Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4954 results about "Cell membrane" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment (the extracellular space) which protects the cell from its environment. Cell membrane is consisted of a lipid bilayer, including cholesterols (a lipid component) that sit between phospholipids to maintain their fluidity under various temperature, in combination with proteins such as integral proteins, and peripheral proteins that go across inside and outside of the membrane serving as membrane transporter, and loosely attached to the outer (peripheral) side of the cell membrane acting as several kinds of enzymes shaping the cell , respectively. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of cells and organelles. In this way, it is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules. In addition, cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, the carbohydrate layer called the glycocalyx, and the intracellular network of protein fibers called the cytoskeleton. In the field of synthetic biology, cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.
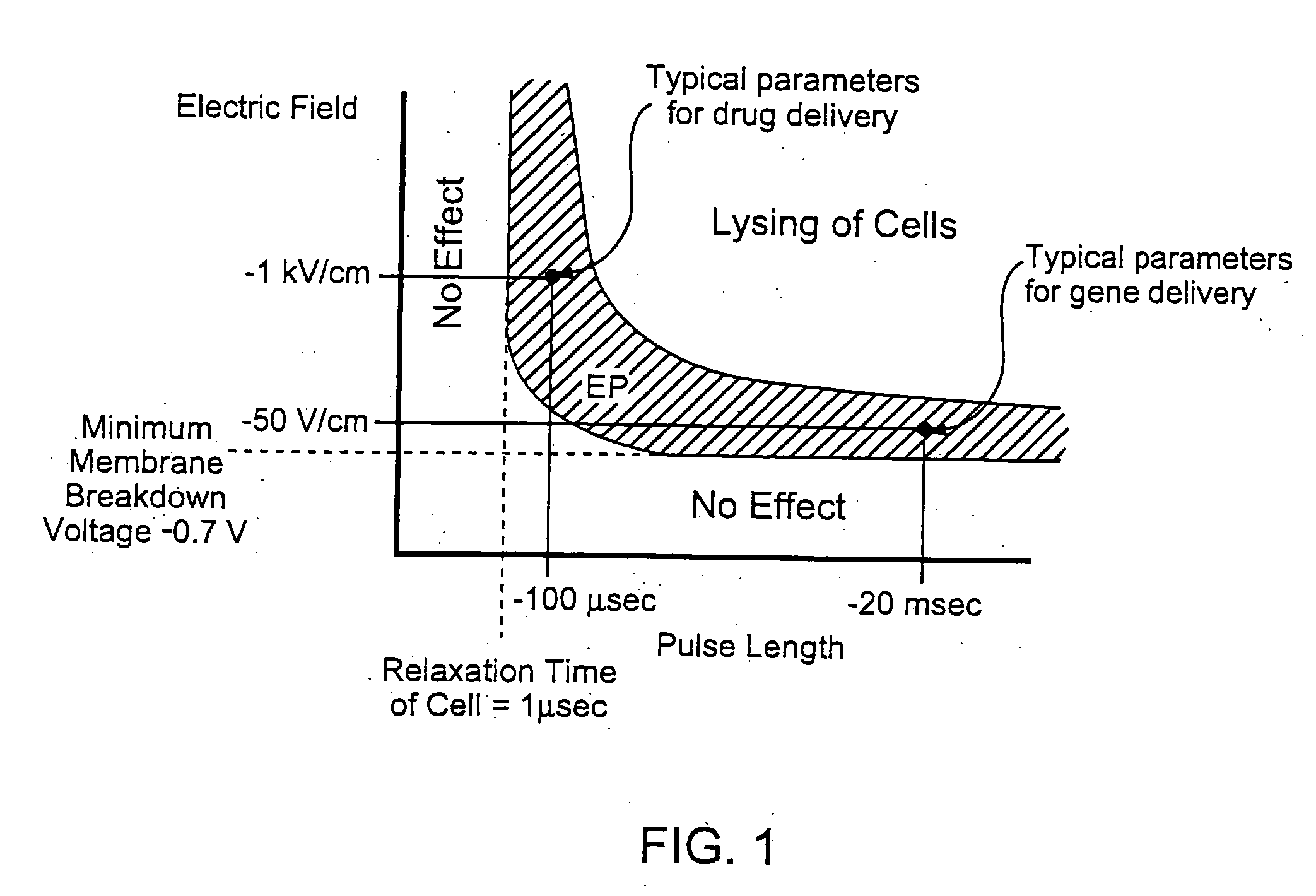
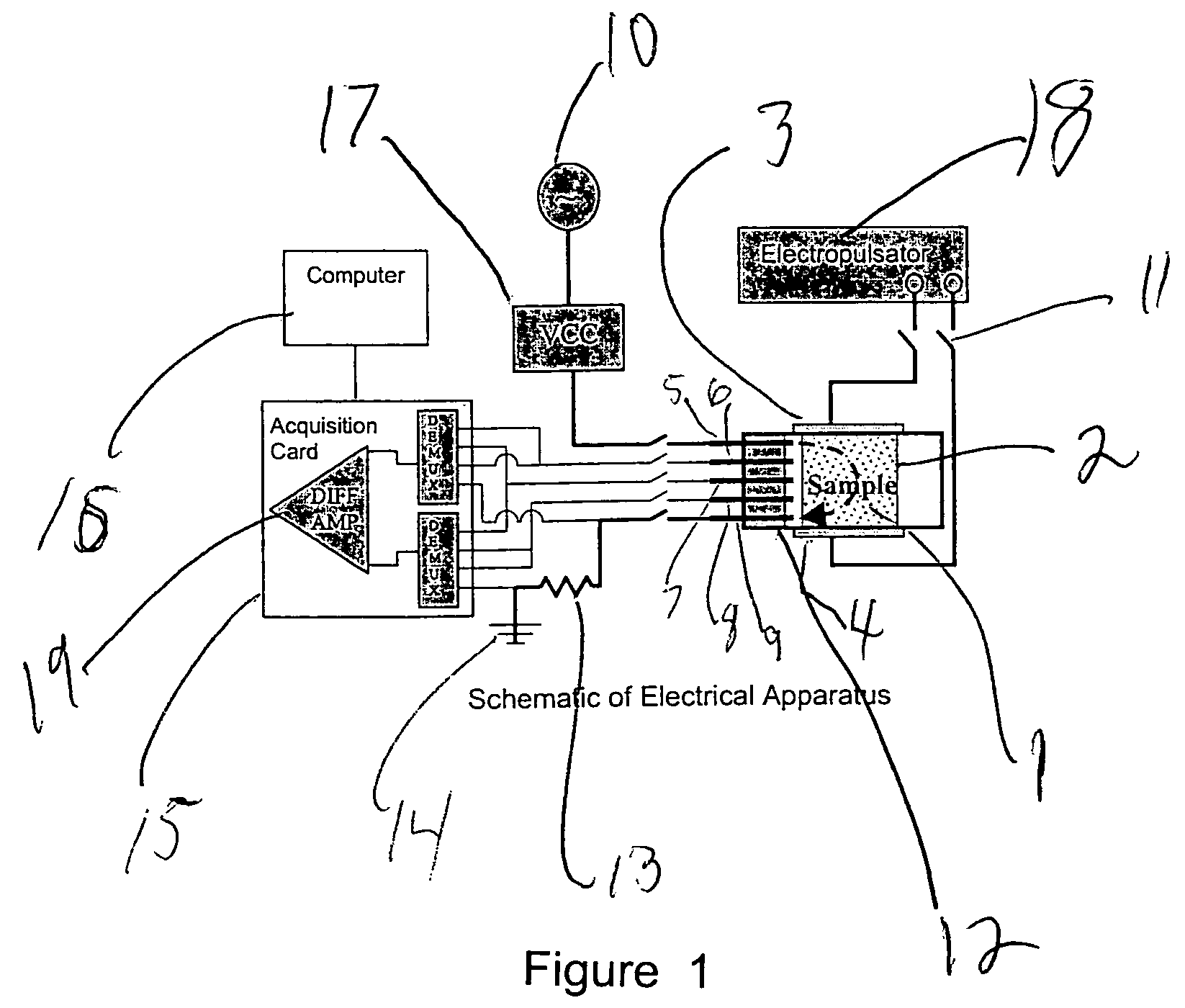
Cell/tissue analysis via controlled electroporation
InactiveUS6482619B1The right amountAvoid cell damageBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological bodyElectrical resistance and conductance
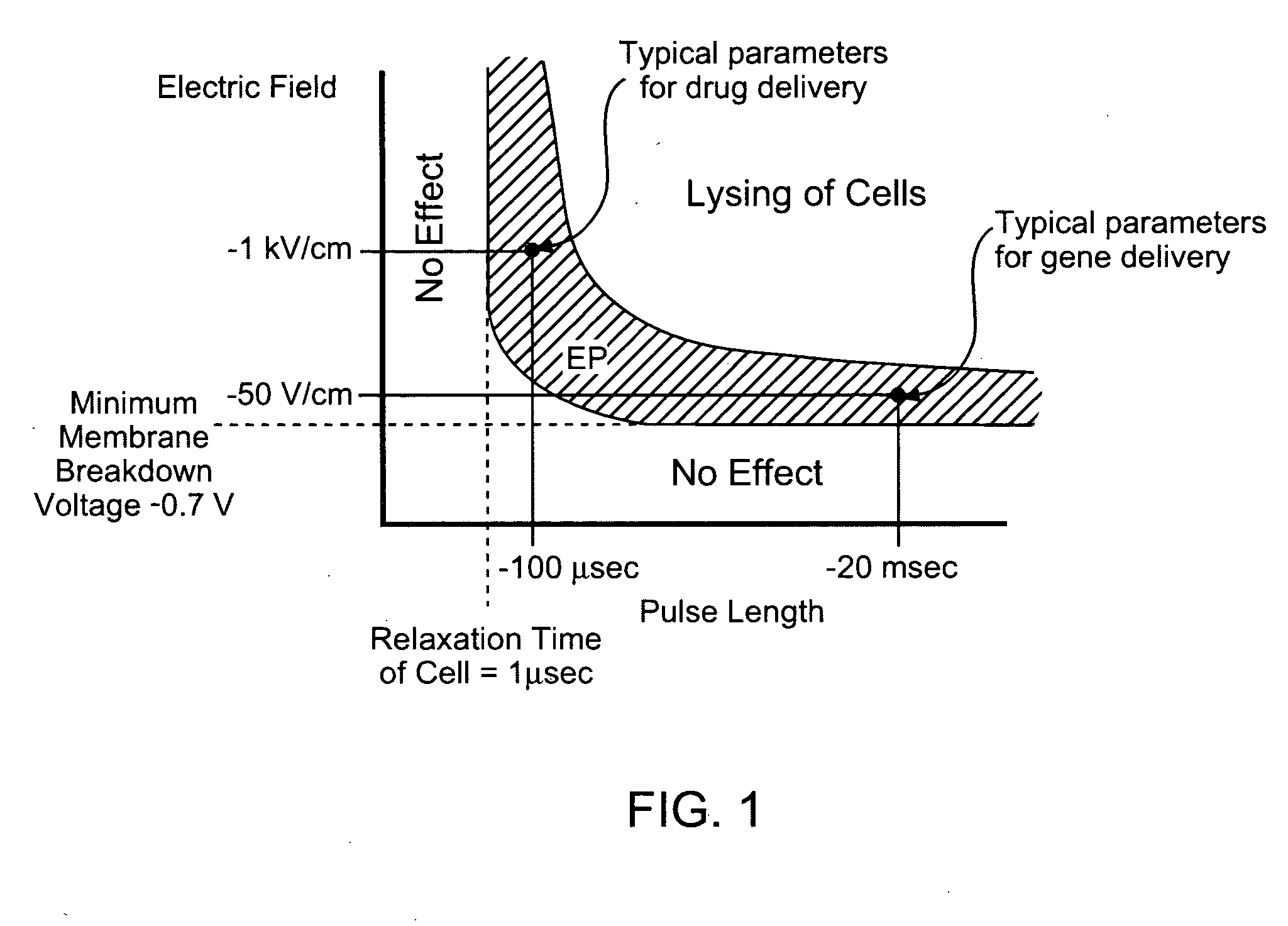
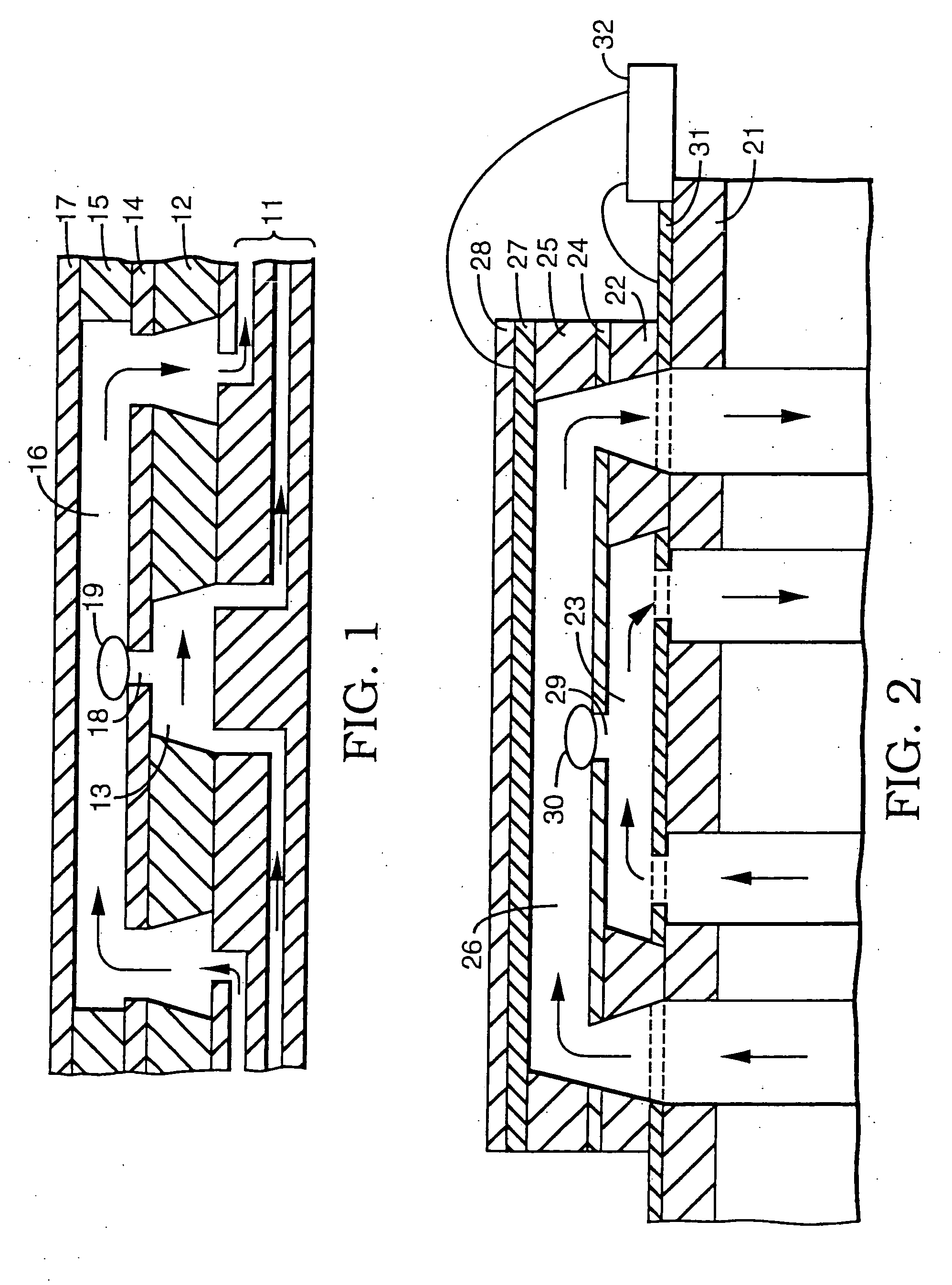
An electrical current is created across an electrically conductive medium comprising a cell which may be part of a tissue of a living organism. A first electrical parameter which may be current, voltage, or electrical impedance is measured. A second electrical parameter which may be current, voltage or a combination of both is then adjusted and / or analyzed. Adjustments are carried out to facilitate analysis and / or obtain a desired degree of electroporation. Analysis is carried out to determine characteristics of the cell membrane and / or tissue.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
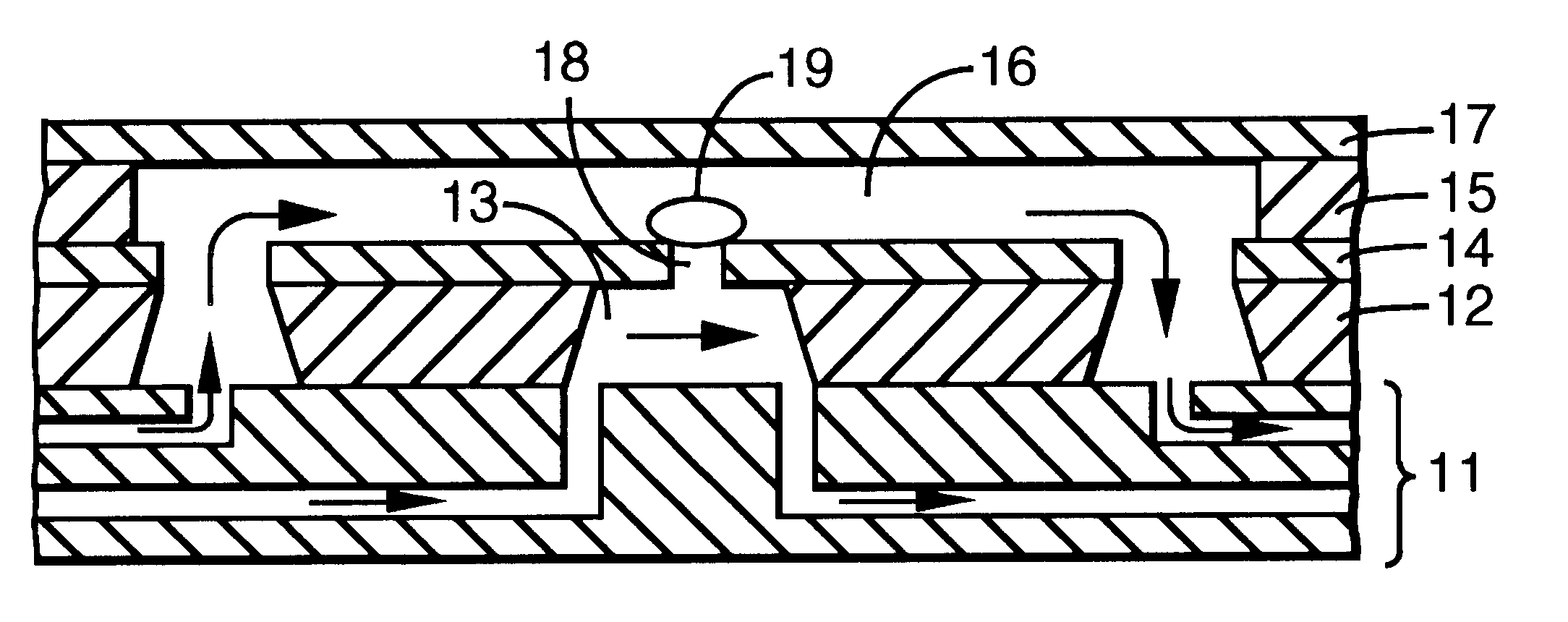
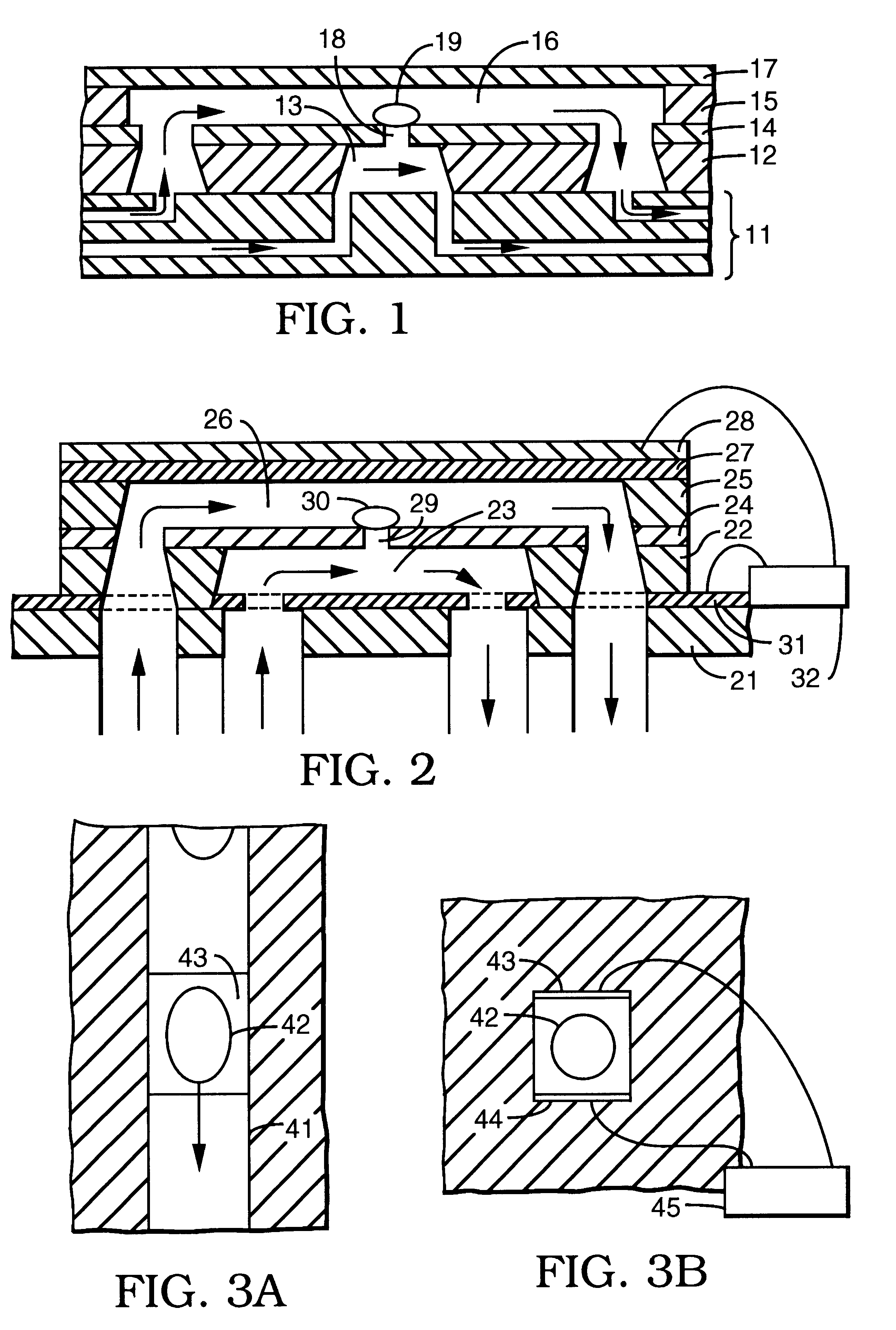
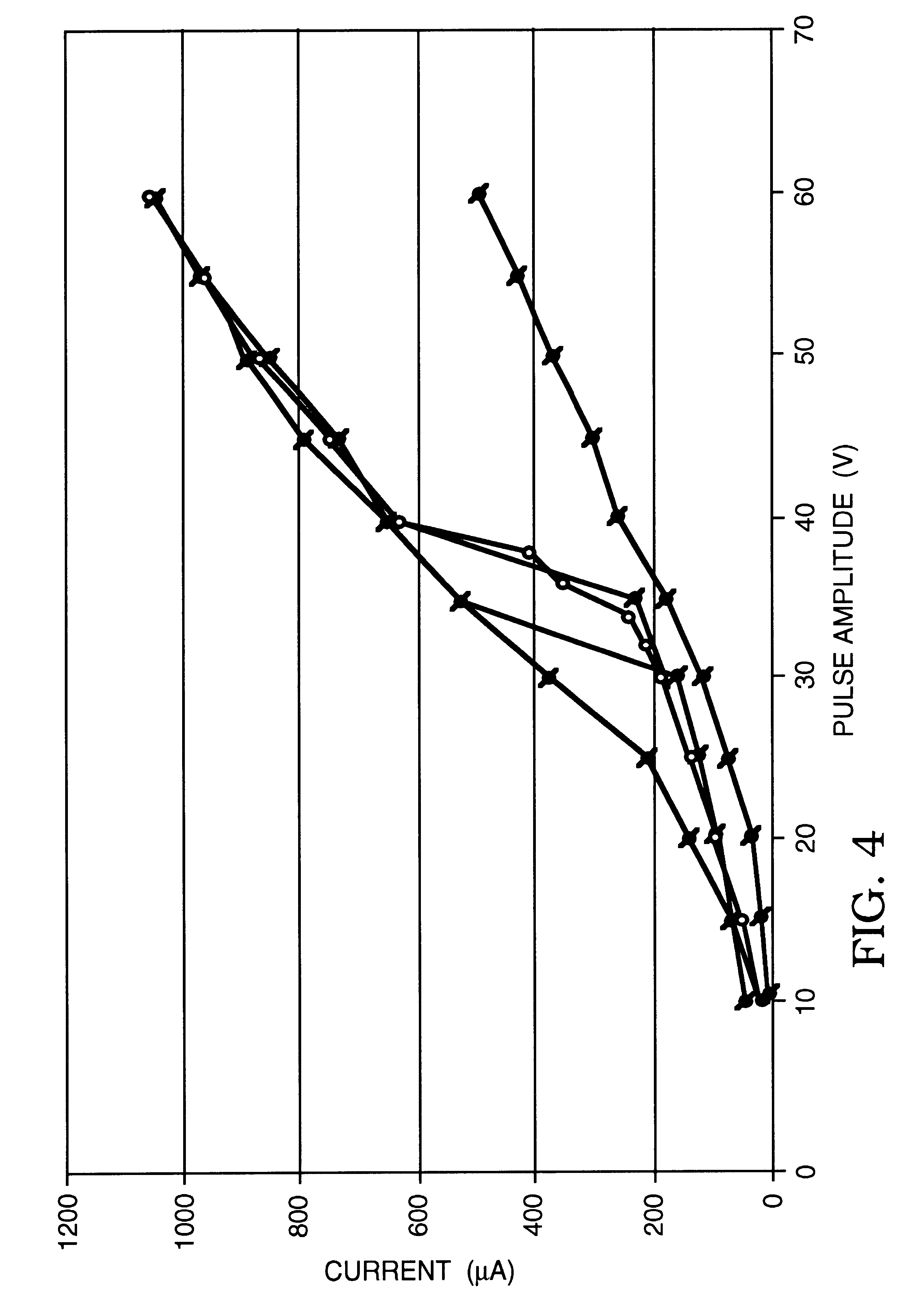
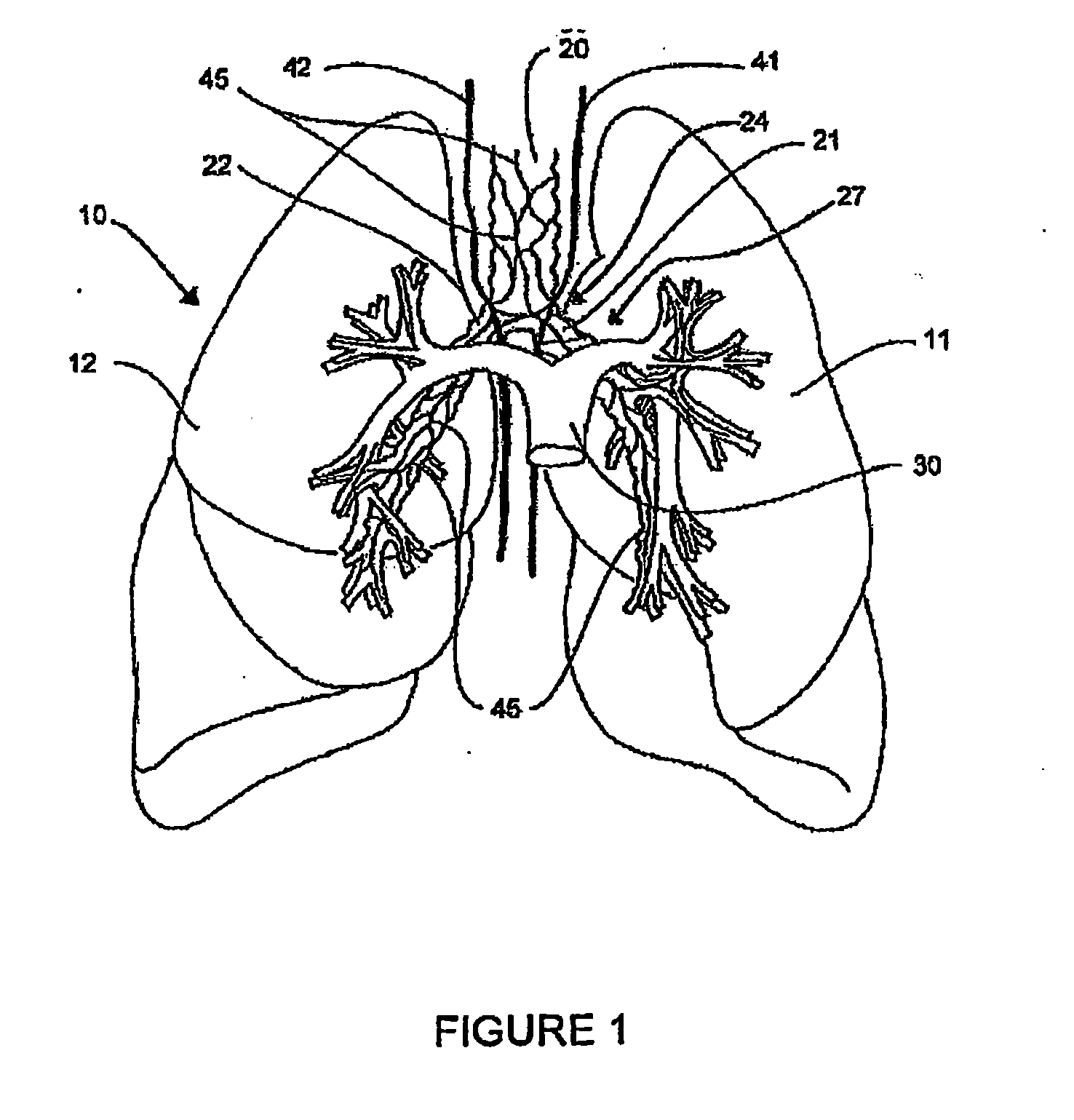
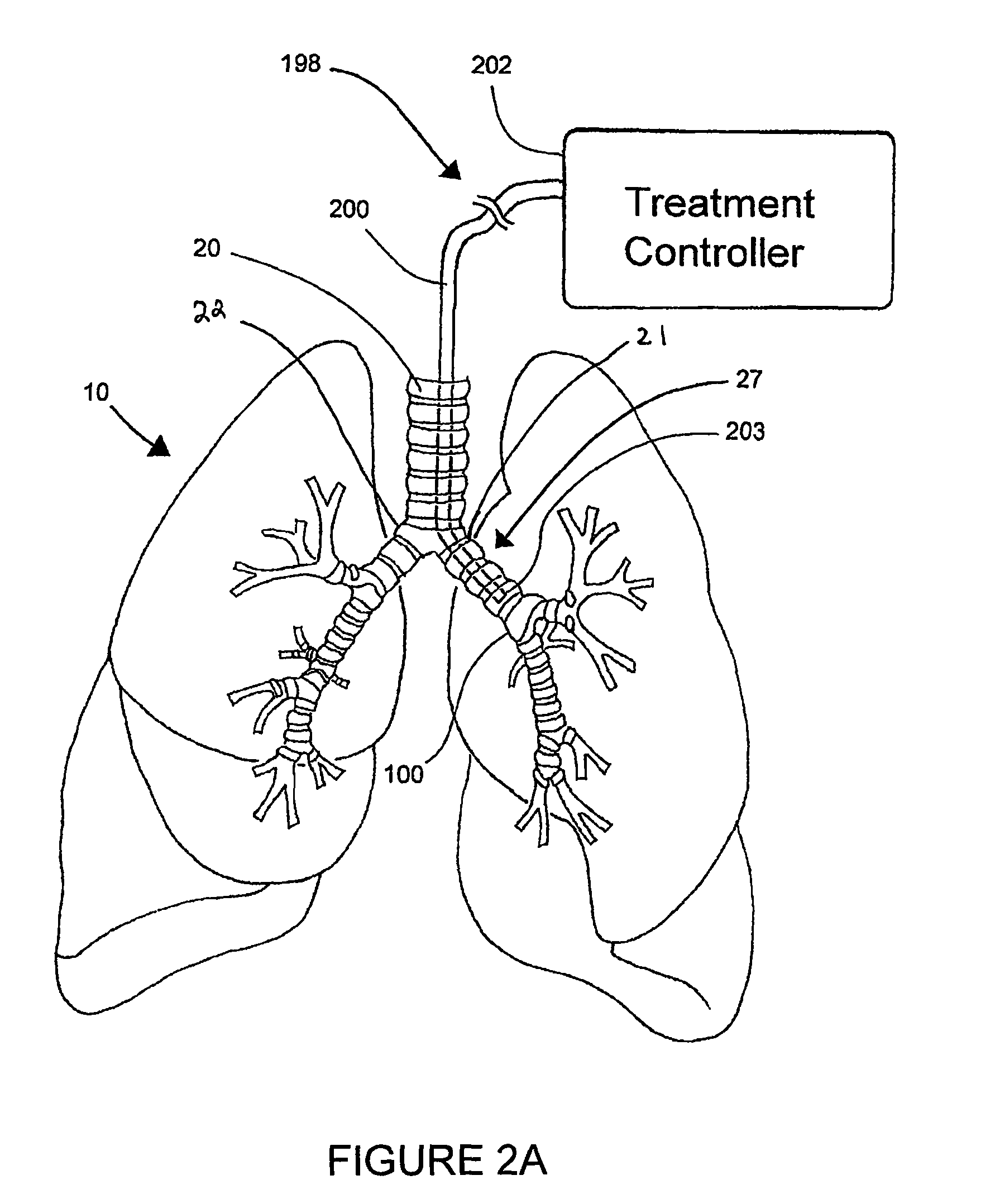
Systems, assemblies, and methods for treating a bronchial tree
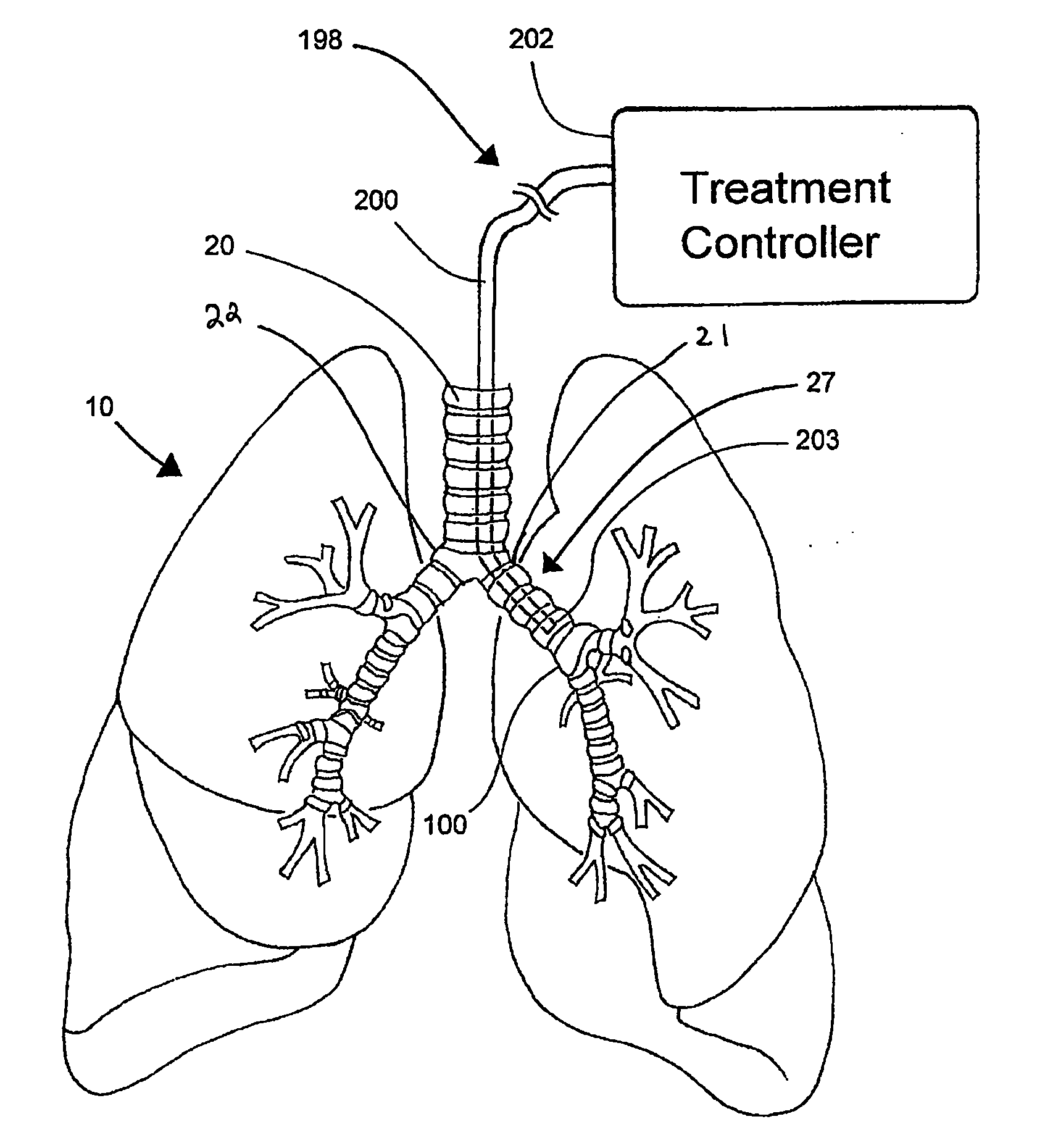
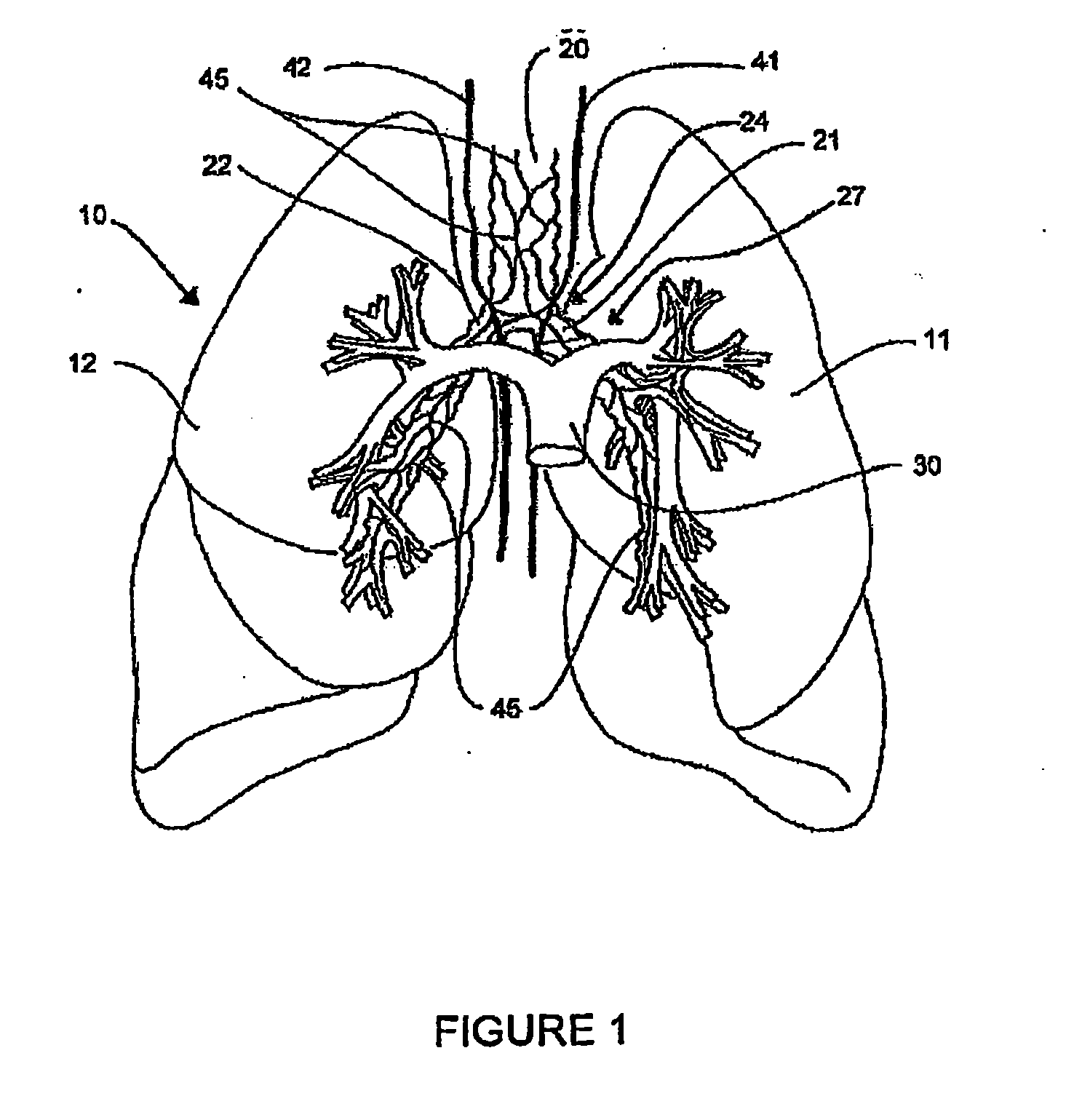
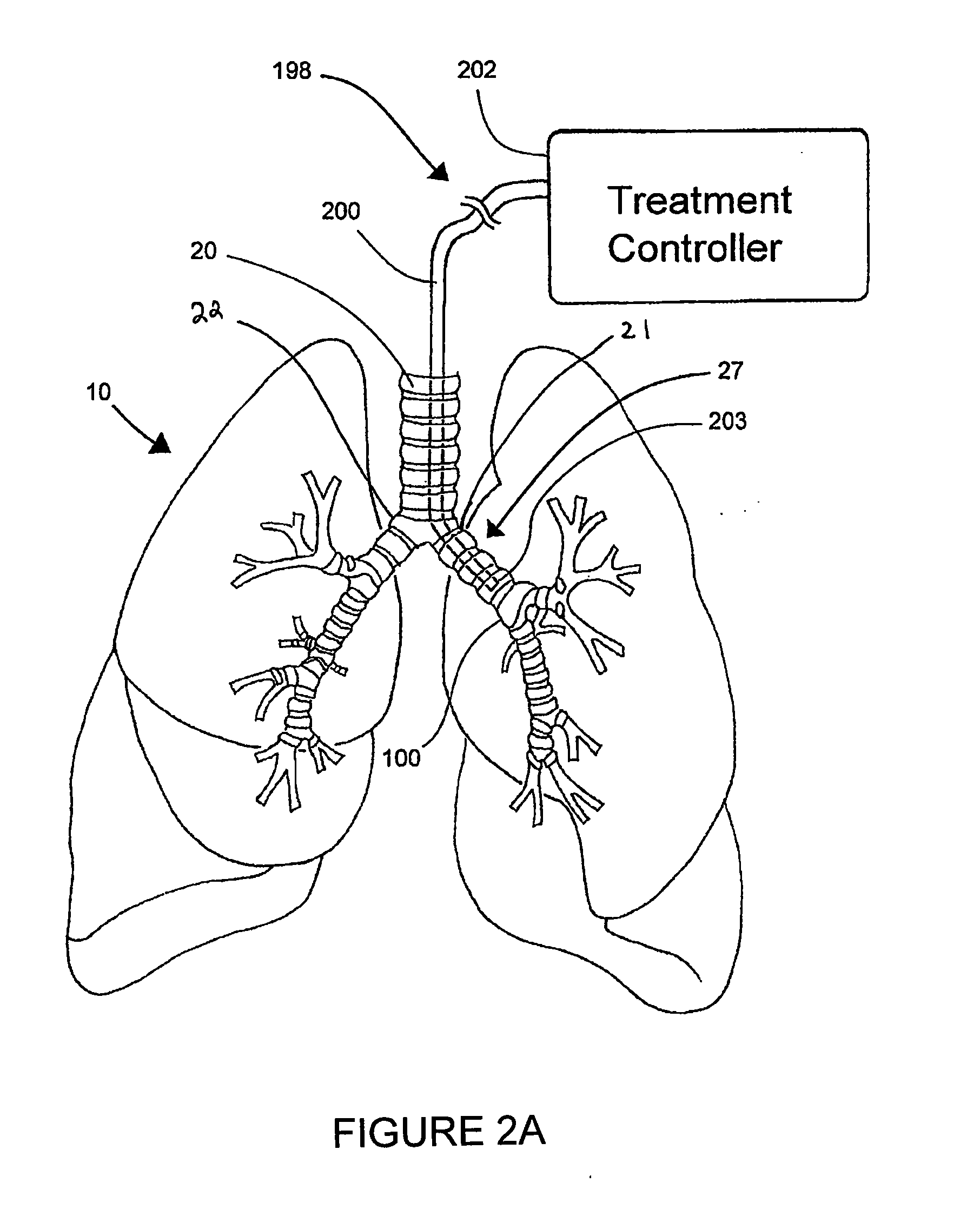
ActiveUS8088127B2Improve the immunityWithout eliminating smooth muscle toneUltrasound therapySurgical needlesNervous systemCell membrane
Systems, assemblies, and methods to treat pulmonary diseases are used to decrease nervous system input to distal regions of the bronchial tree within the lungs. Treatment systems damage nerve tissue to temporarily or permanently decrease nervous system input. The treatment systems are capable of heating nerve tissue, cooling the nerve tissue, delivering a flowable substance that cause trauma to the nerve tissue, puncturing the nerve tissue, tearing the nerve tissue, cutting the nerve tissue, applying pressure to the nerve tissue, applying ultrasound to the nerve tissue, applying ionizing radiation to the nerve tissue, disrupting cell membranes of nerve tissue with electrical energy, or delivering long acting nerve blocking chemicals to the nerve tissue.
Owner:HOLAIRA INC
Electroporation to interrupt blood flow
InactiveUS20050171574A1High level of controlRestricted blood flowSurgical needlesInternal electrodesAbnormal tissue growthBlood flow
A method for disrupting blood flow to undesirable tissue such as cells of a cancerous or non-cancerous tumor is disclosed. It involves the placement of electrodes into or near the vicinity of vessels supplying blood to the undesirable tissue and through the application of electrical pulses causing blood flow disruption. The electric pulses irreversibly permeate the cell membranes, thereby invoking cell death. The irreversibly permeabilized cells are left in situ and are removed by the body immune system. The process may further comprise monitoring blood flow and / or infusion of a material such as a chemotherapeutic agent or marker into the blood.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
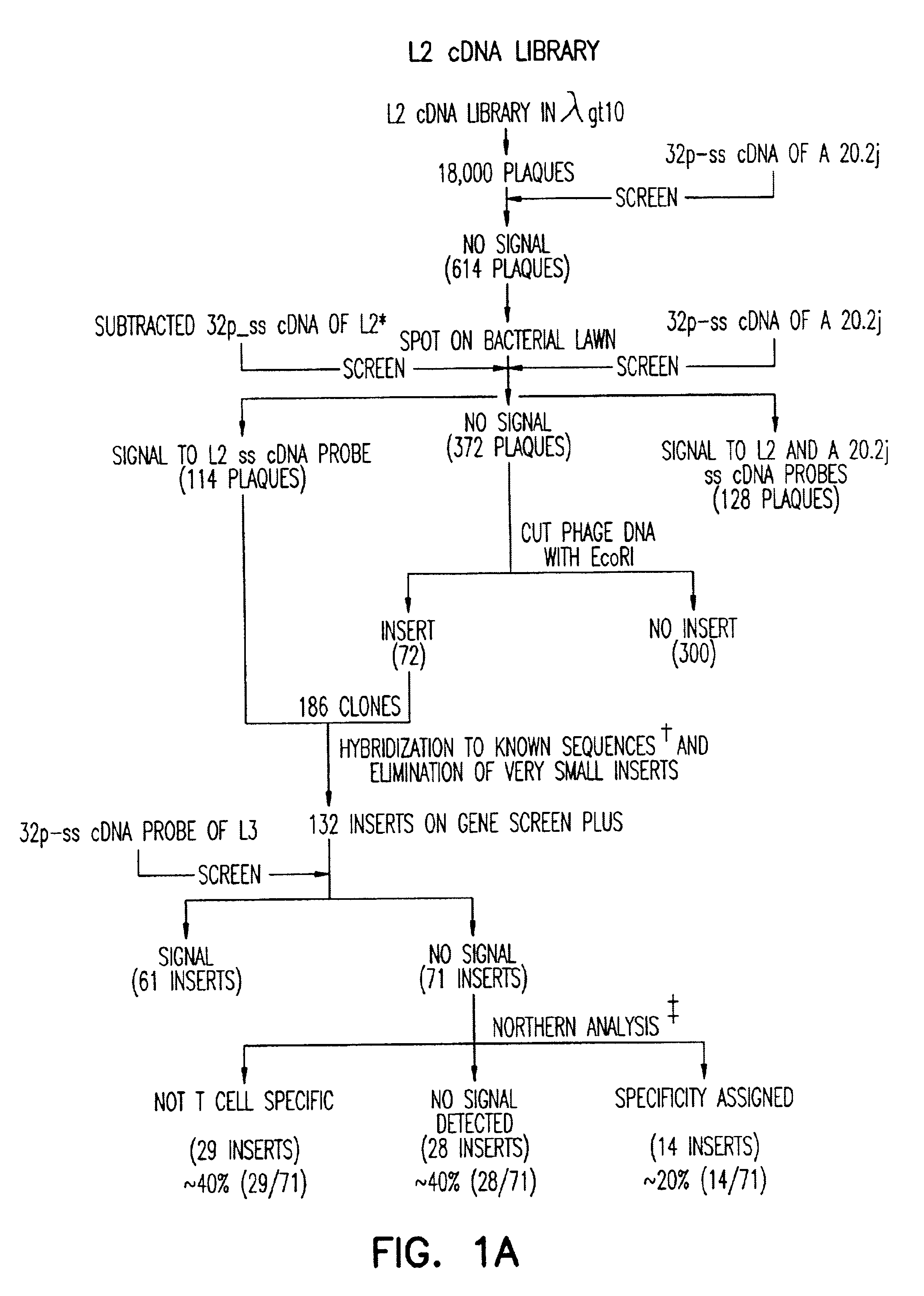
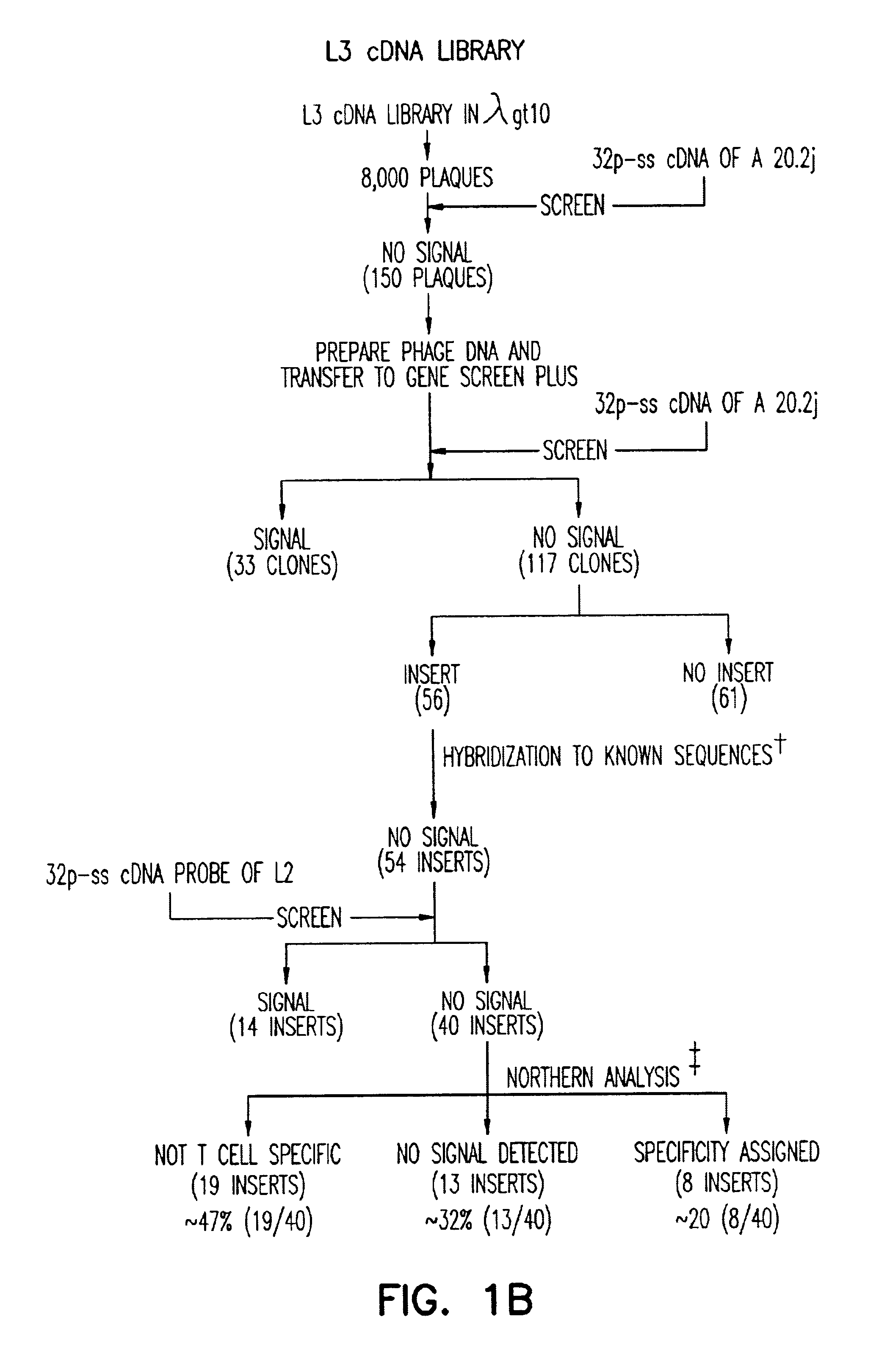
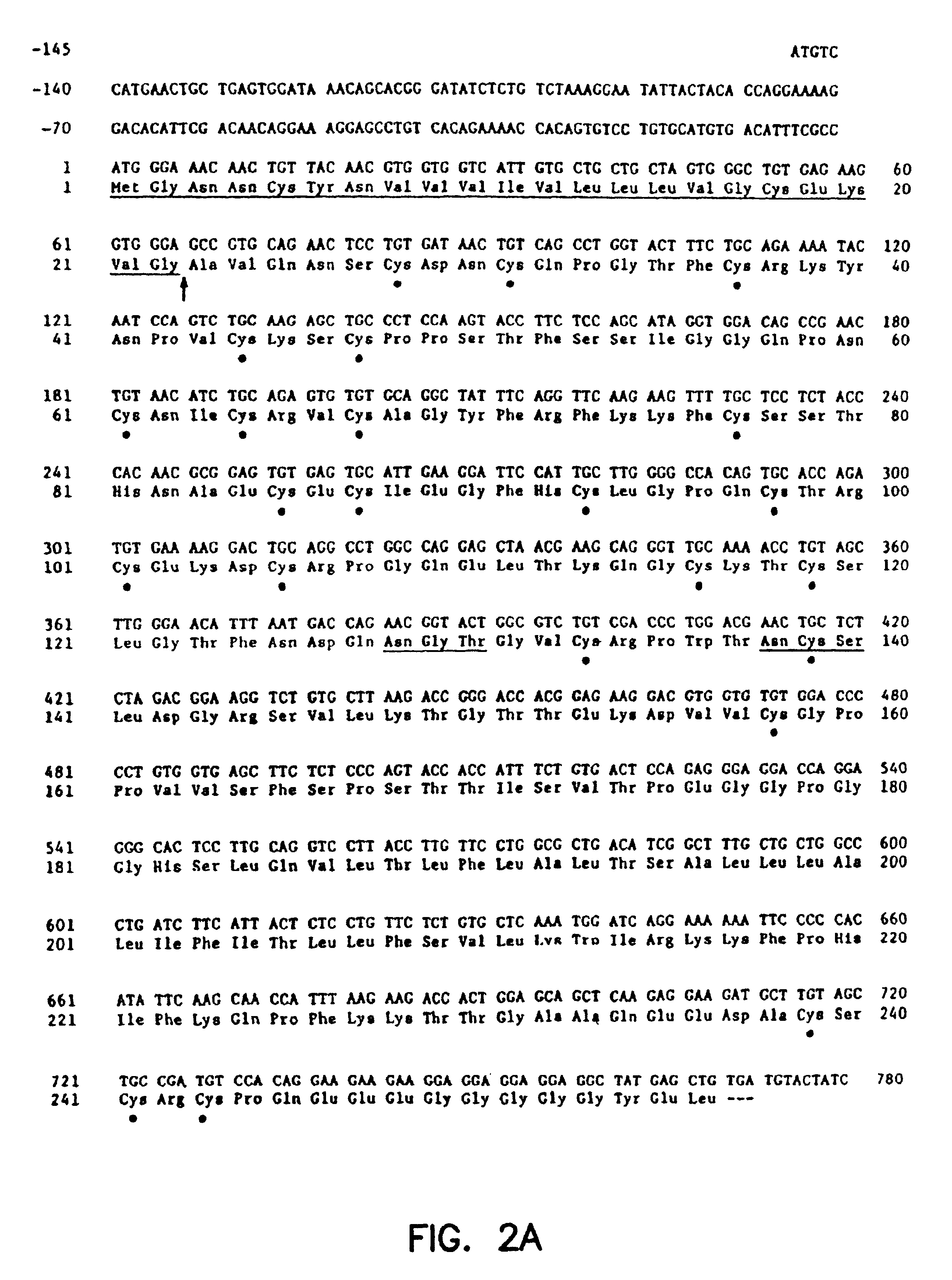
Antibody for 4-1BB
The present invention includes the receptor protein 4-1BB and the cDNA gene encoding for receptor protein 4-1BB. The nucleotide sequence of the isolated cDNA is disclosed herein along with the deduced amino acid sequence. The 4-1BB protein and fragments and derivatives can be used: 1) as a probe to isolate ligands to receptor protein 4-1BB, 2) to stimulate proliferation of B-cell's expressing 4-1BB, or 3) to block 4-1BB ligand binding. A monoclonal antibody against 4-1BB was developed which specifically recognizes an epitope on the extracellular domain of receptor protein 4-1BB. The monoclonal antibody can be used enhance T-cell proliferation and activation by treating T-cells that have expressed receptor protein 4-1BB with the monoclonal antibody. The effectiveness of the treatment was enhanced when conducted in the presence of protein tyrosinase kinase. A fusion protein for detecting cell membrane ligands to receptor protein 4-1BB was developed. It comprises the extracellular portion of the receptor protein 4-1BB and a detection protein bound to the portion of the receptor protein 4-1BB.
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
Systems, assemblies, and methods for treating a bronchial tree
ActiveUS20090306644A1Improve the immunityWithout eliminating smooth muscle toneUltrasound therapyDiagnosticsNervous systemCell membrane
Systems, assemblies, and methods to treat pulmonary diseases are used to decrease nervous system input to distal regions of the bronchial tree within the lungs. Treatment systems damage nerve tissue to temporarily or permanently decrease nervous system input. The treatment systems are capable of heating nerve tissue, cooling the nerve tissue, delivering a flowable substance that cause trauma to the nerve tissue, puncturing the nerve tissue, tearing the nerve tissue, cutting the nerve tissue, applying pressure to the nerve tissue, applying ultrasound to the nerve tissue, applying ionizing radiation to the nerve tissue, disrupting cell membranes of nerve tissue with electrical energy, or delivering long acting nerve blocking chemicals to the nerve tissue.
Owner:NUVAIRA INC
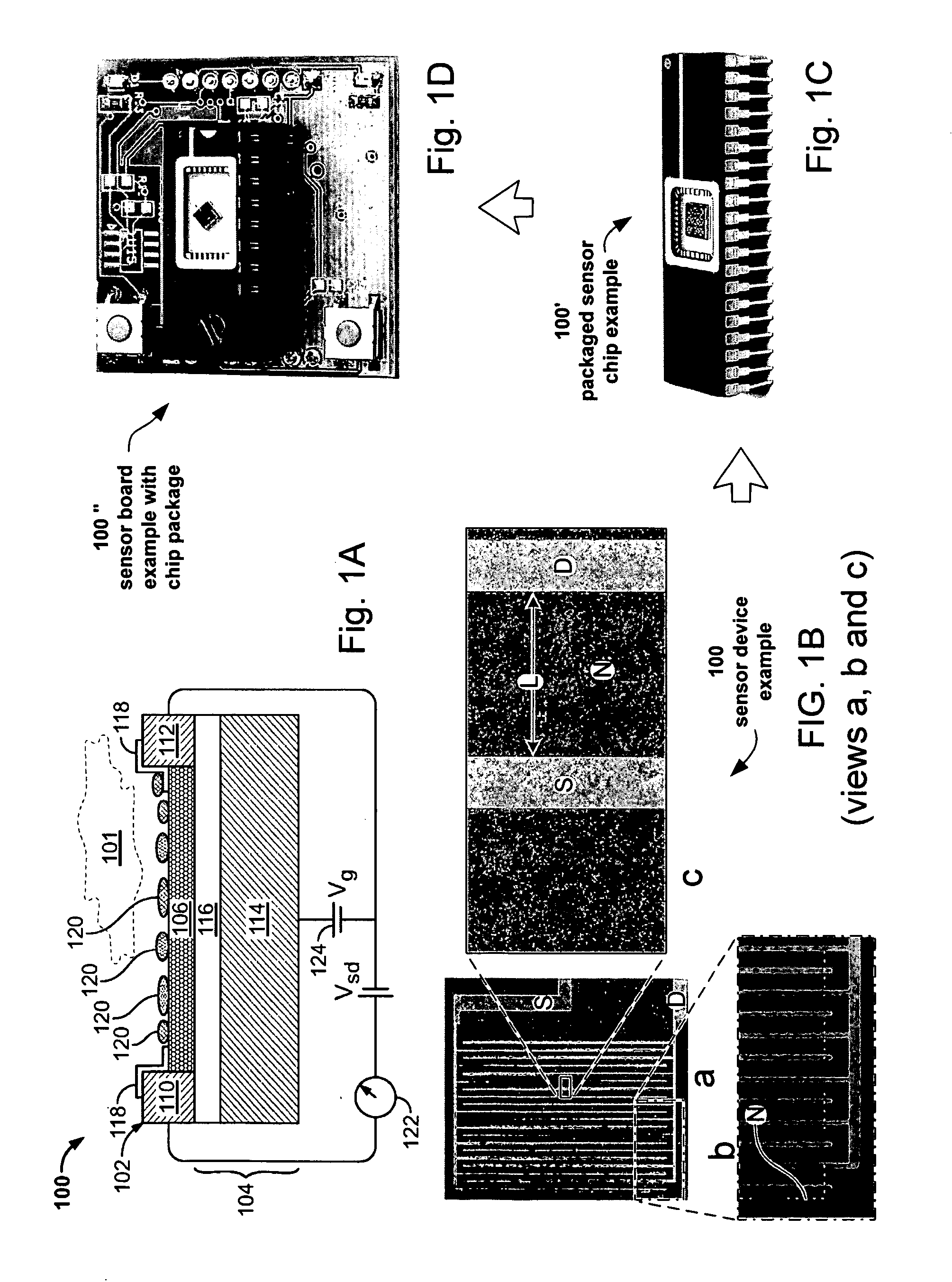
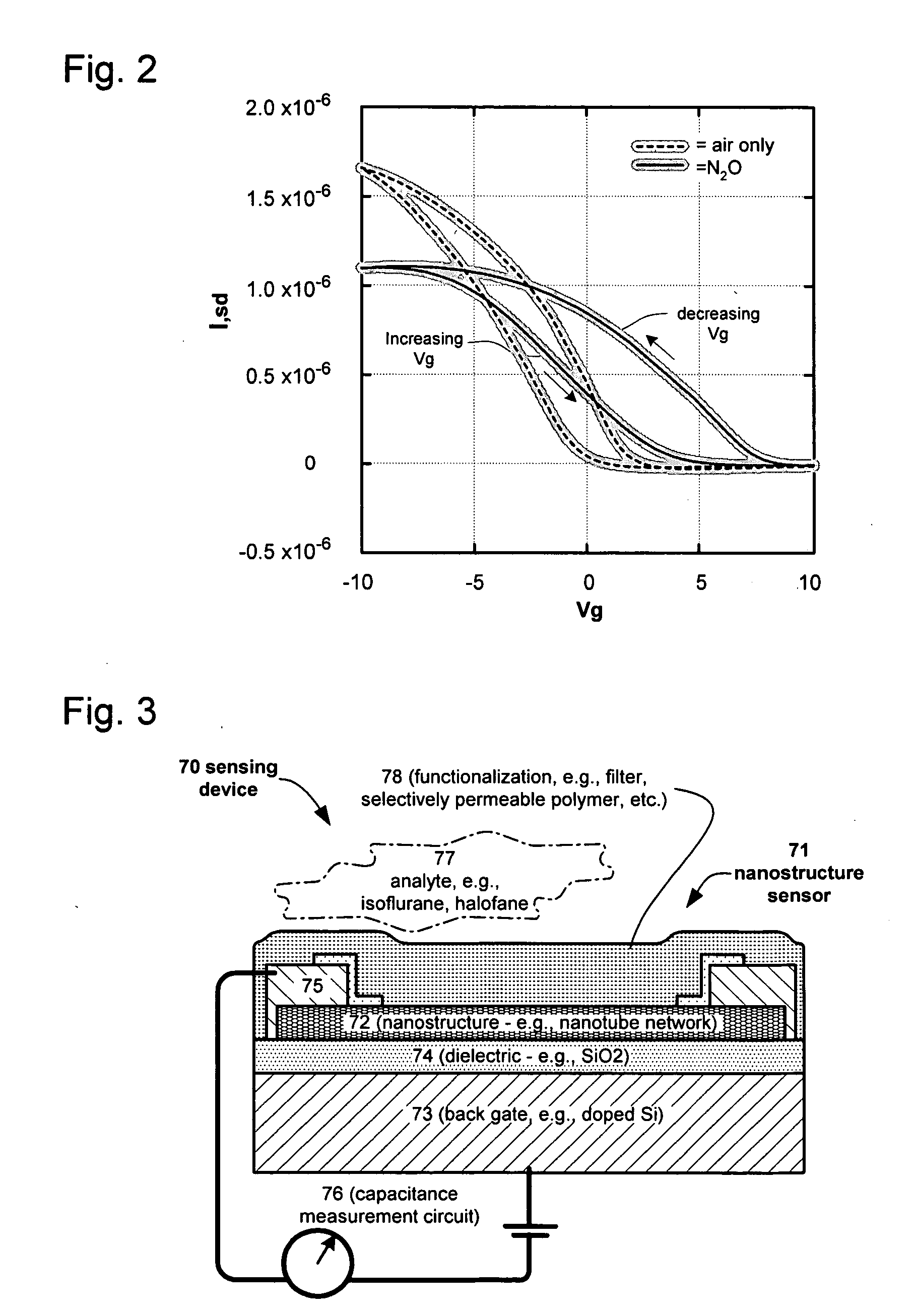
Nano-electronic sensors for chemical and biological analytes, including capacitance and bio-membrane devices
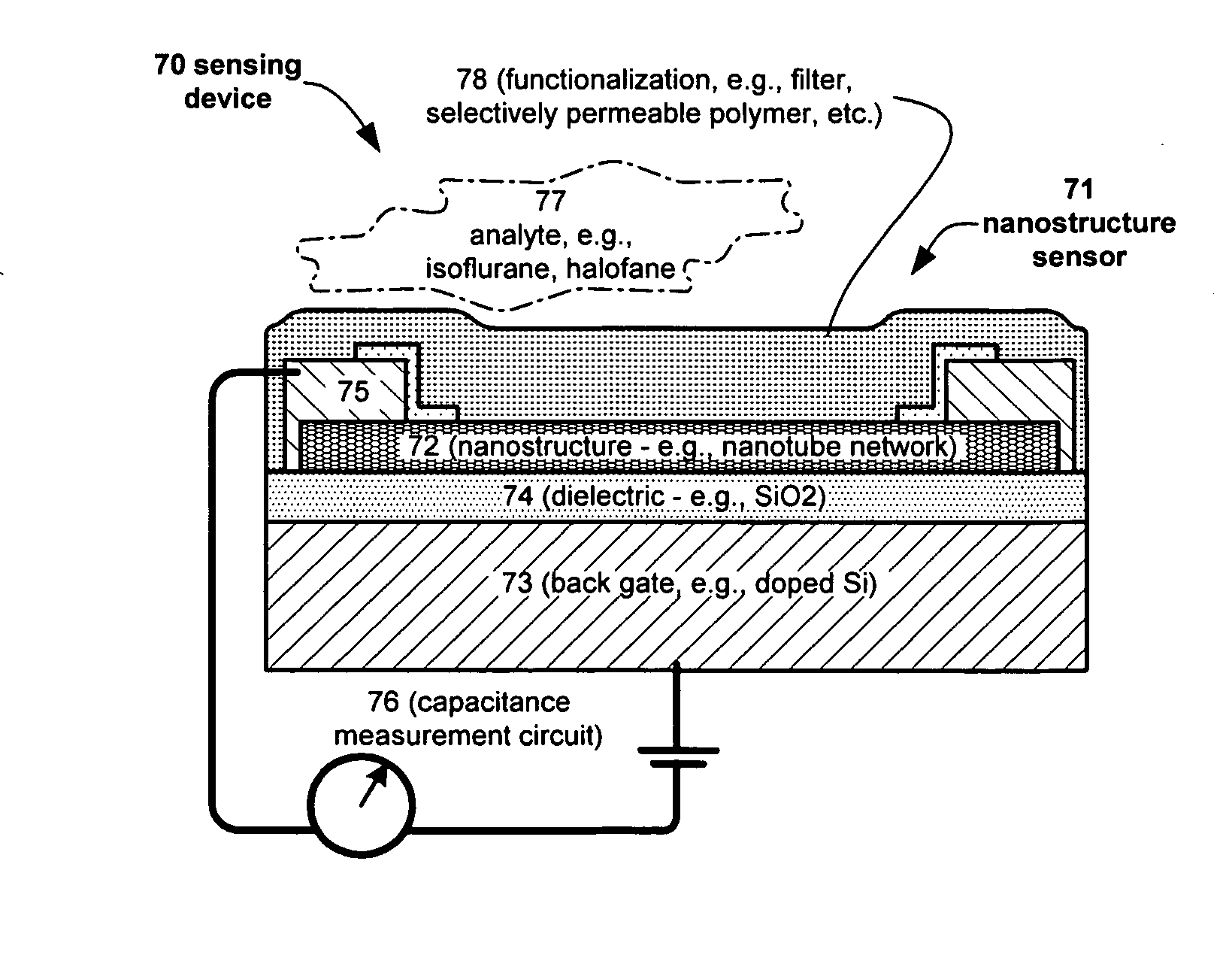
InactiveUS20070132043A1Enhanced signalSmall sizeNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesAnalyteCell membrane
Embodiments of nanoelectronic sensors are described, including sensors for detecting analytes inorganic gases, organic vapors, biomolecules, viruses and the like. A number of embodiments of capacitive sensors having alternative architectures are described. Particular examples include integrated cell membranes and membrane-like structures in nanoelectronic sensors.
Owner:NANOMIX
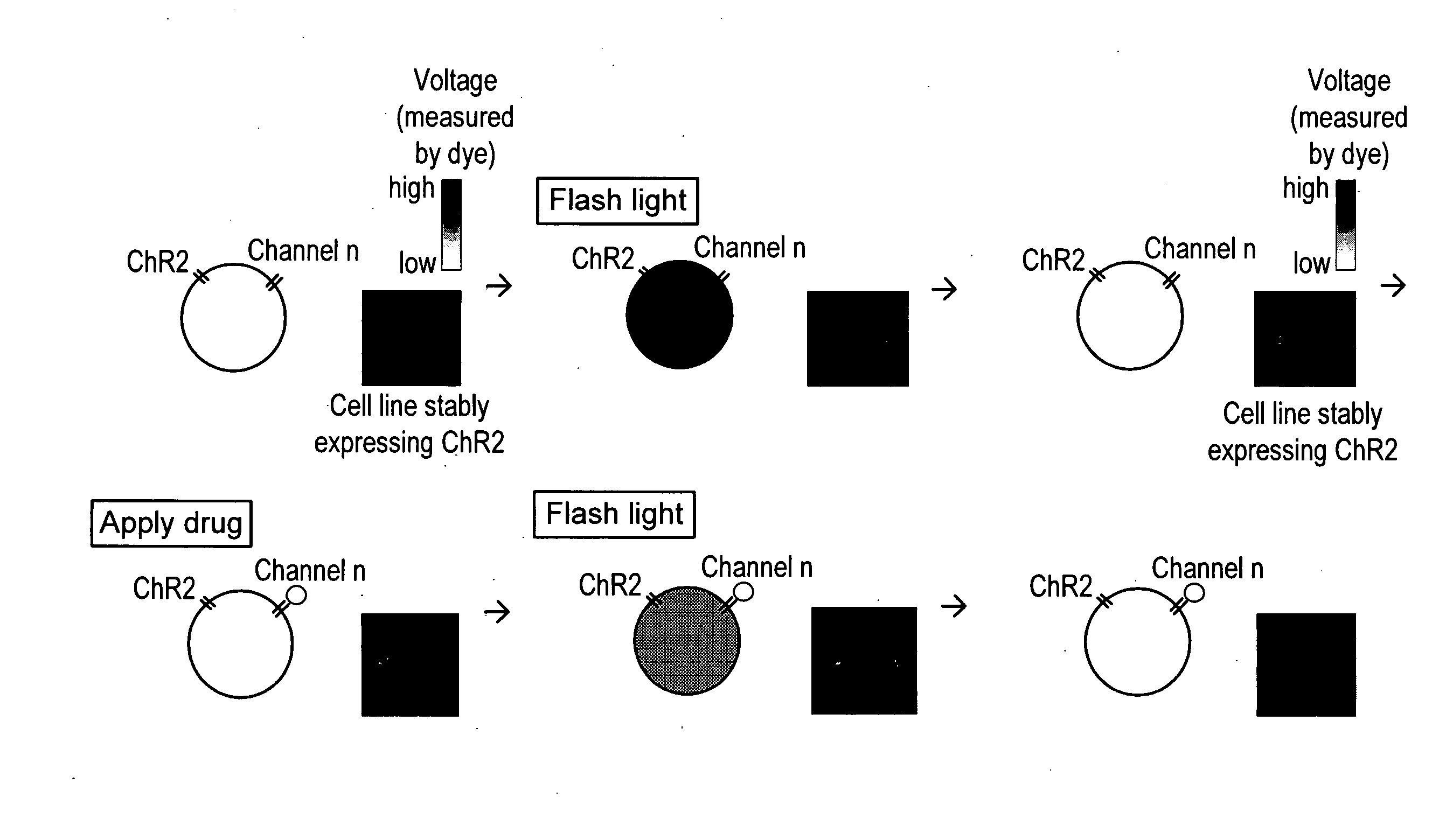
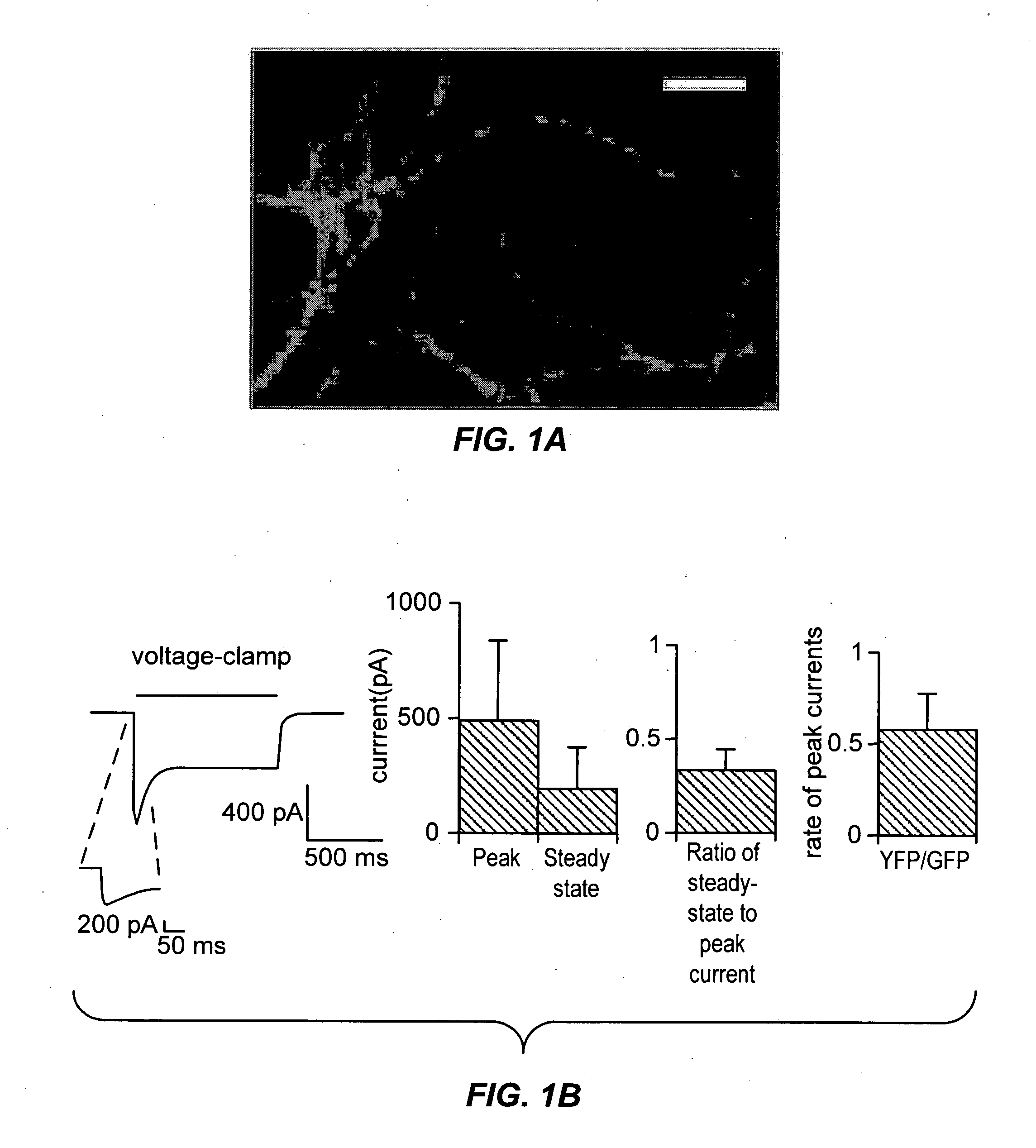
Light-activated cation channel and uses thereof
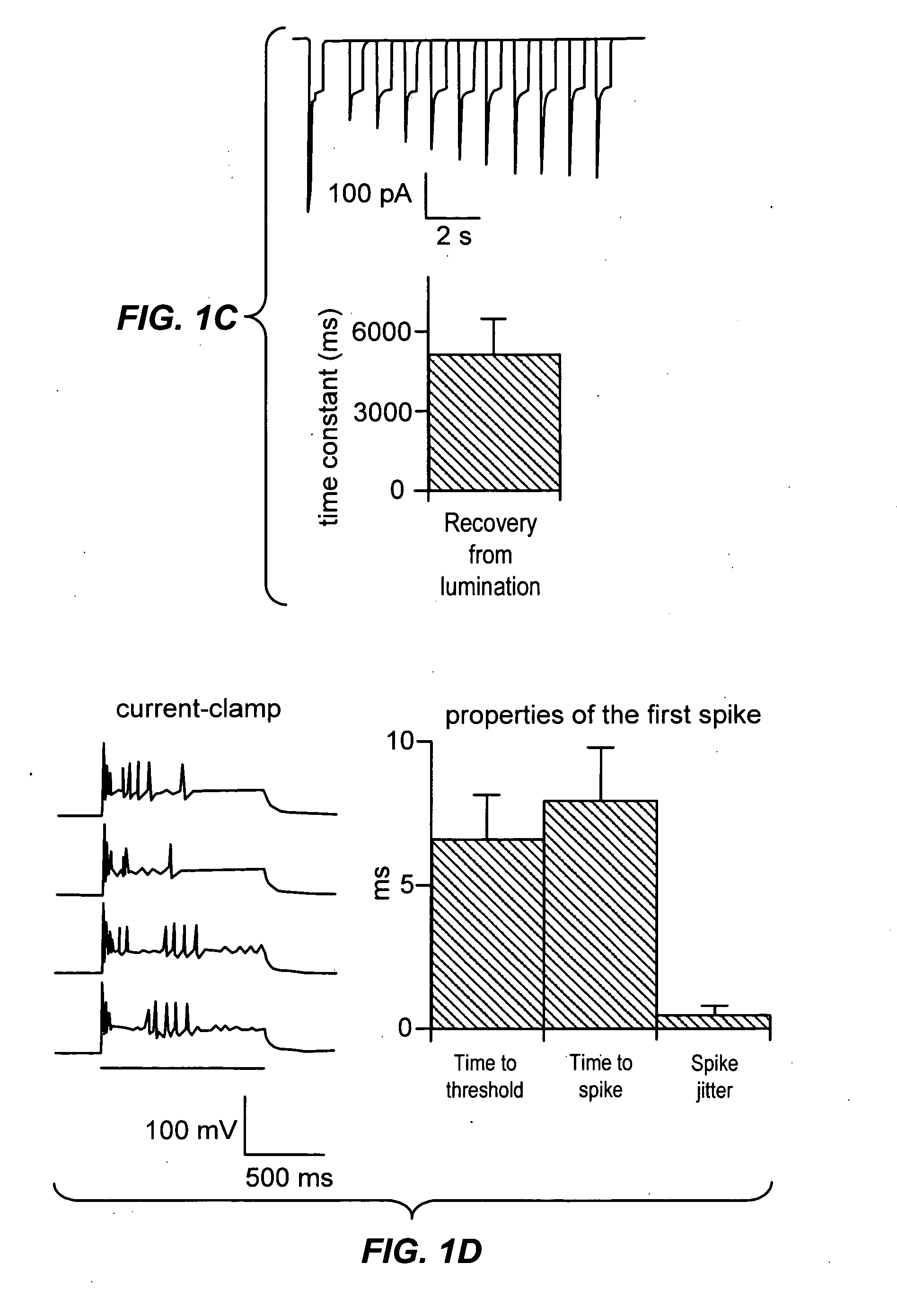
ActiveUS20070261127A1Improve abilitiesOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderCell membraneExcitable cell
The present invention provides compositions and methods for light-activated cation channel proteins and their uses within cell membranes and subcellular regions. The invention provides for proteins, nucleic acids, vectors and methods for genetically targeted expression of light-activated cation channels to specific cells or defined cell populations. In particular the invention provides millisecond-timescale temporal control of cation channels using moderate light intensities in cells, cell lines, transgenic animals, and humans. The invention provides for optically generating electrical spikes in nerve cells and other excitable cells useful for driving neuronal networks, drug screening, and therapy.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Cell viability detection using electrical measurements
InactiveUS6927049B2Quantitative measurementEnhanced informationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectricityCell membrane
A method of determining information about cell viability and other characteristics relating to cell membrane permeability is disclosed. The method involves determining the effect of a cell on current flow and relating that effect to a known standard which standard may be a known healthy cell and thereby deducing the viability of the cell being tested. The cells being tested can be subjected to different environmental conditions such as surrounding chemicals, temperature, pH and pressure to determine the effects of such conditions on cell viability and / or cell permeability. The cell being tested can be in a cell suspension, grown on s ubstarte, in tissue in vitro or in tissue in vivo. The method provides substantially instantaneous results and need not include the use of dyes or other markers.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Controlled electroporation and mass transfer across cell membranes
InactiveUS20060121610A1High levelImprove efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsControl mannerCell membrane
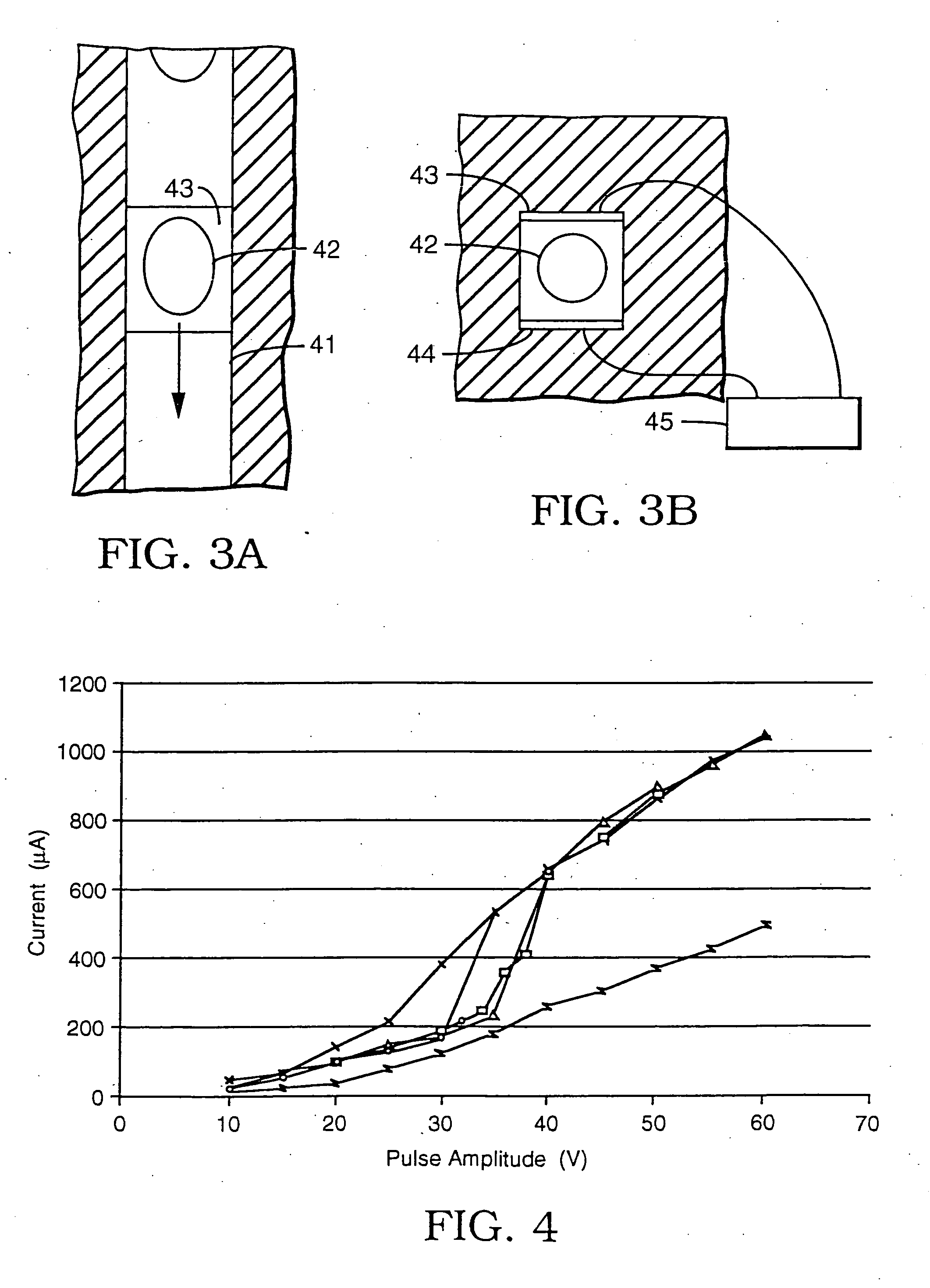
Electroporation is performed in a controlled manner in either individual or multiple biological cells or biological tissue by monitoring the electrical impedance, defined herein as the ratio of current to voltage in the electroporation cell. The impedance detects the onset of electroporation in the biological cell(s), and this information is used to control the intensity and duration of the voltage to assure that electroporation has occurred without destroying the cell(s). This is applicable to electroporation in general. In addition, a particular method and apparatus are disclosed in which electroporation and / or mass transfer across a cell membrane are accomplished by securing a cell across an opening in a barrier between two chambers such that the cell closes the opening. The barrier is either electrically insulating, impermeable to the solute, or both, depending on whether pore formation, diffusive transport of the solute across the membrane, or both are sought. Electroporation is achieved by applying a voltage between the two chambers, and diffusive transport is achieved either by a difference in solute concentration between the liquids surrounding the cell and the cell interior or by a differential in concentration between the two chambers themselves. Electric current and diffusive transport are restricted to a flow path that passes through the opening.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Substance specific to human PD-1
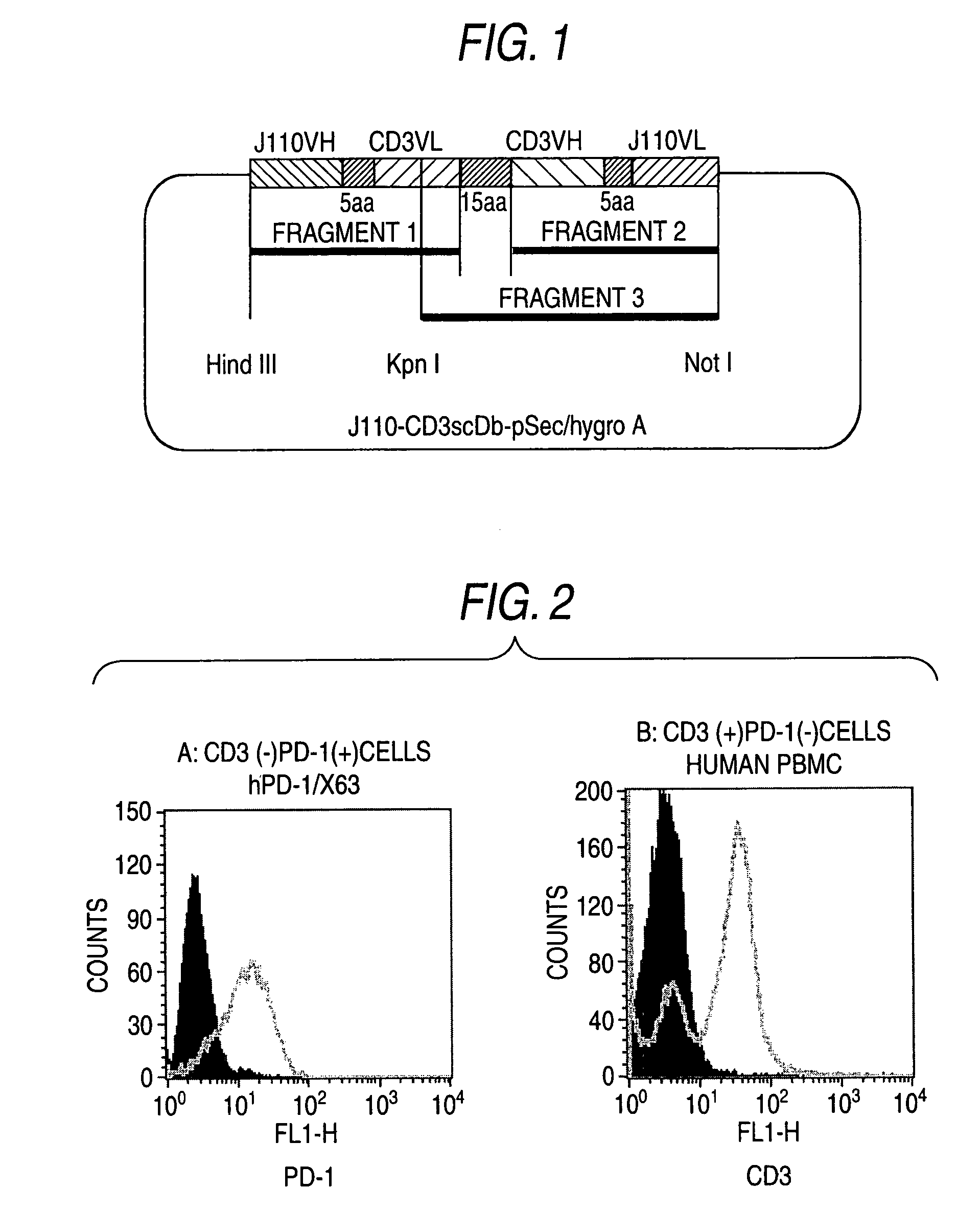
The present invention relates to a substance specific to human PD-1 comprising a part that recognizes human PD-1, a part that recognizes a membrane protein in cell membrane of human PD-1-expressing cells, and linkers. Since the substance specific to human PD-1 selectively can recognize human PD-1 and a membrane protein on cell membrane of human PD-1-expressing cells and can transmit inhibitory signal of human PD-1, it is useful for therapy and / or prevention of diseases caused by immunopathy.
Owner:HONJO TASUKU +1
Light-activated cation channel and uses thereof
ActiveUS20070054319A1Improve abilitiesOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderCell membraneExcitable cell
The present invention provides compositions and methods for light-activated cation channel proteins and their uses within cell membranes and subcellular regions. The invention provides for proteins, nucleic acids, vectors and methods for genetically targeted expression of light-activated cation channels to specific cells or defined cell populations. In particular the invention provides millisecond-timescale temporal control of cation channels using moderate light intensities in cells, cell lines, transgenic animals, and humans. The invention provides for optically generating electrical spikes in nerve cells and other excitable cells useful for driving neuronal networks, drug screening, and therapy.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
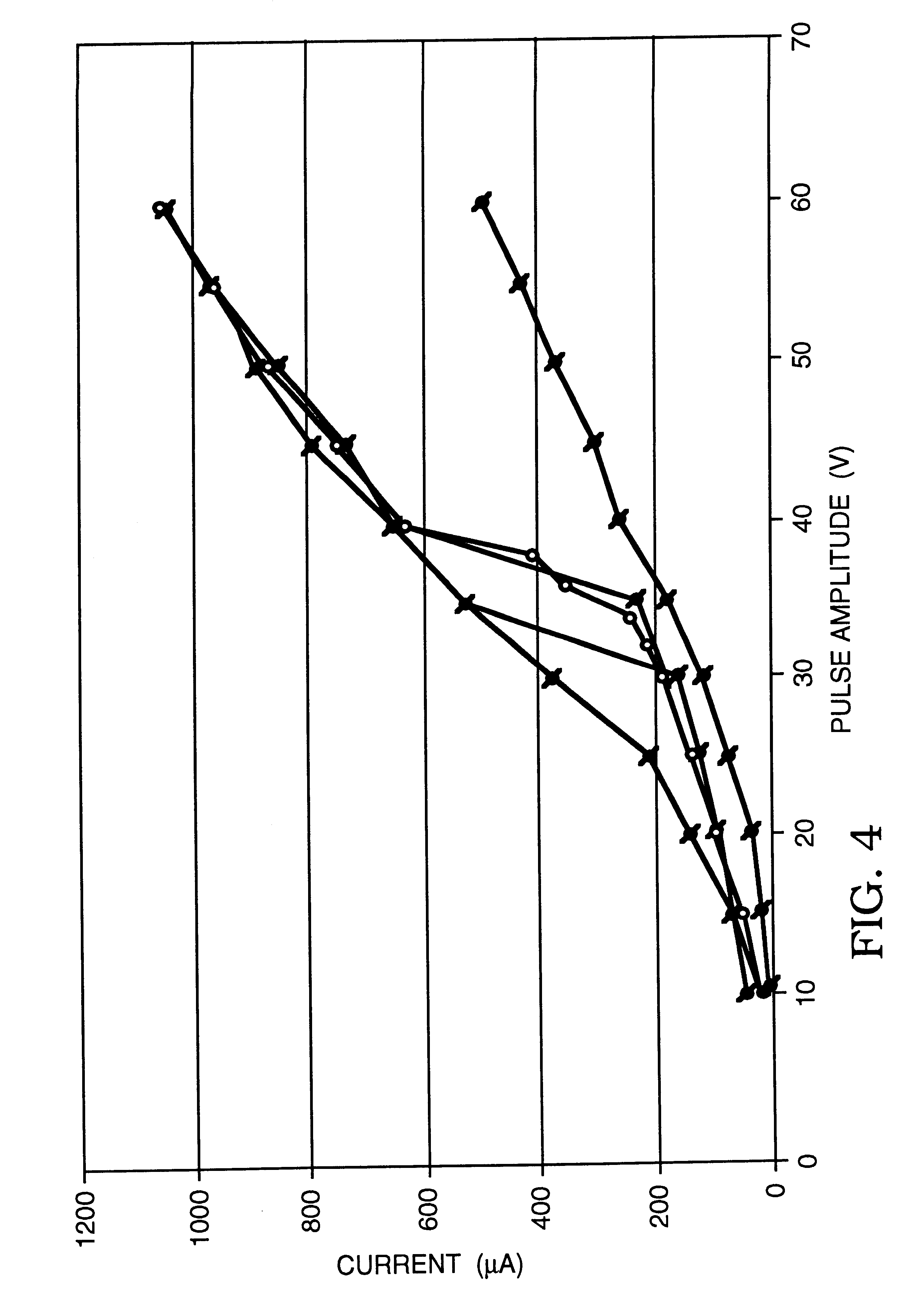
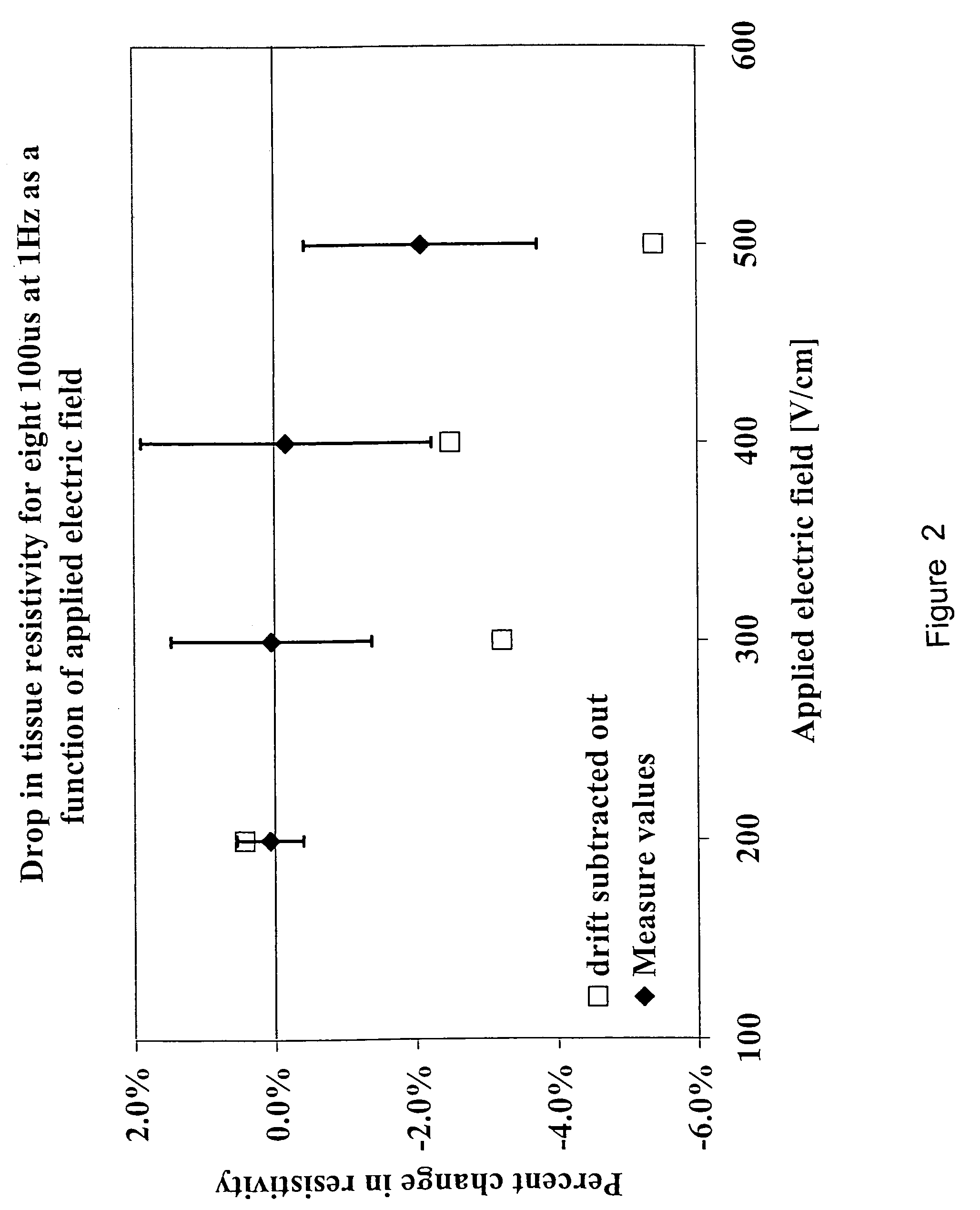
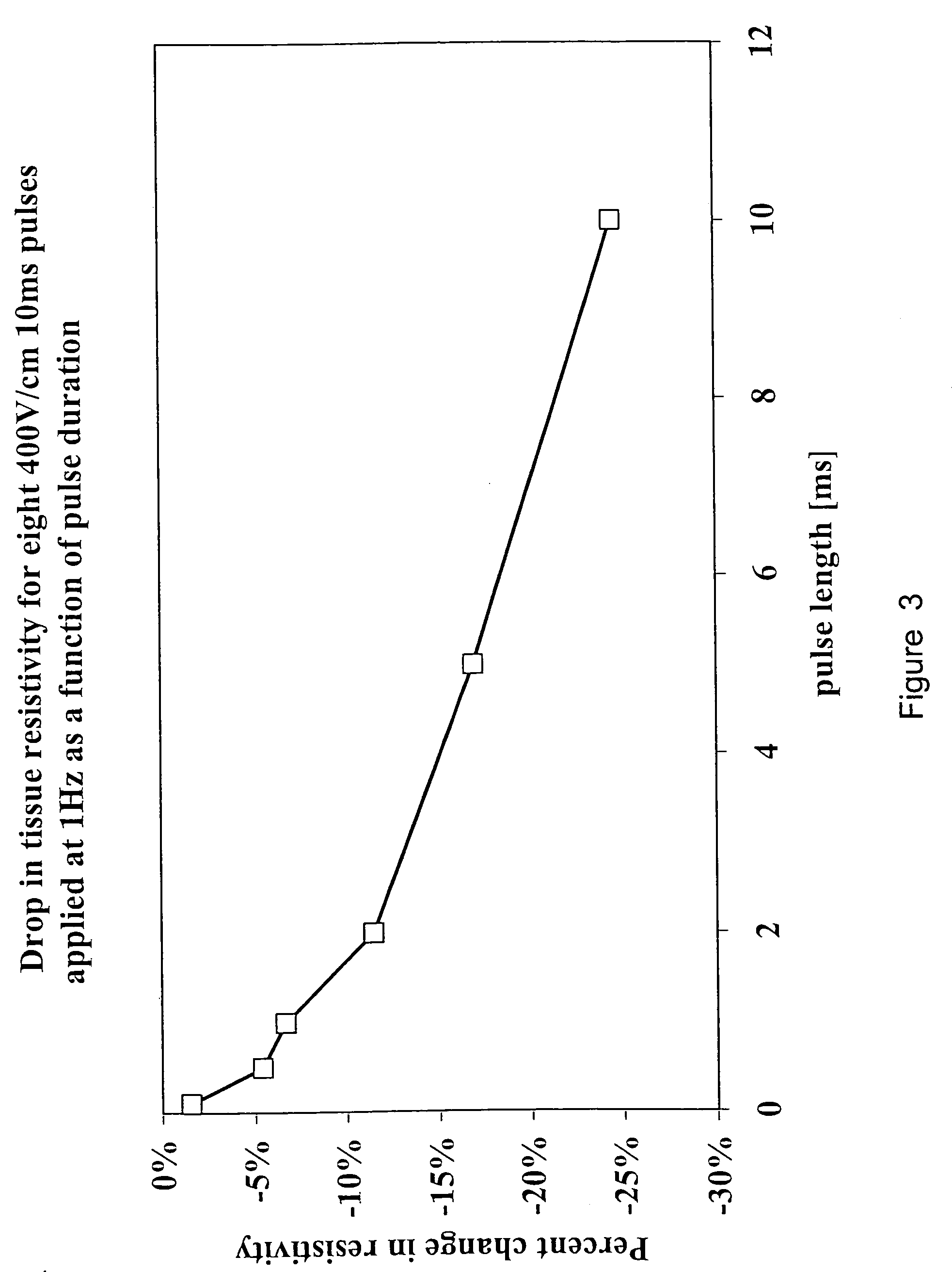
Electrical impedance tomography to control electroporation
InactiveUS6387671B1The right amountAvoid cell damageBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrotherapyElectrical resistance and conductanceElectricity
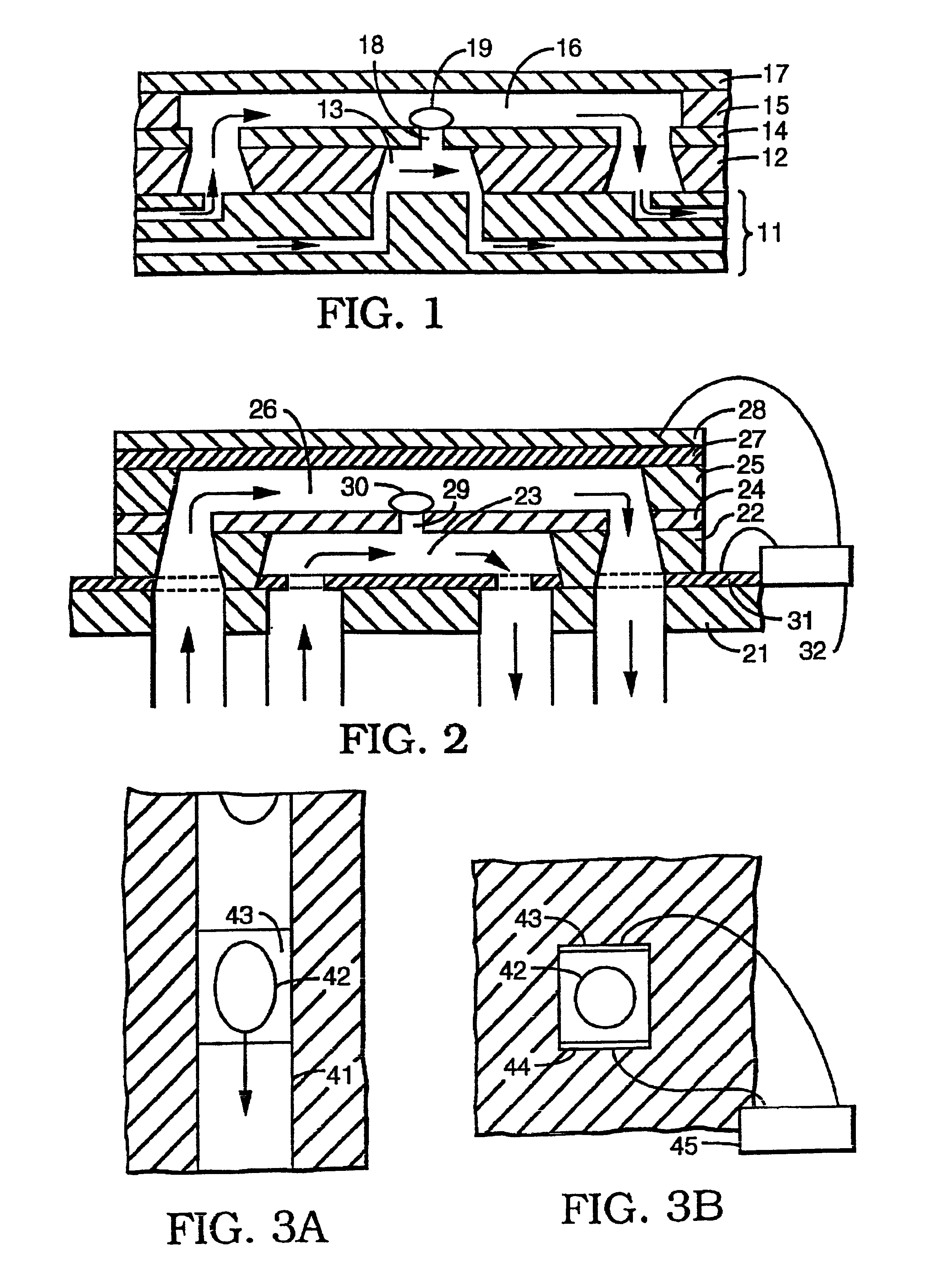
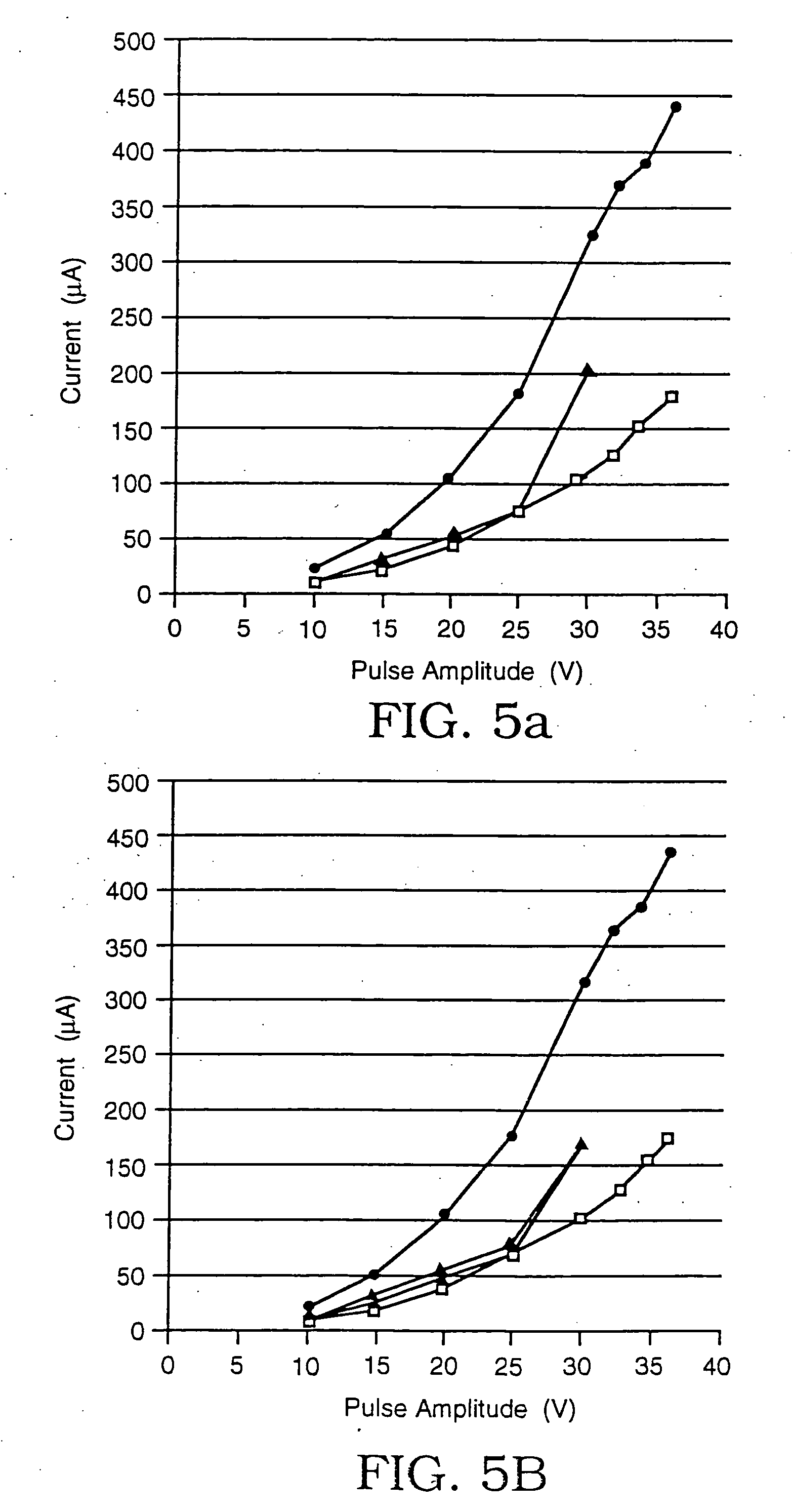
Images created by electrical impedance tomography (EIT) are used to adjust one or more electrical parameters and obtain a desired degree of electroporation of cells in tissue. The parameters include current, voltage and a combination thereof. The cells are subjected to conditions such that they become permeabilized but are preferably not subjected to conditions which result in irreversible pore formation and cell death. The electroporation can analyze cell membranes, diagnose tissues and the patient as well as to move materials into and out of cells in a controlled manner.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Tissue ablation with irreversible electroporation
ActiveUS20070043345A1High level of controlMinimize damageSurgical needlesInternal electrodesAbnormal tissue growthCell membrane
A new method for the ablation of undesirable tissue such as cells of a cancerous or non-cancerous tumor is disclosed. It involves the placement of electrodes into or near the vicinity of the undesirable tissue through the application of electrical pulses causing irreversible electroporation of the cells throughout the entire area of the undesirable tissue. The electric pulses irreversibly permeate the cell membranes, thereby invoking cell death. The irreversibly permeabilized cells are left in situ and are removed by the body immune system. The amount of tissue ablation achievable through the use of irreversible electroporation without inducing thermal damage is considerable.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
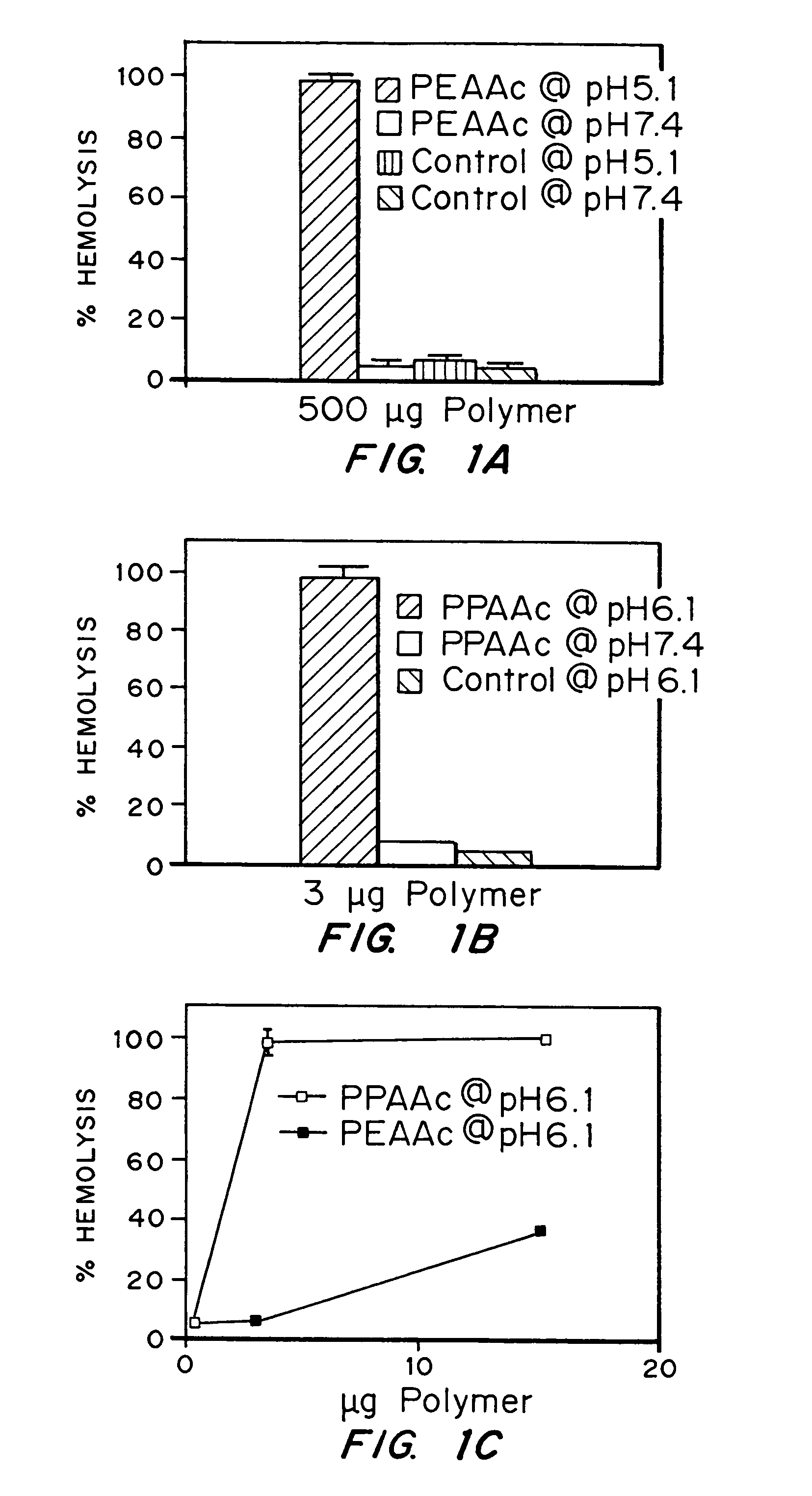
Enhanced transport using membrane disruptive agents
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON +1
Controlled electroporation and mass transfer across cell membranes in tissue
InactiveUS20050282284A1High levelImprove efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrotherapyBiological cellElectricity
Electroporation is performed in a controlled manner in individual and multiple biological cells present in biological tissue by monitoring the electrical impedance, defined herein as the ratio of current to voltage in the electroporation cell. The impedance detects the onset of electroporation in the biological cell(s), and this information is used to control the intensity and duration of the voltage to assure that electroporation has occurred without destroying the cell(s). This is applicable to electroporation in general.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Enhanced transport using membrane disruptive agents
InactiveUS7737108B1Prevent uptakePrevent clearanceBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsMetaboliteCell layer
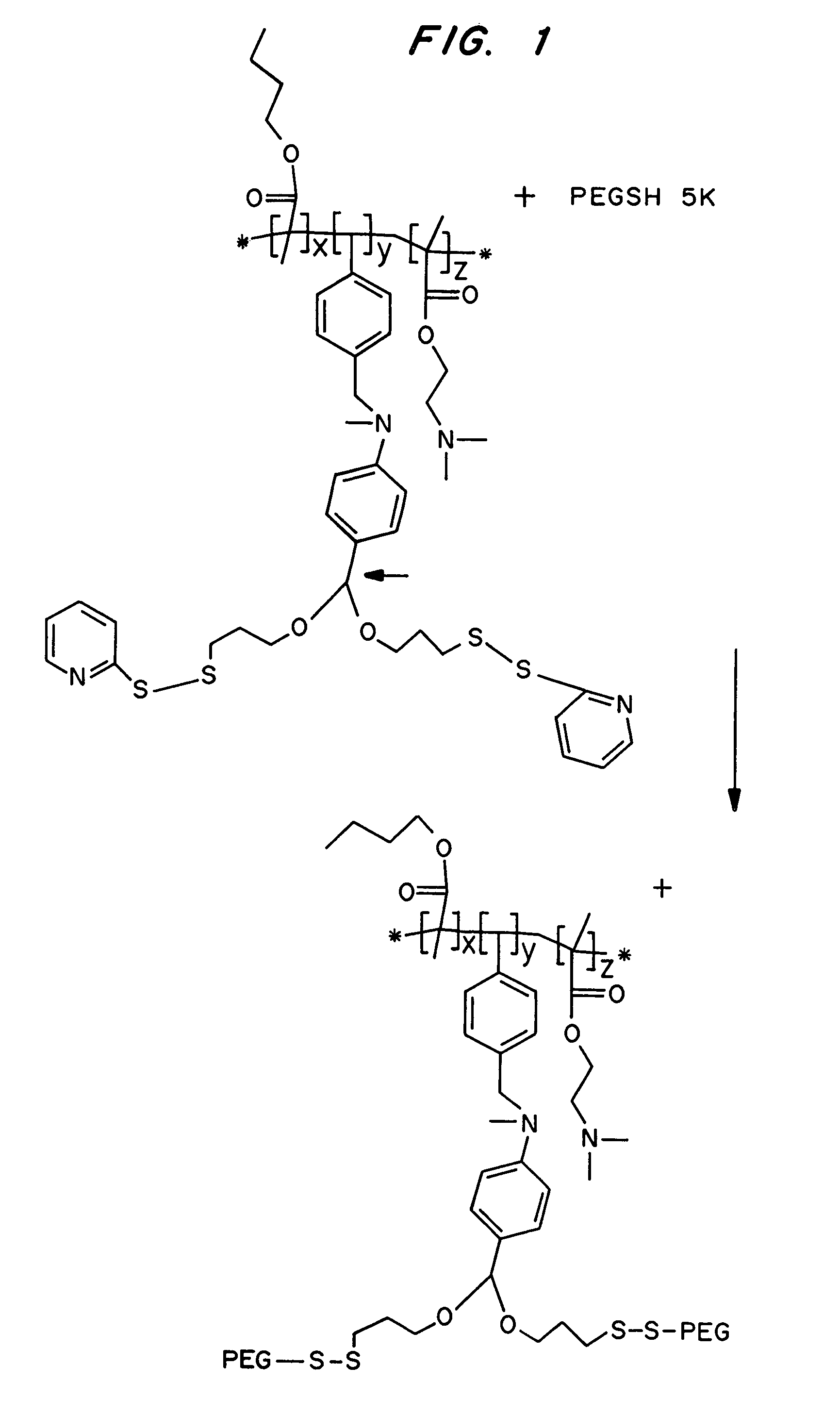
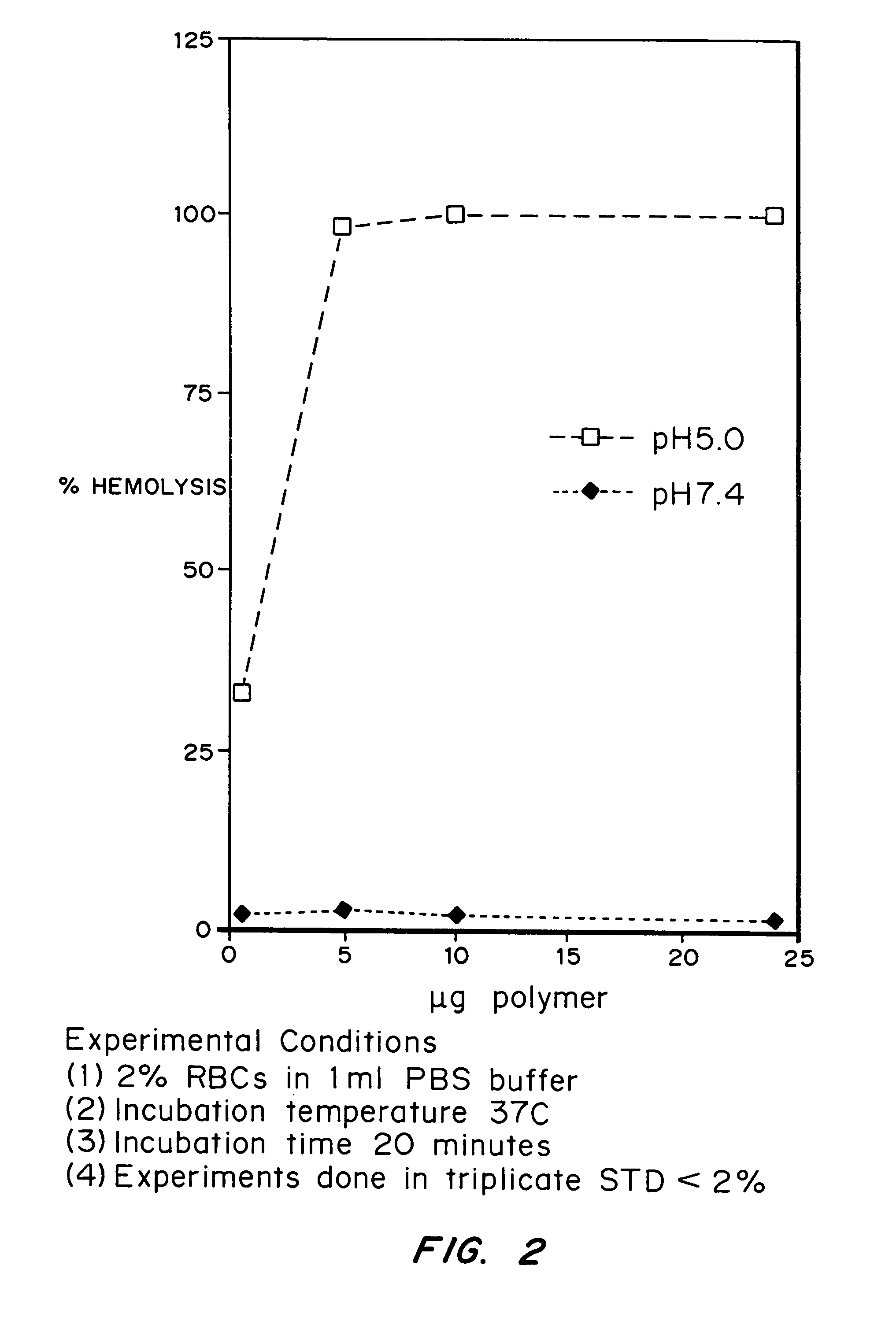
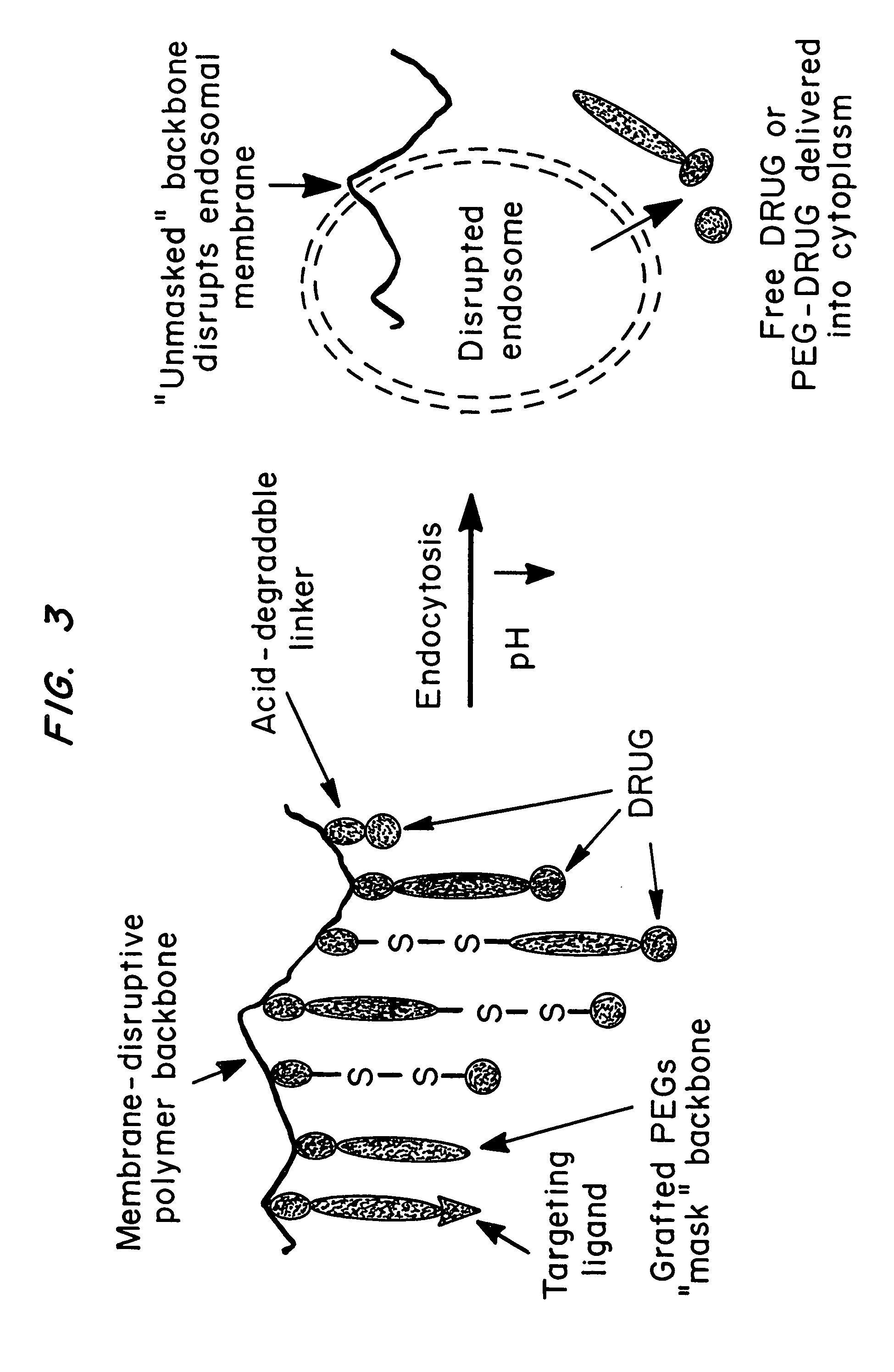
Compositions and methods for transport or release of therapeutic and diagnostic agents or metabolites or other analytes from cells, compartments within cells, or through cell layers or barriers are described. The compositions include a membrane barrier transport enhancing agent and are usually administered in combination with an enhancer and / or exposure to stimuli to effect disruption or altered permeability, transport or release. In a preferred embodiment, the compositions include compounds which disrupt endosomal membranes in response to the low pH in the endosomes but which are relatively inactive toward cell membranes (at physiologic pH, but can become active toward cell membranes if the environment is acidified below ca. pH 6.8), coupled directly or indirectly to a therapeutic or diagnostic agent. Other disruptive agents can also be used, responsive to stimuli and / or enhancers other than pH, such as light, electrical stimuli, electromagnetic stimuli, ultrasound, temperature, or combinations thereof. The compounds can be coupled by ionic, covalent or H bonds to an agent to be delivered or to a ligand which forms a complex with the agent to be delivered. Agents to be delivered can be therapeutic and / or diagnostic agents. Treatments which enhance delivery such as ultrasound, iontopheresis, and / or electrophereis can also be used with the disrupting agents.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
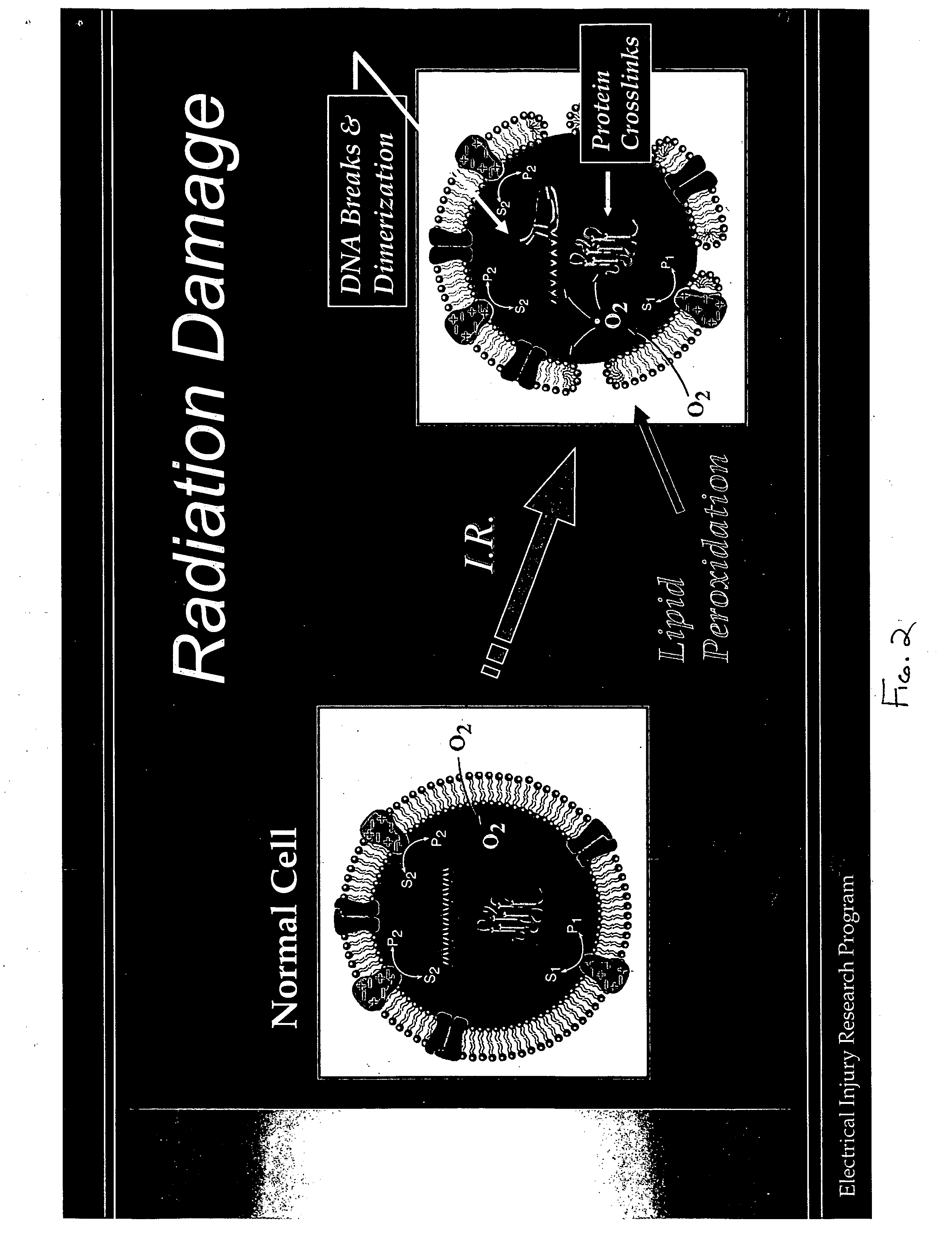
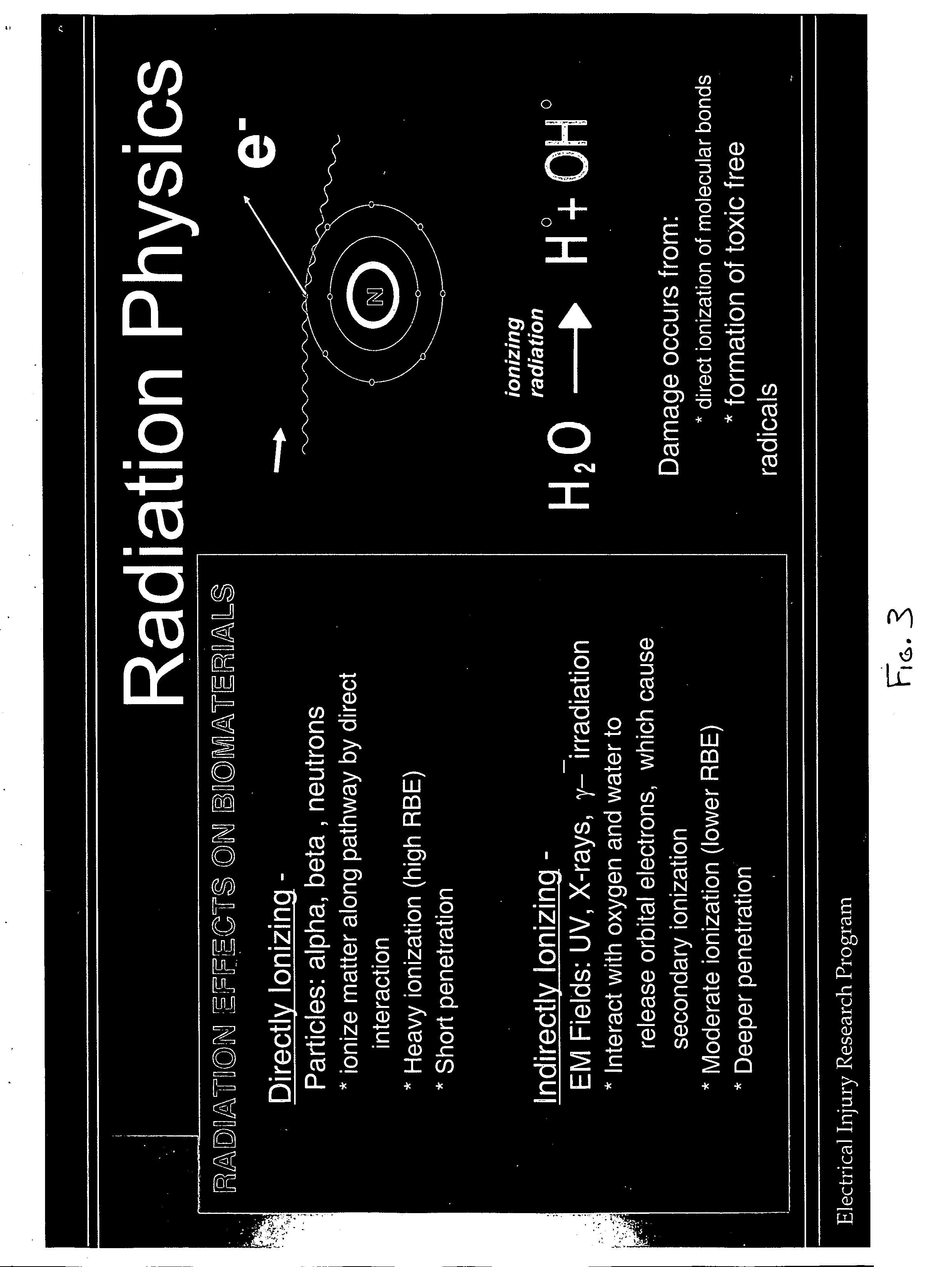
Methods and compositions for treatment of free radical injury
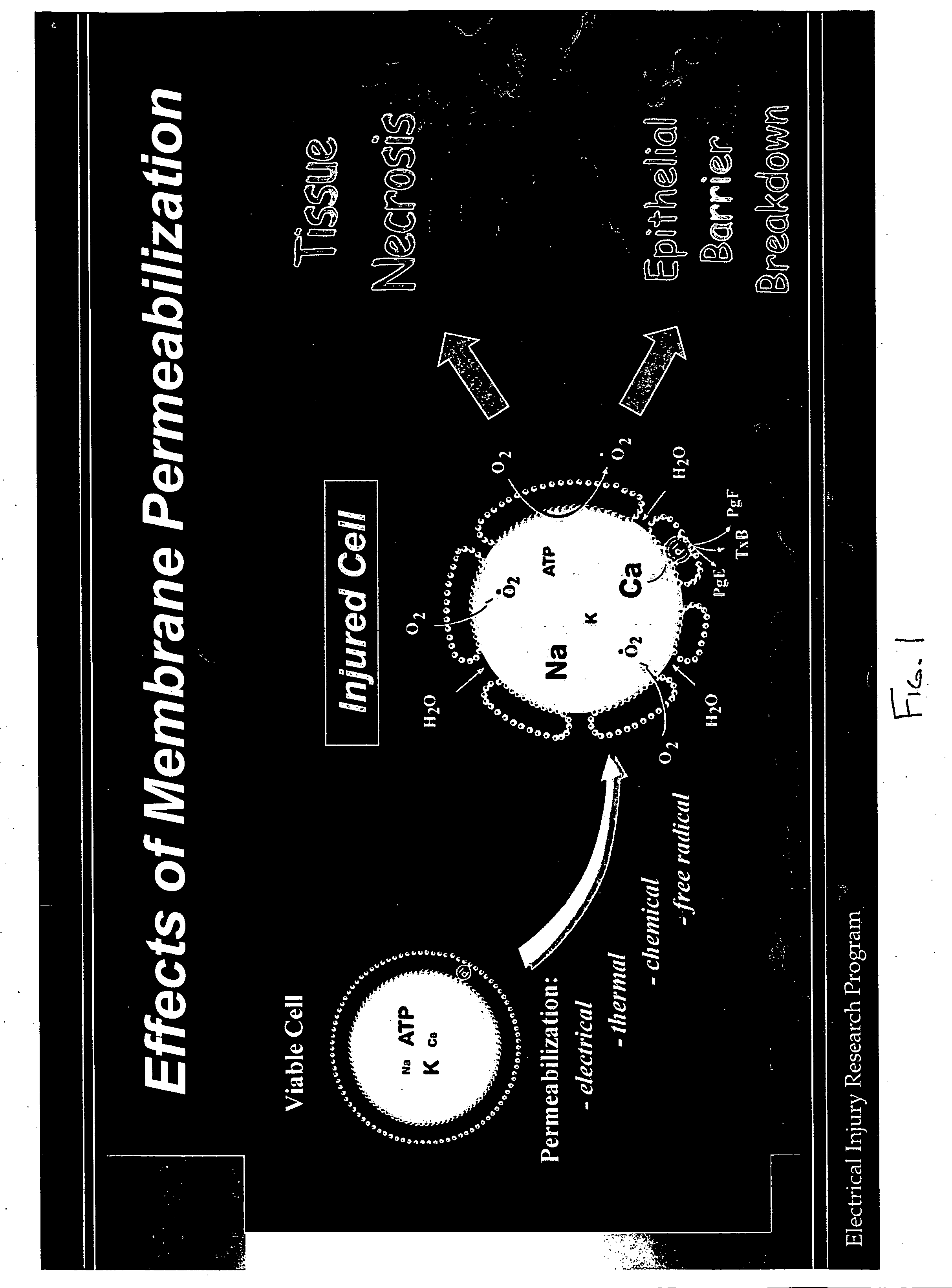
InactiveUS20060121016A1Reduction of tissue level oxidative damage toBiocideDipeptide ingredientsAntioxidantCell membrane
Therapeutic methods and compositions useful for the prevention and / or treatment of cellular membrane damage leading to or resulting from peroxidation of the cellular membrane and a breakdown of the barrier function of the cellular membrane. A therapeutic composition includes a combination of a membrane sealing sealing surfactant and a cofactor treatment consisting of an antioxidant and a cellular energy store. To affect this goal, the permeability of damaged cellular membranes is reestablished by the membrane sealing surfactant, effectively “sealing” the injured membranes. To facilitate rapid tissue recovery, cellular energy levels can be reestablished through addition of a cellular energy source such as, for example, MgCl2-ATP which, serves a further dual benefit of improving the cellular ion balance. Addition of an antioxidant eliminates the generation of Reactive Oxygen intermediates and enhances the metabolism of free radicals.
Owner:MAROON BIOTECH
Controlled electroporation and mass transfer across cell membranes
InactiveUS6403348B1The right amountAvoid cell damageBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrotherapyControl mannerCell membrane
Electroporation is performed in a controlled manner in either individual or multiple biological cells or biological tissue by monitoring the electrical impedance, defined herein as the ratio of current to voltage in the electroporation cell. The impedance detects the onset of electroporation in the biological cell(s), and this information is used to control the intensity and duration of the voltage to assure that electroporation has occurred without destroying the cell(s). This is applicable to electroporation in general. In addition, a particular method and apparatus are disclosed in which electroporation and / or mass transfer across a cell membrane are accomplished by securing a cell across an opening in a barrier between two chambers such that the cell closes the opening. The barrier is either electrically insulating, impermeable to the solute, or both, depending on whether pore formation, diffusive transport of the solute across the membrane, or both are sought. Electroporation is achieved by applying a voltage between the two chambers, and diffusive transport is achieved either by a difference in solute concentration between the liquids surrounding the cell and the cell interior or by a differential in concentration between the two chambers themselves. Electric current and diffusive transport are restricted to a flow path that passes through the opening.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
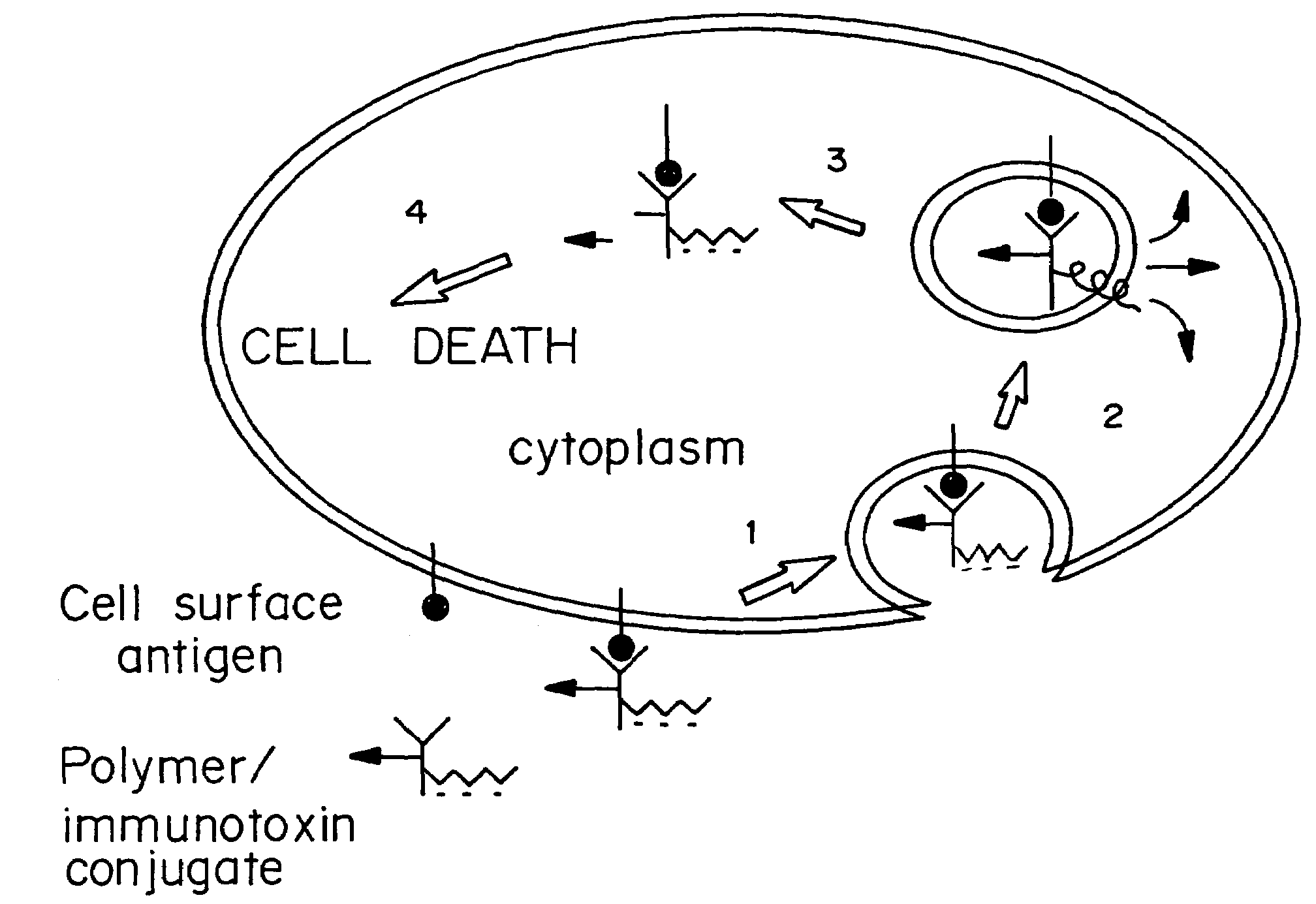
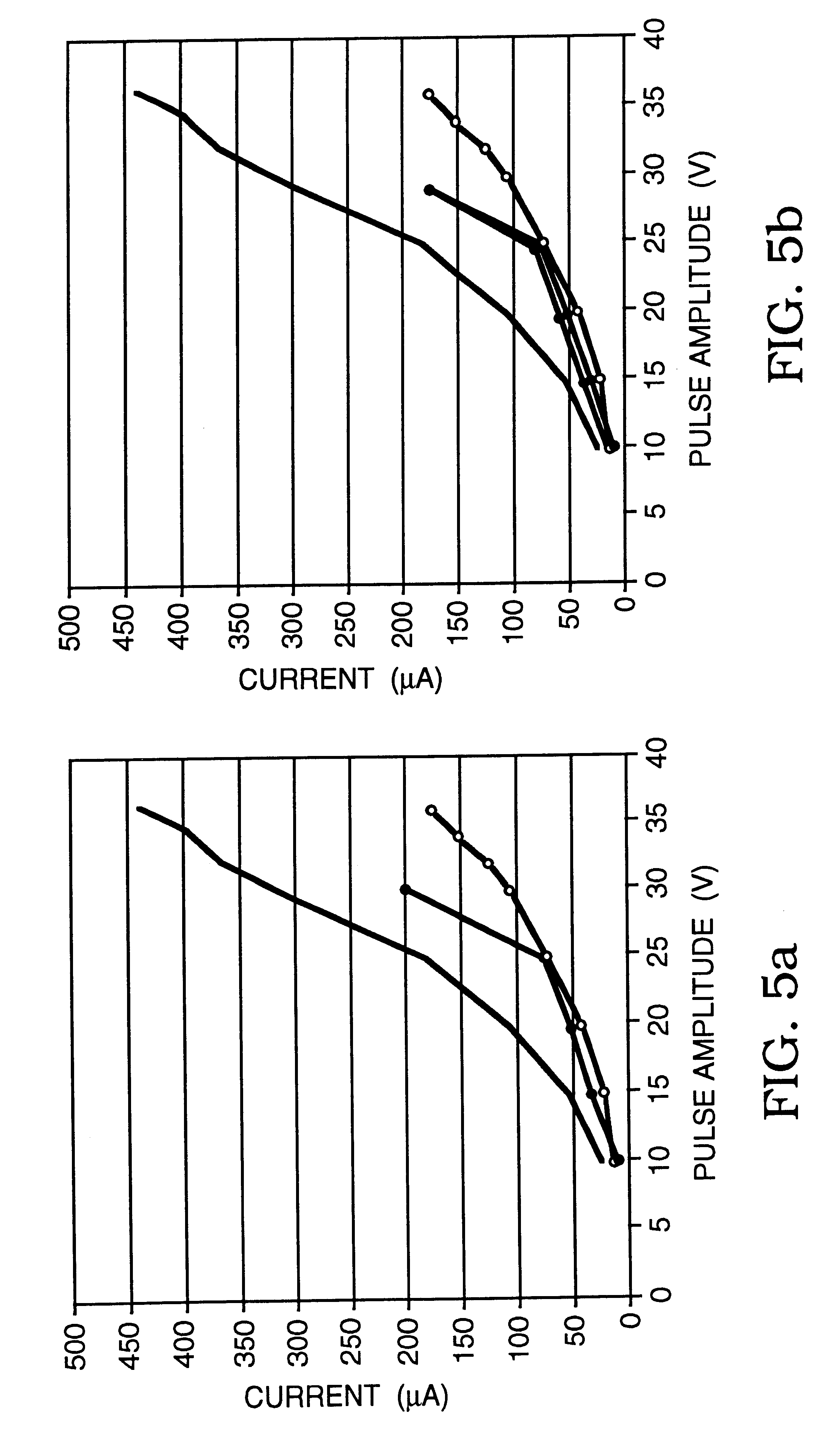
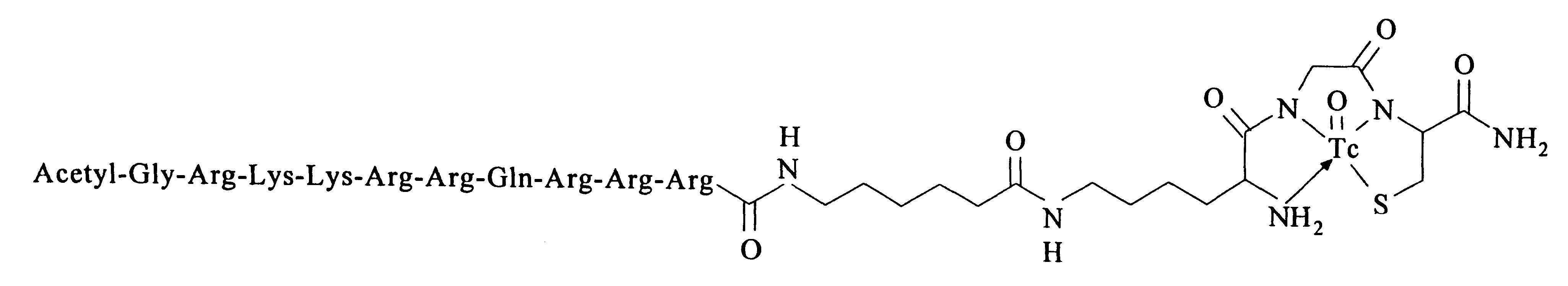
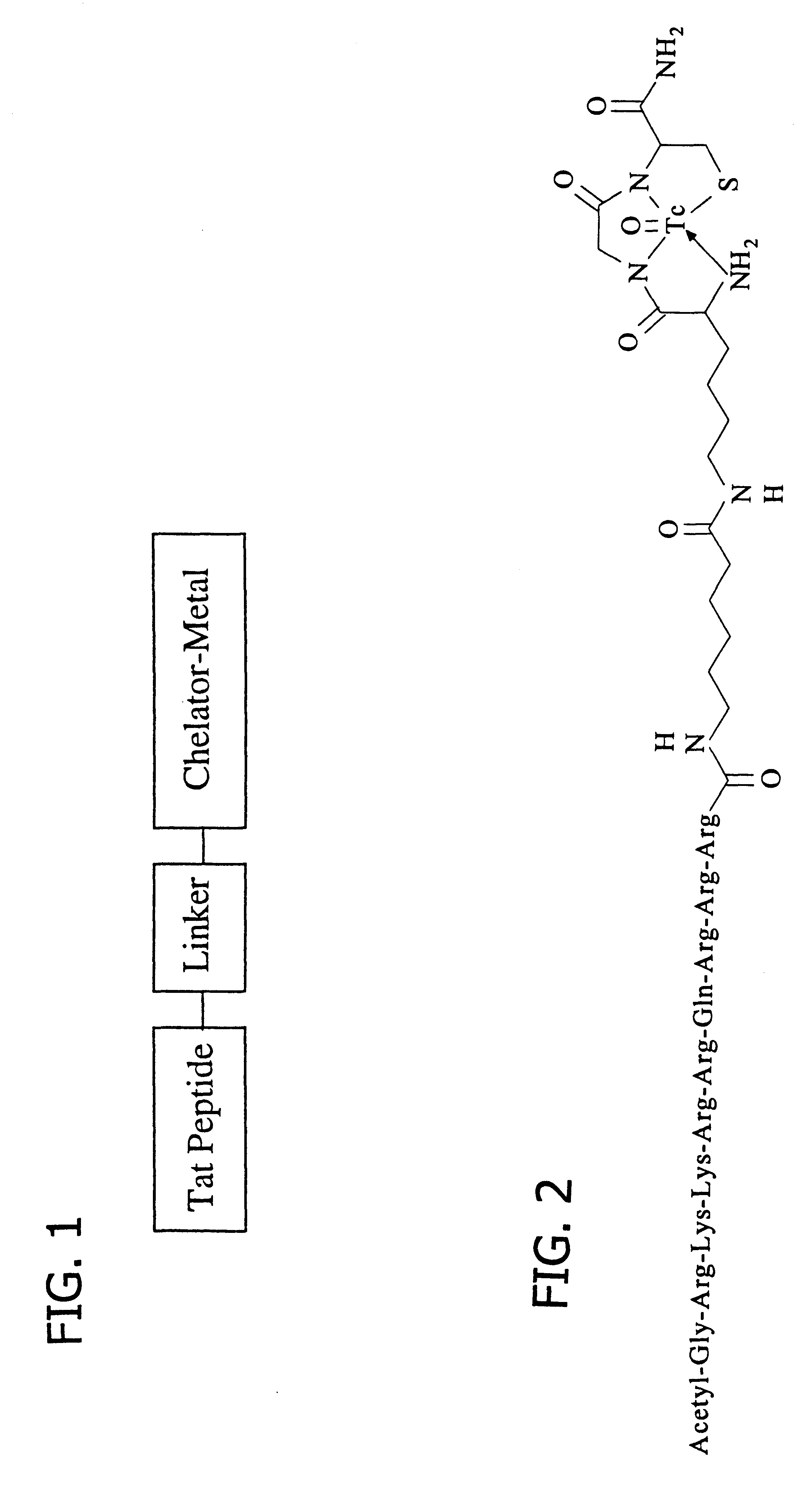
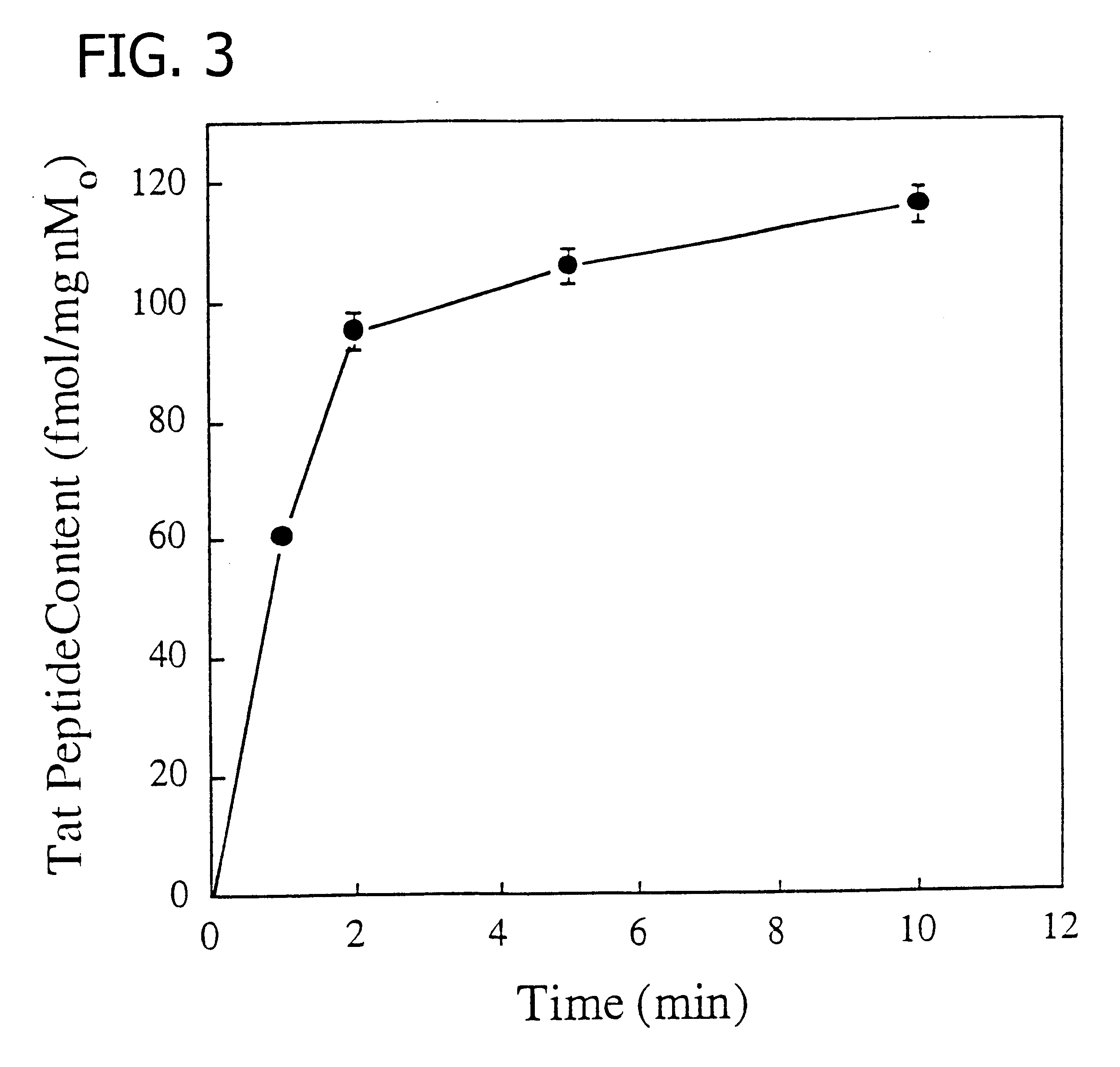
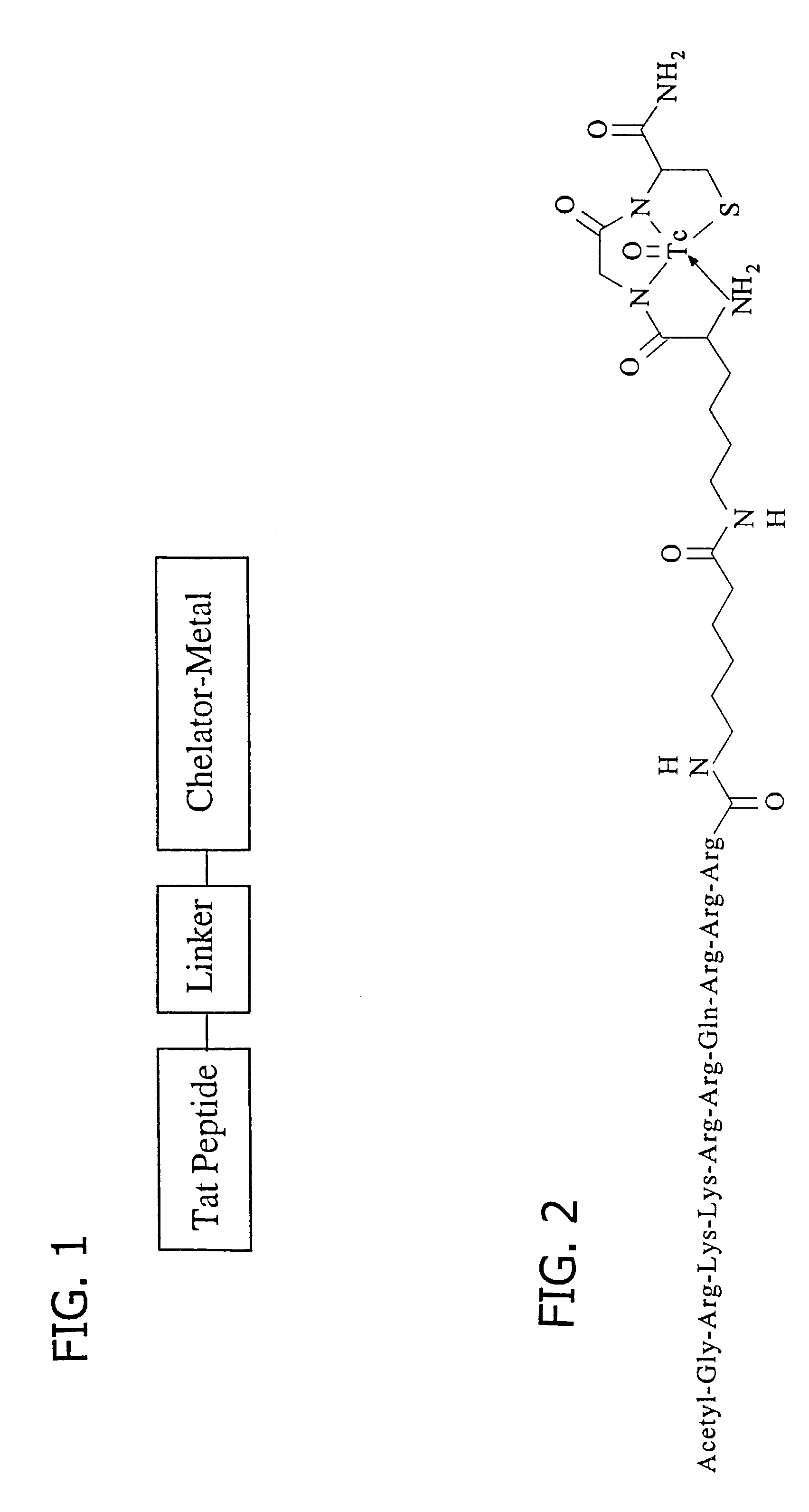
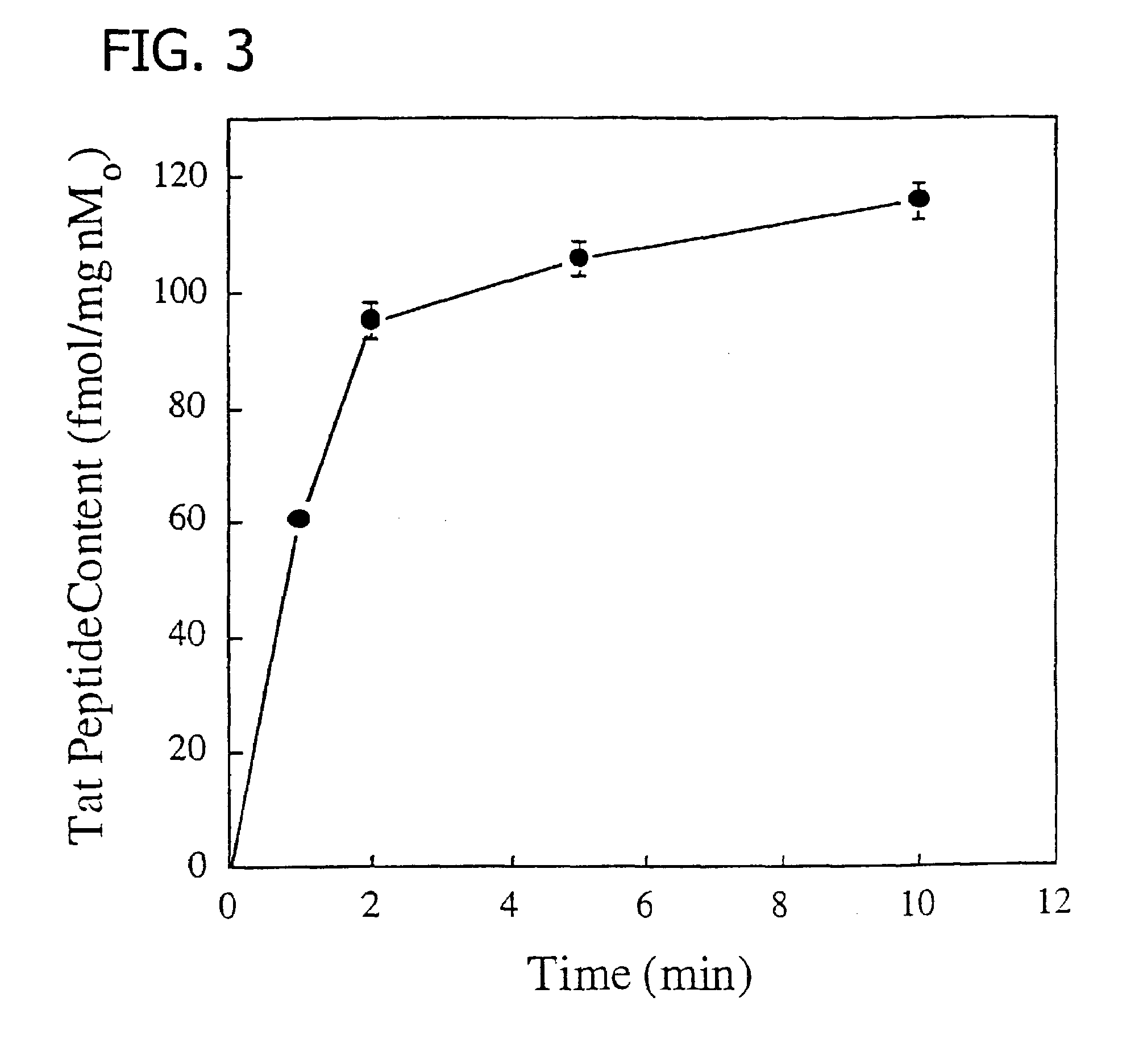
Membrane-permeant peptide complexes for medical imaging, diagnostics, and pharmaceutical therapy
Methods and compositions for medical imaging, evaluating intracellular processes and components, radiotherapy of intracellular targets, and drug delivery by the use of novel cell membrane-permeant peptide conjugate coordination and covalent complexes having target cell specificity are provided. Kits for conjugating radionuclides and other metals to peptide coordination complexes are also provided.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Controlled electroporation and mass transfer across cell membranes in tissue
InactiveUS7053063B2High levelImprove efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrical resistance and conductanceBiological cell
Electroporation is performed in a controlled manner in individual and multiple biological cells present in biological tissue by monitoring the electrical impedance, defined herein as the ratio of current to voltage in the electroporation cell. The impedance detects the onset of electroporation in the biological cell(s), and this information is used to control the intensity and duration of the voltage to assure that electroporation has occurred without destroying the cell(s). This is applicable to electroporation in general.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
System and method for transdermal delivery
InactiveUS20060036209A1Improve transdermal deliveryReduce deliveryElectrotherapyMicroneedlesElectricityActive agent
A system and method for transdermally delivering a biologically active agent comprising one or more electrodes having stratum corneum-piercing projections and a circuit that delivers an electrical signal to the electrodes to electroporate a cell membrane. Preferably, the system is configured to generate homogeneous electrical fields and, more preferably, to generate spherically or semispherically symmetrical electric fields. Methods of the invention include applying a first electric signal to facilitate transdermal transport of the agent and applying a second electric signal to facilitate intracellular transport of the agent.
Owner:ALZA CORP
4-substituted piperidine derivatives
ActiveUS7572913B2Promote neurite outgrowthPotential curative effectAntibacterial agentsBiocideDiseaseCell membrane
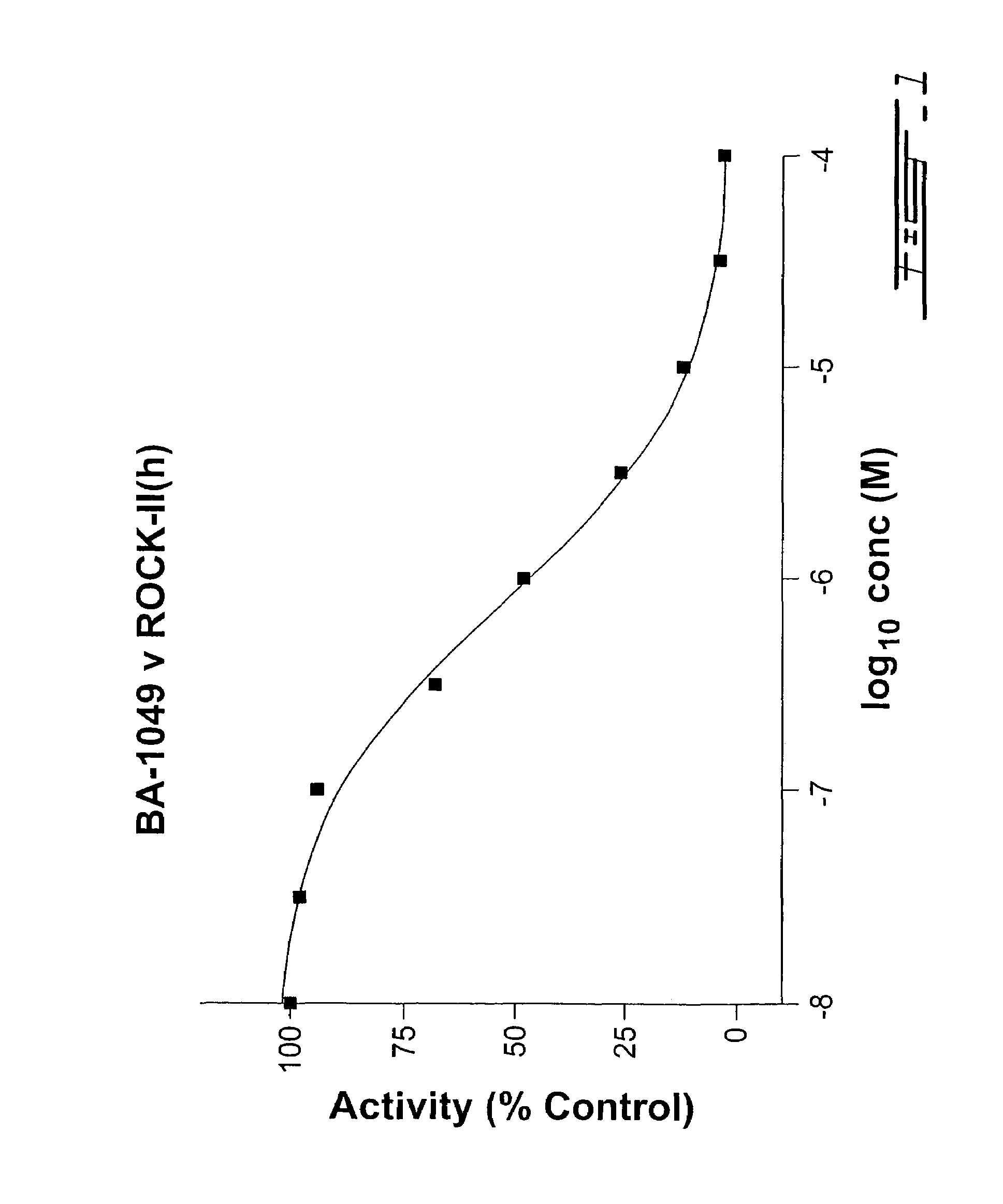
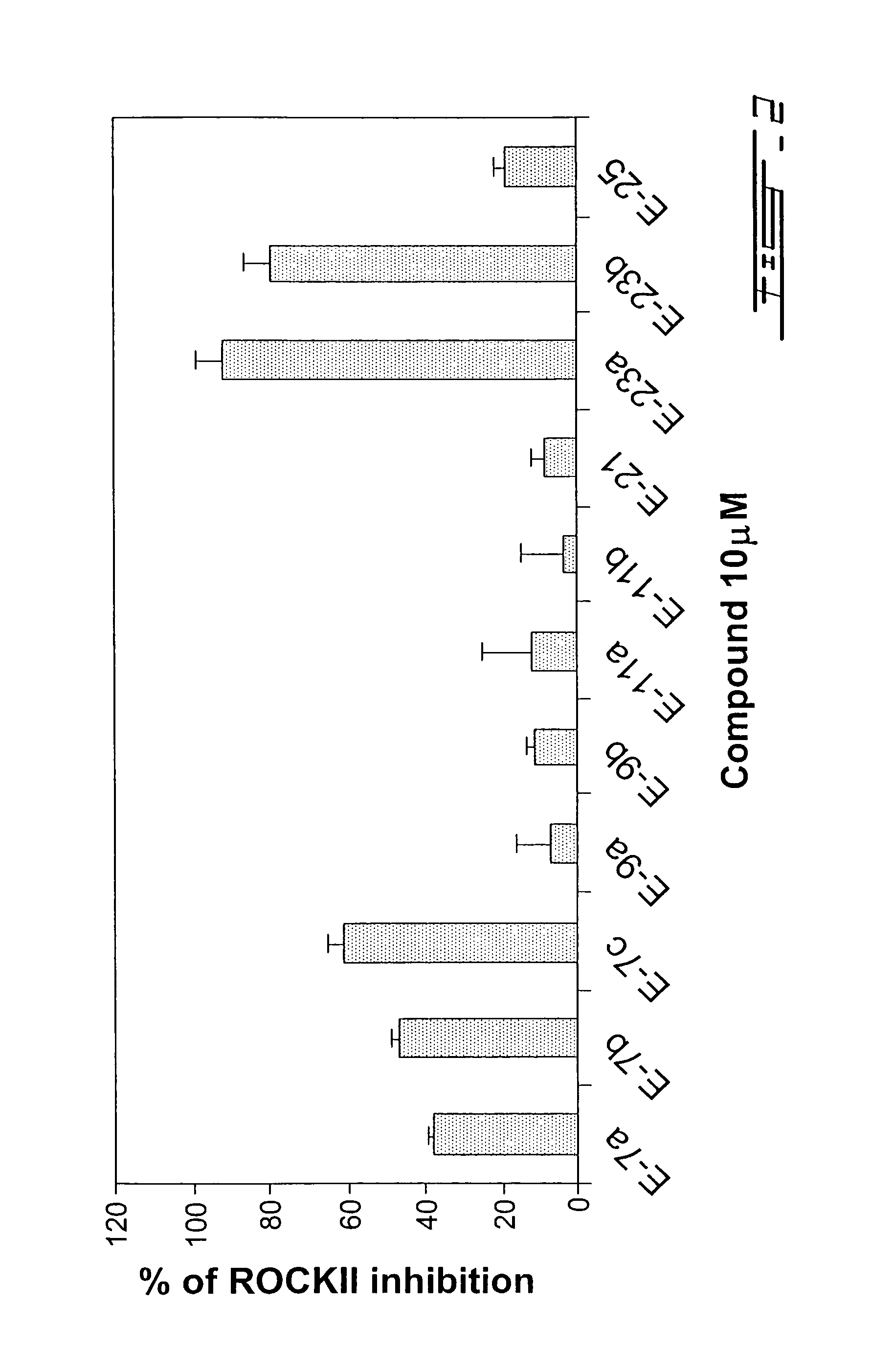
Substituted piperidine compounds represented by the structure I are provided,wherein each of R1a, R1b, R1c, R1d, R1e, R1f, R1g, R1h, R2, R2A, R3, R4, A, X, a, x and n is as defined in the specification. Substituted piperidine compounds of structure I may permeate or penetrate across a nerve cell membrane into the interior of a nerve cell, may inhibit intracellular Rho kinase enzyme found in nerve cells in mammals, and may find utility in repair of damaged nerves in the central and peripheral nervous system of such mammals. These compounds may induce the regeneration or growth of neurites in mammalian nerve cells and may thereby induce regeneration of damaged or diseased nerve tissue. These compounds also find additional utility as antagonists of the enzyme Rho kinase in treatment of disease states in which Rho kinase is implicated. Pharmaceutical compositions containing these substituted piperidine compounds may be useful to promote neurite growth and in the treatment of diseases in which Rho kinase inhibition is indicated.
Owner:BIOAXONE BIOSCI
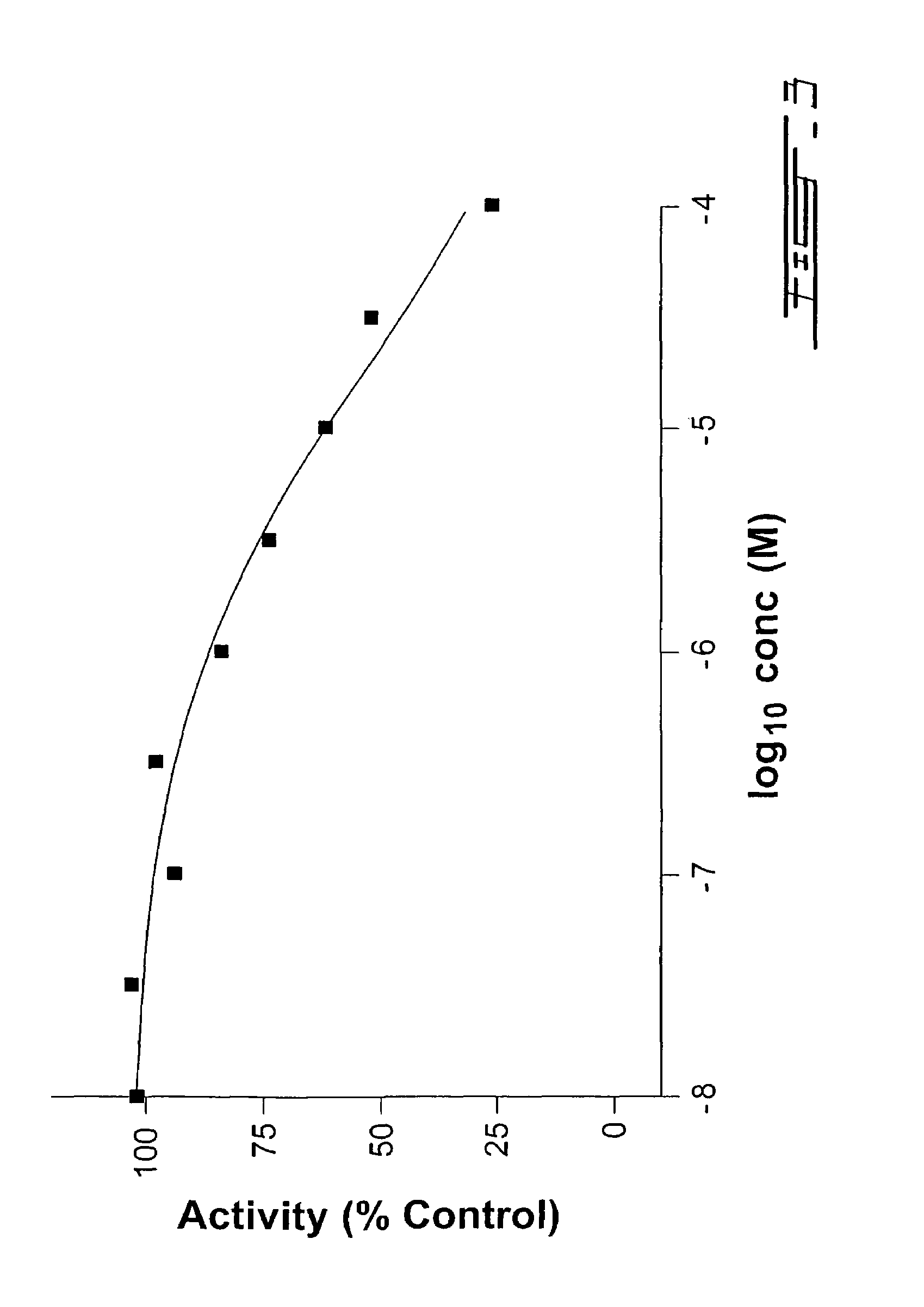
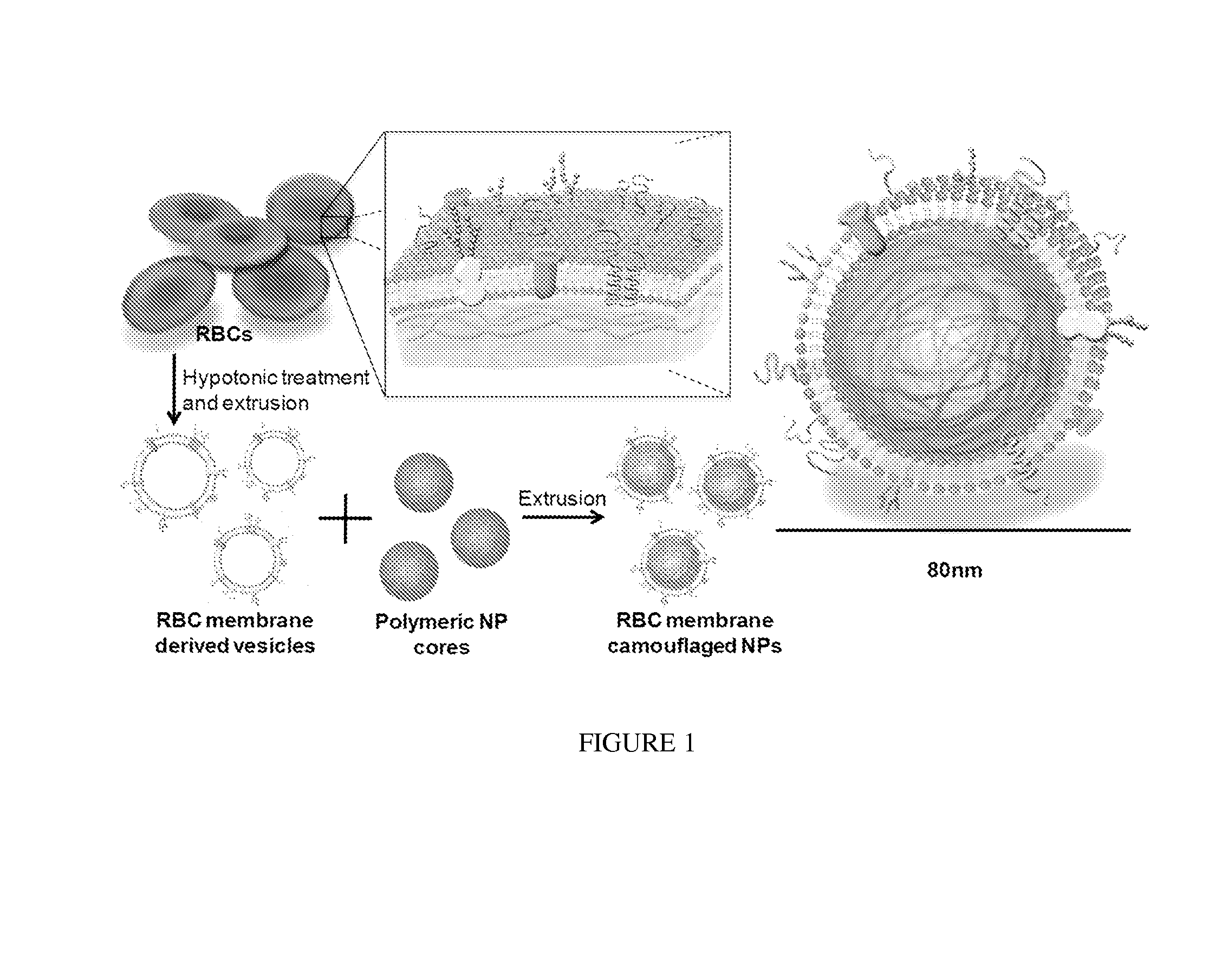
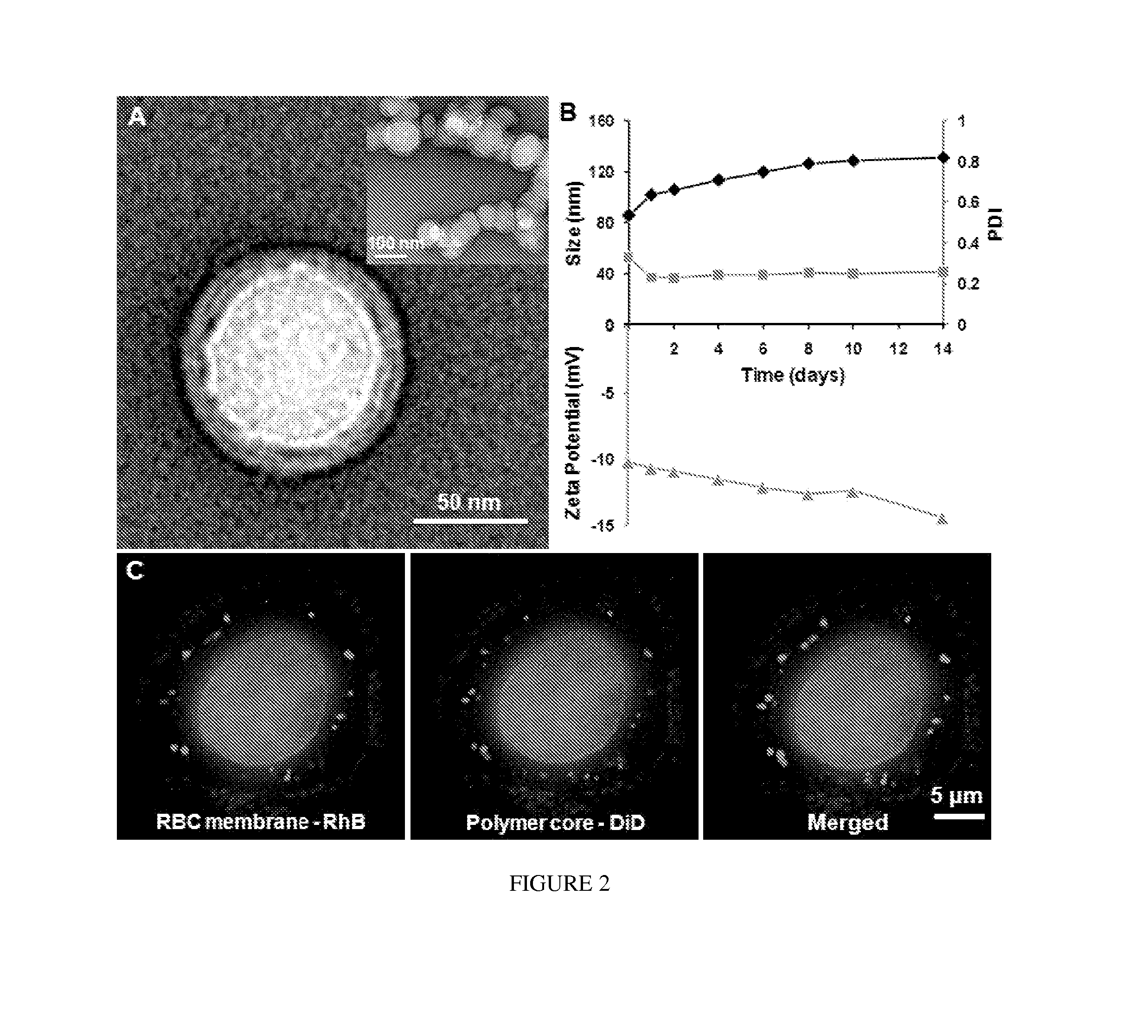
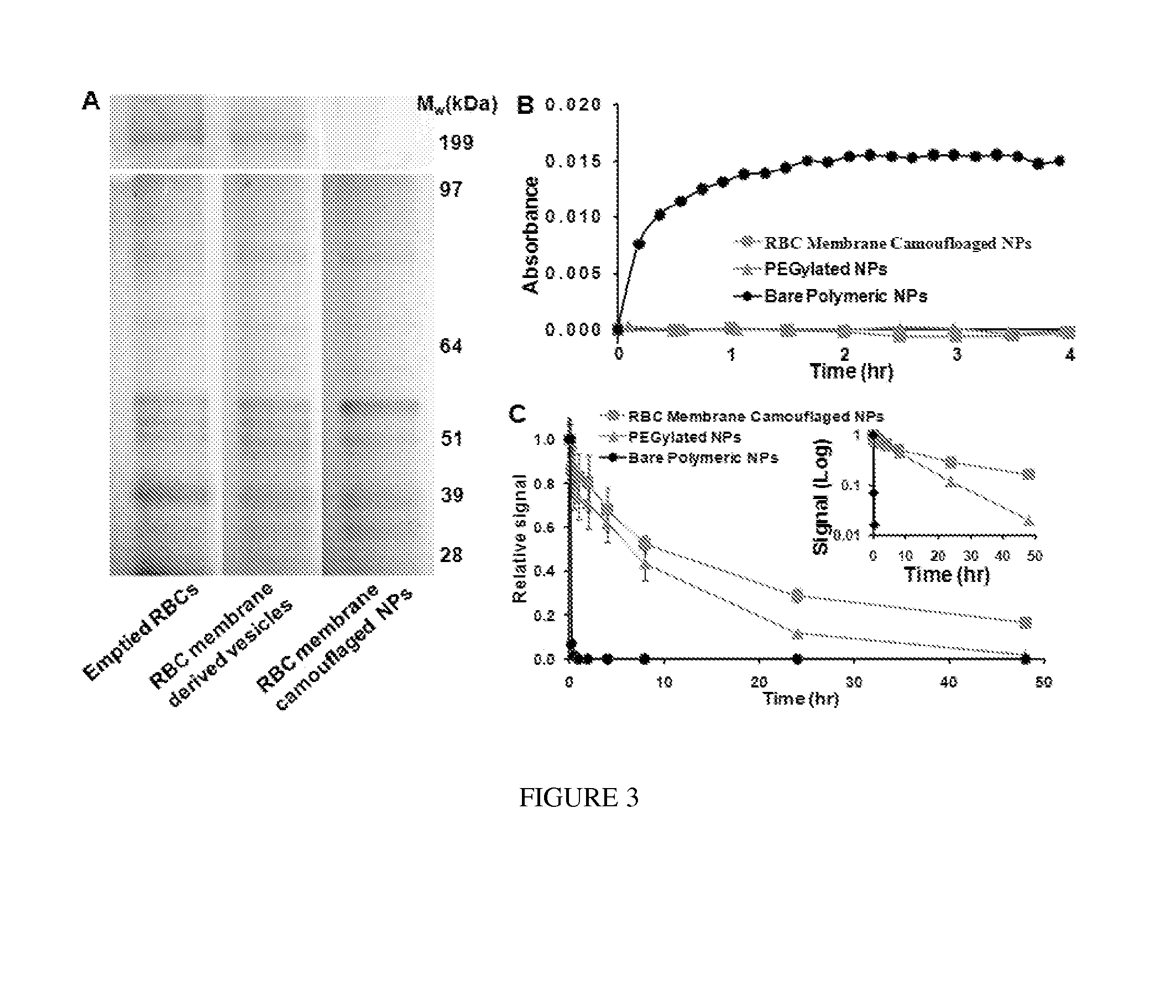
Membrane Encapsulated Nanoparticles and Method of Use
Provided are nanoparticles and methods of using and making thereof. The inventive nanoparticle comprises a) an inner core comprising a non-cellular material; and b) an outer surface comprising a cellular membrane derived from a cell or a membrane derived from a virus. Medicament delivery systems or pharmaceutical compositions comprising the inventive nanoparticles are also provided. Further provided are immunogenic compositions comprising the inventive nanoparticles, and methods of using the inventive immunogenic compositions for eliciting an immune response, and for treating or preventing diseases or condition, such as neoplasm or cancer, or disease or conditions associated with cell membrane inserting toxin. Vaccines comprising the immunogenic composition comprising the nanoparticles are also provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Compositions and methods for treating insulin resistance and diabetes mellitus
Provided are electrokinetically-altered fluids (gas-enriched electrokinetic fluids) comprising an ionic aqueous solution of charge-stabilized oxygen-containing nanostructures in an amount sufficient to provide modulation of at least one of cellular membrane potential and cellular membrane conductivity, and therapeutic compositions and methods for use in treating diabetes and diabetes-associated conditions or disorders (e.g., insulin resistance), or symptoms thereof. Provided are electrokinetically-altered ioinic aqueous fluids optionally in combination with other therapeutic agents. Particular aspects provide for regulating or modulating intracellular signal transduction associated with said inflammatory responses by modulation of at least one of cellular membranes, membrane potential, membrane proteins such as membrane receptors, including but not limited to G-Protein Coupled Receptors (GPCR), and intercellular junctions (e.g., tight junctions, gap junctions, zona adherins and desmasomes). Other embodiments include particular routes of administration or formulations for the electrokinetically-altered fluids (e.g., electrokinetically-altered gas-enriched fluids and solutions) and therapeutic compositions.
Owner:REVALESIO CORP
Polymers for analyte detection
InactiveUS20060127929A1Microbiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceEscherichia coliFluorescence
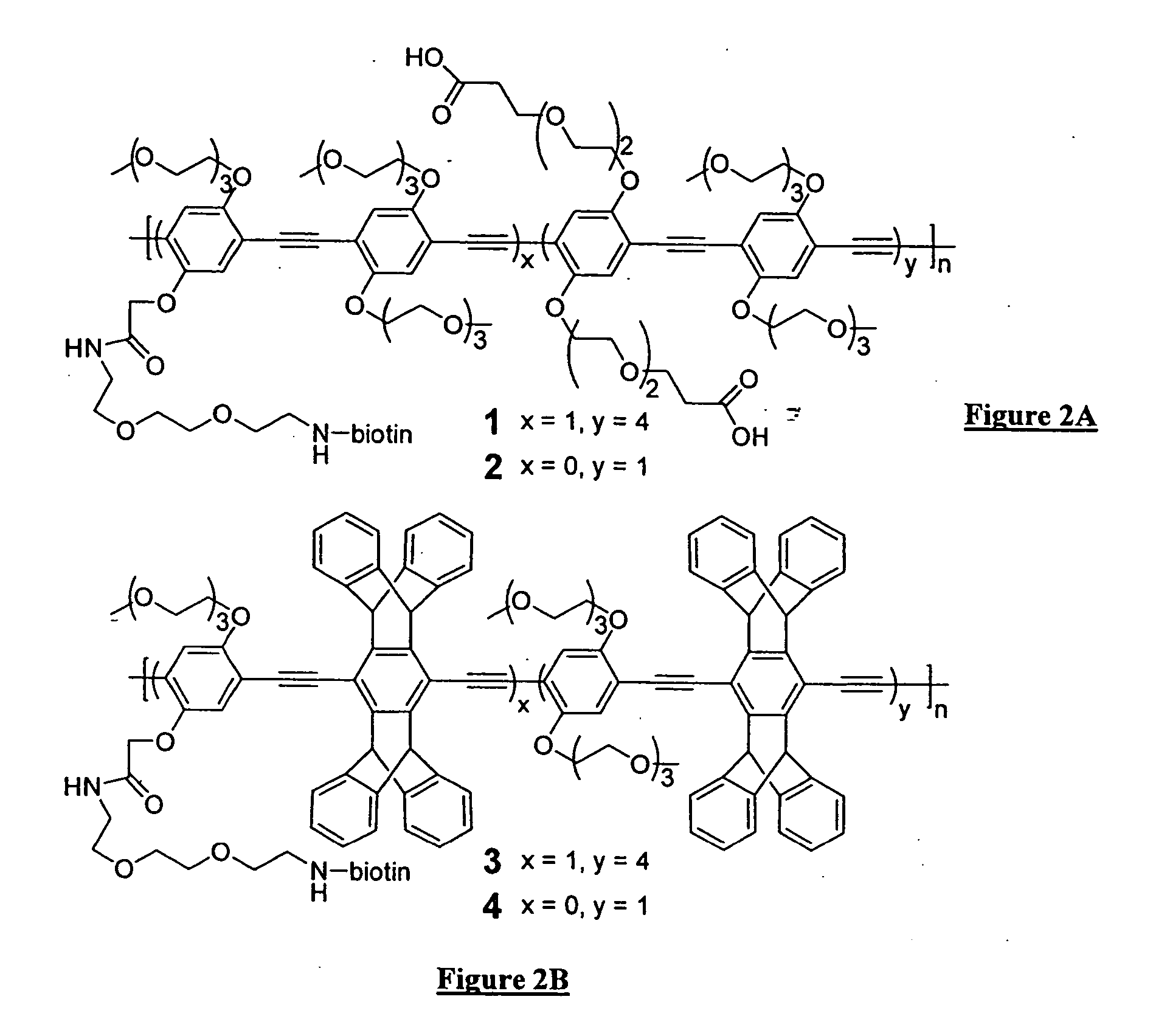
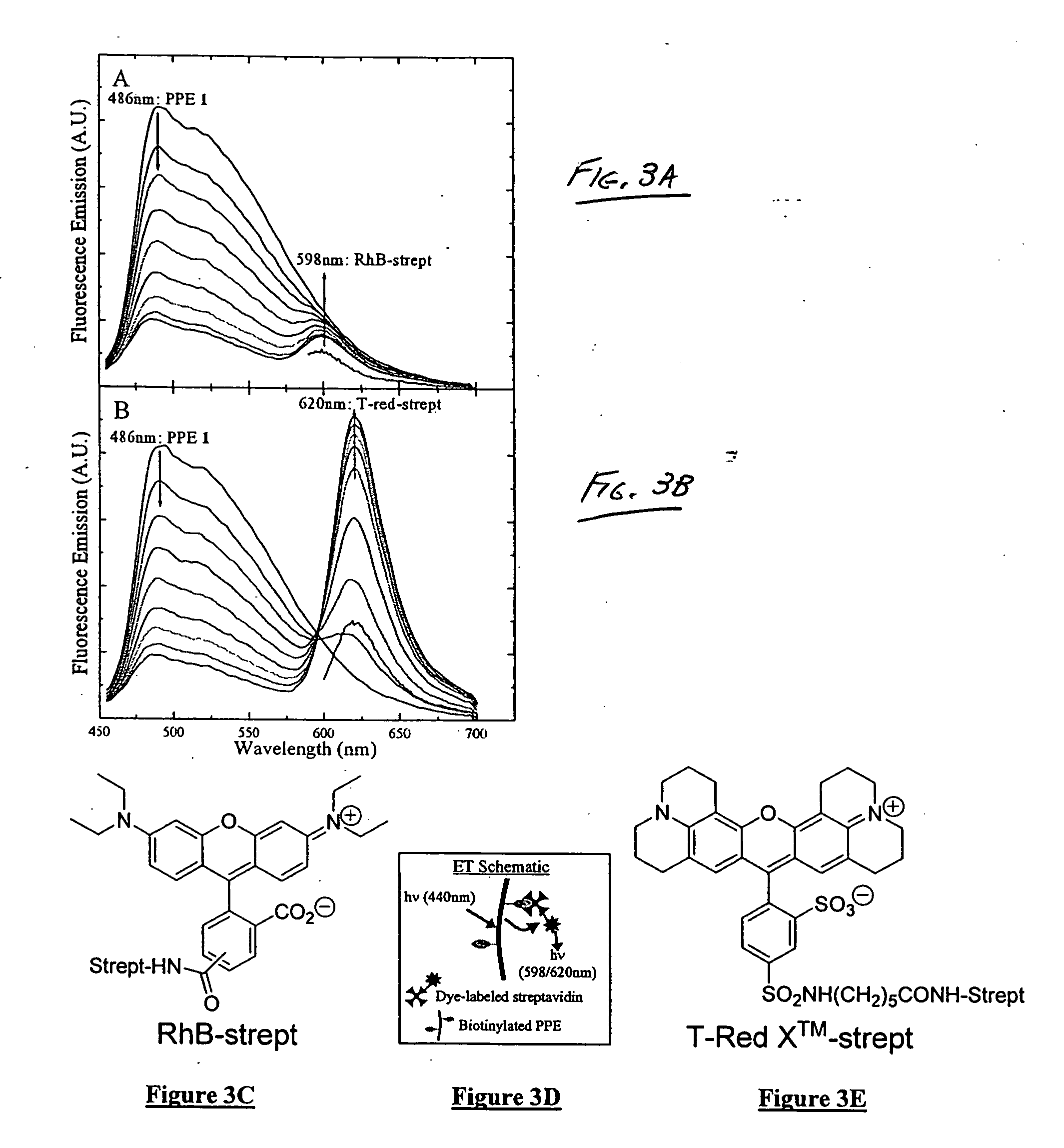
The present invention generally relates to organic polymers able to participate in an analyte-recognition process, where an analyte facilitates an energy transfer between an energy donor and an energy acceptor. Certain embodiments of the invention make use of fluorescent conjugated polymers, such as poly(phenylene ethynylene)s and other polymers comprising pi-conjugated backbones. For example, one aspect of the invention provides a fluorescent conjugated polymer and an indicator that can interact with each other in the presence of an analyte to produce an emissive signal. In some cases, the interaction may include energy exchange mechanisms, such as Dexter energy transfer or the strong coupling effect. The interaction of the conjugated polymer and the indicator, in some instances, may be facilitated through specific interactions, such as a protein / carbohydrate interaction, a ligand / receptor interaction, etc. Another aspect of the invention provides for the detection of biological entities, for example, pathogenic bacteria such as E. coli, or viruses such as influenza virus. In some cases, biological recognition elements may be used to determine the biological entity, for instance, carbohydrates that can be used to specifically interact with at least part of the biological entity, such as a protein in the cell membrane of a bacterium. Still other aspects of the invention involve articles, devices, and kits using any of the above-described systems.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Scalable Production Method for AAV
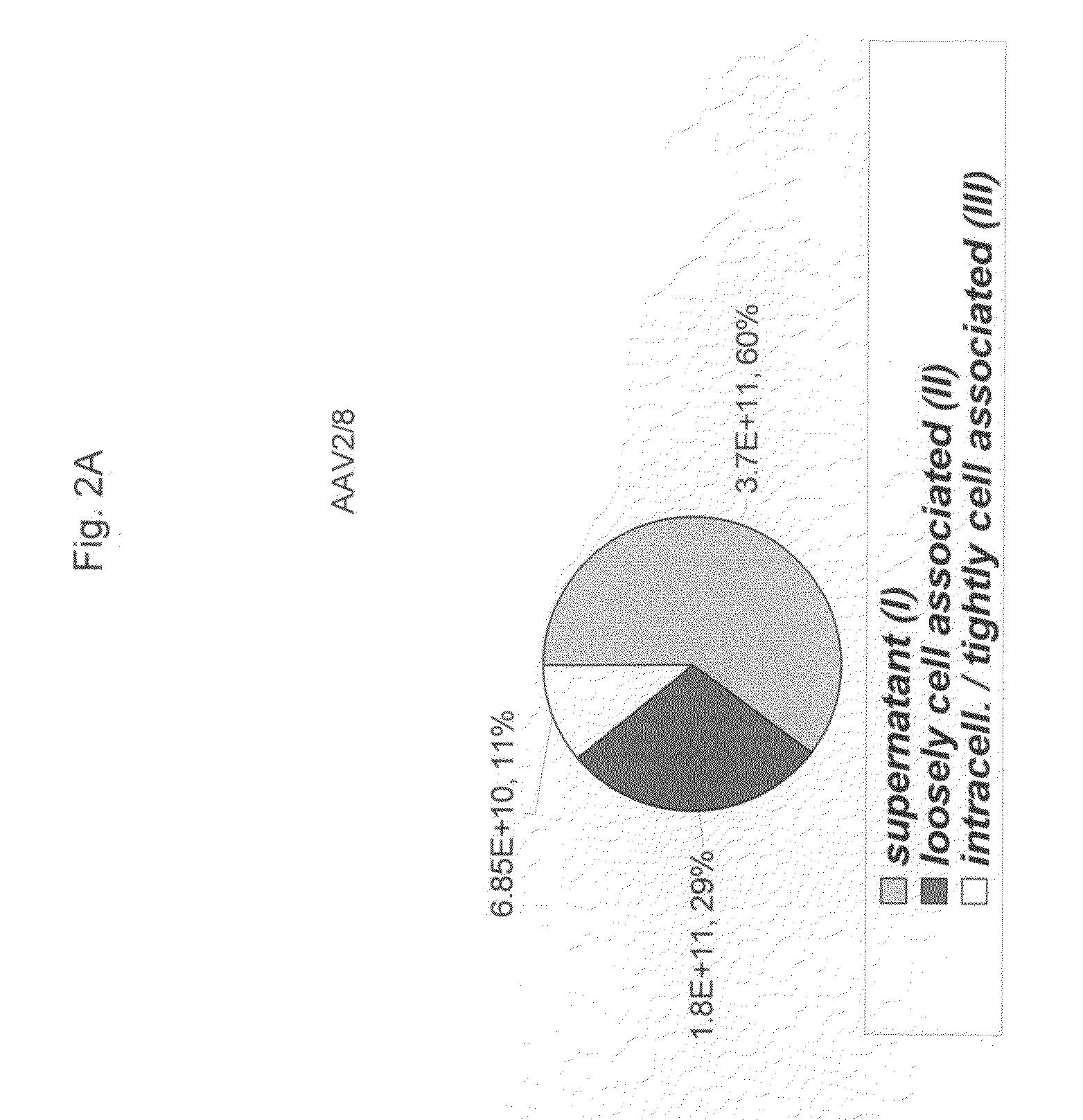
ActiveUS20090275107A1Reduce and eliminate bindingHigh yieldGenetic therapy composition manufactureVirus peptidesLysisBinding site
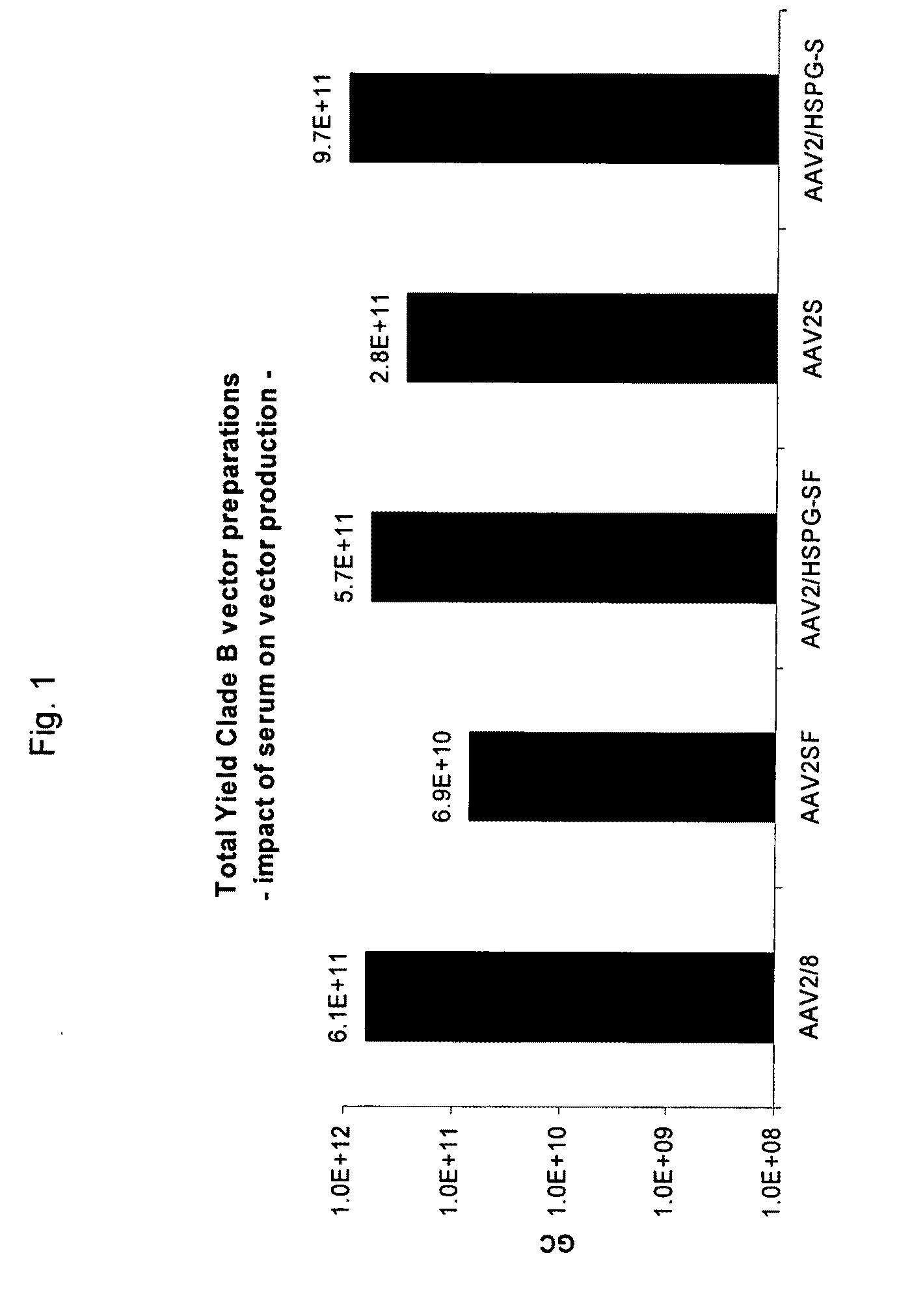
A method for producing AAV, without requiring cell lysis, is described. The method involves harvesting AAV from the supernatant. For AAV having capsids with a heparin binding site, the method involves modifying the AAV capsids and / or the culture conditions to ablate the binding between the AAV heparin binding site and the cells, thereby allowing the AAV to pass into the supernatant, i.e., media. Thus, the method of the invention provides supernatant containing high yields of AAV which have a higher degree of purity from cell membranes and intracellular materials, as compared to AAV produced using methods using a cell lysis step.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Methods of wound care and treatment
InactiveUS20100021464A1Reduce scarsImprove the level ofBiocideSenses disorderCell membraneWound care
Provided are electrokinetically-altered fluids (e.g., gas-enriched electrokinetic fluids) comprising an ionic aqueous solution of charge-stabilized oxygen-containing nanostructures in an amount sufficient to provide modulation of at least one of cellular membrane potential and cellular membrane conductivity, and therapeutic compositions and methods for use in treating a wound to a surface tissue or a symptom thereof. The electrokinetically-altered fluids or therapeutic compositions and methods include electrokinetically-altered ionic aqueous fluids optionally in combination with other therapeutic agents. Particular aspects provide for regulating or modulating intracellular signal transduction associated with said inflammatory responses by modulation of at least one of cellular membranes, membrane potential, membrane proteins such as membrane receptors, including but not limited to G-Protein Coupled Receptors (GPCR), and intercellular junctions (e.g., tight junctions, gap junctions, zona adherins and desmasomes). Other embodiments include particular routes of administration or formulations for the electrokinetically-altered fluids (e.g., electrokinetically-altered gas-enriched fluids and solutions) and therapeutic compositions.
Owner:REVALESIO CORP
Peptide having cell membrane penetrating activity
InactiveUS20130129726A1Prominent penetrating efficiencyTargeting of drugs is required high efficientlyPeptide/protein ingredientsDrug compositionsHistamine releasing factorProtein transduction domain
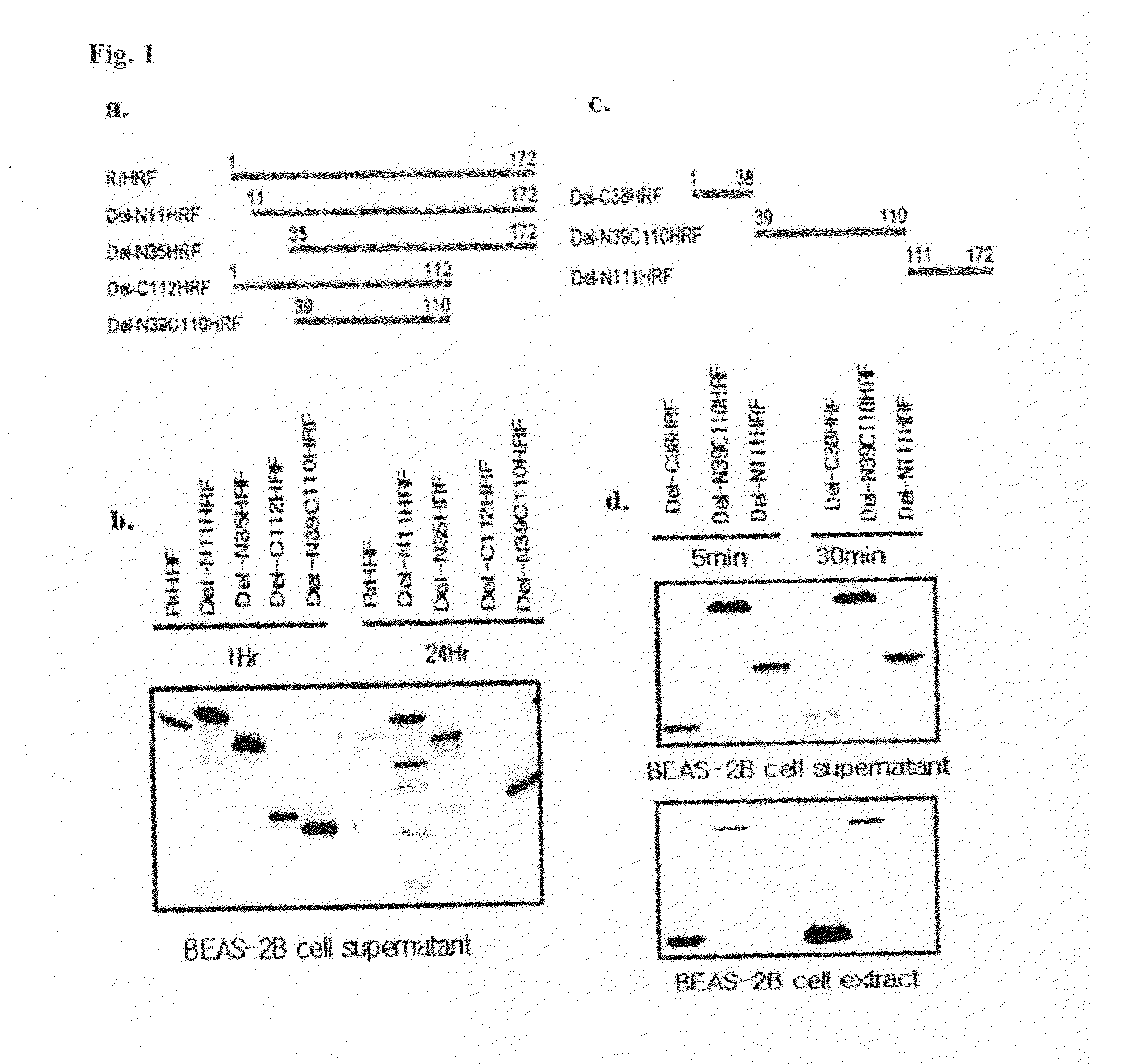
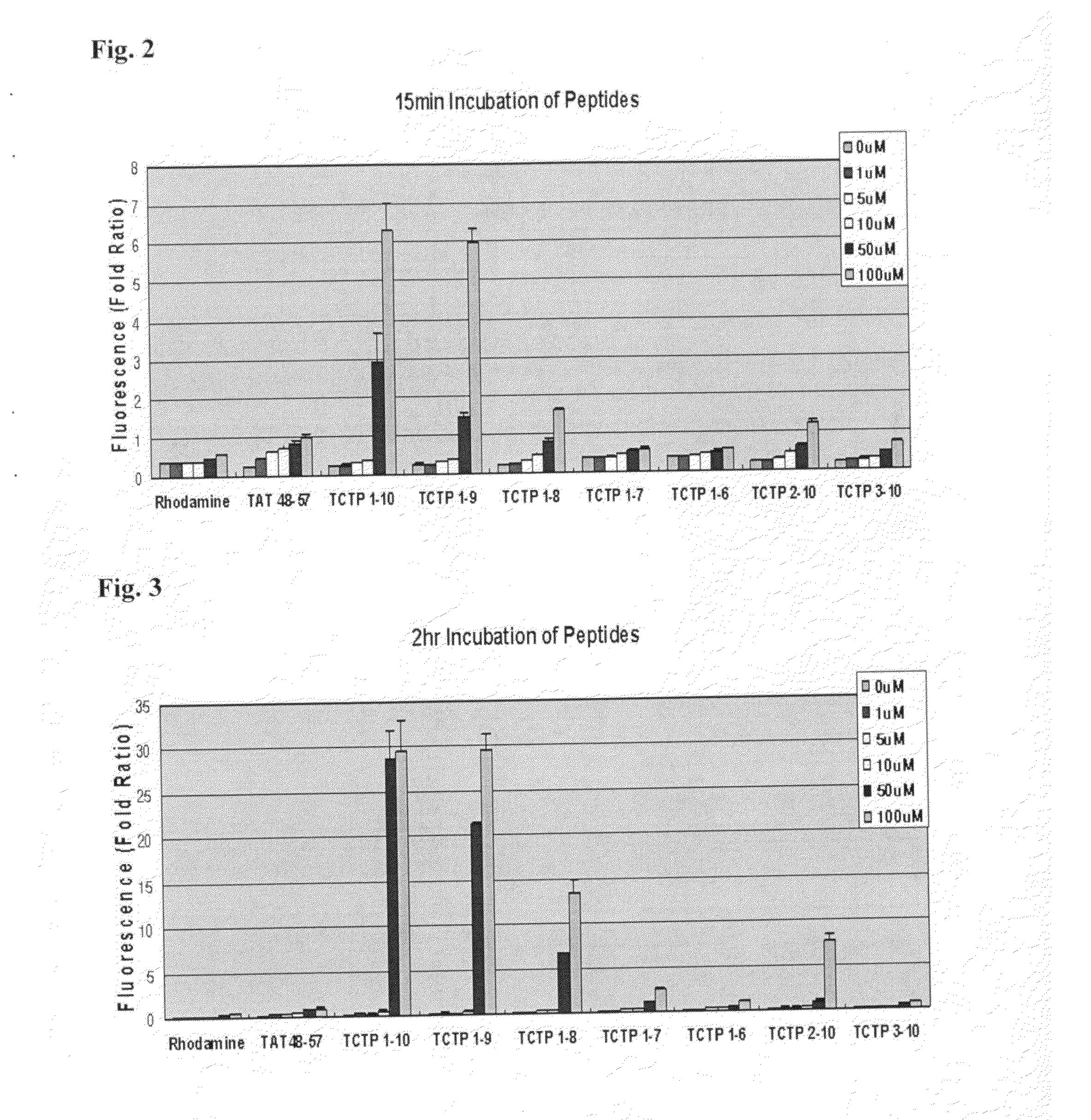
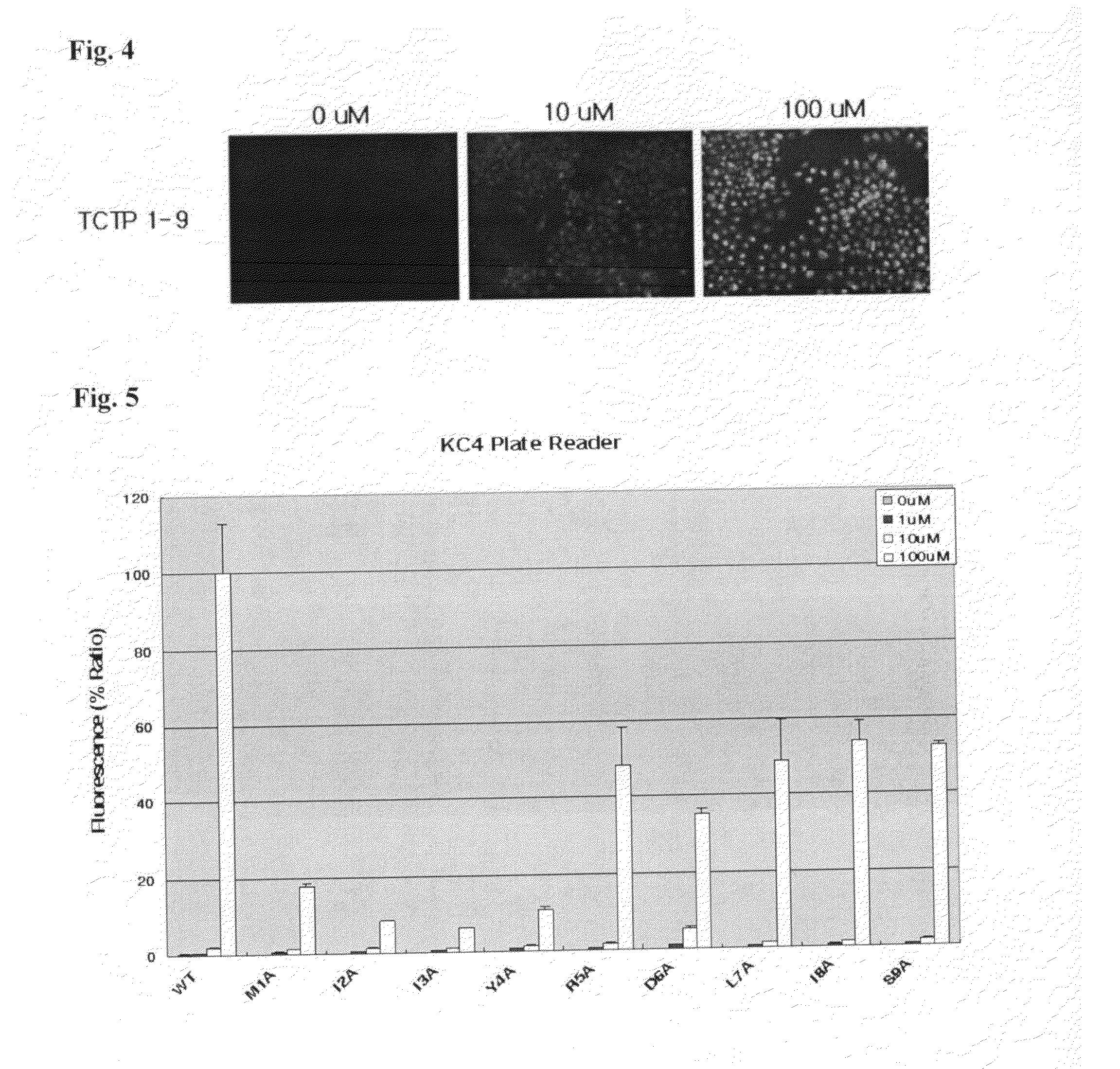
Provided are transmembrane complexes that contain a protein transduction domain (PTD) from the N-terminus of IgE-dependent histamine-releasing factor (HRF) and a target substance that is to be delivered into a cell. Also provided are nucleic acid molecules encoding the transmembrane complex, and methods of delivering the target substance into a cell interior by contacting the transmembrane complex with a cell. Also provided are transfection kits containing the PTD and the target substance.
Owner:EWHA UNIV IND COLLABORATION FOUND
Compositions and methods for treating cystic fibrosis
InactiveUS20100303917A1Increased mucus secretionReduce airflowBiocidePowder deliveryTobramycinCell membrane
Provided are electrokinetically-altered fluids (gas-enriched (e.g., oxygen-enriched) electrokinetic fluids) comprising an ionic aqueous solution of charge-stabilized oxygen-containing nanostructures in an amount sufficient to provide, upon contact with a cell, modulation of at least one of cellular membrane potential and cellular membrane conductivity, and therapeutic compositions and methods for using same in treating cystic fibrosis or a symptom thereof. The electrokinetically-altered fluid compositions and methods include electrokinetically-altered fluids optionally in combination with other therapeutic agents (e.g., antibiotics, albuterol, budesonide, etc.). Particular embodiments comprise use and / or synergy with tobramycin for treating bacterial infection, and use and / or synergy with a bronchiodilator. In certain aspects, the methods comprise regulating intracellular signal transduction by modulation of at least one of cellular membranes, membrane potential, membrane proteins (like, membrane receptors, including but not limited to G protein coupled receptors, and intercellular junctions).
Owner:REVALESIO CORP
Membrane-permeant peptide complexes for medical imaging, diagnostics, and pharmaceutical therapy
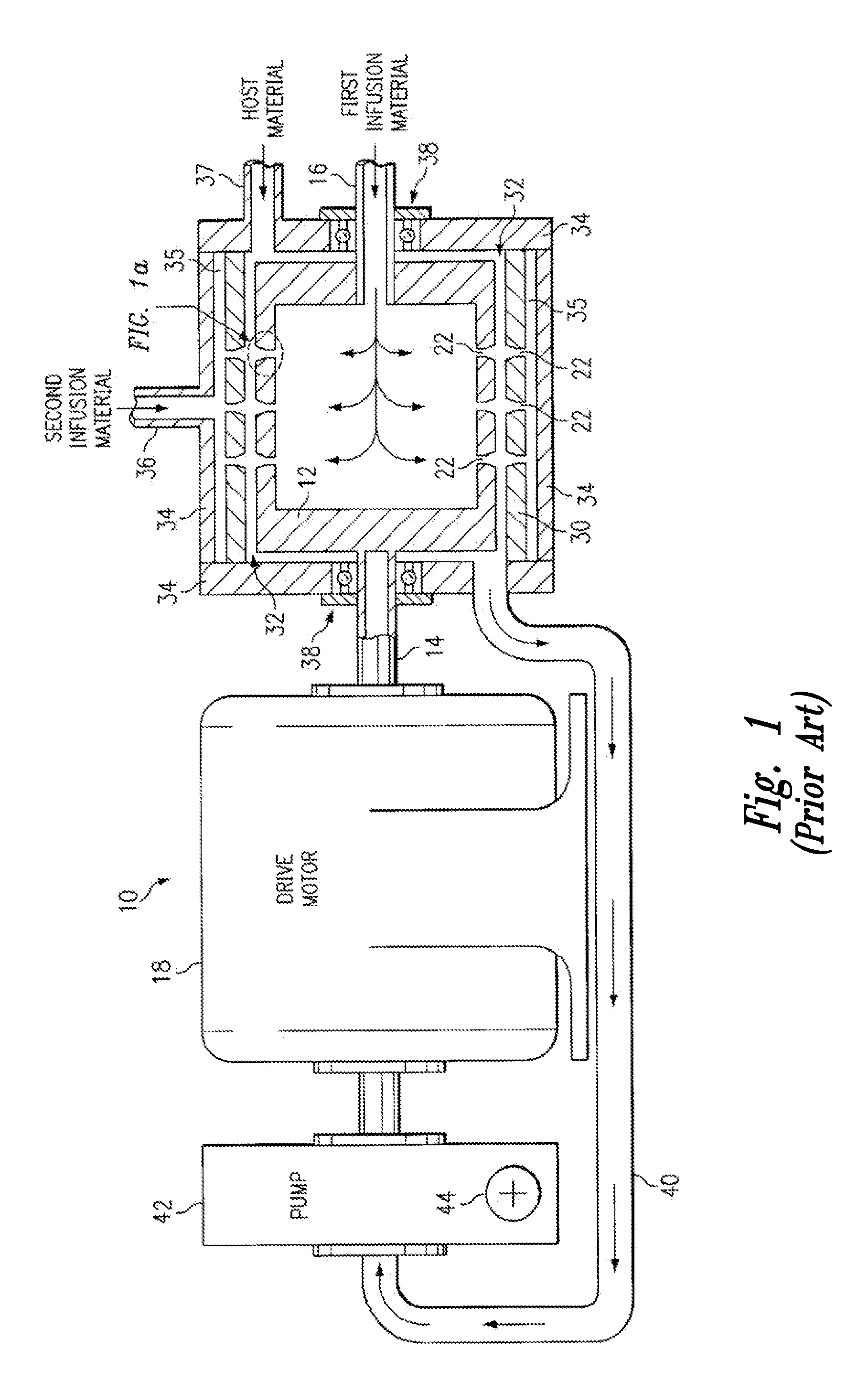
InactiveUS7306783B2Accelerate the accumulation processImprove clearance rateVirusesHydrolasesCell membraneMedical imaging
Methods and compositions for medical imaging, evaluating intracellular processes and components, radiotherapy of intracellular targets, and drug delivery by the use of novel cell membrane-permeant peptide conjugate coordination and covalent complexes having target cell specificity are provided. Kits for conjugating radionuclides and other metals to peptide coordination complexes are also provided.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com