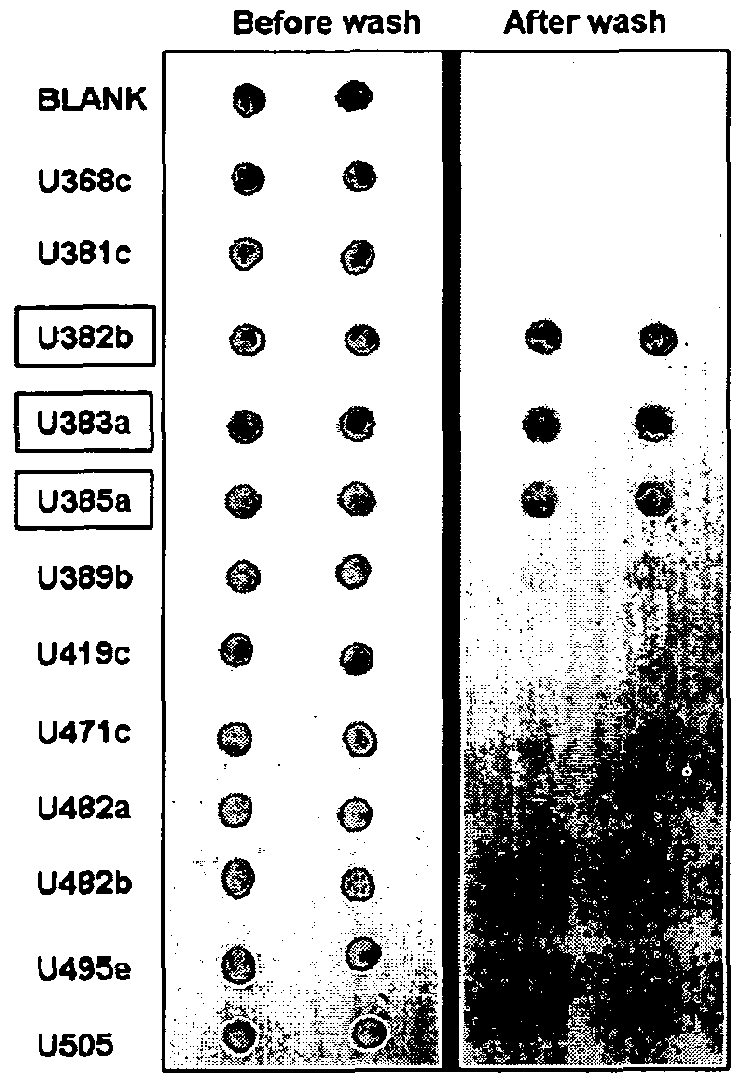
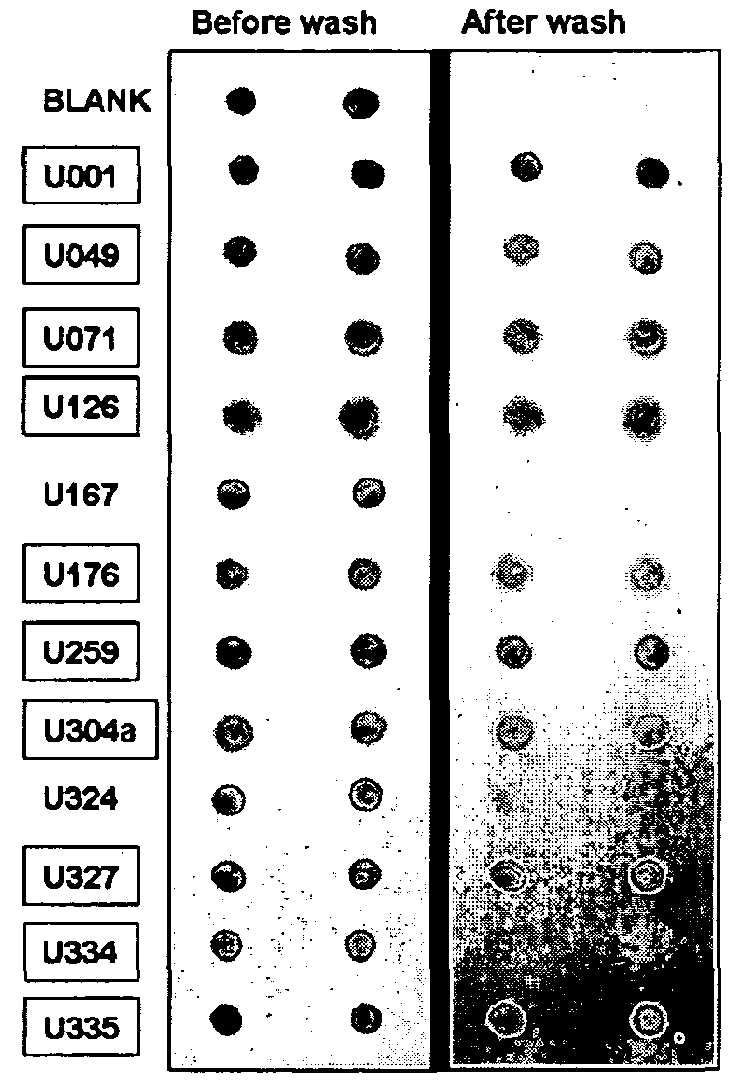
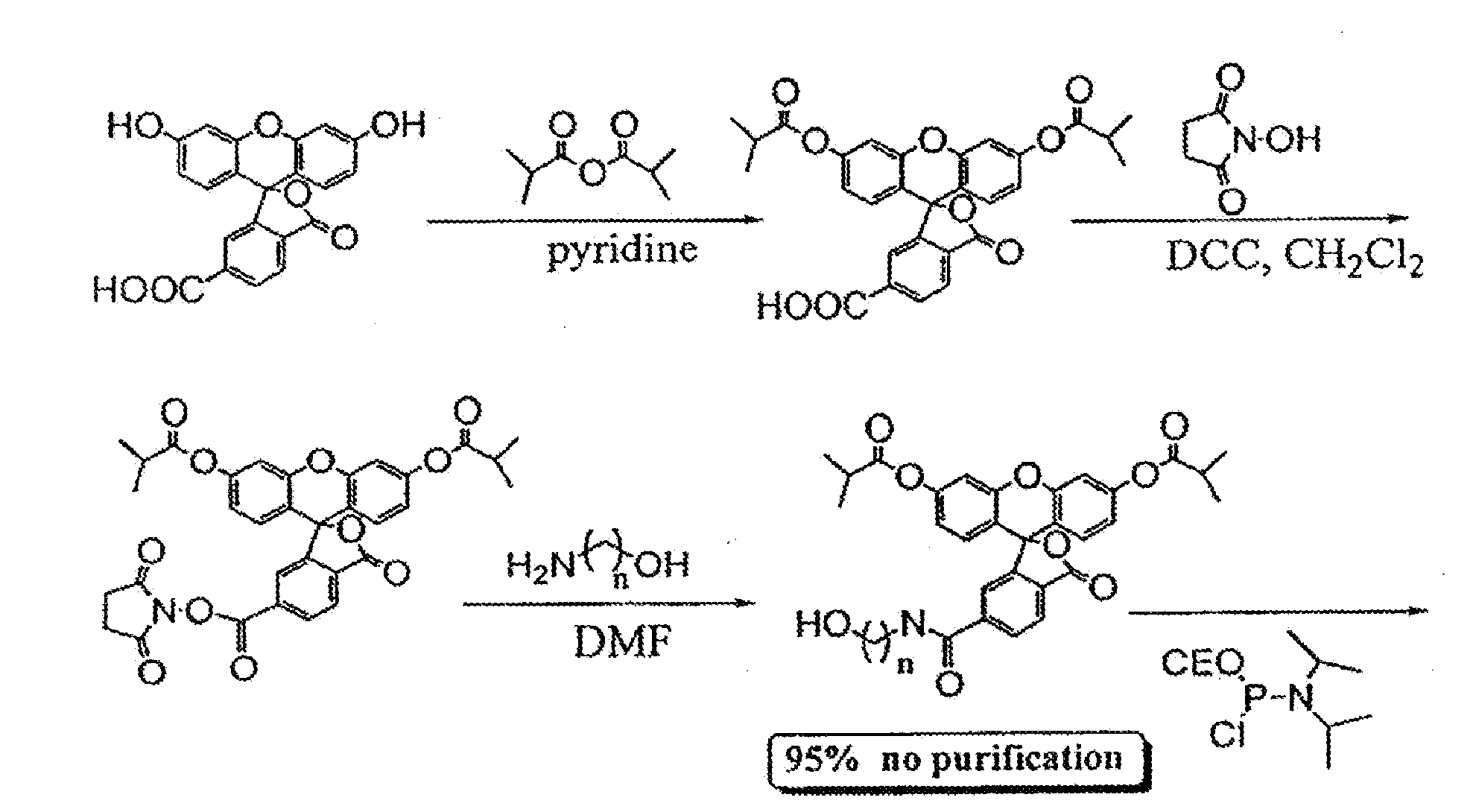
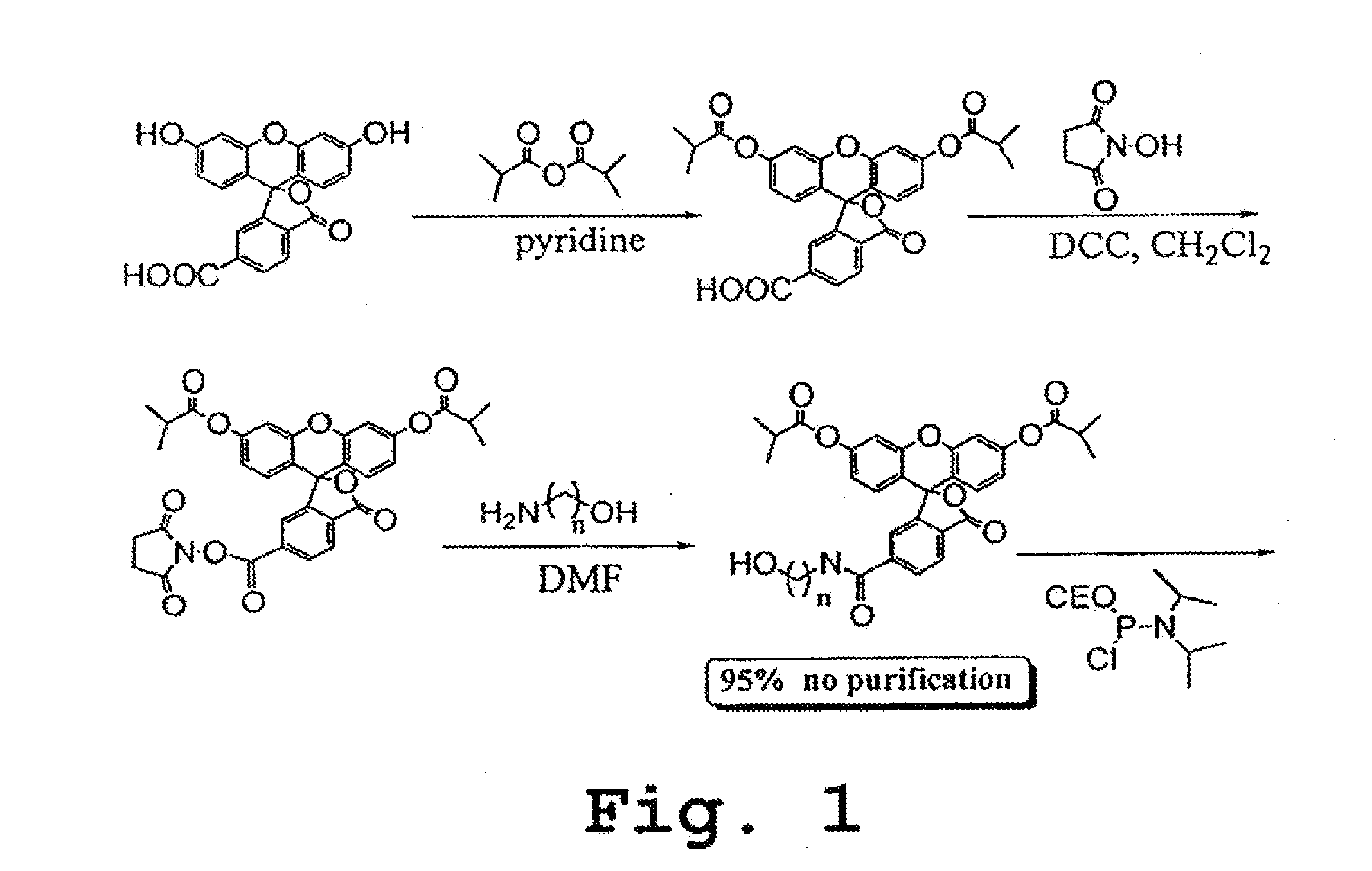
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
140 results about "Protein methods" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Protein methods are the techniques used to study proteins. There are experimental methods for studying proteins (e.g., for detecting proteins, for isolating and purifying proteins, and for characterizing the structure and function of proteins, often requiring that the protein first be purified). Computational methods typically use computer programs to analyze proteins. However, many experimental methods (e.g., mass spectrometry) require computational analysis of the raw data.
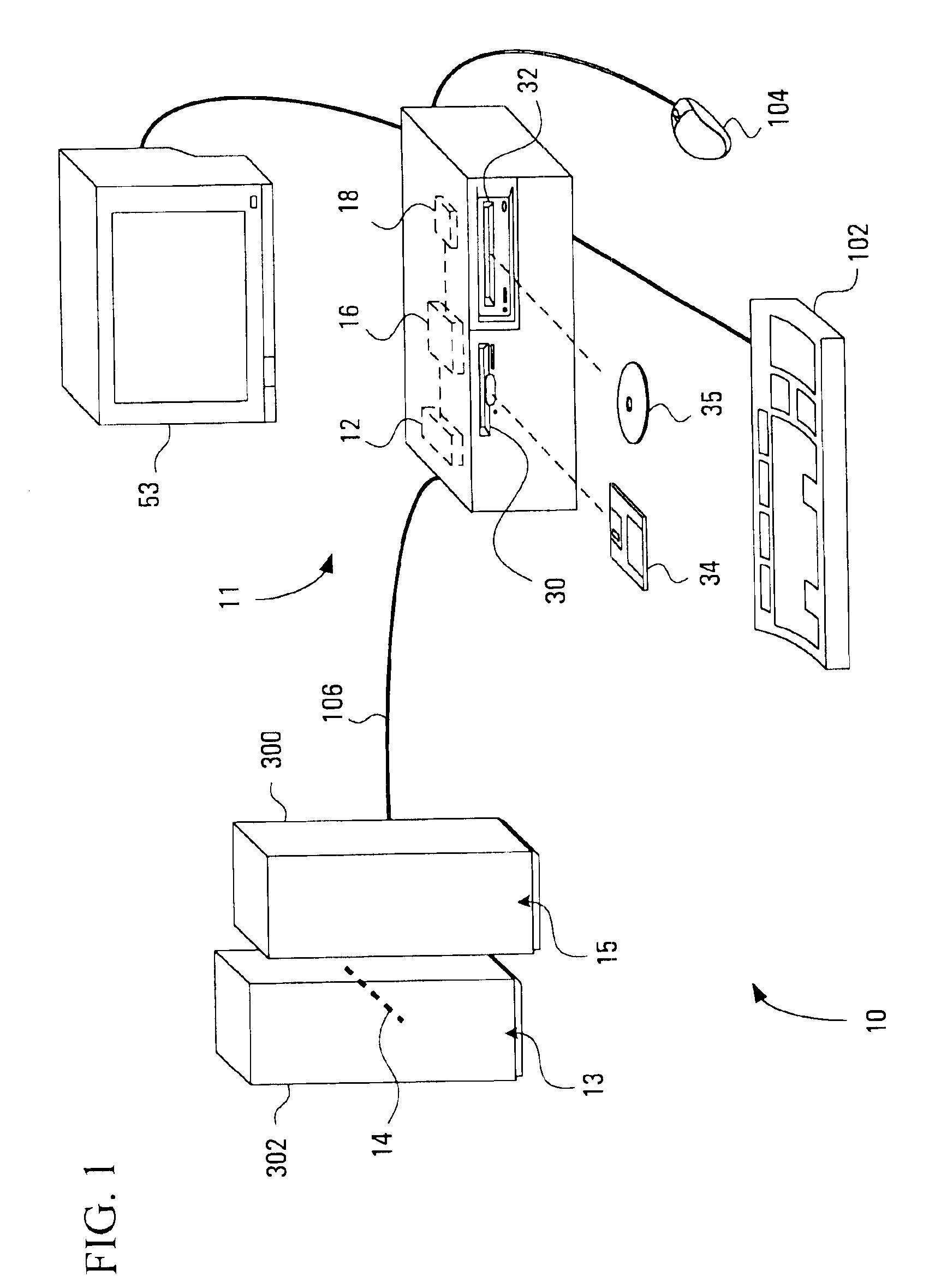
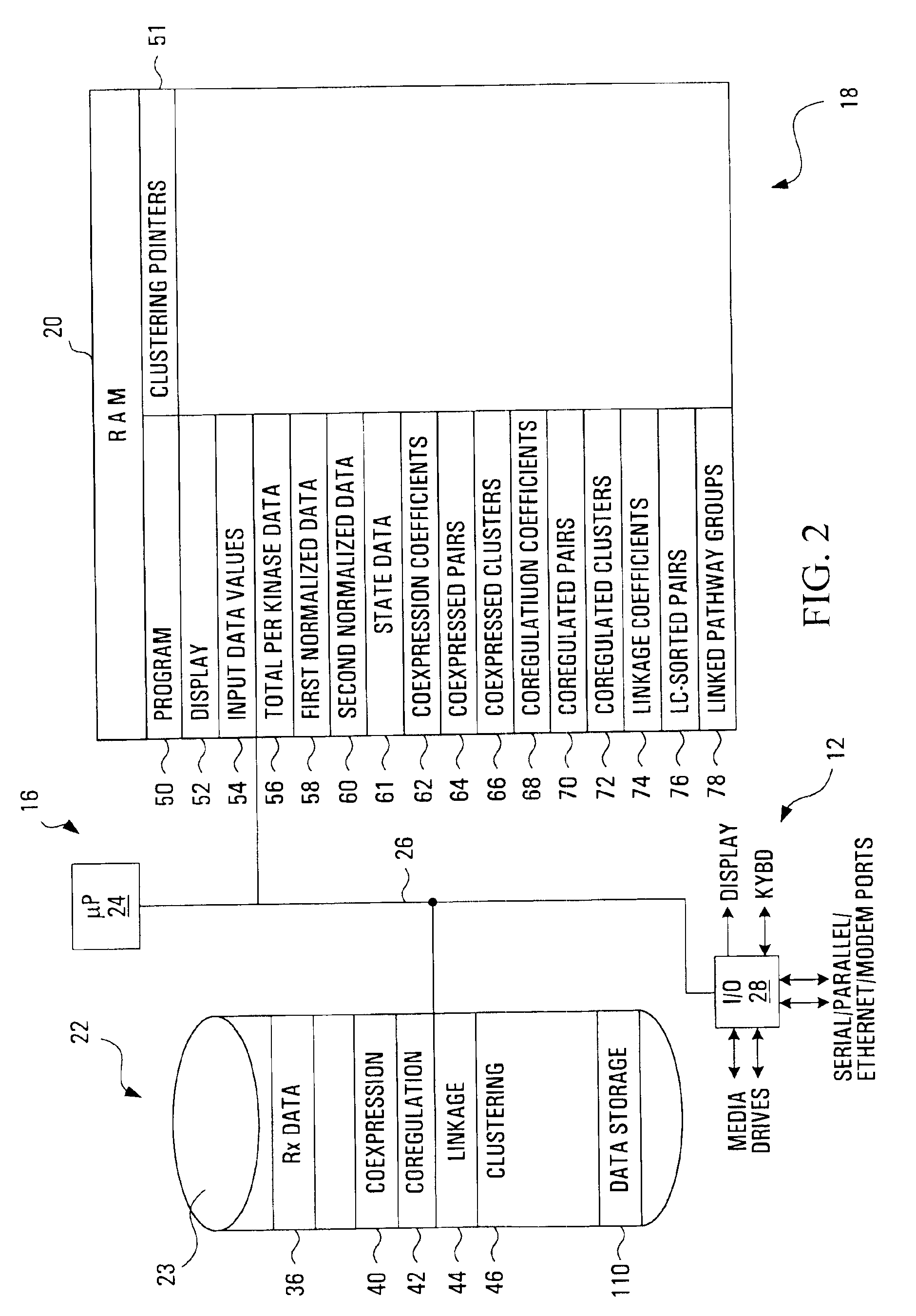
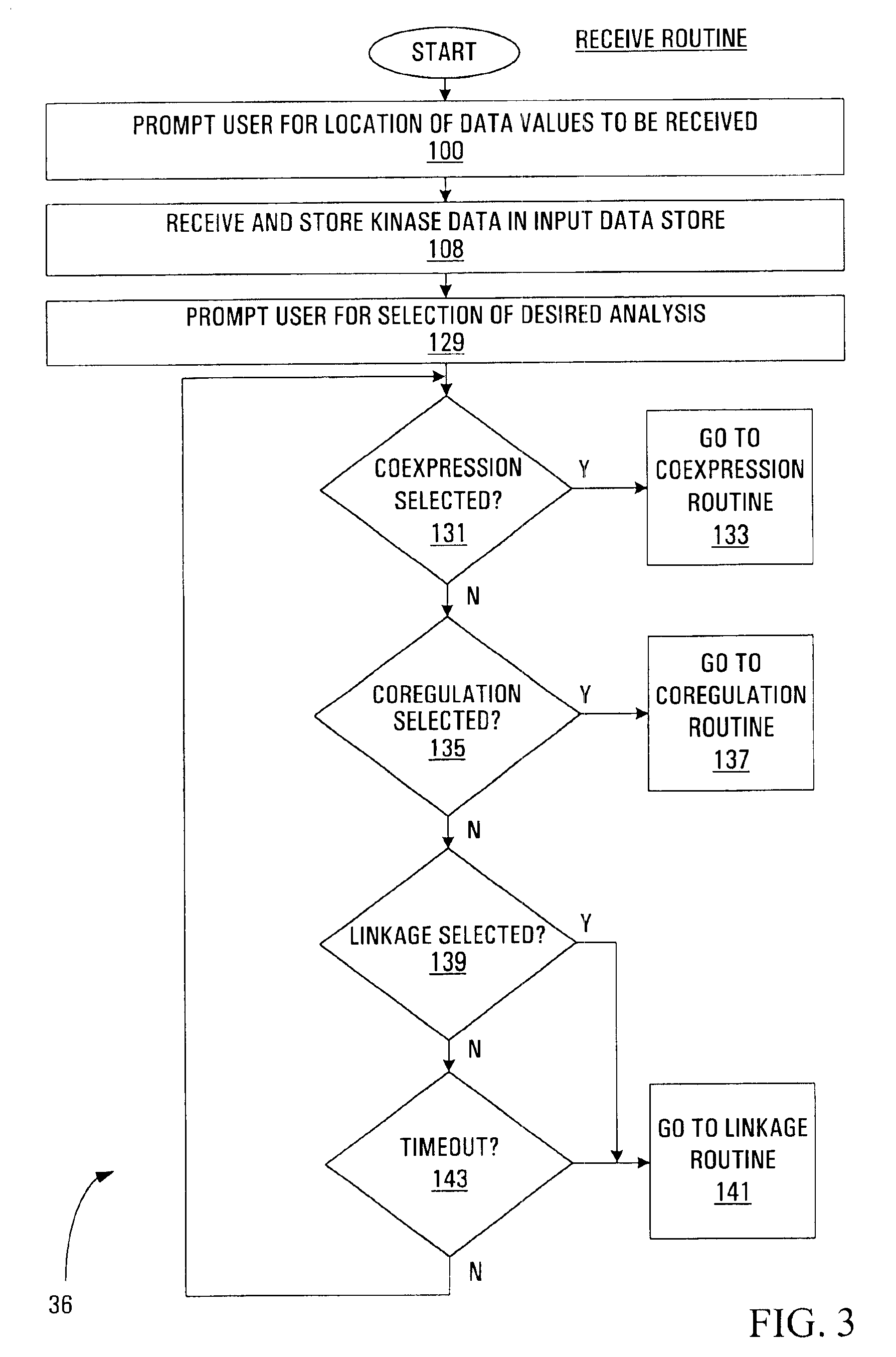
Method, apparatus, media and signals for identifying associated cell signaling proteins
Methods, apparatus, media and signals for identifying associated cell signaling proteins are disclosed. The method involves producing and storing a comparison value for each pair of the cell signaling proteins in response to data values representing physical properties of respective cell signaling proteins. The method further involves identifying cell signaling protein pairs having comparison values satisfying a condition indicative of an association between the cell signaling proteins.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
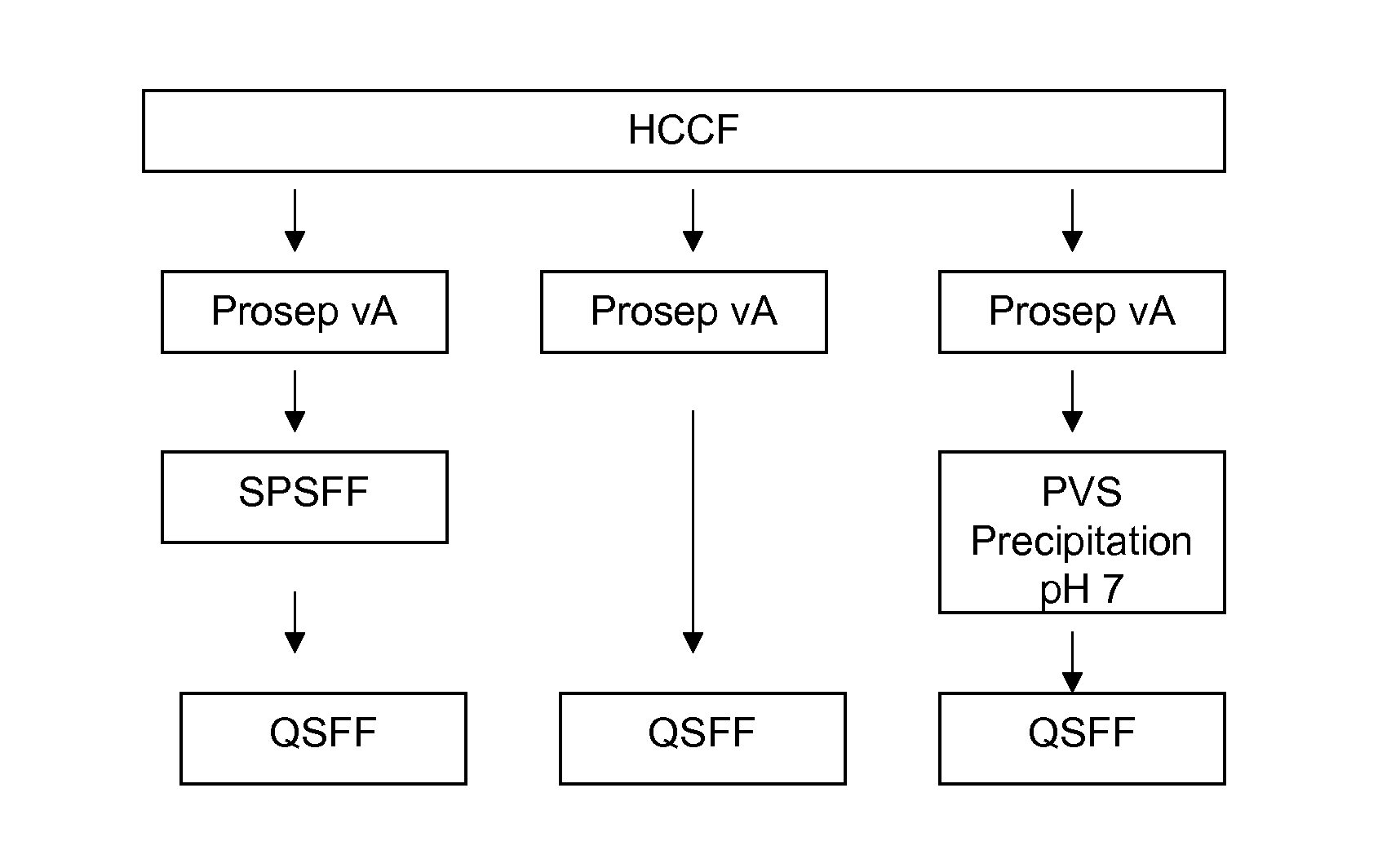
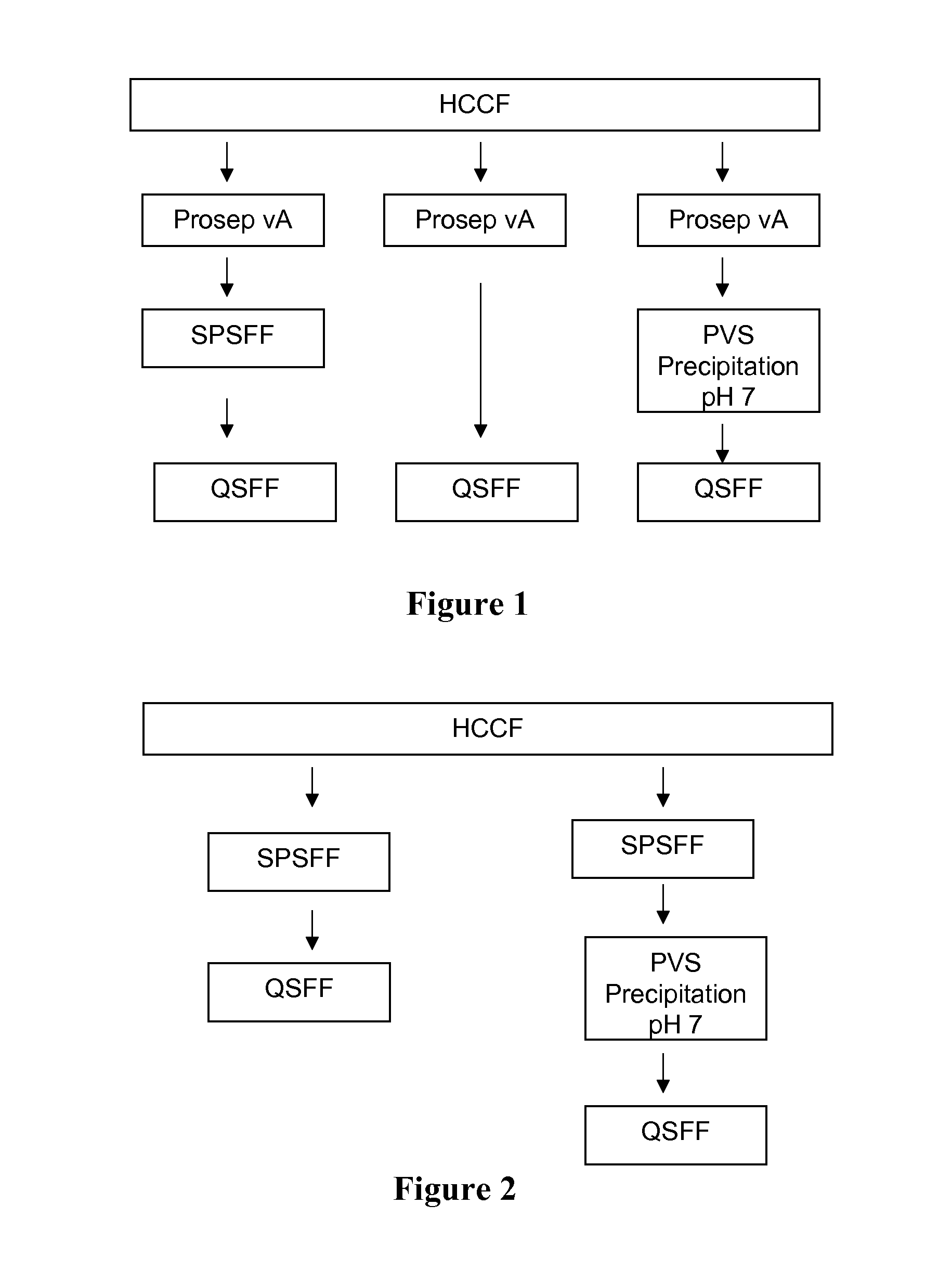
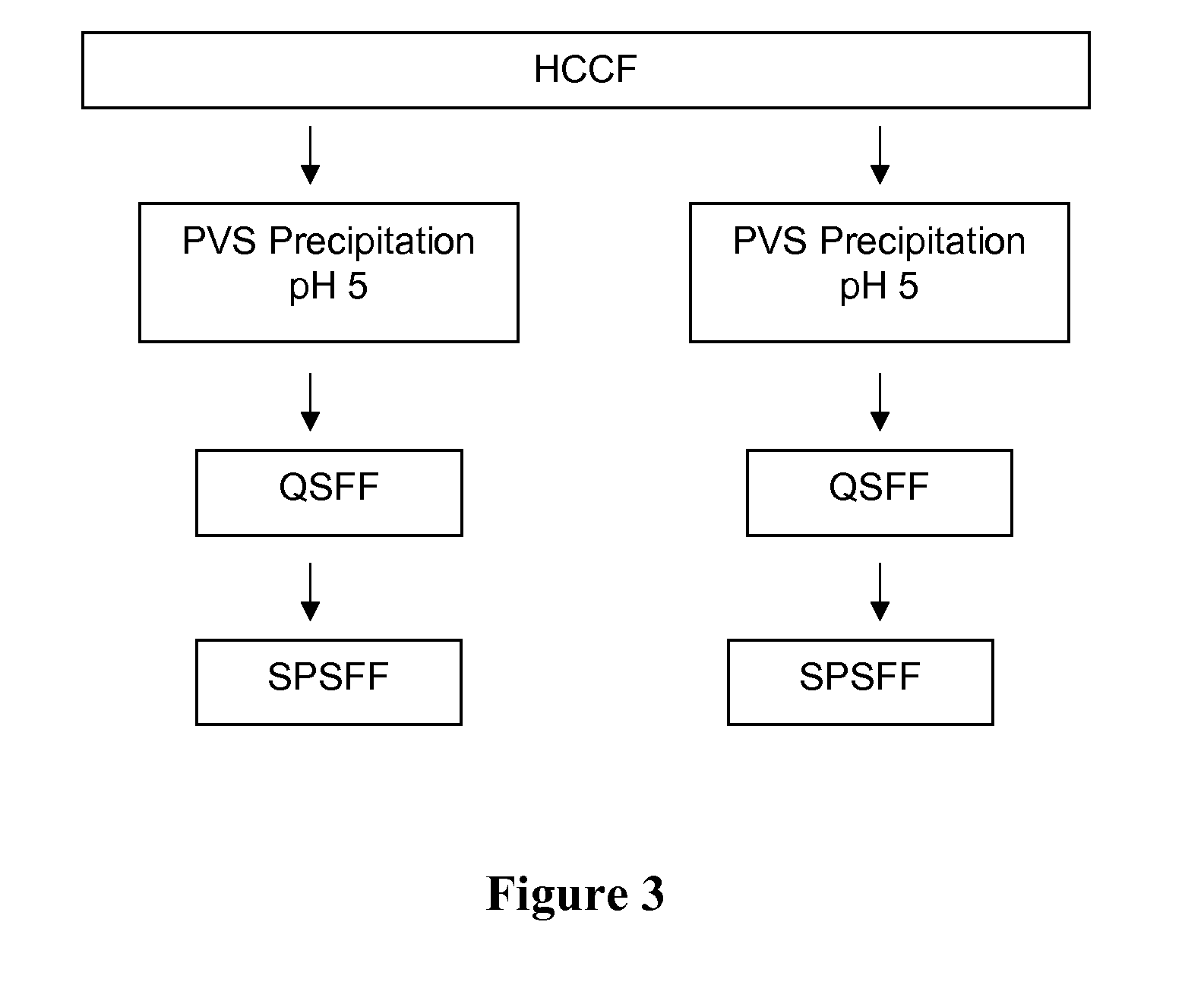
Polyelectrolyte precipitation and purification of proteins
ActiveUS20080193981A1Organic active ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsPolyelectrolyteBiochemistry
Methods are presented for isolating and purifying proteins by adding a polyelectrolyte to a cell culture fluid, such as a harvested cell culture fluid, and precipitating a protein-polyelectrolyte complex or a complex of impurities and the polyelectrolyte.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Methods of therapy for cancers characterized by overexpression of the HER2 receptor protein
InactiveUS7306801B2Promotes therapeutic responseImproved therapeutic responsePowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsDosing regimenAnti her2
Methods for treating a subject with a cancer that is characterized by overexpression of HER2 receptor protein using a combination of interleukin-2 (IL-2) or variant thereof and at least one anti-HER2 antibody or fragment thereof are provided. These anti-tumor agents are administered as two separate pharmaceutical compositions, one containing IL-2 (or variant thereof), the other containing at least one anti-HER2 antibody (or fragment thereof), according to a dosing regimen. Administering of these two agents together potentiates the effectiveness of the anti-HER2 antibody alone, resulting in a positive therapeutic response that is improved with respect to that observed with this anti-tumor agent.
Owner:HEALTH RES INC +1
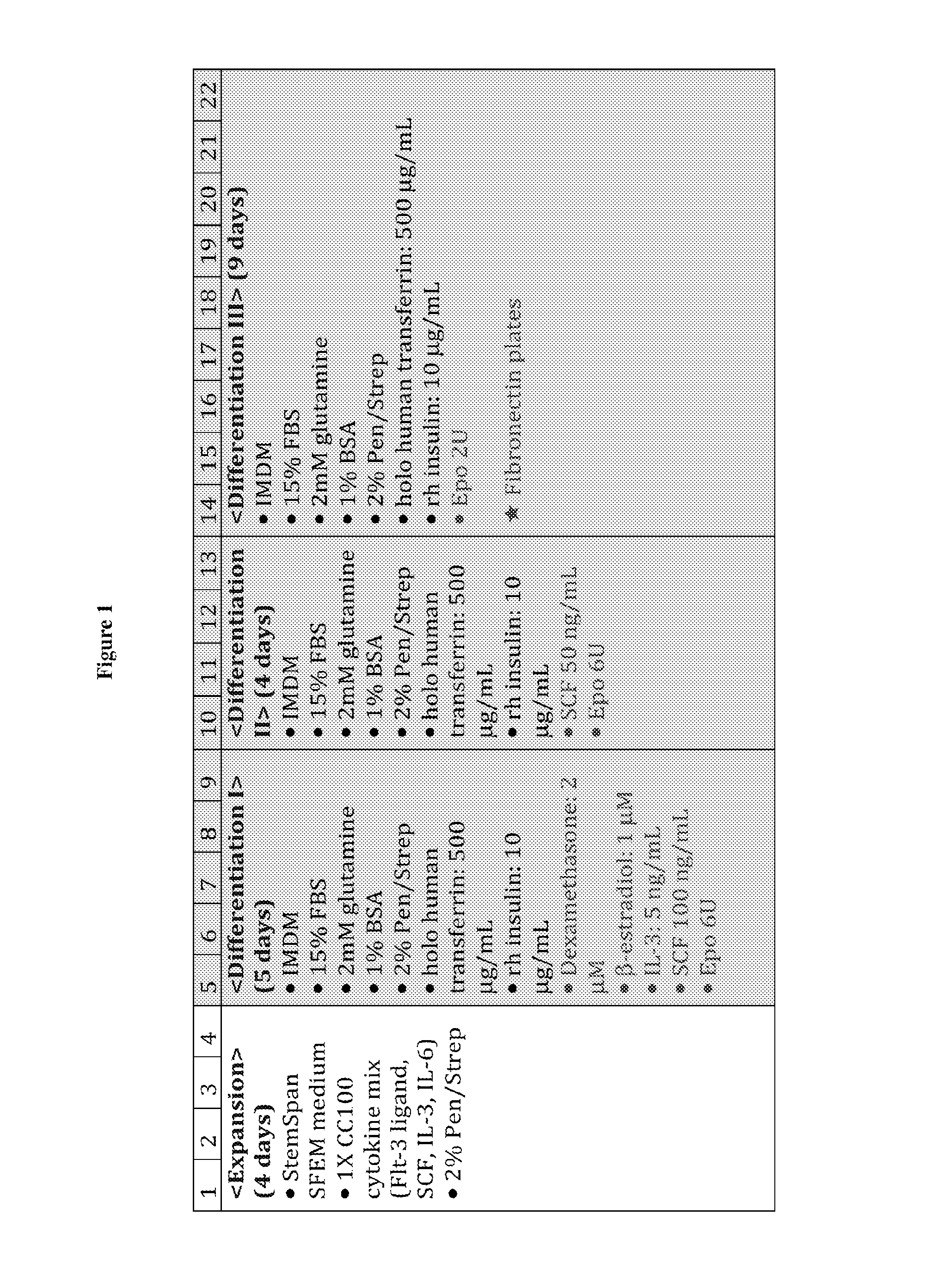
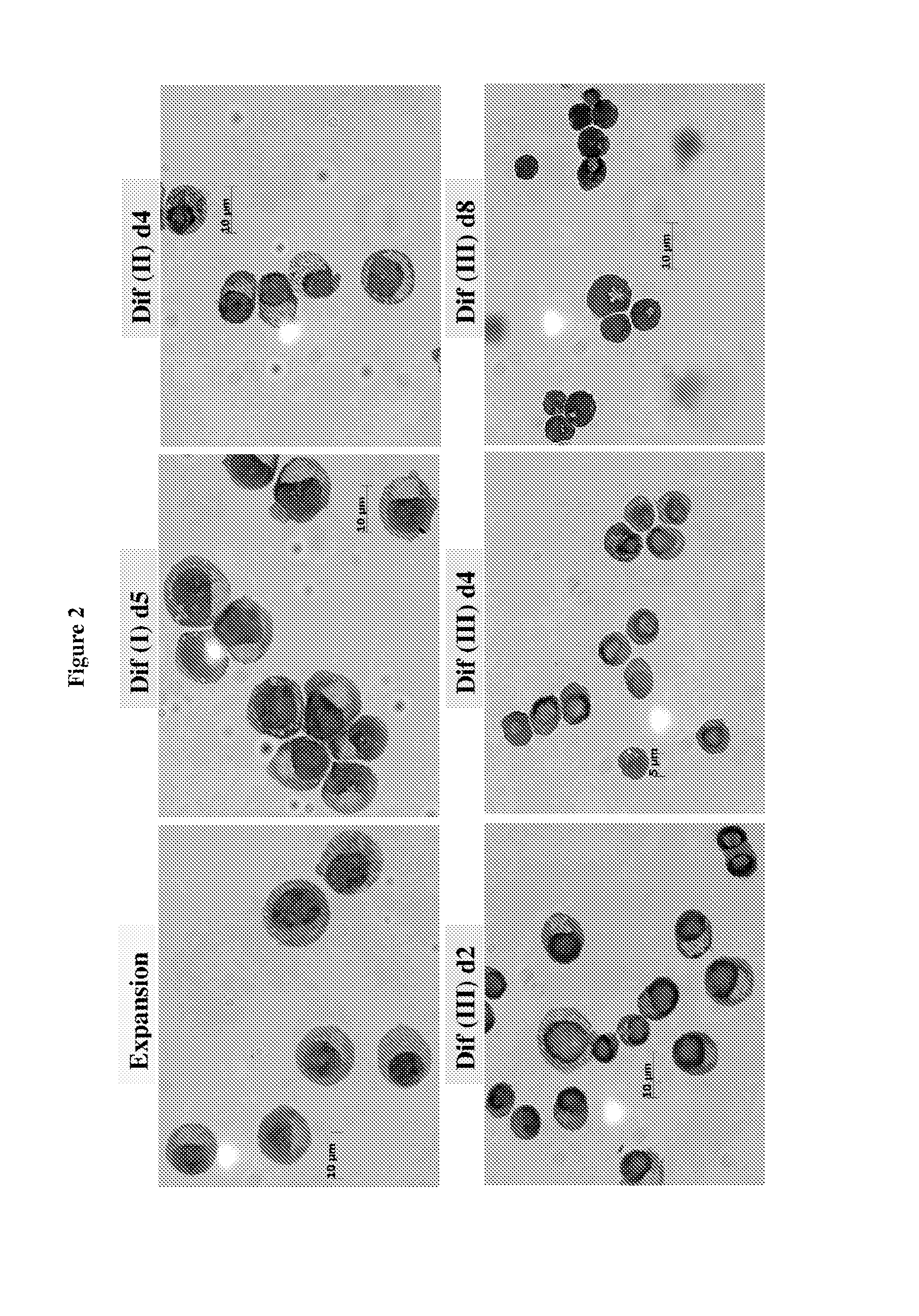
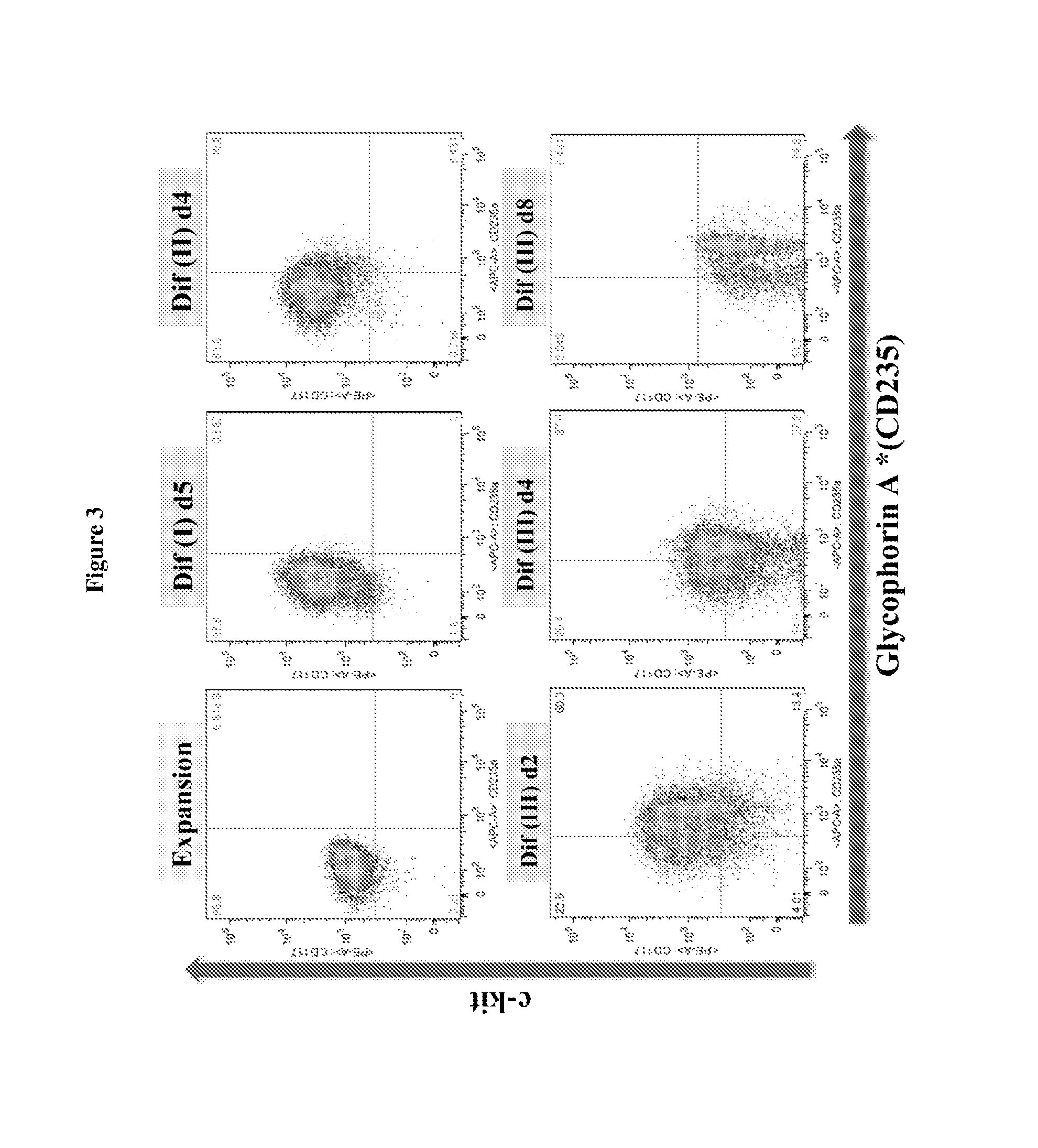
In vitro production of red blood cells with sortaggable proteins
Methods for the in vitro production of enucleated red blood cells and the enucleated red blood cells thus prepared are provided. Such enucleated red blood cells may express a sortaggable surface protein, which allows for surface modification in the presence of a sortase. Also described herein are surface modified enucleated red blood cells, e.g., conjugated with an agent of interest such as a peptide, a detectable label, or a chemotherapeutic agent, and uses thereof in delivering the agent to a subject.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
Methods and compositions for analyzing proteins
InactiveUS7255999B2Electrolysis componentsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorBinding siteElectrophoresis
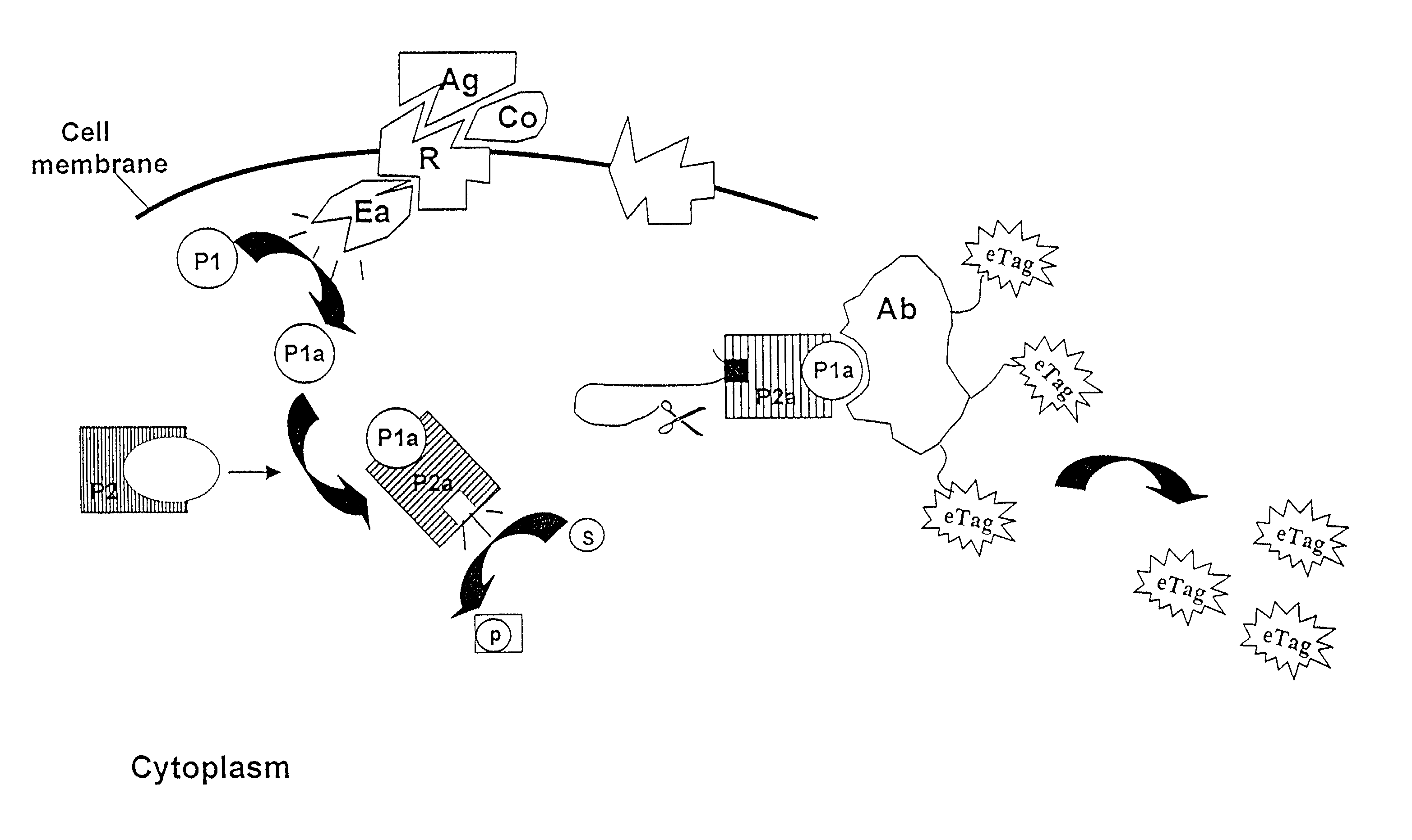
Methods, compositions and kits are disclosed for determining one or more target polypeptides in a sample where the target polypeptides have undergone a post-translational modification. A mixture comprising the sample and a first reagent comprising a cleavage-inducing moiety and a first binding agent for a binding site on a target polypeptide is subjected to conditions under which binding of respective binding moieties occurs. The binding site is the result of post-translational modification activity involving the target polypeptide. The method may be employed to determine the target polypeptide itself. In another embodiment the presence and / or amount of the target polypeptide is related to the presence and / or amount and / or activity of an agent such as an enzyme involved in the post-translational modification of the target polypeptide. The interaction between the first binding agent and the binding site brings the cleavage-inducing moiety into close proximity to a cleavable moiety, which is associated with the polypeptide and is susceptible to cleavage only when in proximity to the cleavage-inducing moiety. In this way, an electrophoretic tag for each of the polypeptides may be released. Released electrophoretic tags are separated and the presence and / or amount of the target polypeptides are determined based on the corresponding electrophoretic tags.
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
Methods for discovering molecules that bind to proteins
InactiveUS20130053541A1Inhibit functionPeptide/protein ingredientsLibrary screeningProtein targetPeptide ligand
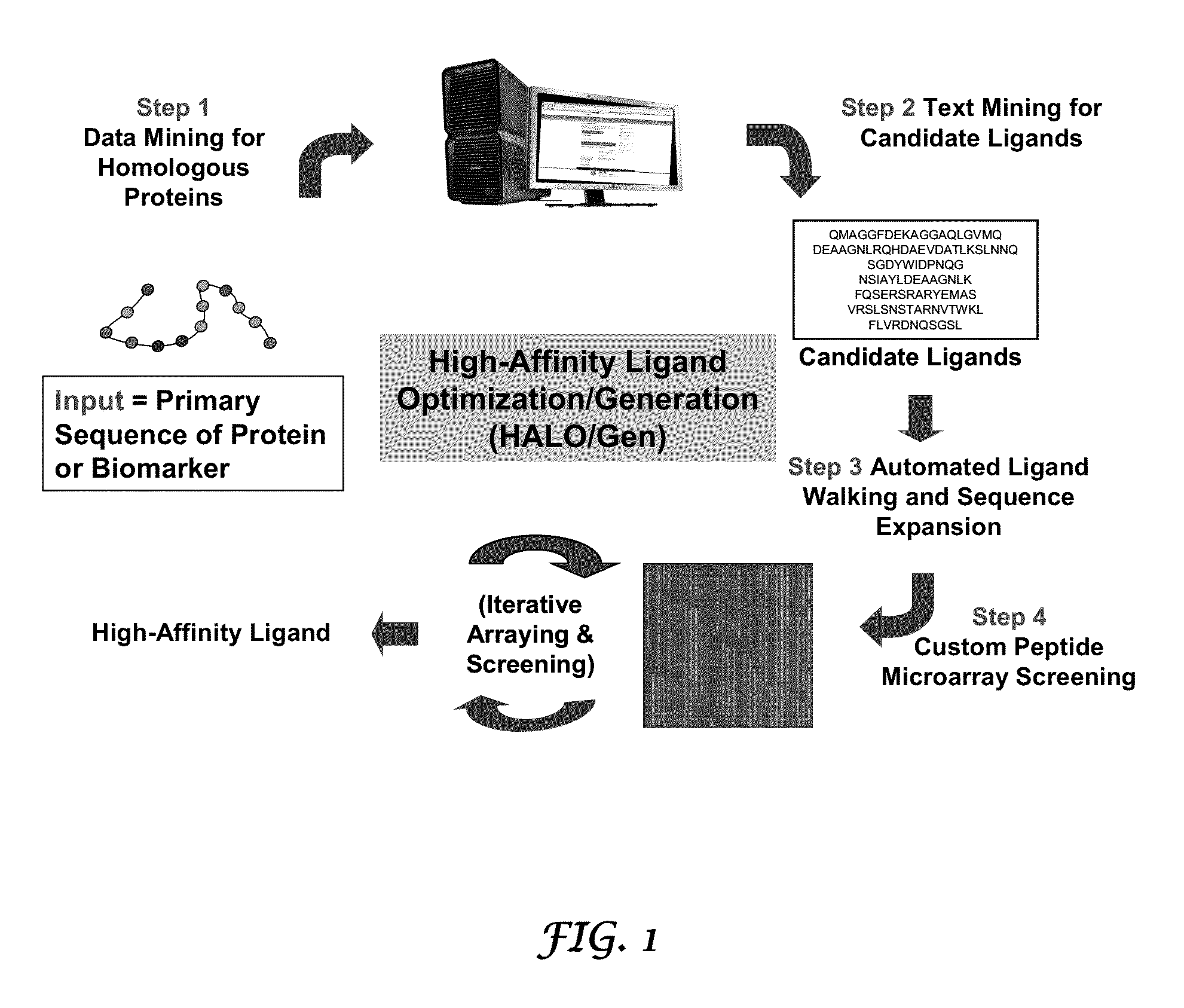
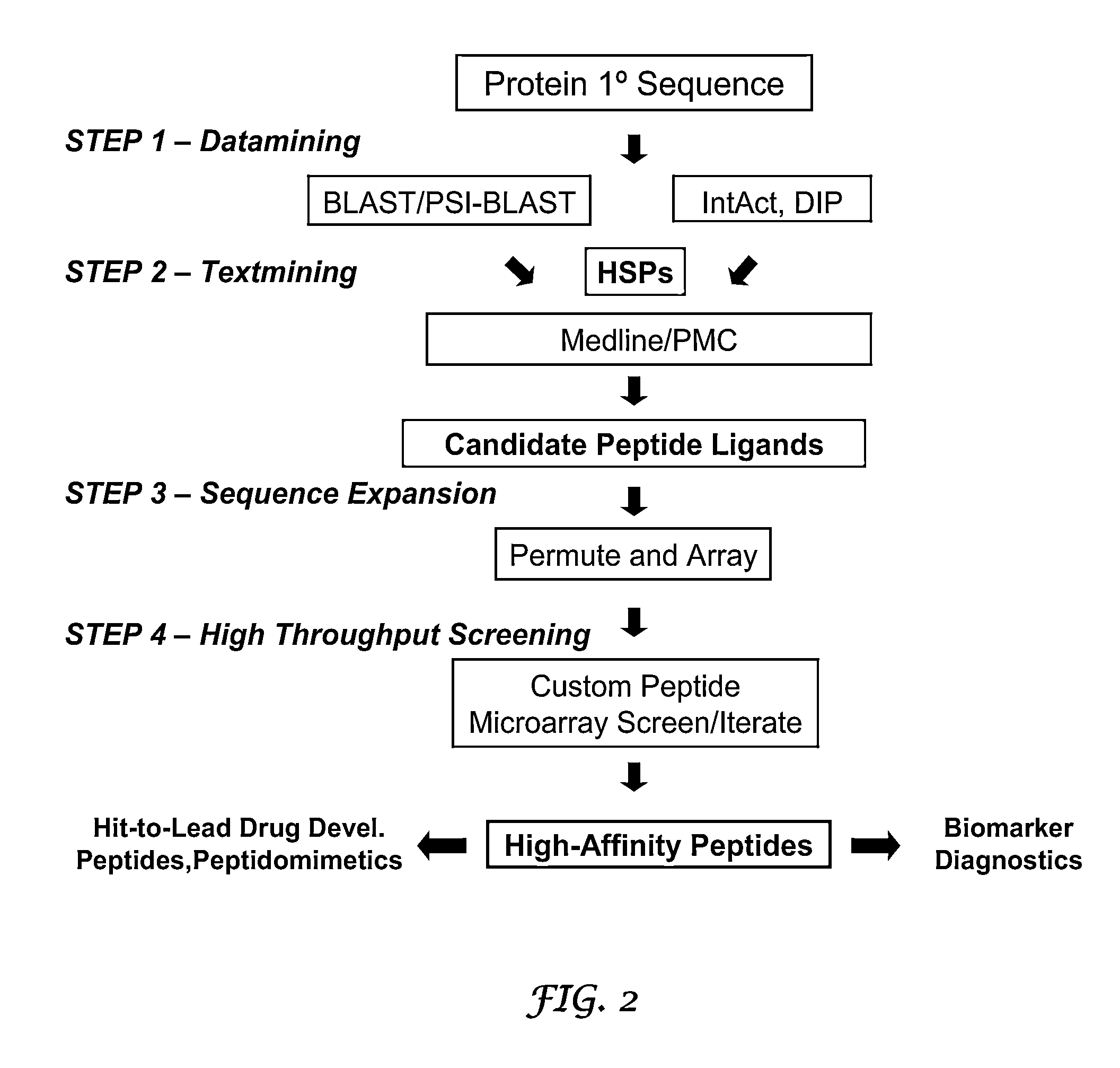
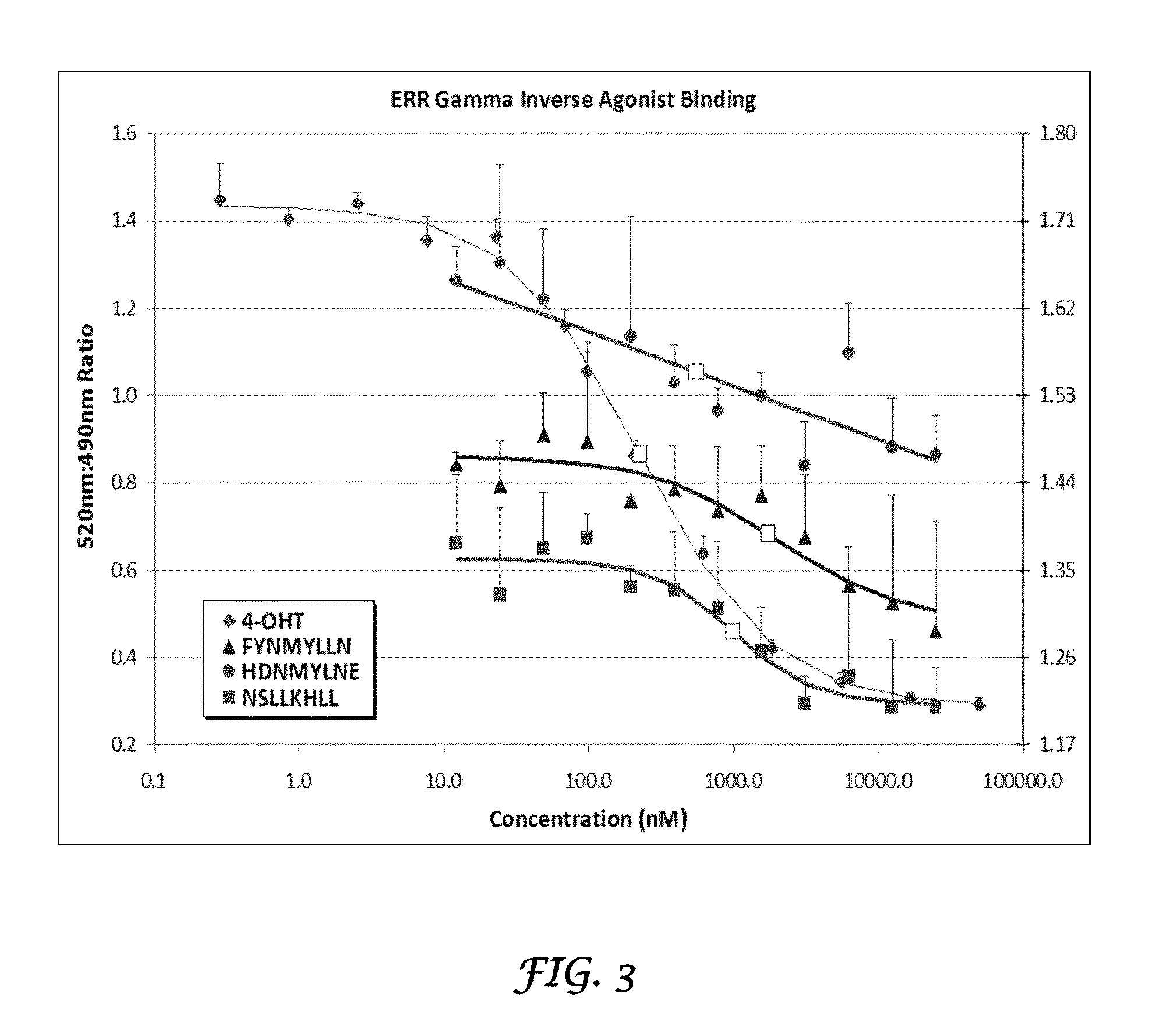
Methods and systems for the discovery of high-affinity peptide ligands and the resulting compositions are described herein. The amino acid sequence of a target protein is used to identify one or more homologous proteins of the target protein. Publications and databases are textmined to retrieve the sequences of peptide ligands that bind to the homologues or the target protein. Complementary proteins, which are proteins that bind to the target or homologous proteins or to DNA, and their target protein- or DNA-binding regions may also be identified. These candidate ligands are predicted to have a high probability of binding to the target protein or the DNA. The library of candidate peptide ligands is modulated by substituting native amino acid residues with suitable amino acids, thus increasing the explored protein space in a knowledge-based manner. Peptides designed in the modulation step are experimentally screened to identify high-affinity binding ligands, and further optimized through iterative application of the modulation and screening steps.
Owner:LYNNTECH
Methods and compositions for preventing oxidative degradation of proteins
InactiveUS20050276823A1Improve the immunityExtend product shelf lifePharmaceutical delivery mechanismImmunoglobulinsScavengerProtein oxidation
Methods and compositions for preventing oxidative damage to proteins, particularly antibodies, are provided. The compositions include a combination of metal chelators, such as DTPA, EGTA, and / or DEF, and can further include one or more free radical scavengers, particularly scavengers of oxygen radicals. Methods for enhancing protein stability using the compositions of the invention are also disclosed.
Owner:MEDAREX INC
Substituted piperidines that increase P53 activity and the uses thereof
In its many embodiments, the present invention discloses novel compounds, as inhibitors of HDM2 protein methods for preparing such compounds, pharmaceutical compositions including one or more such compounds, methods of treatment, prevention, inhibition, of one or more diseases associated with the HDM2 protein or P53 using such compounds or pharmaceutical compositions.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Novel methods of constructing libraries of genetic packages that collectively display the members of a diverse family of peptides, polypeptides or proteins
InactiveUS20060166252A1Peptide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein methodsComputational biology
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Methods and apparatus for performing submicroliter reactions with nucleic acids or proteins
InactiveUS7138254B2Reduce processing stepsAvoid pollutionHeating or cooling apparatusSugar derivativesHigh-fluence-rate responseSystems design
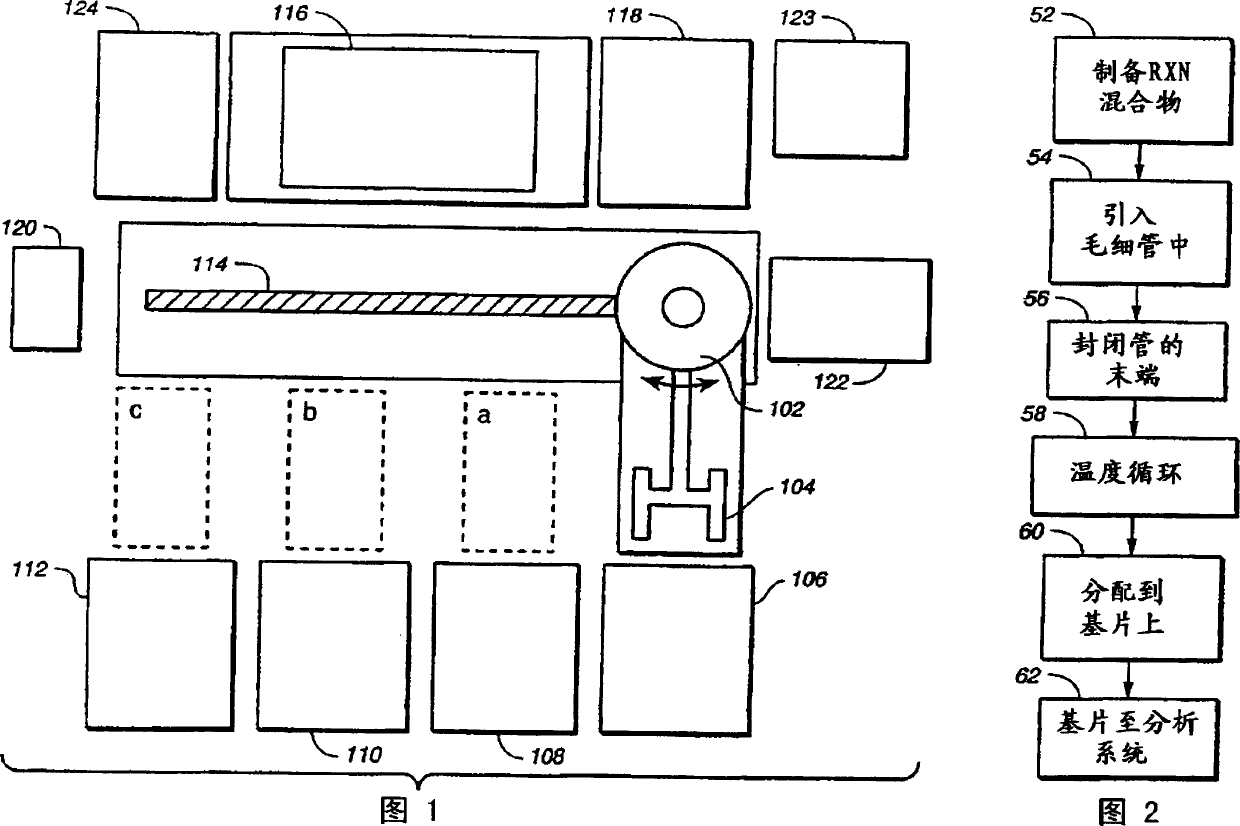
Methods for preparing nanoscale reactions using nucleic acids or proteins are presented. Nucleic acids are captured saturably, yet reversibly, on the internal surface of the reaction chamber, typically a capillary. Excess nucleic acid is removed and the reaction is performed directly within the capillary. Proteins are captured specifically and saturably on the modified inner surface of the reaction chamber, typically a capillary. Excess protein is removed and the reaction is performed directly within the capillary. Devices for effecting the methods of the invention and a system designed advantageously to utilize the methods for high throughput reactions involving nucleic acids or proteins are also provided.
Owner:INTEGENX
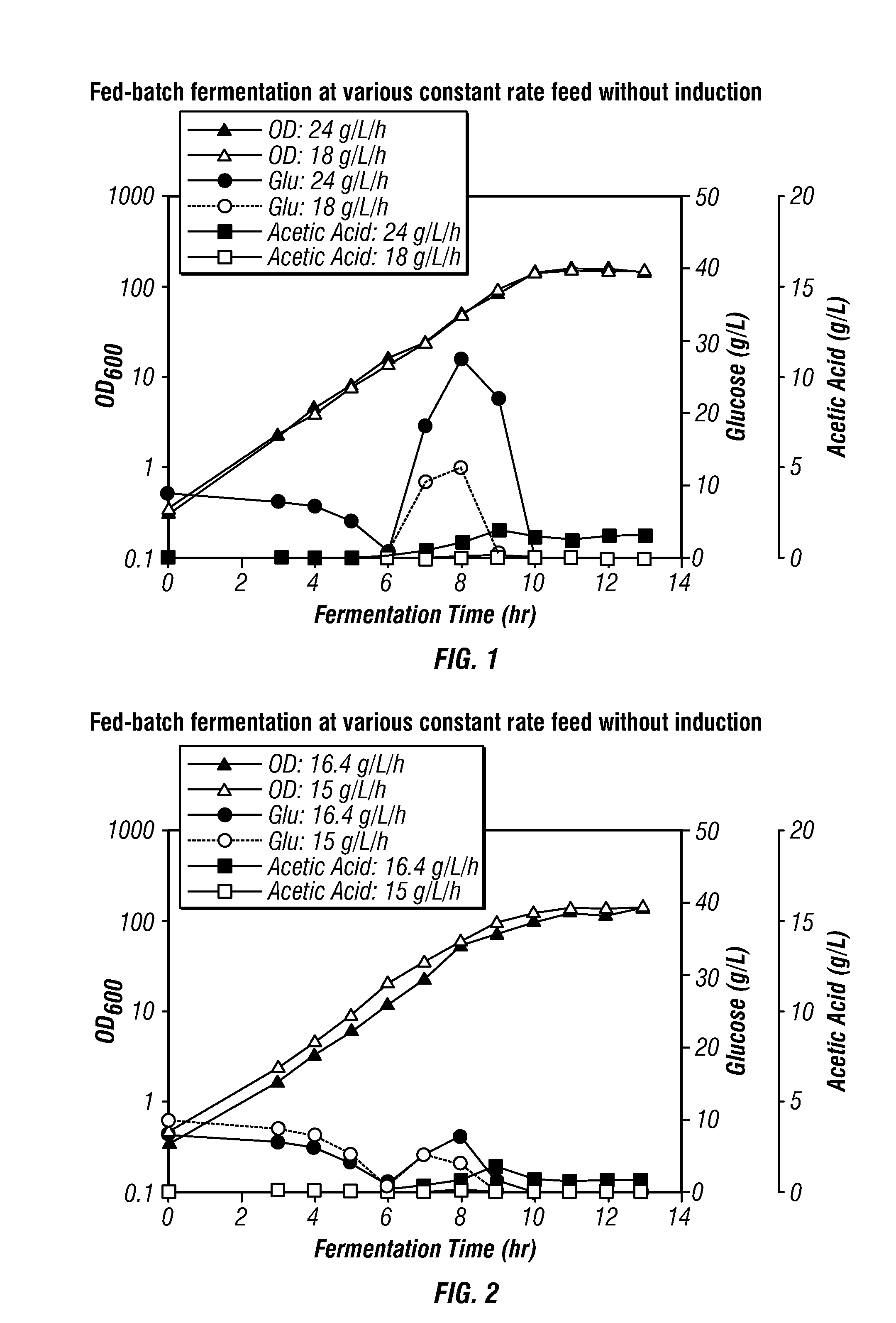
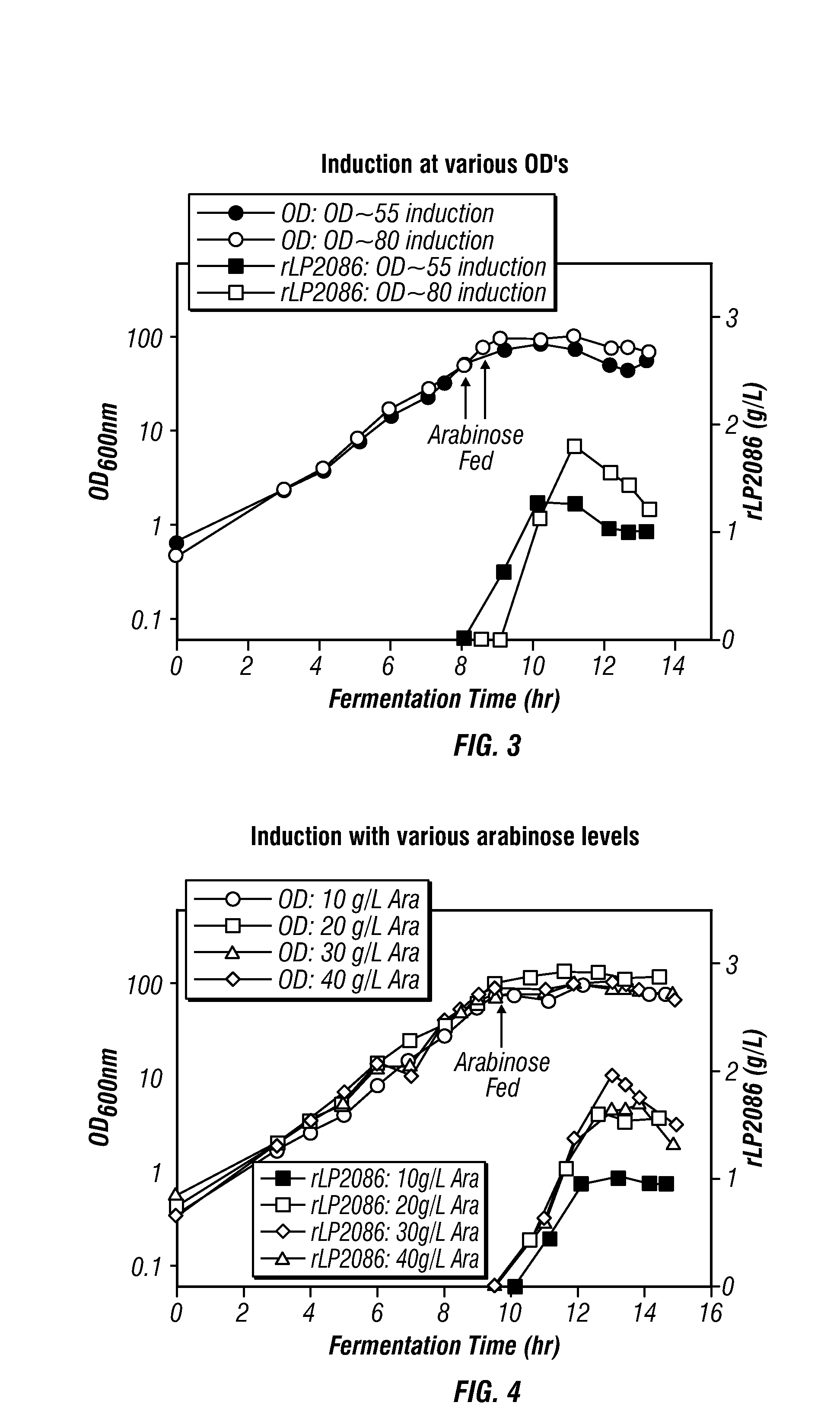
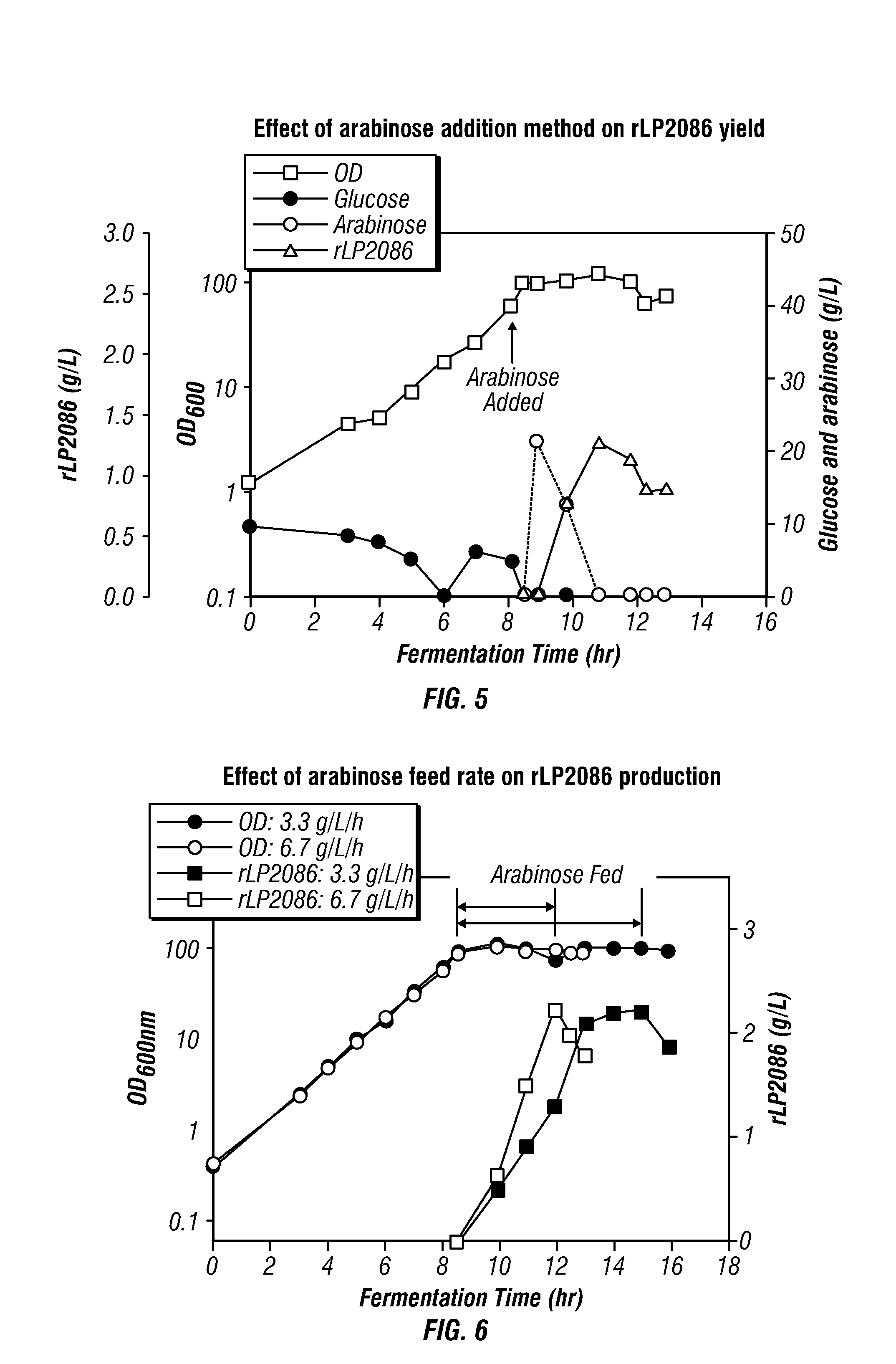
High-cell density fed-batch fermentation process for producing recombinant protein
Methods for producing proteins, for example, recombinant meningococcal 2086 proteins, using fed-batch fermentation with continuous input of an inducer after achieving a threshold parameter, and optionally continuous input of a carbon source, for example, a constant rate input, to improve protein yields, as well as high density protein compositions and compositions for use in the methods of the present invention, are provided.
Owner:WYETH LLC
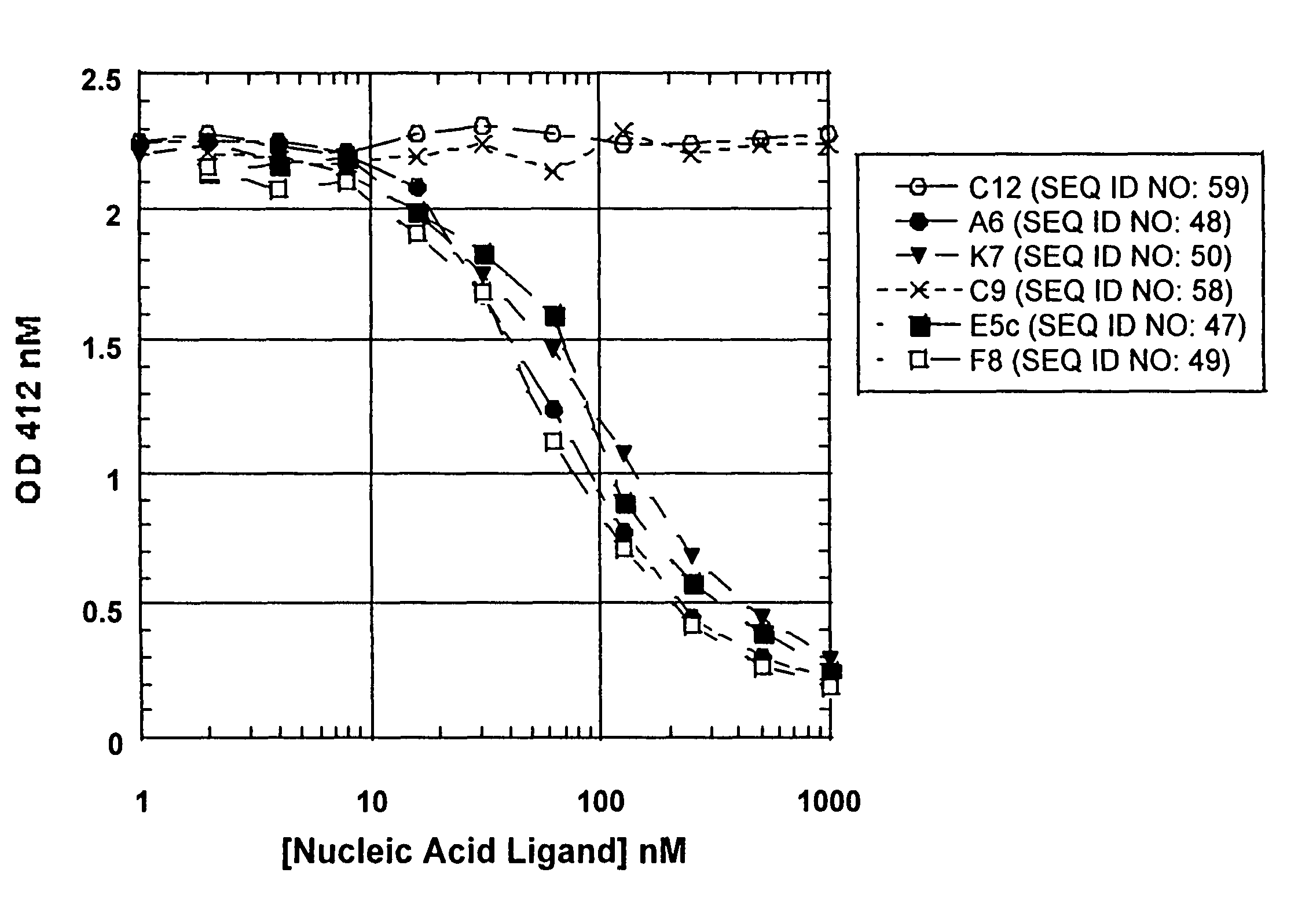
High affinity nucleic acid ligands of complement system proteins
InactiveUS20060079477A1Inhibit functioningNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsComplement systemProtein methods
Methods are described for the identification and preparation of high-affinity Nucleic Acid Ligands to Complement System Proteins. Methods are described for the identification and preparation of high affinity Nucleic Acid Ligands to Complement System Proteins C1q, C3 and C5. Included in the invention are specific RNA ligands to C1q, C3 and C5 identified by the SELEX method.
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
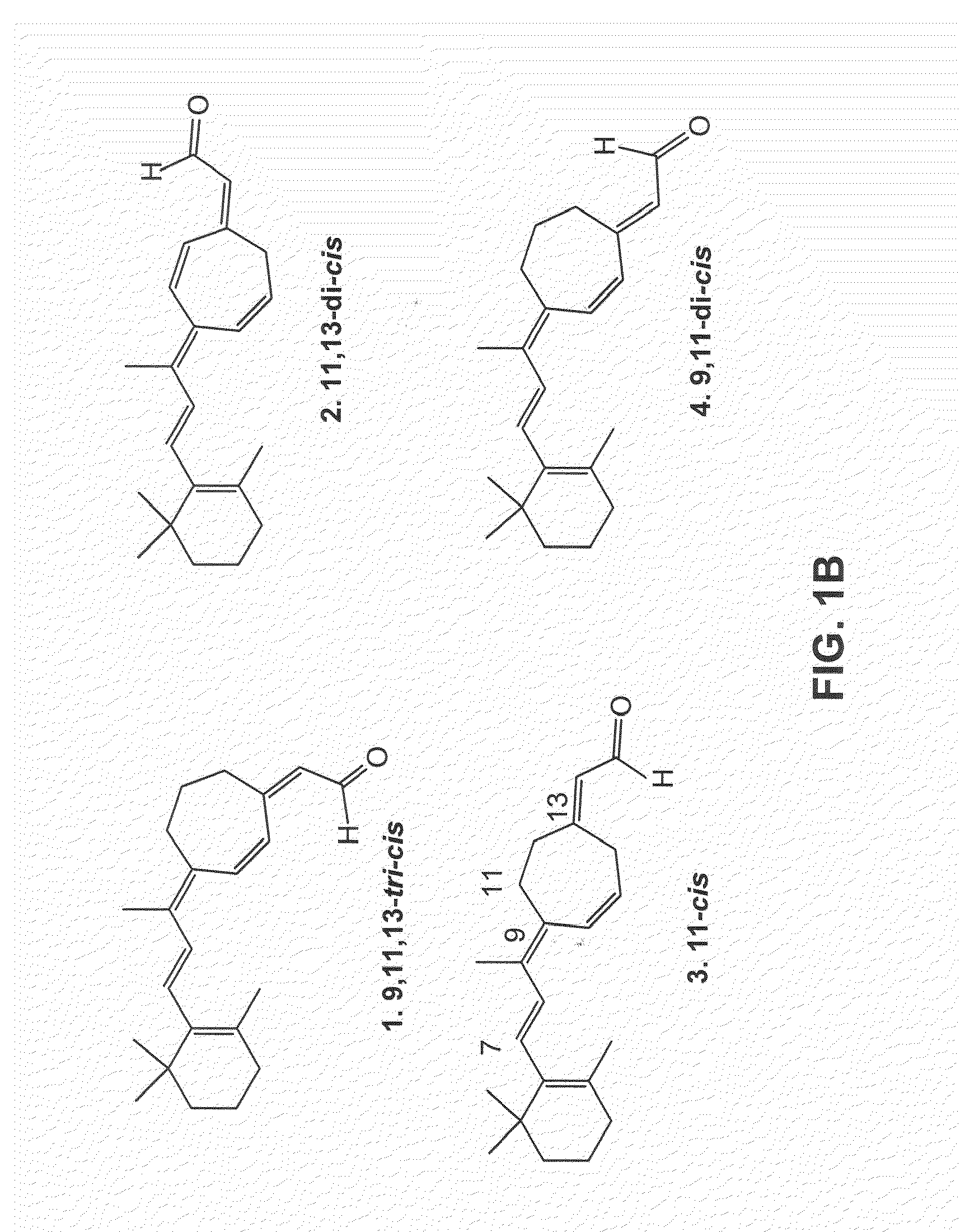
Stabilized mutant opsin proteins
InactiveUS20120041073A1Restoring and stabilizing photoreceptor functionGood effectBiocideSenses disorderOpsin bindingSynthetic retinoid
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON +1
Diagnostic method based on large scale identification of post-translational modification of proteins
InactiveUS20100160177A1Quick filterLibrary screeningDisease diagnosisPost translationalDisease cause
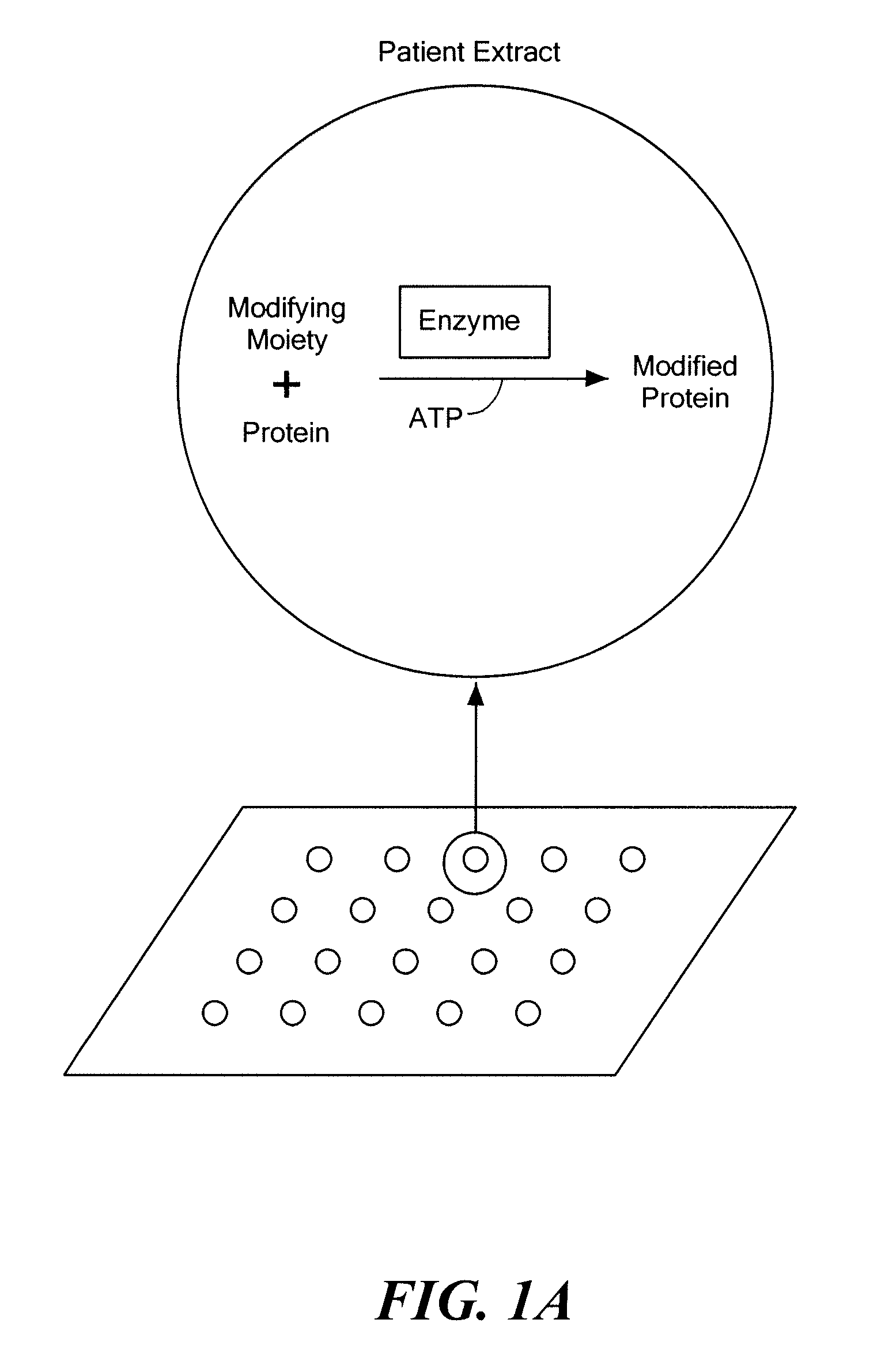
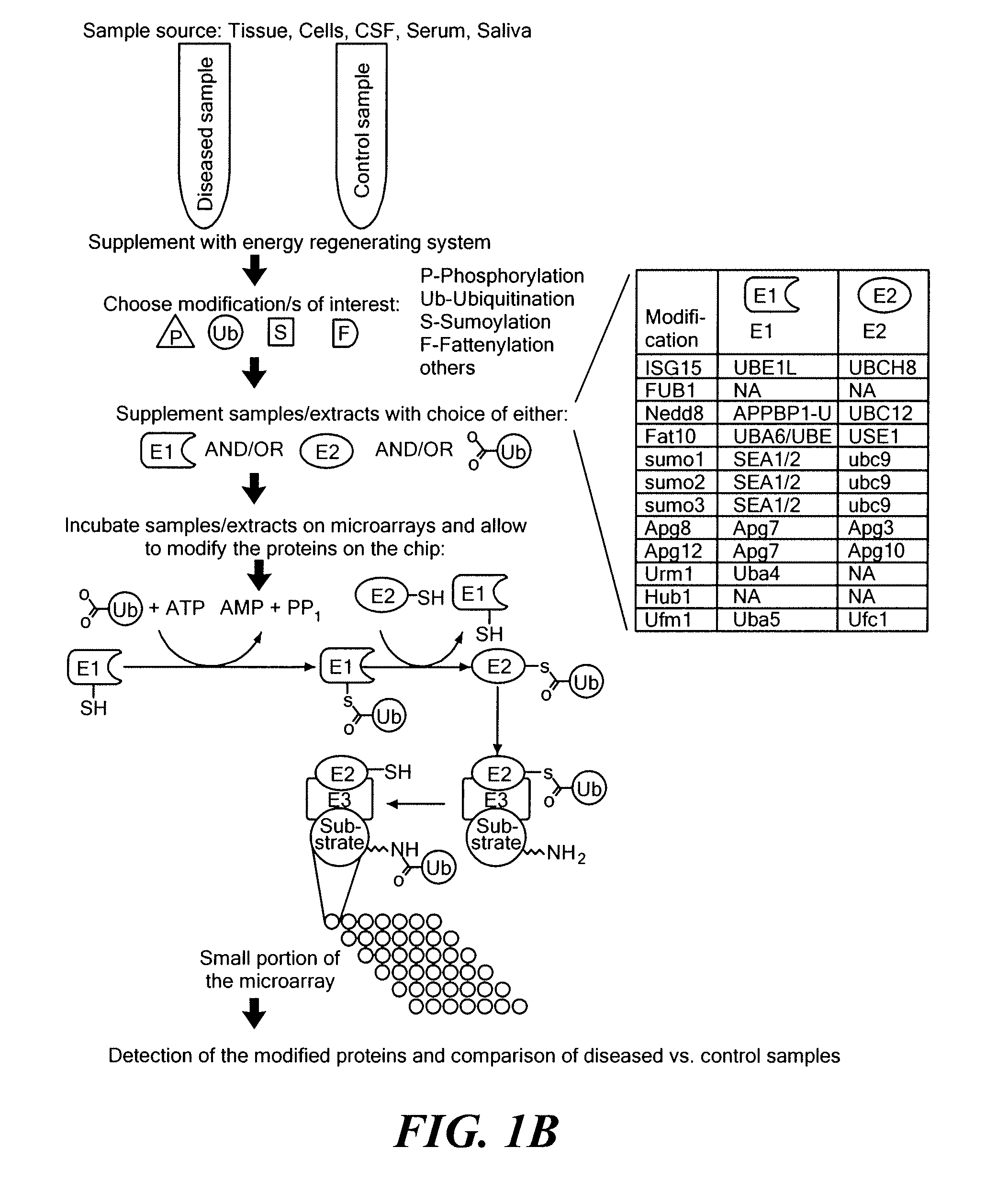
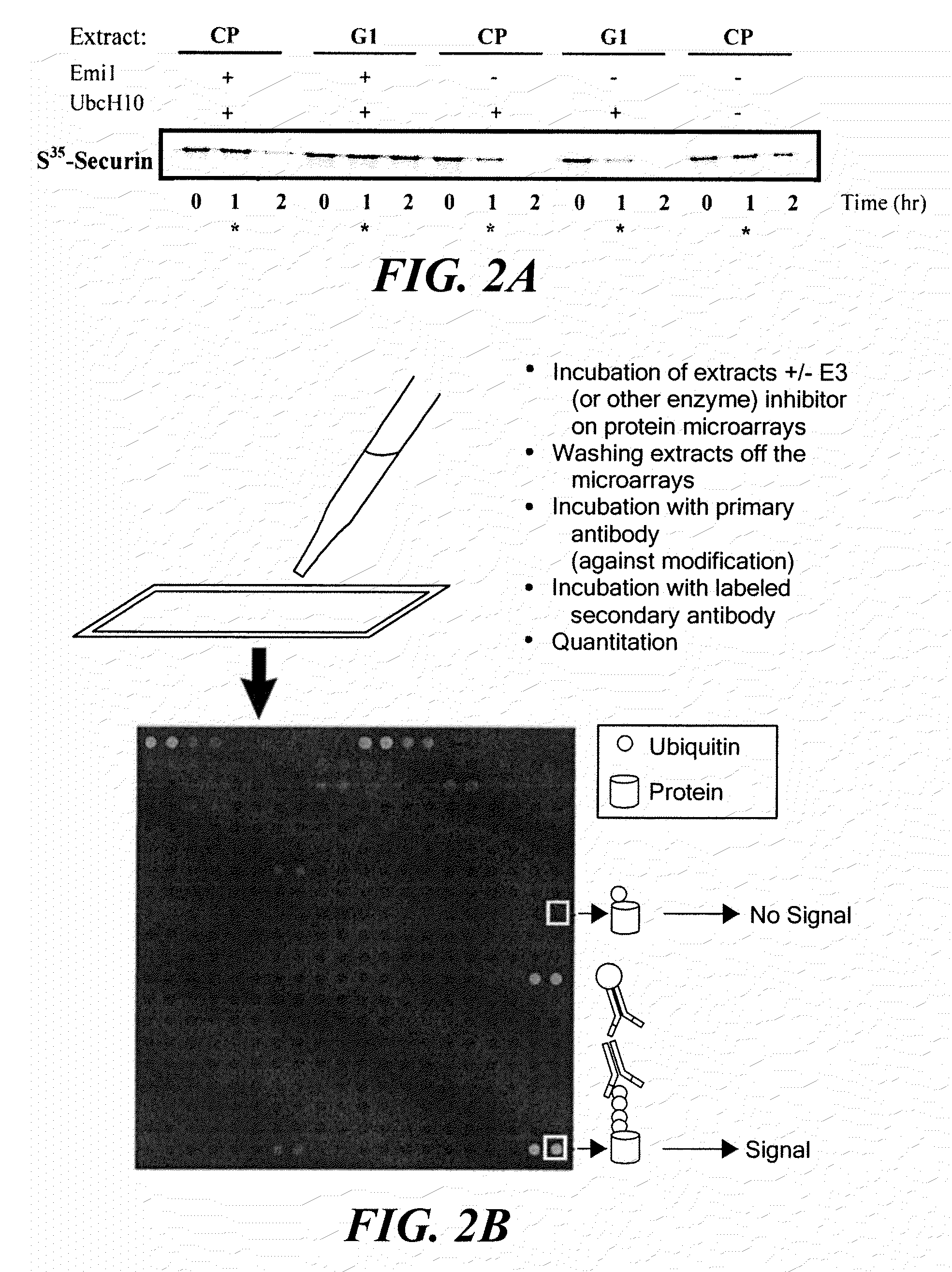
Methods for the large scale identification of post-translational modification states of proteins and enzyme activities for carrying out post-translational modification reactions involve the analysis of functional extracts from fresh and frozen samples using protein arrays. The methods and kits of the present invention can be used to analyze and characterize compounds for their effects on post-translational modifications and their pathways. The methods and kits can also be used to diagnose and characterize a wide variety of diseases and medical conditions, including cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, immune diseases, infectious diseases, genetic diseases, metabolic conditions, and drug effects using cells or body fluids of a patient.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Method and device for performing submicroliter reactions with nucleic acids or proteins
InactiveCN1791680ASteps required to ensure consistencySteps Required to Reduce ConsistencyFermentationHigh-fluence-rate responseSystems design
Methods for preparing nanoscale reactions using nucleic acids or proteins are presented, Nucleic acids are captured saturably, yet reversibly, on the internal surface of the reaction chamber, typically a capillary. Excess nucleic acid is removed and the reaction is performed directly within the capillary. Proteins are captured specifically and saturably on the modified inner surface of the reaction chamber, typically a capillary. Excess protein is removed and the reaction is performed directly within the capillary. Devices for effecting the methods of the invention and a system designed advantageously to utilize the methods for high throughput reactions involving nucleic acids or proteins are also provided.
Owner:AMERSHAM BIOSCI SV
Method for Shielding Functional Sites or Epitopes on Proteins
InactiveUS20100092505A1Eliminate and suppress unwanted biological responseNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsPolymer modifiedBinding site
Methods of site-specifically shielding one or more binding sites within a polypeptide are disclosed, comprising attaching at least one small molecular weight, water-soluble polymer to said polypeptide such that the binding site is masked by said polymer. The shielding of a binding site (e.g., epitope) as per the disclosed methods acts to either eliminate or substantially reduce the biological response induced by the interaction between said binding site and its cognate receptor, helping to refocus the biological response toward unmasked portions of the polypeptide. Pharmaceutical products generated as per the methods described herein (e.g., polymer-modified antigens and vaccine compositions comprising them), as well as the use thereof, induce a specific immune response against unmasked portions of the polypeptides when directly introduced into living vertebrate tissue, preferably a mammalian host such as a human or a non-human mammal of commercial or domestic veterinary importance, generating selective immunoprotection in said mammal.
Owner:IST DI RICERCHE DI BIOLOGIA MOLECOLARE P ANGELETTI
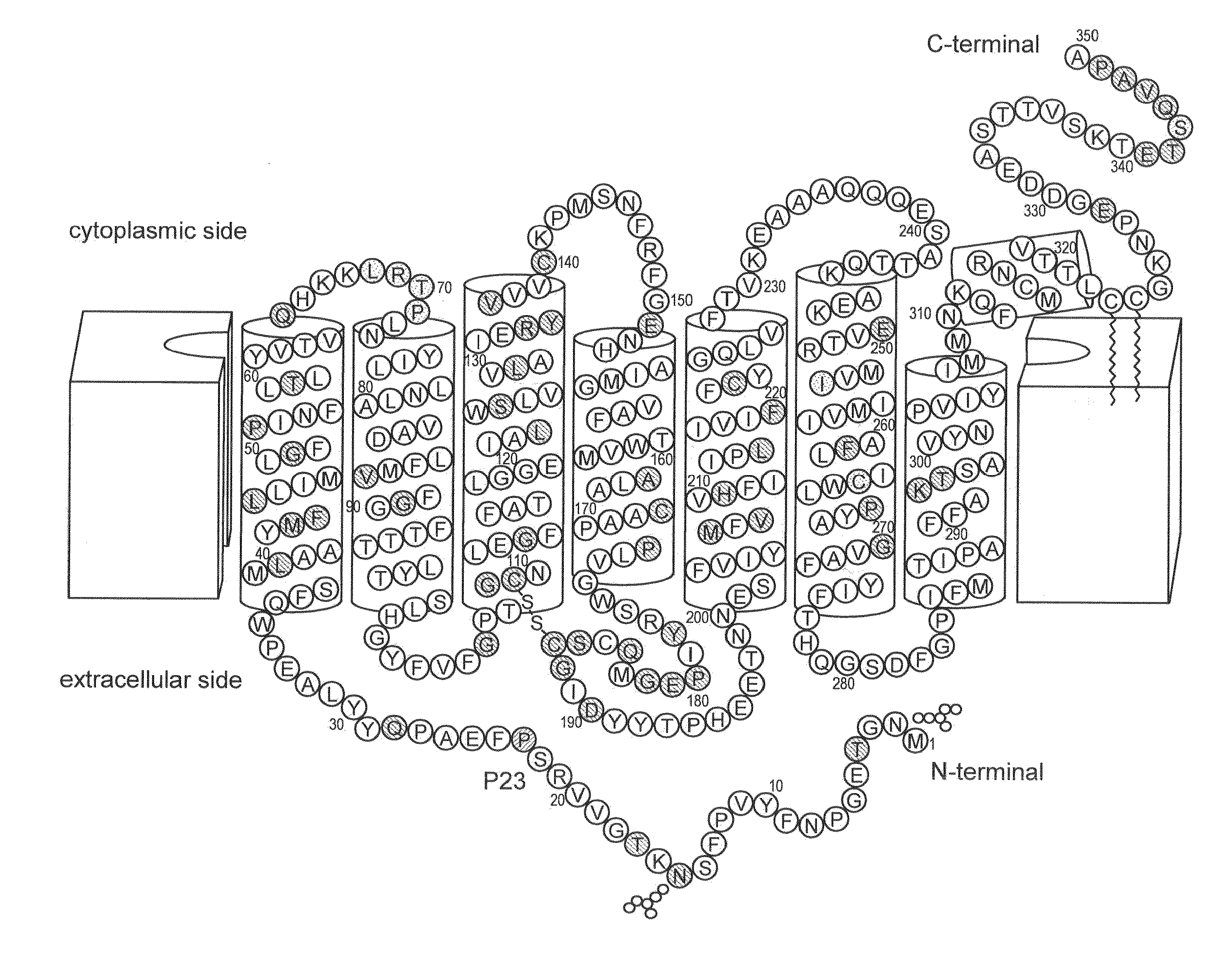
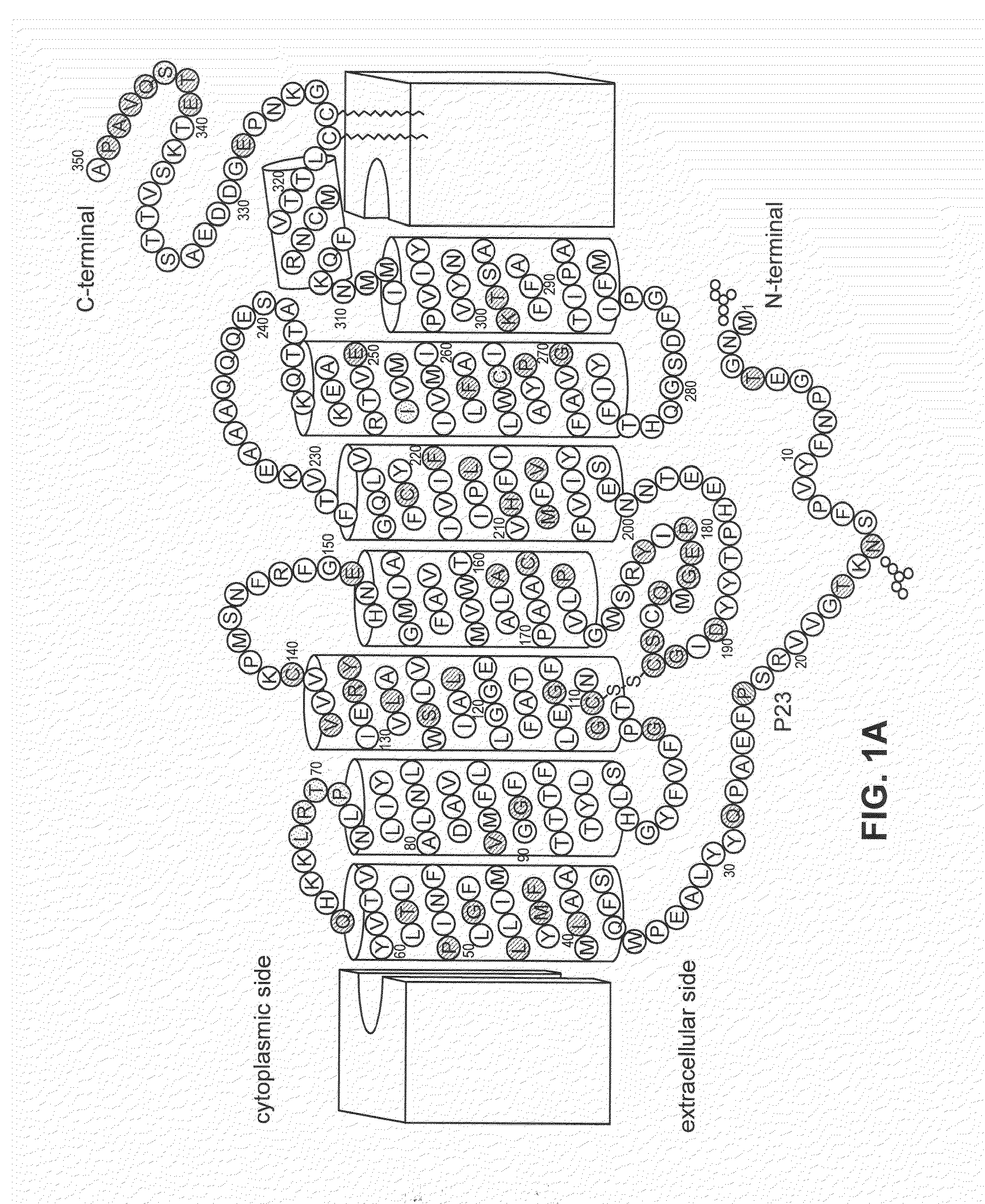
Methods for producing soluble membrane-spanning proteins
InactiveUS20060172385A1Efficient productionHigh yieldBacteriaBacteria peptidesProtein methodsTransmembrane protein
Methods for producing membrane-spanning polypeptides in high yields, with native conformation, and / or in soluble form include solubilizing in non-ionic or zwitterionic detergents, as well as use of promoters and expression vectors for expressing high yields of membrane-spanning polypeptides in bacterial cells. Mutated promoters provide tight control of membrane-spanning polypeptides in bacterial cell hosts.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Design of synthetic nucleic acids for expression of encoded proteins
ActiveUS20100028870A1Digital data processing detailsMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotidePolynucleotide
Methods for determining a property that affects expression of polynucleotides are provided. A plurality of polynucleotides each encoding a polypeptide sequence is constructed. A frequency that a sequence element is used in a first polynucleotide is different than in a second polynucleotide. Each polynucleotide is expressed in an expression system to obtain an expression property value thereby constructing a dataset that contains, for each respective polynucleotide, sequence element occurrence in the respective polynucleotide and the measured expression property value of the respective polynucleotide. A model is computed that describes variation in the measured expression property values as a function of a plurality of variables and weights. From the model, a property that affects expression of polynucleotides in the expression system is determined, where the property is an effect that the frequency of occurrence of one or more sequence elements has on the expression property of polynucleotides in the expression system.
Owner:DNA TWOPOINTO
Algorithmic design of peptides for binding and/or modulation of the functions of receptors and/or other proteins
InactiveUS20050119454A1Improve the immunityImprove actionCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseProtein target
Methods of synthesizing a peptide or peptide-like molecule to a polypeptide or protein target based on mode-matching each member of a set of peptide constituents of the peptide or peptide-like molecule to peptide constituents of the target polypeptide or protein target for treatment of neurological diseases.
Owner:CIELO INST
Methods and kits for detecting misfolded proteins
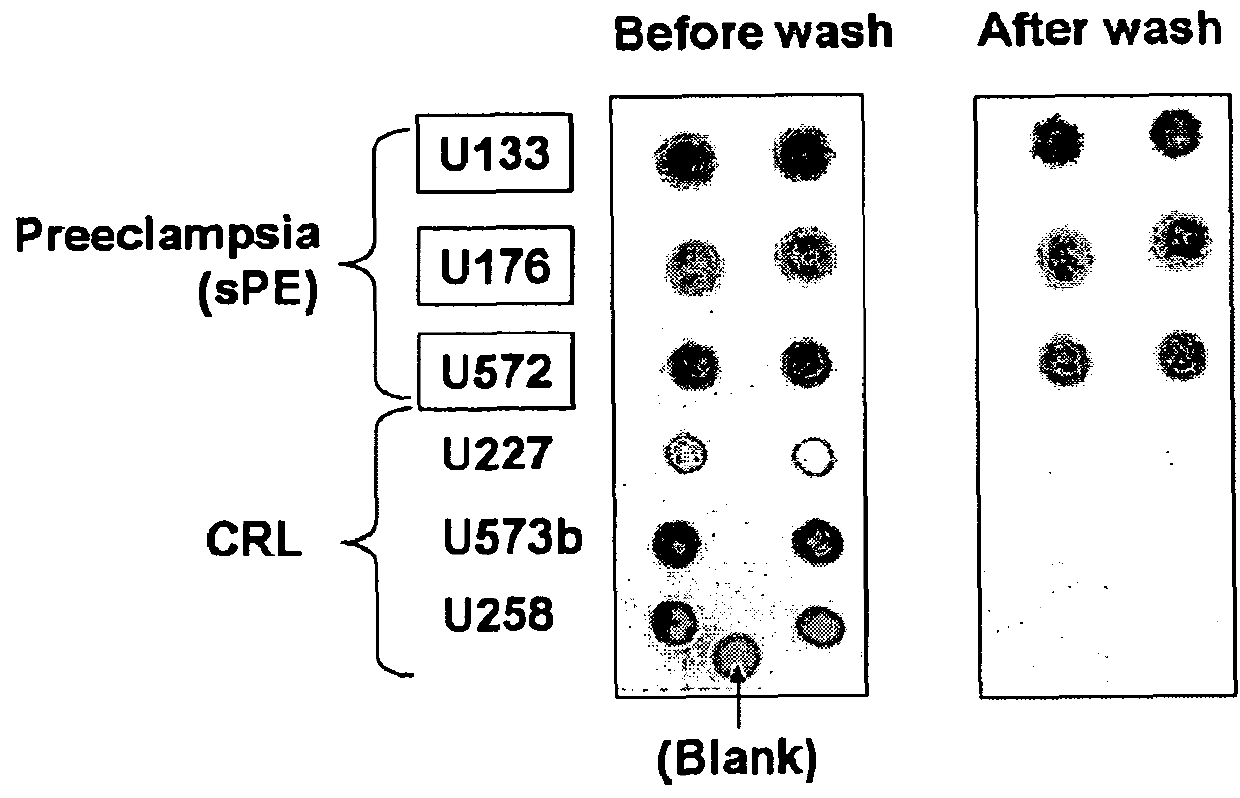
Methods, kits and compounds are provided that relate to the diagnosis, treatment, and / or prevention of preeclampsia.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Methods and compositions for analyzing proteins
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
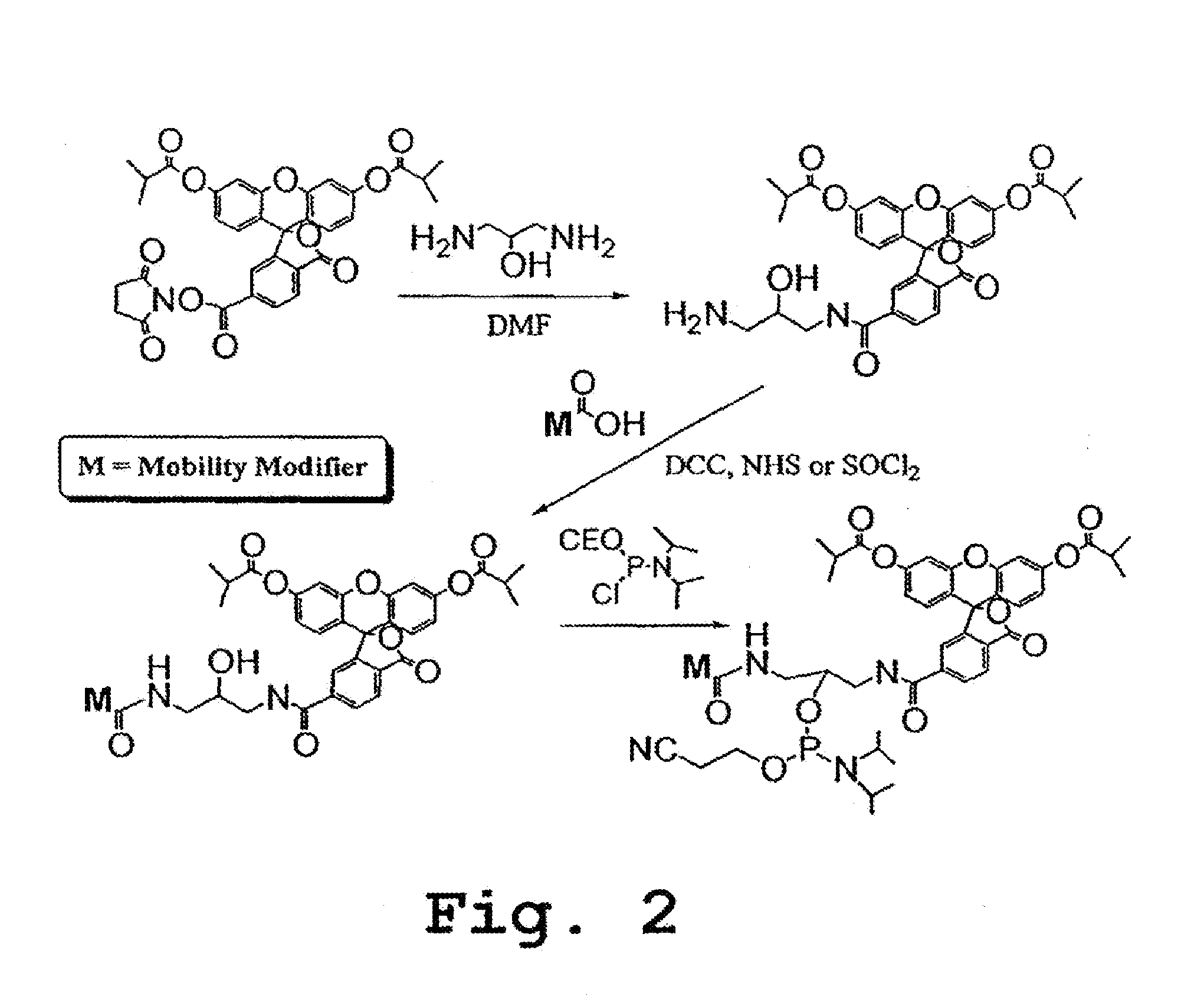
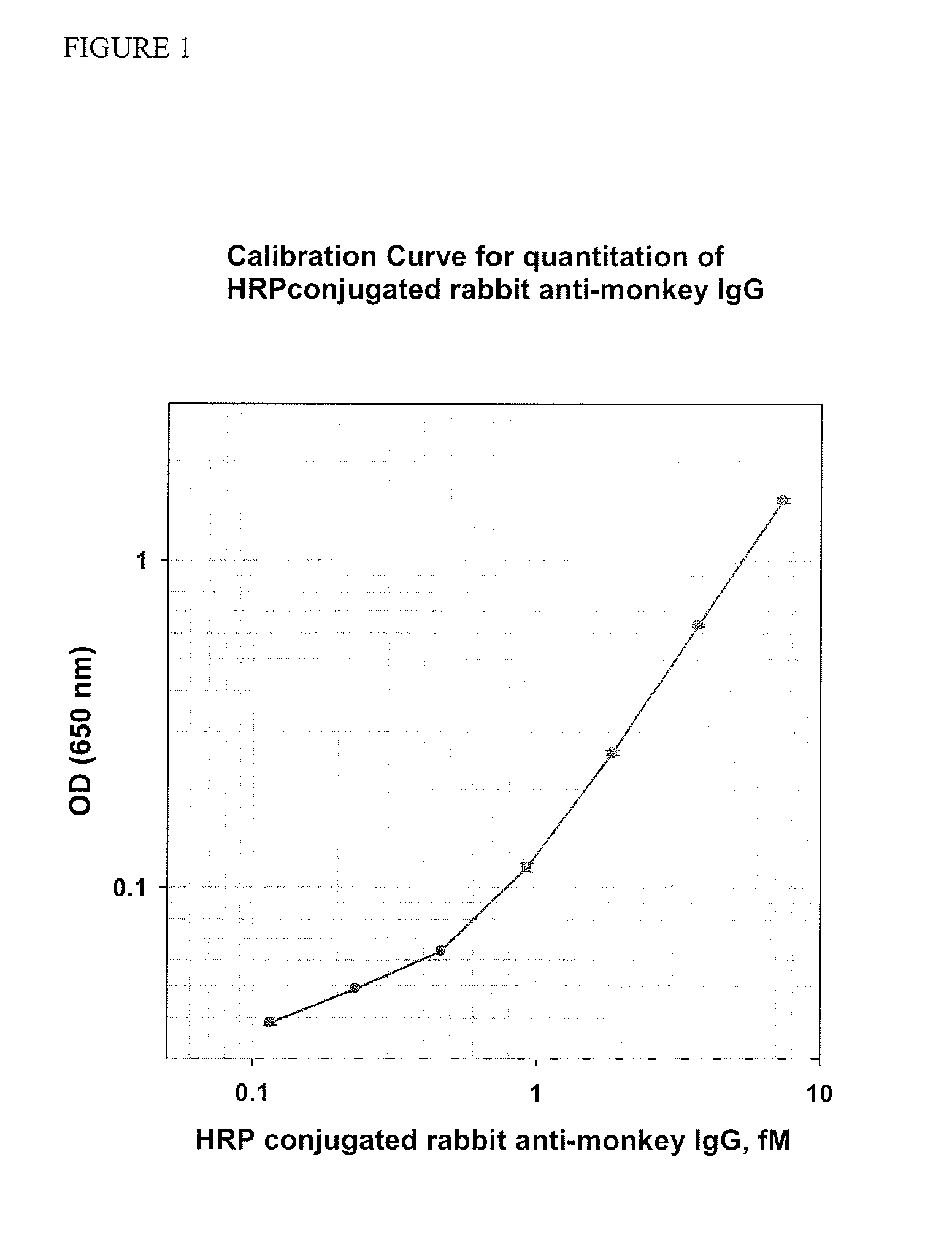
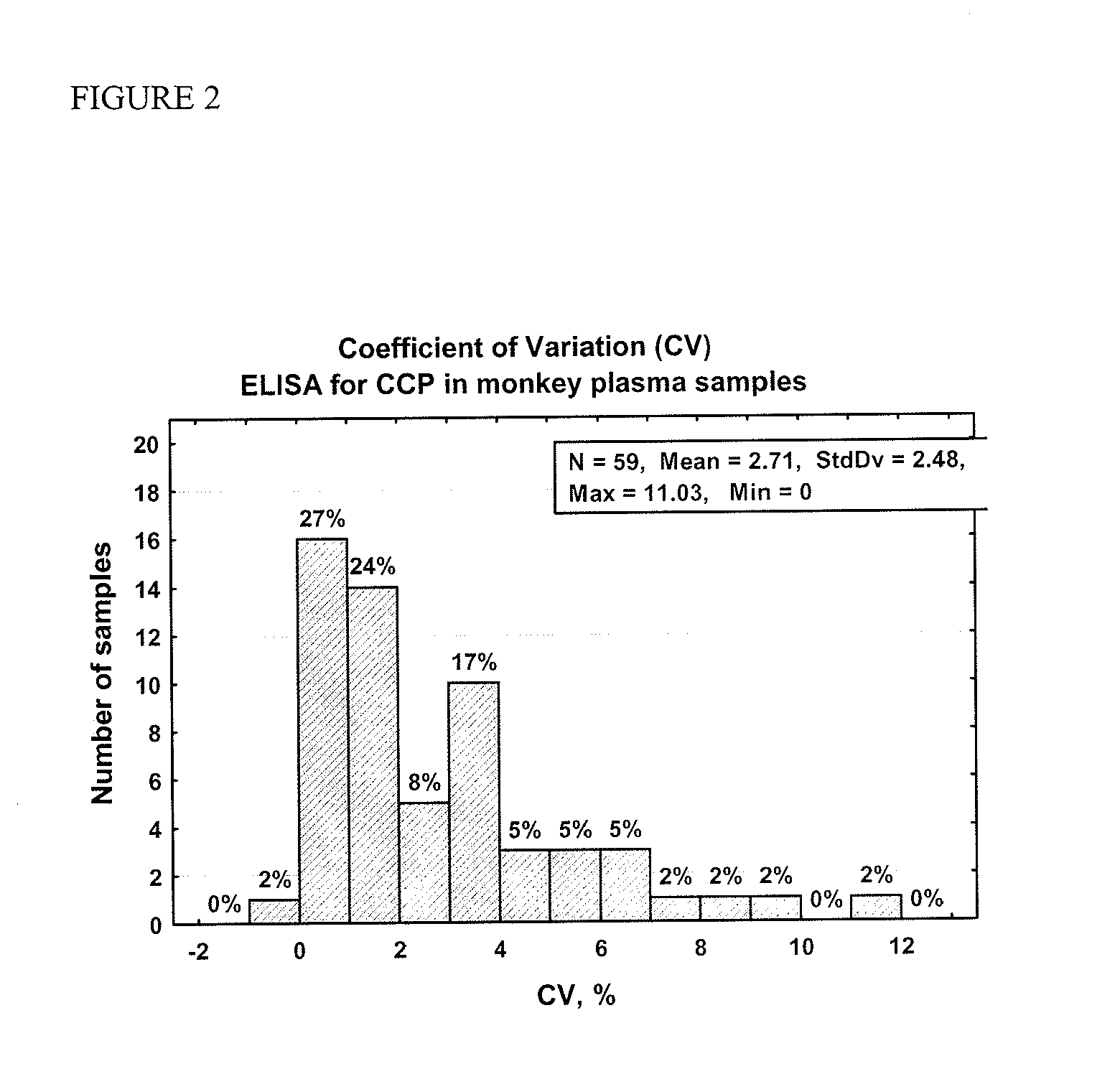
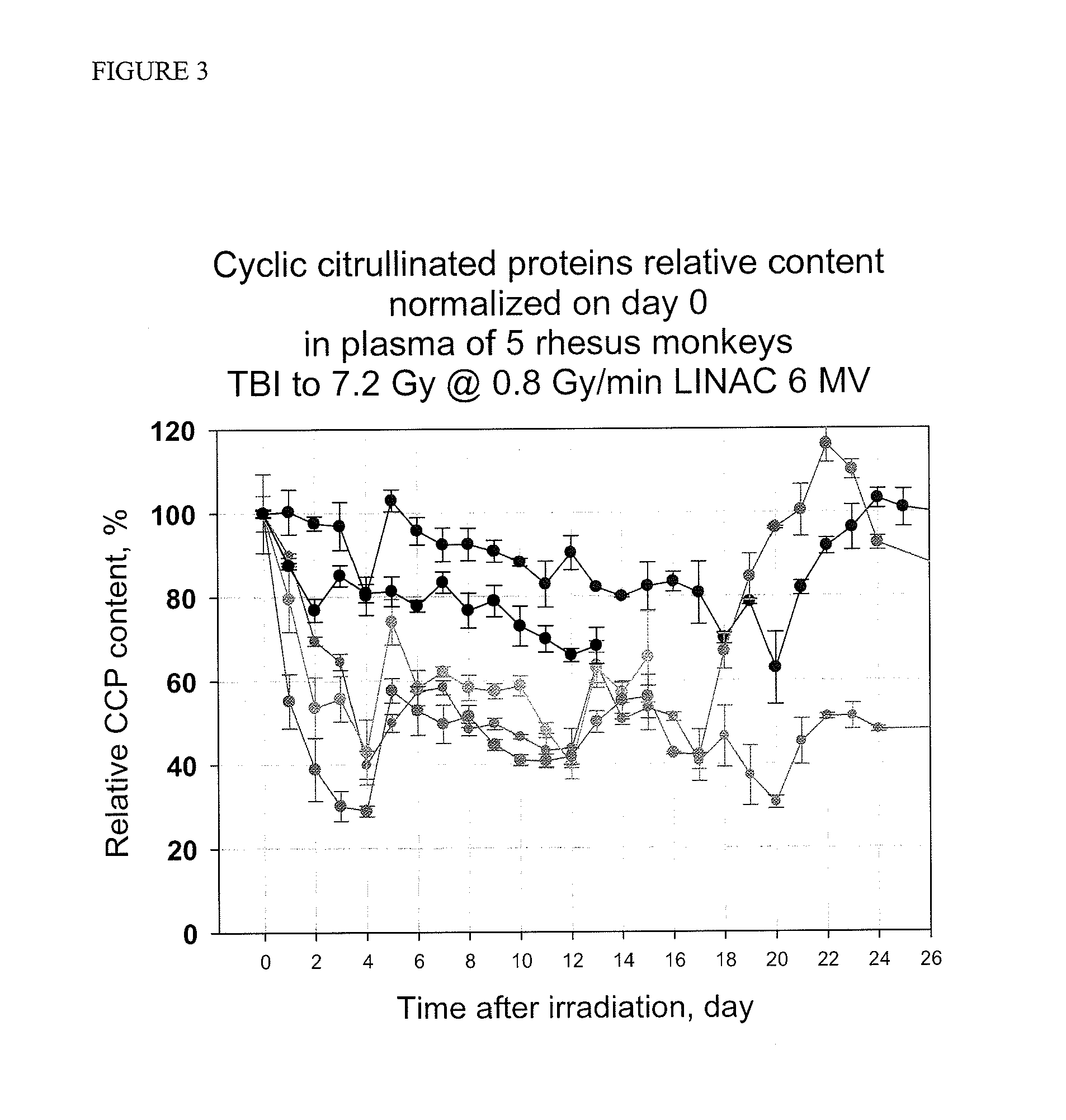
Immunoassays for citrullinated proteins
ActiveUS20110244492A1Reduce in quantityEnhanced radiationDisease diagnosisBiological testingRadiation injuryImmuno assay
Methods and kits are provided for assessing radiation injury and exposure in a mammal. The methods comprise the steps of: obtaining one or more test samples from the mammal, contacting the test samples with an antibody immunoreactive with a citrullinated protein to form an immunocomplex; and detecting the immunocomplex with an ELISA; wherein a decrease in the quantity of the immunocomplex in the test samples, as compared to the quantity of immunocomplexes formed under identical conditions with the same antibody and a control sample from one or more mammals known to have a lower degree of radiation injury or exposure, indicates a higher degree of radiation injury and exposure to the mammal. The information obtained from such methods can be used by a clinician to accurately assess the extent of radiation injury / exposure in the mammal, and thus will provide a valuable tool for determining treatment protocols on a subject by subject basis.
Owner:THE HENRY M JACKSON FOUND FOR THE ADVANCEMENT OF MILITARY MEDICINE INC
Stem cells and lim mineralization proteins
Methods of changing a phenotype of a cell are provided. The methods comprise increasing an amount of an amino acid sequence which is at least 70% identical to an amino acid sequence encoding an LMP protein or a fragment thereof in a cell. The cells may be contacted by either a composition comprising a nucleic acid sequence encoding the amino acid sequence which is at least 70% identical to the amino acid sequence encoding an LMP or its fragment or by a composition comprising acid sequence which is at least 70% identical to the amino acid sequence encoding an LMP or its fragment or any combination thereof. The cells may be contacted either in vivo or ex-vivo.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Methods and systems for designing stable proteins
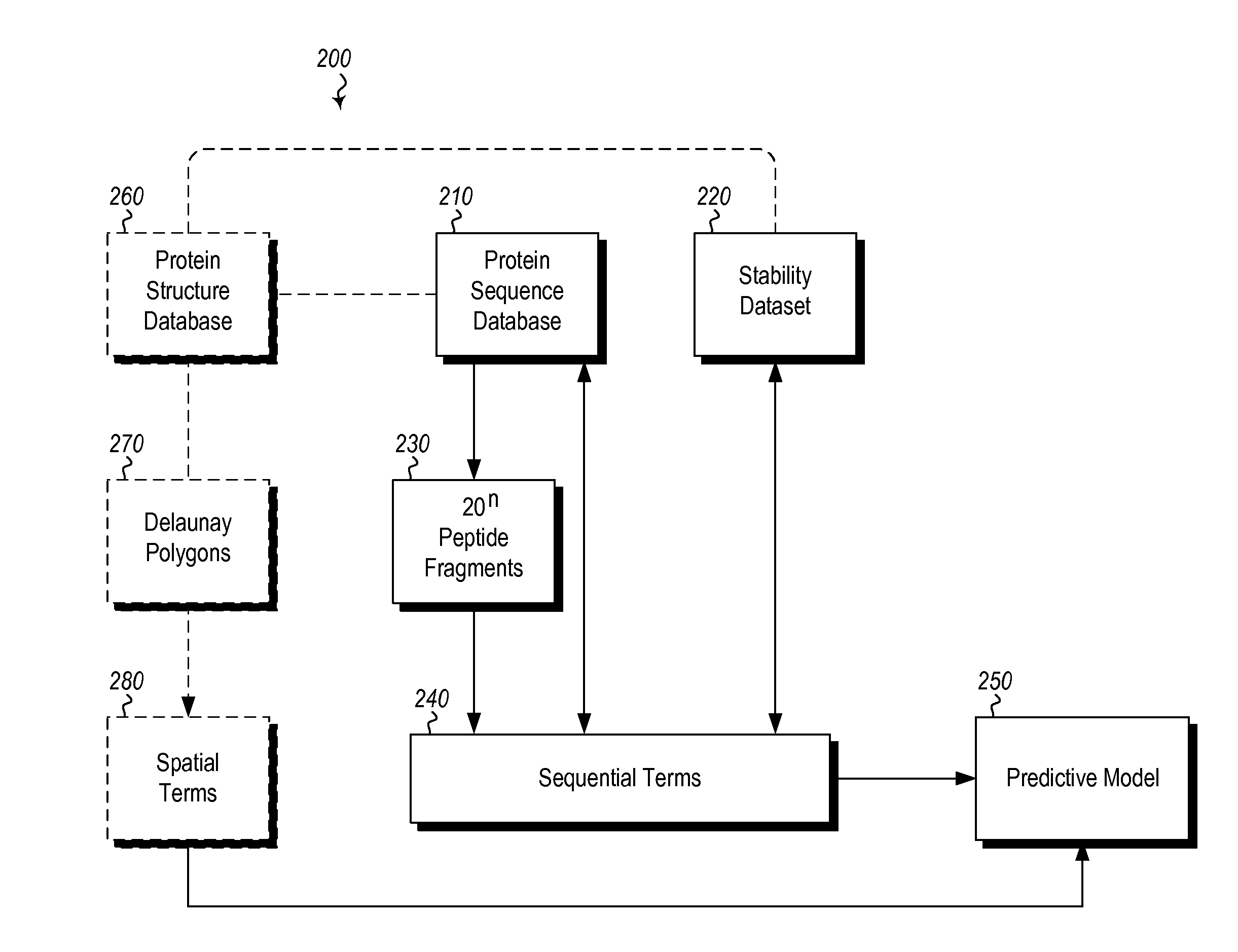
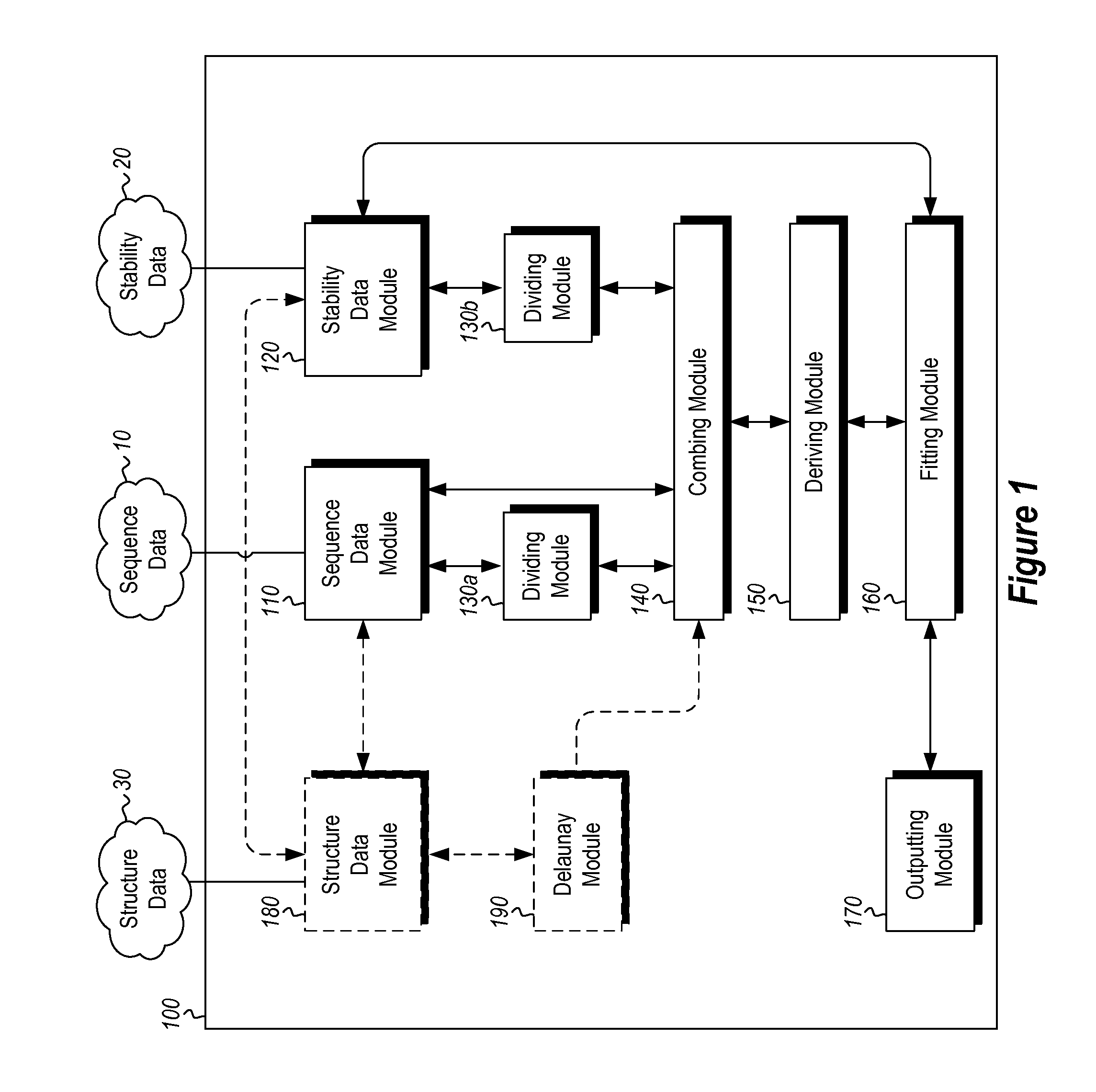
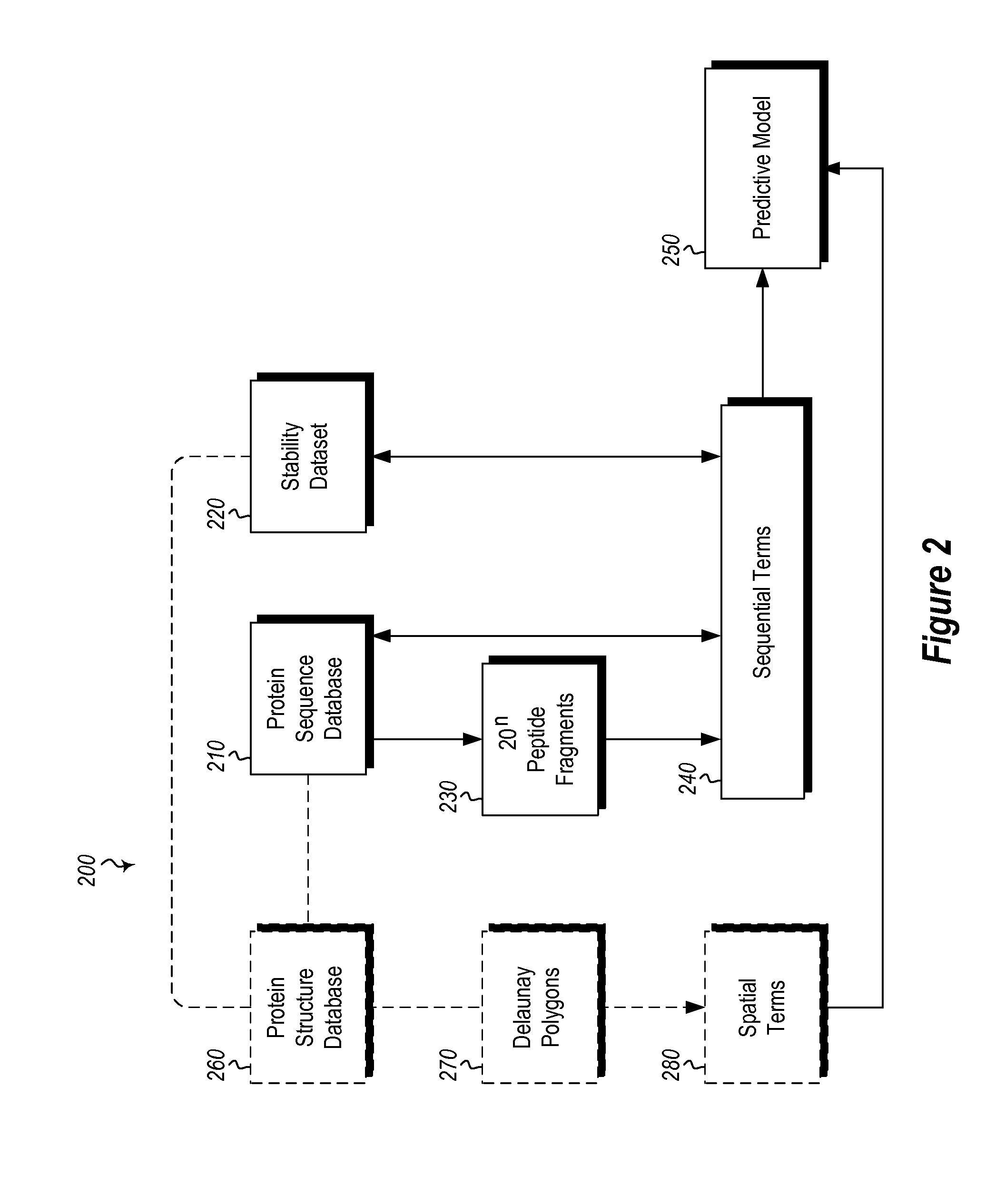
InactiveUS20120265513A1Improve protein stabilityImprove thermal stabilityAnalogue computers for chemical processesProteomicsProtein structureThermophilic organism
Methods and computing systems for generating a protein stability lookup table and a predictive model. These methods and systems are useful for predicting the thermal stability of a protein sequence and for predicting mutations that may enhance the thermal stability of a protein given its amino acid sequence and / or three dimensional structure. The protein stability lookup table and a predictive model are based on a combination and analysis of related protein sequences and, where available, protein structure data, and relative stability data from mesophilic and thermophilic organisms and experimentally determined stability changes of wild type proteins and their mutants.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS
High affinity nucleic acid ligands of complement system proteins
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
Methods for producing factor VIII proteins
InactiveUS20050165221A1Advantage in processing timeReduced monoclonal antibody contaminationFactor VIIPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide ligandIon exchange
Methods are provided for purification of Factor VIII polypeptides by affinity chromatography and ion exchange chromatography, in which the eluate from the affinity column is diluted with a solution comprising higher salt concentration, or lower non-polar agent concentration than that of the elution solution, prior to passing the diluted solution through the ion exchange column. The affinity matrix may comprise a monoclonal antibody or a peptide ligand. The methods result in improved purification without significant yield loss.
Owner:GENETICS INST INC
Reagents and Methods for Appending Functional Groups to Proteins
ActiveUS20080020942A1Minimizes and avoids inactivationMaintain biological activityPeptide librariesPeptide/protein ingredientsInteinLink protein
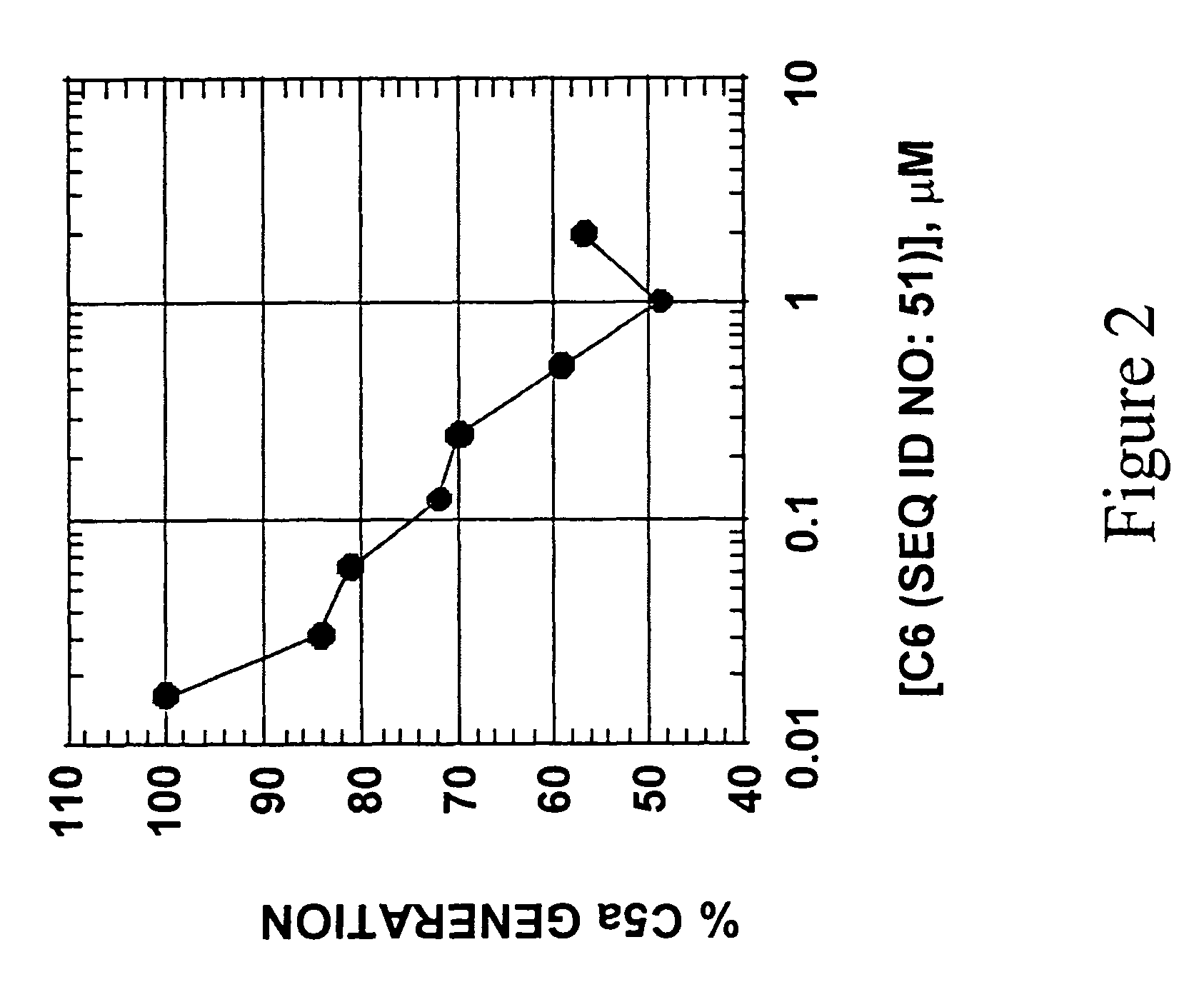
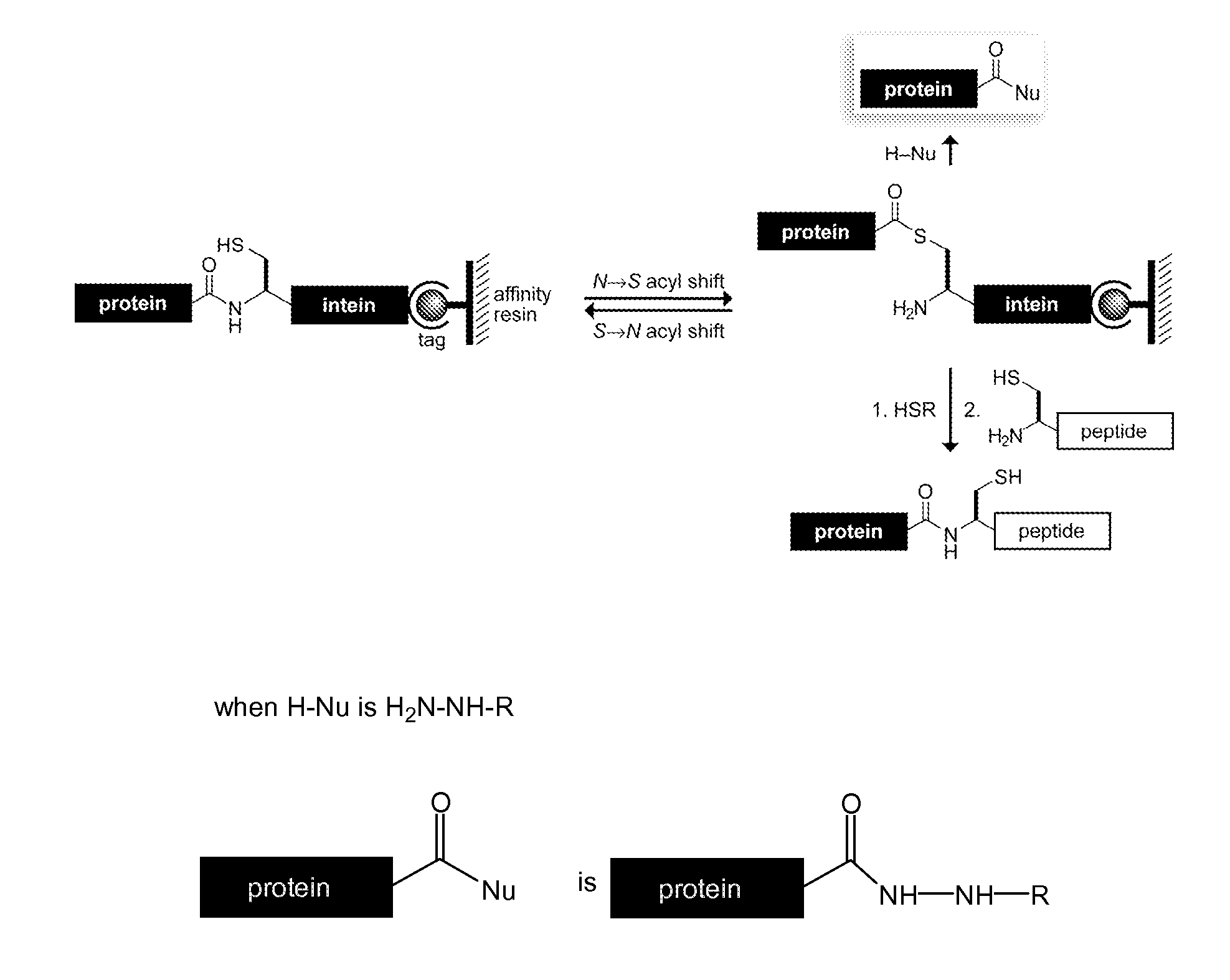
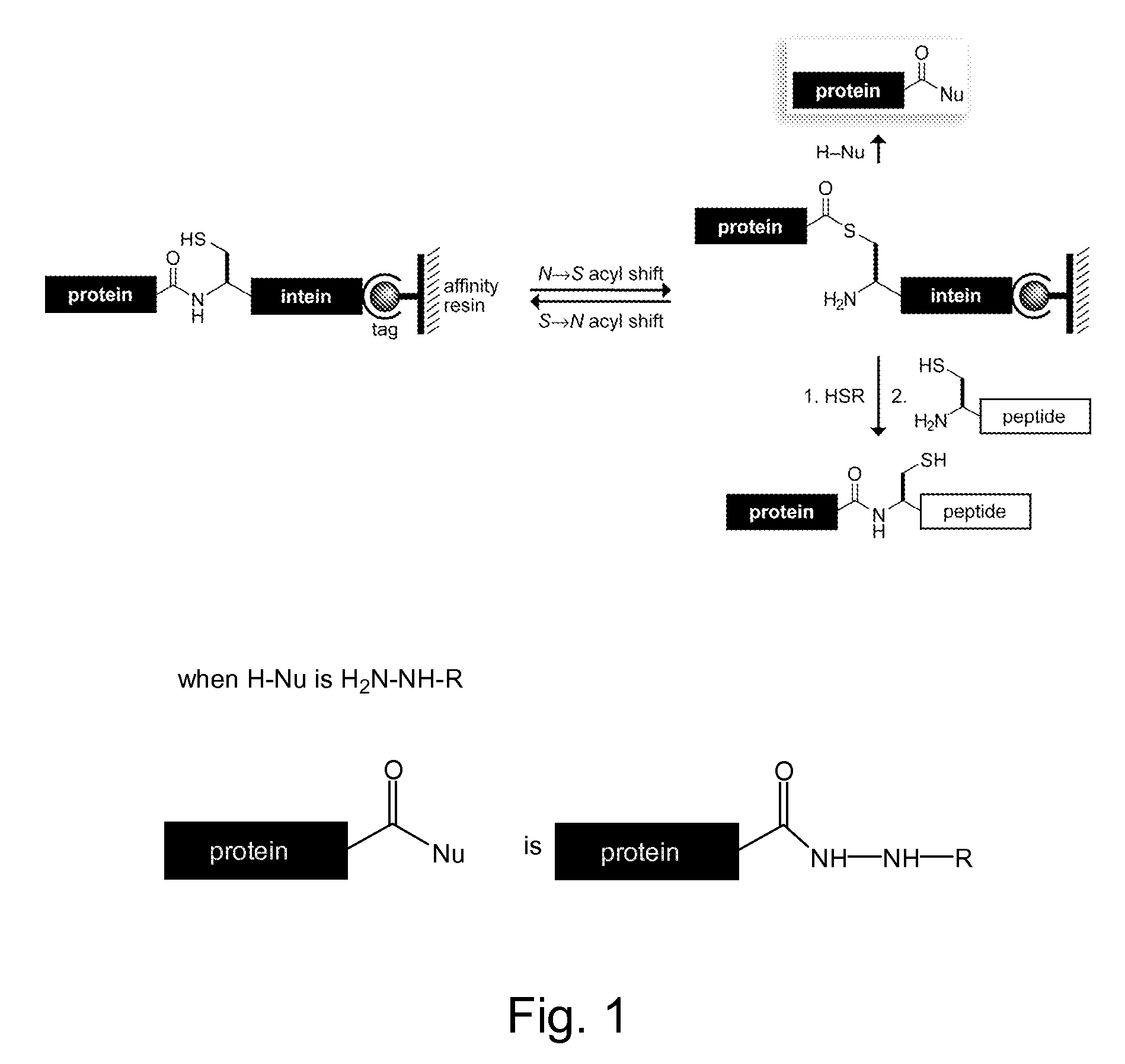
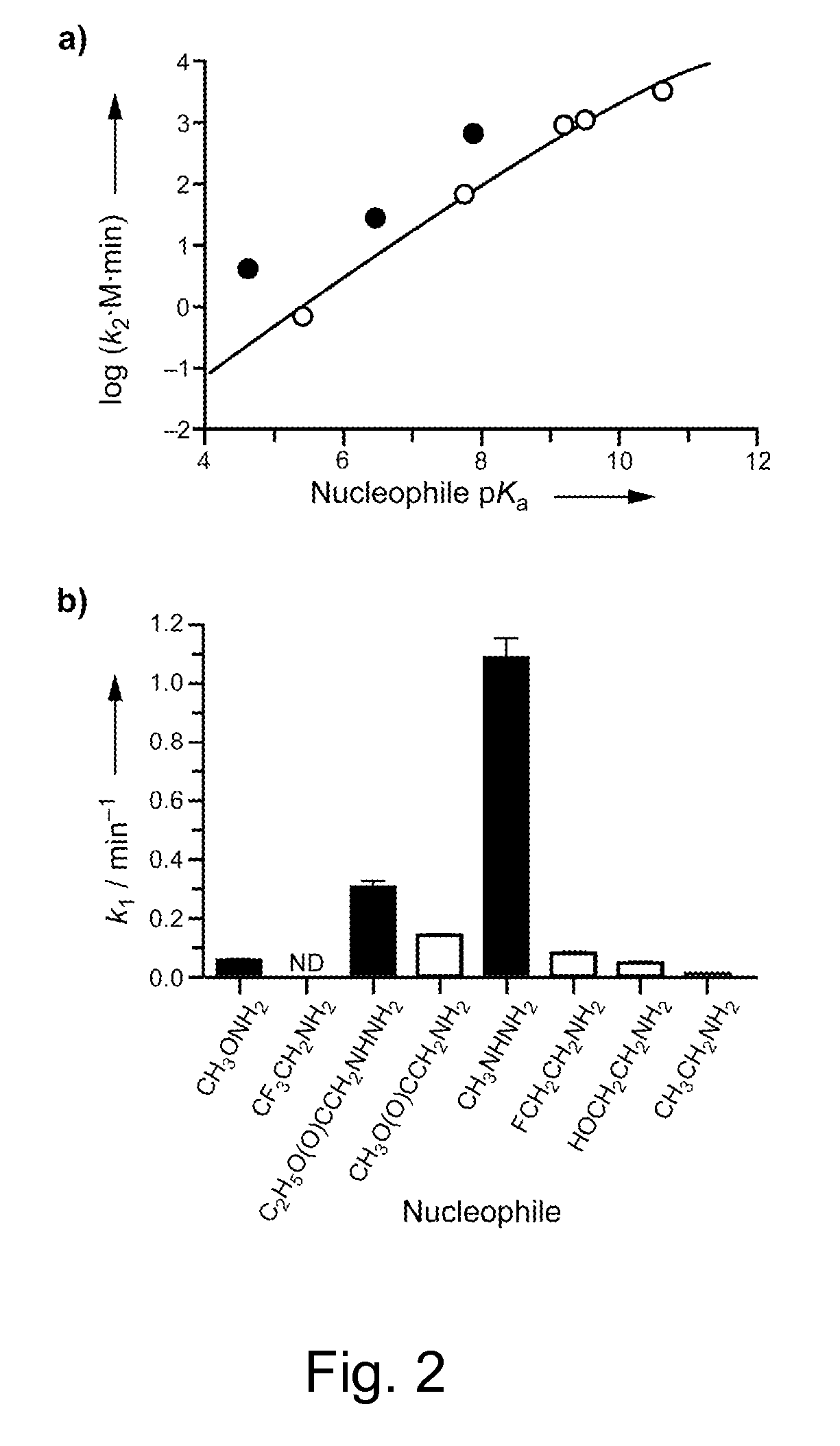
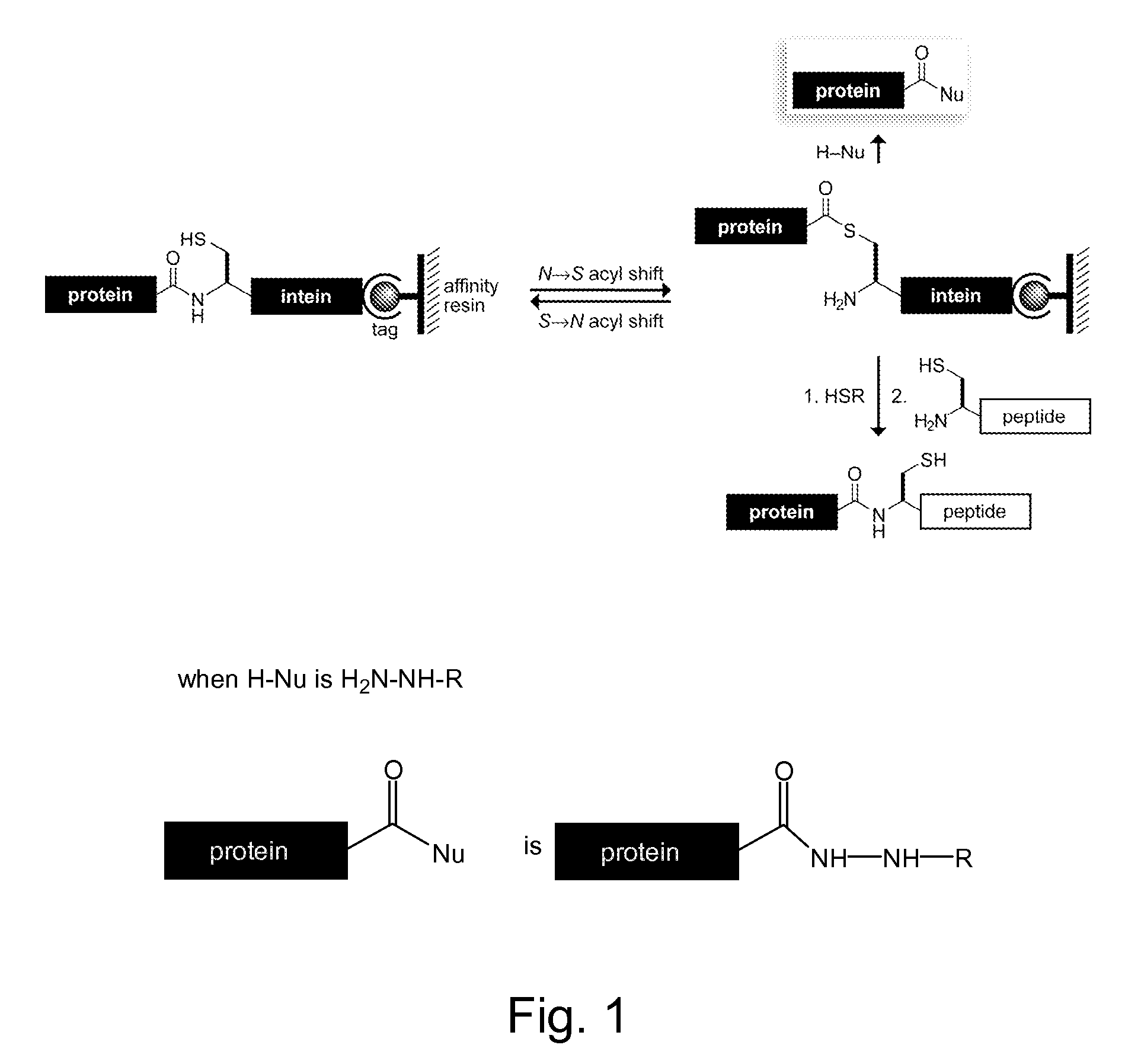
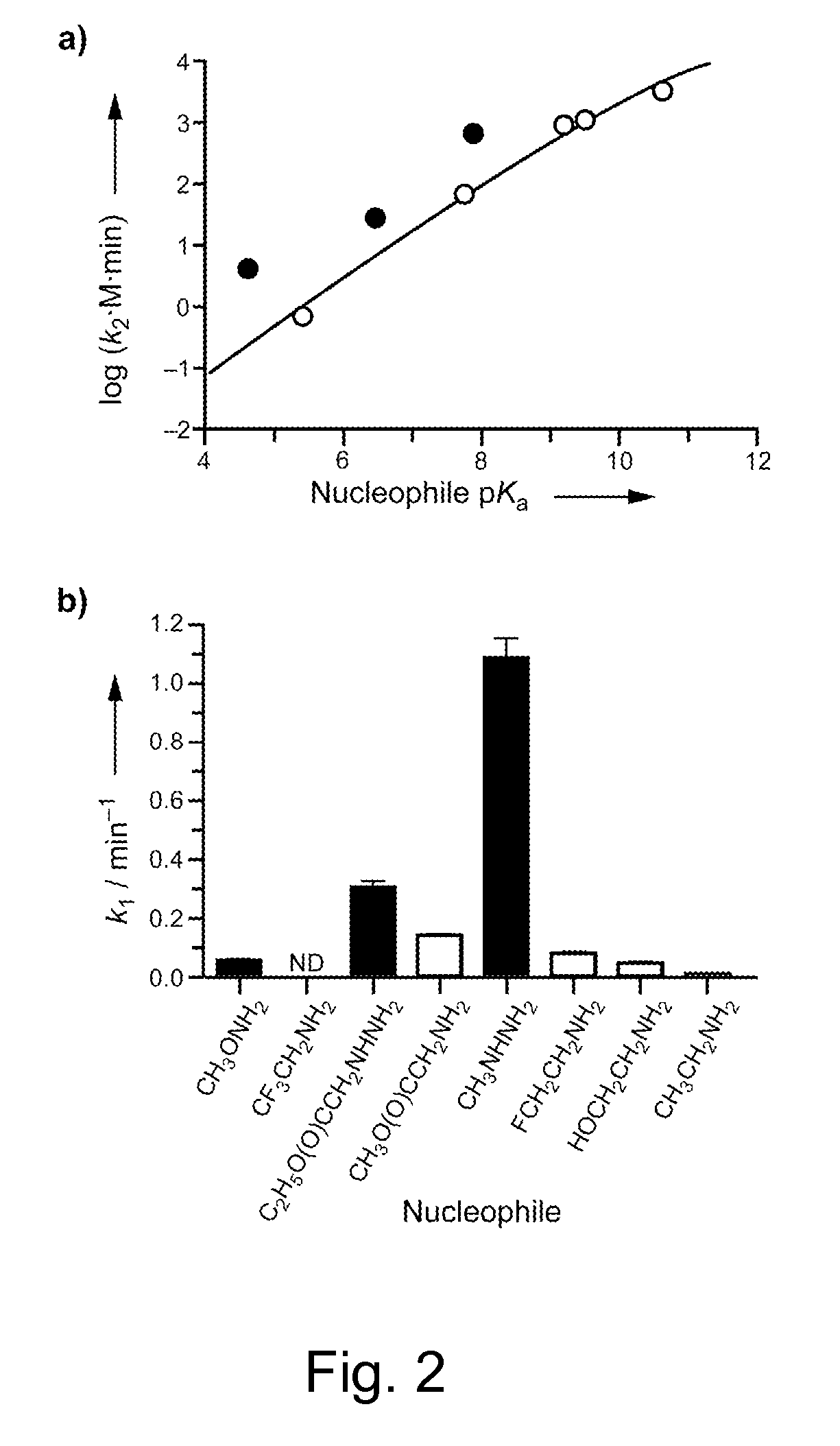
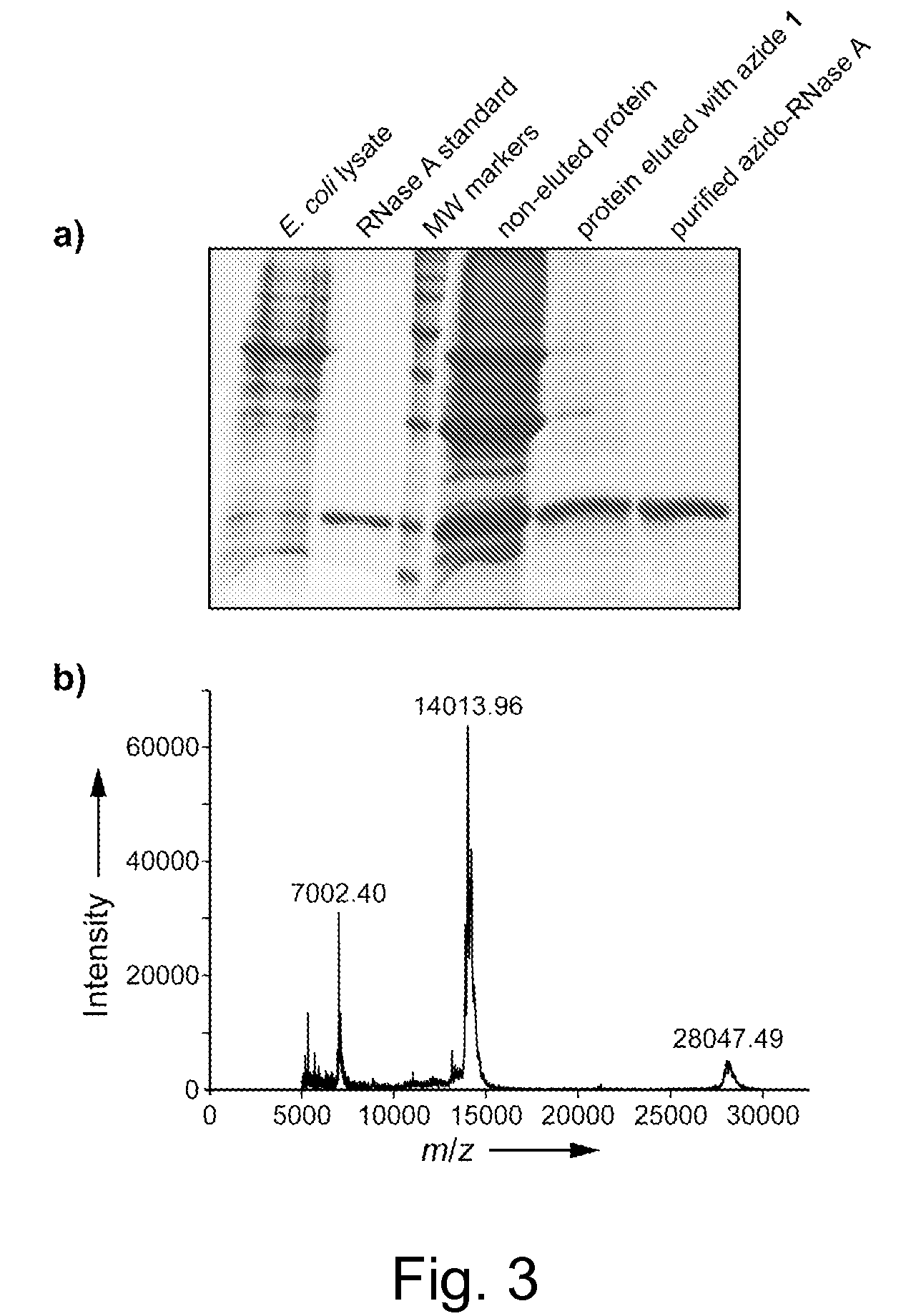
Methods and reagents for site-selective functionalization of peptides and proteins. The methods most generally involve the reaction of a thioester with hydrazine. Reagents include bifunctional reagents of formula:H2N—NH—CH2-M-L-FGand salts thereof where M is a single bond or a chemical group carrying a non-bonding electron pair, such as —C(O)NR′—, where R′ is H, or an alkyl or aryl group; L is an optional linker group as described above; and FG is a functional group having reactivity that is orthongonal to that of the hydrazine group. FG can, among others, be an azide, alkenyl, alkynyl, nitrile (—CN) or triazole group and is preferably an azide group (—N3). Methods and reagents can, for example, be combined with intein-mediated protein splicing to link proteins or fragments thereof to various chemical species or to a surface. Surface immobilization of proteins via the methods herein results in immobilized proteins which substantially retain biological activity and is thus useful for the generation of peptide or protein microarrays. Kits for functionalization and / or immobilization of peptides and proteins are provided as well as microarrays of peptides, proteins or both.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Reagents and methods for appending functional groups to proteins
ActiveUS8242058B2Minimizes and avoids inactivationMaintain biological activityPeptide librariesSugar derivativesInteinHydrazine compound
Methods and reagents for site-selective functionalization of peptides and proteins. The methods most generally involve the reaction of a thioester with hydrazine. Reagents include bifunctional reagents of formula:H2N—NH—CH2-M-L-FGand salts thereof where M is a single bond or a chemical group carrying a non-bonding electron pair, such as —C(O)NR′—, where R′ is H, or an alkyl or aryl group; L is an optional linker group as described above; and FG is a functional group having reactivity that is orthongonal to that of the hydrazine group. FG can, among others, be an azide, alkenyl, alkynyl, nitrile (—CN) or triazole group and is preferably an azide group (—N3). Methods and reagents can, for example, be combined with intein-mediated protein splicing to link proteins or fragments thereof to various chemical species or to a surface. Surface immobilization of proteins via the methods herein results in immobilized proteins which substantially retain biological activity and is thus useful for the generation of peptide or protein microarrays. Kits for functionalization and / or immobilization of peptides and proteins are provided as well as microarrays of peptides, proteins or both.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
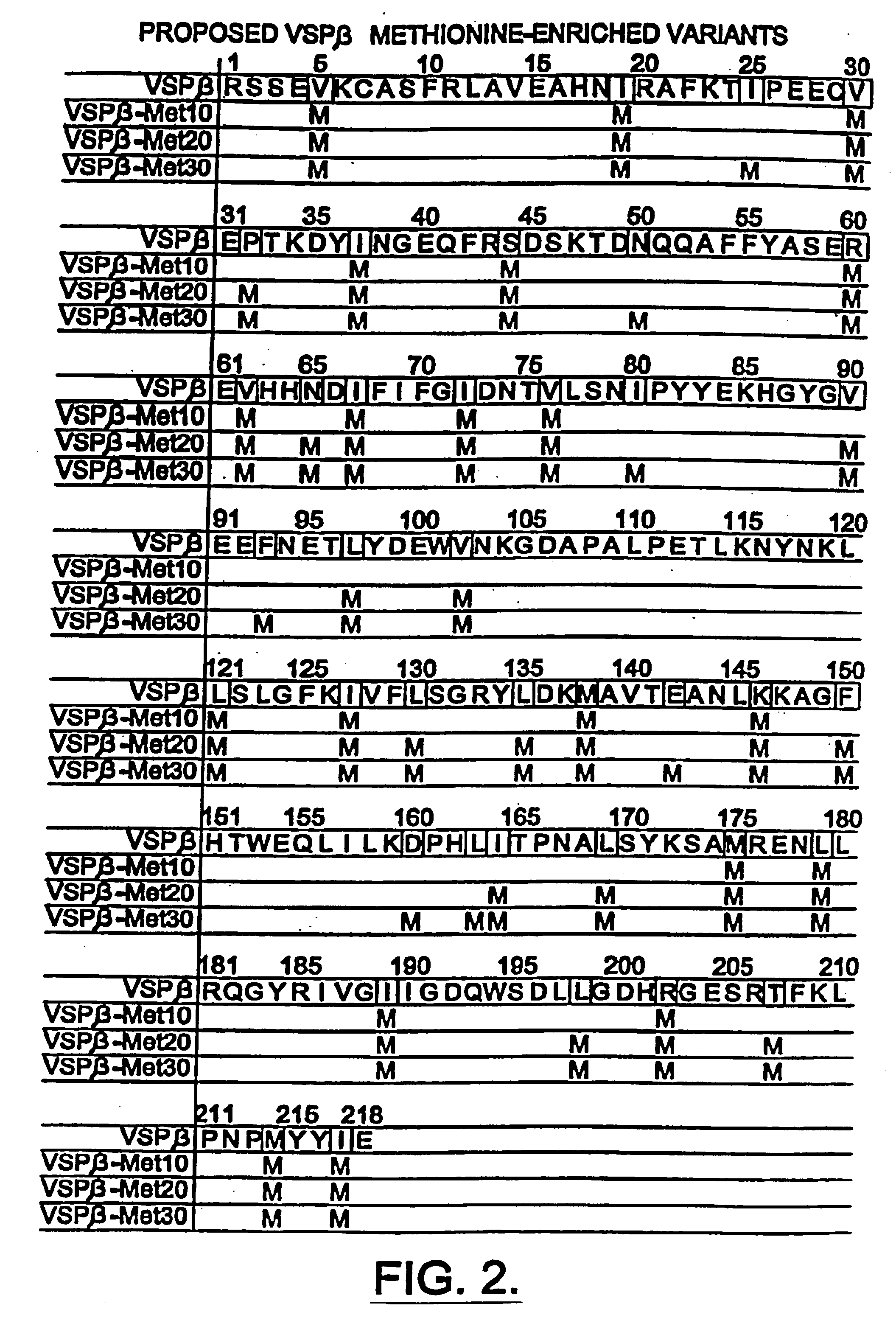
Compositions and methods for altering amino acid content of proteins
InactiveUS6905877B1Increased methionine levelImprove the level ofMicroorganism librariesPlant peptidesAmino acid compositionDrug biological activity
Methods and compositions for altering amino acid composition of a protein of interest are provided, particularly proteins whose three-dimensional structure is unknown. The method comprises creating interacting molecules to the native protein and selecting for engineered proteins which retain the native conformation by antibody binding. In this manner, the levels of essential amino acids in a protein can be increased yet the biological activity of the protein maintained. Also provided is an exemplary plant protein—Glycine max vegetative storage protein (VSP)—in which methionine levels have been increased.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
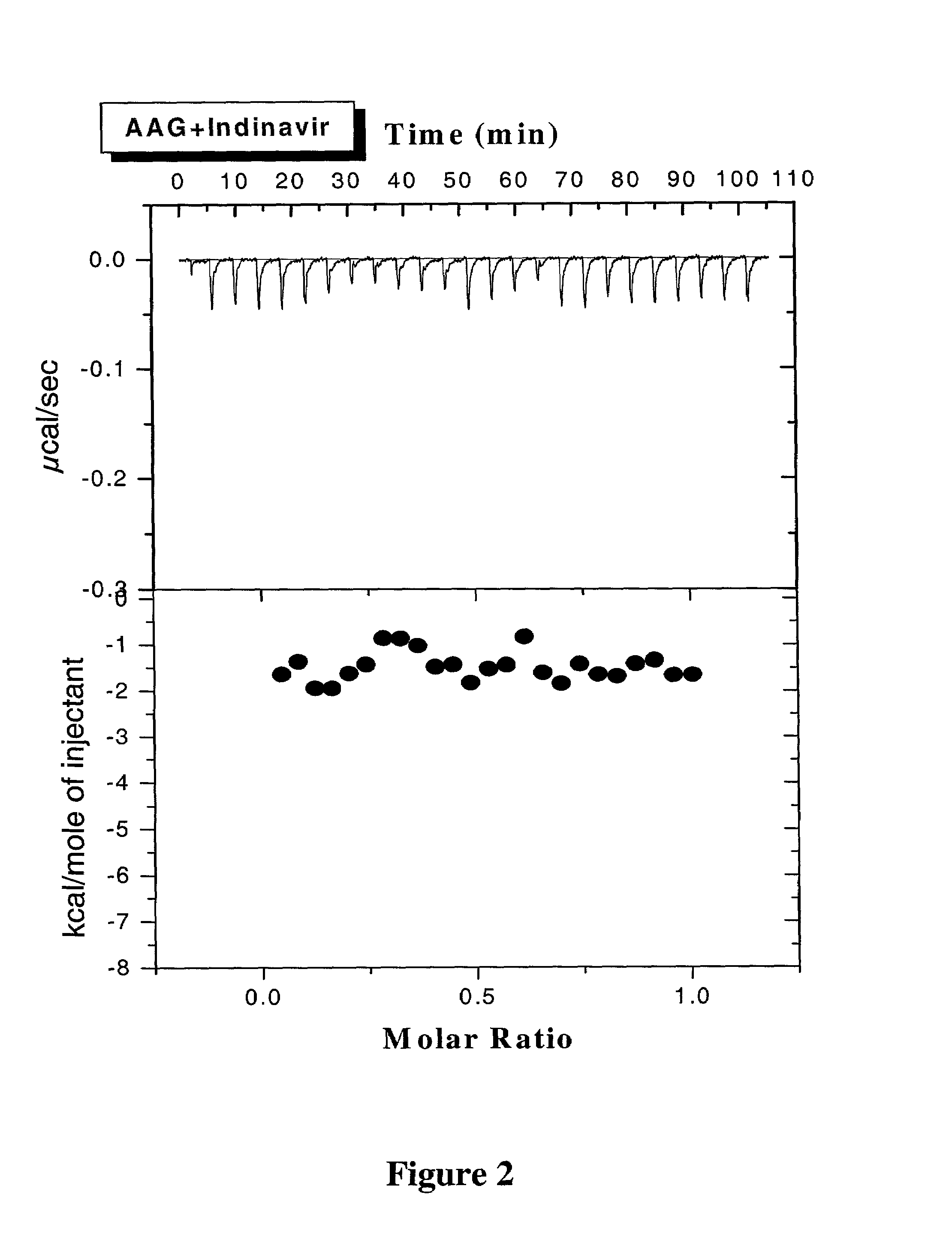
Methods for determining plasma free drug concentration by direct measurement of binding affinity of protease inhibitors to plasma proteins
InactiveUS7087373B2Evaluate the in vivo anti-HIV efficacy of PIsCompound screeningApoptosis detectionRegimenIn vivo
Methods for isothermal titration calorimetry analysis of the binding affinity of protease inhibitors to plasma proteins. A method that can quantitatively calculate free drug concentrations of protease inhibitors in human plasma, as well as a method to calculate therapeutic amounts and dosage regimens. Furthermore, the present invention provides a method that can calculate the effect of plasma proteins on the antiviral activity (EC50 values) of protease inhibitors from their binding affinities to plasma proteins. The present invention provides as well a method that can evaluate the in vivo anti-HIV efficacy of PIs in human plasma.
Owner:TIBOTEC PHARMA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com