Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
77 results about "Ion Channel Protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
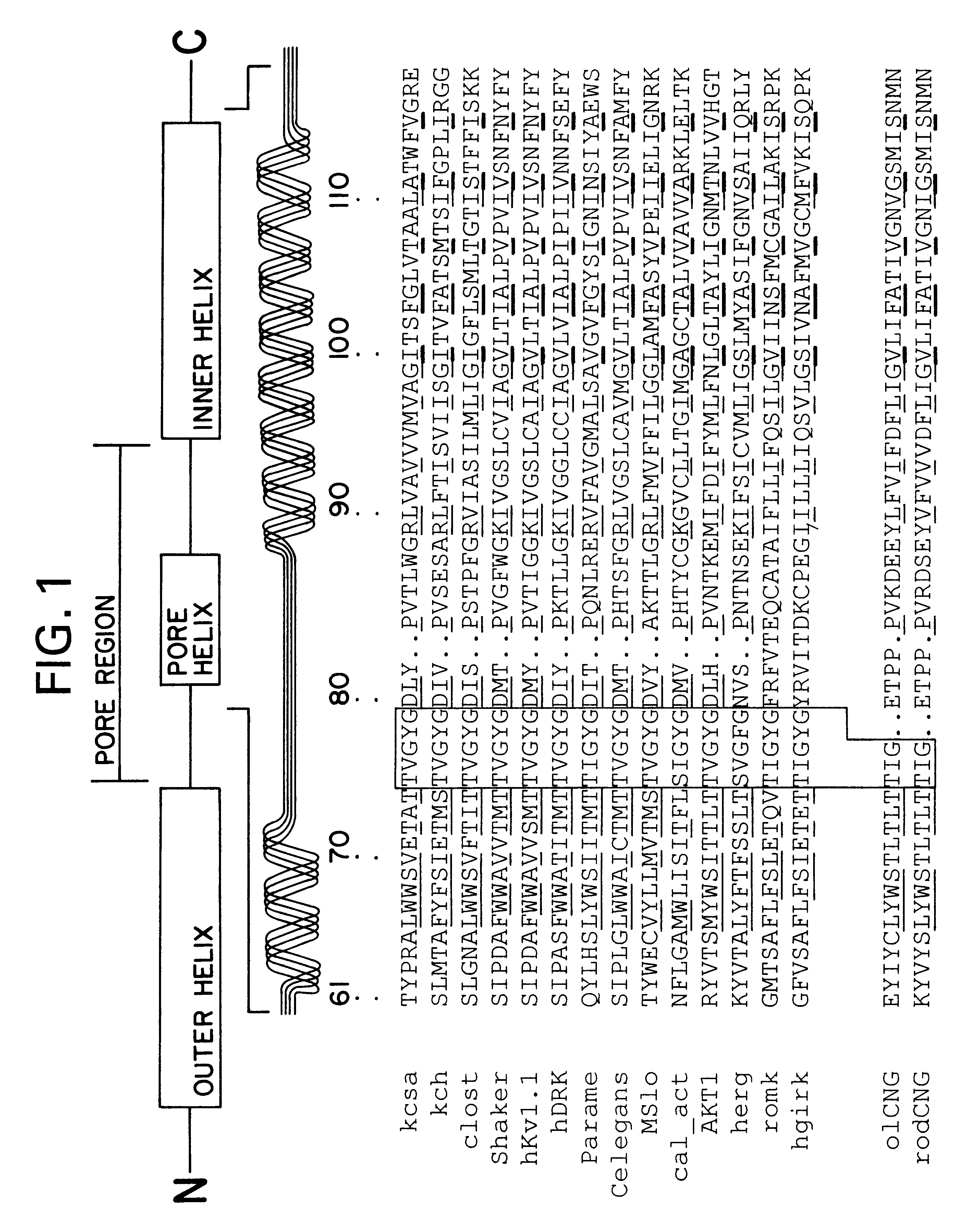
Ion Channel Proteins typically aggregate in membrane-associated complexes forming pores whose activities regulate the movement of ions through cellular membranes to affect cellular homeostatic conditions and/or signaling processes. (NCI)
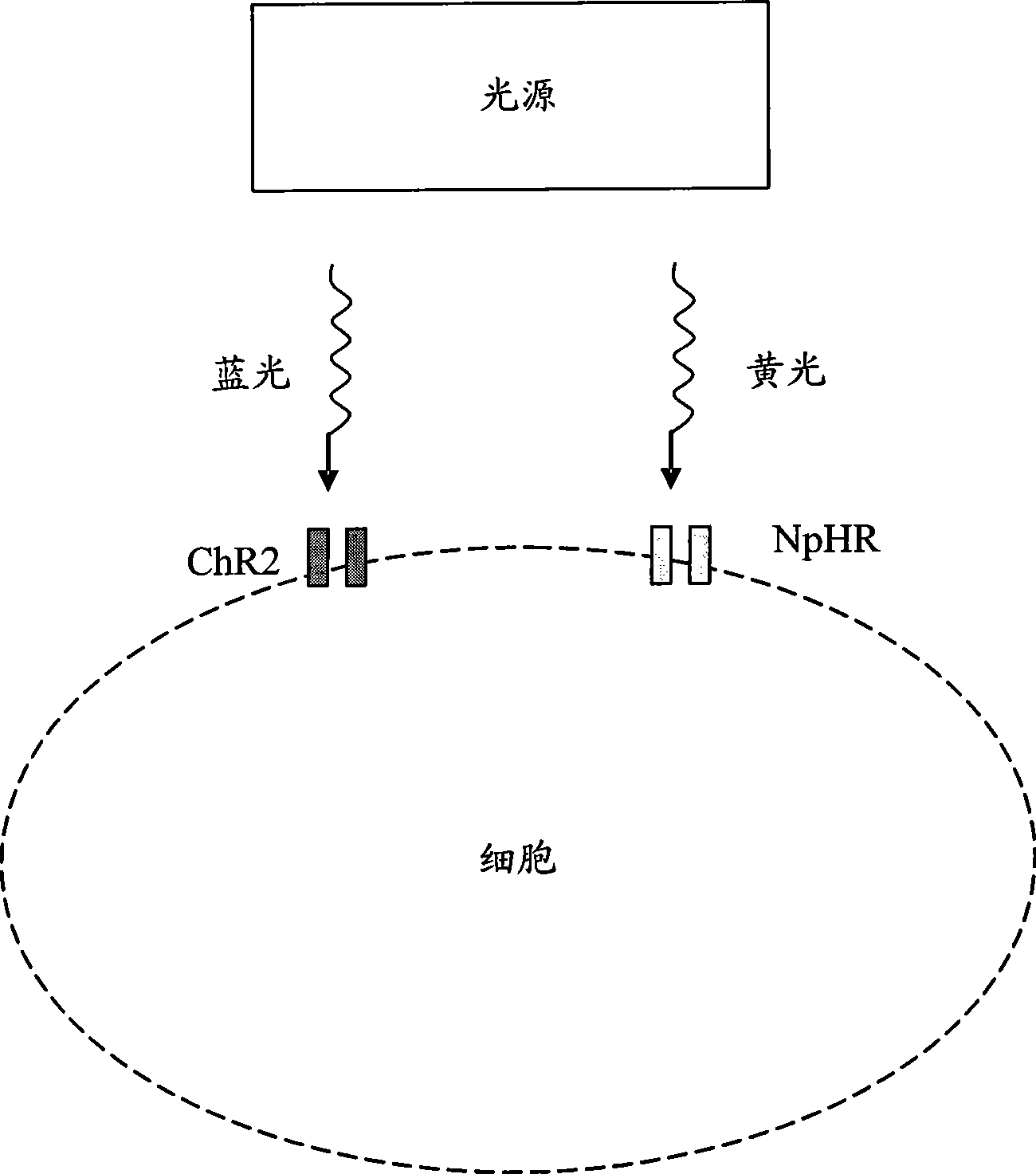
Light-activated cation channel and uses thereof
ActiveUS20070054319A1Improve abilitiesOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderCell membraneExcitable cell
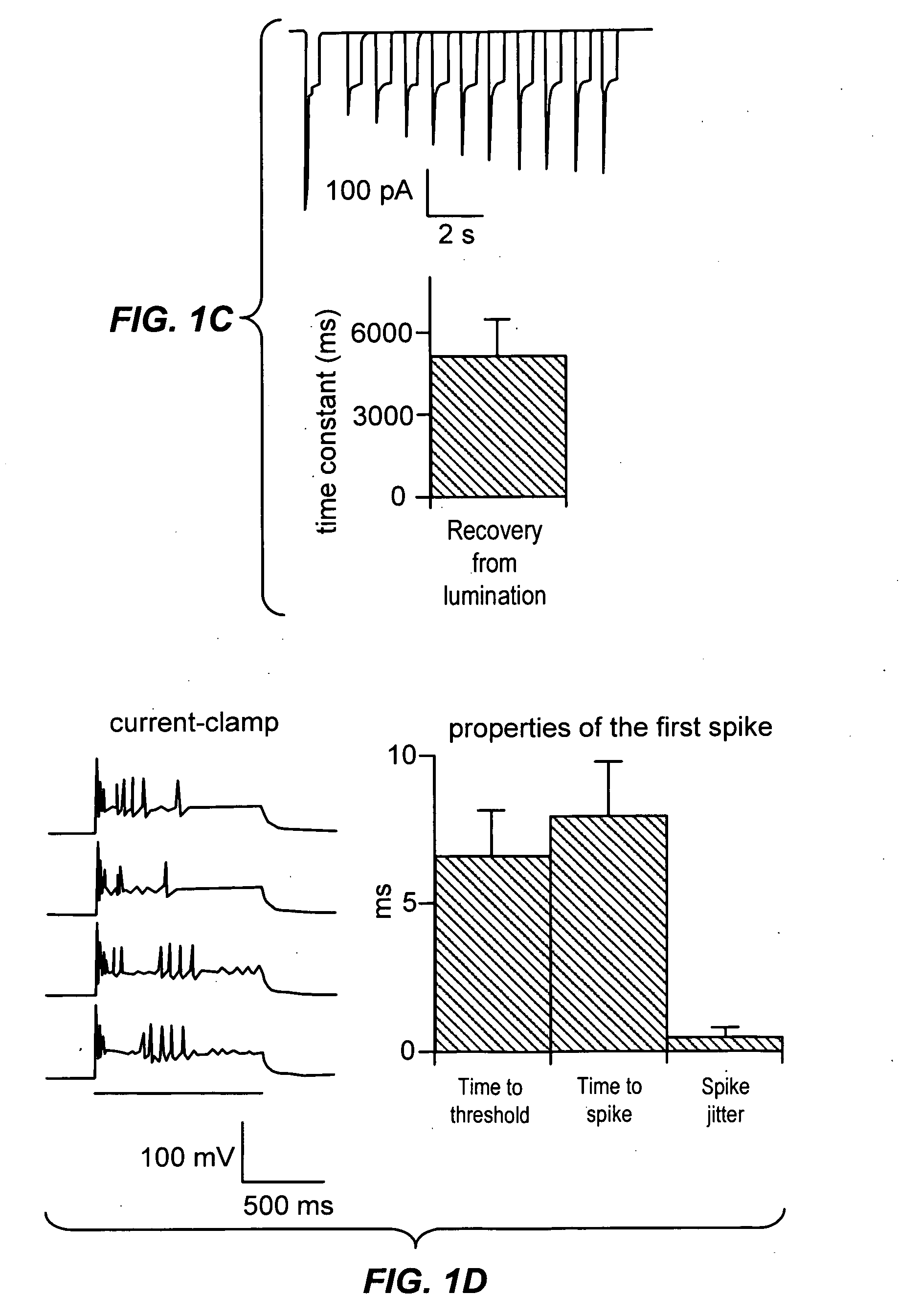
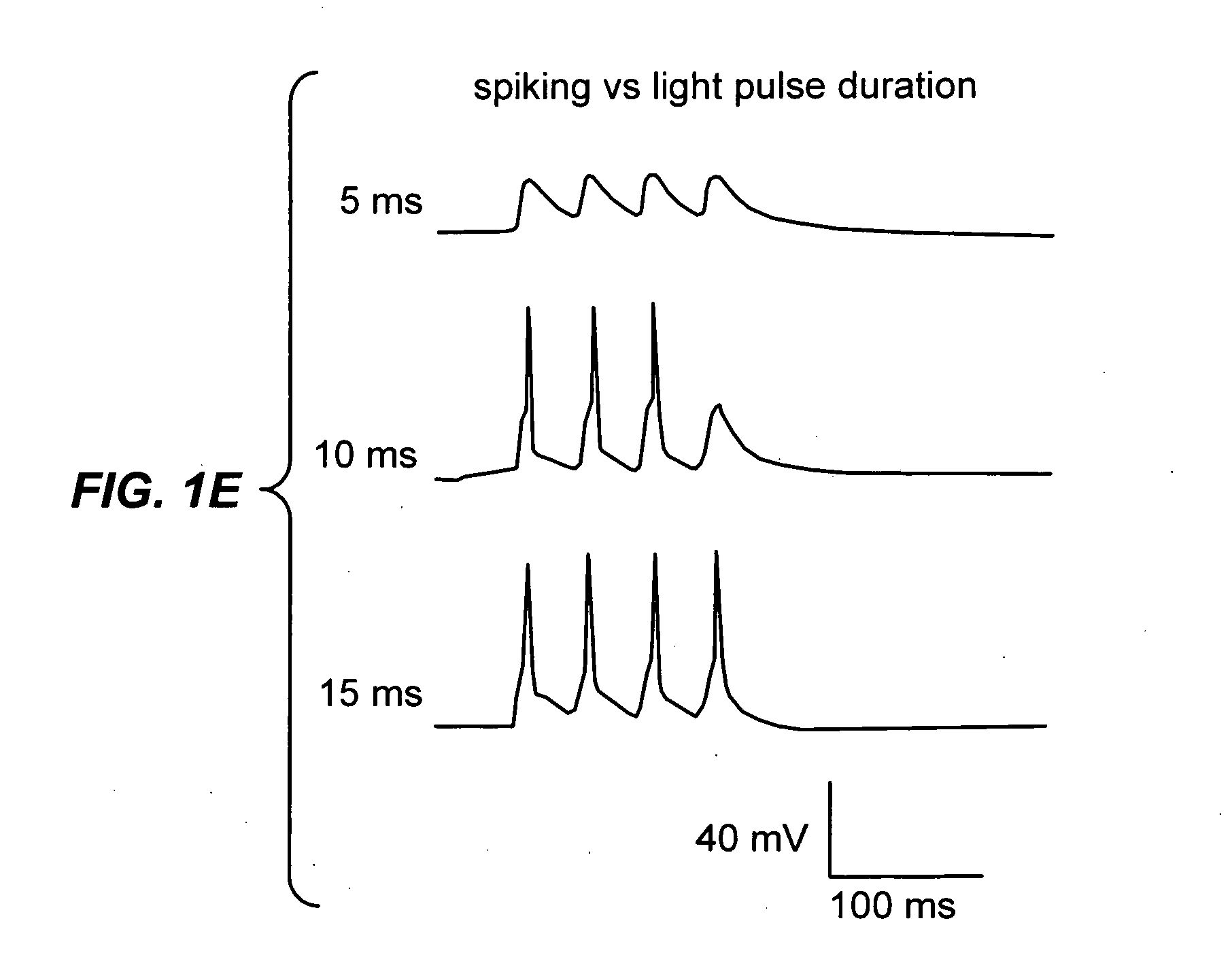
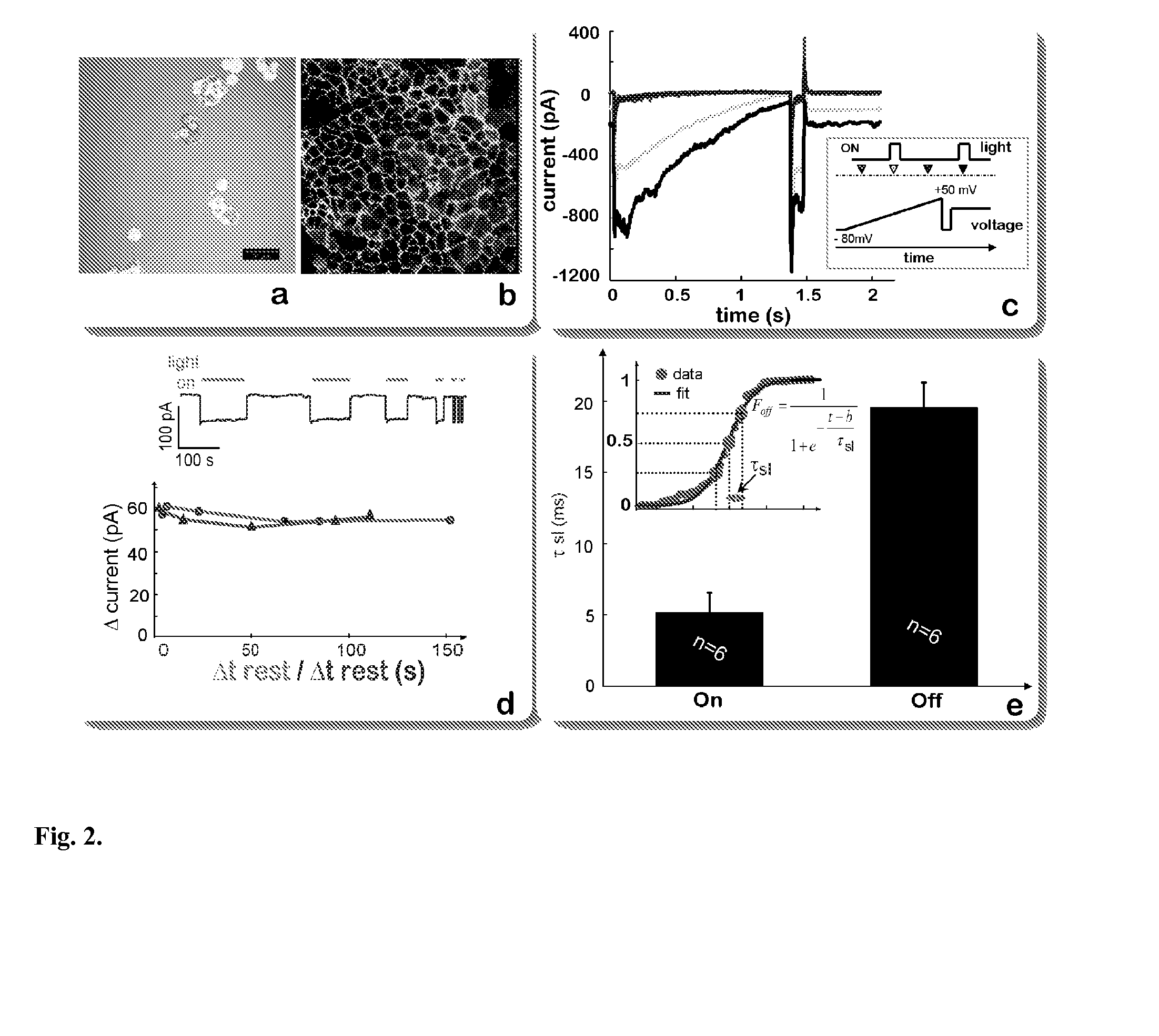
The present invention provides compositions and methods for light-activated cation channel proteins and their uses within cell membranes and subcellular regions. The invention provides for proteins, nucleic acids, vectors and methods for genetically targeted expression of light-activated cation channels to specific cells or defined cell populations. In particular the invention provides millisecond-timescale temporal control of cation channels using moderate light intensities in cells, cell lines, transgenic animals, and humans. The invention provides for optically generating electrical spikes in nerve cells and other excitable cells useful for driving neuronal networks, drug screening, and therapy.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
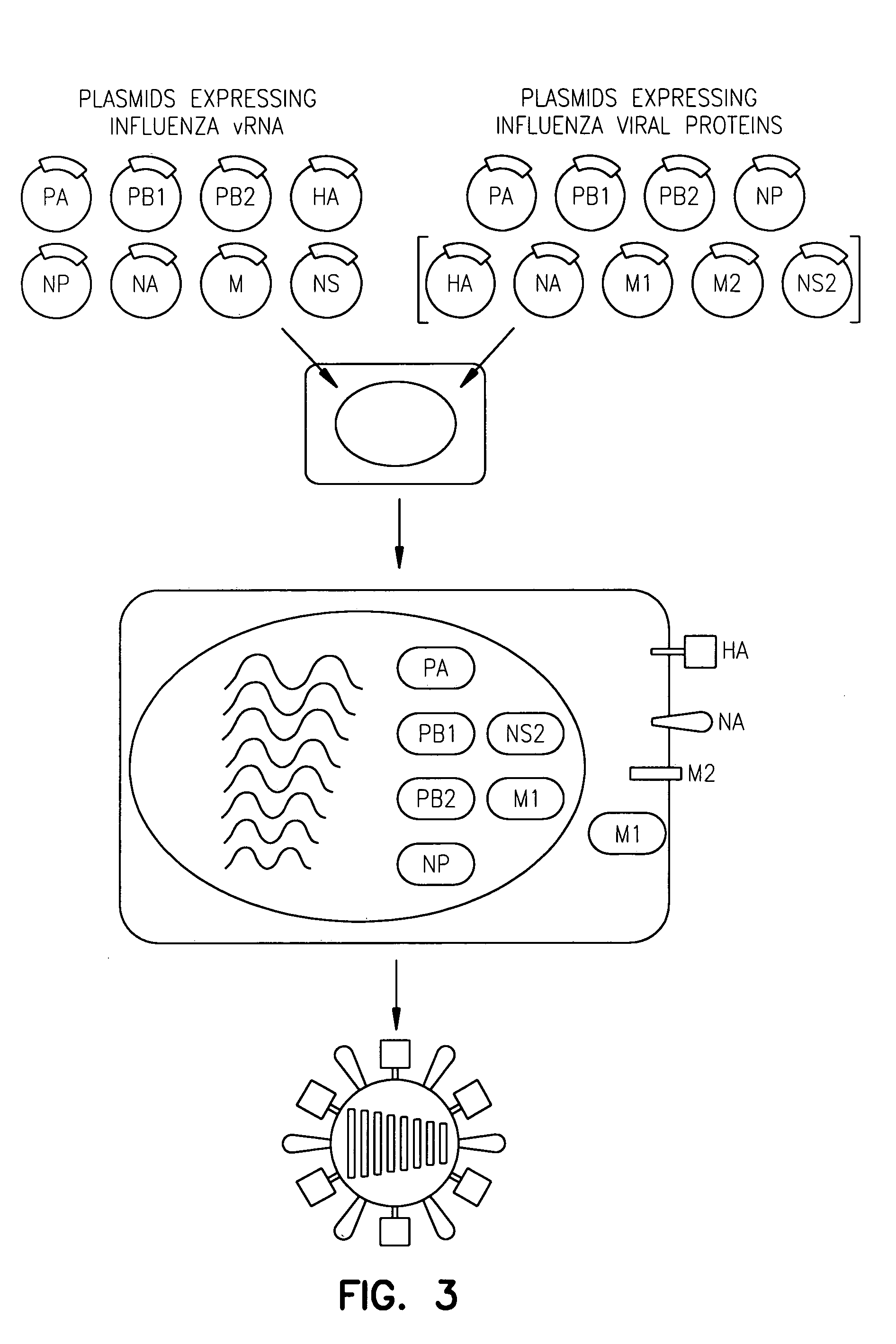
Viruses comprising mutant ion channel protein
InactiveUS20050232950A1Facilitate viral replicationReduce the overall heightSsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideIon Channel ProteinVirus
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Assays for screening compounds which interact with cation channel proteins, mutant prokaryotic cation channel proteins, and uses thereof
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
Methods for Identifying Modulators of Ion Channels
ActiveUS20090137422A1Block functional activityMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementIon Channel ProteinProtein C
Owner:X BODY
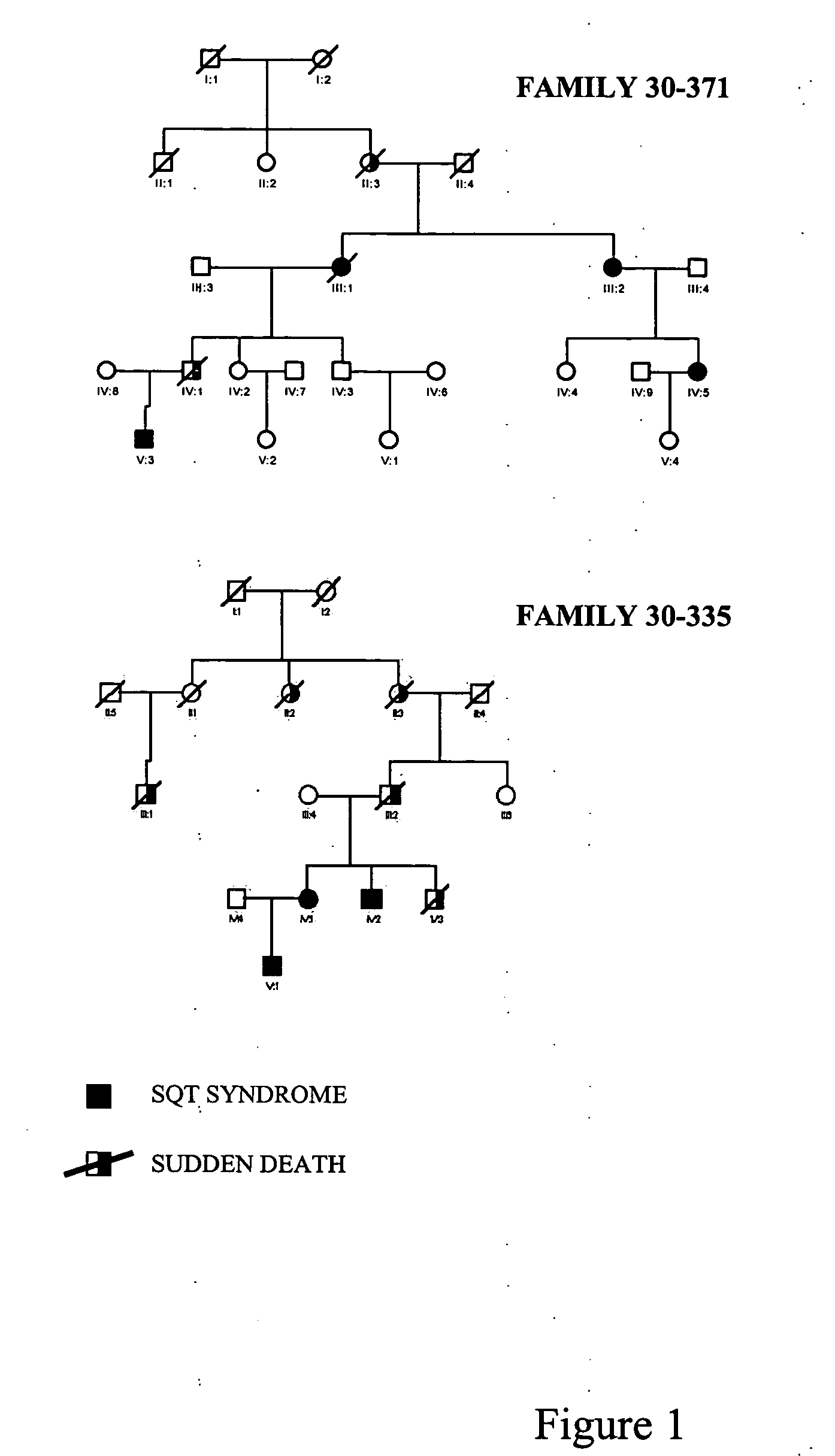
Mutations in ion channel proteins associated with sudden cardiac death
ActiveUS20050130190A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesDiseaseIon Channel Protein
Previously unknown mutations of the KCNH2, SCN5A and KCNQ1 genes are disclosed which are involved in ion channel disruptions associated with short QT syndrome, long QT syndrome, Brugada syndrome and progressive conduction disease. These mutations are utilized to diagnose and screen for short QT syndrome, long QT syndrome, Brugada syndrome and progressive conduction disease, thus providing modalities for diagnosing sudden cardiac death and / or predicting susceptibility to sudden cardiac death. Nucleic acid probes are provided which selectively hybridize to the mutant nucleic acids described herein. Antibodies are provided which selectively bind to the mutant proteins described herein. The mutations described herein are also utilized to screen for compounds useful in treating the symptoms manifest by such mutations.
Owner:MASONIC MEDICAL RES LAB A CORP OF NY
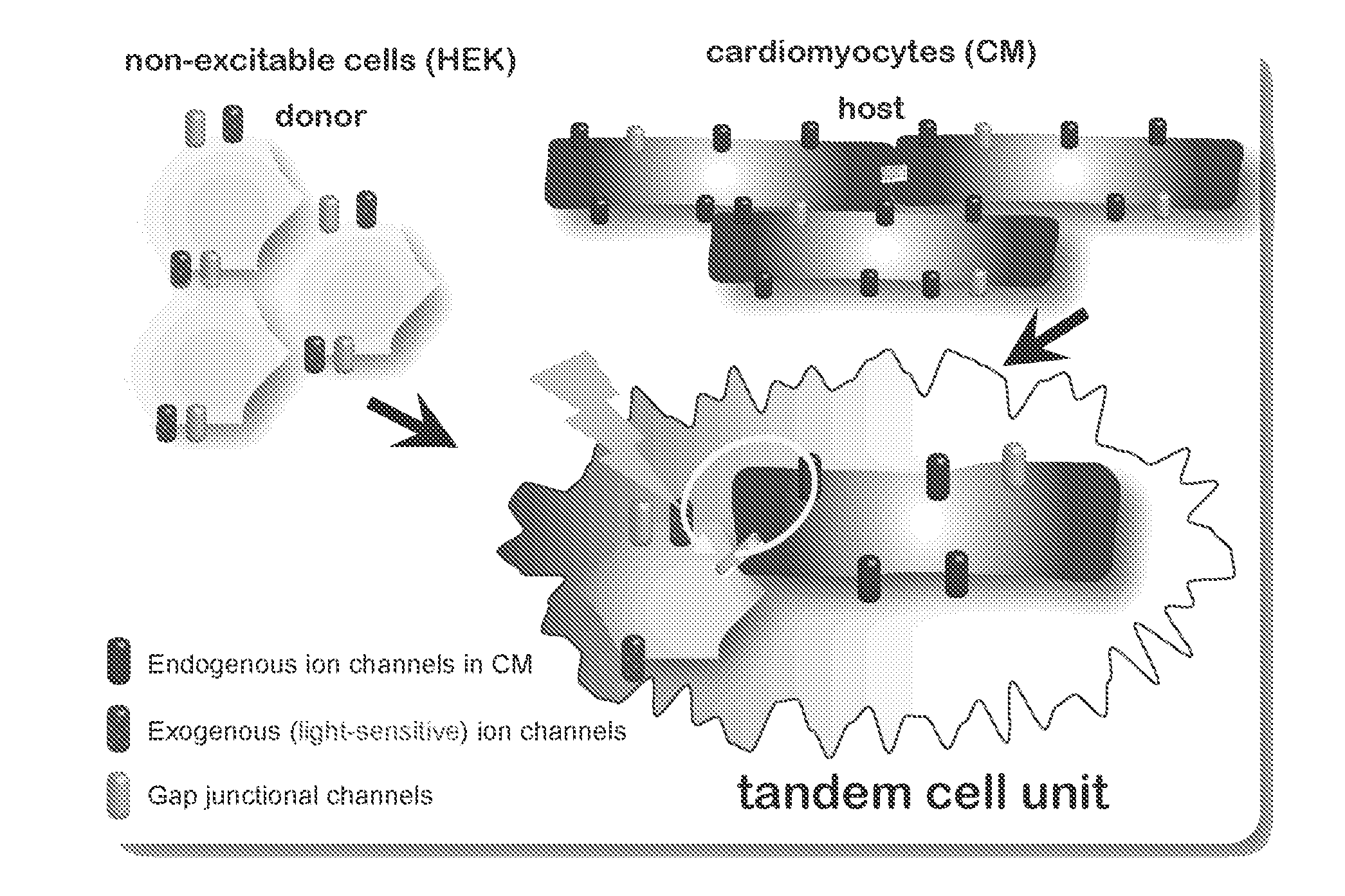
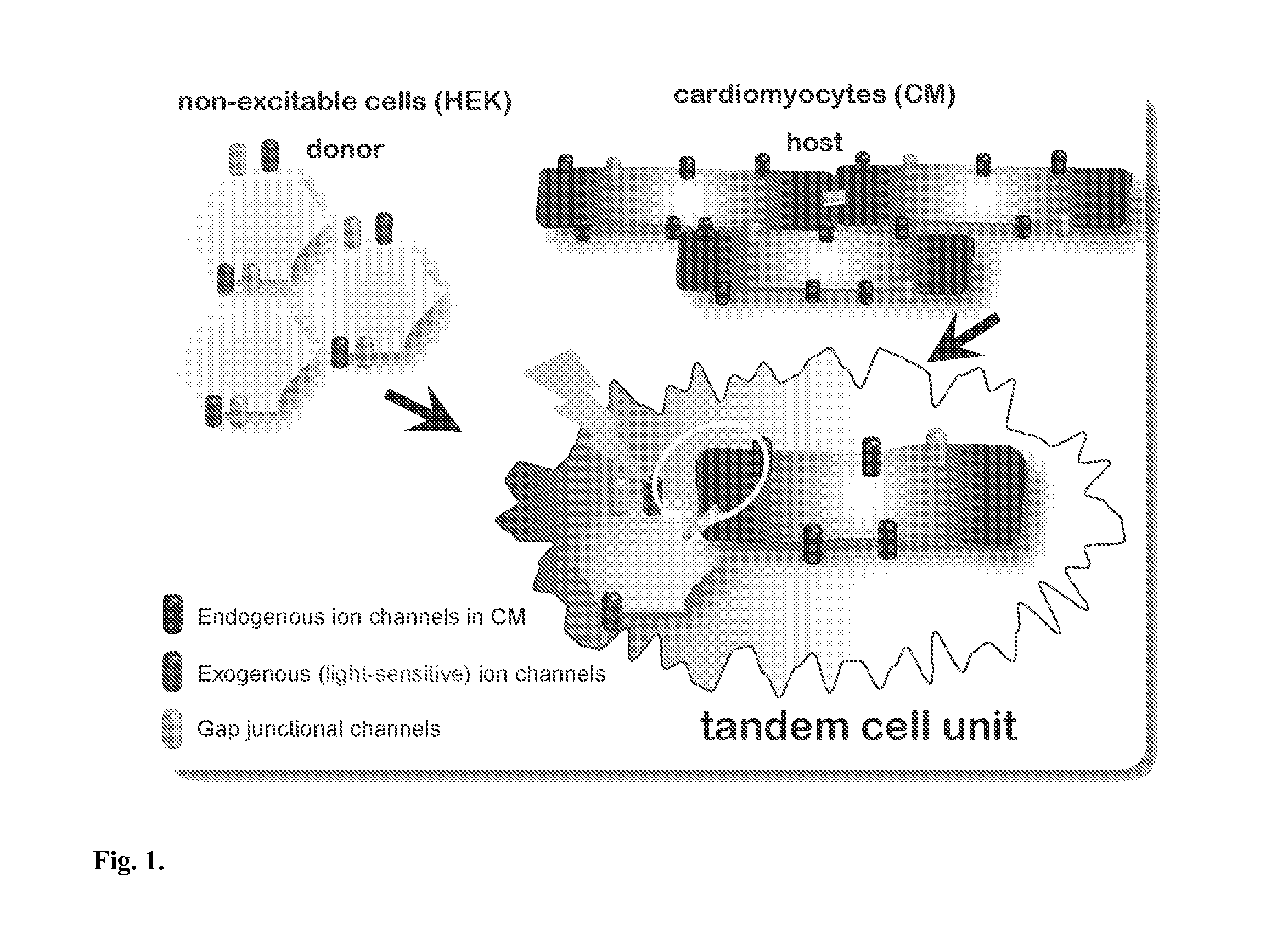
Optical control of cardiac function
InactiveUS20130274838A1Peptide/protein ingredientsImplantable neurostimulatorsIon Channel ProteinIonic Channels
The invention features an optically-controlled biological device that includes a biological component comprising a non-excitable cell expressing a light-gated ion channel protein and capable of forming gap junction channels with a target cell, and an optical stimulation unit.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Novel chimeric ligand-gated ion channels and methods of use thereof
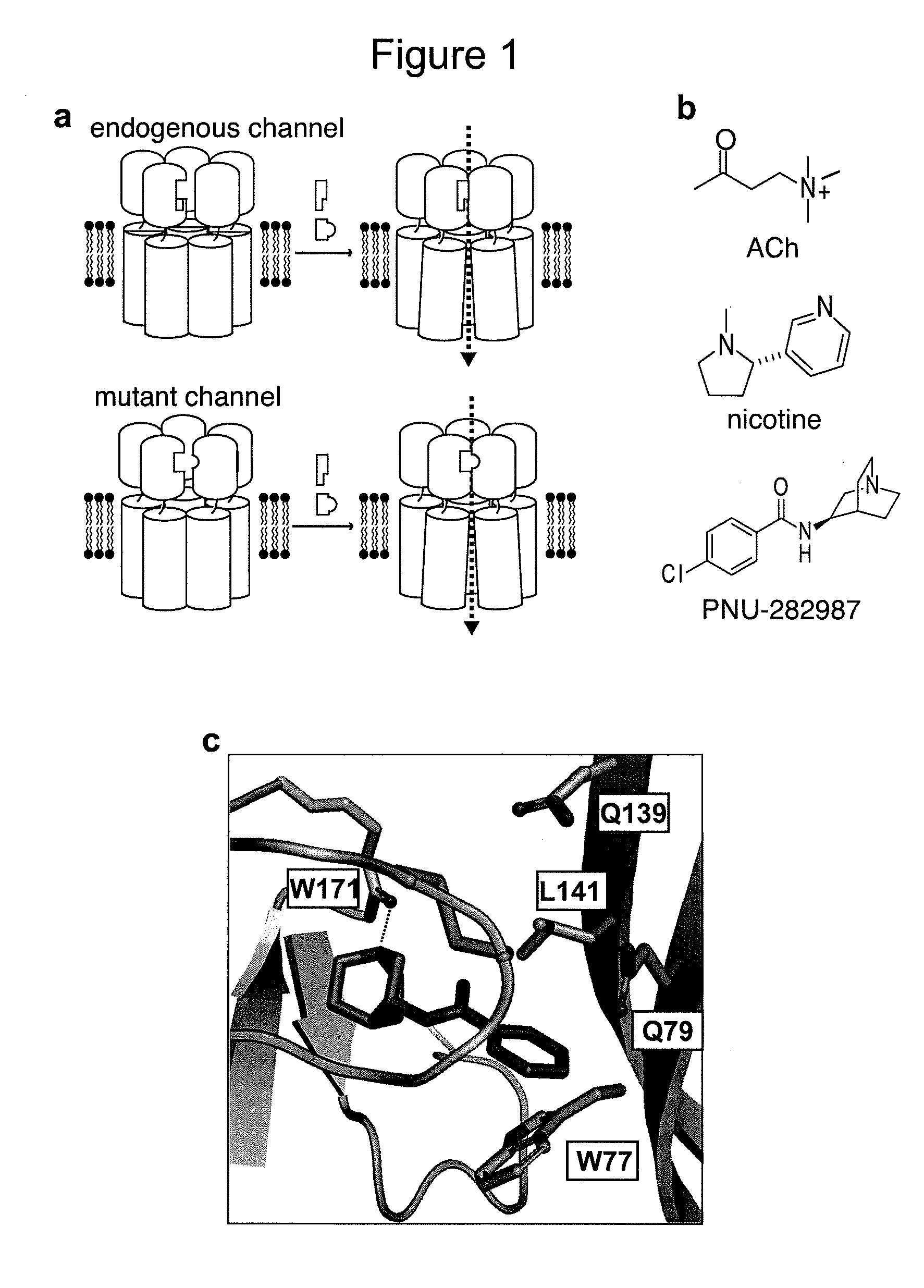
The present invention provides novel chimeric receptors that have unique pharmacology. In particular, the chimeric receptors comprise a mutated ligand binding domain of the α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor fused to a transmembrane or channel domain from a ligand-gated ion channel protein. The mutations in the ligand binding domain confer selective binding of compounds. Methods of using the novel chimeric receptors of the invention as well as compounds that preferentially bind and activate the chimeric receptors are also disclosed.
Owner:HOWARD HUGHES MEDICAL INST
Assays for screening compounds which interact with cation channel proteins, mutant prokaryotic cation channel proteins, and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050272093A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsIon Channel ProteinCation channels of sperm
Owner:MACKINNON RODERICK
Viruses comprising mutant ion channel protein
InactiveUS8057806B2Reduce the overall heightSpeed up the descentSsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideIon Channel ProteinVirus
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
System and method for enhancing cardiac signal sensing by cardiac pacemakers through genetic treatment
InactiveUS7337011B2Enhancing cardiac pacemaker signal sensingImprove and correct signal to noise ratioTransvascular endocardial electrodesGenetic material ingredientsIon Channel ProteinCardiac pacemaker
The present invention provides delivery systems for and methods of delivering ion channel protein genetic material to cardiac cells in areas adjacent to where an electrode is to be positioned in a patient's heart to improve or correct the signal to noise ratio of cardiac signals, such as the P-wave. More specifically, there is provided a system and method for delivering sodium ion channel proteins or nucleic acid molecules encoding sodium ion channel proteins to a site in the heart adjacent to an electrode to increase the expression of the same, thereby enhancing the cardiac signal amplitude and enabling improved sensing of cardiac signals by an implanted pacemaker.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method for labeling a membrane-localized protein
InactiveUS20050191710A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsMicrobiological testing/measurementIon Channel ProteinProtein C
The present invention relates to a method for labeling a membrane-localized protein by introducing a biotin target sequence tag into at least one loop domain of a membrane-localized protein. The method of the invention is useful for labeling an ion channel protein such as CFTR or mutants thereof. A method for identifying an agent which corrects protein misfolding of a membrane-localized protein is also provided.
Owner:HANRAHAN JOHN W +1
Methods for Identifying Modulators of Ion Channels
ActiveUS20090017488A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisIon Channel ProteinProtein C
Owner:X BODY
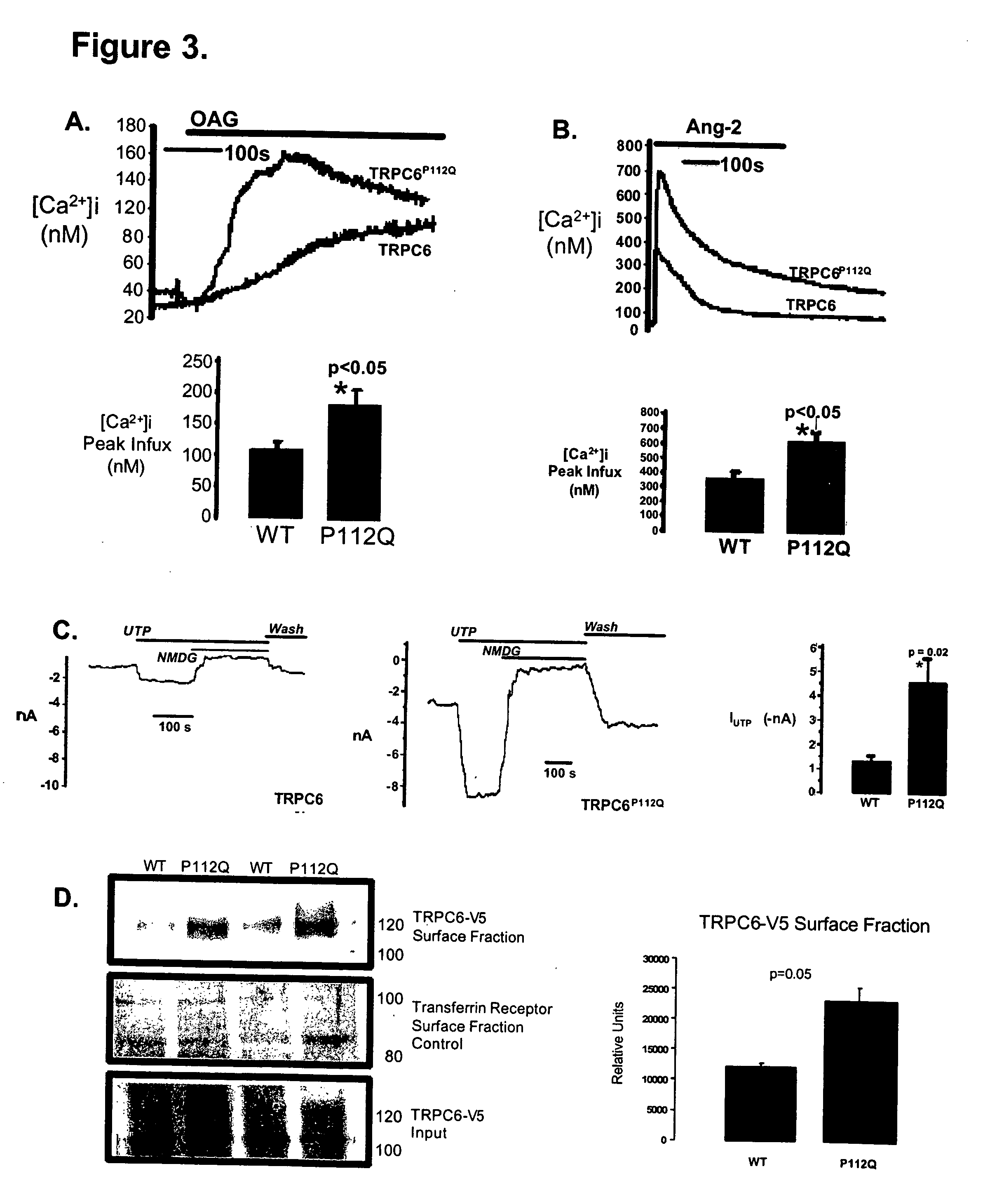
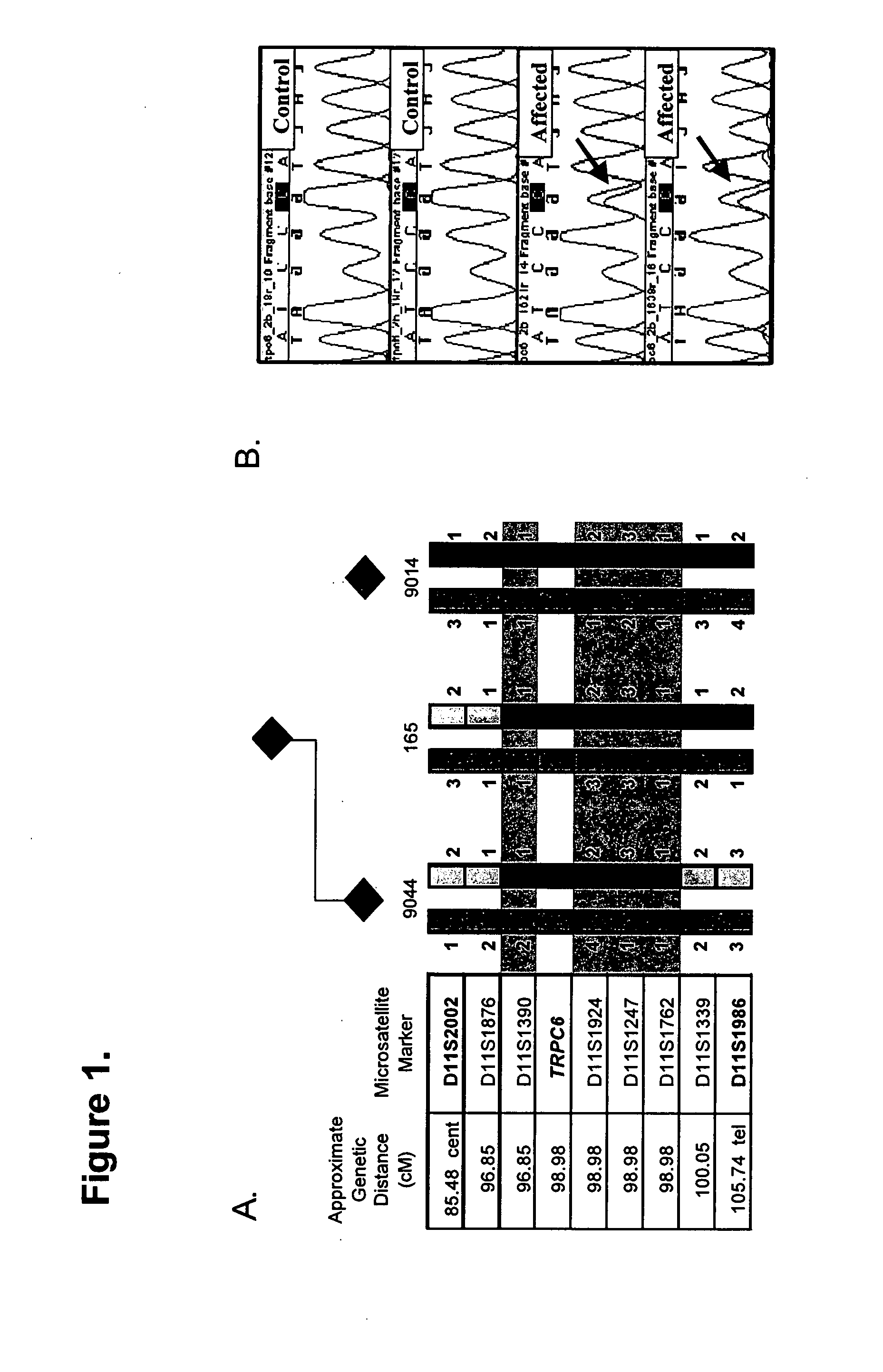
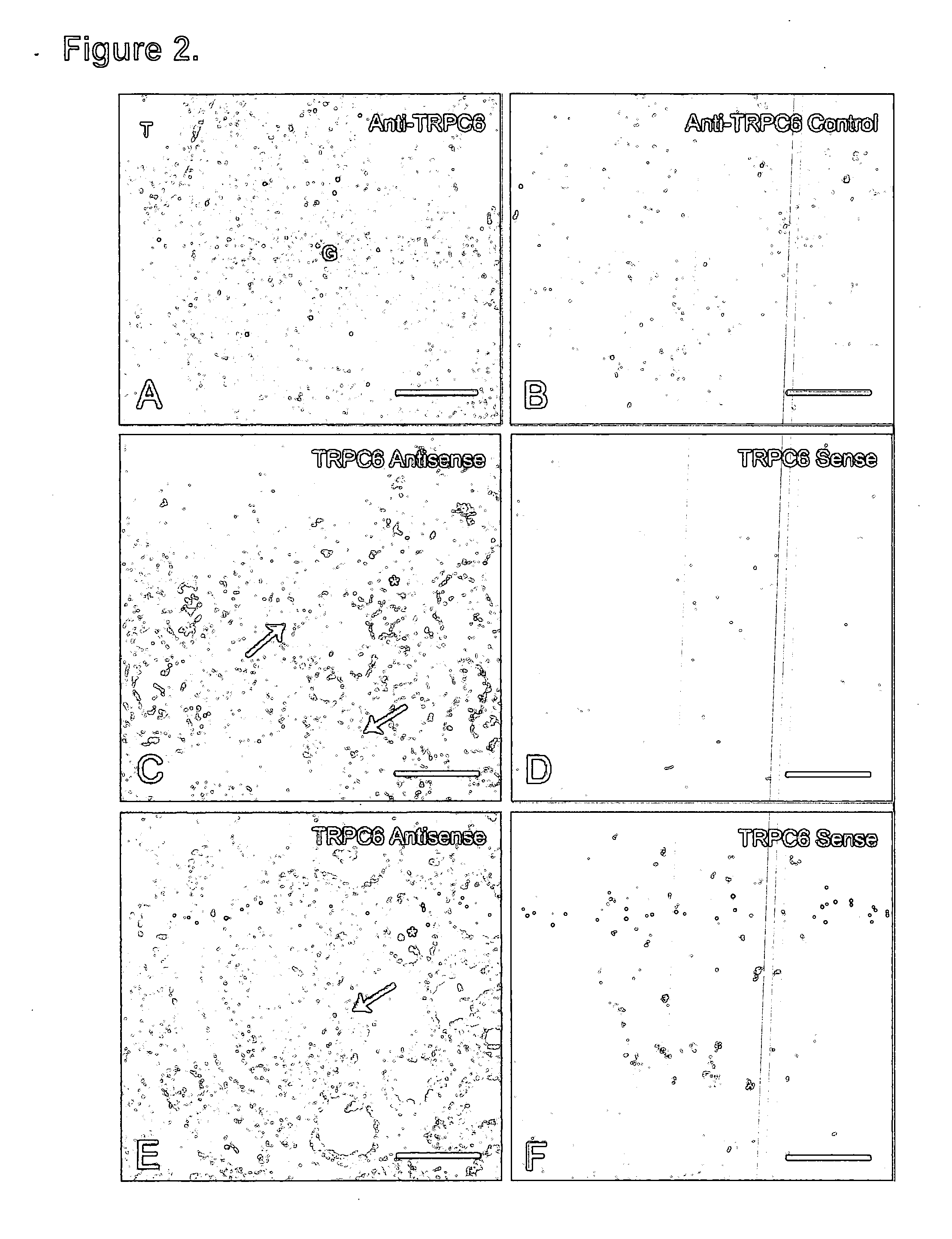
TRPC6 involved in glomerulonephritis
InactiveUS20060257500A1Calcium ion influx is thereby reducedCompound screeningBiocideEtiologyDisease
Focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) is a kidney disorder of unknown etiology and up to 20% of patients on dialysis have this diagnosis. A large family with hereditary FSGS carries a missense mutation in the TRPC6 gene on chromosome 11q, encoding the ion channel protein Transient Receptor Potential Cation Channel 6. The missense mutation is a P112Q substitution, which occurs in a highly conserved region of the protein, enhances TRPC6-mediated calcium signals in response to agonists such as angiotensin II, and alters the intracellular distribution of TRPC6 protein. Previous work has emphasized the importance of cytoskeletal and structural proteins in proteinuric kidney diseases. Our findings suggest a novel mechanism for glomerular disease pathogenesis.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Ion channel medicament screening apparatus and method
InactiveCN101498723AAccurately know the impactIncrease success rateMaterial analysisElectricityIon Channel Protein
An ion channel drug screening method includes the following steps of affusing cells with photosensitive ion channel protein into a chip; performing light treatment to the cells with photosensitive ion channel protein, which is affused into the chip; recording a reference transmembrane electric signal; administration; recording the transmembrane electric signal after administration; analyzing the reference transmembrane electric signal before administration and an administration transmembrane electric signal after administration and judging the affect of a drug to ion channels. Controlling the ion channels by light, the ion channel drug screening method can uniformly control the switches of the ion channels of the cell and facilitate accurately knowing the affect of the drug to the ion channels, thereby improving the success ratio of ion channel drug screening. In addition, the invention also provides an ion channel drug screening device.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
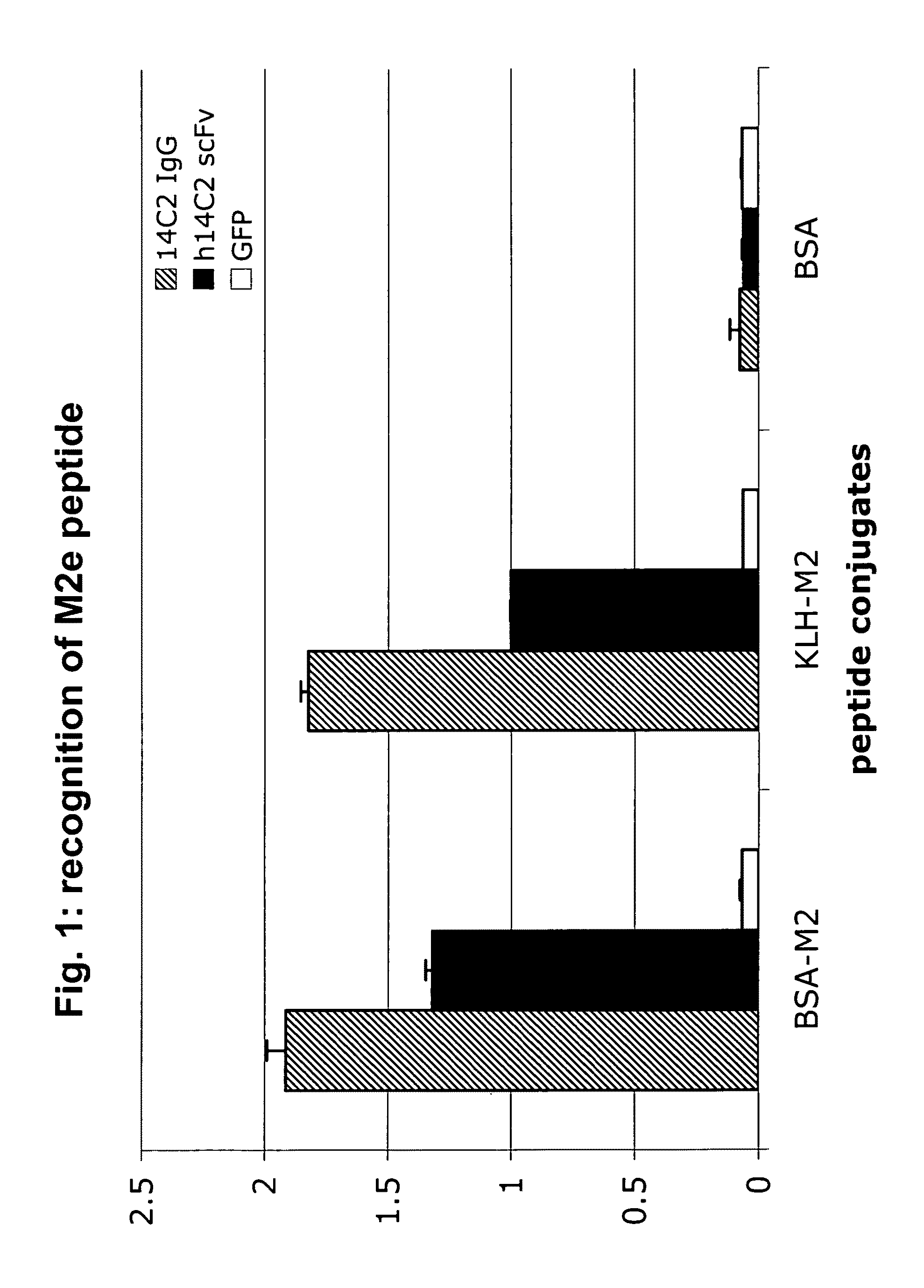
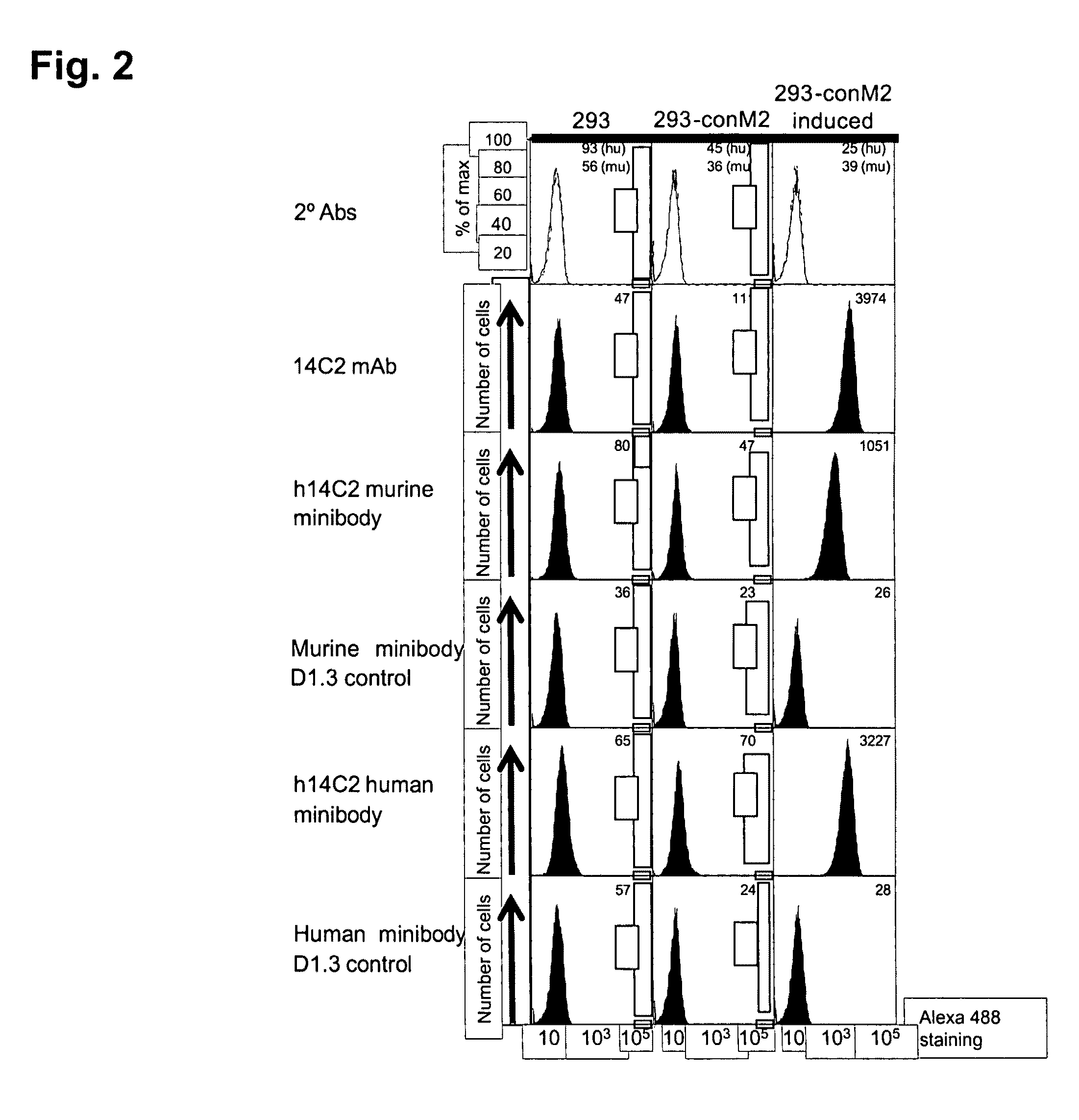
Anti-influenza M2e antibody
InactiveUS20100215662A1Inhibition of replicationSugar derivativesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsIon Channel ProteinMonoclonal antibody
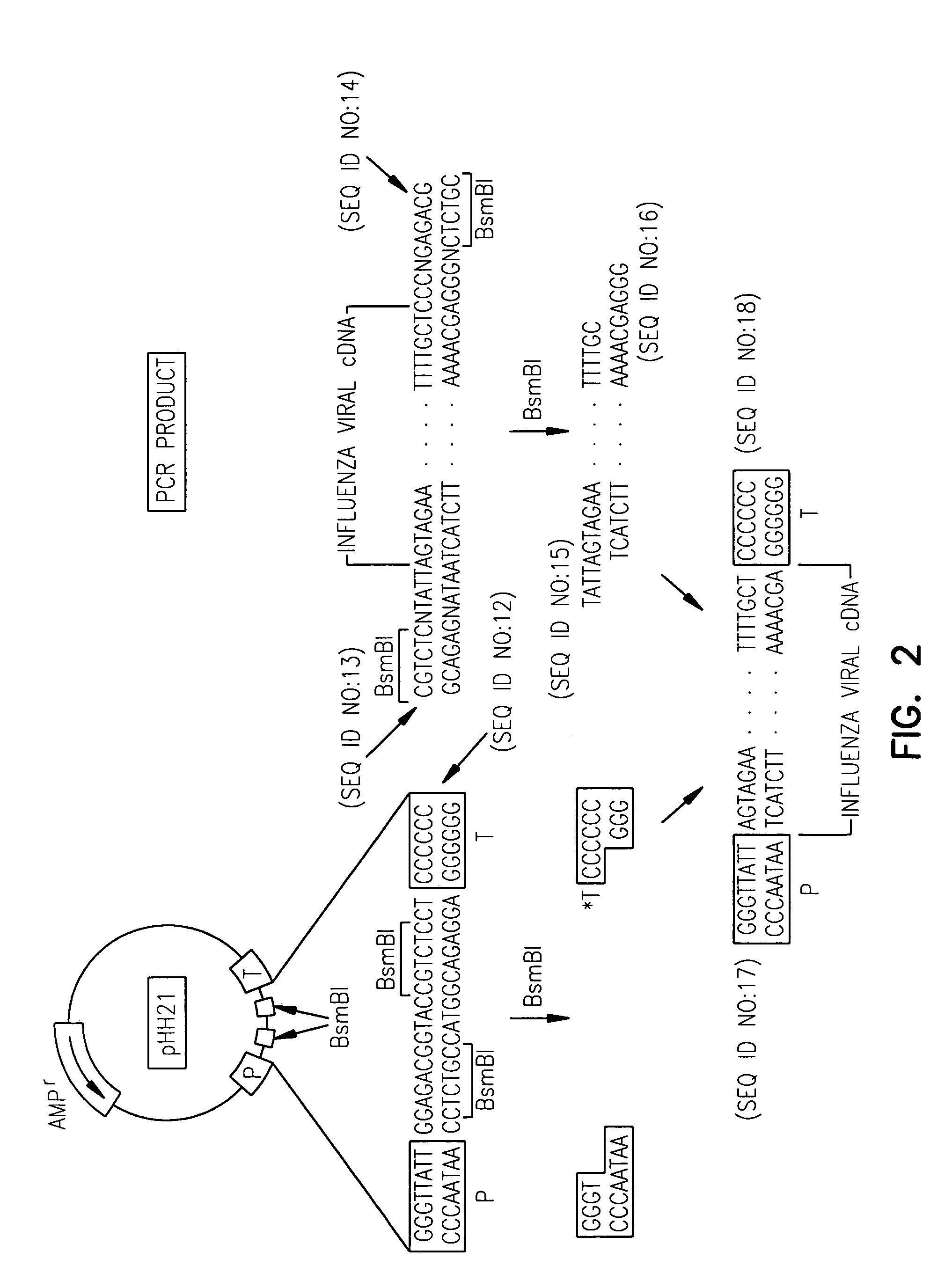
Humanized recombinant and monoclonal antibodies specific for the ectodomain of the influenza virus M2 ion channel protein are disclosed. The antibodies of the invention have anti-viral activity and may be useful as anti-viral therapeutics and / or prophylactic / vaccine agents for inhibiting influenza virus replication and for treating individuals infected with influenza.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
BmCP274 promoter of bombyx mori cuticular protein, recombinant expression vector and application of the promoter
ActiveCN102604953AChange natureFermentationPlant genotype modificationForeign proteinIon Channel Protein
The invention discloses a BmCP274 promoter of bombyx mori cuticular protein. The promoter consists of nucleotide sequences shown in SEQ ID No.1, can drive foreign proteins to specifically express at a front silk gland of the bombyx mori and can be used as a specific promoter at the front silk gland of the silkworm. The invention further discloses a recombinant expression vector containing the promoter, which provides a powerful tool for a next-step study on regulating ion channel protein expression at the front silk gland of the silkworm to affect the behavior of the bombyx mori and improve the performance of the silk fiber.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Engineered light-activated anion channel proteins and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20170095556A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifDrug photocleavageIon Channel ProteinOptogenetics
Aspects of the disclosure include compositions, devices, systems and methods for optogenetic modulation of action potentials in target cells. The subject devices include light-generating devices, control devices, and delivery devices for delivering light-responsive polypeptides, or nucleic acids encoding same, to target cells. The subject compositions and systems include light-activated polypeptides, nucleic acids comprising nucleotide sequences encoding these polypeptides, as well as expression systems that facilitate expression of these polypeptides in target cells. Also provided are methods of using the subject devices and systems to optogenetically manipulate action potentials in target cells, e.g., to treat a neurological or psychiatric condition in a human or animal subject.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Non-invasive near-infrared optically-controlled nano-material for repairing damaged nerves
ActiveCN108686208AGet rid of the bondageInhibit side effectsNervous disorderEnergy modified materialsInfraredFiber
The invention relates to a non-invasive near-infrared optically-controlled nano-material for repairing damaged nerves. The non-invasive near-infrared optically-controlled nano-material converts near-infrared light into visible light and / or ultraviolet light. The non-invasive near-infrared optically-controlled nano-material is an up-converting fluorescent nano-material. The invention discloses newuse of the up-converting fluorescent nano-material. In a repairing process of neurons, electrical stimulation does not need to be applied to the neurons, animals do not need to be surgically implantedwith invasive fibers, and near-infrared light with high tissue penetrability is used for stimulating the up-converting fluorescent nano-material in organisms; the converted up-converting fluorescencecan activate photosensitive ion channel protein on the neuronal cell membrane, stimulate the neuronal cells to produce membrane potential changes and enhance the stimulation of the neural circuits, thus repairing the damaged neurons.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Cycloalkane amine compound as M2 inhibitor and application thereof
ActiveCN101906056AInhibition of replicationTo kill the virusOrganic chemistryAntiviralsIon Channel ProteinMedicinal chemistry
The invention discloses a cycloalkane amine compound of a general formula I or II, or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or substituted group defined in the description; the cycloalkane amine compound of the general formula I or II, or pharmaceutically acceptable salt can be used for preparing medicine for preventing and treating flue; as the M2 ion channel protein inhibitor, the compound can stop copy of the flue virus, and treat influenza, specifically the influenza A.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICINE & HEALTH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Recombined corynebacterium glutamicum as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108085287ANo effect on growth rateHigh expressionBacteriaHydrolasesForeign proteinIon Channel Protein
The invention provides recombined corynebacterium glutamicum, can be used for effectively solving the technical problem that the conventional corynebacterium glutamicum is low in foreign protein expression quantity. The peptidoglycan endonucleases gene mepA, cytomembrane surface anion protein gene porB and endoproteinase gene clpC in the corynebacterium glutamicum are knocked out, meanwhile ACB transporter gene Ncg10909 are over expressed. Moreover the invention further provides a preparation method for the recombined corynebacterium glutamicum and application thereof.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Serum-free induction method of sensory neuronal cells
PendingCN112055746AImprove expression strengthSolve pollutionCompound screeningNervous disorderIon Channel ProteinSerum free
According to the novel human sensory neuron induction culture system provided by the invention, the combination of the small-molecule inhibitor LY2157299 and the growth factor is added into the serum-free basal culture medium, so that compared with a serum-containing induction method, the efficiency of converting pluripotent stem cells into sensory neurons is greatly improved, and the induction efficiency of the pluripotent stem cells is improved. In addition, the expression of various ion channel proteins is obviously improved, so that various induced pluripotent stem cells with different sources are successfully induced into sensory neurons.
Owner:IREGENE THERAPEUTICS LTD
Controllable escherichia coli acid-resistant system based on ion channel and application thereof
InactiveCN104450593AEasy to control survivalGuaranteed survivalBacteriaCarbon-carbon lyasesEscherichia coliIon Channel Protein
The invention discloses a controllable escherichia coli acid-resistant system based on an ion channel and application thereof. The original glutamine-mediated acid-resistant system of escherichia coli is based, and the survival rate of escherichia coli is enabled to be related to the expression quantity of ammonium ion channel proteins and the concentration of ammonium ions in a culture medium under an extreme acidic condition with glutamine by knocking out glutamate decarboxylase GadA and GadB in the original system, so that the acid resistance of escherichia coli can be controlled by regulating the concentration of extracellular ammonium ions and / or the expression quantity of intracellular ammonium ion channel proteins, thus controlling the survival of escherichia coli under the acidic condition. The acid-resistant system can also be used as a mode system for measuring the substrate and functions of the ion channel proteins.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Solid support membranes for ion channel arrays and sensors: application ro rapid screening of pharmacological compounds
The present invention relates to synthetic membranes and provides a solid supported membrane comprising: a support; a chromium layer; a gold layer; an alkyl monolayer, a lipid monolayer; and an ion channel protein, wherein the alkyl monolayer and the lipid monolayer form a bilayer, and further wherein a functionally reconstituted ion channel is supported, and methods for forming them. The invention further provides methods and applications of the membranes in rapid screening for pharmacological agents and as bioelectric smart sensors.
Owner:CUPPOLETTI JOHN
TRPC6 involved in glomerulonephritis
ActiveUS20080038365A1Calcium ion influx is thereby reducedOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsZona glomerulosaDisease
Focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) is a kidney disorder of unknown etiology and up to 20% of patients on dialysis have this diagnosis. A large family with hereditary FSGS carries a missense mutation in the TRPC6 gene on chromosome 11q, encoding the ion channel protein Transient Receptor Potential Cation Channel 6. The missense mutation is a P112Q substitution, which occurs in a highly conserved region of the protein, enhances TRPC6-mediated calcium signals in response to agonists such as angiotensin II, and alters the intracellular distribution of TRPC6 protein. Previous work has emphasized the importance of cytoskeletal and structural proteins in proteinuric kidney diseases. Our findings suggest a novel mechanism for glomerular disease pathogenesis.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Anti-influenza M2e antibody
InactiveUS8080244B2Sugar derivativesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsIon Channel ProteinMonoclonal antibody
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
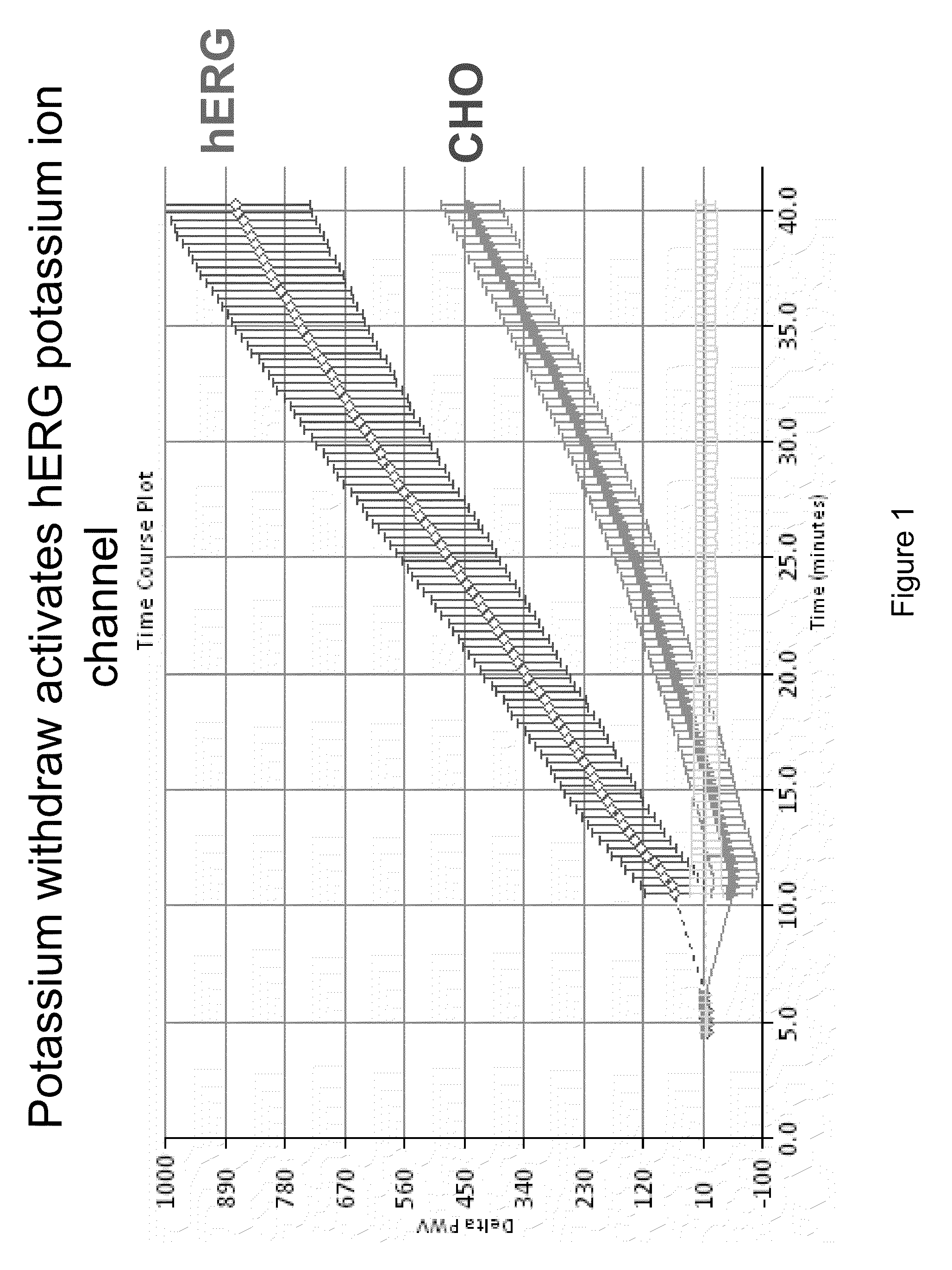
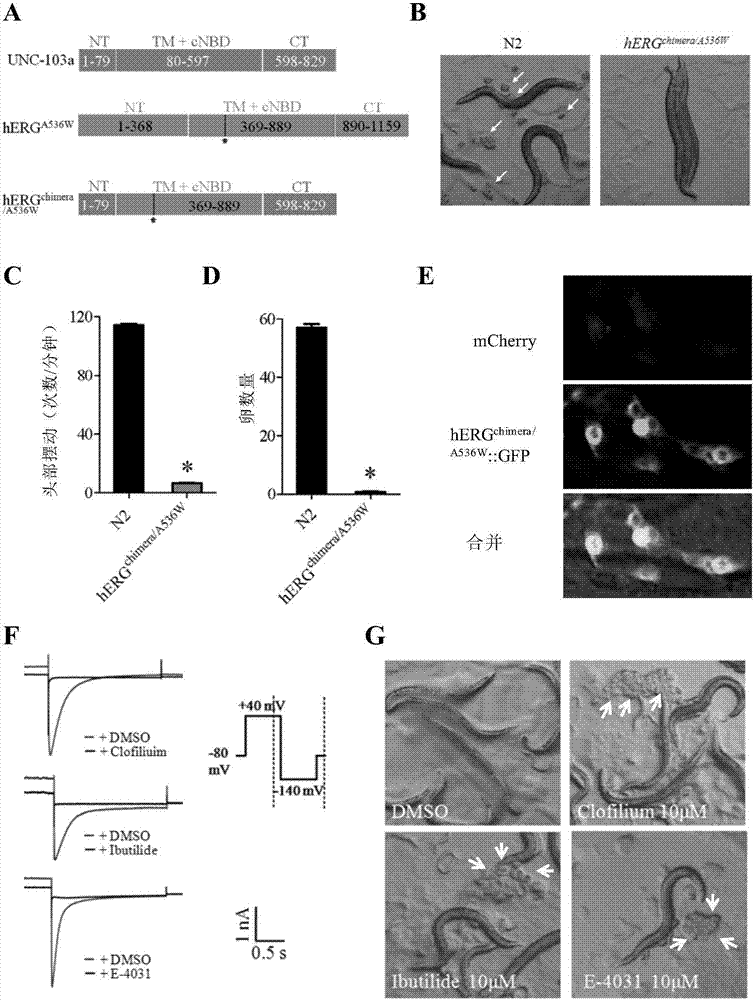
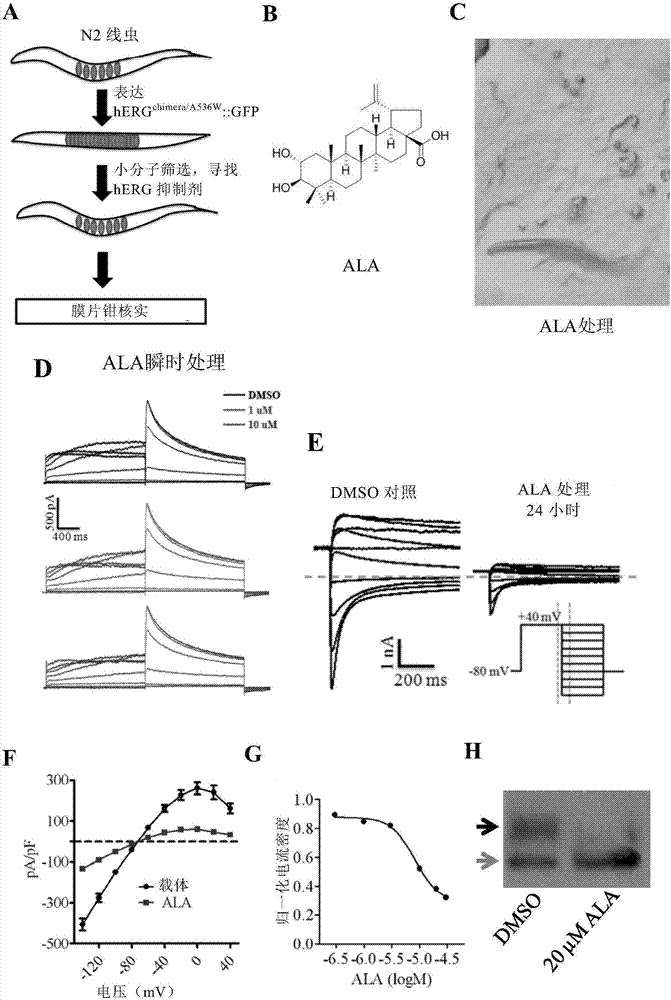
Method for screening hERG potassium ion channel agonist and detecting toxicity
ActiveCN107011444APolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifBiological testingCyclic nucleotide bindingScreening method
The invention relates to a method for screening hERG potassium ion channel agonist and detecting toxicity. Particularly, the invention firstly relates to a fusion protein, which contains a fragment (which is used as the N end of the fusion protein, is from a position between 1st to 85th amino acid residues of the N end of the nemathelminth ERG family potassium ion channels UNC-103 protein and has the length of 75 to 85 amino acid residues), hERG or a fragment at least containing S1-S6 transmembrane domains and cyclic nucleotide binding domains, and a fragment (which is used as the C end of the fusion protein, is from a position between 590th to 829th of amino acid residues of the C end of the UNC-103 protein and has the length of 220 to 240 amino acid residues). The invention also relates to a polynucleotide sequence coding the fusion protein, a relevant transgenic nemathelminth, a relevant screening method and application. The inventor builds an in-vivo hERG-intracellular-transport-influence-recognizable compound molecule screening method for screening hERG inhibitors or LQTS (long QT syndrome) relevant channel mutant functional correcting agents for the first time; the novel path and method are provided for hERG toxicity detection and LQTS treatment medicine screening.
Owner:CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN BRAIN SCI & INTELLIGENCE TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Engineered light-activated anion channel proteins and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS10052383B2Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsIon Channel ProteinOptogenetics
Aspects of the disclosure include compositions, devices, systems and methods for optogenetic modulation of action potentials in target cells. The subject devices include light-generating devices, control devices, and delivery devices for delivering light-responsive polypeptides, or nucleic acids encoding same, to target cells. The subject compositions and systems include light-activated polypeptides, nucleic acids comprising nucleotide sequences encoding these polypeptides, as well as expression systems that facilitate expression of these polypeptides in target cells. Also provided are methods of using the subject devices and systems to optogenetically manipulate action potentials in target cells, e.g., to treat a neurological or psychiatric condition in a human or animal subject.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
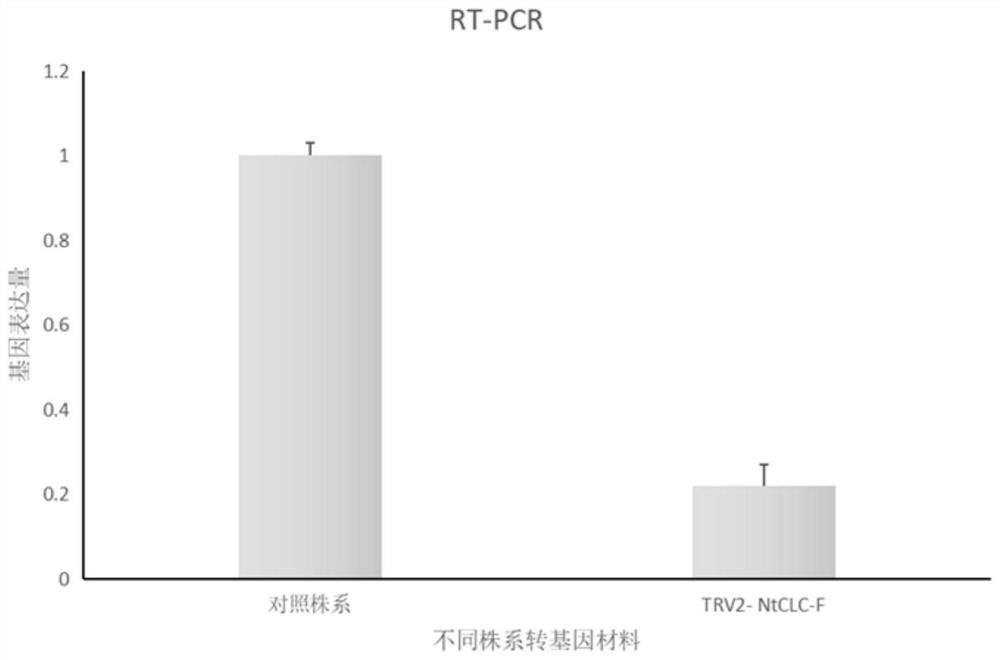
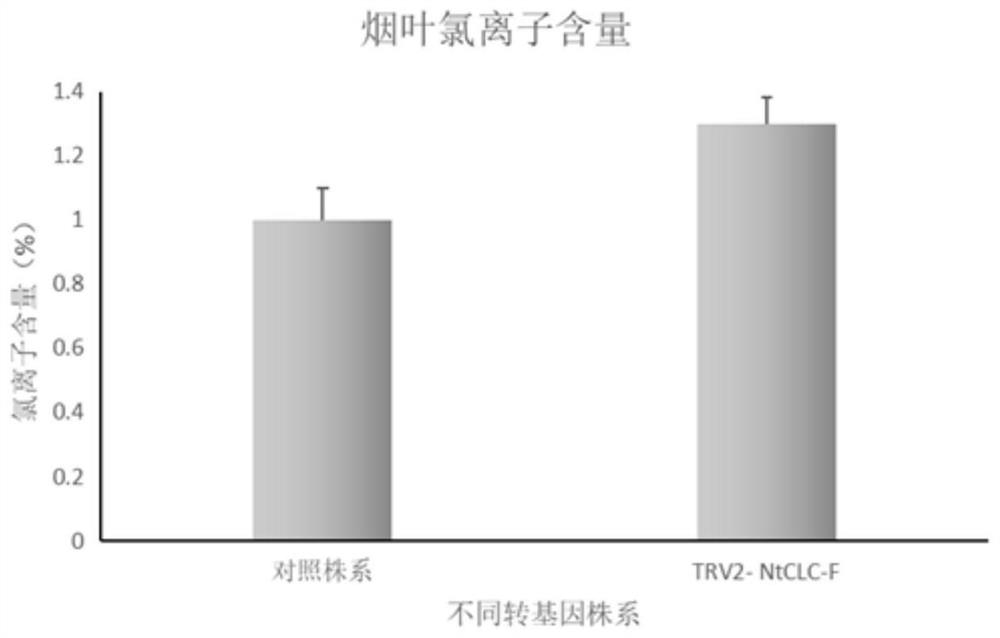
Tobacco chloride ion channel protein gene NtCLC-F and application thereof
InactiveCN112760329AIncreased chloride ion contentPlant peptidesFermentationIon Channel Protein GeneIon Channel Protein
The invention belongs to the technical field of tobacco gene engineering, and particularly relates to a tobacco chloride ion channel protein gene NtCLC-F and application thereof. The base sequence of the gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1. The tobacco chloride ion channel protein NtCLC-F is composed of 726 amino acid residues, wherein the 181st-500th amino acids are conserved chloride ion channel protein structural domains. The protein is related to the chloride ion content of plant leaves, and after the expression of the protein is reduced, the chloride ion content of the leaves is obviously increased. Preliminary research on a specific tobacco chloride ion channel NtCLC-F shows that the specific tobacco chloride ion channel NtCLC-F is highly related to the content of the tobacco chloride ions, and after the gene is silenced, the content of the tobacco chloride ions is obviously increased. Based on the characteristic, a certain application basis and reference can be provided for cultivation of a new tobacco variety with the chlorine ion content regulated and controlled.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO HENAN IND
Method for increasing content of intracellular heme in escherichia coli
ActiveCN111849847AIncreased hemoglobin contentGrowth status did not change significantlyBacteriaTransferasesEscherichia coliIon Channel Protein
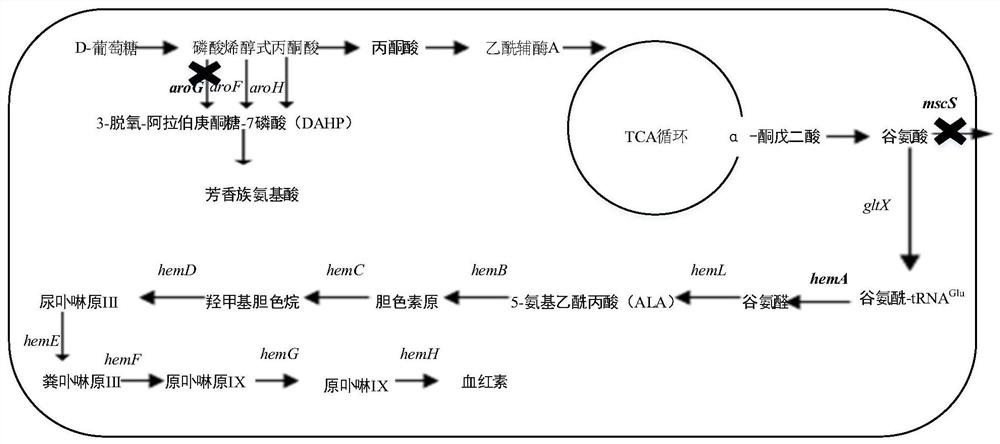
The invention discloses a method for increasing the intracellular heme content of escherichia coli, and belongs to the field of metabolic engineering. The method comprises the following steps: knocking out a gene mscS for encoding a small-conductivity mechanical sensitive ion channel protein, knocking out a gene aroG for encoding 3-deoxy-arabinoheptulose-7 phosphate synthase, or overexpressing a gene hemA for encoding glutamyl-tRNA reductase in escherichia coli. The constructed recombinant bacteria are cultured in an LB culture medium, the heme content can reach 47.6 [mu]mol.L<-1> and is remarkably improved compared with that of a control strain, and the recombinant bacteria have wide application value.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
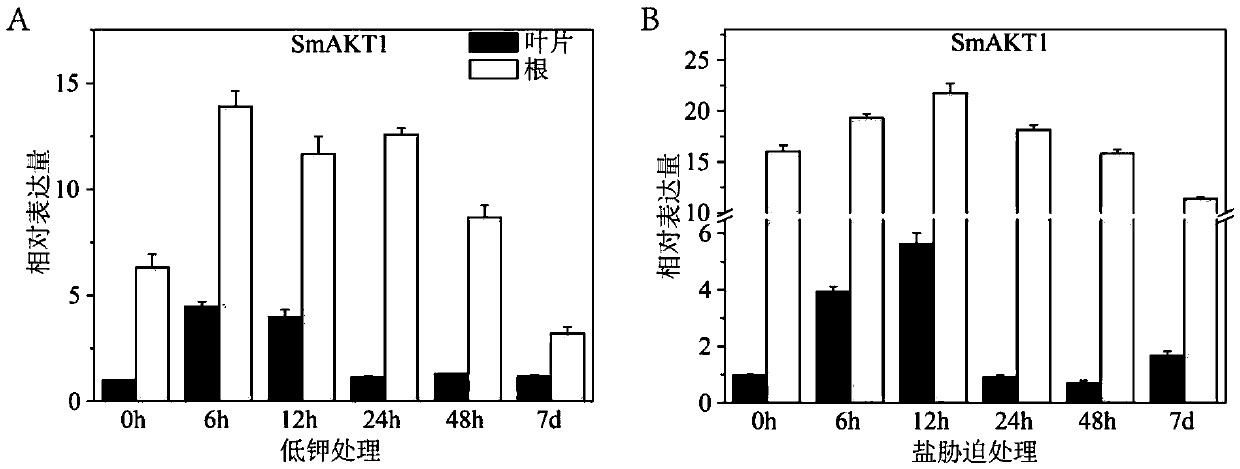
Eggplant potassium ion channel protein SmAKT1 as well as encoding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses eggplant potassium ion channel protein SmAKT1 as well as an encoding gene and an application thereof. The protein SmAKT1 has the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.2, and anucleotide sequence encoding the gene of the protein is shown in SEQ ID NO.1. The gene has expression in roots, stems, leaves, flowers, fruits and sepals, and the expression quantity in a root systemis notably higher than that in other tissue. Under low-potassium and salt stress treatment, the expression quantity of the gene in the leaves and the root system has the trend of first rising and then dropping. The gene function of the protein SmAKT1 is also identified, the gene SmAKT1 is imported in a target defect type yeast strain or an arabidopsis thaliana mutant, and the stress resistance ofthe gene to low-potassium stress and salt stress can be improved. A theoretical basis is provided for cultivation of the low-potassium stress and salt stress resistant eggplants with a gene engineering technology in the future, and the gene has great application value.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com