Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
167 results about "Graft rejections" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A graft rejection is an immune response by the body to destroy foreign cells in transplanted tissue. Graft rejections occur because the transplanted tissue or organ has antigens on its cells that do not match the person's own cell antigens.
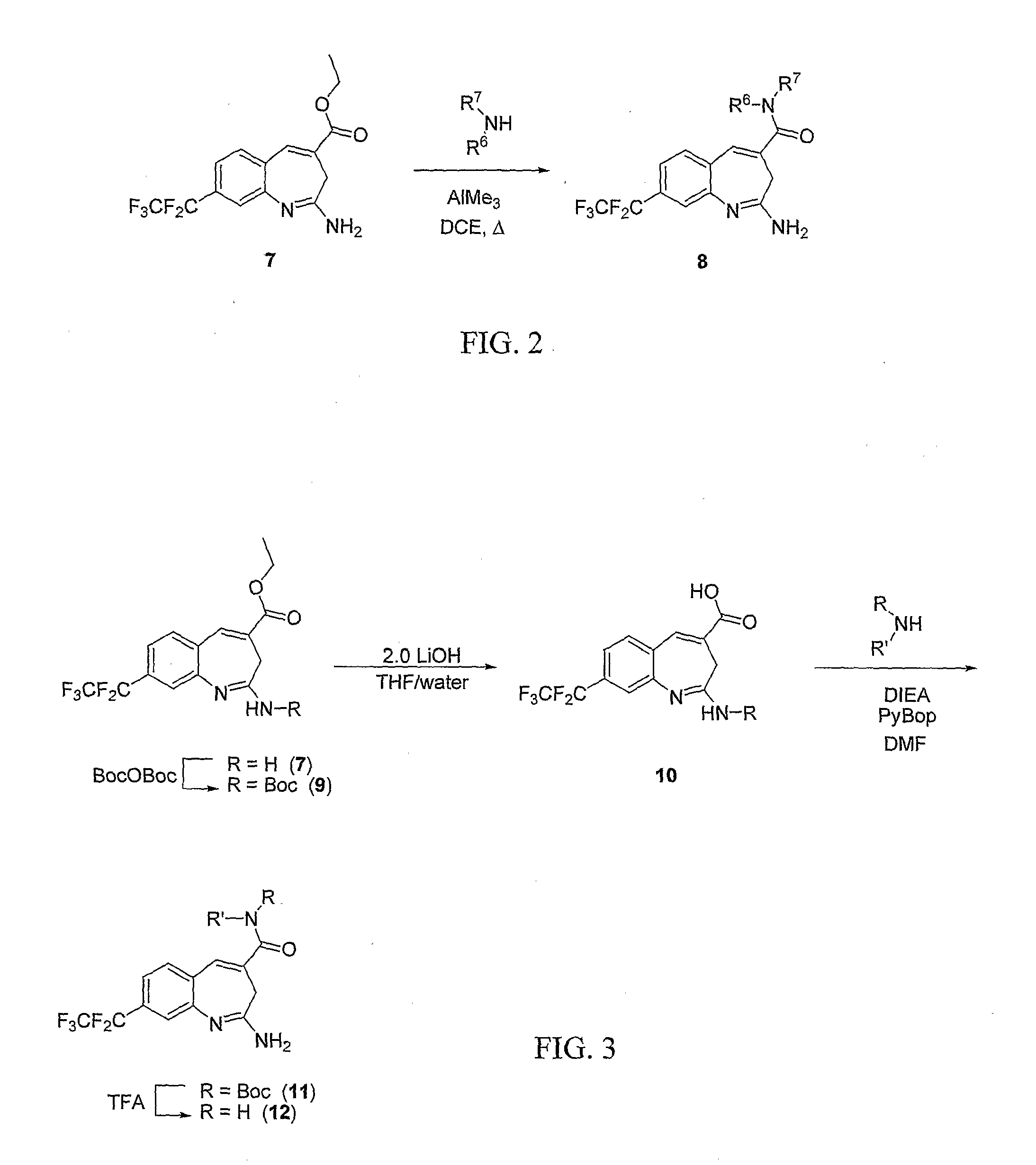
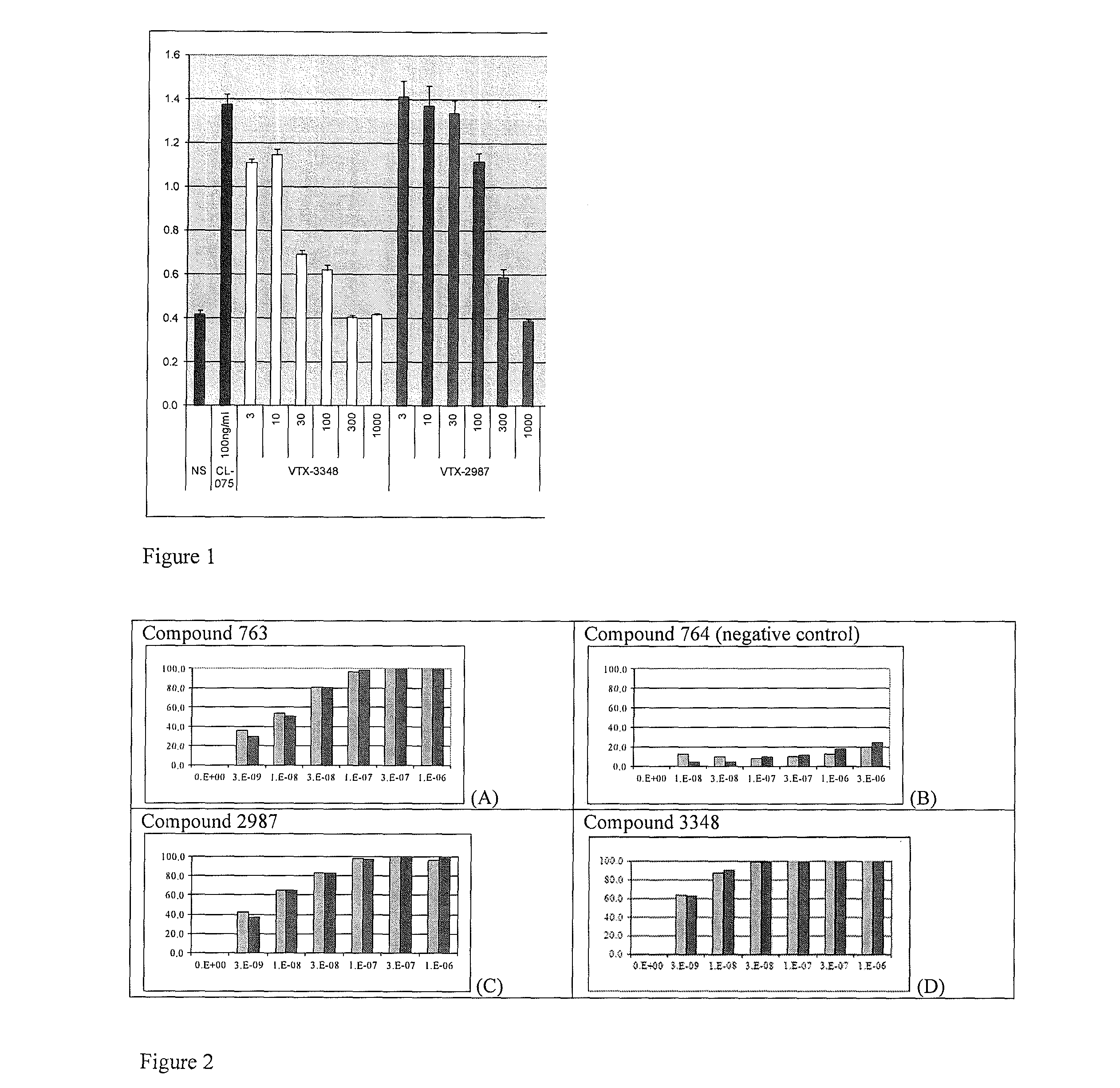
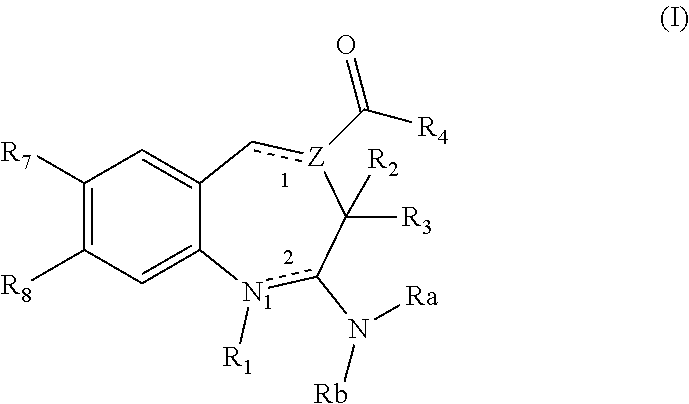
8-Substituted Benzoazepines as Toll-Like Receptor Modulators
Provided are compositions and methods useful for modulation of signaling through the Toll-like receptors TLR7 and / or TLR8. The compositions and methods have use in the treatment of autoimmunity, inflammation allergy, asthma, graft rejection, graft versus host disease, infection, sepsis, cancer and immunodeficiency.
Owner:ARRAY BIOPHARMA
Substituted Benzoazepines As Toll-Like Receptor Modulators
Provided are compositions and methods useful for modulation of signaling through the Toll-like receptors TLR7 and / or TLR8. The compositions and methods have use in treating or preventing disease, including cancer, autoimmune disease, fibrotic disease, cardiovascular disease, infectious disease, inflammatory disorder, graft rejection, or graft-versus-host disease.
Owner:ARRAY BIOPHARMA +1
Antagonizing interleukin-21 receptor activity
InactiveUS20060039902A1Reduce riskSufficient amountCompounds screening/testingCompound screeningWhite blood cellFibrosis
Methods and compositions for inhibiting interleukin-21 (IL-21) / IL-21 receptor (MU-1) activity using antagonists of IL-21 or IL-21 receptor (“IL-21R” or “MU-1”), are disclosed. IL-21 / IL-21R antagonists can be used to induce immune suppression in vivo, e.g., for treating, ameliorating or preventing autoimmune or inflammatory disorders, including, e.g., inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), transplant / graft rejection, psoriasis, asthma, fibrosis, and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Owner:WYETH LLC
Methods and compositions for the inhibition of transplant rejection
InactiveUS20120177645A1Inhibit and reduce transplant rejection of insulin-producingInhibiting and reducing chronic transplant rejectionNervous disorderAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTransplant rejectionT cell
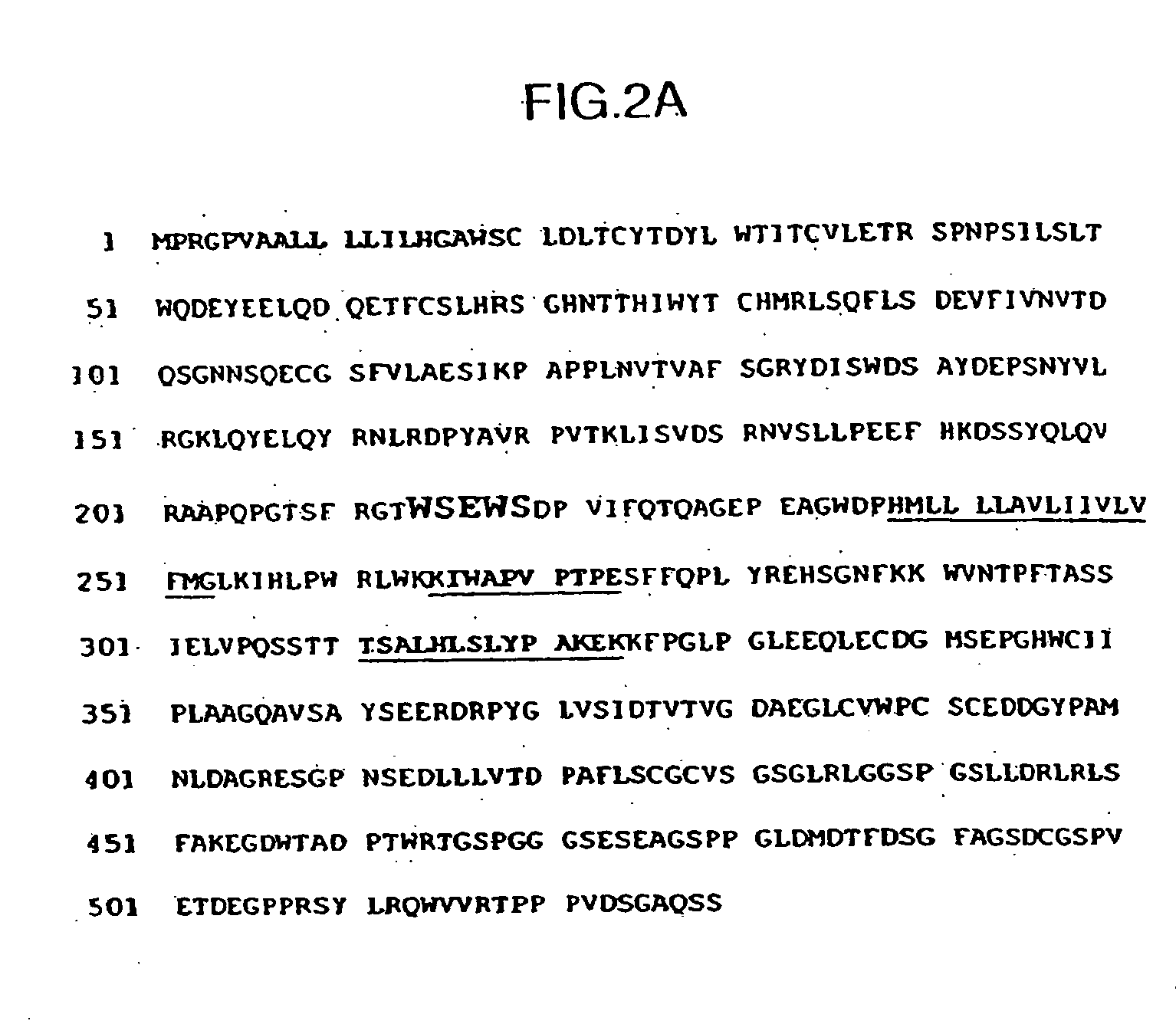
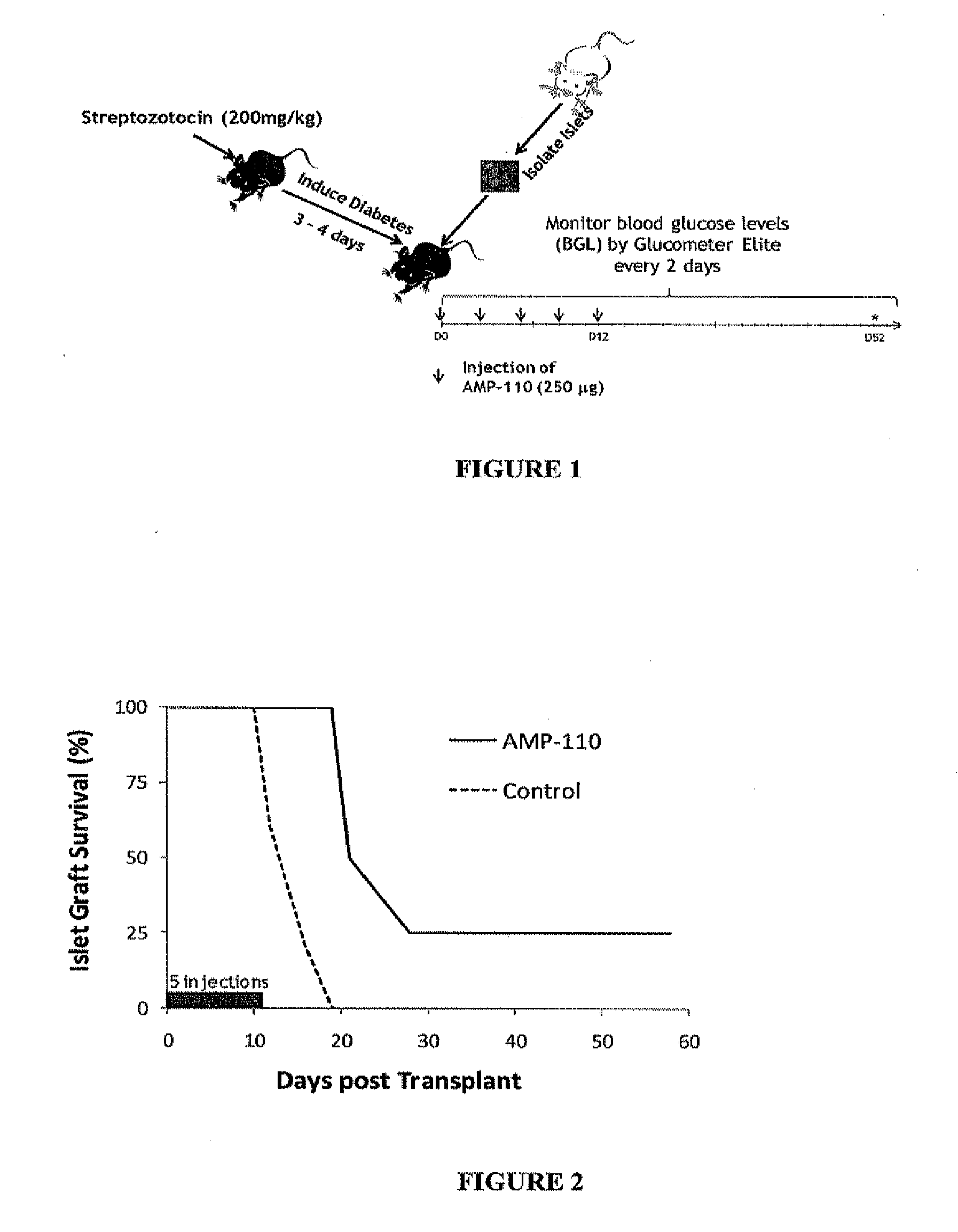
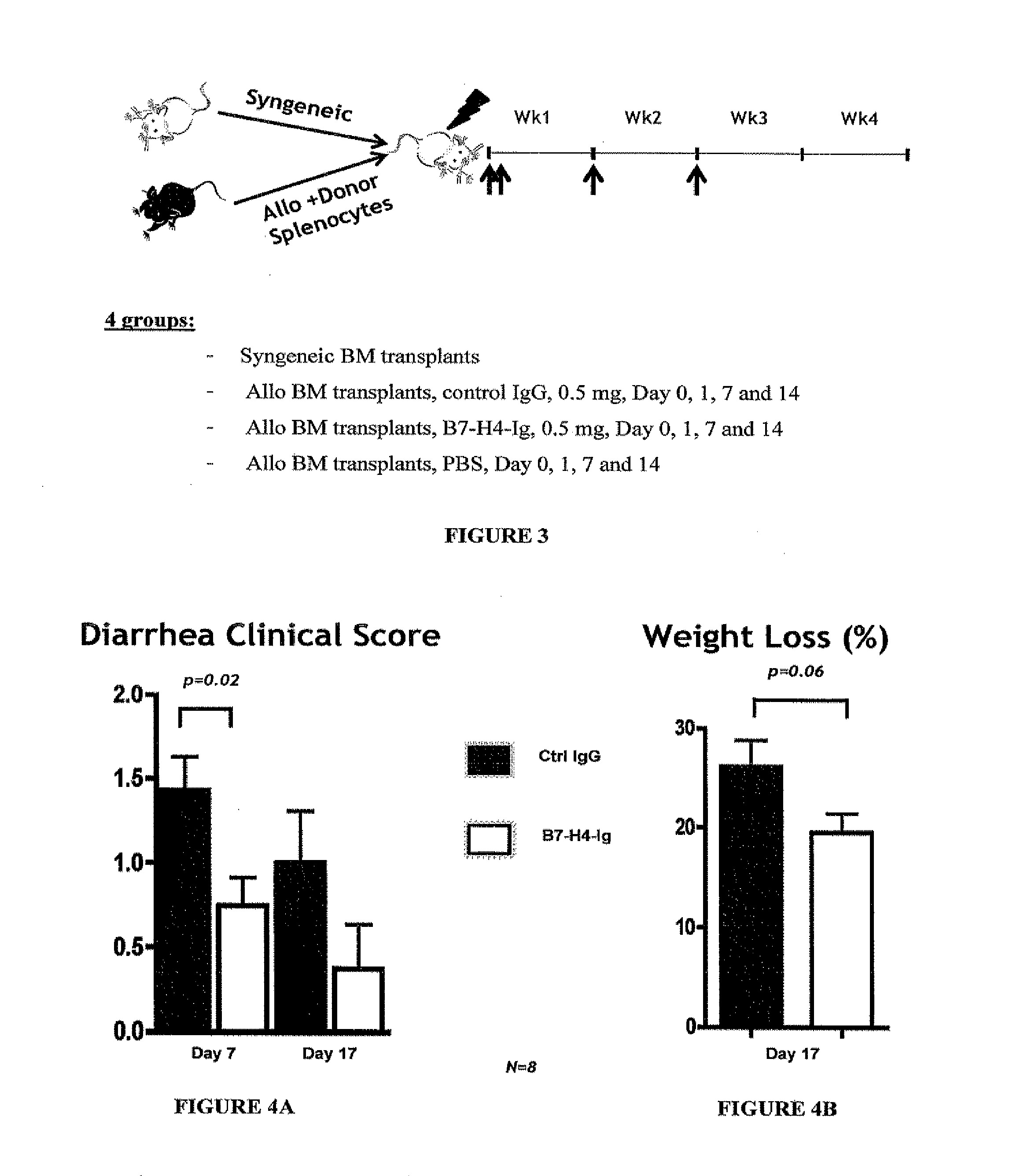
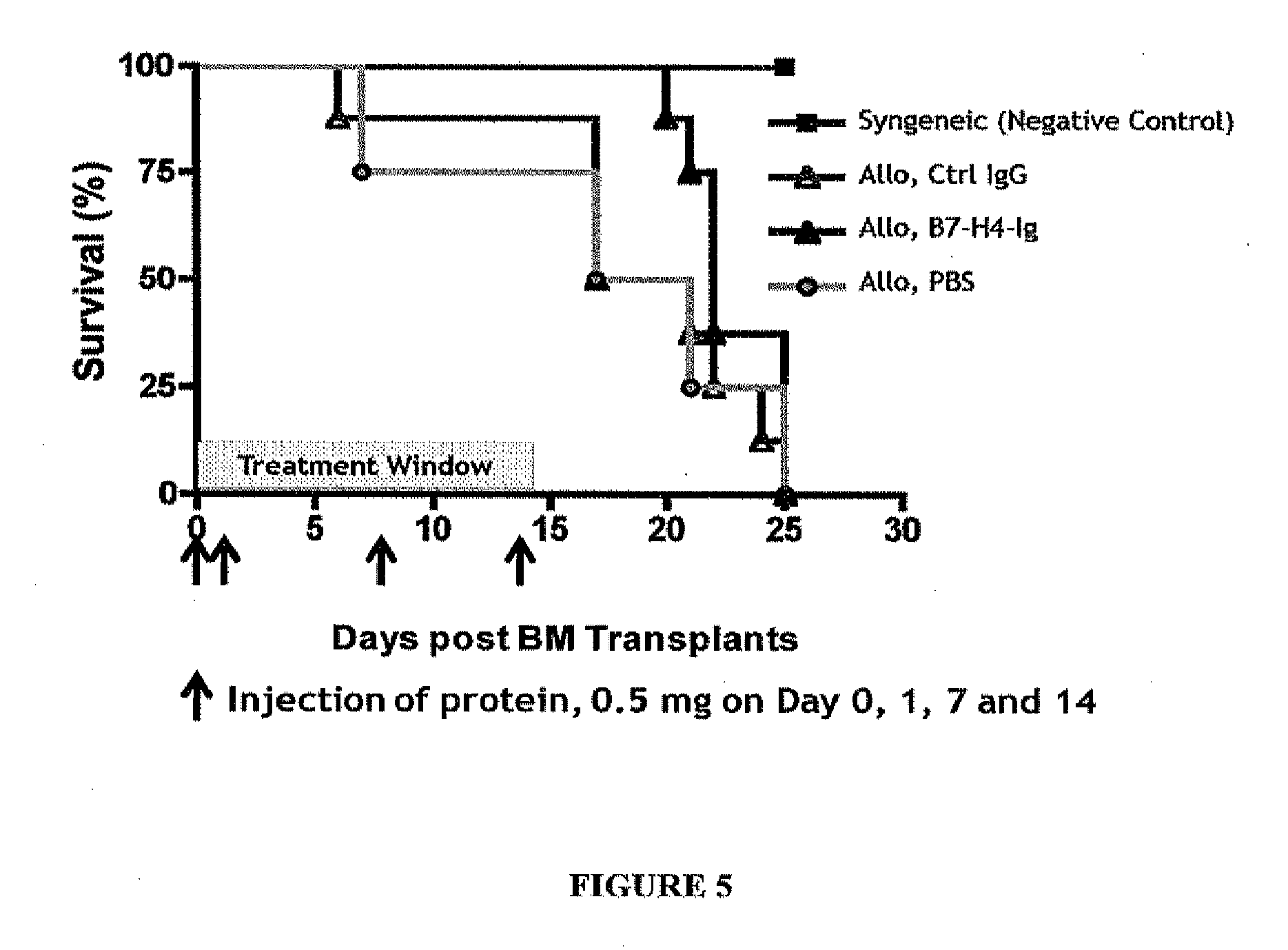
Methods for modulating immune responses in a subject are provided. A preferred embodiment provides methods and compositions for reducing or inhibiting transplant rejection in a subject, preferably a human subject. Transplant rejection can be inhibited or reduced in a subject by administering an effective amount of B7-H4 polypeptide, fragments or fusions thereof to inhibit or reduce the biological activity of an immune cell or to reduce the amounts of proinflammatory molecules at a site of transplant. Th1, Th17 and Th22 cells are exemplary T cells that can be targeted for inhibition by B7-H4 polypeptides, fusion proteins or fragments thereof to inhibit or reduce inflammation.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
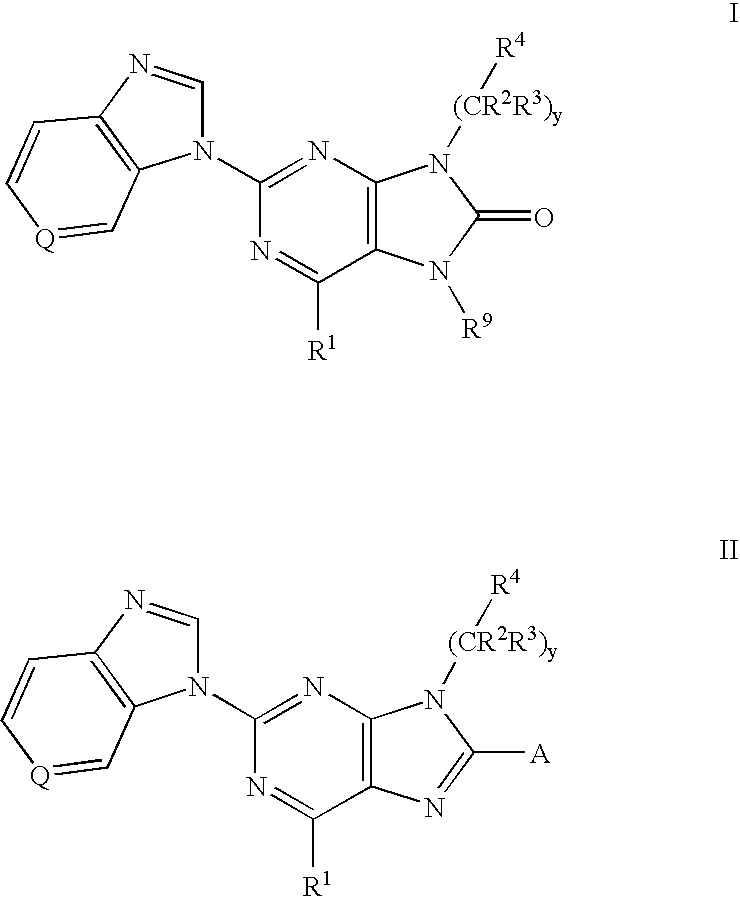
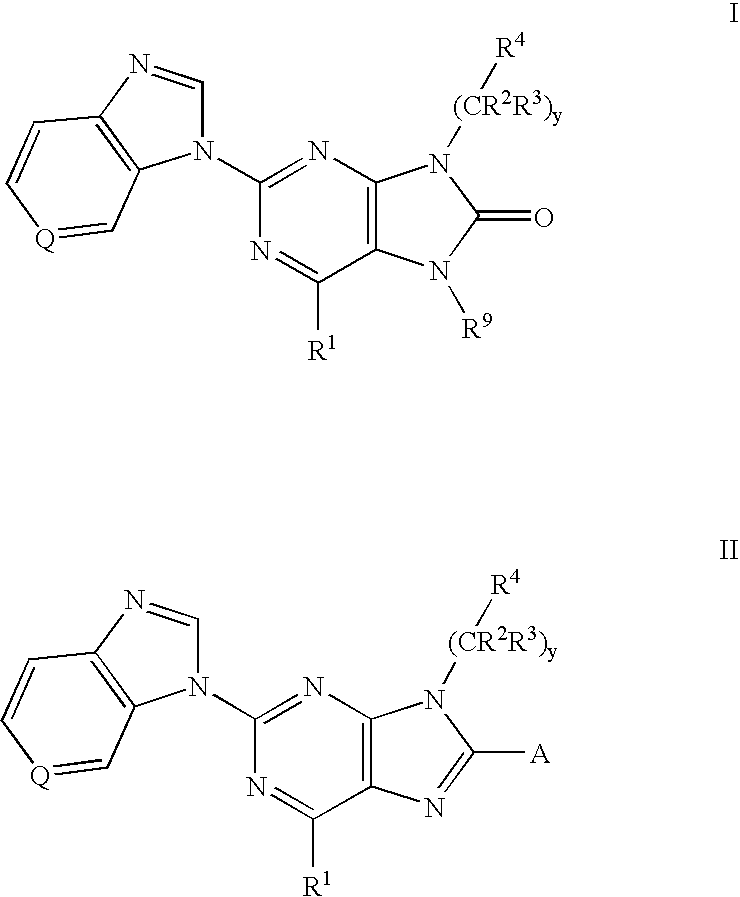
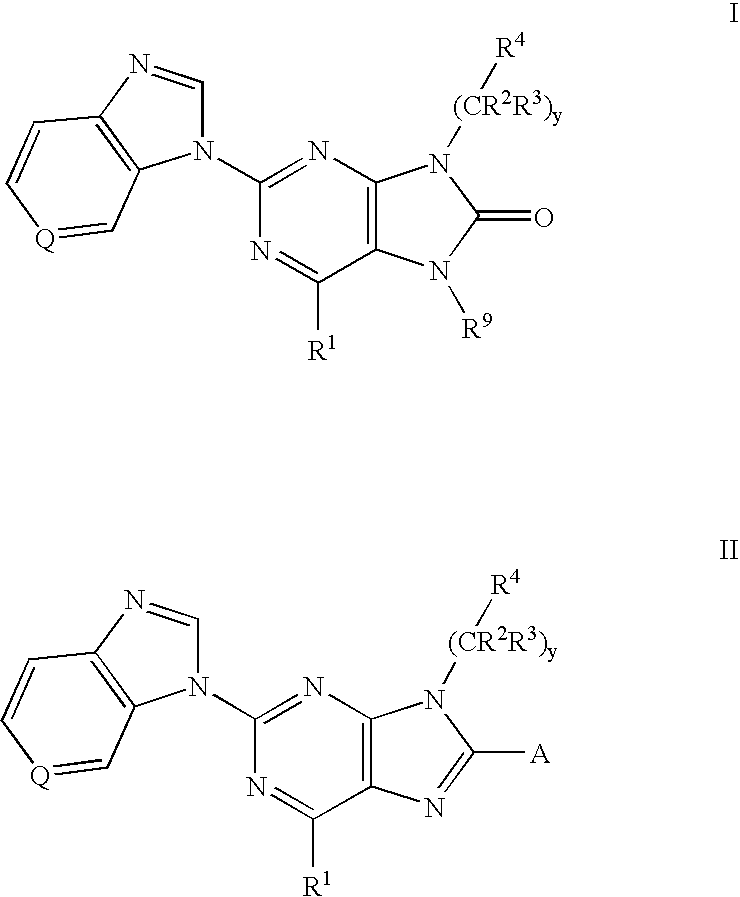
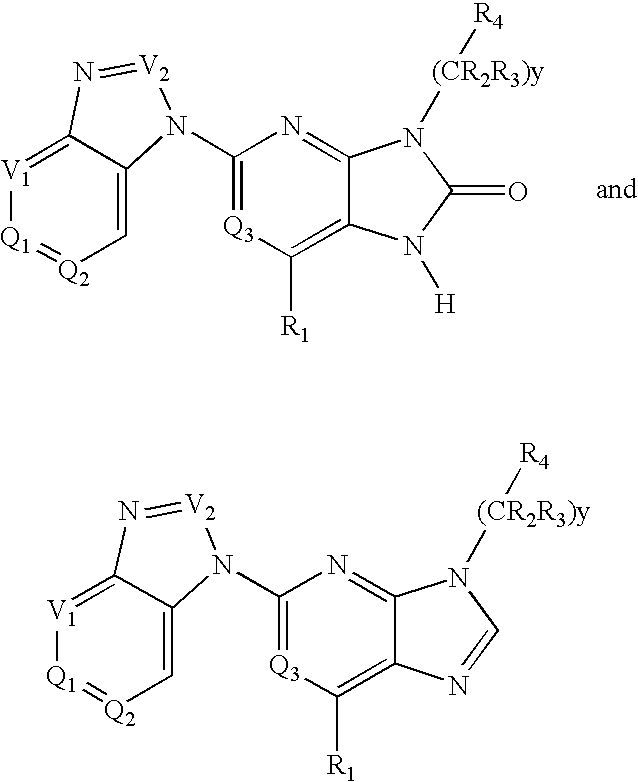
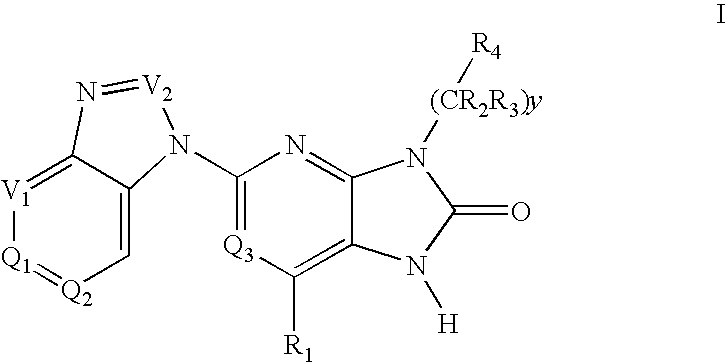
6-substituted 2-(benzimidazolyl)purine and purinone derivatives for immunosuppression
The present invention provides novel purinones and purines useful for the prevention and treatment of autoimmune diseases, inflammatory disease, mast cell mediated disease and transplant rejection. The compounds are of the general formulae I and II:
Owner:WYETH LLC
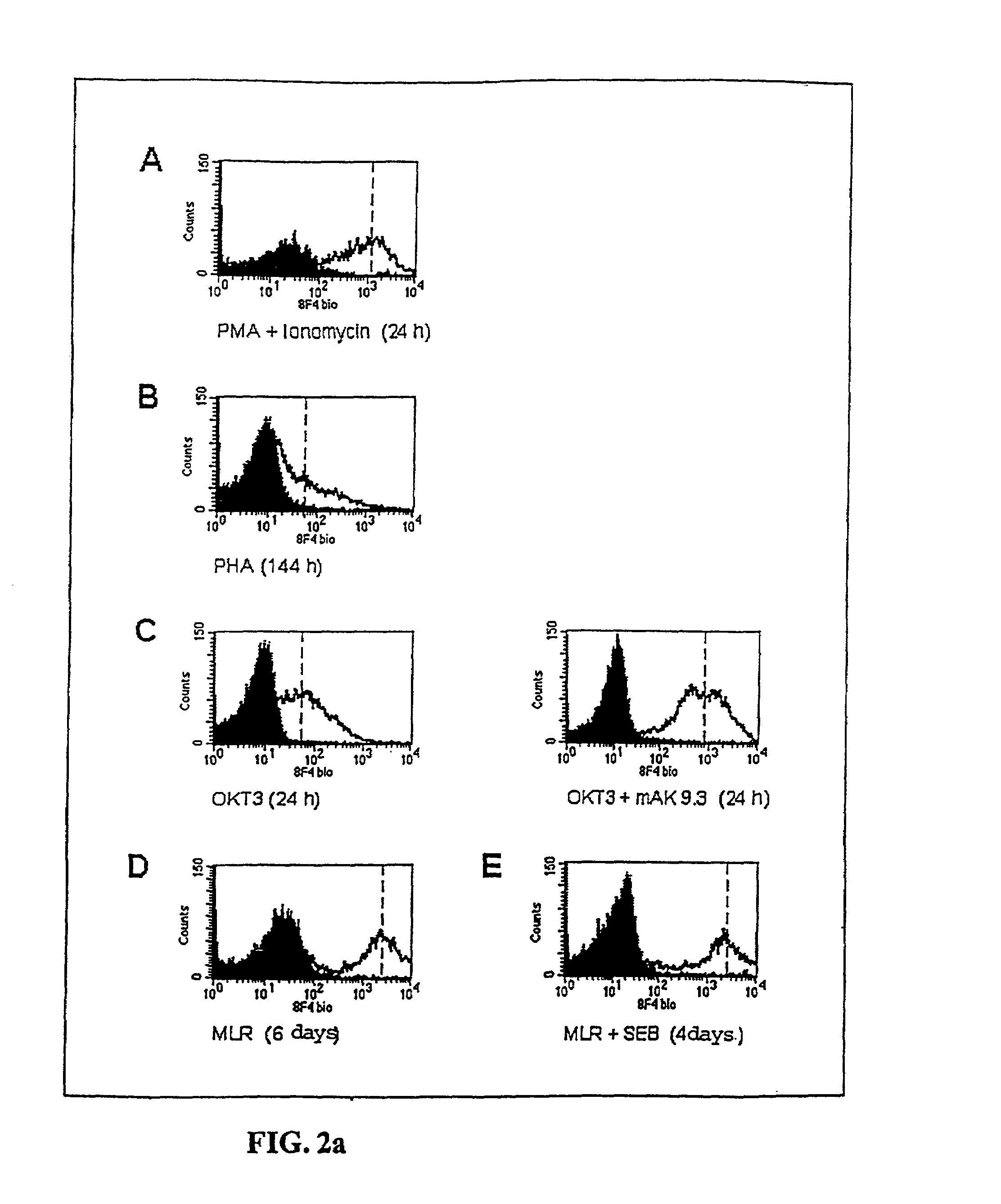
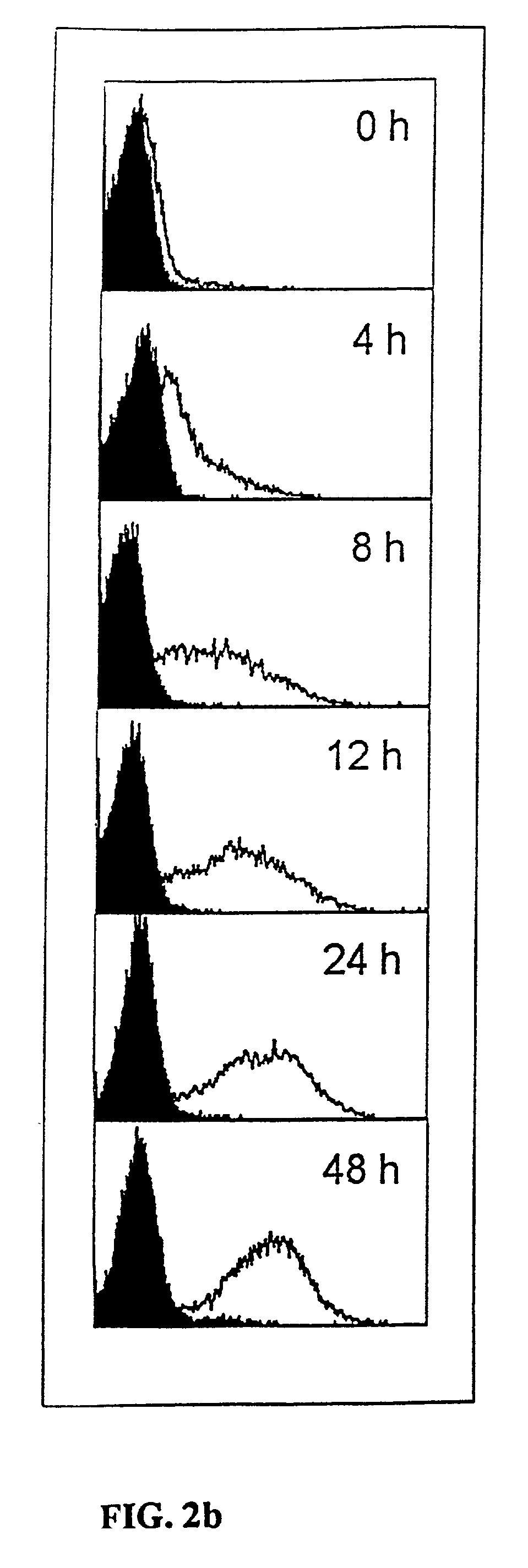
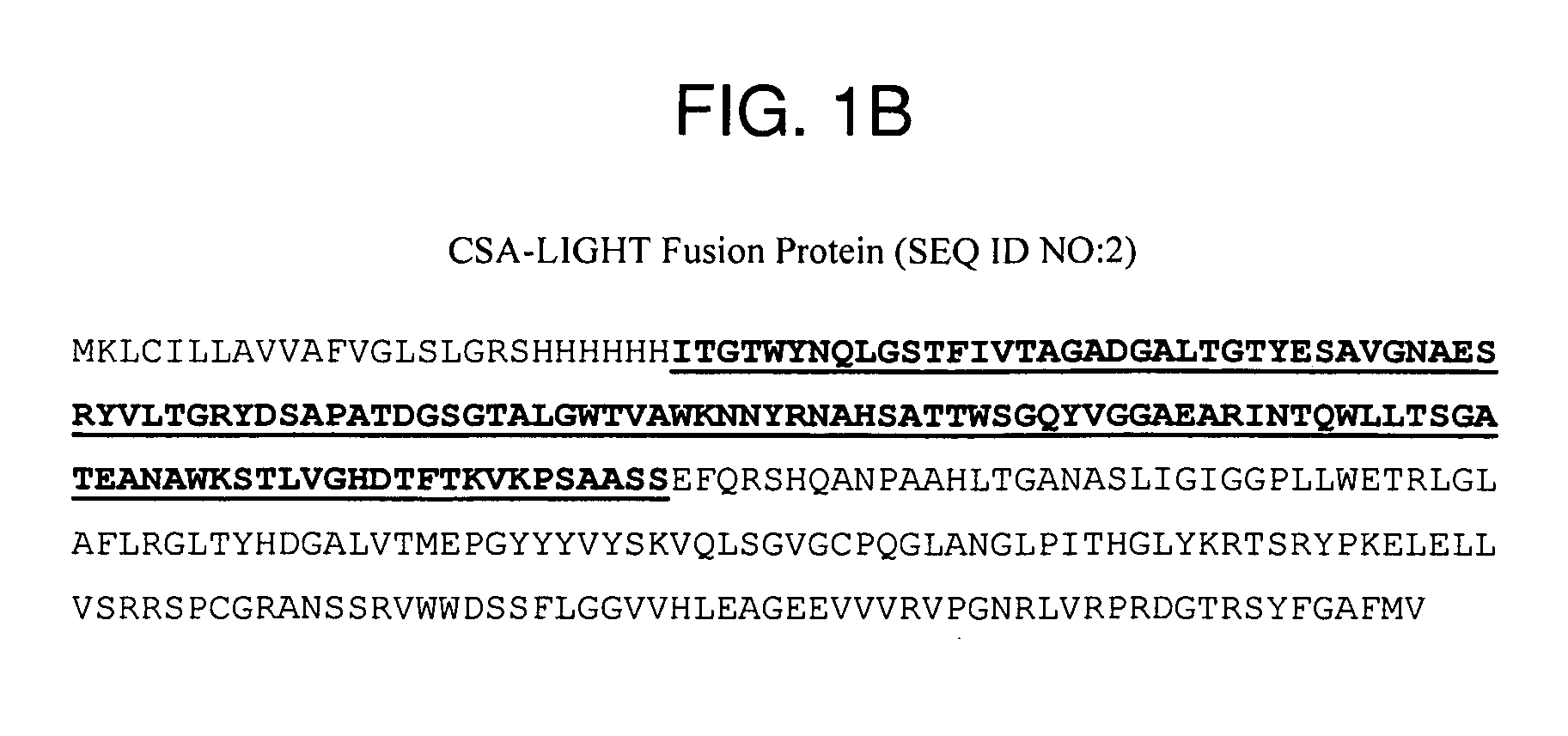
Methods for treatment of asthmatic disorders using a monoclonal antibody to 8F4 polypeptide
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for the prevention and treatment and prevention of immune system disorders, including cancer, AIDS, asthmatic disorders, autoimmune diseases, organ transplant rejection and chronic viral diseases such as HCV or HBV infections. The therapeutic methods of the invention comprise administering molecules that modulate the activity of 8F4, thereby modulating costimulation of T cells. The present invention further provides monoclonal antibodies against the 8F4 molecule and hybridoma cells which produce said monoclonal antibodies. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising molecules that modulate the activity of 8F4 are also provided.
Owner:BUNDESREPUBLIK DEUTSCHLAND
Methods and compositions for expanding T regulatory cells
InactiveUS20070172947A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsType 1 diabetesStem cell
The present invention provides methods and compositions for expanding Treg cells ex vivo or in vivo using one or more conjugates comprising a costimulatory moiety that stimulates at least one of three signals involved in Treg cell development and / or using dendritic cells pulsed with antigens and modified to display TGF-β, or hematopoetic stem cells or bone marrow cells modified to display TGF-β. The methods and compositions are useful, for example, in the treatment and prevention of autoimmune disease, including Type 1 diabetes and in preventing foreign graft rejection, as well as to establish mixed chimerism, induce tolerance to autoantigens, alloantigens or xenoantigens, beta cell regeneration, prevention of foreign graft rejection, and treatment of a genetically inherited hematopoietic disorder.
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE RES FOUND INC
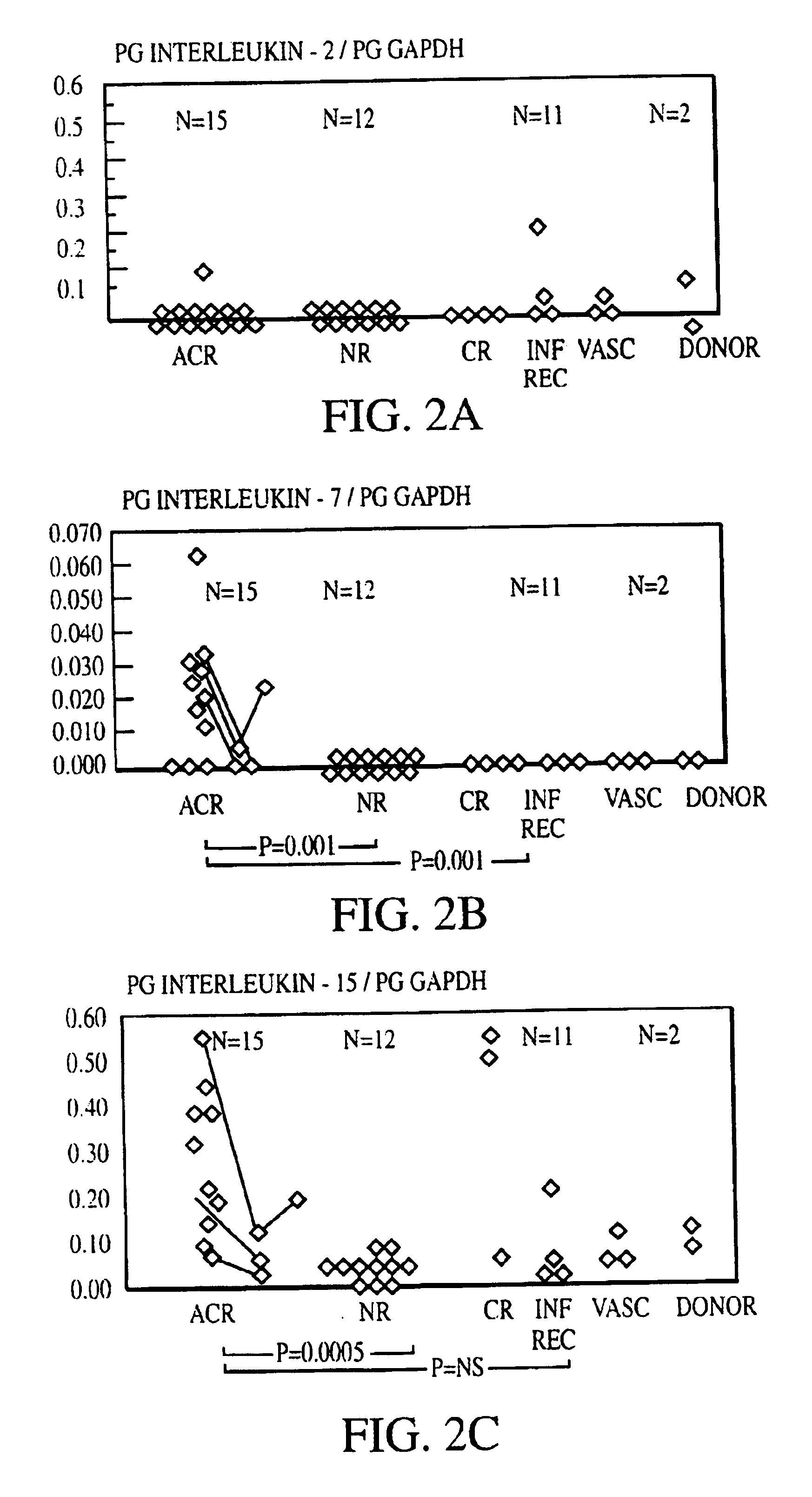
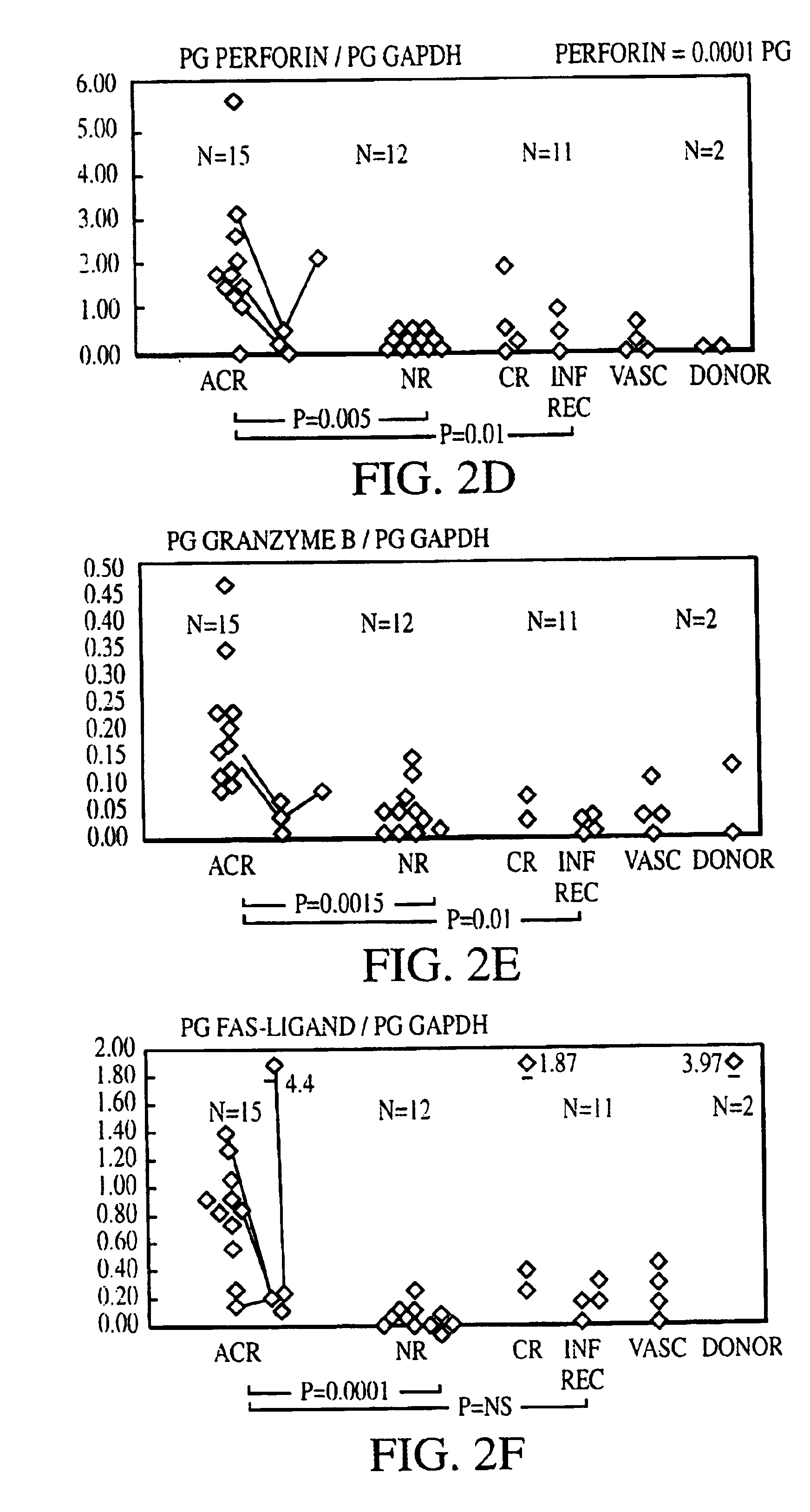
Measurement of protective genes in allograft rejection
InactiveUS6900015B2Quantitative precisionAccurately allograft rejectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisCytotoxicityAllograft rejection
The invention relates to methods of evaluating transplant rejection in a host comprising determining a heightened magnitude of gene expression of genes in rejection-associated gene clusters. The disclosed gene clusters include genes that are substantially co-expressed with cytotoxic lymphocyte pro-apoptotic genes, cytoprotective genes and several other cytokine and immune cell genes.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC +1
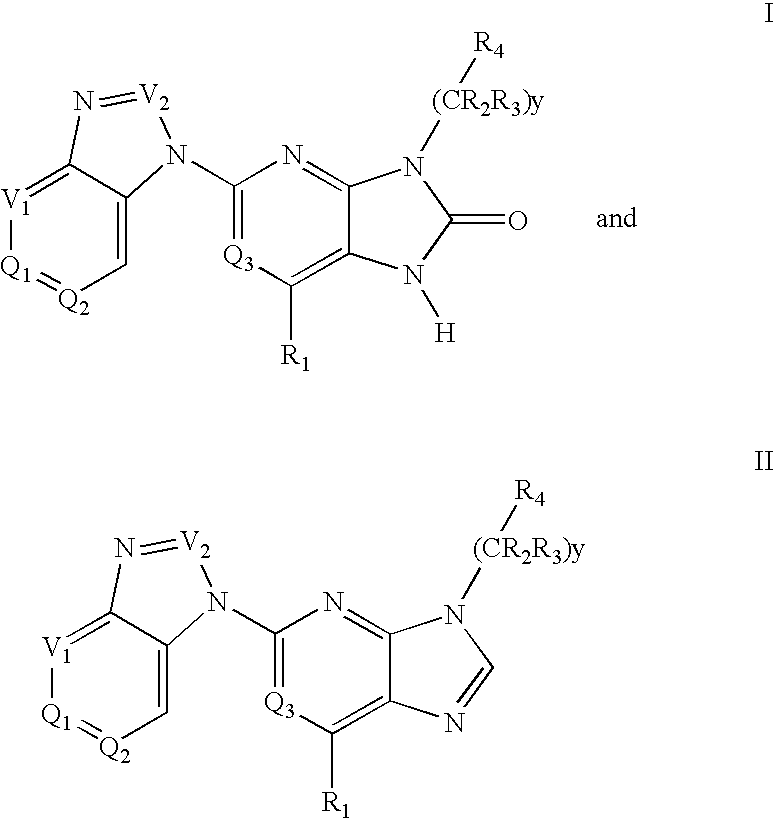
Purine and imidazopyridine derivatives for immunosuppression
The present invention provides novel purine and imidazopyridine derivatives useful for the prevention and treatment of autoimmune diseases, inflammatory disease, mast cell mediated disease and transplant rejection. The compounds are of the general formulas:
Owner:PHARMACOPEIA INC CO LIGAND PHARM INC +1
Treatment methods for autoimmune disorders
ActiveUS20100260781A1Promote regulatory cell-mediated suppressionAvoid seizuresBiocideSenses disorderDiseaseT-regulatory cell
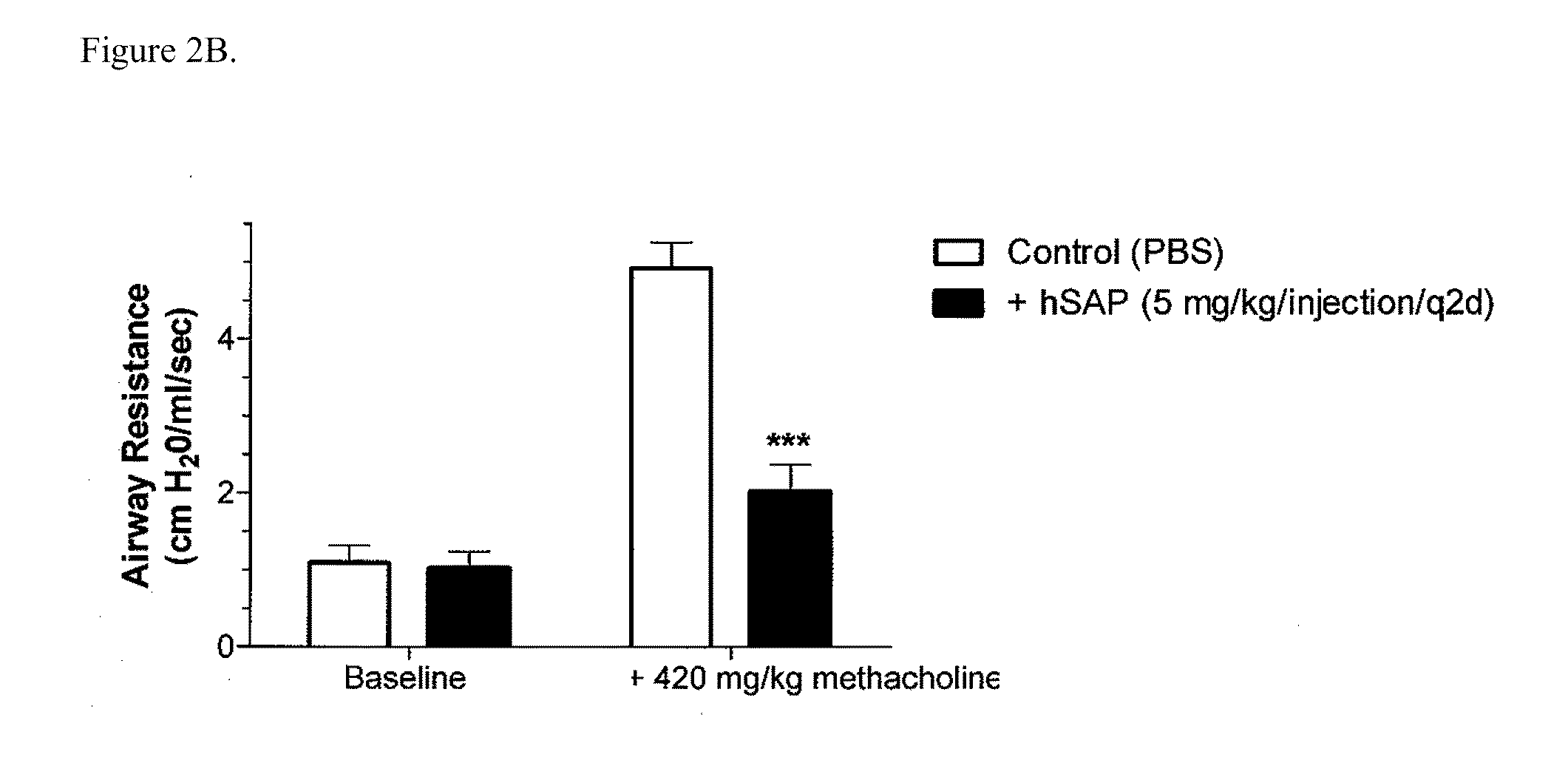
The present invention provides methods and compositions for expanding T regulatory cells ex vivo or in vivo using one or more SAP agonists. The methods and compositions are useful in the treatment of autoimmune diseases and in preventing foreign graft rejection.
Owner:PROMEDIOR
Suppression of transplant rejection
InactiveUS20070166307A1Vertebrate cellsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAutoimmune conditionRegulatory T cell
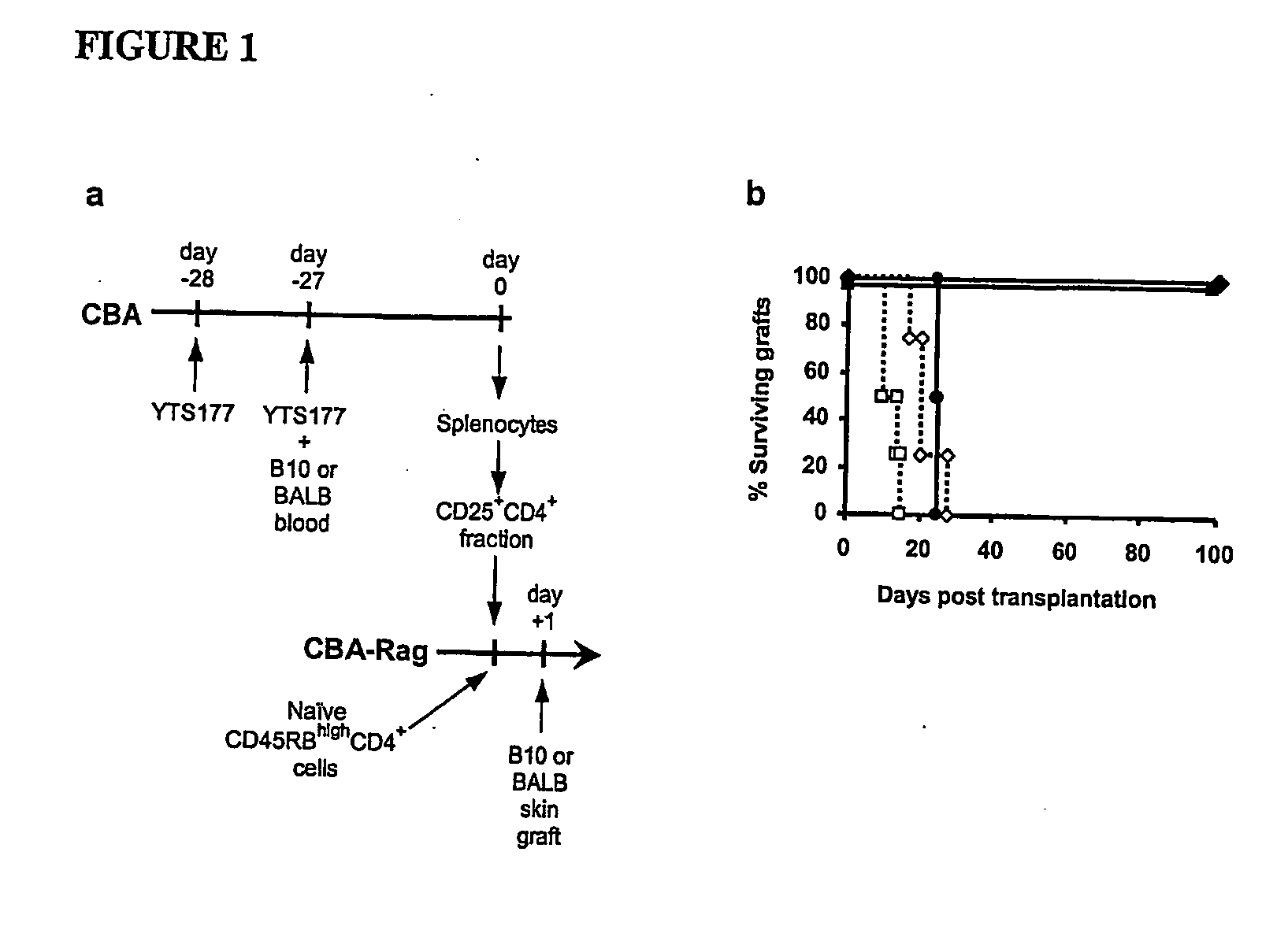
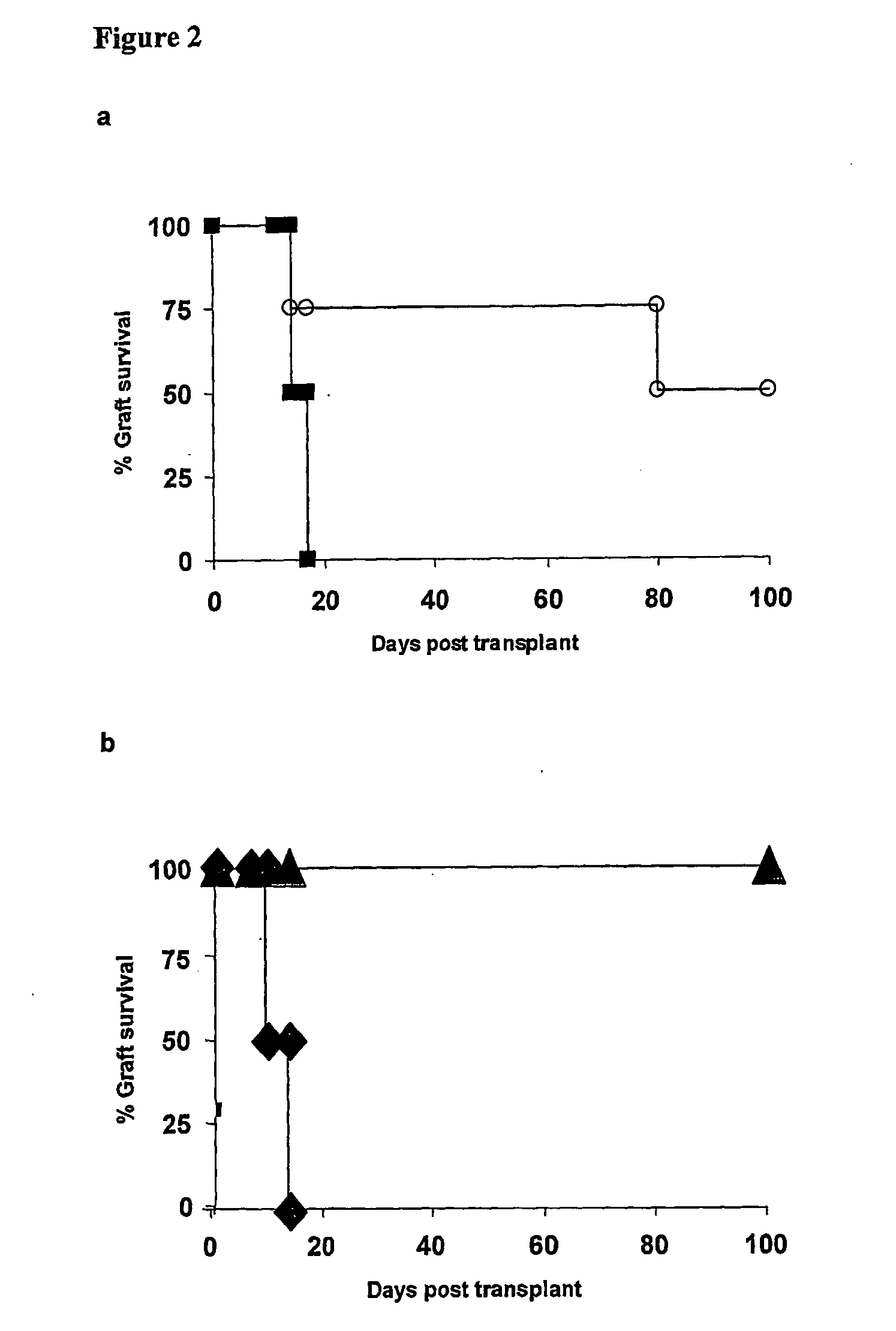
The present invention relates to a transplant rejection in an animal suppressed by administration of an antibody directed at a cell surface antigen selected from the group consisting of CD4, CD8, CD154, LFA-1, CD80, CD86 and ICAM-1, preferably an anti-CD4 antibody, together with a non-cellular protein antigen to generate in the animal a population of regulatory T-lymphocytes; reactivating said population of regulatory T-lymphocytes by further administration to the animal of the non-cellular protein antigen; and transplanting said organ or tissue whilst said population of regulatory T-lymphocytes is activated. Regulatory T cells can be generated ex vivo by culturing T cells with an antibody directed at a cell surface antigen selected from the group consisting of CD4, CD8, CD154, LFA-1, CD80, CD86 and ICAM-1, in the presence of cells that present either alloantigen or a non-cellular protein antigen. Ex vivo generated T-lymphocytes can be used as an alternative method of overcoming transplant rejection or in combination with the in vivo method. A similar approach can be adopted for the treatment of autoimmune conditions.
Owner:ISIS INNOVATION LTD
Dihydro-1h-pyrrolo[1,2-a]indol-1-yl carboxylic acid derivatives which act as s1p1 agonists
The present invention relates to certain (1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrrolo[1,2-a]indol-1-yl carboxylic acid derivatives of Formula (Ia) and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, which exhibit useful pharmacological properties, for example, as agonists of the S1P1 receptor. Also provided by the present invention are pharmaceutical compositions containing compounds of the invention, and methods of using the compounds and compositions of the invention in the treatment of S1P1 associated disorders, for example, psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn's disease, transplant rejection, multiple sclerosis, systemic lupus erythematosus, ulcerative colitis, type I diabetes, sepsis, myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke, acne, microbial infections or diseases and viral infections or diseases.
Owner:ARENA PHARMA
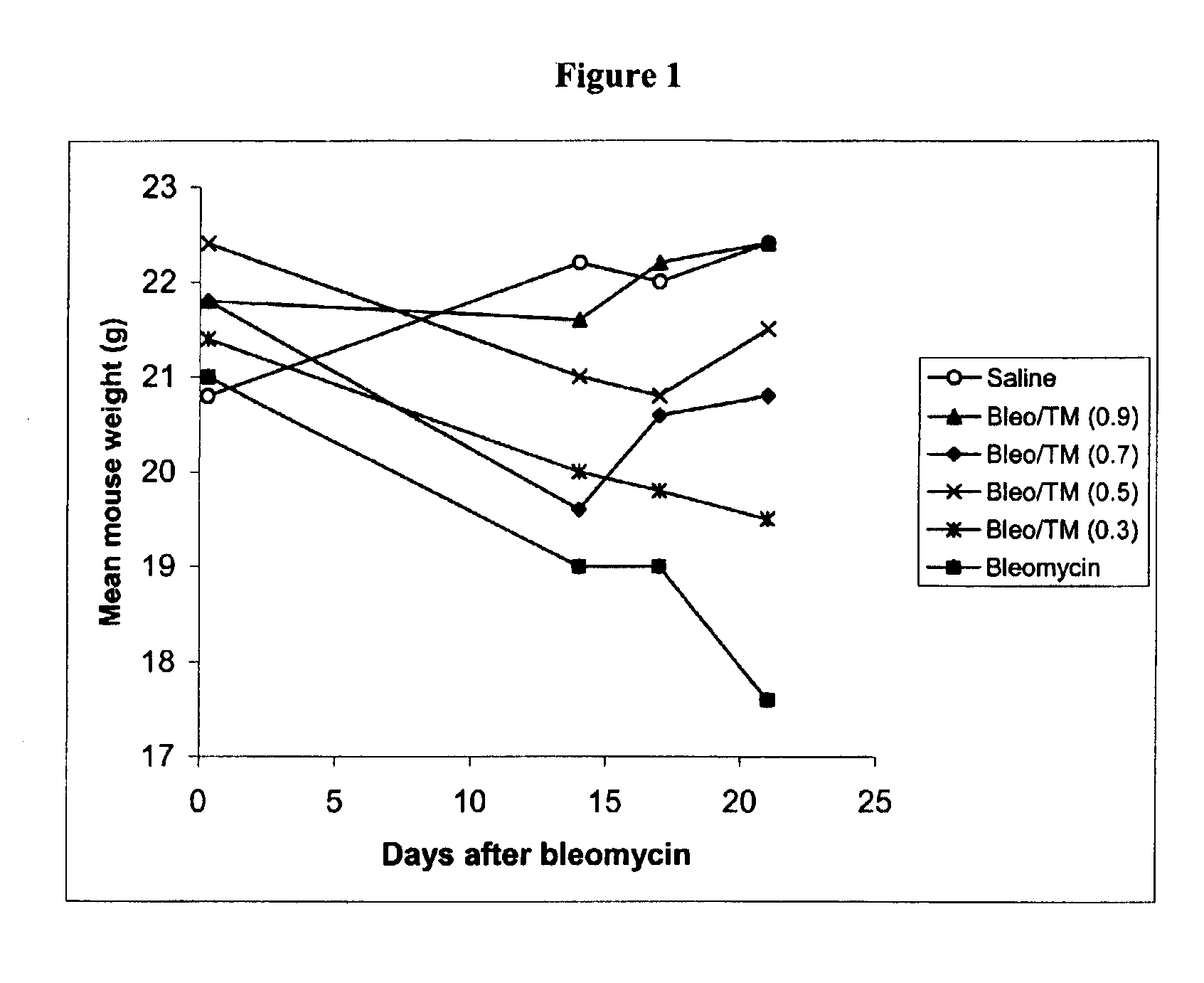
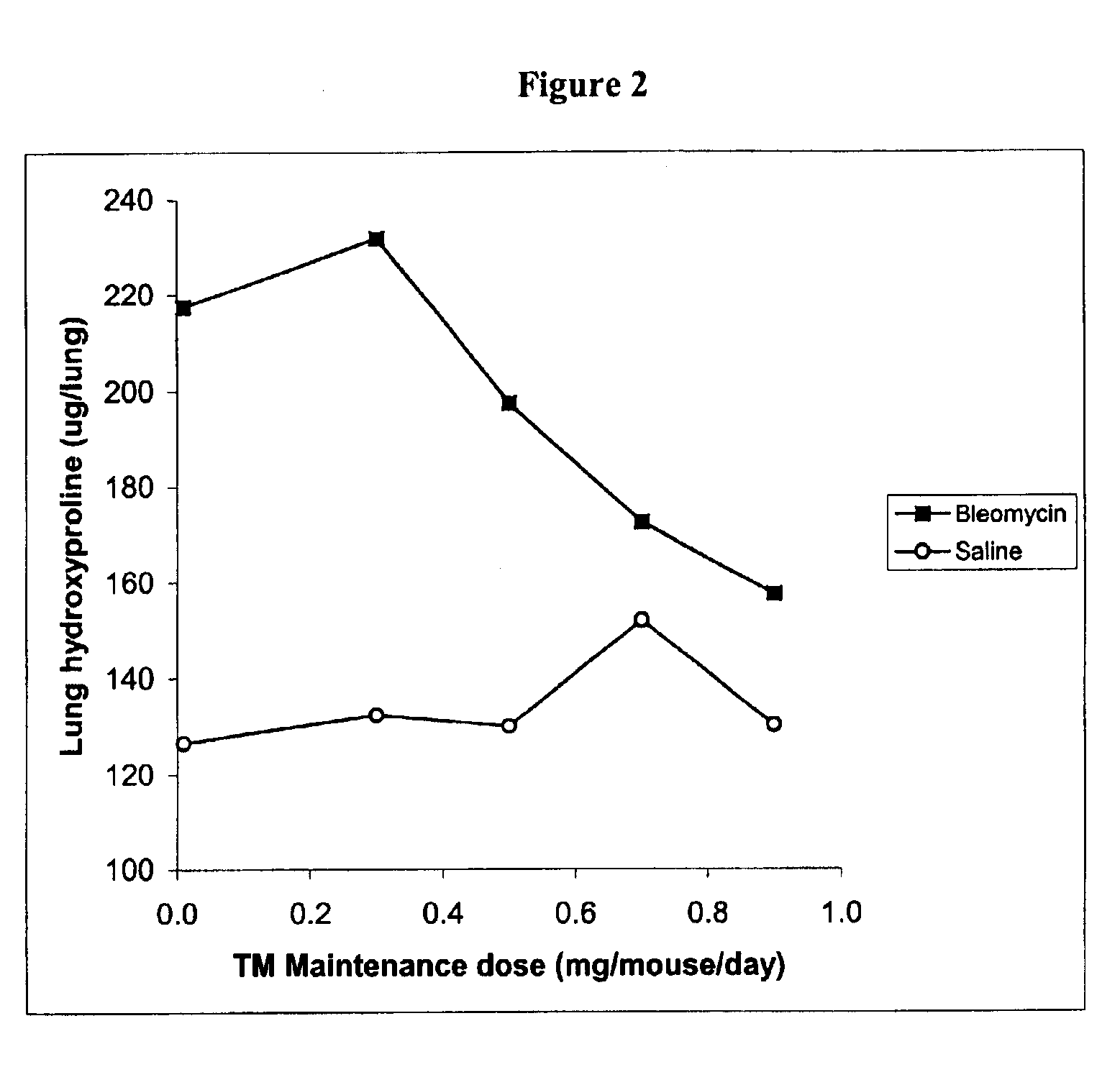
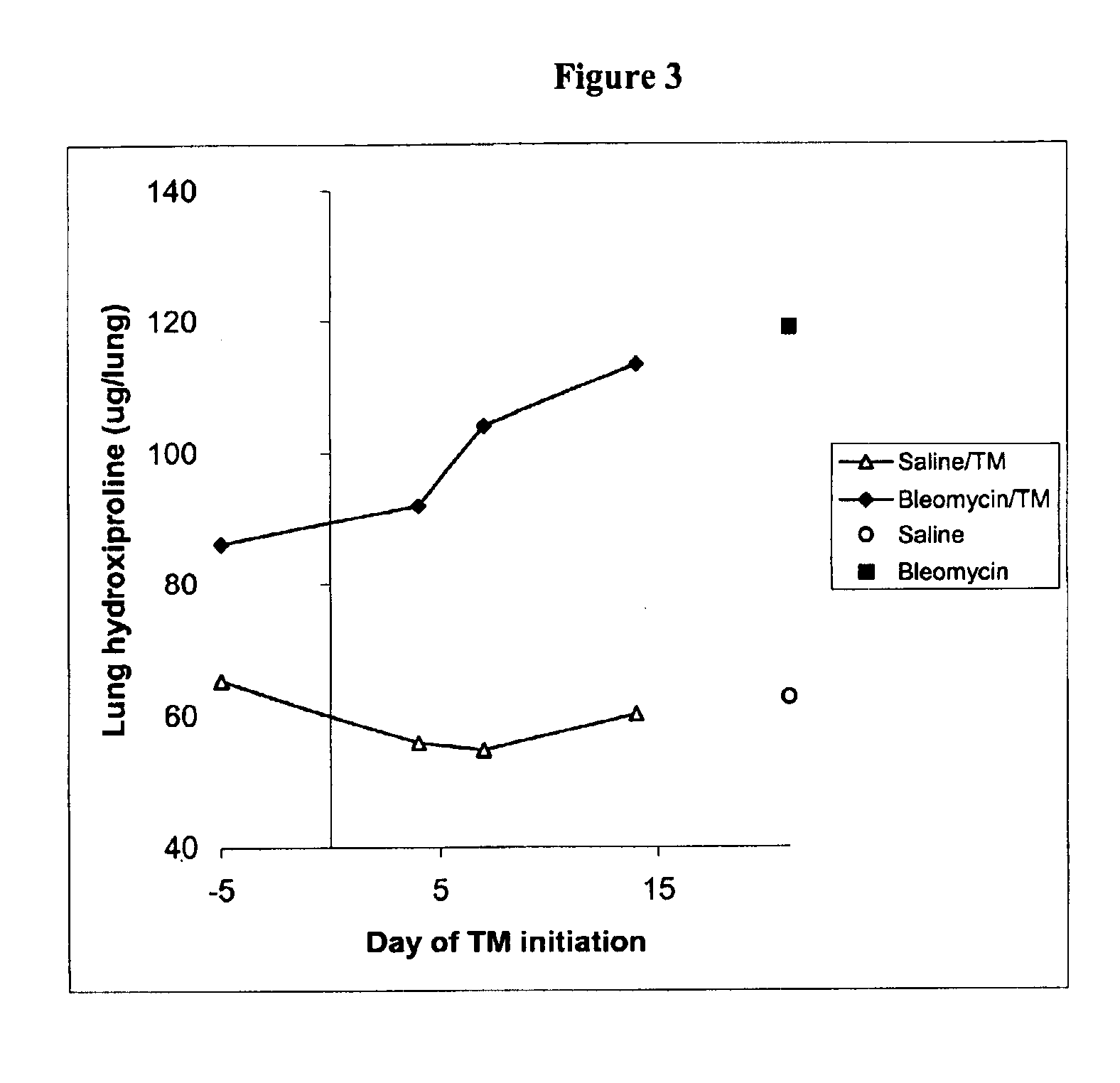
Copper lowering treatment of inflammatory and fibrotic diseases
InactiveUS6855340B2Treatment safetyLower Level RequirementsBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsDithiomolybdateLiver disease
The present invention relates generally to the field of prophylaxis and therapy for inflammatory and / or fibrotic diseases which include responses to injuries. In particular, the present invention is related to agents that can bind or complex copper such as thiomolybdate, and to the use of these agents in the prevention and treatment of inflammatory and / or fibrotic diseases. Exemplary thiomolybdates include mono-, di-, tri- and tetrathiomolybdate; these agents are administered to patients to prevent and / or treat inflammatory and / or fibrotic diseases, such as pulmonary disease including pulmonary fibrosis and acute respiratory distress syndrome, liver disease including liver cirrhosis and hepatitis C, kidney disease including renal interstitial fibrosis, scleroderma, cystic fibrosis, pancreatic fibrosis, keloid, secondary fibrosis in the gastrointestinal tract, hypertrophic burn scars, myocardial fibrosis, Alzheimer's disease, retinal detachment inflammation and / or fibrosis resulting after surgery, and graft versus host and host versus graft rejections.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
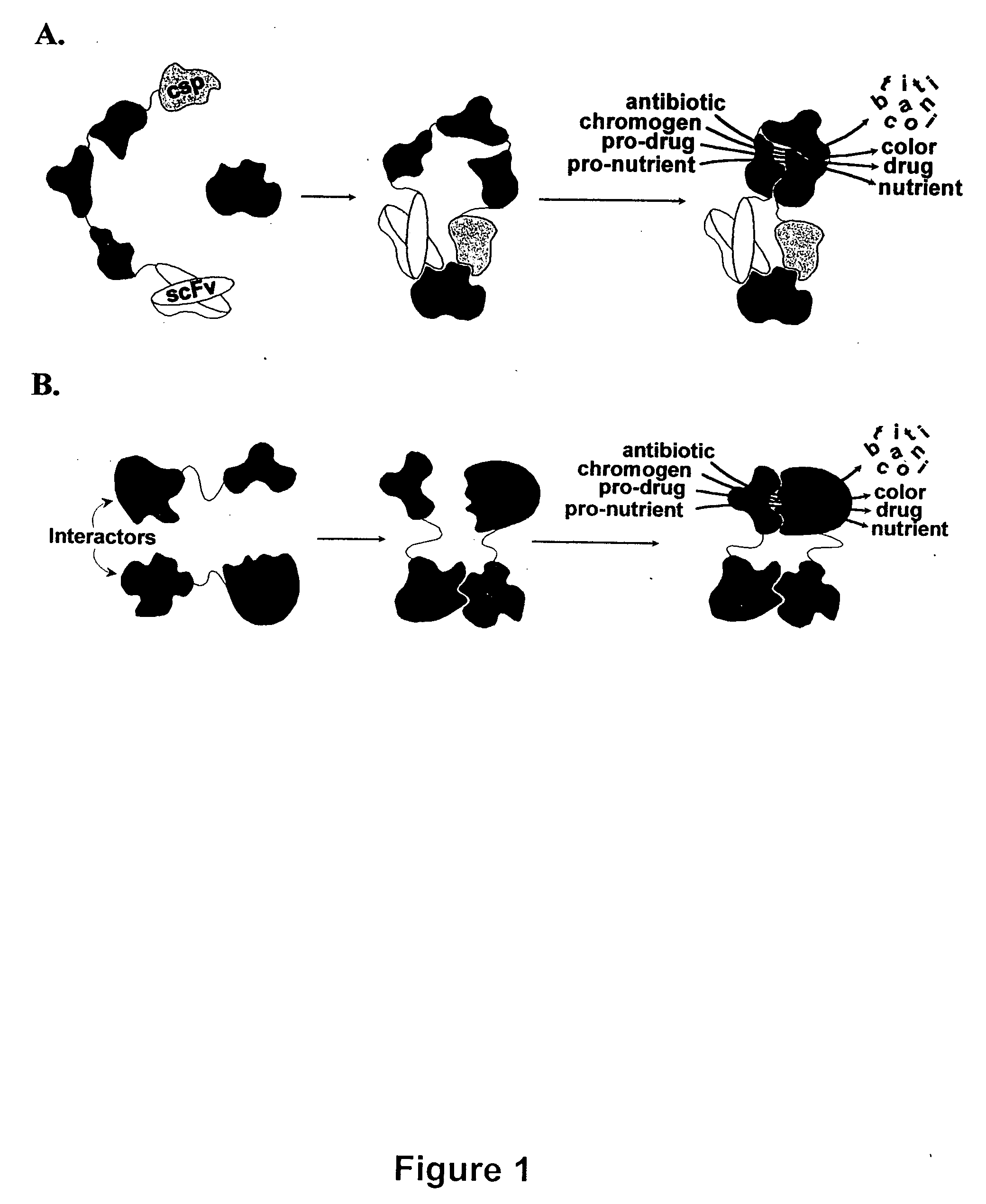
Breakpoint fusion fragment complementation system
InactiveUS20040038317A1Peptide librariesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHeterologousRNA-Protein Interaction
Fragment pairs of a Class A beta-lactamase (TEM-1 of E. coli) are disclosed that depend for their functional reassembly into the parent protein on the interaction of heterologous polypeptides or other molecules which have been genetically or chemically conjugated to the break-point termini of the fragment pairs. In addition, methods are provided for identifying fragment pairs that will optimally reassemble into a functional parent protein. Fragment pairs that comprise molecular interaction-dependent enzymes find use in (1) homogeneous assays and biosensors for any analyte having two or more independent binding sites, (2) tissue-localized activation of therapeutic and imaging reagents in vivo for early detection and treatment of cancer, chronic inflammation, atherosclerosis, amyloidosis, infection, transplant rejection, and other pathologies, (3 cell-based sensors for activation or inhibition of metabolic or signal transduction pathways for high-efficiency, high-throughput screening for agonists / antagonists of the target pathway, (4) high-throughput mapping of pair-wise protein-protein interactions within and between the proteomes of cells, tissues, and pathogenic organisms, (5) rapid selection of antibody fragments or other binding proteins which bind specifically to polypeptides of interest, (6) rapid antigen identification for anti-cell and anti-tissue antibodies, (7) rapid epitope identification for antibodies, (10) cell-based screens for high-throughput selection of inhibitors of any protein-protein interaction.
Owner:KALOBIOS PHARMA
Cells expressing an alphagala nucleic acid and methods of xenotransplantation
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for the reduction of xenotransplantation rejection. Specifically, the present invention relates, first, to transgenic cells, tissues, organs and animals containing transgenic nucleic acid molecules that direct the expression of gene products, including, but not limited to enzymes, capable of modifying, either directly or indirectly, cell surface carbohydrate epitopes such that the carbohydrate epitopes are no longer recognized by natural human antibodies or by the human cell-mediated immune response, thereby reducing the human immune system response elicited by the presence of such carbohydrate epitopes. In a preferred embodiment, the transgenic cells, tissues, organs and animals express nucleic acid molecules encoding functional recombinant alpha-Galactosidase A (alphaGalA) enzyme which modifies the carbohydrate epitope Galalpha(1,3)Gal. In a more preferred embodiment, the transgenic cells, tissues, organs and animals expressing the functional recombinant alphaGalA are transgenic pig cells, organs, tissues and / or animals. Second, the present invention relates to methods for xenotransplantation comprising introducing the transgenic cells, tissues and / or organs into human recipients so that a lower level of hyperacute rejection (HAR) is observed in the human recipients relative to the level of HAR observed in human recipients having received non-transgenic cells, tissues and / or organs.
Owner:THE AUSTIN RES INST +1
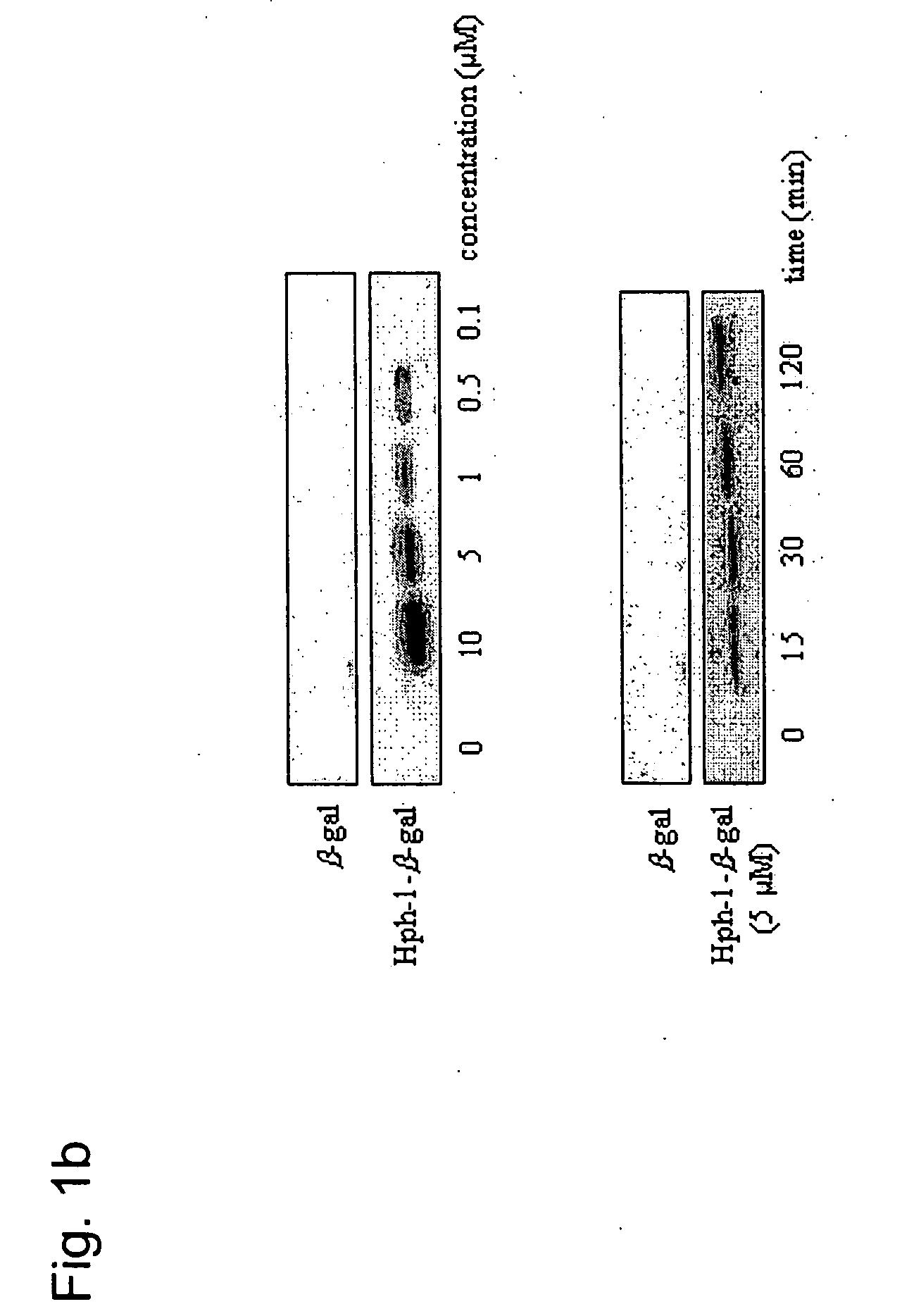
Methods for fusion polypeptide delivery into a cell
InactiveUS20070105775A1Limited utilityLack of tissue specificityNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsMedicineActivation cells
The present invention relates to methods for delivery of fusion polypeptides into cells. Methods are provided for local delivery of fusion polypeptides, e.g., through the skin, eye and the airway, to prevent allergic inflammation, airway hyper-responsiveness and to block T cell activation. Methods for delivery of fusion polypeptides to suppress graft rejection are also provided.
Owner:FORHUMANTECH CO LTD
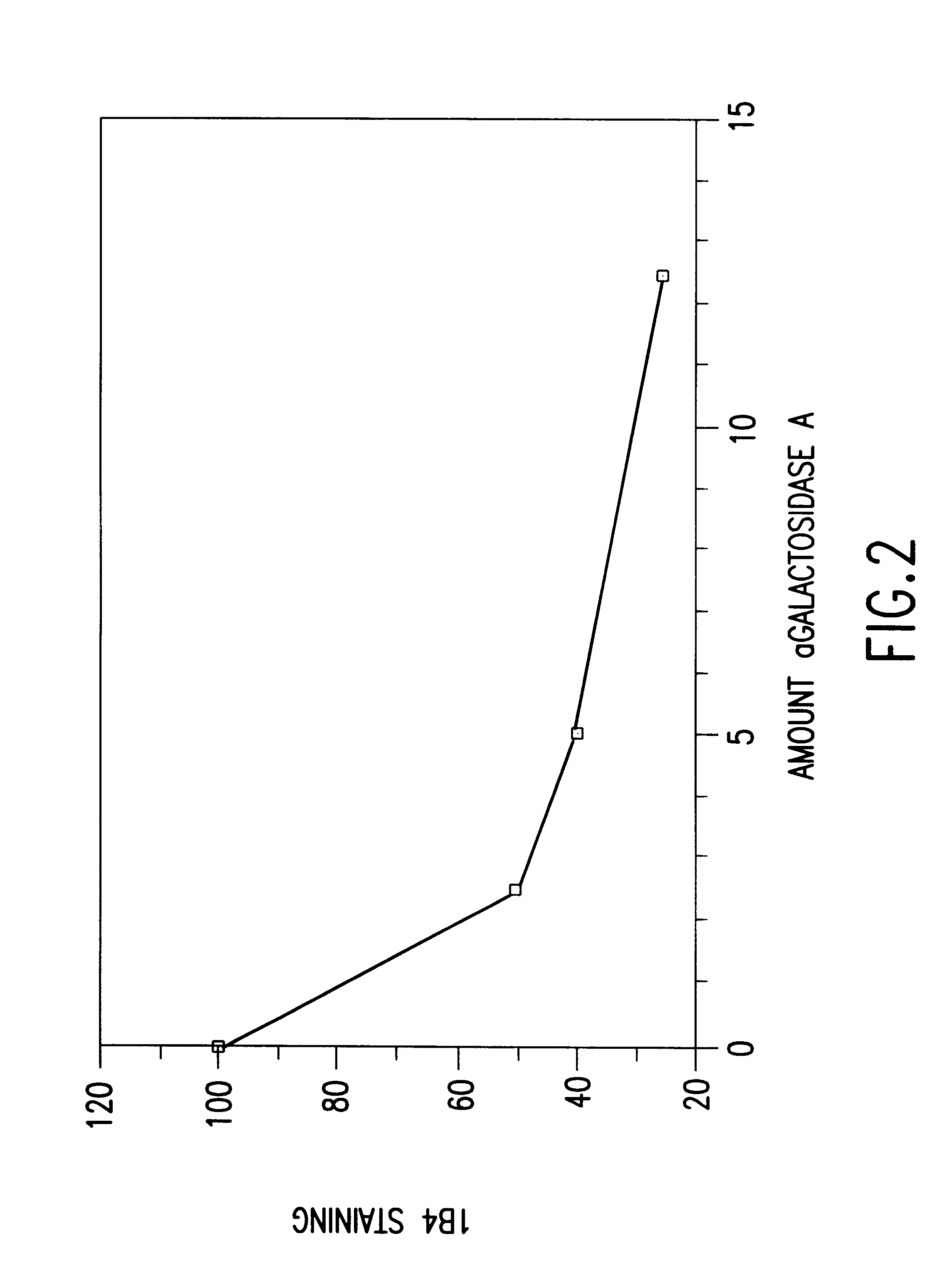
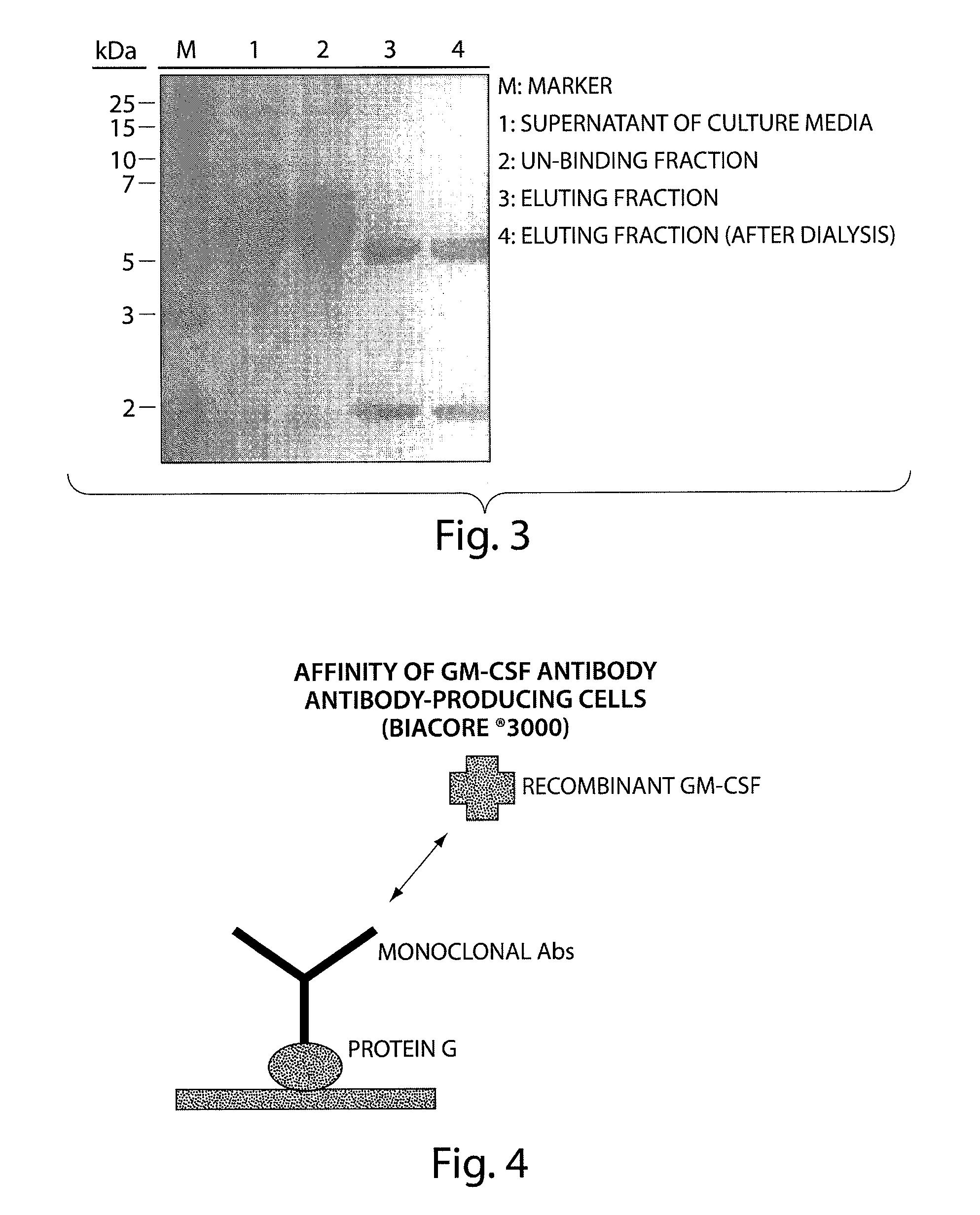
Human monoclonal antibody binding to hGM-CSF and its antigen binding portion
ActiveUS7935795B2High affinityPrevent proliferationSenses disorderAntipyreticComplementarity determining regionAutoimmune disease
The present invention provides a human monoclonal antibody, and antigen-binding portions thereof, capable of binding to human granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor (hGM-CSF) and neutralizing the bioactivity of the hGM-CSF, wherein the anti-hGM-CSF monoclonal antibody has a light chain (L chain) including an amino acid sequence SEQ ID NO:1 and a heavy chain (H chain) including an amino acid sequence SEQ ID NO: 2. Also provided are human monoclonal anti-hGM-CSF antibodies, and antigen-binding portions thereof, characterized by complementarity determining regions (CDRs) or H chain and L chain variable regions related to SEQ ID NO:1 and SEQ ID NO:2. Antibodies, and antigen-binding portions thereof, of the invention are useful in the treatment of diseases associated with overproduction of hGM-CSF, including allergic disease, graft rejection and graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), and autoimmune diseases.
Owner:EVEC
2-Imino-4-(thio)oxo-5-poly cyclovinylazolines for use as p13 kinase ihibitors
The present invention is related to 2-imino-azolinone-vinyl fused-benzene derivatives of Formula (1) in particular for the treatment and / or prophylaxis of autoimmune disorders and / or inflammatory diseases, cardiovascular diseases, neurodegenerative diseases, kidney diseases, platelet aggregation, cancer, transplantation, graft rejection or lung injuries.
Owner:MERCK SERONO SA
Use of b lymphocyte stimulator protein antagonists to promote transplantation tolerance
InactiveUS20110014190A1Decreasing antibody titerInhibiting and reducing immunoglobulin productionOrganic active ingredientsAntibody ingredientsRegimenTolerability
The invention relates to methods of preventing, treating, ameliorating and otherwise inhibiting organ or transplant rejection in a patient by administering B Lymphocyte Stimulator antagonists. In addition, therapeutic treatment regimens are provided to promote transplant tolerance in a patient following the administration of B Lymphocyte Stimulatorantagonists.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA +1
Materials and Methods for Altering an Immune Response to Exogenous and Endogenous Immunogens, Including Syngeneic and Non-Syngeneic Cells, Tissues or Organs
InactiveUS20120308610A1Reduce reduction reactionReduced responseAntipyreticAnalgesicsAutoimmune conditionGraft rejections
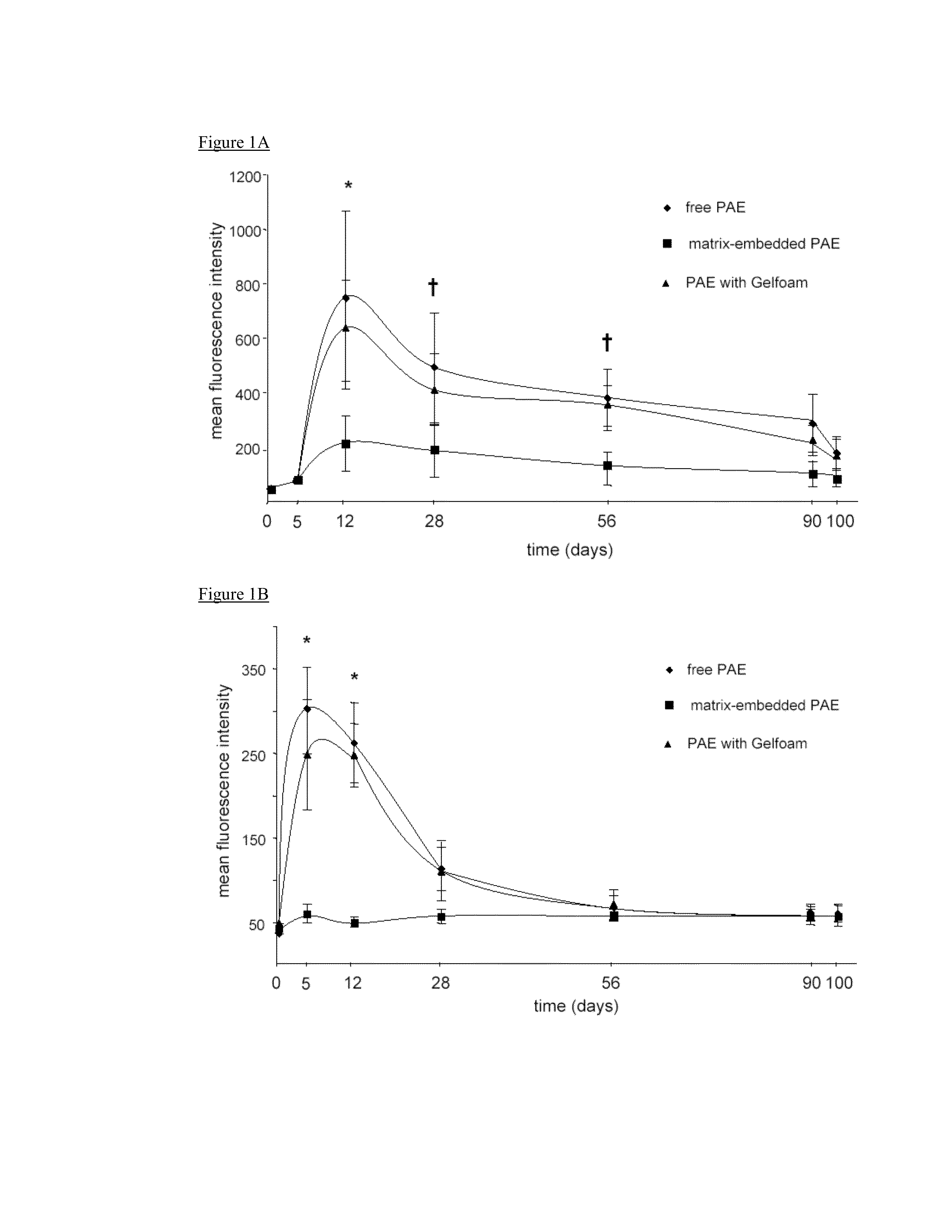
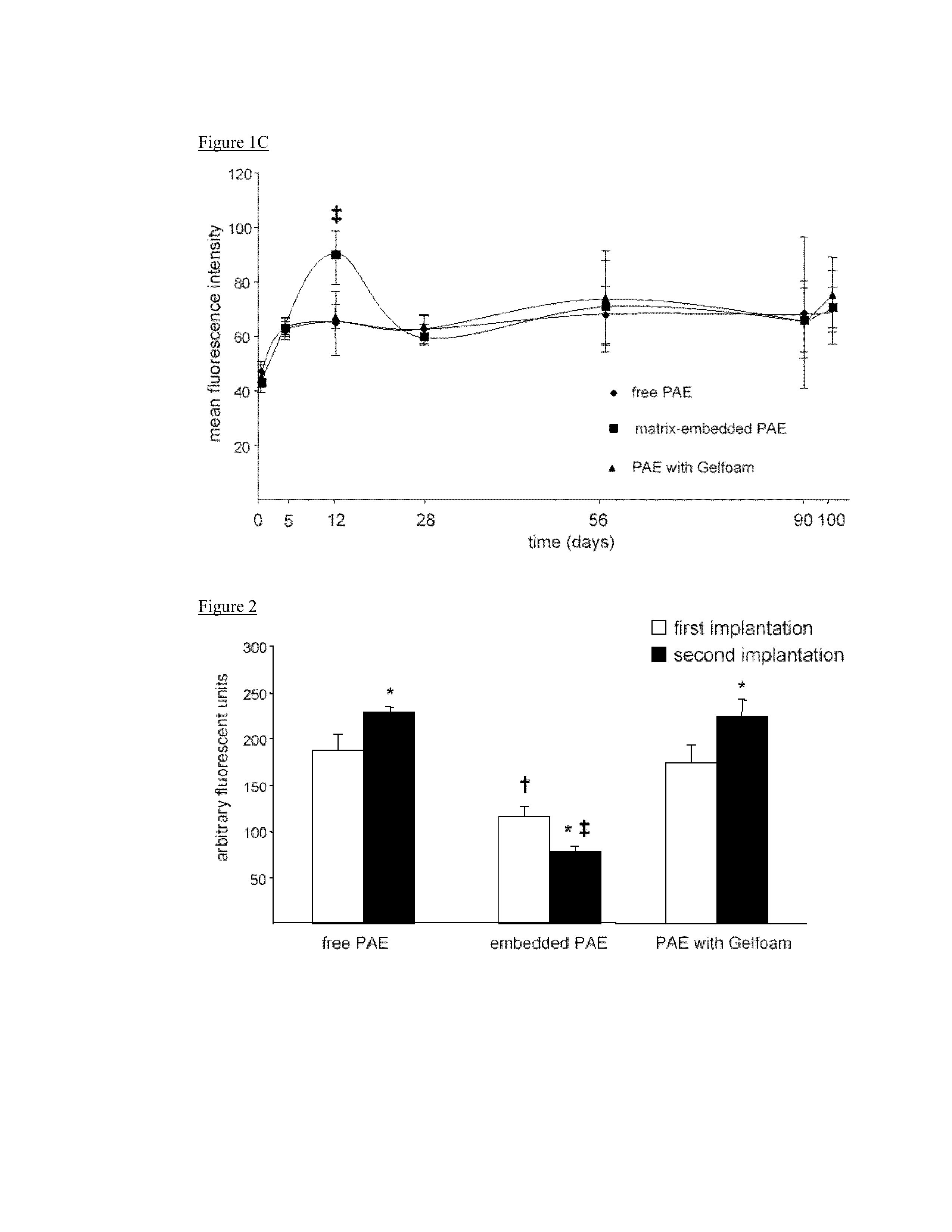
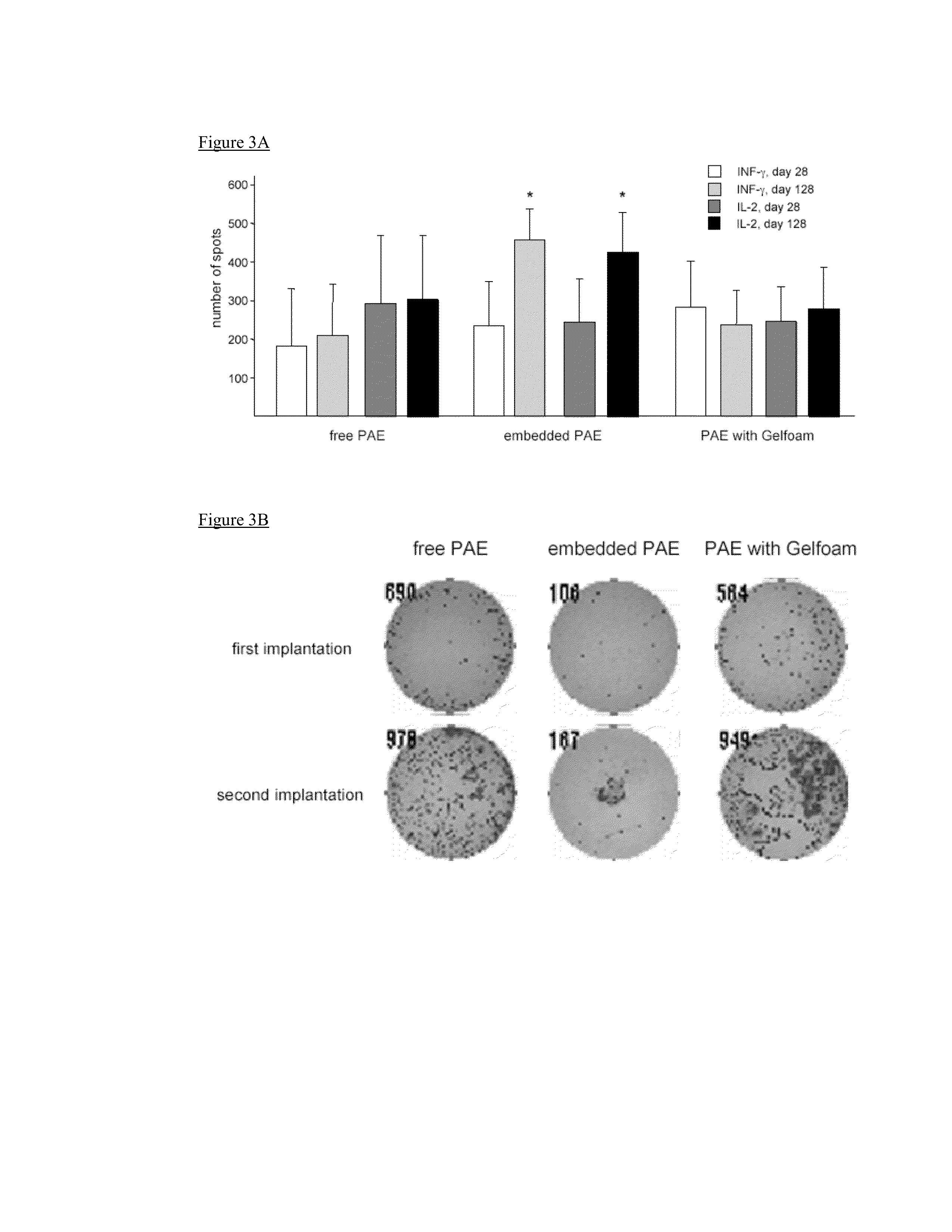
Disclosed herein are materials and methods for modulating an immunologically adverse response to an exogenous or endogenous immunogen, including a cell, tissue, or organ associated immunogen. An implantable material comprising cells, such as but not limited to endothelial cells, anchored or embedded in a biocompatible matrix can modulate an adverse immune or inflammatory reaction to exogenous or endogenous immunogens, including response to non-syngeneic or syngeneic cells, tissues or organs, exogenous immunogens or stimuli, as well as ameliorate an autoimmune condition. The implantable material can be provided prior to, coincident with, or subsequent to occurrence of the immune response or inflammatory reaction. The implantable material can induce immunological acceptance in a transplant patient, reduce graft rejection and reduce donor antigen immunogenicity.
Owner:EDELMAN ELAZER R +2
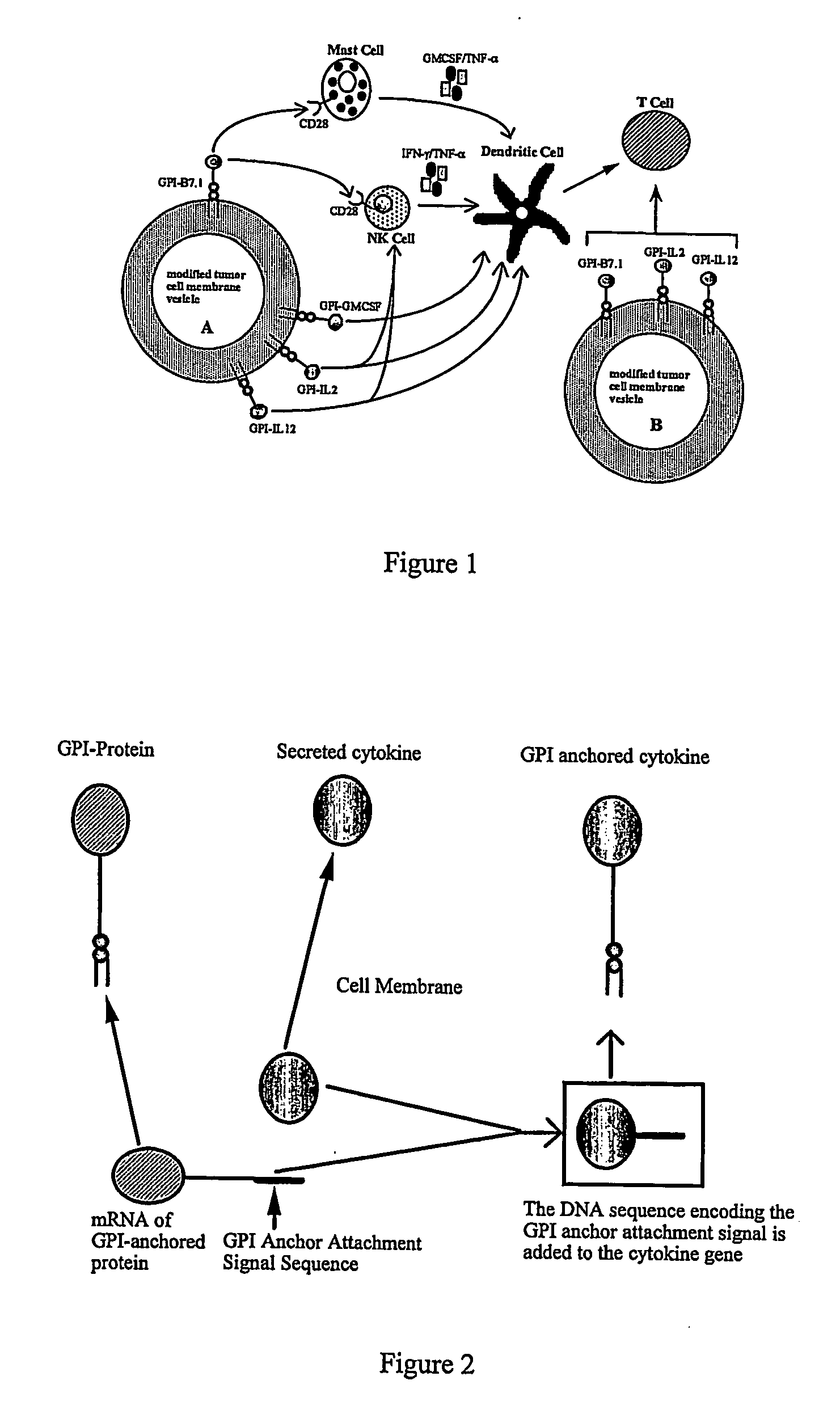
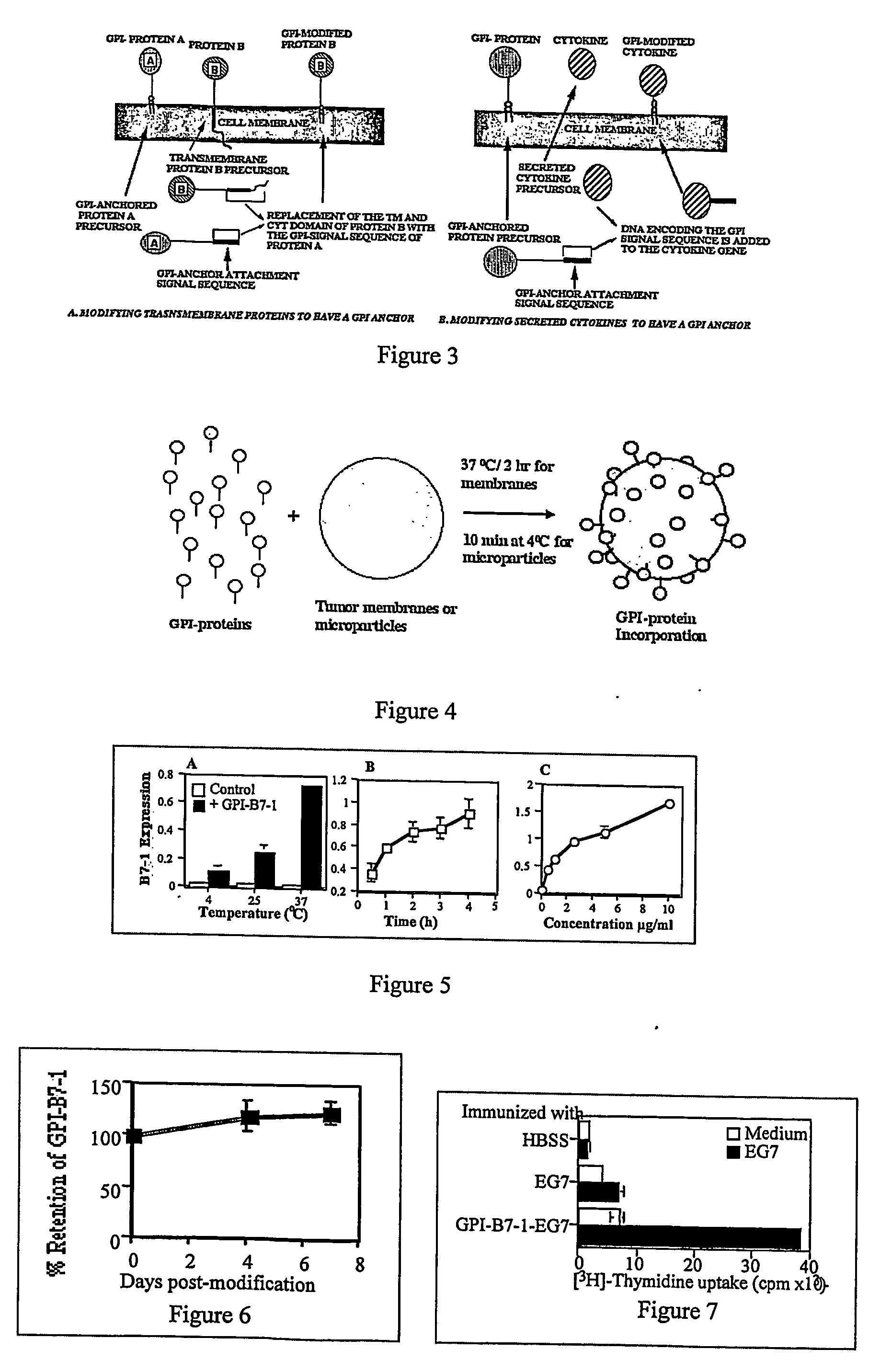
Therapeutic Compositions and Vaccines By Glycosyl-Phosphatidylinositol (Gpi)-Anchored Cytokines and Immunostimulatory Molecules
InactiveUS20070243159A1Induce toleranceSuppress immunityViral antigen ingredientsCancer antigen ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthGlycosyl-Phosphatidylinositol
A therapeutic composition or a vaccine comprising tumor membrane-anchored cytokines or other immunostimulatory or costimulatory molecules are provided. The therapeutic composition or a tumor vaccine can be used for treating a tumor or other disease such as autoimmune disorder, viral diseases, bacterial diseases, parasitic diseases, and transplant rejection.
Owner:IRM +1
Materials and Methods for Altering an Immune Response to Exogenous and Endogenous Immunogens, Including Syngeneic and Non-Syngeneic Cells, Tissues or Organs
InactiveUS20130177600A1Reduce reduction reactionReduced responseAntipyreticAnalgesicsAutoimmune conditionAutoimmune responses
Disclosed herein are materials and methods for modulating an immunologically adverse response to an exogenous or endogenous immunogen, including a cell, tissue, or organ associated immunogen. An implantable material comprising cells, such as but not limited to endothelial cells, anchored or embedded in a biocompatible matrix can modulate an adverse immune or inflammatory reaction to exogenous or endogenous immunogens, including response to non-syngeneic or syngeneic cells, tissues or organs, exogenous immunogens or stimuli, as well as ameliorate an autoimmune condition. The implantable material can be provided prior to, coincident with, or subsequent to occurrence of the immune response or inflammatory reaction. The implantable material can induce immunological acceptance in a transplant patient, reduce graft rejection and reduce donor antigen immunogenicity.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Isolated TNF-alpha peptide and pharmaceutical composition thereof
InactiveUS7892558B2Peptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticTumor necrosis factor alphaAutoimmune diabetes
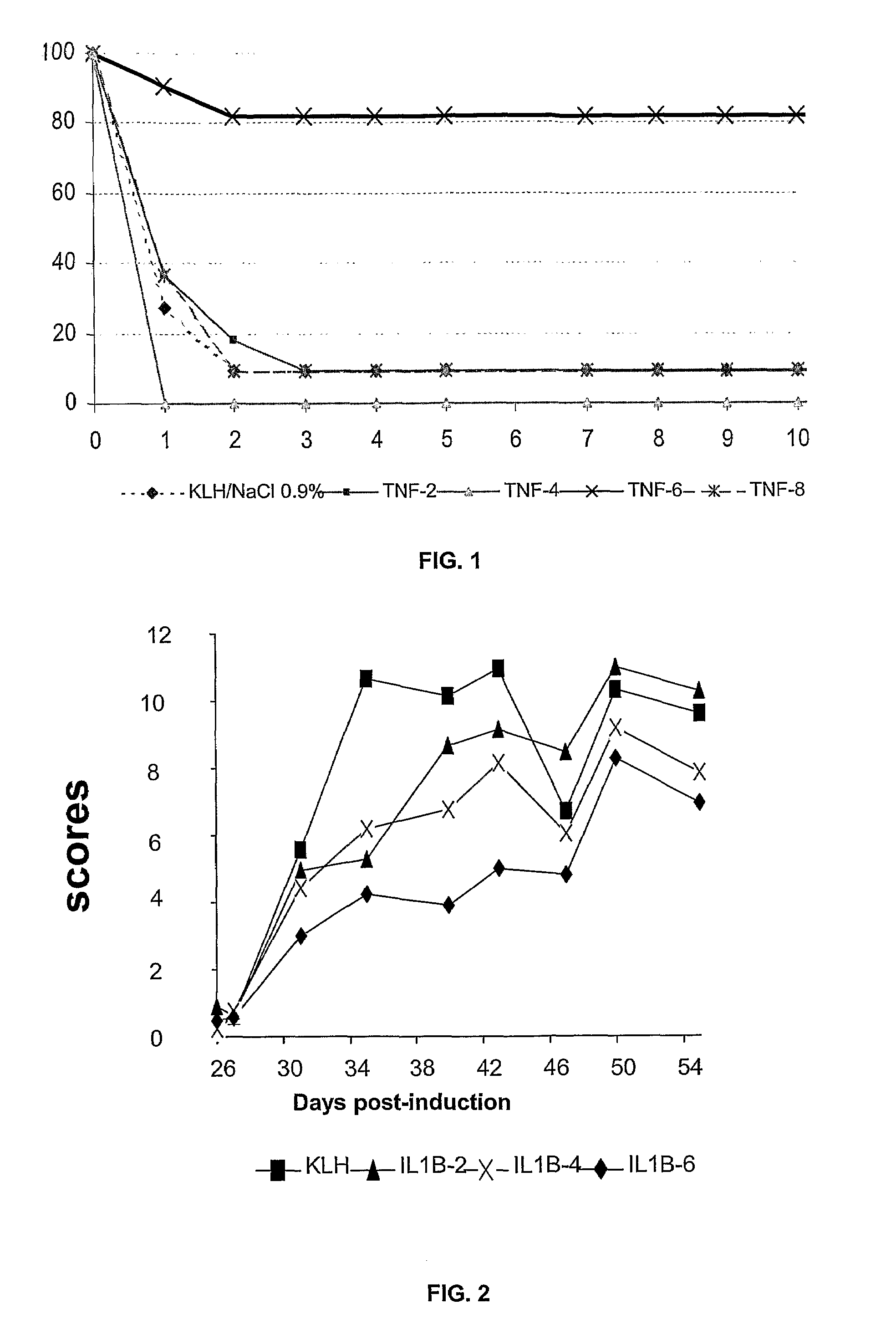
The present invention relates to peptides derived from the proinflammatory cytokines, interleukin-1β, (IL1β) and tumor necrosis factor α, (TNFα), and their use in human or veterinary therapy, such as to generally treat diseases linked to the overproduction of IL1β or TNFα as well as acute or chronic inflammatory diseases, rheumatoid arthritis, septic shock, autoimmune diabetes, graft rejection in the host, etc.
Owner:VAXCONSULTING
Materials and methods for altering an immune response to exogenous and endogenous immunogens, including syngeneic and non-syngeneic cells, tissues or organs
InactiveUS20090087414A1Lower immune responseReduce decreaseBiocideAntipyreticAutoimmune conditionAutoimmune responses
Disclosed herein are materials and methods for modulating an immunologically adverse response to an exogenous or endogenous immunogen, including a cell, tissue, or organ associated immunogen. An implantable material comprising cells, such as but not limited to endothelial cells, anchored or embedded in a biocompatible matrix can modulate an adverse immune or inflammatory reaction to exogenous or endogenous immunogens, including response to non-syngeneic or syngeneic cells, tissues or organs, exogenous immunogens or stimuli, as well as ameliorate an autoimmune condition. The implantable material can be provided prior to, coincident with, or subsequent to occurrence of the immune response or inflammatory reaction. The implantable material can induce immunological acceptance in a transplant patient, reduce graft rejection and reduce donor antigen immunogenicity.
Owner:PERVASIS THERAPEUTICS INC
Methods and compositions for immunotherapy and detection of inflammatory and immune-dysregulatory disease, infectious disease, pathologic angiogenesis and cancer
InactiveUS20080108794A1Antibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDendritic cellAutoimmune condition
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Epitope composition
A pharmaceutical composition for sublingual, buccal or enteric administration comprising at least one substance obtainable by hydrolysis with chymotrypsin of an antigenic structure which induces graft rejection, allergic reaction or autoimmune disease.
Owner:BIOTECH TOOLS
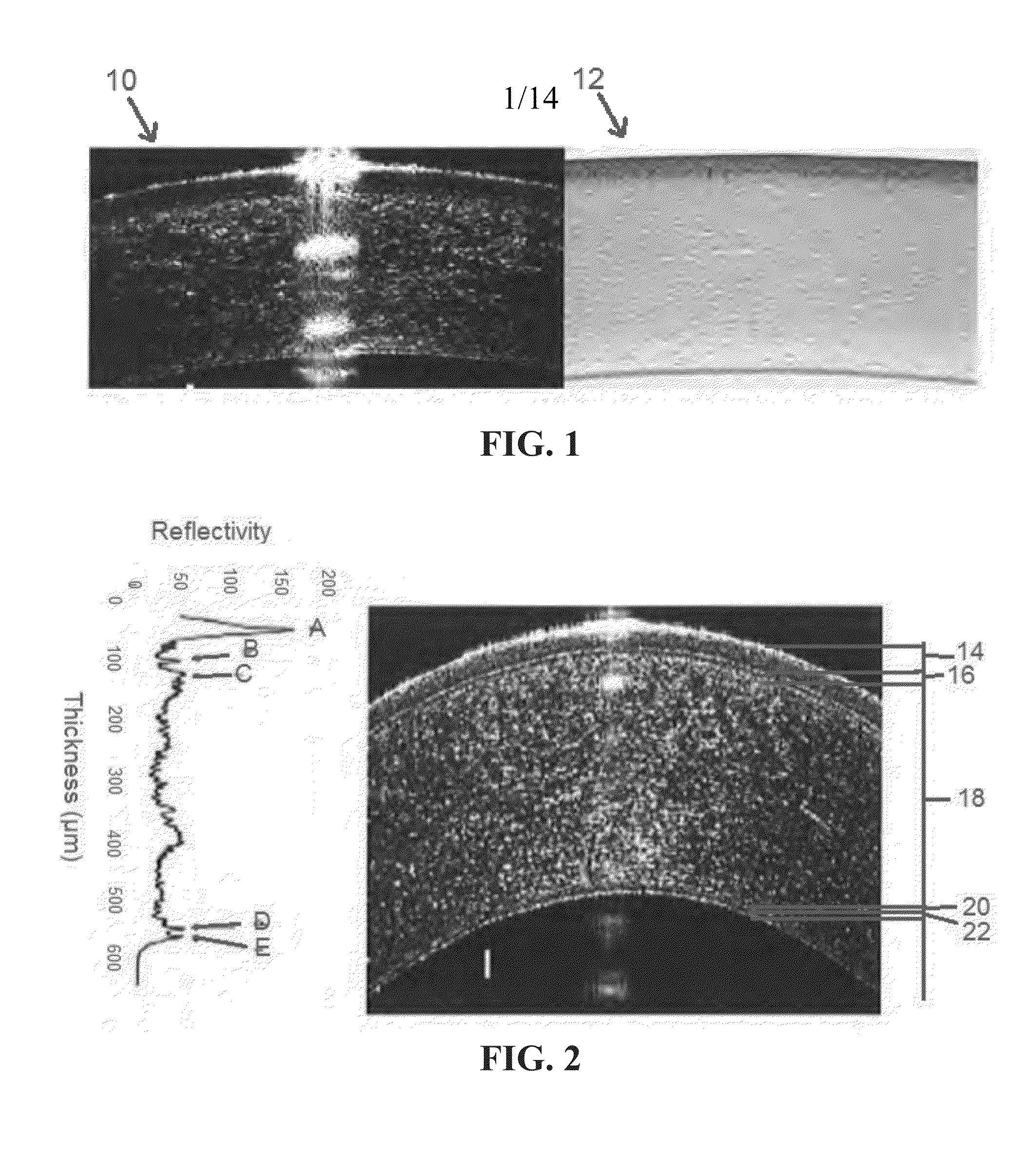
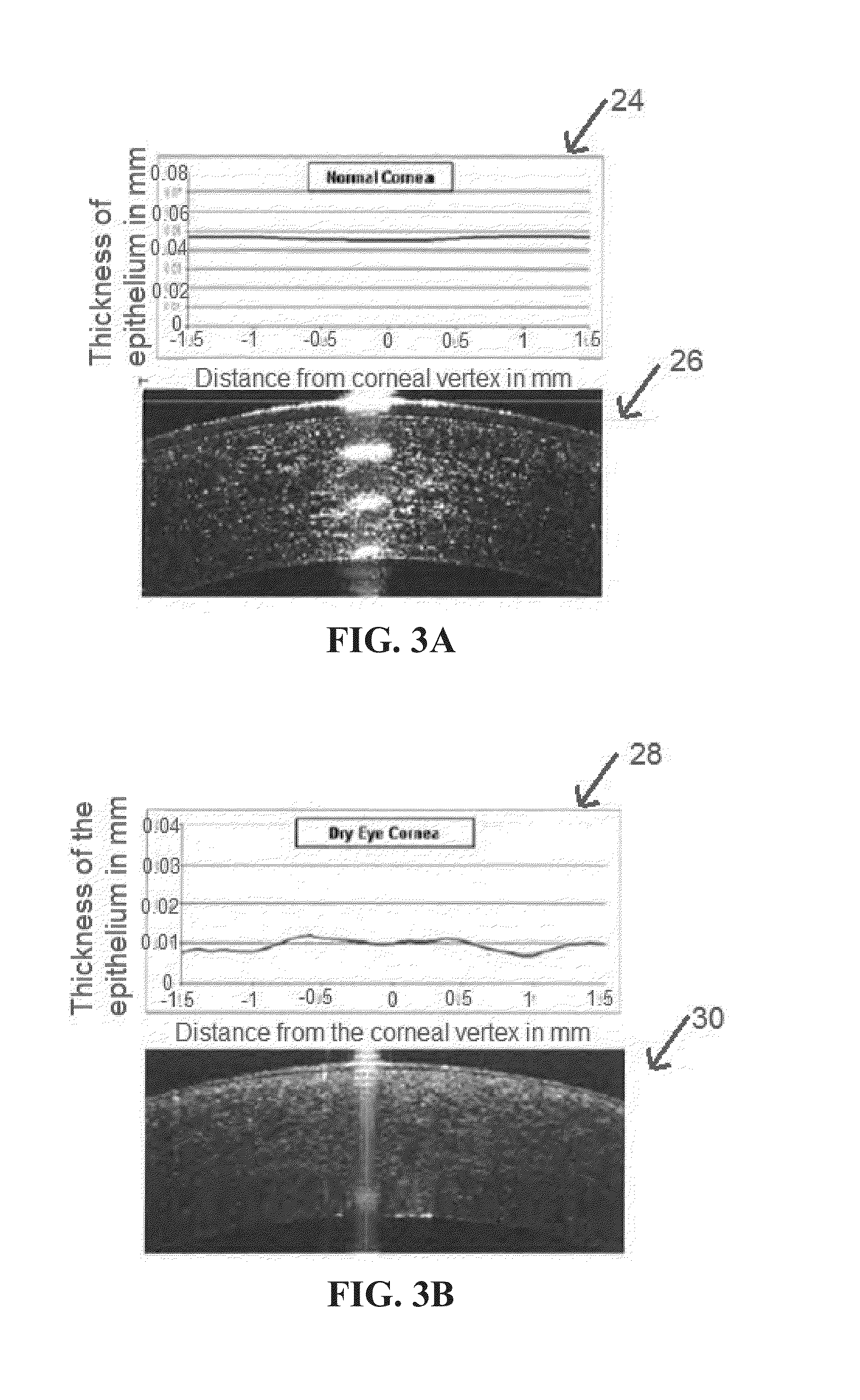
Indices for management of dry eye syndrome, corneal ectasia, keratoplasty graft rejection and failure and fuchs' dystrophy
InactiveUS20140300862A1Easy diagnosisImprove treatmentImage enhancementImage analysisKeratorefractive surgeryHigh resolution image
Improved indices for the diagnosis and evaluation of conditions affecting the eye. Specifically, the indices include an Enhanced Epithelial Irregularity Factor (eEIF) for the diagnosis and evaluation of conditions such as dry eye syndrome (DES), Bowman's Ectasia Index (BEI), including enhanced BEI (eBEI) and BEI-Max, and Bowman's Relative Thinning (BRT) Index for the diagnosis and evaluation of ectatic conditions such as keratoconus, pellucid marginal degeneration, post-refractive surgery ectasia, and keratoglobus, and Descemet's Membrane Thickening Index (DMT), Descemet's Rejection Index (DRI), and Descemet's Membrane Irregularity Factor (DIF) for the diagnosis and evaluation of conditions such as keratoplasty rejection and failure and Fuchs' dystrophy. These improved indices may be incorporated into optical coherence tomography systems, or any other imaging device capable of capturing high resolution images of the cornea, for more sensitive and specific diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring of certain corneal conditions, in addition to the evaluation of new treatments.
Owner:UNIV OF MIAMI
Oral tolerance induction by collagen to prevent allograft rejection
InactiveUS20030078208A1Peptide/protein ingredientsSnake antigen ingredientsAllograft rejectionOral tolerance
The present invention relates to the use of collagen and MHC-like compounds to down regulate immune responses. Methods for administration of such compounds that induce immune tolerance are described. The invention is important in the context of allograft rejection, transplantation, graft rejection, pleural disease and immunotolerance.
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
Competitive inhibitors of invariant chain expression and/or ectopic clip binding
ActiveUS20110118175A1Efficient methodEasy to synthesizeAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderCellular graft rejectionAntigen
The invention relates to methods for modulating the immune function through targeting of CLIP molecules. The result is wide range of new therapeutic regimens for treating, inhibiting the development of, or otherwise dealing with, a multitude of illnesses and conditions, including autoimmune disease, cancer, Alzheimer's disease, allergic disease, transplant and cell graft rejection, HIV infection and other viral, bacterial, and parasitic infection, and AIDS. Methods are also provided for preparing a peptide having the property of being able to displace CLIP by feeding one or more peptide sequences into software that predicts MHC Class II binding regions in an antigen sequence and related products.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Methods and compositions for immunotherapy and detection of inflammatory and immune-dysregulatory disease, infectious disease, pathologic angiogenesis and cancer
InactiveUS20080241141A1Antibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDendritic cellAutoimmune condition
Methods and compositions for immunotherapy of inflammatory and immune-dysregulatory diseases, using multispecific antagonists that target at least two different markers are disclosed. The different targets include (i) proinflammatory effectors of the innate immune system, (ii) coagulation factors, and (iii) targets specifically associated with an inflammatory or immune-dysregulatory disorder, with a pathologic angiogenesis or cancer, or with an infectious disease, wherein the targets included in group (iii) are neither a proinflammatory effector of the immune system nor a coagulation factor. When the multispecific antagonist reacts specifically with a target associated with an inflammatory or immune-dysregulatory disorder, with a pathologic angiogenesis or cancer, or with an infectious disease, it also binds specifically with at least one proinflammatory effector of the immune system or at least one coagulation factor. Thus, the multispecific antagonist contains at least one binding specificity related to the diseased cell or condition being treated and at least one specificity to a component of the immune system, such as a receptor or antigen of B cells, T cells, neutrophils, monocytes and macrophages, and dendritic cells, a modulator of coagulation, or a proinflammatory cytokine. The multispecific antagonists are used in the treatment of various diseases that are generated or exacerbated by, or otherwise involve, proinflammatory effectors of the innate immune system or coagulation factors. Such diseases more particularly include acute and chronic inflammatory disorders, autoimmune diseases, giant cell arteritis, septicemia and septic shock, coagulopathies (including diffuse intravascular coagulation), neuropathies, graft versus host disease, infectious diseases, acute respiratory distress syndrome, granulomatous diseases, transplant rejection, asthma, cachexia, myocardial ischemia, and atherosclerosis. Other diseases also responsive to these therapies include cancers and conditions with pathological angiogenesis.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com






![Dihydro-1h-pyrrolo[1,2-a]indol-1-yl carboxylic acid derivatives which act as s1p1 agonists Dihydro-1h-pyrrolo[1,2-a]indol-1-yl carboxylic acid derivatives which act as s1p1 agonists](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/46052328-f670-4632-9214-3658d5fe9461/US20100292233A1-20101118-D00000.png)
![Dihydro-1h-pyrrolo[1,2-a]indol-1-yl carboxylic acid derivatives which act as s1p1 agonists Dihydro-1h-pyrrolo[1,2-a]indol-1-yl carboxylic acid derivatives which act as s1p1 agonists](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/46052328-f670-4632-9214-3658d5fe9461/US20100292233A1-20101118-D00001.png)
![Dihydro-1h-pyrrolo[1,2-a]indol-1-yl carboxylic acid derivatives which act as s1p1 agonists Dihydro-1h-pyrrolo[1,2-a]indol-1-yl carboxylic acid derivatives which act as s1p1 agonists](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/46052328-f670-4632-9214-3658d5fe9461/US20100292233A1-20101118-D00002.png)