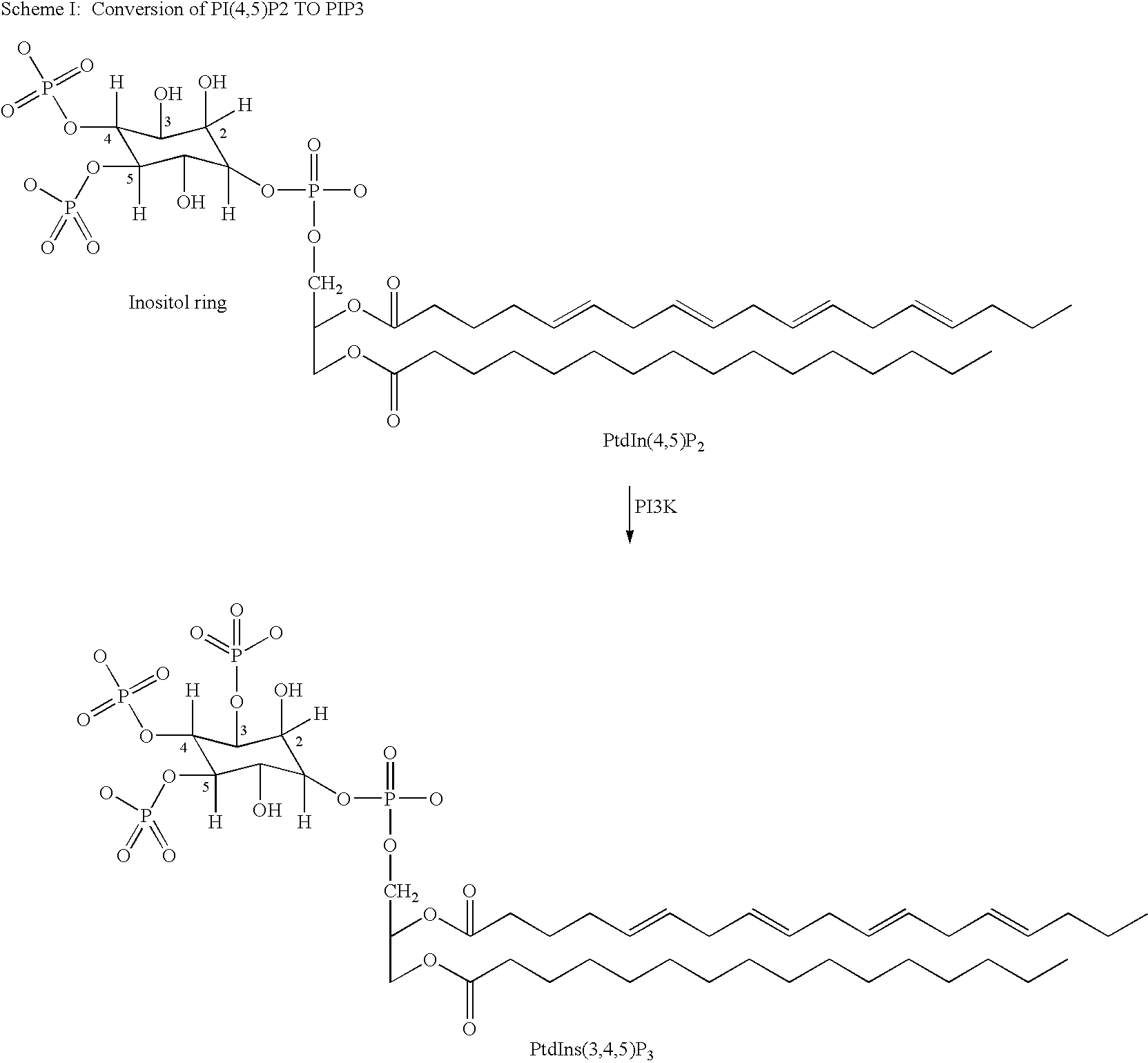
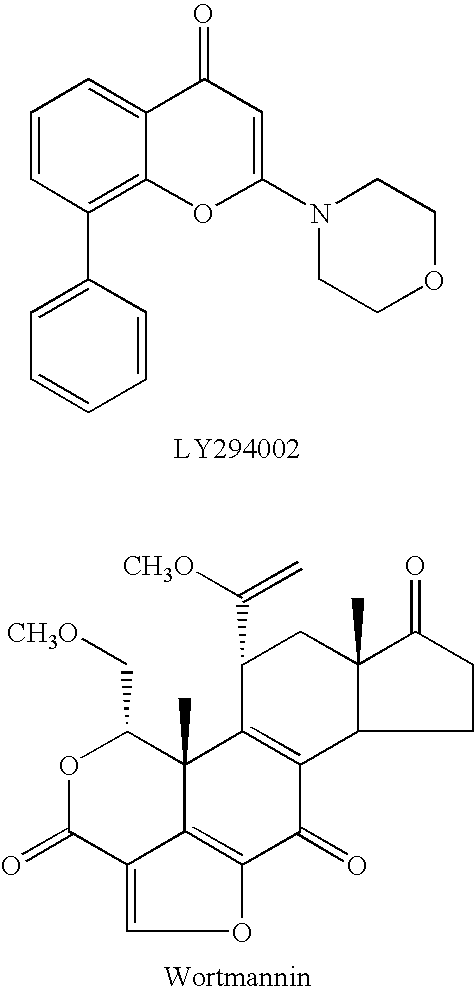
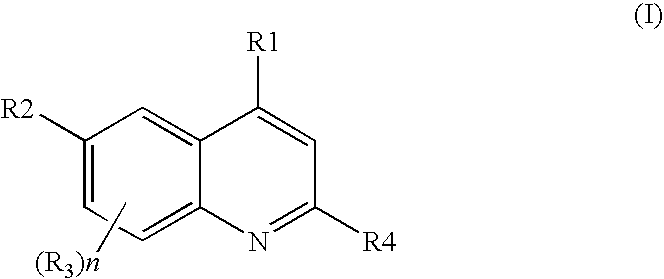
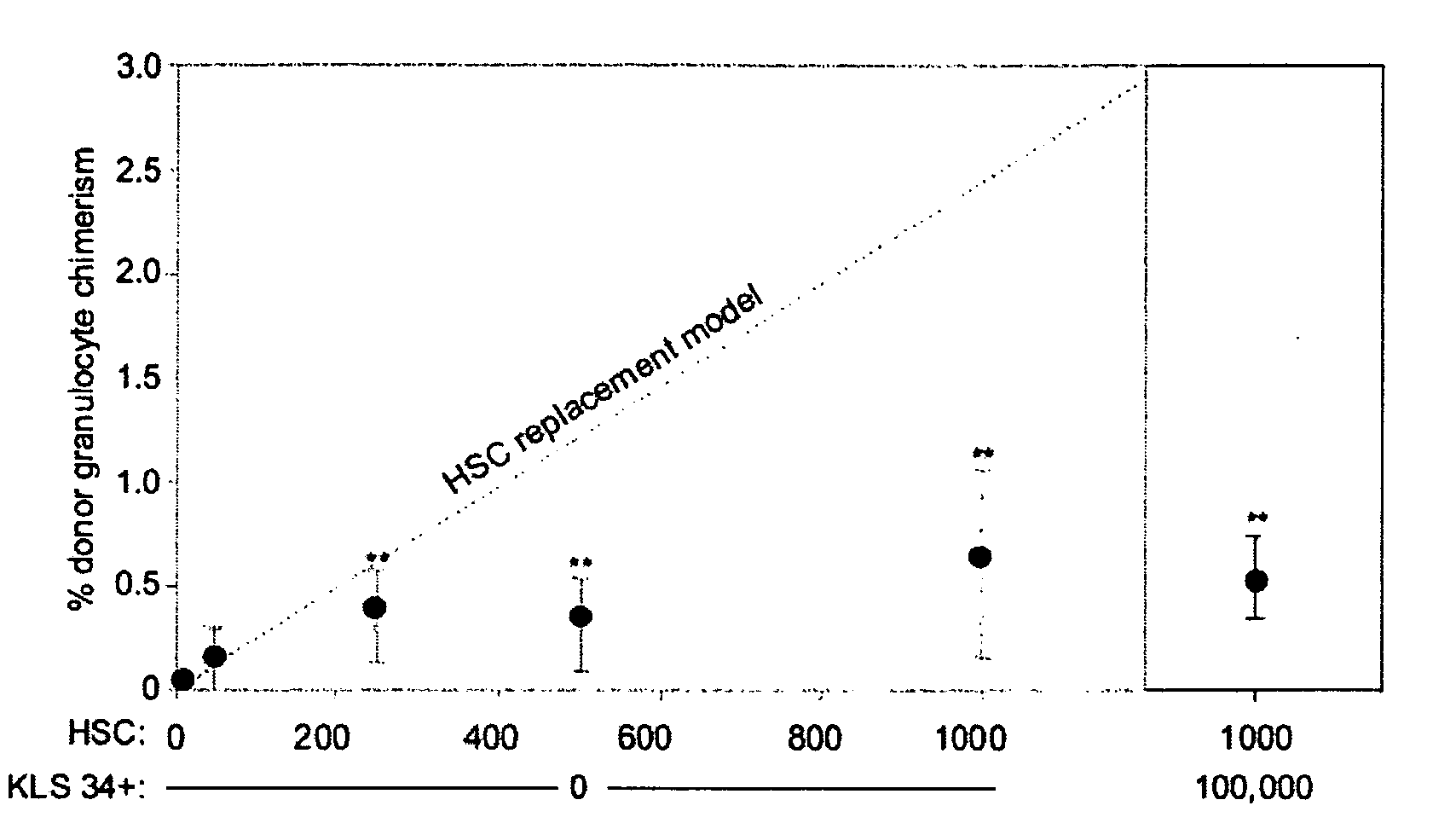
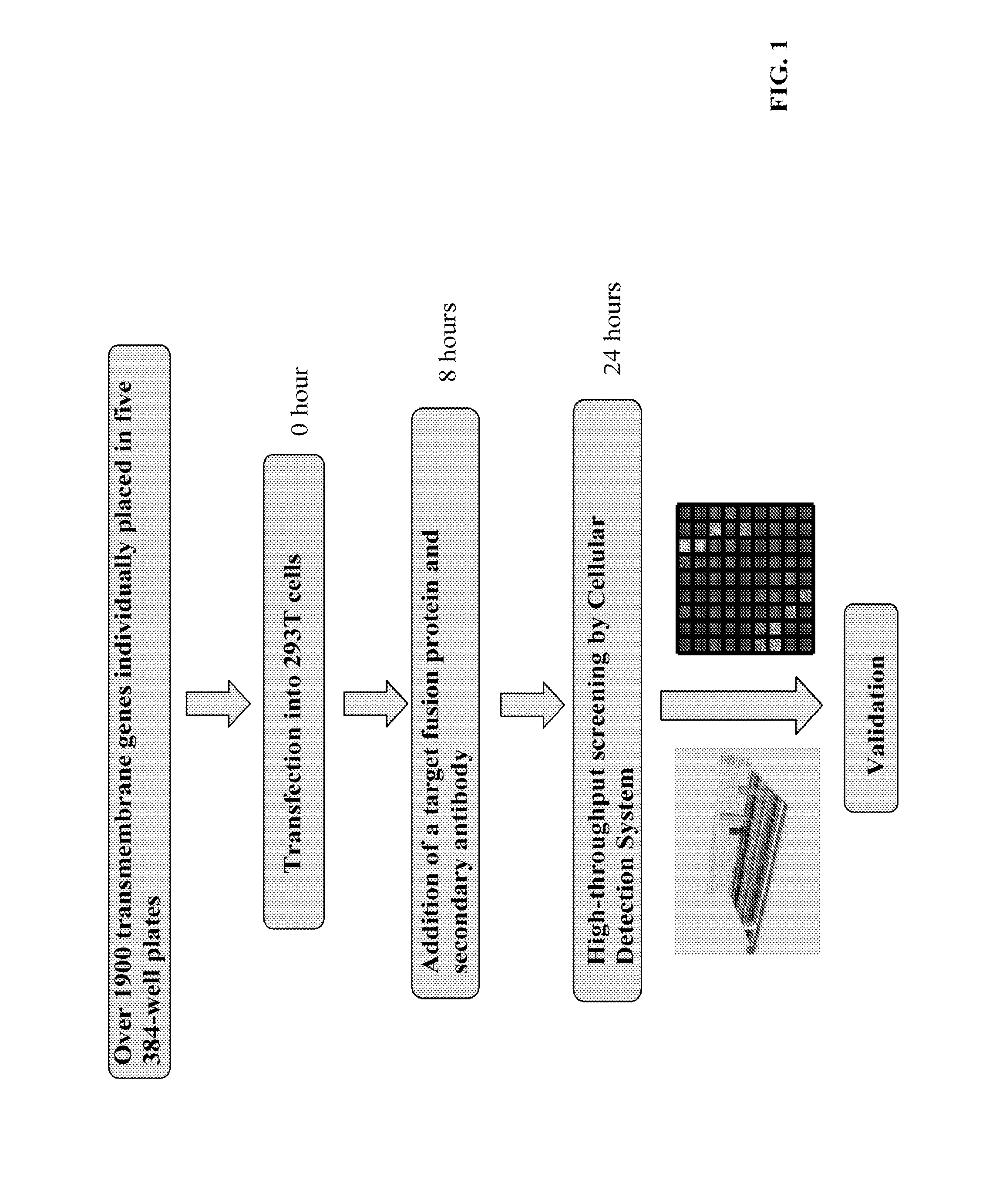
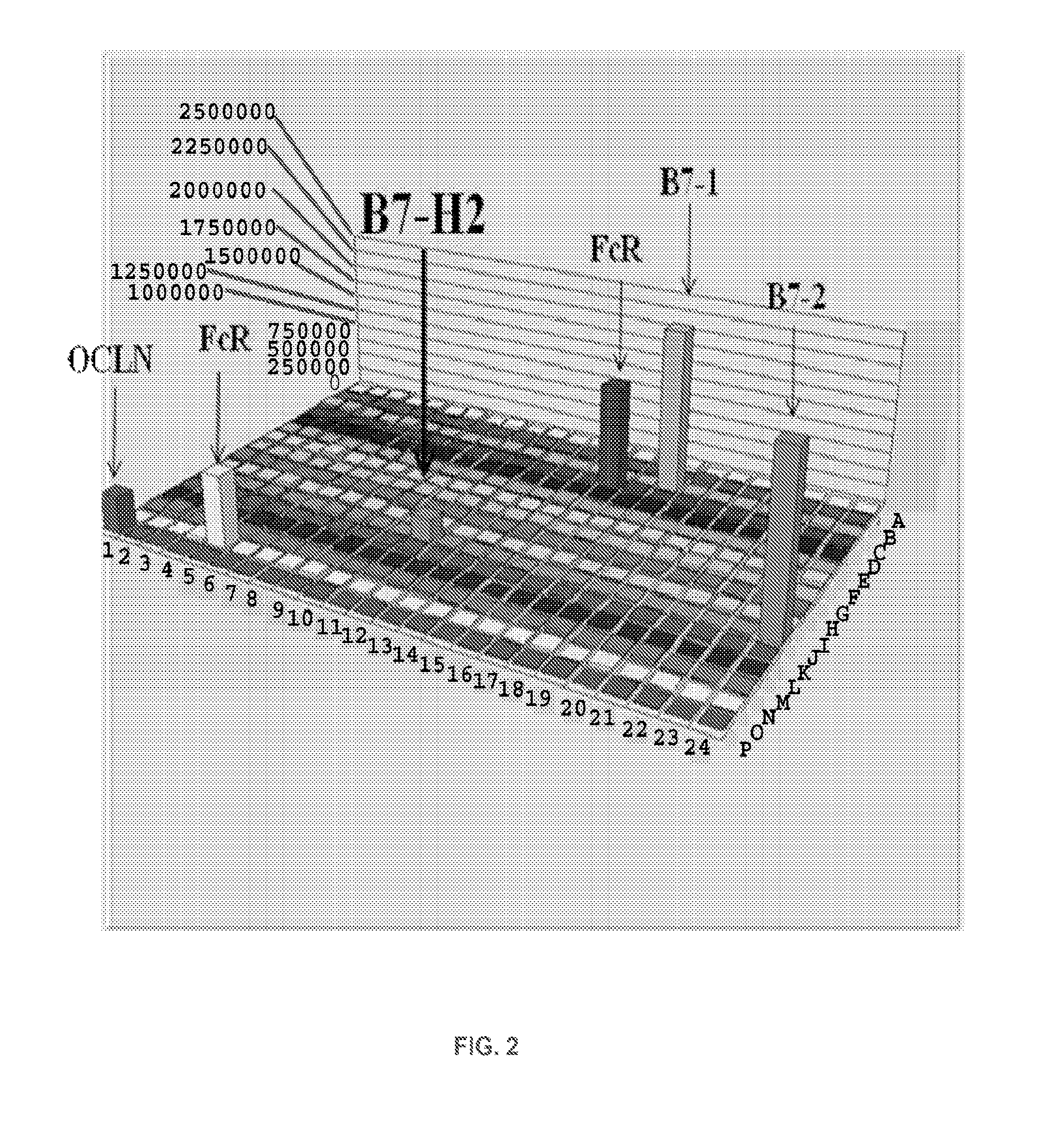
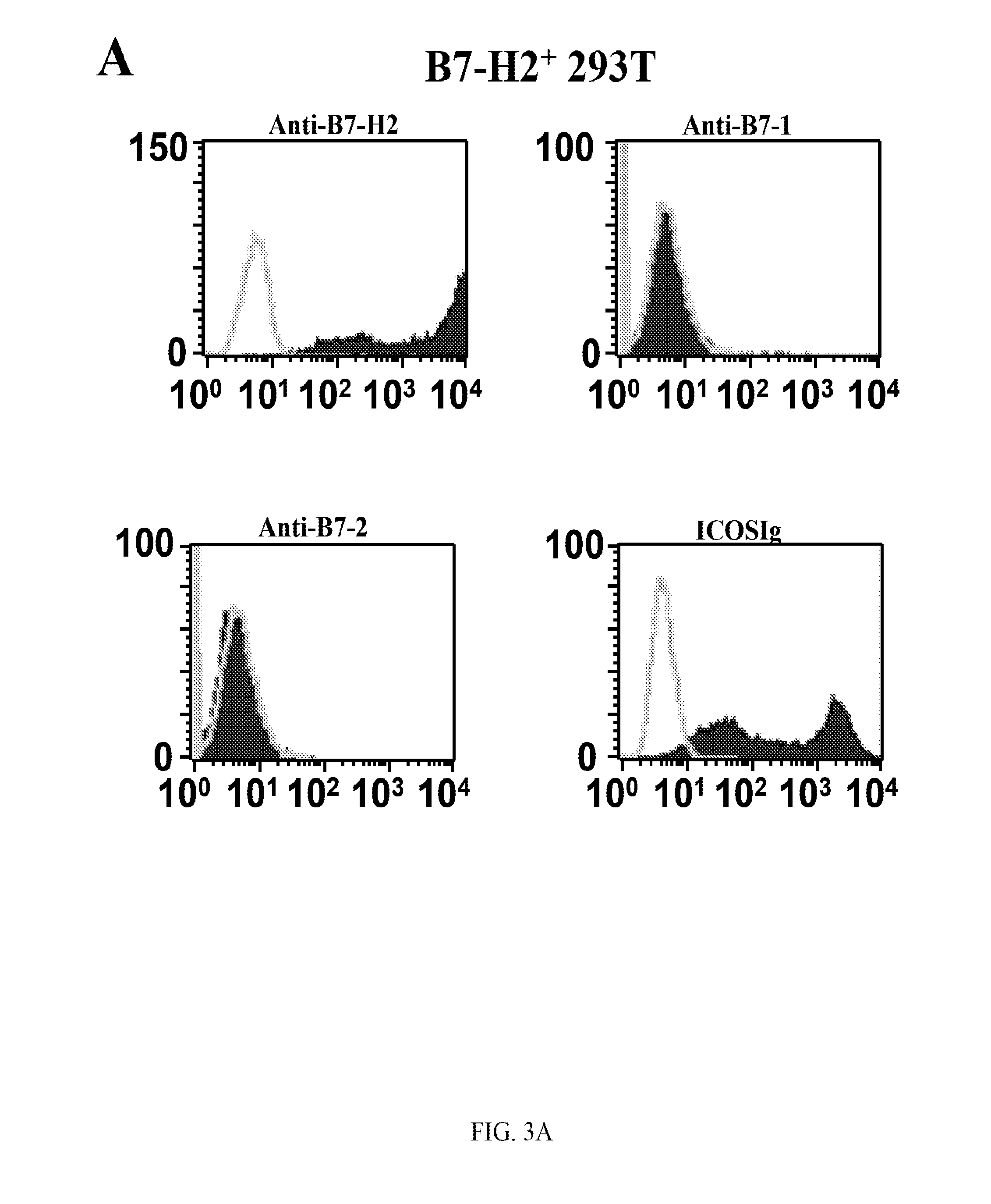
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
369 results about "Graft rejection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A graft rejection is an immune response by the body to destroy foreign cells in transplanted tissue. Graft rejections occur because the transplanted tissue or organ has antigens on its cells that do not match the person's own cell antigens. Only grafts from one identical twin to another are perfect matches,...
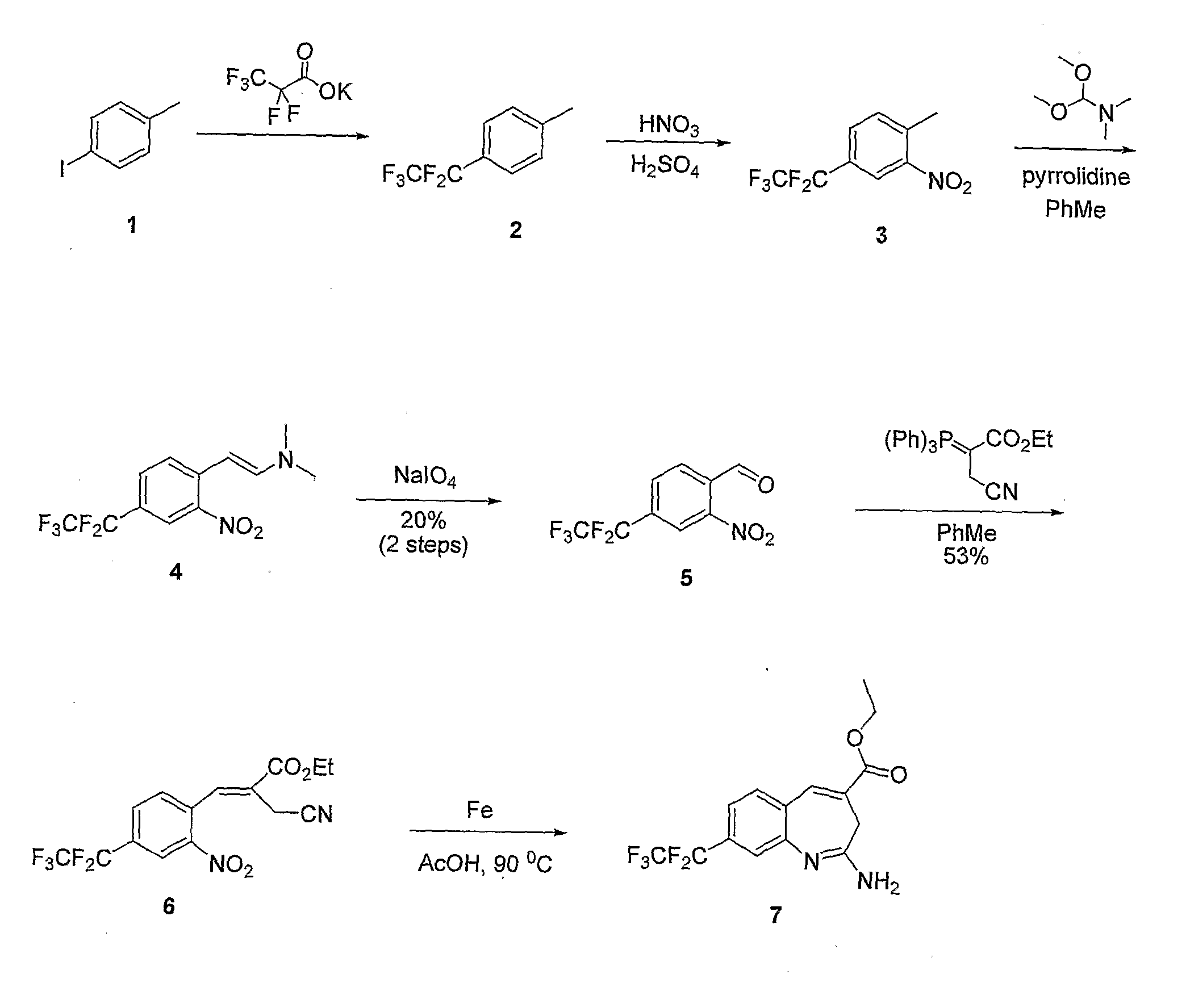
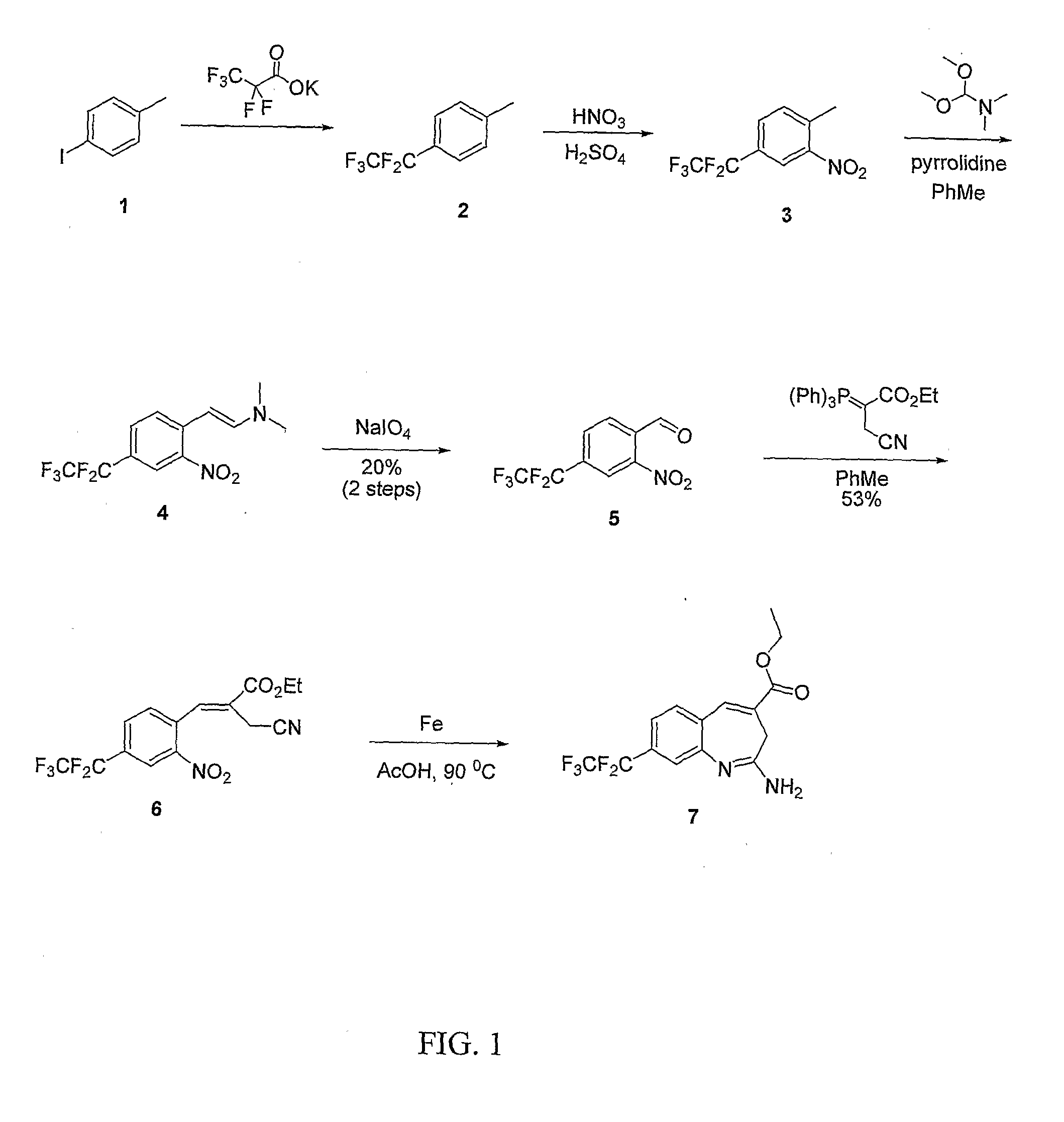
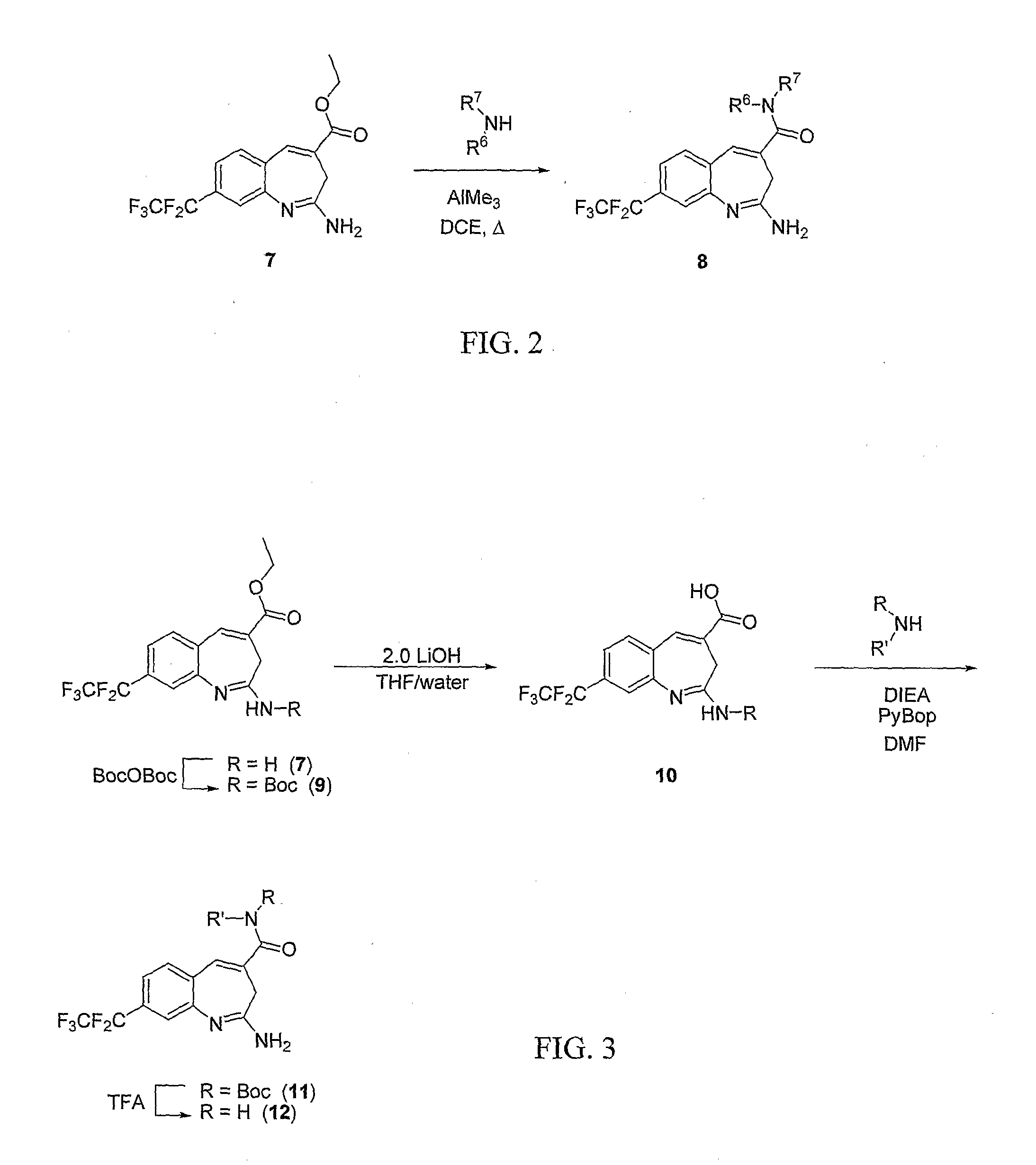
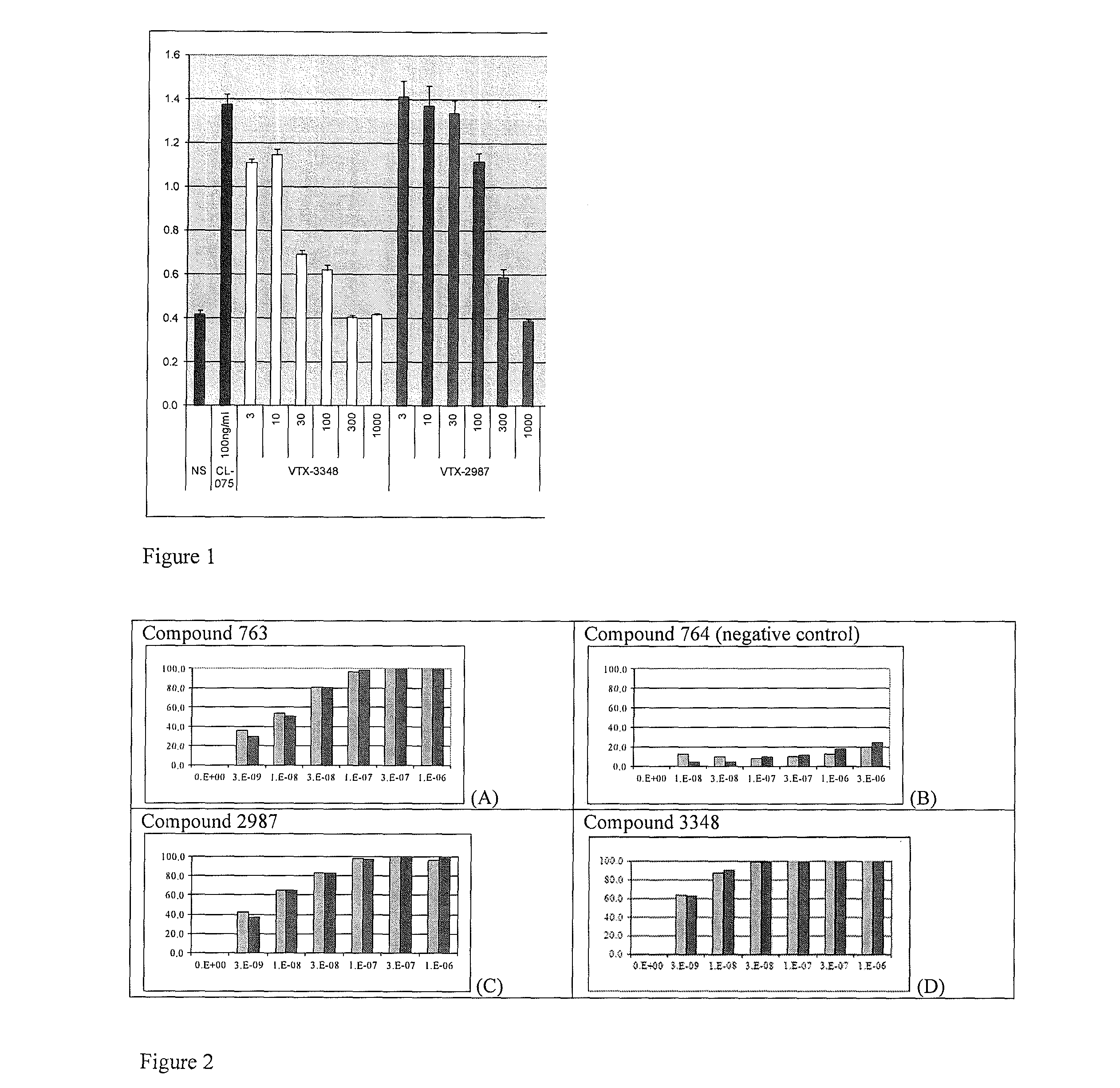
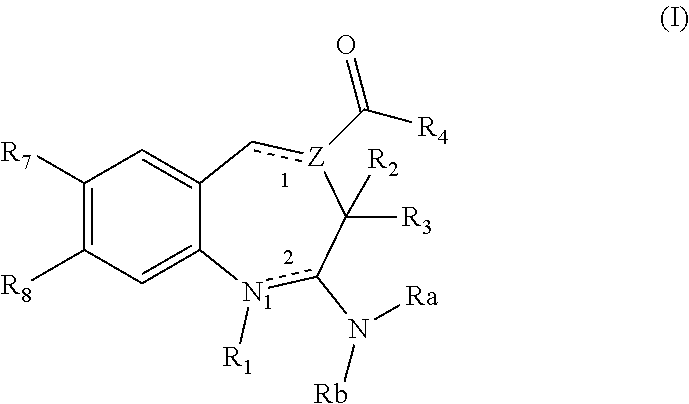
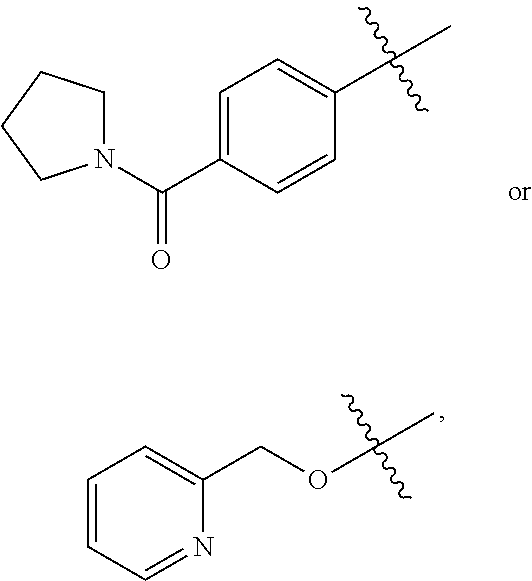
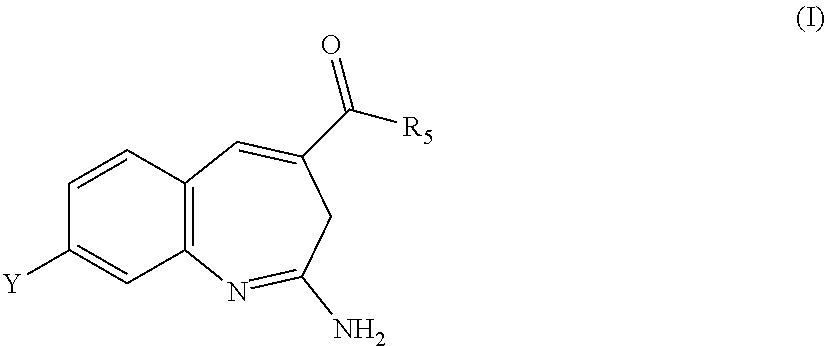
8-Substituted Benzoazepines as Toll-Like Receptor Modulators
Provided are compositions and methods useful for modulation of signaling through the Toll-like receptors TLR7 and / or TLR8. The compositions and methods have use in the treatment of autoimmunity, inflammation allergy, asthma, graft rejection, graft versus host disease, infection, sepsis, cancer and immunodeficiency.
Owner:ARRAY BIOPHARMA
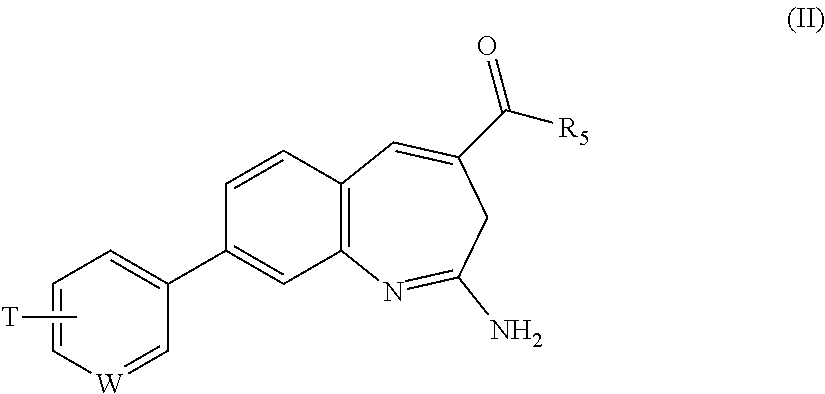
Substituted Benzoazepines As Toll-Like Receptor Modulators
Provided are compositions and methods useful for modulation of signaling through the Toll-like receptors TLR7 and / or TLR8. The compositions and methods have use in treating or preventing disease, including cancer, autoimmune disease, fibrotic disease, cardiovascular disease, infectious disease, inflammatory disorder, graft rejection, or graft-versus-host disease.
Owner:ARRAY BIOPHARMA +1
Small molecule toll-like receptor (TLR) antagonists
The invention provides methods and compositions useful for modulating signaling through Toll-like receptors. The methods involve contacting a TLR-expressing cell with a small molecule having a core structure including at least two rings. Certain of the compounds are 4-primary amino quinolines. Many of the compounds and methods are useful specifically for inhibiting immune stimulation involving at least one of TLR9, TLR8, TLR7, and TLR3. The methods may have use in the treatment of autoimmunity, inflammation, allergy, asthma, graft rejection, graft versus host disease, infection, sepsis, cancer, and immunodeficiency.
Owner:COLEY PHARMA GMBH +1
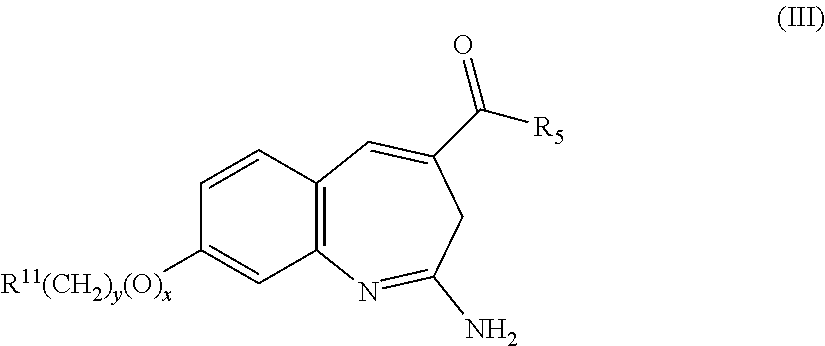
Aminodiazepines as Toll-Like Receptor Modulators
Provided are compositions and methods useful for modulation signaling through the Toll-like receptor TLR8. The compositions and methods have use in the treatment of autoimmunity, inflammation allergy, asthma, graft rejection, graft versus host disease, infection, sepsis, cancer and immunodeficiency.
Owner:ARRAY BIOPHARMA
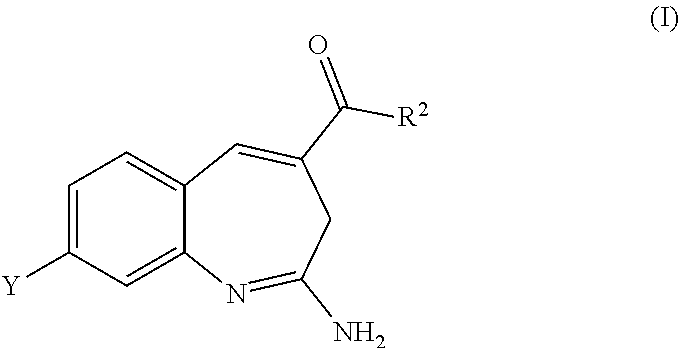
Substituted benzoazepines as toll-like receptor modulators
Provided are compositions and methods useful for modulation of signaling through the Toll-like receptors TLR7 and / or TLR8. The compositions and methods have use in treating or preventing disease, including cancer, autoimmune disease, infectious disease, inflammatory disorder, graft rejection, and graft-verses-host disease.
Owner:ARRAY BIOPHARMA
Substituted benzoazepines as toll-like receptor modulators
ActiveUS20110118235A1Efficient modulationAntibacterial agentsBiocideTLR8Graft versus host disease induction
Provided are compositions and methods useful for modulation of signaling through the Toll-like receptors TLR7 and / or TLR8. The compositions and methods have use in treating or preventing disease, including cancer, autoimmune disease, infectious disease, inflammatory disorder, graft rejection, and graft-verses-host disease.
Owner:ARRAY BIOPHARMA +1
Method of treating transplant rejection
This invention relates to a method of treating transplant rejection comprising administering to a patient a pharmaceutical composition comprising an lck inhibitor and a calcineurin inhibitor or an immunosuppressant.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
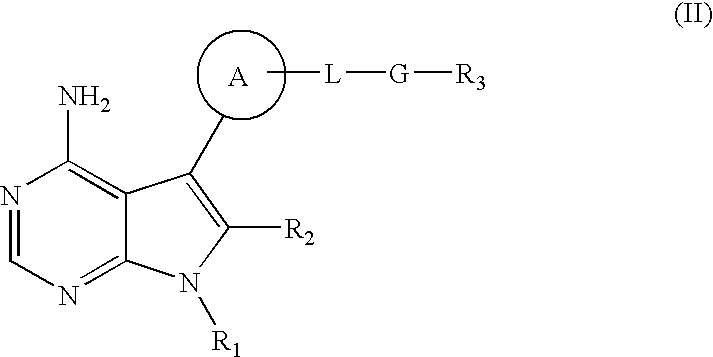
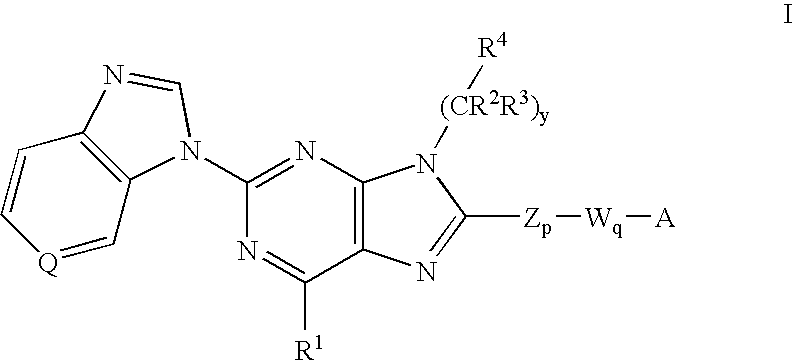
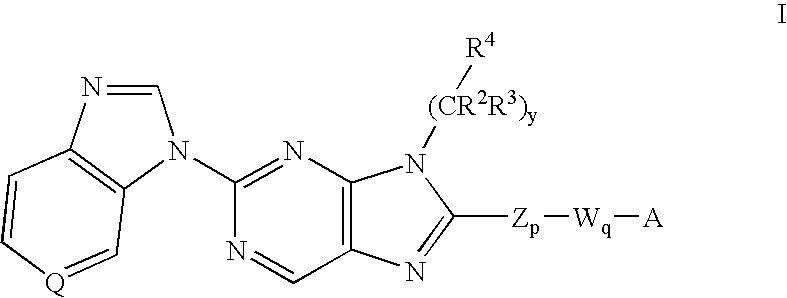
7-Substituted Purine Derivatives for Immunosuppression
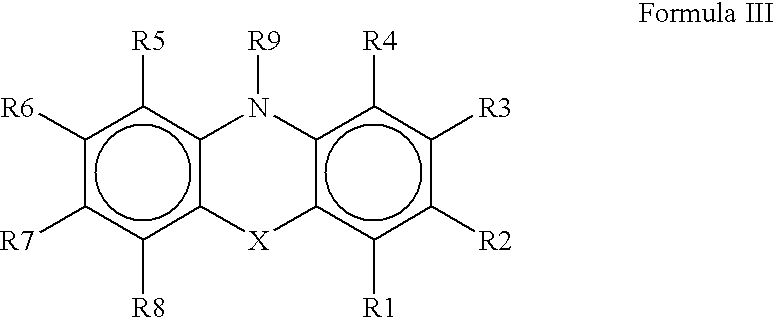
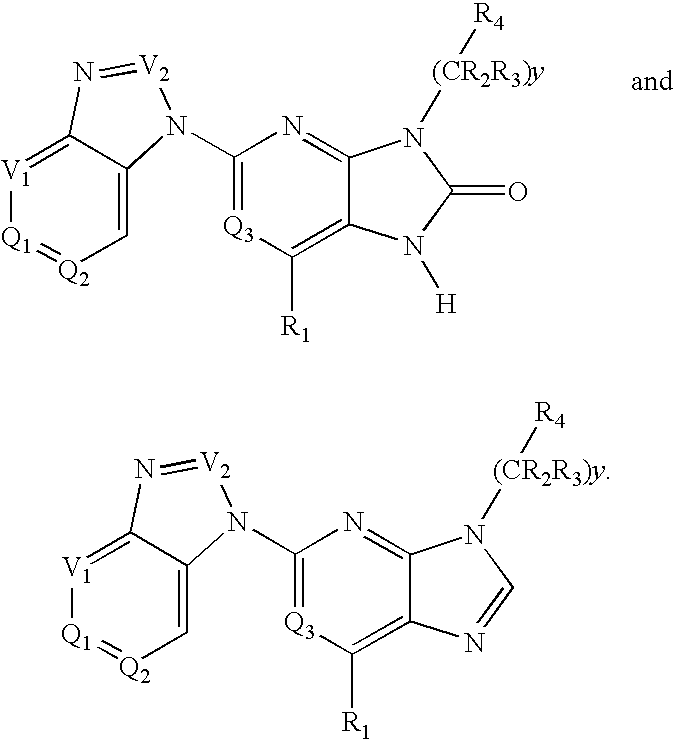
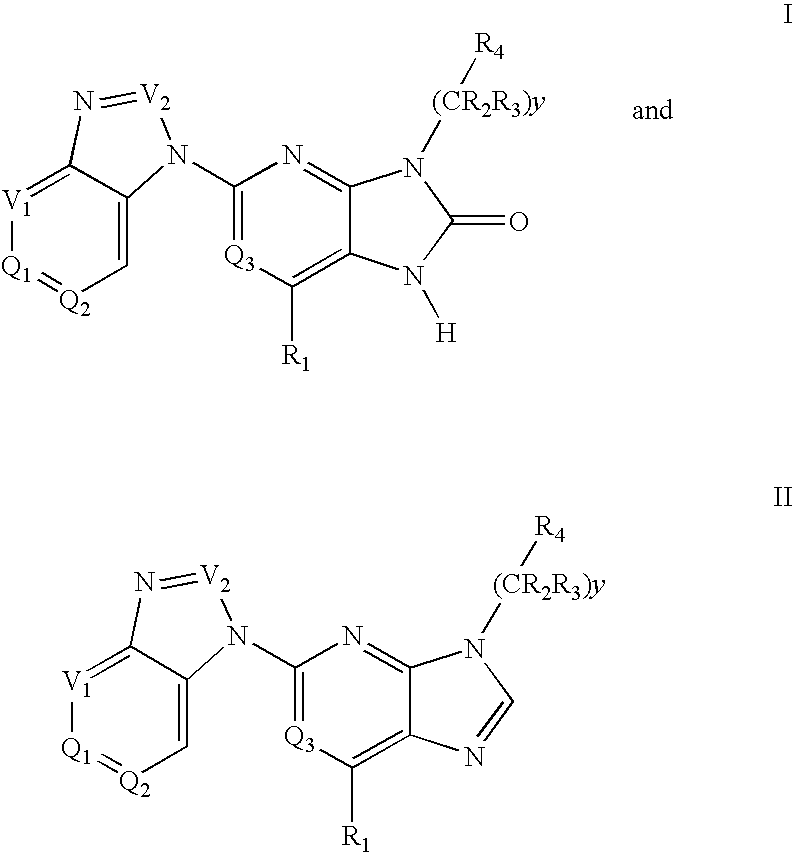
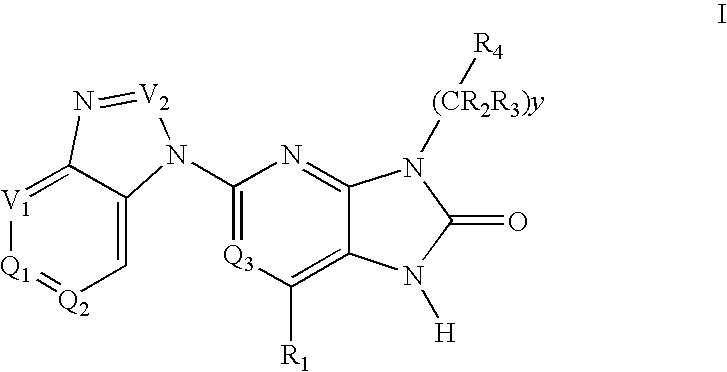
The present invention provides novel purinone and related derivatives useful for the prevention and treatment of autoimmune diseases, inflammatory disease, mast cell mediated disease and transplant rejection. The compounds are of the general formula III:
Owner:WYETH LLC
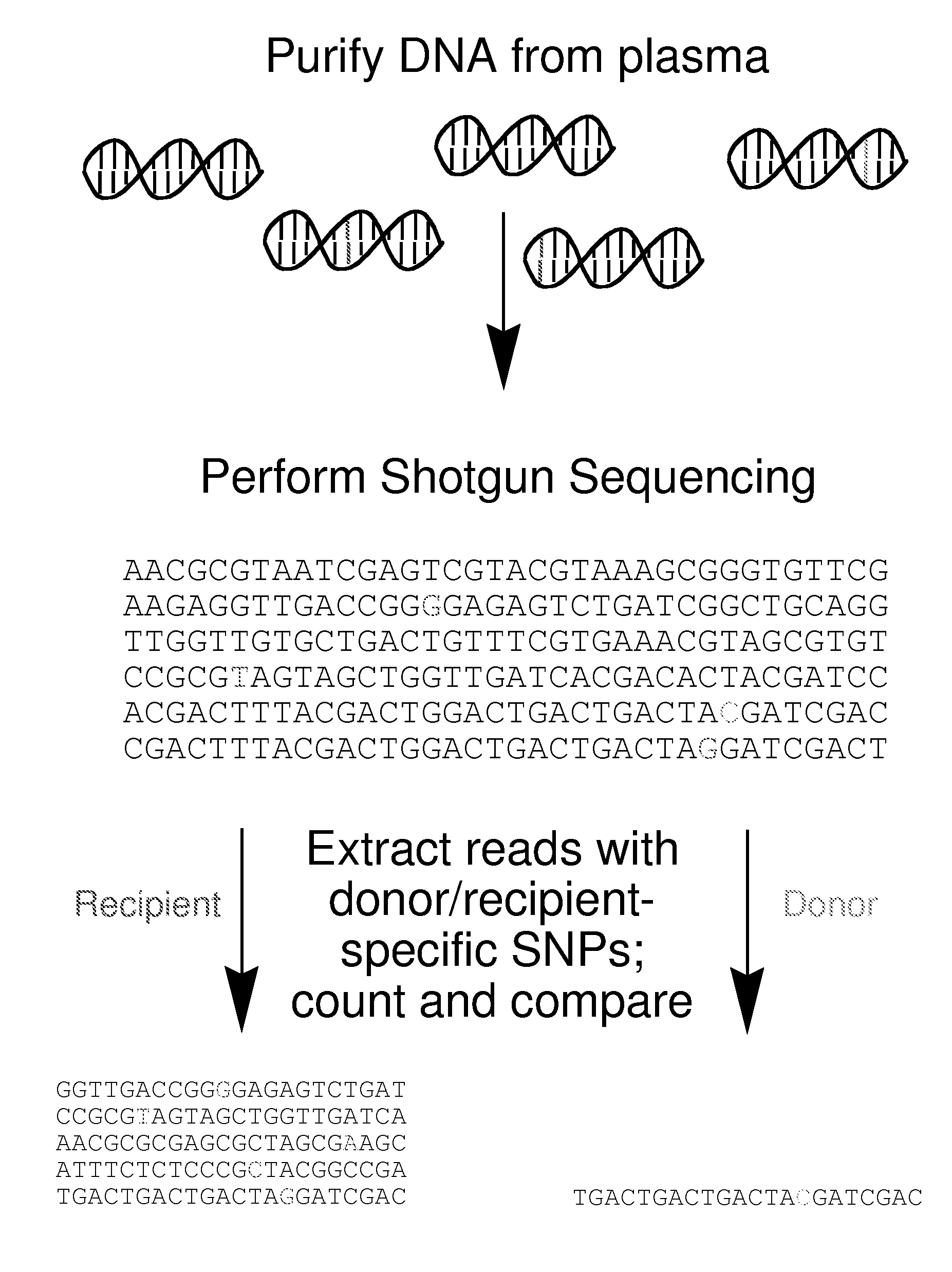
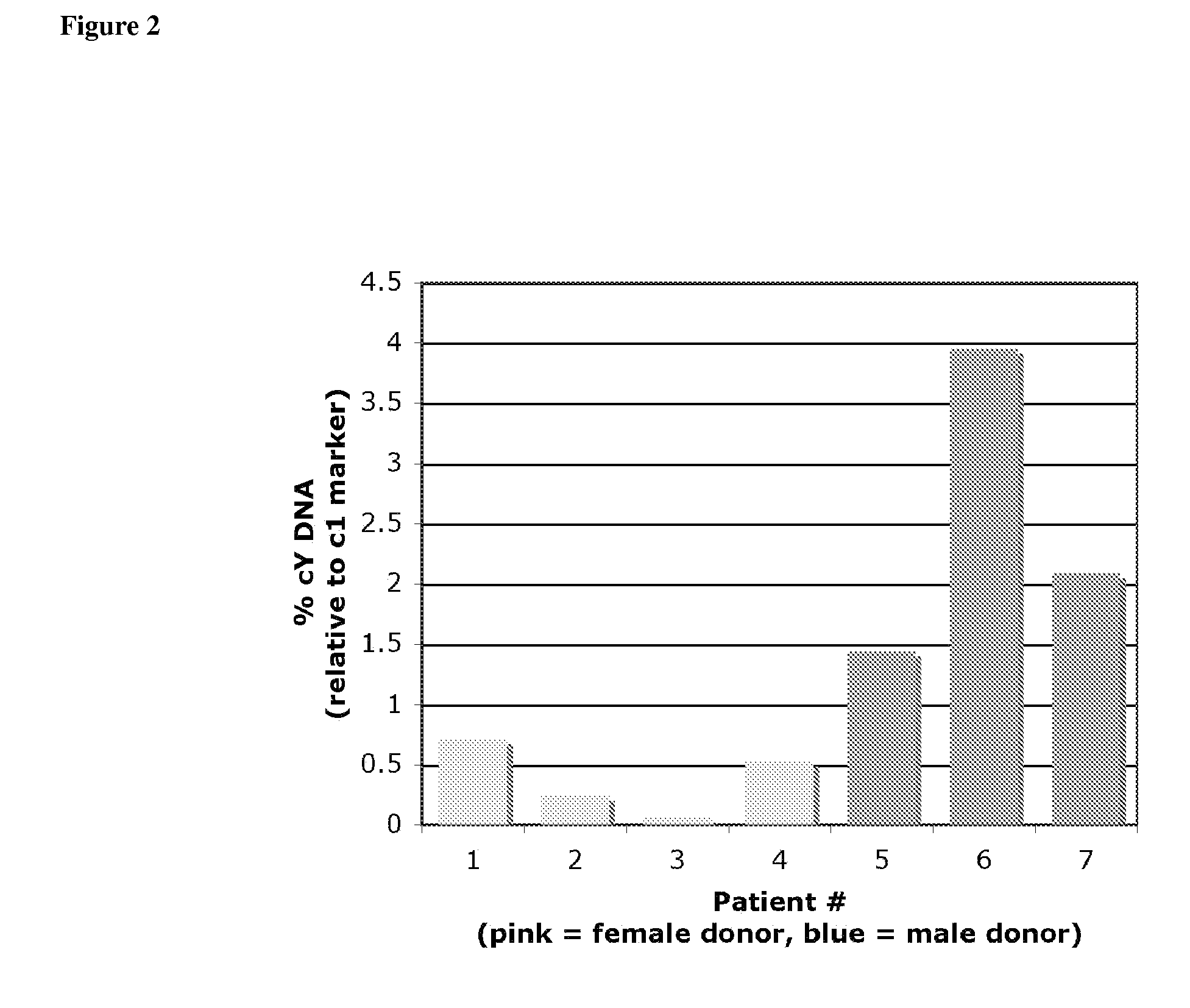
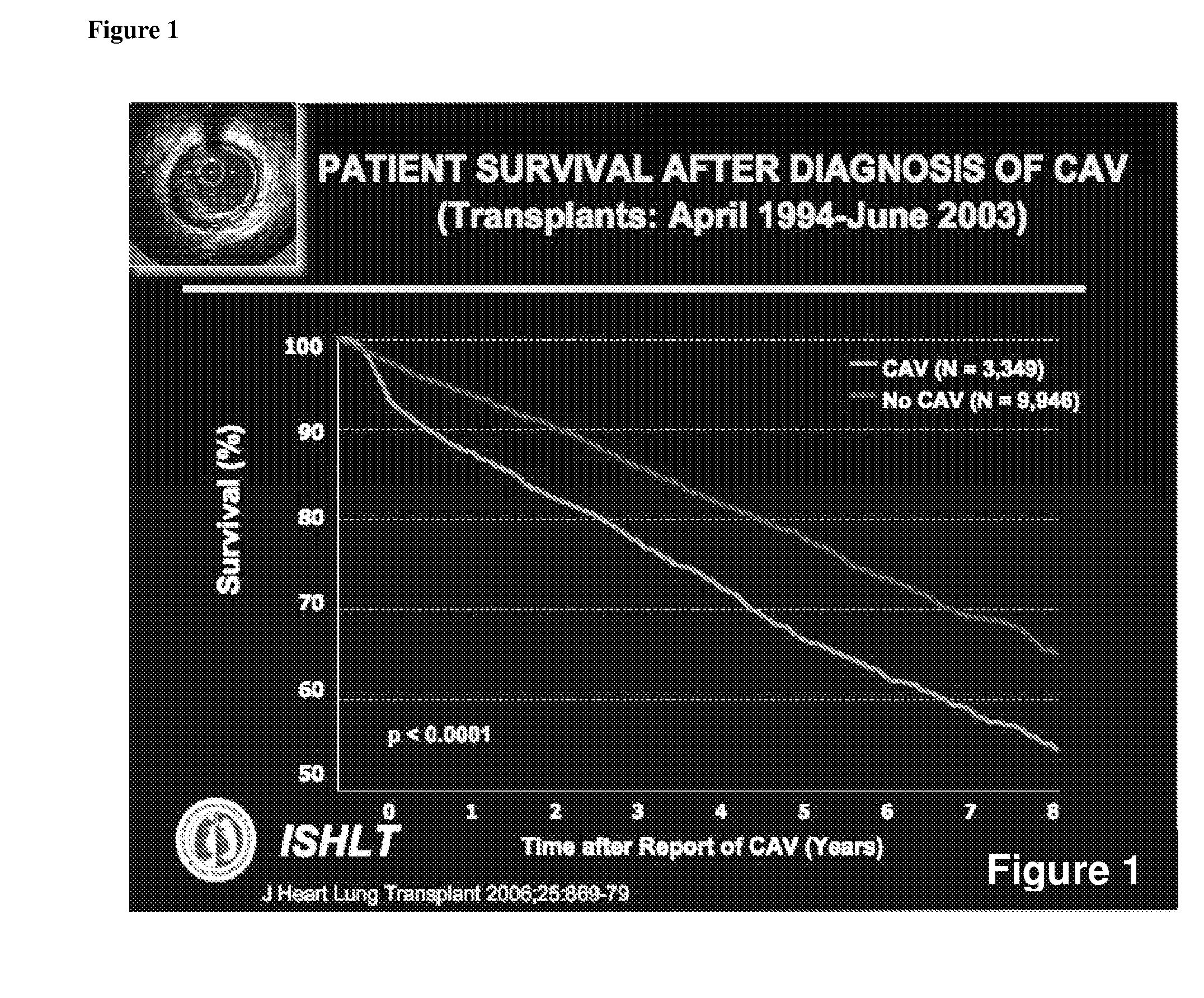
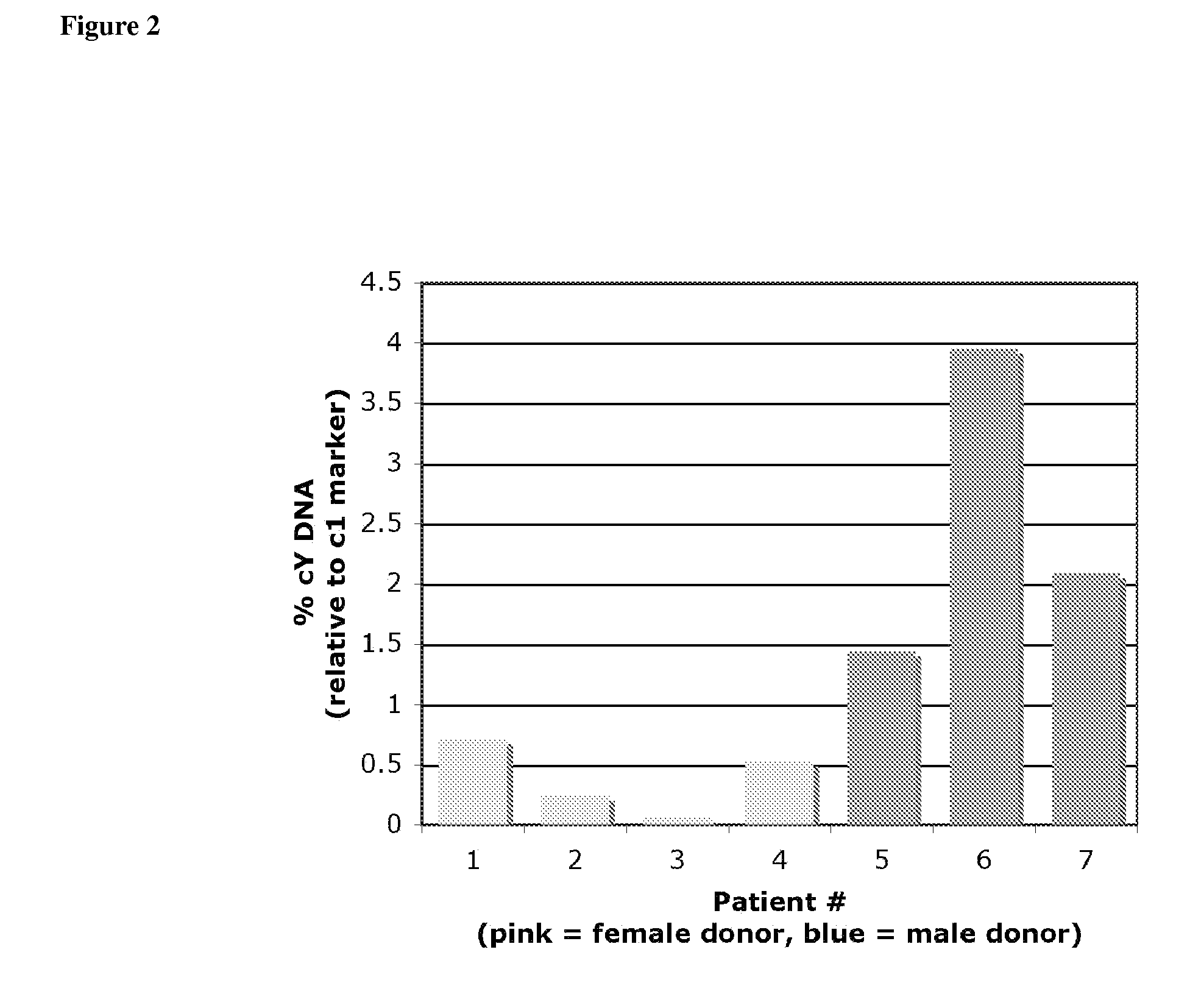
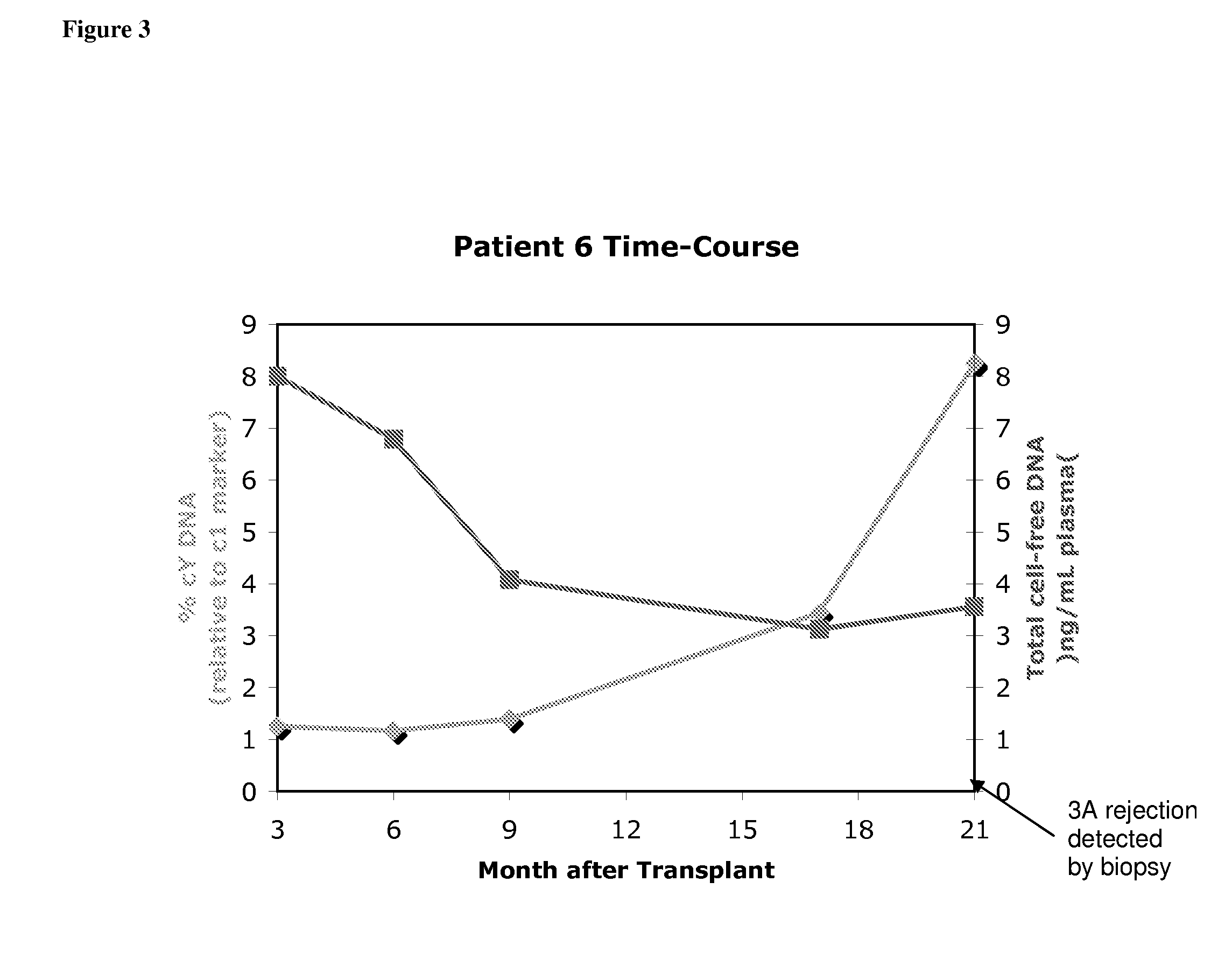
Non-Invasive Diagnosis of Graft Rejection in Organ Transplant Patients
ActiveUS20120295810A1Mechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesMicrobiological testing/measurementTransplant rejectionNon invasive
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
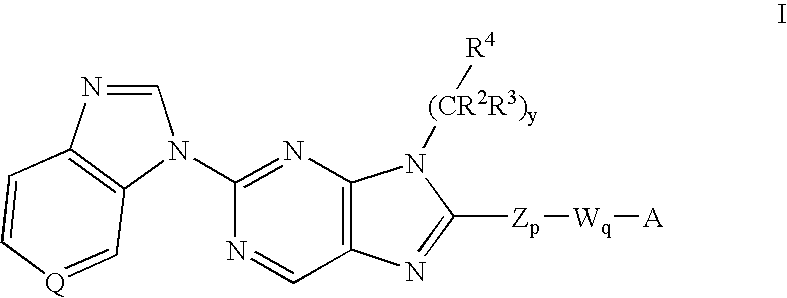
8-substituted 2-(benzimidazolyl)purine derivatives for immunosuppression
The present invention provides novel purines useful for the prevention and treatment of autoimmune diseases, inflammatory disease, mast cell mediated disease and transplant rejection. The compounds are of the general formula I:
Owner:WYETH LLC
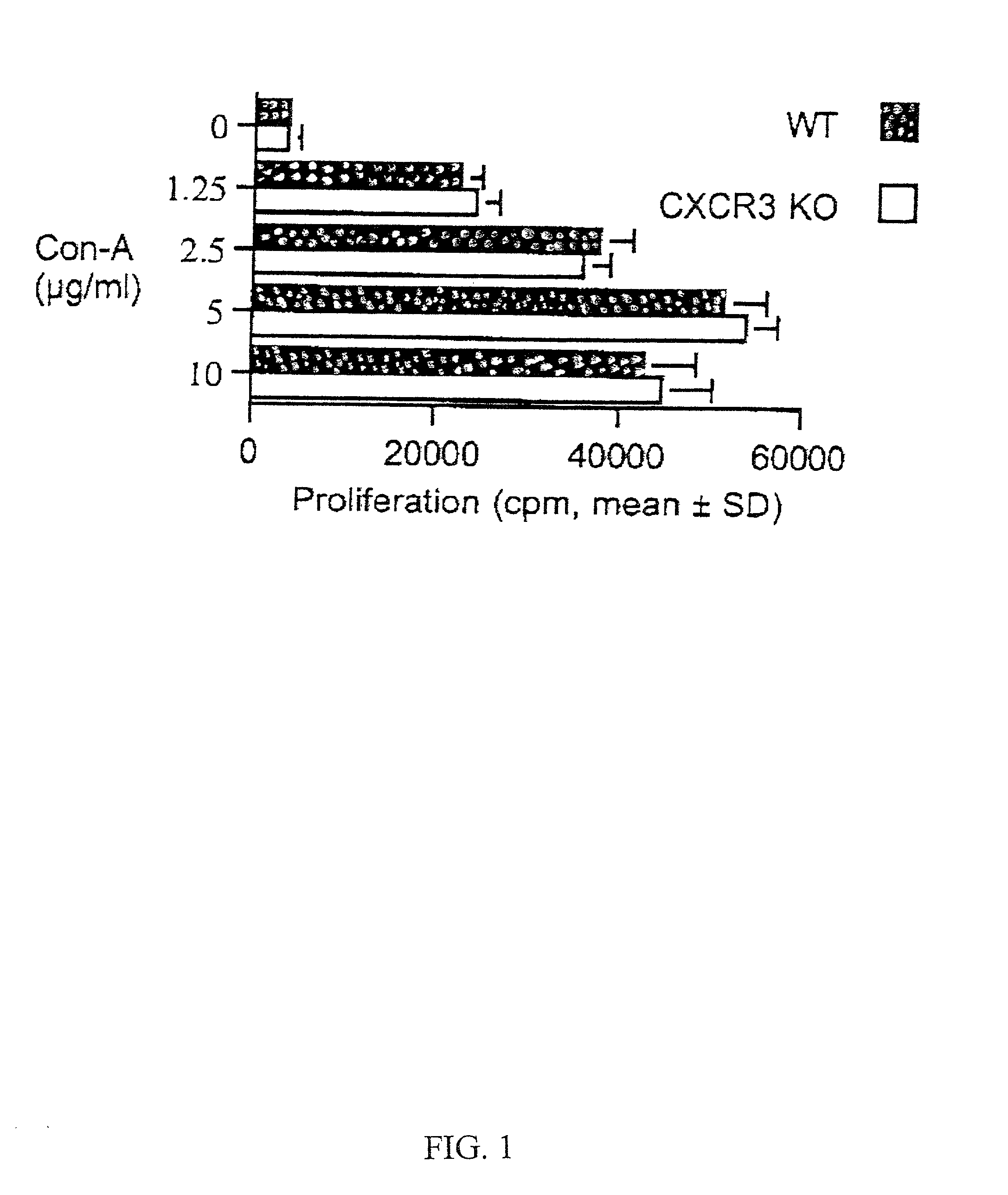
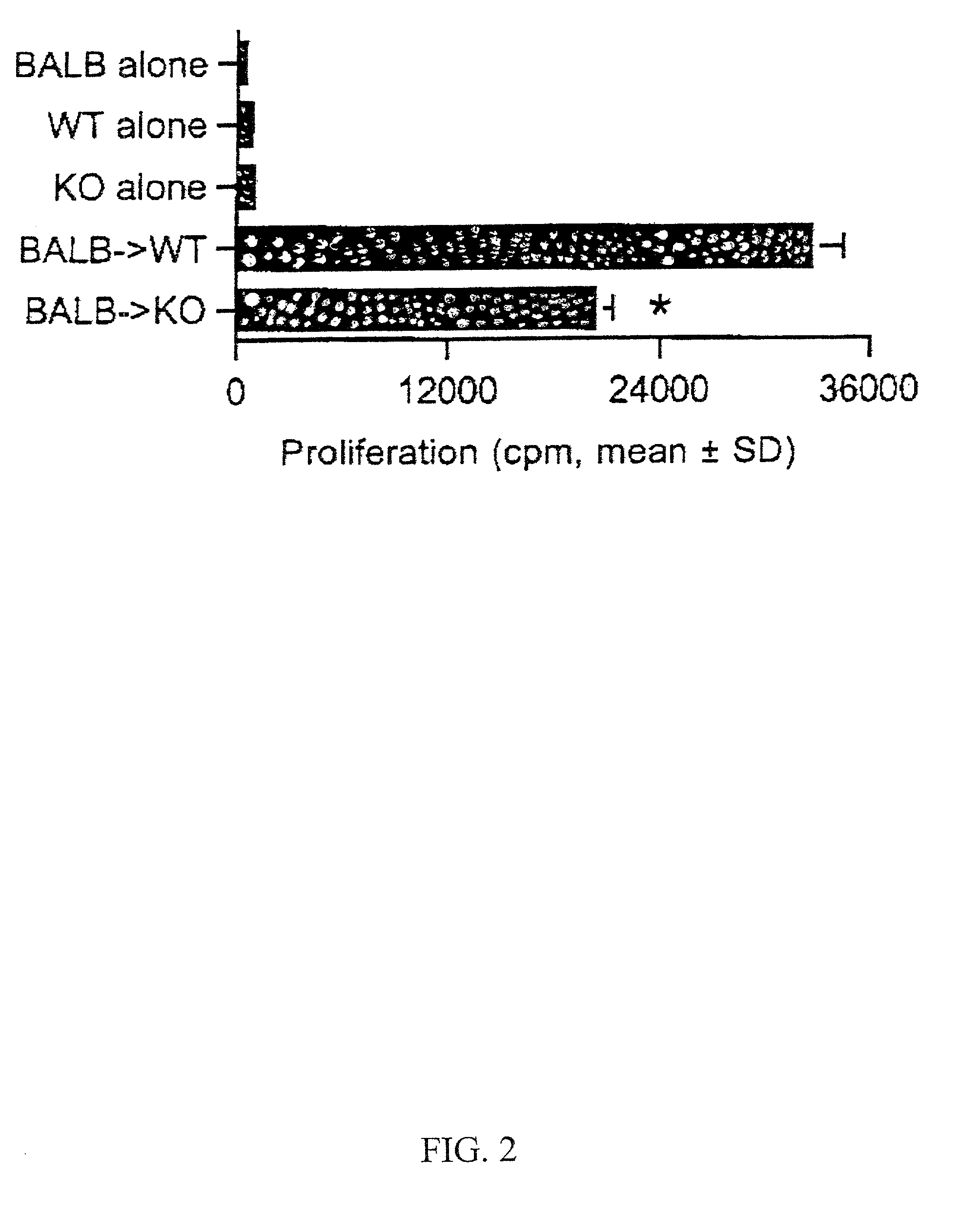
Method of treating graft rejection using inhibitors of CXCR3 function
InactiveUS20020018776A1Improve survivabilityPrevent graft rejectionBiocideBiological material analysisCo administrationSurgery
A method for inhibiting the rejection of transplanted grafts is disclosed. The method comprising administering an effective amount of an antagonist of CXCR3 function to a graft recipient. The disclosed methods can also comprise the co-administration of one or more additional therapeutic agents, for example, immunosuppressive agents.
Owner:MILLENNIUM PHARMA INC
Small molecule toll-like receptor (TLR) antagonists
The invention provides methods and compositions useful for modulating signaling through Toll-like receptors. The methods involve contacting a TLR-expressing cell with a small molecule having a core structure including at least two rings. Certain of the compounds are 4-primary amino quinolines. Many of the compounds and methods are useful specifically for inhibiting immune stimulation involving at least one of TLR9, TLR8, TLR7, and TLR3. The methods may have use in the treatment of autoimmunity, inflammation, allergy, asthma, graft rejection, graft versus host disease, infection, sepsis, cancer, and immunodeficiency.
Owner:COLEY PHARMA GMBH +1
Non-invasive diagnosis of graft rejection in organ transplant patients
ActiveUS8703652B2Mechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesMicrobiological testing/measurementNon invasiveOrgan transplanting
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
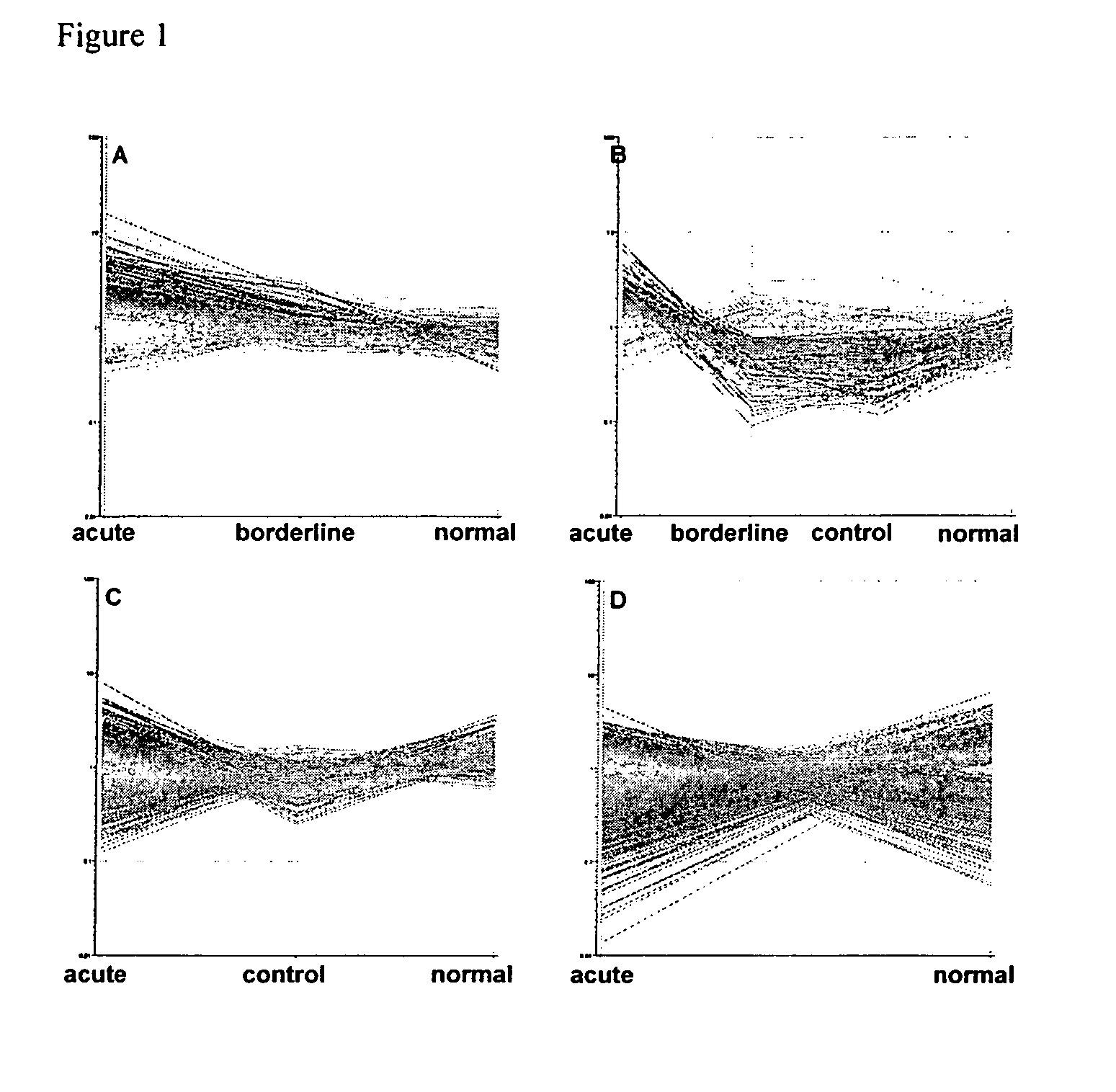
Methods and compositions for assessing acute rejection
InactiveUS20090022730A1Accurate detectionMinimize and personalize immunosuppressionMicrobiological testing/measurementAntibody ingredientsTransplant rejectionGene
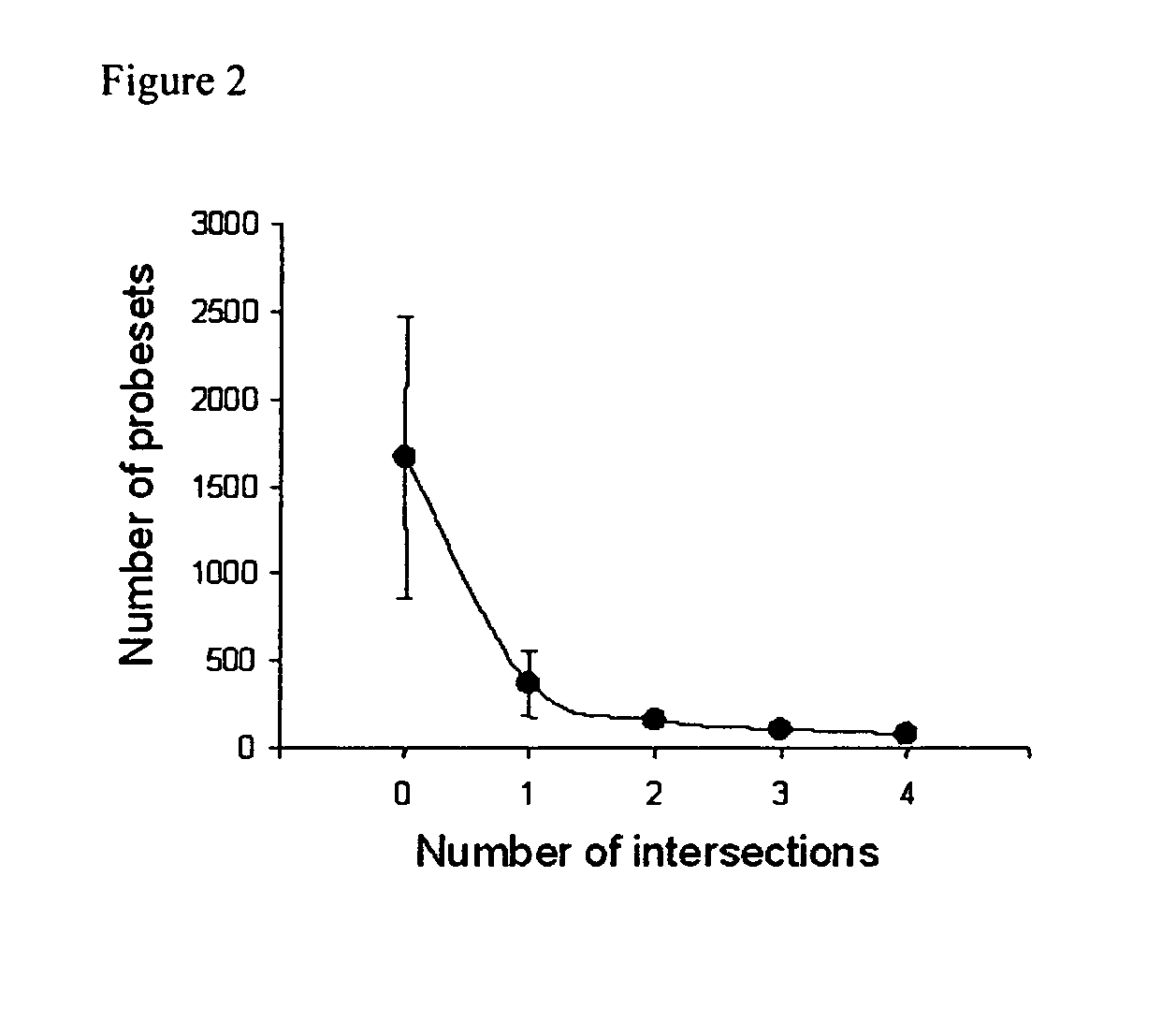
The invention relates to the analysis and identification of genes that are up-regulated simultaneously in transplant rejection. This simultaneous up-regulation of genes provides a molecular signature to accurately detect transplant rejection.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG +1
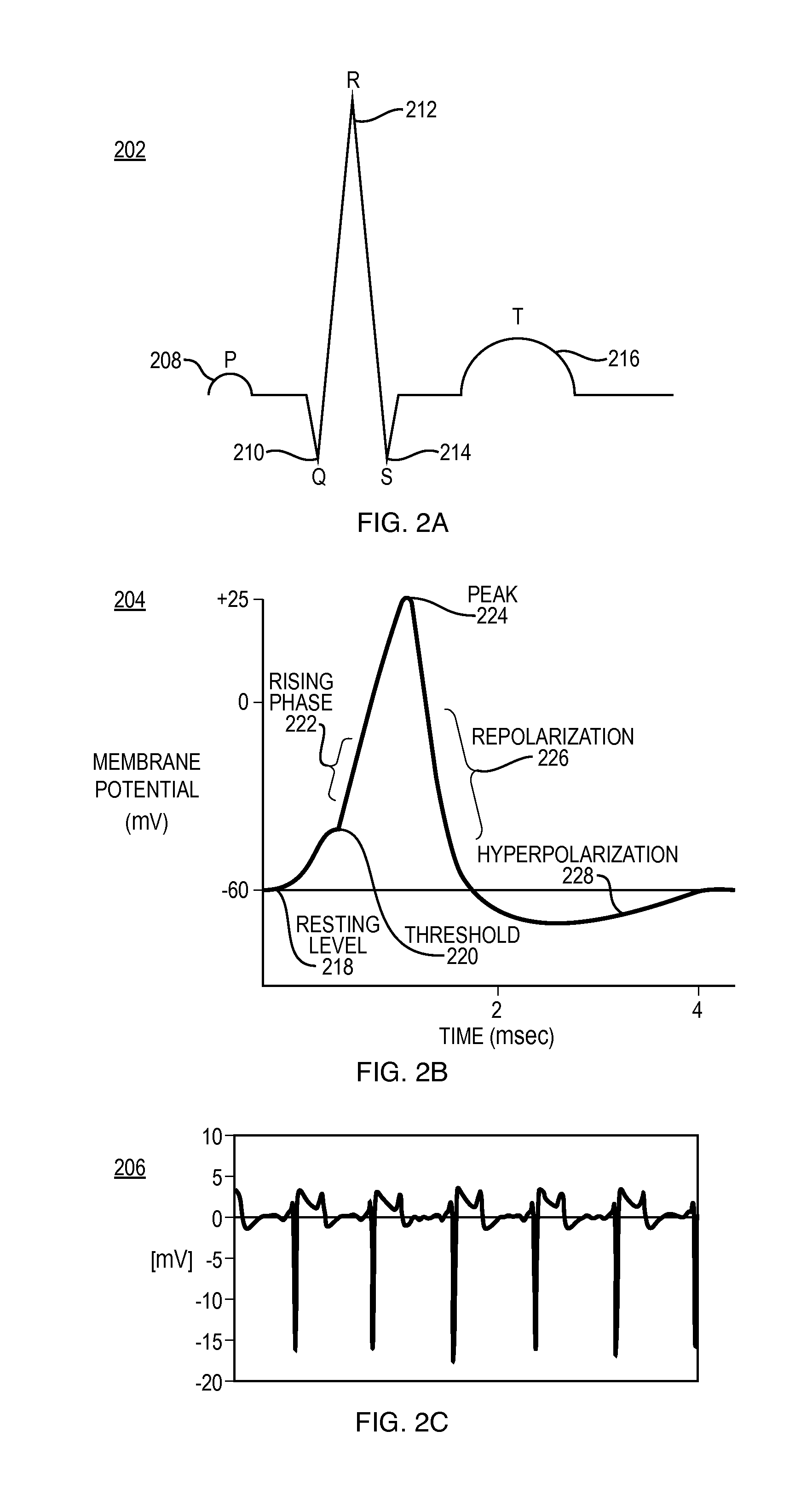
Systems and Methods for Heart and Activity Monitoring
InactiveUS20120165684A1ElectrocardiographyLocal control/monitoringTransplant rejectionCardiac muscle
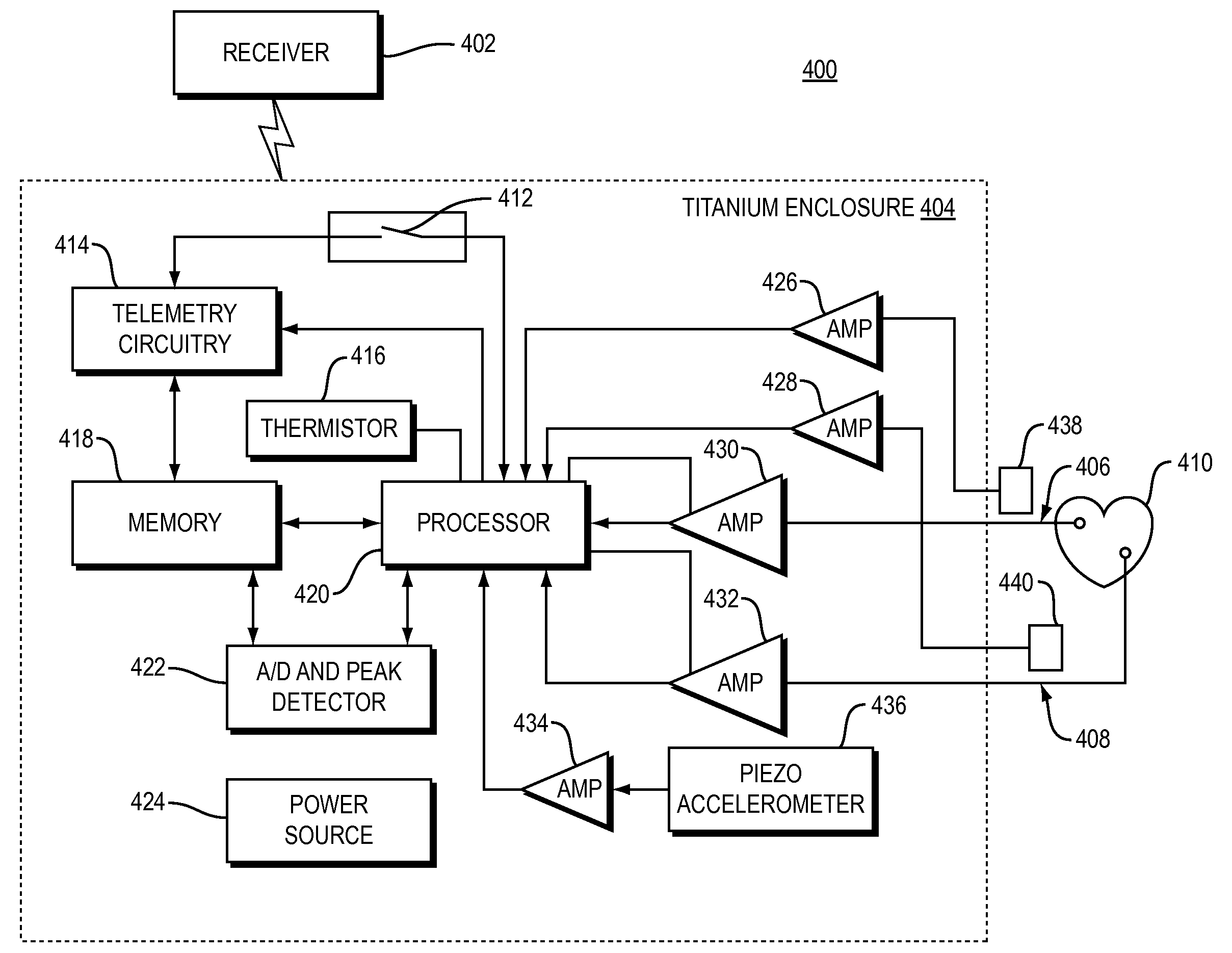
Methods and systems for monitoring a heart failure or transplant rejection status of a patient including use of a device or system to collect intramyocardial electrogram (IMEG) signals from the patient at different times automatically when a detected activity level of the patient is below a preset threshold level for a predetermined amount of time, and use of a device or system to generate a status indicator value proportional to a combination of parameters extracted from at least a portion of the collected IMEG signals. Methods and systems can also include measuring time delay values between IMEG signals collected from different locations in the patient. The IMEG signals can be collected from the right ventricular septum and the right ventricular apex of the patient or from the right and left ventricular myocardium of the patient.
Owner:QRS HEART
Use of glutaminyl cyclase inhibitors
ActiveUS20090068699A1BiocideOrganic active ingredientsMild cognitive impairment (MCI)Percent Diameter Stenosis
An inhibitor of a glutaminyl peptide cyclotransferase, and use thereof for the treatment and / or prevention of a disease or disorder selected from the group consisting of inflammatory diseases selected froma. neurodegenerative diseases, e.g. mild cognitive impairment (MCI), Alzheimer's disease, neurodegeneration in Down Syndrome, Familial British Dementia, Familial Danish Dementia, multiple sclerosis,b. chronic and acute inflammations, e.g. rheumatoid arthritis, atherosclerosis, restenosis, pancreatitis,c. fibrosis, e.g. lung fibrosis, liver fibrosis, renal fibrosis,d. cancer, e.g. cancer / hemangioendothelioma proliferation, gastric carcinomas,e. metabolic diseases, e.g. hypertension,f. and other inflammatory diseases, e.g. neuropathic pain, graft rejection / graft failure / graft vasculopathy, HIV infections / AIDS, gestosis, tuberous sclerosis.Additionally disclosed are a respective diagnostic method, assay and kit.
Owner:VIVORYON THERAPEUTICS NV
Quinoline derivatives as pi3 kinase inhibitors
Invented is a method of inhibiting the activity / function of PI3 kinases using quinoline derivatives. Also invented is a method of treating one or more disease states selected from: autoimmune disorders, inflammatory diseases, cardiovascular diseases, neurodegenerative diseases, allergy, asthma, pancreatitis, multiorgan failure, kidney diseases, platelet aggregation, cancer, sperm motility, transplantation rejection, graft rejection and lung injuries by the administration of quinoline derivatives.
Owner:GLAXO SMITHKLINE LLC
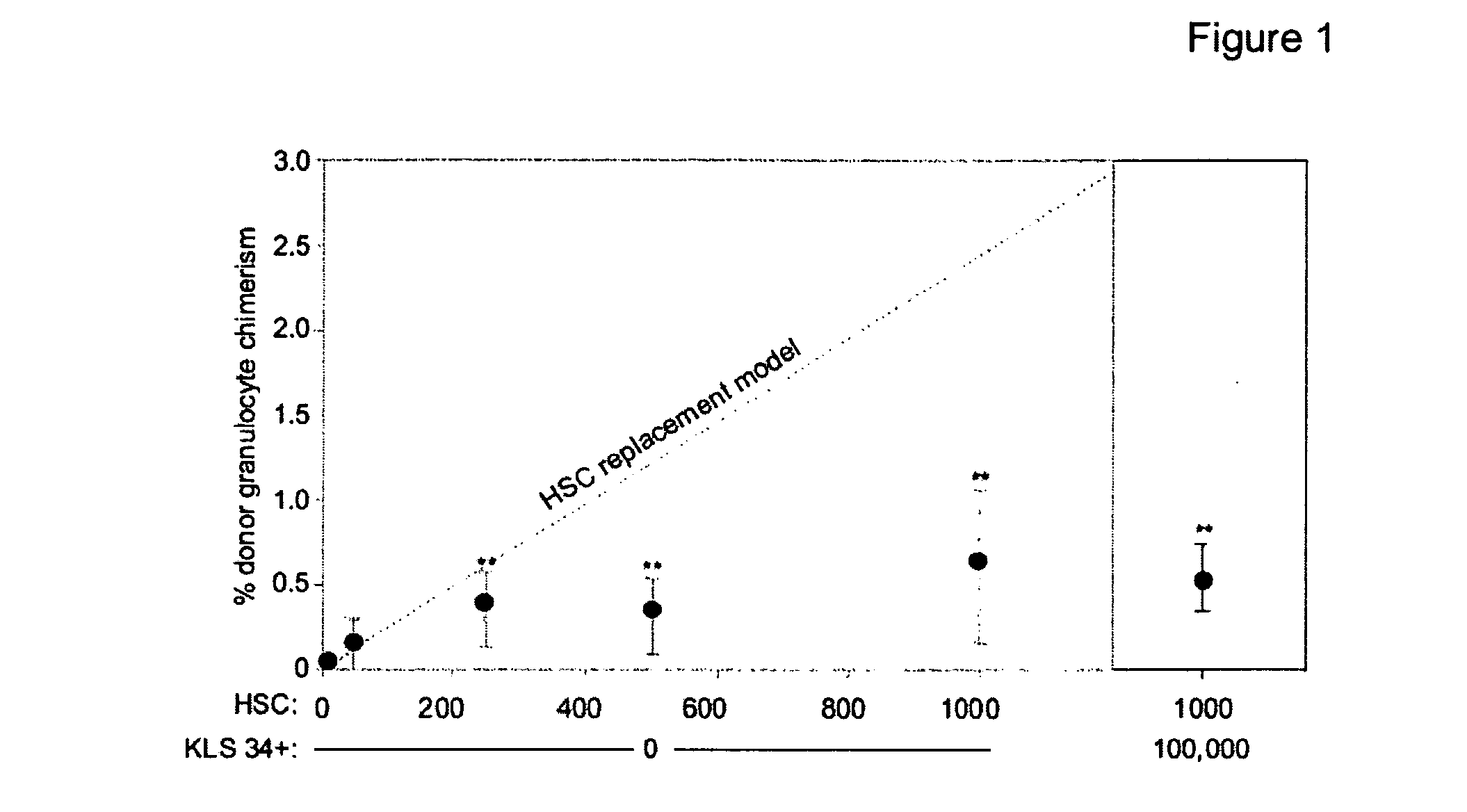
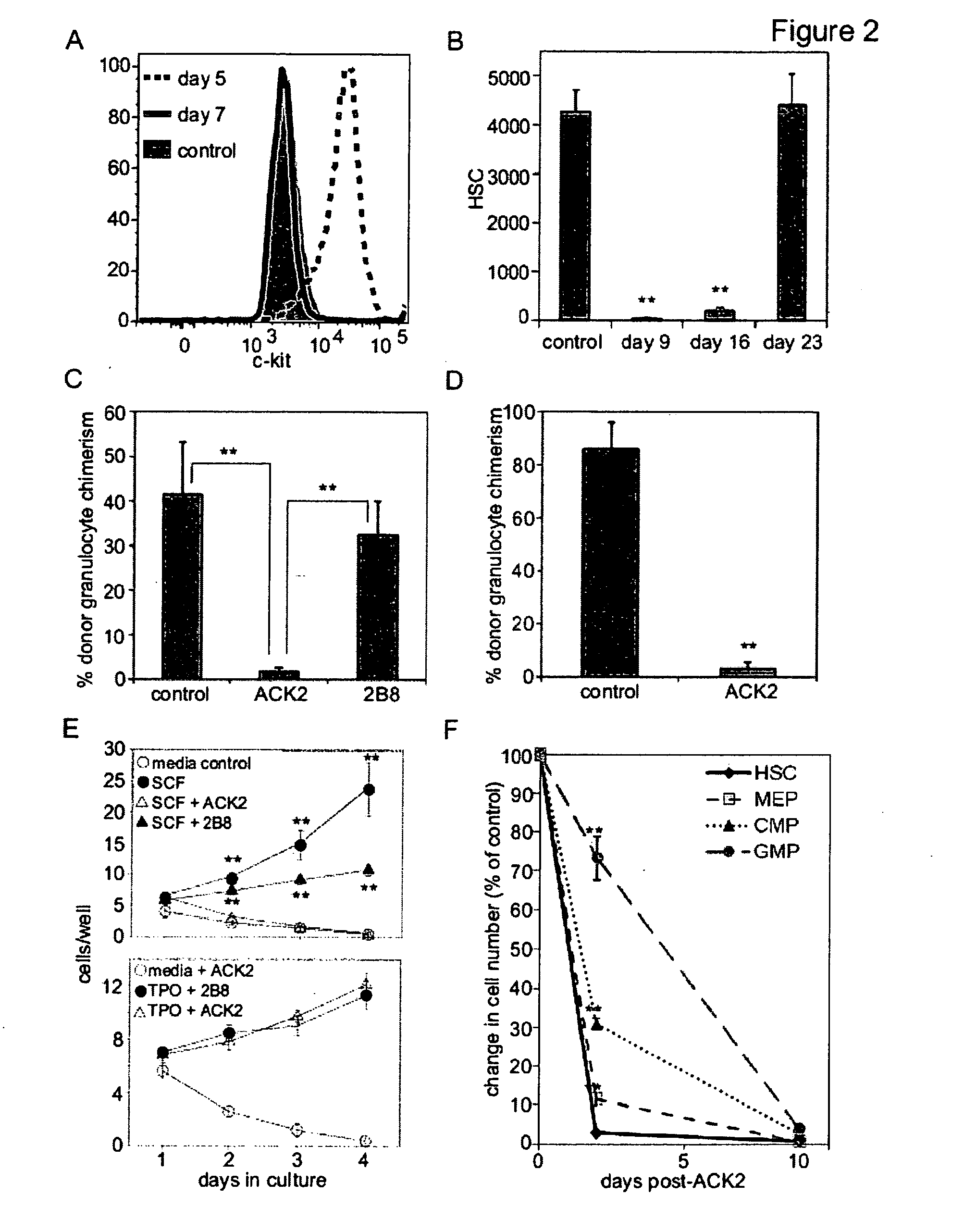
Selective immunodepletion of endogenous stem cell niche for engraftment
InactiveUS20100226927A1Maintain positionFunction increaseBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsImmunocompetenceRadiation therapy
The present invention provides a clinically applicable method of stem cell transplantation that facilitates engraftment and reconstitutes immunocompetence of the recipient without requiring radiotherapy or chemotherapy, and without development of GVHD or graft rejection. Aspects of the present invention are based on the discovery that the depletion of the endogenous stem cell niche facilitates efficient engraftment of stem cells into that niche. In particular, the present invention combines the use of selective ablation of endogenous stem cells, in combination with the administration to the recipient of exogenous stem cells, resulting in efficient, long-term engraftment and tolerance.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
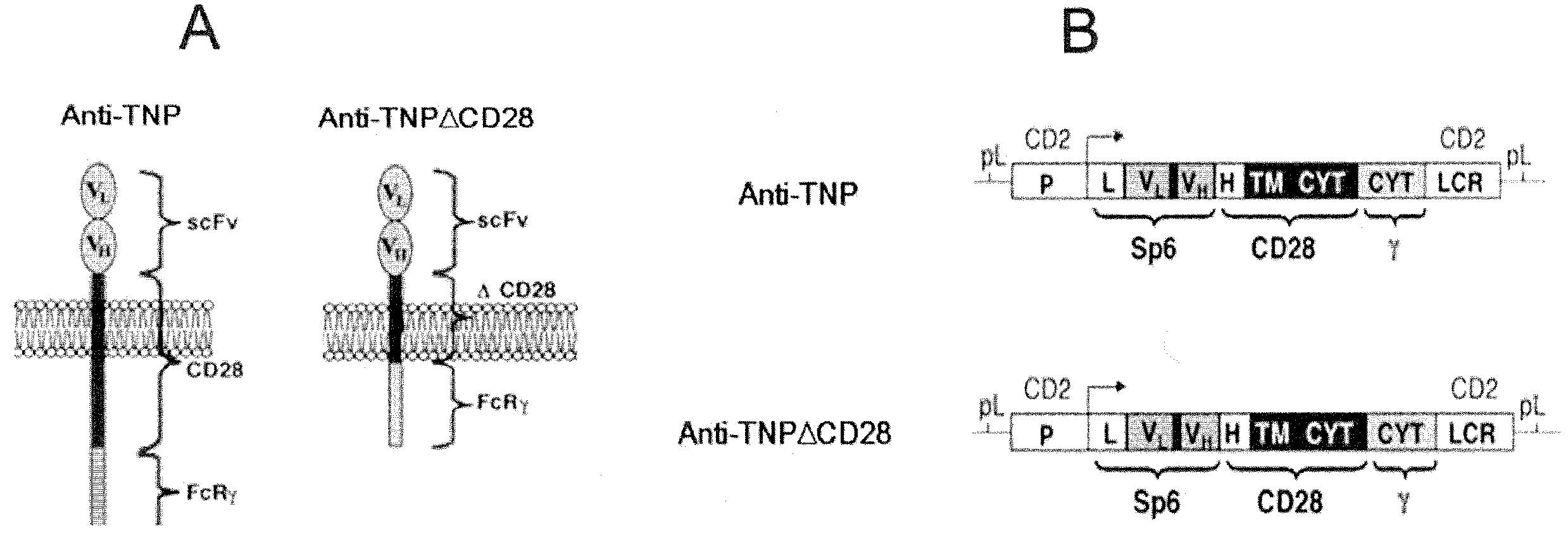
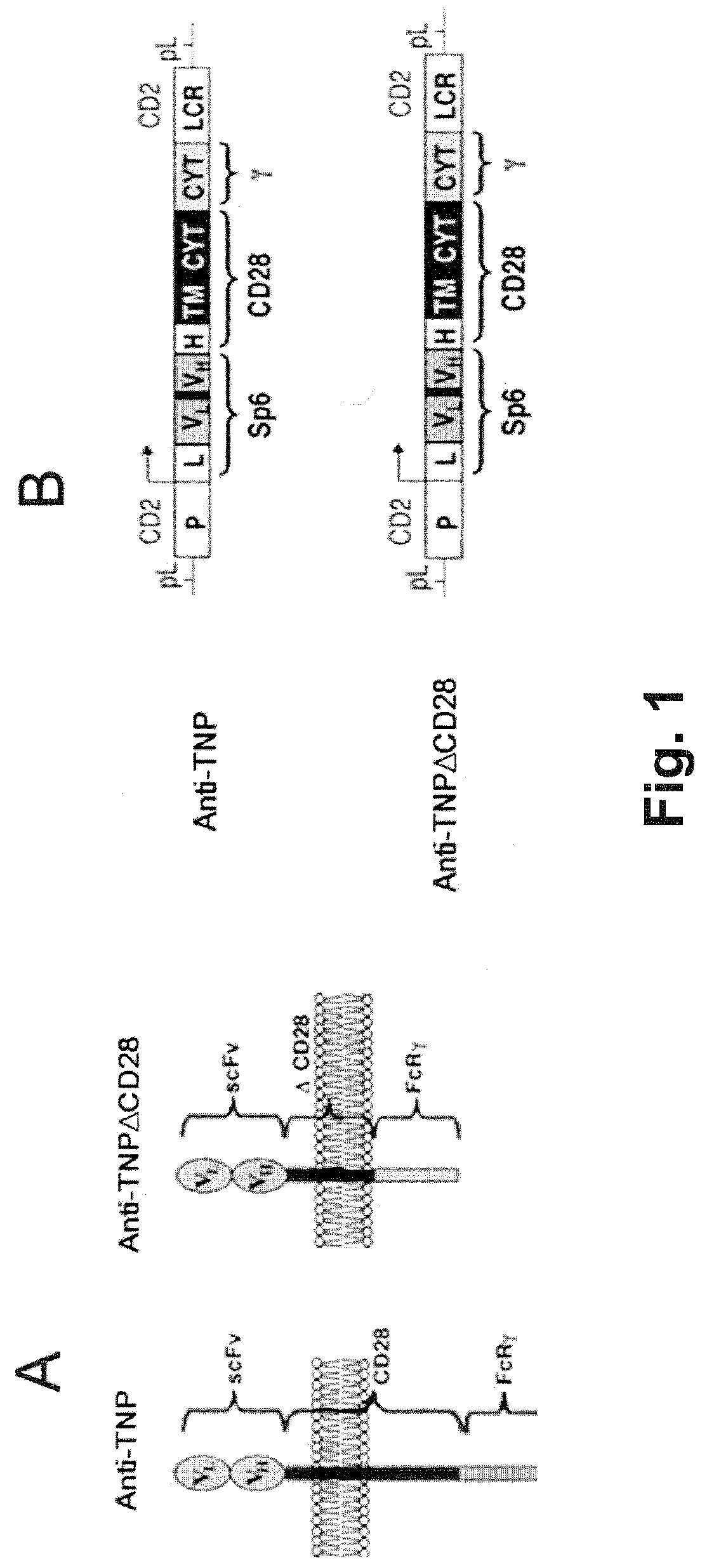
Redirected, genetically-engineered t regulatory cells and their use in suppression of autoimmune and inflammatory disease
InactiveUS20100135974A1Effective quantityOvercome scarcityBiocideAntipyreticIntracellular signallingInflammatory Bowel Diseases
A redirected Treg cell is endowed with specificity toward a selected target antigen or ligand. The cell contains a chimeric receptor polypeptide that is expressed in a single, continuous chain, with an extracellular recognition region displayed on the surface of the cell, a transmembrane region and an intracellular signaling region. The extracellular recognition region is specific for the selected target antigen or ligand. The intracellular signaling region includes a combination of T-cell signaling polypeptide moieties, which combination, upon binding of the extracellular recognition region to the selected target antigen or ligand, triggers activation of the redirected Treg cells to cause suppression of T-cell mediated immunity. Such redirected Treg cells may be used to suppress undesired activity of T effector cells thereby mediating an immune or inflammatory response. They are particularly useful in treating T effector cell-mediated diseases, such as inflammatory bowel disease, transplant rejection and GVH disease.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Compositions and methods of use for alpha-1 antitrypsin having no significant serine protease inhibitor activity
InactiveUS20090203580A1Reduce riskReduce symptom associated with diabetesMetabolism disorderSaccharide peptide ingredientsDiabetes mellitusMedical disorder
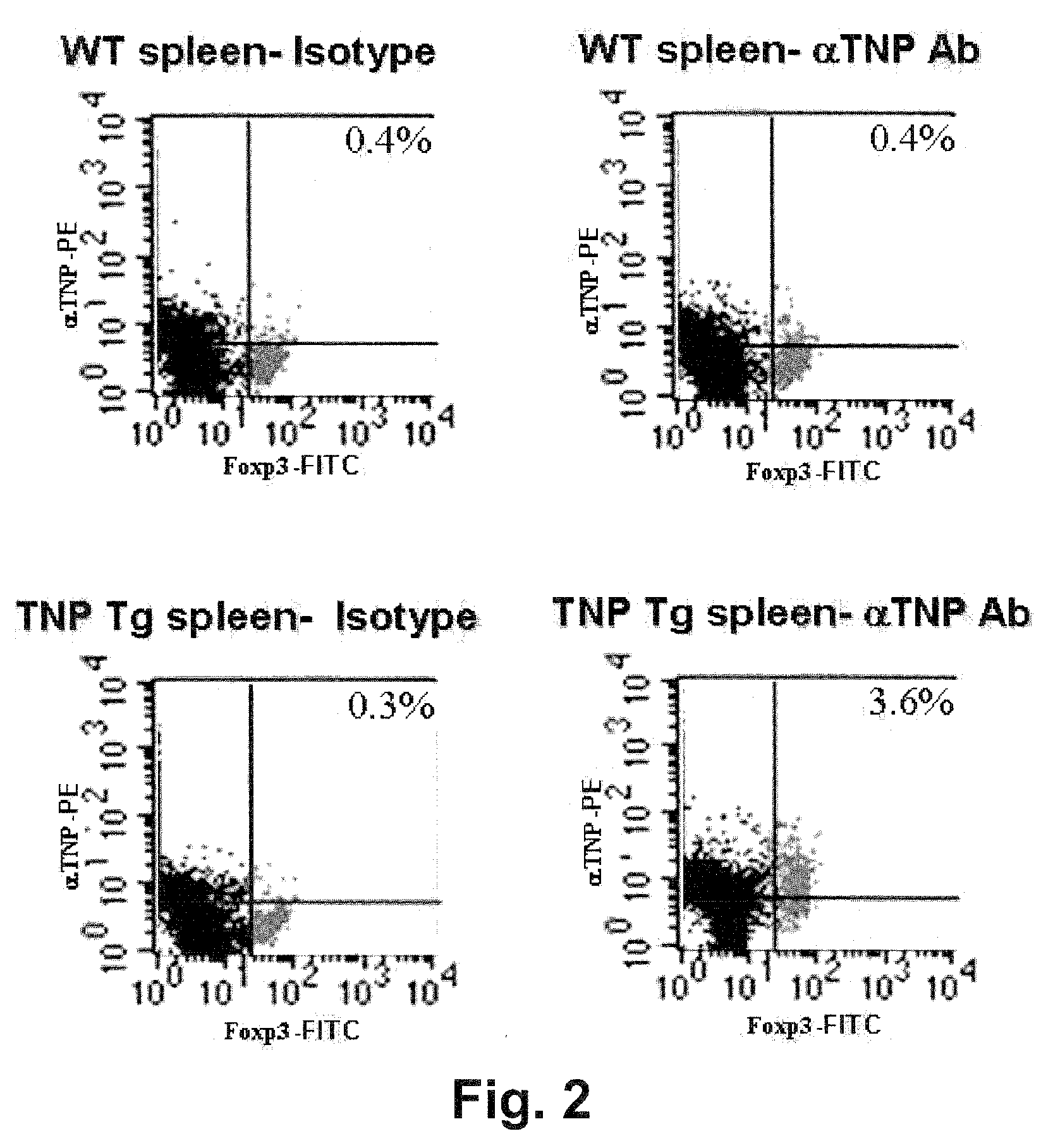
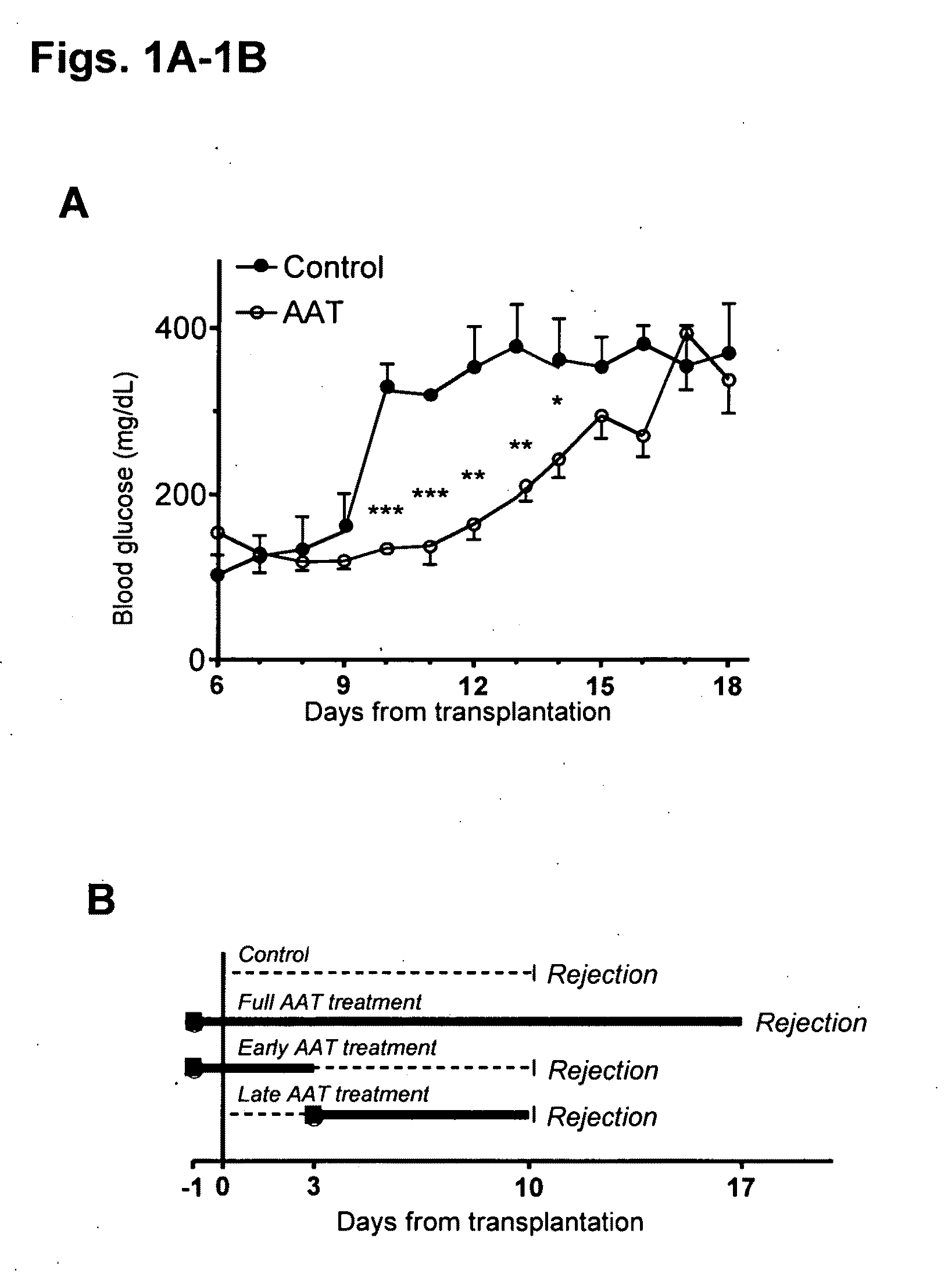
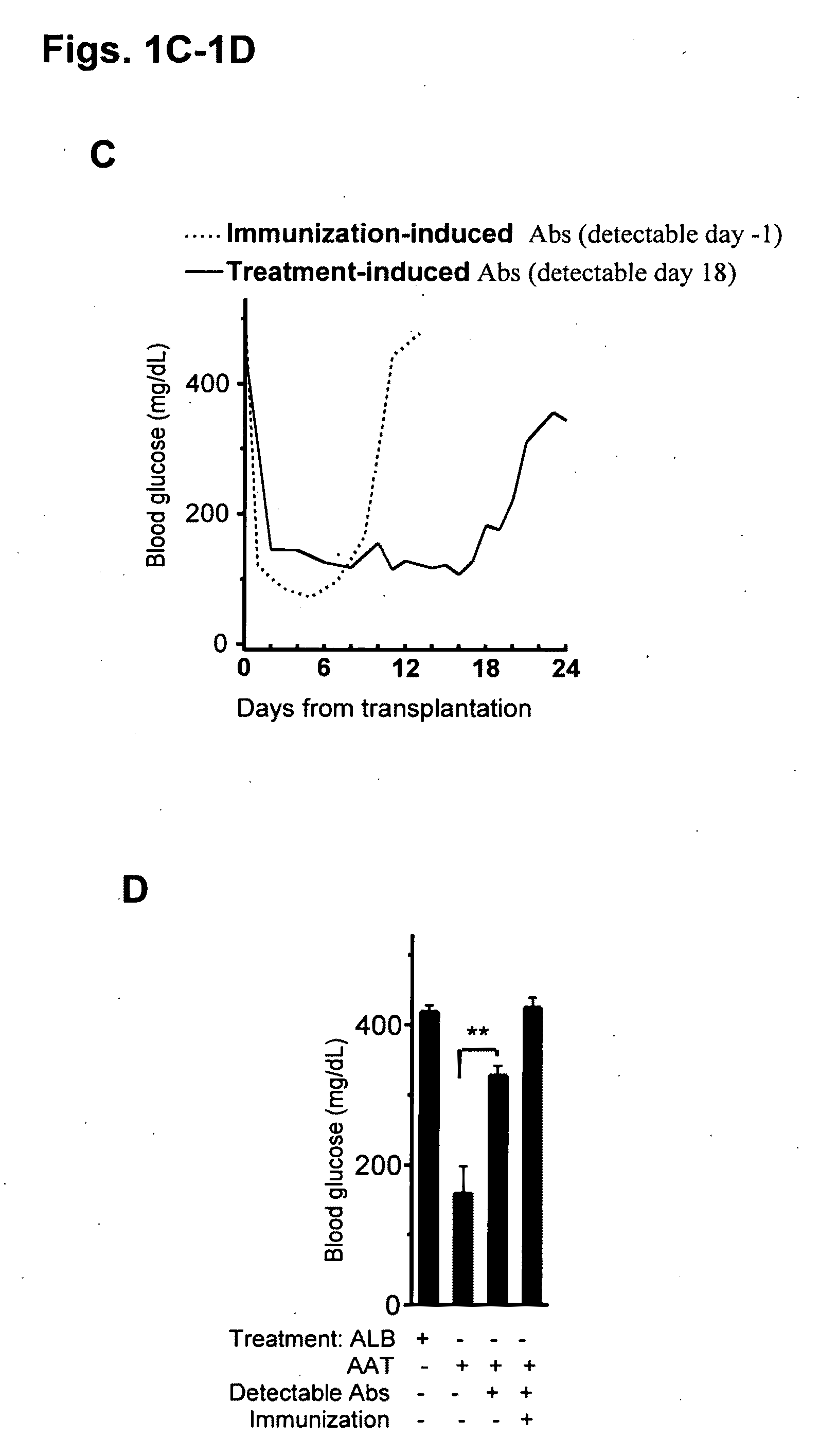
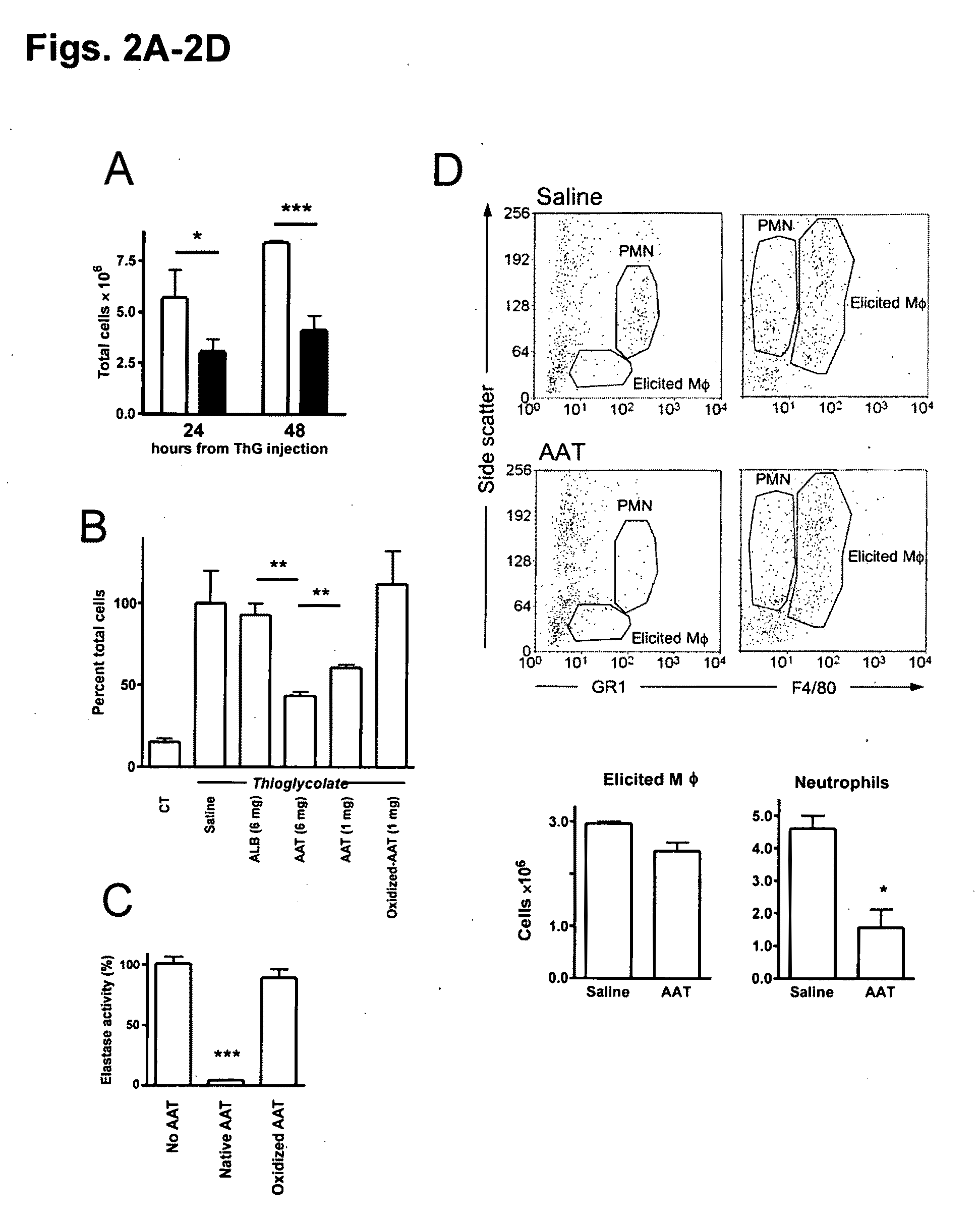
Embodiments herein illustrate methods and compositions for treating medical disorders. In certain embodiments, compositions and methods relate to reducing, inhibiting or treating graft rejection, transplant rejection or diabetes in a subject. Other embodiments herein relate to compounds including naturally occurring and synthetic mutant compositions of alpha-1 antitrypsin, wherein the alpha-1 antitrypsin has no significant serine protease inhibitor activity.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Methods of modulating immune function
ActiveUS20120219559A1Modulate its functionAdjust immune functionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsCTLA-4Autoimmune disease
Presented herein are therapeutic agents that modulate one or more immune functions and uses of such therapeutic agents in the prevention, treatment and management of diseases. In one aspect, the therapeutic agents modulate one or more signal transduction pathways induced by the binding of B7-H7 to B7-H7CR, or the binding of B7-H2 to either ICOS, CD28, or CTLA-4. In another aspect, the therapeutic agents modulate the binding of B7-H7 to B7-H7CR, or the binding of B7-H2 to either ICOS, CD28, or CTLA-4. The therapeutic agents can be used in the prevention, treatment and / or management of diseases in which it might be useful to modulate one or more immune functions (e.g., cancer, infectious disease, autoimmune disease, and transplantation rejection). In another aspect, presented herein are methods for identifying receptor-ligand interactions.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
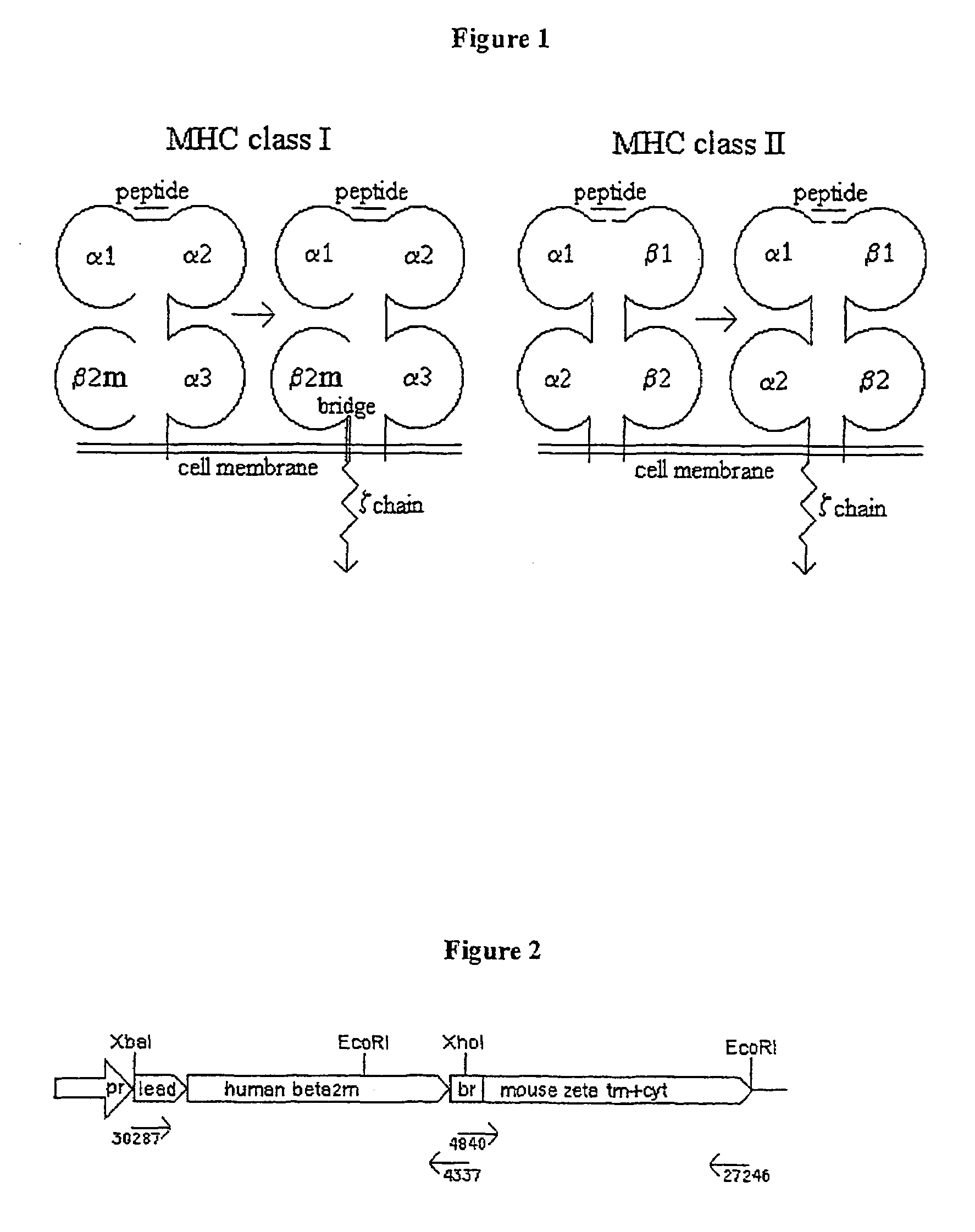
Genetically-engineered MHC molecules
The invention provides DNA molecules encoding a chimeric polypeptide comprising (a) a component of a MHC molecule capable of association on a cell surface with an endogenous MHC molecule component of the same class, and (b) an intracellular region of a signal transduction element capable of activating T cells. Component (a) may be a monomorphic component and is preferably beta 2-microglobulin, or a polymorphic class I or class II component. The signal transduction element (b) capable of activating T cells may be a component of T-cell receptor CD3, preferably the CD3 zeta (zeta) polypeptide, a B cell receptor polypeptide or an Fc receptor polypeptide. Immune cells such as a CTLs expressing said chimeric MHC molecules specifically eliminate or inactivate harmful T cells and are useful for treating graft rejection and autoimmune diseases.
Owner:GAVISH GALILEE BIO APPL
Anti-cd20 antibodies and methods of use
ActiveUS20080089885A1High affinityImproved CDC functionAntipyreticAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsCD20Autoimmune condition
Compositions and methods are provided for treating diseases associated with CD20, including lymphomas, autoimmune diseases, and transplant rejections. Compositions include anti-CD20 antibodies capable of binding to a human CD20 antigen located on the surface of a human CD20-expressing cell, wherein the antibody has increased complement-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (CDC) that is achieved by having at least one optimized CDR engineered within the variable region of the antibody. Compositions also include antigen-binding fragments, variants, and derivatives of the monoclonal antibodies, cell lines producing these antibody compositions, and isolated nucleic acid molecules encoding the amino acid sequences of the antibodies. The invention further includes pharmaceutical compositions comprising the anti-CD20 antibodies of the invention, or antigen-binding fragments, variants, or derivatives thereof, in a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, and methods of use of these anti-CD20 antibodies.
Owner:VACCINEX
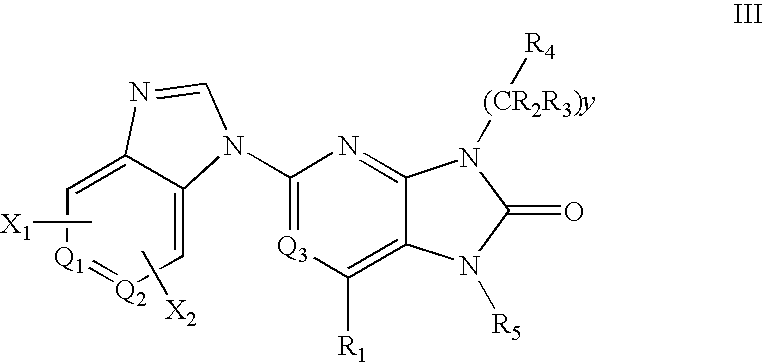
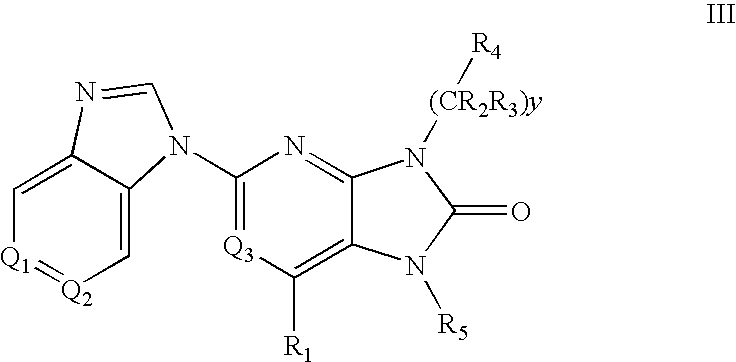
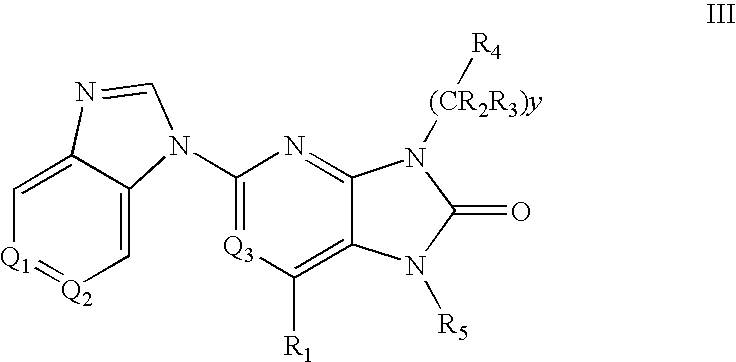
Purine and imidazopyridine derivatives for immunosuppression
The present invention provides novel purine and imidazopyridine derivatives useful for the prevention and treatment of autoimmune diseases, inflammatory disease, mast cell mediated disease and transplant rejection. The compounds are of the general formulas:
Owner:WYETH LLC +1
Methods of inhibiting immune response suppression by administering antibodies to OX-2
InactiveUS6955811B2Inhibited graft survivalReduce miscarriage rateImmunoglobulin superfamilyPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseAutoimmune disease
Methods and compositions for regulating immunity are disclosed. For enhancing an immune response, agents that inhibit OX-2 are administered. Such methods are useful in treating cancer. For suppressing an immune response, an OX-2 protein or a nucleic acid encoding an OX-2 protein is administered. Such methods are useful in preventing graft rejection, fetal loss, autoimmune disease, allergies and in inducing tumor cell growth.
Owner:TRILLIUM THERAPEUTICS
Tumor necrosis factor-gamma
InactiveUS7597886B2Increase blockingInduce inflammatory activityOrganic active ingredientsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsAbnormal tissue growthDisease
Human TNF-gamma-alpha and TNF-gamma-beta polypeptides and DNA (RNA) encoding such polypeptides and a procedure for producing such polypeptides by recombinant techniques are disclosed. Also disclosed are methods for utilizing such polypeptides to inhibit cellular growth, for example in a tumor or cancer, for facilitating wound-healing, to provide resistance against infection, induce inflammatory activities, and stimulating the growth of certain cell types to treat diseases, for example restenosis. Also disclosed are diagnostic methods for detecting a mutation in the TNF-gamma-alpha and TNF-gamma-beta nucleic acid sequences or overexpression of the TNF-gamma-alpha and / or TNF-gamma-beta polypeptides. Antagonists against such polypeptides and their use as a therapeutic to treat cachexia, septic shock, cerebral malaria, inflammation, arthritis and graft-rejection are also disclosed.
Owner:HUMAN GENOME SCI INC
Methods of preparation and composition of peptide constructs useful for treatment of autoimmune and transplant related host versus graft conditions
InactiveUS20060257420A1Effectively eliminate set and subsetTreating or preventing inappropriate autoimmune responsePeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsAutoimmune diseaseApoptosis
The invention is related to peptide constructs, i.e., polypeptides obtained by linking together two or more peptides based on or derived from different molecules, which are useful in the treatment or prevention of autoimmune diseases, asthma, allergies, and host versus graft (or graft versus host) rejection, as well as to compositions containing same, methods for producing same and methods for using same; wherein the peptide constructs have the formula P1-x-P2 where P1 is a peptide associated with autoimmune disease, allergy, asthma, host-versus-graft rejection, myocarditis, diabetes, and immune-mediated disease, which binds to an antigen receptor on a set or subset of T cells; P2 is a peptide which will cause a Th2 directed immune response by the set or subset of T cells to which the peptide P1 is attached or which will bind to a T cell receptor which will cause the set or subset of T cells to which the peptide P1 is attached to initiate, but not complete, an immune response causing the set or subset of T cells to undergo anergy and apoptosis; and x is a direct bond or linker for covalently bonding P1 and P2.
Owner:CEL SCI CORP
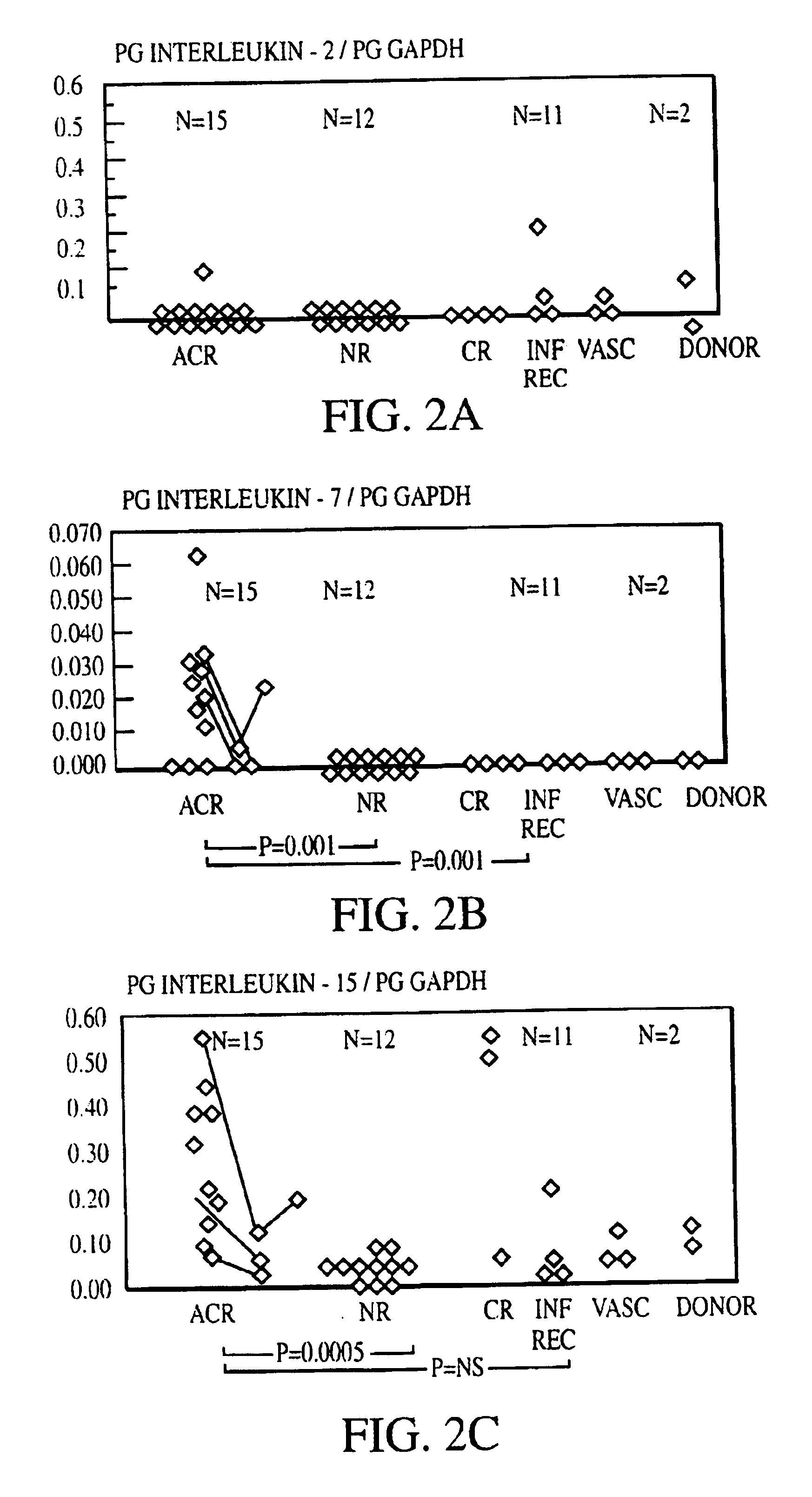
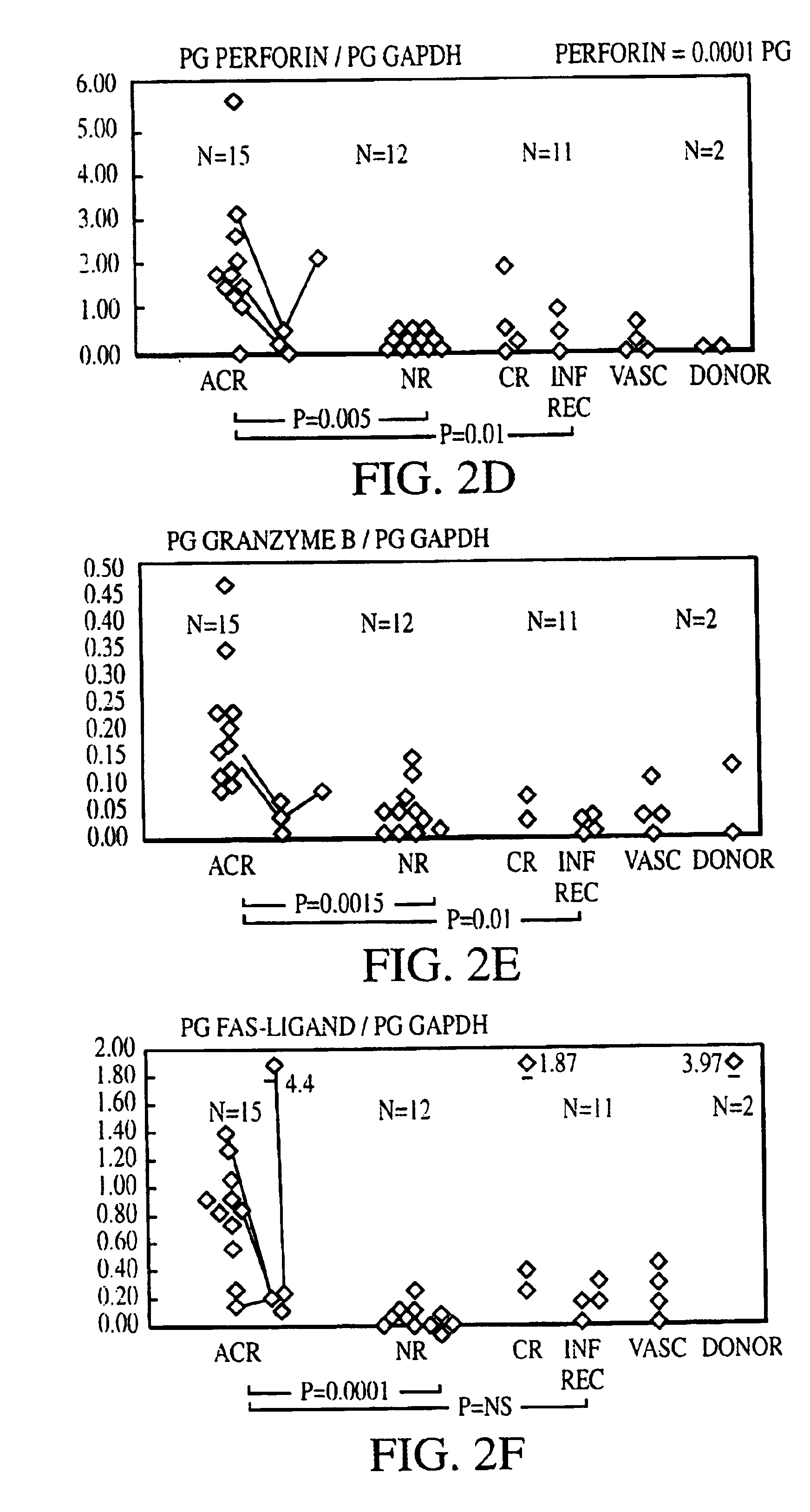
Measurement of protective genes in allograft rejection
InactiveUS6900015B2Quantitative precisionAccurately allograft rejectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisCytotoxicityAllograft rejection
The invention relates to methods of evaluating transplant rejection in a host comprising determining a heightened magnitude of gene expression of genes in rejection-associated gene clusters. The disclosed gene clusters include genes that are substantially co-expressed with cytotoxic lymphocyte pro-apoptotic genes, cytoprotective genes and several other cytokine and immune cell genes.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC +1
Antagonizing interleukin-21 receptor activity
InactiveUS20080241098A1Reduced activityImprove inflammation symptomsCompounds screening/testingPeptide/protein ingredientsWhite blood cellInflammatory Bowel Diseases
Methods and compositions for inhibiting interleukin-21 (IL-21) / IL-21 receptor (MU-1) activity using antagonists of IL-21 or IL-21 receptor (“IL-21R” or “MU-1”), are disclosed. IL-21 / IL-21R antagonists can be used to induce immune suppression in vivo, e.g., for treating, ameliorating or preventing autoimmune or inflammatory disorders, including, e.g., inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), transplant / graft rejection, psoriasis, asthma, fibrosis, and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Owner:WYETH LLC
Mutant Forms of Fas Ligand and Uses Thereof
The invention provides for DNA encoding Fas ligand muteins and chimeras and the proteins encoded thereby. The invention further includes the use of DNA and vectors to produce transformed cells expressing the mutant or chimeric Fas ligand. When the Fas ligand of the invention is a non cleavable form, the cells expressing the Fas ligand are useful in vitro for identifying Fas expressing cells or in vivo for reducing populations of Fas expressing cells. Thus, in other embodiments, the present invention is also directed to a method for treating a patient, for example a mammal, for autoimmune disease or transplant rejection by administering a Fas ligand therapeutic agent. The therapeutic agent is a polypeptide, a polynucleotide encoding the polypeptide or a small molecule. The polypeptides include full-length Fas ligand polypeptide, or a biologically active variant, derivative, portion, fusion or peptide thereof.
Owner:CHU KETING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com