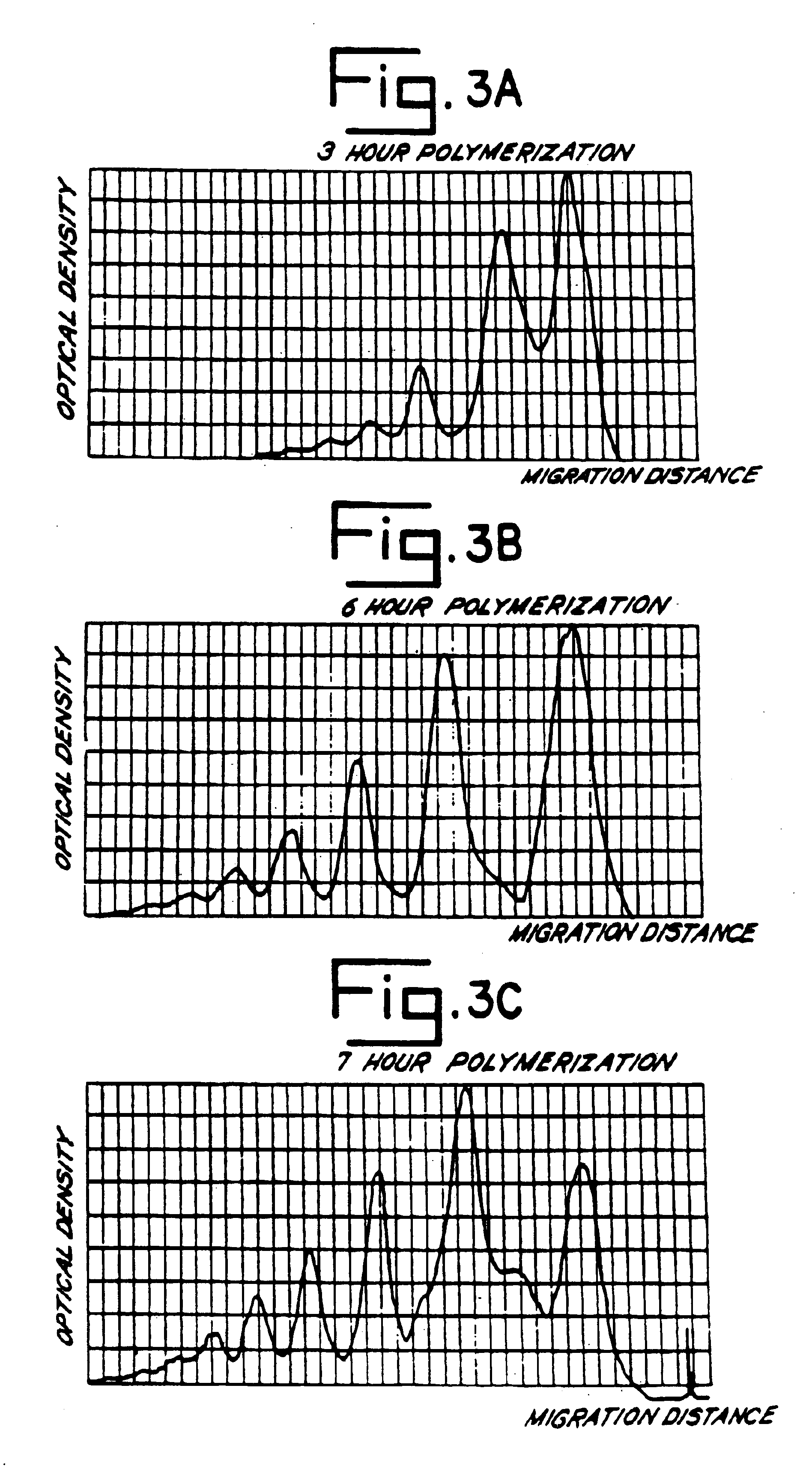
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
37 results about "Erythroblast" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An immature, nucleated erythrocyte occupying the stage of erythropoiesis that follows formation of erythroid progenitor cells and precedes formation of reticulocytes.
In vitro production of red blood cells with sortaggable proteins
Methods for the in vitro production of enucleated red blood cells and the enucleated red blood cells thus prepared are provided. Such enucleated red blood cells may express a sortaggable surface protein, which allows for surface modification in the presence of a sortase. Also described herein are surface modified enucleated red blood cells, e.g., conjugated with an agent of interest such as a peptide, a detectable label, or a chemotherapeutic agent, and uses thereof in delivering the agent to a subject.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
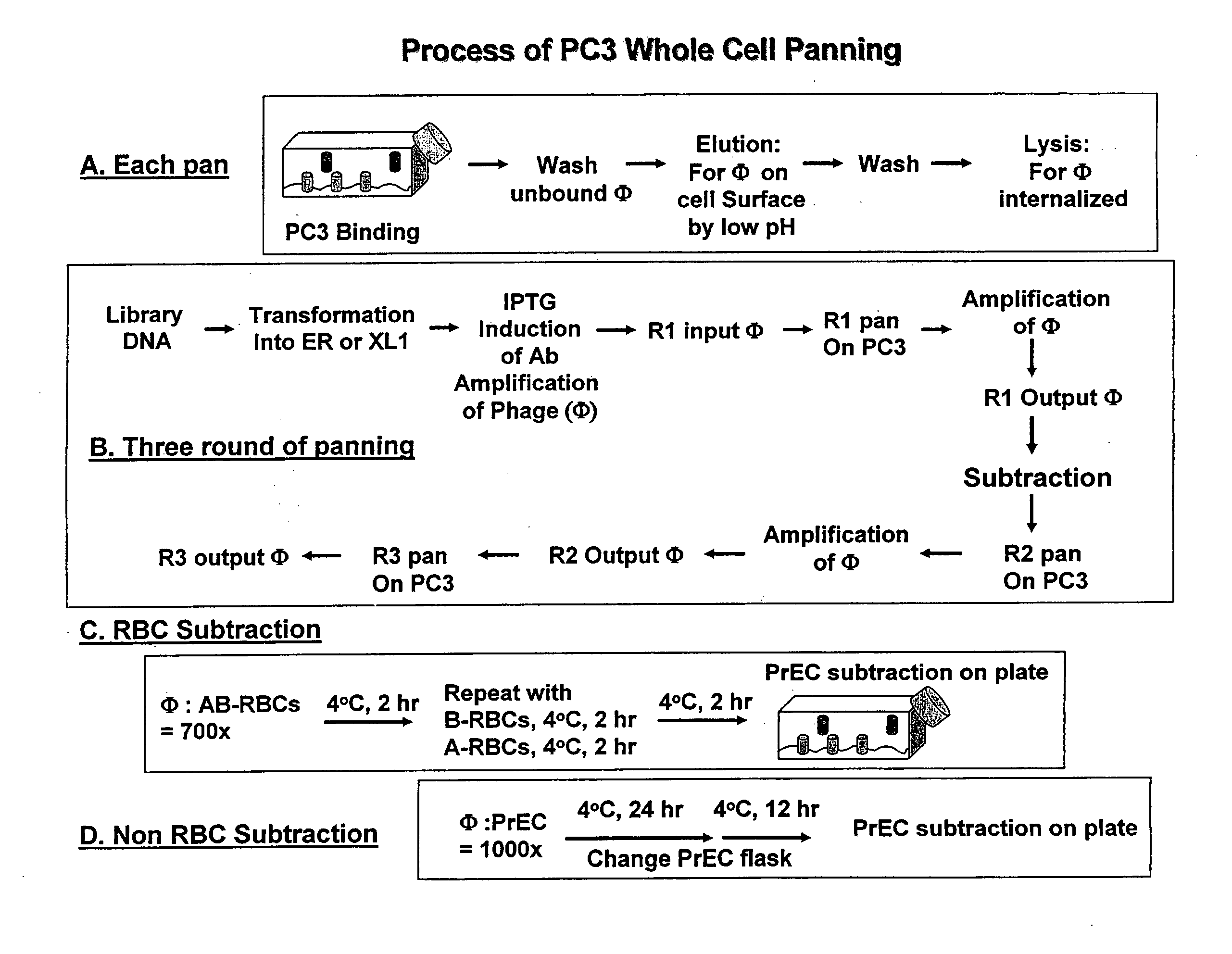
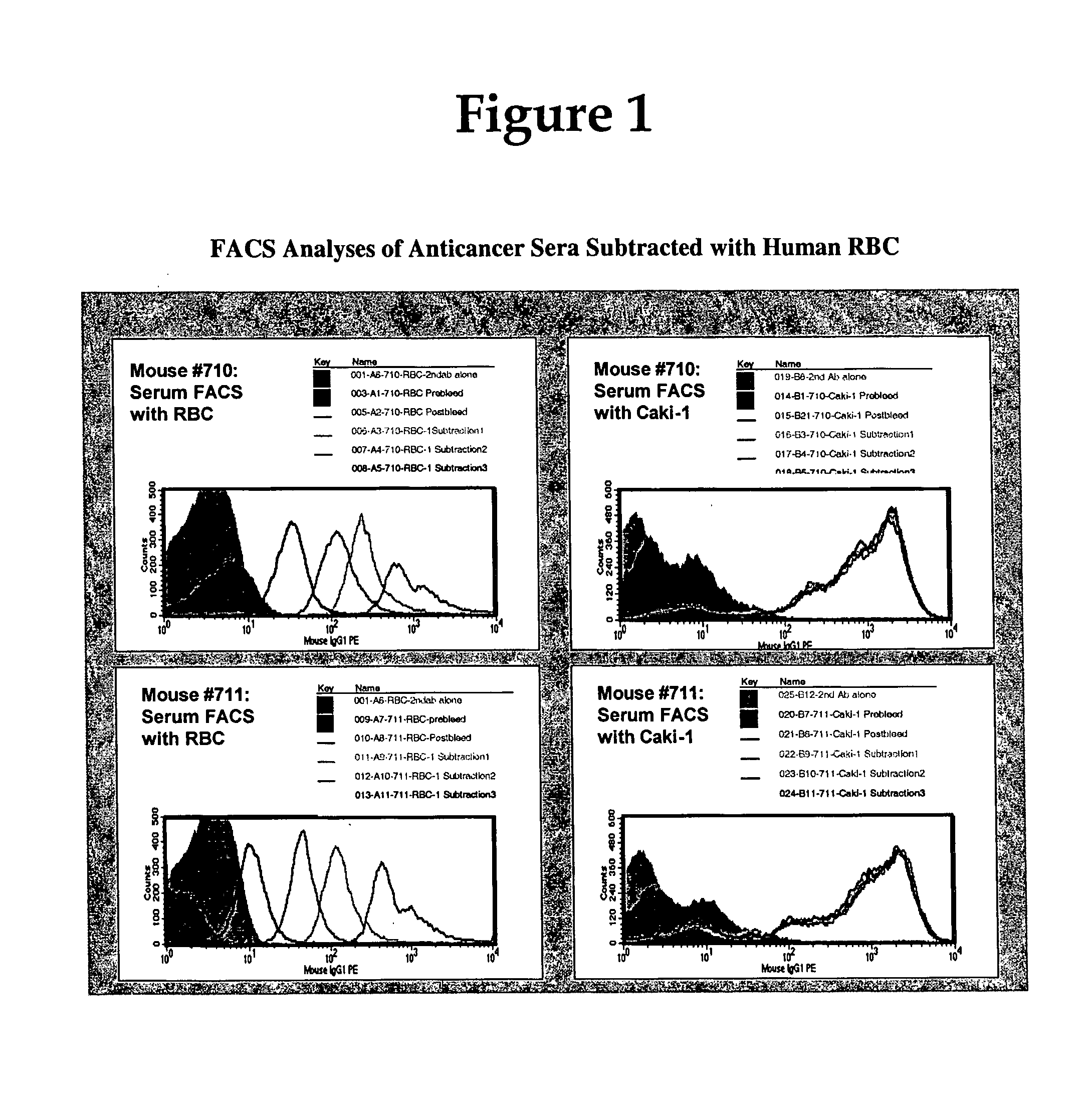
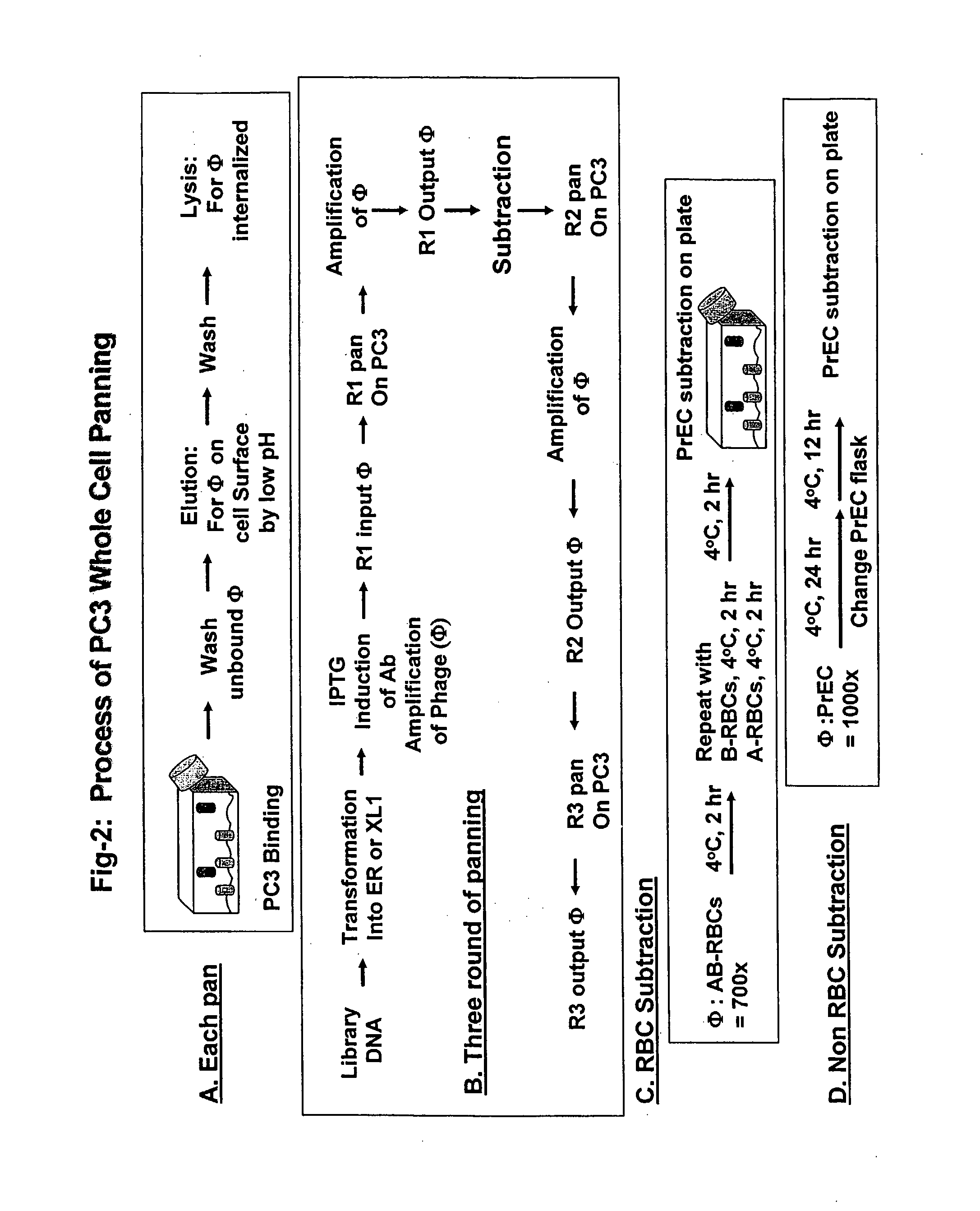
Methods for Discovering Antibodies Specific to Cancer Cells and Antibodies Discovered Thereby
InactiveUS20080287309A1Tumor rejection antigen precursorsSugar derivativesCancer cellWhite blood cell
This disclosure relates to methods for selecting antibodies having desirable characteristics from a population of diverse antibodies. More specifically, this disclosure provides methods for identifying antibodies which bind to cancer cells, but which do not bind to human red blood cells, white blood cells or normal tissue cells. Antibodies of the disclosure can be used for therapeutic and / or diagnostic purposes.
Owner:ALEXION PHARMA INC
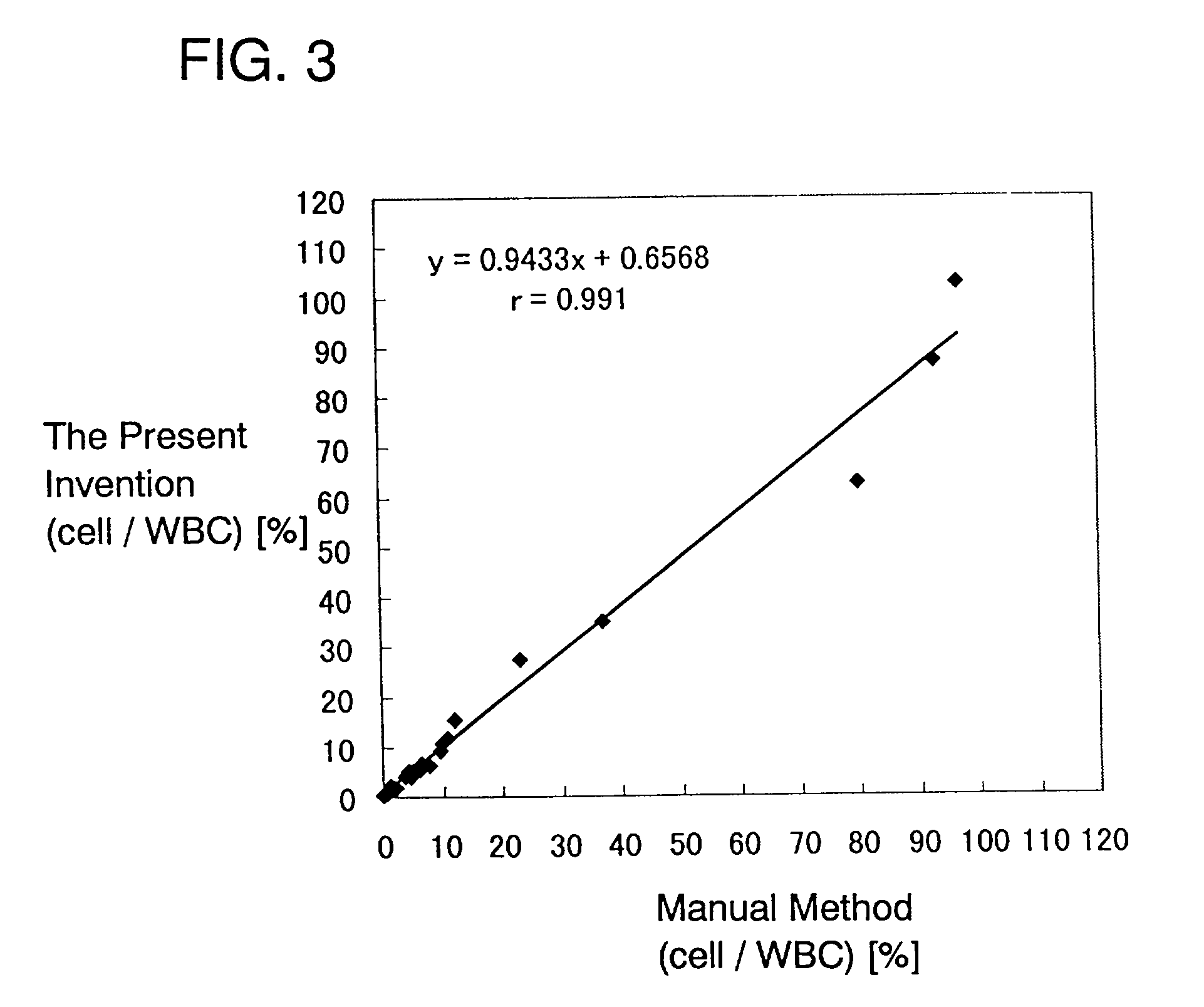
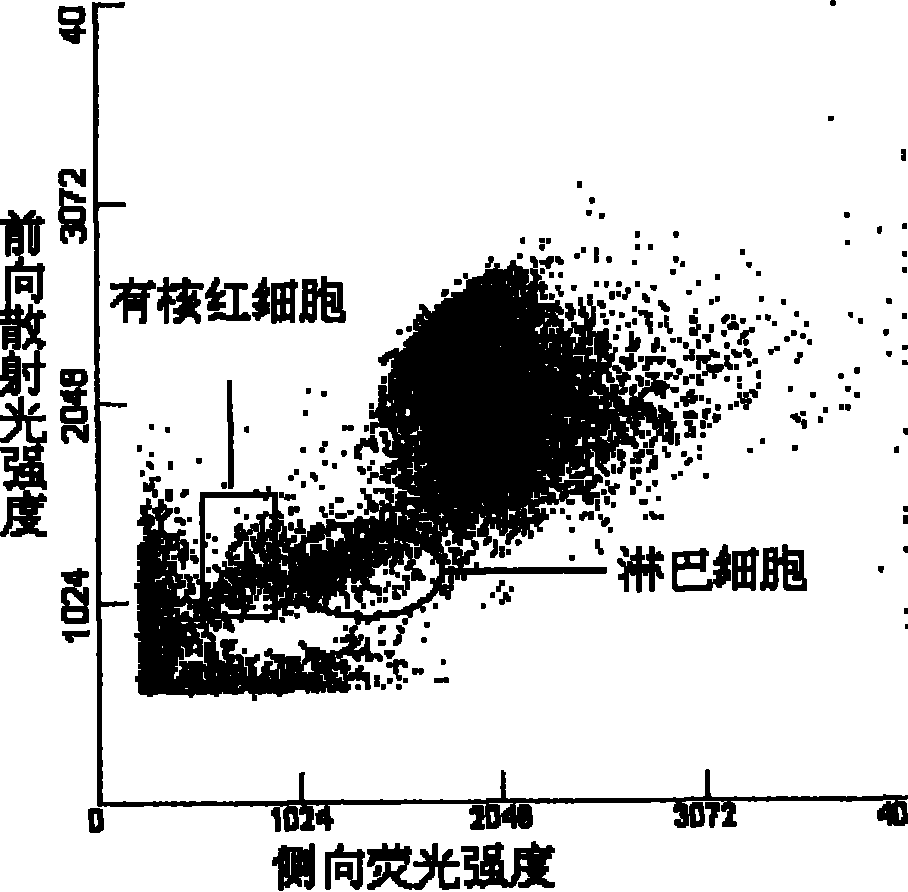
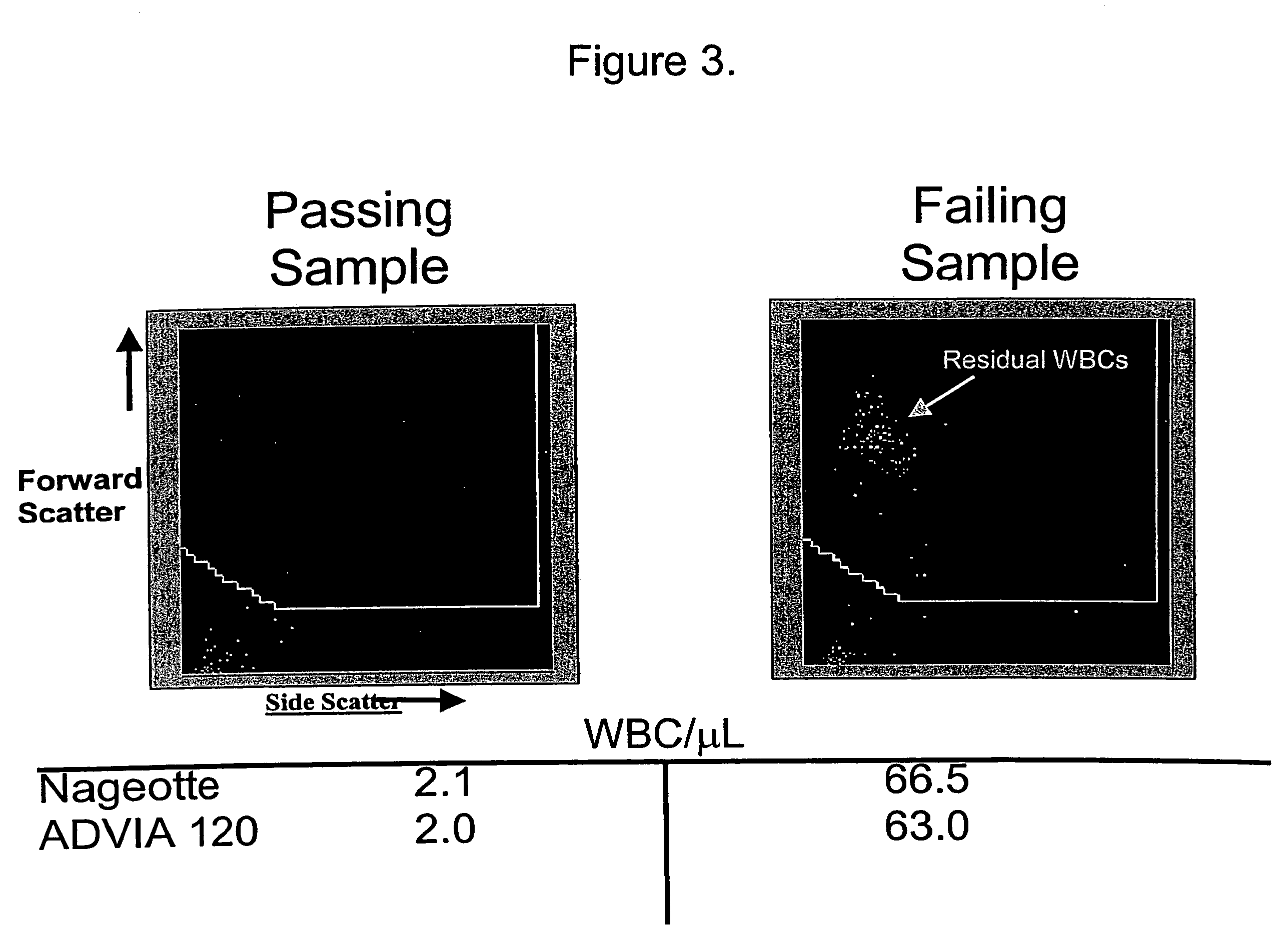
Process for discriminating and counting erythroblasts
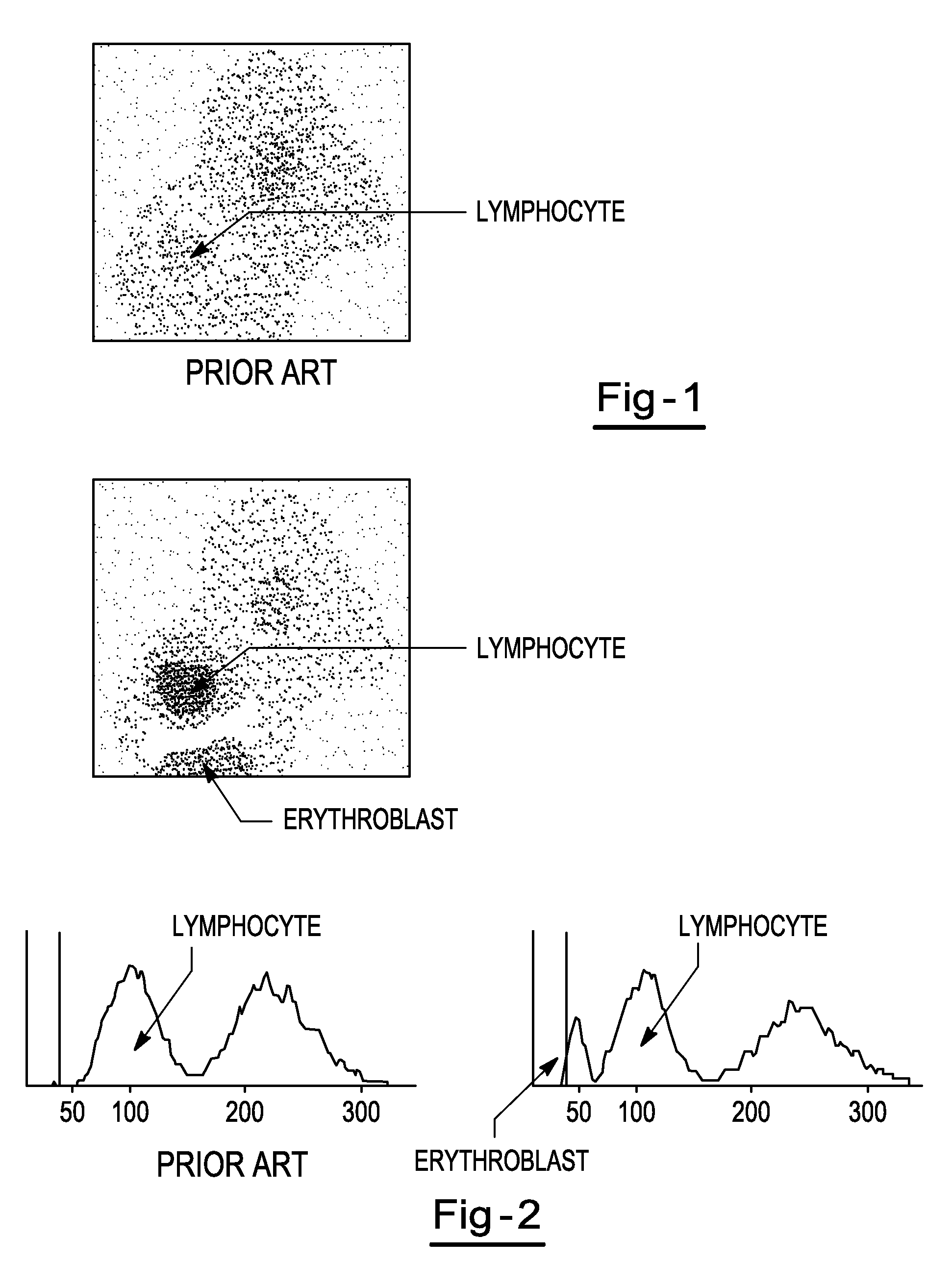
InactiveUS20020006631A1Microbiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceRed blood cellWhite blood cell
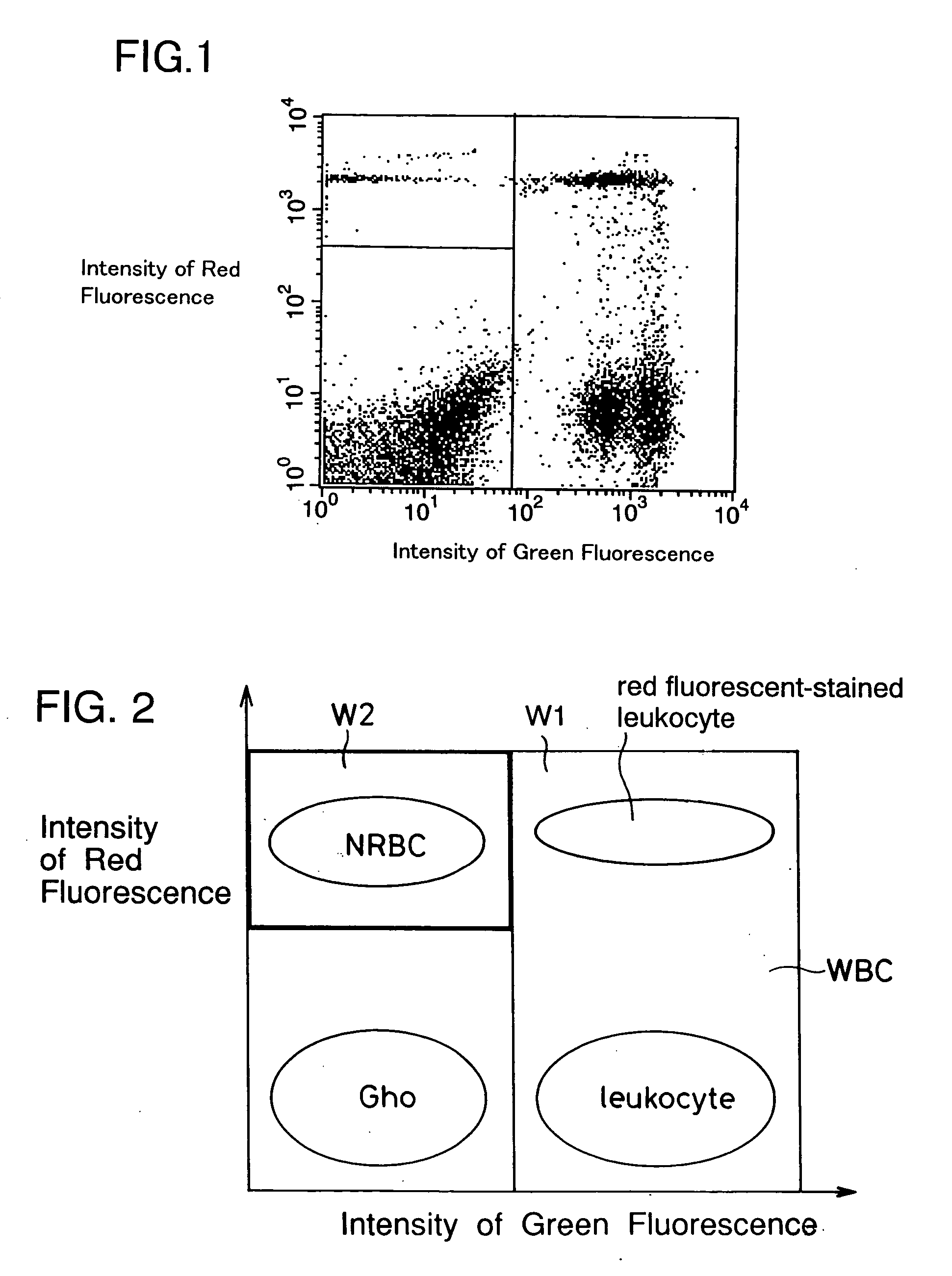
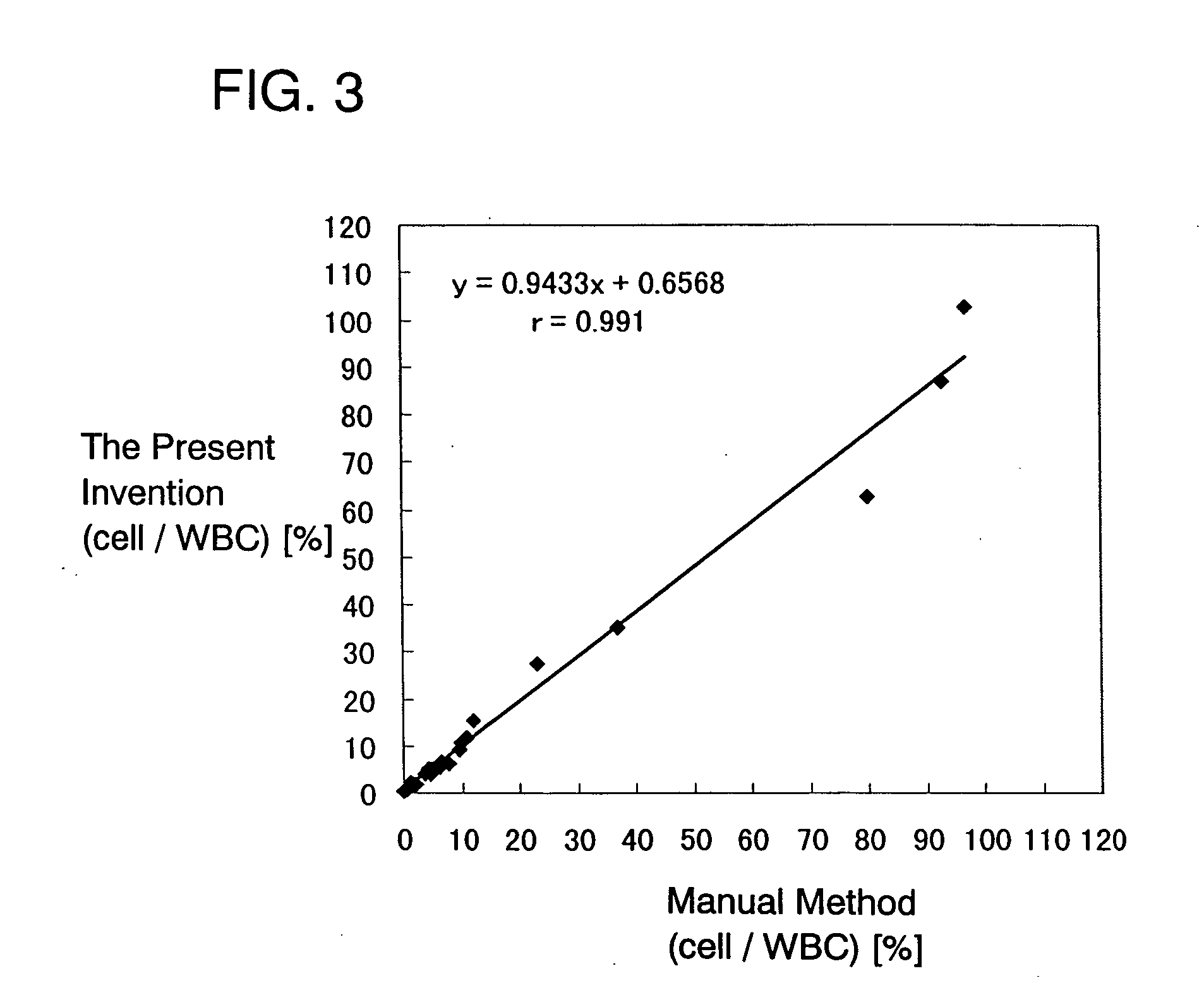
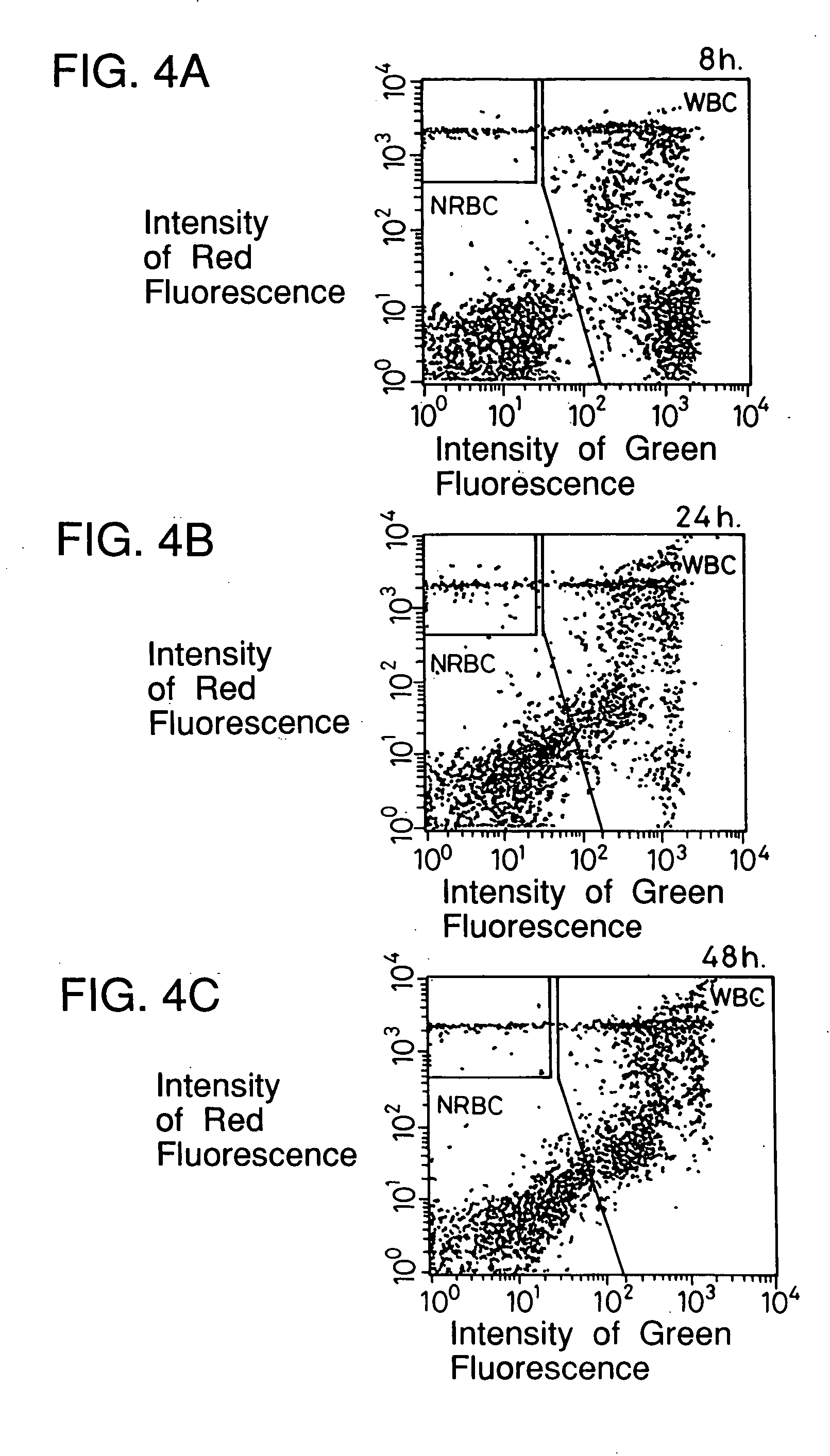
A method for discriminating and counting erythroblasts comprises the steps of: (i) staining leukocytes in a hematologic sample by adding a fluorescent labeled antibody capable of binding specifically with leukocytes to the hematologic sample; (ii) raising the permeability only of cell membranes of erythroblasts in the hematologic sample to a nucleotide fluorescent dye which does not permeate a cell membrane usually, the nucleotide fluorescent dye having a fluorescent spectrum capable of being distinguished from that of a fluorescent labeling compound of the fluorescent labeled antibody in step (i); (iii) staining nuclei of the erythroblasts in the hematologic sample with the nucleotide fluorescent dye; (iv) subjecting the hematologic sample to flowcytometry to detect at least two fluorescent signals from each cell; and (v) discriminating and counting the erythroblasts from difference in intensity between the at least two fluorescent signals.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
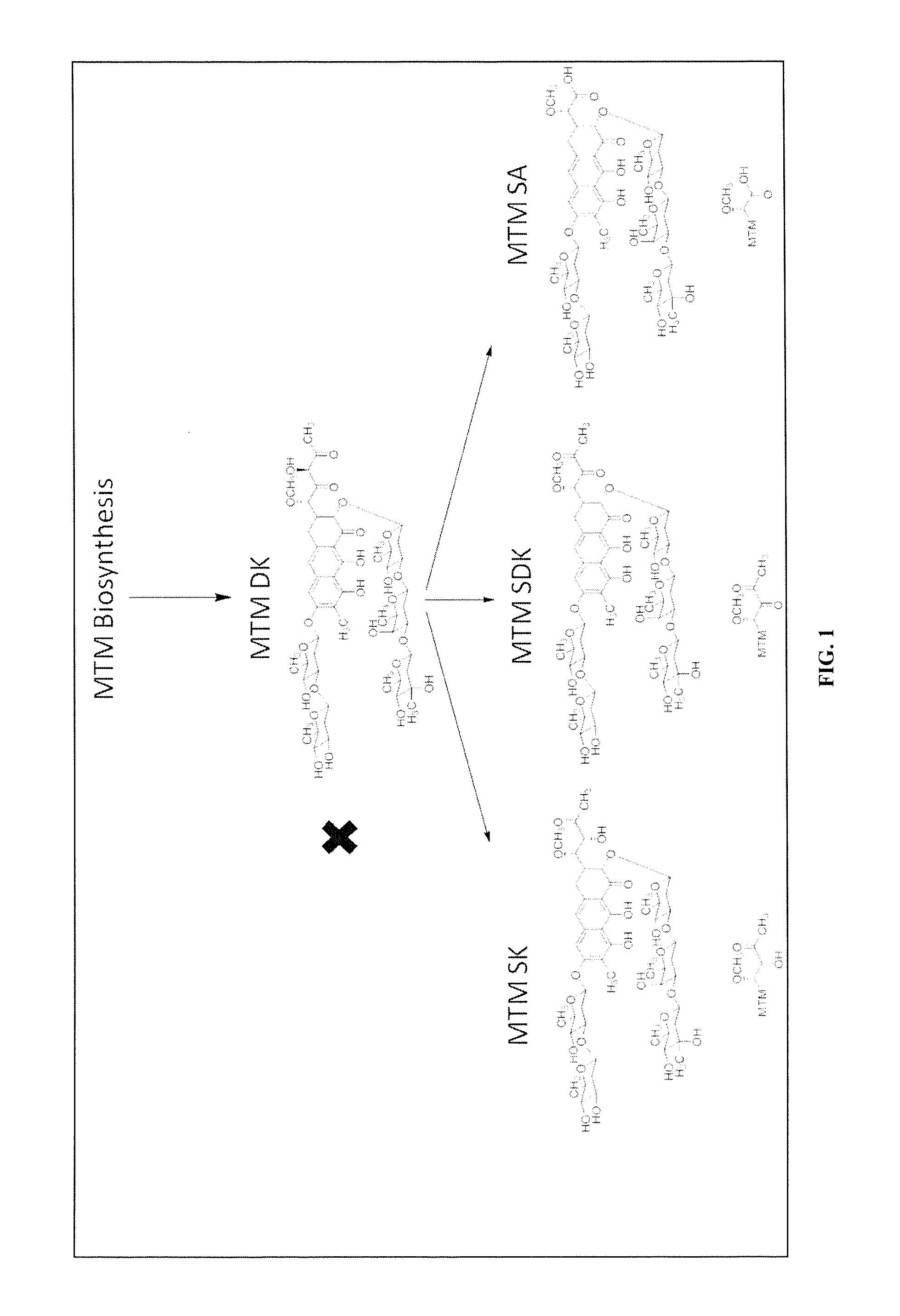
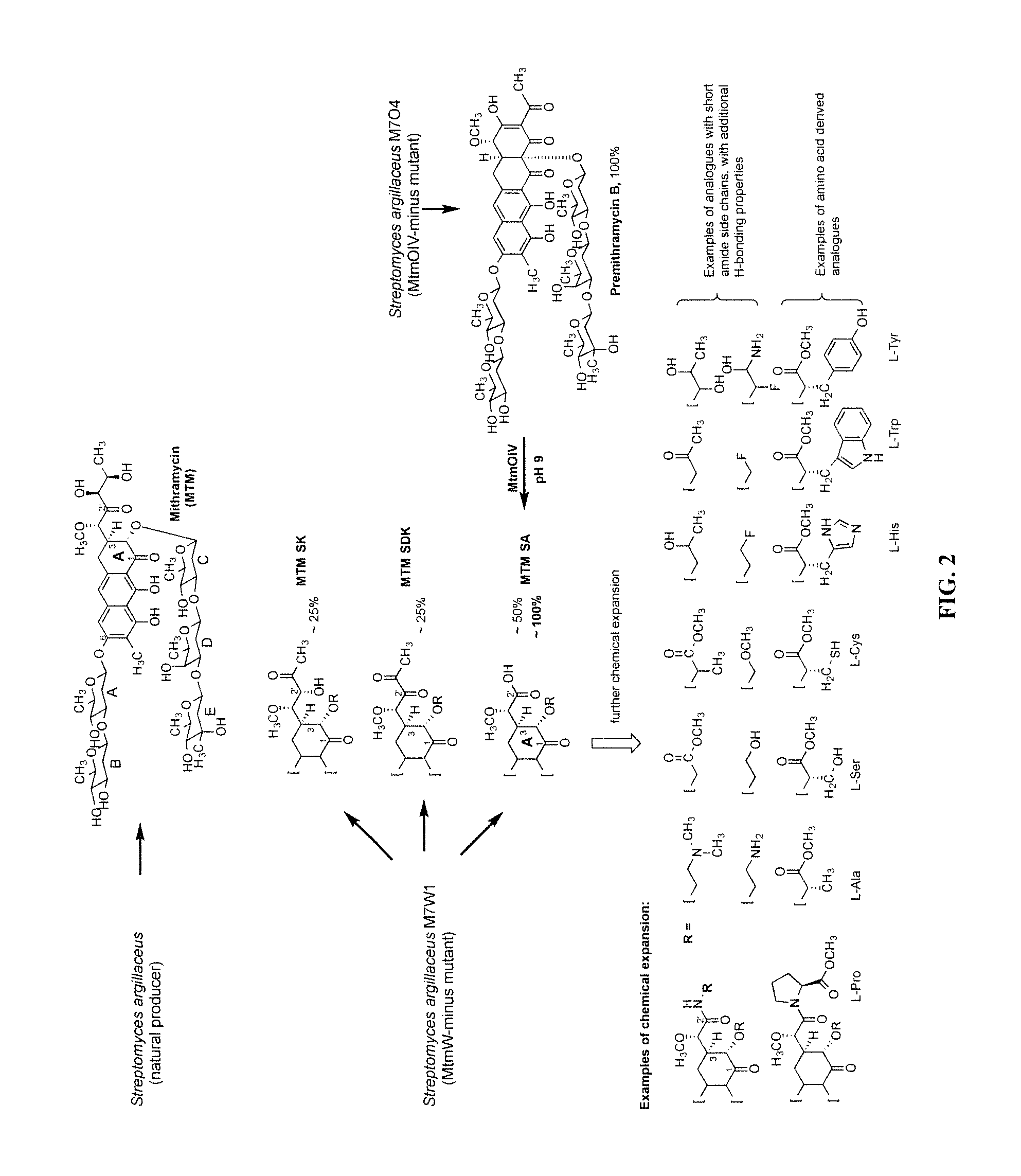
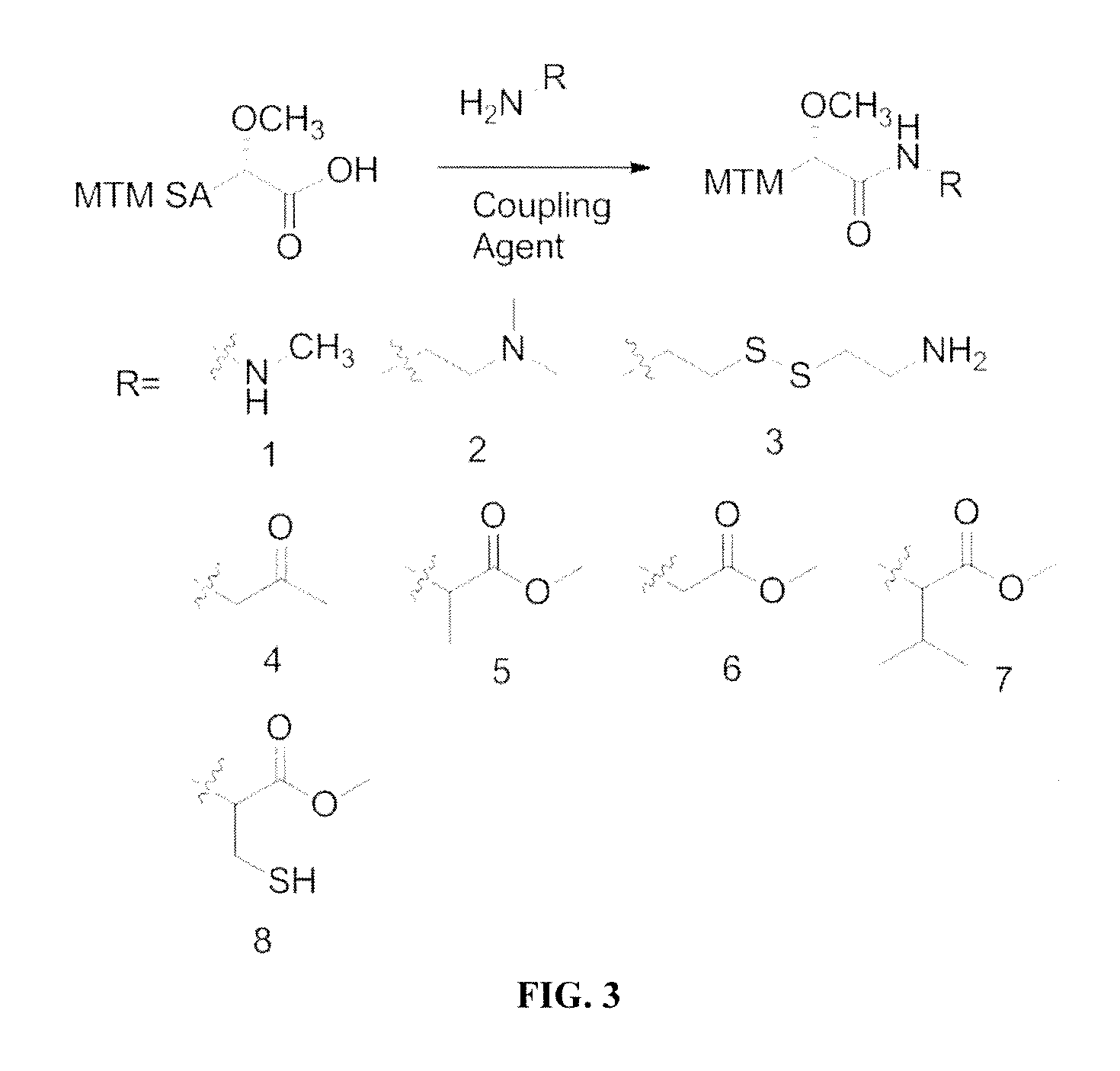
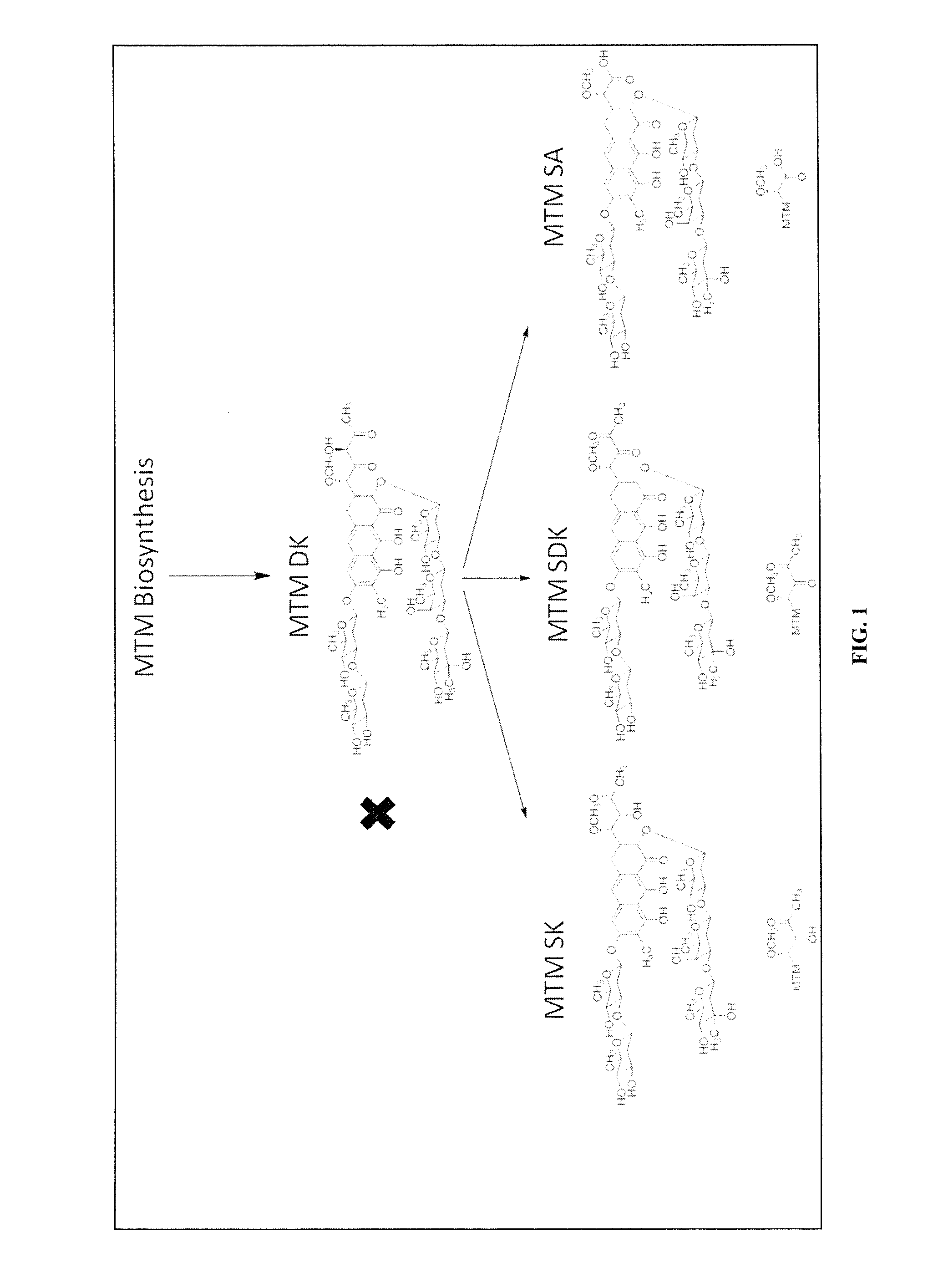
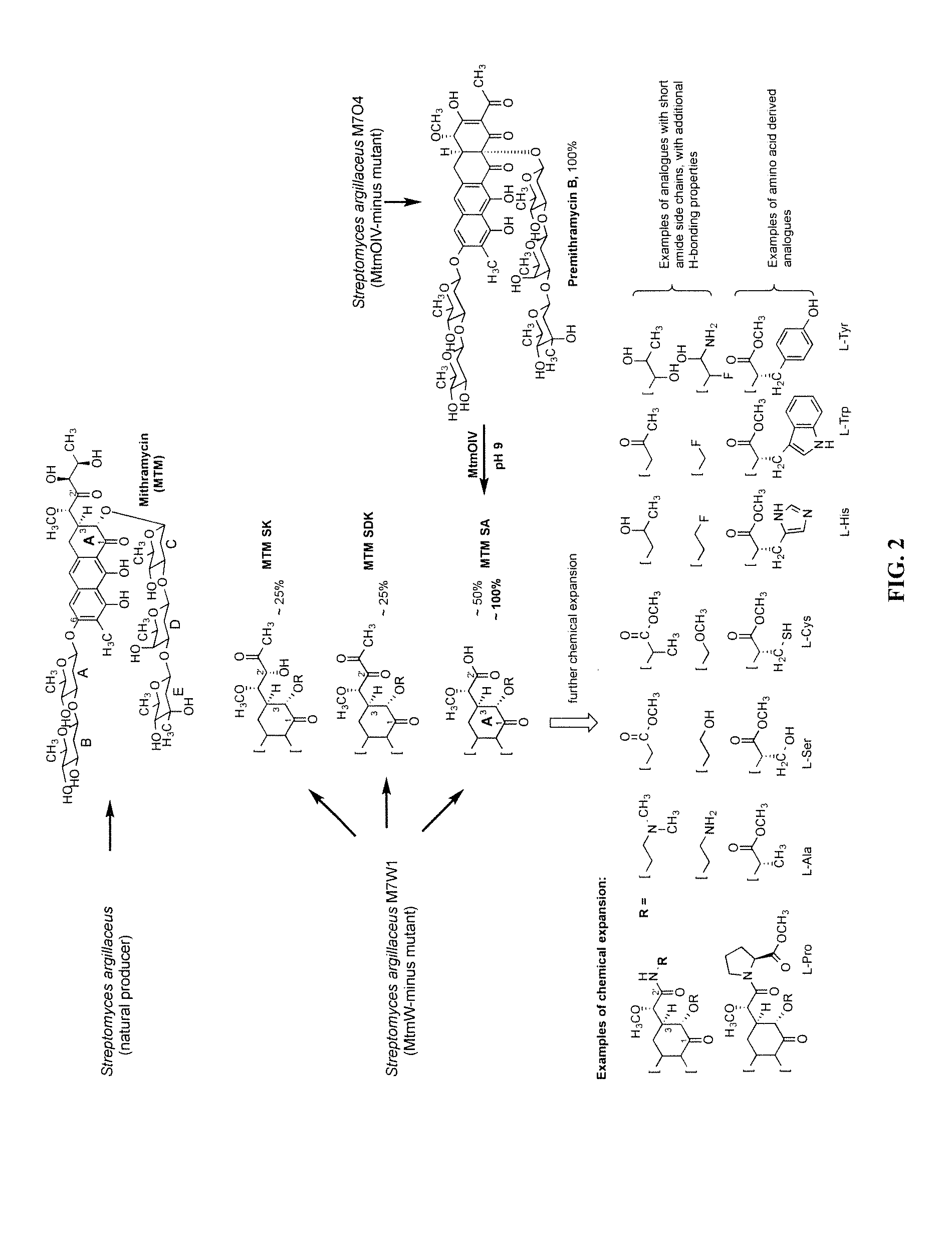
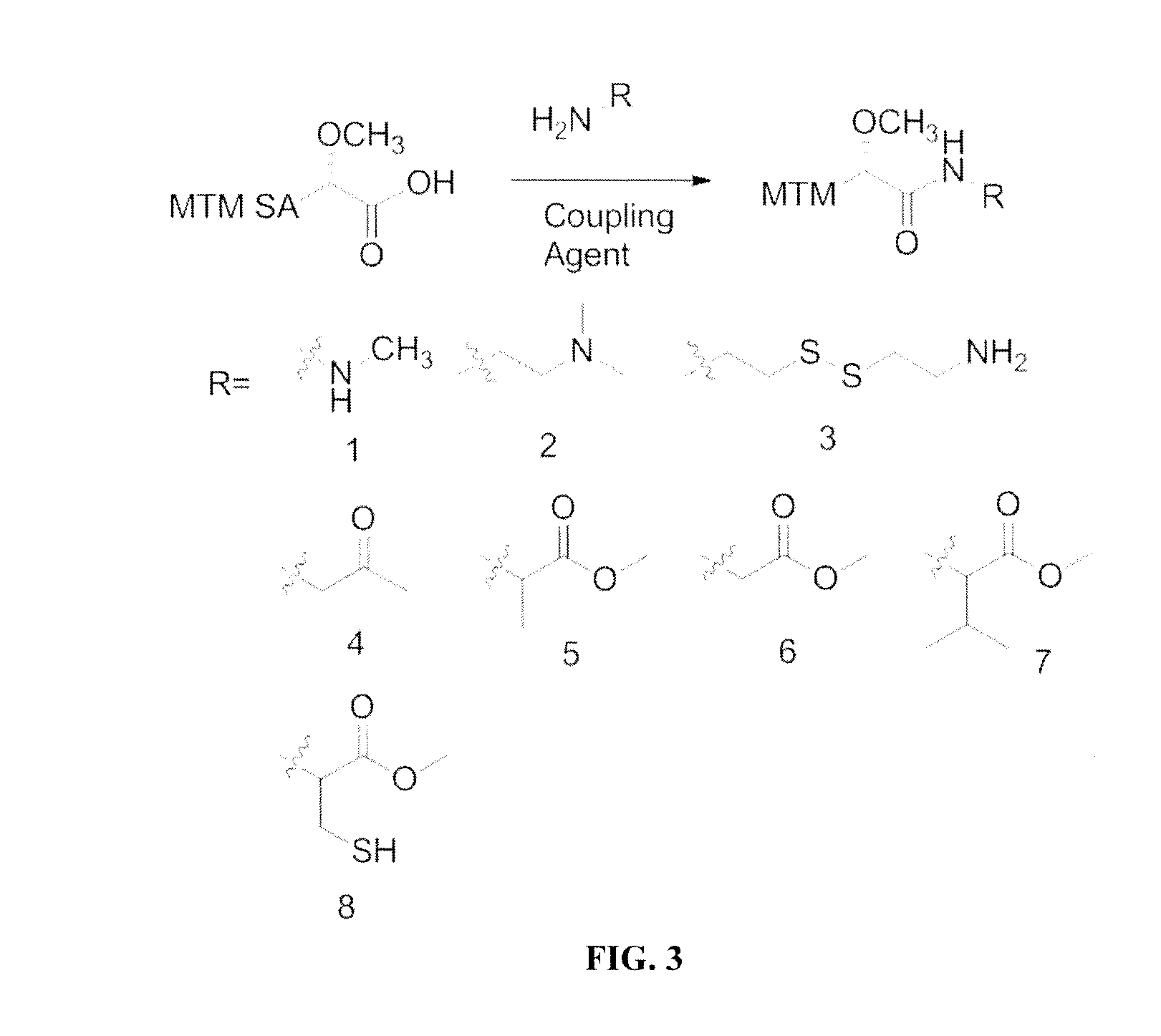
Semi-synthetic mithramycin derivatives with anti-cancer activity
Mithramycin derivatives and their pharmaceutically acceptable salts are disclosed. The mithramycin derivatives can be used in the treatment of Ewing sarcoma or other cancer or neuro-disease associated with an aberrant erythroblast transformation-specific transcription factor.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
Method for separating and authenticating erythroblast of blood
InactiveCN101122601AEasy to identifyPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsBiologyGene
The invention discloses a method for separating and appraising nucleated red blood cells in blood, including the following steps: (1) confecting reagent; (2) preparing anti-degumming slide; (3) selecting the staining method for nucleated red blood cells; (4) getting nucleated red blood cells from blood through microoperation. The method for separating and appraising nucleated red blood cells in blood can effectively identify nucleated red blood cells. Nucleated blood cell can be detected in 40 samples and the detection rate is 100 percent. Each sample is detected to have 2*106 to 6*106 / ml nucleated blood cell. In the invention, after the aniline being stained, the nucleated red blood cell is easy to be identified and skilled microoperation can quickly obtain the single nucleated red blood cell, so that the invention lays a good primary foundation to apply the single red blood cell in gene analysis.
Owner:孙艳萍
Cyanine compound, composition containing same and application in cell detection thereof
ActiveCN102115456AAccurate countEliminate distractionsOrganic chemistryMethine/polymethine dyesOrganic chemistryNonionic surfactant
On one hand, the invention provides a compound with a structure of general formula I or a conjugate thereof, wherein each group is as defined in the description. On the other hand, the invention provides a composition comprising (i) the compound of formula I or the conjugate thereof, and (ii) at least one surfactant selected from cationic surfactants and nonionic surfactants. The invention also provides a preparation method of the composition and a kit containing the composition. The invention still provides a method for the simultaneous identification of nucleated erythrocyte, basophilic granulocyte and lymphocyte and the classification by using the composition disclosed in the invention.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method of prenatal gene screen for down's syndrome using nucleated erythrocyte and kit
InactiveCN101358241ASimple and fast operationAccurate Screening ResultsMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescencePrenatal diagnosisFluorescence
The invention relates to a prenatal gene screening method for Down's syndrome by using nucleated erythrocyte and a kit thereof. The method is that a kit which comprises a nucleated erythrocyte purification reagent, primers and a bichrome Taqman fluorescent probe which are synthesized by the specific sequence DSCR section sequence of chromosome 21 and the GAPDH gene sequence on chromosome 16, and an amplification buffering action reagent of PCR action. The invention realizes that through the following steps: (a) the purification of fetus NRBC and the extraction of DNA; (b) the synthesis of the primers and the bichrome Taqman fluorescent probe respectively by using the specific sequence DSCR section sequence of chromosome 21 and the GAPDH gene sequence on chromosome 16; (c) the co-amplification of two pairs of the primers to obtain the curve of fluorescence quantitative PCR by the bichrome fluorescence quantitative PCR reaction in the amplification buffering reaction system. The invention has simple and convenient operation and high testing throughput, and belongs to a non-invasive prenatal diagnostic method.
Owner:SHANDONG YADA PHARMA
Acellular red blood cell substitute
An acellular red blood cell substitute which comprises an essentially tetramer-free, substantially stroma-free, cross-linked, polymerized, pyridoxylated hemoglobin and a nontoxic, pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, its use and a process for preparing said acellular red blood cell substitute.
Owner:OPK BIOTECH
Process for discriminating and counting erythroblasts
InactiveUS20040241770A1Preparing sample for investigationBiological testingFluorescent spectraStaining
A method for discriminating and counting erythroblasts comprises the steps of: (i) staining leukocytes in a hematologic sample by adding a fluorescent labeled antibody capable of binding specifically with leukocytes to the hematologic sample; (ii) raising the permeability only of cell membranes of erythroblasts in the hematologic sample to a nucleotide fluorescent dye which does not permeate a cell membrane usually, the nucleotide fluorescent dye having a fluorescent spectrum capable of being distinguished from that of a fluorescent labeling compound of the fluorescent labeled antibody in step (i); (iii) staining nuclei of the erythroblasts in the hematologic sample with the nucleotide fluorescent dye; (iv) subjecting the hematologic sample to flowcytometry to detect at least two fluorescent signals from each cell; and (v) discriminating and counting the erythroblasts from difference in intensity between the at least two fluorescent signals.
Owner:HOUWEN BEREND +4
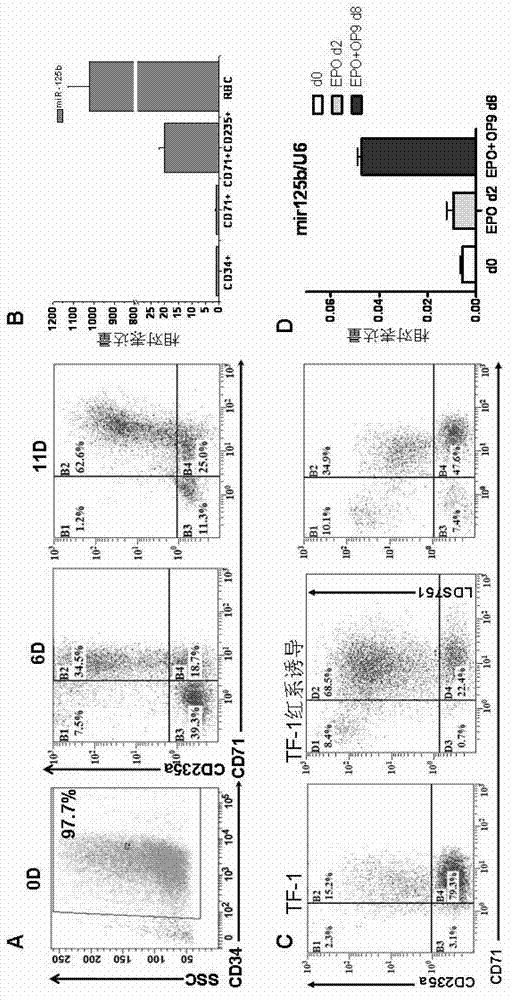
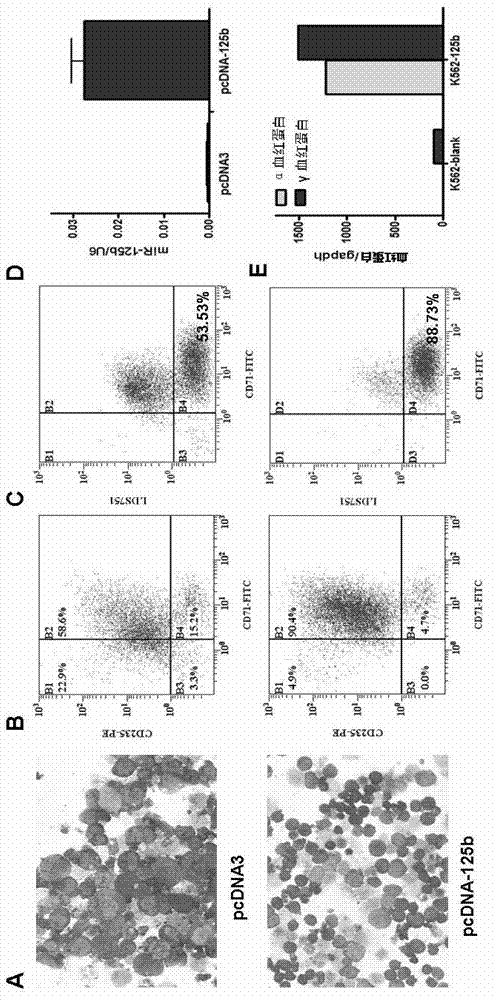
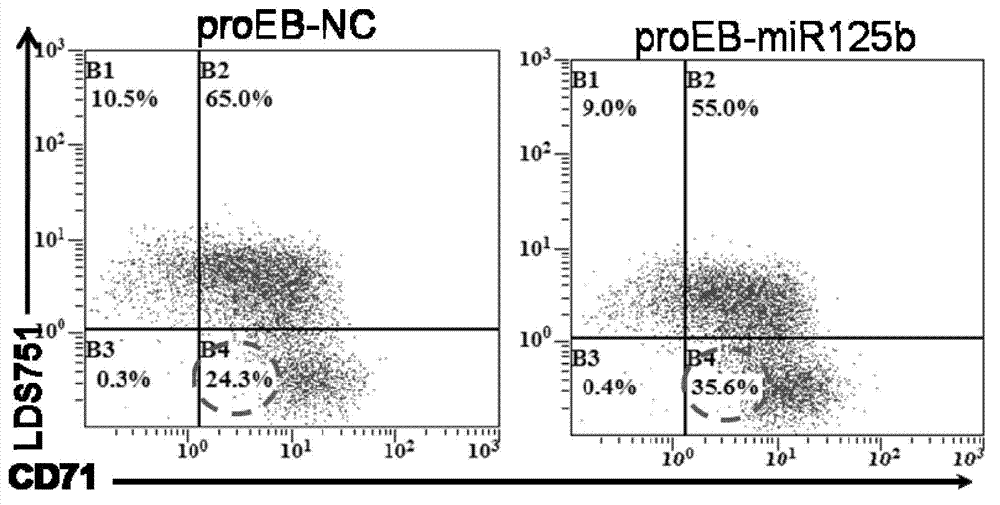
Application of miR-125b in red blood cell maturation
ActiveCN103074354AEfficient manufacturingVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsMir 125bNucleotide sequencing
The invention relates to an application of miR-125b in red blood cell maturation. A method for preparing mature red blood cell comprises the following steps: making precursor cells of the red blood cell to express miR-125b, wherein the miR-125b has a nucleotide sequence shown in a SEQ IDNO:1; and culturing the precursor cells of the red blood cell of the expressed miR-125b to obtain the mature red blood cell; wherein, the precursor cells of the red blood cell can be selected from original erythroblast, polychromatic erythroblast, orthoneutrophil erythroblast and reticulocyte. The method can be used for effectively preparing the mature red blood cell.
Owner:FIELD OPERATION BLOOD TRANSFUSION INST OF PLA SCI ACAD OF MILITARY
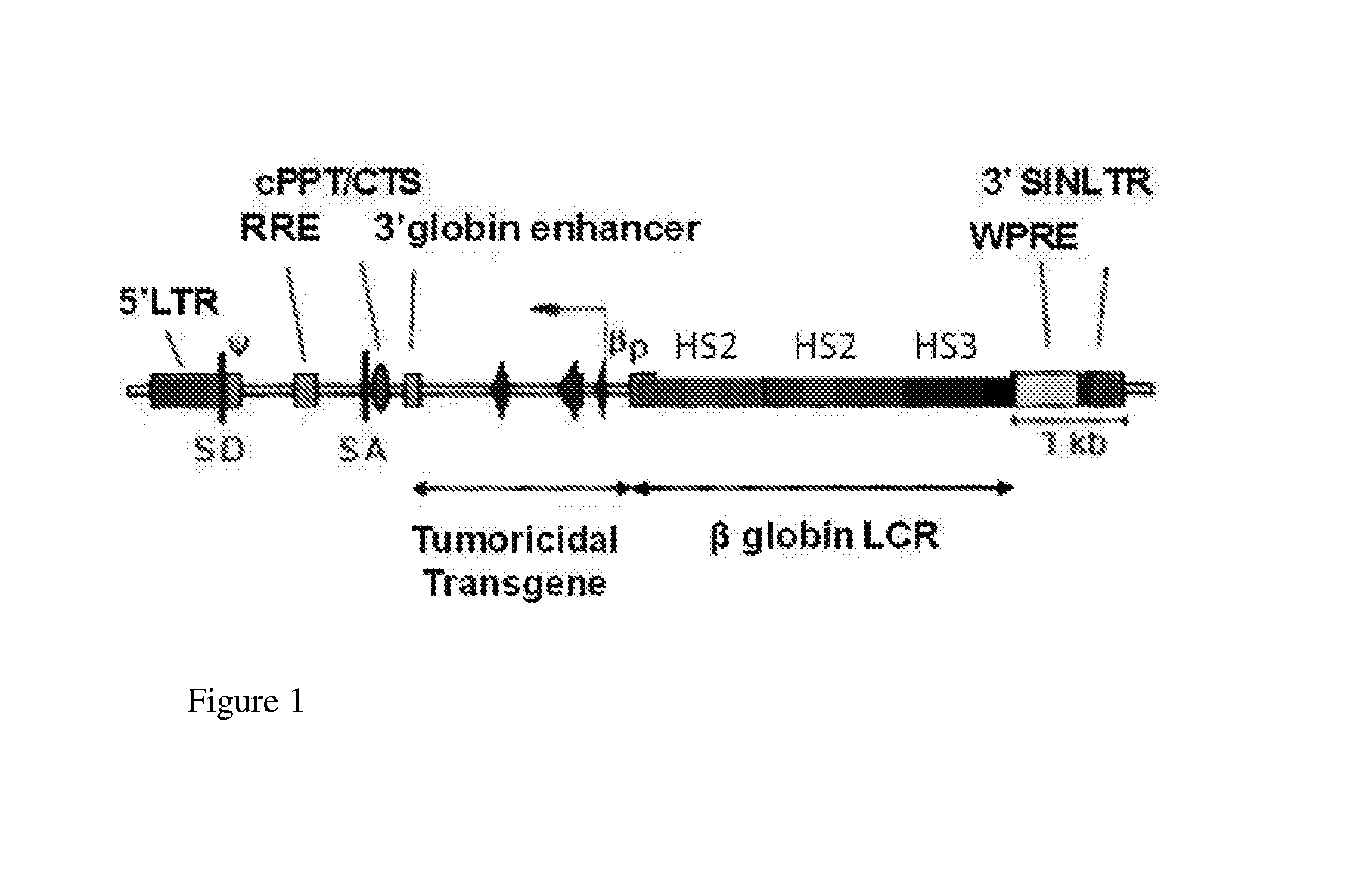
Sickled Erythrocytes and Progenitors Target Cytotoxics to Tumors
The present invention provides therapeutic mammalian cells which synthesize and express SS hemoglobin and a tumoricidal transgene. They are produced by transduction of SS erythroid progenitors / erythroblasts using viral vectors comprising a tumoricidal transgene operatively linked to the coding region of SS β-globin promoter / enhancer. Such transduced SS erythroid cells differentiate into mature SSRBCs that exhibit sustained synthesis and expression of SS hemoglobin, a tumoricidal protein(s). Both mature and progenitor SS-cells carrying tumoricidal transgene(s) are capable of selectively localizing in tumor microenvironment, occluding tumor microvessels and inducing a tumoricidal response.
Owner:TERMAN DAVID S
Hematology controls and methods
InactiveUS20100086962A1Stable hematology controlCost-effective manufacturingMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingCellular componentMedicine.hematology
An integrated hematology control and methods for making the same, including a first cellular component derived from a plurality of processed animal red blood cells other than human blood cells and a second cellular component derived from a plurality of processed animal red blood cells other than human blood cells and a plurality of human blood cells, wherein the control simulates erythroblasts and white blood cells of a human blood sample on an automated blood analyzer.
Owner:STRECK INC
In vitro mass production of human erythroid cells from the blood of normal donors and thalassemic patients
InactiveUS20040229356A1FavorInhibit productionArtificial cell constructsBlood/immune system cellsGlycophorinThalassemia
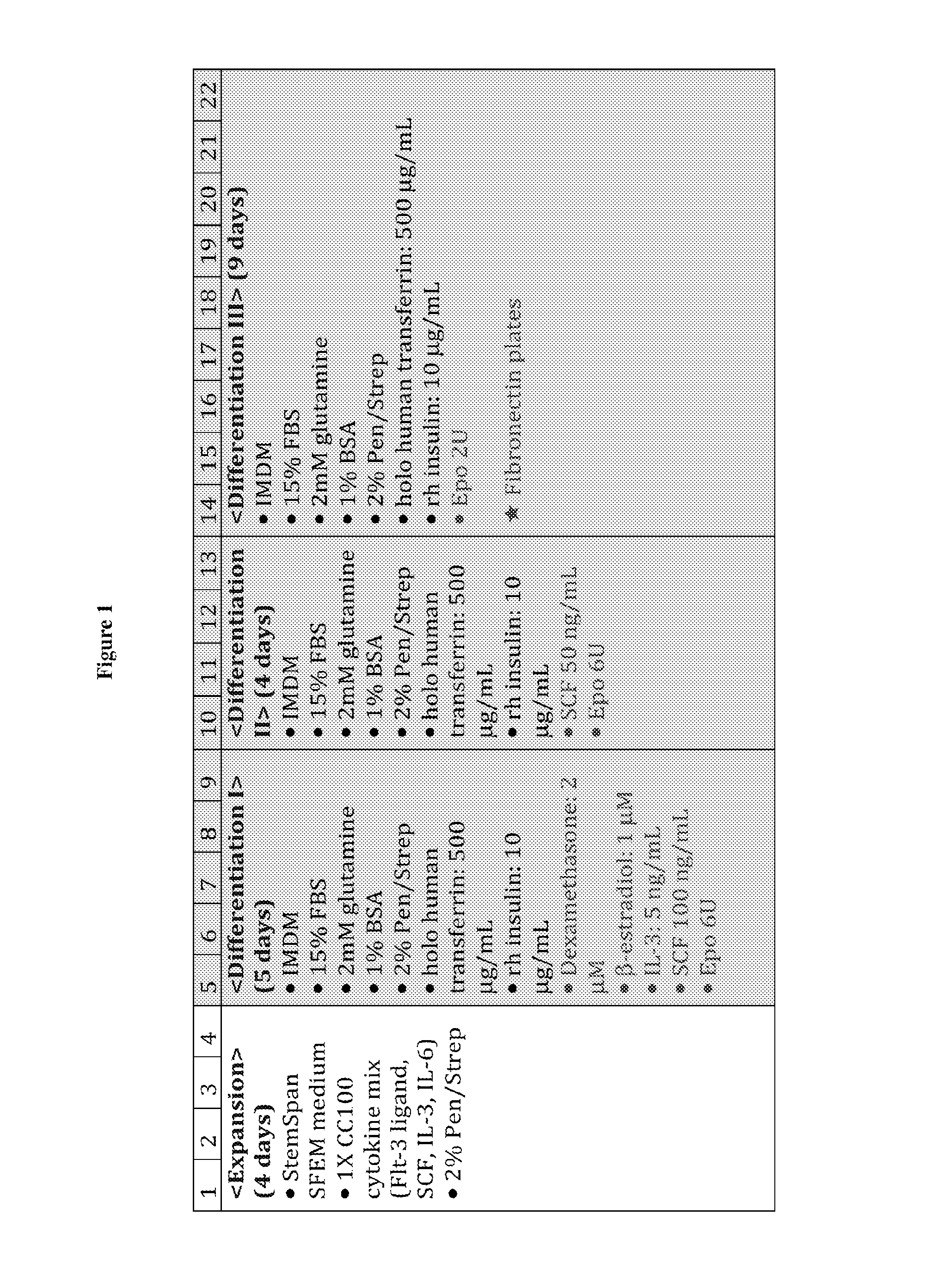
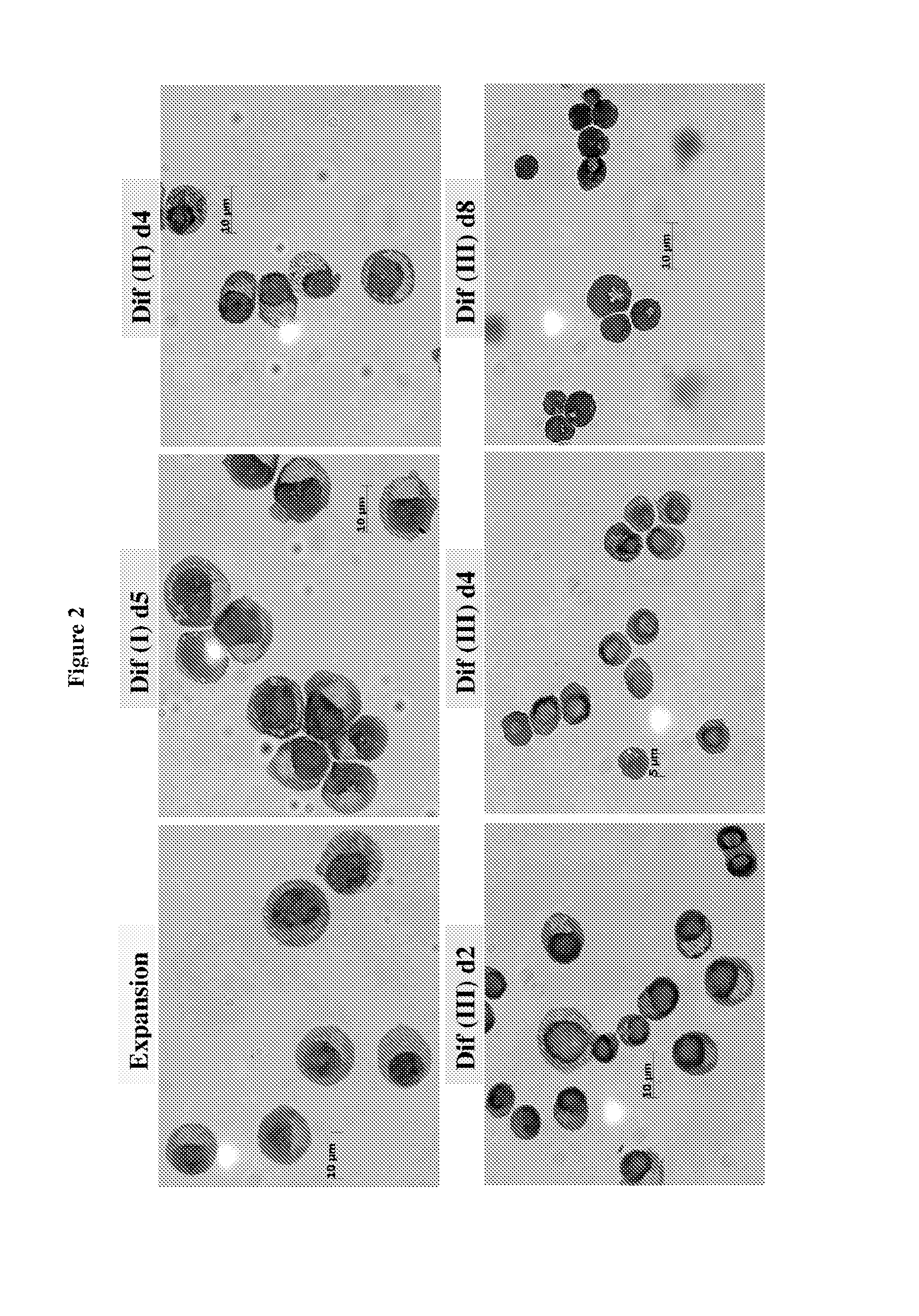
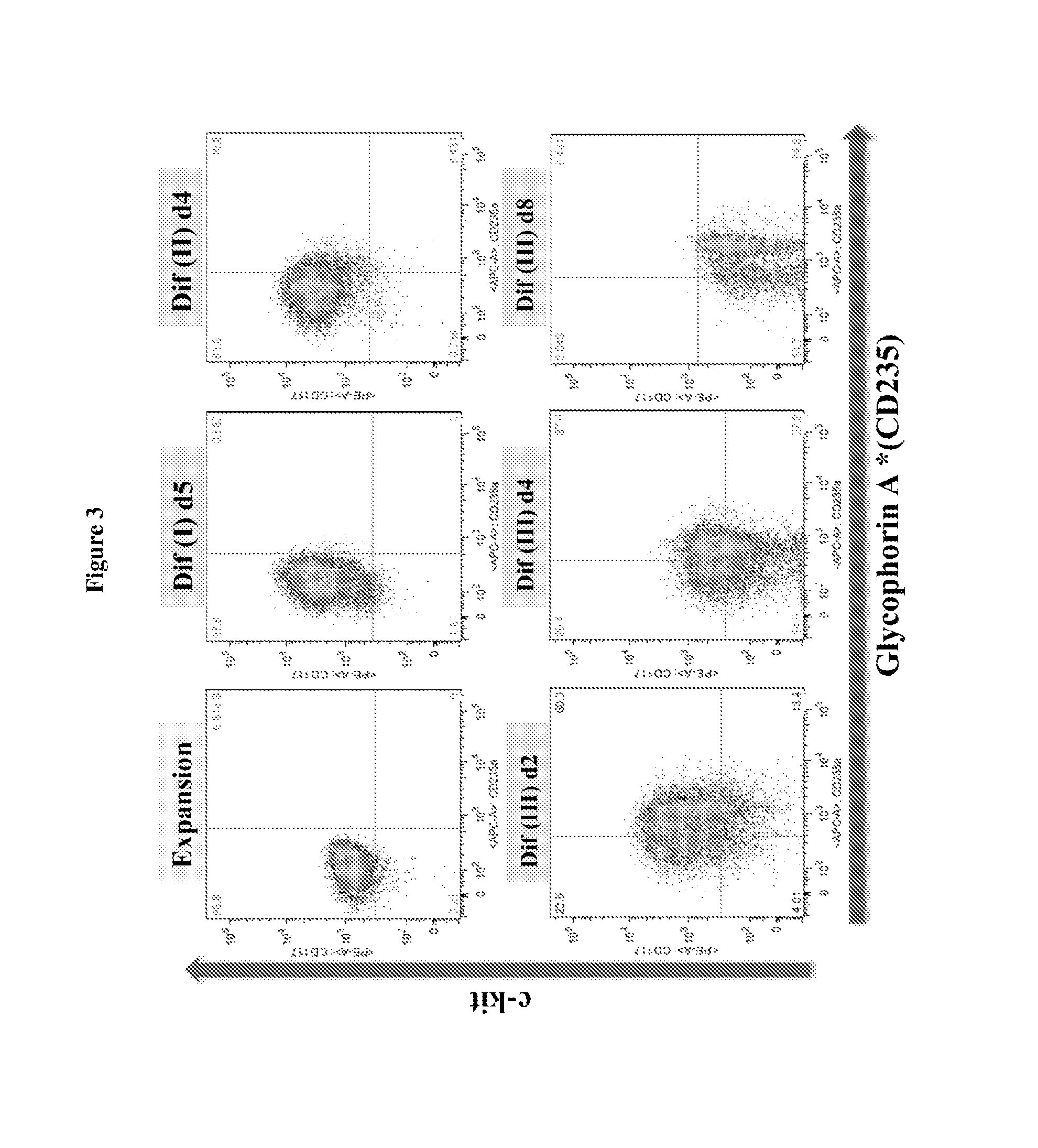
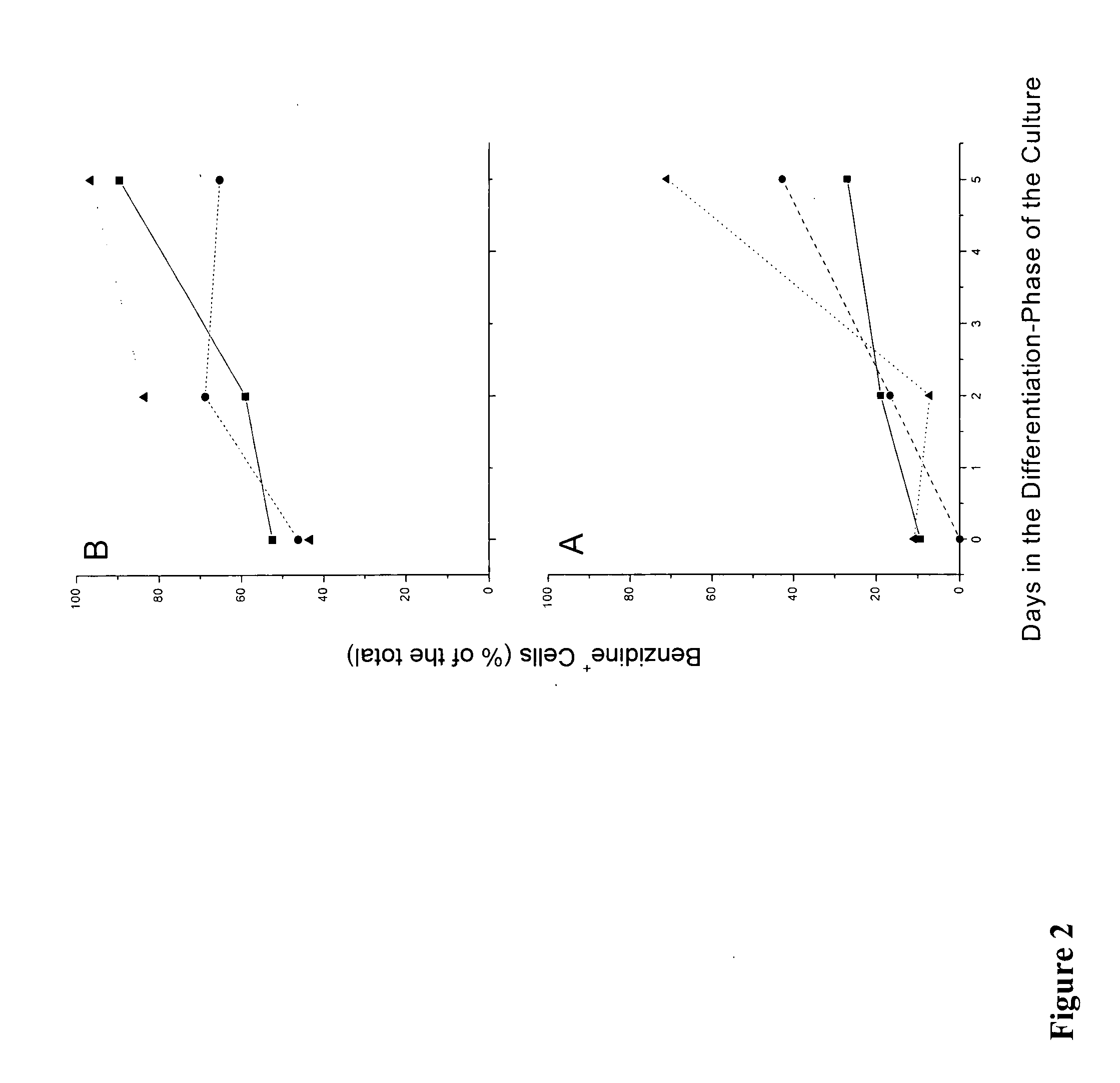
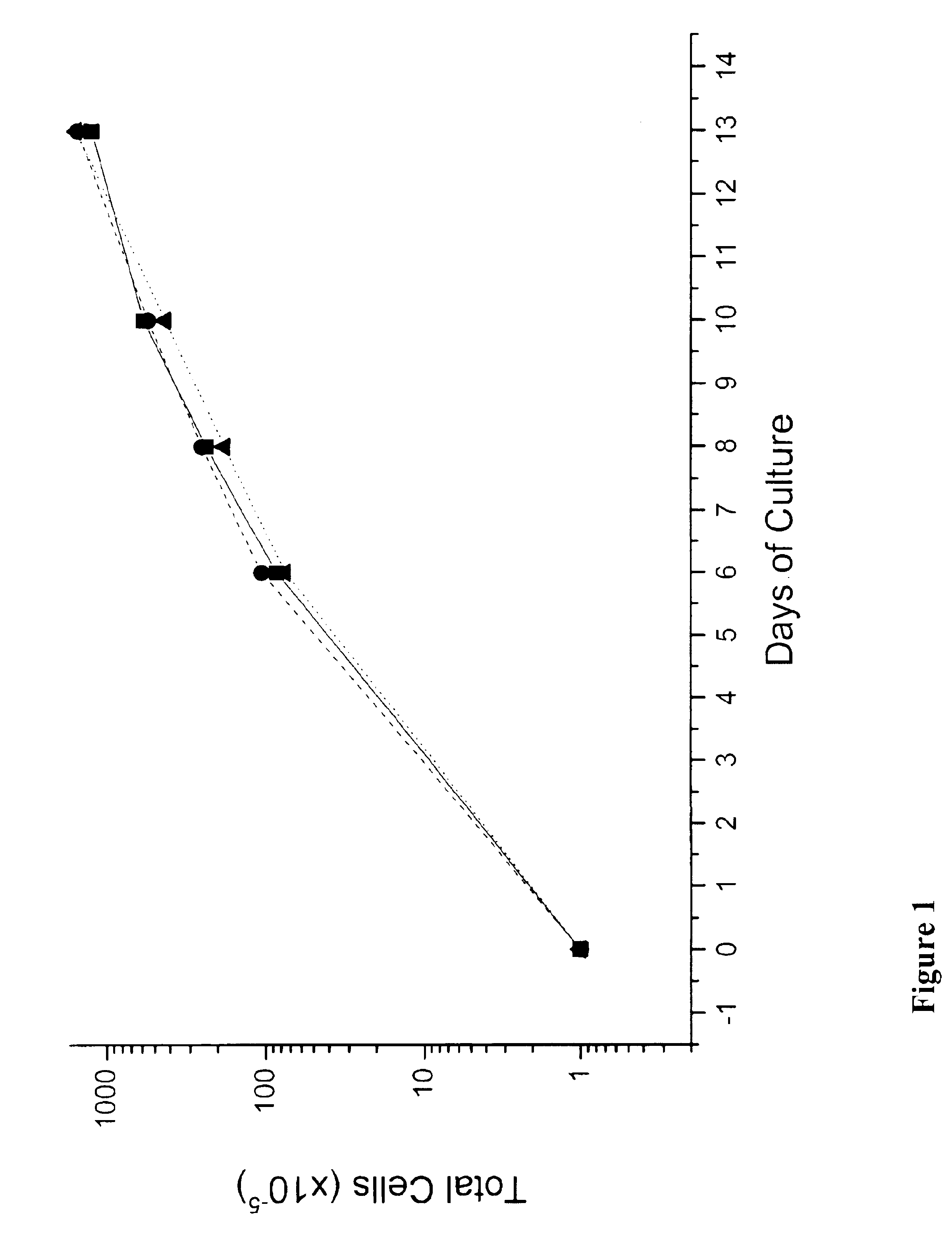
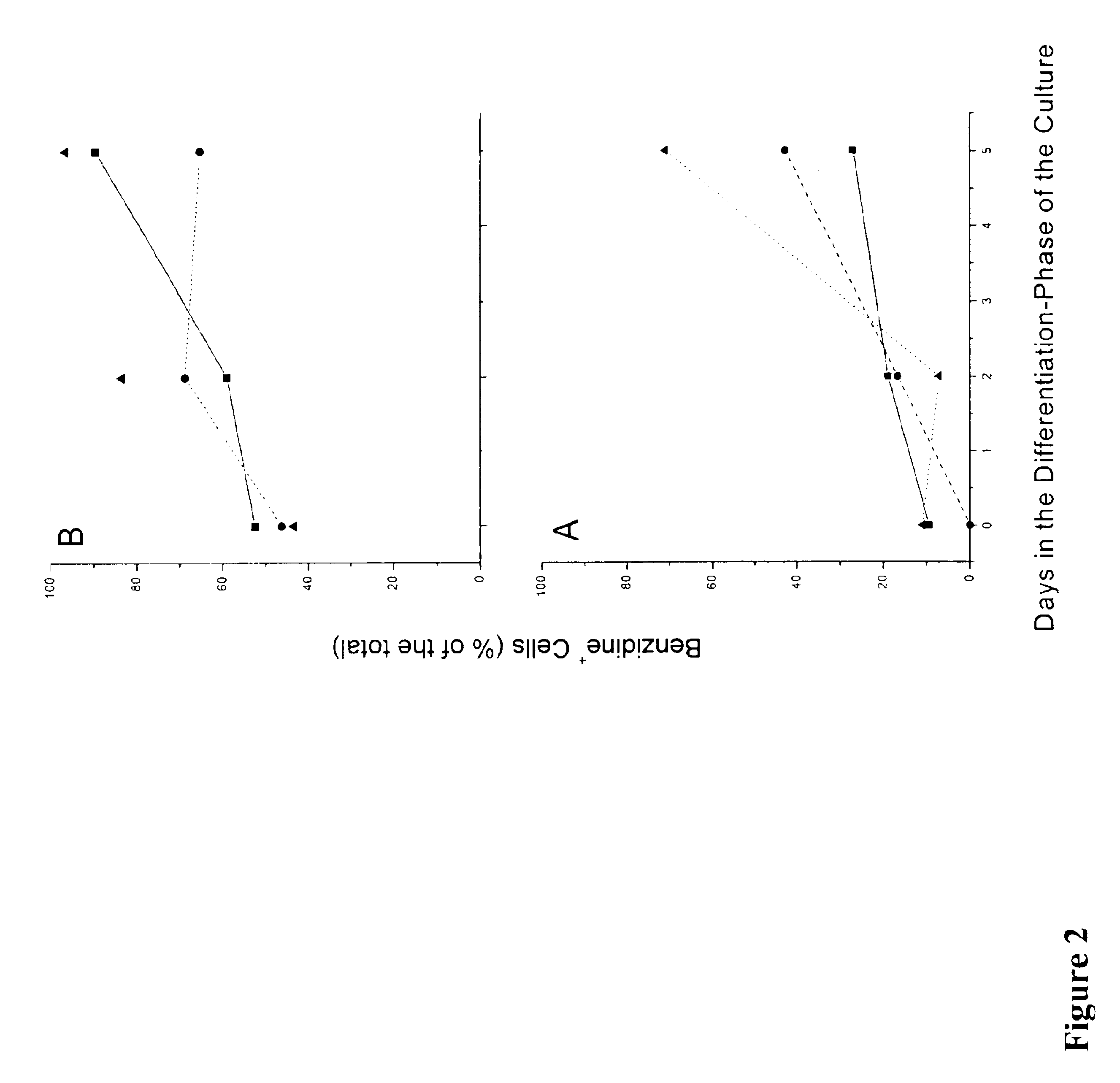
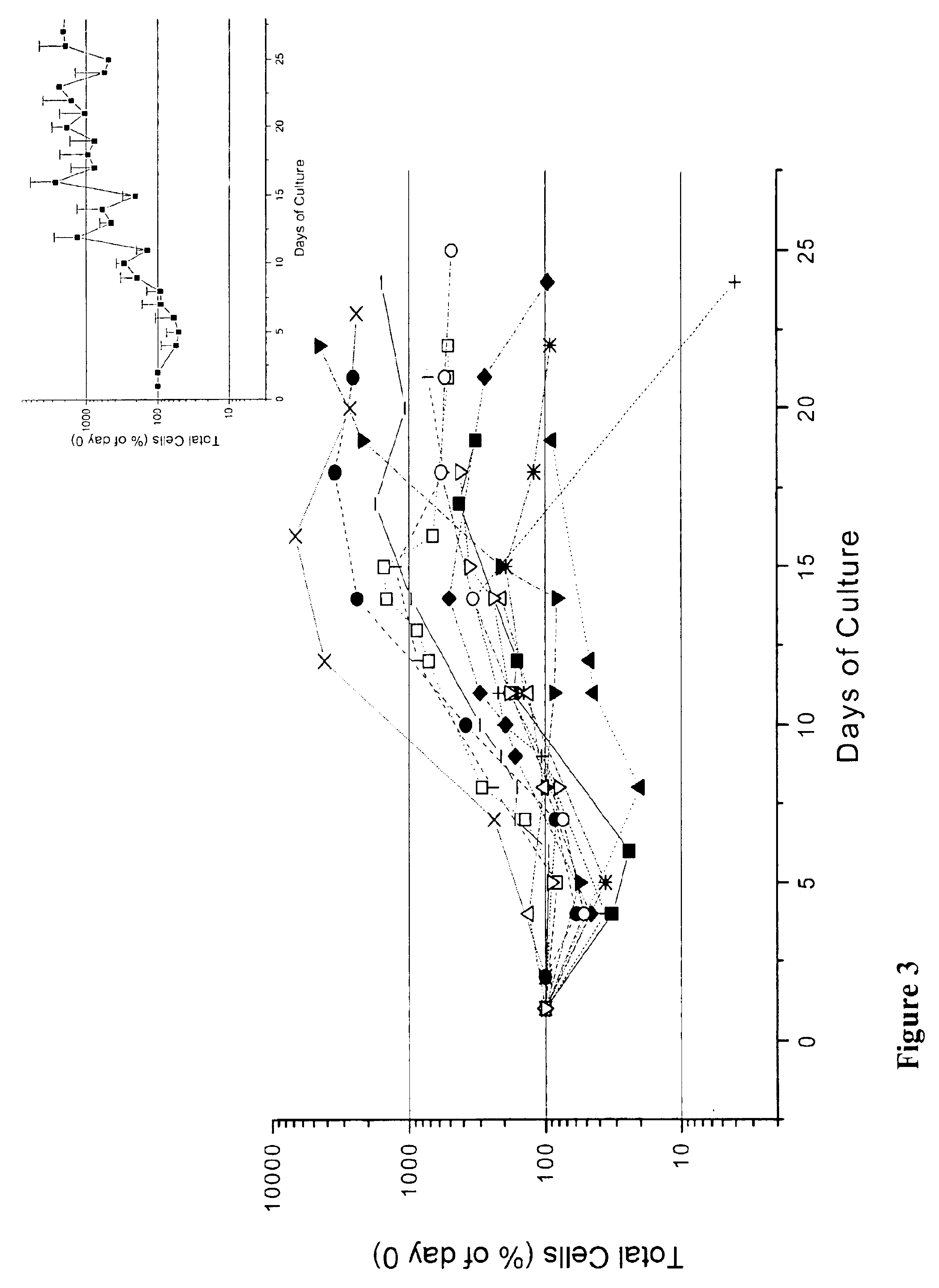
We describe a new two-step culture method for mass production in vitro of erythroid cells from either CD34<+> (10<5 >cells / mL) or light-density (10<6 >cells / mL) cells purified from the blood of normal donors and thalassemic patients. The method includes (i) culture of the cells in the presence of dexamethasone and estradiol (10<-6 >M each) and (ii) the growth factors SCF (50 ng / mL), IL-3 (1 ng / mL), and EPO (1 U / mL). In their proliferative phase, these cultures generated about 1-2x10<7 >erythroblasts for each milliliter of blood collected from normal donors or thalassemic patients. They were composed mostly (90%) of CD45<low> / glycophorin (GPA)<neg> / CD71<low >cells at day 7, 50-60% of which became CD45<neg> / GPA+ / CD71<high >by days 15-20. However, when cells from days 7 to 12 of the proliferative phase were transferred in differentiation medium containing EPO and insulin, they progressed to mature erythroblasts (>90% benzidine<pos >and CD45<neg> / GPA<+> / CD71<medium>) in 4 days. Because of the high number of erythroid cells that are generated from modest volumes of blood, this method will prove useful in donor-specific studies of erythroid differentiation.
Owner:INST SUPERIORE DI SANITA
In vitro mass production of human erythroid cells from the blood of normal donors and thalassemic patients
We describe a new two-step culture method for mass production in vitro of erythroid cells from either CD34+ (105 cells / mL) or light-density (106 cells / mL) cells purified from the blood of normal donors and thalassemic patients. The method includes (i) culture of the cells in the presence of dexamethasone and estradiol (10−6 M each) and (ii) the growth factors SCF (50 ng / mL), IL-3 (1 ng / mL), and EPO (1 U / mL). In their proliferative phase, these cultures generated about 1-2×107 erythroblasts for each milliliter of blood collected from normal donors or thalassemic patients. They were composed mostly (90%) of CD45low / glycophorin (GPA)neg / CD71low cells at day 7, 50-60% of which became CD45neg / GPA+ / CD71high by days 15-20. However, when cells from days 7 to 12 of the proliferative phase were transferred in differentiation medium containing EPO and insulin, they progressed to mature erythroblasts (>90% benzidinepos and CD45neg / GPA+ / CD71medium) in 4 days. Because of the high number of erythroid cells that are generated from modest volumes of blood, this method will prove useful in donor-specific studies of erythroid differentiation.
Owner:INST SUPERIORE DI SANITA
Micro-fluidic chip, manufacturing method thereof and fetus erythroblast capturing and releasing method
ActiveCN108795685AReduce non-specific adsorptionImprove capture efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLength waveMonocyte
The invention discloses a micro-fluidic chip. The micro-fluidic chip comprises a micro-channel and a capturing substance, wherein the micro-channel at least allows target substances such as fetus erythroblasts to pass through; the capturing substance can be specifically combined to the target substances; the capturing substance is fixed in the micro-channel via a connecting arm; the connecting armcomprises at least one locus which can be cut by light; and after more than one locus which can be cut by light is cut by light with selectable wavelength, the connecting arm is broken completely. The invention further discloses a manufacturing method of the micro-fluidic chip and a fetus erythroblast capturing and releasing method. by the micro-fluidic chip, fetus erythroblasts and the like canbe captured specifically, high-efficiency and high-purity separation of the fetus erythroblasts is realized, the captured fetus erythroblasts can further be selectively released on monocyte level in amode of light cutting and the like, and follow-up analysis is facilitated. Meanwhile, the micro-fluidic chip is low in manufacturing cost and simple in process.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Method for differentiation of human pluripotent stem cell lines in suspension culture
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
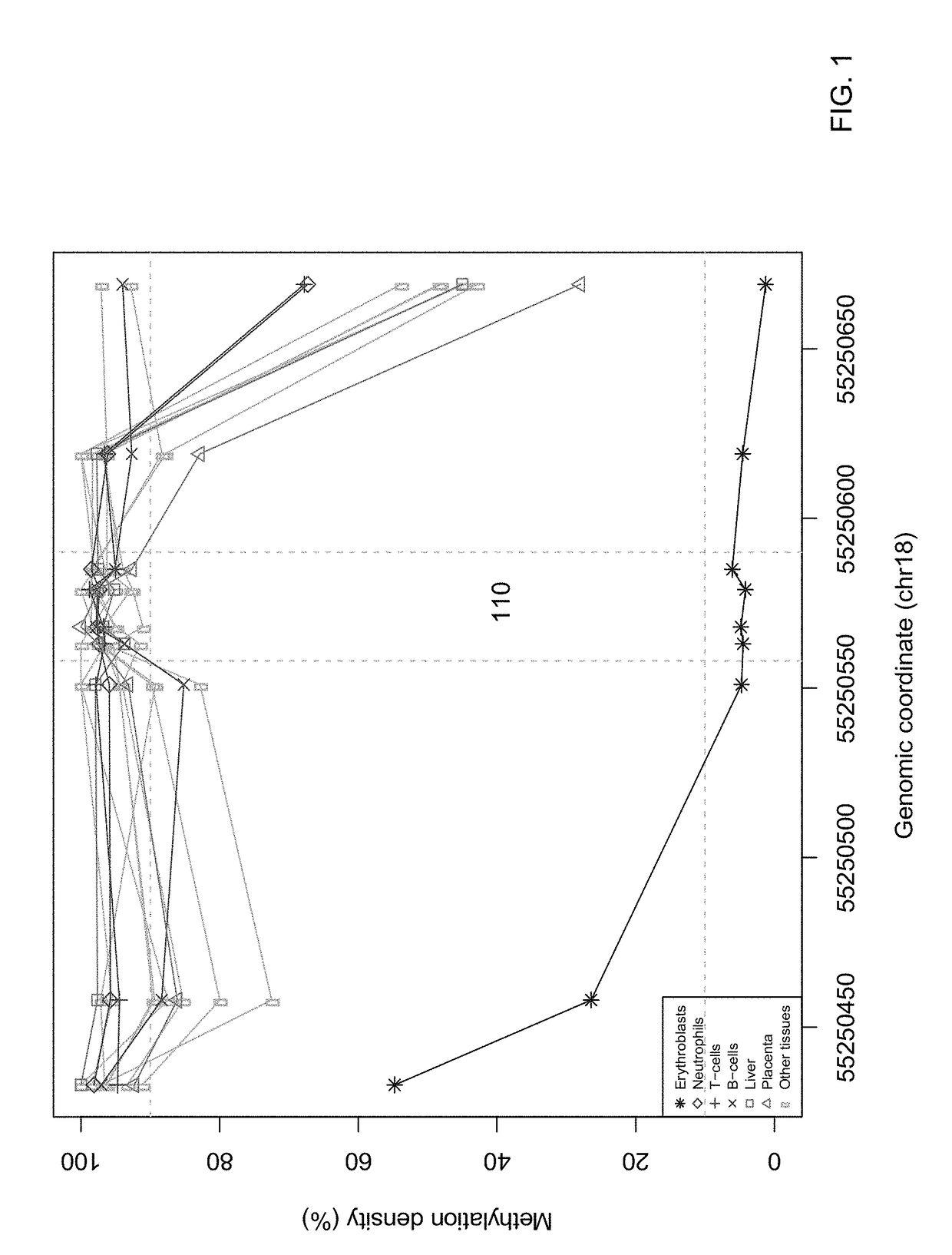
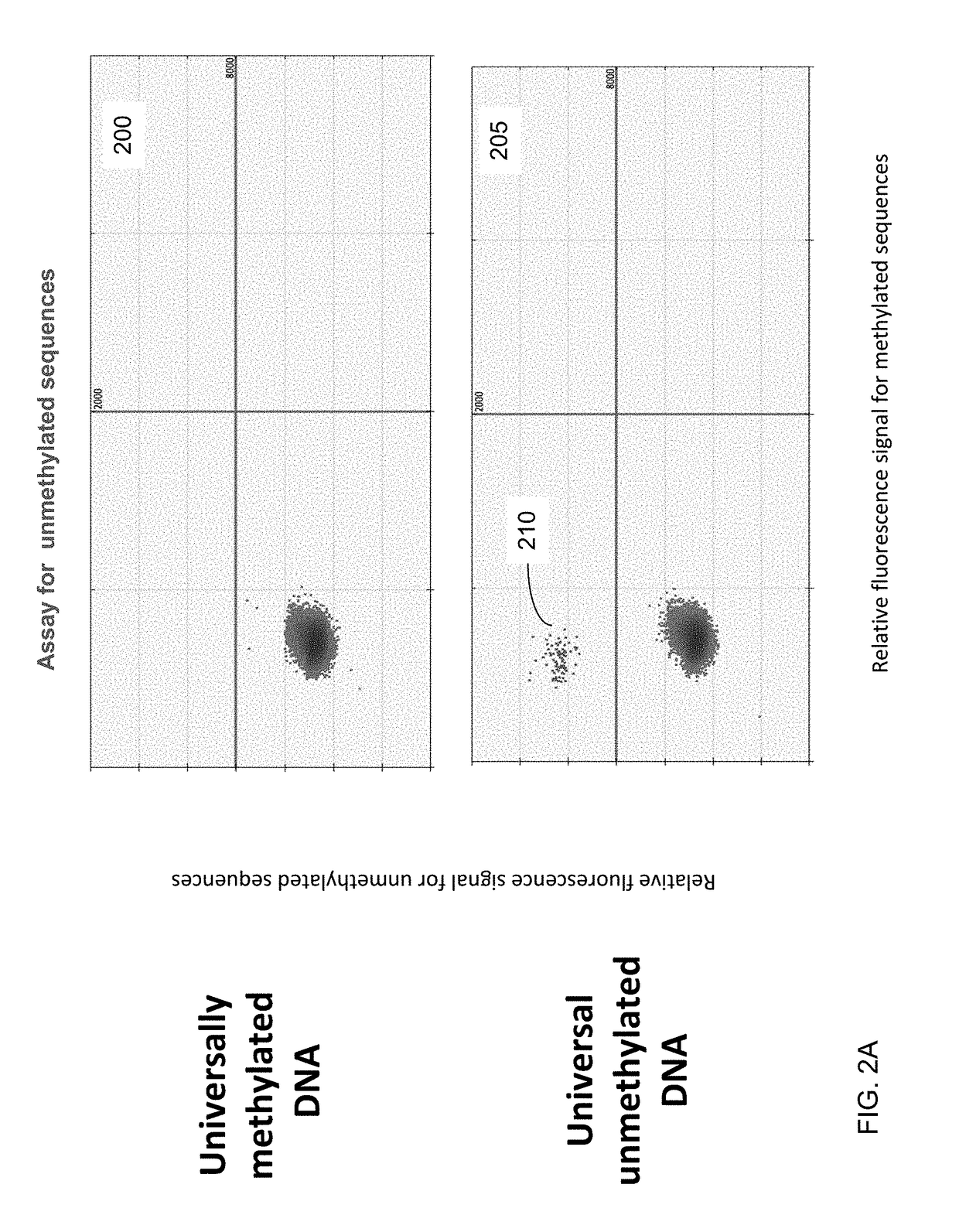
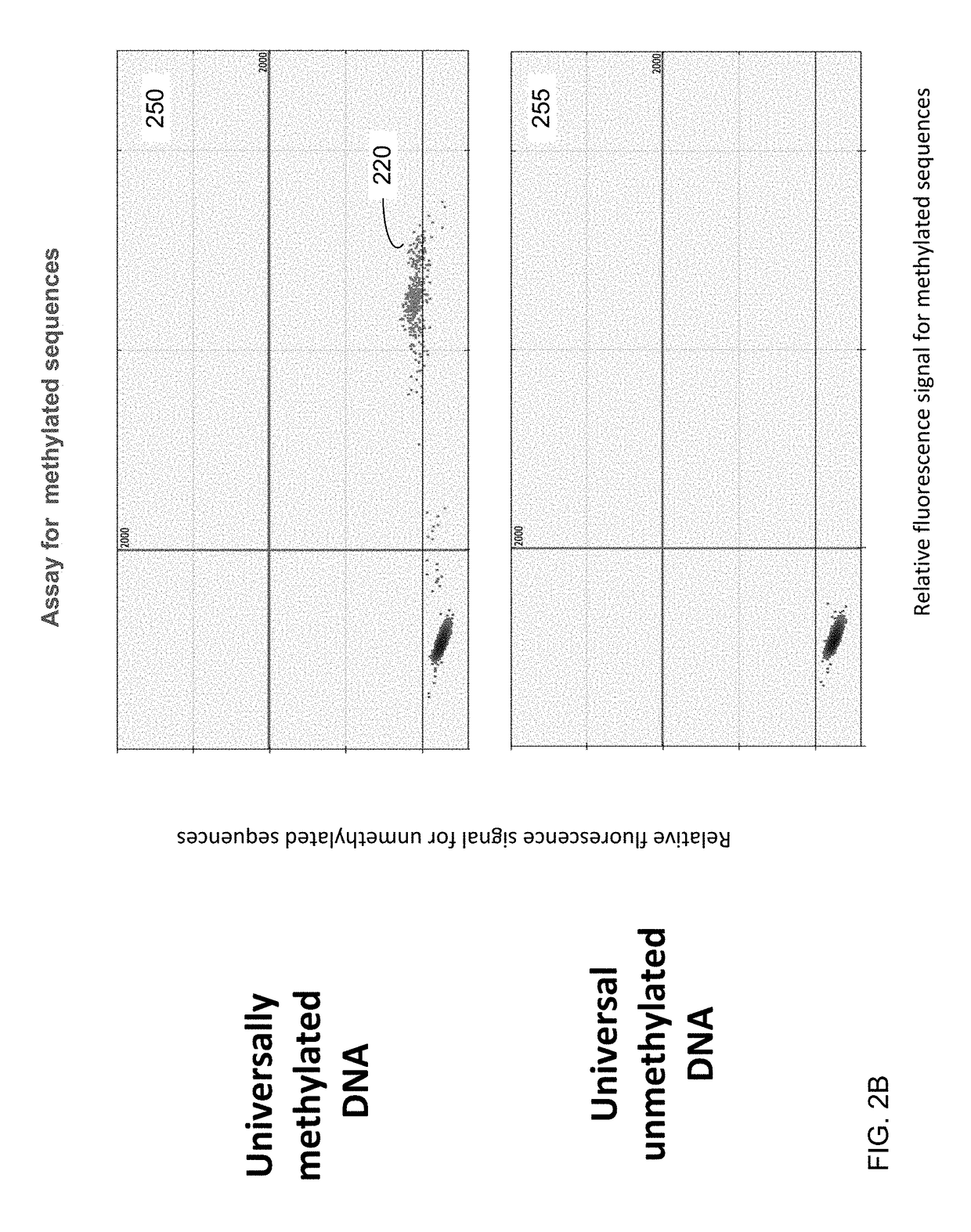
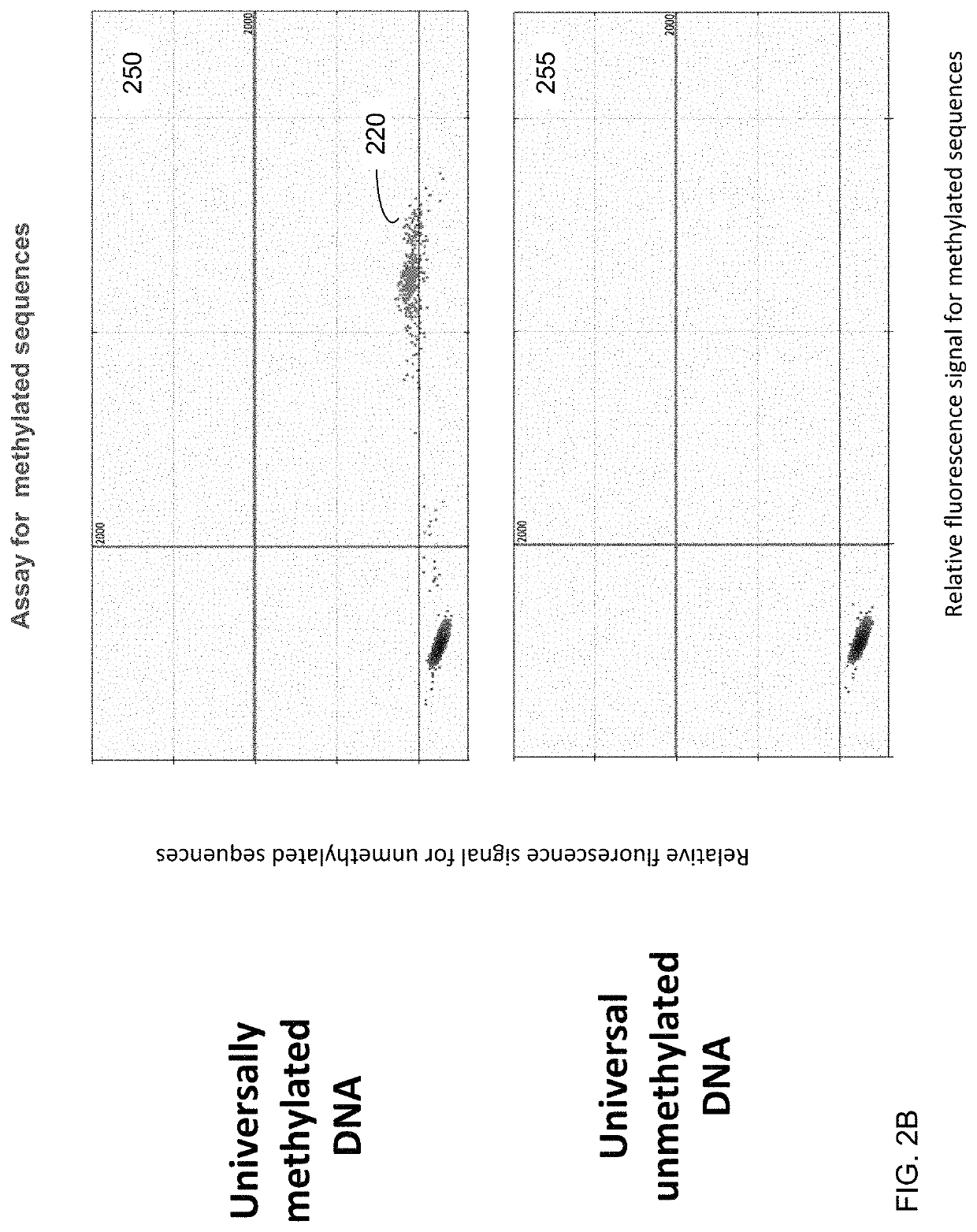
Detecting hematological disorders using cell-free DNA in blood
Techniques are provided for detecting hematological disorders using cell-free DNA in a blood sample, e.g., using plasma or serum. For example, an assay can target one or more differentially-methylated regions specific to a particular hematological cell lineage (e.g., erythroblasts). A methylation level can be quantified from the assay to determine an amount of methylated or unmethylated DNA fragments in a cell-free mixture of the blood sample. The methylation level can be compared to one or more cutoff values, e.g., that correspond to a normal range for the particular hematological cell lineage as part of determining a level of a hematological disorder.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
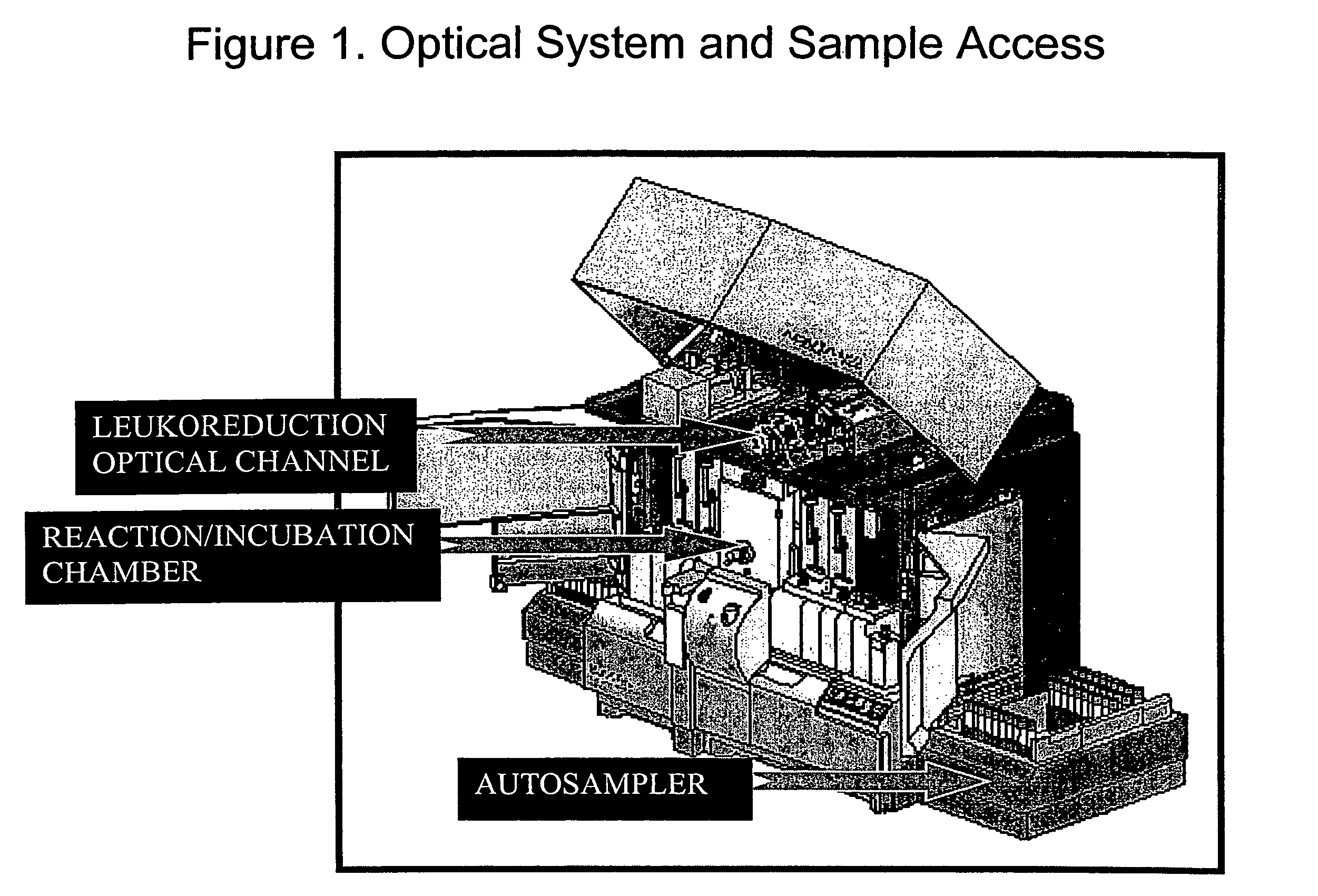
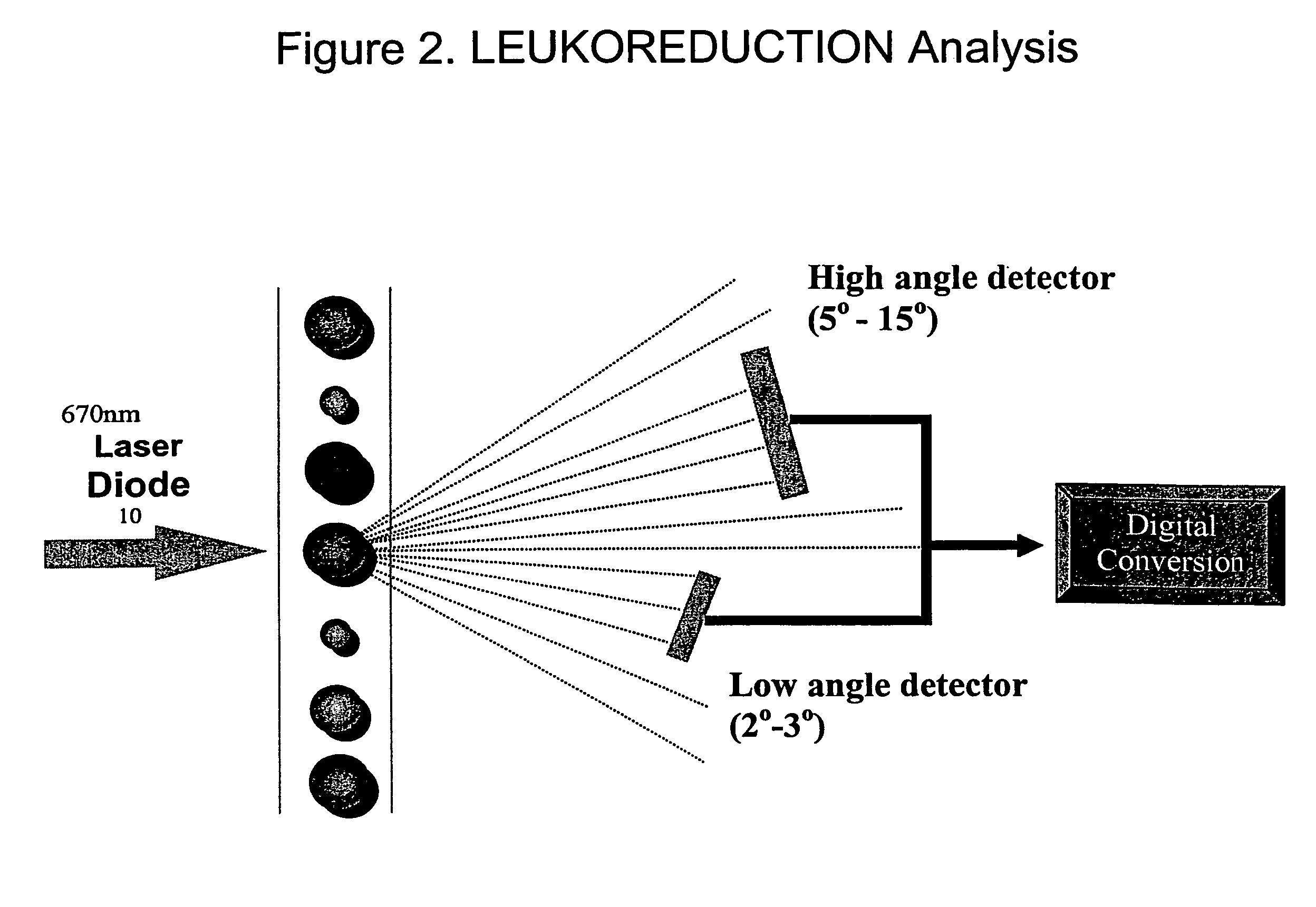
Reagent composition for the analysis of residual white blood cells in leuko-reduced blood banking products
InactiveUS7745219B2Easy to eliminateRapid deteriorationPreparing sample for investigationIndividual particle analysisWhole blood productWhite blood cell
The enumeration and analysis of residual white blood cells in a sample of leukocyte-reduced blood products is conducted by forming a suspension of the leukocyte-reduced blood products with a sufficient amount of a lysing reagent. The lysing reagent comprises a buffer with a low molar concentration, and a non-ionic surfactant. The suspension of leukocyte-reduced blood products and the lysing reagent is incubated for a sufficient time at a temperature sufficient to selectively lyse the platelets and red blood cells without damaging the white blood cells. The white blood cells of the lysed blood products are then contacted with a suitable dye to stain the white blood cells and the number of stained white blood cells is measured. The lysing reagent is free of harsh organic solvents which can damage the plastic components of automated clinical analyzers.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
Sickled Erythrocytes and Progenitors Target Cytotoxics to Tumors
The present invention provides therapeutic mammalian cells which synthesize and express SS hemoglobin and a tumoricidal transgene. They are produced by transduction of SS erythroid progenitors / erythroblasts using viral vectors comprising a tumoricidal transgene operatively linked to the coding region of SS β-globin promoter / enhancer. Such transduced SS erythroid cells differentiate into mature SSRBCs that exhibit sustained synthesis and expression of SS hemoglobin, a tumoricidal protein(s). Both mature and progenitor SS-cells carrying tumoricidal transgene(s) are capable of selectively localizing in tumor microenvironment, occluding tumor microvessels and inducing a tumoricidal response.
Owner:TERMAN DAVID S
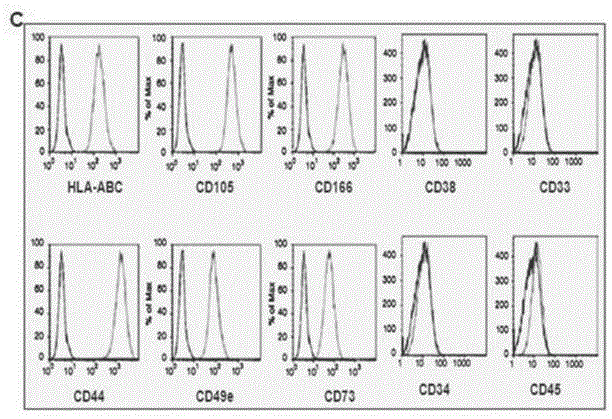
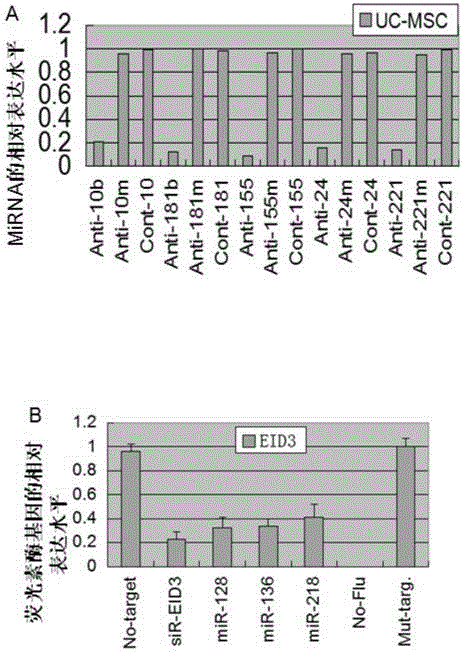
Method for inducing direct transdifferentiation of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells into erythroblasts
ActiveCN106190970ASkeletal/connective tissue cellsBlood/immune system cellsTransdifferentiationSerum free media
The invention discloses a method for inducing direct transdifferentiation of mesenchymal stem cells into erythroblasts, and discloses a method for rapidly inducing the direct transdifferentiation of the mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) into the erythroblasts (EBCs). The method comprises the following steps: S1, separating and purifying the homogeneous umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells; S2, selecting small RNA molecules applicable to the epigenetic regulation of the stem cells; S3, preparing small nucleic acid polypeptide nanoparticles and conducting cell transfection; and S4, conducting amplification culture on the transfected erythroblasts. According to the method disclosed by the invention, neonatal umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells, which are easily acquired, sufficient in source, free from ethical and moral problems and safe and effective, are taken as an induced object and six small RNAs molecules are transfected, so that the large-scale and rapid direct transdifferentiation of the stem cells into the erythroblasts under the action of a special serum-free medium is achieved; and the technical difficulties in the prior art of the artificial hematopoietic technology on the limitation of the source and the quantity as well as directional differentiation of the erythroblasts are solved.
Owner:黄兵 +1
Semi-synthetic mithramycin derivatives with Anti-cancer activity
Mithramycin derivatives and their pharmaceutically acceptable salts are disclosed. The mithramycin derivatives can be used in the treatment of Ewing sarcoma or other cancer or neuro-disease associated with an aberrant erythroblast transformation-specific transcription factor.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
Separation and purification method for foetus erythroblast in maternal blood and separator
InactiveCN111235104AEfficient decompositionEasy to operateCell dissociation methodsBlood/immune system cellsAnimal scienceCord blood stem cell
The invention belongs to the field of cell biology detection, and particularly relates to a separation and purification method for foetus erythroblast in maternal blood and a separator. The method comprises the steps of (1) culturing a CD71 positive cell line (K562) and detecting antigen binding capacity and specificity; (2) establishing a catching system by a CTCBIOPSY-detection system and K562 cells and optimizing capturing conditions by cord blood; and (3) separating the collected foetus erythroblast: enlarging the diameter of target cells by microspheres coupled with a CD71 polyclonal antibody, and through the CTCBIOPSY- detection system, separating the erythroblast in the maternal blood by a filtering principle. The method is high in capturing efficiency, low in cost, simsple in operation steps, short in consumption time and high in sensitivity.
Owner:SHANDONG PROVINCIAL HOSPITAL +1
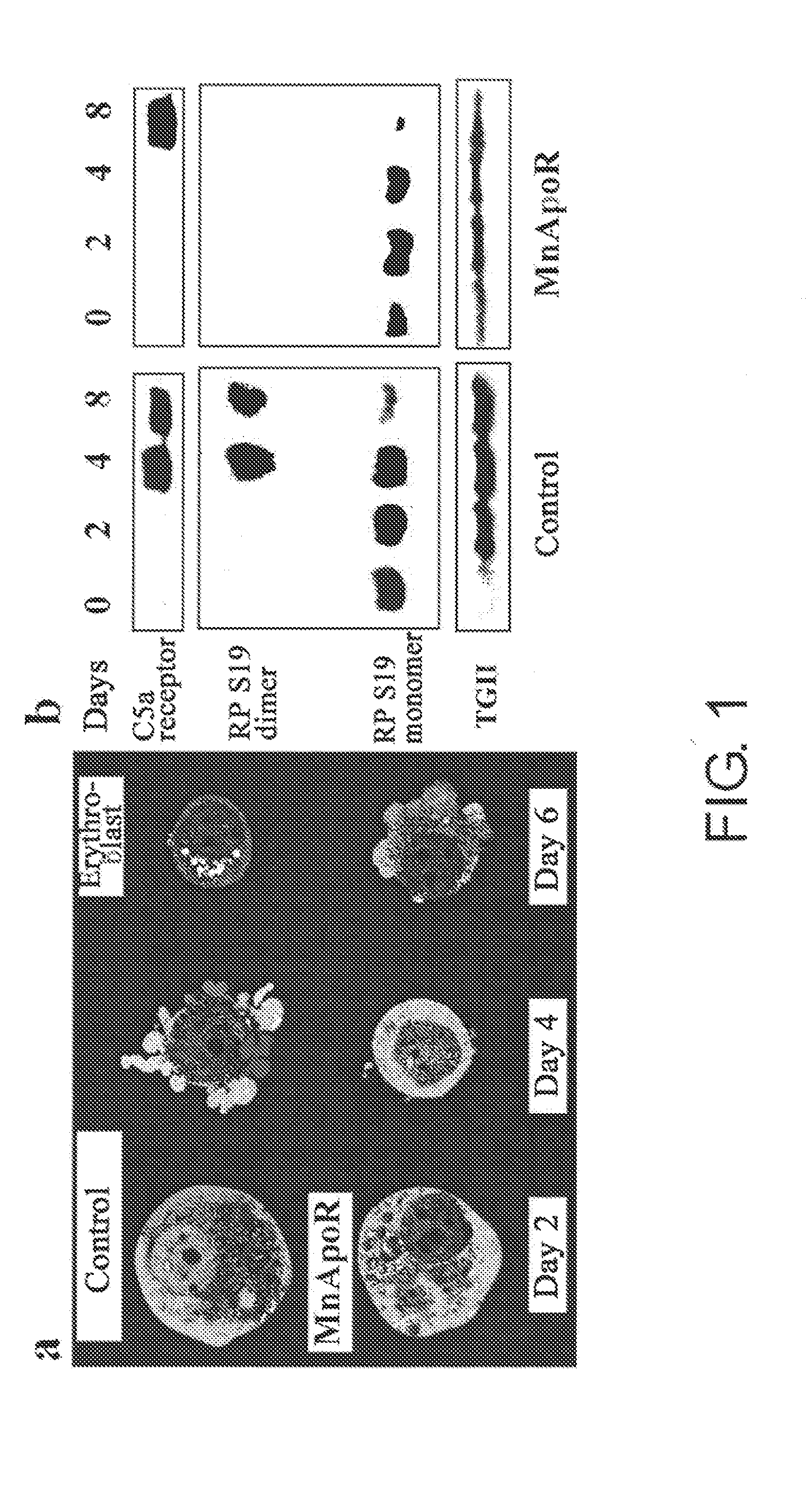
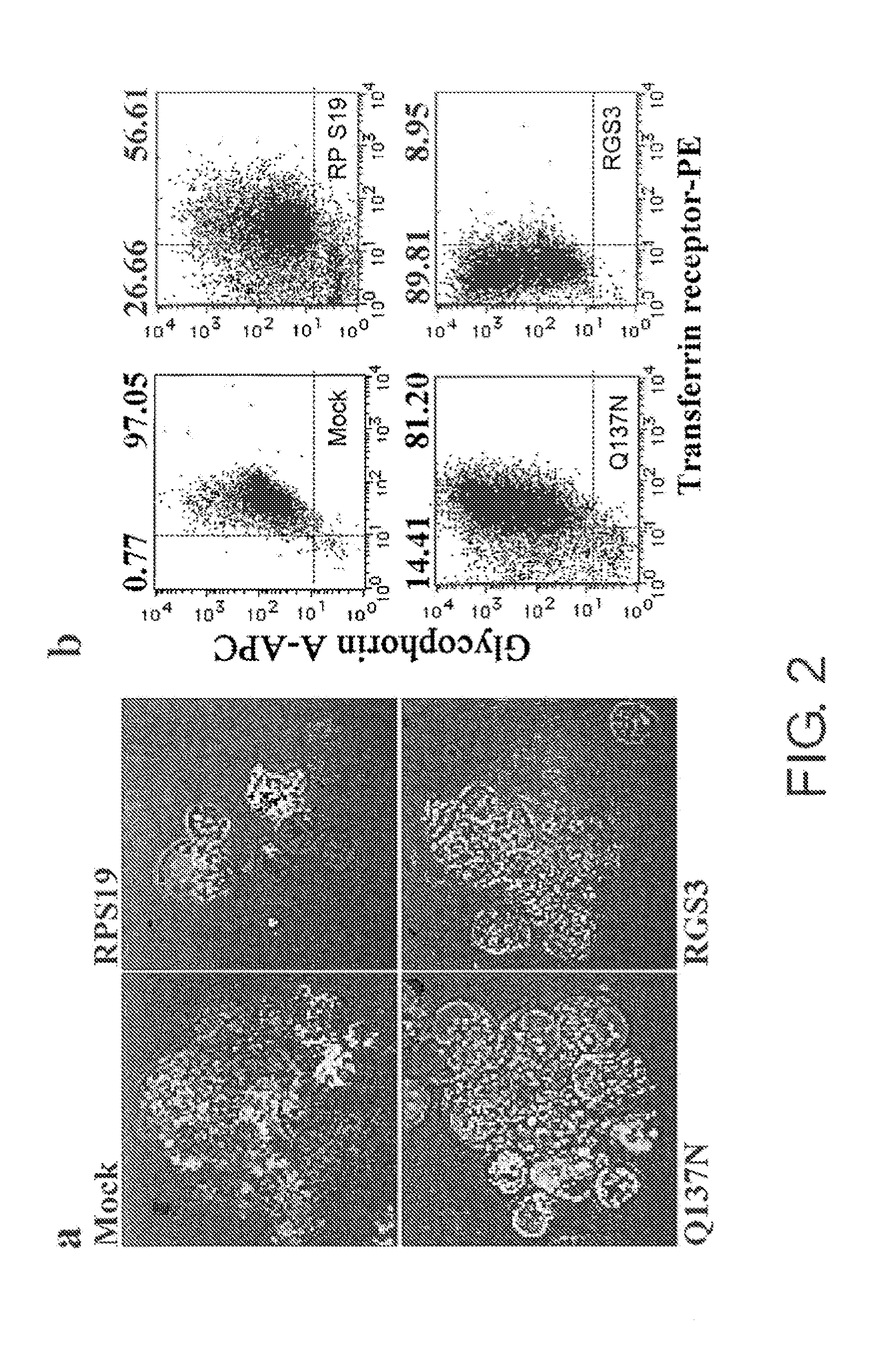
Screening Method for Substance Having Hemocyte Maturation Acceleration Action
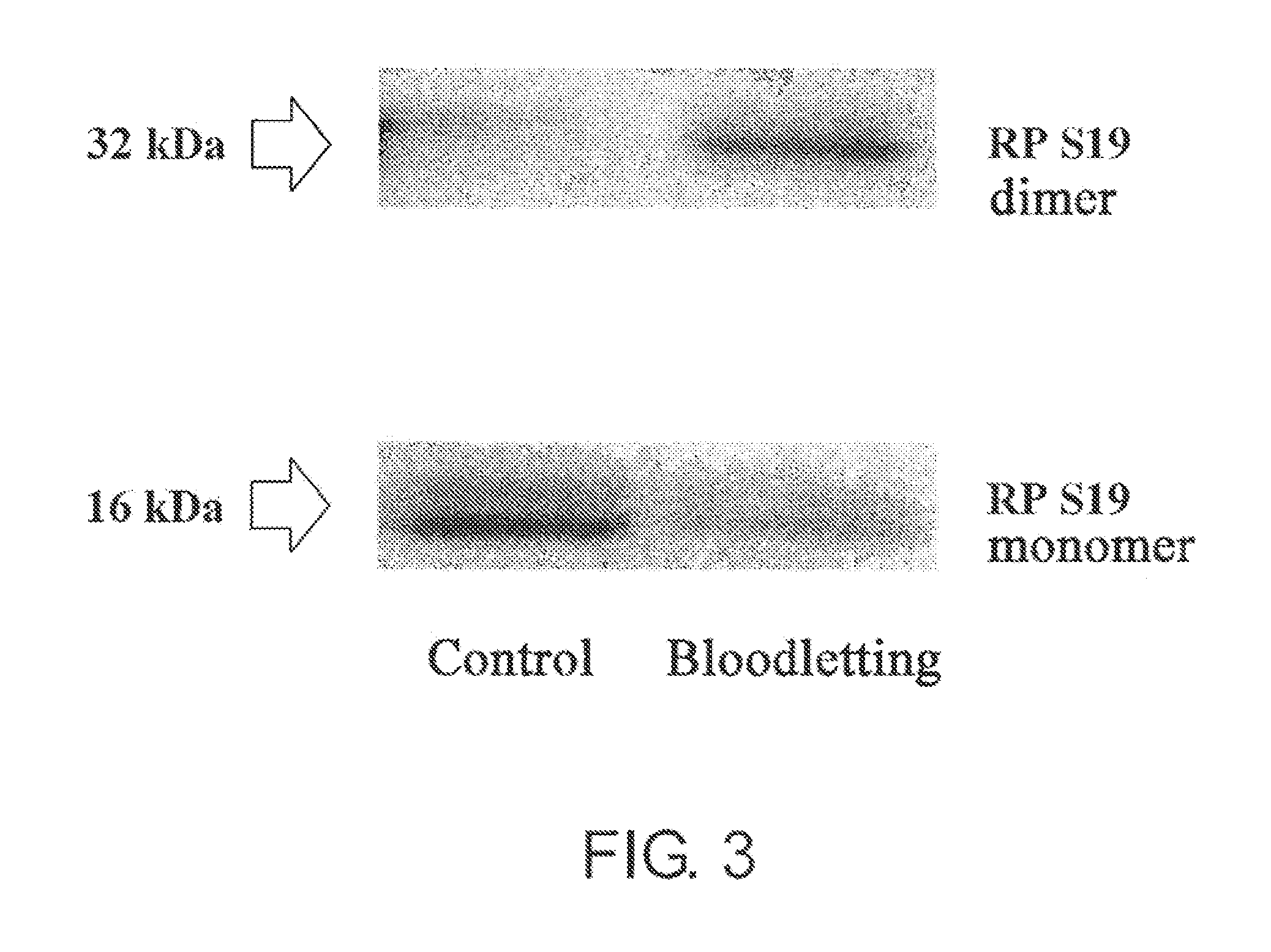
An objective is to provide screening methods for substances having an activity of promoting maturation into hemocytes. It was revealed that in the maturation process of erythrocytes and platelets, RP S19 multimers are released to the outside of the cell and act on the C5a receptors of erythroblasts and megakaryocytes, thereby causing maturation of erythroblasts and megakaryocytes to erythrocytes and platelets. Based on such findings, the present invention provides methods of screening for substances having an activity of promoting maturation into hemocytes by targeting the RP S19 multimers and C5a receptors. The screening methods of the present invention can detect hemocyte maturation using an increase of the R4 RGS family as an indicator. Furthermore, the present invention provides agents for promoting hemocyte maturation, which comprise RP S19 multimers and a substance having an activity of promoting maturation into hemocytes as useful components. The present invention also provides methods for producing erythrocytes and platelets, which include the step of contacting RP S19 multimers and a substance having an activity of promoting maturation into hemocytes with erythroblasts or megakaryocytes.
Owner:BLOOM TECH
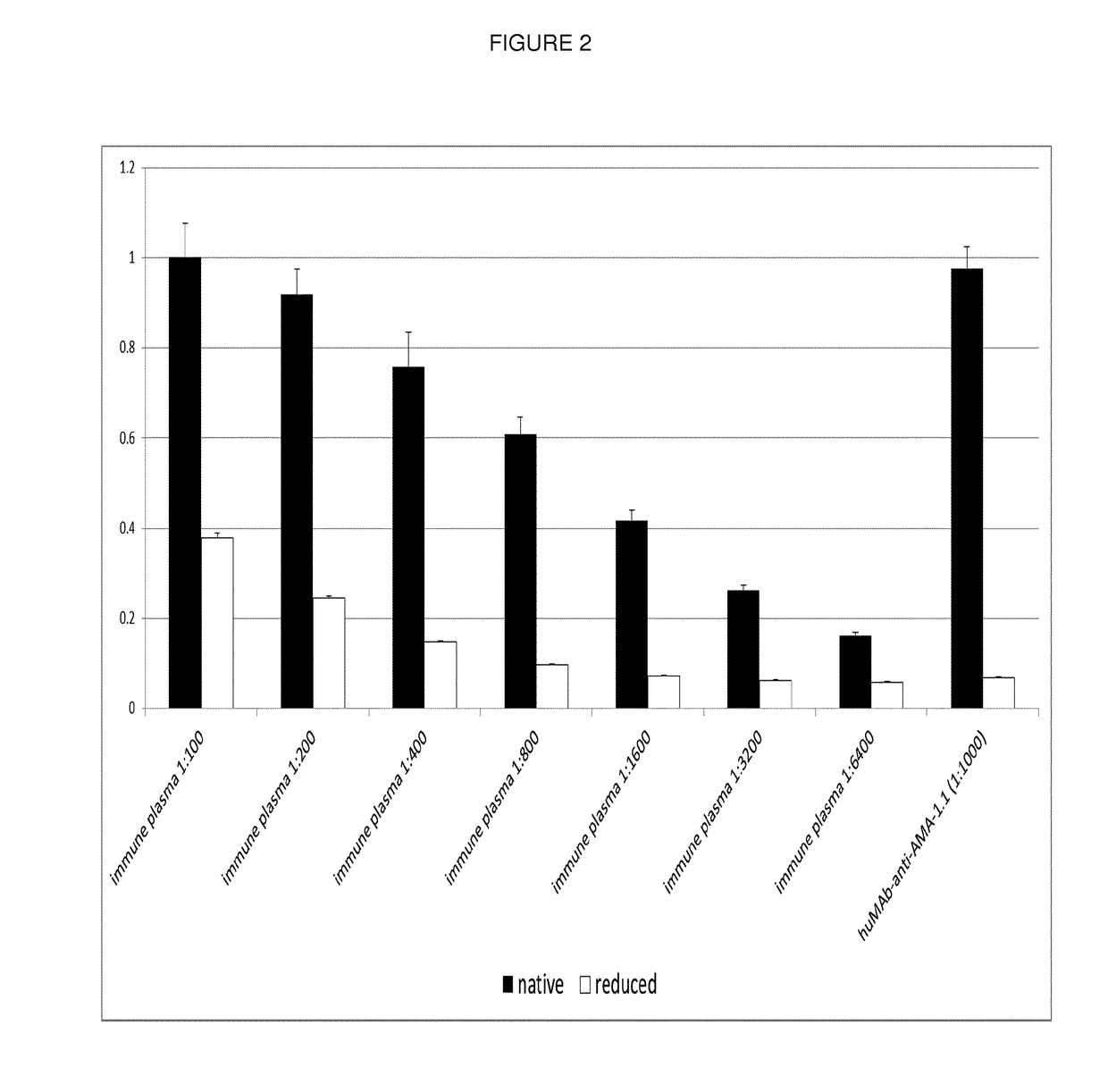
Anti-plasmodium parasite antibodies
The technology provided herein relates to novel human antibodies against Plasmodium parasites, in particular against the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. The present disclosure pertains to antibodies against apical membrane antigen 1 (AMA-1). These antibodies have high affinity e.g. to Plasmodium falciparum schizonts and merozoites, inhibit the reinvasion of merozoites into erythrocytes and thereby neutralize parasitic multiplication.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
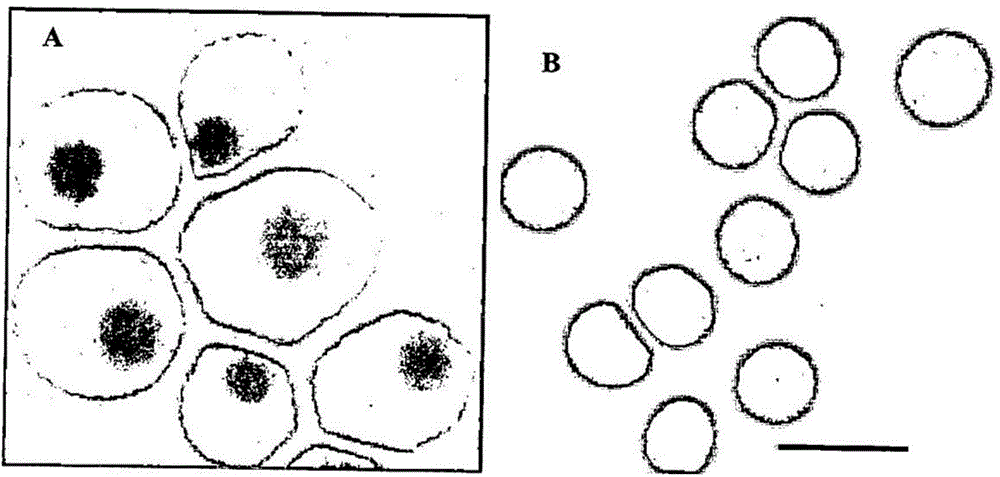
Method of identifying foetal erythroblast
InactiveCN104603618ACell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsMicrobiological testing/measurementIon Channel ProteinIntegral membrane protein
There is provided a method for identifying at least one foetal erythroblast the method comprising: (a) detecting the expression of at least one foetal erythroblast specific marker selected from the group consisting of neutral amino acid transporter B (SLC1A5), solute carrier family 3 (activators of dibasic and neutral amino acid transport) member 2 isoform A (SLC3A2), Splice Isoform A of Chloride channel protein 6, Transferrin receptor protein 1, Splice Isoform 3 of Protein GPR107 precursor, Olfactory receptor 11H4, Splice Isoform 1 of Protein C9orf5, Cleft lip and palate transmembrane protein 1, BCG induced integral membrane protein BIGM103, Antibacterial protein FALL-39 precursor, CAAX prenyl protease 1 homolog, Splice Isoform 2 of Synaptophysin-like protein, Vitamin K epoxide reductase complex subunit 1-like protein 1, Splice Isoform 1 of Protein C20orf22 (ABHD12), Hypothetical protein DKFZp564K247 (Hypoxia induced gene 1 protein) (IPI Accession No. IPI00295621), Hypothetical protein DK-FZp586C1924 (IPI Accession No. IPI00031064), ALEX3 protein variant, Hypothetical protein MGC14288 (IPI Accession No. IPI00176708), protein with IPI Accession No. IPI00639803 and protein with IPI Accession No. IPI00646289, wherein detection of the marker indicates the presence of the foetal erythroblast.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Detecting hematological disorders using cell-free DNA in blood
Techniques are provided for detecting hematological disorders using cell-free DNA in a blood sample, e.g., using plasma or serum. For example, an assay can target one or more differentially-methylated regions specific to a particular hematological cell lineage (e.g., erythroblasts). A methylation level can be quantified from the assay to determine an amount of methylated or unmethylated DNA fragments in a cell-free mixture of the blood sample. The methylation level can be compared to one or more cutoff values, e.g., that correspond to a normal range for the particular hematological cell lineage as part of determining a level of a hematological disorder.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Method of identifying, isolating and/or culturing foetal erythroblasts
ActiveUS20140030724A1High cytoplasmic to nuclear ratioMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisErythroid cellCytoplasm
There is provided a method of identifying at least one foetal erythroblast in a sample, the method comprising analysing the morphology of at least one cell in the sample; wherein at least one analysed cell that is nucleated, is CD45 negative and comprises a relatively high cytoplasmic to nuclear ratio is identified as the foetal erythroblast.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
A method suitable for rapid classification and counting of fish blood cells and its application
ActiveCN107686859BGuaranteed accuracyEnsure reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisWhite blood cellGranular leucocyte
The invention discloses a high-throughput rapid classification and analysis method for blood cells suitable for common fish such as crucian carp and carp. Aiming at the problem that nucleated red blood cells that cannot be removed interfere with white blood cell classification and counting in terms of quantity and shape, an automated measurement and analysis strategy combining fluorescent dyes and multi-channel images is used to separate the interference The red blood cell samples are separated from the white blood cells, and the range of different white blood cell groups that undertake important immune functions such as lymphocytes, monocytes, and granulocytes is divided, and automatic analysis is completed. The difficulty of effectively removing nucleated red blood cells has long plagued the automatic analysis of blood images of many types of animals. This invention combines fluorescent dyes with image analysis, and uses the high-throughput and high-sensitivity measurement modules of the multi-dimensional panoramic analyzer to accurately identify red blood cell groups. Eliminating its interference provides important technical support for focused analysis of leukocyte groups and has broad application prospects.
Owner:TIANJIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
A method for separating and identifying nucleated red blood cells in blood
InactiveCN101122601BEasy to identifyPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsBiologyDetection rate
Owner:孙艳萍
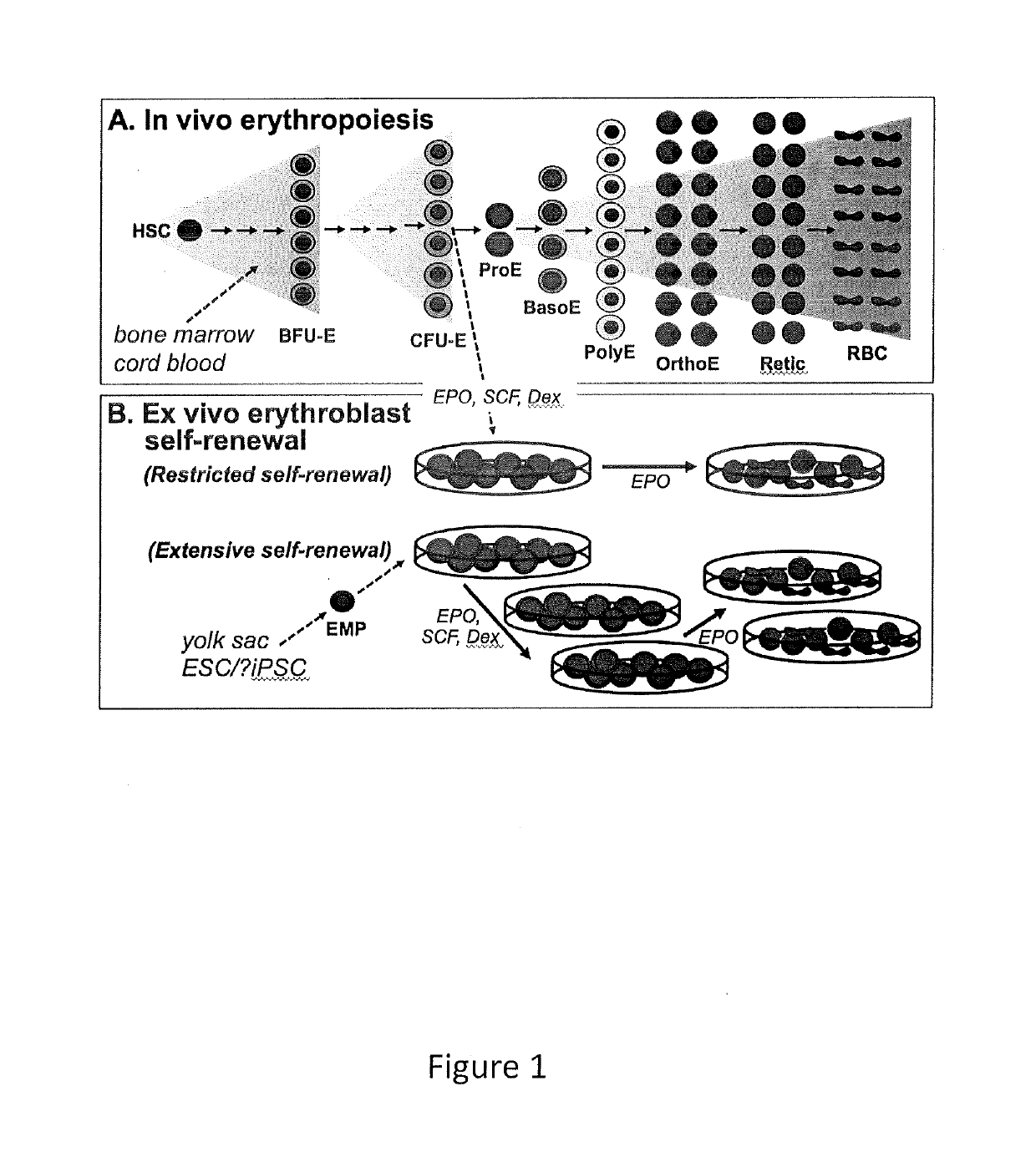
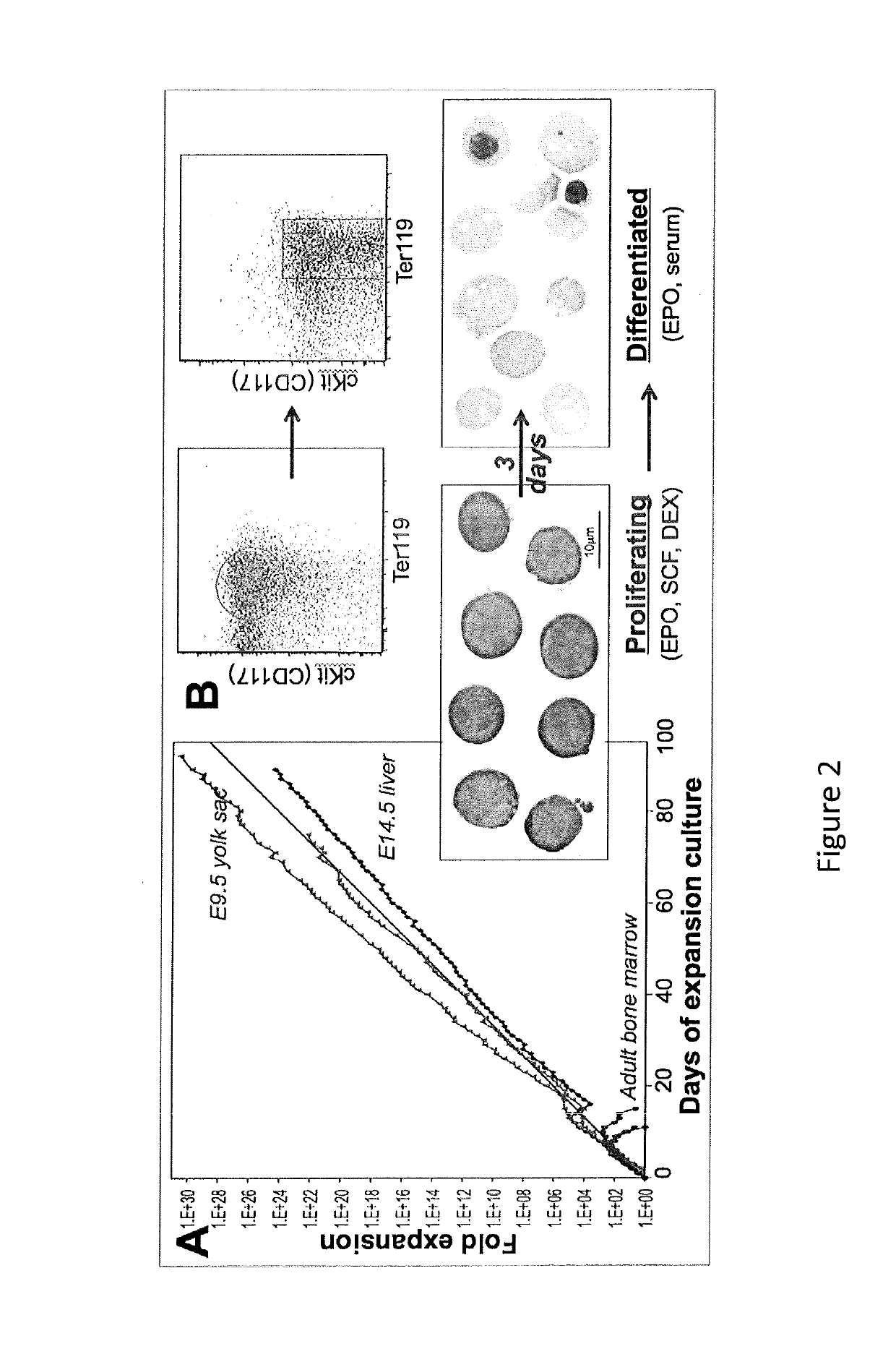
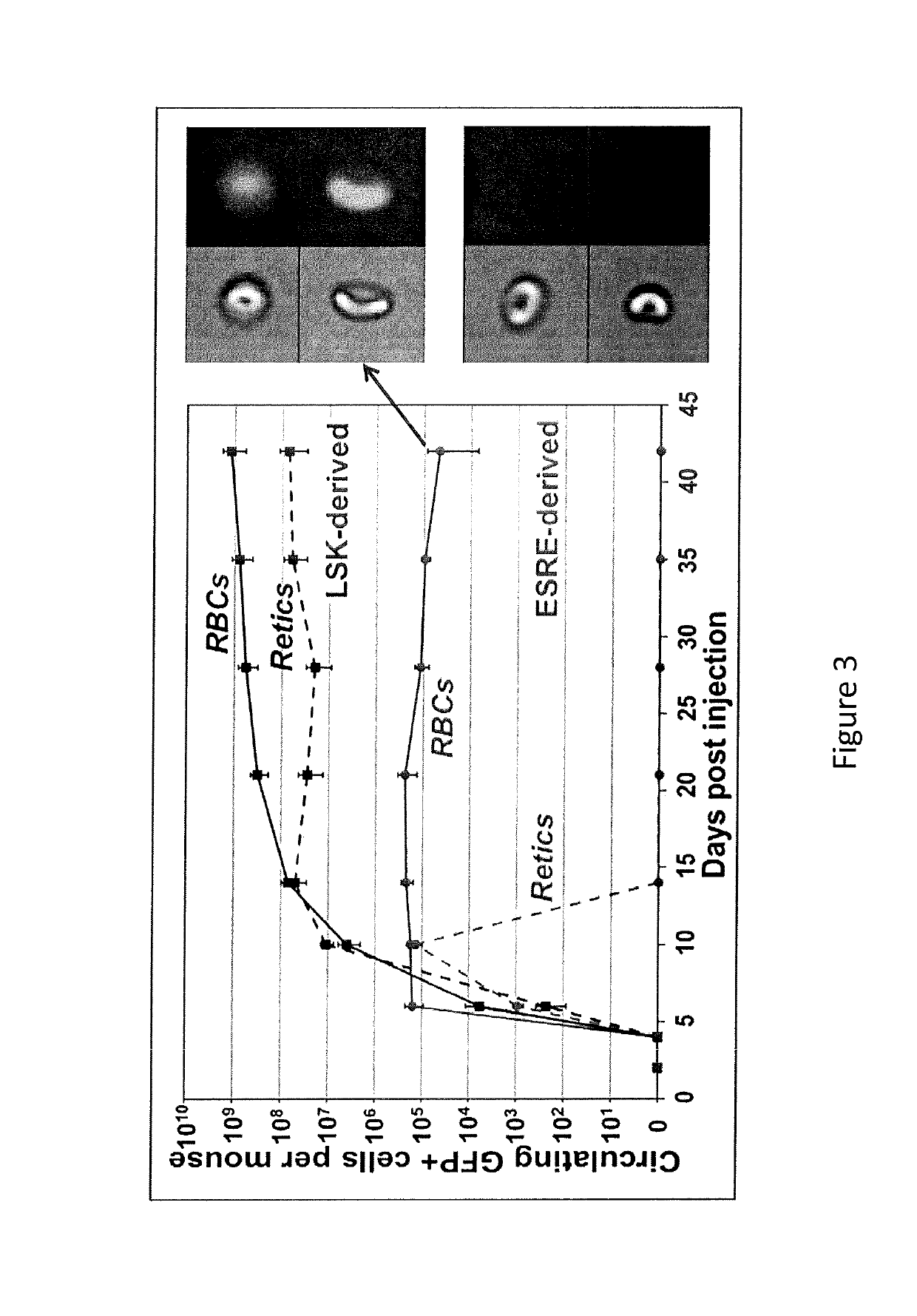
Human extensively self-renewing erythroblasts (ESRE)
The present invention provides a human cell population that can self-renew extensively and yet retain the capacity to differentiate into red blood cells (RBCs). These cells are referred to as extensively self-renewing erythroblasts (ESREs). The cells of the invention serve among other things as a renewable source of transfusable RBCs.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com