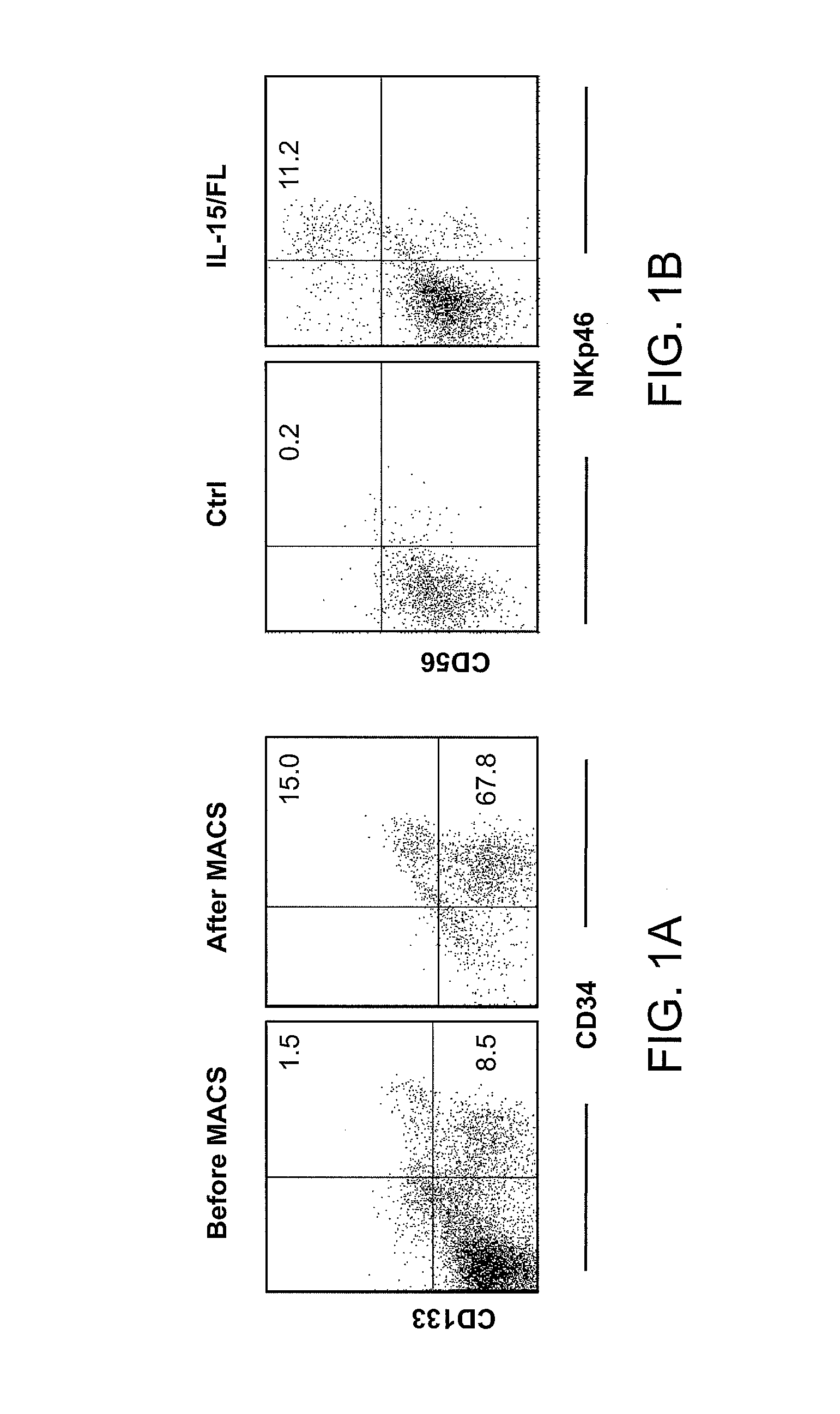
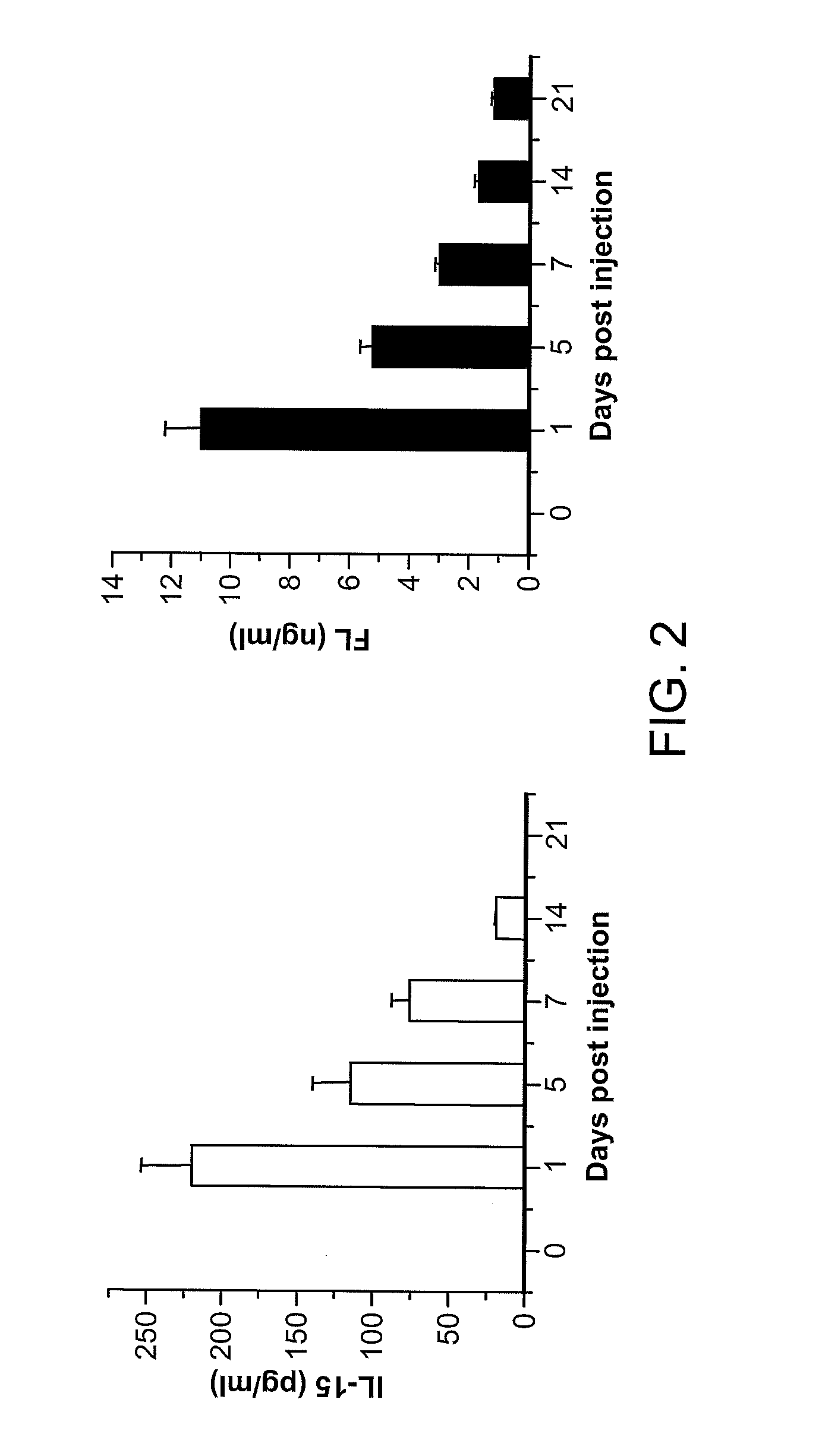
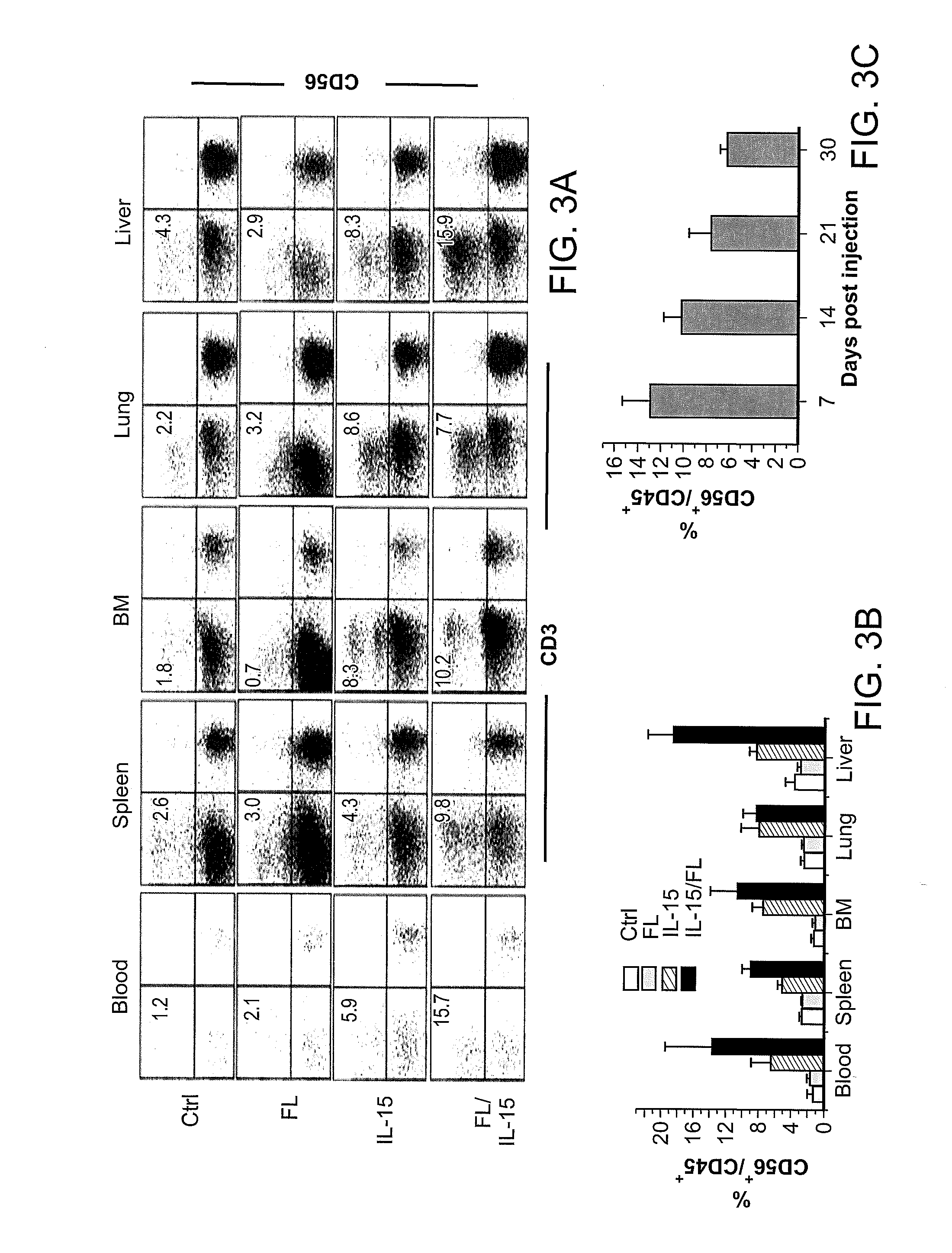
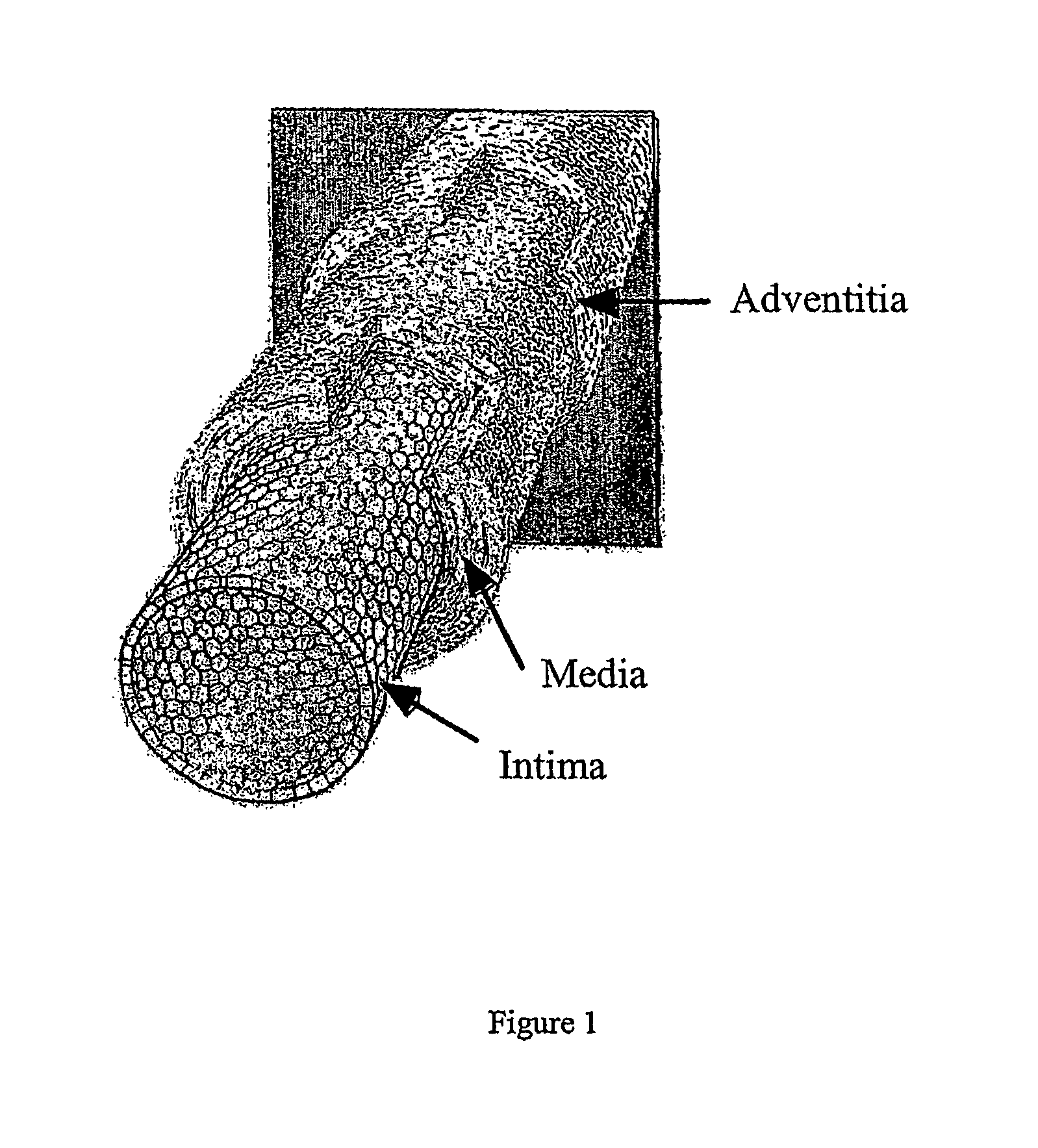
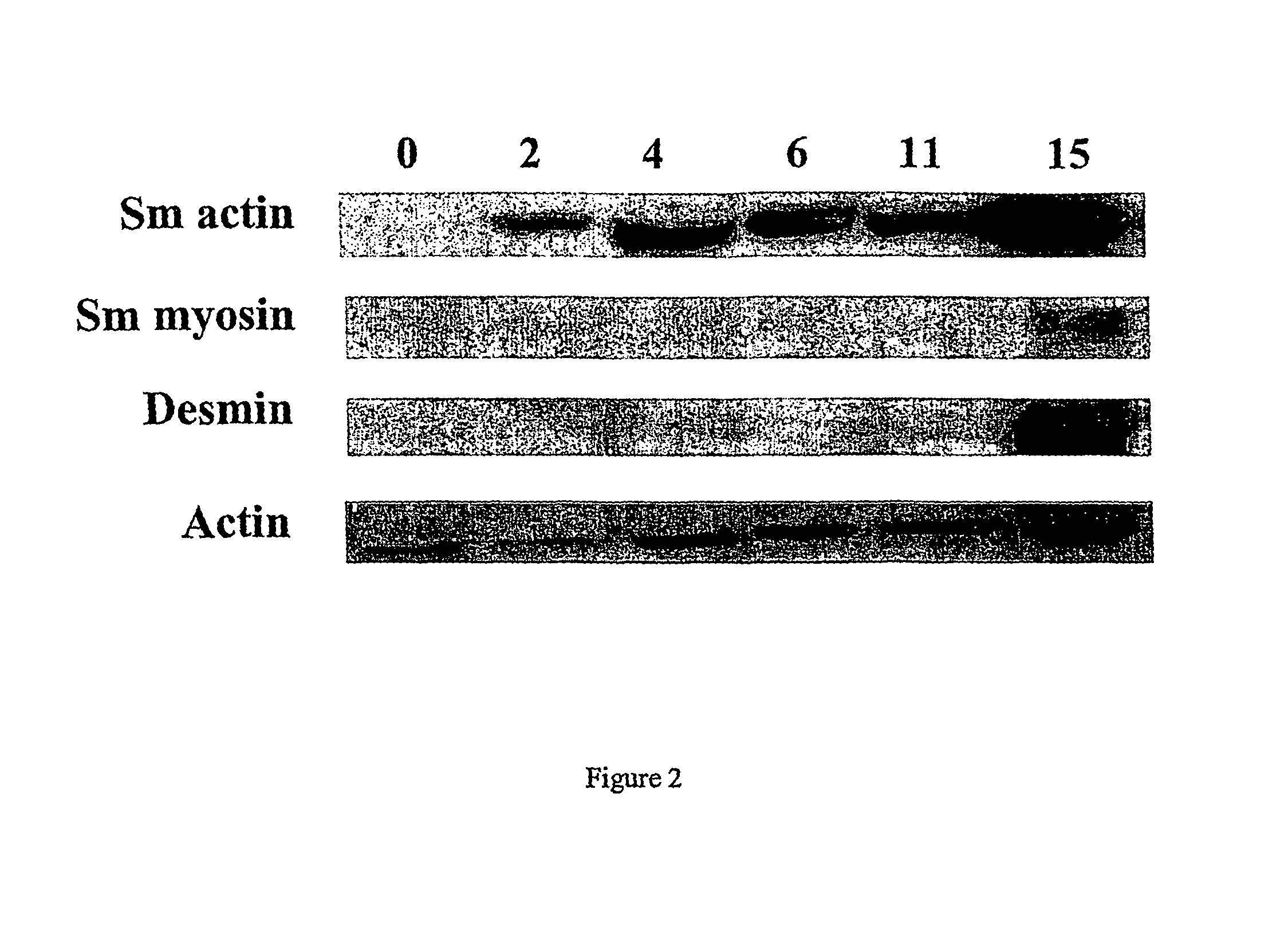
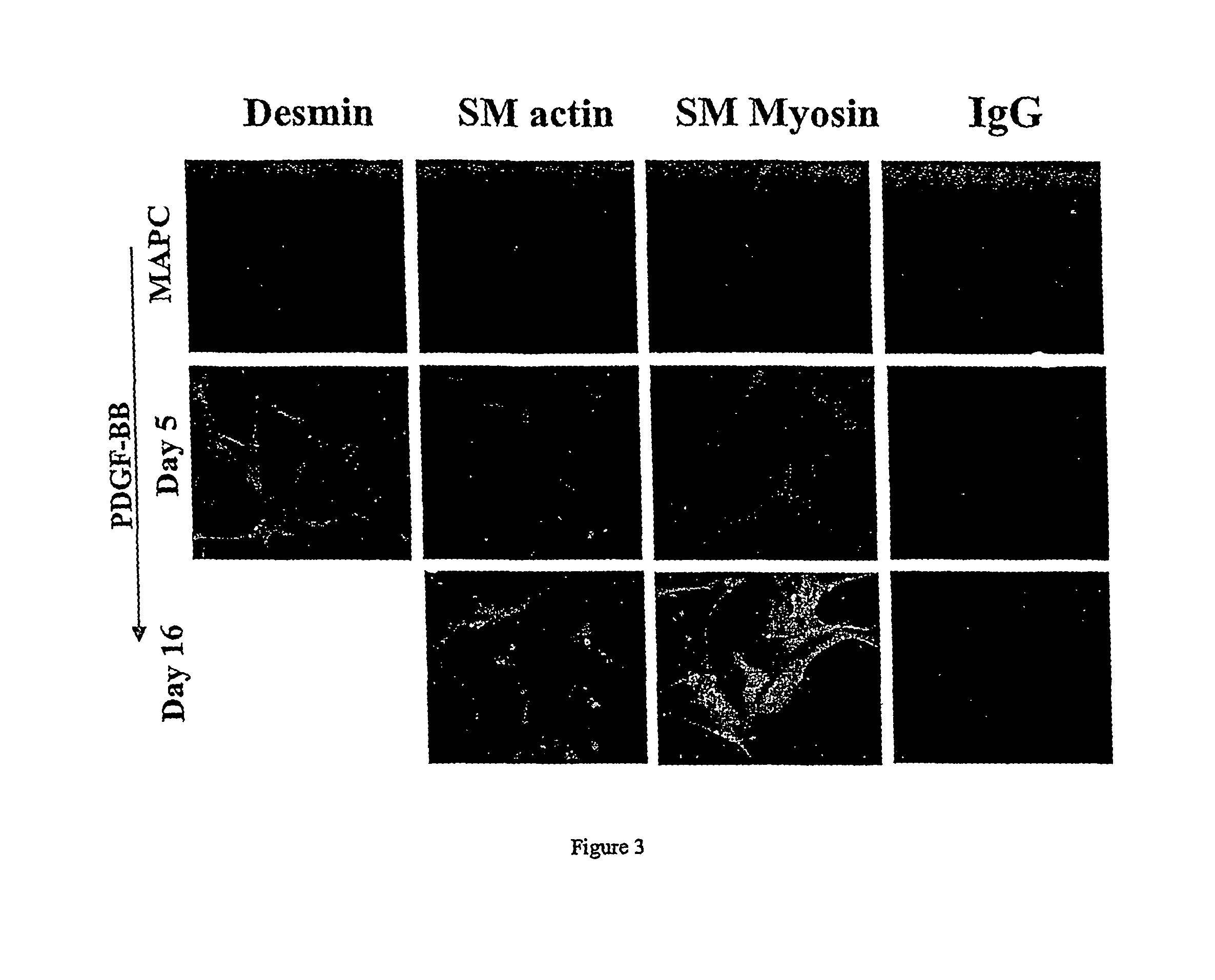
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
128 results about "Cell lineage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cell lineage denotes the developmental history of a tissue or organ from the fertilized embryo. Cell lineage can be studied by marking a cell (with fluorescent molecules or other traceable markers) and following its progeny after cell division. Some organisms, such as C. elegans, have a predetermined pattern of cell progeny and the adult male will always consist of 1031 cells, this is because cell division in C. elegans is genetically determined and known as eutely. This causes the cell lineage and cell fate to be highly correlated. Other organisms, such as humans, have variable lineages and somatic cell numbers.
Endometrial stem cells and methods of making and using same
InactiveUS20090053182A1Rapid rate of cellular divisionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsCell lineageEndometrium
The invention provides pluripotent stem cells and methods for making and using pluripotent stem cells. Pluripotent stem cells, among other things, can differentiate into various cell lineages in vitro, ex vivo and in vivo. Pluripotent stem cells, among other things, can also be used to produce conditioned medium.
Owner:MEDISTEM LAB
Methods and compositions for the differentiation of stem cells
ActiveUS20100216181A1Overcome limitationsPromote cell differentiationMicrobiological testing/measurementCulture processProgenitorInduced pluripotent stem cell
The present invention provides methods and compositions for the production of hematopoietic progenitor cells or endothelial progenitor cells from human pluripotent stem cells using a defined cell culture medium without the need to utilize feeder cells or serum. In some embodiments, differentiation is accomplished using hypoxic atmospheric conditions. The defined medium of the present invention may contain growth factors and a matrix component. The hematopoietic progenitor cells may be further differentiated into cell lineages including red blood cells, macrophages, granulocytes, and megakaryocytes. The endothelial progenitor cells may be further differentiated into endothelial cells. Also disclosed are screening assays for identification of candidate substances that affect differentiation of pluripotent stem cells into progenitor cells.
Owner:FUJIFILM CELLULAR DYNAMICS INC
Engineering three-dimensional tissue structures using differentiating embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS20050031598A1Reduce molecular weightBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsCell lineageSupport matrix
A method of producing a tissue engineering construct. The method includes providing a population of embryonic stem cells, seeding the embryonic stem cells on a cell support matrix, and exposing the embryonic stem cells to at least one agent selected to promote differentiation of the stem cells along a predetermined cell lineage or into a specific cell type. The step of exposing may be performed before or after the step of seeding.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD +1
Engineered blood vessels
The present invention relates to engineered blood vessels and methods of making such vessels using matrices comprising endothelial and smooth muscle cells, or cells capable of differentiating into endothelial and smooth muscle cell lineages (e.g., stem cells, or the progenitors thereof).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
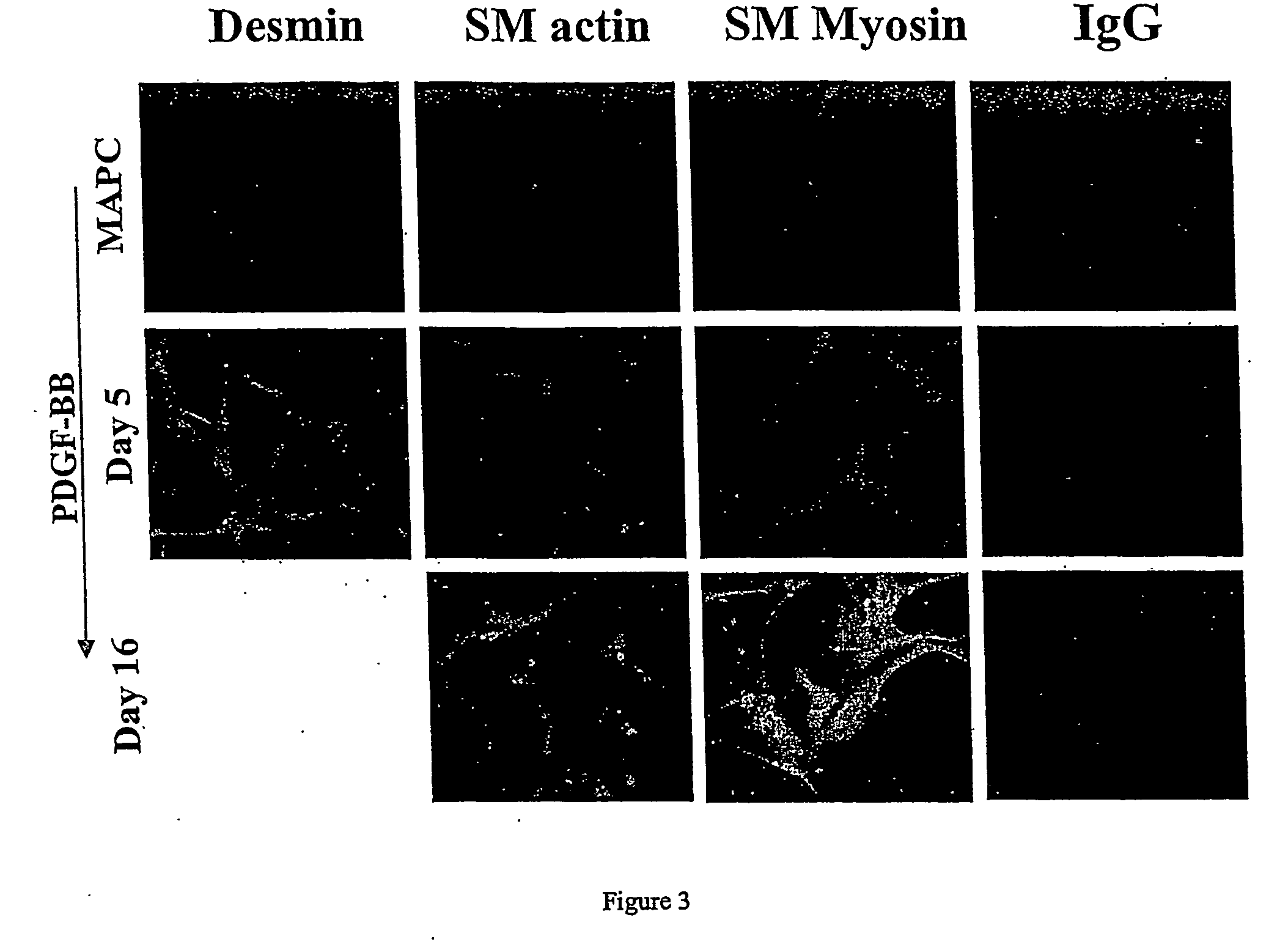
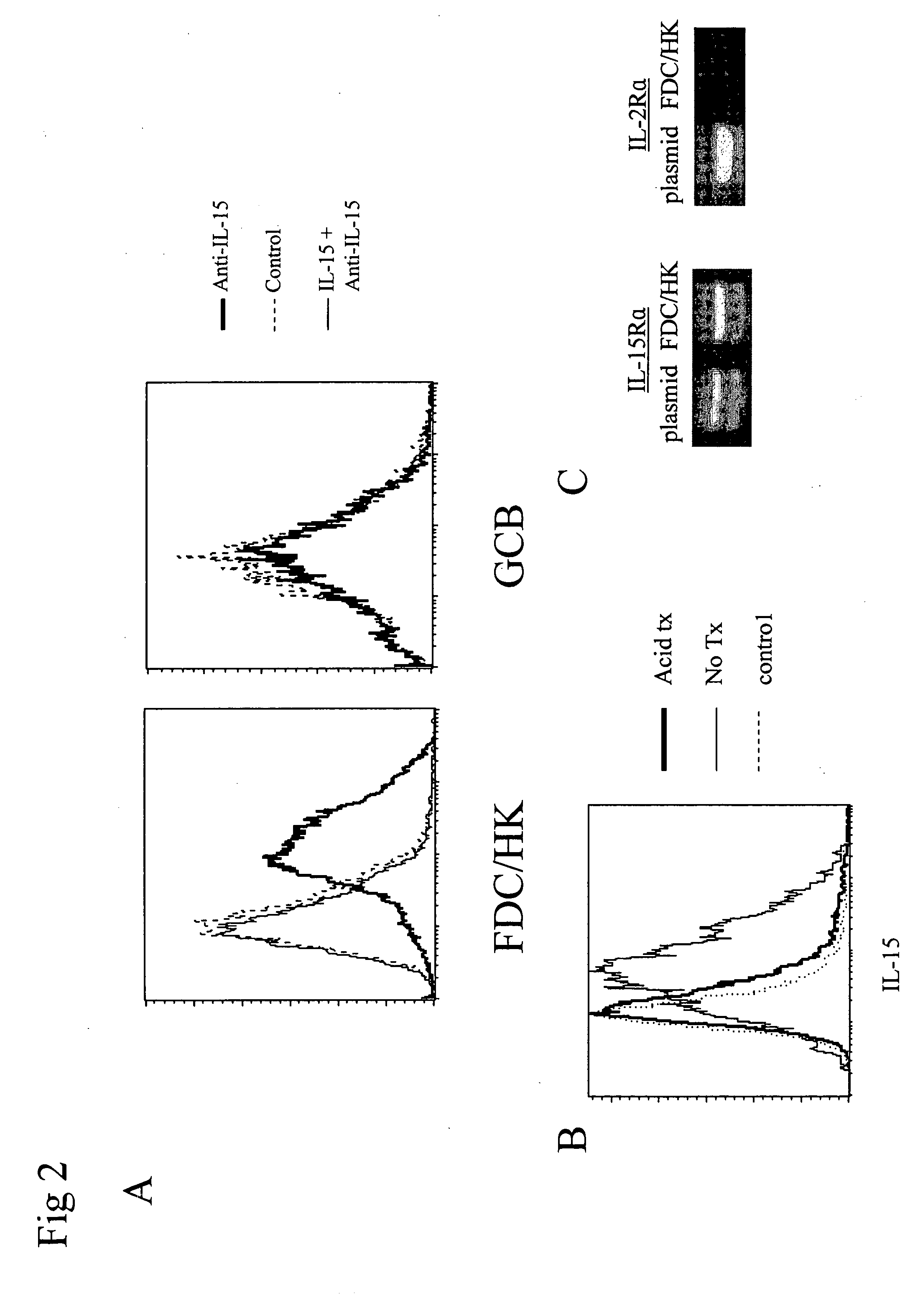
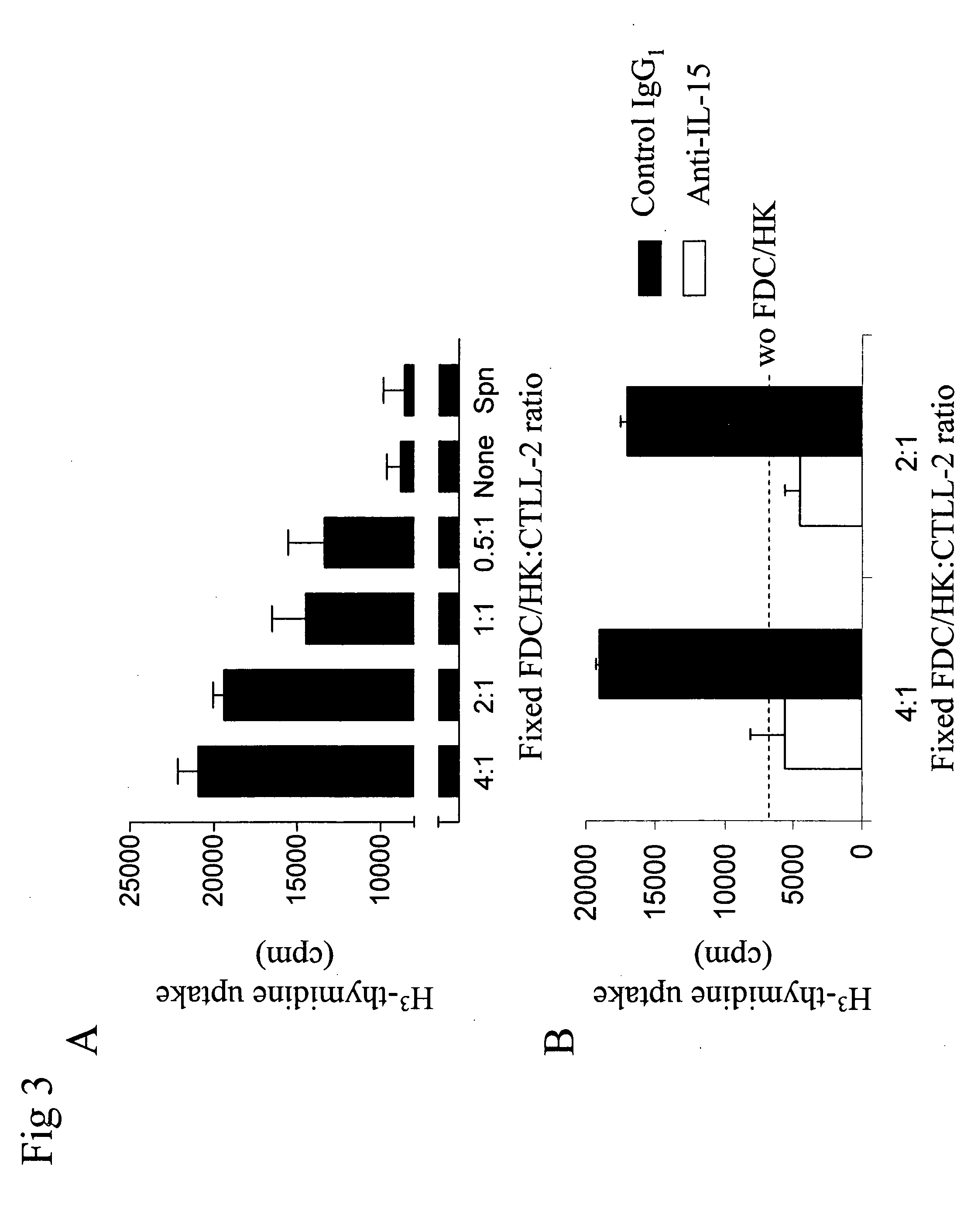
Enhancement of B cell proliferation by IL-15
InactiveUS20060104945A1Prevent proliferationAvoid signalingOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsCell lineageDisease
Compositions and methods for modulating the growth, proliferation, and / or differentiation of B-cells in the germinal center are disclosed, and include use of IL-15 inhibitors, antagonists, and agonists. The compositions and methods find use in treating B-cell-related disorders, including neoplasms of the B-cell lineage.
Owner:OCHSNER CLINIC FOUND
Therapeutic reprogramming, hybrid stem cells and maturation
InactiveUS20050170506A1Minimal oxidative damageTherapeutic applicationNew breed animal cellsArtificial cell constructsCell lineageReprogramming
Therapeutically programmed cells and methods for making such cells are provided. Therapeutically programmed cells are stem cells which have been matured such that they represent either a more differentiated state or a less differentiated state after contact with stimulatory factors. The therapeutically reprogrammed cells are suitable for cellular regenerative therapy and have the potential to differentiate into more committed cell lineages. Additionally, hybrid stem cells suitable for therapeutic reprogramming and cellular regenerative therapy are provided.
Owner:PRIMEGEN BIOTECH LLC
Cartilage-derived stem cells and applications thereof
The invention relates to methods of isolating adult stem cells, to the cells thus isolated and to applications thereof. More specifically, the invention relates to isolated adult stem cells, which are derived from dedifferentiated chondrocytes, which can be differentiated and which can give rise to a series of cell lineages, as well as to specific markers present in said cells, such as cell surface antigens. The cells provided by the present invention can be used, for example, in cell therapy and in the search for and development of novel medicaments.
Owner:CONSEJO SUPERIOR DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS (CSIC) +1
Method for facilitating the production of differentiated cell types and tissues from embryonic and adult pluripotent and multipotent cells
InactiveUS20050153443A1Improve developmentEasy to produceMammal material medical ingredientsArtificial cell constructsGerm layerCell lineage
The invention is concerned with producing differentiated cells, tissues and organs from pluripotent and mutlipotent cells. The methods of the invention are particularly useful for producing differentiated cells from pluripotent cells wherein communication between the cells of more than one embryonic germ layer or more than one organ system are required for development along a specific cell lineage. The invention methods are effected by in vivo or in vitro culturing of embryonic and developing or developed allogeneic or xenogeneic cells.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL TECH INC
Methods Of Producing Humanized Non-Human Mammals
InactiveUS20120157667A1Reconstitution is increasedImprove the level ofAnimal cellsImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsCell lineageMammal
Provided herein are methods of reconstituting functional human blood cell lineages in a non-human mammal comprising introducing human hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) and nucleic acid encoding one or more human cytokines into an immunodeficient non-human mammal. The non-human mammal is maintained under conditions in which the nucleic acid is expressed and the human HSCs differentiate into functional human blood cell lineages in the non-human mammal, thereby reconstituting functional human blood cell lineages in the non-human mammal. Also provided are methods of producing human antibodies directed against an immunogen in a non-human mammal, hybridomas that secrete the monoclonal antibodies as well as antibodies (e.g., polyclonal antibodies; monoclonal antibodies) produced by the B cells and non-human mammals produced by the methods.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Endometrial stem cells and methods of making and using same
InactiveUS20130156726A1Rapid rate of cellular divisionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsCell lineageEx vivo
The invention provides pluripotent stem cells and methods for making and using pluripotent stem cells. Pluripotent stem cells, among other things, can differentiate into various cell lineages in vitro, ex vivo and in vivo. Pluripotent stem cells, among other things, can also be used to produce conditioned medium.
Owner:XON CELLS
Reprogramming of adult human testicular stem cells to pluripotent germ-line stem cells
Methods for therapeutically programming human adult stem cells into pluripotent cells are provided. Cell therapeutically programmed from adult testicular cells are disclosed. The therapeutically reprogrammed cells are suitable for cellular regenerative therapy and have the potential to differentiate into more committed cell lineages.
Owner:PRIMEGEN BIOTECH LLC
Human mesenchymal progenitor cell
InactiveUS20050059147A1Microbiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsProgenitorBone marrow transplantations
The present invention provides isolated pluri-differentiated human mesenchymal progenitor cells (MPCs), which simultaneously express a plurality of genes that are markers for multiple cell lineages, wherein the multiple cell lineages comprise at least four different mesenchymal cell lineages (e.g., adipocyte, osteoblast, fibroblast, and muscle cell) and wherein each of the markers is specific for a single cell lineage. The present invention also method for isolating and purifying human mesenchymal progenitor cells from Dexter-type cultures for characterization of and uses, particularly therapeutic uses for such cells. Specifically, isolated MPCs can be used for diagnostic purposes, to enhance the engraftment of hematopoietic progenitor cells, enhance bone marrow transplantation, or aid in the treatment or prevention of graft versus host disease.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Therapeutic reprogramming of germ line stem cells
InactiveUS20070020759A1Minimal oxidative damageCulture processArtificial cell constructsCell lineageReprogramming
Pluripotent therapeutically programmed cells and methods for making such cells are provided. The pluripotent therapeutically programmed cells are post-natal stem cells which have been matured such that they represent either a more differentiated state or a less differentiated state after contact with stimulatory factors. The pluripotent therapeutically reprogrammed cells are suitable for cellular regenerative therapy and have the potential to differentiate into more committed cell lineages. Also disclosed are culture media for therapeutically reprogramming post-natal stem cells.
Owner:PRIMEGEN BIOTECH LLC
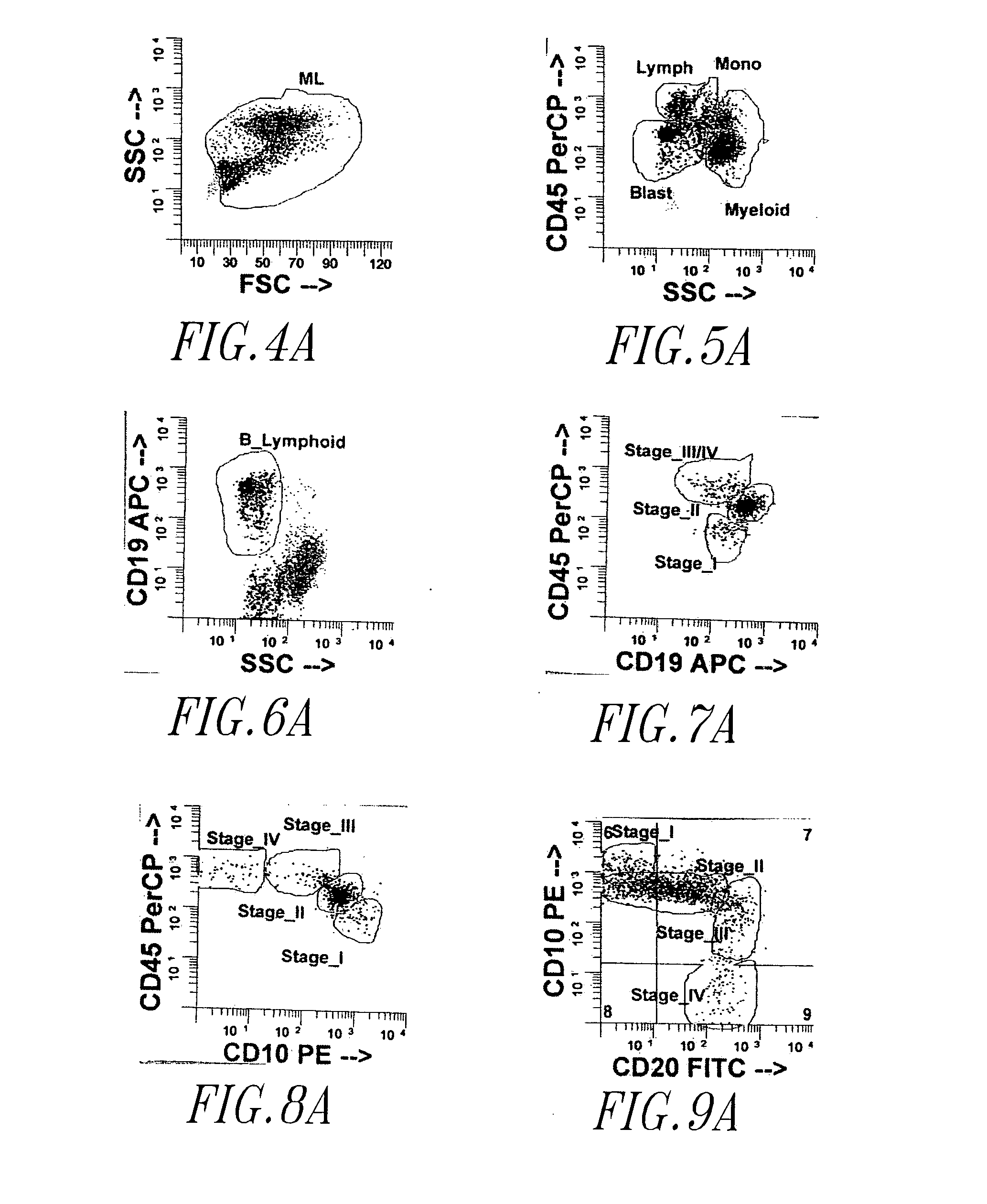
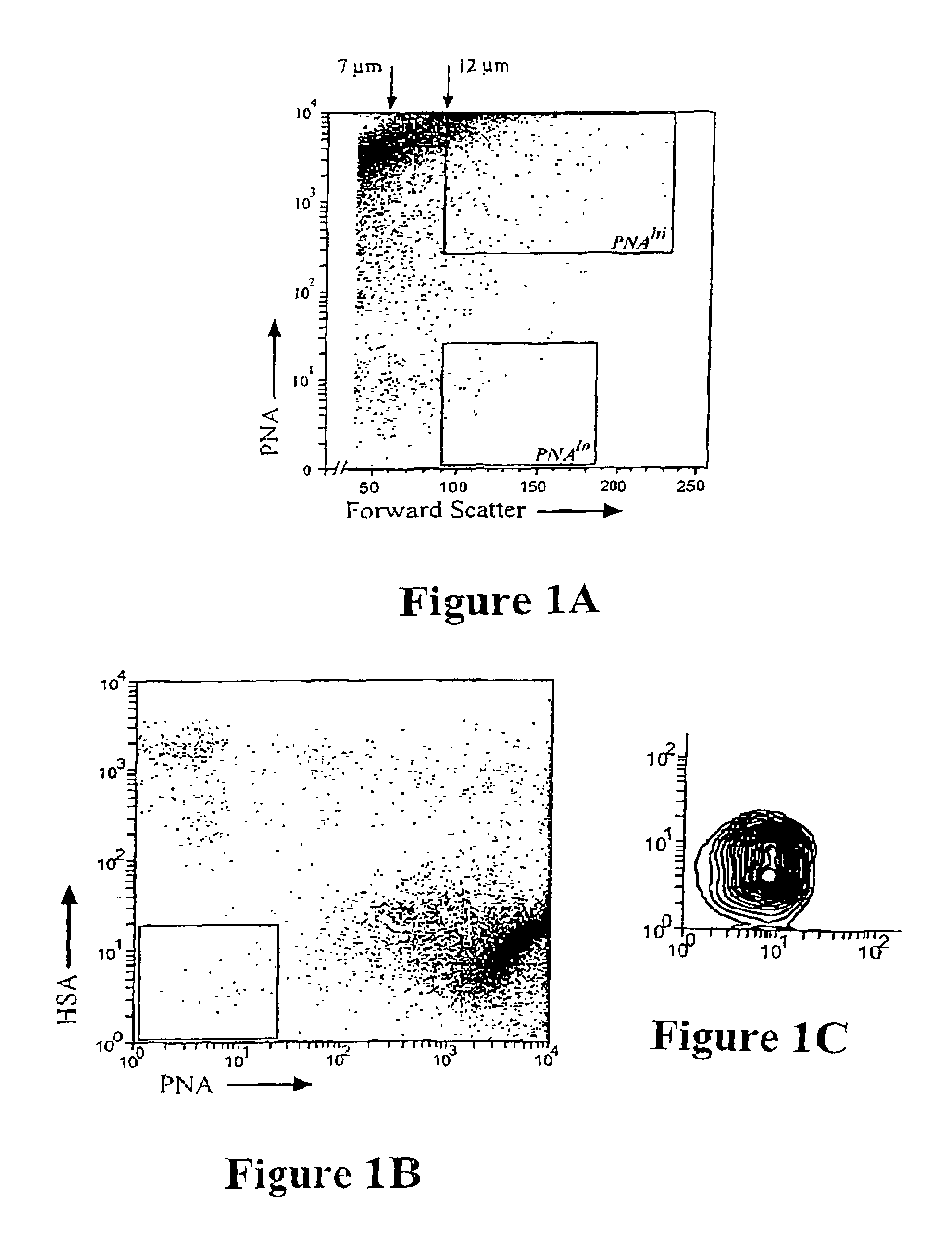
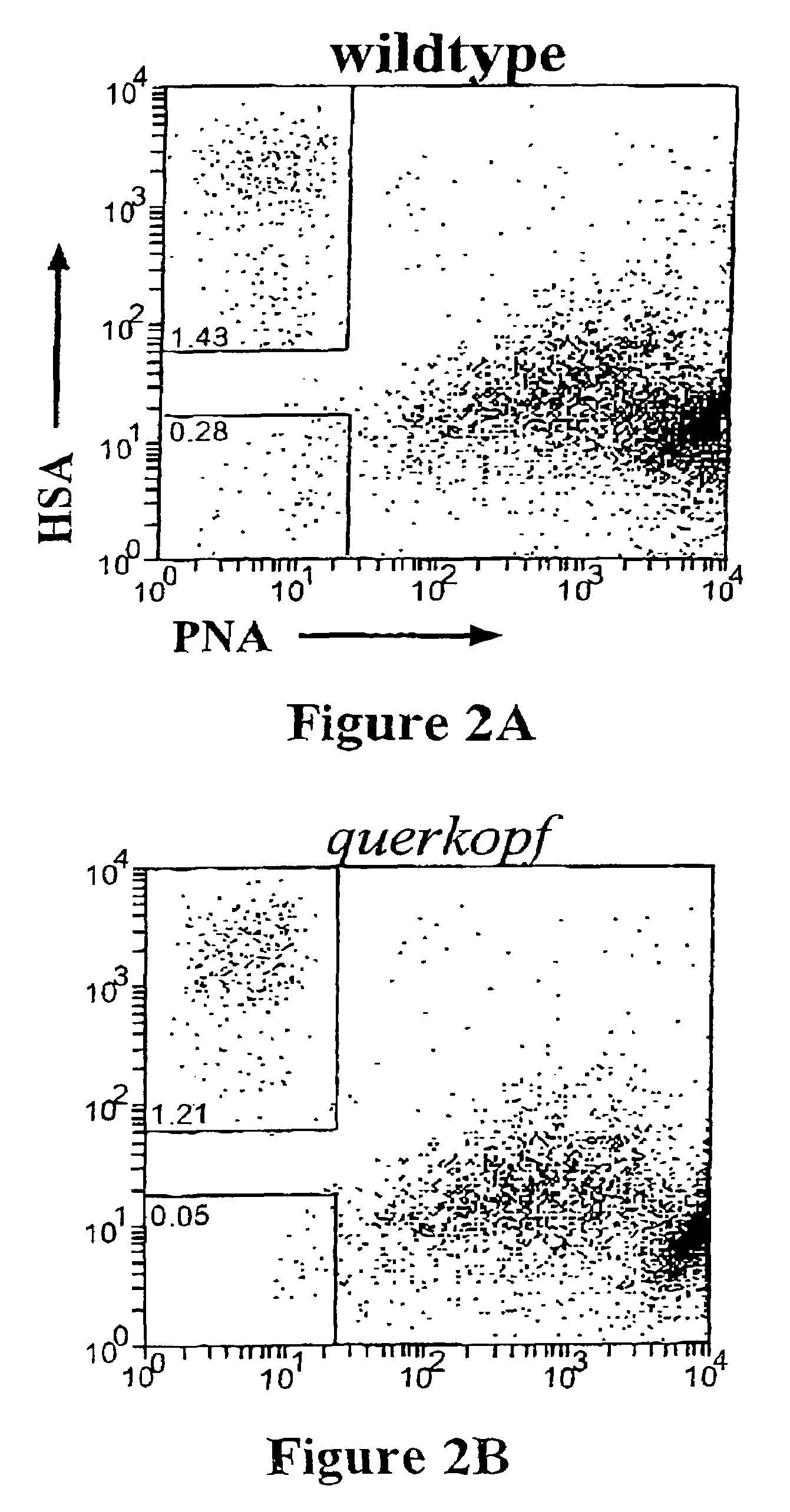
System, method, and article for detecting abnormal cells using multi-dimensional analysis
ActiveUS20060263833A1Easy to detectWell representedData visualisationBiological particle analysisCell lineageBiological cell
A system, method, and article for diagnosing a test set of biological cells. For example, in one embodiment a normal set of cells is characterized using flow cytometry. A centroid and radius are defined for a set of clusters in an n-dimensional space corresponding to a normal maturation for a cell lineage in the normal set of cells. A test set of cells is characterized using flow cytometry and the characterization is compared to the set of clusters.
Owner:HEMATOLOGICS
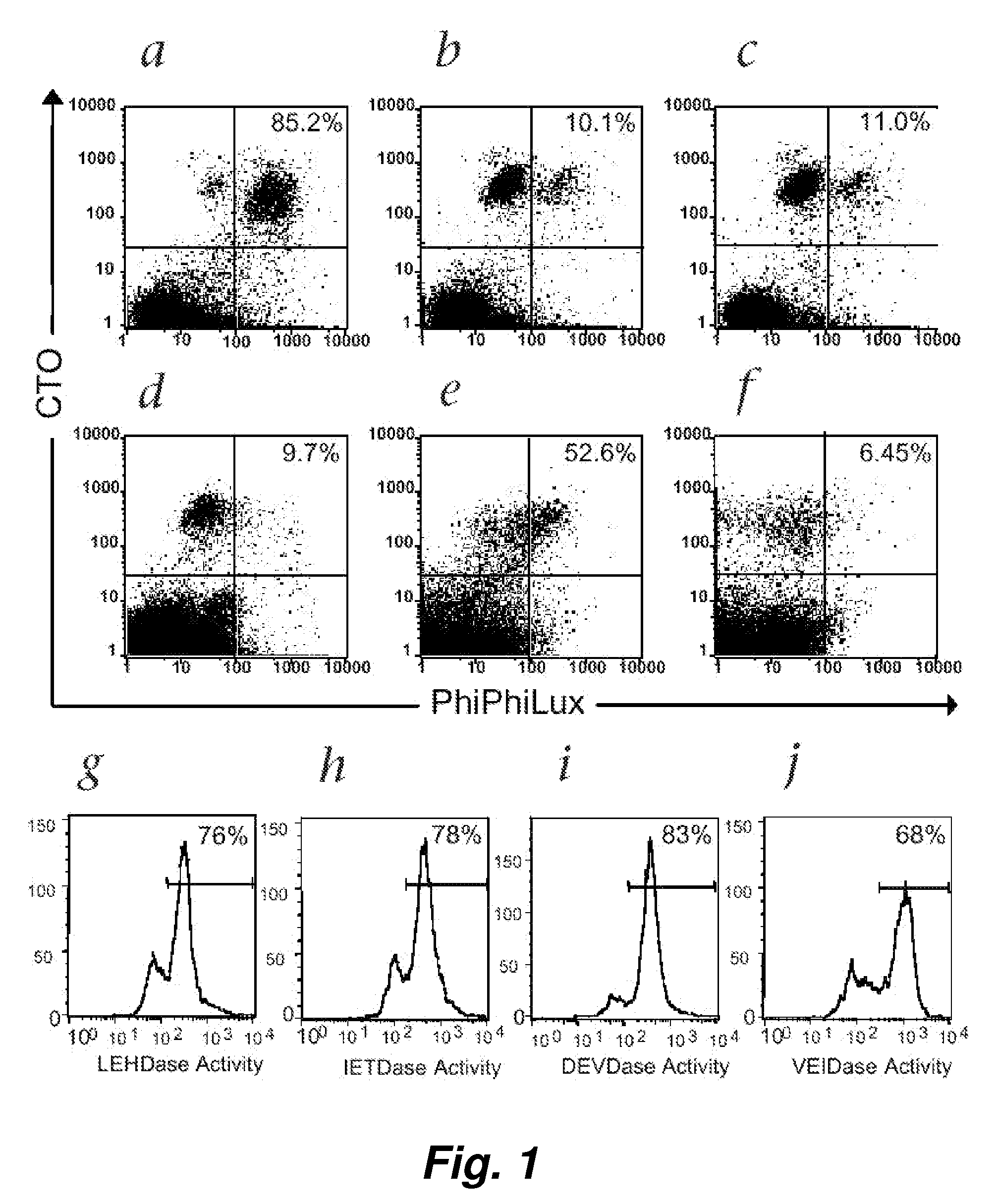
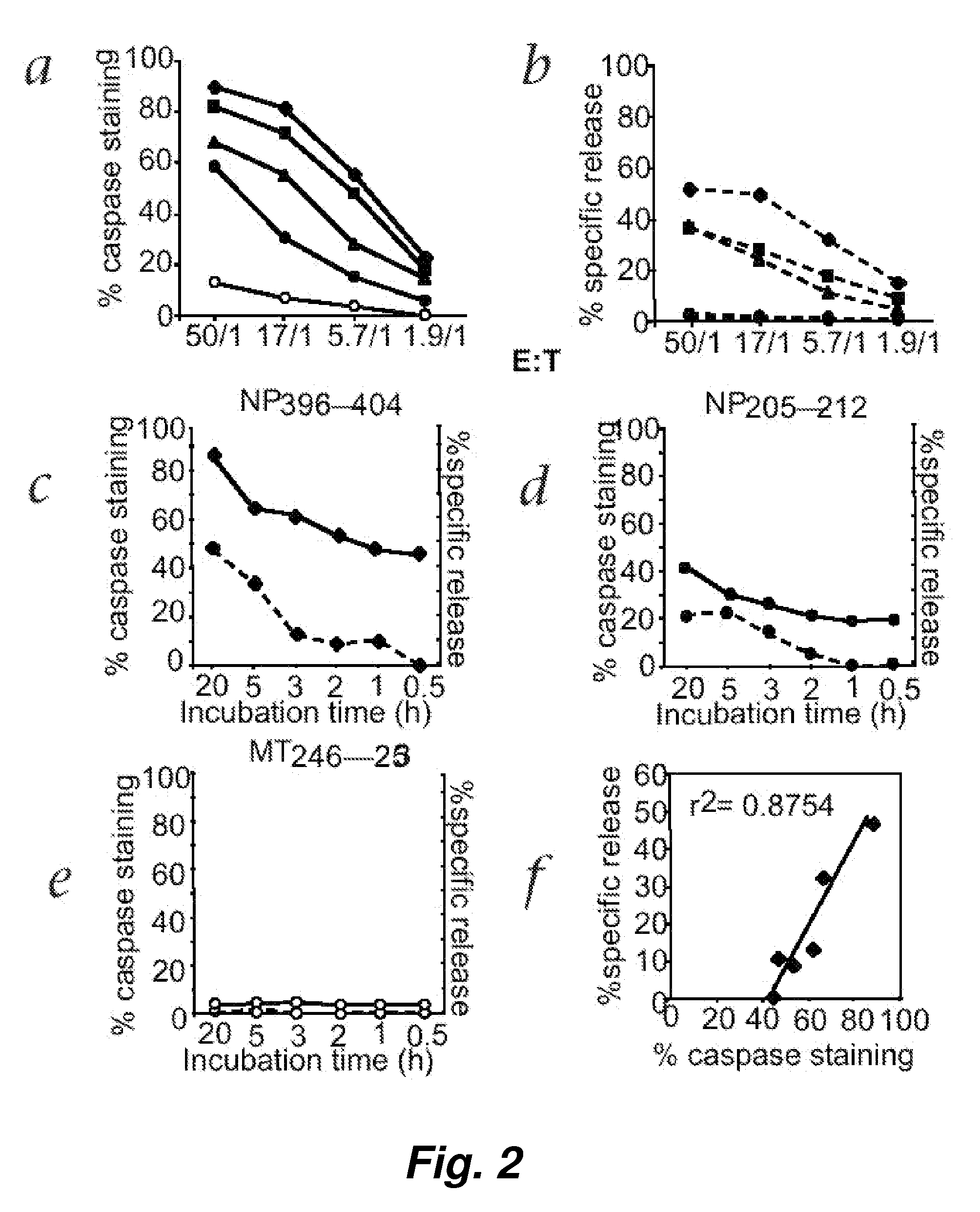
Visualization and quantitation of cellular cytotoxicity using cell-permeable fluorogenic protease substrates and caspase activity indicator markers
ActiveUS20070184493A1Microbiological testing/measurementTetrapeptide ingredientsFluorescenceApoptosis pathways
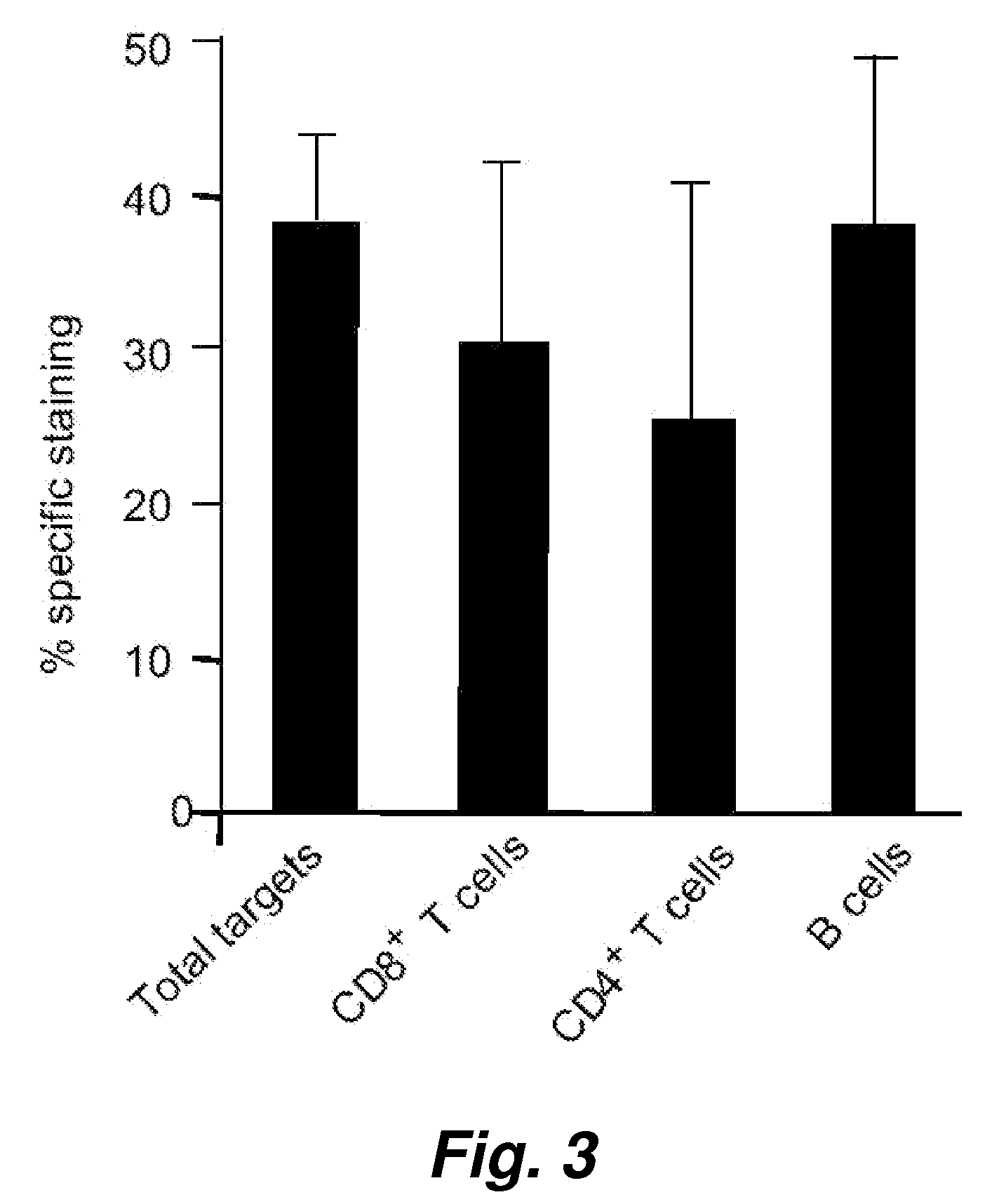
This invention provides a non-radioactive assay to monitor and quantify the target-cell killing activities mediated by cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs). This assay is predicated on the discovery that apoptosis pathway activation and, in particular, granzyme B activity, provides a measure of cytotoxic effector cell activity. In one embodiment, measurement of CTL-induced granzyme B activation in target cells is achieved through detection of the specific cleavage of fluorogenic granzyme B substrates. This assay reliably detects antigen-specific CTL killing of target cells, and provides a more sensitive, more informative and safer alternative to the standard 51Cr-release assay most often used to quantify CTL responses. The assay can be used to study CTL-mediated killing of primary host target cells of different cell lineages, and enables the study of antigen-specific cellular immune responses in real time at the single-cell level. As such, the assay can provide a valuable tool for studies of infectious disease pathogenesis and development of new vaccines and immunotherapies.
Owner:ONCOIMMUNIN
Methods of producing humanized non-human mammals
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Methods and compositions for promoting attachment of cells of endothelial cell lineage to medical devices
InactiveUS20070160644A1Promote disseminationPromote one or more of healingPeptide/protein ingredientsPretreated surfacesCoated surfaceCell lineage
The present invention provides compositions and methods for an improved coating for medical devices. Provided is a biofunctional coating composition comprising at least one binding domain that has binding specificity for a surface material of a medical device, and at least one binding domain that has binding specificity for cells of endothelial cell lineage. Methods for coating a surface of a medical device, and for manufacturing of a medical device, comprise contacting the surface to be coated with the biofunctional coating material in an amount effective to form a coating, and may further comprise contacting the coated surface with cells of endothelial cell lineage to bind the cells of endothelial cell lineage to the coated surface.
Owner:AFFINERGY INC
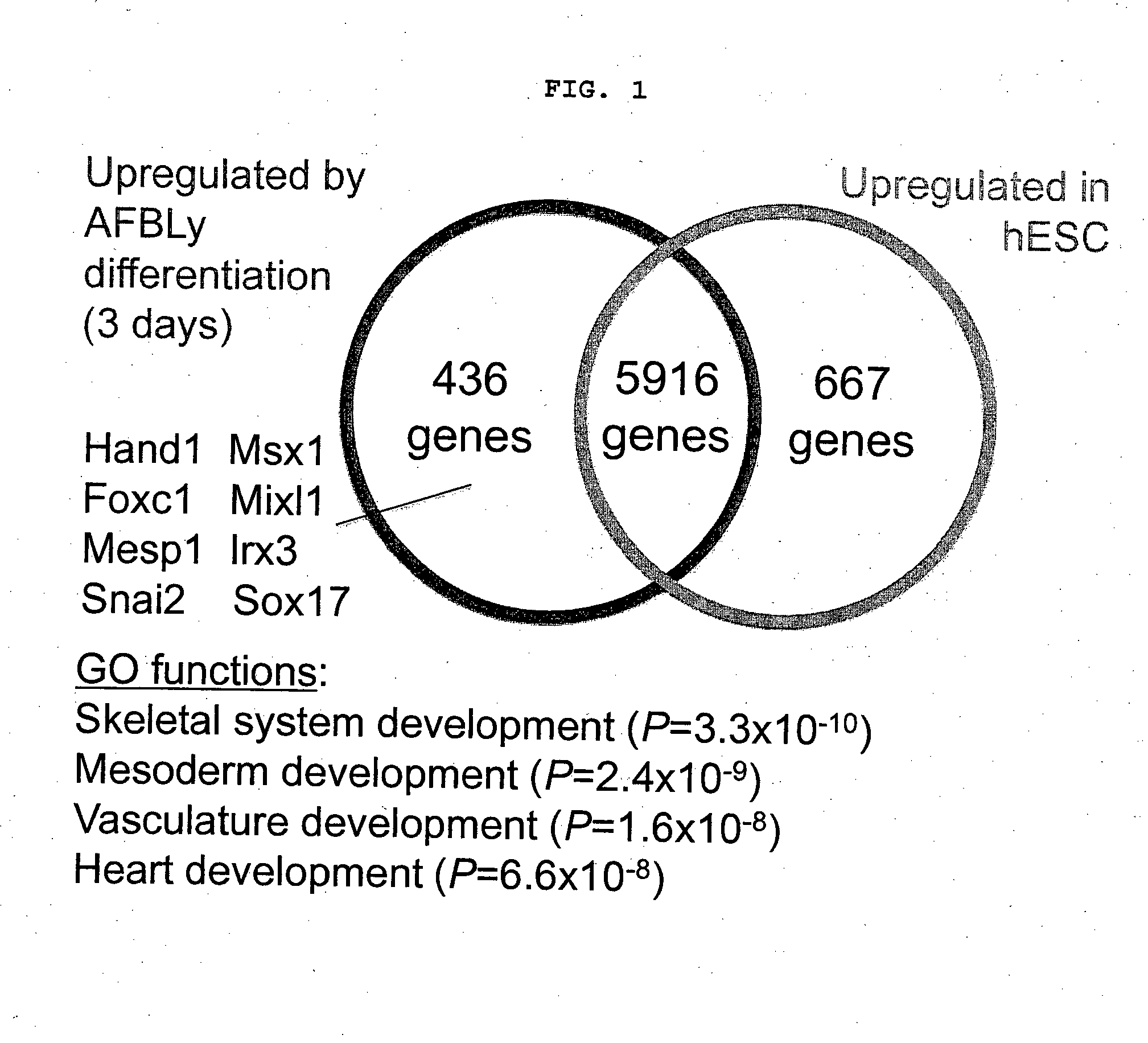
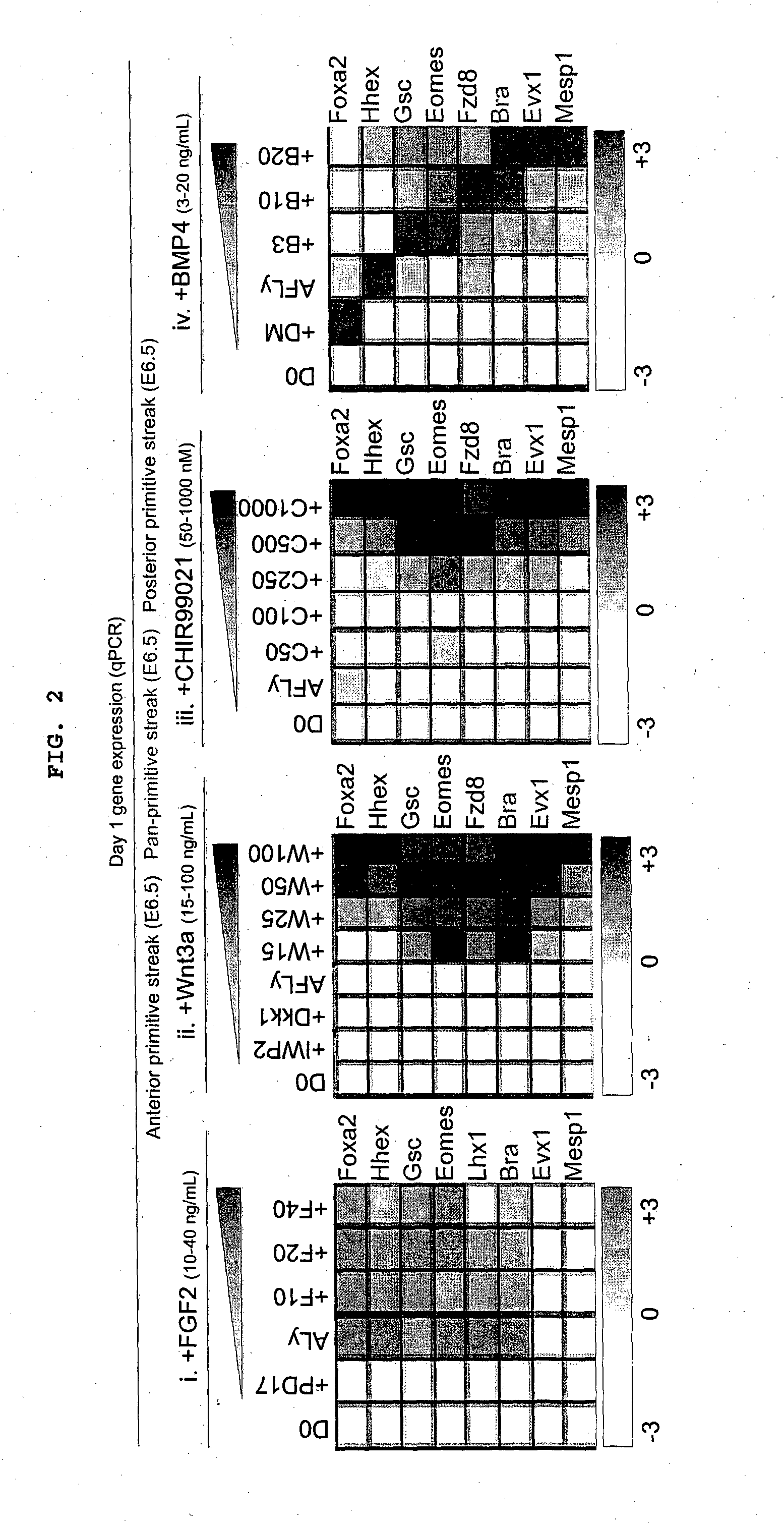
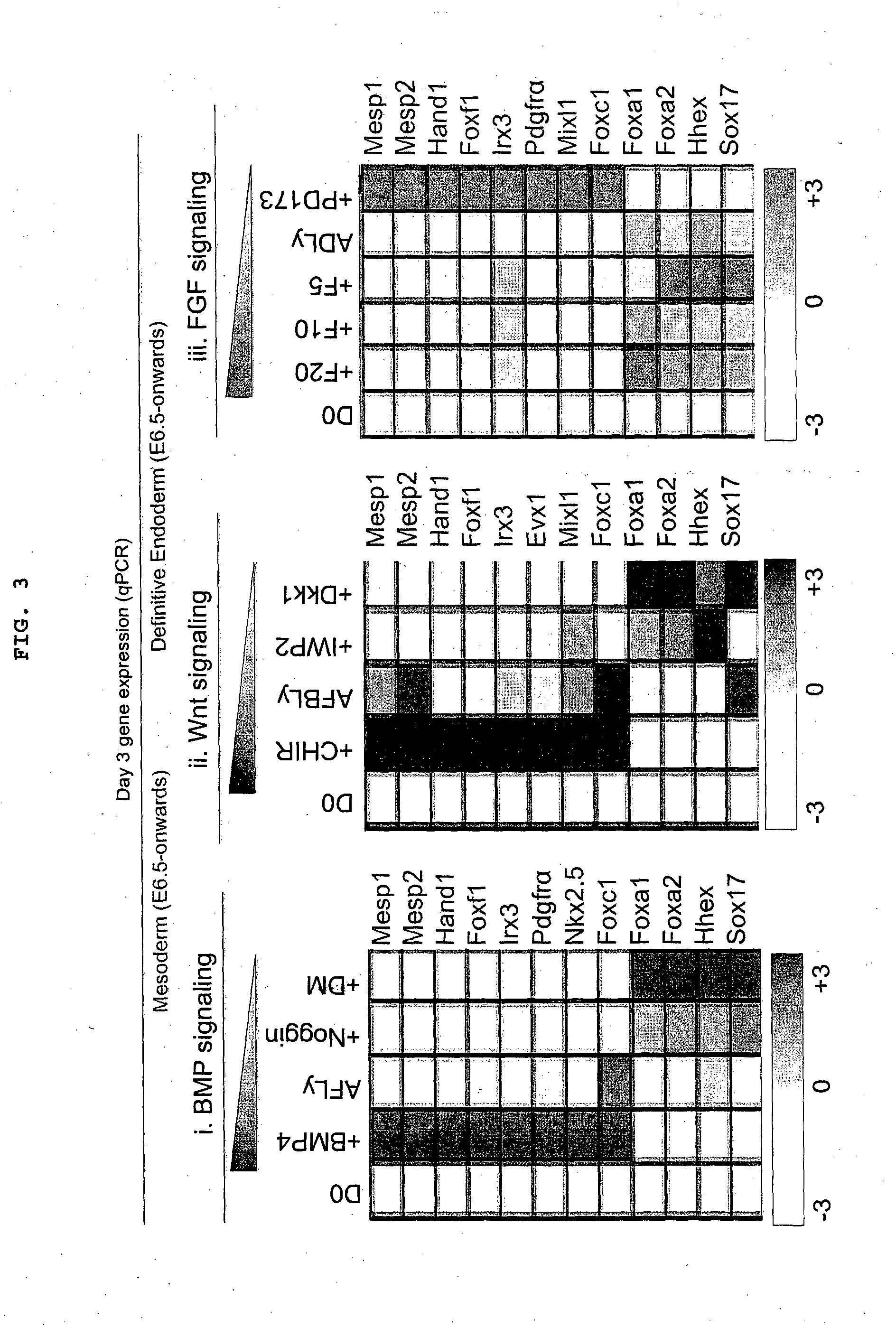
Methods of differentiating stem cells into one or more cell lineages
The present disclosure provides an understanding of the regulation of the developmental phases of stem cells and their induction into relevant cell lineages, such as primitive streak, endoderm, mesoderm, or subterrotories of endoderm's. In particular, the present disclosure provides methods, culture medium and kits for the maintenance and differentiation of stem cells into relevant cell lineages.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
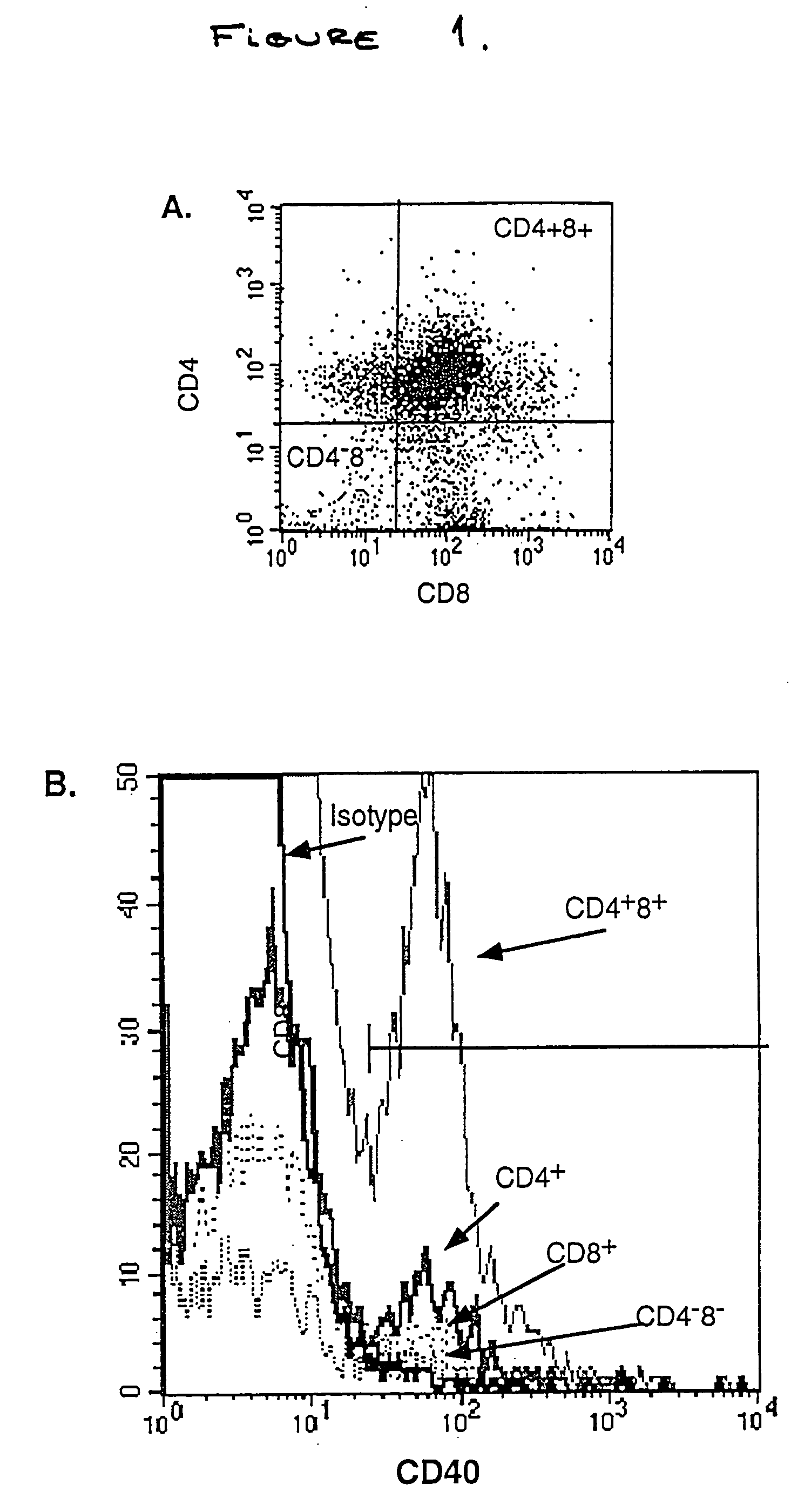
Use of CD40 engagement to alter T cell receptor usage
InactiveUS20050048055A1Promote maturitySpecificity can be alteredSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenCell lineage
The invention relates to methods for altering and enhancing the immune response toward an antigen. More specifically, the present invention relates to methods of using CD40 engagement on T cells to induce T cell receptor gene rearrangement and enhance T cell affinity for a particular antigen. The invention also relates to methods for promoting developmental maturation of an immature cell of the T cell lineage.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF VERMONT +1
Method for identifying and purifying smooth muscle progenitor cells
InactiveUS20040234972A1Increase chanceImprove efficacyGenetically modified cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementProgenitorCell lineage
The present invention relates to purified smooth muscle progenitor cells and a method for isolating such cells. The purified smooth muscle progenitor cells of the present invention are capable of being induced into the smooth muscle cell lineage at high efficacy (i.e. greater than 60% conversion). The method comprises the steps of transforming cell populations that contain totipotent or pluripotent cells with DNA constructs that are expressed only in the smooth muscle cell lineage, inducing a portion of those cells and identifying those cells that express the construct only after the cells are induced.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
CD123+ dendritic cells in blood and lymphoid tissues
InactiveUS6294381B1Artificial cell constructsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsCell lineageDendritic cell
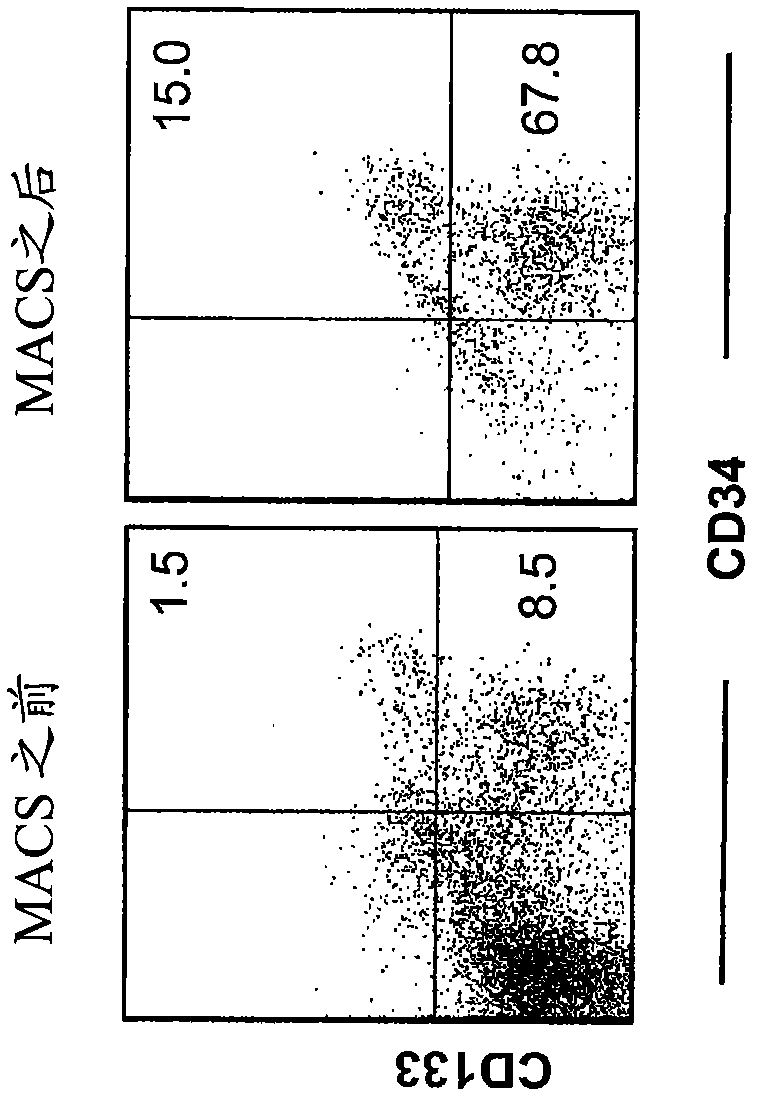
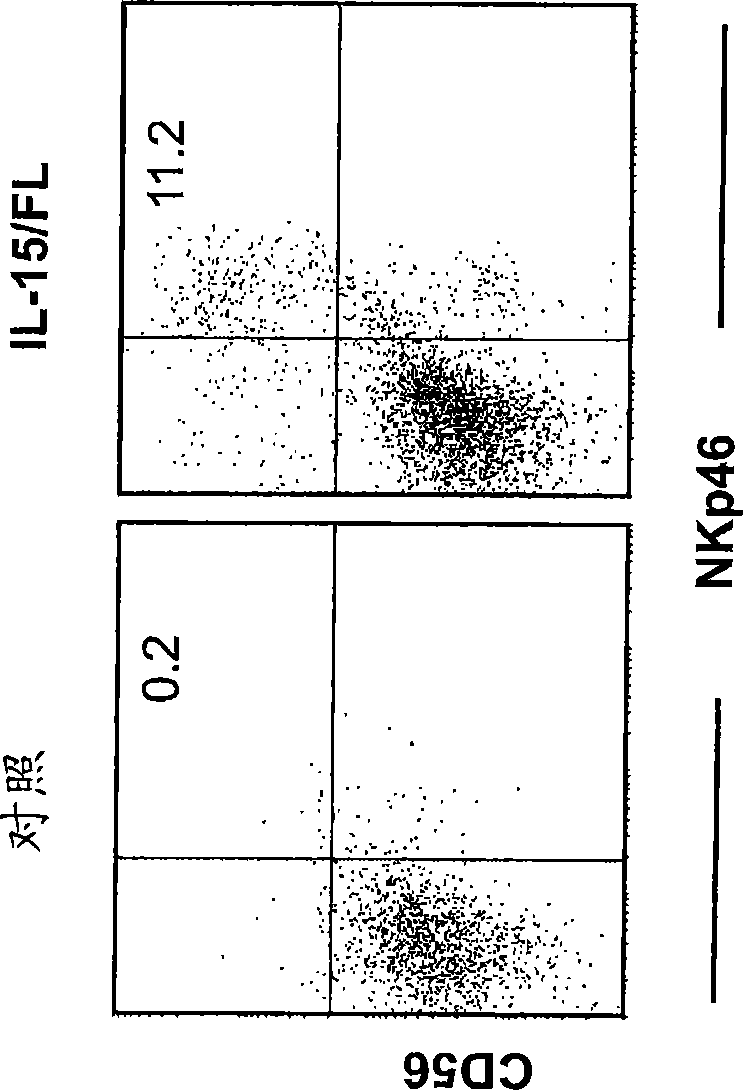
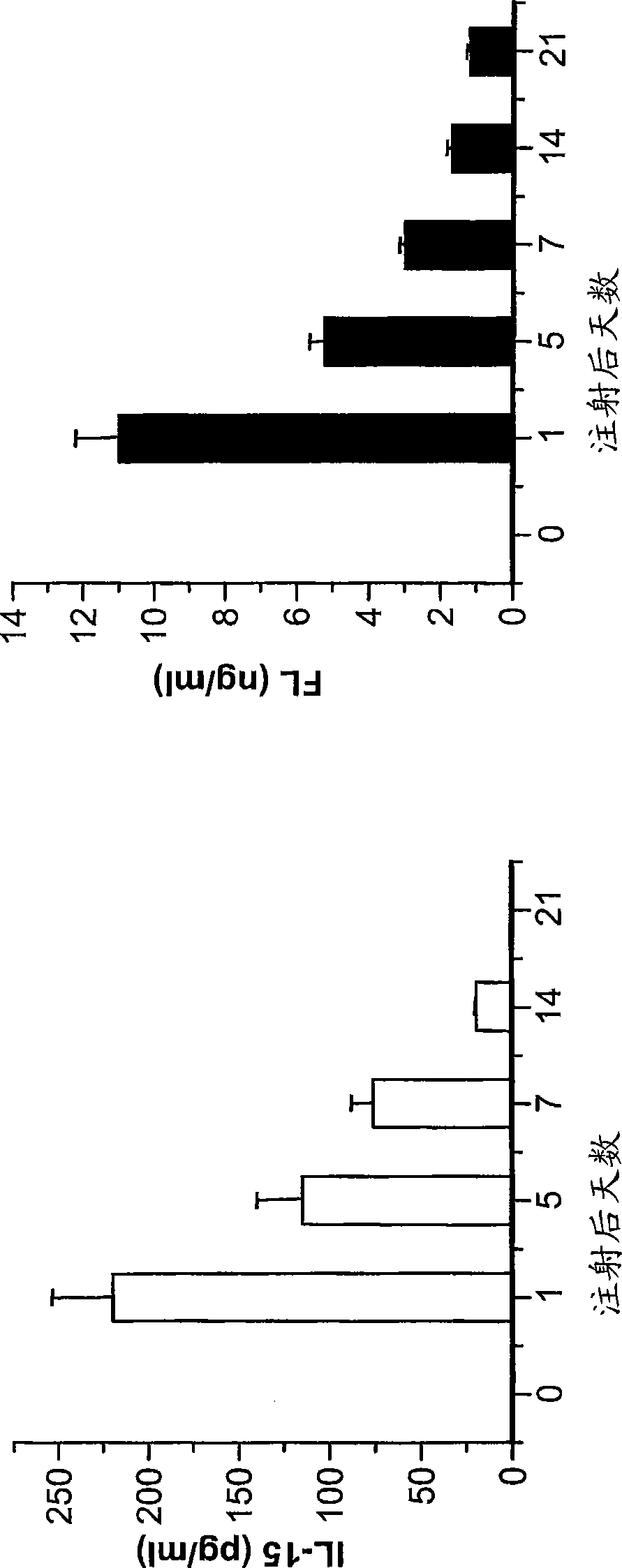
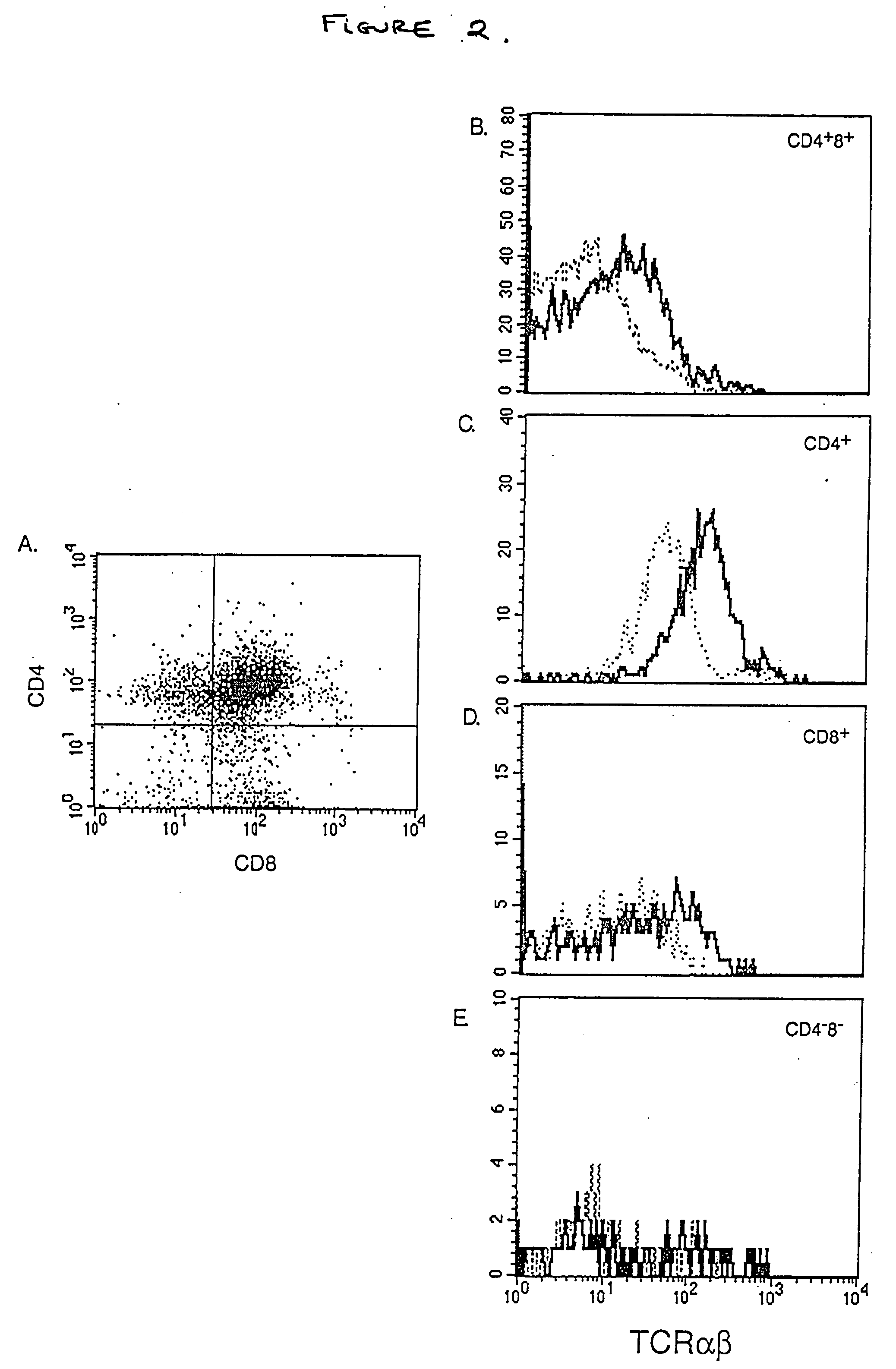
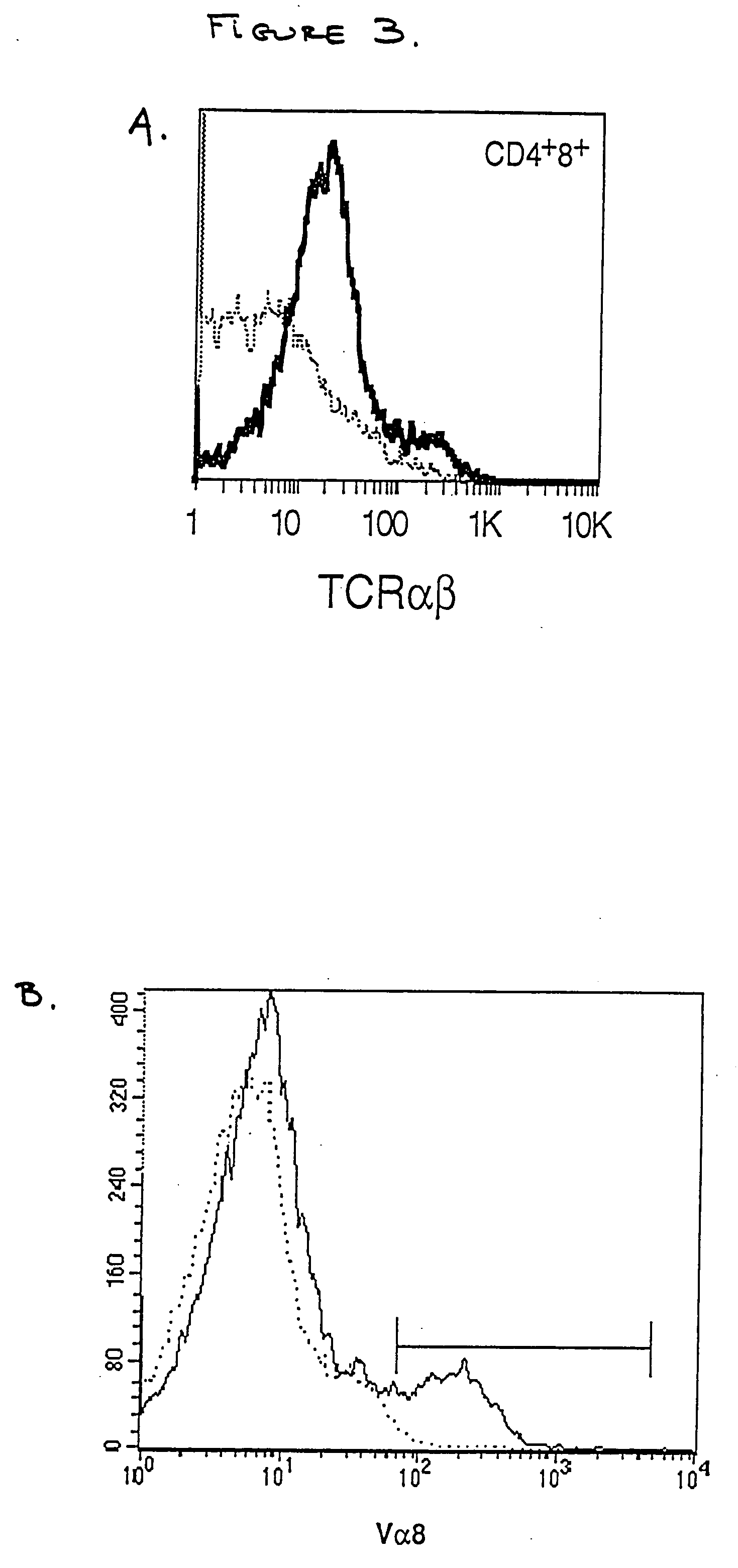
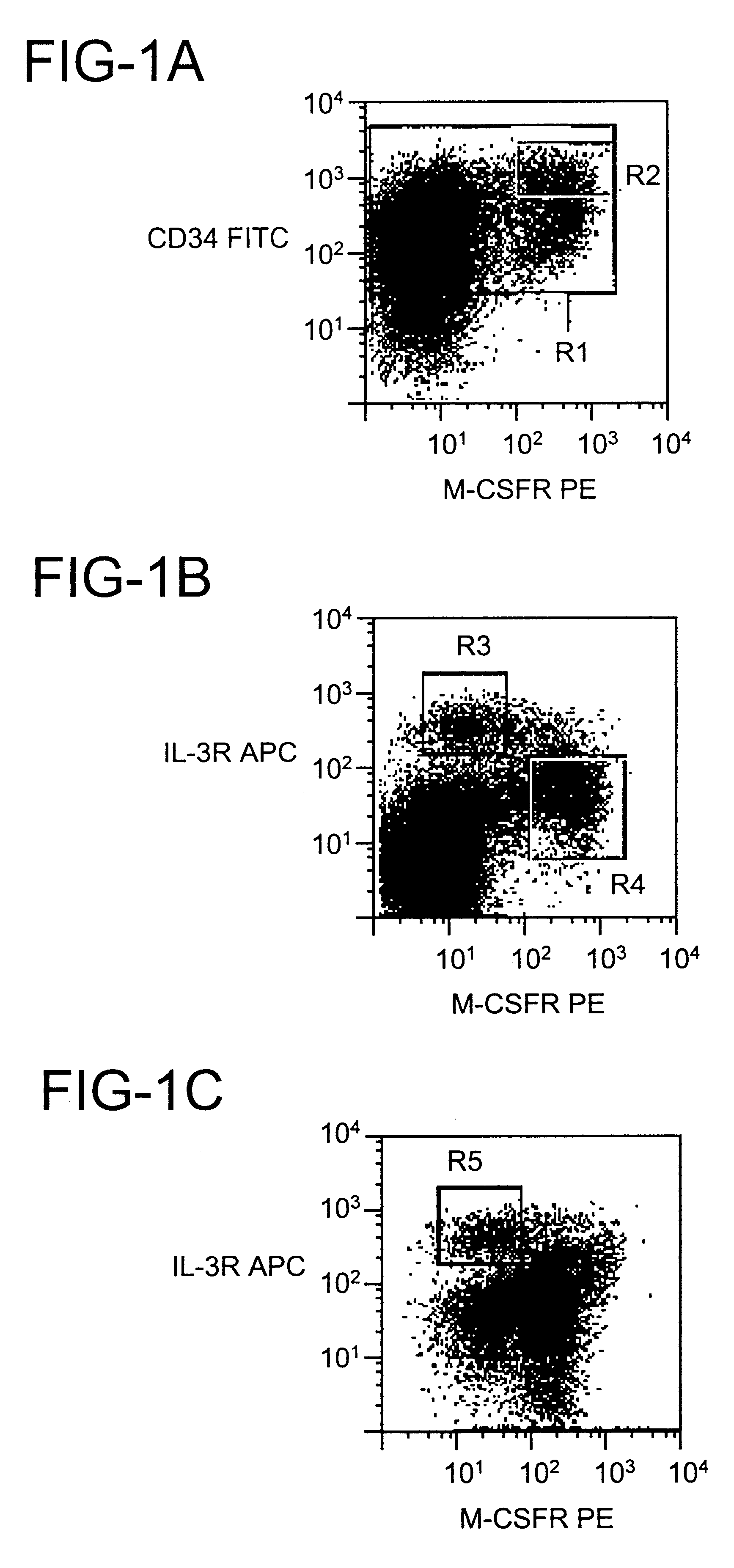
Dendritic cells (DCs) are the primary antigen presenting cells during the initiation of T cell-dependent immune responses. The cells originate from the bone marrow and have been suggested to represent a distinct cell lineage. However, distinct DC precursors have not been identified in bone marrow, and mature monocytes can also give rise to DCs. The instant invention presents a distinct DC precursor among bone marrow CD34+ cells. The cells express high levels of the interleukin-3 receptor alpha chain and CD4 and can be uniquely identified also in blood and lymphoid tissues by this phenotype.
Owner:OLWEUS JOHANNA +1
Method for programmed differentiation of stem cells
Provided is a method for programming the differentiation of stem cells and for the identification of the signals responsible for cell lineage establishment of differentiated cells.
Owner:KHILLAN JASPAL S
Engineered blood vessels
The present invention relates to engineered blood vessels and methods of making such vessels using matrices comprising endothelial and smooth muscle cells, or cells capable of differentiating into endothelial and smooth muscle cell lineages (e.g., stem cells, or the progenitors thereof).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Method of differentiating stem cells
ActiveUS20130224857A1Efficient power generationCell dissociation methodsCulture processCell lineageGerm layer
The present disclosure provides methods of generating germ layers from stem cells comprising culturing the stem cells in a culture media having osmolality ranges that promote the generation of specific germ layer progenitor cells. The present disclosure also includes a method to generate different cell lineages from the germ layers as well as to detect them by immunological methods. The present disclosure further provides methods for the generation, isolation, cultivation and propagation of committed progenitor cells and for the production of differentiated cells from the three germ layers. The present disclosure also provides culture media and kits for use in inducing the three germ layers.
Owner:STEMCELL TECHNOLOGIES
Method of Differentiating Stem Cells
ActiveUS20110086379A1Cell dissociation methodsMicrobiological testing/measurementCell lineageProgenitor
The present disclosure provides methods of generating germ layers from stem cells comprising culturing the stem cells in a culture medium having an osmolality less than 340 mOsm / kg. The present disclosure also includes a method to generate different cell lineages from the germ layers as well as to detect them by immunological methods. The present disclosure further provides methods for the generation, isolation, cultivation and propagation of committed progenitor cells and for the production of differentiated cells from the three germ layers. The present disclosure also provides culture media for use in inducing the three germ layers.
Owner:STEMCELL TECHNOLOGIES
Titration of differentiation medium components
ActiveUS20120129211A1Improve efficiencyMass productionCell differentiationMicrobiological testing/measurementCell lineageCulture mediums
Methods and composition for differentiation of pluripotent stem cells are provided. For example, in certain aspects methods including screening of optimal differentiation conditions for a selected stem cell clone in a selected batch of culture medium and use of the determined optimal condition for differentiation into a specific cell lineage.
Owner:FUJIFILM CELLULAR DYNAMICS INC
Mesenchymal-like stem cells derived from human embryonic stem cells, methods and uses thereof
ActiveUS20150191699A1Efficient productionHigh purityBiocideNervous disorderAutoimmune conditionAutoimmune disease
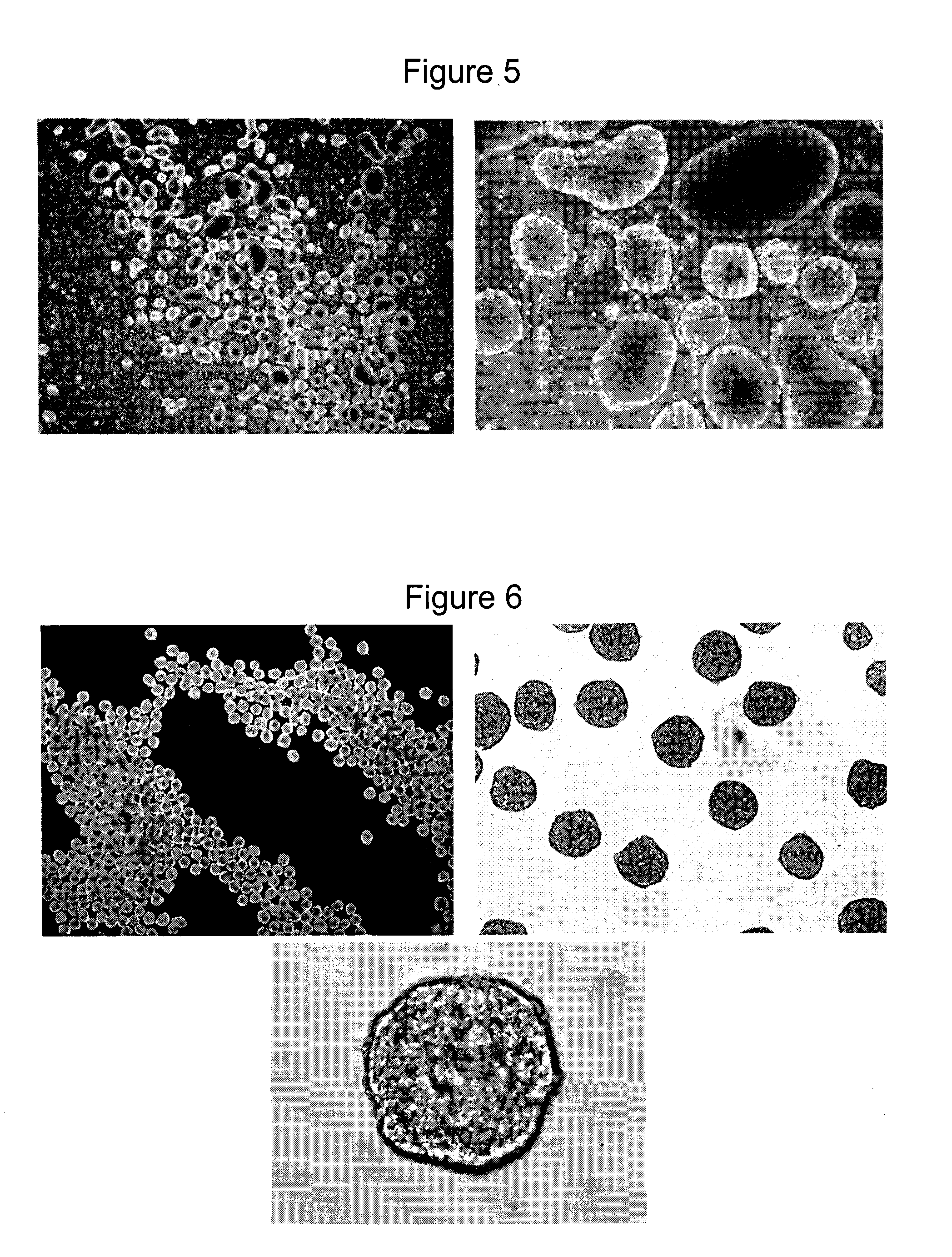
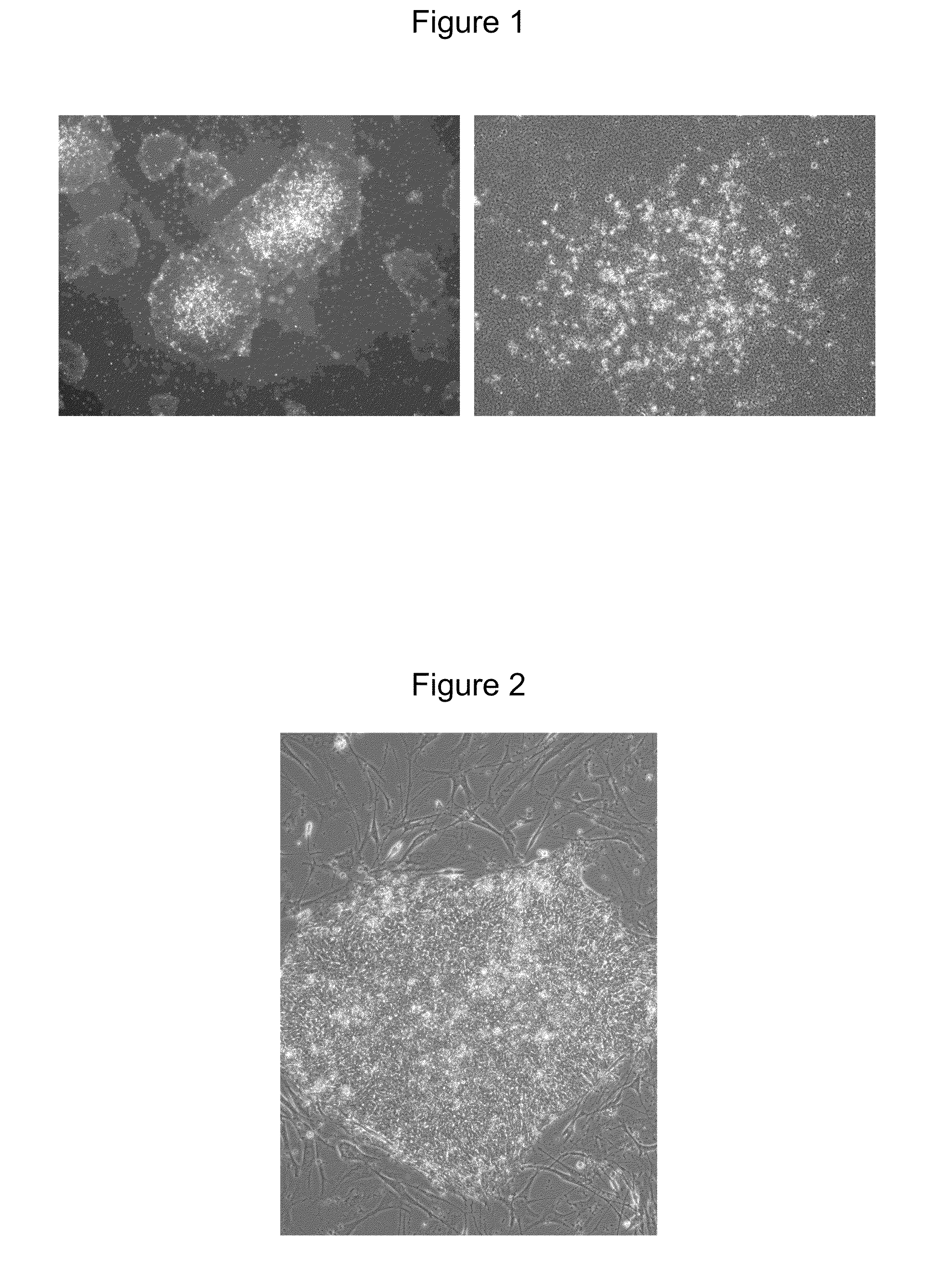
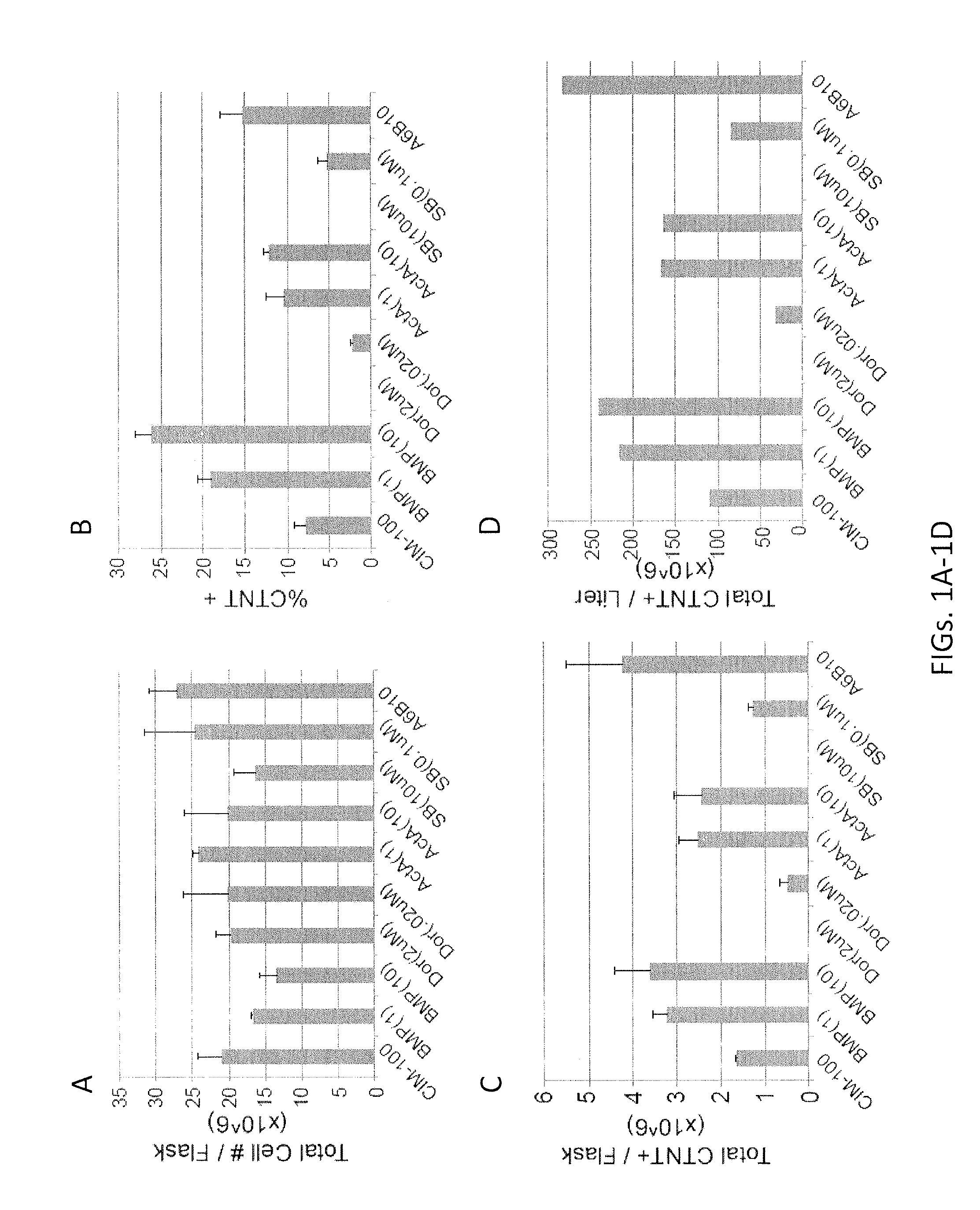
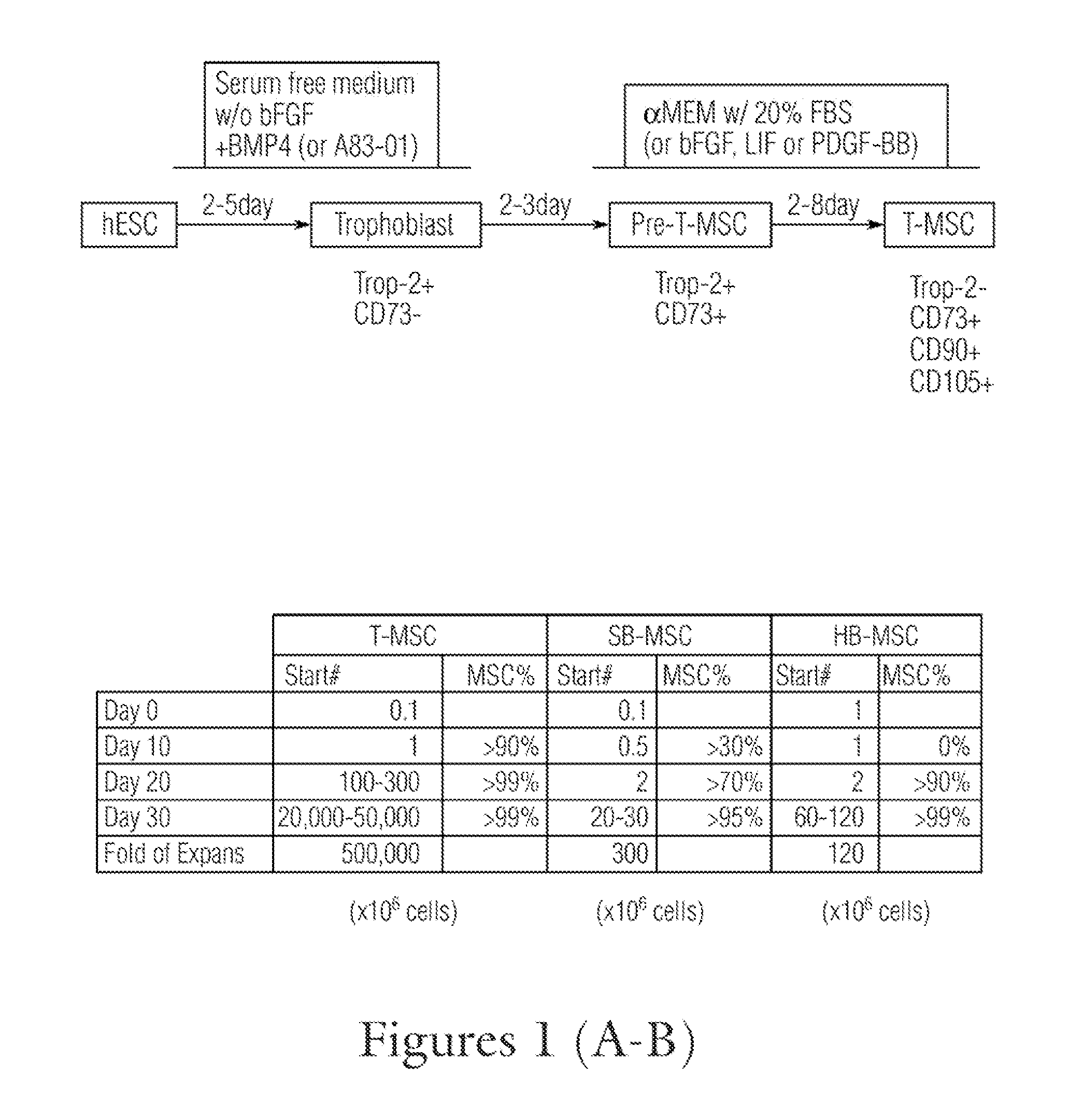
The disclosure provided herein relates generally to mesenchymal-like stem cells “hES-T-MiSC” or “T-MSC” and the method of producing the stem cells. The method comprises culturing embryonic stem cells under conditions that the embryonic stem cells develop through an intermediate differentiation of trophoblasts, and culturing the differentiated trophoblasts to hES-T-MSC or T-MSC, T-MSC derived cells and cell lineages “T-MSC-DL” are also described. Disclosed also herein are solutions and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the T-MSC and / or T-MSC-DL, methods of making the T-MSC and T-MSC-DL, and methods of using the T-MSC and T-MSC-DL for treatment and prevention of diseases, specifically, T-MSC and T-MSC-DL are used as immunosuppressive agents to treat multiple sclerosis and autoimmune diseases.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT +1
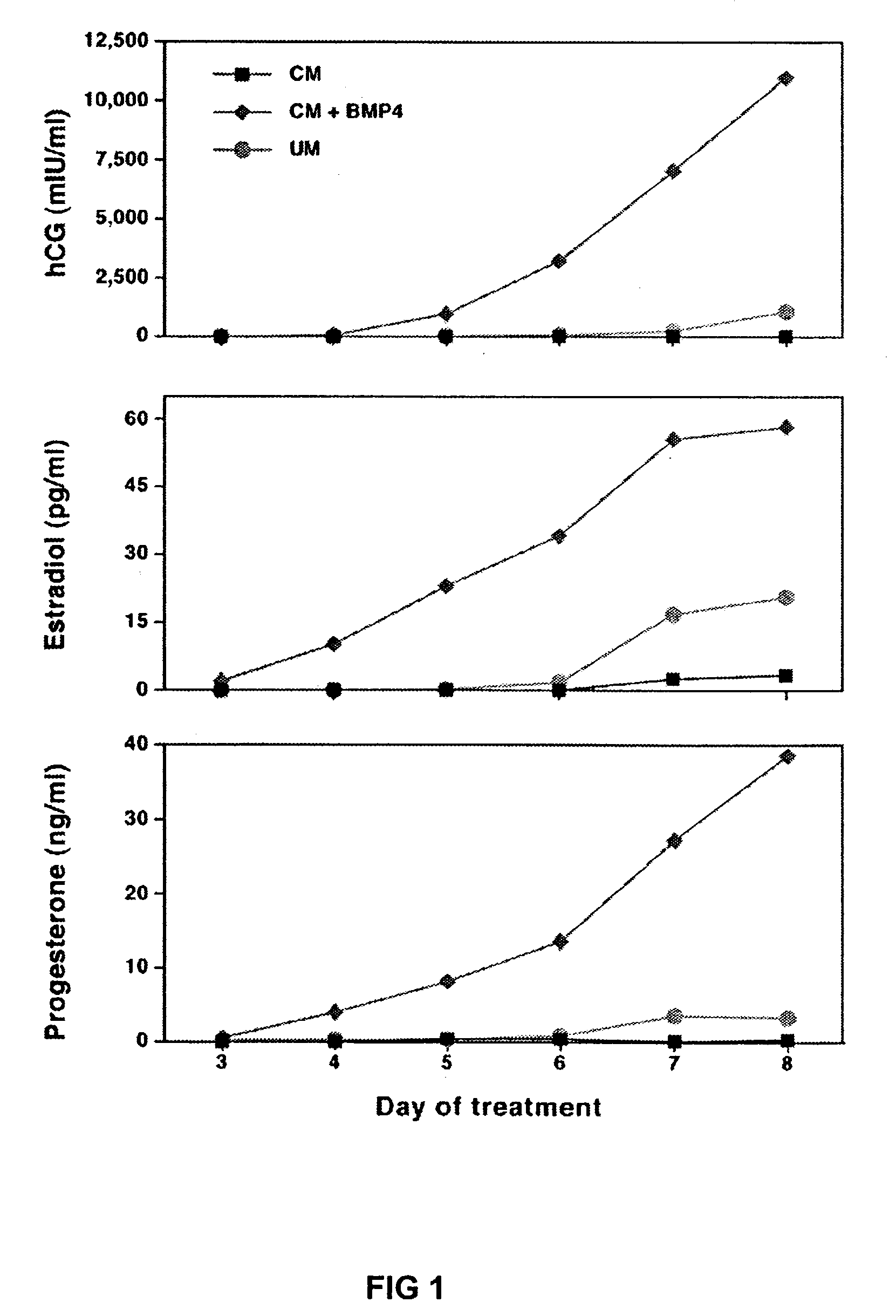
Method for generating primate trophoblasts
The first method to cause a culture of human and other primate stem cells to directly and uniformly differentiate into a committed cell lineage is disclosed. Treatment of primate stem cells with a single protein trophoblast induction factor causes the cells to transform into human trophoblast cells, the precursor cells of the placenta. Several protein factors including bone morphogenic protein 4 (BMP4), BMP2, BMP7, and growth and differentiation factor 5 can serve as trophoblast-inducting factors.
Owner:WICELL RES INST
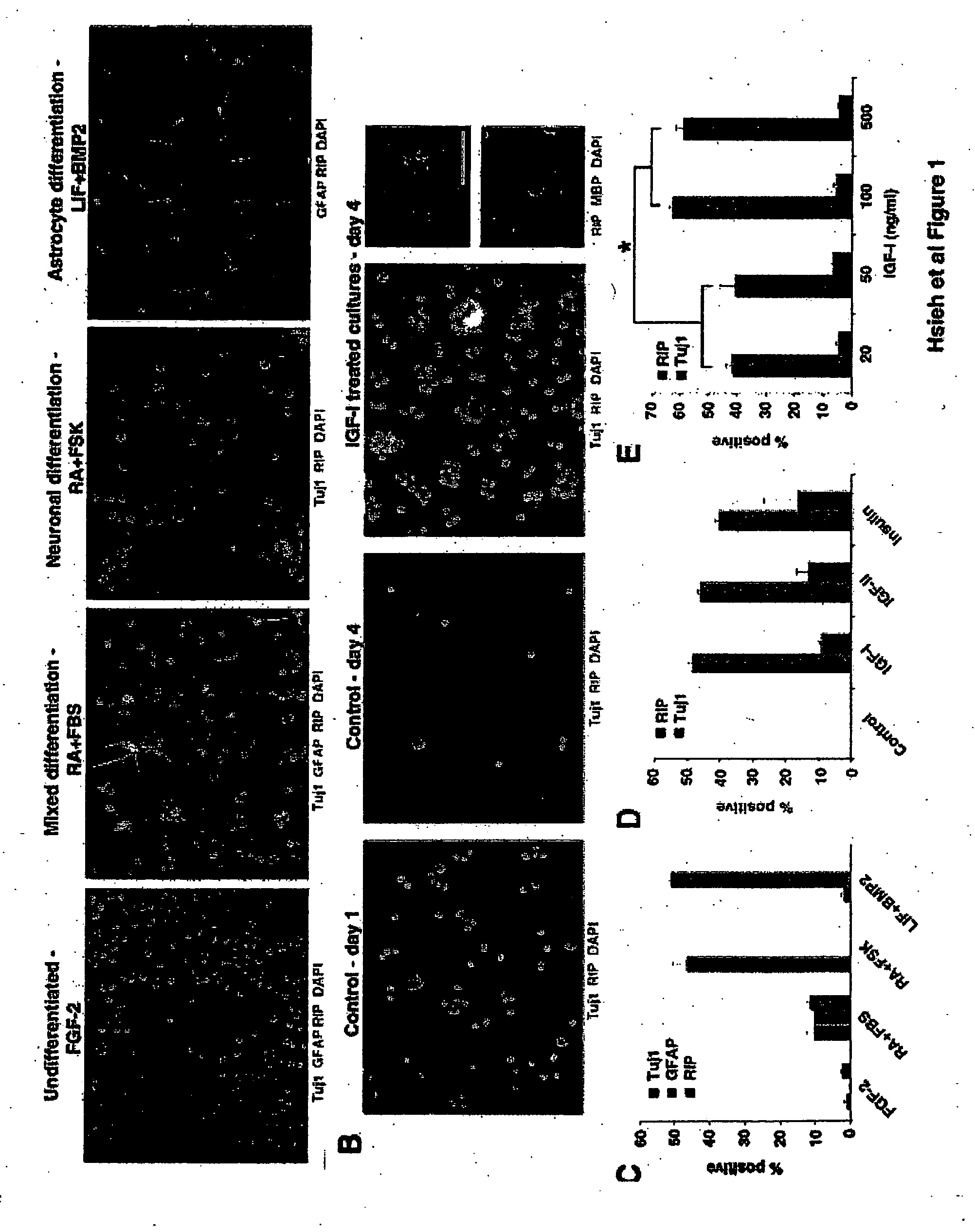
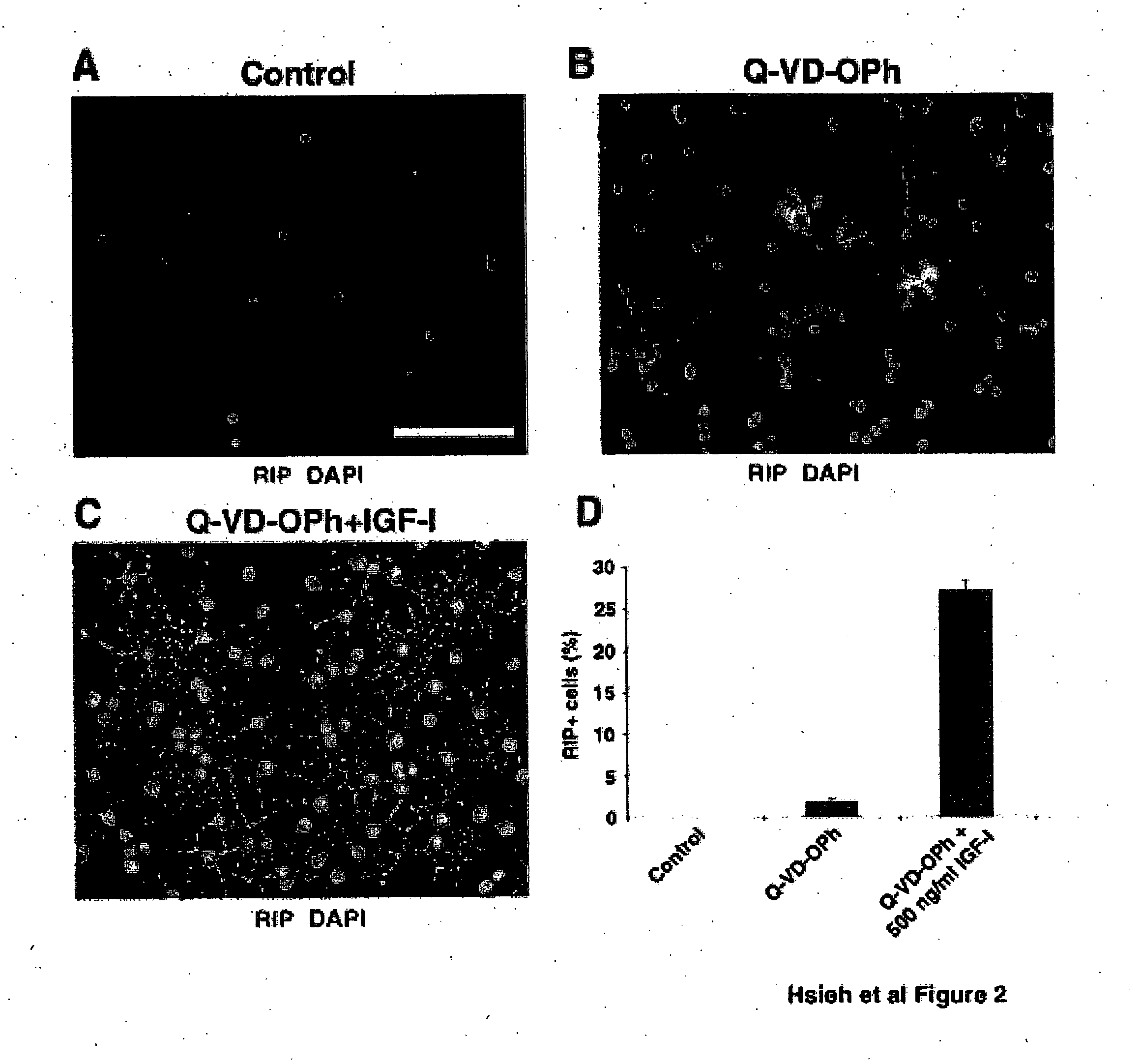
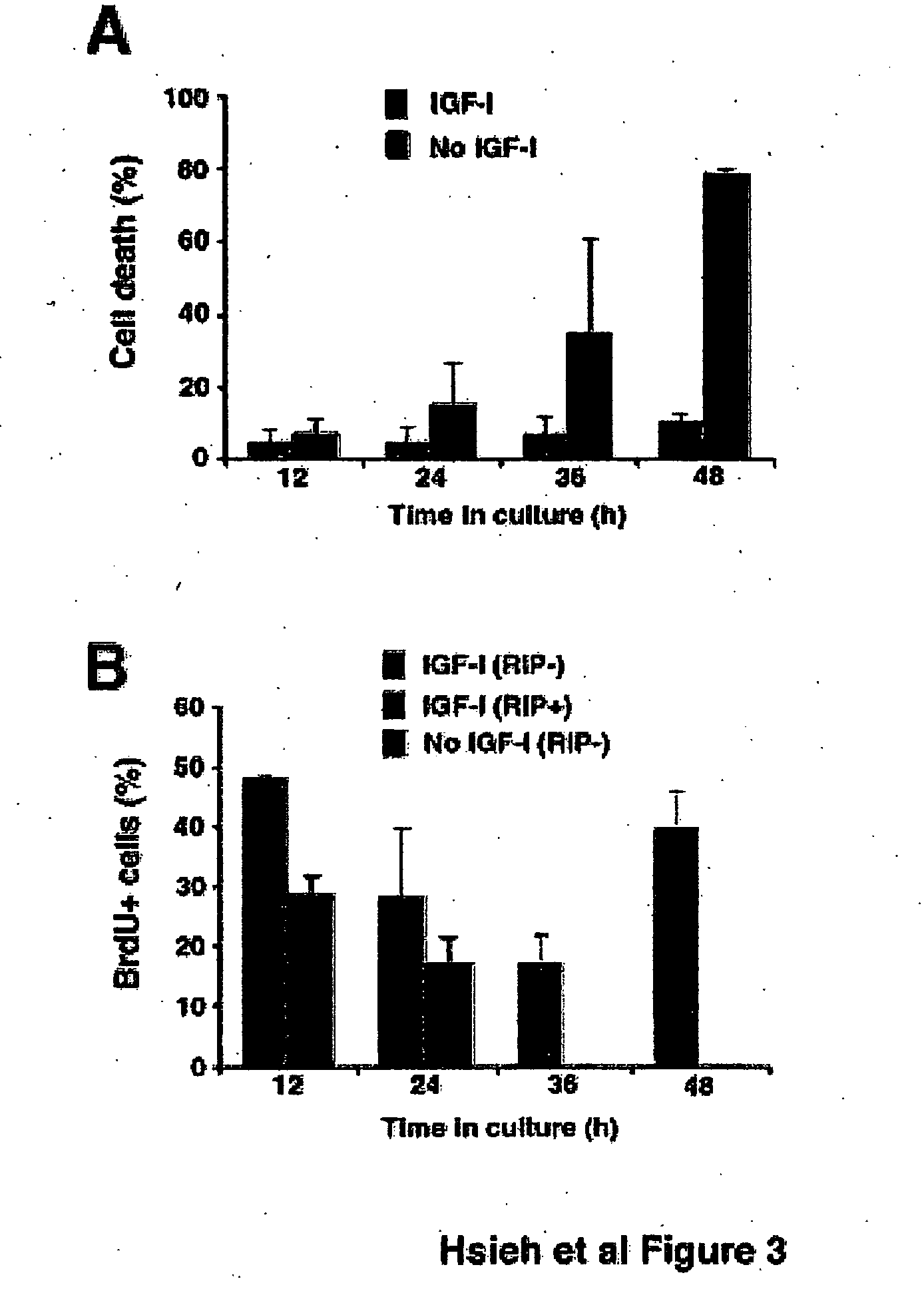
IGF-1 instructs multipotent adult CNS neural stem cells to an oligodendroglial lineage
InactiveUS20050148069A1Promote differentiationStimulate immune responseNervous disorderNervous system cellsProgenitorInsulin-like growth factor
Adult neural stem cells differentiate into neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes in the mammalian CNS, but the molecular mechanisms that control their differentiation are not yet well understood. Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) can promote the differentiation of cells already committed to an oligodendroglial lineage during development. However, it is unclear whether IGF-I affects multipotent neural stem cells. Here we show that IGF-I stimulates the differentiation of multipotent adult rat hippocampus-derived neural progenitor cells into oligodendrocytes. Modeling analysis indicates that the actions of IGF-I are instructive. Oligodendrocyte differentiation by IGF-I appears to be mediated through an inhibition of BMP signaling. Furthermore, overexpression of IGF-I in the hippocampus leads to an increase in oligodendrocyte markers. These data demonstrate the existence of a single molecule, IGF-I, that can influence the fate choice of multipotent adult neural progenitor cells to an oligodendroglial lineage.
Owner:GAGE FRED H +1
Method of purification of cells
The present invention relates generally to a method for the generation of a substantially homogeneous population of undifferentiated cells. More particularly, the present invention relates to the purification of a substantially homogeneous population of stem cells and their progenitor or precursor cells. Even more particularly, the present invention provides a population of neural stem cells (NSCs). The subject invention is particularly directed to NSCs and precursor cells with the capacity to differentiate into cells and cell lineages required for the development, maintenance or repair of the central nervous system in an animal such as a mammal. The present invention is further directed to NSCs and progenitor and / or precursor cells which are capable of proliferation and differentiation into multiple cell lineages, such as but not limited to neurons, oligodendrocytes, glia and astrocytes. The subject invention further contemplates the use of NSCs and / or precursor cells for the repair or regeneration of tissue, such as tissue associated with the central nervous system, in an animal including a mammal. The NSCs of the present invention may be used to identify naturally occurring molecules such as cytokines as well as molecules obtained from natural product screening or screening of chemical libraries which induce proliferation of the NSCs. Such molecules are useful in the development of therapeutics.
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com