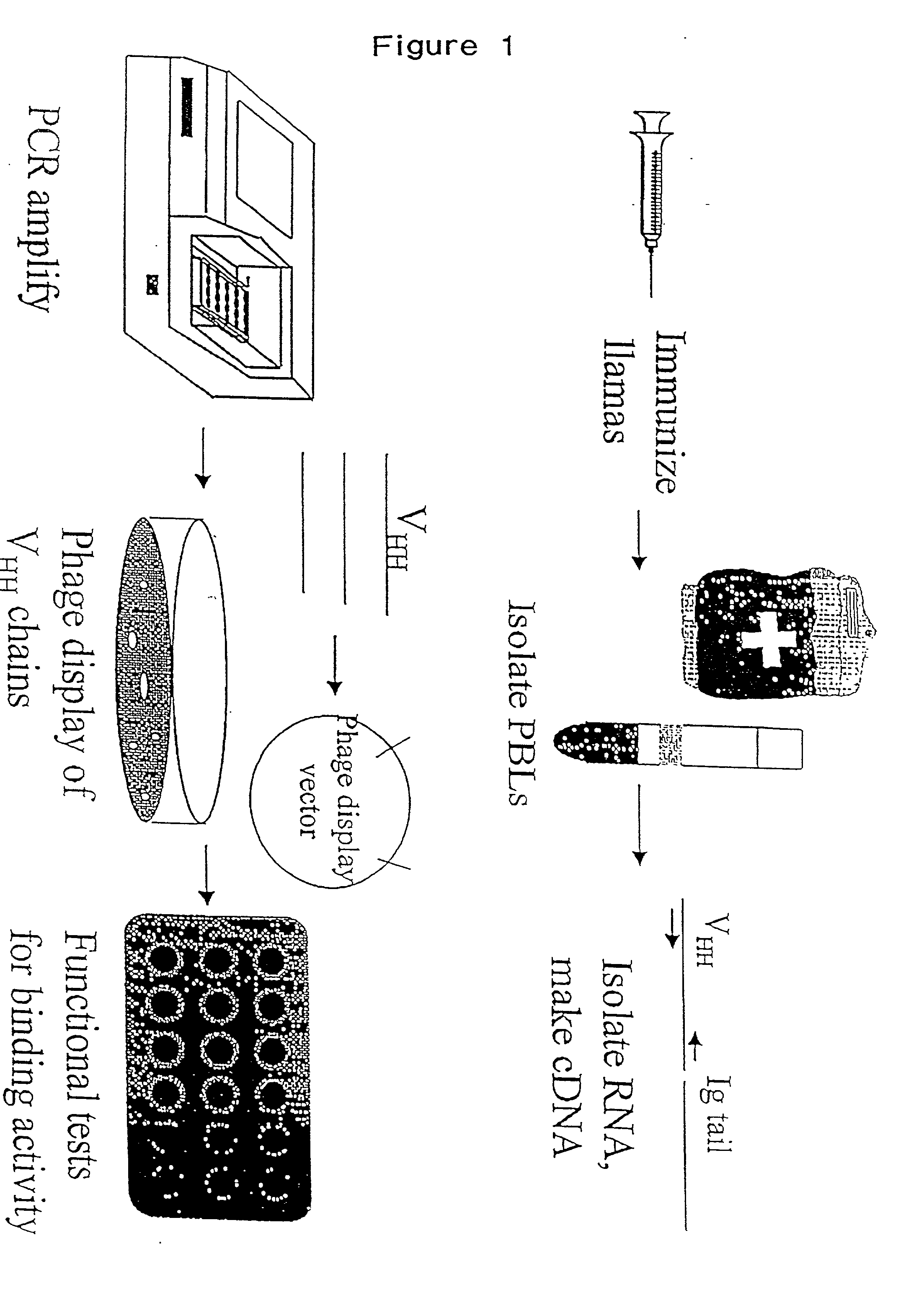
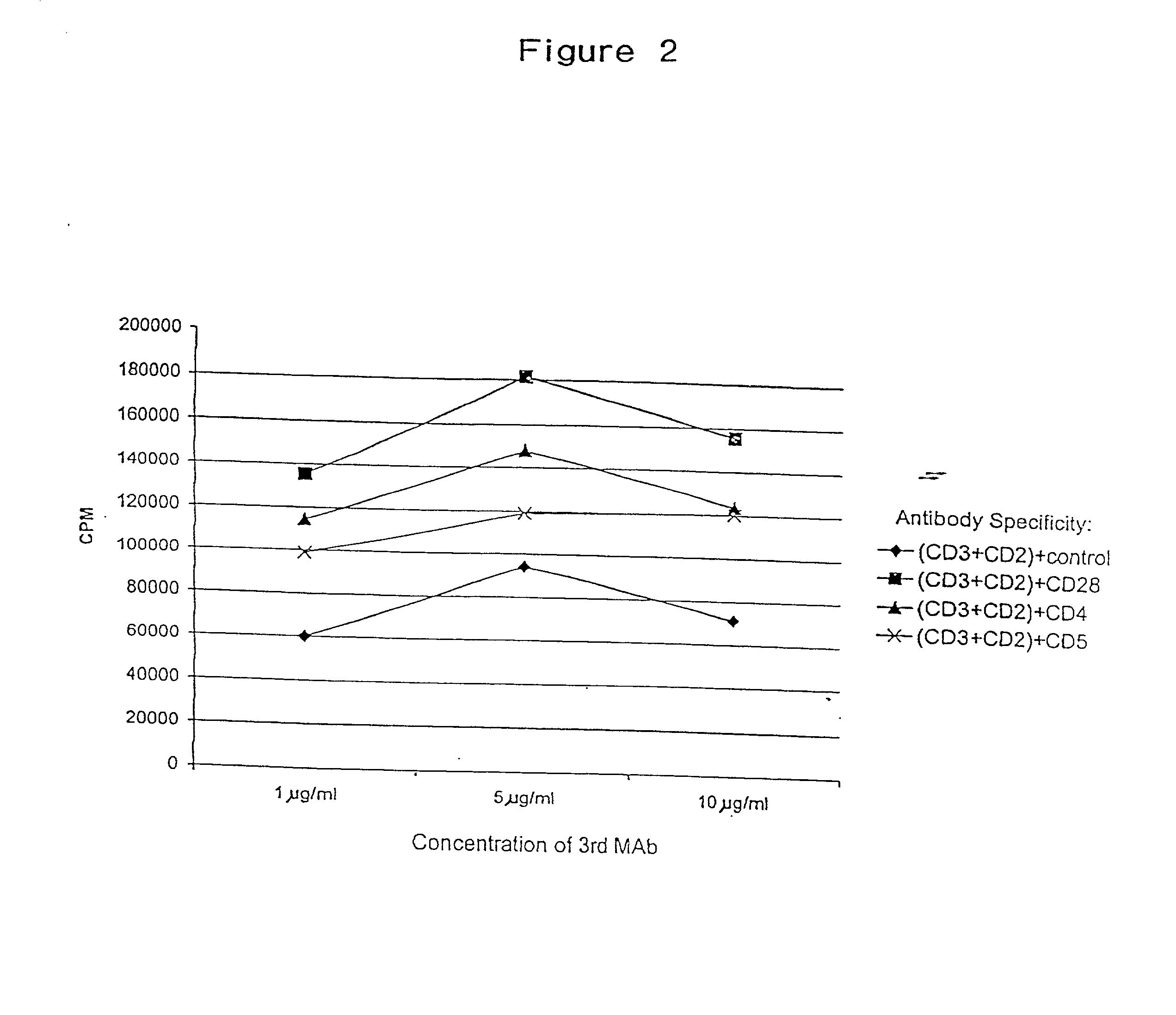
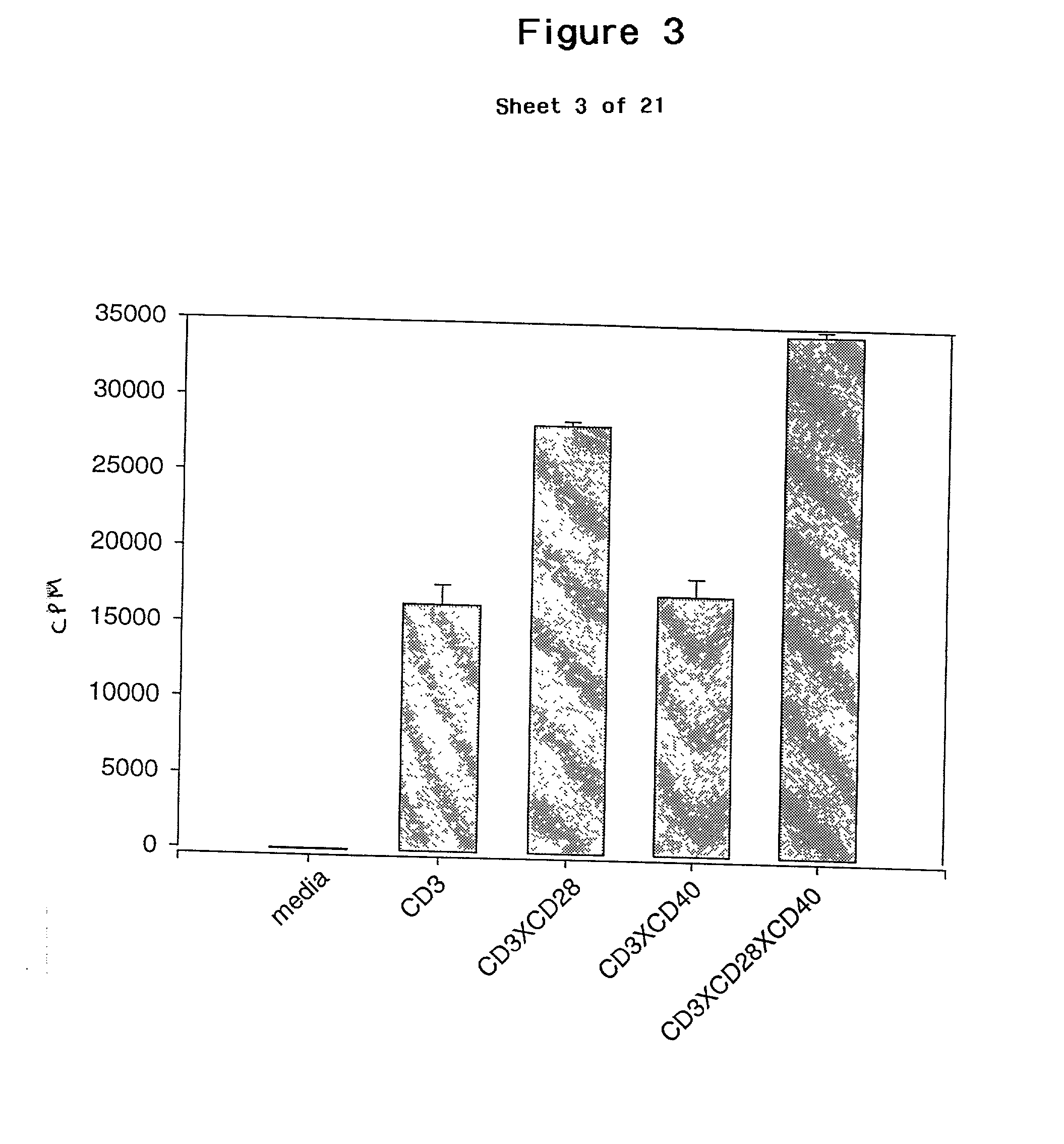
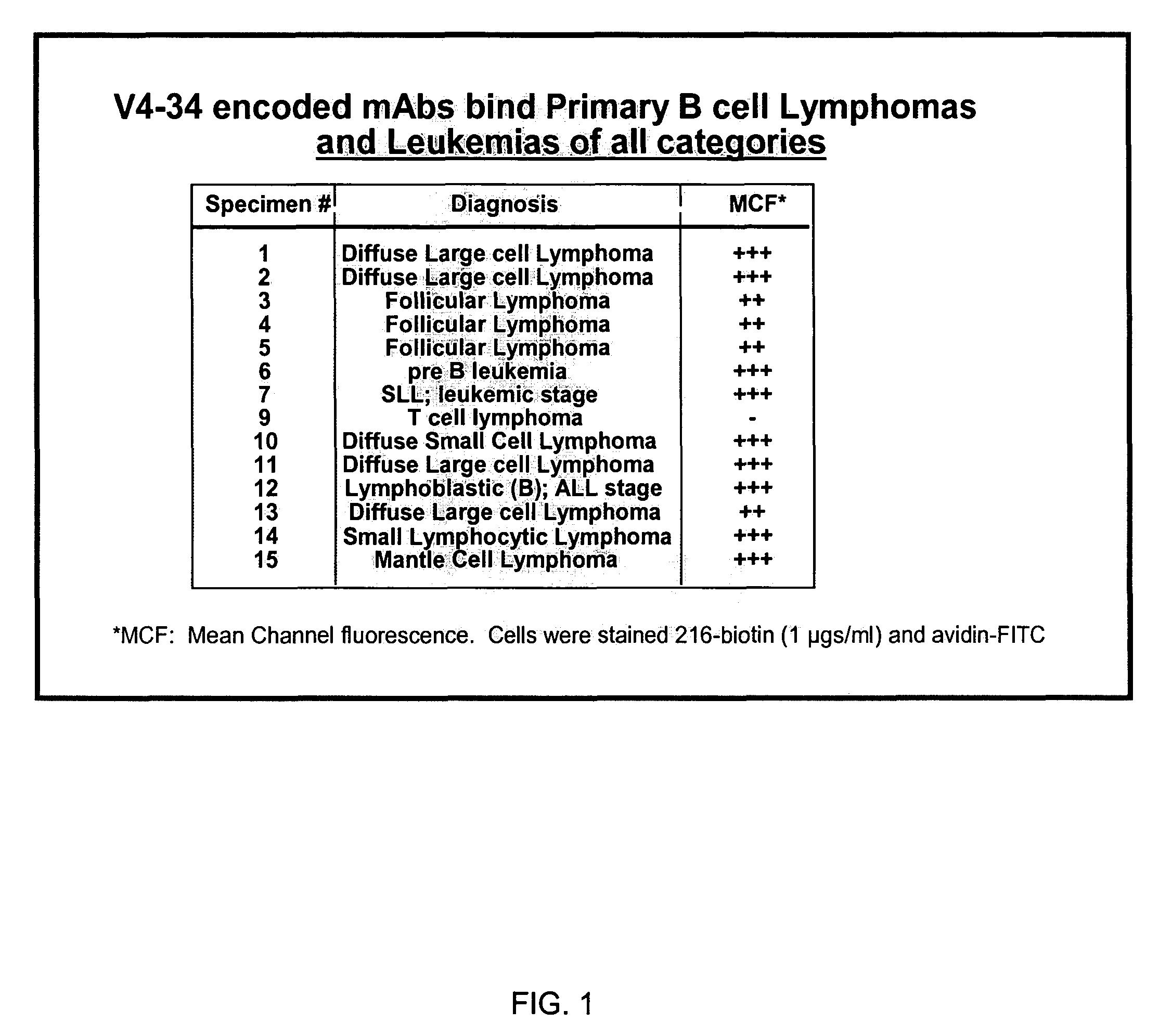
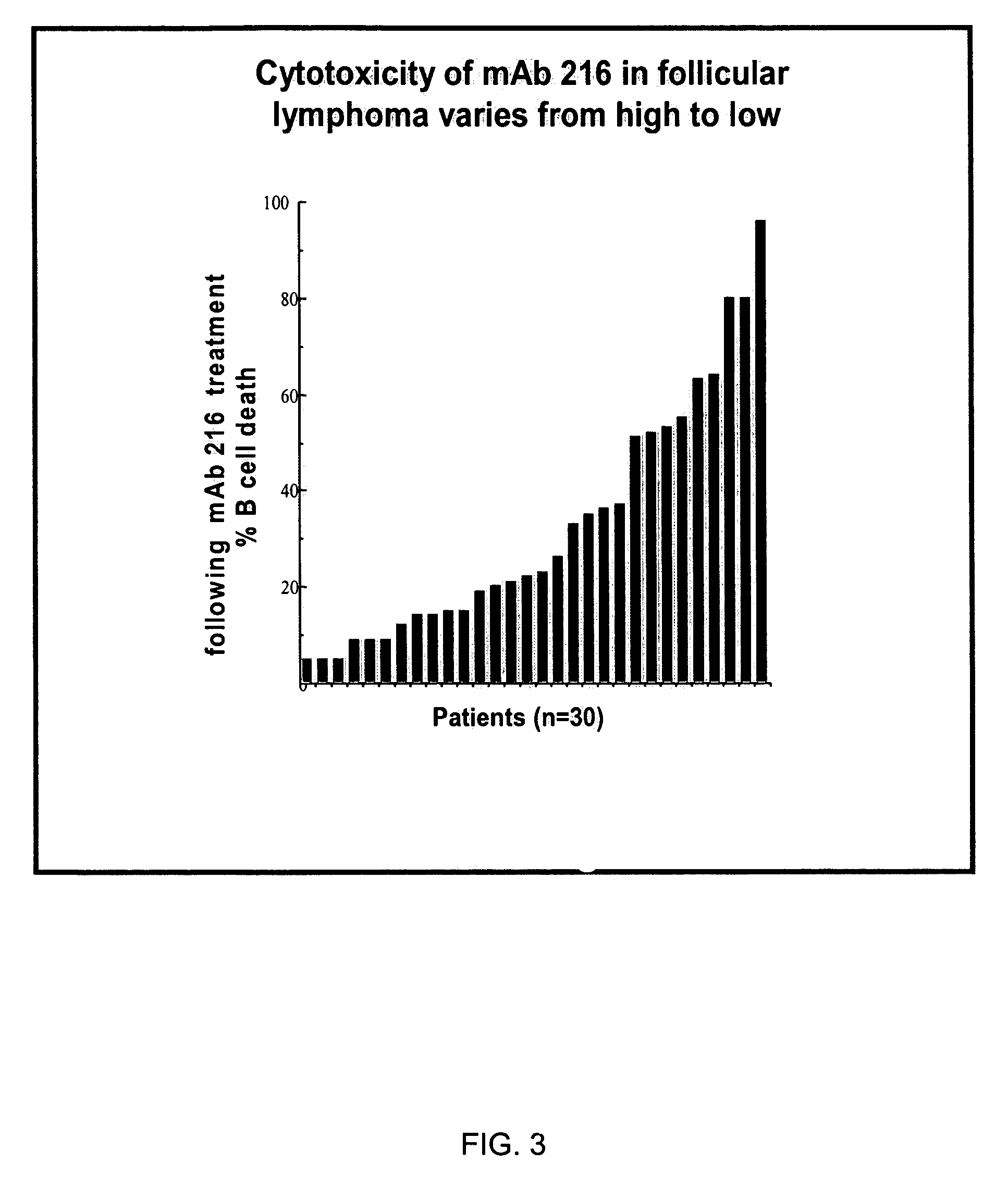
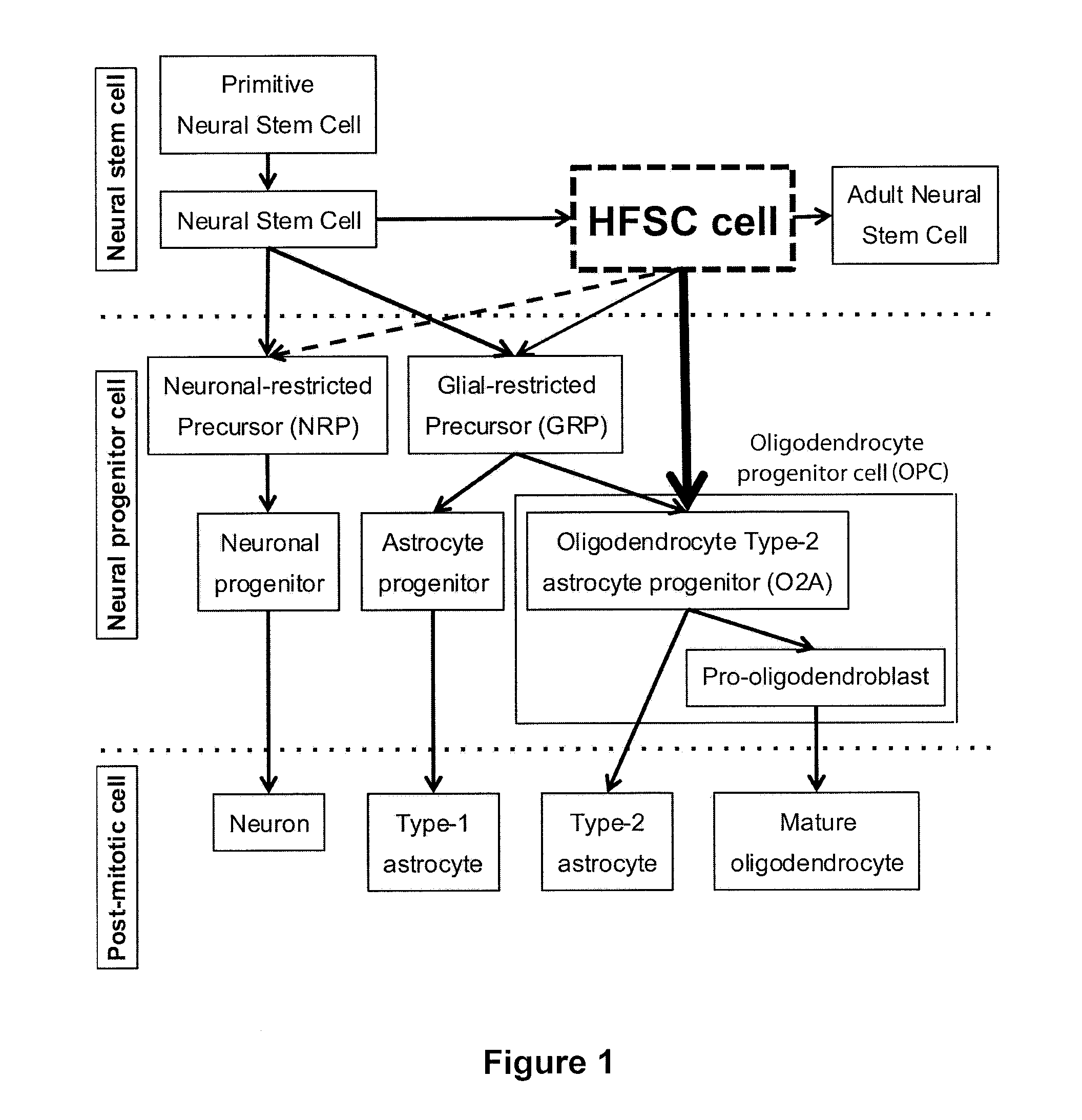
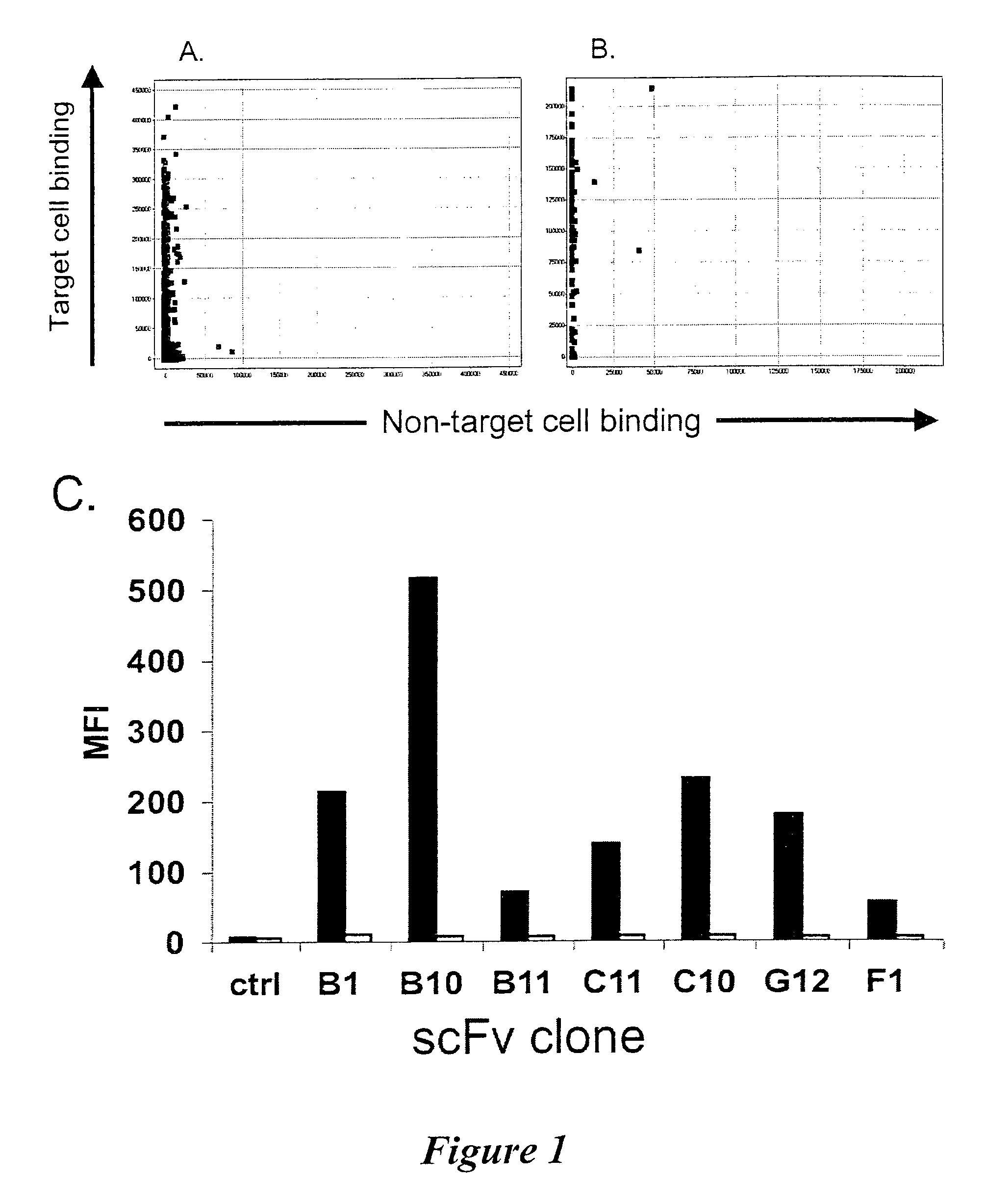
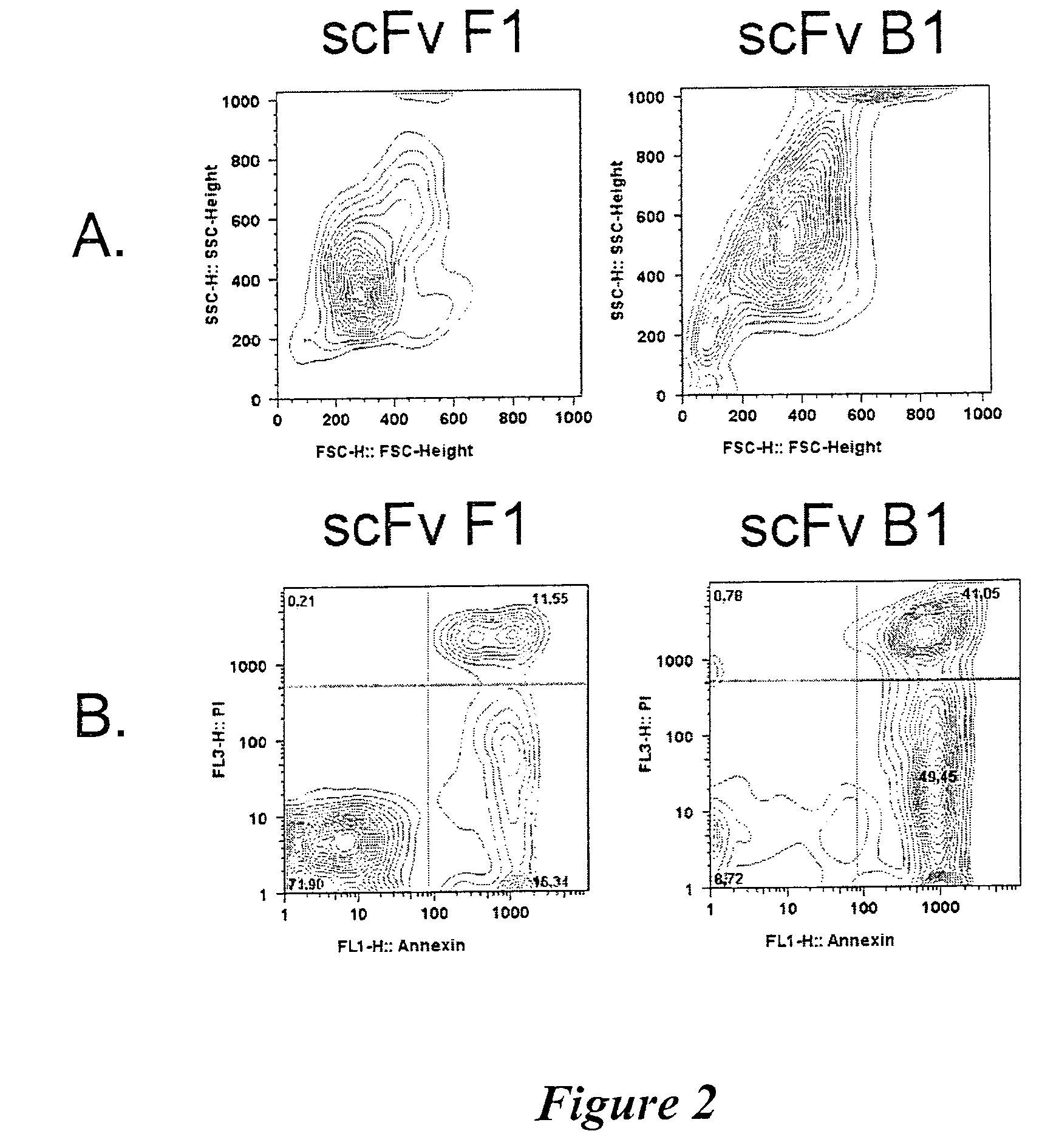
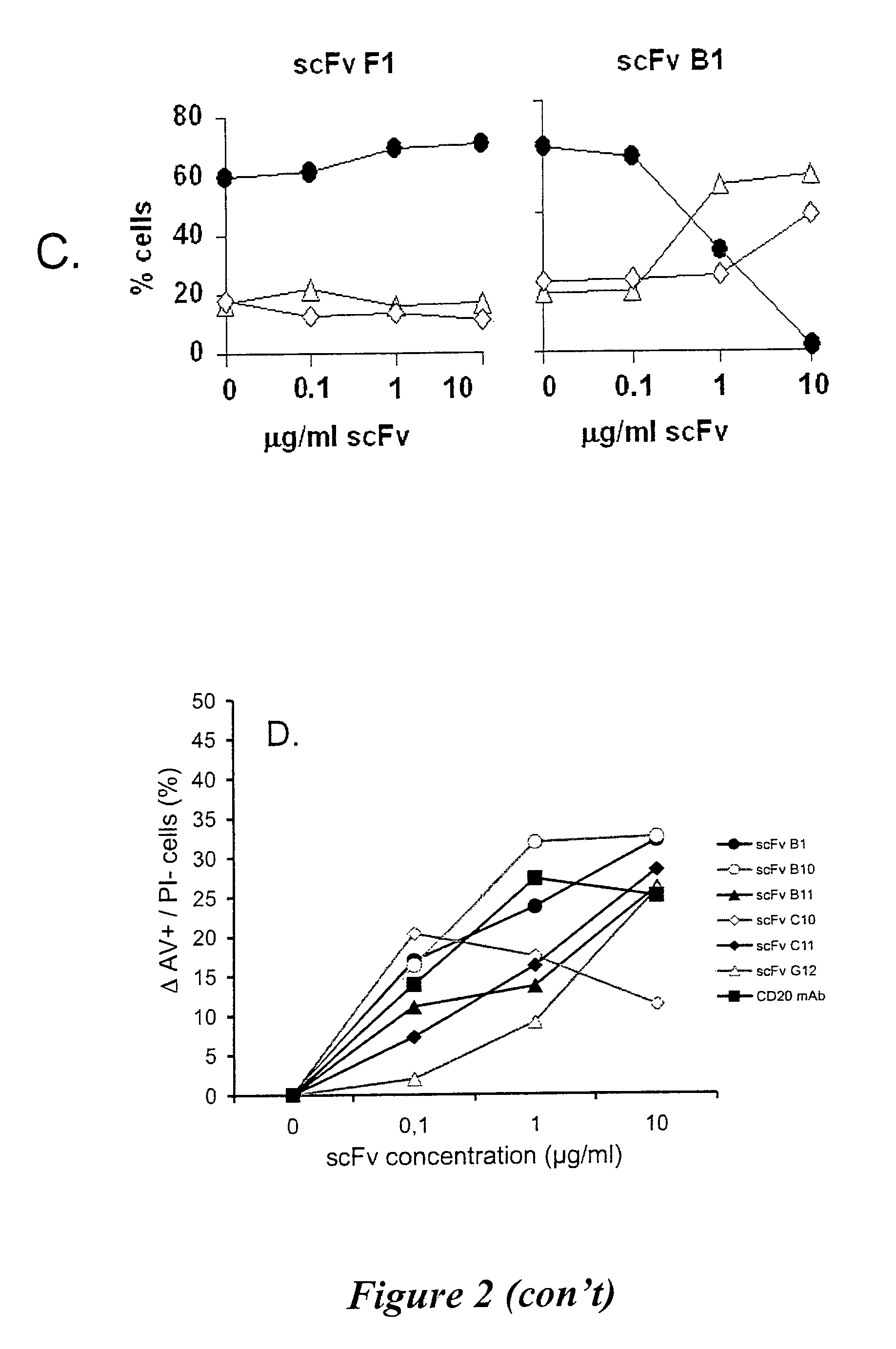
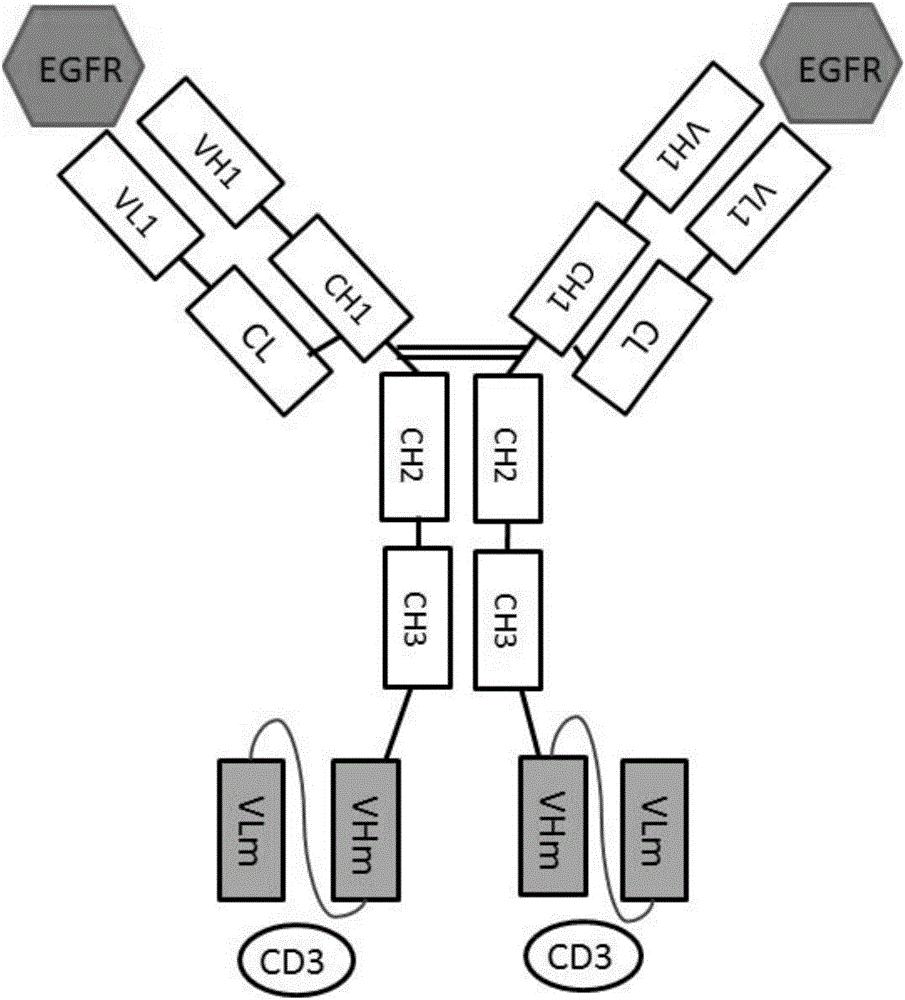
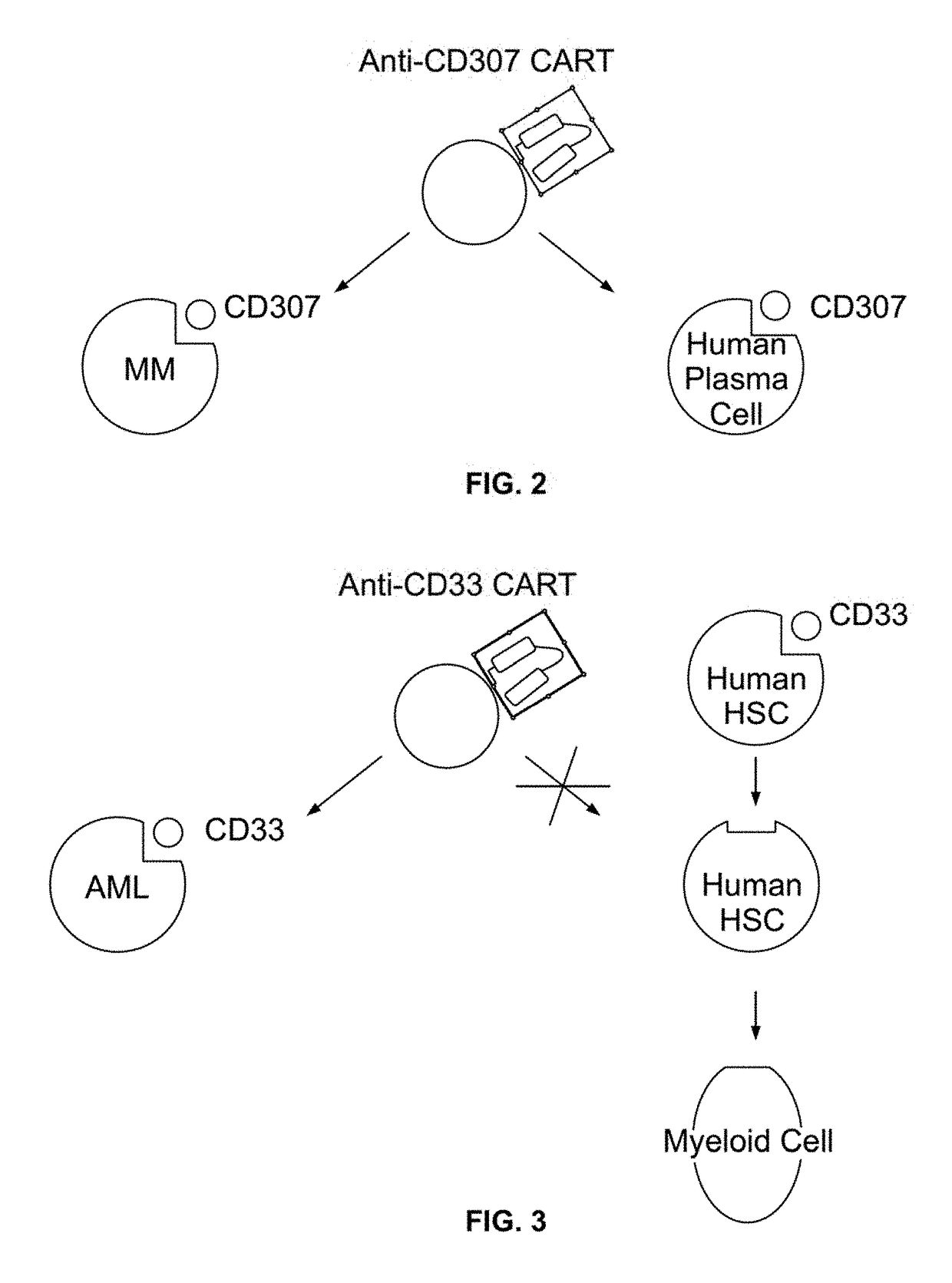
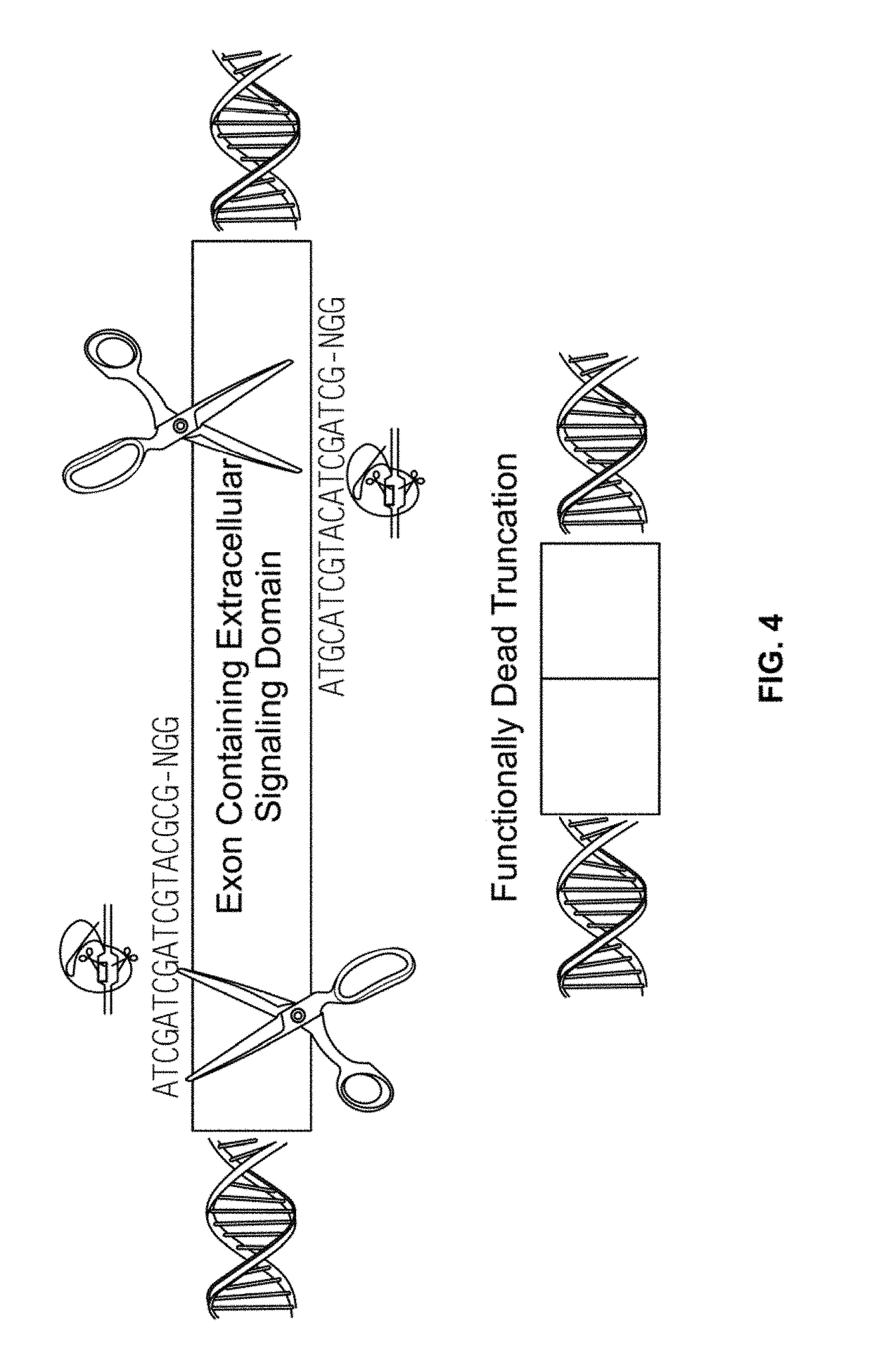
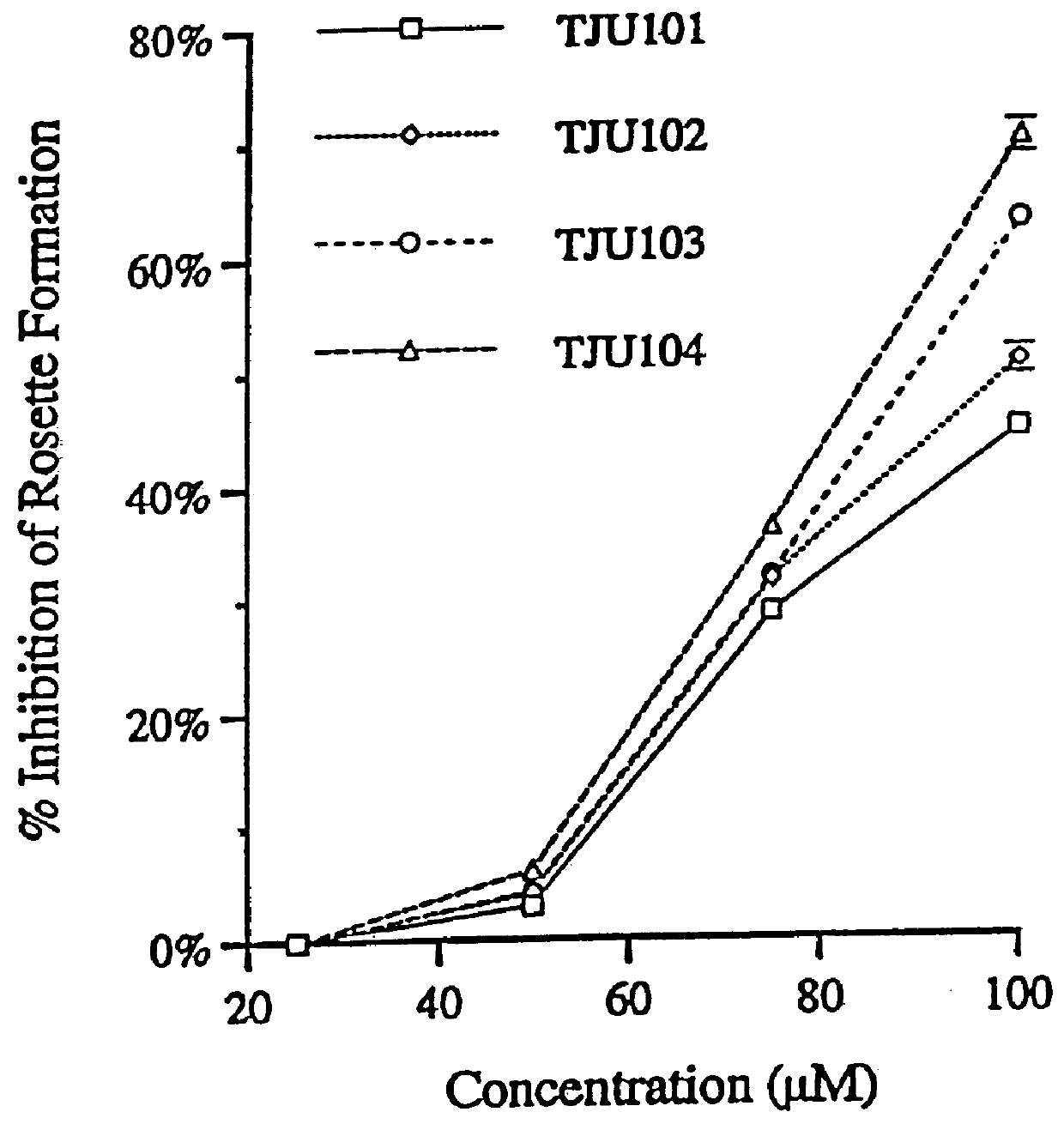
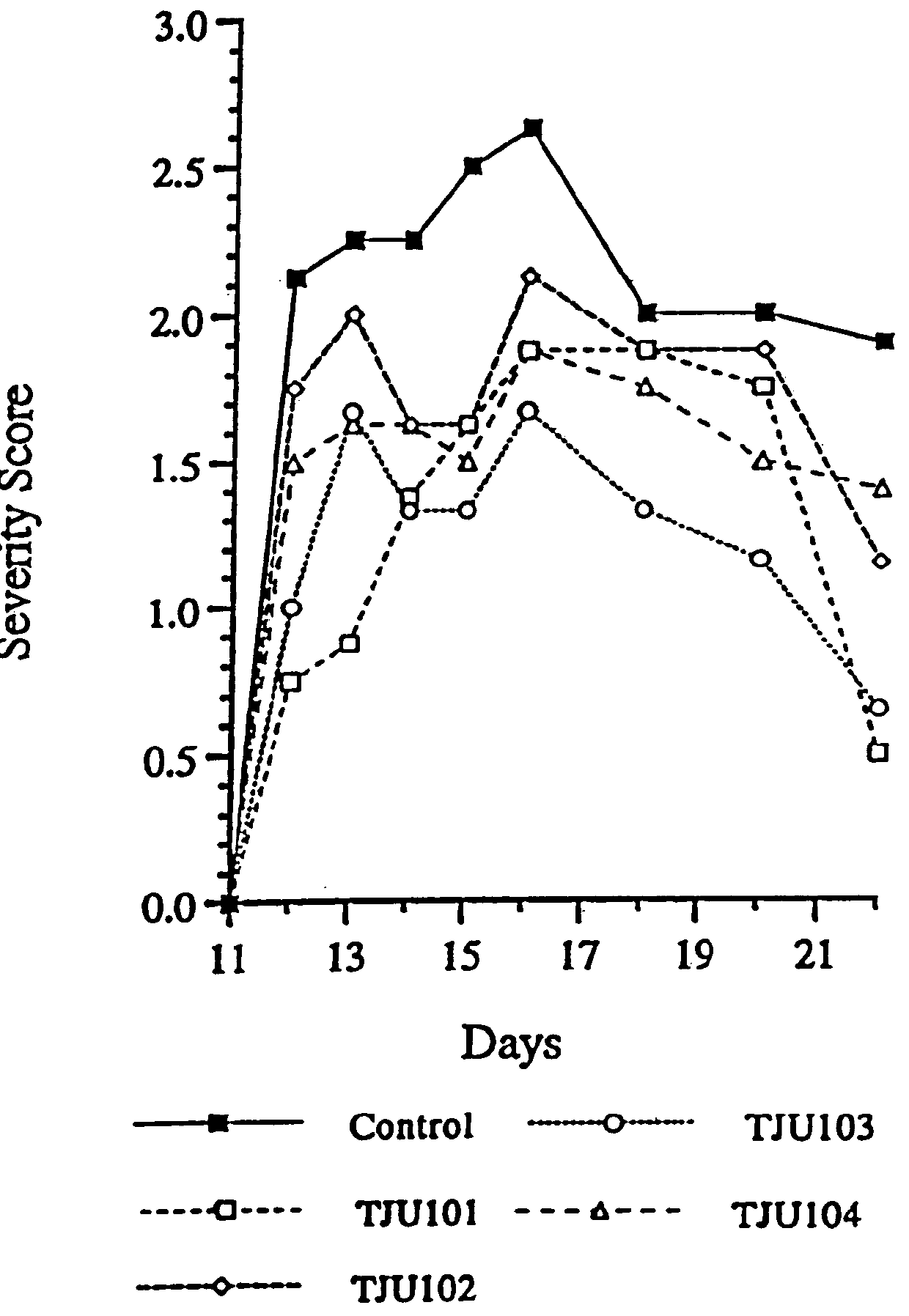
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
222 results about "Cell Surface Antigens" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Mammalian cell surface antigens; related reagents
InactiveUS7025962B1Abnormal immune responseFacilitated DiffusionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMammalT cell
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Compositions for targeting the vasculature of solid tumors
InactiveUS6051230AEffectively compete for bindingReduce TEC-4 or TEC-11 bindingHybrid immunoglobulinsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenCell Surface Antigens
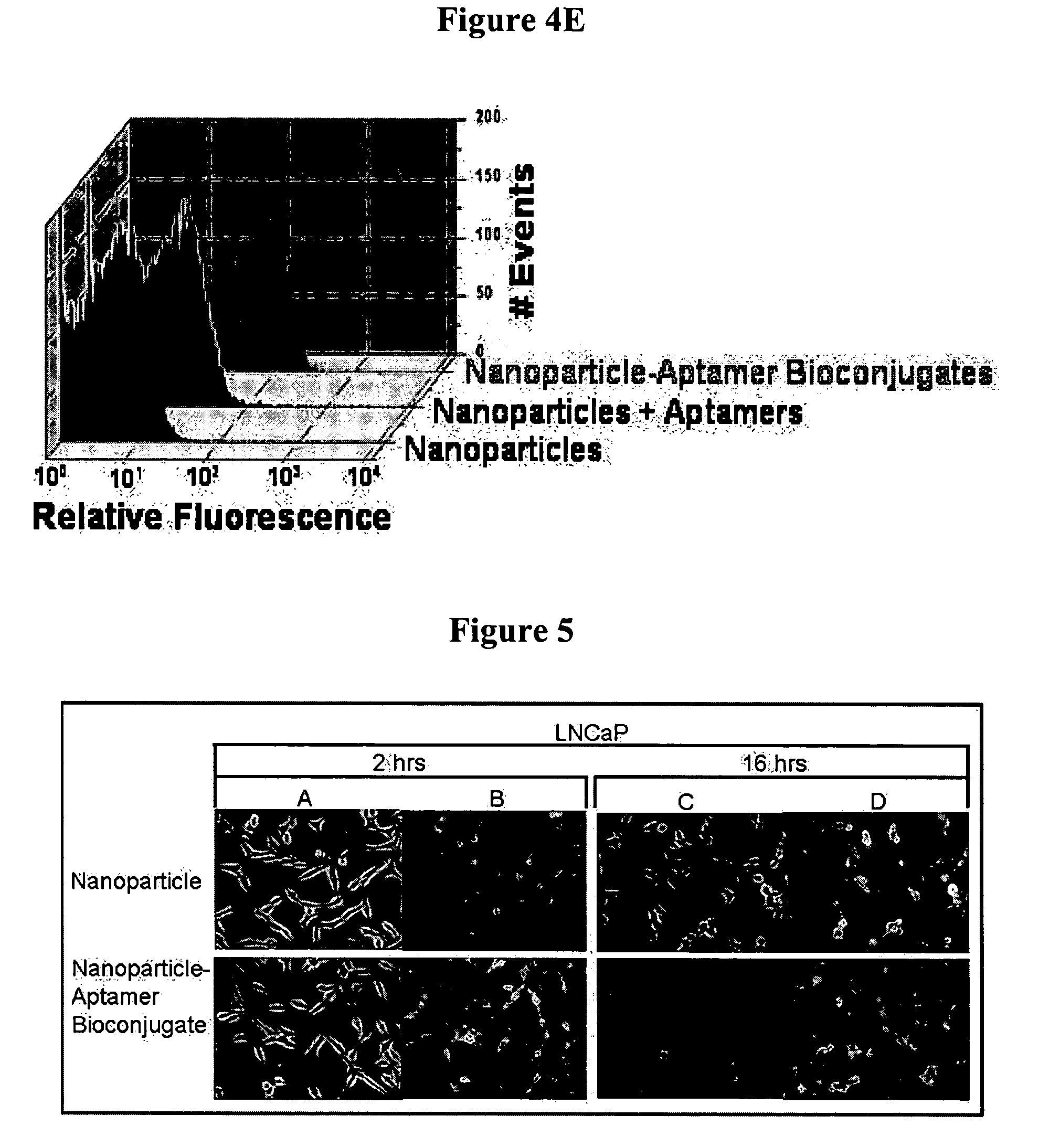
The present invention relates generally to methods and compositions for targeting the vasculature of solid tumors using immunological- and growth factor-based reagents. In particular aspects, antibodies carrying diagnostic or therapeutic agents are targeted to the vasculature of solid tumor masses through recognition of tumor vasculature-associated antigens, such as, for example, through endoglin binding, or through the specific induction of endothelial cell surface antigens on vascular endothelial cells in solid tumors.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Targeted delivery of controlled release polymer systems
ActiveUS20050037075A1Strong specificityHigh affinityPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsControlled releaseCell Surface Antigens
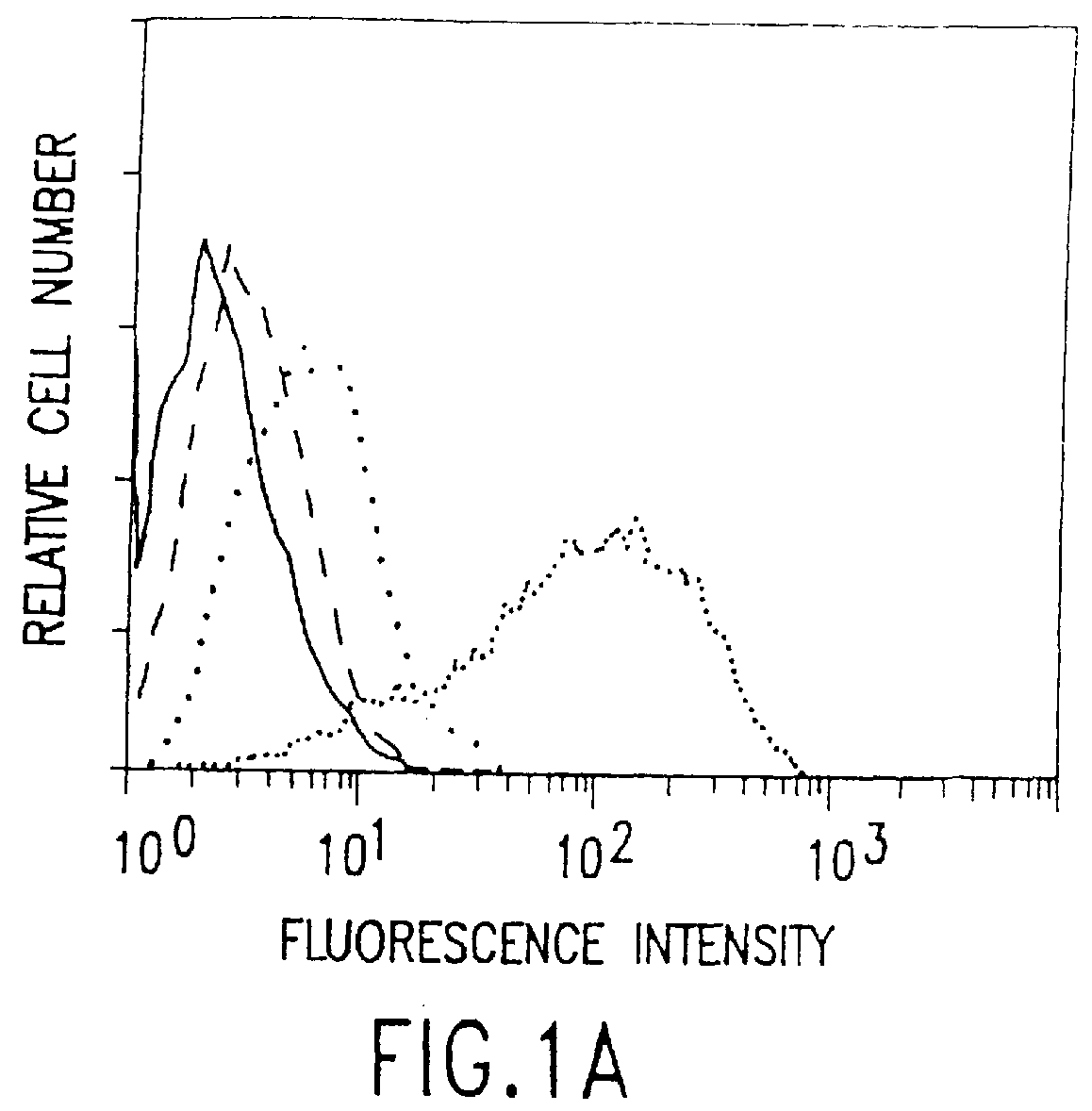
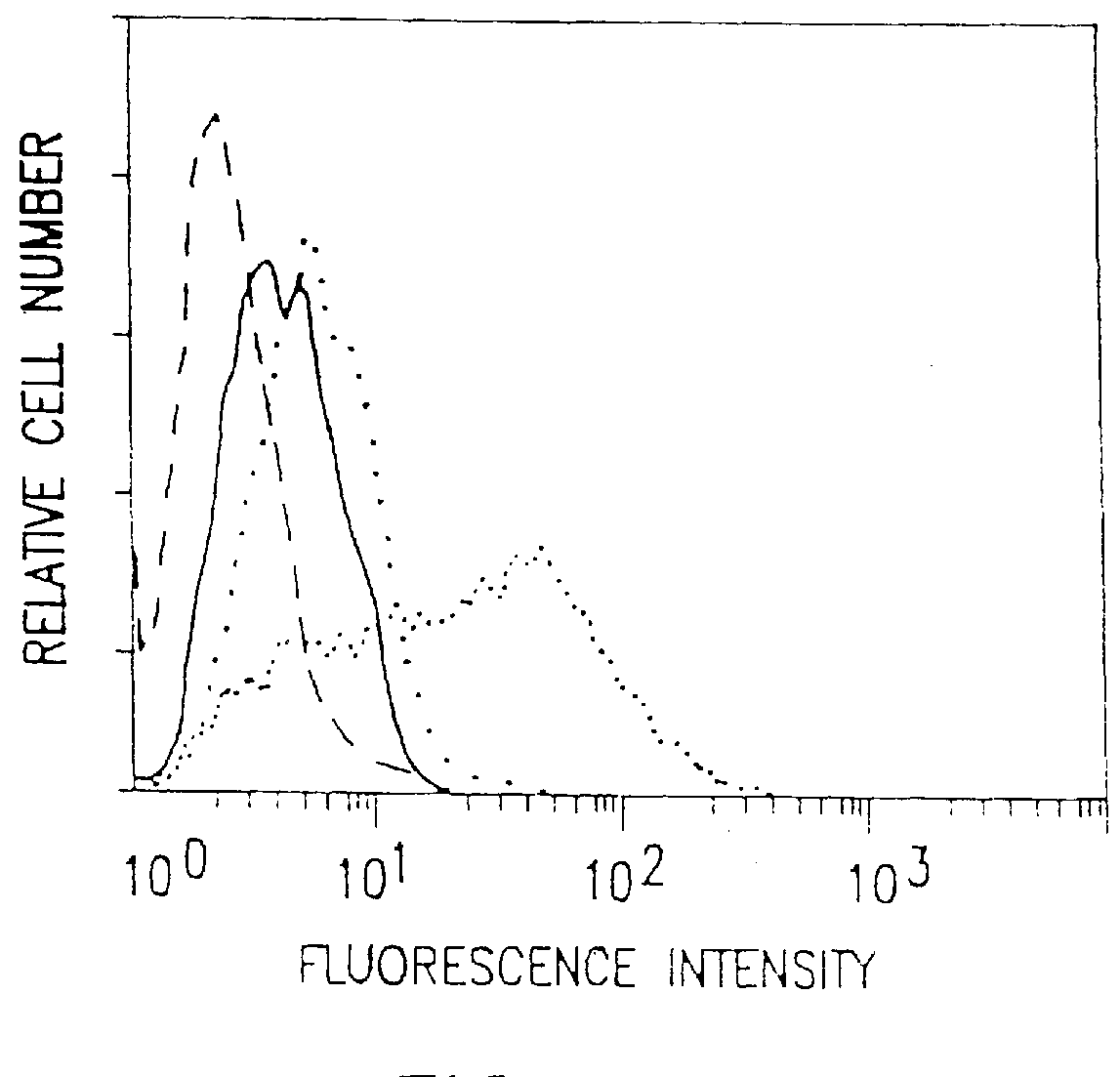
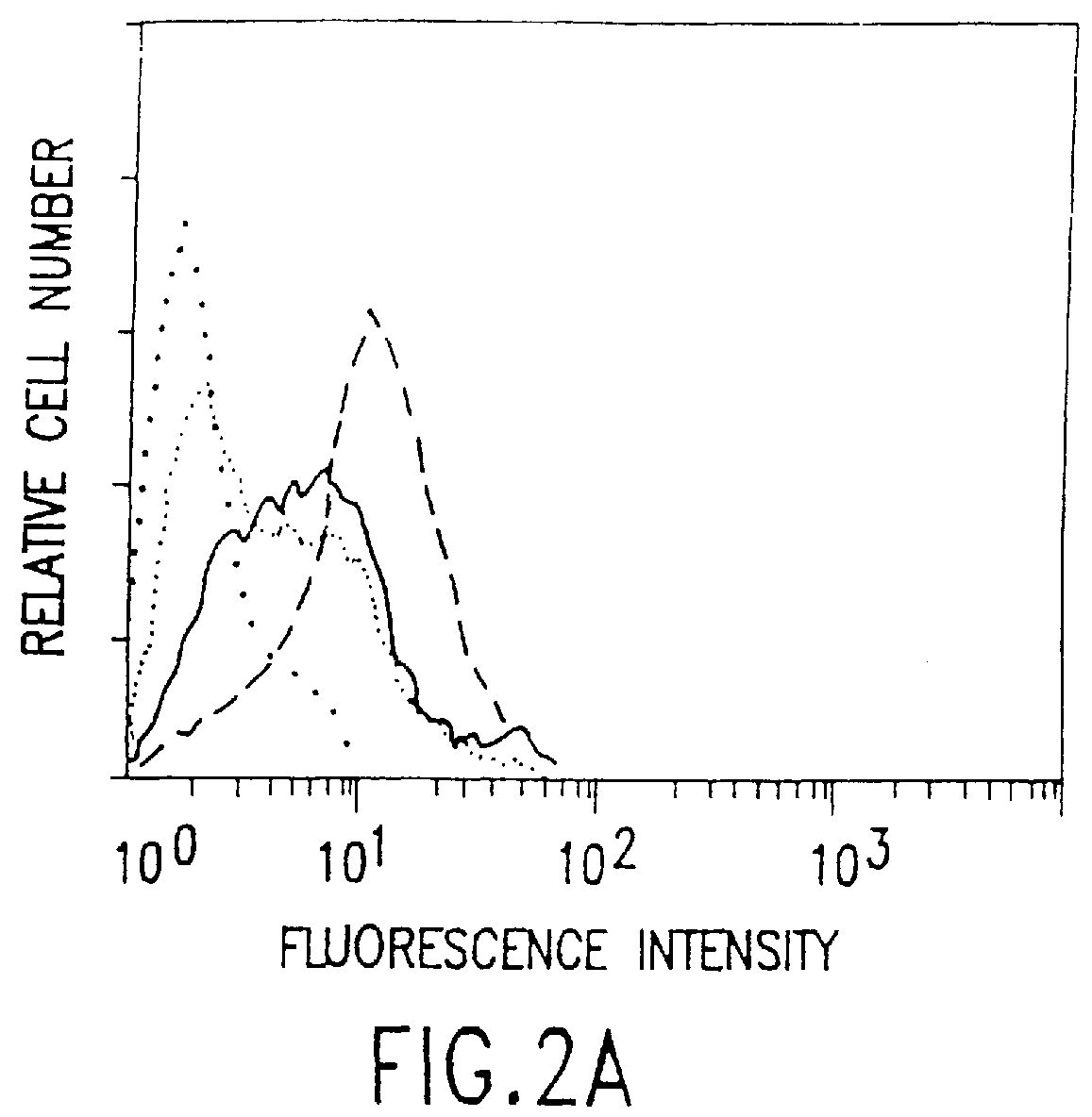
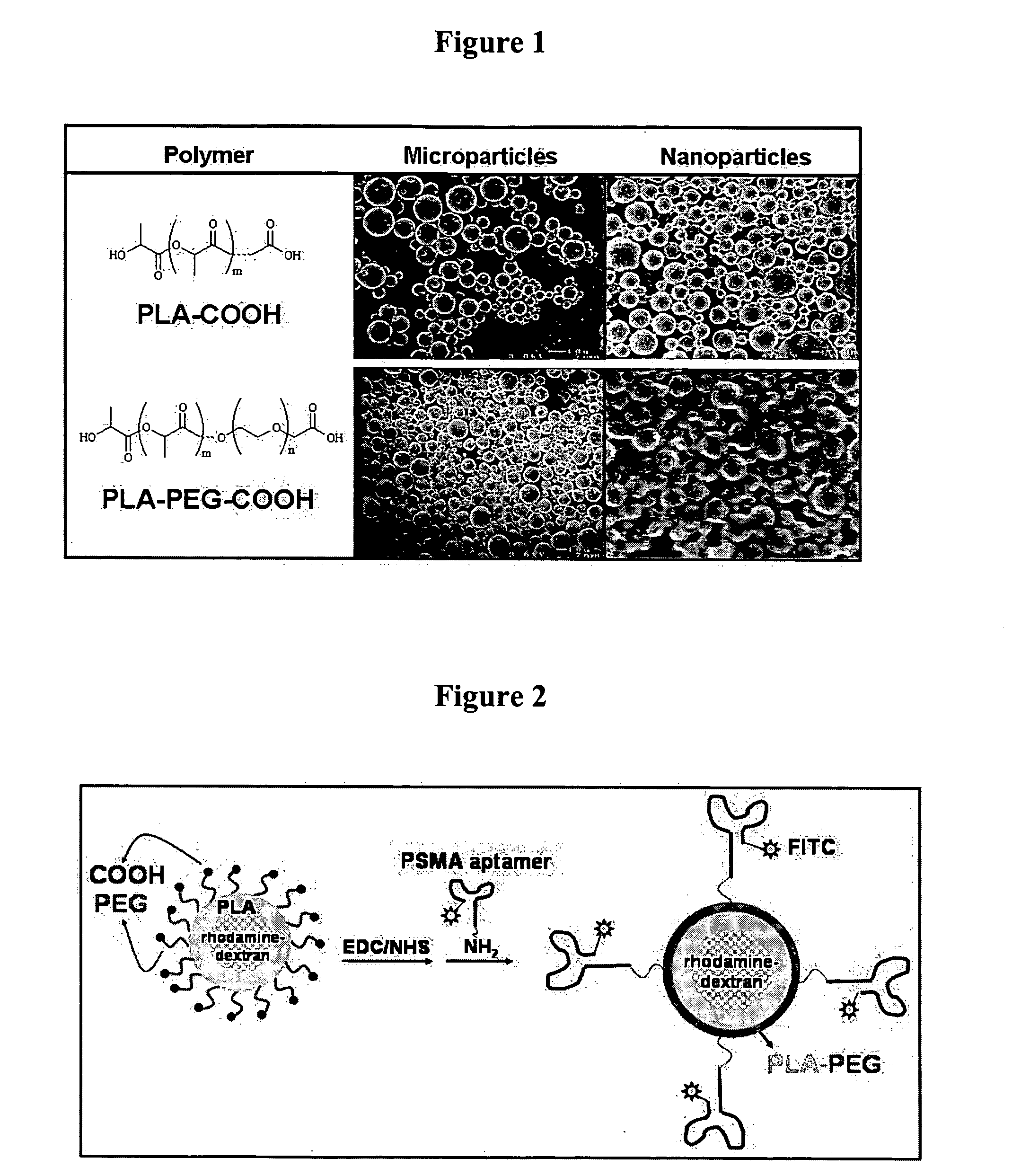
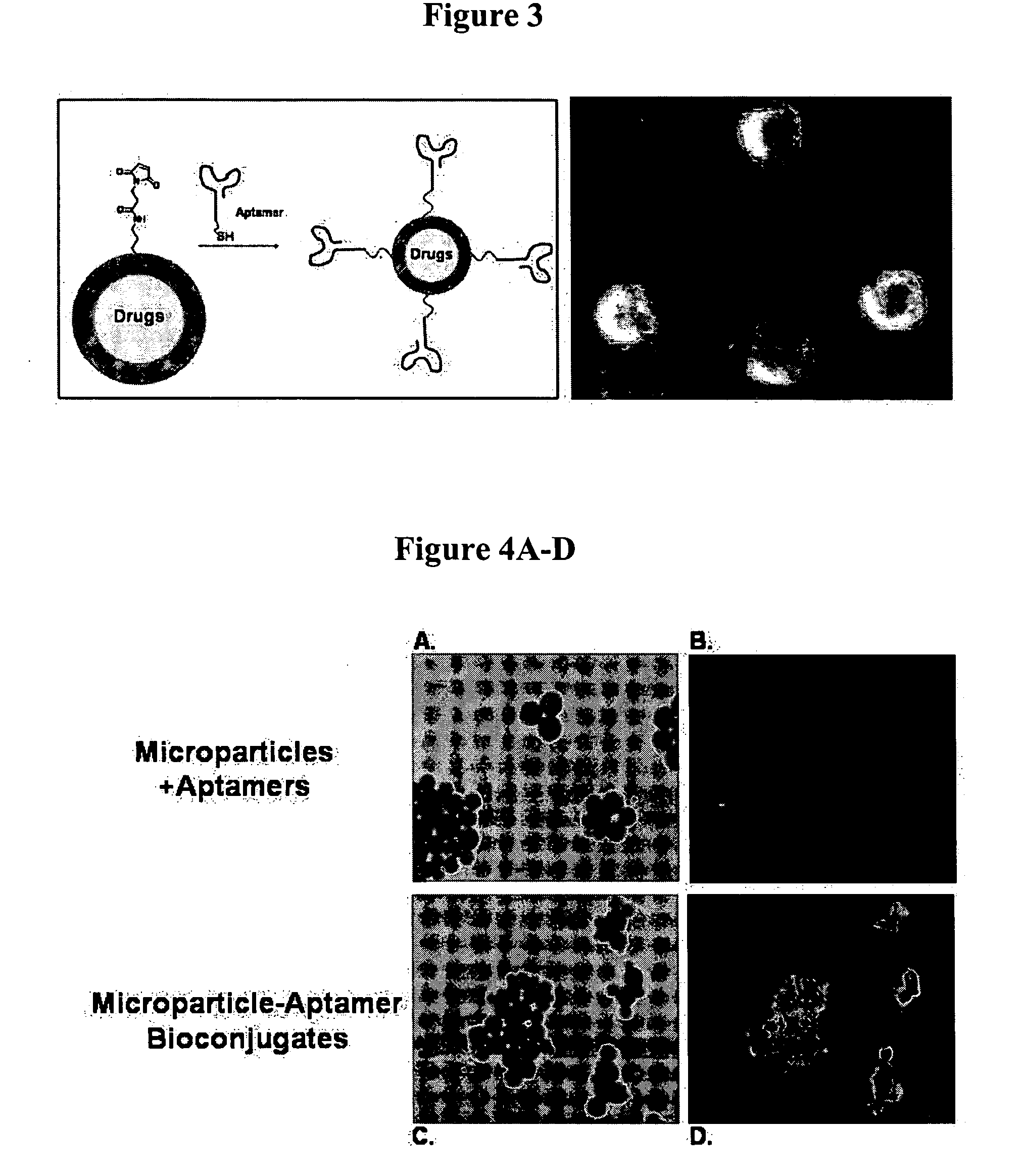
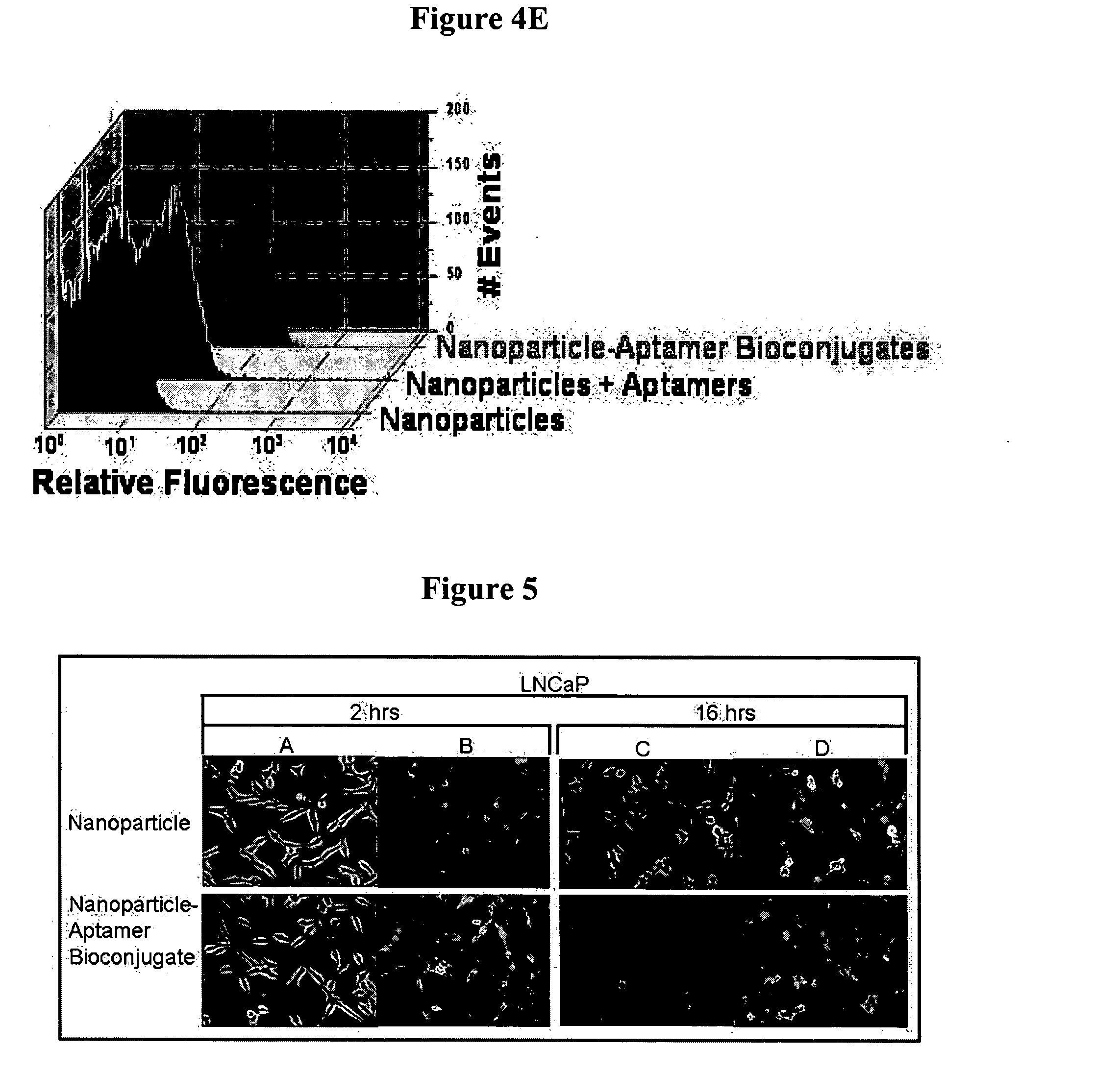
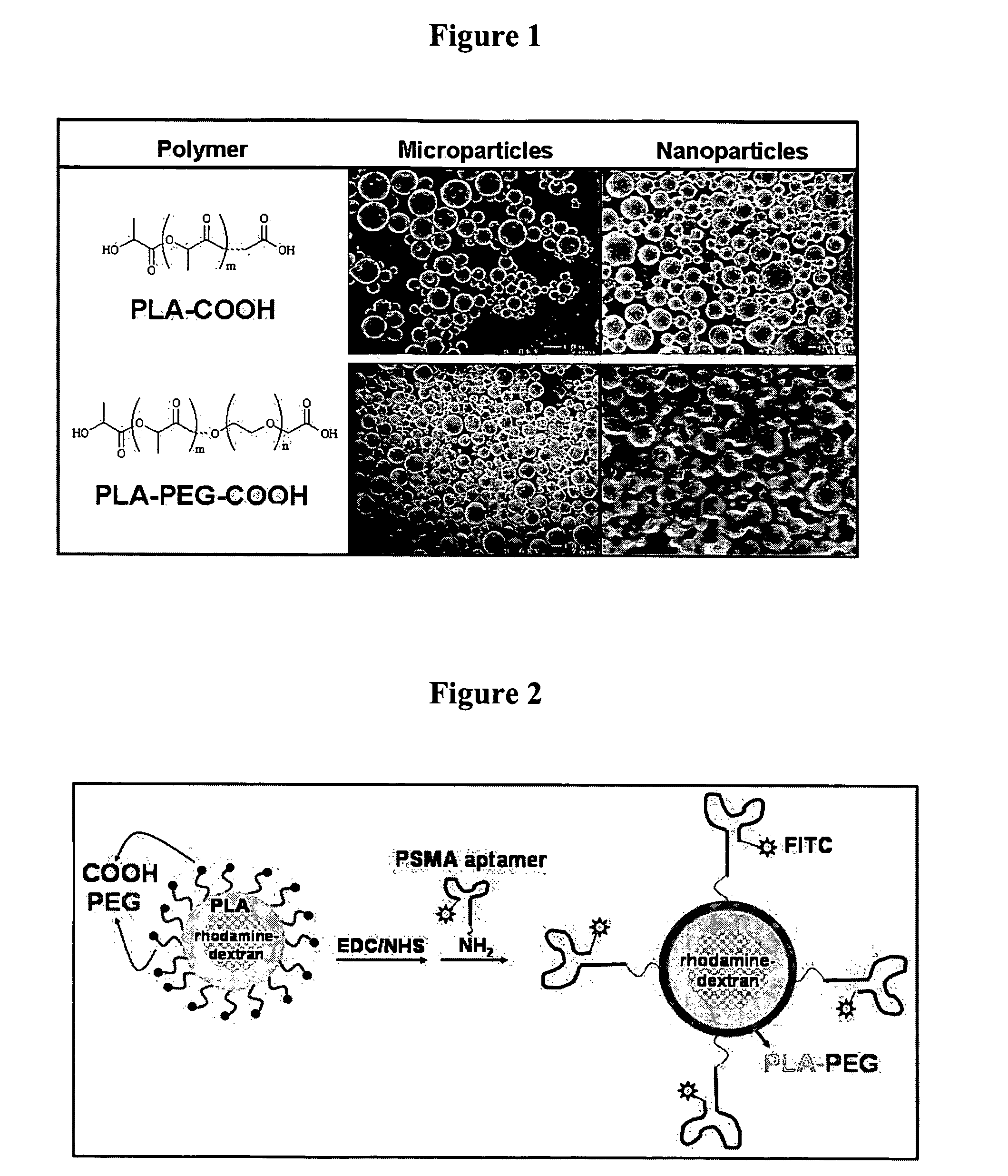
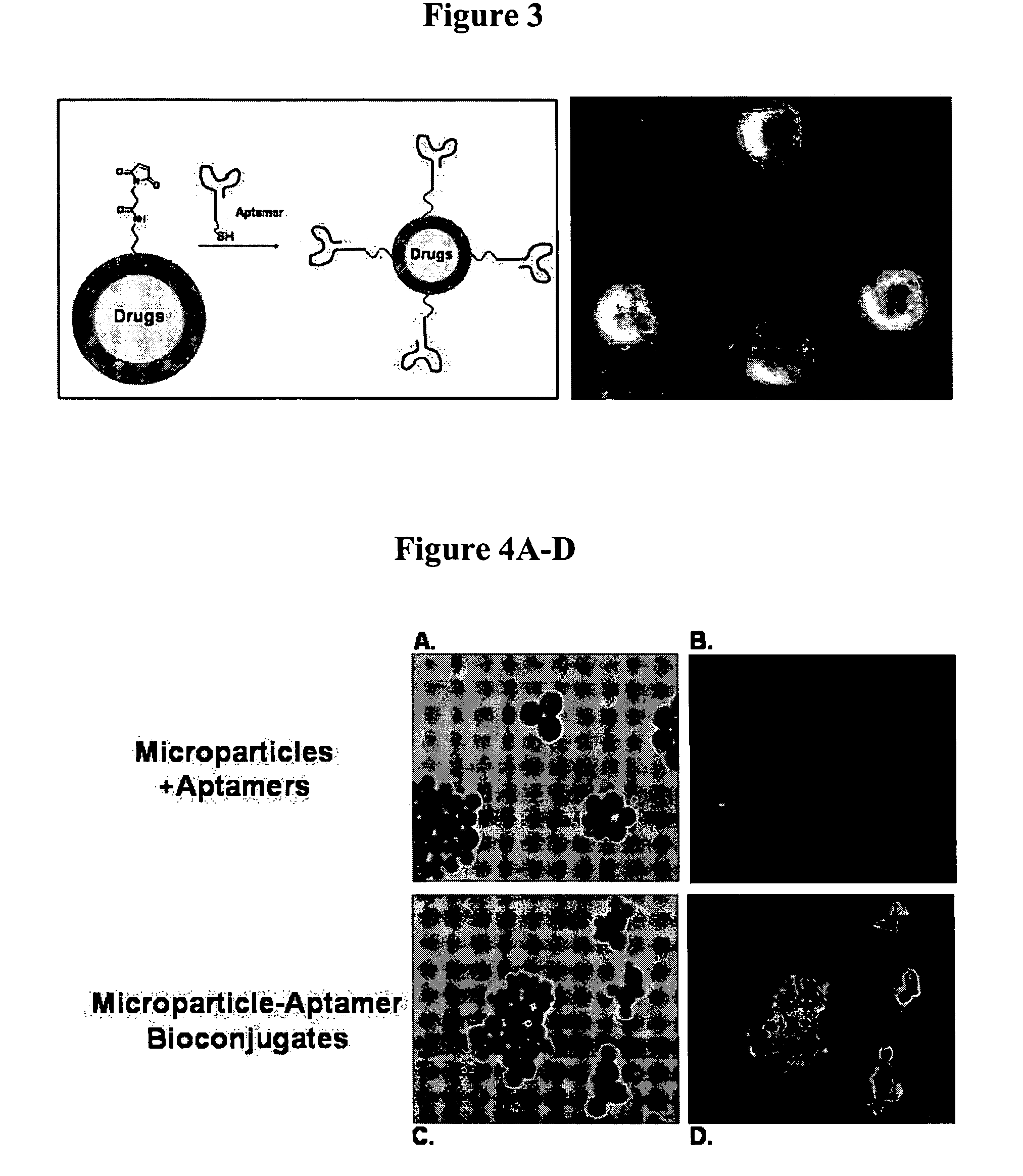
The present invention relates to a conjugate that includes a nucleic acid ligand bound to a controlled release polymer system, a pharmaceutical composition that contains the conjugate, and methods of treatment using the conjugate. The controlled release polymer system includes an agent such as a therapeutic, diagnostic, prognostic, or prophylactic agent. The nucleic acid ligand that is bound to the controlled release polymer system, binds selectively to a target, such as a cell surface antigen, and thereby delivers the controlled release polymer system to the target.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Controlled release polymer nanoparticle containing bound nucleic acid ligand for targeting
The present invention relates to a conjugate that includes a nucleic acid ligand bound to a controlled release polymer system, a pharmaceutical composition that contains the conjugate, and methods of treatment using the conjugate. The controlled release polymer system includes an agent such as a therapeutic, diagnostic, prognostic, or prophylactic agent. The nucleic acid ligand that is bound to the controlled release polymer system, binds selectively to a target, such as a cell surface antigen, and thereby delivers the controlled release polymer system to the target.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Medical device with coating that promotes endothelial cell adherence
InactiveUS7037332B2Prevent restenosisMaterial nanotechnologyPeptide/protein ingredientsCell Surface AntigensPercent Diameter Stenosis
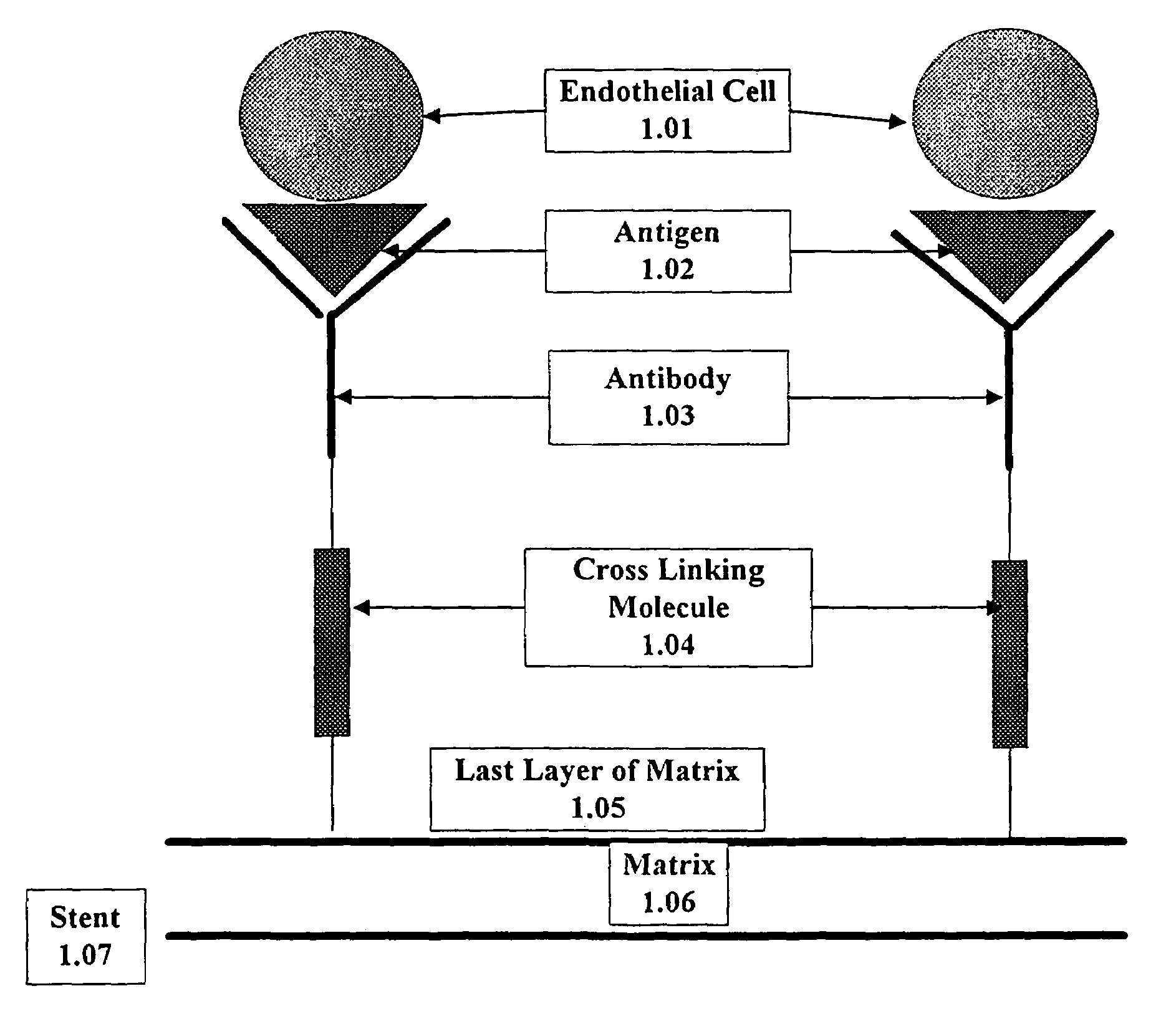
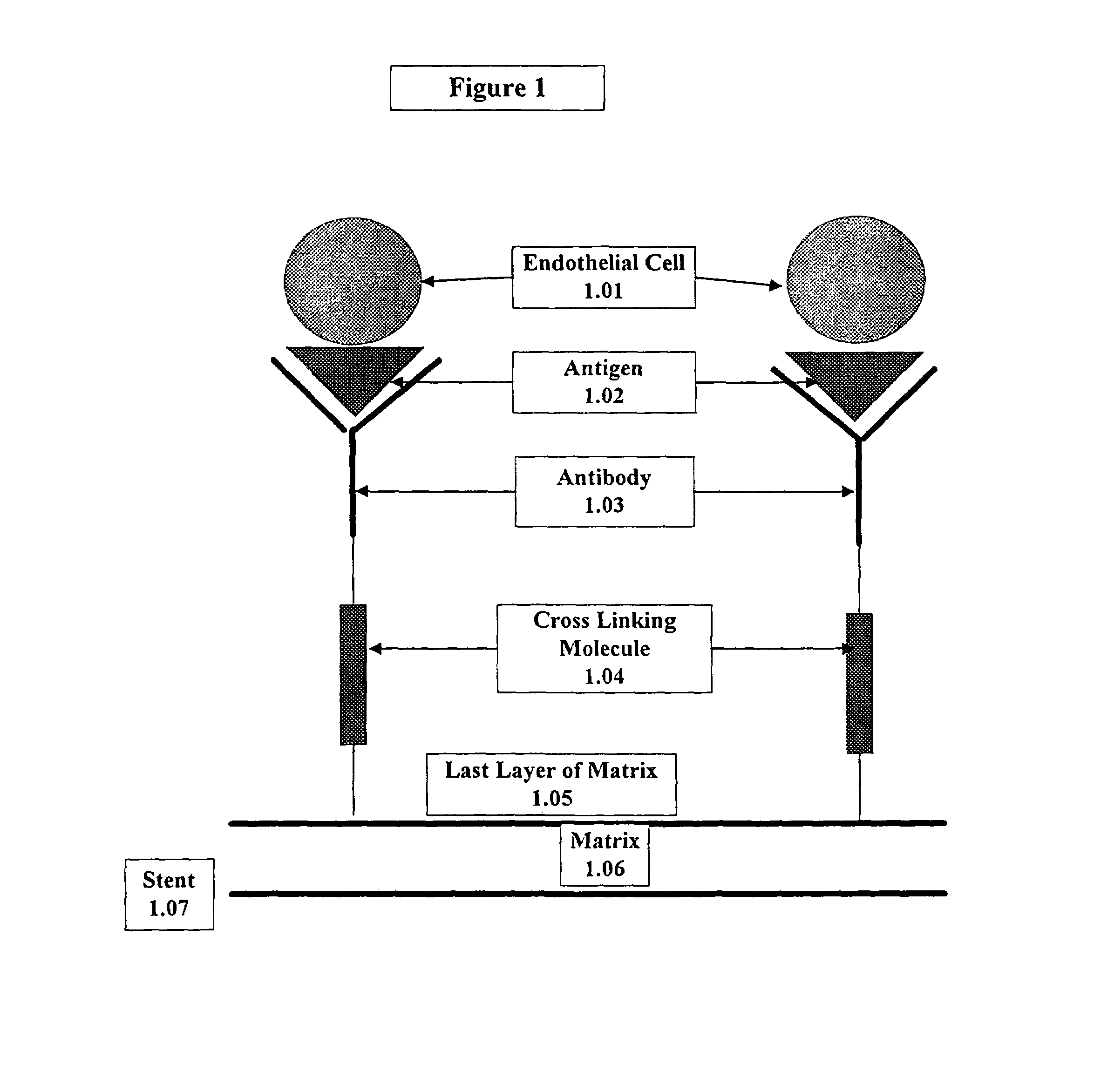
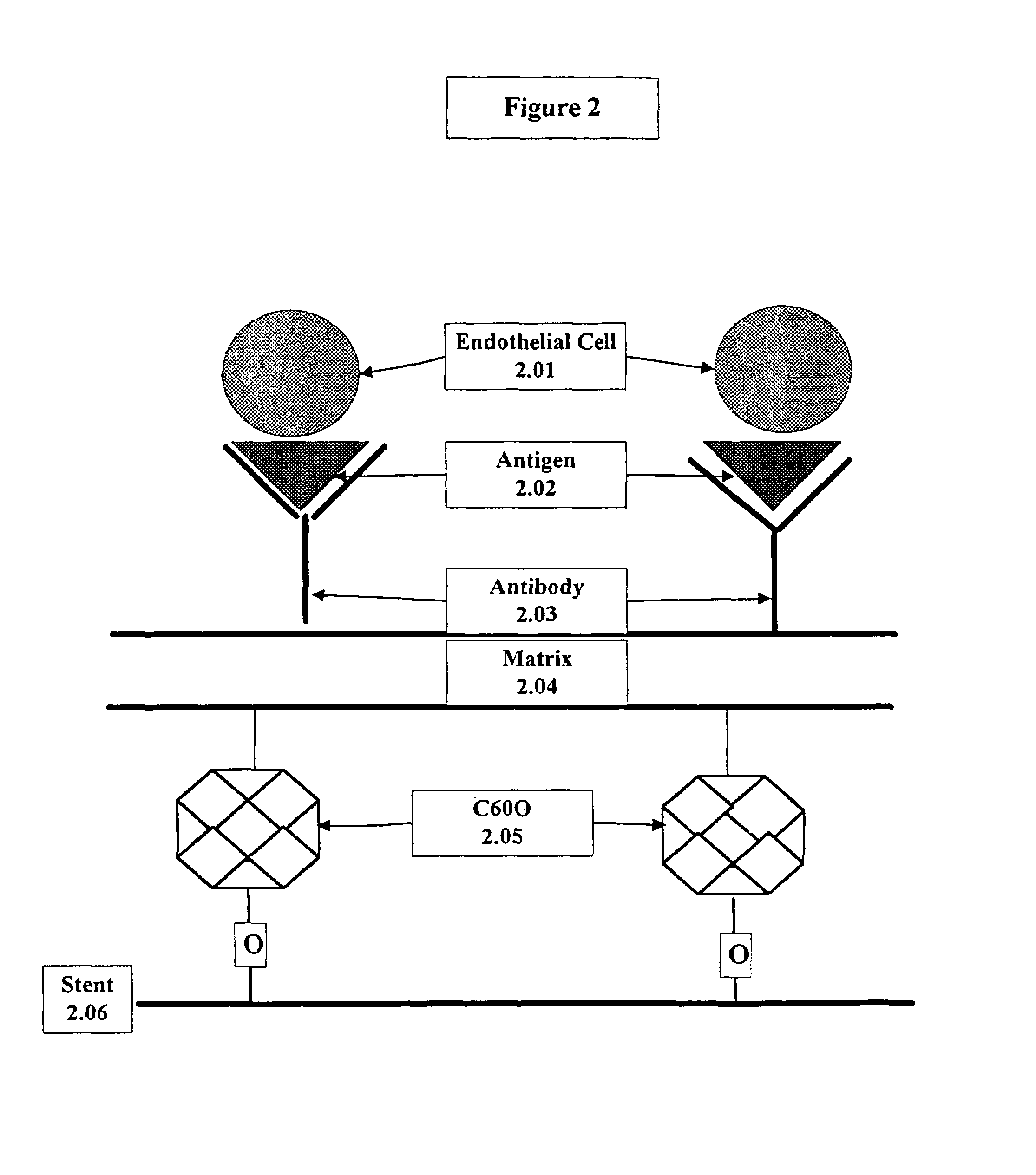
A medical device coated with one or more antibodies and one or more layers of a matrix is disclosed. The antibodies or fragments thereof react with an endothelial cell surface antigen. Also disclosed are compositions and methods for producing the medical device. The matrix coating the medical device may be composed of a synthetic material, such as a fullerene, or a naturally occurring material. The fullerenes range from about C60 to about C100. The medical device may be a stent or a synthetic graft. The antibodies promote the adherence of cells captured in vivo on the medical device. The antibodies may be mixed with the matrix or covalently tethered through a linker molecule to the matrix. Following adherence to the medical device, the cells differentiate and proliferate on the medical device. The antibodies may be different types of monoclonal antibodies. By facilitating adherence of cells to the surface of the medical device, the disclosed methods and compositions will decrease the incidence of restenosis as well as other thromboembolic complications resulting from implantation of medical devices.
Owner:ORBUSNEICH MEDICAL PTE LTD
Controlled release nanoparticle having bound oligonucleotide for targeted delivery
The present invention relates to a conjugate that includes a nucleic acid ligand bound to a controlled release polymer system, a pharmaceutical composition that contains the conjugate, and methods of treatment using the conjugate. The controlled release polymer system includes an agent such as a therapeutic, diagnostic, prognostic, or prophylactic agent. The nucleic acid ligand that is bound to the controlled release polymer system, binds selectively to a target, such as a cell surface antigen, and thereby delivers the controlled release polymer system to the target.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
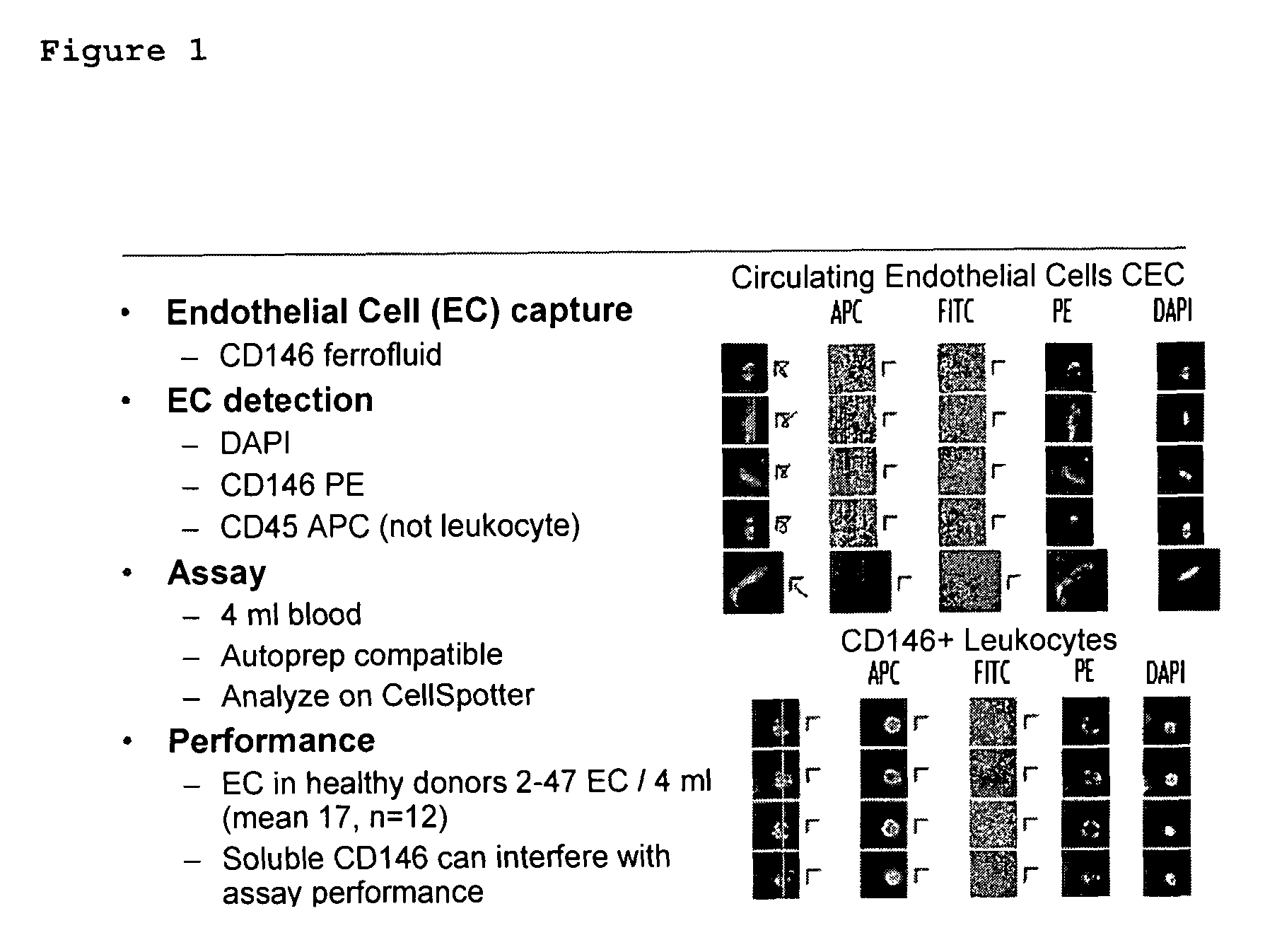
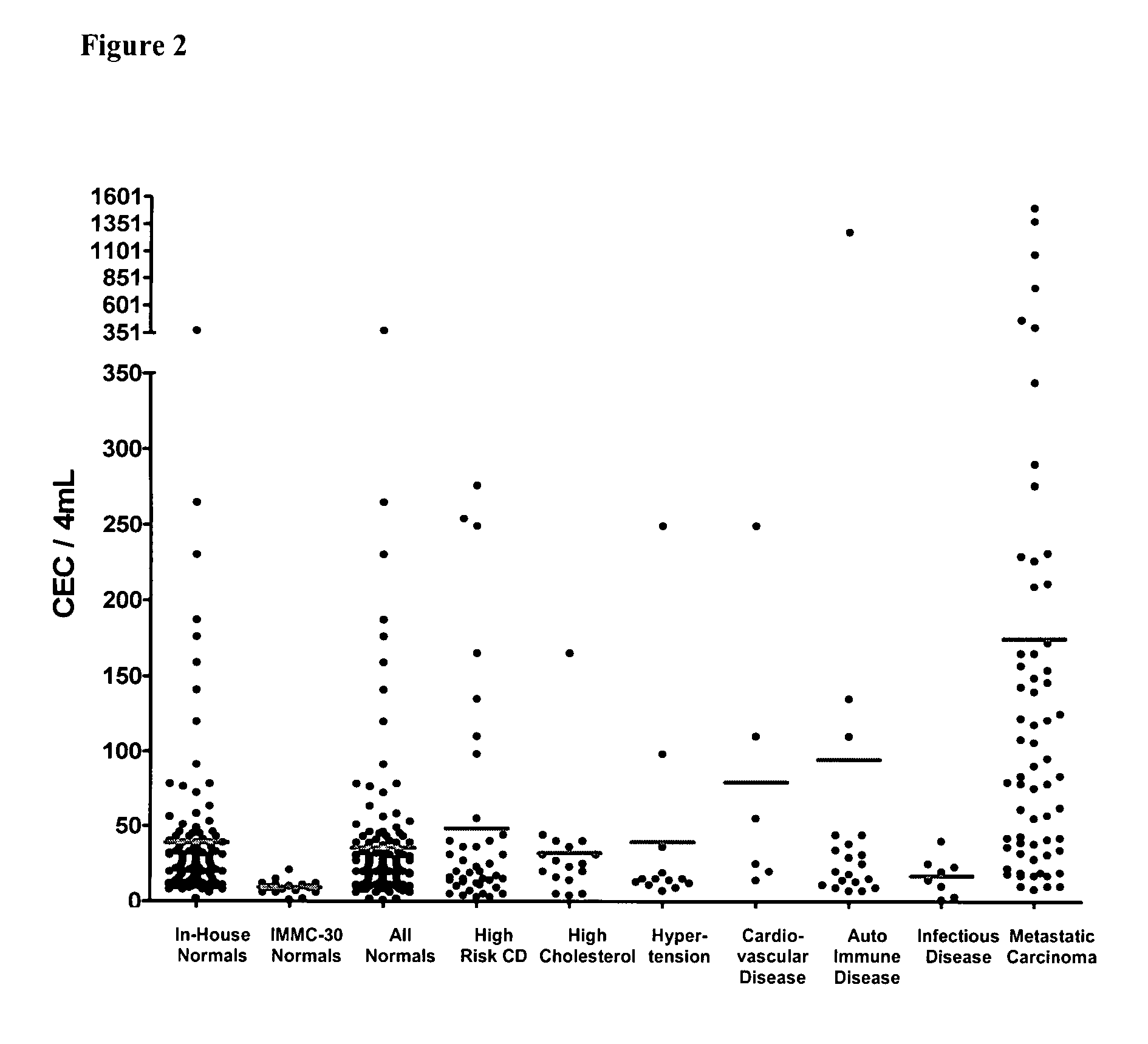
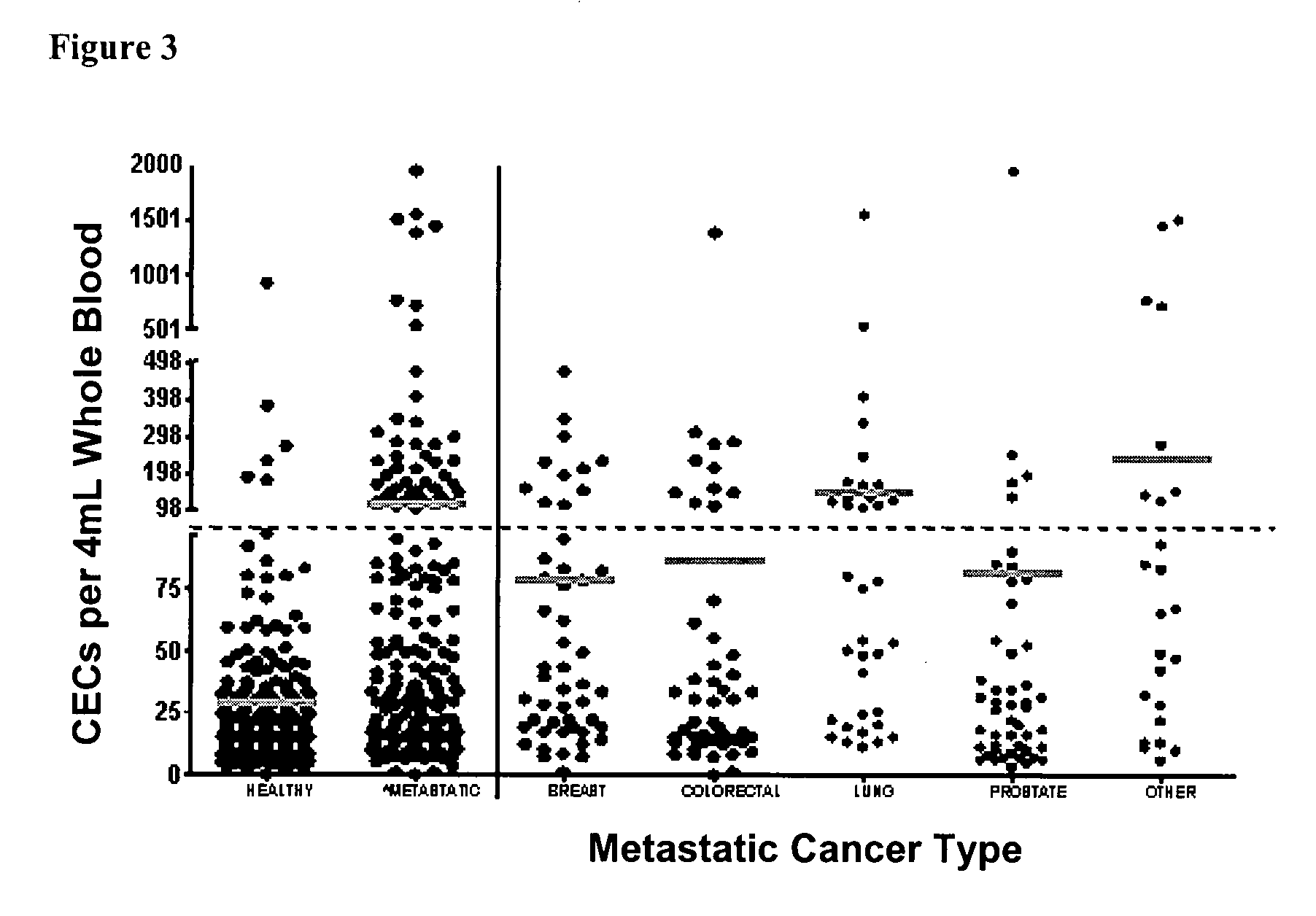
Method for assessing disease states by profile analysis of isolated circulating endothelial cells
ActiveUS7901950B2Confident diagnosticConfident prognosticBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAntigenCirculating endothelial cell
Owner:MENARINI SILICON BIOSYSTEMS SPA
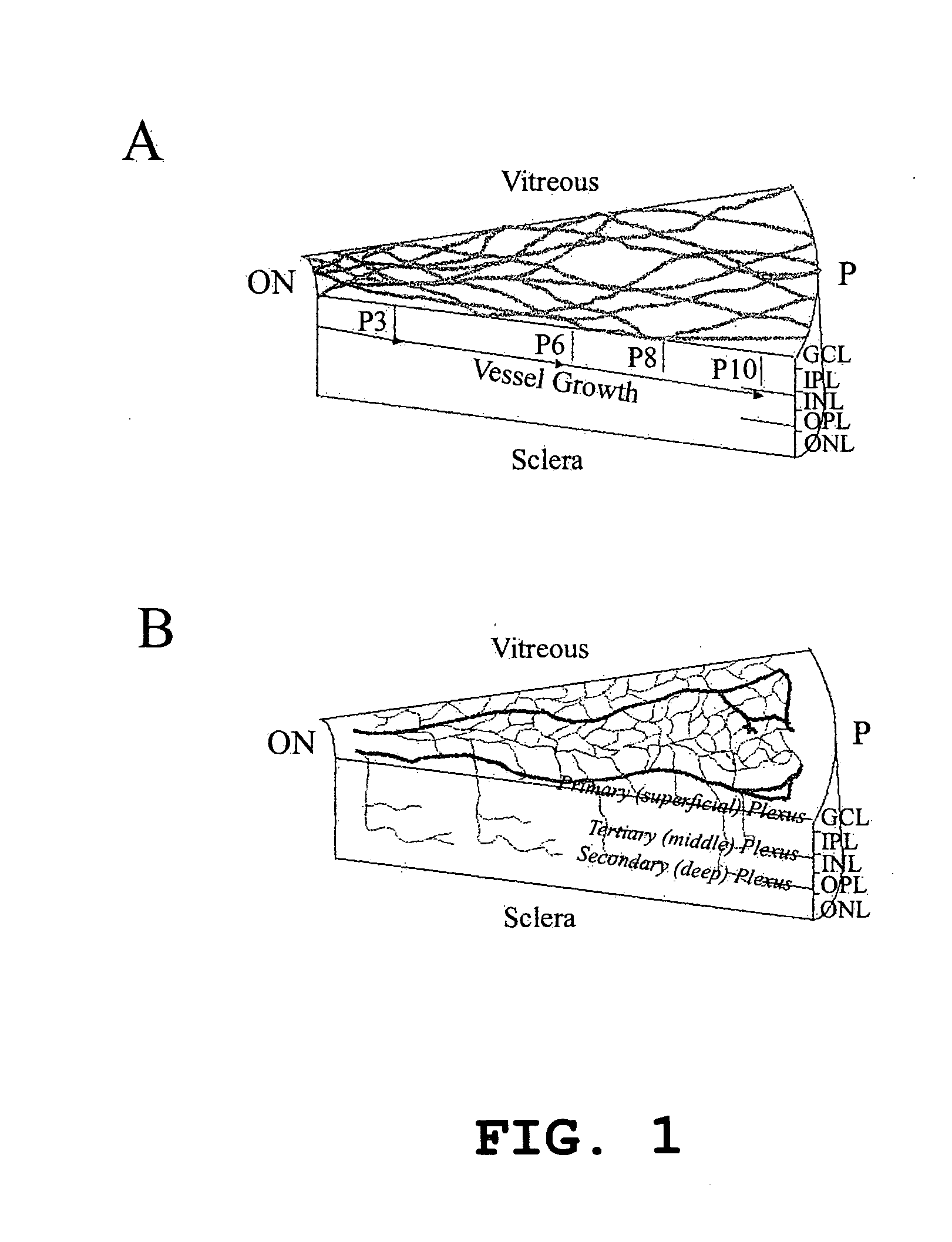
Hematopoietic stem cells and methods of treatment of neovascular eye diseases therewith
InactiveUS20050063961A1Stably incorporated into neovasculature of the eyePromote repairBiocideSenses disorderDiseaseProgenitor
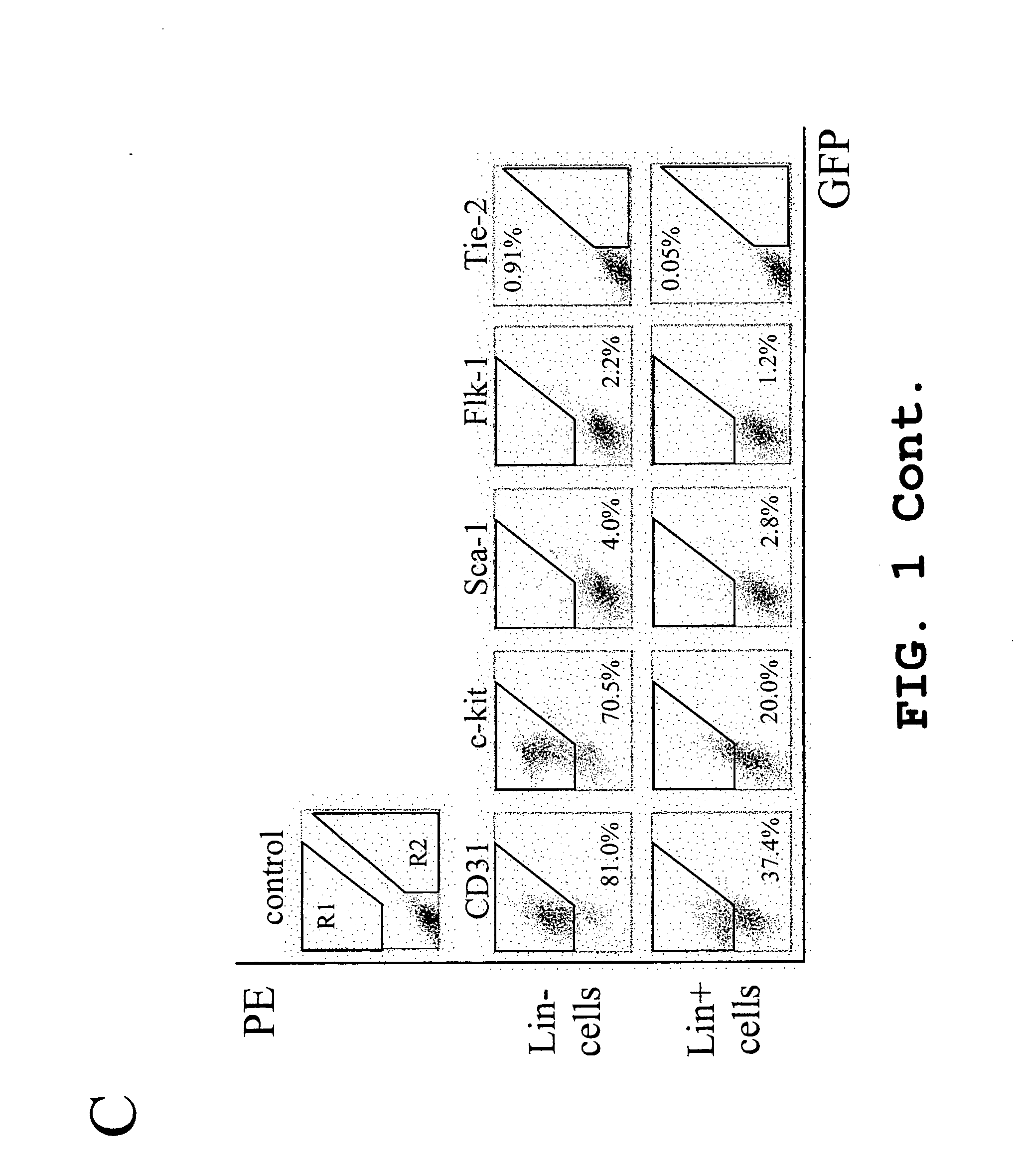
Isolated, mammalian, adult bone marrow-derived, lineage negative hematopoietic stem cell populations (Lin− HSCs) contain endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) capable of rescuing retinal blood vessels and neuronal networks in the eye. Preferably at least about 20% of the cells in the isolated Lin− HSCs express the cell surface antigen CD31. The isolated Lin− HSC populations are useful for treatment of ocular vascular diseases. In a preferred embodiment, the Lin− HSCs are isolated by extracting bone marrow from an adult mammal; separating a plurality of monocytes from the bone marrow; labeling the monocytes with biotin-conjugated lineage panel antibodies to one or more lineage surface antigens; removing of monocytes that are positive for the lineage surface antigens from the plurality of monocytes, and recovering a Lin− HSC population containing EPCs. Isolated Lin− HSCs that have been transfected with therapeutically useful genes are also provided, and are useful for delivering genes to the eye for cell-based gene therapy. Methods of preparing isolated stem cell populations of the invention, and methods of treating ocular diseases and injury are also described.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Method of classifying antibody, method of identifying antigen, method of obtaining antibody or antibody set, method of constructing antibody panel and antibody or antibody set and use of the same
InactiveUS20090203538A1Labor moreMany timesPeptide librariesLibrary screeningAntigenCell Surface Antigens
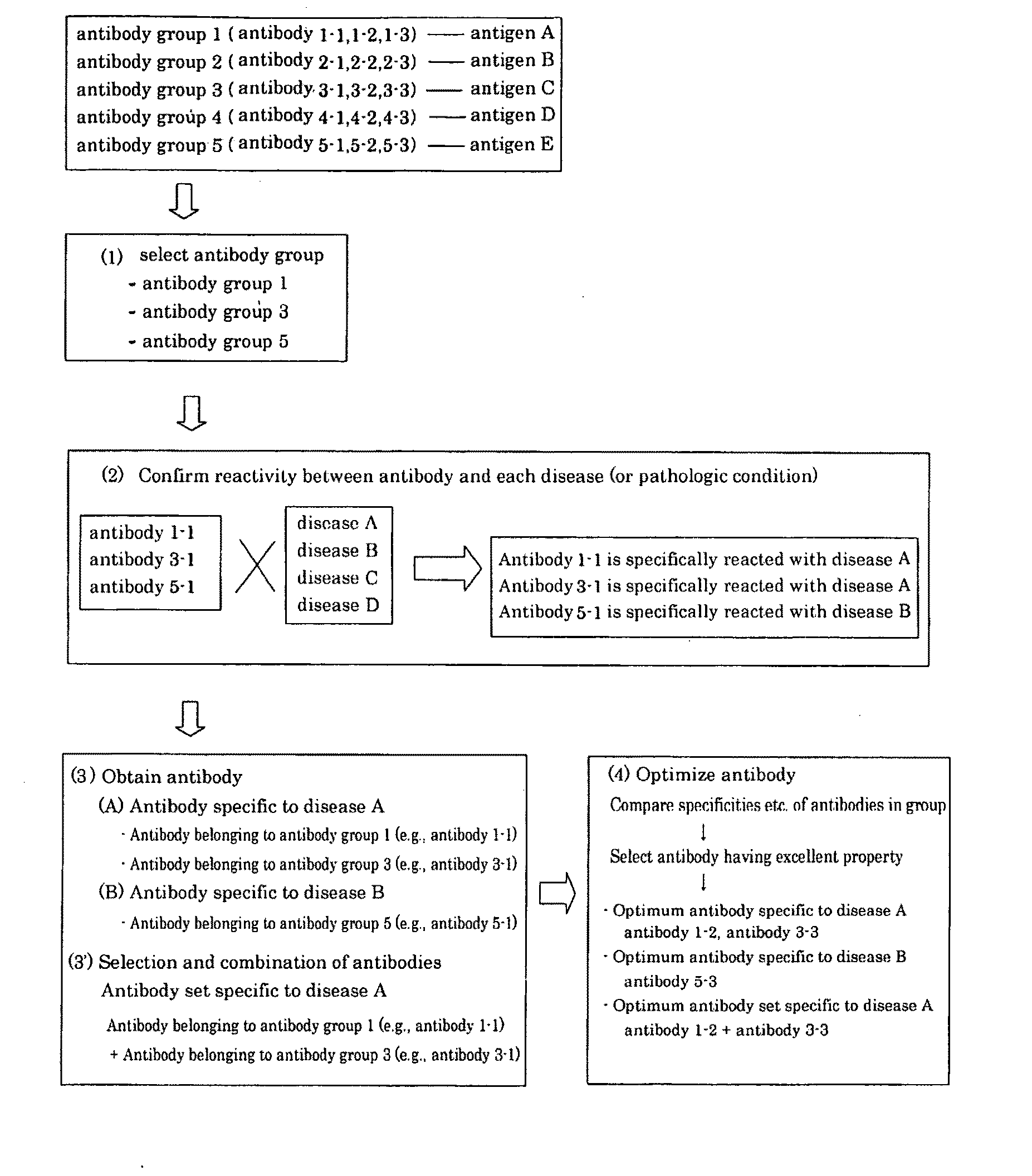
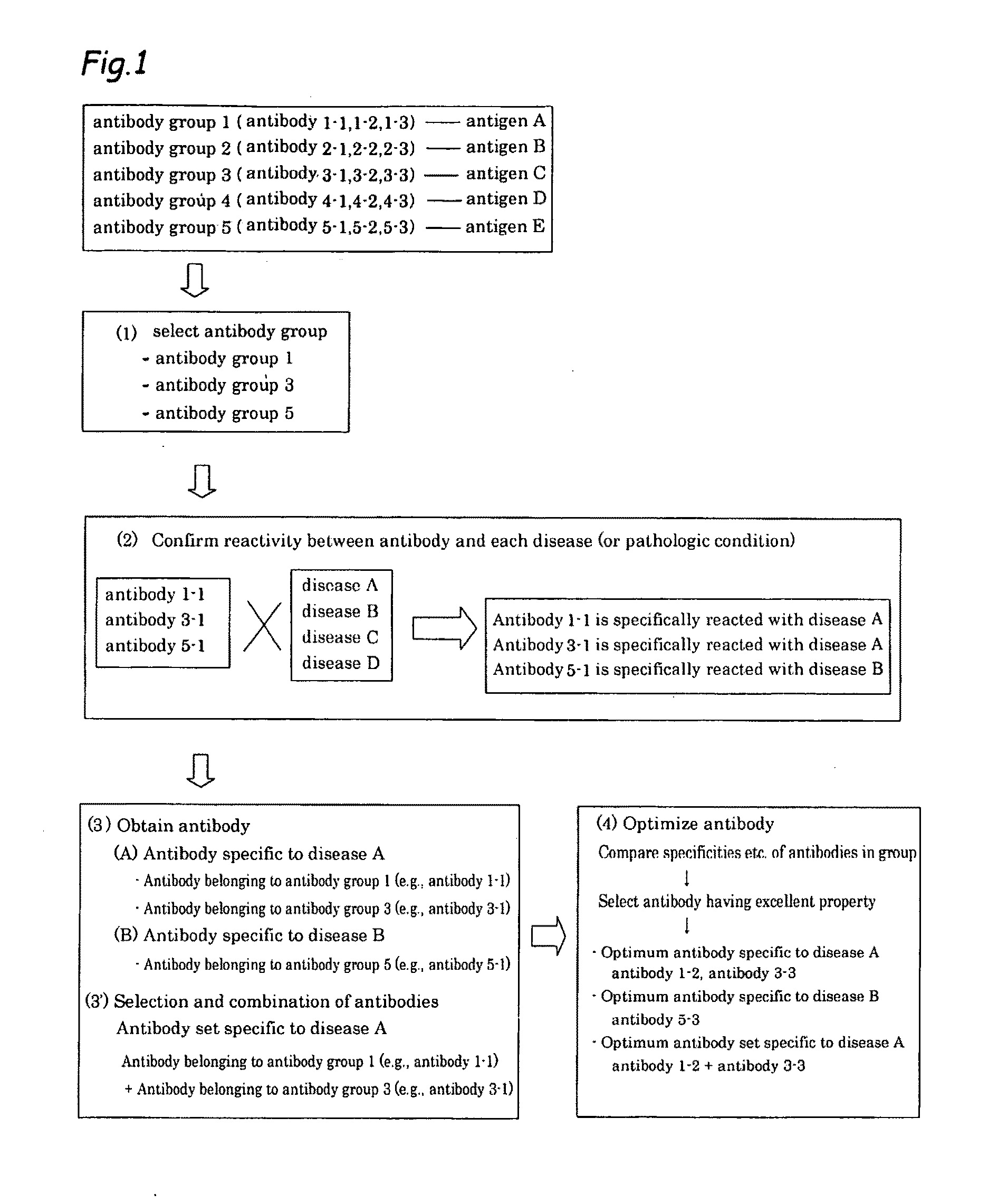
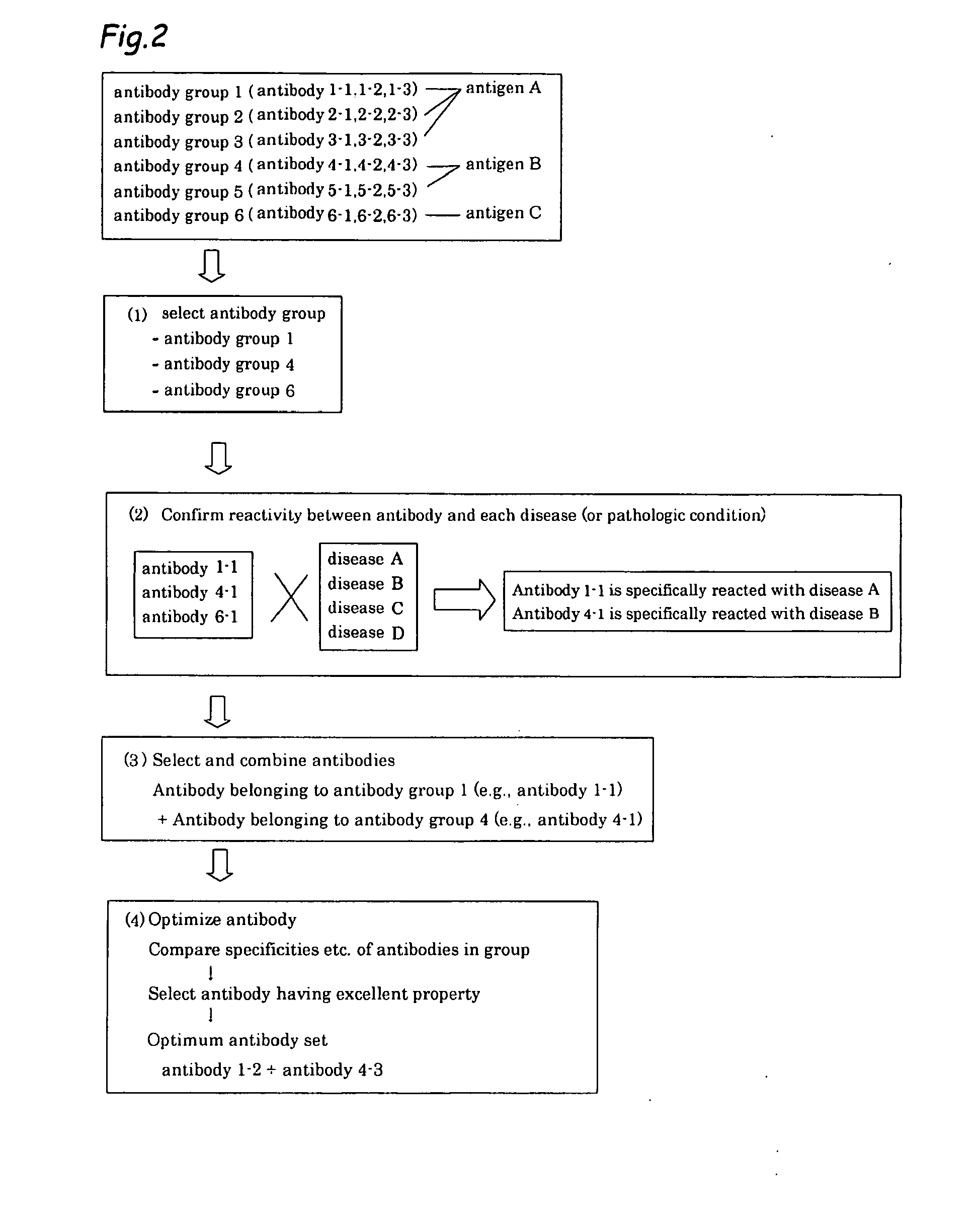
It is intended to provide a method whereby a plural number of antibodies against cell surface antigens are quickly classified and to provide a method whereby antigens of the thus classified antibodies are quickly identified. Further, it is intended to provide a method of promoting the utilization of the useful data obtained by the above methods. Furthermore, it is intended to provide an antibody which is effective in treating or diagnosing cancer. Namely, a method of classifying antibodies which comprises: (1) the step of preparing a plural number of antibodies respectively recognizing cell surface antigens; (2) the step of bringing each of these antibodies into contact with a cell of the same species; (3) the step of analyzing each of the cells having been treated in the step (2) by flow cytometry and thus obtaining data indicating the reactivity of each antibody with its cell surface antigen; and (4) the step of comparing the thus obtained data and classifying the individual antibodies depending on the similarity. A method of identifying antigens which further comprises: (5) the step of selecting one to several antibodies from each antibody group formed in the step (4) and identifying antigens thereof; and (6) on the assumption that antigens of the antibodies belonging to a single antibody group are the same or highly related to one another, making relations between the antigens having been identified in the step (5) and the antibody groups to thereby identify the antigens. An antibody against HER1, an antibody against HER2, an antibody against CD46, an antibody against ITGA3, an antibody against ICAM1, an antibody against ALCAM, an antibody against CD147, an antibody against C1qR, an antibody against CD44, an antibody against CD73, an antibody against EpCAM and an antibody against HGFR, each obtained by using the above methods.
Owner:FUJITA HEALTH UNIVERSITY
Compositions and methods for regulating lymphocyte activation
InactiveUS20020155604A1Increased proliferationHigh affinityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsCell activationCell Surface Antigens
The present invention relates to regulation of lymphocyte activation. In particular, it relates to compositions and methods for regulating lymphocyte activation by selectively binding multiple cell surface antigens expressed by the same lymphocyte.
Owner:CYCLACEL PHARMA
Antibodies against epitopes with homology to self antigens, methods of preparation and applications thereof
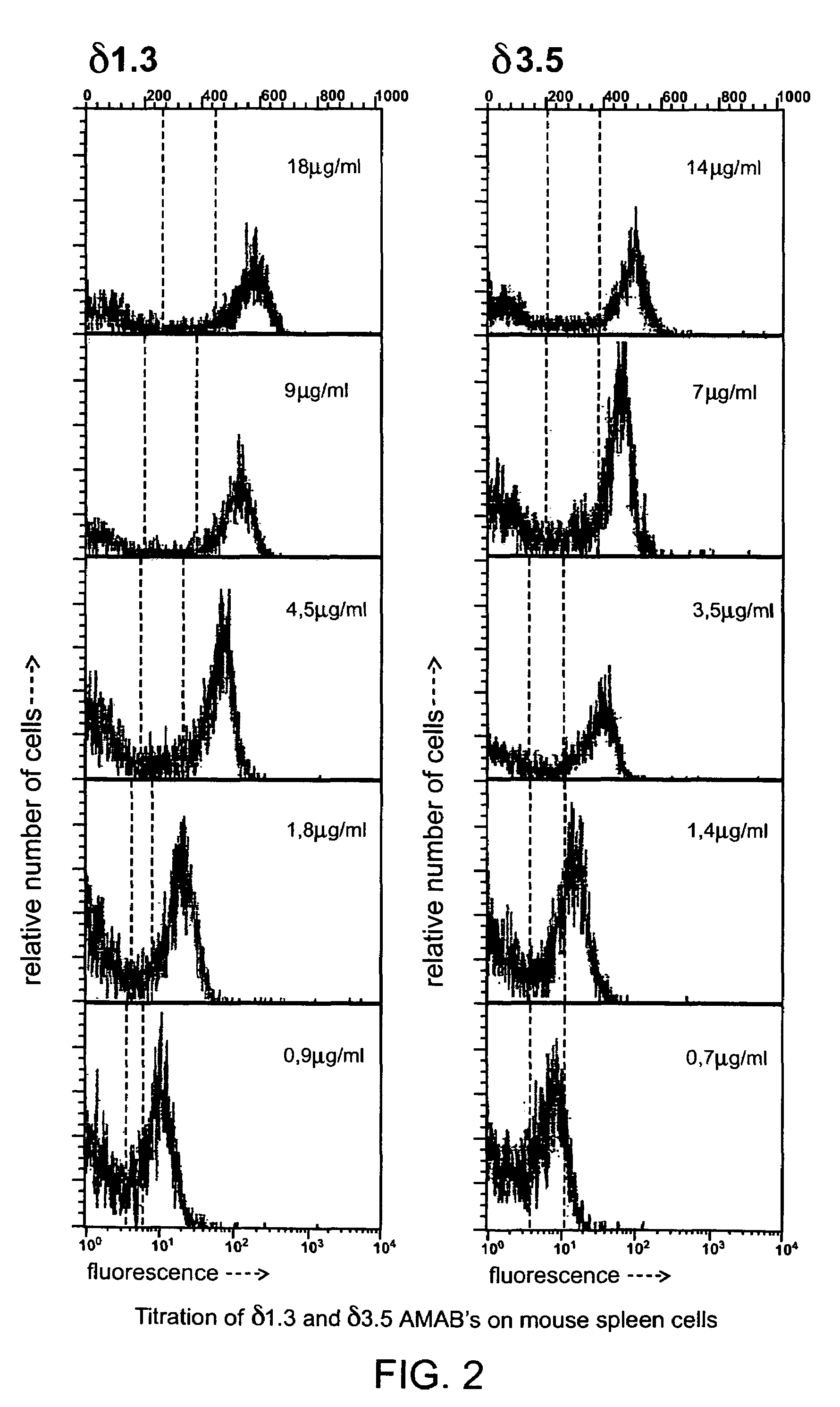
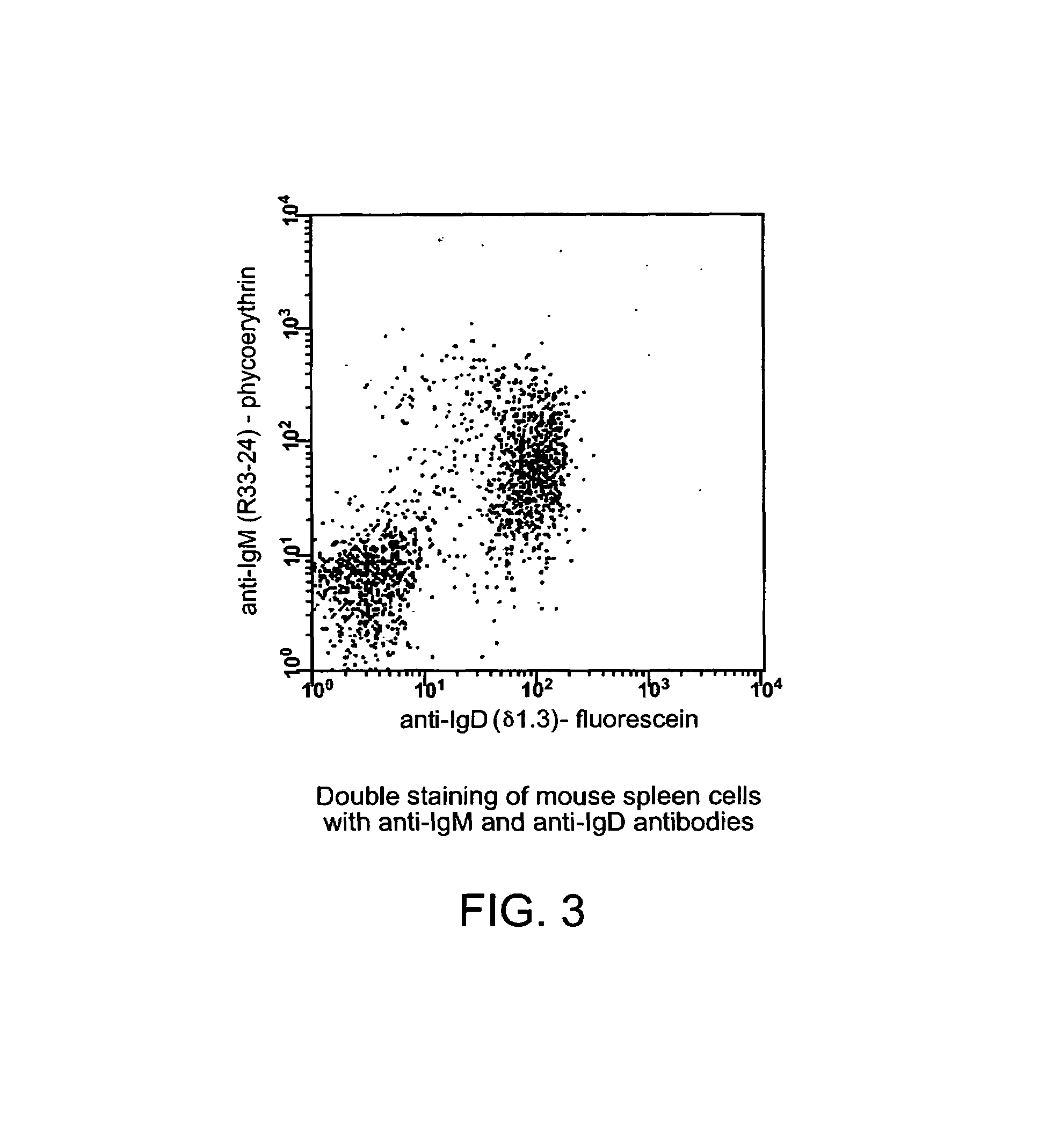
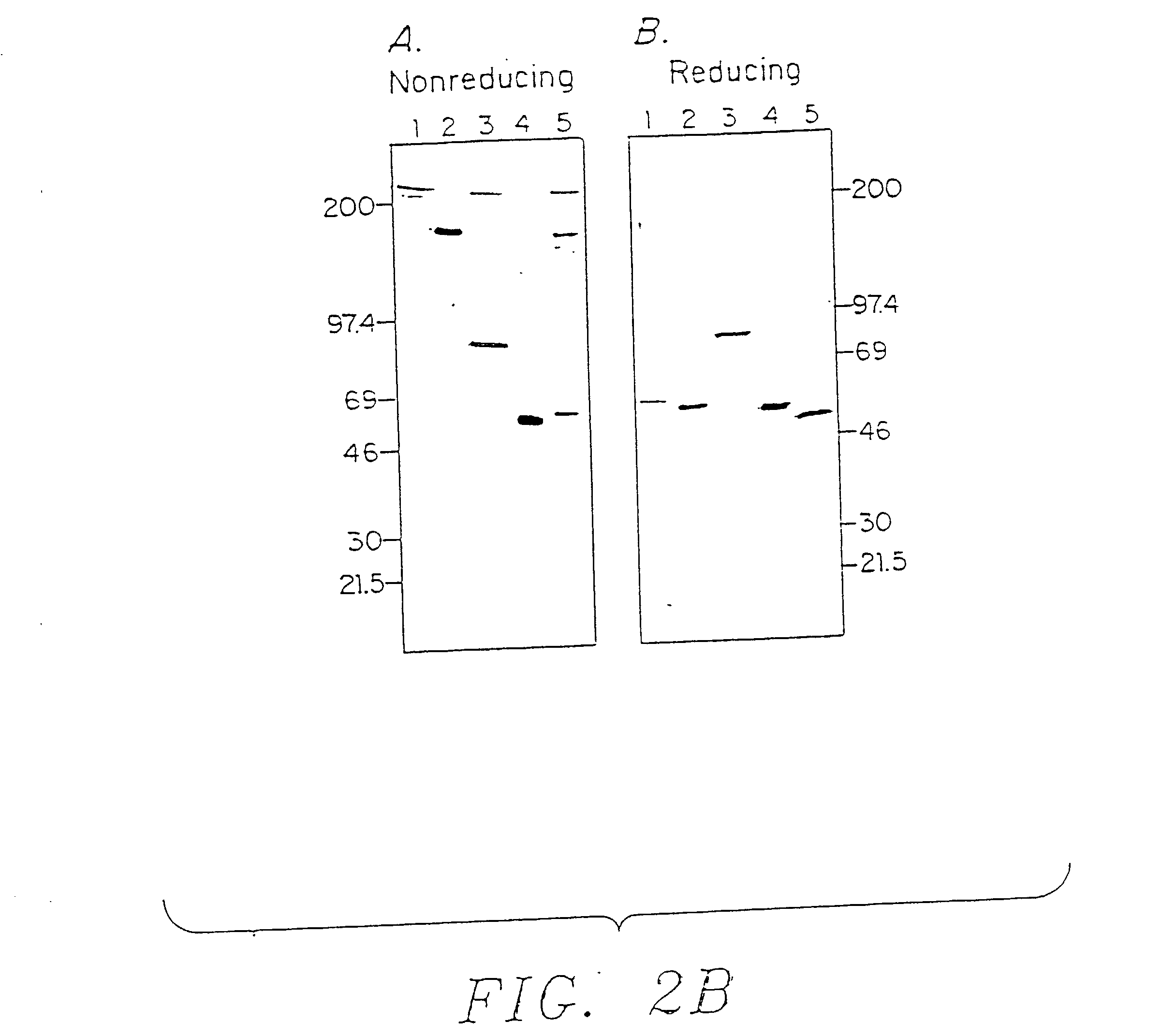
This invention provides novel methods of obtaining autologous monoclonal antibodies (AMABs) to self-antigens or homologs thereof. The method involves obtaining a genetically engineered host animal that does not biosynthesize at least one epitope of the antigen and utilizes the lack of self-tolerance of the host to the epitope to produce antibodies specific to the antigen. The invention also encompasses the AMABs produced by the methods. The invention further encompasses methods of isolating cells comprising the use of such AMABs that have specificity for a cell surface antigen.
Owner:MILTENYI BIOTEC
Expression vectors encoding bispecific fusion proteins and methods of producing biologically active bispecific fusion proteins in a mammalian cell
The present invention provides an expression vector encoding monospecific or bispecific fusion protein. In one embodiment the expression vector encodes a monospecific fusion protein, which vector comprises a recombinant monospecific single chain cassette comprising a DNA sequence encoding a first binding domain capable of binding a cell surface antigen. In another embodiment the expression vector encodes a bispecific fusion protein, which vector comprises a recombinant bispecific single chain cassette comprising a DNA sequence encoding a first binding domain capable of binding a cell surface antigen and a DNA sequence encoding a second binding domain capable of binding a cell surface antigen, each domain capable of binding a different antigen. The present invention also provides a method for producing a biologically active monospecific or bispecific fusion protein in a mammalian cell. This method comprises: (a) transfecting the mammalian cell with the recombinant expression vector of the invention; (b) culturing the mammalian cell so transfected in step (a); and (c) recovering the biologically active bispecific fusion protein so as produced by the cultured mammalian cell.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
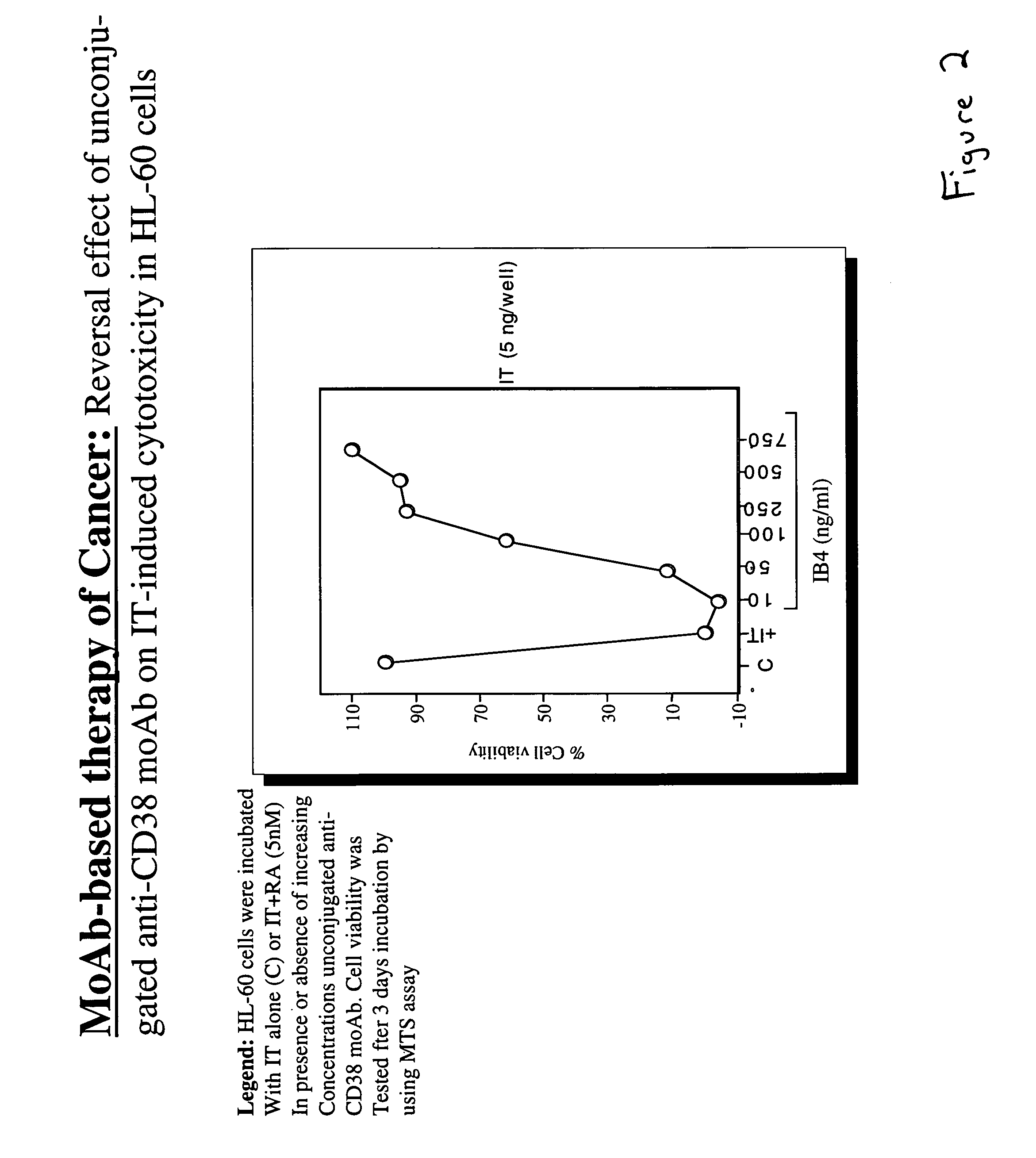
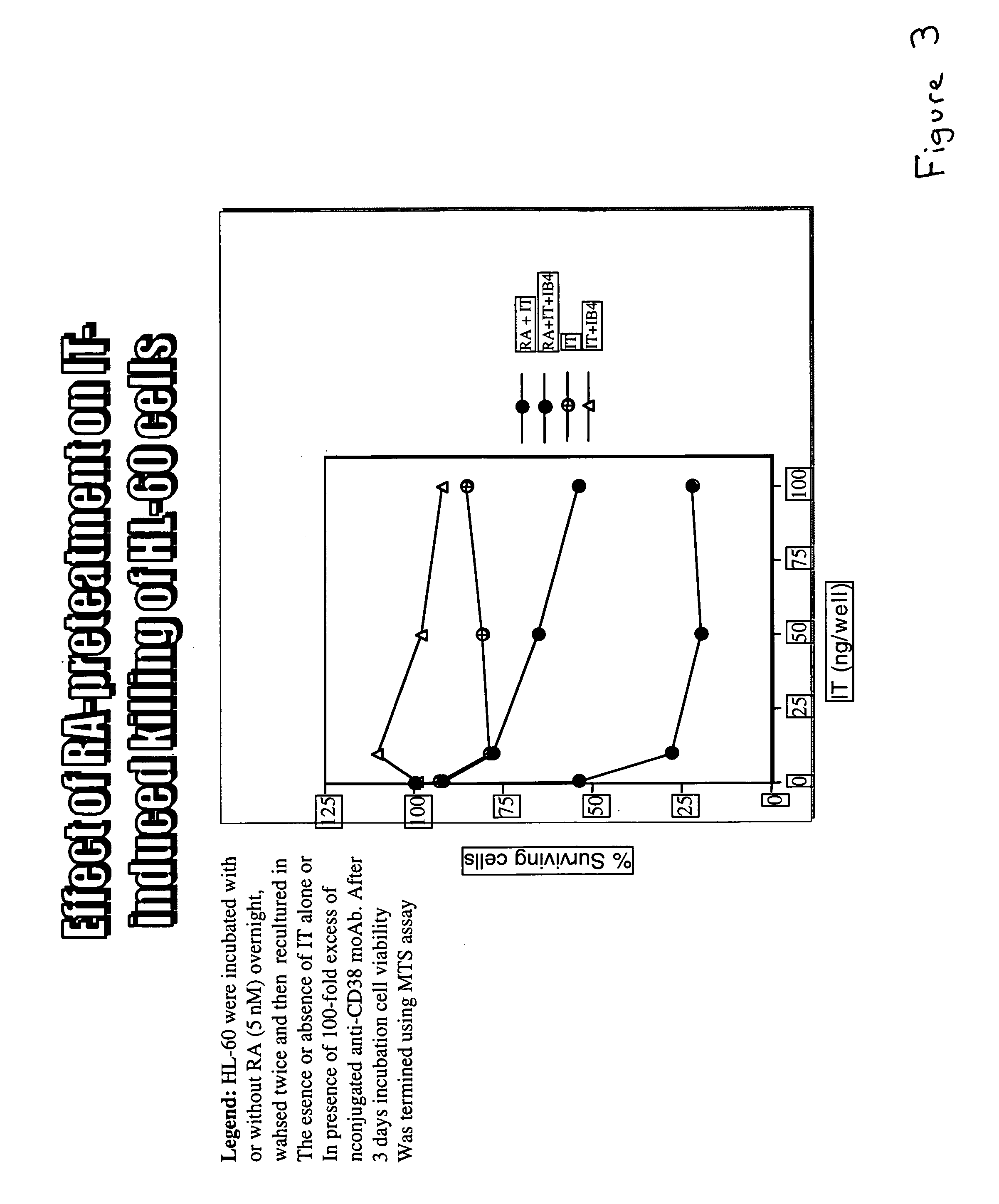
Potentiation of anti-CD38-Immunotoxin cytotoxicity
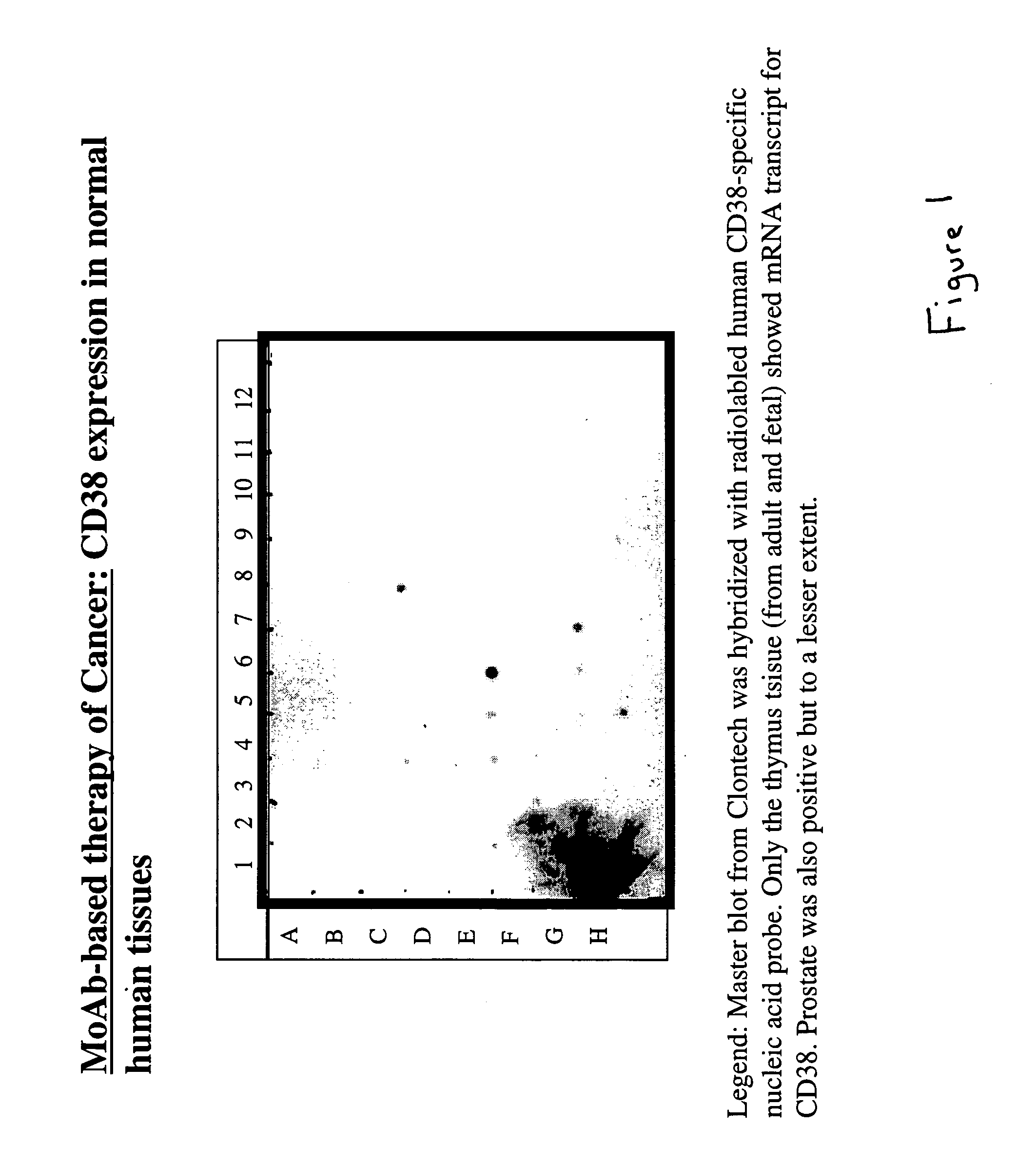
The present invention is directed to the use of agents that induce high levels of cell surface molecules to provide targets for immunotoxins directed against the same cell surface molecules. A specific example is given in which all-trans-retinoic acid (RA) is used to induce high levels of CD38 cell surface antigen expression in several myeloid and lymphoid leukemia cells. CD38 was then used as target for delivering plant toxin (gelonin) to leukemia cells. Treatment of leukemia cells with RA induced high levels of CD38 in those cells that otherwise had low CD38 expression. The RA-induced leukemia cells then became exquisitely sensitive to an immunotoxin constructed from an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody conjugated to the plant toxin gelonin.
Owner:BOARD OF REGENTS
Methods for treating fibrotic conditions
The present invention is directed to methods for treating fibrosis conditions, such as liver, kidney and lung fibrosis, as well as fibrosis conditions of other tissues of the body. The methods of the invention comprise administering to a patient in need of such treatment a therapeutically effective amount of a B-cell antagonist. Exemplary B-cell antagonists that can be used in the practice of the methods of the invention include antibodies against B-cell surface antigens (e.g., antibodies against CD20), and BAFF antagonists.
Owner:BIOGEN INC
Cartilage-derived stem cells and applications thereof
The invention relates to methods of isolating adult stem cells, to the cells thus isolated and to applications thereof. More specifically, the invention relates to isolated adult stem cells, which are derived from dedifferentiated chondrocytes, which can be differentiated and which can give rise to a series of cell lineages, as well as to specific markers present in said cells, such as cell surface antigens. The cells provided by the present invention can be used, for example, in cell therapy and in the search for and development of novel medicaments.
Owner:CONSEJO SUPERIOR DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS (CSIC) +1
Methods for enhancing anti-tumor antibody therapy
InactiveUS9005619B2Improve anti-tumor effectEnhances target cell killingBiological material analysisImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsCell Surface AntigensAgonist
Methods of enhancing the efficacy of antibody-directed cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) for therapy directed to killing of tumor cells are disclosed. Cancer specific cell surface antigens are bound by monoclonal antibodies, thereby stimulating a cytotoxic T cell response characterized by an upregulation of cell surface expression of costimulatory molecules on the T cell. The ADCC response is augmented by the subsequent administration of a second antibody that is an agonist of the costimulatory molecule.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Suppression of transplant rejection
InactiveUS20070166307A1Vertebrate cellsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAutoimmune conditionRegulatory T cell
The present invention relates to a transplant rejection in an animal suppressed by administration of an antibody directed at a cell surface antigen selected from the group consisting of CD4, CD8, CD154, LFA-1, CD80, CD86 and ICAM-1, preferably an anti-CD4 antibody, together with a non-cellular protein antigen to generate in the animal a population of regulatory T-lymphocytes; reactivating said population of regulatory T-lymphocytes by further administration to the animal of the non-cellular protein antigen; and transplanting said organ or tissue whilst said population of regulatory T-lymphocytes is activated. Regulatory T cells can be generated ex vivo by culturing T cells with an antibody directed at a cell surface antigen selected from the group consisting of CD4, CD8, CD154, LFA-1, CD80, CD86 and ICAM-1, in the presence of cells that present either alloantigen or a non-cellular protein antigen. Ex vivo generated T-lymphocytes can be used as an alternative method of overcoming transplant rejection or in combination with the in vivo method. A similar approach can be adopted for the treatment of autoimmune conditions.
Owner:ISIS INNOVATION LTD
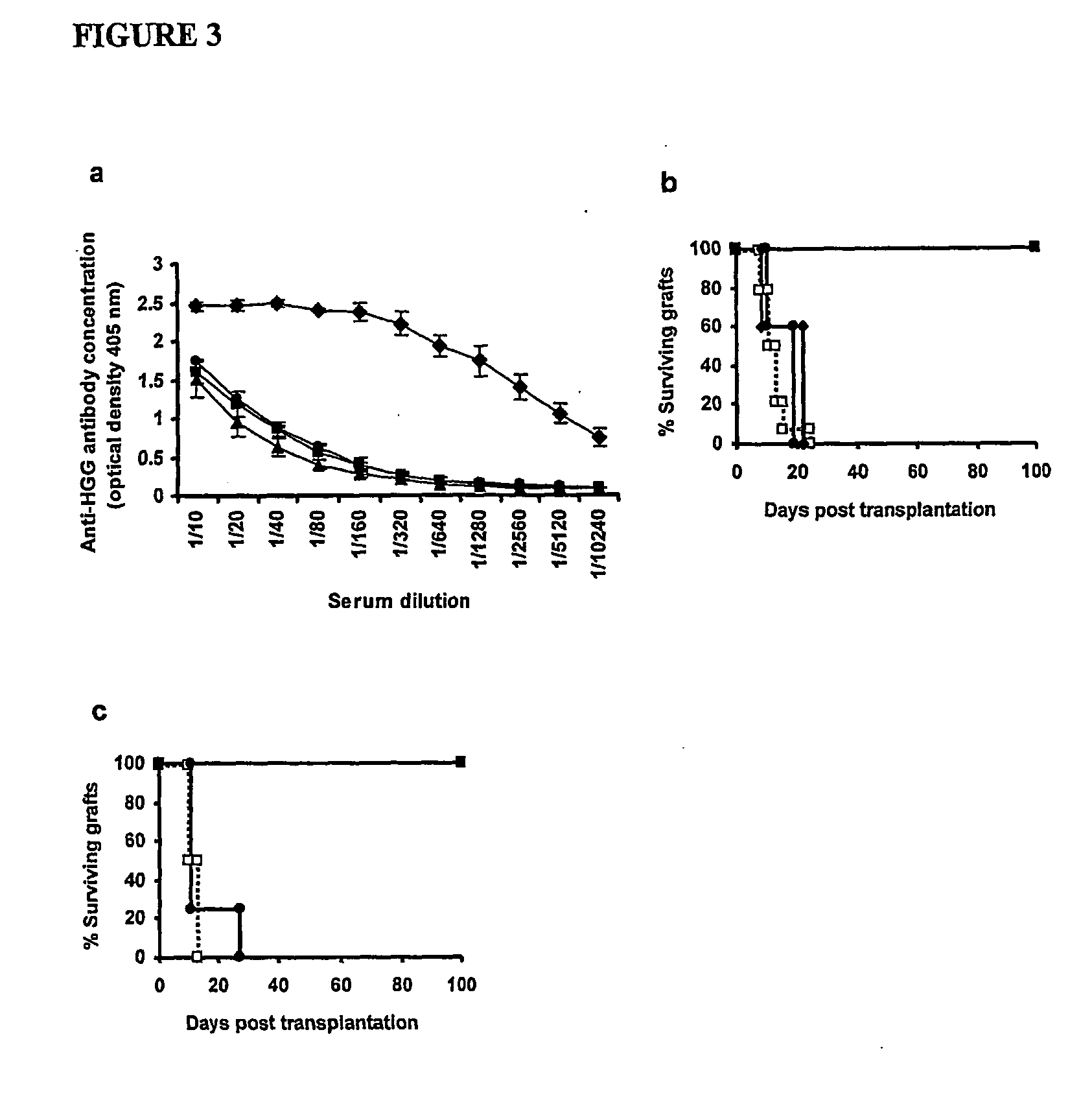
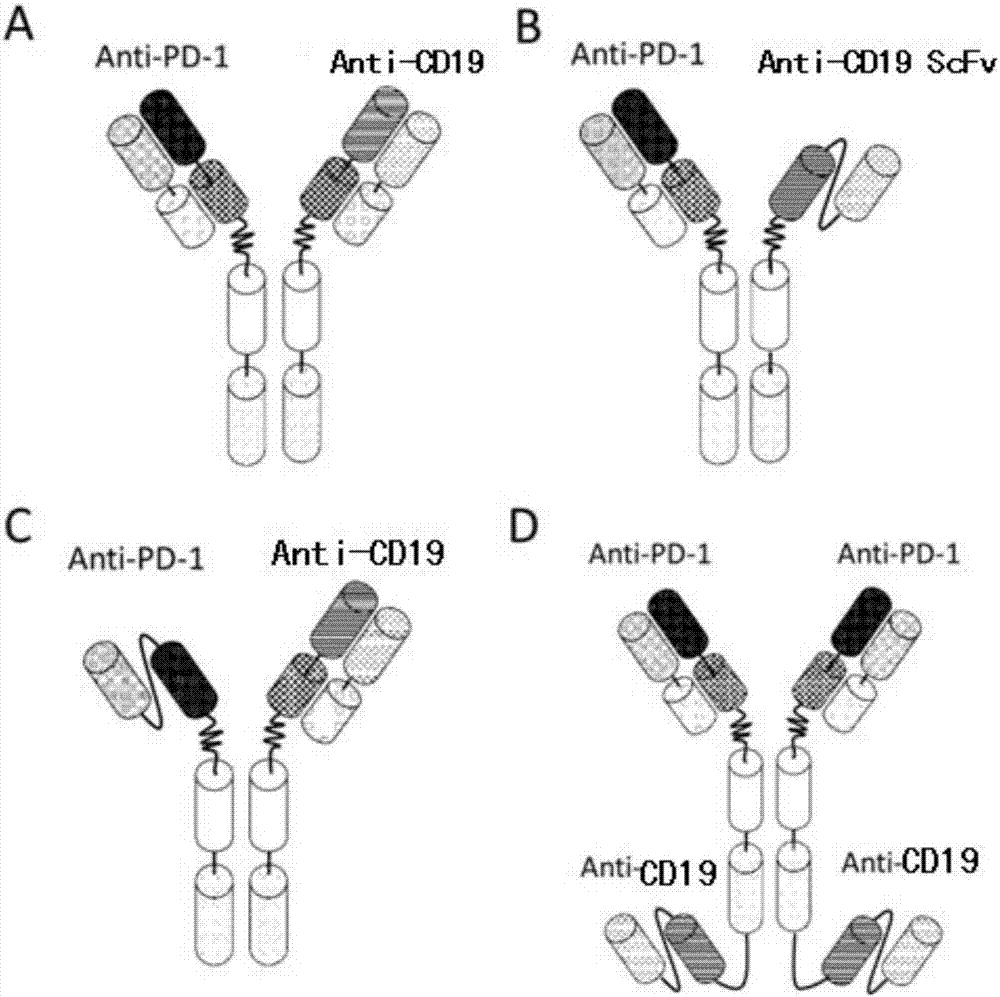
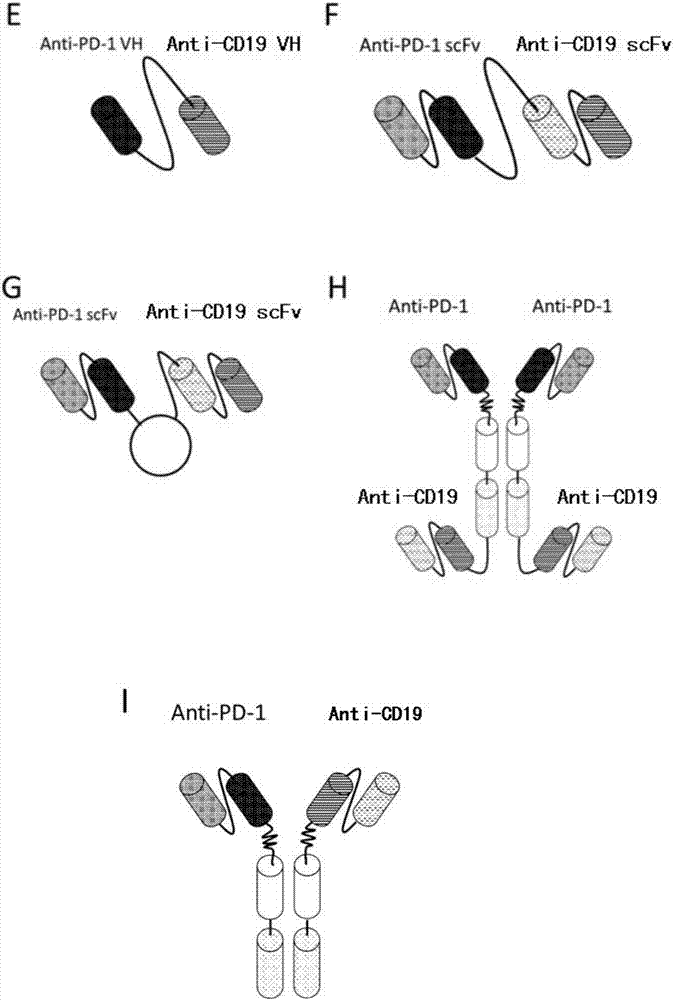
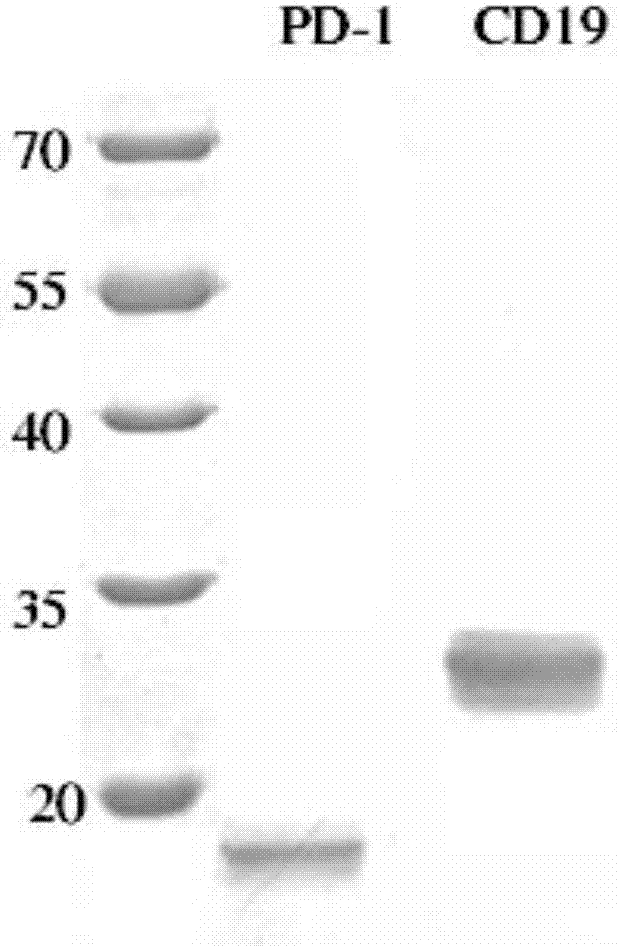
Anti-PD1 and anti-CD19 bispecific antibody and applications thereof
ActiveCN106939050AImprove biological activityGood biological stabilityHybrid immunoglobulinsAntibody ingredientsCell Surface AntigensTherapeutic effect
The present invention relates to anti-PD1 and anti-CD19 bispecific antibody and applications thereof, wherein the anti-PD1 and anti-CD19 bispecific antibody, or a variant, or a functional fragment thereof comprises: a domain capable of specifically recognizing and binding an immune cell surface antigen PD-1, wherein the domain comprises the heavy chain variable region (anti-PD-1 VH) of an anti-PD-1 specific antibody; and a domain capable of specifically recognizing and binding CD19, wherein the domain comprises the heavy chain variable region (anti-CD19 VH) of an anti-CD19 specific antibody. According to the present invention, the bispecific antibody has the whole human sequence, such that the occurrence of HAMA in clinical treatment application is effectively avoided, the occurrence of drug resistance can be effectively reduced, and the utilization efficiency and the treatment effect of the medicine can be improved; and the anti-PD-1 and anti-CD19 bispecific antibody can well mediate T cells to efficiently and specifically kill B-lymphocyte derived tumor cells compared to the existing anti-PD-1 specific antibody and the existing anti-CD19 specific antibody.
Owner:SHUNHAO CELL BIOTECHNOLOGY (TIANJIN) CO LTD
Antibody induced cell membrane wounding
ActiveUS8377435B2Enhanced cell membrane wounding and killing of cellReduced viabilityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAntigenCell Surface Antigens
Compositions and methods for inducing cell membrane wounding, cell permeabilization and cell killing are provided. The composition comprises a polyvalent agent that binds to a highly expressed cell surface antigen present on the surface of a cell. Preferably, the cell surface antigen is associated with the cytoskeleton of the cell. A preferred polyvalent agent is an IgM, and enhanced cell wounding and killing can be provided by the addition of a crosslinking agent. At sublethal concentrations in vivo, the cell wounding antibodies permeabilize cells and dramatically enhance response to chemotherapeutic agents, even in patients refractory to the chemotherapeutic agents.
Owner:MCURE BIOSCIENCES INC +1
Culture method to obtain and maintain a pure or enriched population of mammalian neural stem cells and/or neural/progenitor cells that are prone to differentiate into oligodendrocyte-lineage cells in vitro
An isolated expandable human neural stem or progenitor cell wherein the cell is a progenitor cells or stem cell, maintains its capability to differentiate into neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes, maintains its ability to differentiate into oligodendrocyte lineage cells efficiently throughout subsequent passages, and the cell expresses at least cell surface antigens CD133 and CD140α. Also provided is a method of in vitro culturing an expandable neural progenitor or stem cell isolated from a mammalian central nervous system, and the culture itself, wherein said cell maintains its capability to differentiate into neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes and its ability to differentiate into oligodendrocyte-lineage cells efficiently. In addition, a method of treating a condition caused by a loss of myelin or a loss of oligodendrocytes is provided as is a composition comprising an isolated expandable neural stem cell or one cultured by the methods of the invention.
Owner:KIDO TSUNEO
ICAM-1 binding antibodies
InactiveUS7943744B2Efficacious in eliminating activated B cellSuitable characteristicAntibacterial agentsAntipyreticCell Surface AntigensPharmaceutical drug
The invention provides binding molecules, including antibody molecules which selectively bind to a cell surface antigen of a target cell, and wherein the binding molecules, on binding the cell surface antigen, induce apoptosis of the target cell. There is also provided methods of and pharmaceutical compositions for apoptosis induction and uses thereof.
Owner:BIOINVENT INT AB
Selective antibody targeting of undifferentiated stem cells
This invention provides a system for producing differentiated cells from a stem cell population for use wherever a relatively homogenous cell population is desirable. The cells contain an effector gene under control of a transcriptional control element (such as the TERT promoter) that causes the gene to be expressed in relatively undifferentiated cells in the population. Expression of the effector gene results in expression of a cell-surface antigen that can be used to deplete the undifferentiated cells. Model effector sequences encode glycosyl transferases that synthesize carbohydrate xenoantigen or alloantigen, which can be used for immunoseparation or as a target for complement-mediated lysis. The differentiated cell populations produced are suitable for use in tissue regeneration and non-therapeutic applications such as drug screening.
Owner:ASTERIAS BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC +1
Anti-EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) and anti-CD3 (cluster of differentiation 3) bispecific antibody and application thereof
ActiveCN106632681AConducive to biological functionsConducive to biological functionHybrid immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsDiseaseAntigen
Owner:BEIJING DONGFANG BIOTECH +1
Rapid immunoselection cloning method
InactiveUS7119183B2Large amount of proteinImprove efficiencyPeptide librariesPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenCDNA library
A simple and highly efficient method for cloning cDNAs including CD27 (SEQ ID NO:28) from mammalian expression libraries based on transient expression in mammalian host cells has been discovered. Novel expression vectors allowing highly efficient construction of mammalian cDNA libraries are disclosed. The cloning method of the invention which has been used to clone genes for cell surface antigens of human lymphocytes, has general application in gene cloning. Cell surface antigens cloned according to the present invention have been purified, and the nucleotide and amino acid sequences determined. These antigens have diagnostic and therapeutic utility in immune-mediated infections in mammals, including humans.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
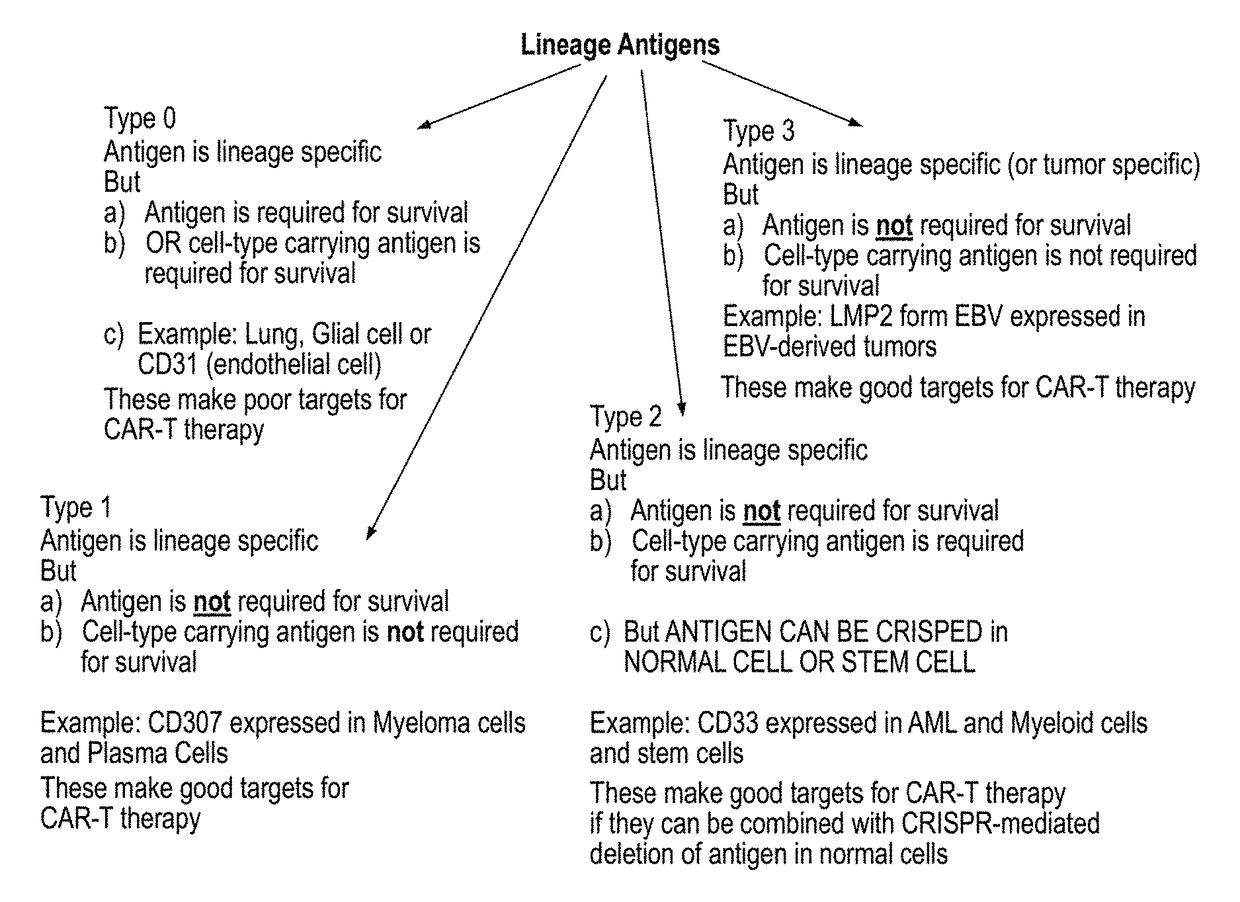
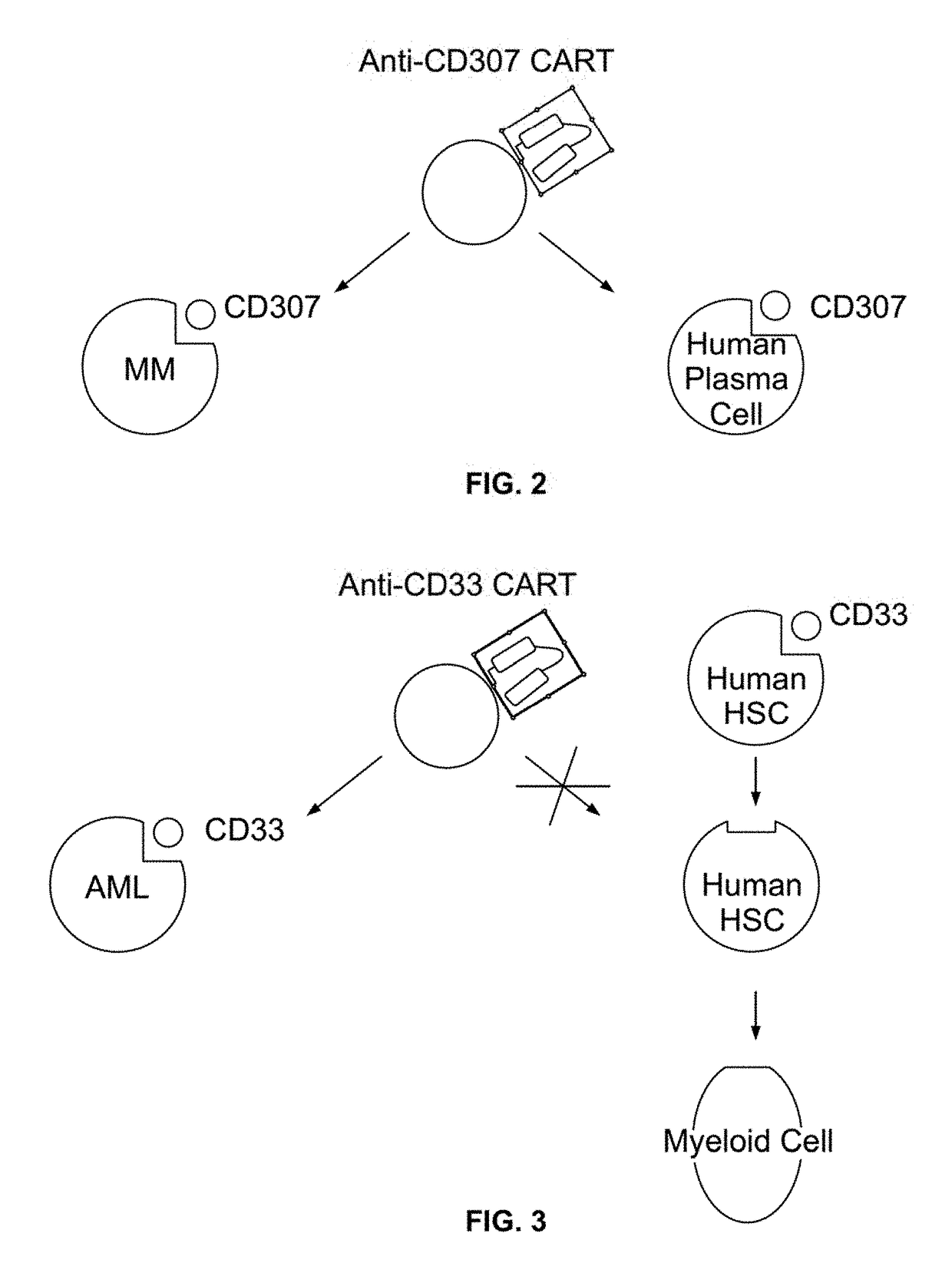
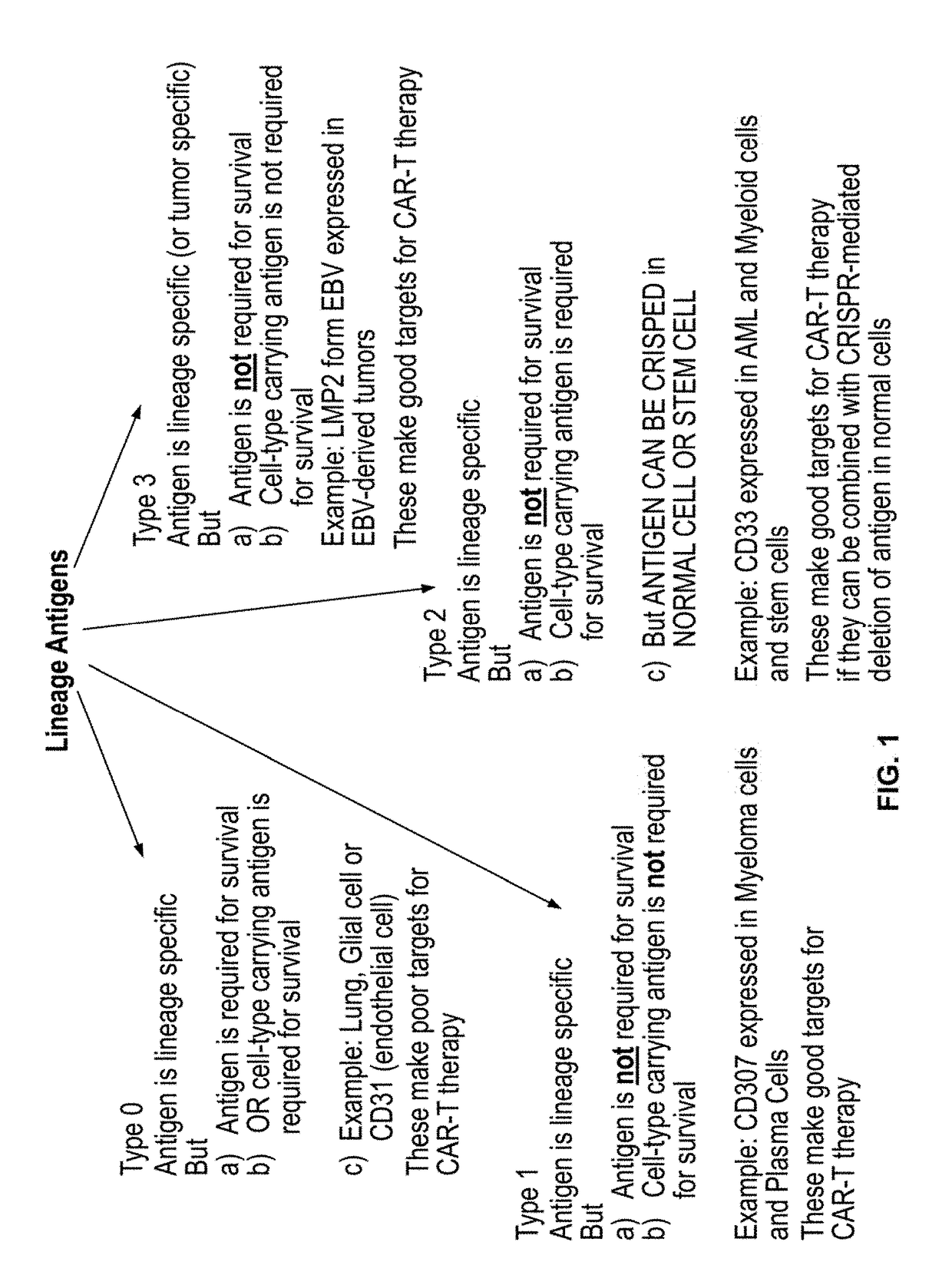
Compositions and methods for inhibition of lineage specific antigens
ActiveUS20170326179A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyAntigenHematopoietic cell
Disclosed herein are methods of administering an agent targeting a lineage-specific cell-surface antigen and a population of hematopoietic cells that are deficient in the lineage-specific cell-surface antigen for immunotherapy of hematological malignancies.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Compositions and methods for inhibition of lineage specific antigens
ActiveUS10137155B2Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyAntigenHematopoietic cell
Disclosed herein are methods of administering an agent targeting a lineage-specific cell-surface antigen and a population of hematopoietic cells that are deficient in the lineage-specific cell-surface antigen for immunotherapy of hematological malignancies.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Use of CD4-binding small molecules to inhibit immune responses
InactiveUS6127387AInhibition formationInhibits T cell activationBiocideOrganic chemistryCD4 LymphocyteCell Surface Antigens
The application concerns a method of identifying compounds that can be used to inhibit undesired human CD4+ T cell immune responses by identifying compounds that block the interaction of CD4 and class II MHC gene products and a method of treatment which comprises administering such an identified compound. The compounds that inhibit undesired human CD4+ T cell immune responses can be used to treat disease such as multiple sclerosis and to prevent graft rejection and graft versus host disease. More specifically, the application concerns compounds having molecular weights between about 500 and 150 that bind to the GFCC'C'' portion of the D1 domain of human CD4 lymphocyte cell surface antigen.
Owner:UNIV THOMAS JEFFERSON
Polypeptide for enrichment, separation and detection of circulating tumor cells and application thereof
ActiveCN103923192AGood reproducibilityEasy to separatePeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesDiseaseLymphatic Spread
The invention provides a polypeptide for enrichment, separation and detection of circulating tumor cells and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the polypeptide is shown as SEQ ID NO:1. The invention also includes a polypeptide-magnetic nanoparticle, which contains the magnetic nanoparticle and the polypeptide that is coupled to the magnetic nanoparticle and used for specific recognition of tumor cells. In addition, the invention discloses application of the polypeptide and the polypeptide-magnetic nanoparticle in preparation of products for enriching, separating or detecting circulating tumor cells or drugs for treating tumor metastasis related diseases. The invention provides a new method for utilizing a polypeptide cell surface antigen to conduct specific recognition, puts forward the new polypeptide-magnetic nanoparticle substance for enrichment, separation and detection of CTC, provides a fast, accurate and low-cost detection technology for enrichment, separation and detection of CTC, and provides an effective method for diagnosis, treatment and prognosis of clinical tumor metastasis patients.
Owner:北京中科纳泰科技有限公司
CIK cell cryopreservation liquid
ActiveCN105248413AProliferation effect is goodHigh activityDead animal preservationAntigenGrape seed
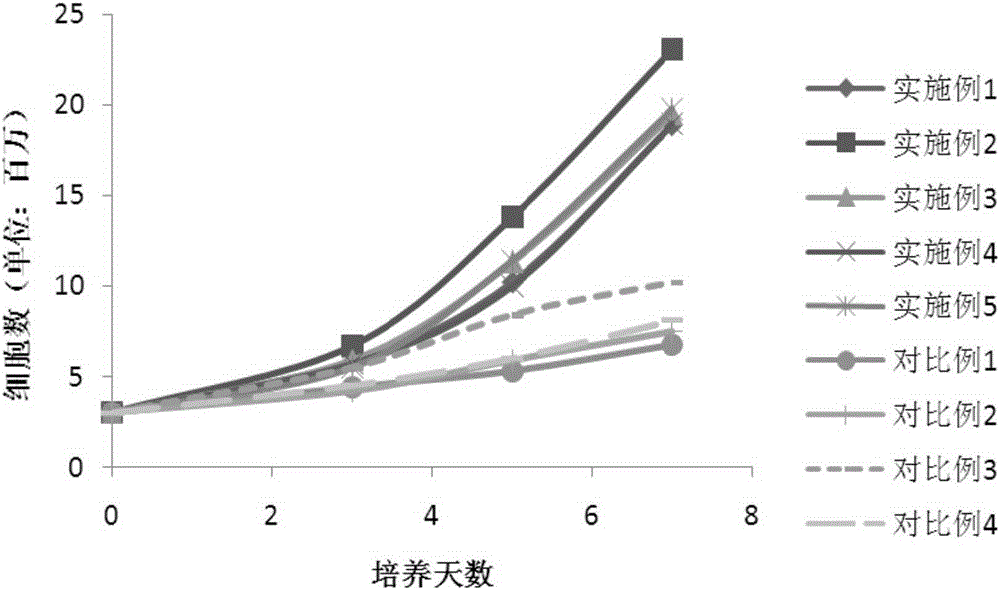
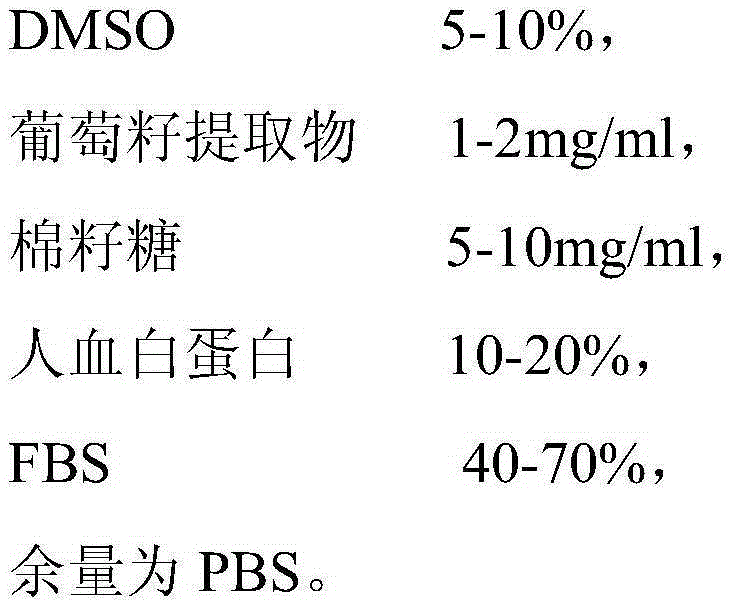
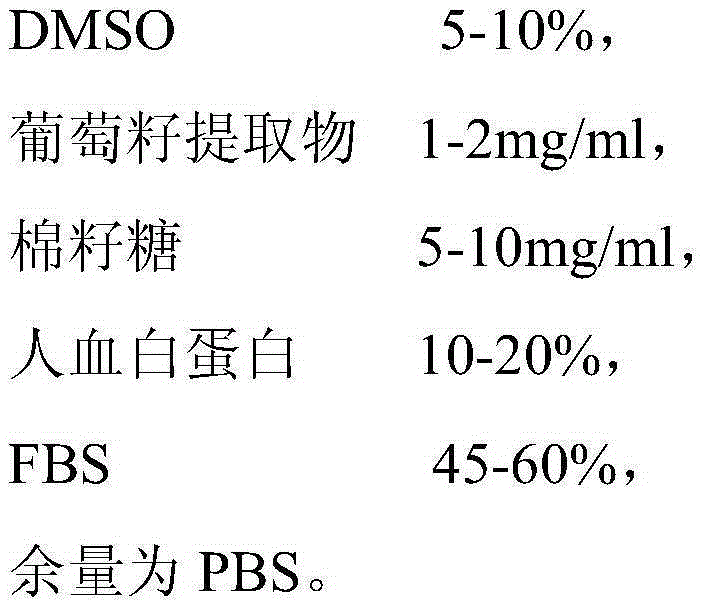
The invention relates to CIK cell cryopreservation liquid. The CIK cell cryopreservation liquid is prepared from, by volume and concentration, 5-10% of DMSO, 1-2 mg / ml of grape seed extracts, 5-10 mg / ml of raffinose, 10-20% of human albumin, 40-70% of FBS and the balance PBS. Due to the fact that raffinose, grape seed extracts and human albumin are added, cell survival time is prolonged, and the cellular structure is prevented from being damaged by free radicals. By the adoption of the CIK cell cryopreservation liquid, cell viability can be better maintained, loss of cell surface antigens is reduced, and cells still have high multiplication capacity and killing activity after recovery.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SALIAI STEMCELL SCI & TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com