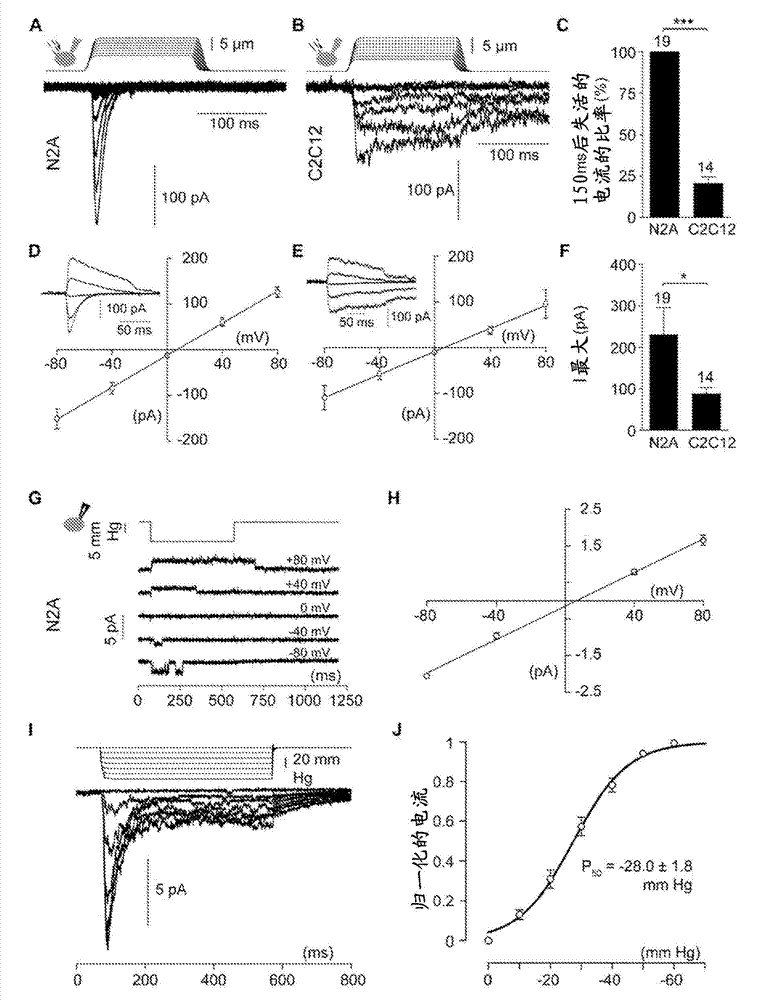
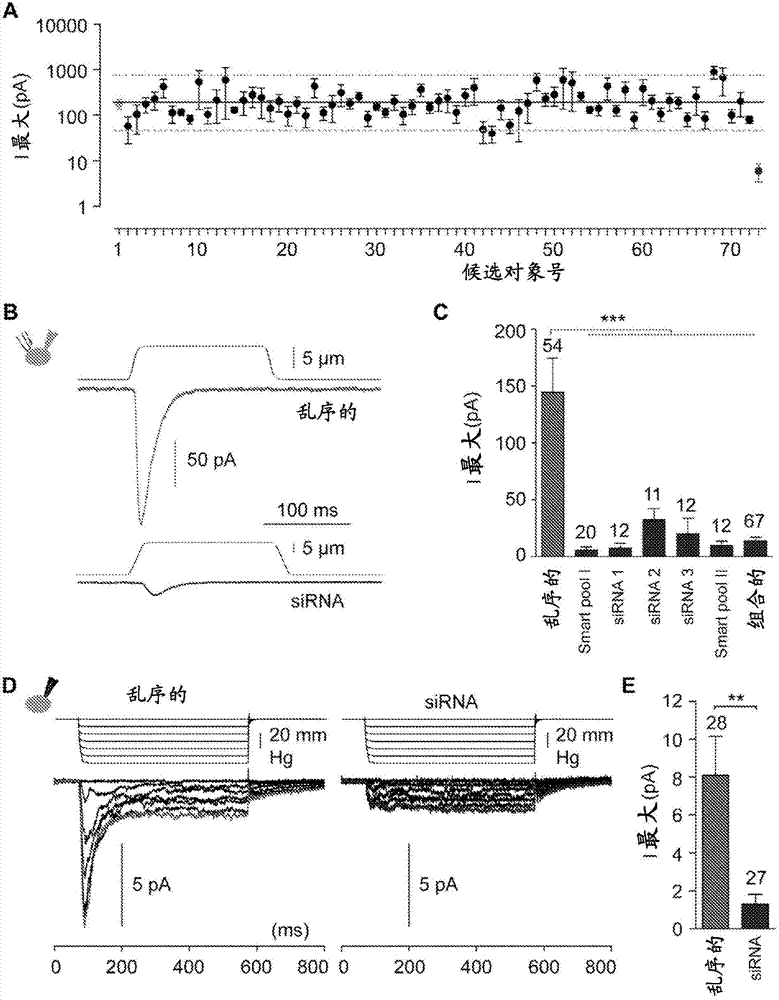
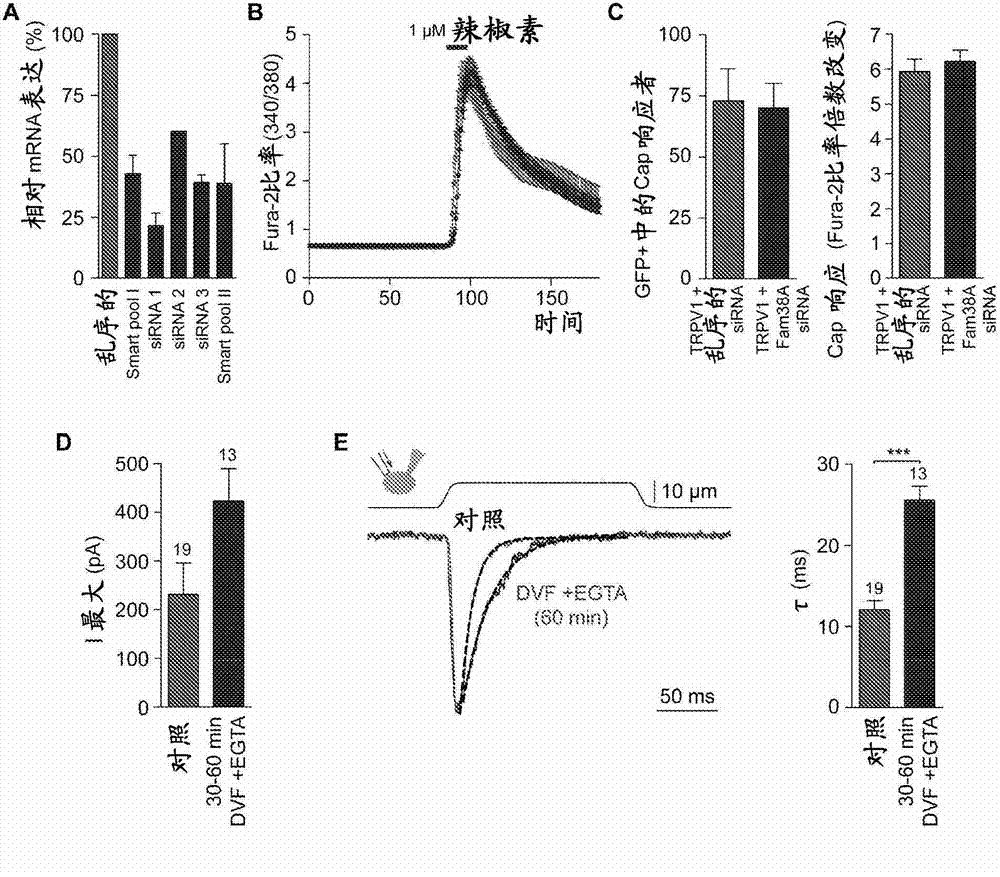
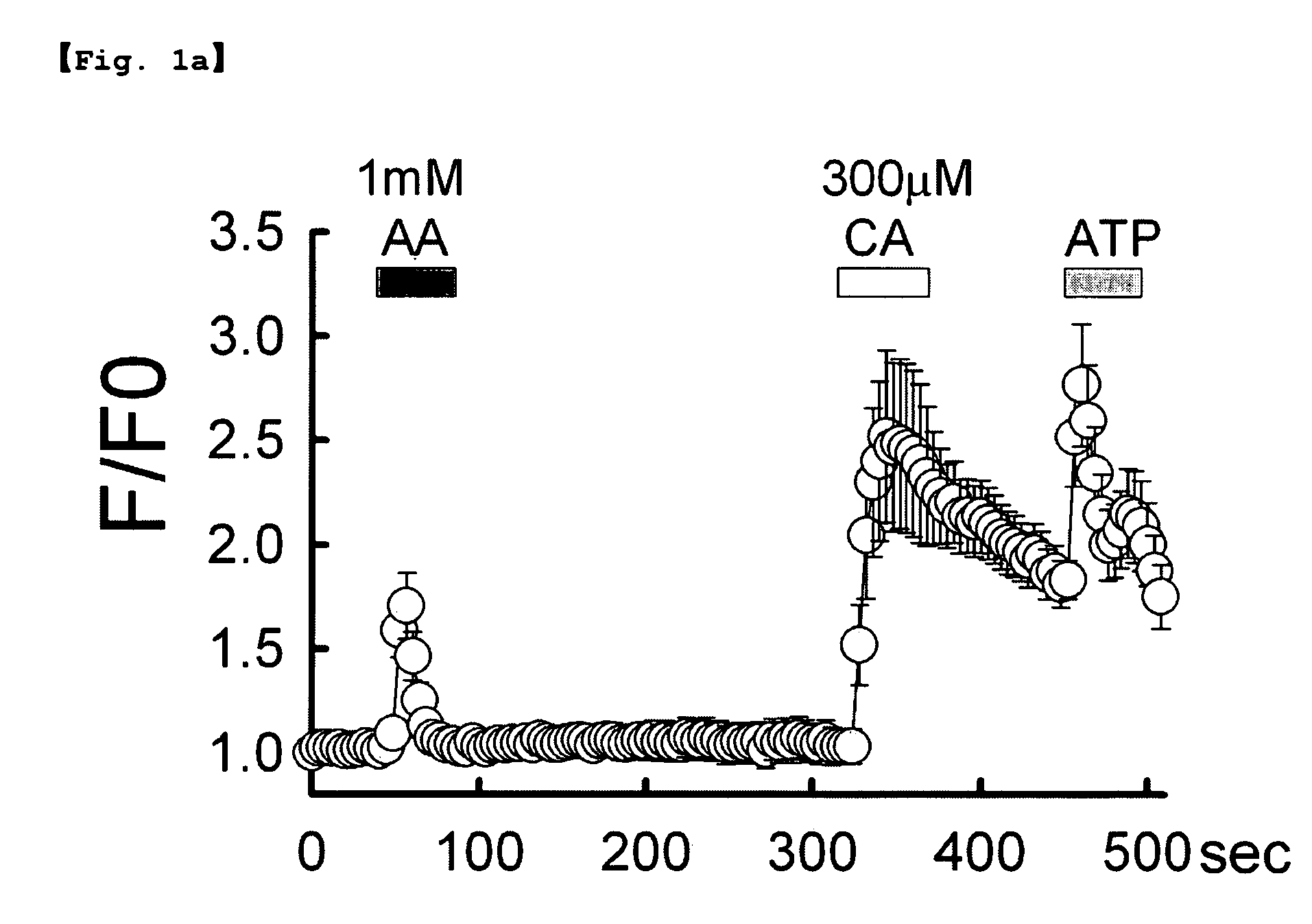
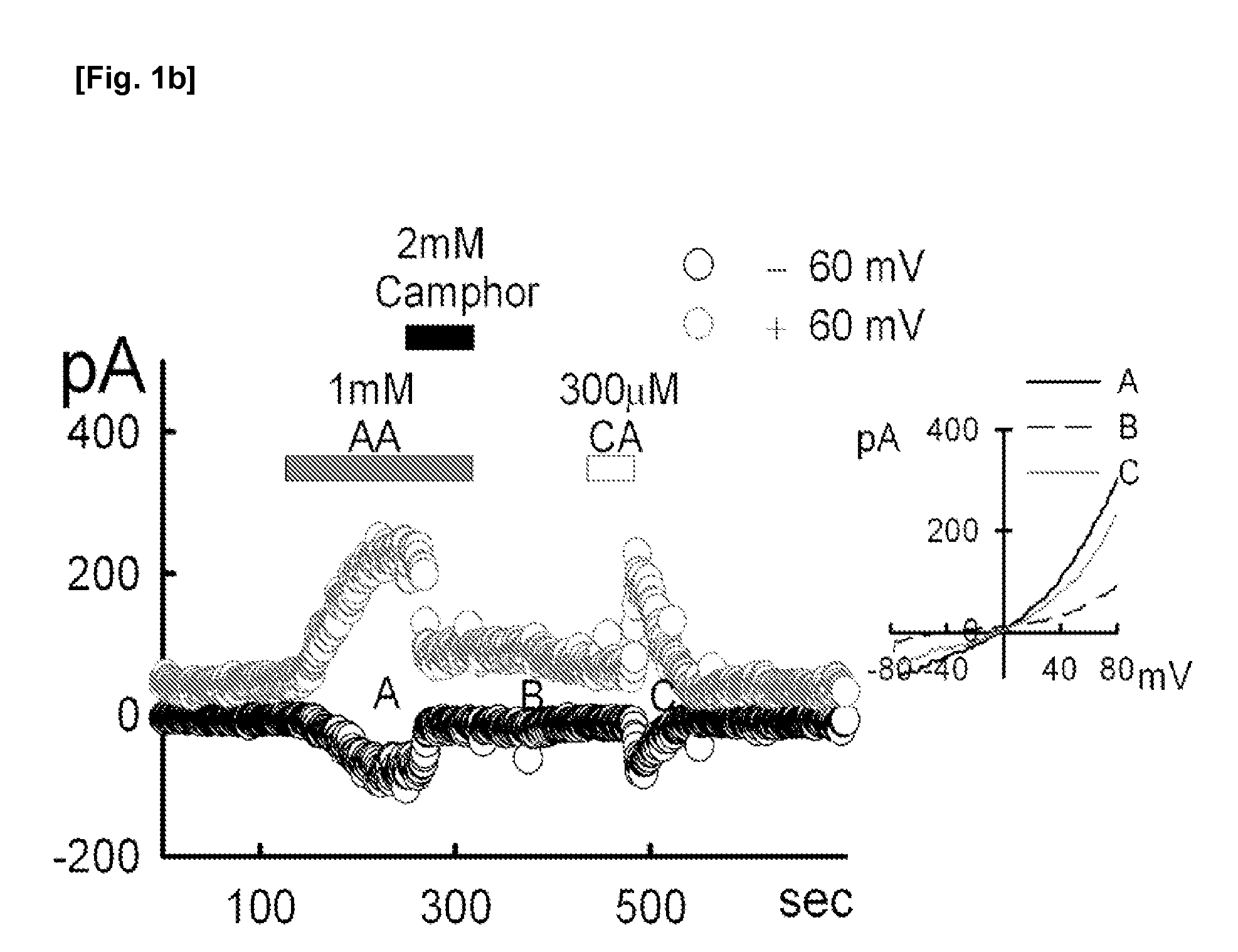
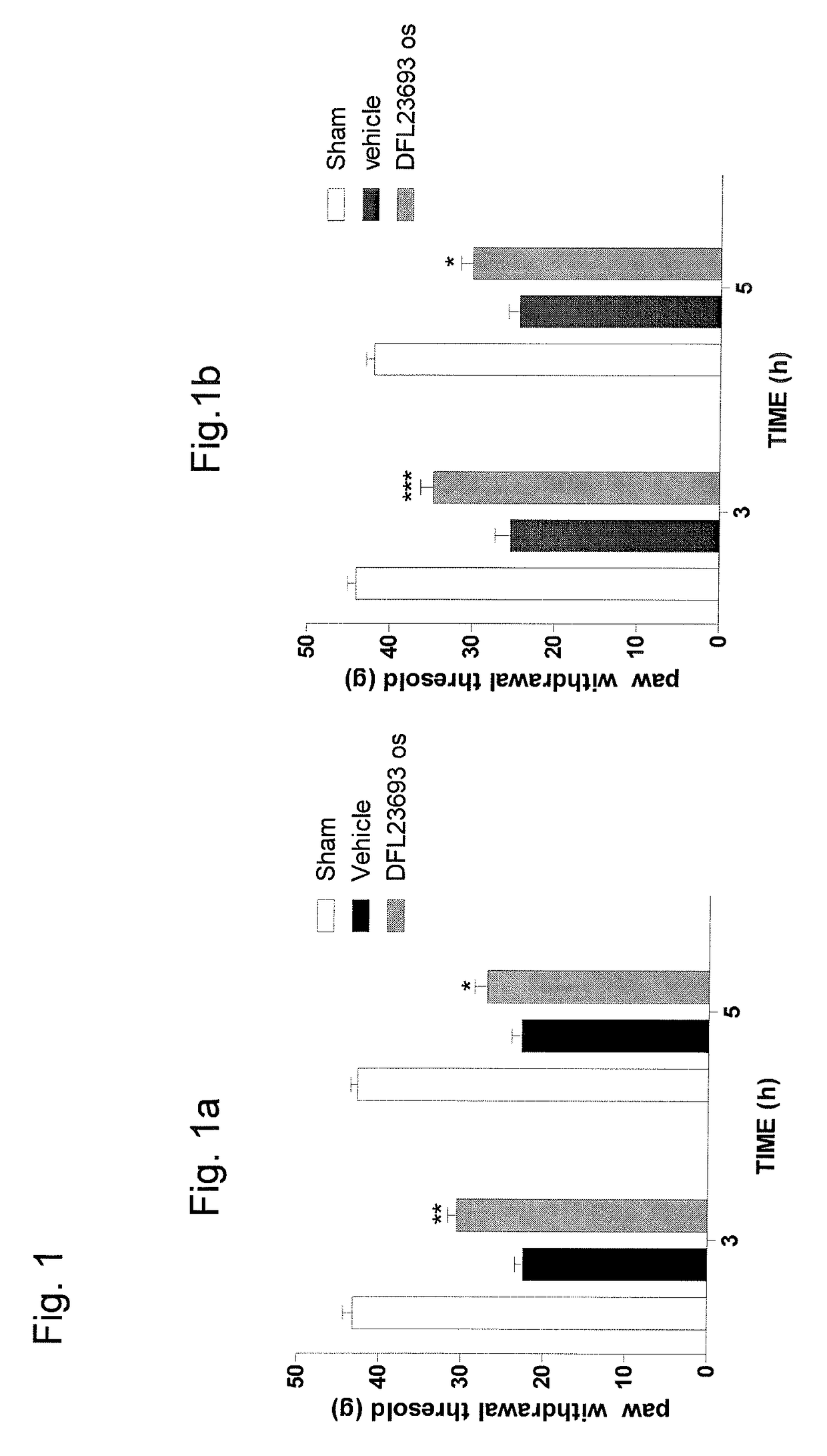
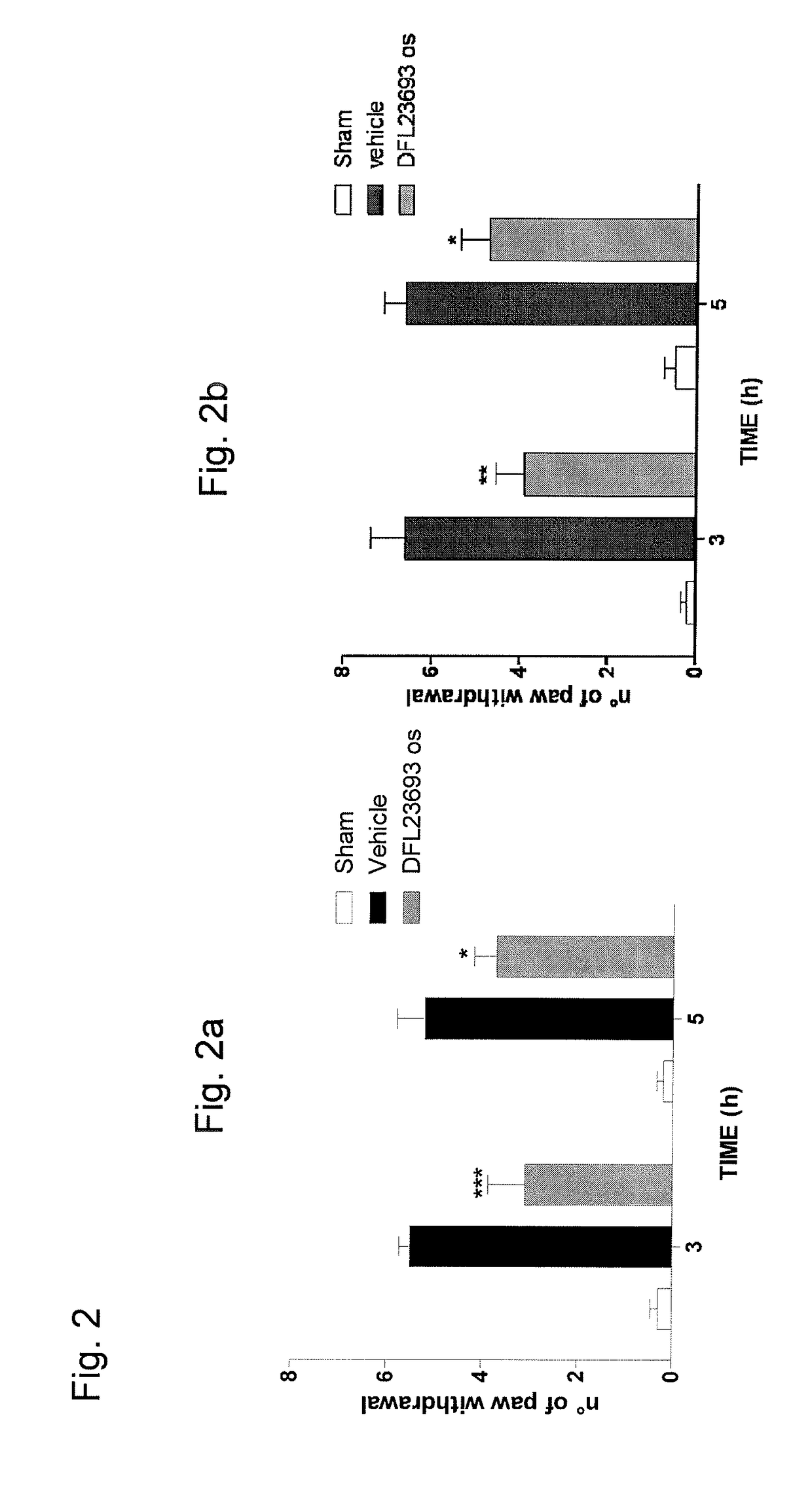
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
42 results about "Cation channels of sperm" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
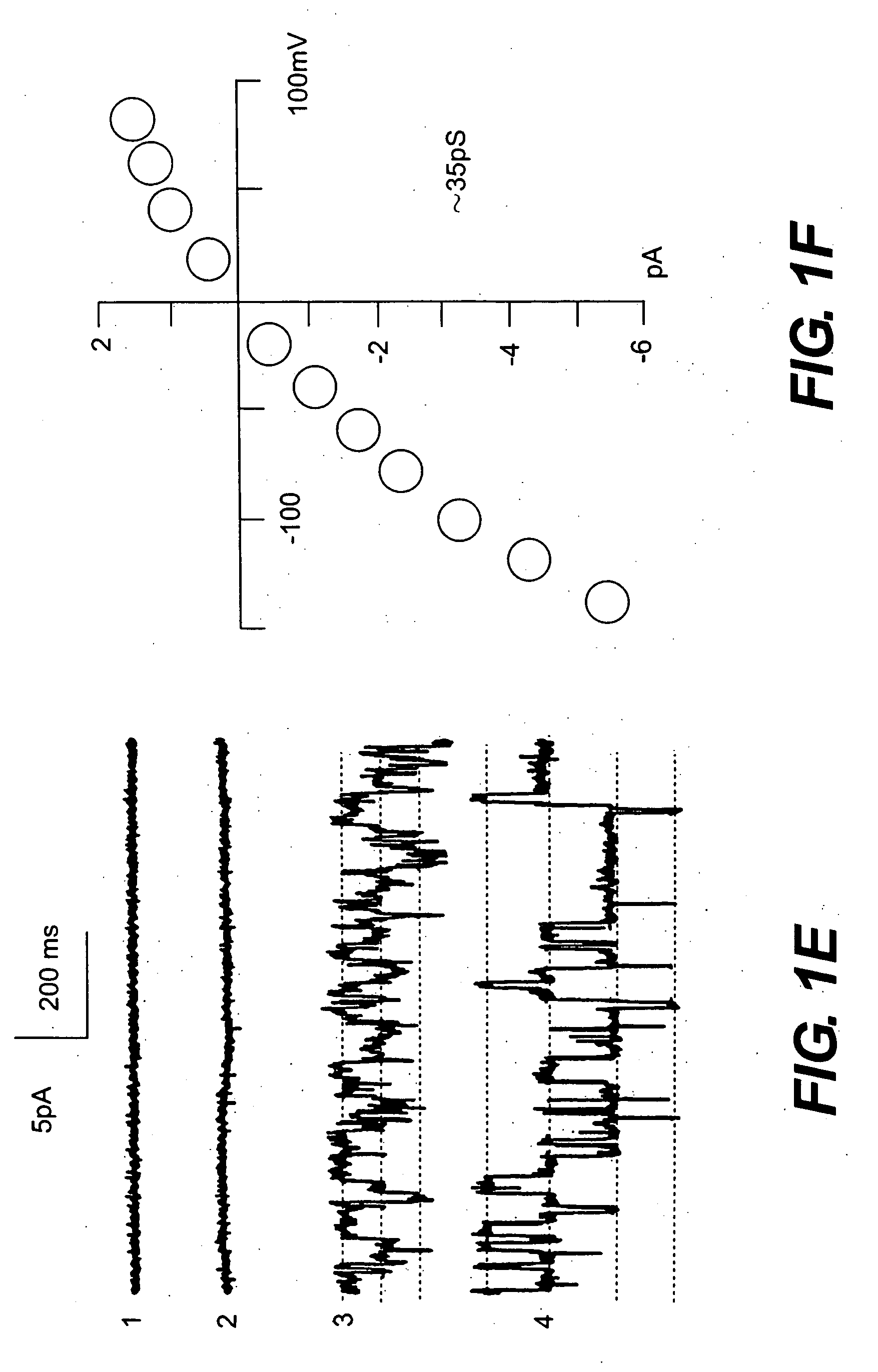
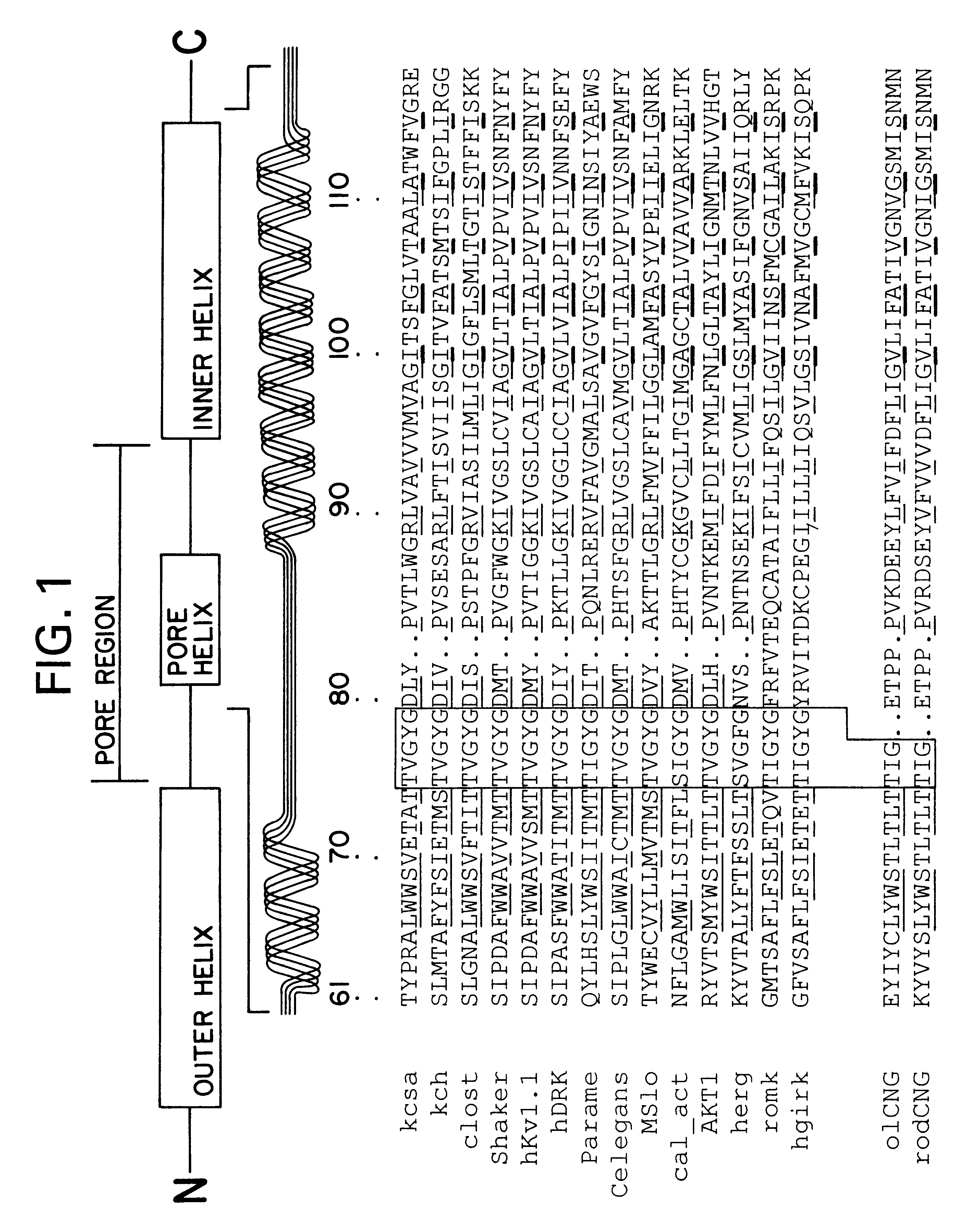
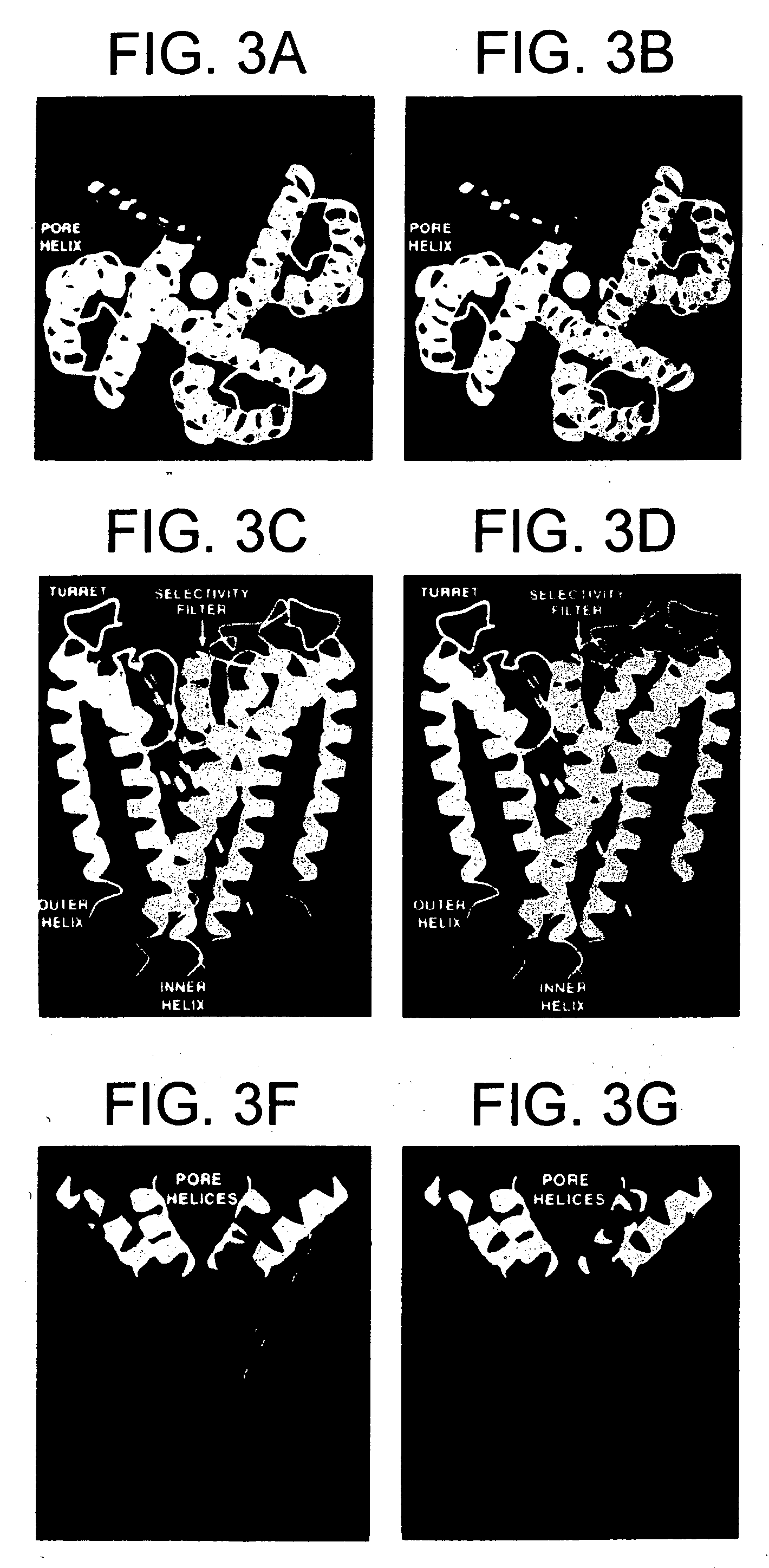
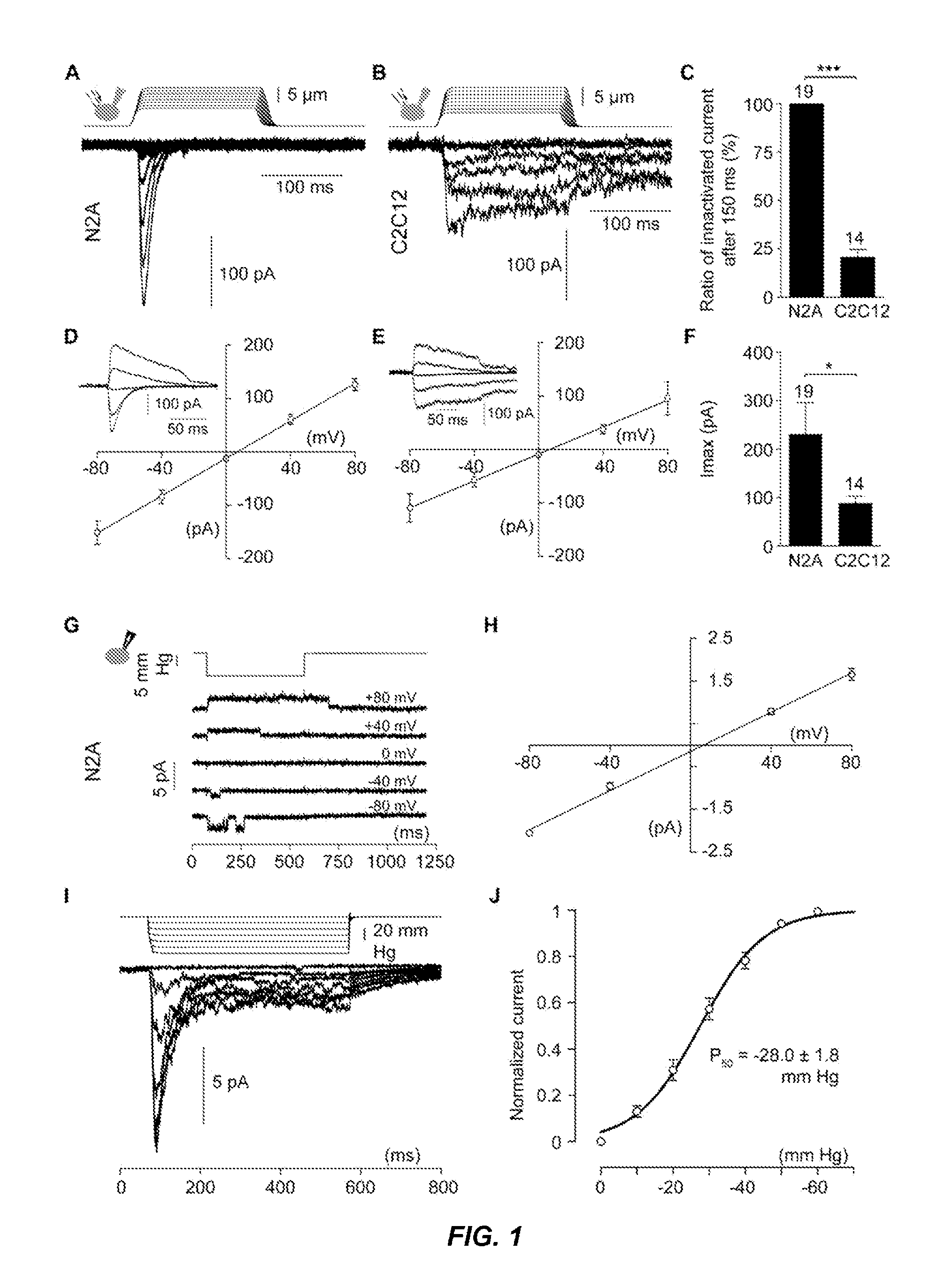
The cation channels of sperm also known as Catsper channels or CatSper, are ion channels that are related to the two-pore channels and distantly related to TRP channels. The four members of this family form voltage-gated Ca²⁺ channels that seem to be specific to sperm. As sperm encounter the more alkaline environment of the female reproductive tract, CatSper channels become activated by the altered ion concentration. These channels are required for proper fertilization. The study of these channels has been slow because they do not traffic to the cell membrane in many heterologous systems.
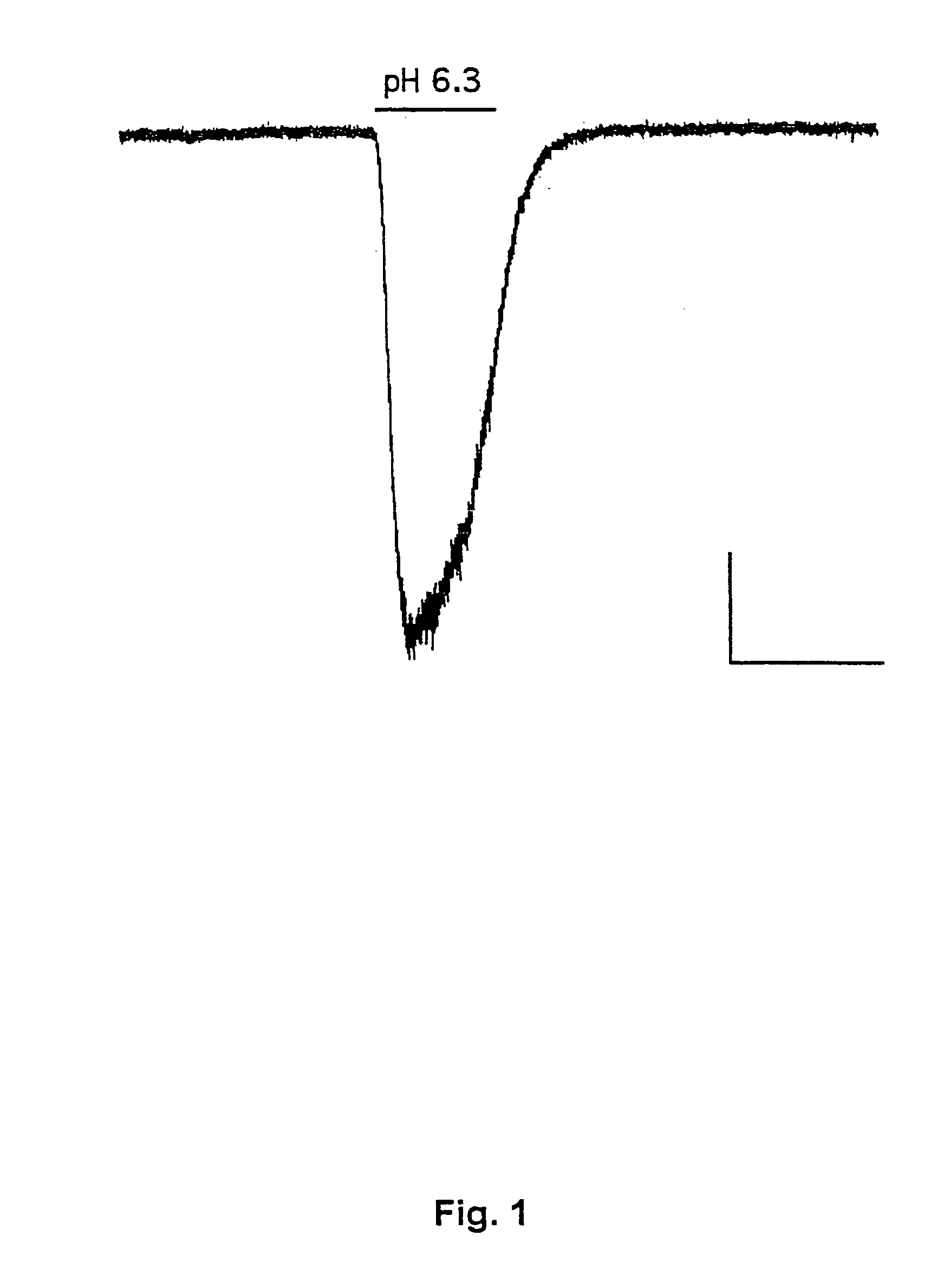
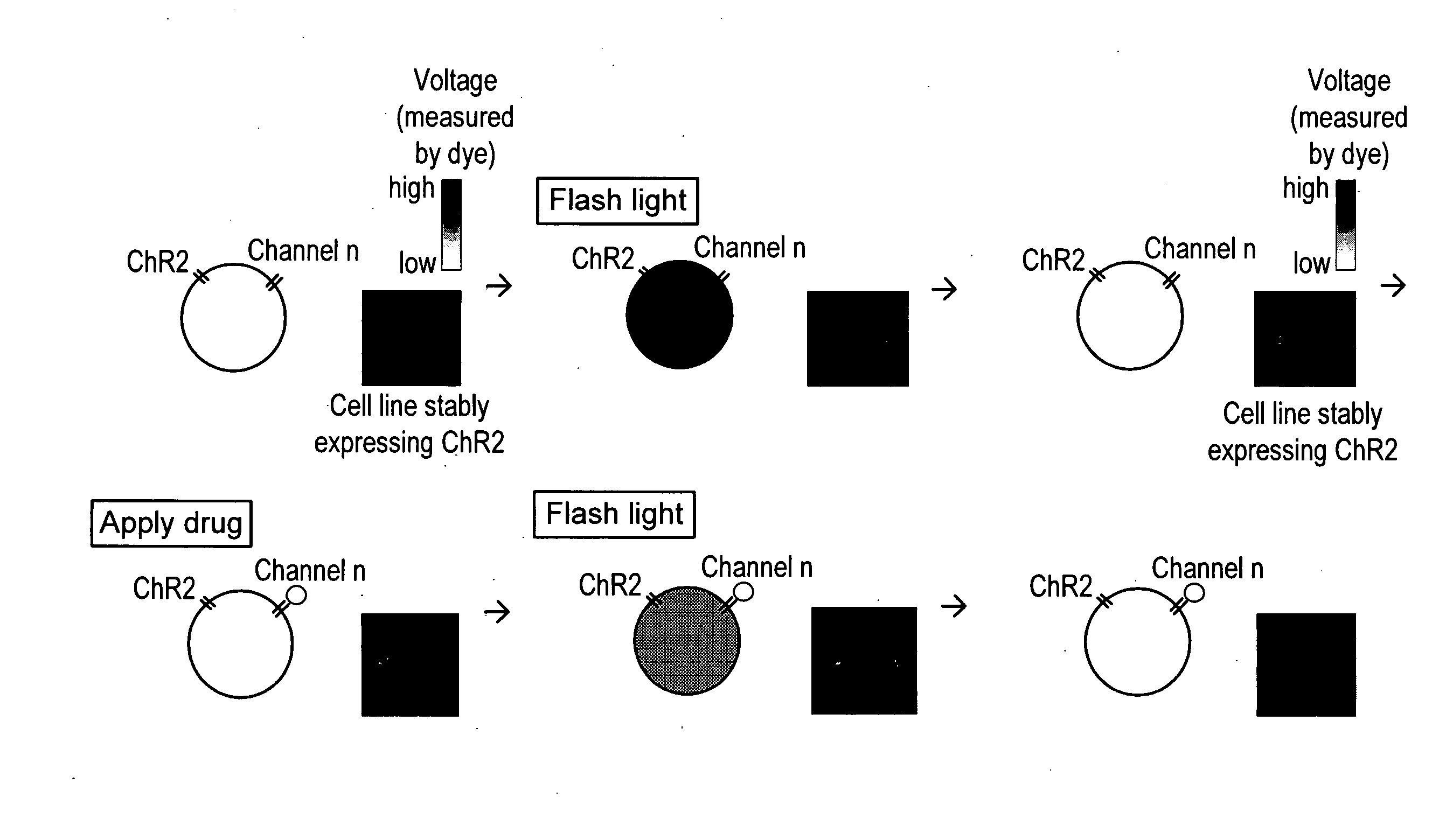
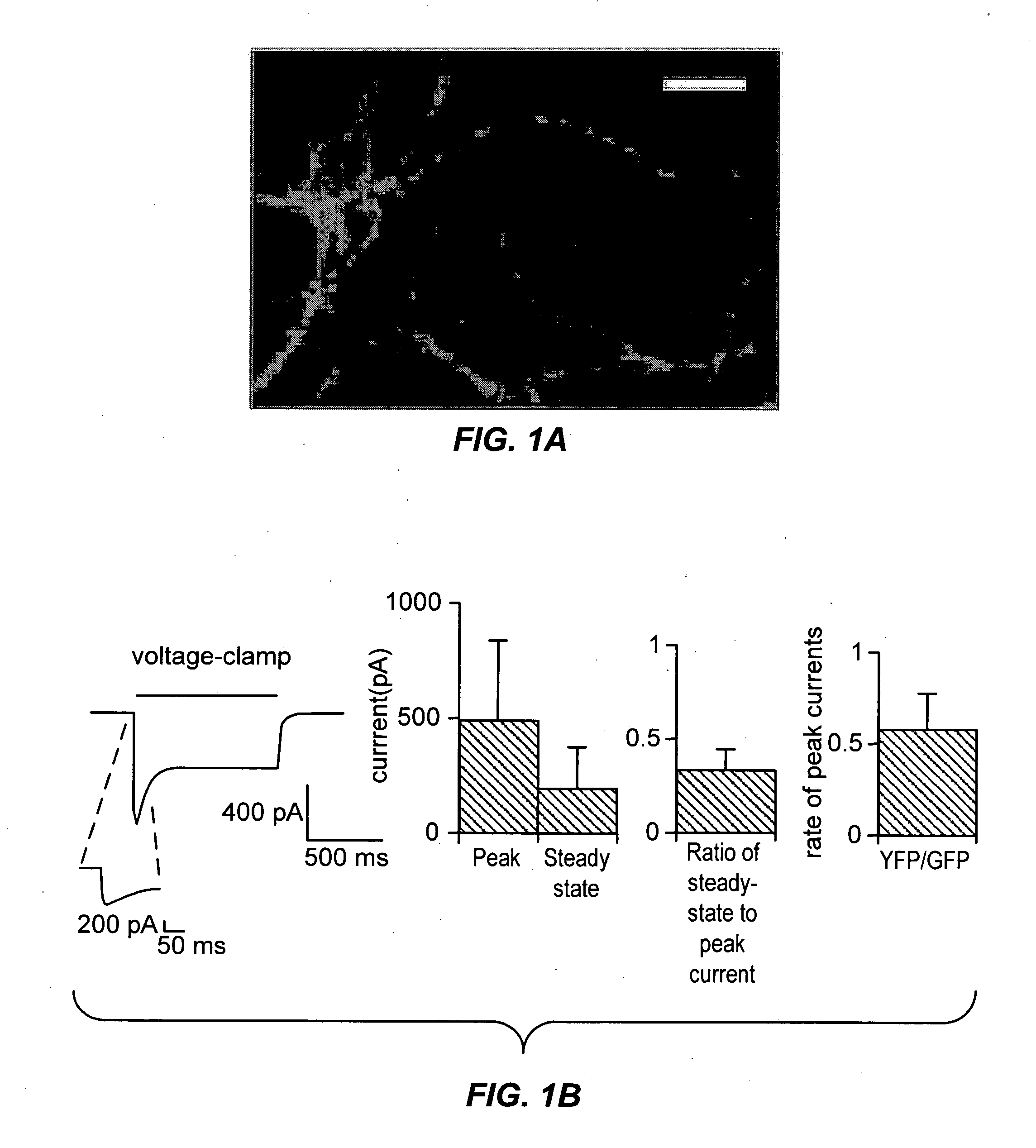
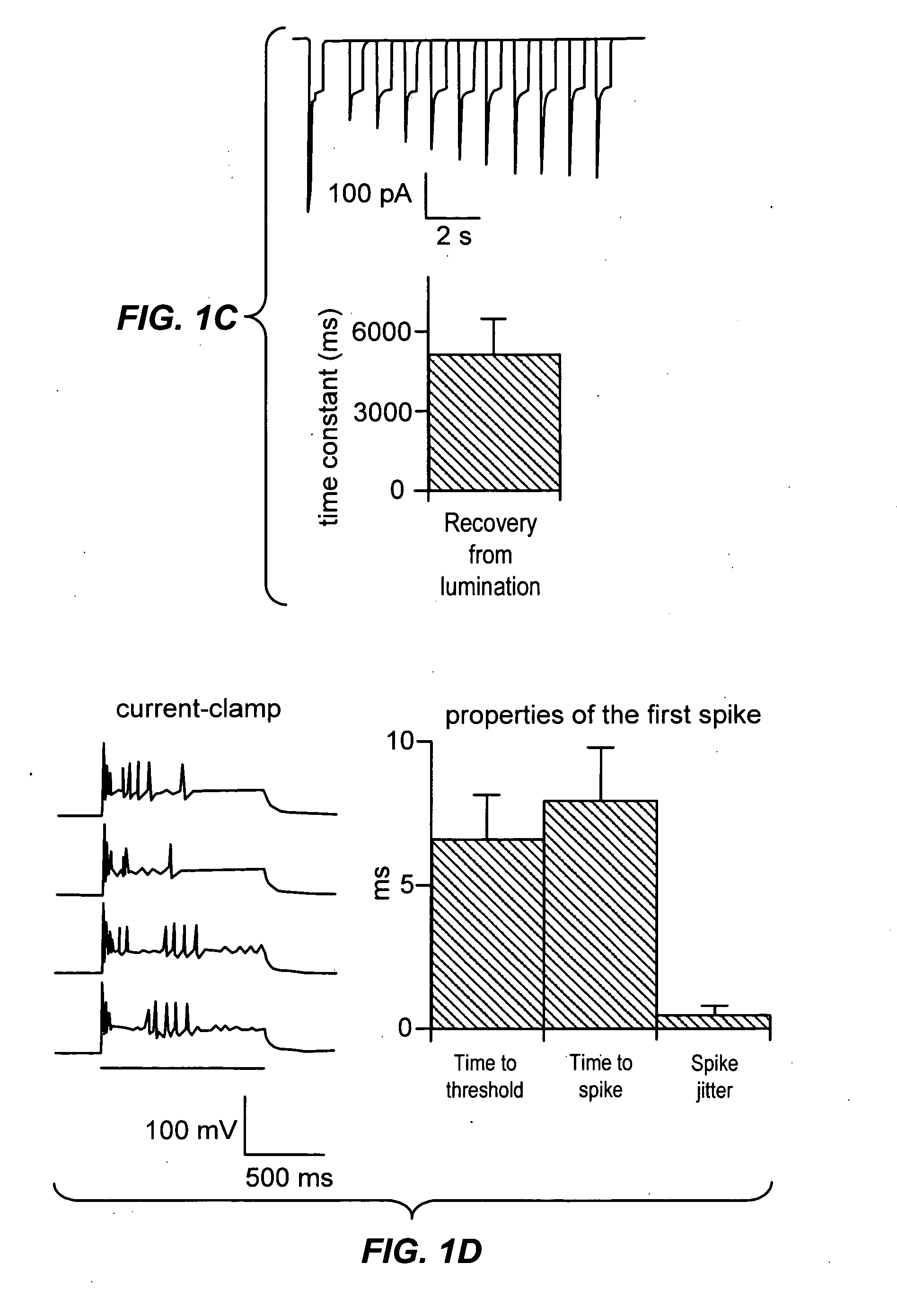
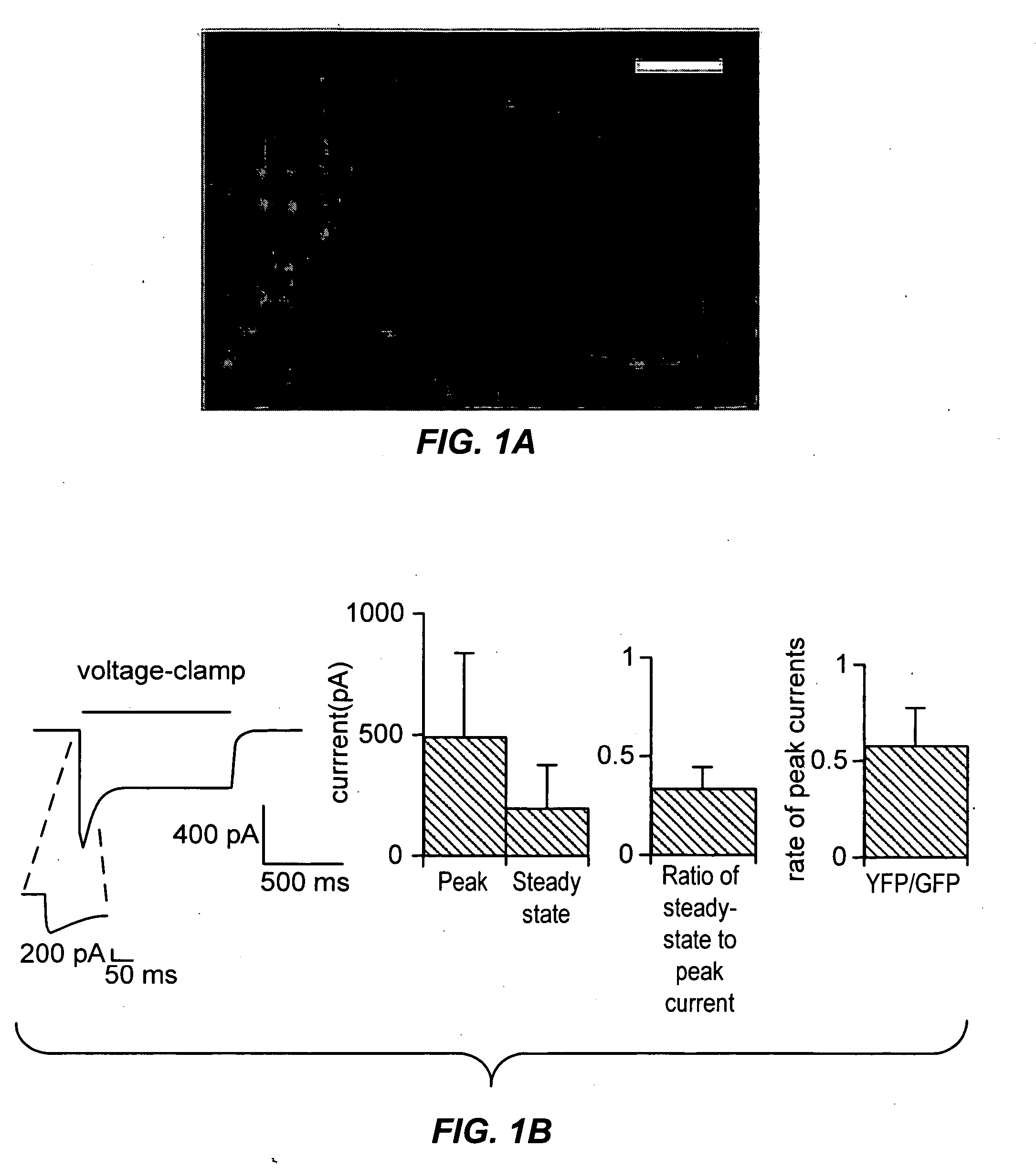
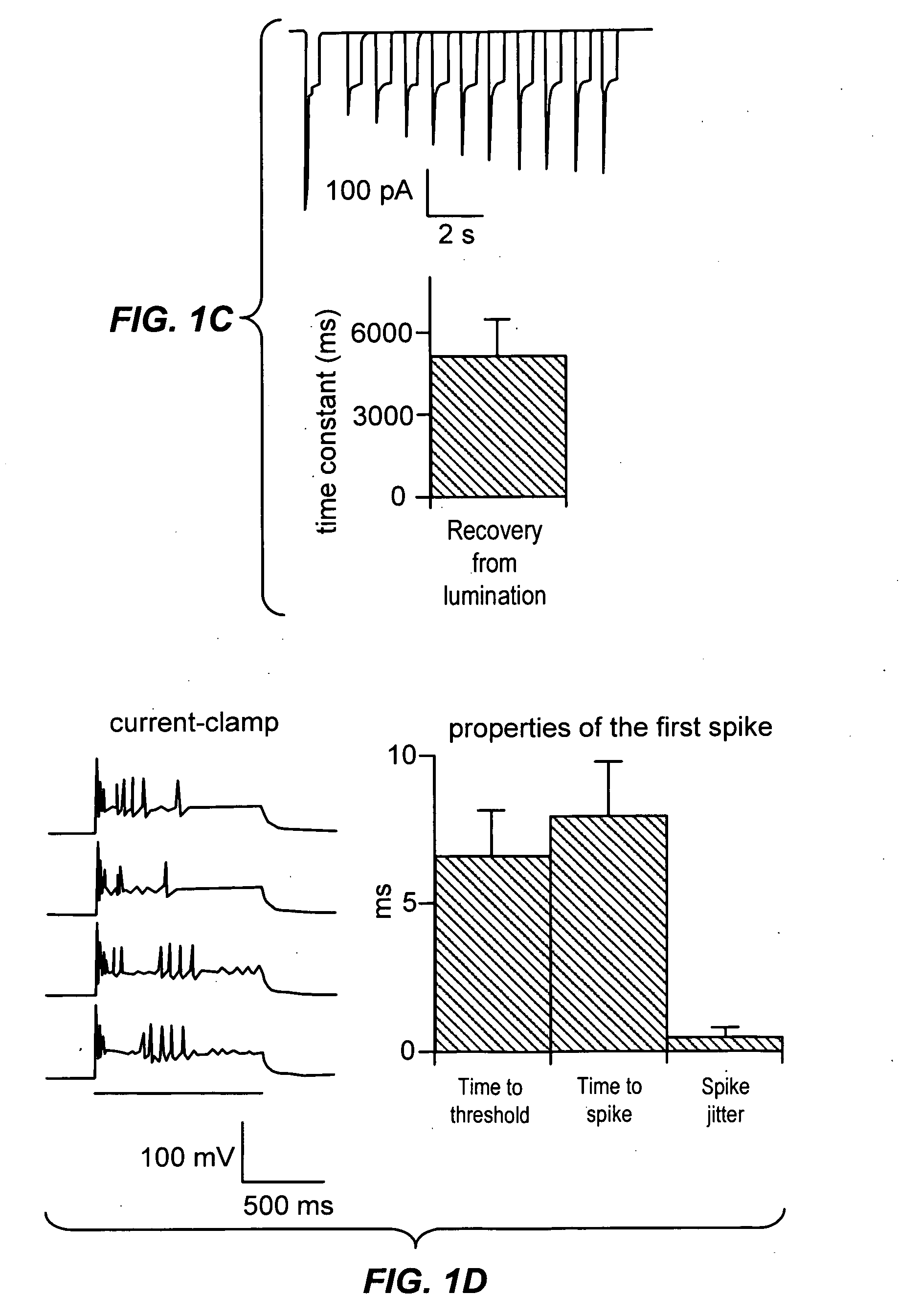
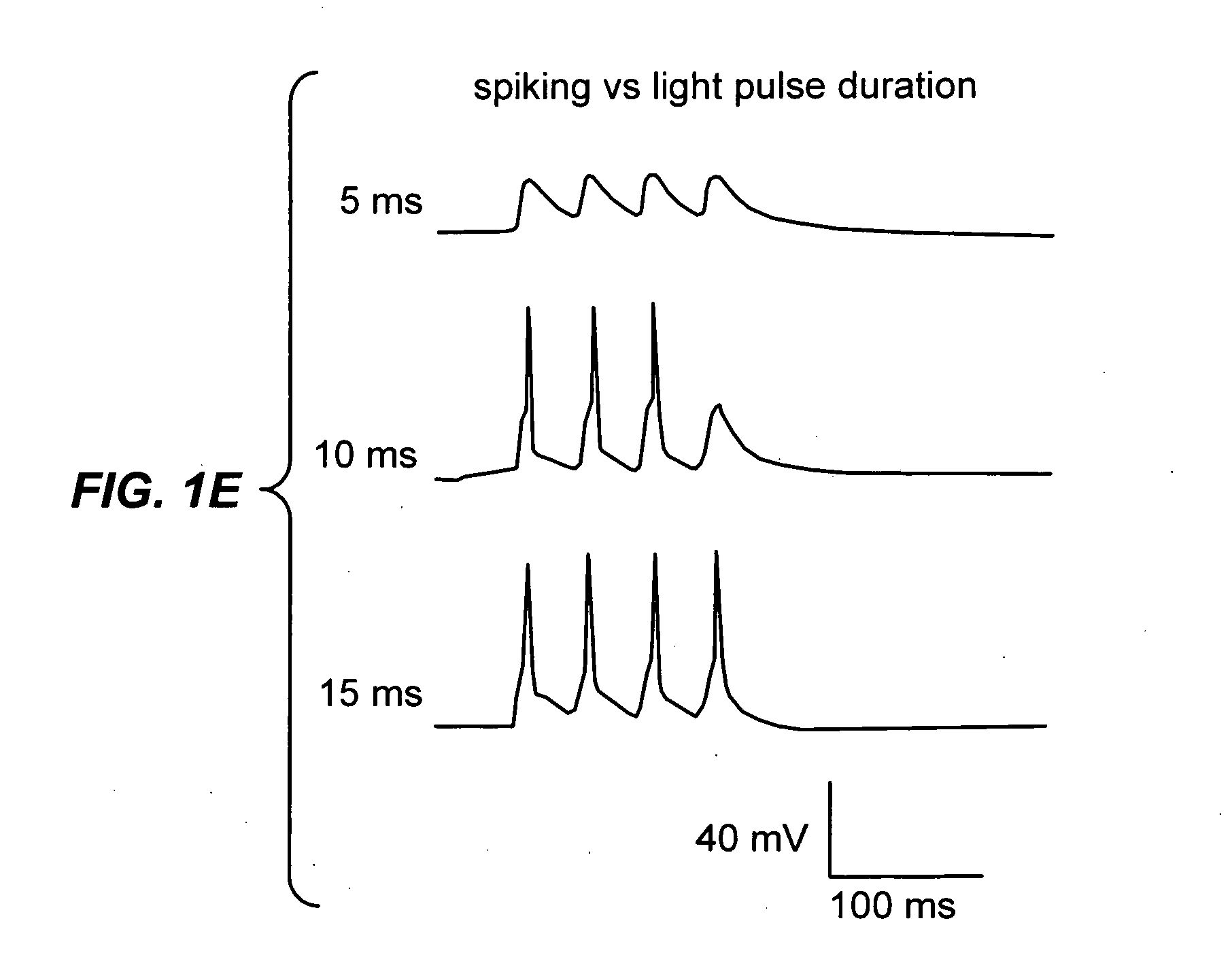
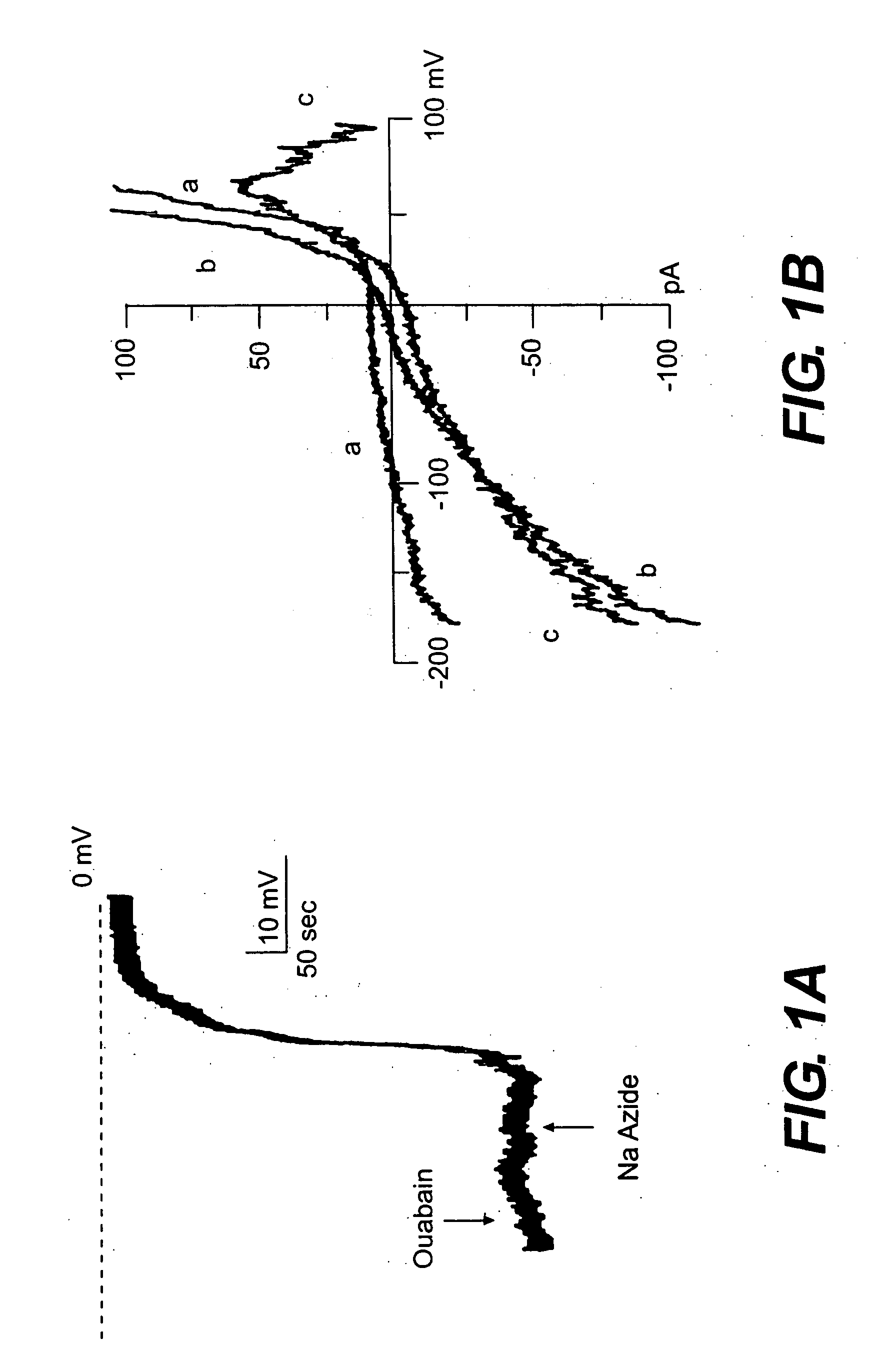
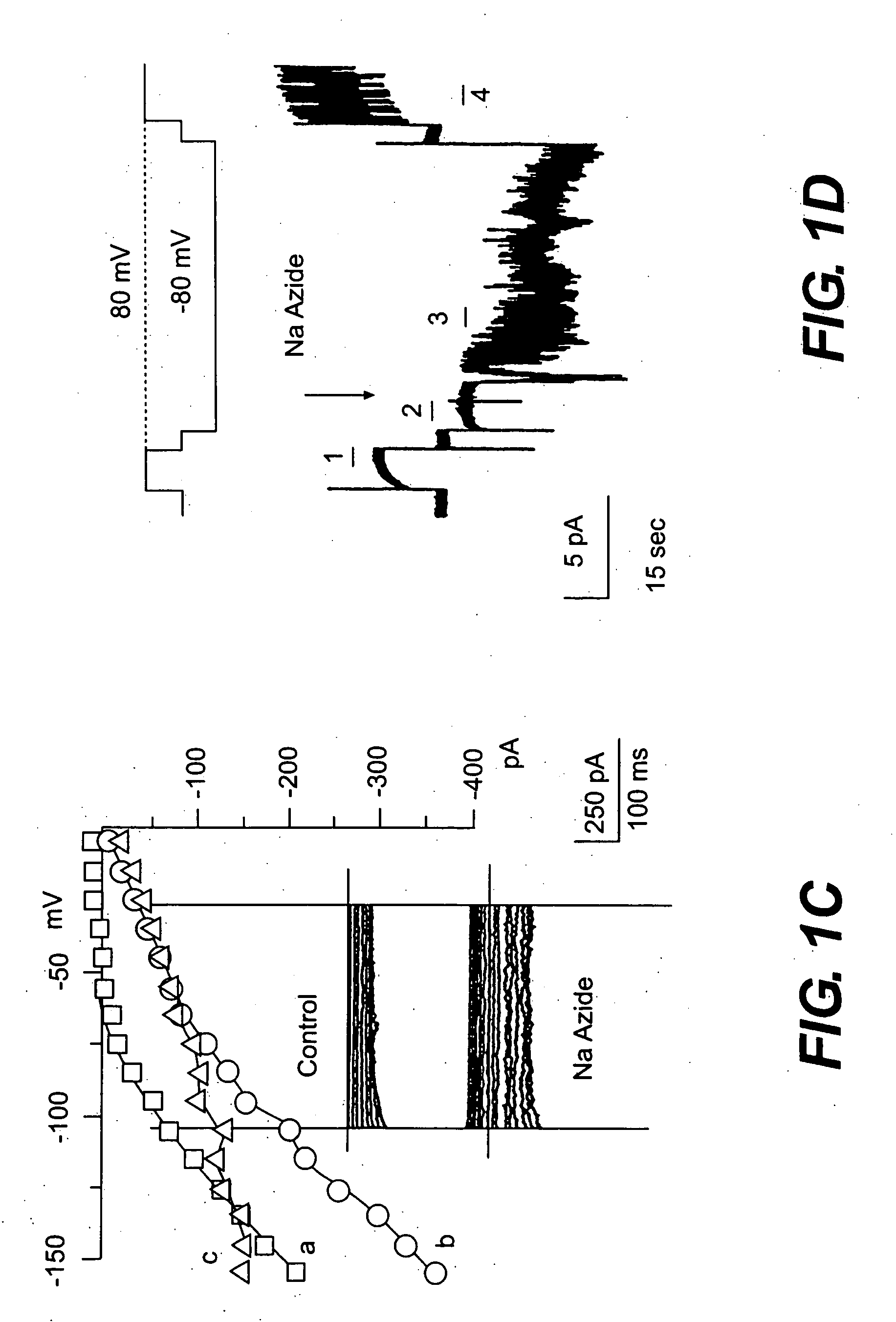
Light-activated cation channel and uses thereof
ActiveUS20070261127A1Improve abilitiesOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderCell membraneExcitable cell
The present invention provides compositions and methods for light-activated cation channel proteins and their uses within cell membranes and subcellular regions. The invention provides for proteins, nucleic acids, vectors and methods for genetically targeted expression of light-activated cation channels to specific cells or defined cell populations. In particular the invention provides millisecond-timescale temporal control of cation channels using moderate light intensities in cells, cell lines, transgenic animals, and humans. The invention provides for optically generating electrical spikes in nerve cells and other excitable cells useful for driving neuronal networks, drug screening, and therapy.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Light-activated cation channel and uses thereof
ActiveUS20070054319A1Improve abilitiesOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderCell membraneExcitable cell
The present invention provides compositions and methods for light-activated cation channel proteins and their uses within cell membranes and subcellular regions. The invention provides for proteins, nucleic acids, vectors and methods for genetically targeted expression of light-activated cation channels to specific cells or defined cell populations. In particular the invention provides millisecond-timescale temporal control of cation channels using moderate light intensities in cells, cell lines, transgenic animals, and humans. The invention provides for optically generating electrical spikes in nerve cells and other excitable cells useful for driving neuronal networks, drug screening, and therapy.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Novel non-selective cation channel in neuronal cells and methods for treating brain swelling
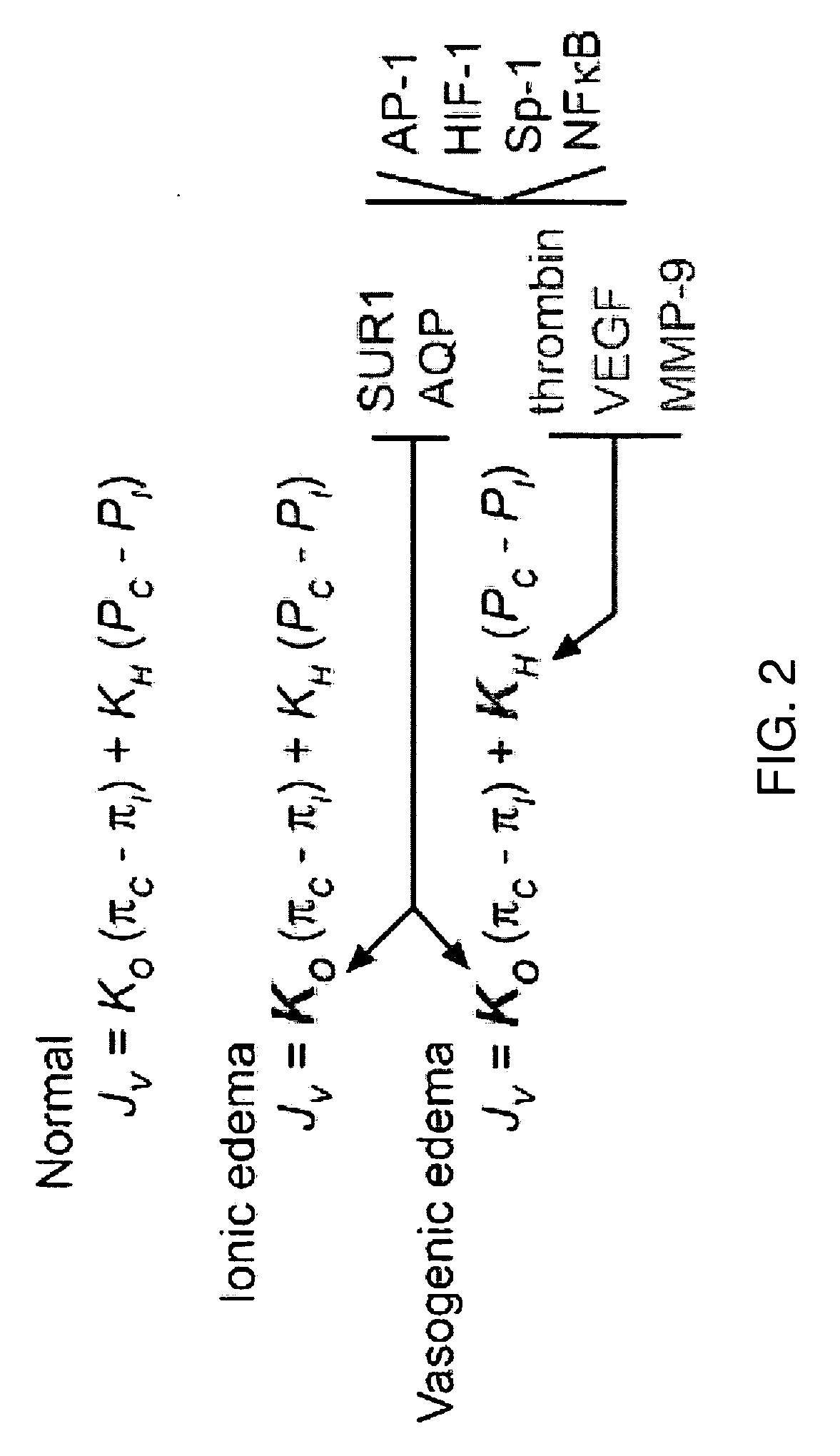
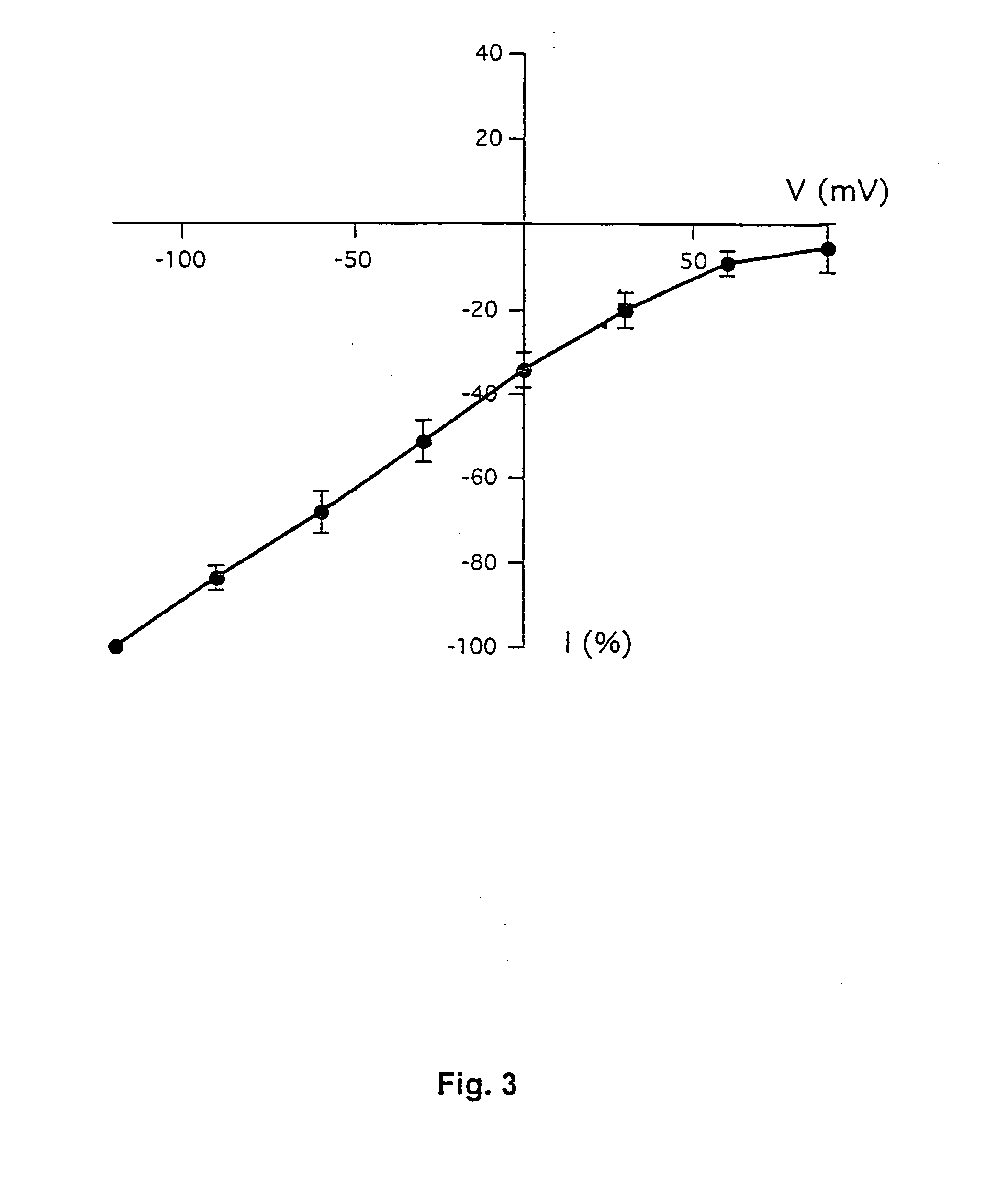
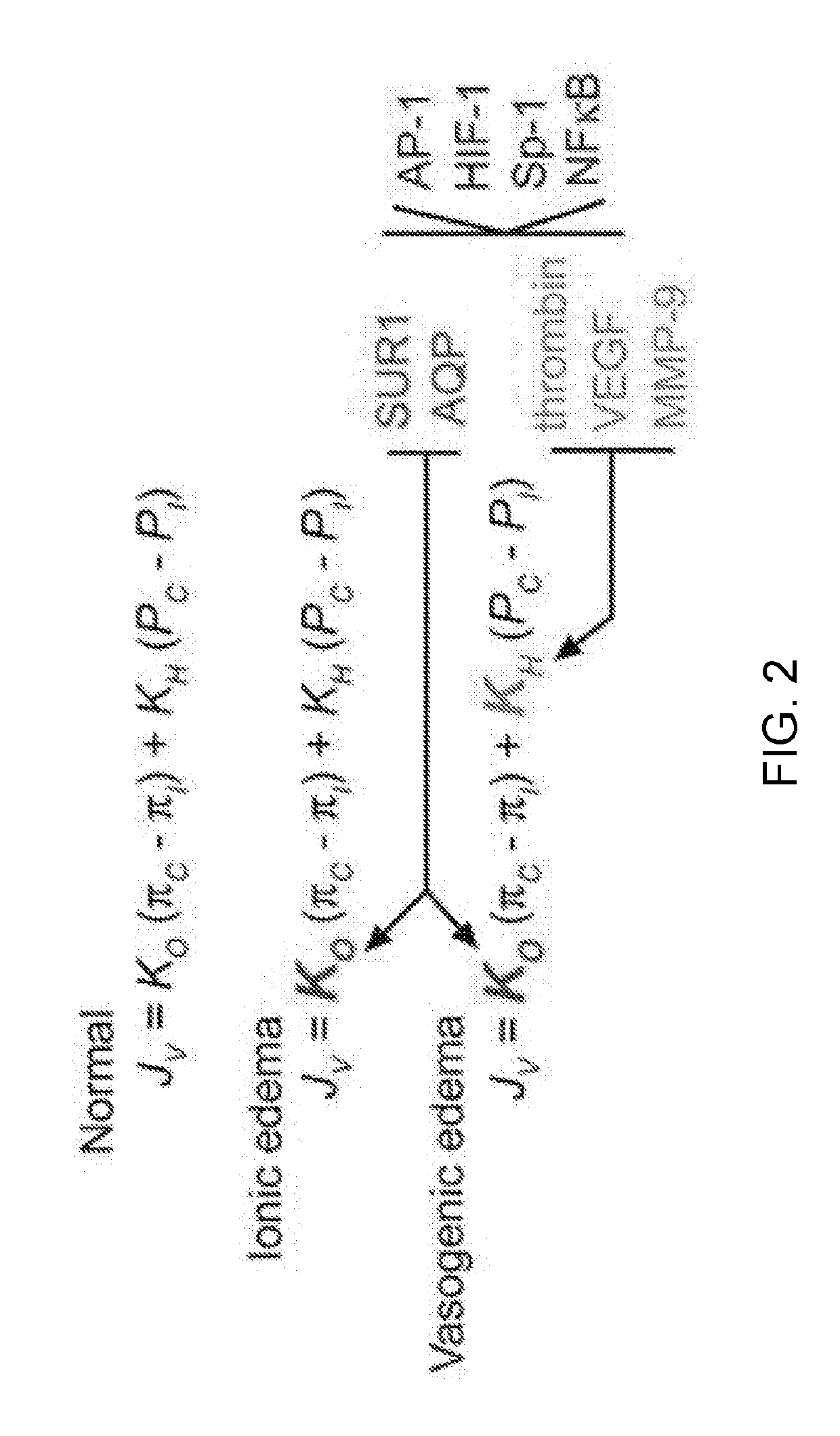
The present invention is directed to therapeutic compounds, treatment methods, and kits affecting the NCCa-ATP channel of neural tissue, including neurons, glia and blood vessels within the nervous system, and methods of using same. The NCCa-ATP channel is newly expressed in neural tissue following injury such as ischemia, and is regulated by the sulfonylurea receptor SUR1, being inhibited by sulfonylurea compounds, e.g., glibenclamide and tolbutamide, and opened by diazoxide. Antagonists of the NCCa-ATP channel, including SUR1 antagonists, are useful in the prevention, diminution, and treatment of injured or diseased neural tissue, including astrocytes, neurons and capillary endothelial cells, that is due to ischemia, tissue trauma, brain swelling and increased tissue pressure, or other forms of brain or spinal cord disease or injury. Agonists of the NCCa-ATP channel may be are useful in the treatment neural tissue where damage or destruction of the tissue, such as a gliotic capsule, is desired.
Owner:U S GOVERNMENT REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS
Nucleic acid molecules and polypeptides for a human cation channel polypeptide
InactiveUS20030096249A1Increase calciumAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTissue cultureRisk strokeNeurological disorder
The present invention relates to novel human nucleic acid molecules encoding novel human cation channels, and proteins and polypeptides encoded by such nucleic acid molecules. More specifically, the nucleic acid molecules of the invention include the novel human gene designated HBMYCNG. The proteins and polypeptides of the invention represent a novel cation channel that may be therapeutically valuable targets for drug delivery in the treatment of human diseases which involve calcium, sodium, potassium or other ionic homeostatic dysfunction, such as central nervous system (CNS) disorders, e.g., stroke, anxiety and depression, or degenerative neurological disorders such as Alzheimer's disease or Parkinson's disease, or other disorders such as cardiac disorders, e.g., arrhythmia, diabetes, chronic pain, hypercalcemia, hypocalcemia, hypercalciuria, hypocalciuria, or ion disorders associated with immunological disorders, gasto-intestinal (GI) tract disorders, or renal or liver disease.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Antagonists of a non-selective cation channel in neural cells
InactiveUS20100092469A1Reduce mortalityReduces stroke sizeBiocideNervous disorderDiseaseNervous system
The present invention is directed to a combination of therapeutic compounds and treatment methods and kits using the combination. In particular, one of the combination affects the NCca-ATP channel of neural tissue, including neurons, glia and blood vessels within the nervous system. Exemplary SUR1 and / or TRPM4 antagonists that inhibit the NCca-ATP channel may be employed in the combination. The combination therapy also employs one or more of a non-selective cation channel blocker and / or an antagonist of VEFG, NOS, MMP, or thrombin. Exemplary indications for the combination therapy includes the prevention, diminution, and / or treatment of injured or diseased neural tissue, including astrocytes, neurons and capillary endothelial cells, that is due to ischemia, tissue trauma, brain swelling and increased tissue pressure, or other forms of brain or spinal cord disease or injury, for example. In other embodiments, there are methods and compositions directed to antagonists of TRPM4, including at least for therapeutic treatment of traumatic brain injury, cerebral ischemia, central nervous system (CNS) damage, peripheral nervous system (PNS) damage, cerebral hypoxia, or edema, for example.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS
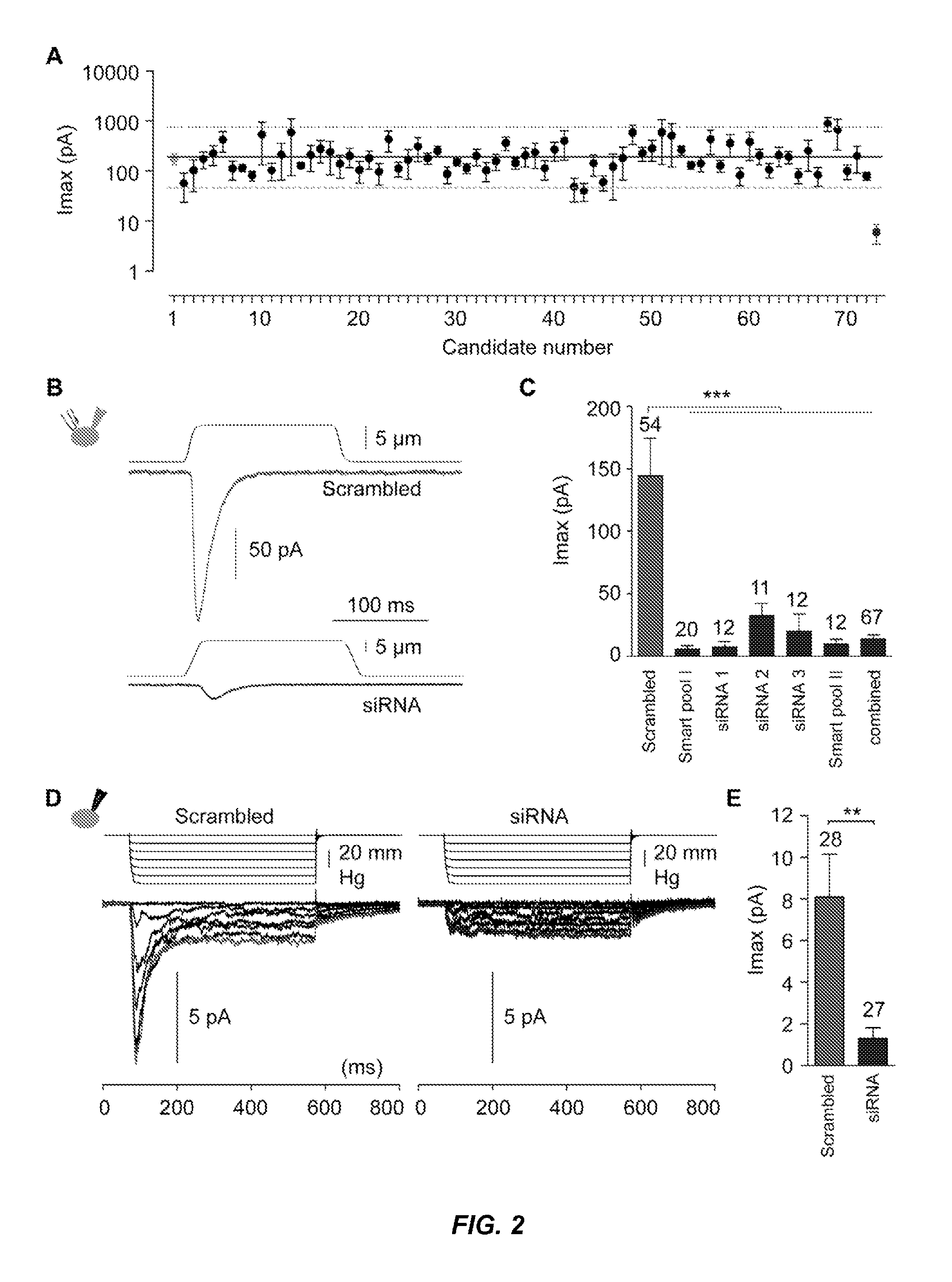
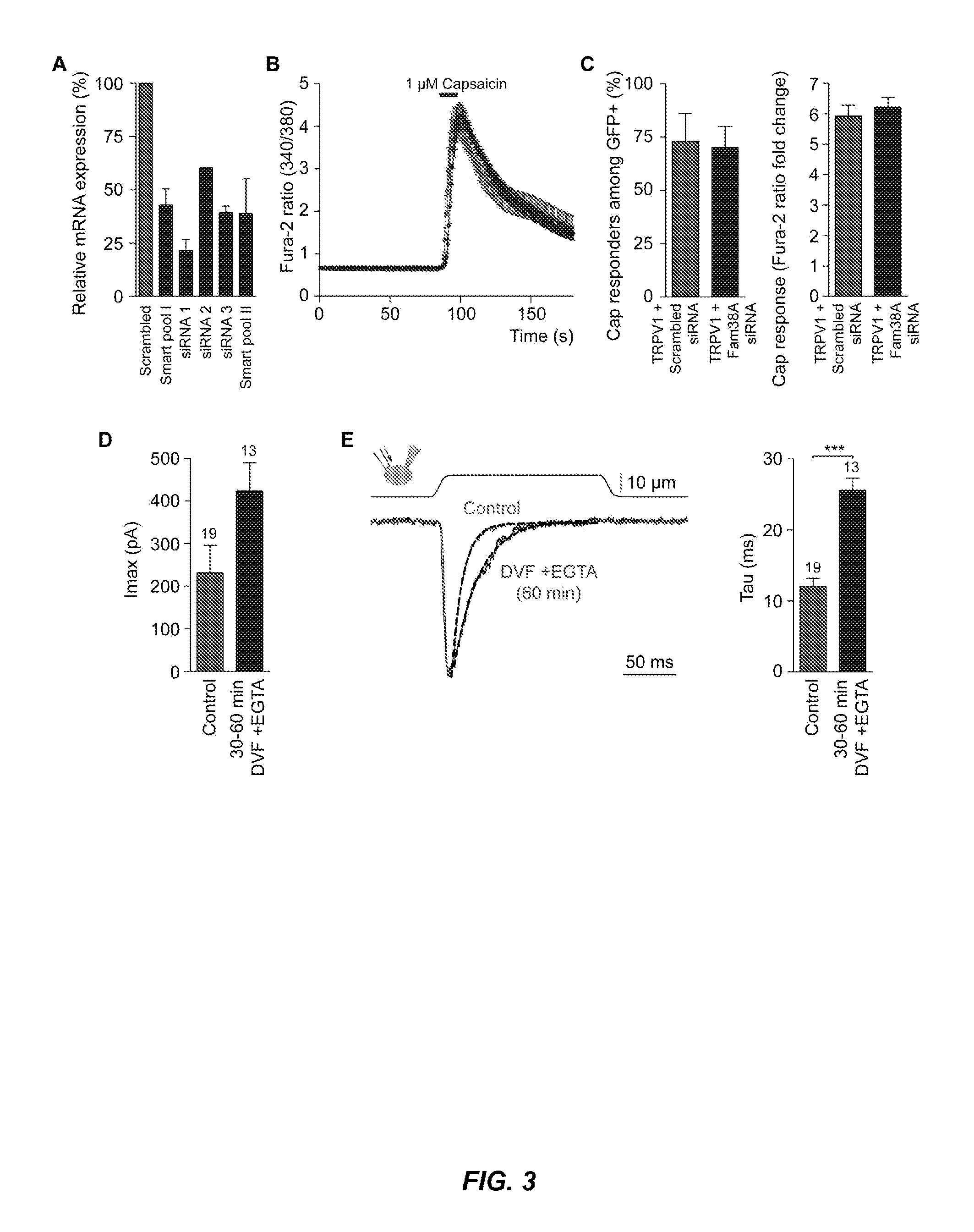
Assays for screening compounds which interact with cation channel proteins, mutant prokaryotic cation channel proteins, and uses thereof
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
Assays for screening compounds which interact with cation channel proteins, mutant prokaryotic cation channel proteins, and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050272093A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsIon Channel ProteinCation channels of sperm
Owner:MACKINNON RODERICK
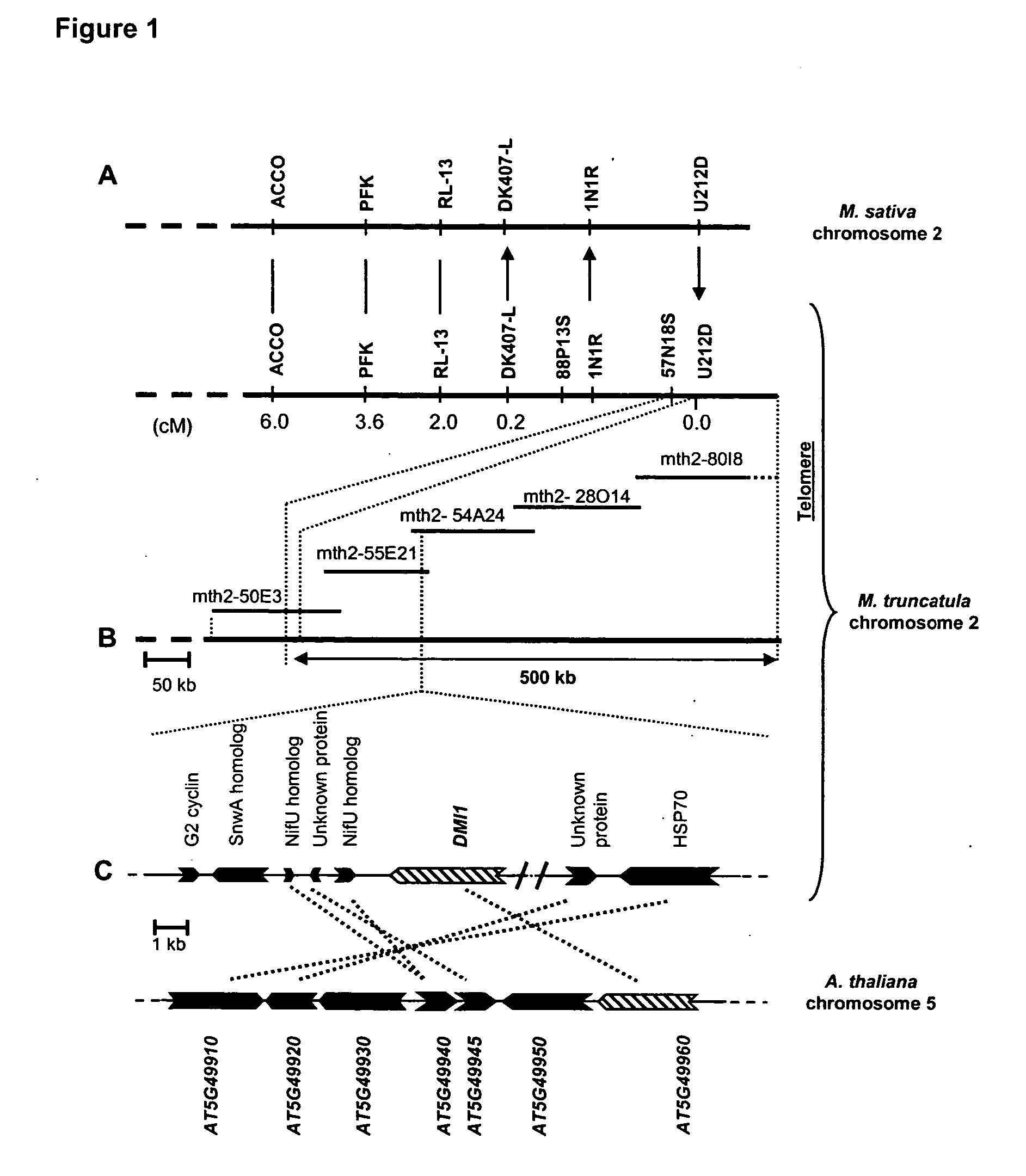
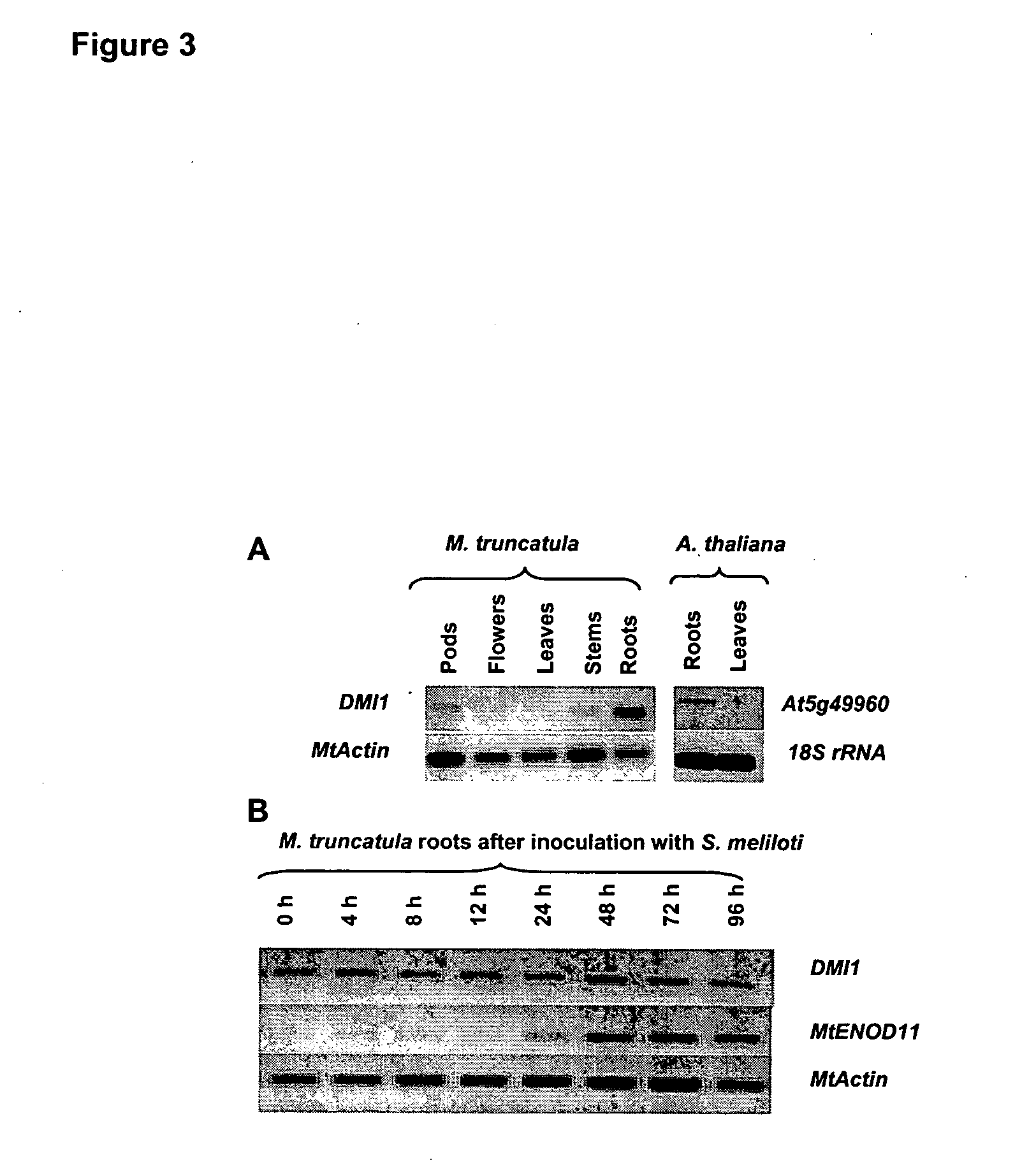
The DMI1 gene encodes a protein that is required for the early steps of bacterial and fungal symbioses
InactiveUS20050081262A1Enhanced nitrogenEnhanced phosphorous acquisitionBryophytesSugar derivativesBacteroidesPlant nodule
Mycorrhizal and rhizobial associations represent the two most important symbiotic relationships between higher plants and microorganisms, providing access to otherwise limiting supplies of phosphate and nitrogen, respectively. Although many higher plants are able to establish a symbiotic relationship with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, legumes are unusual among plants because they also form associations with nitrogen fixing soil bacteria called rhizobia. This symbiosis requires the production of bacterial signals, “Nod factors” that trigger several key developmental responses in the host plant (Dénarié et al., 1996). The DMI1 gene of the model legume M. truncatula plays a major role both in the early steps of Nod factor signaling and in the establishment of mycorrhizal symbiosis. Dmi1 mutants do not exhibit many of the early responses to Nod factors and are incapable of forming nitrogen fixing root nodules. Here we describe the cloning and preliminary characterization of DMI1. The DMI1 gene encodes a novel protein with low global similarity to ligand-gated cation channels of archaea. The protein is highly conserved in angiosperms and ancestral to land plants. Interestingly a putative A. thaliana DMI1 orthologous gene is expressed in roots. As A. thaliana is unable to establish a mycorrhizal symbiosis, this finding suggests that DMI1 may also exhibit a function that is independent of symbiotic interactions.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL DE LA RECHERCHE AGRONOMIQUE +1
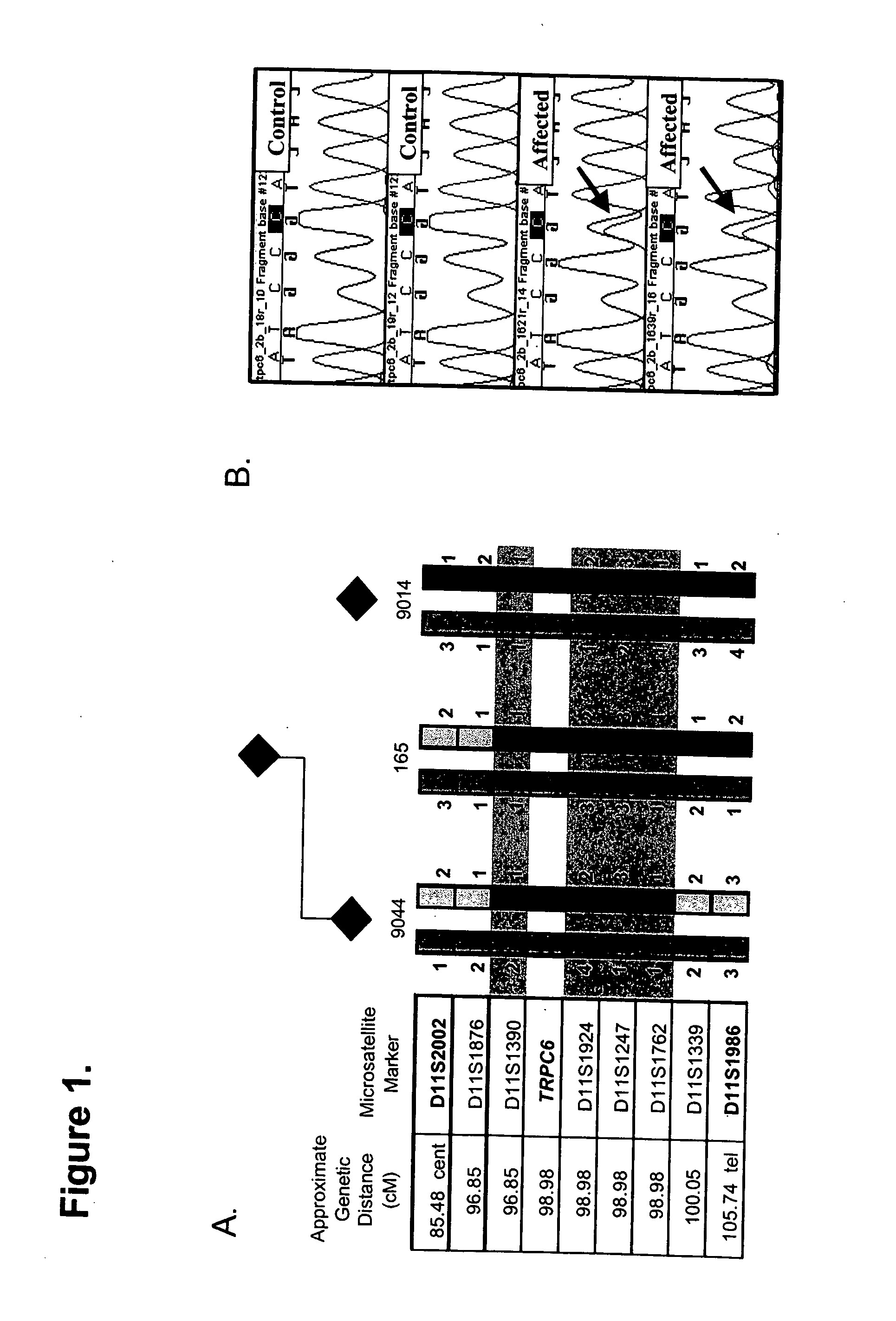
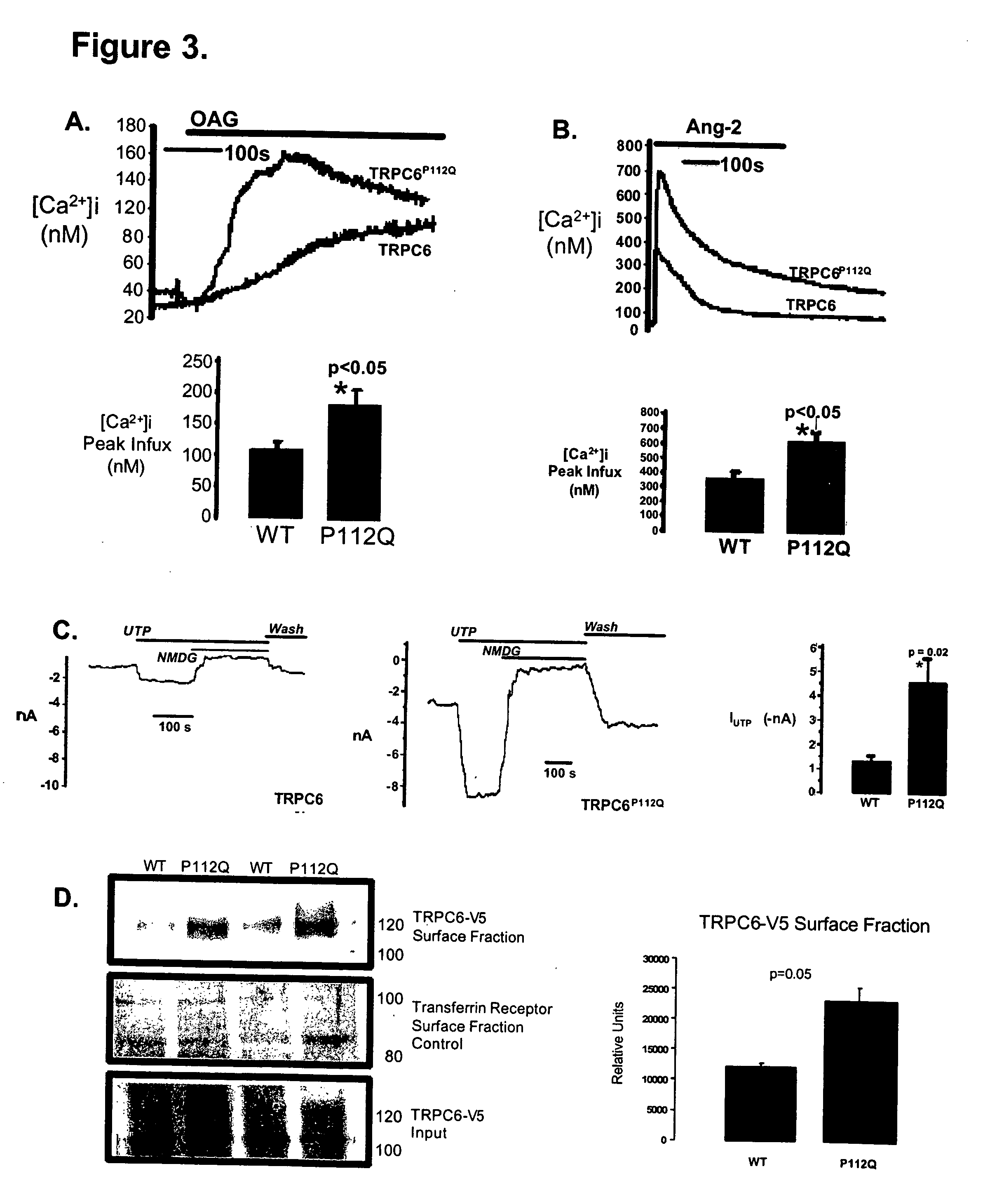
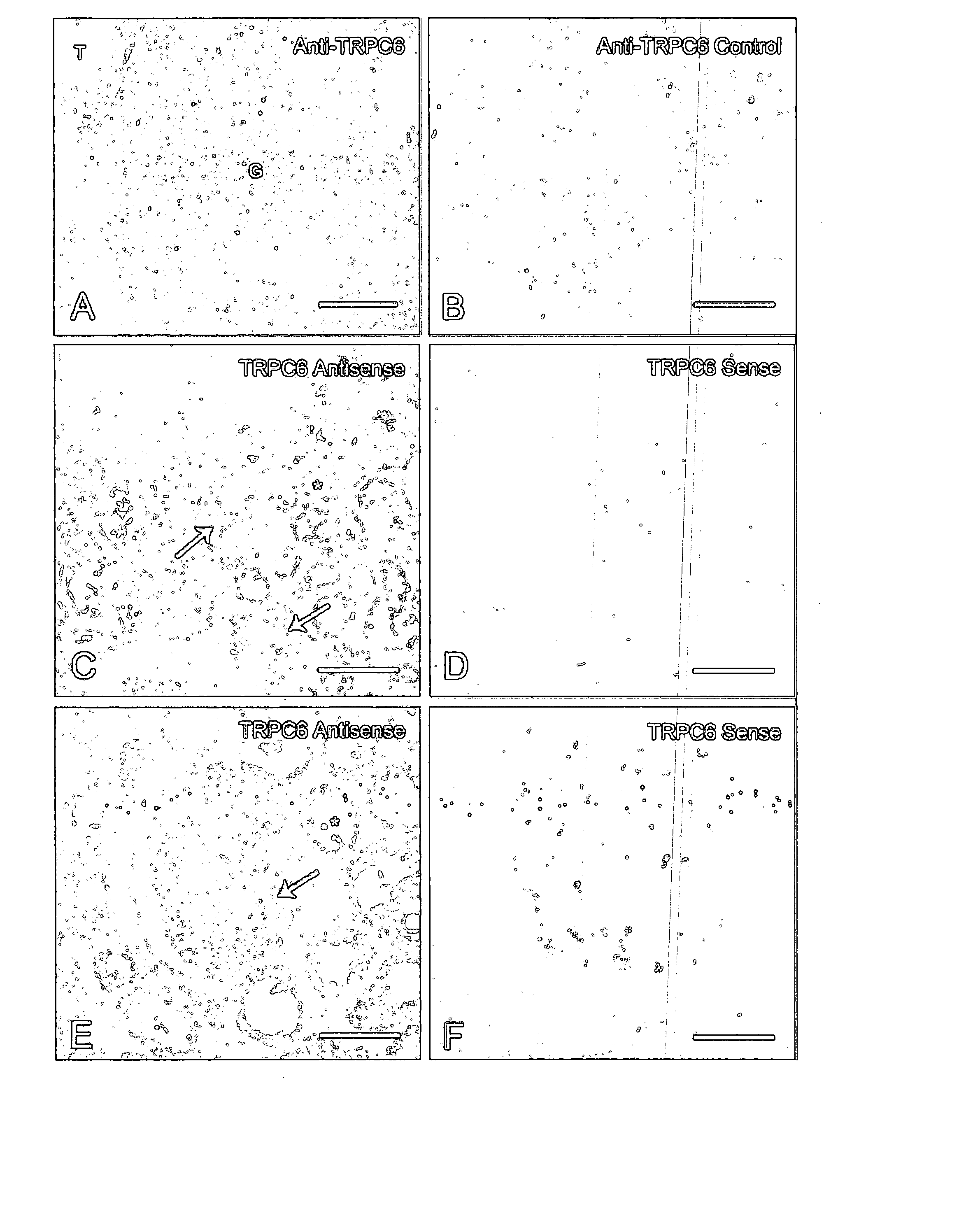
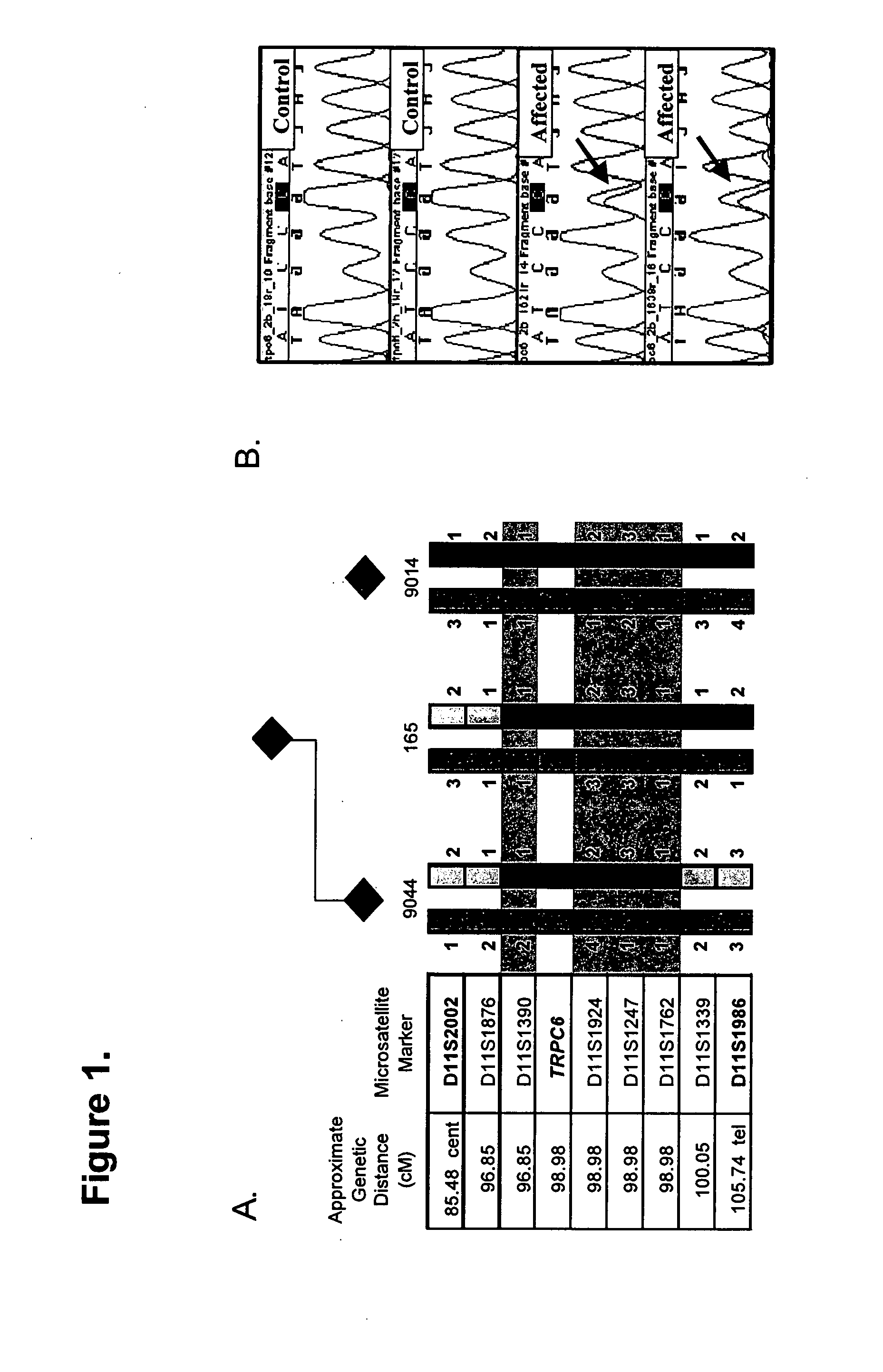
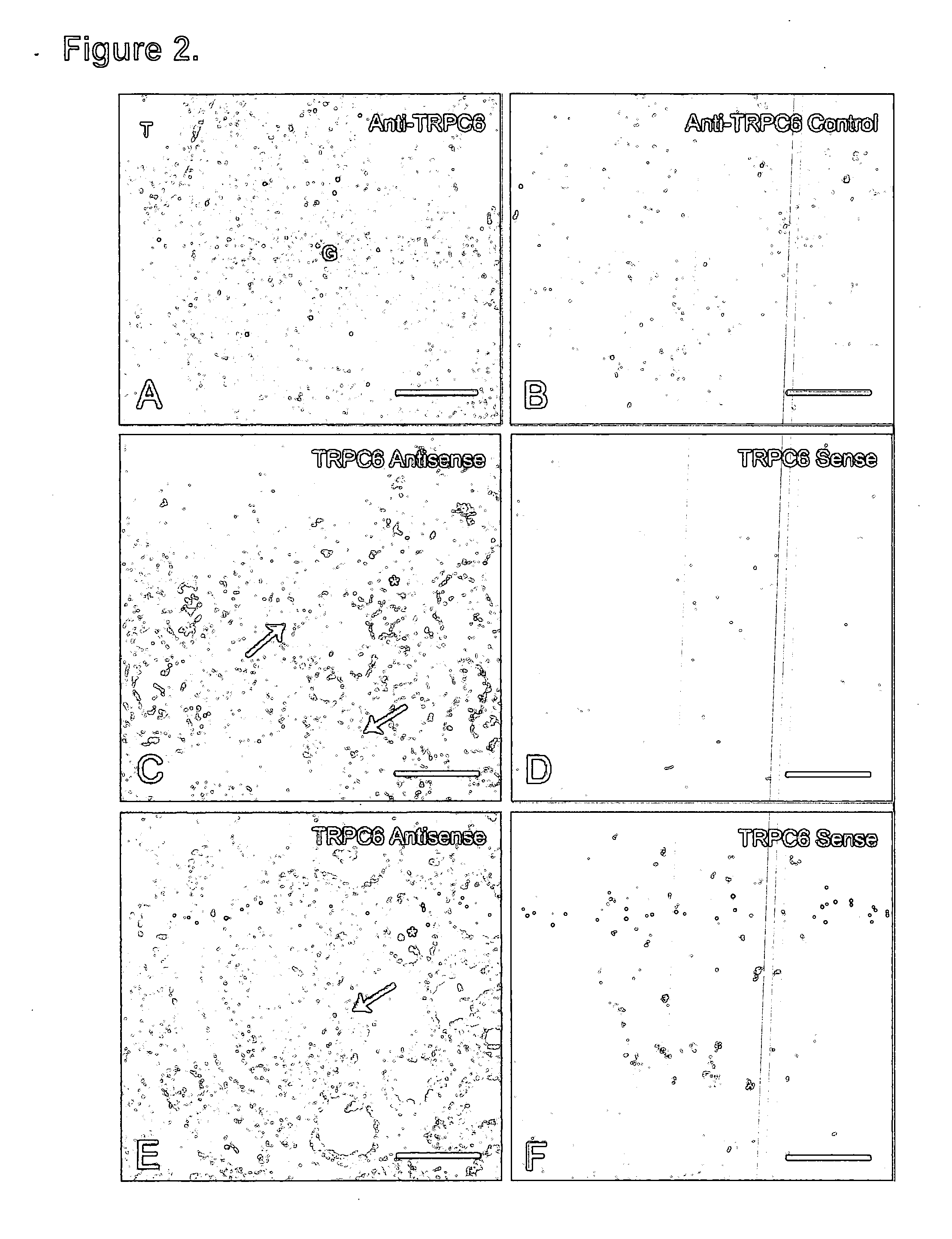
TRPC6 involved in glomerulonephritis
InactiveUS20060257500A1Calcium ion influx is thereby reducedCompound screeningBiocideEtiologyDisease
Focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) is a kidney disorder of unknown etiology and up to 20% of patients on dialysis have this diagnosis. A large family with hereditary FSGS carries a missense mutation in the TRPC6 gene on chromosome 11q, encoding the ion channel protein Transient Receptor Potential Cation Channel 6. The missense mutation is a P112Q substitution, which occurs in a highly conserved region of the protein, enhances TRPC6-mediated calcium signals in response to agonists such as angiotensin II, and alters the intracellular distribution of TRPC6 protein. Previous work has emphasized the importance of cytoskeletal and structural proteins in proteinuric kidney diseases. Our findings suggest a novel mechanism for glomerular disease pathogenesis.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
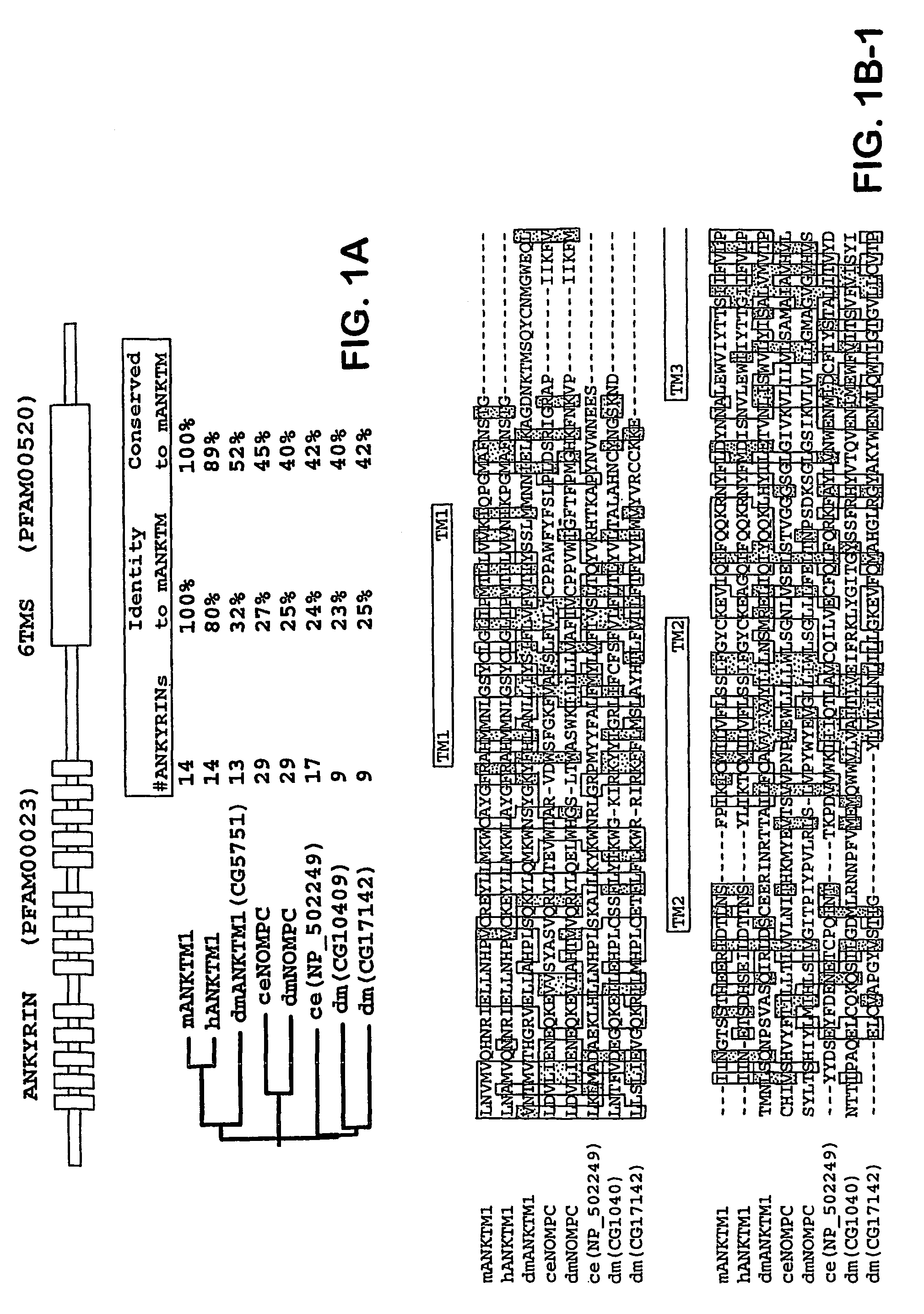
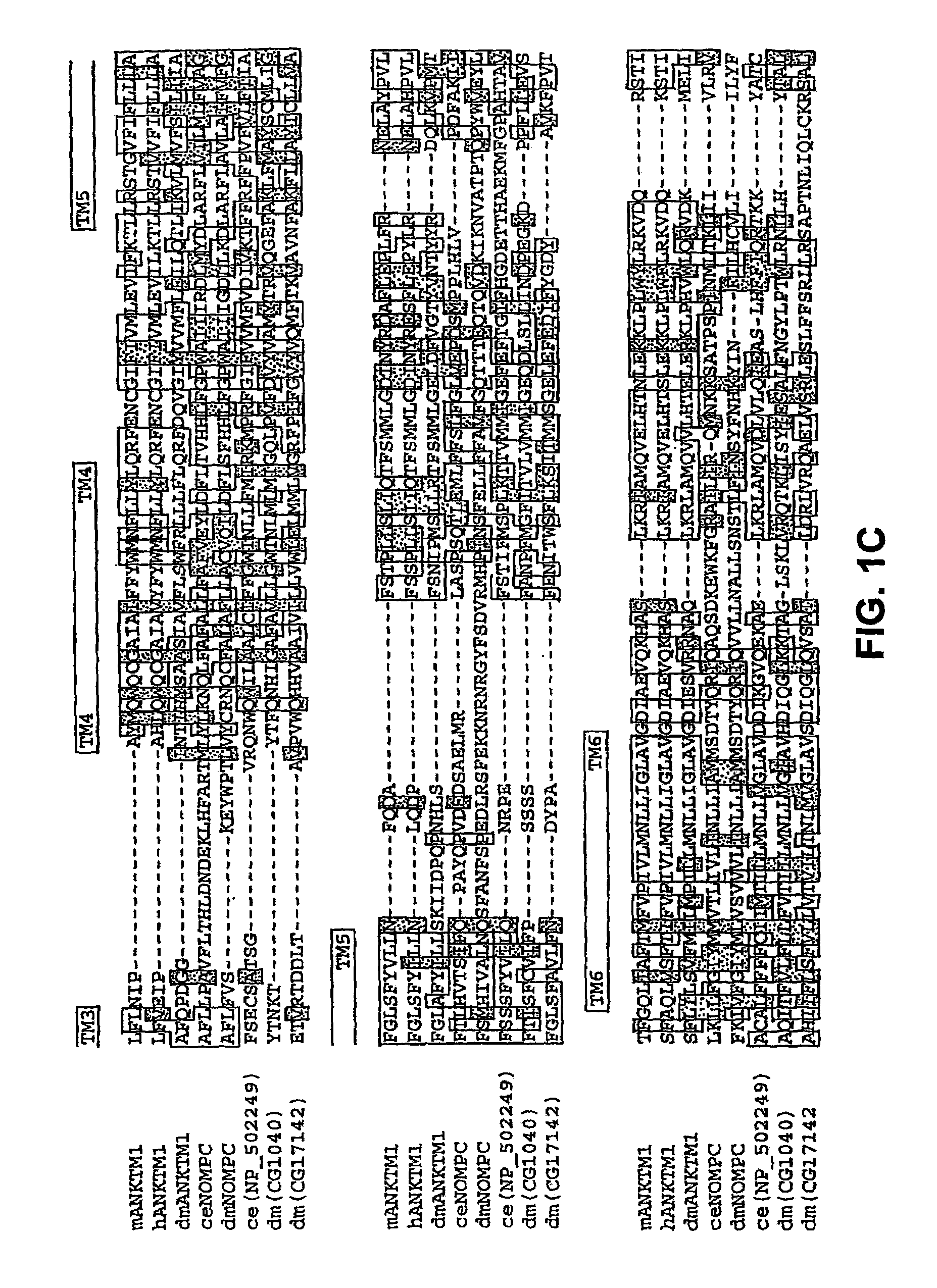
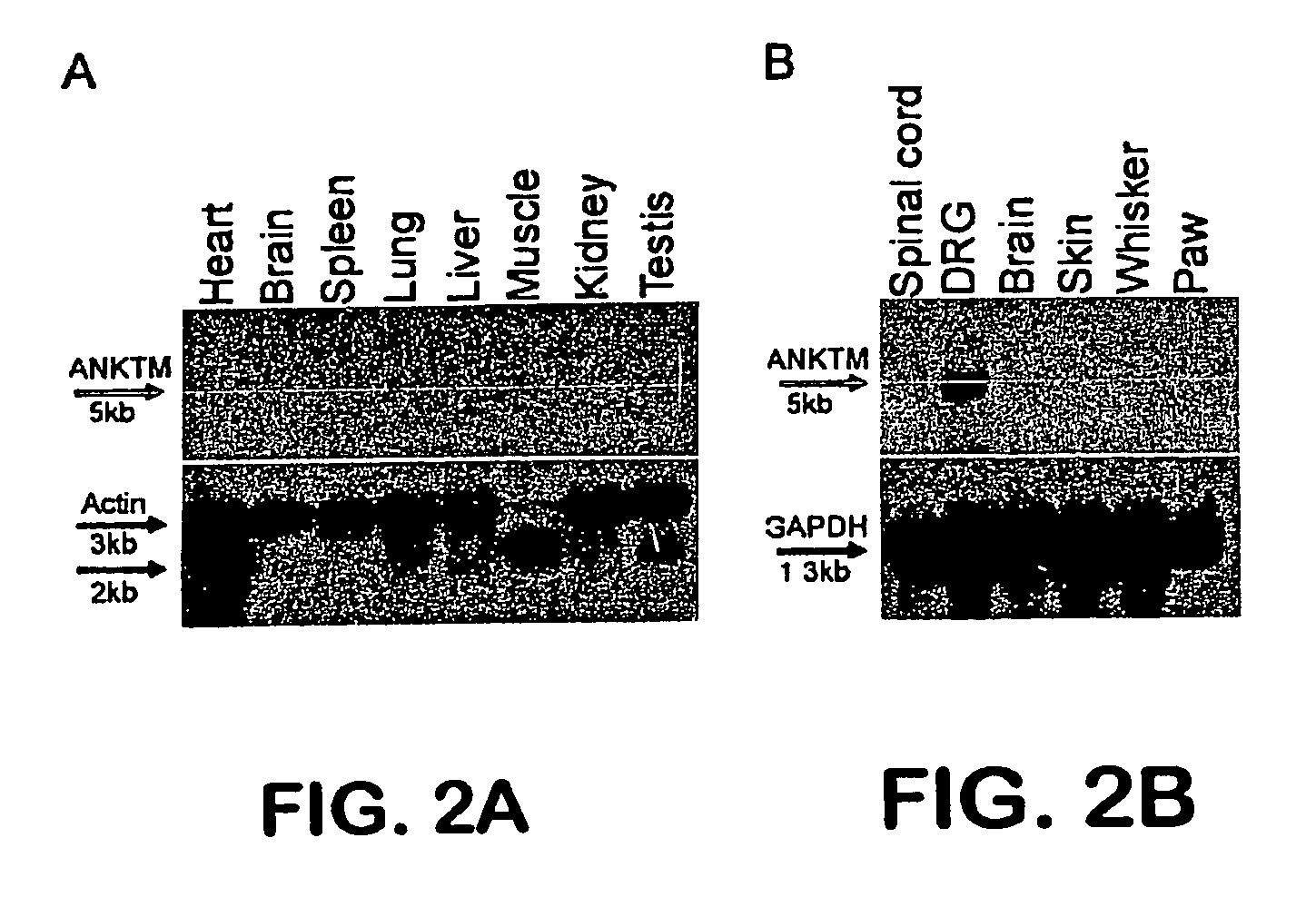
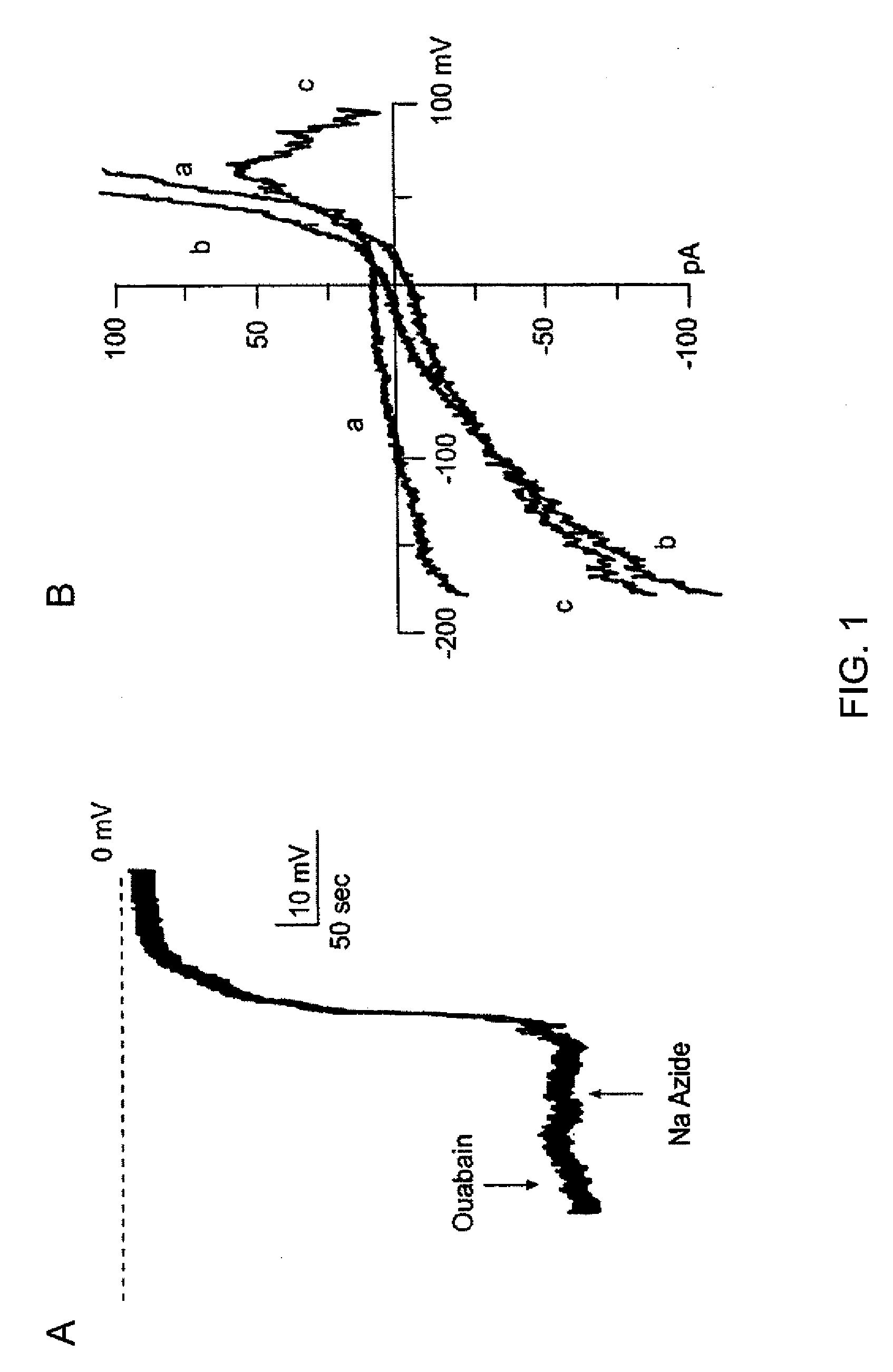
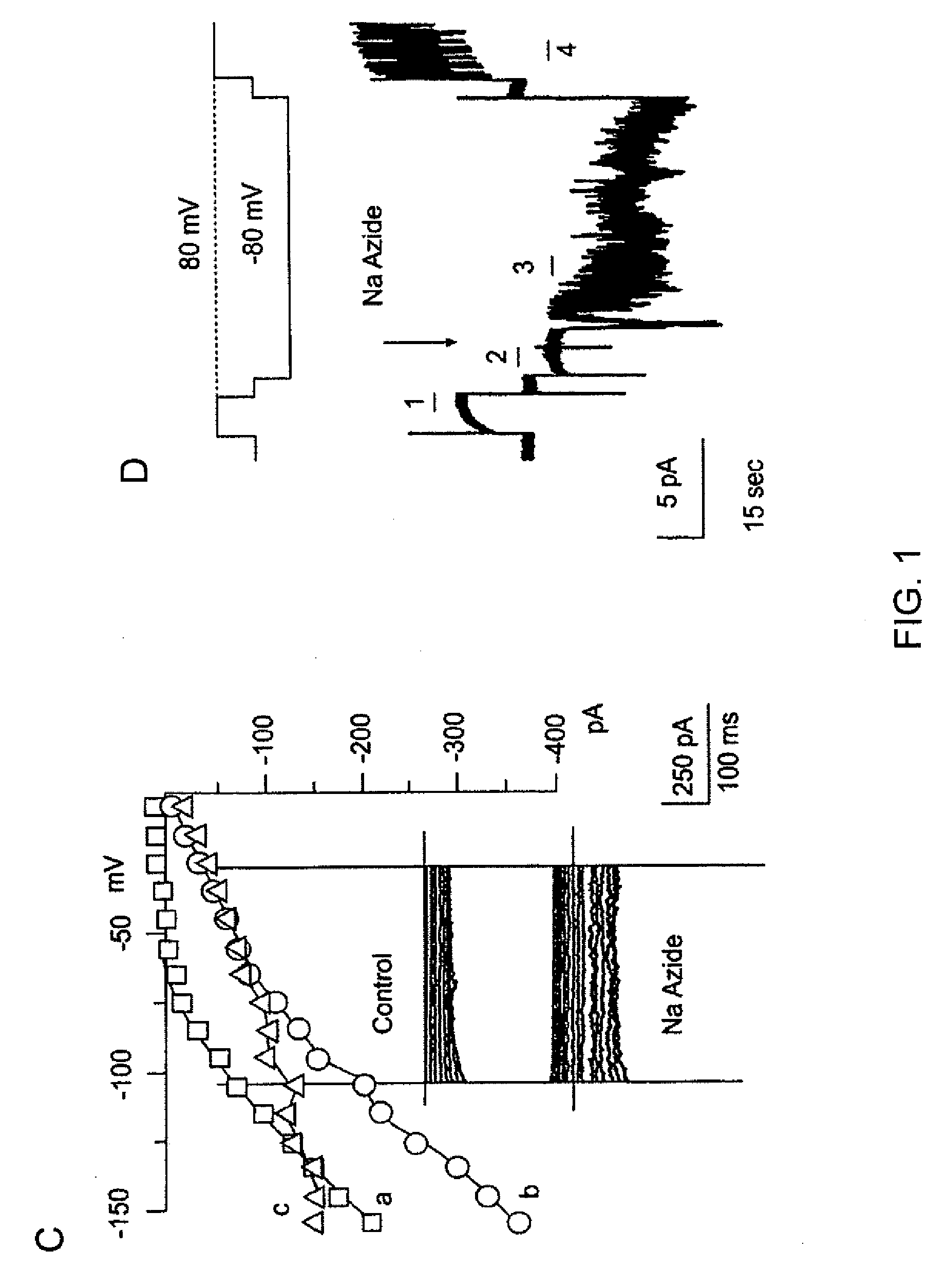
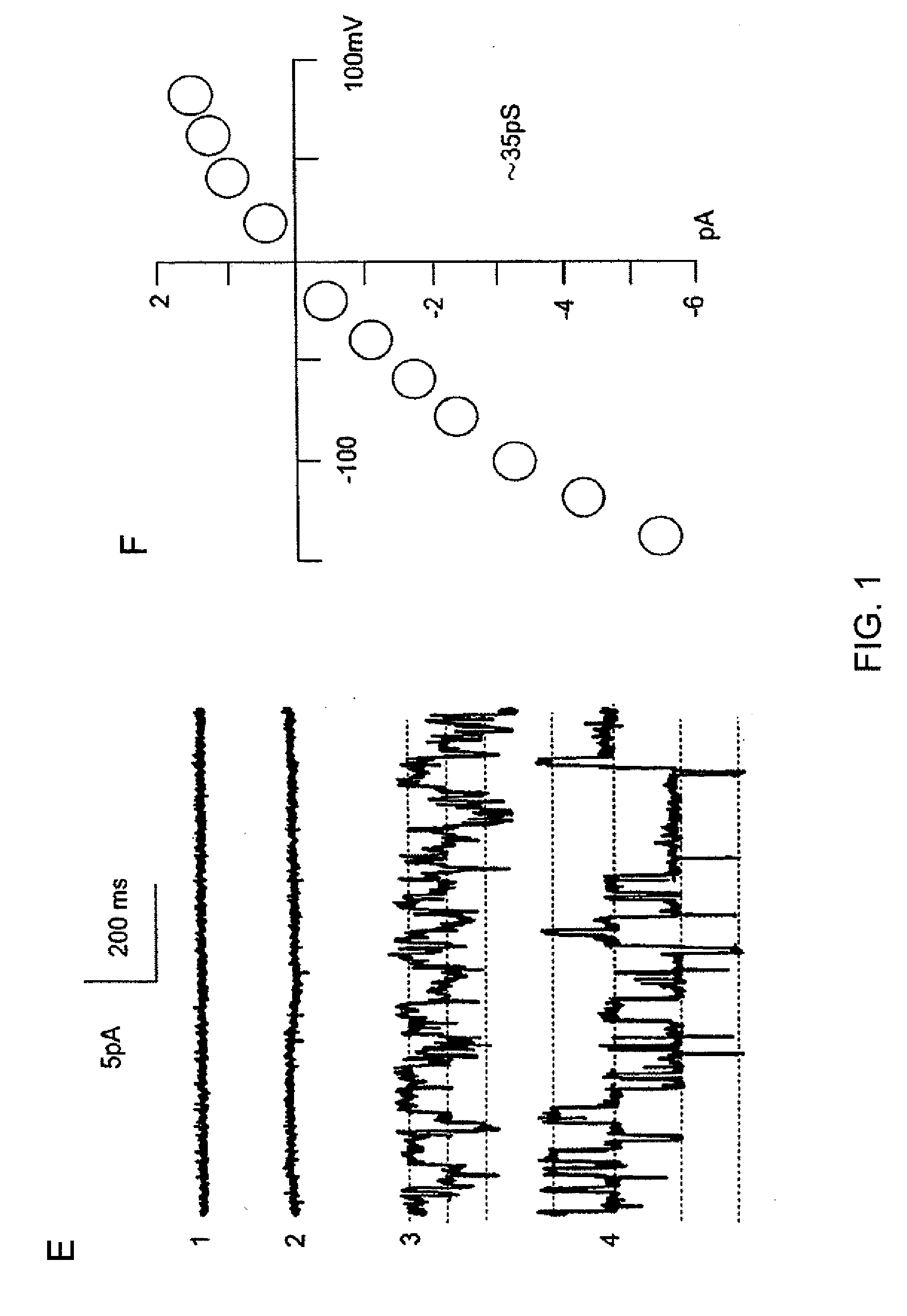
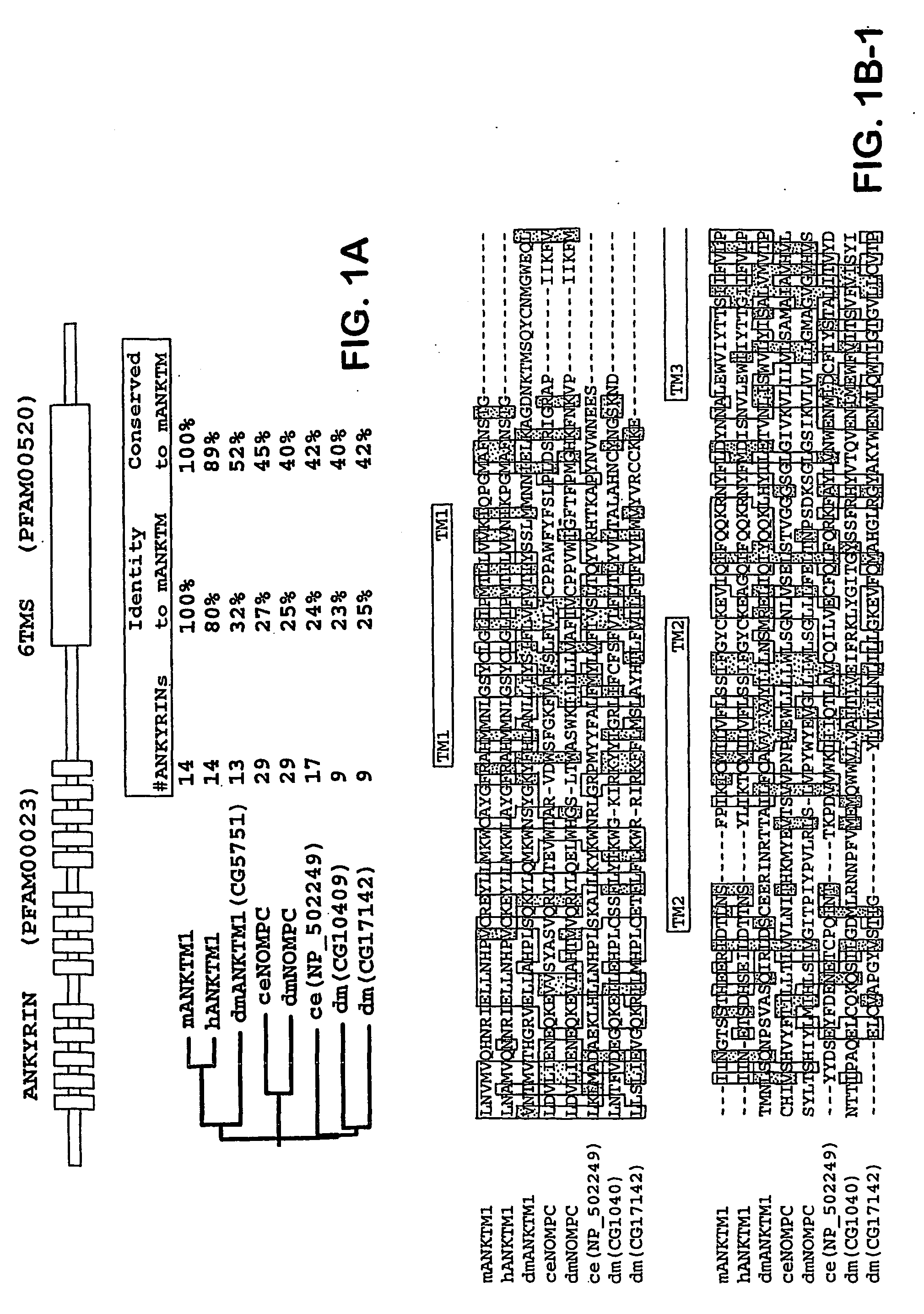
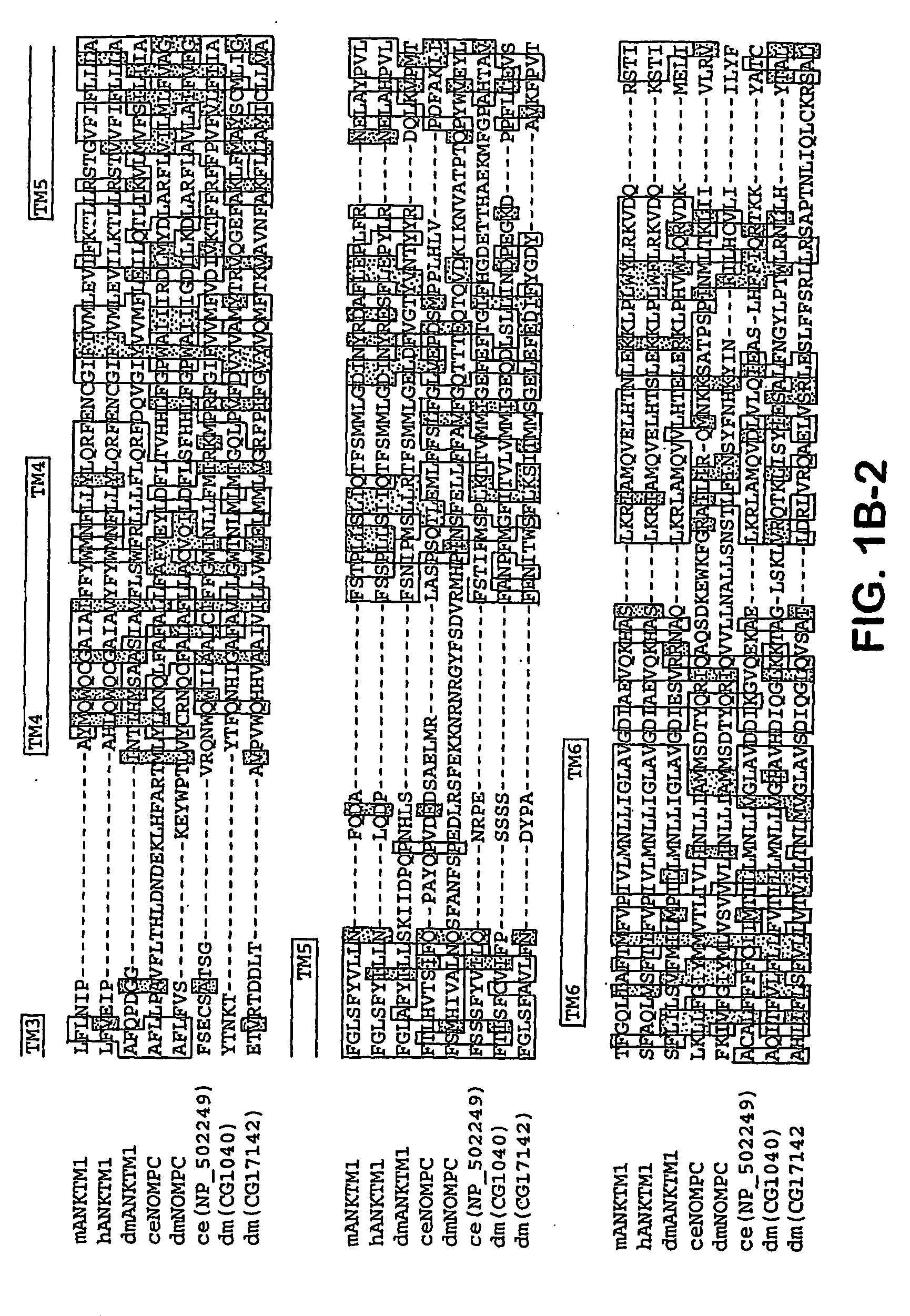
ANKTM1, a cold-activated TRP-like channel expressed in nociceptive neurons
The methods and compositions of the invention are based on a method for measuring nociceptive responses in vertebrates, including humans and other mammals utilizing a newly discovered thermoreceptor belonging to the Transient Receptor Potential (TRP) family of non-selective cation channels that participates in thermosensation and pain. This receptor, designated ANKTMI, is associated with nociceptive pain, such as hyperalgesia. Accordingly, the invention provides isolated polypeptides and polynucleotides associated with nociception as well as methods for identifying or screening agents that modulate nociception.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG +1
Novel non-selective cation channel in neuronal cells and method for treating brain swelling
The present invention is directed to therapeutic compounds, treatment methods, and kits affecting the NCCa-ATP channel of neural tissue, including neurons, glia and blood vessels within the nervous system, and methods of using same. The NCCa-ATP channel is newly expressed in neural tissue following injury such as ischemia, and is regulated by the sulfonylurea receptor SUR1, being inhibited by sulfonylurea compounds, e.g., glibenclamide and tolbutamide, and opened by diazoxide. Antagonists of the NCCa-ATP channel, including SUR1 antagonists, are useful in the prevention, diminution, and treatment of injured or diseased neural tissue, including astrocytes, neurons and capillary endothelial cells, that is due to ischemia, tissue trauma, brain swelling and increased tissue pressure, or other forms of brain or spinal cord disease or injury. Agonists of the NCCa-ATP channel may be are useful in the treatment neural tissue where damage or destruction of the tissue, such as a gliotic capsule, is desired.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Anktm1, a cold-activated trp-like channel expressed in nociceptive neurons
InactiveUS20060142547A1Reducing nociceptive painReduce painNervous disorderBacteriaThermoreceptorMammal
The methods and compositions of the invention are based on a method for measuring nociceptive responses in vertebrates, including humans and other mammals utilizing a newly discovered thermoreceptor belonging to the Transient Receptor Potential (TRP) family of non-selective cation channels that participates in thermosensation and pain. This receptor, designated ANKTMI, is associated with nociceptive pain, such as hyperalgesia. Accordingly, the invention provides isolated polypeptides and polynucleotides associated with nociception as well as methods for identifying or screening agents that modulate nociception.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG +1
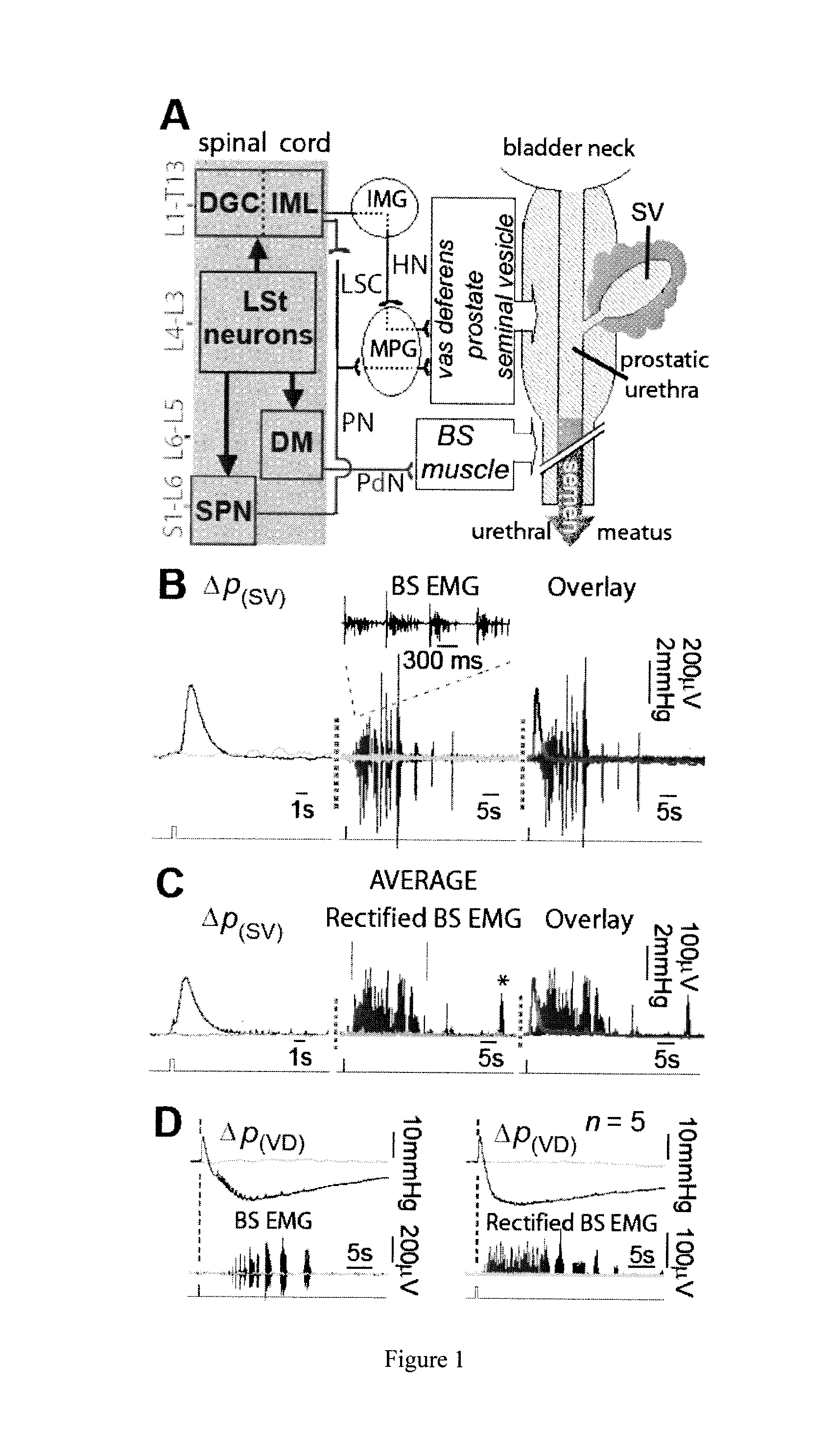
Method for Restoring an Ejaculatory Failure
The present invention relates to a method for eliciting ejaculation in a male individual, comprising delivering one or more stimulation pulses to lumbar spinothalamic (LSt) cells via a light stimulus, wherein said LSt cells express a light-activated cation channel protein.
Owner:PELVIPHARM
Functional composite membrane capable of recognizing alkali metal ions and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102068926AIncrease evaporation rateSemi-permeable membranesWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisCation channels of spermAlkali metal
The invention belongs to the field of functional polymer materials, in particular to a functional composite membrane capable of recognizing alkali metal ions and a preparation method thereof. The functional composite membrane provided by the invention is prepared by coating a carbamido-containing silicon compound capable of carrying out molecular self-assembly to form an ionic channel on the surface of a microporous planar supporting layer or blending a carbamido-containing silicon compound capable of carrying out molecular self-assembly to form an ionic channel with a polymer forming a microporous supporting layer. The compact-surface composite membrane comprises the microporous planar supporting layer and a surface-coated compact layer of the carbamido-containing silicon compound or comprises the compact layer and the microporous supporting layer, wherein the compact layer with the carbamido-containing silicon compound on the surface is prepared by blending the carbamido-containing silicon compound and the polymer forming the microporous supporting layer. The compact layer of the carbamido-containing silicon compound contains crosslinked siloxane network cation channels so as torealize the recognition and the transmission of the functional membrane to alkali metal ions.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Mechanically-activated cation channels
InactiveCN103249878AInhibition of endogenous MA currentsCompound screeningNervous disorderActive agentBiochemistry
Owner:IRM有限责任公司,特拉华有限责任公司 +1
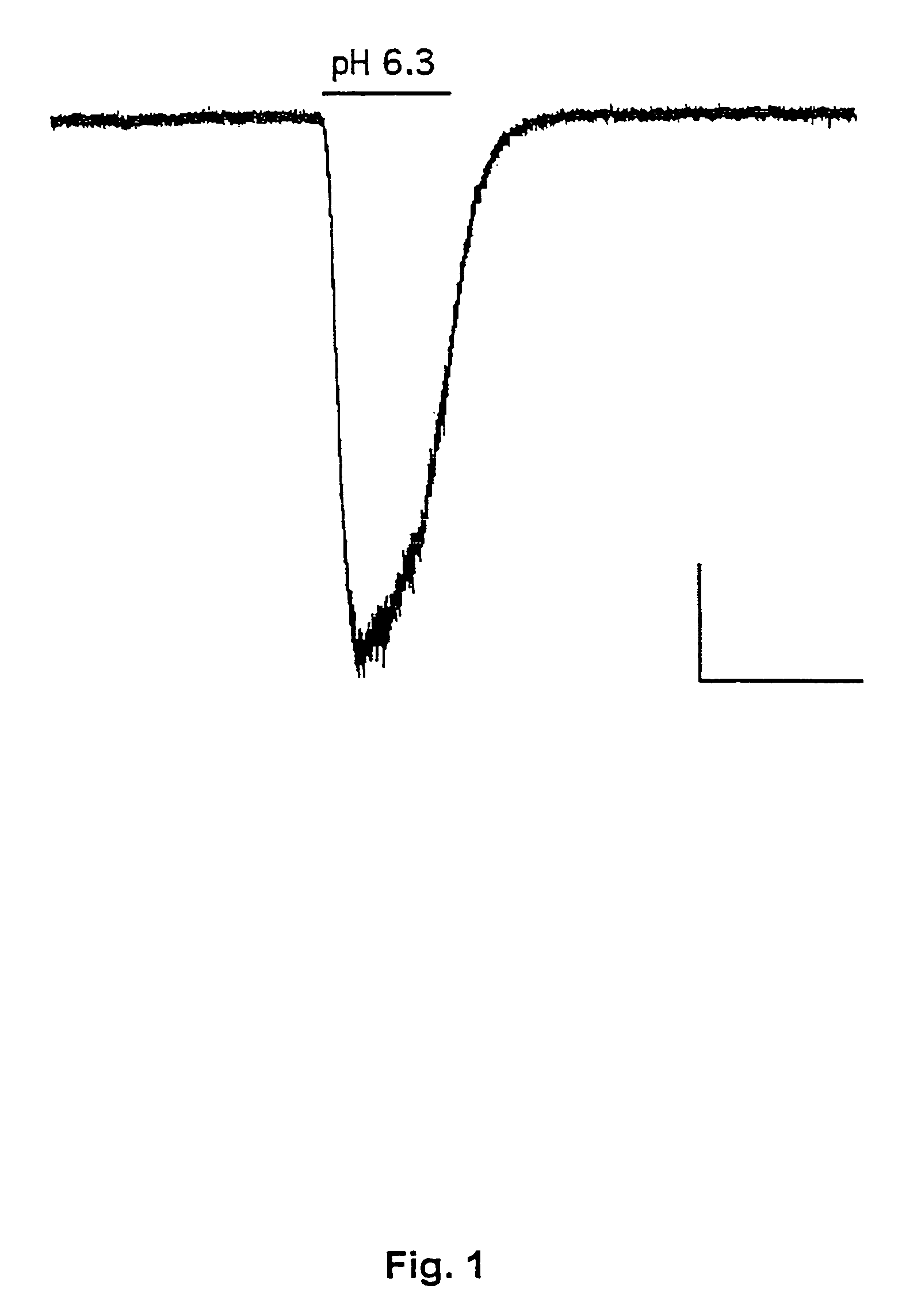
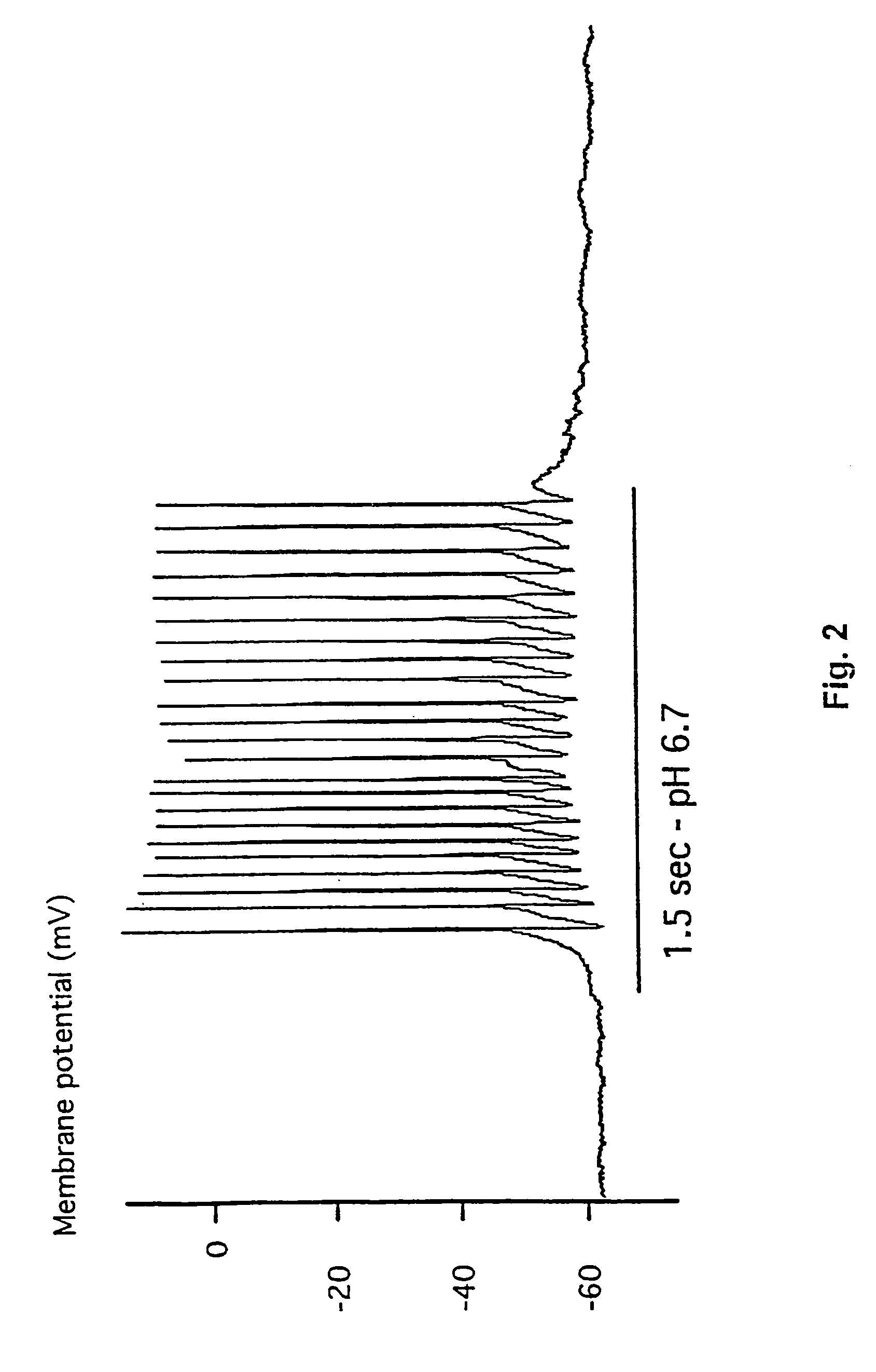
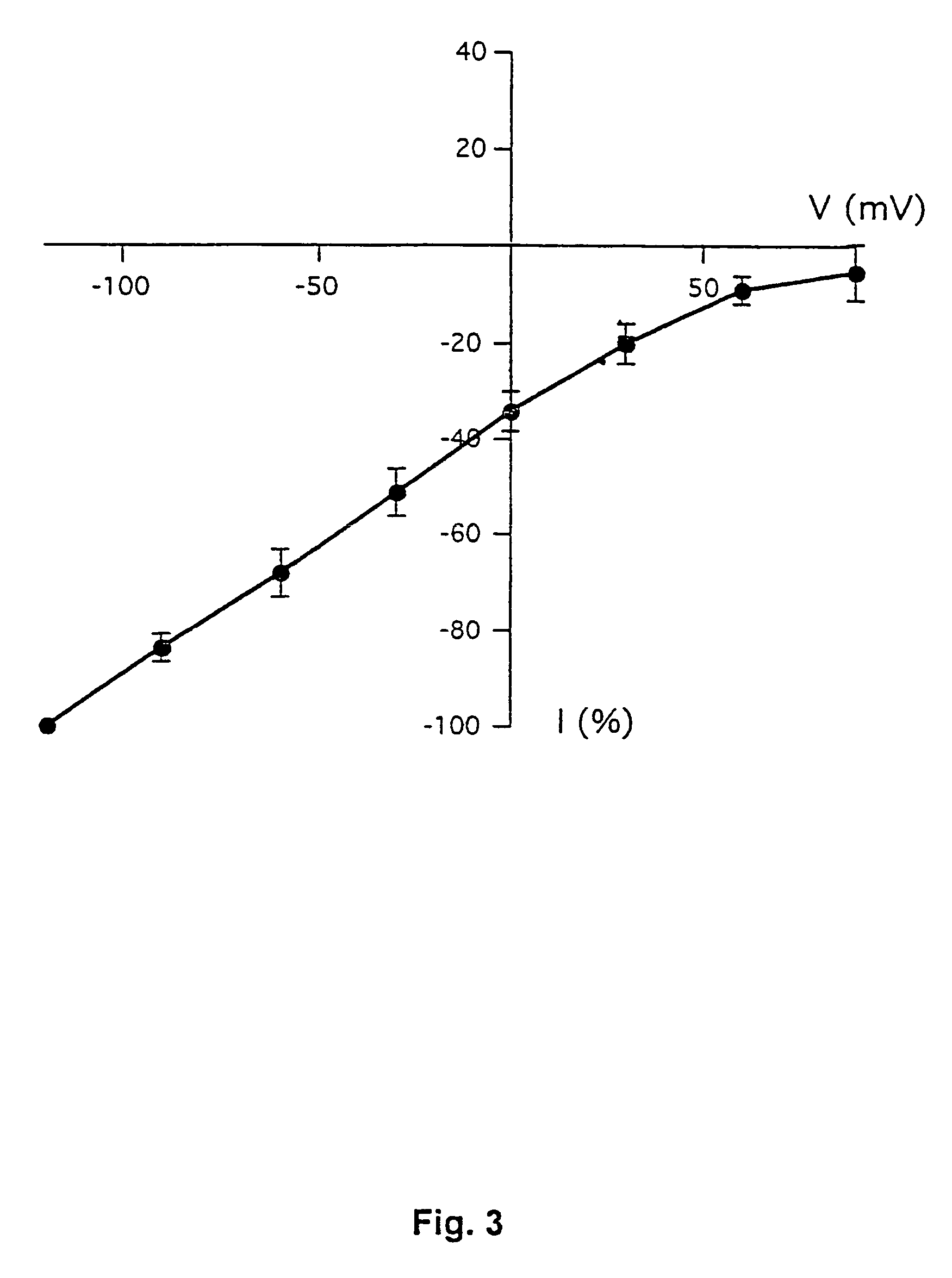
Inhibitors of proton-gated cation channels and their use in the treatment of ischaemic disorders
This invention relates to the use of compounds capable of inhibiting the activity of a proton-gated cation channel in the treatment of alleviation of diseases or disorders associated with, or mediated by a drop in extra cellular pH.
Owner:AROS PHARMA APS
TRPC6 involved in glomerulonephritis
ActiveUS20080038365A1Calcium ion influx is thereby reducedOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsZona glomerulosaDisease
Focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) is a kidney disorder of unknown etiology and up to 20% of patients on dialysis have this diagnosis. A large family with hereditary FSGS carries a missense mutation in the TRPC6 gene on chromosome 11q, encoding the ion channel protein Transient Receptor Potential Cation Channel 6. The missense mutation is a P112Q substitution, which occurs in a highly conserved region of the protein, enhances TRPC6-mediated calcium signals in response to agonists such as angiotensin II, and alters the intracellular distribution of TRPC6 protein. Previous work has emphasized the importance of cytoskeletal and structural proteins in proteinuric kidney diseases. Our findings suggest a novel mechanism for glomerular disease pathogenesis.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Methods for generating functional hematopoietic stem cells
Methods for preparing populations of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), e.g., autologous and / or allogenic HSCs, using mechanical stretching or transient receptor potential cation channel-subfamily vanilloid member 4 (Trpv4) agonists, and methods of use of the HSCs in transplantation are provided. Specifically, the methods comprising providing population cells comprising hemogenic endothelial (HE) cells, contacting the HE cells with an amount of an agonist of Trpv4; and / or subjecting the cells to cyclic 2-dimensional stretching, for a time and under conditions sufficient to stimulating endothelial-to-HSC transition. Further disclosed are methods of treating malignant or non-malignant hematologic, metabolic, or immune disorders comprising administering to a subject a therapeutically effectiveamount of HSCs obtained by the methods.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC +1
Method for activation of transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily a, member 1 using acetaldehyde
ActiveUS20090269280A1Improve isolationEasy to useMicrobiological testing/measurementTissue cultureSensory potentialSensory neuron
The present invention relates to a method for activation of TRPA1 (transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily A, member 1) using acetaldehyde, more precisely a method for selecting a candidate for TRPA1 activation blocker from neurons activated by acetaldehyde. Acetaldehyde of the present invention works on TRPA1 specifically so that it facilitates the isolation of sensory neurons expressing TRPA1. Therefore, acetaldehyde of the invention can be effectively used for the studies on TRPA1 mechanisms and the development of a TRPA1 based anodyne.
Owner:HANBAT NAT UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOPERATION FOUND
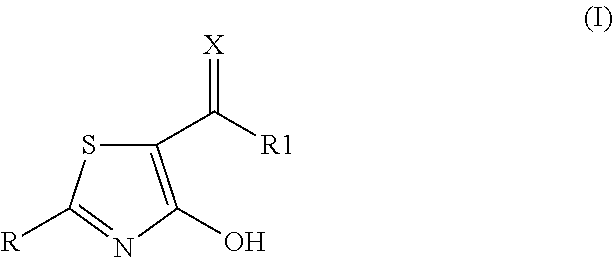
2-aryl-4-hydroxy-1,3-thiazole derivatives useful as trpm8-inhibitors in treatment of neuralgia, pain, COPD and asthma
ActiveUS20170190678A1High selectivityAdequate pharmacokinetic profileOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderIrritable bowelRisk stroke
The invention relates to compounds acting as selective antagonists of Transient Receptor Potential cation channel subfamily M member 8 (TRPM8), and having formula (I).Said compounds are useful in the treatment of diseases associated with activity of TRPM8 such as pain, inflammation, ischaemia, neurodegeneration, stroke, psychiatric disorders, itch, irritable bowel diseases, cold induced and / or exacerbated respiratory disorders and urological disorders.
Owner:DOMPE FARM SPA
Novel non-selective cation channel in neural cells and method for treating brain swelling
InactiveUS20050181980A1Compounds screening/testingOrganic active ingredientsNeural cellSulphonylurea compounds
A composition comprising a novel Ca2+-activated, [ATP]i-sensitive nonspecific cation (NCCa-ATP) channel is described. The channel is found in mammalian neural cells and exhibits a different sensitivity to block by various adenine nucleotides, and is activated by submicromolar [Ca]i. The NCCa-ATP channel is activated under conditions of ATP depletion, which causes severe cell depolarization, followed by cell swelling. The NCCa-ATP channel is regulated by a sulfonylurea receptor and is inhibited by sulfonylurea compounds glibenclamide and tolbutamide. Methods employing compositions comprising the NCCa-ATP channel to screen for compounds that block the channel and the use of such antagonists as therapeutics in preventing brain swelling and damage are described. In addition, methods employing compositions comprising the Kir2.3 channel to screen for compounds that open the channel and the use of such antagonists as therapeutics in preventing brain swelling and damage are described.
Owner:U S GOVERNMENT REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS
Gene vaccine of sperm-specific cationic channel protein CatSper1 and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101816799APrevent movementLower average litter rateGenetic material ingredientsAntibody medical ingredientsBALB/cCholesterol
The invention relates to a vaccine, in particular to a gene vaccine of sperm-specific cationic channel protein CatSper1. The vaccine is an immune-stimulating complex type vaccine composed of CatSper1-BAFF digenic recombinant eukaryotic vector, saponin Quil A, cholesterol and lecithin; and the vaccine can inhibit the movement of sperms, perform specific reduction of the average farrowing rate and number born of BALB / c mouse and have good application prospect in the immunological contraception field. The invention also relates to a preparation method of the vaccine which has simple operation and low cost.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Method for screening olfactory sensibility inhibitor
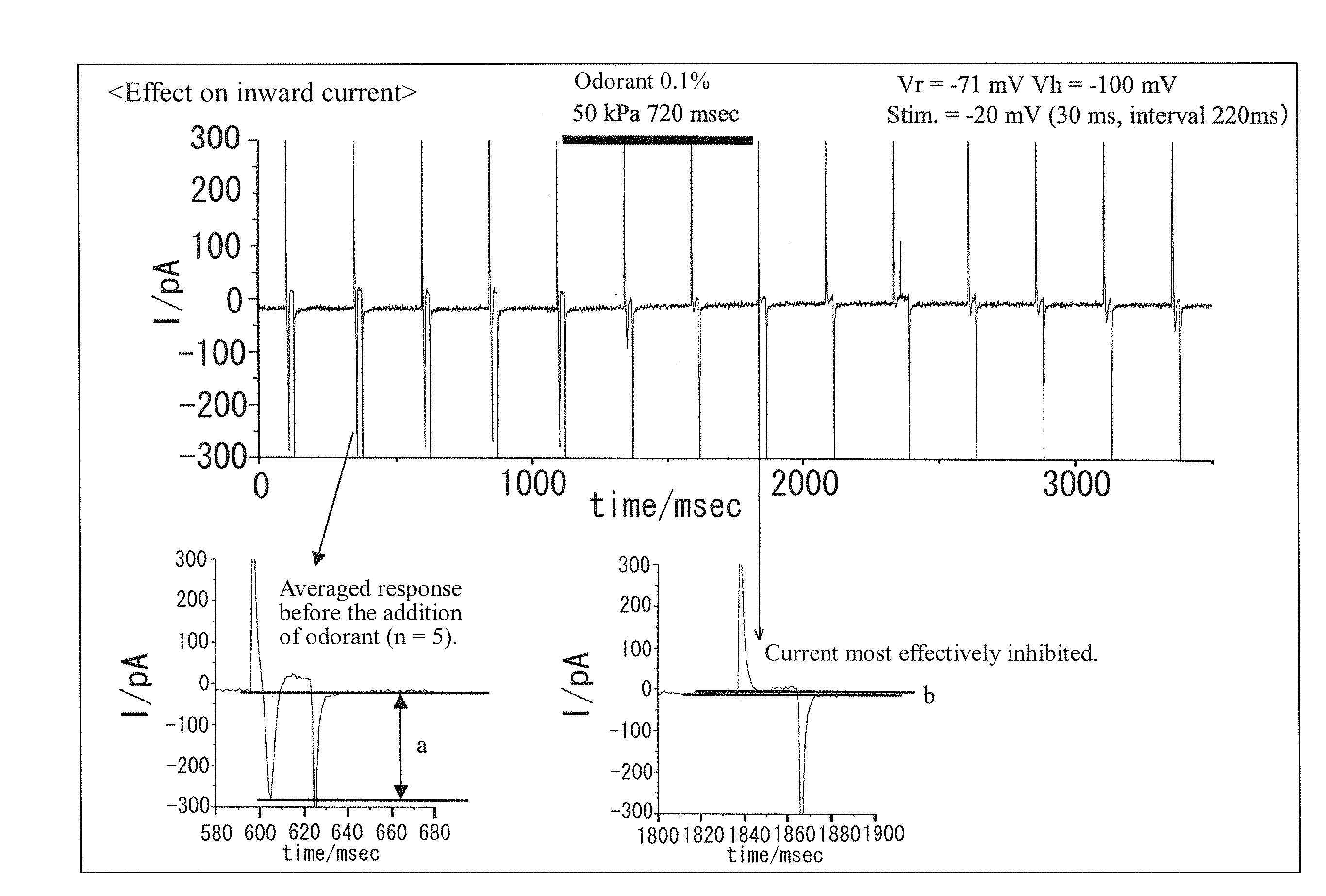
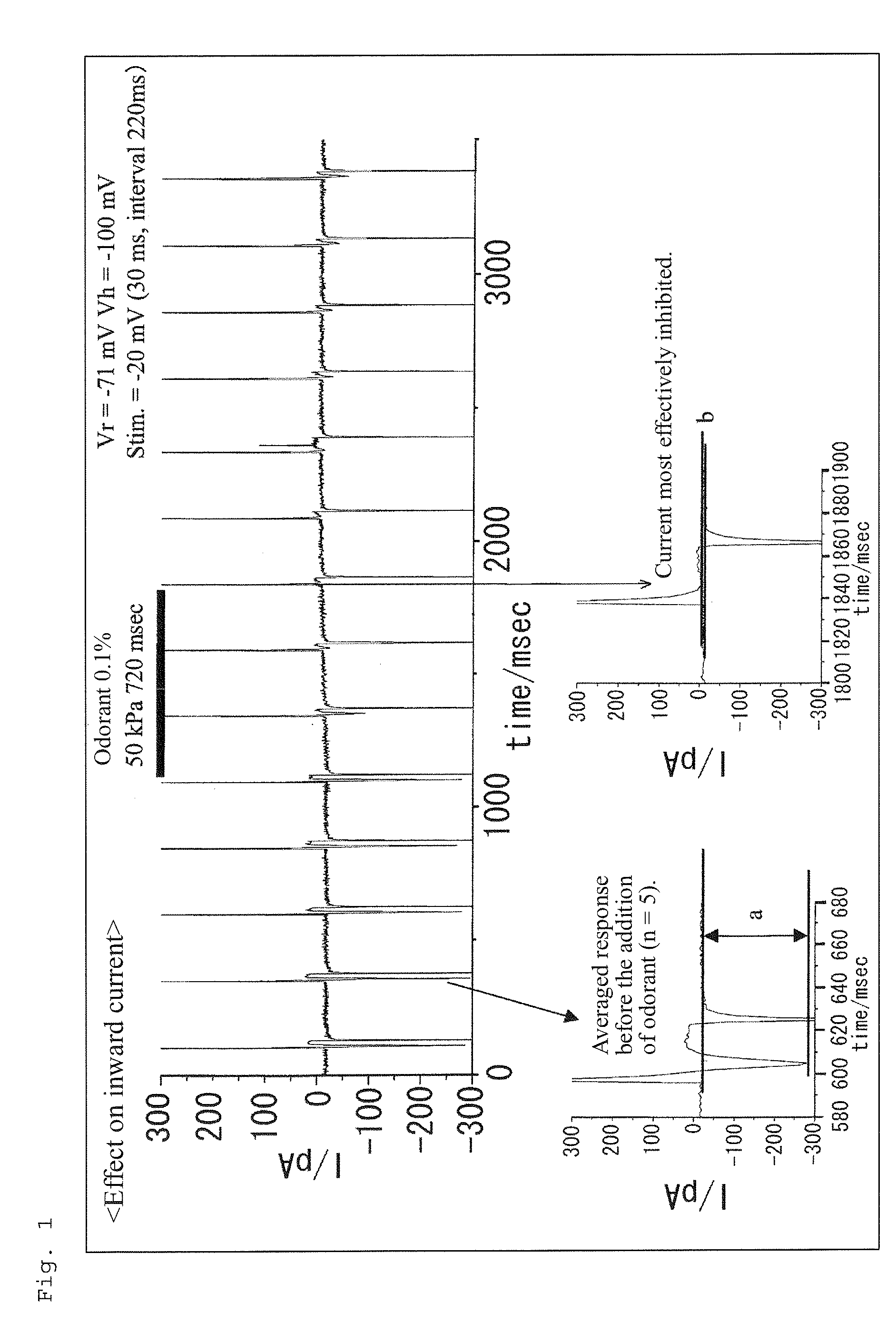
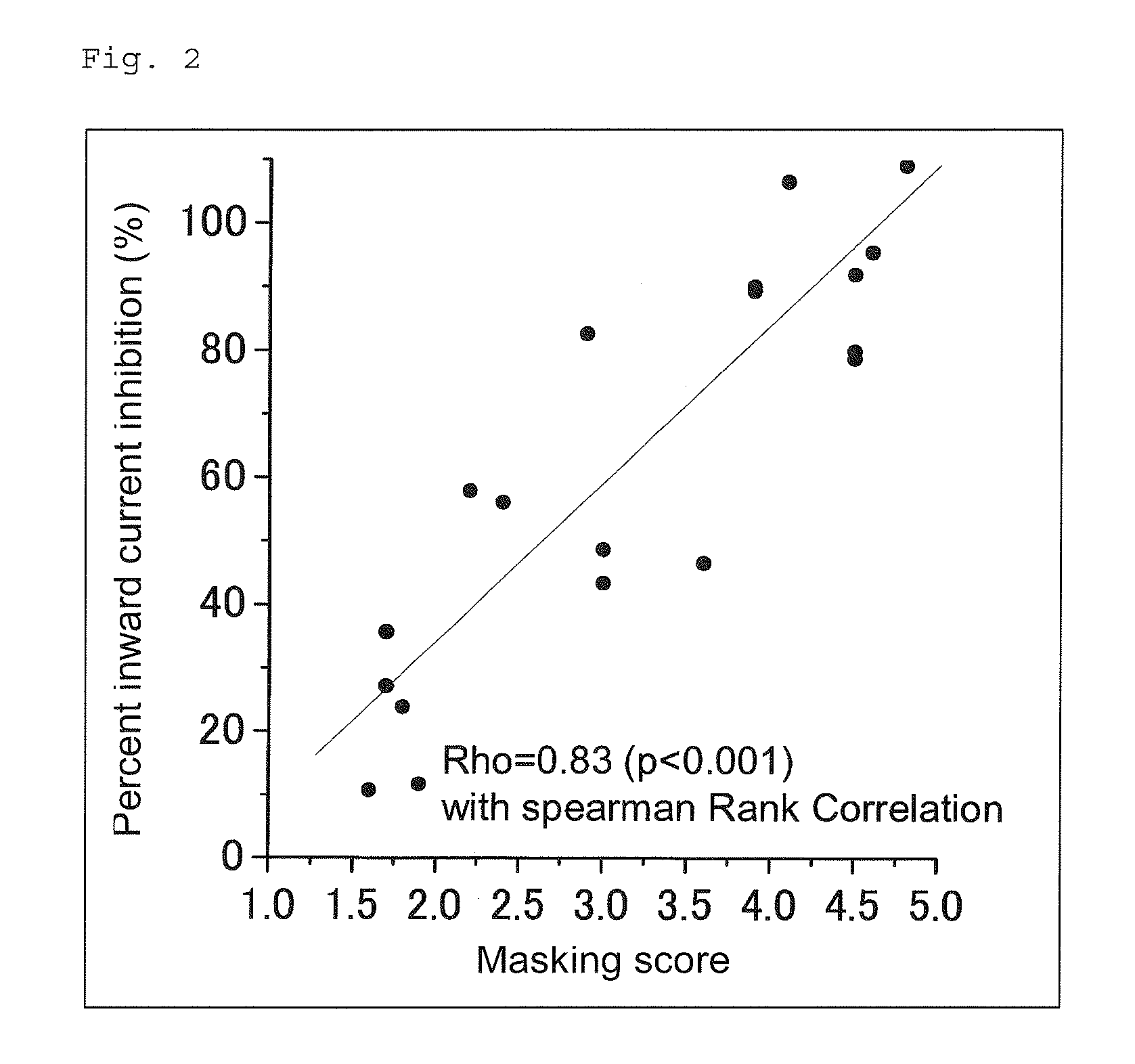
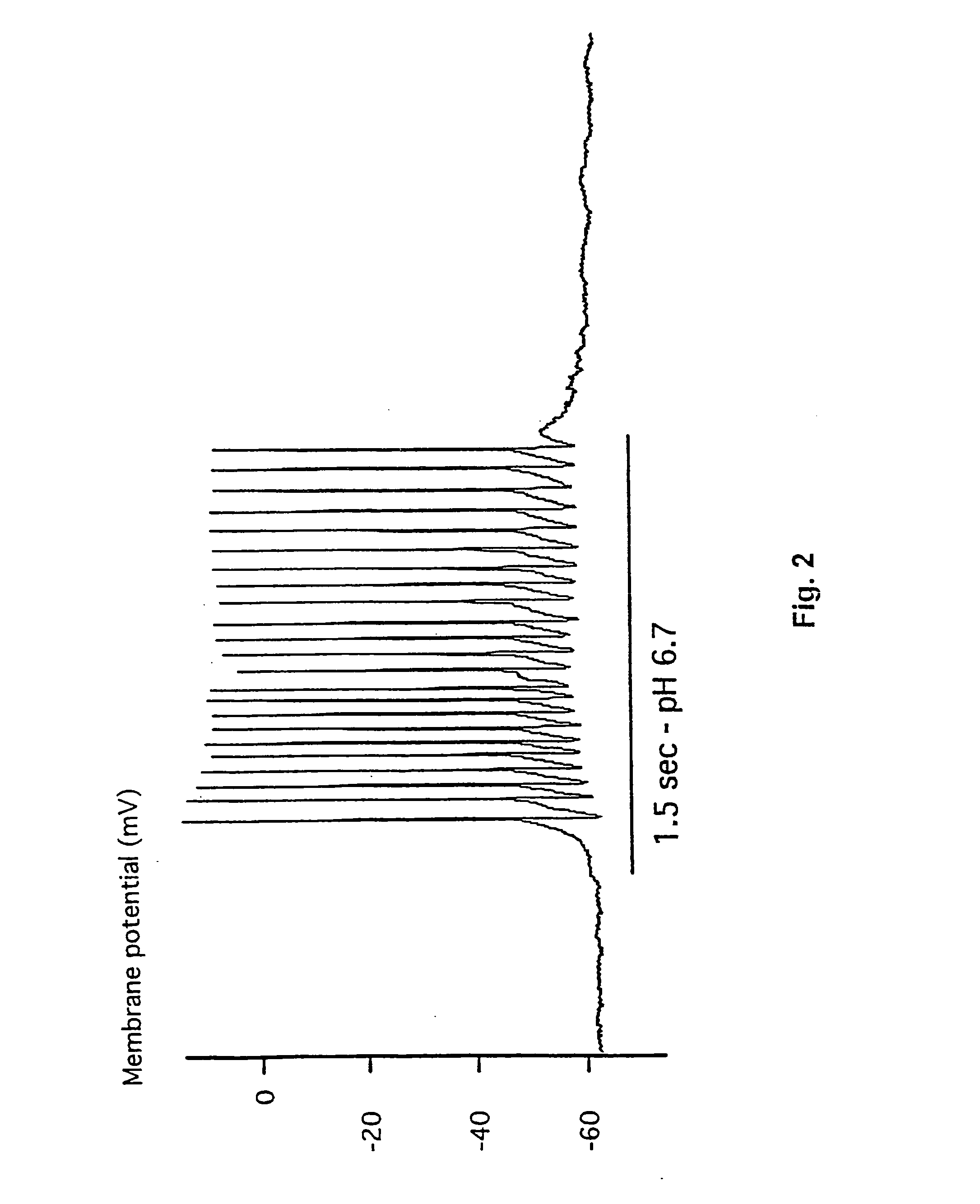
To provide a method for objectively evaluating or screening to identify a substance which is capable of suppressing or regulating olfaction. A method of evaluating or screening to identify an agent for suppressing olfactory sensitivity, including adding a test substance to a substrate having a voltage-dependent cation channel and evaluating or selecting a substance that inhibits an electrical activity caused by the cation channel. A method of evaluating or screening to identify an agent for suppressing olfactory sensitivity, including the following steps (1) to (4): (1) adding a test substance to a substrate having a voltage-dependent cation channel; (2) measuring electrical activity caused by the voltage-dependent cation channel; (3) comparing the electrical activity measured in step (2) with the corresponding electrical activity in a control group; and (4) evaluating or selecting the test substance that inhibits the electrical activity as an agent for suppressing olfactory sensitivity, based on the results obtained in step (3).
Owner:KAO CORP
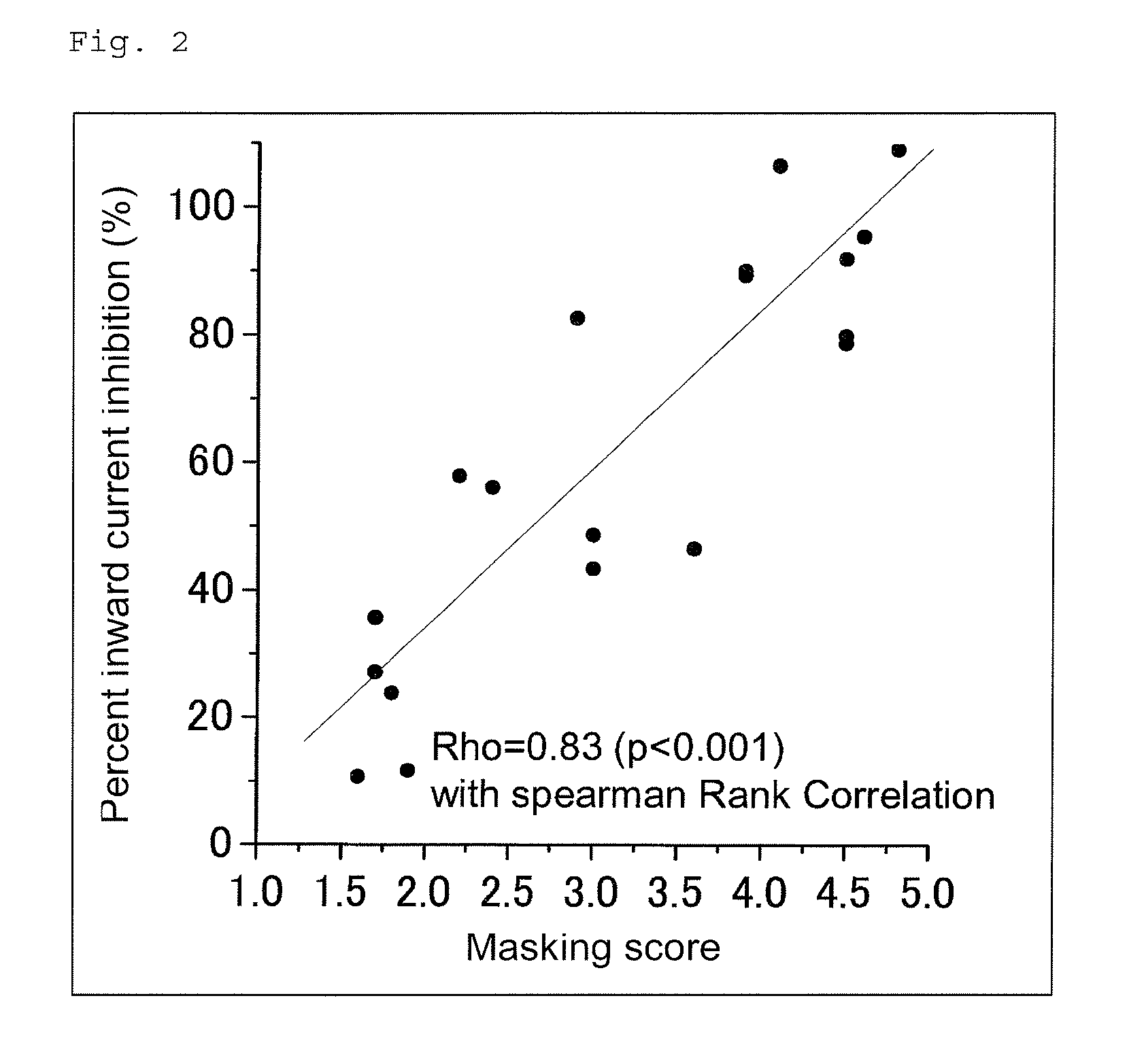
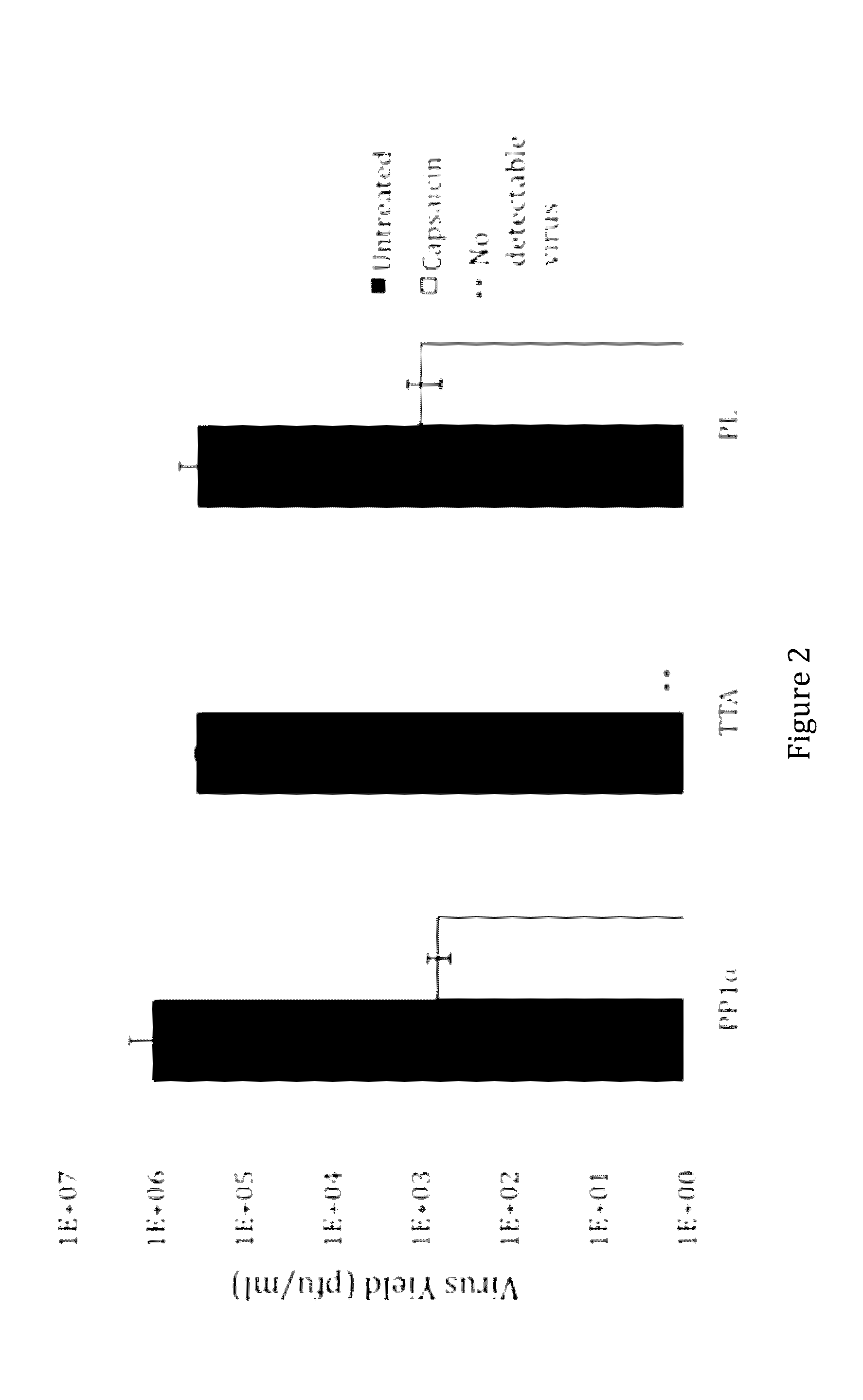
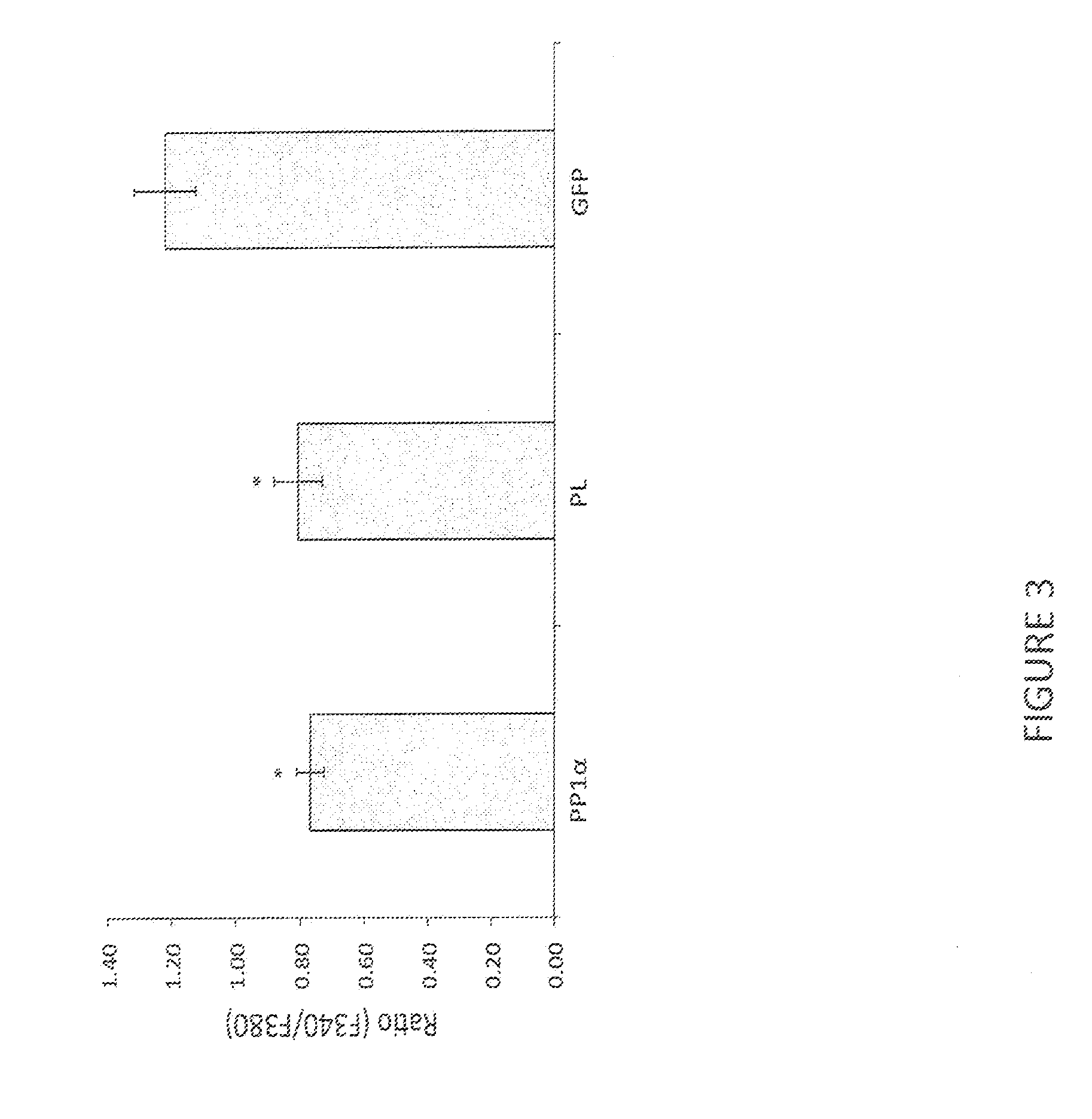
TRPV1 modulatory gene product that affects TRPV1-specific pain behavioral responses identified in a functional screen of an HSV-based cDNA library
ActiveUS9580699B2Eliminate side effectsReduce sensitizationVectorsPeptide/protein ingredientsCDNA libraryNeurophysins
The invention provides a method for ameliorating chronic pain signaling involving transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 1 (TRPV1) by expressing PP1α in neurons. The invention also provides HSV vectors for expressing PP1α within neurons and compositions comprising such vectors.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Method for Screening Olfactory Sensibility Inhibitor
ActiveUS20110050246A1Suppressing olfactory sensitivityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionCation channels of spermIon channel
To provide a method for objectively evaluating or screening to identify a substance which is capable of suppressing or regulating olfaction. A method of evaluating or screening to identify an agent for suppressing olfactory sensitivity, including adding a test substance to a substrate having a voltage-dependent cation channel and evaluating or selecting a substance that inhibits an electrical activity caused by the cation channel. A method of evaluating or screening to identify an agent for suppressing olfactory sensitivity, including the following steps (1) to (4): (1) adding a test substance to a substrate having a voltage-dependent cation channel; (2) measuring electrical activity caused by the voltage-dependent cation channel; (3) comparing the electrical activity measured in step (2) with the corresponding electrical activity in a control group; and (4) evaluating or selecting the test substance that inhibits the electrical activity as an agent for suppressing olfactory sensitivity, based on the results obtained in step (3).
Owner:KAO CORP
Inhibitors of proton-gated cation channels and their use in the treatment of ischaemic disorders
This invention relates to the use of compounds capable of inhibiting the activity of a proton-gated cation channel in the treatment of alleviation of diseases or disorders associated with, or mediated by a drop in extra cellular pH.
Owner:AROS PHARMA APS
Methods for antagonists of a non-selective cation channel in neural cells
InactiveUS20190111137A1Avoid depolarizationReduce and preventOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseNervous system
The present invention is directed to a combination of therapeutic compounds and treatment methods and kits using the combination. In particular, one of the combination affects the NCCa-ATP channel of neural tissue, including neurons, glia and blood vessels within the nervous system. Exemplary SUR1 and / or TRPM4 antagonists that inhibit the NCCa-ATP channel may be employed in the combination. The combination therapy also employs one or more of a non-selective cation channel blocker and / or an antagonist of VEFG, NOS, MMP, or thrombin. Exemplary indications for the combination therapy includes the prevention, diminution, and / or treatment of injured or diseased neural tissue, including astrocytes, neurons and capillary endothelial cells, that is due to ischemia, tissue trauma, brain swelling and increased tissue pressure, or other forms of brain or spinal cord disease or injury, for example. In other embodiments, there are methods and compositions directed to antagonists of TRPM4, including at least for therapeutic treatment of traumatic brain injury, cerebral ischemia, central nervous system (CNS) damage, peripheral nervous system (PNS) damage, cerebral hypoxia, or edema, for example.
Owner:U S GOVERNMENT REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS
Gene vaccine of sperm-specific cationic channel protein CatSper1 and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101816799BPrevent movementEasy to prepareGenetic material ingredientsAntibody medical ingredientsBALB/cCholesterol
The invention relates to a vaccine, in particular to a gene vaccine of sperm-specific cationic channel protein CatSper1. The vaccine is an immune-stimulating complex type vaccine composed of CatSper1-BAFF digenic recombinant eukaryotic vector, saponin Quil A, cholesterol and lecithin; and the vaccine can inhibit the movement of sperms, perform specific reduction of the average farrowing rate and number born of BALB / c mouse and have good application prospect in the immunological contraception field. The invention also relates to a preparation method of the vaccine which has simple operation and low cost.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
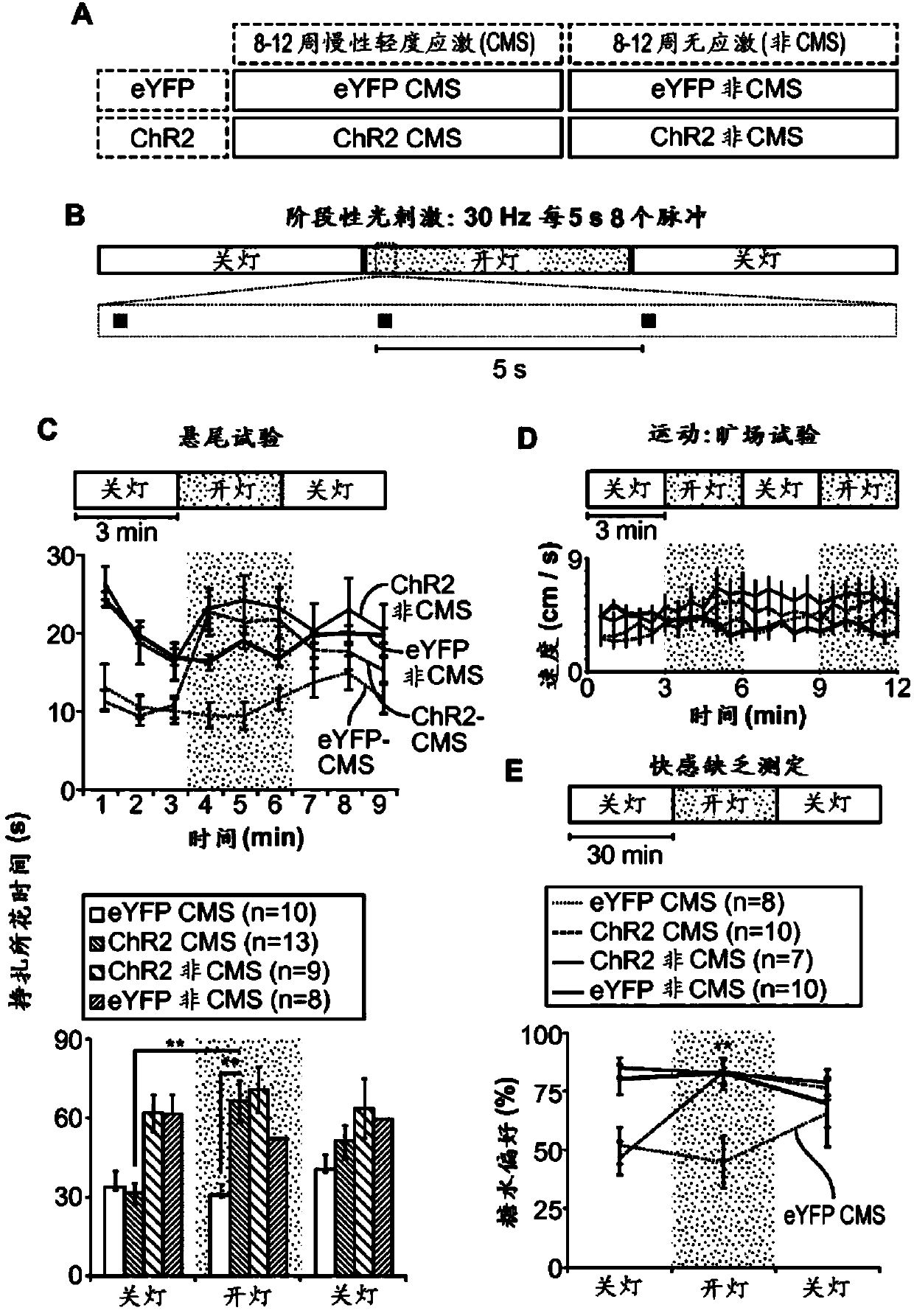
Non-human animal models of depression and methods of use thereof
InactiveCN104270942ACompounds screening/testingElectrotherapyLight responsiveCation channels of sperm
The disclosure provides non-human optogenetic animal models of depression. Specifically, non-human animals each expresses a light- responsive opsin in a neuron of the animal are provided. The animal models are useful for identifying agents and targets of therapeutic strategies for treatment of depression. Examples of using the non-human animals expressing light-responsive opsin including Halorhodopsin family of light-responsive chloride pumps and Channelrhodopsin family of light-responsive cation channel proteins are described.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Mechanically-Activated Cation Channels
InactiveUS20130156762A1Reduces and inhibits electrophysiological changeIncreases electrophysiological changeCompound screeningNervous disorderCation channels of spermCation channel activity
Owner:IRM +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com