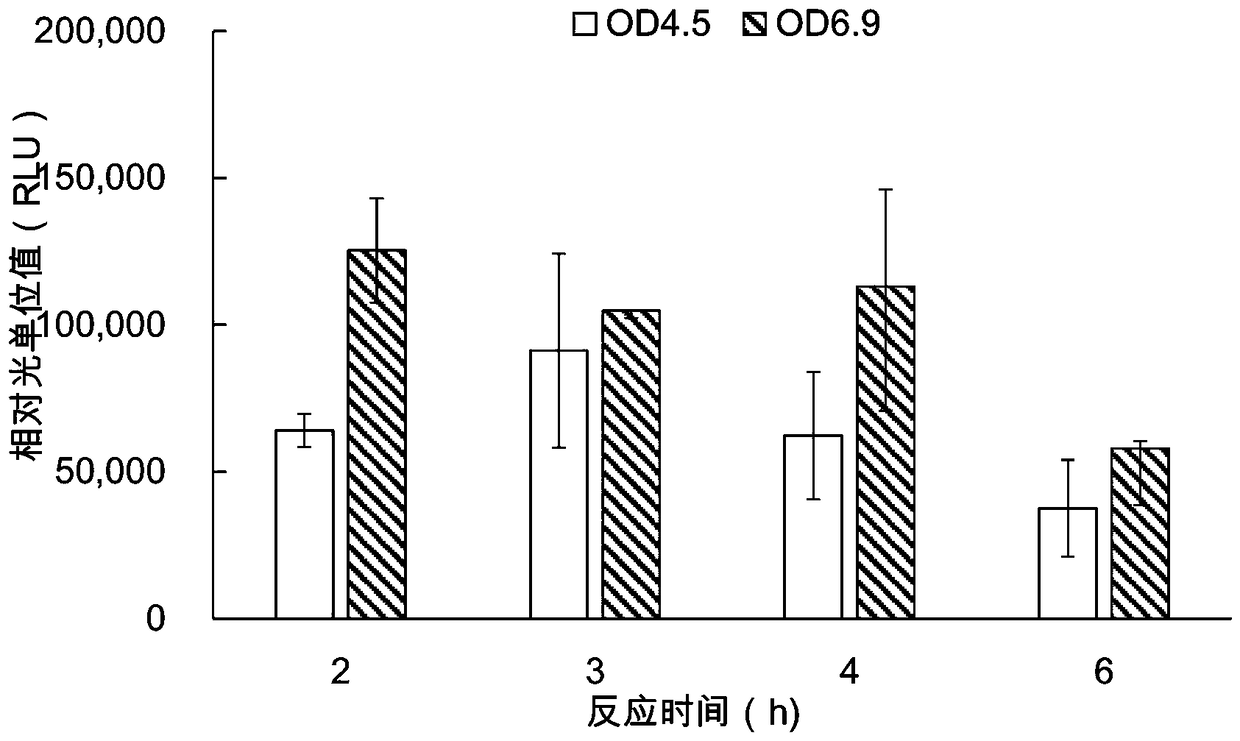
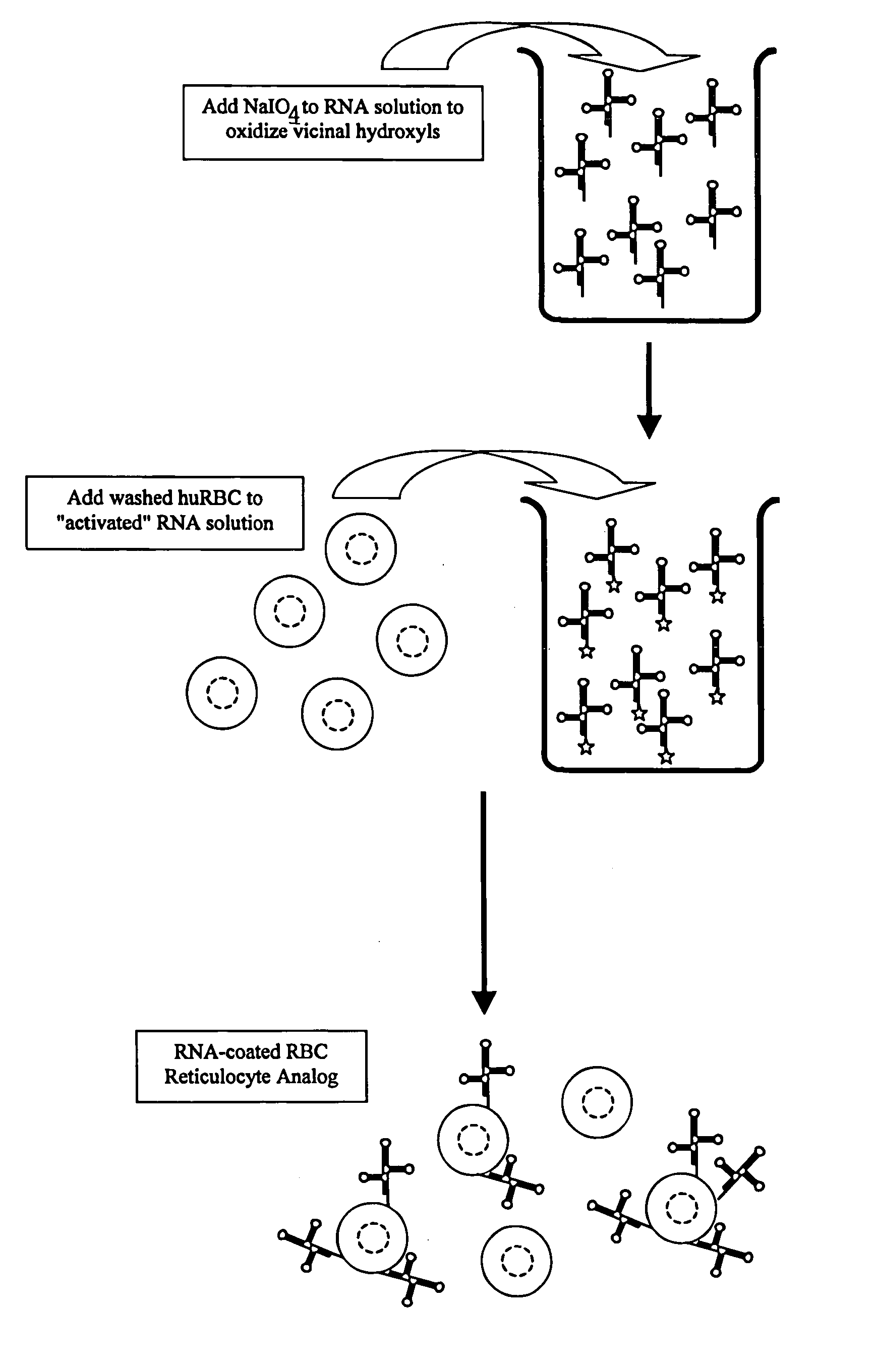
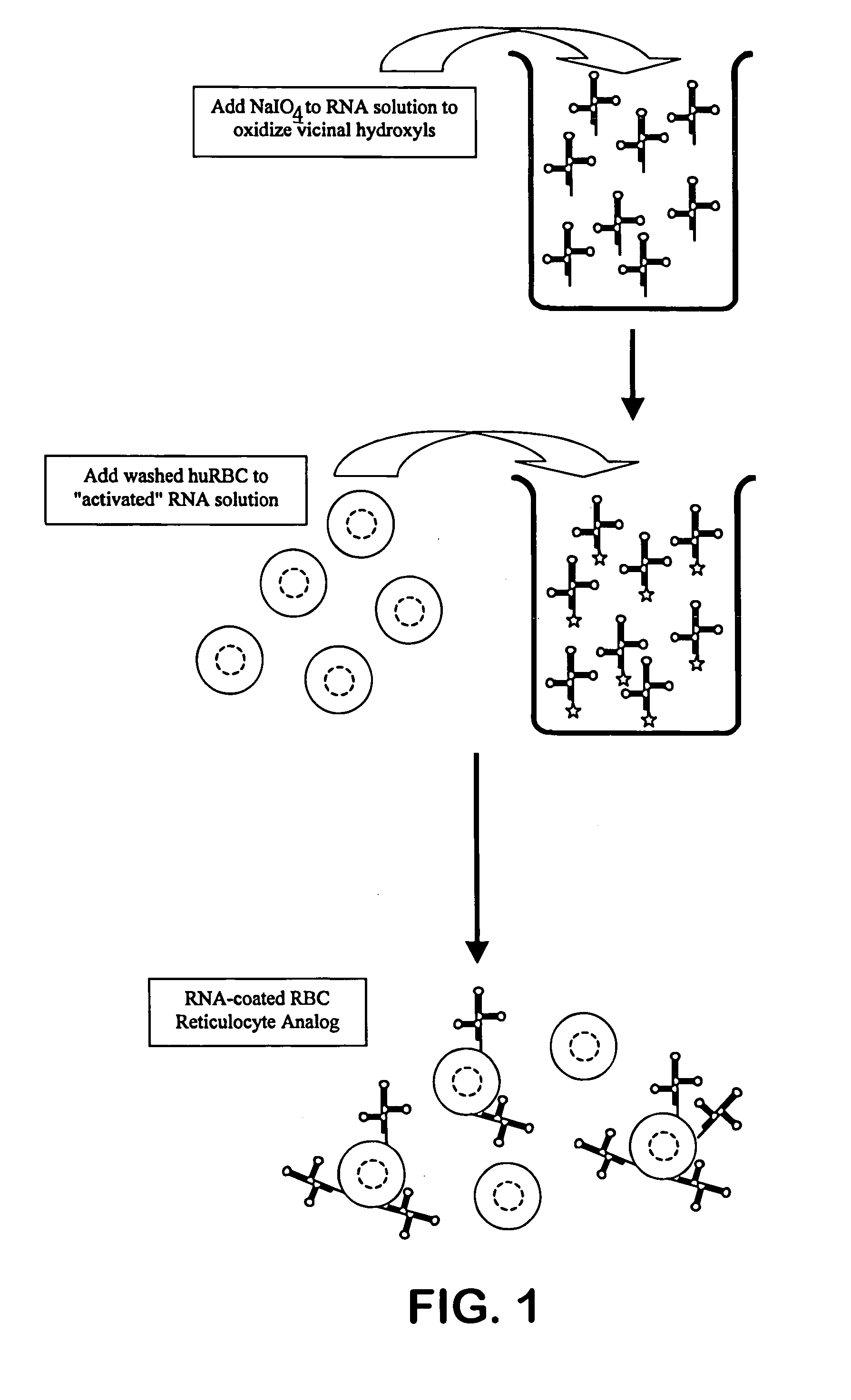
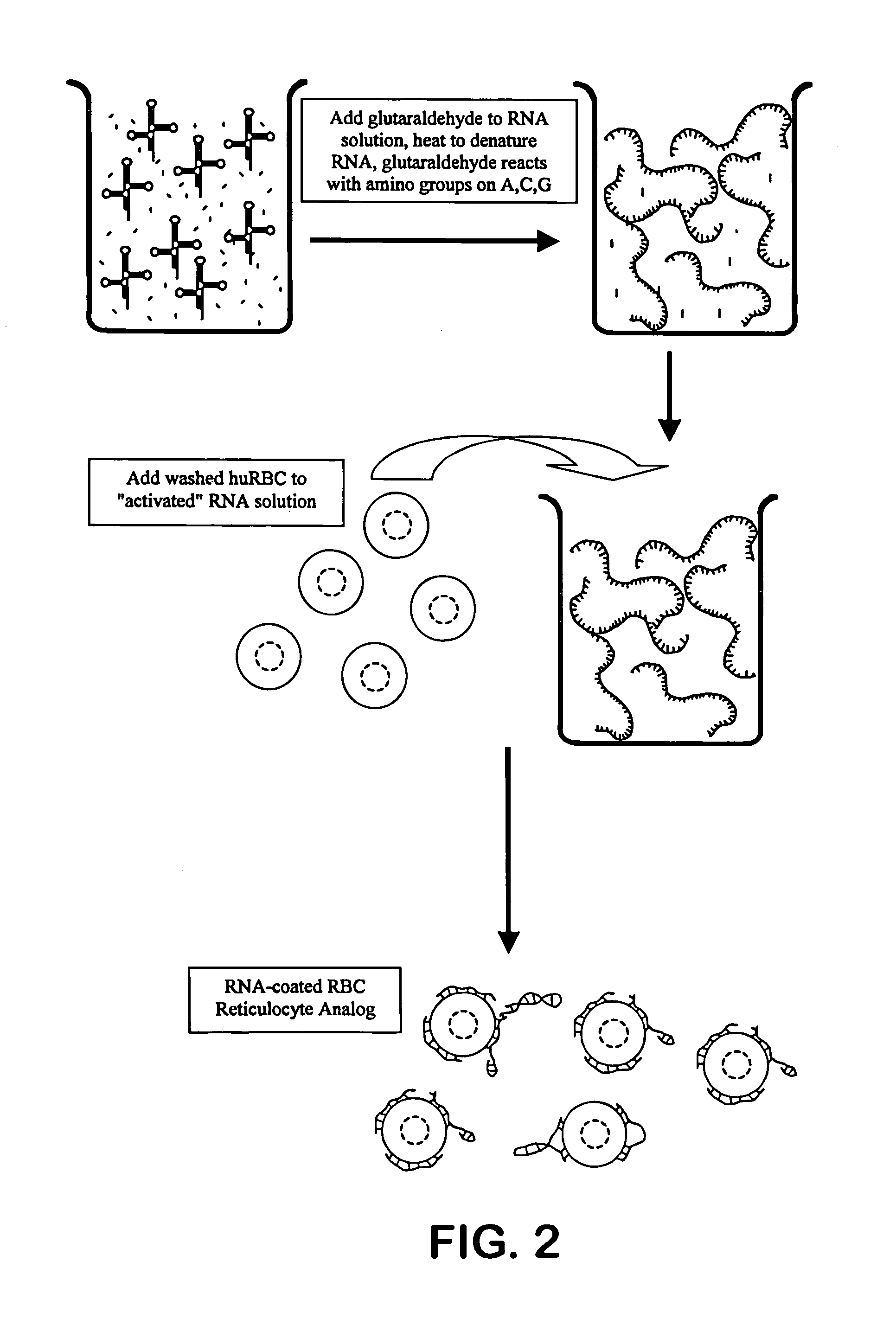
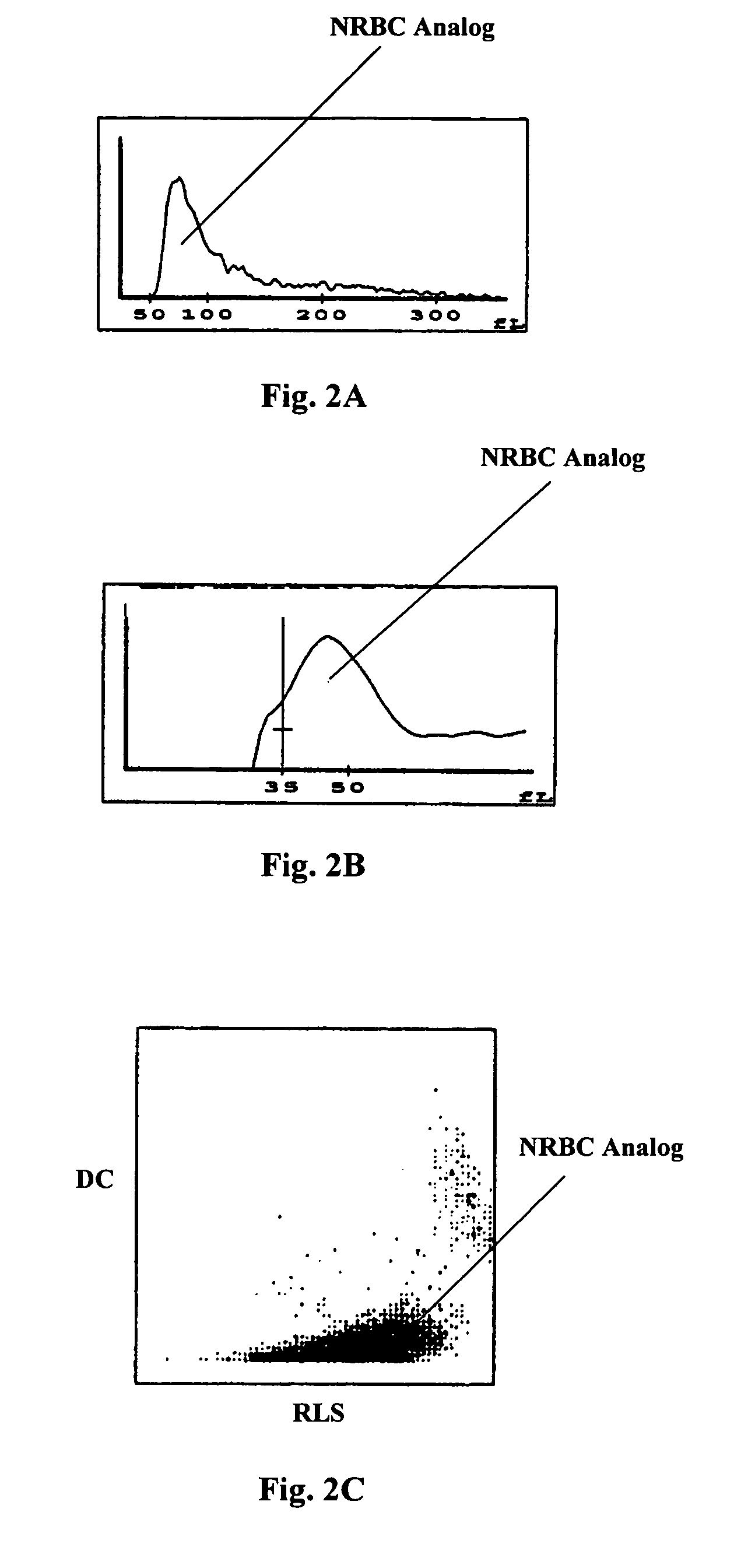
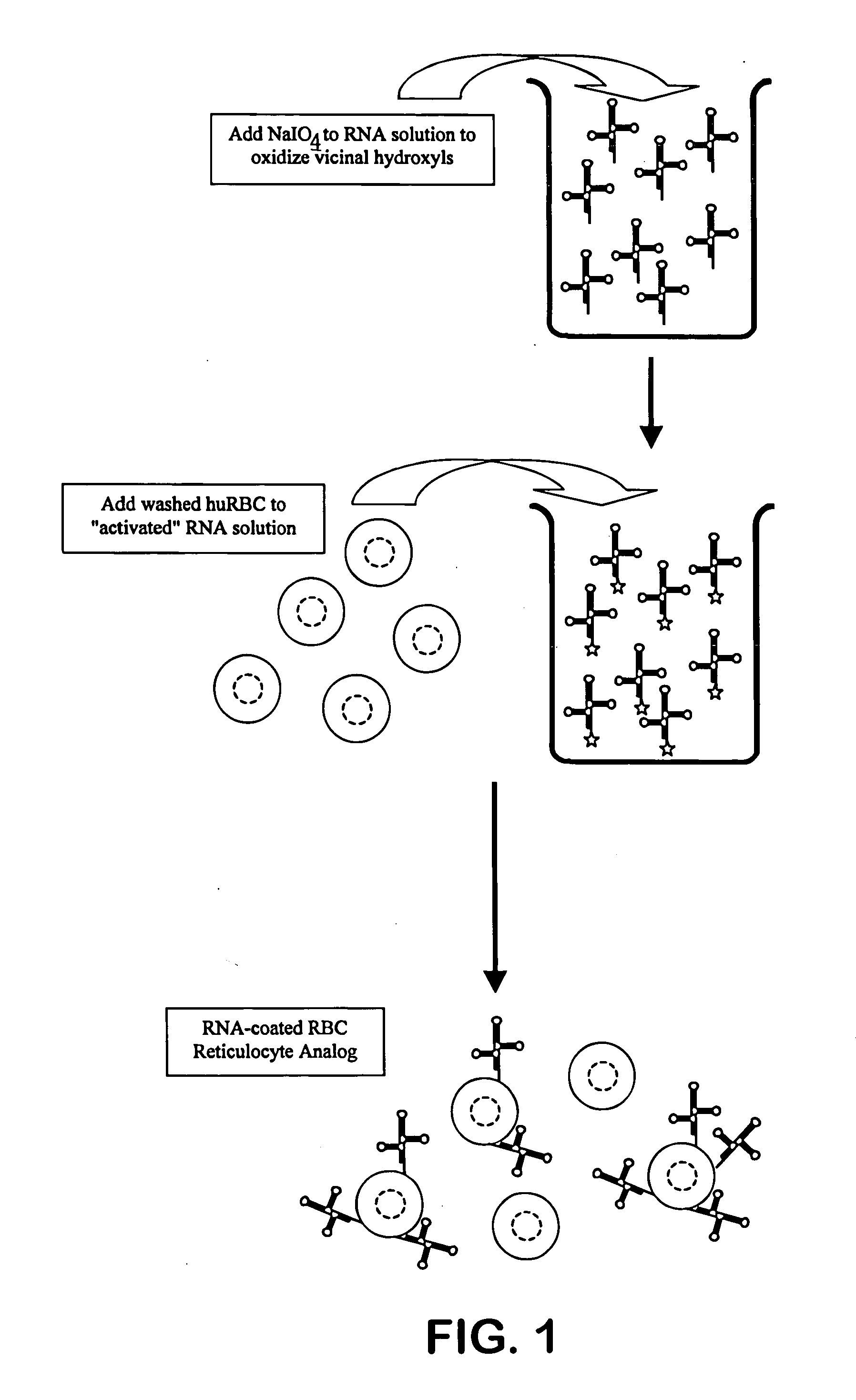
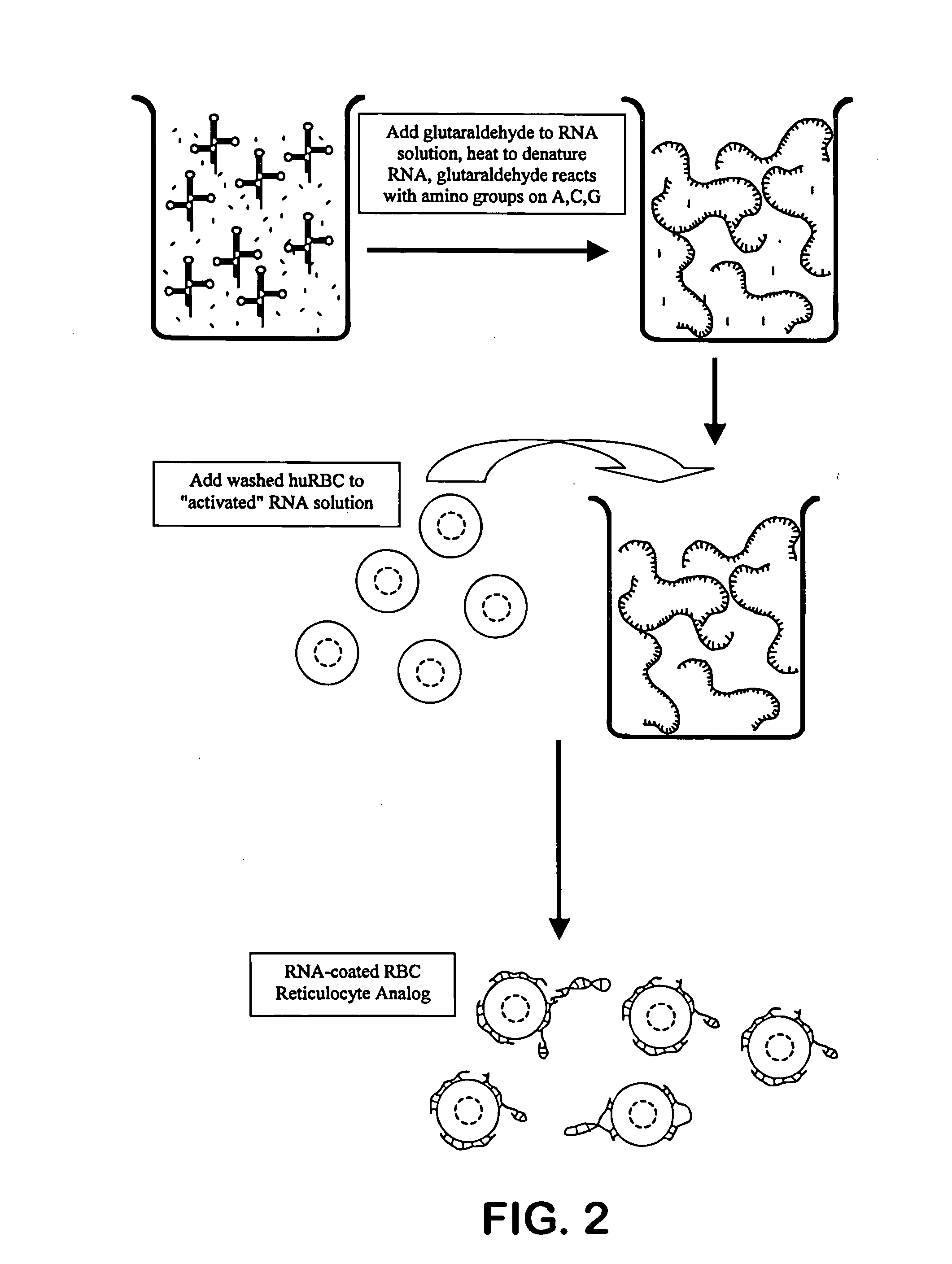
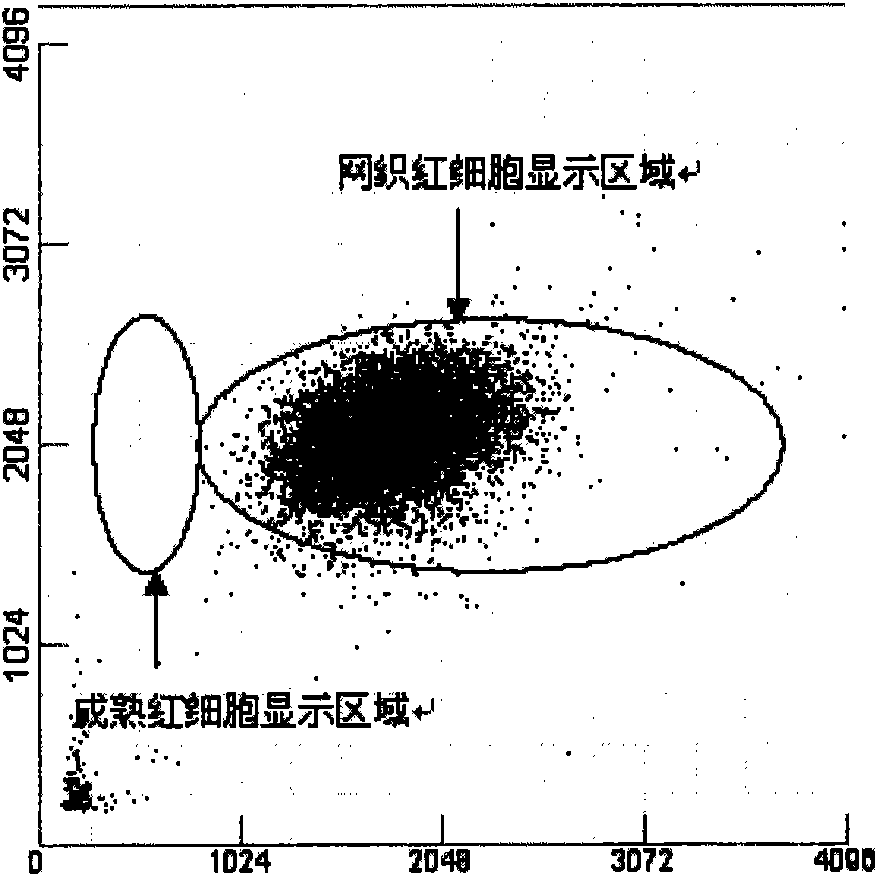
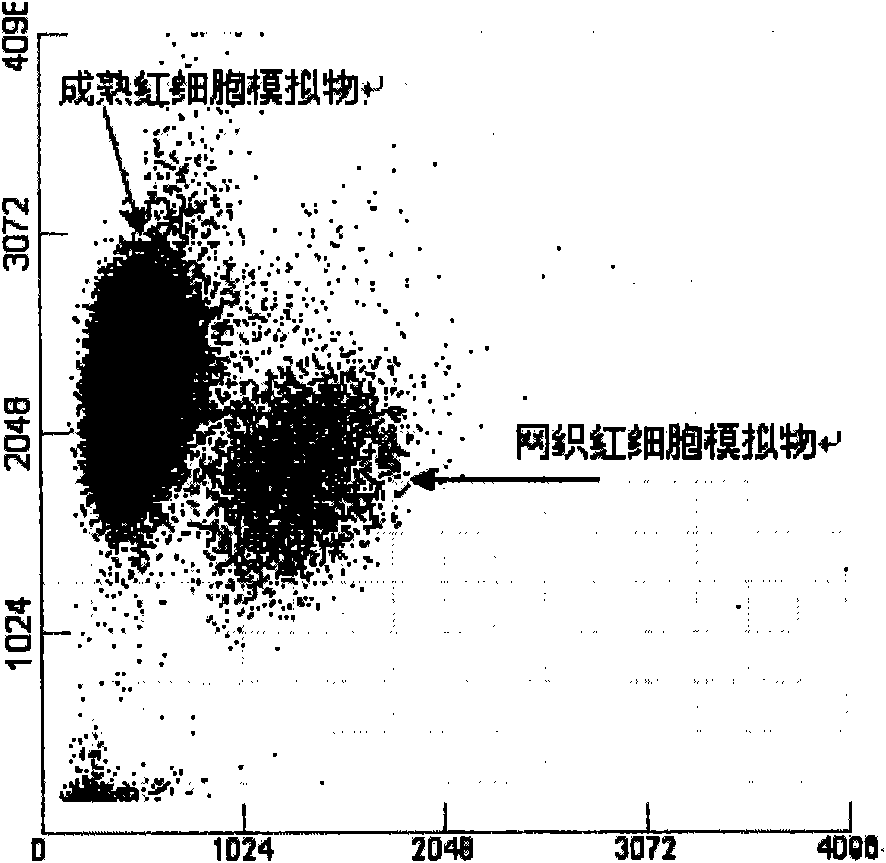
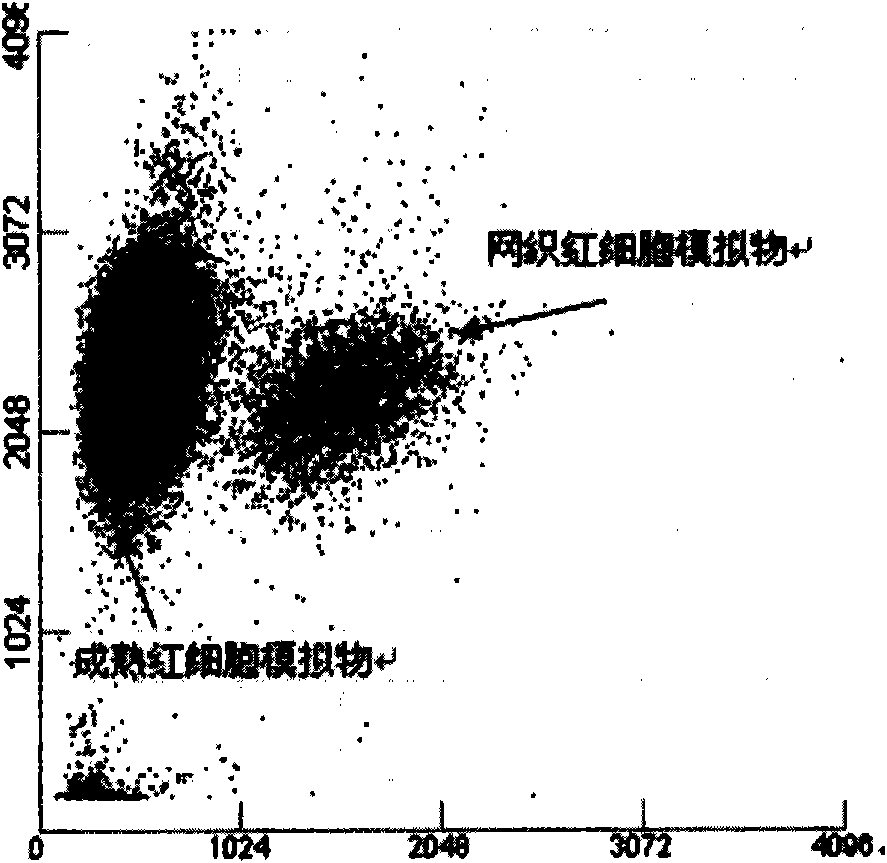
Reticulocyte mimics and preparation method thereof
On one aspect, the invention provides a method for preparing reticulocyte mimics, and on the other aspect, the invention provides reticulocyte mimics which is obtained from the method. On another aspect, the invention provides a whole blood quality control substance which contains the reticulocyte mimics provided by the invention.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for measuring in vivo mutation frequency at an endogenous gene locus
ActiveUS7824874B2Fast and reliable and accurateUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsRed blood cellWild type
The present invention relates a method for the enumeration of in vivo gene mutation. The method utilizes differential staining of GPI-anchor deficient erythrocyte populations to distinguish between wild-type and pig-a gene mutants. Quantitative analyses can be conducted on erythrocytes and / or reticulocytes, and is based upon fluorescent emission and light scatter following exposure to an excitatory light source. Counting of mutant erythrocytes or reticulcoytes relative to the number of total erythrocytes or reticulocytes can be used to assess the DNA-damaging potential of an exogenous chemical agent, the DNA-damaging potential of an exogenous physical agent, the effects of an exogenous agent which can modify endogenously-induced DNA damage, and the effects of an exogenous agent which can modify exogenously-induced DNA damage. Kits for practicing the invention are also disclosed.
Owner:LITRON LAB
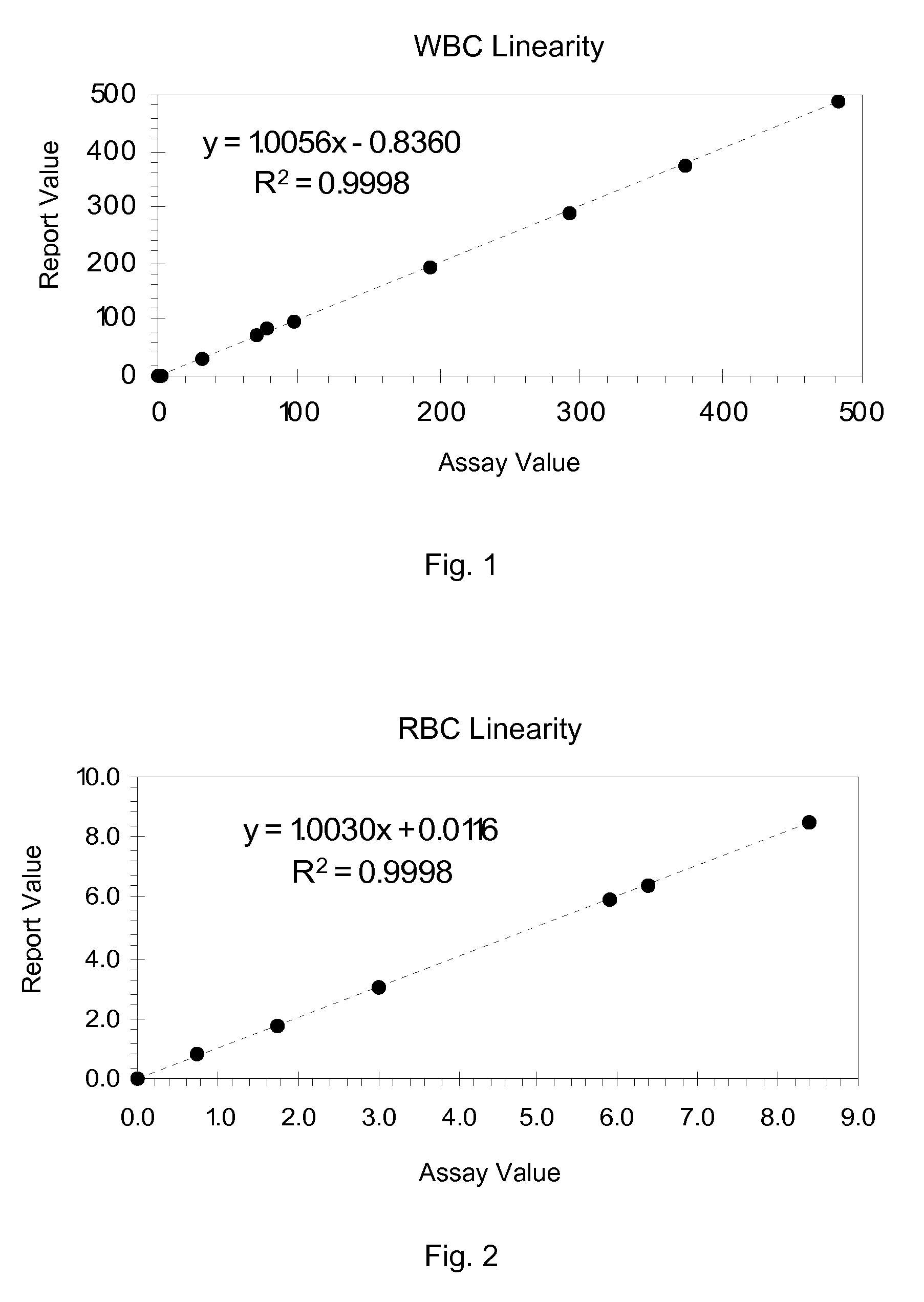
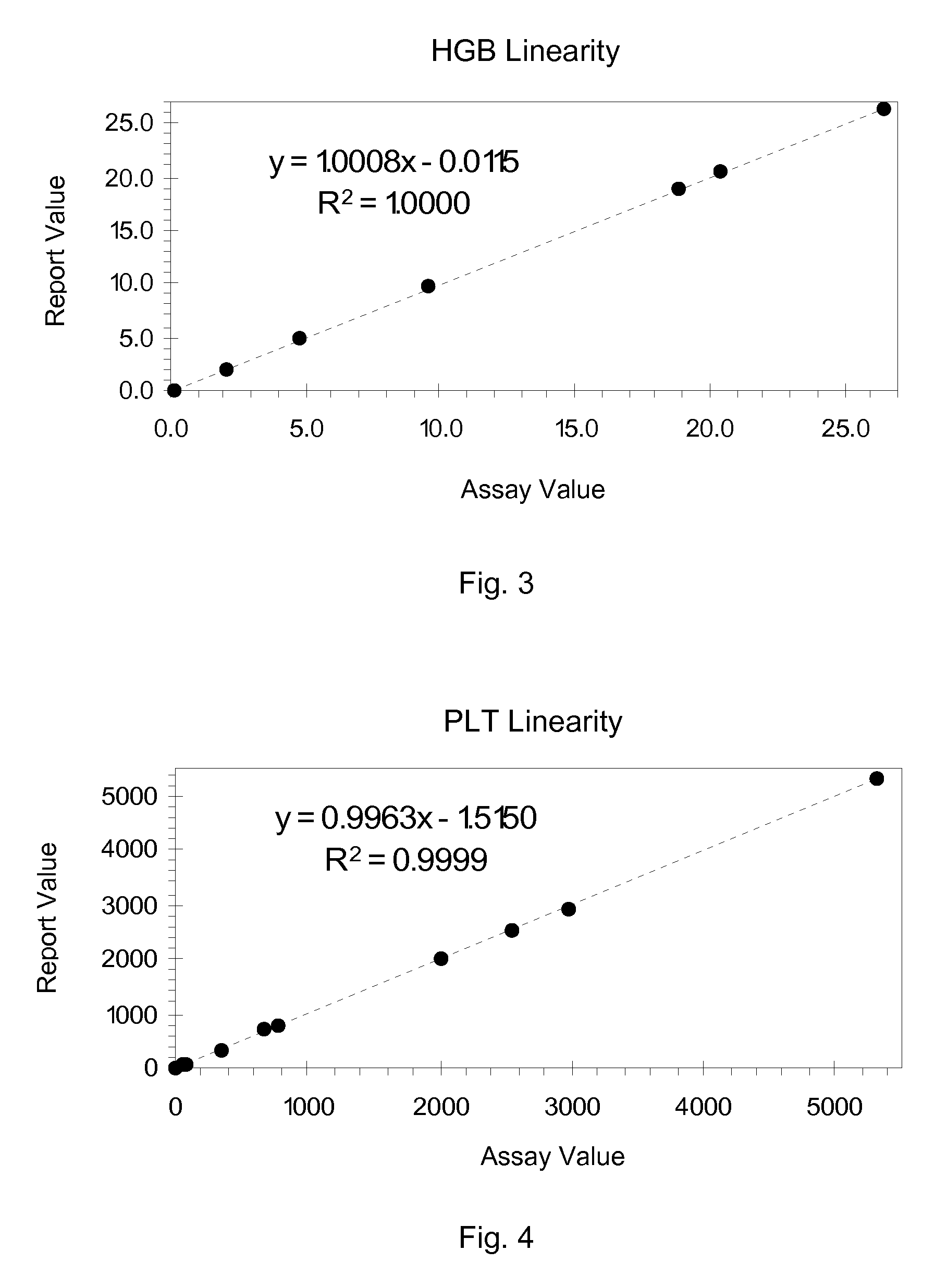
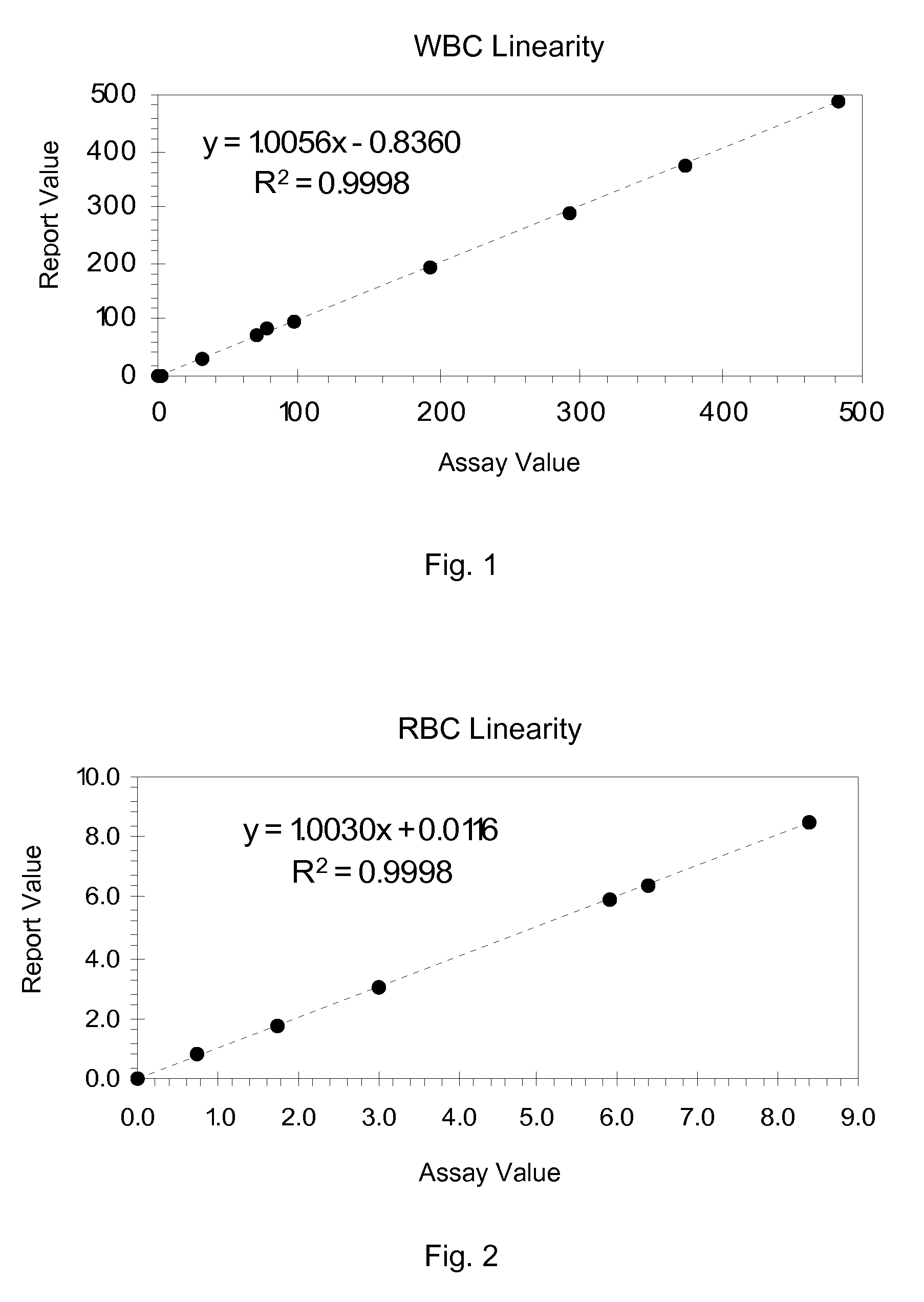
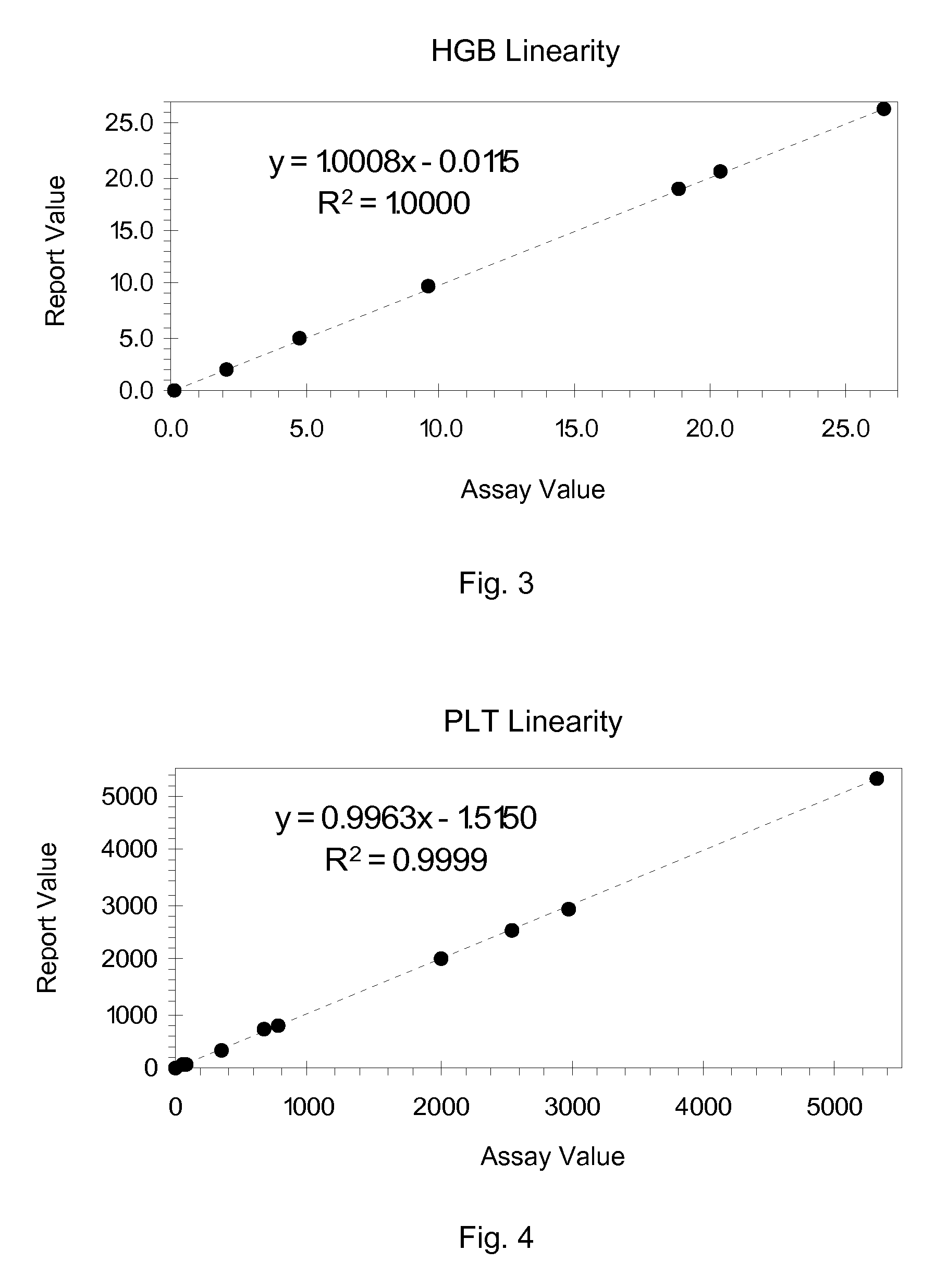
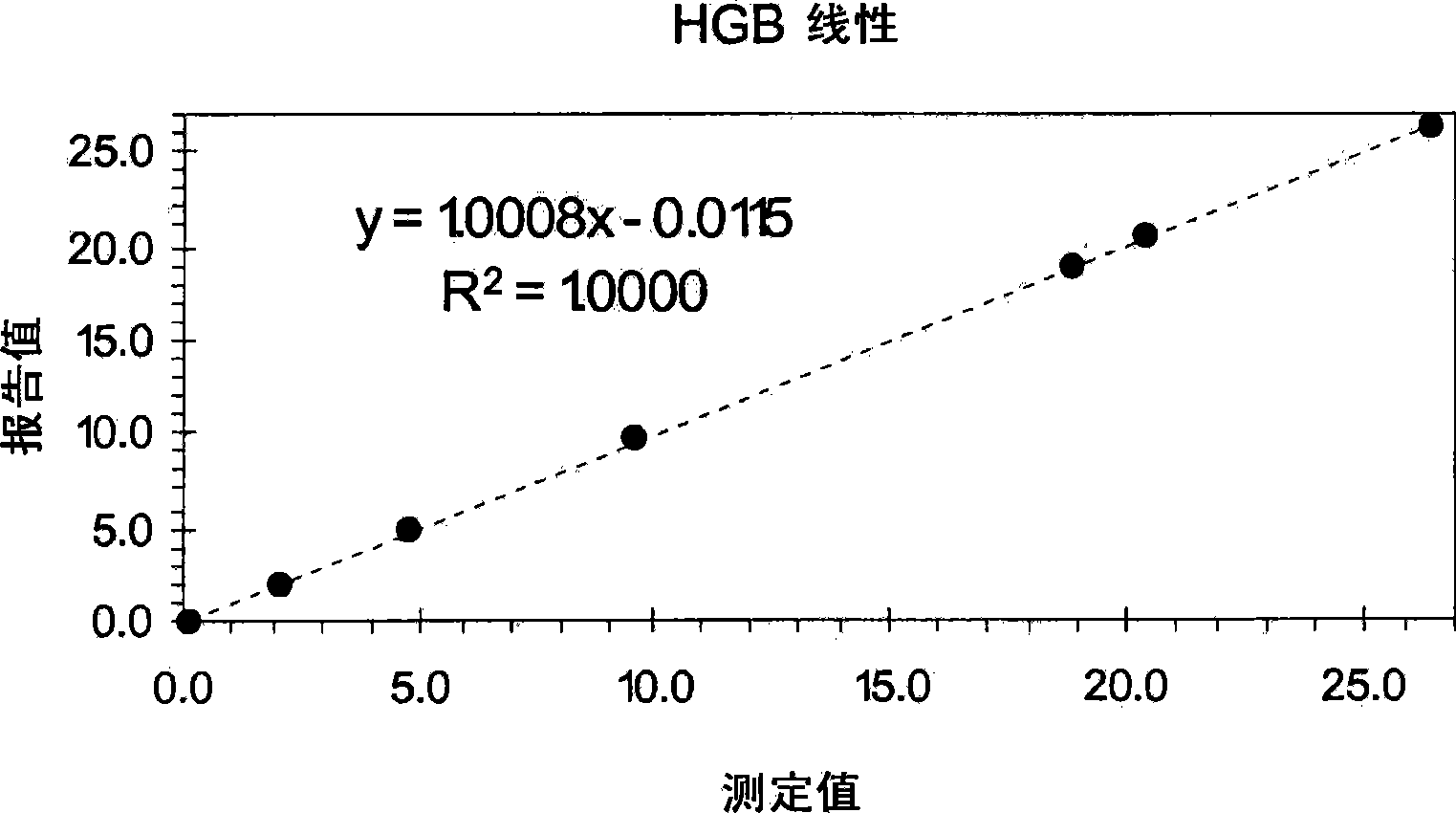
Hematology Linearity Control Composition, System and Method of Use
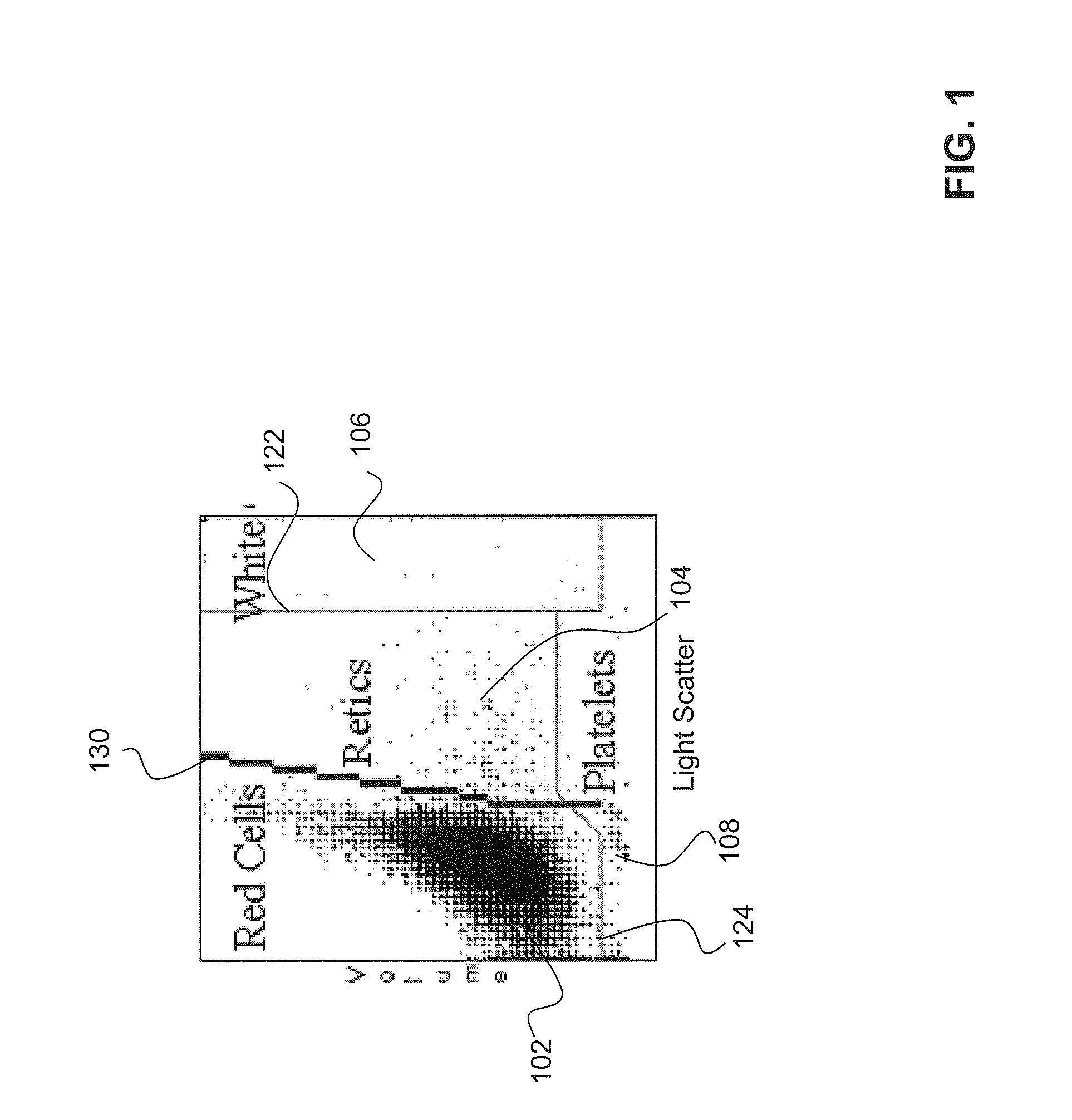
ActiveUS20080113438A1Affect measurementReduce concentrationDead animal preservationIndividual particle analysisMedicine.hematologyWhite blood cell
A linearity control system includes a series of linearity control compositions, each thereof includes white blood cell analogs and stabilized red blood cells in a suspension medium. The concentration of the white blood cell analogs in the series of control compositions increases from 0.2×103 to 800×103 analogs per microliter, and the concentration of the white blood cell analogs in at least one control composition is greater than 120×103 analogs per microliter. The stabilized red blood cells facilitate mono-dispersion of the white blood cell analogs in the suspension medium by gently mixing. The control compositions further include platelet analogs, or additionally include reticulocyte and / or nucleated red blood cell analogs. The linearity control system allows the verification of the reportable measurement range and linearity of the measurements of hematology analyzers for white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets in extended concentration ranges.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
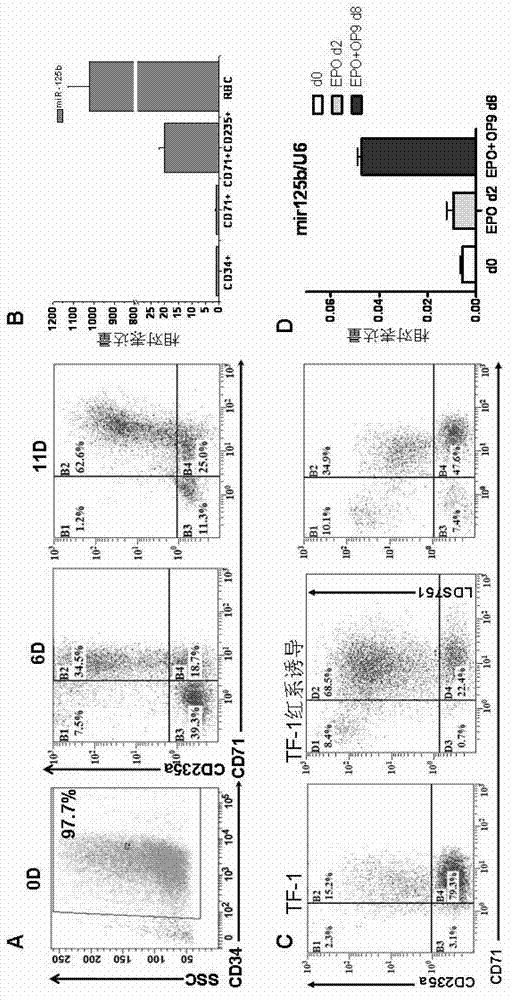
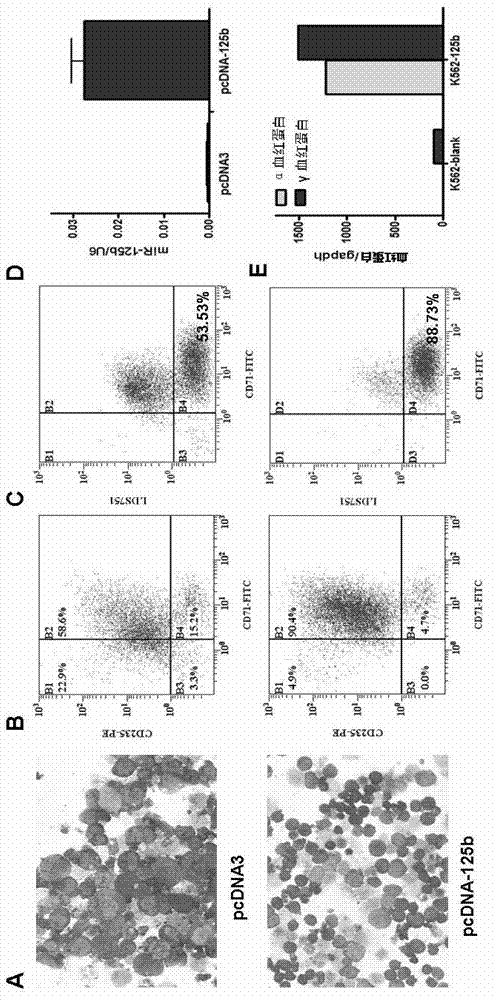
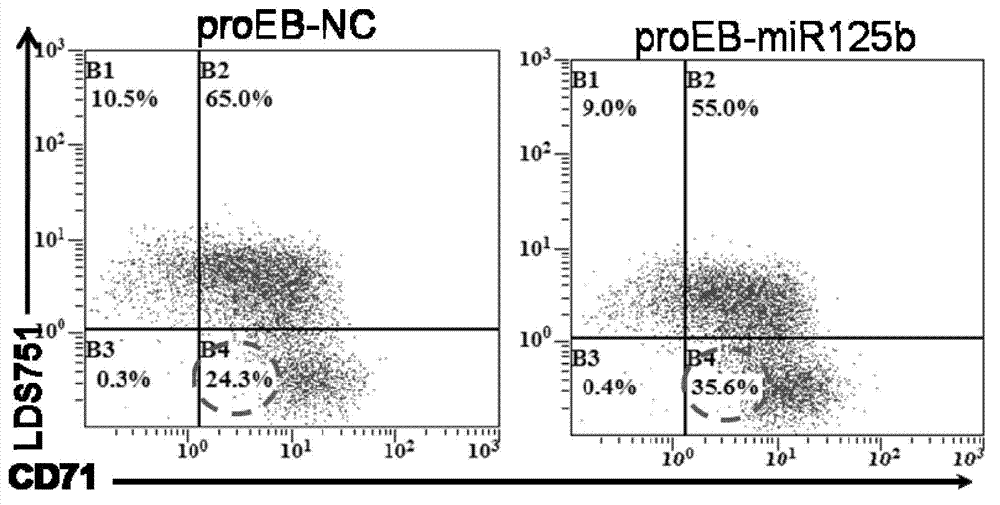
Application of miR-125b in red blood cell maturation
ActiveCN103074354AEfficient manufacturingVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsMir 125bNucleotide sequencing
The invention relates to an application of miR-125b in red blood cell maturation. A method for preparing mature red blood cell comprises the following steps: making precursor cells of the red blood cell to express miR-125b, wherein the miR-125b has a nucleotide sequence shown in a SEQ IDNO:1; and culturing the precursor cells of the red blood cell of the expressed miR-125b to obtain the mature red blood cell; wherein, the precursor cells of the red blood cell can be selected from original erythroblast, polychromatic erythroblast, orthoneutrophil erythroblast and reticulocyte. The method can be used for effectively preparing the mature red blood cell.
Owner:FIELD OPERATION BLOOD TRANSFUSION INST OF PLA SCI ACAD OF MILITARY
Hematology linearity control composition, system and method of use
ActiveUS7754487B2Affect measurementReduce concentrationDead animal preservationIndividual particle analysisMedicine.hematologyWhite blood cell
A linearity control system includes a series of linearity control compositions, each thereof includes white blood cell analogs and stabilized red blood cells in a suspension medium. The concentration of the white blood cell analogs in the series of control compositions increases from 0.2×103 to 800×103 analogs per microliter, and the concentration of the white blood cell analogs in at least one control composition is greater than 120×103 analogs per microliter. The stabilized red blood cells facilitate mono-dispersion of the white blood cell analogs in the suspension medium by gently mixing. The control compositions further include platelet analogs, or additionally include reticulocyte and / or nucleated red blood cell analogs. The linearity control system allows the verification of the reportable measurement range and linearity of the measurements of hematology analyzers for white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets in extended concentration ranges.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Reference control composition containing a nucleated red blood cell component made of non-nucleated blood cells
A reference control composition containing a nucleated red blood cell component and the method of making are disclosed. The reference control composition includes a nucleated red blood cell component made of fixed non-nucleated blood cells and a suspension medium. The non-nucleated blood cell has a natural cell size substantially similar to a size of nucleus of said nucleated red blood cell of said blood sample. The nucleated red blood cell component can be made of equine, ovine, bovine, feline, canine, or porcine red blood cells; and it is substantially free of nucleic acid. The reference control composition can further include a white blood cell component, a red blood cell component, a platelet component, a reticulocyte component, or combinations thereof. Further disclosed are the methods of using the reference control composition for measurement of nucleated red blood cells on a blood analyzer.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
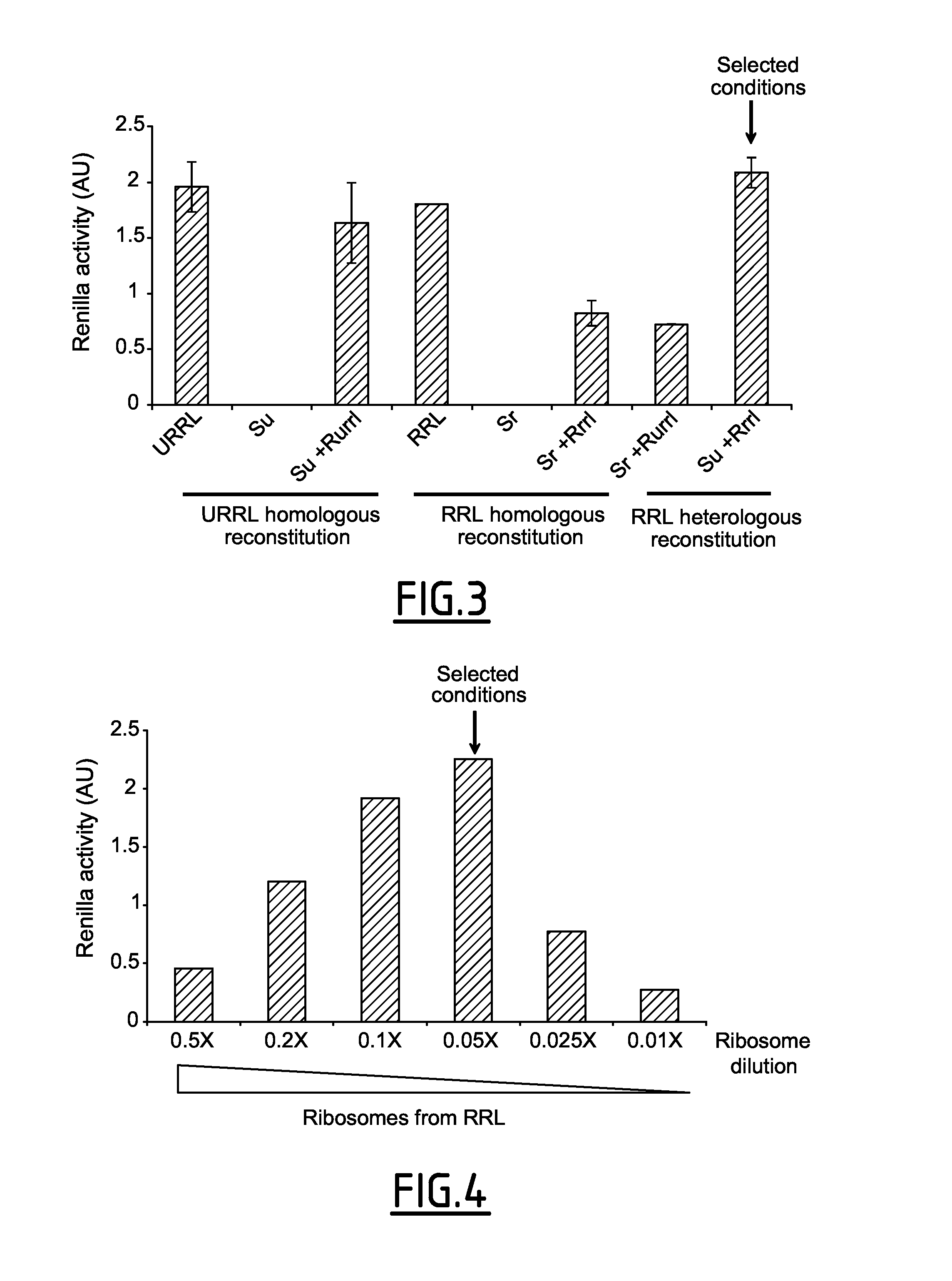
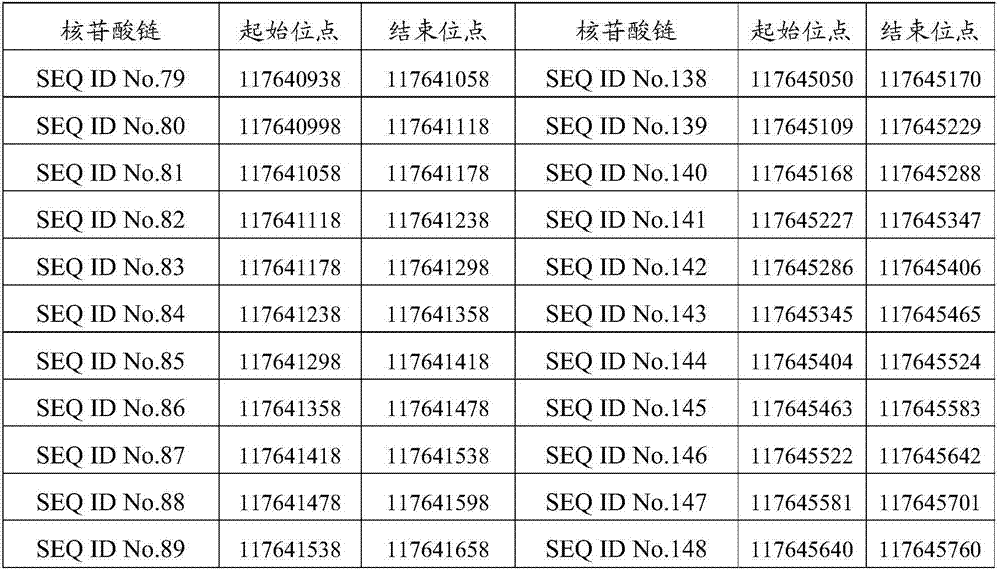
Cell-Free Translation System
The present invention relates to a new cell-free translation system. In particular, the invention relates to a cell-free reaction system for translating in vitro a RNA into a protein, said reaction system comprising a ribosome-depleted red blood cell lysate and ribosomes isolated from eukaryotic cells, with the proviso that (1) when the ribosome-depleted red blood cell lysate is obtained from a nuclease untreated rabbit reticulocyte lysate, the eukaryotic cells from which ribosomes are isolated are not nuclease untreated rabbit reticulocytes, and (2) when the ribosome-depleted red blood cell lysate is obtained from a nuclease treated rabbit reticulocyte lysate, the eukaryotic cells from which ribosomes are isolated are not nuclease treated rabbit reticulocytes. The invention also pertains to a method for translating in vitro a ribonucleic acid template into an amino acid sequence of interest using the cell-free reaction system of the invention. The invention also relates to the use of (i) a ribosome-depleted red blood cell lysate, and (ii) ribosomes isolated from eukaryotic cells, with the proviso that (1) when the ribosome-depleted red blood cell lysate is obtained from a nuclease untreated rabbit reticulocyte lysate, the eukaryotic cells from which ribosomes are isolated are not nuclease untreated rabbit reticulocytes, and (2) when the ribosome-depleted red blood cell lysate is obtained from a nuclease treated rabbit reticulocyte lysate, the eukaryotic cells from which ribosomes are isolated are not nuclease treated rabbit reticulocytes, for producing a cell-free translation system.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +2
Detection chip for tumor driving gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a detection chip for a tumor driving gene and application thereof. The detection chip for the tumor driving gene comprises an ALK (anaplastic lymphoma kinase) fusion detection agent, an EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) fusion detection agent, an RET (reticulocyte) fusion detection agent and an ROS1 (reactive oxygen species 1) fusion detection agent. Proofed by the results of clinical detect, after fusion probes corresponding to the ALK, the EGFR, the RET and the ROS1 are specifically designed, the detection chip has the advantages that the sensitivity is high, and the gene fusion between a particular site area of the ALK, the EGFR, the RET and the ROS1 and fusion segments is specifically detected. The invention further discloses a detection chip for detecting a second sequence group of the gene mutation and a third sequence group of the gene amplification; after detecting once, the gene fusion, gene mutation and gene amplification of the multiple tumor driving genes, such as the ALK, BRAF (aserine / theroninespecific kinases), DDR2 (discordin domain receptor 2), the EGFR, ERBB2 (receptor tyrosine kinase 2), FGFR1 (fibroblast growth factor receptor 1), KRAS (kirstenrat sarcoma viral oncogene), MET (methionine), NRAS, PIK3CA (phosphatidylino-sitol 3-kinases), the RET and the ROS1.
Owner:常州桐树生物科技有限公司
Reference Control Containing a Nucleated Red Blood Cell Component
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Method of measurement of cellular hemoglobin
A method of measuring cellular hemoglobin of a blood sample includes mixing a blood sample with a permeation reagent, and incubating the sample mixture to permeate cellular membrane of red blood cells and to cause hemoglobin aggregation within the cells; adding a neutralization reagent to inhibit further reactions of the permeation reagent; performing a cell-by-cell measurement of side scatter signals of the red blood cells in the sample mixture on a flow cytometer; and obtaining cellular hemoglobin (Hgbcell) of each red blood cell using the obtained side scatter signals. The method further includes measuring cellular hemoglobin of reticulocytes (Hgbretic) by differentiating reticulocytes using a simultaneous fluorescence measurement. The method also includes measuring cellular percentage of a hemoglobin variant in mature red blood cells or reticulocytes by adding a fluorescent antibody in the neutralization reagent and detecting fluorescence signals of antibody bound hemoglobin variant.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Hematology linearity control composition system and method of use
ActiveCN101535804AMonodisperse goodIndividual particle analysisBiological testingWhite blood cellPlatelet
A linearity control system includes a series of linearity control compositions; each thereof includes white blood cell analogs and stabilized red blood cells in a suspension medium. The concentration of the white blood cell analogs in the series of control compositions increases from 0.2x103 to 800x103 analogs per microliter, and the concentration of the white blood cell analogs in at least one control composition is greater than 120x103 analogs per microliter. The stabilized red blood cells facilitate mono-dispersion of the white blood cell analogs in the suspension medium by gently mixing. The control compositions further include platelet analogs, or additionally include reticulocyte and / or nucleated red blood cell analogs. The linearity control system allows the verification of the reportable measurement range and linearity of the measurements of hematology analyzers for white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets in extended concentration ranges.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
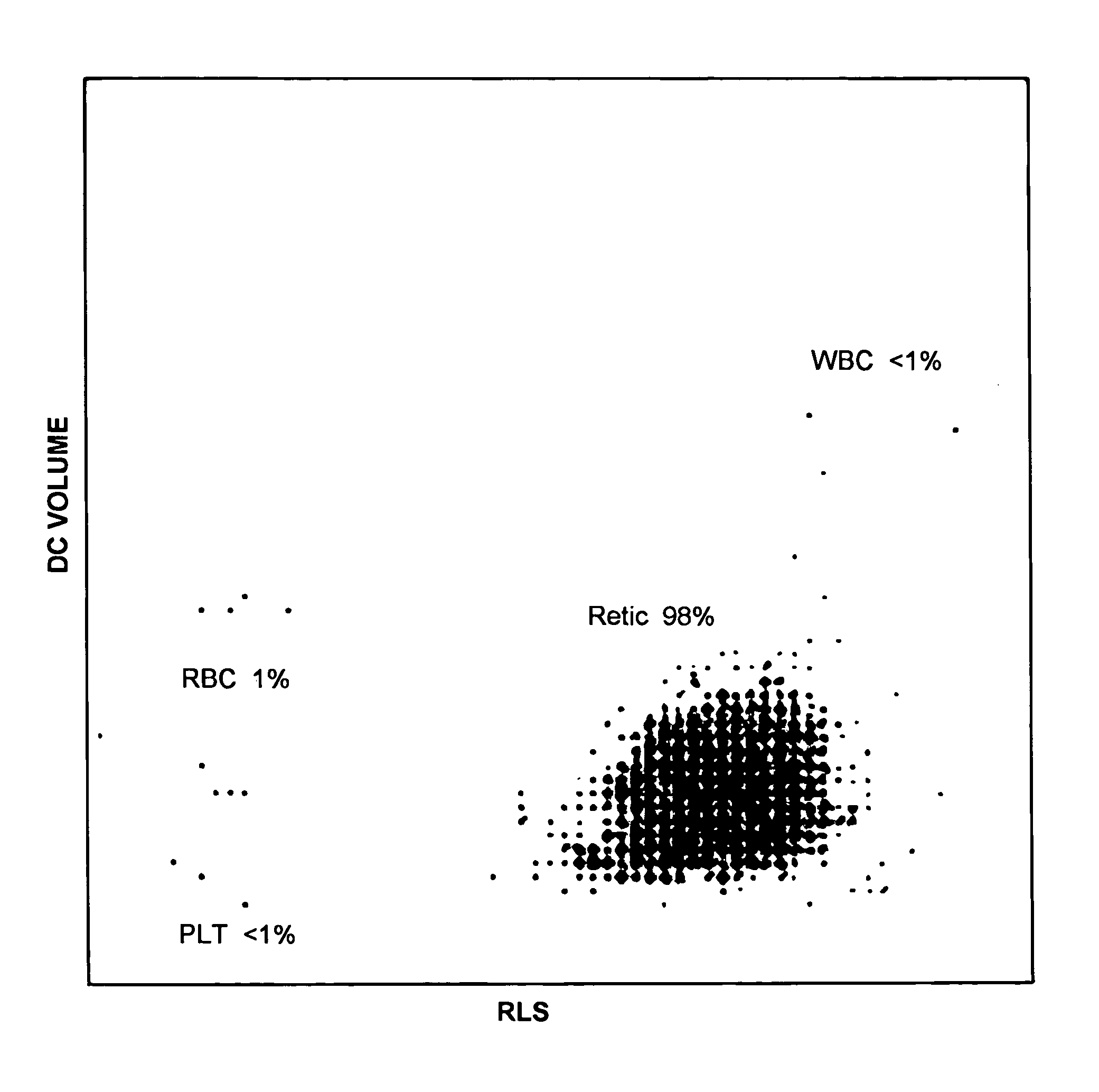
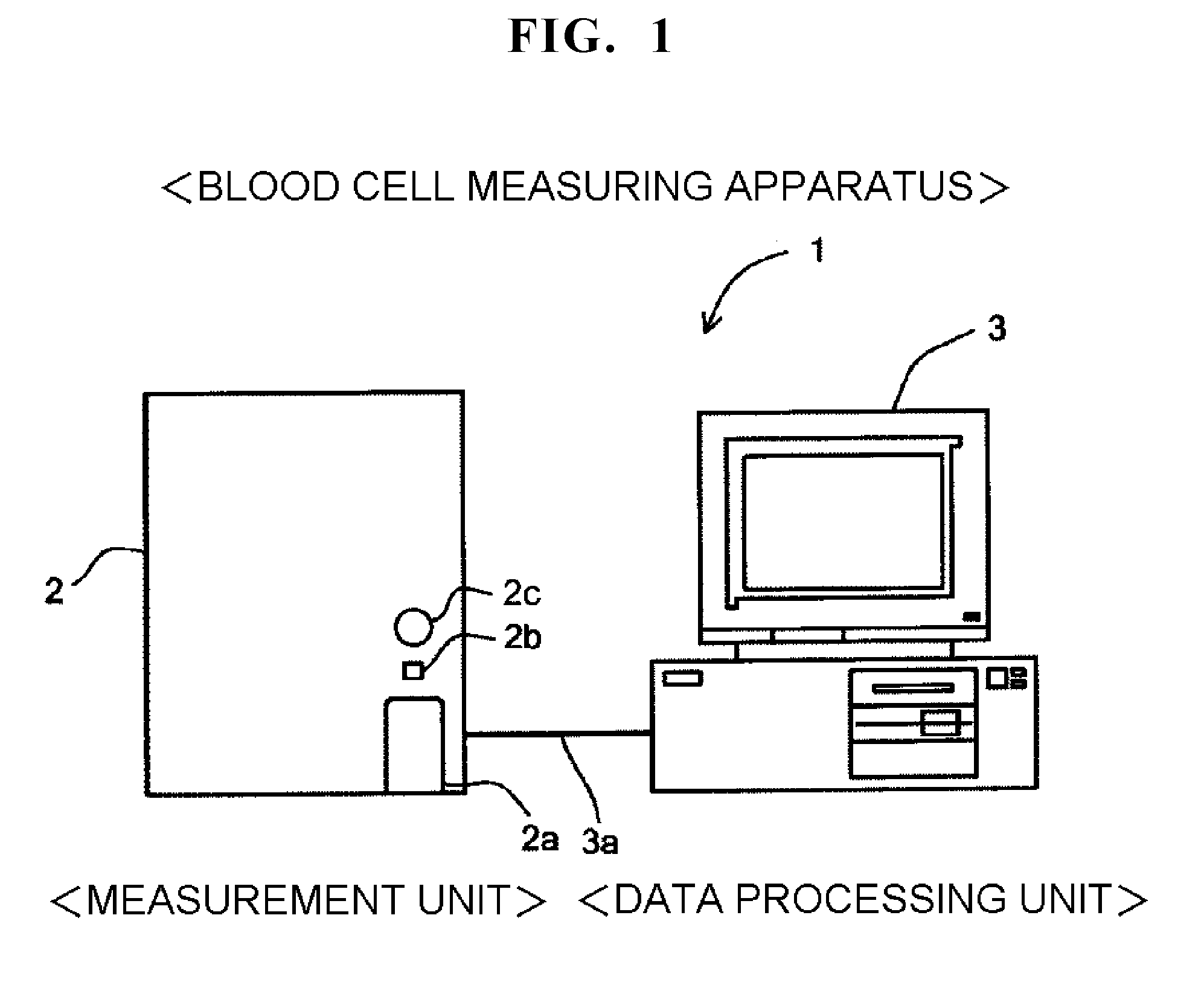
Animal blood cell measuring apparatus
ActiveUS20100248349A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAcquired characteristicMedicine
An animal blood cell measuring apparatus comprising: a specimen preparation section for preparing a measurement specimen from blood of an animal; a characteristic information obtaining section for obtaining characteristic information indicating a characteristic of the measurement specimen, from the measurement specimen prepared by the specimen preparation section; and a controller configured for performing operations comprising: (a) classifying aggregate reticulocytes contained in the blood from other blood cells, based on the characteristic information obtained by the characteristic information obtaining section; and (b) outputting information regarding a number of the classified aggregate reticulocytes.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
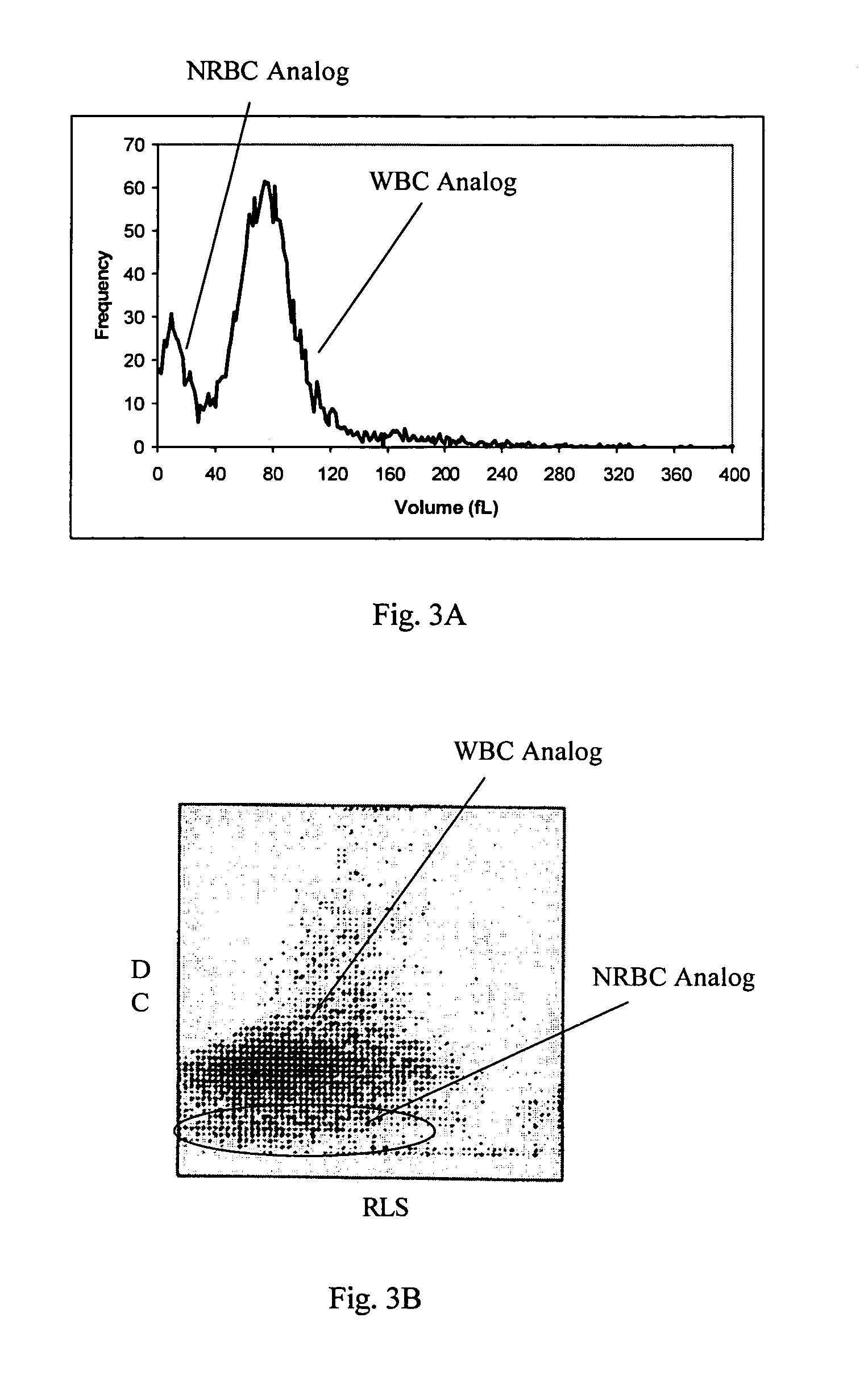
Immature Reticulocyte Fraction Reference Control and Related Methods
InactiveUS20120308985A1Rapid introductionArtificial cell constructsDead animal preservationSufficient timeAutomated analyzer
A composition (and associated methods) including a plurality of treated red blood cells for simulating reticulocytes, and particularly an immature reticulocyte fraction, of whole blood when processed as a sample in an automated analyzer capable of detecting reticulocytes. A method for making the composition or other simulated reticulocyte may include steps of contacting a suspension of a plurality of red blood cells each having a membrane in an initial state that surrounds an interior volume of a cell with an effective amount of a hypertonic permeabilizing solution including dimethyl sulfoxide and a hypotonic loading agent delivery solution including a loading agent, for a sufficient time to form a plurality of pores in the membrane, for permitting the loading agent to enter into the interior volume of the cells.
Owner:STRECK INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com